1 引言
2020年底召开的全国农村工作会议提出坚持把解决好“三农”问题作为全党工作的重中之重,举全党全社会之力推动乡村振兴,促进农业高质高效、乡村宜居宜业、农民富裕富足。2021年中央一号文件强调新发展阶段“三农”工作依然极端重要,须臾不可放松,提出全面推进乡村产业、人才、文化、生态、组织振兴的实施方案。落实乡村振兴战略已上升为全社会的重要战略,为巩固脱贫攻坚成果,夯实三农“固本安邦”基础,衔接两个一百年奋斗目标提供坚实保障。推进乡村振兴战略难度大,如何立足“大国小农”基本国情[1],在构建新发展格局的过程中,基于制度性的集成创新,汇聚更多具有重大牵引作用的惠农举措,形成多轮驱动的乡村振兴格局,将具有重要现实意义。
实施乡村振兴战略需要在认识乡村发展阶段和规律的前提下进行,乡村振兴对象是一个多体融合的地域系统[1]。以乡村地域系统理论为基础,探究中国乡村地域类型及分区发展途径,开展多尺度、多层次的乡村地域类型和功能识别,科学把握乡村地域系统类型及空间分异规律[2,3,4],为振兴乡村提供保障。城乡二元体制下乡村发展长期受到资源、劳动力、资金等要素供给的制约,需要改变城乡不平衡、乡村发展不充分的现状,推动城乡关系进入新阶段[1, 5-6]。《乡村振兴促进法》为乡村振兴战略实施提供多方面的保障。当前,乡村振兴研究在理论基础和实施路径上有了一些探索,面向国家战略需求,有关乡村振兴的理论逻辑,体制机制等学理性问题仍待加强,科学体系仍待凝练[7,8,9]。
面向国家治理现代化需求,立足中国城乡转型的现实背景,构建具有中国特色的乡村振兴体系具有理论和实践创新意义。城乡发展要素自由流通与乡村空间开发密切相关[10],乡村空间治理是破解要素配置困境,实现乡村转型发展的重要抓手。从发达国家经验看,欧洲经历了由“自上而下”主导要素分配模式到“自下而上”城乡要素交互流通的乡村发展政策转变过程。从治理内容看,“自上而下”模式下政府开展基础设施建设和土地开发项目,转变为“自下而上”以国土治理为代表,注重乡村自我发展能力的营建[11,12,13]。乡村空间是乡村发展的物质基础,有学者尝试从乡村物质空间治理及物质空间承载的非实体空间治理为切入点,以促进城乡融合发展为突破口,深化乡村空间治理体系研究[2, 5]。乡村空间作为空间治理体系的底层空间,在落实国土空间用途管制基础上构建适应农村基本经营制度的乡村空间治理理论体系和实施路径,有利于完善空间治理体系和提高空间治理能力[14,15]。乡村空间治理从关注物质空间治理拓展到空间价值分配和空间效益优化[16,17],乡村空间治理的理论内涵和应用价值不断明晰。
乡村空间治理以乡村空间为治理对象,通过对乡村物质空间及其承载的空间关系治理,构建城乡要素流动通道,优化乡村空间结构,促进乡村转型发展[7, 18]。乡村空间治理推动乡村可持续发展,对应乡村振兴的目标诉求[19]。在快速城镇化进程中城进村退局面下,以城乡融合为关键突破的乡村振兴落实路径仍待研究[20]。在农村基本经营制度和村民自治制度背景下,以空间治理手段破解乡村发展困境的理论体系和实施路径亟待深化[2, 16, 21]。在城乡地域系统一体化发展背景下,乡村振兴的地域差异性与乡村空间治理措施组合的适应性衔接机理仍需探索[22,23]。乡村空间治理以打破乡村空间发展障碍为着力点,与破解乡村振兴难点形成逻辑连接[24]。空间治理完善乡村空间地域结构与功能,推进城乡地域系统可持续发展,为乡村振兴战略提供落地抓手[25]。新技术体系下,“时空压缩”带来的发展要素跨尺度流动,通过乡村空间治理提高乡村转型发展能力的机制和路径仍待研究[26,27,28]。“科学、高效、有序”的空间治理体系有利于推动国家发展战略的传导,提升空间开发利用水平,推动空间可持续利用,实现可持续发展目标。相反,“紊乱、低效、失序”的空间治理将带来空间开发利用的不可持续,进而削弱国家治理能力,抵消空间治理弹性,造成系统性治理障碍[2, 5, 18]。
2021年4月《中共中央 国务院关于加强基层治理体系和治理能力现代化建设的意见》指出,通过加强基层治理能力建设,使乡镇围绕全面推进乡村振兴等任务开展相关工作。乡村空间治理在巩固农村基本经营制度的前提下,强化基层组织能力,培育底层内生动力,推动乡村振兴的内在机制仍待探究[2, 11]。本文在解析乡村振兴诉求的基础上,重点探索当前开展乡村空间治理应着力解决的现实问题。从乡村空间综合治理理论体系构建出发,探讨乡村空间治理与乡村振兴的内在逻辑关系。基于此,从乡村空间治理的“效应→路径→策略”出发,进一步探讨基于空间治理的乡村振兴逻辑体系,在逻辑关系与逻辑体系研究的基础上,构建基于空间治理的乡村振兴逻辑分析架构,深化乡村空间治理和乡村振兴战略的互动逻辑研究。
2 面向乡村振兴的空间治理理论解析
2.1 新时期乡村空间治理诉求
2.1.1 可持续乡村振兴路径待完善 乡村振兴是推动乡村可持续发展的有效路径,乡村可持续发展为乡村振兴的实现提供保障。乡村作为城乡地域系统的有机组成部分[3],城乡空间分割,发展权益不均,要素流通阻隔,成为乡村发展衰退的重要原因[5, 29]。当前,乡村空间价值难显化、发展空心化、组织零散化,成为乡村可持续转型的重要障碍。乡村可持续发展强调乡村在自然资源环境承载力的基础上,既能服务本地居民生产与发展需求,也能为城市居民提供必要的综合服务,强调乡村特征的维持,乡村特色的保护,乡村性的有序维系[30,31]。乡村可持续发展为乡村振兴指明了方向,乡村可持续发展不是乡村景观城市化,也不是乡村性逐步衰落的“城进乡退”,而是乡村价值的重构,包含价值体系(目标体系、内涵体系、效应体系等),价值分配(城乡分配、区域分配、主体分配等),价值实现(空间实现、权利实现、制度实现等)的重构。乡村价值重构是落实乡村振兴战略的重要前提,通过振兴方案设计,振兴路线探索,振兴主体参与,将有利于开辟乡村可持续发展的科学路径。
空间载体的一致性决定乡村可持续发展与乡村振兴具有天然的共同性。空间价值及其实现方式是落实乡村振兴目标的关键。乡村可持续转型是乡村振兴的应有之义,乡村生产发展的经济可持续转型,农户生计的社会可持续转型[32],乡村弹性提升的生态可持续转型[33],均为乡村振兴目标落实和实践路径提供可行方案。当前,乡村振兴路径不通也多与空间利用问题密切相关。长期以来,乡村规划中产业发展空间受限,产业空间用地审批难,催生了乡村非正规产业用地[10],产业振兴空间供给紧缺。乡村人地关系优化是人才振兴的前提,村庄“空心化”与“人地分离”的土地管理制度直接相关。乡村公共空间和传统村落是传统乡村文化的重要物质载体,文化振兴渠道不顺畅与乡村文化价值难以得到有效确认,传统文化传承的收益分配不均等现实问题有关。生态振兴前提是乡村空间生态价值的重构与实现,乡村空间功能的多样性和复合性决定了乡村空间生态价值被严重低估[2, 33],成为限制乡村空间实现持续生产的关键环节。乡村组织振兴并不仅仅是乡村治理体系的重组,乡村空间及其组织体系与组织振兴关系紧密,乡村组织空心化、零散化、族群化,需要从空间组织上寻找突破口[34]。
2.1.2 新发展阶段乡村振兴迎挑战 新发展阶段对乡村发展战略提出新要求,应对百年未有之大变局下的国家发展阶段转型,乡村发展迎来全新挑战。乡村是畅通国内大循环的主战场,农村拥有巨大市场潜力,城乡互动发展是优化国际和国内双循环的重要基础。城乡地域系统中发展要素流通不畅、结构功能紊乱等系统性障碍,成为阻隔城乡循环的关键内容[2, 7]。新发展阶段,社会经济发展降速、内外部发展压力挤压、城乡关系矛盾堆积,新旧问题叠加成为城乡转型发展的常态[8]。城镇化将面临城市对乡村外出人口吸引力和容纳力下降的挑战,乡村人口城镇化和市民化的难度和成本不断加大,试图通过城镇化解决“乡村病”的路径存在众多不确定因素[1]。新时期,城乡关系与乡村振兴均面临战略调整,乡村作为国家稳定发展的战略后盾逐渐显现,乡村振兴对于稳固中国中长期发展战略的作用日益凸显。战略转型期也是发展机遇期,城乡二元割裂的管控体系和运营模式已难以适应国家发展的现实需求,破解乡村振兴领域的体制和机制障碍到了迫在眉睫的关键时期,城乡关系优化也成为培育可持续乡村转型路径的重要依据。
城乡空间用途一体化管控和发展权利公平化配置困境也是乡村振兴的核心待解难题[2]。新发展阶段,推进城乡空间开发权利、价值分配、管理体系的一体化,推进空间开发价值流向重新塑造,将有利于重构城乡关系,进而服务乡村振兴。城镇化进程中,大量乡村空间被置换成城镇空间,而空间增值绝大部分被城市政府获取,造成了城乡发展不平衡,加剧了城乡差距的扩大[16]。城乡空间管理模式差异,使得乡村空间价值的溯源主体不明确,并往往处于博弈关系的弱势方,造成乡村空间价值大量流失,失地农民与失业农户显著增多,乡村不稳定因素逐渐累积。以乡村空间治理为突破口,重构乡村发展权益,推动城乡要素流动,激活乡村空间价值,增强乡村发展动力和能力,进而开辟乡村内需新增长点,突破城乡空间发展的异构格局[35]。
2.2 乡村空间治理体系理论建构
乡村空间治理,以乡村空间为治理对象,在乡村多元主体(政府、市场、社会群体等)的共同参与下,通过规划和协商等方式,治理不适应乡村发展的空间形态,落实乡村空间用途管制策略,进而实现乡村空间结构与功能优化,推动城乡空间公平配置的综合治理过程。乡村空间形态表征一段时期内乡村国土空间开发与利用状态,乡村空间结构的不连续性、功能的多样性、关系的复杂性、价值的复合性,决定乡村空间形态既包含显性的物质空间形态,也包括物质空间承载的社会经济系统等空间隐性形态,其中空间权属关系和空间组织形式是其中重要内容。乡村空间治理包含物质空间治理、空间组织治理、空间权属治理,进而重构物质空间结构功能,重组空间组织关系,重塑空间价值分配,实现对乡村空间的综合治理[7]。
乡村空间治理以乡村空间形态为治理对象,在强调乡村空间结构功能特性的基础上,强化乡村空间权属和空间组织治理,突出乡村空间治理的特殊定位。乡村空间治理成为破解乡村发展困境的重要突破口,强化乡村空间治理能力提升将为构建有序的空间治理体系提供保障。正如前文所述,落实乡村振兴目标、推进乡村可持续转型、构建新发展阶段均与乡村空间密切相关,可以说乡村空间开发与利用形态决定了乡村地域系统的运转状态。然而,“城乡分治”的国土空间管理体系、“人地分离”的乡村人地关系格局、“组织零散”的空间组织体系、“权利模糊”的空间权属体系等乡村空间形态,成为限制乡村空间高效利用、公平分配、有序开发的障碍,乡村空间治理势在必行[1]。
乡村空间治理立足空间形态治理,优化乡村地域系统整体运行状态。乡村治理是社会学和政治学长期关注的话题,与其聚焦国家与乡村社会接触过程中形成的各种关系不同,乡村空间治理从空间承载性、空间复杂性、空间异质性出发,核心探讨通过治理空间形态,改变乡村人地关系的地域格局,进而服务乡村发展的现实需求。乡村治理重点关注了乡村社会管理和乡村自治对乡村发展的影响,与本文关注的空间治理存在较大差异。乡村空间治理通过凸显空间治理的尺度特征、综合特征、区域特征,强化国土空间在乡村发展中重要作用,具有鲜明的学科特征。已有研究从乡村空间治理推动城乡国土空间用途管制、城乡主体公平博弈、城乡发展要素流动、城乡权利均衡配置等方面推进城乡关系优化。可以看出,乡村空间治理重点从城乡空间形态的结构性矛盾出发,尝试从空间多元治理手段入手,建构扎根于国土空间的乡村空间治理分析框架。
2.3 乡村空间治理与乡村振兴逻辑关系
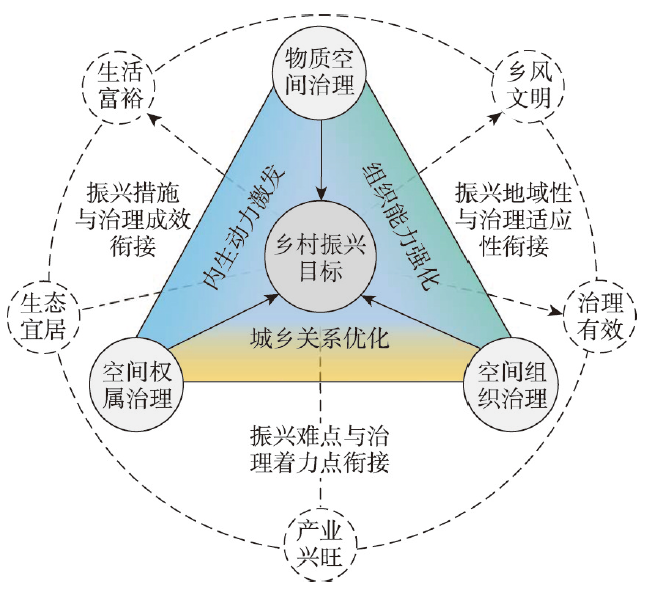
乡村振兴难点与乡村空间治理的着力点是二者连接的逻辑起点。乡村振兴战略难落实与失配的人地关系、异化的城乡关系、失衡的价值流向密切相关,破解城乡融合发展的体制和机制障碍正是推进乡村振兴的前提条件(图1)。当前,乡村空间开发存在结构功能不协调、价值低估、权属不明、组织零散等问题,同时也是抑制乡村跃升发展的阻力。乡村空间治理瞄准乡村空间开发利用的不适宜形态展开针对性治理,为打通振兴乡村发展的路径扫除空间障碍。具体表现为物质空间治理协调乡村空间地域结构与功能,空间权属治理打通乡村空间价值实现渠道,空间组织治理凝聚乡村发展活力。进而重新配置乡村人地关系地域格局,改变“城乡分治”“人地分离”的状态,这将重新塑造乡村发展的空间基础。
图1
图1
乡村空间治理与乡村振兴衔接关系
Fig. 1
The cohesive relationship between rural spatial governance and rural revitalization
乡村振兴措施与乡村空间治理成效的对应性构成二者在乡村振兴科学体系中的衔接关节点。“产业振兴、人才振兴、文化振兴、生态振兴、组织振兴”为核心的乡村振兴举措体系为乡村空间治理指明了方向。产业振兴是落实乡村振兴的根本前提,需要在完善基层集体经营制度前提下构建现代产业体系[34],空间治理服务乡村产业振兴是其核心治理目标。人才振兴是乡村振兴的坚实保障,缺乏人才振兴的乡村将难以持续运营,空间综合治理增强乡村吸引力将是完善人才振兴的关键举措。文化振兴是防止乡村性削弱的重要前提,脱离传统乡村地域文化的振兴策略将成为“无源之水”,乡村空间治理维持乡村地域特色的差异化治理策略,凸显乡村公共空间文化传承作用的治理方案将为有效落实文化振兴路径创造机遇。生态振兴与乡村空间的价值化和产品化紧密相关,通过乡村空间治理强化乡村空间生态价值特征及其实现方式将为乡村振兴注入活力。组织振兴与乡村组织程度及其风险应对能力紧密关联[35],乡村空间组织治理将重点解决乡村振兴的组织困境。
乡村振兴的地域差异性与乡村空间治理措施组合的适应性是二者逻辑衔接的基石。因地制宜实施乡村振兴政策是破解乡村振兴战略难落地的关键举措,乡村振兴的地域特色离不开区域国土空间的承载性和社会文化的特殊性。乡村空间地域特征凸显了乡村资源环境本底的重要性[36],突破地域限制性因素也是乡村实现跨越式发展的重要路径。不论是贫困区资源环境的诅咒效应,还是发达地区乡村空间的消费化,都表明结合乡村空间的自然基础是保障乡村振兴落地的关键所在。乡村空间治理举措的差异化组合表现为立足区域特征,识别核心限制性因素,以乡村空间关键环节治理为突破,撬动整个乡村转型发展格局。江苏省立足乡村公共空间治理,推动乡村集体经济大发展的成功经验,充分说明乡村空间治理举措的适应性将有效推动区域乡村实现快速发展[5]。
乡村空间治理通过物质空间治理、空间权属治理、空间组织治理,正契合了乡村振兴目标的核心诉求。乡村空间利用问题是乡村病频发的重要诱因,相反乡村空间治理将是打开乡村振兴的重要钥匙,探讨乡村空间治理与乡村振兴的内在逻辑关系,将具有现实意义。下文将从乡村空间治理的振兴效应、振兴路径、振兴策略出发,深化二者逻辑关系。
3 空间治理的乡村振兴效应
3.1 乡村空间治理与城乡互动关系优化
乡村空间治理改变城乡互动格局,有利于完善城乡地域系统转型的理论基础。乡村空间治理通过改变城乡空间用途的二元轨道,尝试建构城乡空间用途一体化管控平台和公平置换机制,进而推进城乡土地市场交易的一体化,突破乡村空间长期处于被动接受的定位。乡村物质空间治理是推进城乡互动的动力源,通过物质空间治理挖掘乡村空间开发潜力,为置换乡村发展资本创造条件。乡村空间权属治理显化乡村空间价值,推动空间价值增值的公平化分配,创造空间价值向乡村流动的条件[37,38]。乡村空间组织治理强化乡村破碎空间的重组,优化空间主体组织方式,为推进市民化为代表的城镇化扫除基本障碍。通过乡村空间治理,打破城乡空间物理隔离、价值割裂、组织分裂的困境,进而为优化城乡关系提供破题路径。
乡村空间治理通过改变城乡互动“强度”和“通道”实现对城乡关系的优化。城乡互动强度与城乡发展要素流动的顺畅度和牵引力成正比,同城乡空间阻隔和城乡差异鸿沟成反比,乡村空间治理优化城乡发展要素流动格局、城乡空间结构特征、城乡空间功能体系,进而建立起全新的城乡互动关系,提升互动强度。乡村空间“物质—组织—权属”治理体系通过改变城乡互动通道优化城乡关系[2]。城乡空间发展权、物权、经营权等权利体系的不对等(图1),使得乡村空间权利被城市持续挤占,通过空间治理打通城乡权利互动通道,将是激活乡村空间开发潜力的关键环节[37]。此外,城乡互动的要素流通通道、一二三产业融合通道、基础设施连通通道、公共服务网络通道均将在乡村空间治理过程中得到强化。通过城乡互动强度延伸和通道疏通,实现城乡空间开发格局的重构,为构建公平的城乡关系奠定基础。
3.2 乡村空间治理与乡村内生动力激发
乡村空间是乡村发展的物质基础,利用乡村空间培育内生发展动力,关键在于打破传统空间利用模式和价值实现路径。城镇化进程中,以“空心化”为代表的村庄衰退趋势“不留人、不养人”,乡村发展动力持续衰减。因此,破解乡村发展动力流失的关键是留住本乡人,招来外乡人,培育干事能人,“有人气”的村庄才可能被活化。此外,村庄内生动力培育需要激发主体参与建设的积极性,村庄创新发展的自适应能力培育是关键,外来因子的引入仅是翘板。乡村产业难发展,动力培育将难以为继,产业持续引入与再造才是乡村内生动力持续发酵的源泉[11, 34]。乡村人地关系转型背景下,通过乡村空间治理激发乡村内生动力的条件已具备,部分先行先试、市场化程度高的地区已经树立众多成功案例。以山东曹县为代表的数字电商乡村发展模式,充分说明依托乡村本土空间资源衔接跨尺度交互作用的市场网络,乡村内生动力激发具备现实的可行性。解析乡村空间治理对乡村内生发展动力的激发效应,有利于揭示乡村转型发展的内在机理。
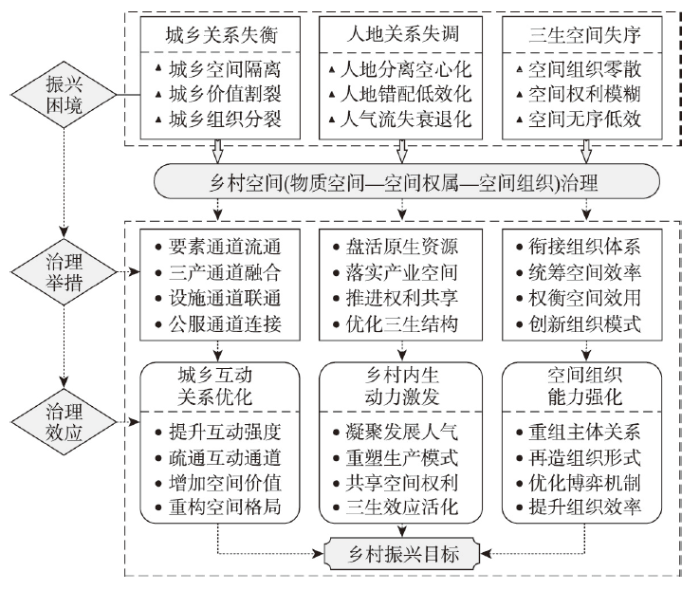
乡村空间治理激发乡村内生动力可通过空间保障、权利保障、组织保障等形式得以体现。乡村物质空间治理解决乡村人地错配问题(如宅基地合理退出),空间权属治理提升乡村人口空间处置权和收益物权,充分激活乡村空间价值服务本地居民的潜力,调动多元主体参与乡村建设和产业开发的积极性,从而凝聚乡村“人气”。空间组织治理推动乡村生产和生活模式重组,创新新型合作组织方法,凝聚新的乡村经济组织形式。以上分析可知,乡村空间综合治理在打破乡村“空心化”,破解乡村衰退无后劲等问题上具有重要作用[38]。乡村内生动力的激发需要空间基础,空间综合治理通过盘活存量空间,挖掘潜在空间,优化空间结构,推进混合利用等方式,落实乡村内生发展的空间保障。城乡空间价值公平分配是调动乡村主体创业的重要推动力,乡村空间权利赋予过程,也是城乡空间价值二次配置过程,空间治理推动乡村土地利用价值增值,正是乡村内生动力培育所急需的权利保障。乡村空间利用“散、乱、空”状态[39],带来乡村空间组织“低效、无序、混乱”,阻碍了乡村生产和生活模式的更新,“小农”生产组织模式与现代市场对接需要通过空间治理加以衔接[1],推动空间组织与乡村生产组织有序转型,进而从组织保障层面加快构建乡村内生发展渠道。通过空间保障、权利保障、组织保障,内生动力激发更具现实可操作性(图2),也为构建乡村产业发展和创新生产模式创造条件。
图2
图2
空间治理的乡村振兴效应
Fig. 2
The effect of spatial governance for rural revitalization
3.3 乡村空间治理与空间组织能力强化
乡村空间治理重组乡村空间体系,重聚乡村发展活力,强化基层组织能力将为乡村振兴提供坚实保障。中国乡村由小规模家庭为单位向现代生产组织体系转型是乡村转型面临的重要挑战。以日本和韩国为代表的发达国家转型经验表明,乡村人口流出过程需要与农户结构体系重组,生产模式重组,城乡关系重组紧密结合起来。东亚发达国家转型经验中,强化农户协商机制的自组织体系成为保障农户发展权益,调动农户参与积极性,发挥乡村基层组织力的重要渠道[2]。集体经营性资产紧缺,公共服务能力羸弱,组织号召力缺失,这些已经成为阻碍乡村振兴的关键环节。立足中国小农基本经营制度的前提,破解乡村组织能力涣散问题必须得到足够关注。乡村空间治理从乡村空间权利分配重组、用途管制重组、主体关系重组等方面出发,强化乡村地域系统内部生产和生活组织体系的重组,将为强化乡村空间组织能力提供支撑。
乡村空间治理通过乡村空间组织体系、组织效率和组织效用等方面强化基层组织能力,提升乡村发展组织程度。乡村空间综合治理在强化村域尺度村民自治制度和农户尺度家庭联产承包责任制的基础上,强化村集体的空间组织能力,协调村支两委和村民经济合作组织在村庄组织中的地位和定位,突出乡村空间组织的统筹能力,进而破解乡村组织体系零散化、空心化、悬空化等弊端[31]。乡村空间治理与治理效率提升主要表现为治理主体明确,治理组织高效,治理方式多样等方面。乡村空间综合治理强化物质空间与空间关系一体化治理,空间权利与空间组织统筹治理,正切合了乡村组织体系重组的现实需求。乡村空间治理作用与组织效率提升还可通过空间利用效率,城乡组织效率,主体博弈效率等方面施加影响,进而全方位促进乡村组织效率的提升,服务构建新型空间治理格局。乡村空间治理强化基层组织能力可从优化组织效用入手服务乡村振兴,主要通过再造基层组织模式,提升基层组织博弈能力,优化多元主体参与机制等方面促进乡村发展新格局的形成。
4 基于空间治理的乡村振兴路径探讨
乡村空间治理在重构城乡互动关系、乡村内生发展体系、基层组织能力等方面具有显著的正向效应,这些正向效应通过合理的体制和机制设计,将为构建新时期乡村振兴可行路径提供强有力的支撑。不同类型的乡村振兴路径适用于不同发展阶段和地域特征的乡村。因此,开展空间治理导向的振兴路径理论研究,核心是阐述如何通过空间治理搭建具有普适特征的乡村振兴可行方案,进而推进乡村转型发展进入良性通道。综合前文分析,本文构建了3种空间治理导向乡村振兴可行路径,分别为城乡融合路径,内生发展路径和组织强化路径,与空间治理效应体系紧密结合,逻辑体系较为严密。
4.1 城乡融合路径
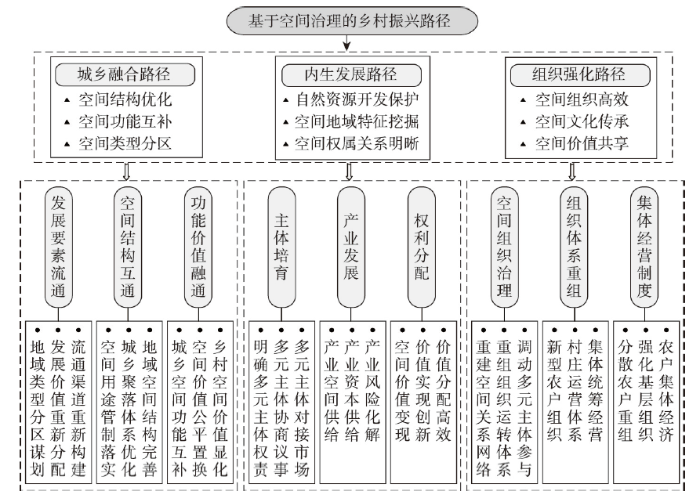
