本文首先界定经济地理思想史范畴,随后分析中国经济地理思想的阶段特征,然后梳理贯穿各个阶段并承继下来的主题脉络,最后从历史发展角度分析中国经济地理研究思想的走向,并简要对一些问题进行反思。
1 经济地理思想史界定
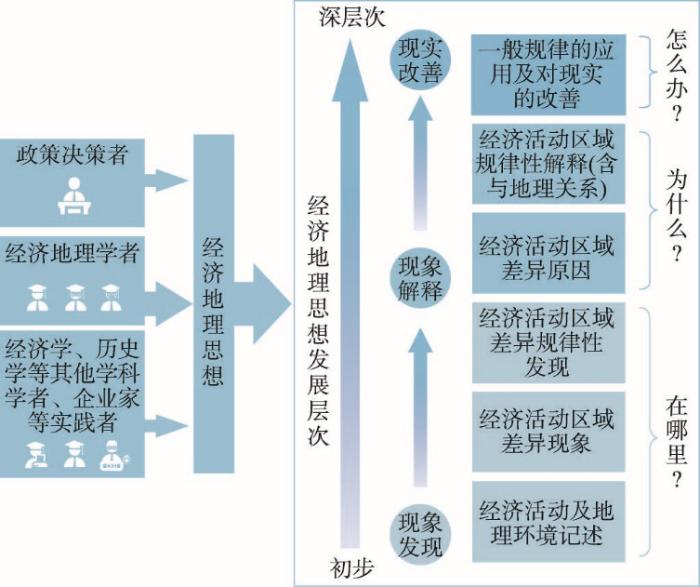
参照科学思想史定义[14]和地理学思想史[3⇓-5]、经济学思想史[10]中的研究框架,科学思想史更突出科学概念及思想体系的演变,而一个国家某学科的思想史在此导向下,可突出不同历史时期实际出现的相关思想的具体变化历史。经济地理思想,包括学科形成前对各地经济活动现象的认识、差异的描述、特征的概括、原因的理解等,学科形成后的经济地理学研究对象、相关概念、哲学思维、假设、定律、理论、方法、研究重心等[15]。具体一点,包括经济地理研究方向的变化,对经济活动区位、空间格局的认识、特点归纳,对其背后原因尤其是与地理环境关系的特点、相关规律的探索,以及指导人们更好地利用地理环境,有效地、可持续地进行满足人类需求的经济活动的思想等(图1)。
经济地理思想史关注不同时期相关思想的关联,如早期阶段人们对地理环境和物产的认识和记述:记述什么地方有什么山水、植物、动物、矿物以及相应的作物种植、动物养殖,金属器皿的制造等(图1“在哪里”)。这些记述为之后认识物产的地域特点、物产与地理条件的关系提供了基础事实。从比较自然条件与物产、土壤与作物、水与农业、矿物出产地的差别,逐步得出规律性的解释(图1“为什么”)。这些规律性的发现,可用来指导实践,以使人类更好地利用自然条件,进行更有效的经济活动(图1“怎么办”)。近代及现代经济地理思想,具有更多内涵,如经济活动与地理现象关系一般规律、经济活动区位及空间格局规律、经济地理学研究的哲学思想、经济地理研究方法、经济地理成果的应用方向等。随着历史进步,经济地理思想逐步走向深入(图1)。
图1
在该学科形成之前,古代哲学、地理、历史、文学等方面的相关记述,是经济地理思想的重要来源。学科出现后,经济地理思想主要来自经济地理学者的相关研究结果。此外,中国政府领导人的有些观点,含有经济地理思维,尤其在区域发展战略上,如孙中山[16]、毛泽东[17]、邓小平[18]、胡锦涛[19]的区域发展战略思想,习近平新发展理念中的“协调”“共享”思想等,都具有明确的经济地理指导意义。此外,在一些相近学科,如经济学、地理学中的一些分支(城市地理学、自然地理学、地理信息科学等),也有一些研究对经济地理思想有所贡献。经济活动实践者(如企业家),在相关经济活动实施中,有不少涉及区位和与地理环境关系的决策。他们的决策过程及其结果,也成为经济地理思想的一个来源(图1)。
2 经济地理思想发展的阶段特征
表1 中国经济地理思想发展历史分期及其特点简表
Tab. 1
| 历史时期 | 起止时间 | 分期理由 | 经济地理思想阶段特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 古代时期 | 先秦至1840年第一次鸦片战争 | 中国地理学发展研究中以第一次鸦片战争之前作为古代地理学阶段[3,8],鸦片战争之后,中国政治、经济发生转折性变化,经济地理研究出现众多新特点。 | 人类对地理环境的适应:农业耕作因地制宜,农业分区,物产和商业区域差异,城镇区位;区域综合研究;城乡规模与腹地关系,实地考察研究(游记、探险等)。 |
| 近代时期 | 1840—1949年中华人民共和国成立 | 该时期为中国近代历史阶段。政治、经济发生多种变化,经济地理出现较快发展。经济地理学作为一个学术领域出现。 | 经济地理学定义,农业地理、工业地理专门研究;提出区域发展战略思想;开始对经济地理格局进行解释;在研究中使用新的地图技术。 |
| 现代时期I: 计划经济时期 | 1949—1978年 | 这是中华人民共和国成立后,计划经济起主导作用的特殊时期,经济地理研究带有明显的计划经济特征。 | 经济地理学为政府服务;关注生产布局要求与地理条件的关系,重视自然条件对生产布局的影响;均衡战略起主导作用;关注对地理环境利用和改造。 |
| 现代时期II: 20世纪后期 | 1979年至20世纪末 | 改革开放带来了中国经济管理体制变革和经济迅速发展,市场经济改革以及西方经济地理思想引入。 | 国土整治与国土规划;区域不平衡战略;提出“点—轴系统”理论等经济空间结构理论;发现区域经济差异扩大趋势并建议适当调控;提出区域可持续发展诊断方法及实施思路;外资与区域发展关系;多种新的研究方法、视角的引入。 |
| 现代时期III: 21世纪前20 年 | 2000—2020年 | 在社会经济快速发展基础上,经济地理现象快速变化,经济地理学在服务经济发展的同时,关注经济增长所出现的问题。 | 区域差异与区域协调;新因素对经济活动地理格局的影响;产业集聚、都市经济区、特大城市群地区经济发展,农业、农村、农户的地理研究;人地关系思想与主体功能区划分;空间分析与大数据结合,进行预测性研究。 |
2.1 古代时期
该时期始于先秦而止于1840年第一次鸦片战争。始于春秋战国的历史典籍常常包含有丰富的地理描述,其经济地理思想主要包括:
(1)经济活动不同产业(如作物种植、畜牧业、自然物产、矿藏及采矿业、仓储、漕运等)的发生地及其各地差异(见《山海经》《管子》《禹贡》《史记》等)。也有一些文献的记述,隐含有经济活动与地理条件的关系和经济地理区划思想(如《史记·货殖列传》《齐民要术》)。尽管几千年变化很大,但主要思想是人类如何通过对自然环境的适应和有限利用进行经济活动。古代时期人类的经济活动以自然农业为主[10],自然农业以生物的自然再生产为基础,这种生产与地理环境,尤其是气候、土壤、地形等,关系密切。这一时期的经济地理思想突出表现在人类利用不同的自然地理条件和自然资源,进行适宜的作物种植[20-21]。在对不同地区资料收集与分析的基础上,2000多年前人们就进行土壤分类[22]以及地理分区[27-28]。古人的土地研究思想被承继发扬,一直发展到现代经济地理中的土地利用和空间规划。
(3)区域综合研究思想。作为记述各级行政区域的综合著作,地方志蕴含着可贵的经济地理内容,包括所记述的自然资源情况(如煤、铁、金、银、铜、锡、石油、天然气、井盐等),土产、特产情况(如谷、蔬、菌、果、花、木、药、羽、毛、鳞、食货等)。局部地方志书源于东汉[4,8],唐代以后,地方志中加入地图,给这种思想以直观的表达[2],到南宋发展较快,其记述也更加详细,甚至带有地理位置说明[7]。它不仅提供了所记述地区经济地理的珍贵史料,还有地域经济活动特征及区域差异的阐述。随着历史的发展,人类经济活动覆盖的地域范围逐步扩展,经济活动种类也逐步增加,地方志中相关记述对各个地区开发过程、经济活动扩散及经济空间联系思想发展也具有重要意义。
(4)经济地理研究中的考察思想。《穆天子传》描述穆王出游沿途的交通等地理情况[26]。西汉张骞探险考察了中国西北及阿富汗、巴基斯坦以及土库曼斯坦等国的山川地势、交通及市场货物[27]。东汉班超出使西域、东晋的法显、唐朝的玄奘、宋末的丘处机等游历西部、北部和南部边境国家并有重要记述[28-29]。唐代的玄奘游历110个国家和地区描述其各地面积、都城、地形、水利、农产、服饰、货币等地理内容[30-31]。15世纪郑和对南亚和印度洋沿岸一些国家探险考察[32]。17世纪徐霞客按照中国古代科学所倡导的务实精神从事地理考察,所记述的经济地理现象包括矿产、手工业、居民点、物价等。他还提出人类活动对自然的影响,如太和山森林之所以保存,是“盖国禁也”;嵩山、少室山之所以无森林,是因为“樵伐无遗”[33]。英国著名学者李约瑟曾称“他(指徐霞客—引者注)的游记读来并不像是17世纪学者所写的东西,倒像是一位20世纪的野外勘测家所写的考察记录”[34]。
2.2 近代时期
近代经济地理思想中首次提出中国区域发展的战略。孙中山在《实业计划》中提出,以北、东、南3个世界级大港为中心,将中国划分为3个经济区。在每个经济区建立一个经济中心。通过水系和铁路系统,带动全国发展[16]。该思想对于之后中国经济地理格局产生重要影响。
2.3 现代时期I:1949—1978年
该时期是中国历史上计划经济起完全主导作用的时期。在总体上,该时期的经济地理研究带有深刻的苏联烙印。学者以服务国家需求为唯一方向,通过自然条件、自然资源的评价、产业布局的研究,积累理论基础。其经济地理思想可以概括为:
(3)产业布局理论。农业地理集中于农业区划研究,区划的基本原则包括:① 农业生产与农产品需求相结合;② 合理利用自然条件并考虑改造自然的可能性;③ 农业生产地域分工与综合发展相结合;④ 合理利用劳动力资源;⑤ 农业生产原有基础的利用和必要的改造;⑥ 保持一定的行政区划完整性但不完全局限于现有区划[48]。其主要思想体现了利用地理条件特点确定农业发展方向。
2.4 现代时期II:20世纪后期
该时期从1979年到20世纪末,为中国历史上非常特殊的转折阶段。改革开放改变了完全计划的经济体制。家庭联产承包责任制促进了农村商品经济的发展,带来了乡镇企业兴起。企业在市场经济中的主体地位逐渐显现出来。国家对经济管理权逐步下放,不断缩小指令性计划[19]。为了吸引外商投资,先后设立经济特区、沿海开放城市、沿海经济开放区以及一些沿边和内陆省会开放城市,国家或地区经济出现高速增长。与此相应,这一时期的经济地理思想有以下特点:
(1)区域不平衡发展战略思想。邓小平的“两个大局”③(③ “两个大局”是指东部沿海地区加快对外开放,使之先发展起来,中西部地区要顾全这个大局;当发展到一定时期,国家要拿出更多力量帮助中西部地区发展,东部沿海地区也要服从这个大局[18]。)思想是该战略的核心。在经济地理学术界,刘再兴等[53]提出“立足沿海、循序西移、中间突破”,陈栋生[54]提出“东靠西进,逐步展开”等观点。胡序威主持完成国家自然科学基金首个人文—经济地理重点项目,研究发现到20世纪末,沿海城镇密集区经济集聚和扩散均存在,但以集聚为主要倾向[55]。陆大道等研究发现90年代以来区域经济绝对差距不断扩大,建议应减缓其加剧趋势[49]。
(3)经济发展空间格局理论。陆大道的“点—轴”渐进式扩散以及逐渐完善的“点—轴系统”理论[62],科学阐释了经济空间形成机理,是经济活动空间演化规律的重要探索,对于不同等级的国土空间规划具有重要指导作用。在具体表现形式上,由于地理发展条件差异,经济空间结构可以呈现不同形式。根据东部海岸带和长江沿岸带的条件,陆大道提出了国土开发和经济布局的“T”型空间格局[63],被写入《全国国土规划纲要》(1997年草案)和23个省、自治区的国土规划。陆玉麒[64]提出一些特殊地理条件下形成的“双核结构模式”。魏后凯[65]、覃成林等[66]分别提出网络格局和多级网络空间思想。在经济空间结构与自然地理的联系上,叶大年发现一个大区域的经济地理的对称分布,与自然地理的对称性有关[67]。这些开创性研究,推动中国经济地理学理论大步前行。
2.5 现代时期III:21世纪前20年
本时期中国经济地理发展环境条件有以下特点:经过20多年的快速发展,区域经济不均衡具扩大趋势;长期经济增长引起人口、资源、投资、体制等支撑要素出现新变化,经济发展进入转折期;城市群经济迅速崛起,已形成的或培育的城市群在国家经济中占主导地位;城乡差距明显,农村地区衰退状况令人关注。在交通设施上,高速公路、高速铁路增长迅速,高铁里程超过世界其他所有国家总和,速度引领世界;信息技术快速发展,信息化水平居世界前列,并快速运用于经济部门和人民生活中。与此相关,经济地理思想有以下特点:
该时期经济地理学发展中,有一些特色思路。如贺灿飞根据大量中国实际研究,在演化经济地理、政治经济地理、创新地理等方面提出了一些新思想[111]。王铮等对理论经济地理学进行了梳理,把演化经济地理理论与区域发展结合,提出区域进化学说[112]。在总结学科发展中,樊杰等指出中国经济地理学实践性成果很多,但对理论关注不够,批判性思维薄弱[113];刘卫东等对经济地理学理论进行了反思,强调其独特之处在于整体性思维,并提出一些非常值得大家认真考虑的问题[114]。此外,国内评价体系引入国际SCI和SSCI后,带来学者在国际上发表论文数量快速增长[115]。相应地,学者的研究方法和思维逐渐接近这些期刊偏好的西方评价标准。最近几年,中国强调论文要“写在中国的大地上”,开始加强国内评价及中文成果的分量,学者们开始中国特色的经济地理学探索[116]。
3 经济地理思想历史演化脉络
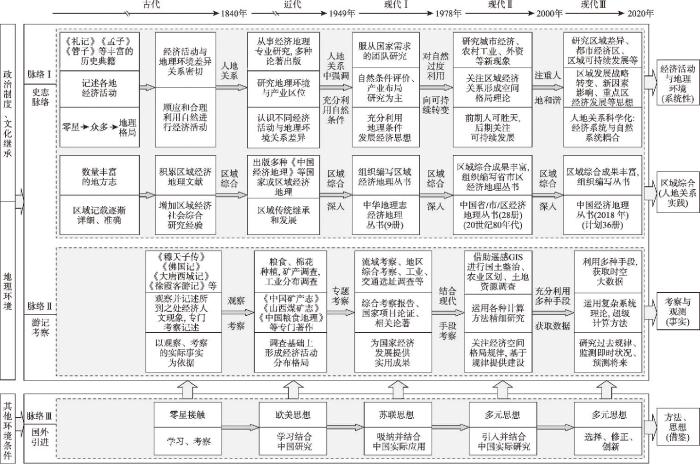
根据前后持续传承并形成主要经济地理思想轴线的原则,参考这些思想的主要来源文献以及其背后的研究考察工作特点,将其梳理为史志脉络和实地考察脉络。近现代以来其他国家经济地理思想的引入并结合中国实际的创新,可作为第3支脉络(图2)。