城乡融合在重构城乡关系与振兴乡村双重层面具有建设目标的一致性,建设手段的共通性,建设过程的融合性。城乡融合发展既是城乡关系的重新构建,也是乡村振兴的应有之义,没有城乡融合发展的乡村振兴难以实现,离开乡村振兴的城乡关系也难以融合发展。刘彦随指出城市和乡村是一个有机体,城乡交错的地域系统是推进城乡关系重构的关键,构建城乡融合体是推进城乡关系转型的核心策略[1]。构建城乡融合体可从空间要素配置体系、空间结构传导体系、空间功能优化中寻找突破。乡村空间治理瞄准城乡关系领域存在的要素流通难、价值互通难、功能置换难等问题展开针对性治理,正契合了城乡关系重构与融合的目标。空间治理带来的城乡发展要素配置体系重构主要包括组合搭配重新谋划,发展价值重新分配,流通渠道重新构建。通过推动发展要素有序流动和重新配置,打通乡村振兴要素流通渠道。乡村空间治理优化空间结构传导体系主要通过空间用途管制落实、城乡聚落体系优化[40]、乡村地域空间结构完善等方面传导乡村振兴政策。空间治理优化城乡功能体系是推动城乡融合发展机制落实的重要内容,通过空间治理落实城乡空间功能交换与价值置换相匹配,推动乡村空间价值显化和城乡空间功能互补,进而服务城乡融合发展[5, 7]。
乡村空间治理推动城乡发展要素流通、空间结构互通、功能价值融通的融合过程,正是乡村振兴实现的可行路径。城乡发展要素自由和高效流通是保障乡村振兴的基础动力,推动城乡迁移人口市民化、工商业资本有序下乡、科技和技术支持乡村发展、保障返乡劳动力就业并加强培训。这将带来城乡发展要素由单向流通向双向流通,进而为落实乡村振兴创造条件。城乡文化差异及其空间承载地域分异,通过乡村空间有序治理将有利于城乡文化的交互,为传承乡土文化,推进文化振兴创造条件。城乡空间结构互通是打通乡村振兴的关键环节[41],城乡空间三生空间结构、聚落体系结构、空间网络结构、空间关系结构等结构体系互通目标的落实,将有利于完善乡村振兴目标的实现。城乡空间价值融通是落实乡村振兴目标的重要突破,核心在于空间治理破解城乡空间功能和价值体系的异化格局,推动城乡空间价值的公平配置(图3)。乡村空间治理通过改变城乡发展要素的空间配置格局,释放乡村空间的经济价值,推动城乡社会关系的互动,有利于建立城乡统一的市场机制、价值分配机制、功能互补机制。结合乡村空间地域类型,制定适应地方需求的治理手段,重点击破“问题区域”的“区域振兴问题”。通过乡村空间综合治理,推动城乡发展要素有序流动,疏通城乡融合发展的障碍“堵点”,破解乡村振兴的落实“难点”,打通振兴政策的传导“断点”。
图3
图3
基于空间治理的乡村振兴路径
Fig. 3
The path of rural revitalization based on spatial governance
4.2 内生发展路径
乡村内生发展动力、机制和路径的落实是乡村振兴需要破解的重要命题。离开乡村内生发展的振兴将难以持续运营,乡村性也难以持续维持,乡村转型与重构的动力基础不牢。长期以来,以项目制输入为代表的外缘动力介入乡村发展虽起到短期发展效果,但乡村自适应发展能力仍是短板。以内生发展能力提升为工具,内生发展渠道构建为手段,内生发展参与机制营造为目标,构建乡村内生发展路径将有效完善乡村发展动力基础,夯实乡村振兴可行路径。乡村内生发展与乡村自然资源本底和地域特征密不可分,基于乡村空间开发与利用的内生动力培育具有现实的可操作性与必要性。乡村内生发展路径深化可从“主体培育、产业发展、权利分配”上寻找突破口[2, 11]。乡村发展主体既包含以“小农户”为核心群体的分散主体,也包含乡村新型主体(乡村能人、企业主、工商户等)。乡村空间治理与主体培育主要通过明确主体权责关系,调动主体参与乡村振兴的积极性,完善多元主体协商与议事机制,衔接多元主体与市场的对接等层面展开。乡村产业发展可通过空间治理对产业空间供给,产业资本供给,产业风险化解等几个方面施加影响,进而为乡村内生产业发展提供动力。乡村空间治理瞄准国土空间不合理利用形态,通过实施全域土地综合整治实现土地利用结构调整和功能优化,进而凸显地域空间特色,完善乡村内生发展基础。通过空间治理开辟产业振兴新空间,解决产业用地短缺问题,通过乡村空间价值多元实现路径,培育产业发展增长极。针对乡村生态空间进行综合治理,打通完善乡村地域系统的整体功能,凸显乡村空间综合价值,全面服务乡村生态振兴诉求。
空间治理带来乡村空间权利生成、实现和分配的体系优化有利于保障乡村内生发展路径的实践。落实空间资源向空间价值的转化过程,契合了乡村内生发展的现实诉求。乡村空间治理推动城乡空间“同价同权”,通过空间用途分区与管制制度保障空间价值生成的合理性,落实空间价值公正配置[42]。空间权利的实现方式除了空间价值变现,也包含价值实现方式的创新。空间权属治理重点解决空间权利关系模糊和空间权利落地缺少抓手等问题,有利于打通乡村空间权利的实现路径。空间权利公平和有效分配是保障乡村内生发展实施的重要环节,进而协调不同利益主体参与乡村建设的积极性和主动性,填补乡村发展的“权利真空”和“主体缺少”状态。乡村空间治理通过明晰空间产权关系,明确多元主体经济利益来确立乡村发展权益的分配机制,完善乡村空间价值体系,拓展空间价值实现方式,提升空间价值分配效益(图3)。通过空间权利分配,突出乡村空间的生态价值和社会价值,进而完善乡村内生发展的支撑体系。
4.3 组织强化路径
乡村空间治理强化乡村组织能力对破解乡村衰退趋势具有重要作用。乡村组织体系衰落面临的核心问题是乡村人口流失产生的人才队伍缺和组织结构乱。乡村空间治理以物质空间治理为基础,改善乡村地域系统结构,提升空间组织效率,理顺乡村空间组织体系。乡村权属治理明确不同乡村主体利益关系,明晰公共空间权属体系,优化乡村社会空间关系,激发乡村多元主体参与发展的活力,落实乡村空间文化传承。受制于组织体系不畅的振兴难题,乡村空间治理从乡村物质空间和乡村空间关系两方面组织治理出发,破解乡村发展中的组织困境。一方面改善乡村发展组织散乱,构建乡村三生空间的高效组织方式;另一方面优化农村基本经营制度,在保证农村集体经营制度有效运转的前提下,从空间组织入手强化对分散农户的重组,发展新型农村集体经济,强化村“两委”的领导作用,进而提升乡村基层组织力,深化“多治合一”与“智慧治理”,夯实基层执政基础。乡村空间治理打破乡村发展多元主体难以参与乡村振兴的桎梏,为乡村组织振兴提供治理保障。空间组织治理通过重建乡村空间关系网络,重组空间组织运转体系,调动多元主体参与乡村振兴。
组织强化路径提振乡村发展能力可通过新型农户组织模式和村庄运营体系加以强化。当前,培育多元主体参与乡村振兴缺乏有效可行的组织渠道,分散农户无法及时对接市场的变化,企业主难以统筹应对乡村治理困境,多级政府“自上而下”的治理体系在基层缺乏落地抓手。乡村空间治理导向的组织强化过程破解了当前乡村振兴面临的组织困境。以强化集体统筹经营能力为目标的组织体系重组,为落实“产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕”总体目标创造条件。集体经济和农户合作组织统筹能力增强,有利于乡村产业的升级与再造,也为完善乡村自治体系提供空间载体。在深入推进农村土地制度改革,创新农村集体经营性用地制度和乡村生态用地科学保护的情况下,空间治理既能保障农民集体经济收益的提升,也能服务生态宜居目标。乡村组织体系重组对落实乡风文明和治理有效目标具有直接作用,乡村文化体系传承和可持续乡村性保护有路可循,落实治理有效目标和防止公地悲剧更具可行性。集体经济组织统筹能力与乡村公共服务配置和供给能力有关,强化组织力将为生活富裕目标落实提供保障[43]。
5 面向乡村振兴的空间治理策略
面向乡村振兴的空间治理策略体系是实现乡村空间治理目标,落实乡村振兴战略的重要内容。乡村空间治理以全域乡村空间为治理对象,乡村国土空间及其承载的空间关系治理是其核心内容。构建完善的乡村空间治理策略与国家空间治理体系优化紧密相关,《关于建立国土空间规划体系并监督实施的若干意见》和《关于加强村庄规划促进乡村振兴的通知》,要求在城镇开发边界外编制“多规合一”实用性村庄规划,并试图通过规划构建“全域、全要素、全类型”的乡村国土空间用途管制体系。当前,乡村规划实施缺位导致发展粗放,叠加粮食安全、村庄人居环境整治、基础设施和公共服务完善等压力,对乡村空间治理提出更高要求。多元主体参与乡村规划与运营是落实空间治理目标的重要手段,服务组织强化路径构建。统筹乡村空间用途管制的“刚性约束”与“弹性引导”相结合需将乡村空间权利的共享机制囊括进去,进而推进乡村空间治理激发乡村内生发展动力,疏通城乡发展要素流通的渠道。面向乡村振兴的空间治理策略应瞄准现实需求,实际的可操作性,目标的紧迫性加以设计[44]。本文尝试从“上下结合型”“多元主体参与型”“权利共享型”3个层面尝试探索空间治理策略体系。
5.1 “上下结合型”空间治理与乡村振兴
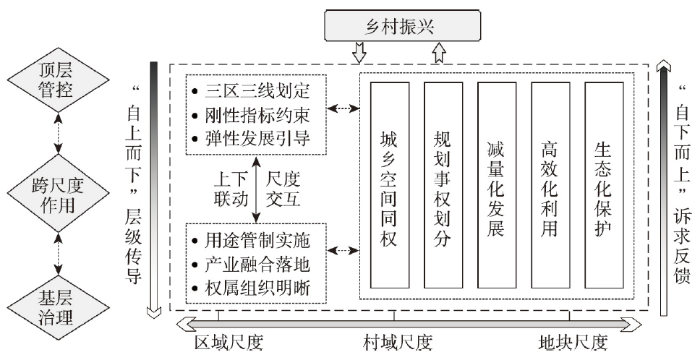
“上下结合型”空间治理逻辑为应对乡村振兴面临的空间挑战和组织挑战提供解决方案。传统“自上而下”空间治理模式从国土空间管控层级传导目标出发,强调顶层治理政策对于多级空间用途管制的传导,并且与各级政府的事权体系相匹配。乡村空间因处底层空间,缺乏事权也难以对空间实现有效管控,难以支撑当前乡村振兴的现实诉求。构建“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的乡村空间治理体系,有利于顶层管控政策传导与基层治理诉求相结合,将多级政府事权体系与乡村空间综合治理结合起来,在多方博弈中实现空间开发权利的合理配置。“上下结合型”空间治理策略重点在于将底层空间发展诉求以合理方式实现反馈,进而保障乡村发展的空间诉求。“自下而上”的空间治理重点在于将破碎化、低效化、模糊化的空间实现有效治理。并且能够通过主体参与、乡村规划、用途管制等措施体系加以落实。“上下结合型”空间治理策略有利于推进多元主体有效参与空间治理,进而满足乡村振兴发展的组织需求[2]。
“上下结合型”空间治理推动城乡关系重构有利于落实振兴政策。现有国土空间规划体系中落实乡村优先发展的体制和机制不健全,城乡空间的差异化所有权实现方案,城乡空间一体化治理体制机制不完善成为新时期阻碍城乡共治,抑制城乡融合共进的重要屏障。“上下结合型”空间一体化治理体系与规划事权划分紧密结合,是保障城乡融合发展目标和乡村振兴政策落实的重要保障。适应“减量化”发展、“高效化”利用、“生态化”保护的现实需求[42],在明确乡村国土空间管控目标的前提下,落实国土空间规划“三区三线”的约束性指标传导、构建“刚性约束”与“弹性引导”结合的管控策略、探索适应乡村振兴需求的管控体系、满足农村一二三产业融合发展的产业发展空间诉求、对接农村土地制度改革的衔接管控体系等,进而完善乡村振兴的支撑体系(图4)。
图4
图4
“上下结合型”空间治理策略与乡村振兴
Fig. 4
"Top-down" and "bottom-up" combined spatial governance strategy for rural revitalization
空间治理的跨尺度效应与“上下结合型”空间治理策略相匹配将显著改善乡村振兴的基础条件。现代通讯和交通网络带来的“时空压缩”使城乡发展要素可以实现跨空间尺度的传递,乡村空间治理在新技术体系下“跨尺度交互”为乡村发展带来全新机遇[21]。乡村空间治理畅通乡村内部组织体系,强化群体的自组织能力和自我学习能力,这将为外部发展要素进入乡村,快速传播,并起到激发效用提供保障。在跨尺度空间治理视角下,乡村空间治理推动乡村治理实现尺度连通,确保多元主体参与乡村转型发展路径的有效性。乡村空间治理地域多样性也随着地域空间影响因素的跨尺度传导趋于复杂,乡村地域系统的内外因素交互影响、远程耦合、跨尺度作用,也对乡村空间治理尺度选择提出更高要求,选择合适的尺度开展乡村空间治理,不同尺度间治理措施的有效传导,将是未来重要的优化方向。乡村振兴应该是城市和乡村共同发展视域下的城乡融合过程,“上下结合型”空间治理与跨尺度要素流动为城乡融合发展提供发展路径,跨尺度交互的空间治理为乡村振兴发展提供机制保障。
5.2 “多元主体参与型”空间治理与乡村振兴
多元主体参与空间治理的渠道、能力与效应构成乡村振兴推进的有利保障。以分散农户为代表的社会主体,多级政府为代表的行政主体,资本和企业主为代表的市场主体,分别构成了“社会力”“政府力”“市场力”多元博弈主体[17]。乡村发展不同阶段多元主体博弈格局因时而异,如何调动多元主体参与空间治理的积极性和可靠性与空间治理制度设计相关。以农户为代表的“社会力”博弈能力越强,越有利于提高乡村空间价值服务乡村振兴的能力。“政府力”与空间事权关系相关,并且成为左右空间治理转型方向的关键力量,“政府力”越强,其他主体力量则越弱。“市场力”越活跃的地区,城乡发展要素流动越频繁,乡村发展的活力越强。“多元主体参与型”空间治理需要在培育“社会力”,监督“政府力”,引导“市场力”方面做好文章,统筹优化多元主体的博弈力量,形成合力推动乡村振兴动力集聚。多元主体在乡村空间治理中的参与程度越高,越有利于建立多元力量协同作用机制。多元力量与多元主体协同应以服务本地乡村振兴作为第一要务,落实多元力量协同需要提升“市场力”在牵引城乡发展要素流动中的作用,也要明确资本下乡的管控渠道,防治资本“跑马圈地”。此外,“社会力”和“政府力”在乡村空间治理过程需强化机制的创新,落实管控治理清单与议事协商制度,全面推进乡村空间治理水平和能力上台阶。“社会力”的强弱与农户组织体系、社会自组织能力、空间产权配置体系相关,并服务于内生动力培育和组织能力强化。多元主体在空间开发中进行博弈,进而落实空间发展目标,推进公平权益体系的建设,完善乡村振兴的体制与机制。
“多元主体参与型”空间治理的效应体系与主体间博弈关系相关,并作用于乡村振兴路径的实现。乡村可持续振兴与农户可持续生计体系的构建直接相关,如何完善农户生计体系,增强农户应对风险的扰动能力,进而服务乡村可持续振兴的诉求,可从多元主体博弈的关系入手寻找突破[2]。“市场力”与“政府力”应以提升“社会力”为核心目标,强化市场收益的本地化和多级分配体系的构建,这将有利于完善农户自组织为特征的振兴体系[45]。农户自组织模式与博弈能力的培养将决定乡村空间开发利用的方向,并且能够影响“政府力”在基层空间治理中的作用效果。多元主体参与乡村空间治理需要强化对博弈弱势群体的保护和强势群体的约束,多元主体的多轮博弈虽然可能在一定程度上降低空间治理的效率,但持续且有效的参与机制,将为构建可持续的乡村振兴渠道奠定基础。此外,多元力量参与乡村空间形态的改造过程,不能脱离本地自然资源环境的约束,尊重资源环境承载能力和本地社会文化适应性的乡村空间治理举措和乡村振兴措施需要加以强化。多元力量的博弈过程,也是乡村空间治理体系完善和制度健全的过程,有利于防止部分力量压倒性优势带来的力量失衡。
5.3 “权利共享型”空间治理与乡村振兴
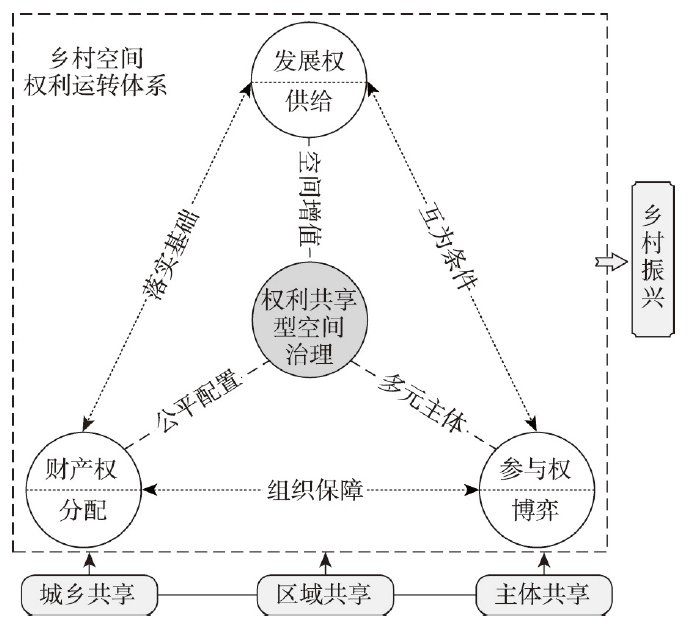
空间权利是推动乡村振兴的基础保障,空间权利共享过程是优化空间社会经济关系的重要手段,也是乡村空间治理需要突破的重要领域。空间治理落实权利共享的机制和手段创新,同乡村空间发展权的供给、财产权的分配、参与权的博弈有关[16]。城乡空间发展权利的差异格局成为乡村空间发展权利受到挤压与侵占的重要表征,乡村空间发展权利缺失与供给不足是乡村发展不充分,城乡差异显著的重要诱因。空间发展权利共享与空间财产配置,权利的公平分配相辅相成,没有乡村空间价值的显化和空间财产权的配置,乡村空间发展权的落实将难以现实。同样,空间发展权的持续供给是破解乡村空间价值低效化,财产价值被严重低估的核心突破口。通过空间发展权和财产权的公平配置,将为落实多元主体空间参与权的博弈创造条件(图5)。参与权的落实与共享是乡村空间治理保障乡村振兴组织与机制构建的核心,农户作为乡村空间治理的核心社会主体,创新农户参与空间治理的共享机制和模式,将为落实乡村振兴提供组织保障,进而服务组织强化路径的实施。
图5
图5
“权利共享型”空间治理策略与乡村振兴逻辑关系
Fig. 5
The logical relationship between "right-sharing" spatial governance strategy and rural revitalization
“权利共享型”空间治理可在城乡共享、主体共享和区域共享中落实乡村振兴目标。空间发展权城乡转移与区域配置将为欠发达地区乡村提供振兴急需的资金保障,基于空间用途管制政策创新推动空间发展权的主体博弈,进而从空间发展权的公平供给,推动乡村振兴政策的落实。自然资源管理的制度创新是乡村空间权利共享策略落实的重要手段,结合激励和约束等不同类型的制度配套,创新空间开发权利、空间财产权的实现方式。主体共享机制核心是落实乡村空间发展权、财产权和参与权在不同利益主体间的分配,保障乡村空间价值增值是推进发展权落实的核心诉求。空间财产权的主体间公平分配,空间参与权的多元主体路径优化,均成为推进乡村振兴的重要依据。
自然资源本底的承载力和国土空间开发的适应性成为明确空间开发主导功能的核心依据,进而成为区域乡村空间治理的主导性用途管制策略,乡村地域主导功能和空间开发时序是乡村空间发展权利差异的重要来源。农业生产主导型与非农生产主导型乡村空间价值具有天然的差异,发达地区与欠发达地区乡村空间权利,在多种因素作用下显著不同。此外,乡村空间开发时序的差异也是乡村空间权利区域差异的内在生成机制,先期开发地区占据区域和政策管控优势,而后发地区则管控强度更大,空间权利约束条件更多。乡村地域主导功能差异带来的空间权利冲突需要在跨区域空间权利交换中创新机制,强化乡村空间综合价值核算的理论和实践研究,探索乡村空间综合价值变现与交易核算路径。乡村空间权利共享需要在国家顶层空间权利分配上探索新方法,其中包括乡村空间发展权和参与权的共享需要在城乡空间权利分配中创新落实路径,探索乡村空间权益的跨区域和跨尺度流动,有益于完善“权利共享型”空间治理策略的落实。乡村空间财产权的配置与空间权益实现方式密切相关,开辟乡村空间多元利用方式、综合开发渠道,突出乡村空间复合功能和价值,推动乡村空间财产权与收益分配权落地。
6 结论与讨论
6.1 结论
构建乡村振兴科学体系对于应对乡村发展不确定性和地域差异性具有重要学科价值。乡村空间治理瞄准乡村空间开发利用过程中出现的结构性难题和功能性障碍,寻求多重治理手段,为乡村振兴提供落地抓手。本文从乡村振兴面临的困境出发,尝试从空间治理视角解构振兴乡村的可行性和内在机制。主要结论如下:
(1)乡村价值重构是落实乡村振兴目标的关键,主要包括价值体系、价值分配、价值实现的重构。乡村空间作为乡村价值重构的物质载体,振兴困境也同其开发利用紧密相关,破解城乡空间管控和发展权利配置难题也可以从乡村空间治理视角寻找突破。
(2)乡村空间治理基于物质空间治理、空间组织治理、空间权属治理,进而重构物质空间结构功能,重组空间组织关系,重塑空间价值分配;空间治理振兴乡村的效应可从城乡互动关系优化、乡村内生动力激发、基层组织能力活化等层面加以强化。
(3)空间治理效应与乡村振兴目标相对应成为明确振兴路径的主要着力点,乡村空间治理推动城乡发展要素流通、空间结构互通、功能价值融通的城乡融合发展路径是落实乡村振兴的可行路径;空间治理带来乡村空间权利生成、实现和分配的体系优化是乡村内生发展路径实现的重要依据;空间治理优化新型农户组织模式和村庄运营体系保障组织强化路径。
(4)构建“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的乡村空间治理体系,有利于顶层管控政策传导和基层治理诉求相结合,推动权利博弈实现空间开发权利的合理配置;多元主体参与空间治理的渠道、能力与效应体系,推动空间发展目标实现和公平权益体系建设,完善乡村振兴的体制与机制;空间治理落实权利共享的机制和手段创新,同乡村空间发展权的供给、财产权的分配、参与权的博弈有关,“权利共享型”空间治理可在城乡共享、主体共享和区域共享中落实乡村振兴目标。
6.2 讨论
乡村空间范畴因研究视角不同存在认知范围的差异,本文研究的乡村空间主要聚焦乡村国土空间,及其延伸的空间形态(空间权属关系和空间组织体系等)。也有学者认为乡村空间除此以外还包括社会空间和文化空间等非物质空间,进而探讨乡村非物质空间治理与乡村振兴的内在关系。乡村物质空间与非物质空间共同构成了乡村空间,乡村空间治理在某种程度上也应在非物质空间治理领域进行尝试和探索。本文在物质空间治理的基础上,尝试从空间权属治理和空间组织治理入手,探索乡村空间综合治理的理论内涵,从空间隐性形态治理的视角对乡村非物质空间治理进行了关注。深入探讨乡村空间多元融合治理是未来乡村空间治理的重要研究方向,深化乡村社会文化空间治理将有利于完善乡村空间治理理论体系。
本文从乡村空间治理理论内涵解析出发,尝试分析空间治理与乡村振兴的内在关系,并分别从“效应→路径→策略”出发,探讨了乡村空间治理推动乡村振兴的可行方案。但以上研究只是初步的探索。新发展阶段,乡村振兴已成为实现第二个百年目标必须攻克的难题,深入研究乡村空间治理与乡村振兴互动作用机制,发挥乡村地理学在乡村振兴科学领域的作用意义重大。当前,瞄准生态文明建设与高质量发展的现实诉求,立足乡村空间价值和权益研究,充分论证乡村空间权利实现机制和路径,进而探索优化城乡发展趋势的科学手段和方案,仍需要进一步深化。立足地域空间特征的乡村空间治理举措和实施路径仍需结合典型案例和样区研究,总结具有可复制和可推广的空间治理经验,完善乡村空间治理的科学机制。
致谢:匿名审稿专家针对乡村空间治理理论完善提出了宝贵的修改意见,广州地理研究所杨梦琪博士在语言精炼上提供了支持,一并感谢。
参考文献
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 7]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 7]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Rural spatial governance for territorial spatial planning in China: Mechanisms and path
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 13]