图2
图2
中国经济地理思想发展脉络
Fig. 2
Evolution threads of the ideas on Chinese economic geography
3.1 史志与人地关系思想脉络
该脉络以史志为载体,从经济活动差异到其与地理关系的研究,形成中国经济地理的思想主线。史志记载的早期思想以经济活动的地方差异为主,其历史延续时间很久。但对其原因的探究,就必然论及与地理环境关系。如《礼记·王制》中的“广谷大川异制,民生其间异俗”[23],含有地理环境影响不同区域经济形态、生活习俗和社会制度的观点。《孟子·公孙丑下》中的“天时不如地利,地利不如人和”[117],含有人定胜天的思想。《管子》中《地员》篇提到的“地者政之本也,辨于土而民可富”[24],《齐民要术·种谷第三》中的“顺天时,量地利,则用力少而成功多,任情返道,劳而无获”[21],含有顺应和合理利用自然进行农业生产的道理[118](图2脉络Ⅰ)。
中国古籍中,地方志体现的区域综合研究思想,不断积累经济活动与地理关系的经验研究。古代如此,近现代经济地理发展中也如此。如,20世纪50年代出版的“中华地理志经济地理丛书”(共9册),20世纪80年代的“中国省市区经济地理丛书”(共28册)以及正在陆续出版的“中国经济地理丛书”(计划36册)。在实际研究的基础上,学者进行理论总结形成区域经济地理学[119]。
从经济地理现象差异,到其原因的解释所形成的人地关系传统,在近代体现在工农业区位与地理环境关系研究中,在现代体现在自然资源评价、经济地理空间格局、主体功能区、区域可持续发展等研究之中。经济地理学发展中,人地关系思想一直作为学科命脉主线,愈来愈显示旺盛的生命力(图2脉络I)。且逐渐由认识自然、利用自然、改造自然(或过度利用),到对自然的可持续利用、人地和谐转变。其研究也由哲学层面的思考,逐渐深入到对两者关系的实际情况的认识,以及不同条件下两者关系演变的科学表达。
3.2 游记考察与事实获取及分析脉络
在地理学发展中,观测、考察作为信息获取的重要手段[120],对学科科学化起着重要作用。与史志脉络并行发展的,是来自于旅行记述的游记脉络(图2脉络II)。这支脉络强调实地考察和观测,从而形成对经济活动及其相关地理环境的形态、位置、功能及其变化的感性认识。从公元前的《穆天子传》[26]到公元4世纪的《佛国记》[29],再到唐代玄奘的西行记述[121]、明代郑和下西洋记述[32]和徐霞客游记[33],游记是中国地理学思想史的重要组成部分[4]。从经济地理角度,这些古代的游记是各种人文经济现象调查考察的最早形式。它们和近现代的考察和观测可以连成中国经济地理发展史中一支重要发展脉络。沿着这一脉络,人们得以观察和研究经济现象的地理格局,发现这种格局的形成规律。
游记脉络形成考察、记述和分析的传统,在近代和现代经济地理学发展中,不断发扬光大。20世纪50年代之后,中国地理学家进行大量自然资源综合考察工作[46]。1978年改革开放之后,伴随着遥感和地理信息技术的发展,借助现代计算科学和现代通讯科学,地理学家可以利用多种手段快速获取海量经济空间数据,并进行科学分析。尽管今非昔比,但其研究的思想逻辑具有一定的历史传承。
3.3 国外引进与多元思想本土化脉络
古代经济地理发展中,也有零星的国外接触。但在清初之前,国外思想的影响较小[4]。16世纪中叶,西方地理大发现的相关知识传入中国,对地理学研究(包括经济地理研究)有一定启发。1840年鸦片战争之前,传教士和商人已传播了一些西方地理思想。之后不少国外地理学著作在中国翻译出版。此外,中国一些有志青年,到欧美和日本留学,接受近代地理学教育,回国后从事教育和科学研究。人文经济领域侯仁之、吴传钧、鲍觉民、曹廷藩、李旭旦、周立三等曾于20世纪30—40年代在英国和美国留学,多数获得硕士或博士学位。他们将西方思想与中国社会经济实际相结合,引领20世纪后半期经济地理发展。
国外经济地理思想的引入,经历学习、消化、融合、改进、创新的过程。在20世纪上半叶,一些受教于西方的中国学者受法国学者地理环境决定论、人地相关论等影响,1935年白吕纳的《人地学原理》被翻译出版[122],中西不同来源的人地关系思想汇合。1949年后的一段时间内,苏联的经济地理思想在中国占主导。1978年改革开放以来,大批中国地理学者赴其他国家留学或交流访问,一些国外学者来华从事教学科学研究工作,地理学家可以更为便捷地学习各国经济地理思想。国外引进的多元化思想,被用于中国实践的研究,有逐渐本土化趋势(图2脉络III)。其中,区位论在一段时间内对中国经济地理学理论具有重要影响[123]。这些来自世界各国的经济地理思想,尤其是通过方法、技术及科学思维的贡献,催生解释中国特殊经济地理实际问题的创新成果,也促进传统的经济活动与地理环境关系思想逐步科学化。
4 中国经济地理思想发展趋势走向
4.1 历史发展走向
对经济地理区域差异的原因追溯,离不开各地地理条件和资源的差异。中国经济地理思想发展中,最为重要的是,在解释经济地理现象时提出人地关系思想。梳理几千年的中国经济地理发展脉络,可以认为,经济活动与地理环境的关系是经济地理思想形成和发展的“纲”。丰富的地方志文献所形成的区域综合研究,则进一步围绕这个“纲”,并通过不同类型区域特殊性的比较,使理论思考与丰富的实践结合起来。在经济地理学发展中,来自于游记的考察发现,尽管涉猎内容很多,但所发现的经济活动与地理环境的大量事实及考察者的感性认识,为人地关系的一般性和特殊性分析提供了可贵的基础。在中国地理环境条件下,不断发展的经济地理思想,多注意经济与地理所形成的系统的整体性、和谐性。而西方科学发展中对方法和技术的重视,可使整体思想与现代科学研究方法结合,科学地解释人地关系机理。国外引进的脉络中的演绎思维、空间分析、计量方法等,从实证角度,促进中国经济地理思想的新发展。中国经济地理思想的发展走向,是3支发展脉络的融合(图3)。在融合中,中国几千年形成的经济活动与自然环境和谐思想得以逐步强化。游记—考察—实地调研—遥感、大数据等现代技术手段获取客观数据的发展脉络,提供了这一思路的事实支持;国外引进的各种思维和分析方法,进一步加强经济活动与地理环境和谐思想的科学化和理论化。
图3
图3
中国经济地理思想发展走向
Fig. 3
Relations of the three threads of the ideas on Chinese economic geography
4.2 历史走向的国际比较
中国智慧与西方智慧所强调的思维逻辑有所不同[124-125]。相应地,中国历史文化根植下的中国经济地理思想发展中,着重考虑经济活动与地理环境相互作用的整体性。数千年历史发展的各个阶段的经济地理思想,都很注重经济中各产业发展与地理环境关系。与此相比,西方经济地理发展中,虽然早期受环境决定论的影响,关注地理环境对经济活动的重要作用,但很快就以区域差异研究、区位分析、空间结构等为重点,用逻辑推理和数学模型分析经济区位问题。尤其是20世纪以来,从规律分析到实证分析、行为主义分析,再到结构主义分析、文化与制度转向、演化经济地理等,在研究“术”方面不断走向精细。2008年以新经济地理学著称的克鲁格曼获得诺贝尔经济学奖,更进一步扩大了空间经济范式对经济地理学的影响。中西两种不同文化中发展的经济地理学,各有侧重。其互相学习,可促进经济地理学的发展。但经济空间差异的实质,在均质的地理条件下,经济规律起主导作用;其他条件下,地理条件差异对经济活动的排斥程度,与集聚收益的经济规律之间的权衡,决定着经济空间的分布。地理条件是经济空间格局的前提,经济规律是经济空间格局的动因。
长时期积淀,使中国和西欧等国在地理环境和经济动因两者权衡中,形成不同的分析侧重。中国国土广阔而地域差异巨大,使得在其中生活的人,首先是从全国整体角度对地理环境认识,排除条件恶劣地区,选择适宜环境。而西欧国家多数国土面积较小,地理环境差距也远小于中国,其对经济活动排斥程度较弱,促成其主流思维中对经济规律(动因)的重点关注。相应地,其经济地理研究,多从人类在某些阶段的行为动因出发,假设地理条件均一且决策者为理性经济人,推理出经济区位选择、经济格局集聚与分散的一般规律(图4)。这些研究所遵循的是自然科学的逻辑,所追求的是错综复杂的表象背后被简化了的本质因果关系:地理环境尽管复杂,其相互作用的本质具一般性;受长期文化积淀影响,人类行为虽也具有差异性,但对经济利益追求上,具有共同之处。根据还原论思维,可以把复杂现象打碎成基本因素,把高层次的现象看作更低层次现象的组合,用低层次的规律解释高层次现象[126]。西方经典区位论以及新经济地理研究,均依据还原论的方法,取得许多标志性成果。但是,随着经济地理研究视野的扩大,在全球尺度上人们面临更大的地理环境差异。同时,适宜经济集聚地区的经济高度发展,导致资源环境劣化,从而转向从人地系统角度考虑经济活动区位及其空间格局。从长远观点看,基于中国文化背景所形成的经济地理整体思想将逐渐显示优势(图4)。
图4
图4
经济地理思想变化趋势
Fig. 4
Development trend of the ideas on Chinese economic geography
但从另一方面看,任何科学规律,均是在一定条件下成立的。经济地理学为自然科学与社会经济科学的交叉学科,其主要理论更受制于特定的条件。如果一个国家经济地理活动空间格局形成机理与其他国家不同,应该产生这个特定条件下的经济地理理论。与西方经济地理学所追寻的“一般规律”对应,这是一个寻求一定类型条件下适应的规律,或称“条件规律”的思维(图4)。如前所述,中国经济地理学注重“人地和谐”,所探求的目标是经济活动空间格局受地理环境影响的机理。进而,中国强大的政府力量,以及各级政府主要对上级负责、文化传统中人们对政府的依赖,使得政府有能力决定国有经济的空间格局,影响其他所有制企业的区位,形成中国特色的“环境条件”和“经济空间格局”的关系规律[116]。这一规律有中国的历史传统(古代当权者有谋划经济活动的传统[15]),更有中国的现实事实依据。随着人们对西方经济地理学理论实质的进一步了解,以及不同类型区域环境条件重要性的认识加深,中国及其他具有独特环境条件的国家,将会逐渐重视“条件规律”的研究。进而,在中国这样的大国之内,不同类别区域的经济地理“条件规律”研究,也将成为另一个重要研究方向。
4.3 问题反思
(1)中国经济地理研究中的问题:如果我们把中国几千年的经济地理思想发展,与经济地理学的研究现状联系起来,同时把中国经济地理思想放在国际坐标系中观察,会发现一些值得思考的问题。① 中国经济地理学研究中,非常重视经济地理现象描述,对其原因解释,尤其是上升到原理层面的解释不够④(④ 詹姆斯等在《地理学思想史》中谈到,中国传统地理学“偏重于所观察的事物和过程,较少理论的公式”(普雷斯顿·詹姆斯, 等. 地理学思想史. 李旭旦, 译. 北京: 商务印书馆, 1989: 74)。)。尤其是长期形成经济现象与地理环境关系机理的科学发现,还在期望之中。② 中国经济地理学的现实需求导向研究多,学科问题导向成果少;在政府需求导向中,对相关战略解释性研究较多,建设性批评或纠编性研究少[114]。③ 与前两个问题关联,中国经济地理学较多关注现实状况研究以及对过去事实的变化分析,但对未来仍起作用的基本原理,以及用这些原理进行预测性研究少。④ 与西方关注一般规律的传统不同,近几十年中国经济地理学利用各种方法的经验研究成果多,思想类成果少[113]。
(2)经济地理思想史对未来研究的启迪:研究思想史可从长期趋势上启迪当下研究,最为重要的有以下两点。① 注意经济现象与地理环境之关系规律性研究。作为中国几千年传承的核心研究领域,人类经济活动与地理环境关系的科学精细研究,非常具有前景。中国的特殊国情,中国不同地区的差异,可以在条件规律研究中有新的发现。未来研究方法的创新,也会有助于在该研究上获得突破。② 鼓励有思想性的研究,培育批判性思想。坚持批判性思维,才能在研究中发现前人肩膀的位置。把前人最高点作为自己的起点,才能走得更高。在肯定中国传统经济地理思想中整体性和辩证思维的同时,要承认还原论以及演绎思维在发现已有研究存在问题的重要性。从不同逻辑视角对已有研究的质疑,对中国经济地理学发展至关重要。
致谢
感谢匿名评审专家非常有见地的评审意见,感谢贺灿飞、龚胜生、汤茂林、孙俊等教授对论文初稿的修改建议,感谢河南大学、河南财经政法大学图书馆在文献收集中的帮助。
参考文献
Development evaluation and new framework proposal of economic geography
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201310010
[本文引用: 1]