Under the background of unified management of urban and rural space, rural spatial governance has become an important part of the spatial governance system. Conducting in-depth theoretical and practical research on rural spatial governance and analyzing the mechanisms and path of rural spatial governance in national spatial planning will be conducive to improving the planning and control system of rural space. Starting from the connotation rural spatial governance, this paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of rural spatial governance based on the comprehensive perspective of spatial governance, discusses the internal mechanism and feasible paths of rural spatial governance in territorial spatial planning, and then realizes the theoretical and practical research of rural spatial governance. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Rural spatial governance starts from the coordination theory of human-land relations in the rural regional system. Through planning and negotiation, it realizes effective control of rural space usage, and orderly allocation of space rights. Rural spatial governance highlights the comprehensive governance process that combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" participation by multiple subjects. (2) Through the "action-efficiency-target" system, the comprehensive governance analysis framework of "matter-organization-ownership" in rural space provides an effective scheme for the construction of multiple rural spatial governance that combines rigidity and flexibility, interaction between material space and space relationship, and superposition of spatial ownership and spatial organization. (3) The rural spatial governance features of interconnecting various scales (region-village-plot) are conducive to improving the rural spatial governance system. (4) The multiple governance means, participation modes and value-sharing mechanisms of rural spatial governance are conducive to enriching the territorial spatial planning system, promoting the integration of multiple regulations, refining the control of territorial space use, and ensuring good rural governance and ecological governance. (5) Rural spatial governance uses mobilization strategies of "top-down" and "bottom-up", and creates conditions for the implementation of practical village planning and revitalization strategies through the construction of new village operation models and reconstruction of organizational mechanisms.
面向国土空间规划的乡村空间治理机制与路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 13]

城乡国土空间统一用途管制背景下,乡村空间治理成为国土空间治理体系的重要组成部分。从乡村空间治理的理论内涵出发,构建了乡村空间治理理论分析框架,探讨了乡村空间治理作用于国土空间规划的内在机制和可行路径。结论如下:① 乡村空间治理是以乡村空间为治理对象,通过规划和协商等方式,实现乡村空间用途有效管制,空间权利有序配置,凸显多元主体参与的“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的综合治理过程;② 通过“举措—效能—目标”体系,构建了刚性与弹性结合、物质空间与空间关系交互、空间权属与空间组织叠加的乡村空间“物质—组织—权属”综合治理分析框架;③ 多级尺度互联互通(区域—村域—地块)的乡村空间治理特征有利于完善乡村空间治理体系;④ 乡村空间治理通过多种手段并施、多元主体参与、多重价值共享,完善国土空间规划体系,推进多规融合,细化国土空间用途管制,促进乡村善治和生态治理;⑤ 乡村空间治理通过“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的动员和行动策略,构建新型村庄运营模式和组织机制,为落实实用性村庄规划和乡村振兴战略创造条件。
Rural regional system and rural revitalization strategy in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 2]

Rural regional system is a spatial system with certain structure, function and inter-regional relationship, which is composed of humanity, economy, resources and environment that are connected and interacted with each other. It is a regional multi-body system, including urban-rural integrity, rural synthesis, village-town organism, and housing-industry synergy. Targeting the rural regional system and supporting the rural revitalization strategy provides new opportunities and challenges for innovation of Chinese geography in the new era. Guided by the theory of regional system of human-land system and the science of human-land system, the research on rural revitalization geography should serve national strategy by finding solutions to problems hindering rural sustainable development, and make contribution to the comprehensive study of rural regional system structure, transformation process, evolution mechanism, differentiation pattern, regional function, and rural revitalization path and model under the interaction of surface's human-land system. There is an urgent requirement to better understand and reveal differences in the types of rural regional system and their differentiation law. Taking 39164 townships in China as research object, this paper used quantitative and qualitative methods to detect and identify the dominant factors that restrict the sustainable development of rural regional systems in China. Then we divided the types of Chinese rural regional systems, revealed the pattern of rural regional differentiation and further proposed scientific approaches to rural revitalization in different areas. Results demonstrate that topographic conditions, climate conditions, ruralization level, land resources endowment, population mobility and aging level are the dominant factors restricting the sustainable development of rural regional system, of which reflects the level of resource endowment, endogenous power and external aid of rural development. Through cluster analysis and spatial overlay of dominant factors, China's rural regional system can be divided into 12 first-class zones and 43 second-class zones. The first-class zones are named by means of 'geographical location + driving force of dominant factors', and the second-class zones are named by means of 'regional scope + driving force of dominant factors + economic development level'. The driving force of rural sustainable development in different regional types are varied. The regional pattern and path of rural revitalization in different types of areas are varied, and promoting the rural revitalization strategy should be based on local conditions to realize the coordination and sustainable development of rural economy, society, culture and ecosystem.
中国乡村地域系统与乡村振兴战略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 2]