This paper examines the development of economic geography and proposes a new framework for further development of this research area.Previous studies on economic geography placed too much emphasis on practice of several developed countries,geographical background of several economies,and fundamental principals of economics rather than on geography.By overcoming this weakness,this study proposes a new framework of economic geography which is specifically situated at the special geographical context of Chinese economic development.This framework attempts to stress on special relationship among population,resources and environment,on special relationship between government and society,on special cultural tradition,and on special academic philosophy.Compared with current main steam economic geography,economic development,man-land harmony, important role played by government,inter-regional relationship among regions under national territory,and close links with physical geography,become foci in this proposal.Moreover, methodologies of both scientific research and social science research are imbalanced.Six important issues under this framework are suggested in Chinese economic geography:(1) changing economic geography after fast economic growth during the past several decades,(2) geographical consequence of involving or overcoming the middle-income trap at both the national and regional levels,(3)regional development and spatial structure of economic actors(enterprises,households and non-government organizations)with strong government intervention,(4)coordinated development among agricultural modernization,urbanization, industrialization and informatization,(5)man-land harmony and regional development,and (6)evolution of spatial patterns of rural settlements during the long history and recently under rapid rural-urban migration.China is a big country with many unique factors affecting economic development,thus,economic geography in China deserves much more attention in the discipline of economic geography in the world.
经济地理学发展审视与新构思
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201310010
[本文引用: 1]