乡村地域系统是由人文、经济、资源与环境相互联系、相互作用下构成的、具有一定结构、功能和区际联系的乡村空间体系,是一个由城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体等组成的地域多体系统。以乡村地域系统为对象,服务支撑国家乡村振兴战略,为新时期地理学创新研究提供了新机遇和新挑战。乡村振兴地理学研究,亟需以问题为导向、战略为指向,以人地关系地域系统理论和人地系统科学为指导,致力于地表人地系统交互作用下乡村地域系统结构、转型过程、演变机理、分异格局、地域功能,以及乡村振兴途径与模式综合研究,科学把握乡村地域系统类型及其分异规律。本文以全国39164个乡镇为基本单元,采用定量和定性相结合的研究方法,诊断识别了制约中国乡村地域系统可持续发展的主导因子,划分了中国乡村地域系统类型,揭示了乡村地域系统分异格局,探明了不同类型区乡村振兴科学途径。结果表明:① 地理环境、村镇化水平、资源禀赋、人口流动程度和老龄化水平等是乡村地域系统分异的主导因子,反映了乡村发展自然本底特征以及外援动力、内生动力的大小。② 通过主导要素聚类和空间叠加分析,将中国乡村地域系统划分为12个一级区、43个二级区。一级区采用“地理区位+主导要素驱动力/约束力”的方法命名,二级区采用“地域范围+主导要素驱动力/约束力+乡村经济发展水平”命名。③ 不同类型区乡村振兴地域模式和路径不同,乡村振兴战略与规划的落地要因地制宜、分类施策。
Land consolidation and rural vitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810002
[本文引用: 1]

The core objective of rural vitalization is to systemically establish a coupling pattern of various rural development elements including population, land and industry. As one of the prerequisites, land resources is required to be optimally allocated via land consolidation. Consequently, land consolidation contributes greatly in population agglomeration, industry development and resources support under the context of combating rural decline. In light of these facts, this paper conducts an elementary analysis on the connotation of land consolidation and rural vitalization in the new era, as well as their relationships. Furthermore, the issues on the alternative paths for achieving rural vitalization via land consolidation in different regions were also discussed. Main conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) It is manifested that rural vitalization in the new era can be explained as a comprehensive process of tackling the loss and decline of rural development elements through political, economic and cultural means. Most importantly, vitalizing the interior motivation and absorbing the external power are essential for the efficient reconfiguration and utilization of rural population, land and industry, thus achieving the goals of arousing rural vitality, optimizing elements structure, enhancing territorial function and restructuring rural morphology. (2) From the perspective of rural vitalization, land consolidation, which adheres to the path of connotative development, should not only target at stimulating the key elements of rural development, but also place emphasis on the coordination of material space and spirit core, so as to realize the co-prosperity of the urban and the rural areas. (3) Regional natural indigenous factors and the corresponding phases of socio-economic development should be both taken into account in the process of implementing rural land consolidation. Following the principle of adjusting measures to local conditions, appropriate paths or modes are supposed to be chosen in different regions constrained by the territorial development pattern. Finally, focusing on a series of problems and new concepts, which is aimed at achieving urban-rural integration development and boosting socio-economic growth in rural areas, we propose further discussions.
论土地整治与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810002
[本文引用: 1]

乡村振兴的核心目的是系统构建人口、土地、产业等多种发展要素的耦合格局。土地整治在乡村振兴过程中肩负着为人口集聚、产业发展提供资源支撑的基础性作用。本文基于影响乡村发展的关键要素阐释了新时代乡村振兴和土地整治的内涵及其互馈关系,剖析了乡村振兴背景下土地整治的区域实施路径。最后,就未来乡村振兴视角下土地整治的方向进行了展望与讨论。结论如下:① 乡村振兴的内涵在于为应对乡村内部要素的流失与衰退,通过经济、政治及文化建设等手段激发内部动力和吸纳外部资源来重新组合、优化配置和高效利用乡村人口、土地和产业等发展要素,从而优化要素结构、提升地域功能、重塑乡村形态,实现乡村地域经济、社会及生态的全面复兴和城乡融合发展的新格局;② 乡村振兴视角下土地整治要激活乡村人口、土地和产业等关键发展要素,统筹物质空间振兴与精神内核提升;③ 开展农村土地整治要与区域自然本底条件和社会经济发展阶段相适应,按照分区统筹、分类施策的原则在国土空间开发格局的框架下因地制宜地采取相应的模式与路径;④ 未来有必要重塑土地整治的价值取向,在统一空间规划体系下统筹土地整治规划与乡村振兴规划,大力发展土地整治与多功能农业相结合的新模式。
Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 6]