分析了现今国际经济地理学发展中基于少数发达国家的经济发展、基于少数国家地理背景、基于经济学原理的偏颇,提出基于中国特殊的地理环境、特殊的人口、资源、环境关系、特殊的政府与社会关系、特殊文化、特殊的学科背景建立中国特色的经济地理学。中国特色的经济地理学应侧重经济社会发展、侧重人地和谐,侧重政府的特殊作用、侧重国内区域间关系与全球的影响、侧重与自然地理的关系,在研究中注重自然科学方法与社会科学方法的兼顾。中国持续高速增长的经济地理研究、中等收入陷阱的国家与地区跨越、政府特殊作用下的区域发展、城镇化、信息化、工业化与农业现代化关系、人地和谐与区域发展、农村聚落格局的演变趋势等,均可作为重要的研究问题。
Development of Chinese economic geography in recent 50 years
50年来我国经济地理学的发展
The development of Chinese economic geography: A review on papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica from 1934 to 2013
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408006
[本文引用: 1]

Papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica are academically regarded as of high quality, speciality and practice-oriented studies. Reviewing these papers can help us better sketch the contours of the development of economic geography in China. This article examined 421 economic geography papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica from 1934 to 2013 based on the number of papers, evolution tracks, research paradigm, topics, and the development of sub-disciplines, and concluded that economic geography research in China has made considerable progress. But this progress remains uneven among sub-disciplines of economic geography. It has shown a close link to new issues in economic development, changing from studies on economic growth to sustainable development, from studies pertinent to nature elements to those pertinent to anthropogenic elements, and the study areas having shifted from industries providing tangible goods to economic activities on services aspects. Sub-disciplines focused on regional, industrial, and agricultural studies before the 1980s, while a growing number of papers have since then been published on transportation, service industries, and urban studies. Research ideas in the 80 years originated from various sources, leading to research by using multiple spatial scales and dynamic quantificational methods. In summary, Chinese economic geographical research has always stood close to the nation's requirements, leaning towards macro studies, economic growth, and practical characteristics. However, studies at the micro scale, with comprehensive features and theoretical deductions are emerging increasingly.
从《地理学报》看80年的中国经济地理学发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408006
[本文引用: 1]

《地理学报》发表的论文具有“高、精、特、实”的特点,评述《地理学报》的经济地理学论文可更加简洁地勾勒出经济地理学的整体“骨骼”。本文基于80年来《地理学报》发表的421篇经济地理论文,从论文数量、发展脉络、研究范式、面向国家需求、学科发展变化等方面梳理了中国经济地理学发展,总结了相关研究特点。论文统计表明,经济地理学研究不断发展,各学科发展很不均衡。呈现密切联系经济发展中的新问题、从经济增长研究转向可持续发展研究、从与自然关系密切的要素研究转向人文要素的研究、研究领域从注重物质生产转向非物质领域等特征。分支学科发展侧重于区域、工业和农业,但交通、商业服务业、城市等也呈增长趋势。学术思想来源多元化、研究尺度多样化、研究方法定量化。总的来看,中国经济地理学呈现出紧密服务国家需求、侧重宏观研究、侧重经济增长、侧重应用型研究的研究特点,但在微观研究、综合研究、理论凝炼方面逐步加强。
The historical evolution, current characteristics and development strategies of economic geography in China
我国经济地理学历史沿革、现状特征与发展策略
My view of history of scientific thinking
我所理解的科学思想史
The analysis of Chinese geographical history research path: From science history to intellectual history and the shift of geographical traditions
中国地理学史研究的理路分析: 兼论中国地理学传统的流变
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201403017
[本文引用: 2]

中国地理学史研究历程的考察表明其具有一定阶段性——从科学史研究到思想史研究:①20世纪40-80年代主要是科学史研究,建构了中国古代地理学的知识体系和学科体系,经历了梳理知识体系、建构学科体系和彻底重构学科体系三个阶段;②80年代后的思想史研究阶段是对科学史研究的深化,一方面建构了地理学科学方面的思想体系和“元问题”系统研究,另一方面对中国古代人文地理学思想给予了重新建构和评估。由此同时尝试回答中国地理学传统的流变,大致历程是:①公元前具有关注人文世界和注重考察、研究自然的传统;②公元前后到19世纪中叶这段时间以关注人文世界为主,考察和研究自然的传统有所弱化;③19世纪中叶以来中国地理学传统与欧美地理学传统有深厚渊源关系。同时也说明了中国古代有地理学,其传统与欧美地理学既有共通之处,又有所差别。
Research on the thought of economic geography in Yugong
《禹贡》经济地理思想研究
The progress of Chinese geography in the past two decades
近二十年来中国地理学之进步(三)
DOI:10.11821/xb193601006
[本文引用: 2]

近年中国人类地理之研究,亦取分工合作之法,其一用地质学之方法,搜寻原人踪迹;其二用考古学之方法,推证远古文化;其三用人类学之方法,测验华人体性;其四用民族学之方法,调查初民生活;其五用语言学之方法,厘定方言区域;其六用医药学之方法,探究疾病分布。
Comment on theory of location of industries
工业区位的理论与中国工业区域
DOI:10.11821/xb194400002
[本文引用: 3]

一、绪言在正统经济学中,区位问题常被忽视。经济学的理论对经济事实的性质分析精详,但对它们的区位却不加深究。其实,经济事实是生根在地上的,研究它们的如何(How),与研究它们的分布在何处(Where),实属同样重要。前者是纯粹经济学的任务,后者则为经济地理学的范畴。
Evaluation of pre-war industrial location: Location of industrial construction
DOI:10.1111/1468-0041.00042 URL [本文引用: 1]
战前工业区位的评价: 工业建设的区位问题之二
The urban geography of Chungking
重庆都市地理
DOI:10.11821/xb194300006
[本文引用: 1]

一、引言重庆为一江畔山城,位於四川盆地东部,扼长江与嘉陵江两江之交,向为我国西南各省中之最大商埠;亦川束门户也。民国二十六年七月抗战军兴,十一月国府西迁,重庆以天然位置优越,形势巩固,遂跃为战时首都,六载以来,领导抗战建国大业,蔚为国际政治重心。
Agricultural regions of China
DOI:10.11821/xb193601001
[本文引用: 1]

Various attempts have been made to divide China into regions of agricultural significance. Both the divisions of Nyhus and Cressey are not very satisfatory. According to my recent study, China may be divided into nine greater agricultural regions which are quite similar to the climatic regions of Co-ching Chu.
中国之农业区域
DOI:10.11821/xb193601001
[本文引用: 1]

我国幅员辽阔,全境面积,计达一千一百余万方公里,约与欧洲全洲面积相当;惟欧洲纬度,介于北纬三十五度至七十度之间,南北狭而东西宽,全洲各地气候差别不多;我国国境,位於北纬十五度至五十五度之间,纬度延长,计较欧洲多出五度.
Thirty years of discussions on the basic theory of economic geography in the People's Republic of China(1950-1979)
三十年来我国经济地理学的基础理论研究
Special research fields and future tasks of geography
地理学的特殊研究领域和今后任务
The evaluation of natural conditions in economic geography: The preliminary summary on 1962 Academic Meeting of Economic Geography Professional Committee
经济地理学对自然条件的评价: 中国地理学会经济地理专业委员会1962年学术会议讨论初步总结
Evaluation of natural conditions in economic geography
经济地理学中的自然条件评价问题
Some problems on the allocation of transport in industrial bases
工业基地交通运输布局问题
DOI:10.11821/xb198102004
[本文引用: 1]

交通运输对地区资源开发,工业基地的形成与发展具有重要作用,对地区内城市的分布也有很大影响。在地区发展和工业基地建设中除了各个部门按系统进行规划与布局外,还必须在地域范围内从多方面加以综合平衡,交通运输是其中之一。
Several problems on the development and allocation of transport in China
当前我国交通运输发展与布局中的几个问题
On the distribution strategy of China's productive forces
论我国生产力布局战略
Land development and regulation zoning and production layout
国土开发整治区划和生产布局
Types and basic functions of land (renovation) planning
关于国土(整治)规划的类型及基本职能
A theoretical development of territorial planning: On the study of regional structure
DOI:10.11821/xb198903002
[本文引用: 1]

Reginnal structure is defined here as the spatial combination of the natural, ecological,economic and social structures of a region. It can be divided into some subsystems. Sinceterritorial plannings are usually made in certain regions, the study of regional structure beco-mes an important theoretical work for geographers to do in territorial planning.The study of regional structure should be concentrated in:1. The characters of regional structure. Comprehensive analysis and generalization fromquality to quantiiy.2. The mechanism of regional structural changes. Under the conditions without outerinfluences or with strong outer influences from macro-en-vironment.3. The openness of regional structure. Orderly relations existing among relevant regionswith open unbalanced structure.4. The development stages of regional structure. division in time and space.5. The rationality of regional structure. From five aspects.The study of regional structure can help us to understand the function and differences ofregiona and give scientific basis for defining the utilization dircction of territorial resources,determining the scale and direction of economic development as well as the adjustment of mac-ro-distribution, and planning the industrial structure in accordance with economic performingmechanism a and urban systems.
国土规划的理论开拓: 关于地域结构的研究
DOI:10.11821/xb198903002
[本文引用: 1]

Reginnal structure is defined here as the spatial combination of the natural, ecological,economic and social structures of a region. It can be divided into some subsystems. Sinceterritorial plannings are usually made in certain regions, the study of regional structure beco-mes an important theoretical work for geographers to do in territorial planning.The study of regional structure should be concentrated in:1. The characters of regional structure. Comprehensive analysis and generalization fromquality to quantiiy.2. The mechanism of regional structural changes. Under the conditions without outerinfluences or with strong outer influences from macro-en-vironment.3. The openness of regional structure. Orderly relations existing among relevant regionswith open unbalanced structure.4. The development stages of regional structure. division in time and space.5. The rationality of regional structure. From five aspects.The study of regional structure can help us to understand the function and differences ofregiona and give scientific basis for defining the utilization dircction of territorial resources,determining the scale and direction of economic development as well as the adjustment of mac-ro-distribution, and planning the industrial structure in accordance with economic performingmechanism a and urban systems.
Academic value of "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction" and our research in recent years//The Editorial Group
“人地关系地域系统”理论的学术价值与近年来我们的研究进展. 《纪念吴传钧先生诞辰100周年文集》编辑组
An analysis of spatial structure and optimal regional development
DOI:10.11821/xb200102001
[本文引用: 1]

This paper is a further analysis of the “Pole Axis Theory” and related “T shaped” spatial structure of the industrial allocation in China, which was developed by the author a decade ago. It starts with an analysis of the relationship between different types of spatial structure and regional development, and of how to achieve optimal regional development through optimal spatial organization as well. Then, based upon existing theories and practices in China, it discusses the formation of the “pole & axis” system by disclosing the evolution of socio economic organization and demonstrates that such a system is the most efficient spatial structure that can lead to optimal regional/national development. Lastly, the paper concludes that the strategy of a “T shaped” spatial structure of industrial allocation, which is an application of the “Pole Axis Theory”, has played a very important role in the spatial economic development in China in the last decade.
论区域的最佳结构与最佳发展: 提出“点—轴系统”和“T”型结构以来的回顾与再分析
DOI:10.11821/xb200102001
[本文引用: 1]

通过阐述各种型式空间结构与发展之间的关系及如何通过区域的最佳组织使其达到最佳发展,从理论和实践的结合上论证了社会经济空间组织的客观过程和“点 -轴系统”的形成,说明“点 -轴系统”理论可以导致区域或国家的最佳发展,因而该系统是最有效的区域开发模式。根据对十多年来我国区域发展实践效果的分析,指出“T”型结构的战略对我国发展起到了巨大作用。
Research on regional development theory
区域开发理论研究
The symmetrical distribution of the cities in China
中国城市的对称分布
The research about an indicator system of sustainable development in Shandong province
DOI:10.11821/yj1996040003
[本文引用: 1]

Shandong is one of the fast developing provinces in the coastal area,and it also is a typical representative in the aspects of natural conditions, regional disparities and impending problems such as population, resources and environment.In the paper, the basic principles to establish an indicator system of sustainable development were studied (scientific principle, practicable or operatable principle, estative principle, perfective principle and dynamic principle).Based on the analysis of the provincial characteristics of Shandong, the strategic thinking for sustainable development was brought out.① Sustainable and fast development should be stressed.② Coordination and soundness in social system should be guaranteed.③ Special considerations should be given to rational resources exploration, ecological environment protection and management.④ Sustainability should be emphsized.The indicator system of sustainable development in Shandong province consists of 3 estates, 4 kinks, 15 groups and 90 indicators, in which, the economic growth kind divides total amount, intensivity and effectivity as 4 groups, 18 indicators; the social progress kind makes population index,living quality, social stability and social ensurance as 4 groups 30 indicators; the sustainance of resources and enviroment contains resources index, pollution index, environmental harness index and ecological index as 4 groups 26 indicators; the sustainability kind includes economic ability, intelletual capacity, environmental resources capability and mangement ability as 4 groups 16 indicators.After the analysis with the AHP method, the proportion of each kind and group was got as follows: economic growth,32 points; social progress, 28 Points; resources and environmental sustainance, 22 points; sustainability,18 points.Finally a comprehensive index was sumed up with their proportions, it was used as an assessment for Shandong's development.According to the assessment,the superhigh economic growth in the past 16 years was a result of large investment,large amount consumption of labour and resources with a result of lower economic benefits and a damage to ecological system and environment, so it could not accommodate the need of sustainable strategy.In the coming 15 years,its sustainable developmental target should coordinate society,population, resource use and environmental protection.That is,the economy should increase appropriately; living conditions should be improved 1 population increase should be controlled effectively;resources.exploration should be reasonable and ecological environment should have a recycling development.
山东省可持续发展指标体系初步研究
DOI:10.11821/yj1996040003
[本文引用: 1]