The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
论乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 6]

构建现代乡村治理体系成为推动城乡融合发展和乡村振兴的重要内容。破解乡村空间利用过程中出现的发展空间受限、权属关系不明和组织体系不畅等系统性问题,成为乡村空间治理的首要任务。本文从乡村空间“物质—权属—组织”综合治理的视角出发,尝试解析乡村空间治理在推动乡村空间重构、权属关系重塑和组织体系重建中的作用机制,并进一步探讨乡村空间治理优化城乡格局、改善城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的可行路径。结论如下:物质空间治理可作为乡村空间结构和功能优化的重要手段,空间权属治理有助于保障乡村空间不同参与主体的发展权利,空间组织治理可提升乡村空间的组织效率;乡村空间治理导向的“人口—土地—产业”转型过程为“深化空间治理—活化乡村空间—优化人地关系—改善城乡格局”的分析思路创造条件;乡村空间治理推动城乡发展格局不断演化,城乡互动关系改善成为推动城乡融合发展和破解乡村发展困境的重要依据。最后,本文构建了乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展互动分析框架,并探讨了乡村空间治理与国土空间规划的内在关系及研究趋势。
Rural multifunctional evolution and rural settlements transformation
论乡村多功能演化与乡村聚落转型
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 5]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 5]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Research progress of urban-rural relations and its implications for rural revitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 2]

With the implementation of rural vitalization strategy, China has stepped into a critical period with the dramatic changes of urban-rural relations and the accelerating transformation development of rural territorial system. Scientifically understanding the research progress of urban-rural relation theory and evolution rule is of great significance for boosting rural vitalization, narrowing urban-rural disparity, adjusting urban-rural structure and optimizing urban-rural patterns. This paper elaborates the research progress of urban-rural relations and rural development in China from the dimensions of economy, society, ecology and culture based on the review of foreign urban-rural relations and the characteristics of domestic rural development, as well as the evolution of urban-rural relation. Furthermore, prospect of research focus or key fields in the future were given. Firstly, transforming the development idea from productivism oriented to post-productivism oriented and attaching importance to the multiple values of rural areas should be emphasized. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out intensive studies about the mechanism, regional path selection and development mode of rural vitalization based on the theory of rural multiple function transition. Understanding the relationship of different functions is essential for dealing with rural decline and realizing the comprehensive vitalization. Meanwhile, we should focus on the mechanism and format of rural vitalization based on different territorial types. Against the context of rural-urban integrated development, we should promote the supply-side reform and activate the forces of socio-economic growth in underdeveloped areas. As for the developed rural areas, the “hybridity” should be emphasized and further studies should be conducted. In some rural areas, the phenomenon of the hybridity of development agents, the combination of production space and living space, the mixture of rurality and modernism have emerged. Accordingly, more emphasis should be placed on the heterogeneity and diversity in the process of rural restructuring. Secondly, with the emergence of new factors or new technologies, we should focus on the new morphology of rural development, such as characteristic towns, rural complex and “Taobao village”. In recent years, China's rural areas have undergone intensive restructuring motivated by e-commerce, which has triggered a new wave of rural rejuvenation. But how e-commerce affects rural development and the characteristics of this process are still unclear, and this is important for understanding the urban-rural relations under the context of informatization. Thirdly, the mechanism and format of urban-rural spatial restructuring should be emphasized. From the perspective of urban-rural interaction, the theory of urban-rural network may be practical and meaningful for optimizing the spatial distribution of infrastructure construction and industrial development. Lastly, creating or improving the theory and improving the path of rural vitalization according to the national conditions are meaningful for realizing the strategy.
城乡关系研究进展及其对乡村振兴的启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 2]

随着乡村振兴战略的实施,我国已经进入城乡关系变革及乡村发展快速转型的关键时期。科学认知国内外城乡关系理论发展和演变规律对实施乡村振兴战略、缩小城乡差距、调整城乡结构和优化城乡格局具有重要意义。本文在系统梳理国外城乡关系理论及我国乡村发展与城乡关系演进的阶段性特征的基础上,从经济、社会、生态及文化的视角阐述了我国乡村发展与城乡关系研究的相关进展,并在此基础上探讨了未来重点的研究领域和方向。乡村发展思维应由生产主义导向转向后生产主义,关注乡村多元价值,深化基于乡村多功能转型理论的乡村振兴机制、区域路径与模式研究;在科技迅速发展,新事物新因素大量涌现的新时代,应关注特色小镇、田园综合体、民宿及乡村电子商务等新兴乡村转型发展形态的形成机制;同时,基于不同地域类型的乡村振兴的机制与模式研究也应得到重视,结合国际乡村地理学前沿,深入开展发达地区乡村的混杂性研究。广泛的城乡空间重构进程对乡村地区产生剧烈的影响与挑战,对于乡村振兴视角下城乡空间重构的动力机制与模式的研究仍需持续关注;根据我国的特殊国情,创新适合我国基本国情与发展实际的乡村振兴理论与实现路径,推动城乡融合发展。
Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization: Theory, mechanism and implementation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

Rural revitalization and urban-rural integration aim at narrowing the gap between urban and rural areas, promoting balanced development and realizing the equivalent life quality between urban and rural residents. Spatial equilibrium and its quantitative expression provide a new perspective to explain the pattern, process and mechanism of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. Through the analysis of basic theory, this study discusses the scientific content and interaction between urban-rural integration and rural revitalization, sets up the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, defines the urban-rural development isolines, works out the way to implement the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China, and addresses the potential for further research. The results show that: (1) Theory of regional system of man-land relationship and theory of spatial structure are the important theoretical basis for urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. The urban-rural integrated development depends on the all-round development of economy, society and environment with optimized spatial layout and innovative system, and rural revitalization mainly refers to the "pentagon of rural revitalization" and "people-land-capital-industry"; Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization strategy support each other, and the process of urban rural integration and rural revitalization is a dynamic equilibrium process between urban and rural areas. (2) The key issues of implementing rural revitalization and urban-rural integration can be illustrated through the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, and the overall per capita benefits in rural areas gradually tend to be the same as that in cities by the re-optimization of urban-rural factors and population mobility; the dynamic process and mechanism of urban-rural integration spatial equilibrium is further interpreted via the urban-rural development isolines. (3) Exploring the implementation path of scientific rural revitalization strategy can achieve the goal of urban-rural integration and urban-rural spatial equilibrium development. The scientific path of rural revitalization is discussed from the perspectives of policy system construction, "pole-axis" spatial progressive diffusion, sub-area classification and typical development pattern, and it can provide theoretical reference for the strategy implementation of China's rural revitalization.
城乡融合与乡村振兴: 理论探讨、机理阐释与实现路径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

缩小城乡差距,促进城乡均衡发展,实现城乡居民生活质量等值,是乡村振兴和城乡融合发展的重要目标。通过基础理论的分析,探讨了城乡融合与乡村振兴科学内涵,剖析了城乡融合与乡村振兴的相互关系,构建了城乡空间均衡模型和定义城乡等值线,提出了中国城乡融合与乡村振兴实现途径及需要深入研究的方向。结果表明:① 城乡融合发展是基于空间布局优化和制度供给创新的经济、社会、环境全面融合发展,“乡村振兴五边形”和“人—地—钱—业”是乡村振兴的核心内涵;城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相互支撑,城乡融合和乡村振兴的过程是城乡空间动态均衡的过程。② 城乡发展的空间均衡模型可以较好地阐释促进城乡融合发展、实施乡村振兴的关键问题,通过城乡要素的重新优化配置和人口的流动,城乡人均综合发展效益逐渐趋于相等;城乡等值线可以进一步解释城乡发展空间均衡的动态过程与传导机理。③ 从政策制度构建、“点轴”渐进扩散、分区分类推进、典型发展模式提炼等方面探讨乡村振兴的科学路径,可以为中国乡村振兴战略实施提供理论参考。
Spatial differentiation and mechanisms of typical rural areas in the suburbs of a metropolis: A case study of Beicun Village, Baiyun District, Guangzhou
广州市城郊典型乡村空间分化过程及机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908010
[本文引用: 2]

全球生产方式变革和社会制度改革加速了城市化进程,城乡要素流动加快了城郊乡村空间分化,以空间生产和博弈论为理论基础,针对广州市城郊北村的空间分化过程及机制进行解析,以期丰富乡村空间分化和治理的理论。结果表明:① 20世纪80年代以来,北村的发展经历了农业发展、工业发展和服务业发展等3个阶段,业态结构从单一的农业逐渐转向为多元,兼有农业去中心化向农村社区化发展转变过程。② 伴随村域经济发展转型,北村土地利用类型和结构趋向多元分化,各类用地空间关系变得更加复杂化,呈现出商住混合和工商混合的用地新特征,空间上逐渐形成“公共服务设施—传统居住区和现代居住区—商业区—农业区和工业区”的圈层式布局模式。③ 乡村物质空间的多元分化动力主要源于新产业介入和主导产业的更替转变。内生的土地流转方式和外生的城市资本共同推动乡村工业化进程,市场力推动了产业发展向服务业转型。④ 乡村工业化驱动了村社组织对历史建筑功能的置换,改变了乡村以宗族血缘和地缘为主的社会关系,产生了由外来务工人员和城市低收入阶层组成的业缘关系,乡村社会关系逐渐多元化。⑤ 城郊乡村空间多元分化遵循着资本和土地利益博弈逻辑。本地村民、代耕农民、经济合作社、工业经营主体和服务业经营主体等行为主体对空间进行争夺和利益博弈,村社组织起着关键的中介作用。
Rural governance and local involvement: Assessing state community relations in the Scottish Highlands
DOI:10.1016/S0743-0167(01)00048-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Routledge International Handbook of Rural Studies
From governance to rural-urban co-governance: Research frontiers, trends, and the Chinese paths
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

Governance has become an important theoretical and practical issue of multi-disciplinary concern. In the context of rapid urbanization and wide rural-urban disparity, rural-urban governance is particularly important for China. Based on the Chinese and international governance theories, the key aspects of governance include: an open system, self-organization, and the interactive relationship between power and rights. Internationally the research frontier focuses on the governance of social-ecological systems, while urban governance has grown significantly, and rural governance has also risen in recent years. The research trend and policy evolution of governance in China indicate that China has undergone a comprehensive transformation from management to governance by top-level design, and rural-urban governance is becoming a key issue. The main path of China's rural-urban governance in the future lies in three aspects. First, it is necessary to shift from power-oriented to rights-oriented governance. Second, equal attention needs to be paid to both ecological environment and social governance instead of focusing only on social, single-dimensional, and urban governance systems, and form a rural-urban co-governance system with the participation of multiple subjects. Third, it should be launched to assist rural and urban vulnerable groups actively. Rural-urban co-governance will become a new growth point for theories, and multi-disciplinary, multi-subject, and multi-department collaboration is much needed.
从治理到城乡治理: 国际前沿、发展态势与中国路径
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

治理已经成为多学科关注的重要理论与现实问题。在快速城镇化和城乡差距居高不下的背景下,城乡治理对中国而言尤为重要。论文通过梳理国内外治理理论,概括治理的要点为开放系统、自组织、权力与权利的交织3个方面。国际研究强调社会生态系统的治理,城市治理增势显著,乡村治理研究开始兴起。中国在顶层设计上经历了从管理到治理的全面转型,城乡治理逐渐成为研究和政策实践的关键议题。未来中国城乡治理的主要路径在于:从权力导向转向权利导向;从只注重社会维度、一元化的、城市偏向的治理模式转向生态环境与社会治理并重,形成多元主体参与的城乡共治体系;积极开展城乡弱势群体的扶持救助工作。城乡共治将会成为新的理论增长点,需要进行多学科、多主体、多部门的协同工作。
Rethinking on the basic issues of territorial and spatial use control in China
中国国土空间用途管制的基础性问题思考
The reform of the natural resource property rights system and the innovation in territorial spatial governance
自然资源产权改革与国土空间治理创
Spatial governance: Political economy of China's urban and rural planning transformation
空间治理:中国城乡规划转型的政治经济学
Grain production transformation mechanism and the security effects in traditional farming areas: The perspective of rural spatial governance
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210618 URL [本文引用: 2]
传统农区粮食生产转型机制及其安全效应: 基于乡村空间治理视角
Rural revitalization and sustainable development: Typical case analysis and its enlightenments
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180879
[本文引用: 1]