山东省作为我国沿海地区经济发展较快的省区之一,无论从自然条件、经济发展的区域差异,还是从当前发展中所面临的人口、资源及环境问题,在全国均具有较强的代表性与典型性,可作为研究中国可持续发展的一个“缩影”.本文探讨了建立可持续发展指标体系的基本原则、山东省实施跨世纪可持续发展战略的主要思路,在此基础上提出了指标体系的基本框架及实际应用。
A preliminary analysis of rural economic types in Jiangsu province
DOI:10.11821/yj1989030010
[本文引用: 1]

In this article a classification of rural economic types in Jiangsu Province is carried out by coefficient of mode ratio on the basis of 1980 statistics. The following indexes are used for classification.1. Gross rural social product per head of rural labour, 2. Percentage of rural labour with non-agricultural occupation, 3. Net income per head of rural population, 4.Pencentage of rural industy in gross rural social product, 5.Ratio of rural industrial and agricultural output value, 6.Percentage of crops farming in gross agricultural output value, 7. Ratio of crops farming and stockraising plus fishing output value.As the result 65 counties of Jiangsu Province are divided into 8 rural economic types.Ⅰ.Developed industrial type, Ⅱ.eveloped industrial-agricultural type, Ⅲ.Medium developed industrial-agricultural type, Ⅳ:Medium developed agricultural-industrial type, Ⅴ.Less developed agricultural-industrial type, Ⅵ.Less developed agricultural type, Ⅶ.Least developed agricultural, industrial type,.Ⅷ.Least developed agricultural type.Some of types are subdivided into subtypes 1 (with more diverse agriculture) and 2 (with less diverse agriculture).
江苏省乡村经济类型的初步分析
DOI:10.11821/yj1989030010
[本文引用: 1]

本文采用模比系数法,按乡村经济发展水平、产业结构和农业结构三类指标,将江苏省65个县(县级市)划分为8个乡村经济类型(含12个亚类型),以便为乡村发展的宏观决策和分类指导提供参考,为开展江苏乡村地理的选点调查打下基础,对乡村经济类型的研究方法作初步尝试。
An analysis of the economic features and regional difference of China's rural industrialization
DOI:10.11821/xb199605002
[本文引用: 1]

Before the reform, the industrialization of China took the way of "taking the cities as key areas and the investment from the state as the main resource for industrial construction".In 1978 the industrial output value of rural area accounted for only 9% of that of the whole of China. In the recent 10 years, the economic structure in rural China has gradually changed and the industry has become the main body.Of the total economic volume,the industrial output value increased from 19% in 1978 to 57%,Which was 41% of the total industrial value of China.The development of industry in rural areas was the significant characteristic of Chinese industrialization in this stage. The correlation analysis indicates that the rural industry is the base for the rural economic prosperity. The ocrrelation coefficient reached 0.985 in 1992 compared to only 0.729 in 1980. The results of the field work in 7 towns of 6 provinces have proved this correlation with regard to two aspects.First of all,the rural industry by turning over profit (10% of the net profit of the enterprise) and management fee (5% of the sales income) and social expenditure(10% of the profit) contributed to the town construction; secondly,in general the income of workers in township enterprises was 2 to 3 times higher than that of local peasants and 79% of them had a monthly income between 100 and 250 Yuan RMB.There is a great regional difference in the development level and distribution of rural industry.In 1980 the gravity centre of me rural industry was located at 116,13E and 33.08N,which was in the middle of Anhui province.The development between eastern areas and western areas was seriously unequal and the deviation coefficient was 1.15. The gravity centre moved continuously towards East until 1988 and the deviation coefficient reached its peak with 1.28. The rural industrial output value in the coastal provinces amounted to 74% of the total China. After moving North for one year the gravity centre has moved towards South continuously till 1992 which resulted in a decreasing difference between the East and the West and a slight increase of difference between the North and the South. The degree of deviation has kept stable. From the proportion of rural industry in rural economy and the proportion of rural industry in total provincial industry can we see that most of the provinces in the hinterland had a relatively backward rural industry.
中国农村工业化的经济分析及省际发展水平差异
DOI:10.11821/xb199605002
[本文引用: 1]

本文以7个建制镇的农村工业发展的实地调研为基础,对比研究我国乡镇工业发展的一般特点和共性规律,比较深入细致地探讨了以镇区农村工业为主的乡镇企业产生和发展的机制、农村工业发展在农村现代化进程中的作用、农村工业化水平的地域差异性等问题。
Analysis framework of the impact of high-tech industrial development zone on regional development
高新技术产业开发区对区域发展影响的分析构架
Transnational corporations and their impact on regional economic imbalance: Evidence from China
DOI:10.3828/twpr.20.4.043570528305p5q3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Inter-firm linkages and regional impact of transnational corporations: Company case studies from Shanghai, China
DOI:10.1111/j.0435-3684.1999.00049.x URL [本文引用: 1]
The development of economic geography and its function on strategy consultation
经济地理学的发展及其战略咨询作用
High-quality development of national territory space governance and regional economic layout during 14th five-year plan in China
我国“十四五”时期高质量发展的国土空间治理与区域经济布局
Discrimination method and its application analysis of regional transport superiority
中国区域交通优势的甄别方法及应用分析
Economic geography for spatial governance
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408007
[本文引用: 1]

Economic geography is a discipline that studies geographical practices in the real world and plays an important role in supporting the state's strategic decision-making on spatial development and helping to understand spatial issues and solutions in contemporary society. Thus, the discipline's vitality lies with its capability to satisfy the demands of the state and society. At present, the development of economic geography in China is facing two critical challenges or opportunities. First, the Communist Party of China, the ruling party, lists modernization and enhancement of national governance capability as a major target of deepening reforms in China, which indicates reforms in the country are moving from target-oriented (i.e., crossing the river by feeling the stones) to institutional building and capability enhancement. Second, recently the International Council for Science and the International Social Science Council co-launched a large scientific program, i.e. the Future Earth, which calls for inter-disciplinary research for managing the Earth's environment and moving towards sustainable development, and China has established its national committee on Future Earth. The program emphasizes the connection of research to decision-making of both the state and society. Against these two opportunities, this paper suggests an economic geography for spatial governance to lift the discipline's capability to engage with the state and society. Then the paper gives a general discussion of the political, administrative and cultural basis on which China's unique governance structure has developed, as well as a general picture of major tools that the Chinese government has taken for spatial governance, including planning, land, Hukou, and fiscal and tax systems. This paper argues economic geographers can do a better job only if they have a better understanding and theorization of China's national governance structure although they were inclined to do research either at local and global scales or global-local connections and ignored the national scale in the past.
经济地理学与空间治理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408007
[本文引用: 1]

经济地理学是一门研究真实世界的学科,在社会实践中发挥着重要作用。满足国家和社会的需求,是这个学科发展的生命力所在。针对当前全面深化改革的新形势以及“未来地球”计划的提出,本文倡导开展面向空间治理的经济地理学研究,提高该学科服务于国家战略决策的能力。之后本文阐述了中国空间治理的政治文化基础;分析了中国空间治理的主要手段,包括规划体制、土地制度、户籍制度和财税体制。本文认为,只有客观、全面地观察中国的空间治理体系,并将其理论知识化,才能使经济地理学研究具有更大的科学价值和实践意义,也才能为国家提高空间治理能力提供科学支撑。
Characteristics of clustering and economic performance of urban agglomerations in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201404004
[本文引用: 1]

The 11th Five-Year Plan (2006-2010) states that city agglomerations should be regarded as the main form of urbanization, and the 12th Five-Year Plan (2011-2015) puts more emphasis on improving the structure of city agglomerations to promote urbanization in China. It means that city agglomerations have been and will still be the major region into which the population and other economic elements concentrate in China. More importantly, the spatial structure of city agglomerations would have an important influence on the quality and level of urbanization through affecting economic performance. This article aims to examine the clustering of China's urban agglomerations and find out the relationship between economic clustering and growth rate of urban agglomerations. Our data are obtained from Gross Domestic Production (GDP) and population statistics of 20 urban agglomerations of China from 1995 to 2010. The conclusions can be obtained as follows. (1) Generally speaking, it is evident that the degree of clustering of urban agglomeration has been ever increasing in the past several years. Although there is a relatively large gap in the degree of concentration between population and economy, the data shows a strong positive linear correlation between them. (2) The 20 city agglomerations can be classified into four groups according to their clustering characteristics. Gini indices and the proportion of GDP of primary city are employed to detect the clustering characteristics of city agglomerations. As a result of investigation, four groups include strong singe-center clustering; multi-centers clustering; weak singe-center clustering and weak centers clustering. (3) As the relationship between clustering of population and growth rate is still unclear, there exists an obvious inverted-U-shaped relationship between economic clustering and growth rate of urban agglomerations. The result further indicates that when Gini indices of GDP in large and medium-sized urban agglomerations are about 0.2 and the primary city's proportion of GDP in small urban agglomerations is about 65%, the fastest growth rate can be achieved in China.
中国城市群集聚特征与经济绩效
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201404004
[本文引用: 1]