Rural decline is a global phenomenon as the world endeavors to promote its urbanization and industrialization. China has been one of such countries which experienced rapid urbanization development while its countryside is suffering depopulation and the related challenges such as labor shortage, economic recession and land abandonment which are referred as the hollowing-out villages. Rural decline is not solely existing in China. Generally, the current developed countries such as the US, Sweden, UK and France etc. all experienced rural decline while the states took measures and produced policies to revitalize the countryside. In 2017, the Chinese Central Government initiated its rural revitalization strategy which covers a period until 2050. How to implement this strategy? What experiences from the world can be borrowed to China? The paper aims to investigate typical cases from abroad and draw experiences which may be applied in China. By referring to cases from Germany, Japan and Sweden, the paper introduces separately the roles of rural land consolidation, special industry development and social capital cultivation in coordinating human-land relationship, improving endogenous capability and constructing new rural subjects. The analysis finds that these measures have contributed to the coupling development of rural people, land and industries. The enlightenments lie in three aspects. First, land consolidation optimizes rural production, living and ecology spaces and provides rural development with a platform through which local industries can develop by inputting resources. Second, local stakeholders' initiatives and the development of new rural subjects are the key elements to improve villages' endogenous capability. Third, the good values, trust, responsibility and social networks contribute to the cohesion and synergy of rural society and improve the production efficiency of the rural inputs of physical capital and human capital. The paper further discusses the applicability of these experiences in China. It points out that China has large territory and villages differ a lot in resources endowments, development stages, advantages and disadvantages. It is necessary to investigate the current situation of rural system of different areal types, and to figure out the suitable ways to deal with problems and challenges so as to revitalize the countryside. And in this process, the endogenous development and local peasants' initiatives are important to achieve sustainable rural development in the long run.
乡村振兴与可持续发展: 国际典型案例剖析及其启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180879
[本文引用: 1]

基于对国际典型案例剖析,系统阐释了土地整治、特色产业发展、社会资本培育在协调乡村人地关系,提升内生动力,构建乡村新型主体,实现乡村地域“人-地-业”耦合发展中的重要作用。实施土地整治适应了乡村人地关系变化,有利于提高土地资源利用效率,优化乡村生产、生活、生态空间,为乡村转型发展提供载体。依托优势资源,发展特色产业是提升乡村内生动力的重要抓手,有利于激活乡村人口、土地、产业等要素活力。而民众主观能动性、新型经营主体的构建是增强乡村内生动力的关键因素。乡村社会良好的价值观、信任、责任及其社会网络的培育与构建有助于提高乡村主体凝聚力与协作力,提高乡村地区发展质量,提升物质资本及人力资本的产出效益。
Approaches to rural transformation and sustainable development in the context of urban-rural integration
城乡融合背景下乡村转型与可持续发展路径探析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

探究乡村转型发展规律对于系统认识乡村发展阶段、研判乡村发展趋势、明确乡村可持续路径、促进乡村转型与振兴具有重要意义。首先基于马斯洛需求层次理论、产业结构演变理论、区域空间结构理论等演绎乡村转型发展阶段,然后结合典型乡村发展历程分析进行实证检验,进而探讨对于新时期乡村可持续发展的启示。研究结果:① 乡村转型发展在理论上可分为4个阶段,一是生产力均匀分布下以实现温饱需求为目标的土地整治促增产阶段,二是城乡联系增强下以改善生活水平为目标的农业结构调整促增收阶段,三是区域联系增强下以提升生活质量为目标的产业结构调整促致富阶段,四是城乡互动融合下以城乡等值为目标的公服设施建设促均等阶段。② 典型发达乡村的发展历程在一定程度上印证了乡村转型发展阶段特征。③ 因资源基础、区位条件、市场规模、发展主动性等因素的差异,乡村实际发展过程可能存在阶段的跃迁或并行的现象。根据发展过程中不同主体发挥作用的变化,每个阶段又可细分为初始阶段、过渡阶段和成熟阶段。④ 基于乡村转型发展规律分析,城乡融合背景下不同类型地区乡村可持续发展路径可分为土地整治集聚路径、特色产业发展路径、产业平台集散路径和社区功能集约路径等4类。
High-quality Development of national territory space governance and regional economic layout during 14th five-year plan in China
我国“十四五”时期高质量发展的国土空间治理与区域经济布局
Rural restructuring: Theory, approach and research prospect
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 1]

For the sake of adapting to the changes of elements in both kernel system and external system of rural development, rural restructuring is a process of optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements affecting rural development, reshaping social and economic structures in rural areas and optimizing spatial pattern in rural territory, and approaching the structure optimization and function promotion of rural territorial system as well as the structure coordination and function complementation of urban-rural territorial system. Based on elaborating the concept and connotations of rural restructuring and the mechanism of promoting rural restructuring due to the evolution of "elements-structure-function", the paper probed the approaches of rural restructuring from the aspects of spatial restructuring, economic restructuring and social restructuring. In order to meet the current national strategic demands and meet the challenges of rural development in the process of urban-rural development transformation, it is in great urgency to strengthen the study on the patterns and processes, dynamic mechanism, differentiated development models, rural planning technology systems, strategies and policies for rural development, and the impacts of globalization on China's rural restructuring in the future. Finally, focusing on a series of problems in the implementation of some important government intervention policies, which is aimed at boosting the social and economic development of rural areas in recent years, a critical analysis and discussion is carried out.
论乡村重构
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 1]

快速城镇化进程驱动中国乡村地域发生巨大变化。乡村重构,即为适应乡村内部要素和外部调控的变化,通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局,以实现乡村地域系统内部结构优化、功能提升以及城乡地域系统之间结构协调、功能互补的过程。本文在界定乡村重构的概念内涵,构建基于“要素—结构—功能”演变助推乡村重构的理论框架基础上,从空间重构、经济重构、社会重构视角探讨了乡村重构的实现路径,并着眼于服务当前国家重大战略需求和解决城乡转型发展进程中乡村地域系统面临的现实困境,提出了未来中国乡村重构研究需重点关注的内容。最后,就现有旨在促进乡村社会经济发展的重大引导性战略和政府干预性政策及其在实践操作中引发的一系列问题,展开批判性分析和讨论。
The process of rural development and paths for rural revitalization in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106007
[本文引用: 1]

China is a large agricultural country, and issues concerning agriculture, rural areas and farmers are closely related to national economic and social development. To achieve the "Two Centenary Goals", rural revitalization strategy has become the choice to resolve unbalanced urban-rural development and inadequate rural development in China. Rural development is a comprehensive process of cycle accumulation and dynamic evolution of rural regional system. Thus, it is of great significance to systematically analyze the process and regional pattern of rural development to scientifically promote the implementation of rural revitalization strategy in the new era. Based on the theory of human-earth areal system and human-earth system science, this study examines the process and features of rural development in China from 1978 to 2050, discusses the internal relationship between rural transformation and rural revitalization, reveals the spatial pattern of the level of county rural revitalization in 2017, and finally puts forward the key problems and countermeasures for rural revitalization in the new era. Results show that the evolution of China's rural development in the period of 1978-2050 can be divided into three stages, i.e. solving the problem of food and clothing (1978-2005), building a well-off society (2005-2020) and realizing prosperity (2020-2050). In general, it is a dynamic and continuous process from low-level and basic-type to high-quality and innovation-type. Rural revitalization is a special stage of rural transformation, and a strategic choice to solve the prominent problem in rural development when it has evolved to a certain stage, thus boosting rural development to a higher stage. In 2017, when rural revitalization strategy was initiated, the level of rural revitalization in 57.3% of the counties in China was between 0.40 and 0.50, and there was an obvious gradient differentiation from the east to the west, with significant clustering characteristics and positive correlation. Specifically, the counties featured by "high-high (H-H)" clustering were mainly distributed in the third step of the terrain and the middle of Sichuan Basin; while the counties featured by "low-low (L-L)" clustering were concentrated in western China except Sichuan Basin, the eastern part of Inner Mongolia and the north of Tianshan Mountains. Due to the regionalism, stage and the difference in constraints of rural development, the focuses of rural revitalization in the new era lie in scientifically identifying the targeting areas of rural revitalization, comprehensively judging the trends of rural development, and systematically diagnosing the dominant constraints of different types of rural areas, so as to take targeted measures to make up for the shortcomings of the modernization of agriculture and rural areas. Besides, it is necessary to fully understand the interactions between urban and rural areas, thus promoting urban-rural integrated development.
中国乡村发展进程与乡村振兴路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106007
[本文引用: 1]

乡村发展是乡村地域系统循环累积与动态演化的结果,全面梳理乡村发展历史脉络与地域分异格局,对于科学推动新时代乡村振兴战略落实具有重要意义。基于人地关系地域系统理论和人地系统科学认知,本文解析了1978—2050年中国乡村发展演化进程,探讨了乡村转型发展与乡村振兴的内在逻辑,揭示了中国县域乡村振兴水平的空间格局,进而提出了新时代乡村振兴的关键问题及其路径对策。研究表明:① 中国1978—2050年的乡村发展可划分为解决温饱、小康建设和实现富裕三个主要阶段,是一个由低水平、基础型向高质量、创新型不断发展的过程;② 乡村振兴本质上是乡村转型发展的一个特殊阶段,是乡村发展演化到一定阶段后,为解决其面临的突出问题以向更高层次迈进的战略选择;③ 2017年中国57.3%的县域乡村振兴综合水平介于0.40~0.50之间,在空间上呈现出明显的东中西地域分异,并具有显著的聚集特征和正相关性;④ 新时代乡村振兴战略的落实重在科学识别乡村振兴的瞄准区域,综合研判乡村发展演化的趋势,系统诊断乡村地域类型的主导制约因素,全面认知城乡耦合互动的逻辑关系,进而采取针对性措施推进农业农村现代化。
Research progress and prospect of rural transformation and reconstruction in China: Paradigms and main content
中国乡村转型重构研究进展与展望: 逻辑主线与内容框架
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.08.009
[本文引用: 1]

伴随快速城镇化,乡村地域正经历着经济社会发展方式转变为主导的人文过程,前瞻性地研究乡村转型发展过程格局、演进机理及空间优化重组研究意义重大。本文系统梳理乡村发展转型内涵、过程格局、驱动机制、类型模式、乡村空间重构、农村发展理论及农村空心化等系列成果研究进展,并进行简要研究评述。在此基础上,对中国乡村发展转型与重构的研究核心内容和逻辑主线加以凝练总结。未来乡村发展转型与重构研究应以人地关系地域系统理论为指导,以揭示不同地域类型区的乡村转型发展过程及演进机制为核心,以建构乡村空间优化重组理论和探究模式途径为目标,综合集成遥感与GIS、抽样调查和模型方法,重点研究不同典型地域的乡村转型发展的多尺度过程规律、地域类型、动力机制,深化乡村空间体系演化规律和优化重组的内外机制,及乡村社会文化网络、技术制度转型重组等方面的研究,进行乡村多维空间重组的情景模拟。结合典型案例实证研究,解构乡村多维空间重构理论与模式的成长机制与区域主导地理要素;比较分析典型模式的演化过程和要素互馈作用机制;探寻推进乡村良性转型发展及空间优化重组的地域模式和科学途径。
China's rural land reform and rural vitalization
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.09.015
[本文引用: 1]

There is a huge gulf between the dilemmas of rural development and the strategic goals of rural vitalization in China. This study examined the trend and characteristics of land reform and rural development in China since 1949, and then explored the interactive mechanisms based on the functional system of rural land reform. Alternative pathways and typical models of rural vitalization promoted by rural land reform were also discussed. The main conclusions are as follows: 1) Rural land reform is the breakthrough point to address the current dilemmas of rural development and promote rural vitalization. In essence, it is the readjustment of production relations in the new era to adapt to the development of urban-rural productive forces, both of which are urgent, integrative, and challenging. Since 1949, changes in rural land institution and rural development have been generally coupled and linked. 2) In the new era, rural land reform has multifunctional values. It promotes rural reconstruction and rural multifunctional development by reinforcing weak links and gives play to the multiplier effect of institutional linkages, urban-rural integration, and economy transformation, to promote rural vitalization and drive the optimization of urban-rural territorial system functions. 3) Along the path of integrating elements, restructuring structures, and optimizing functions, rural land reform promotes the change of regional functions and rural vitalization according to local conditions. 4) In the future, it is necessary to give full play to the stimulating effect of rural land reform, pay attention to potential policy frictions, deepen the positive feedback of rural vitalization on rural land reform, and carefully consider the coordination of rural land reform measures and rural development.
农村土地制度改革与乡村振兴
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.09.015
[本文引用: 1]