城市群作为中国城镇化的主要载体,社会经济要素将会向城市群大规模的集中,人口和经济集聚对城市群的空间结构和经济发展产生重要影响。通过对1995-2010年间中国20个城市群人口和经济集聚程度进行研究,表明中国城市群集聚程度整体仍是一个增加的过程,且经济集聚度高于人口集聚度,两者呈现很高的线性正相关关系;进一步采用城市基尼指数和首位城市集聚度两种方法分别对城市群集聚程度进行测度和分析,认为20个城市群可以分为强单中心、弱单中心、多(双) 中心以及弱中心4 种城市群集聚类型;使用局部加权回归的方法对城市群集聚水平和经济增长率之间的关系进行探索性分析,发现城市群经济集聚度与经济增长之间关系整体上符合倒U型假说的特征,而人口集聚与经济增长没有表现出明显的规律性特征。
Identification of urban clusters in China based on assessment of transportation accessibility and socio-economic indicators
基于交通、人口和经济的中国城市群识别
The classification and analysis of areal topology in extended metropolitan area of Pearl River Delta
珠江三角洲都市经济区地域构成的判别与分析
Distributions of population and employment and evolution of spatial structures in the Beijing metropolitan area
DOI:10.11821/xb201206010
[本文引用: 1]

This study aims to examine the characteristics and changes of the spatial structure in the Beijing Metropolitan Area with the rapid urban growth and decentralization, through analyzing the spatial distributions of urban population and employment. To demonstrate the spatial evolution of population and employment distributions in the Beijing Metropolitan Area, we apply the nonparametric analysis in this study. Our study finds that the significant population and employment subcenters in the suburbs of the Beijing Metropolitan Area, characterized by the polycentric urban spatial structure. Since the 1980s, with the suburbanization of population, the number of population subcenters has increased in the Beijing Metropolitan Area, and the distribution of population subcenters has expanded from the inner suburbs to the outer suburbs. The overall trend toward the decentralization and polycentrification of population is evident, whereas the spatial extent of the decentralization of population is limited in the Beijing Metropolitan Area. Contrary to the decentralization of population, our study finds that the centralization of employment in the Beijing Metropolitan Area from 2004 to 2008 has led to the weakening influences of the outer suburban employment subcenters as well as the decline of the polycentricity of the spatial structure. This implies the spatial pattern of the Beijing Metropolitan Area may still be highly centralized, and the nature of the monocentric urban spatial structure may not be fundamentally changed. Meanwhile, the decentralization of population and the centralization of employment may lead to the overall jobs-housing imbalance. Therefore, to form the polycentric spatial structure, it is necessary to reinforce the agglomeration economies of suburban subcenters and improve the overall jobs-housing balance in the Beijing Metropolitan Area.
北京都市区人口: 就业分布与空间结构演化
DOI:10.11821/xb201206010
[本文引用: 1]

本研究应用非参数计量方法,实证刻画北京都市区人口—就业空间分布演化,揭示在快速城市化和城市增长背景下,北京都市区空间结构特征及发展趋势。研究发现,北京都市区人口和就业分布都呈现多中心空间结构。20 世纪80 年代以来,随着人口郊区化,北京都市区人口次中心数量不断增加,并由近郊向远郊扩展,人口分布呈现明显的分散化和多中心化趋势,但人口分散的空间范围还比较有限。与人口的分散化趋势不同,2004-2008 年,北京都市区就业仍呈现向心集聚的趋势,造成远郊就业次中心的影响不断被弱化,都市区空间结构的多中心性有所降低。这说明北京都市区的单中心或强中心结构可能并未从根本上改变,且人口的分散化和就业的向心集聚导致宏观面上人口—就业的空间失衡。北京都市区多中心空间结构的形成,需要强化郊区次中心的集聚能力,同时注重人口—就业的平衡布局,这是未来北京都市区空间结构调整的重点。
Spatial effects of high-speed rails on interurban economic linkages in China
高速铁路对中国城市空间相互作用强度的影响
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201412009
[本文引用: 1]

高速铁路作为一种新型的交通方式,其快速发展将会带来交通运输史上一次重大的飞跃,且其对区域空间结构、人口流动、经济联系和土地利用等的影响也越来越成为人们关注的焦点。在中国区域经济一体化进程不断加快的背景下,研究高速铁路对城市空间相互作用强度的影响,对加强区域间经济联系、促进区域经济发展和地域空间组织模式的重构具有重要意义。本文基于GIS网络分析工具,构建时间成本矩阵,研究中国333个地级行政单元和4个直辖市对外经济联系总量和城市对间经济联系强度的空间分布特征,构建无高铁、高铁现状和规划高铁三种情景,并对三种情景进行模拟与探讨。结果显示:① 城市空间相互作用呈现出明显的地带性和“廊道效应”,反映了高速交通在重塑区域空间结构中的作用;② 高速铁路建设提升了城市对外经济联系强度总量,且逐渐从追求“效率”转向“公平性”;③ 高速铁路建设缩小了全国城市对外经济联系总量的差异,但却扩大了城市对间经济联系强度的差异;④ 三大城市群成为城市对外经济总量绝对获益量最大的地区,而其毗邻的中小城市成为提升速率最大的城市。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Development of specialized villages in various environments of less developed China
DOI:10.11821/xb201206006
[本文引用: 1]

Theoretical framework on formation of specialized villages was proposed by using rational small household, division of labour and specialization and distance decay and neighbourhood affect theories. These theories from economics and geography determined the formation of specialized villages, but the types of the specialization are related to resources endeavor and environmental conditions of the villages. The paper illustrates the change of the economic structure of villages by applying mathematical models, stating that various geographical conditions surrounding a village leads to different marginal production efficiency, therefore forming specified production structure. If a village's environment proves suitable for certain production or service, then a relevant type of specialized village may emerge. Based on theoretical analysis, we use the census data of specialized villages in Henan Province in 2010, applying dummy variables representing 16 types of specialized villages, and selecting environmental variables such as landform, location, arable land area and labour force from a spatial database from government authorities. The regression results from the OLS models indicate a significant impact of village environmental conditions on village specialization: (1) more labour force leads to lower specialization; (2) abundant arable land benefits specialization; (3) the closer location to its county site results in higher probability of specialization on agricultural processing industry; (4) existence of a wholesale market may increase specialization on relevant villages, especially for agricultural processing and animal husbandry industries; (5) the villages located in hilly terrain show less probability on specialization than others, mainly caused by difficulties in transportation and shortage in arable land; while mountainous environment provides resources for the development of specialization. Results from qualitative models indicate diverse environmental impact in different types of specialized villages. Positive impacts of land availability are observed in tea plantation, tree nursery and fruit farm. Labour force assists the formation of labour intensive production such as floristry. Accessibility benefits specialization in fruit, vegetable production and floristry. Results of this study can be applied to policy making for guidance of specialization under various environmental conditions.
欠发达区地理环境对专业村发展的影响研究
DOI:10.11821/xb201206006
[本文引用: 1]

基于经济学和地理学中的“理性小农”、“劳动分工与专业化”和“距离衰减与邻里效应”理论,并考虑资源环境条件,建立了解释专业村形成机理和形成类型的理论框架。用数理方法推理了村产业结构的发展变化和专业村的形成。在理论分析的基础上,运用2010 年河南省的专业村数据,选择地形、区位、土地和劳动力等环境变量和16 类专业村的虚拟变量,使用最小二乘法进行回归,结果表明村环境资源条件对专业化率有显著影响:① 村劳动力资源越多,专业化率越低;② 村土地越多越利于专业化生产;③ 村离县级市距离越近,越有利于形成农产品加工专业村;④ 具有批发市场可以提高所有专业村的专业化率,对养殖业和加工业专业村更是如此;⑤如果其他环境相同,丘陵地区的专业化率比其他地区低;这主要与丘陵地区交通条件不畅、人均耕地较少等有关。采用定性模型分析表明:环境影响在不同类别的专业村有所不同。土地丰裕程度对茶叶、林业和水果种植等类专业村形成有正面影响,劳动力资源对花卉等专业村的形成产生影响;地域通达性对水果、蔬菜和花卉等时鲜产品专业村的形成产生正面影响。该研究结果的实践引申,在不同环境条件的地区,可以制定相应的适宜专业化发展的引导政策。
A study on the formation and evolution of specialized rural villages
农区专业村的形成与演化机理研究
The scientific foundation of major function Oriented Zoning in China
我国主体功能区划的科学基础
Spatial organization pathway for territorial function-structure: Discussion on implementation of major function zoning strategy in territorial spatial planning
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190865
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial organization law of territorial function-structure is the basic theoretical problem of human-earth system coupling research, as well as the basic theory of carrying out territorial spatial planning and shaping sustainable geographical pattern. Starting from the discussion of geography on the repetition, prediction, regulation and optimization of geographical processes, this paper explains that the spatial governance system is an important way for modern geography to regulate and optimize the sustainable geographical processes and patterns. The spatial and temporal evolution characteristics of the spatial structure of territorial function composed of ecological-life-production (also known as three living spaces) are adopted to express the spatial order law of territorial function - structure, and explain some spatial organization goals, e.g., the coordination between territorial function and natural geographical environment, the minimization of various functions and conflicts between different units in the same region, the effective transmission of territorial functions in different spatial scales, and the maximization of comprehensive benefits in a long time scale. On the one hand, from the perspective of sustainability, the concept of four attributes of natural elements -- resources, environment, ecology and disasters -- is proposed. Through the integration of the four attributes, the natural carrying capacity is constructed, and the function of the original value, remaining value and potential value of carrying capacity in spatial planning is analyzed, so as to form the basic method of analyzing spatial organization from bottom to top. On the other hand, starting from new spatial equilibrium, the basic method of top-down spatial organization analysis is formed based on the territorial functional suitability of carrying capacity, integrated position and spatial structure parameters. Furthermore, the basic and strategic values of the major function zoning formed by the two methods for spatial organization and planning are discussed, and a new idea of separation and interrelation of the zoning, strategy, system with planning of utilization is proposed. With the implementation of the strategy of major function zoning as the main line, the spatial scale-down conduction of major functions as the core scientific problem, and the key constraint parameters as the control indicators of spatial structure, this paper discusses the database and territorial function pedigree, functional and scale-dependent carrying capacity evaluation method and model, and the construction framework of "Three Zones and Three Lines" (Three Zones represent ecological space, agricultural space, and urban space; Three Lines represent ecological conservation redline, permanent capital farmland, and urban development boundary), and demonstrates the way to implement the strategy of major function zoning in spatial planning. Finally, the paper puts forward some suggestions that geography should strengthen the construction of scientific and technological support system, e.g., the basic theory, method and technology of large and medium spatial scale (regional) territorial spatial planning.
地域功能—结构的空间组织途径: 对国土空间规划实施主体功能区战略的讨论
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190865
[本文引用: 1]

地域功能-结构的空间组织规律是人地系统耦合研究的基本理论问题,也是开展国土空间规划、塑造可持续地理格局的基础理论。从地理学对地理过程的重复、预测、调控、优化的讨论入手,阐释了空间治理体系是现代地理学用于调控和优化可持续地理过程与格局的重要途径。采用生态-生活-生产等三生空间构成的地域功能空间结构呈现的时空演变特征,表达了地域功能-结构的空间有序性法则,阐释了地域功能与自然地理环境相协调、同一地域单元各类功能及不同单元之间冲突最小化、地域功能在不同空间尺度有效传导、以及长时间尺度综合效益最大化等空间组织目标。从可持续性出发,建立自然要素的资源、环境、生态和灾害四大属性的概念,并通过四大属性集成构成自然承载力,分析承载力的原值、余量和潜力在空间规划中的作用,形成自下而上解析空间组织的基本方法。从新空间均衡出发,基于承载力、融入位置和空间结构参量后构成的地域功能适宜性,形成自上而下解析空间组织的基本方法。进而讨论了集成两种方法形成的主体功能区具备的对空间组织与规划的基础价值和战略价值,提出主体功能区的区划、战略、制度和规划用途分离及相互关联的新思路。以实施主体功能区战略为主线、以空间降尺度传导主体功能为核心科学问题、以关键约束参数为空间结构控制性指标,讨论了数据库与地域功能谱系、功能和尺度依赖的承载力评价方法与模型库、“三区三线”的建构框架,论证了空间规划实施主体功能区战略的途径,提出地理学应着力加强大、中空间尺度(区域性)国土空间规划基础理论和方法、强化技术等科技支撑体系建设的建议。
Comprehensive evaluation on China's man-land relationship: Theoretical model and empirical study
中国人地关系综合评价的理论模型与实证
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系是地理学研究的经典问题,也是中国人文—经济地理学在国际地理学研究中具有突出贡献的命题。人地关系在动态演变过程中不断出现新的时代内涵,如何科学表征中国现代人地关系的状态,是精准认知现代人地关系进而寻求协调人地矛盾路径的基础。基于人地关系地域系统理论,在梳理中国现代人地关系时代特征的基础上,构建人地关系综合评价的理论框架,从人类活动的施压强度、核心资源要素的承压能力、生态环境系统的约束力度以及人—地系统的开放程度4个层面选取表征指标,秉承分级评价、逐级修正的思想,以县级单元为基础对全国层面的人地关系状态进行综合评价。结果发现:中国的人类活动强度具有明显的东西分异性及依托核心城市群布局的特征,而核心资源要素的综合支撑能力空间布局较为分散,且土地、水、核心能矿资源以及人类活动强度四者之间的空间错配度较高,在一定程度上增加了区域人地关系的紧张状态。生态环境系统的约束紧密区多集中在胡焕庸线两侧及青藏高原西南部,全国层面上人—地系统的开放程度不高,开放程度较高的区域主要集中在中国经济发达地区。综合评价结果显示,全国大约85.56%的区域人地关系状态以宽松为主,但是局部地区尤其是东南沿海地区人地矛盾突出,西部地区人地关系相对宽松,但人地系统演进的等级也相对较低。
Recognition of the spatial characteristics and influencing factors of leading industries in China's national level ETDZs
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180875
[本文引用: 1]

Under the new normal of China's economy development, it is necessary to recognize the leading industries in China's special development zones for promoting economic transformation and industrial upgrading. In this paper, spatial characteristics and influencing factors of leading industries in China's national level economic and technological development zone (ETDZs) are studied based on Ripley's K function and geographically weighted regression methods. The results show that: (1) The manufacturing industry has the absolute advantage in the leading industries of the ETDZs. The spatial agglomeration of leading industries shows the characteristics of spatial scale differentiation and attenuation. (2) From the perspective of industrial organization in the ETDZs, the single and double elements mode play a major role in leading industrial organization. (3) The conditions of the ETDZs have a relatively limited effect on promoting the agglomeration of technology-intensive industries. The supporting function of the city to the industrial agglomeration is negatively related to the investment intensity of the urban fixed assets. The ability of utilizing international capital has a strong correlation with industrial upgrading in the ETDZs. Toward to China's economic transformation and industrial upgrading, the ETDZs should deepen reform in this field. At the same time, two "capital relations" should be handled well, namely, the investment relationship between the ETDZs and the city as well as the relationship between the ETDZs and the international capital.
面向转型升级发展的开发区主导产业分布及其空间集聚研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180875
[本文引用: 1]

国际与国内发展环境双重变革下,开发区“二次创业”乃至“三次创业”的呼声不断高涨。为此,有必要重新审视开发区的主导产业分布、集聚及其影响因素,以促进其转型升级发展。以国家级经济产业开发区为例,在系统梳理中国219家国家级经开区主导产业基础上,采用核密度分析法与Ripley's K函数可视化其空间分布格局与空间集聚状态;并面向转型发展与产业升级,采用GWR方法探讨影响技术密集型产业分布与集聚的主要因素及其空间异质性。研究表明:① 国家级经开区主导产业以制造业为主,产业空间集聚存在尺度分异与空间衰减特征。② 从产业组织来看,以单一/双要素密集的主导产业组织模式为主。③ 开发区自身条件对技术密集型产业集聚的促进效果相对有限;城市对开发区产业集聚的支撑作用与城市固定资产投资强度存在一定的反向联系;开发区参与全球化的深度,尤其是利用国际资本的能力与技术密集型产业集聚具有较强关联性。面向转型升级发展,开发区自身应持续改革,主动探索;同时要处理好两个“资本关系”,即开发区与所在城市固定资产投资以及与国际资本的关系。
Identifying commuting pattern of Beijing using bus smart card data
利用公交刷卡数据分析北京职住关系和通勤出行
The simulation of spatial distribution patterns of China's HSR-economic zones based on the 2D time-space map
基于二维时空地图的中国高铁经济区格局模拟
Competition and cooperation of high-speed rail and air transport in China: A perspective from spatial service market view
中国高铁与民航的空间服务市场竞合分析与模拟
Internationalization of Chinese economic geography
中国经济地理学的国际化
The modern meaning of Aristotle's logic
亚里士多德逻辑的现代意义
Systems, Thinking, Systems Practice: Includes a 30-year Retrospective