乡村发展现实困境与乡村振兴战略目标之间存在巨大鸿沟。论文总结了1949年以来农村土地制度改革与乡村发展的演进态势与时代特征,基于农村土地制度改革的功能体系,剖析了二者的互动机制,探讨了农村土地制度改革助推乡村振兴的发展路径与典型模式,并进行了研究展望。结论如下:① 农村土地制度改革是破解当前乡村发展困境、推进乡村振兴的突破口,本质是新时期为适应城乡生产力发展的生产关系再调整,二者均具迫切性、交融性与攻坚性的时代特征。1949年以来农村土地制度与乡村发展总体耦合联动、互促互馈。② 新时期,农村土地制度改革具有多功能价值,通过补短板促进乡村重构与乡村多功能发展,发挥制度联动、城乡融合与经济转型的乘数效应,助推乡村振兴,并带动城乡地域系统功能优化。③ 农村土地制度改革沿整合要素、重组结构、优化功能的路径,因地制宜、分类推进乡村地域功能演变与乡村振兴。④ 未来需发挥农村土地制度改革的制度联动作用,同时重视改革的政策性摩擦,深化乡村振兴对农村土地制度改革的正反馈,并权衡农村土地制度改革举措与乡村发展的适应性问题。
Diversified agriculture and rural development in China based on multifunction theory: Beyond modernization paradigm
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

There is a big gap between general rural modernization paradigm and huge empirical rural geography studies. This gap results in impotent development strategies on regionally differentiated countryside. Based on multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory which emerged in Western World as a new paradigm, this paper discusses the multiple objectives, differentiated pathways and policies of agriculture and rural development in China. Firstly, this paper reflects the problems and challenges caused by modernization paradigm in rural China on economic, social, and environmental aspects, as well as that of western developed countries. It can be concluded that conventional agricultural and rural modernization is developed largely at the expense of rural environment, social fabric and economic viabilities. Obviously, "modernization development paradigm" alone is not enough for healthy agricultural and rural development in such booming economy as China. A better paradigm should be developed which takes economic development, social justice and environmental sustainability into account at the same time. After a brief review of multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory overseas, the multiple objectives of agriculture and rural development in China are put forward. These multiple objectives, however, should not and could not be a burden on rural space indiscriminatingly due to the enormous differentiation of natural and socio-economic conditions. Thus, the final but main part of this paper envisions the differentiated pathways and policy portfolios of agricultural and rural development in China from the perspective of territorial division.
基于多功能理论的中国乡村发展多元化探讨: 超越“现代化”发展范式
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

传统的乡村现代化发展范式和地理学关于乡村的区域差异研究之间存在缝隙,不足以为快速演化分异的乡村地域发展提供直接理论支撑。本文引入西方近20年来逐渐兴起的多功能农业与多功能乡村理论,从新的视角观察思考中国乡村多元化发展的目标、路径及对策。首先从经济、社会和环境三个方面反思中国乡村现代化的基本历程与得失,以及西方国家乡村现代化产生的问题,指出传统的农业农村现代化发展在很大程度是以牺牲乡村环境和乡村社会机理脆弱化为代价的,也造成了乡村经济对外部支持的过度依赖,仅仅强调“现代化”发展范式显然是不够的;然后简要介绍了国外多功能农业与多功能乡村理论;在此基础上,从功能角度提出中国农业农村发展的多元目标,推演探讨农业农村发展的区域差异化路径及对策。
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
Discussion on rural sustainability and rural sustainability science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004006
[本文引用: 1]

In the face of global environmental challenges, sustainable development has received much attention worldwide, and sustainability science has emerged in the 21st century as a globally well-recognized new area of science. Rural sustainability science, as an important part of sustainability science, is a use-inspired science aimed at understanding and improving the dynamic relationship between people and the rural environment from a transdisciplinary and multiscale perspective. In tandem with urban sustainability science, it provides much needed scientific support for dealing with rural decline and promoting rural sustainable development. In this paper, we first discuss the concepts of sustainability, rural sustainability, and rural sustainability science, and then propose a transdisciplinary integrated framework of rural sustainability science that focuses on agricultural sustainability, community sustainability, and rural human well-being. China is a nation with deep rural roots, complex problems involving interactions among agriculture, farmers, and villages, and huge urban-rural socioeconomic gaps. Since the reform and opening-up in 1978, China's rural areas have developed rapidly, but they still face numerous tough challenges. Rural revitalization strategies are needed for promoting the rural transition toward sustainability, but the necessary scientific basis and appropriate guidelines for formulating such strategies are still lacking. We argue that rural sustainability science can provide theoretical, technical, and decision-making support for the implementation of rural revitalization strategies. Our analysis of the current status of China's rural sustainable development indicates that the transition to sustainability is urgently needed, and so is the science that guides the transition. To address these problems, we call for transdisciplinary research that couples rural society and its environment, focusing on nine core issues in line with the needs of China's rural development and aiming to transfer knowledge of rural sustainability into local adaptive actions.
论乡村可持续性与乡村可持续性科学
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004006
[本文引用: 1]

面对全球环境挑战,可持续发展备受关注,成为21世纪举世瞩目的新兴领域。乡村可持续性科学作为可持续性科学的重要组成部分,是一门以跨学科思维、多尺度视角来理解和改善乡村人地关系的、以应用为导向的整合型学科。与城市可持续性科学相互对应并相互联系,乡村可持续性科学是应对乡村衰退、促进乡村可持续发展所急需的科学支撑。本文在讨论可持续性、乡村可持续性与乡村可持续性科学概念基础上,以农业可持续性、社区可持续性与农民福祉为主要内容,构建了一个多学科综合的乡村可持续性科学研究框架。中国是一个农业大国,城乡差距明显,“三农”问题复杂,1978年改革开放以来,乡村发展迅速,但也面临艰巨挑战。乡村振兴战略的实施是推动中国乡村向可持续发展转型的有效途径,但其理论与实践体系尚不完善。具有中国特色的乡村可持续性科学的发展,可以为乡村振兴战略实施提供理论、技术与决策支撑。为此,本文对中国乡村可持续发展现状进行了分析,并基于文献分析探讨了中国乡村可持续研究的不足。结论显示,中国乡村迫切需要向可持续发展转型,但乡村可持续性科学基础薄弱,需借鉴国际经验,立足本国国情,强化跨学科研究与人地系统耦合研究,聚焦9个适应中国当前乡村发展需求的核心议题,并因地制宜地将乡村可持续性研究成果转化为指导乡村振兴发展的行动策略。
Rural transformation development and new countryside construction in eastern coastal area of China
中国东部沿海地区乡村转型发展与新农村建设
Spatio-temporal differentiation and differentiated regulation of the vulnerability of rural production space system in Chongqing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008009
[本文引用: 1]

Vulnerability, one of the major properties of rural production space system (RPSS), is an effective measure in how system will be susceptible to negative effects or damage, as well as the way to achieving sustainable development of the system. This study establishes an evaluation index system and model of the vulnerability of RPSS and quantitatively measures the RPSS vulnerability of Chongqing from 2007 to 2017 to reveal its spatio-temporal differentiation. Accordingly it identifies vulnerability types and proposes targeted regulation strategies. The results are shown as follows. (1) The vulnerability of the RPSS is a comprehensive measure of the operating state of the system consisting of exposure, sensitivity and adaptability. It embodies the balance relationship of mutual influence and interaction that lies between rural diversified subjects centered on "human" and the rural production space centered on "land". (2) On the whole, the exposure of the RPSS shows an upward trend and a spatial pattern of "partly prominent, high in the north and low in the south"; the sensitivity shows a downward trend of fluctuation and a spatial pattern of "high in the east and low in the west"; the adaptability shows a rapidly increasing trend and a spatial pattern of "high in the west and low in the east". The overall vulnerability of RPSS presents a downward trend and the spatial pattern of "high in the east and low in the west". (3) After dividing the vulnerability of the RPSS into four types, namely, including adaptability type, exposure-sensitivity type, sensitivity-adaptation type, and strong comprehensive type, and based on the principle of "ecological priority - classified regulation - highlight emphasis - local adaptation", this study proposes differentiated "vulnerability reduction" strategies for different types, so as to guide the sustainable development of RPSS.
重庆市乡村生产空间系统脆弱性时空分异与差异化调控
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008009
[本文引用: 1]

脆弱性作为乡村生产空间系统的重要属性,是探讨系统易受负面影响或损害程度的有效度量、解析系统可持续发展趋势的有效途径。以重庆市为研究区,以2007—2017年为研究时段,建立乡村生产空间系统脆弱性评价指标体系和评价模型,以定量测度乡村生产空间系统脆弱性,揭示其时空分异特征,进而划分脆弱性类型并提出差异化调控策略。结果表明:① 乡村生产空间系统脆弱性是系统运行状态的综合度量,包含暴露度、敏感性和适应能力3个要素,其体现了以“人”为核心的乡村多元主体与以“地”为核心的乡村生产空间之间相互影响、相互作用的互动制衡关系。② 乡村生产空间系统暴露度总体呈上升趋势及“局部突出、北高南低”的空间格局特征;敏感性总体呈波动下降趋势及“东高西低”的空间格局特征;适应能力总体呈快速上升趋势及“西高东低”的空间格局特征;脆弱性总体呈下降趋势及“东高西低”的空间格局特征。③ 将重庆市乡村生产空间系统脆弱性划分为适应能力脆弱型、暴露—敏感脆弱型、敏感—适应脆弱型和强综合脆弱型4种类型,并按照“生态优先—分类调控—重点突出—因地施策”原则针对不同类型提出差异化“降脆”策略,以引导乡村生产空间系统可持续发展。
The cognition and path analysis of rural revitalization theory based on rural resilience
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910004
[本文引用: 2]

The rural decline which emerged in the process of human development and transformation has become a global trend, and rural revitalization is urgently needed. It is the only way to realize rural revitalization and sustainable development by scientifically and systematically grasping the development and evolution of rural regional systems, revealing the interaction mode of rural system and external development environment, as well as improving the rural resilience to resist and adapt to changes in the external environment. The article analyzes the development and evolution of rural regional systems and rural revitalization from the perspective of rural resilience. The study found that: (1) Rural resilience includes the resilience, adaptability and transformation ability of the rural system to the impact of external disturbances. (2) Rural development evolution differentiation is a comprehensive representation of the interaction between rural regional systems and the dominant factors of external development. In this process, the resilience of rural systems in different regions to resist external development disturbances has been improved or declined. (3) Creating multi-functional villages, implementing rural rectification projects, and cultivating rural social capital play an important role in promoting the construction of rural resilience. The article emphasizes that the rural regional system should be scientifically identified and differentiated implementation plans are formulated to cultivate and enhance rural resilience to achieve balanced function, structure and operation of rural system.
基于乡村弹性的乡村振兴理论认知与路径研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910004
[本文引用: 2]

在人类社会发展转型过程中出现的乡村衰退问题已成为全球性趋势,亟需实施乡村振兴。科学、系统把握乡村地域系统的演化规律,深入揭示乡村系统与外界发展环境的交互作用模式,提升乡村自身抵御、适应外界环境变化的弹性,是实现乡村振兴与可持续发展的必由之路。本文从乡村弹性视角理论解析了乡村地域系统演化与乡村振兴。研究发现:① 乡村弹性包含乡村系统对外界扰动冲击的抵御能力、适应能力与实现全新发展的转型能力。② 乡村演化分异是乡村地域系统与外界发展主导因素交互作用的结果。在此过程中,乡村弹性决定着不同发展阶段乡村地域系统的演化方式和结果。③ 打造多功能乡村、实施乡村整治工程、培育乡村社会资本对构建弹性乡村起着重要的推动作用。文章强调应科学识别乡村地域系统,差异化制定培育与提升乡村弹性的实施方案,实现乡村系统功能、结构及运行达到均衡状态。
Agricultural development status and industrial prosperity path under the background of rural revitalization in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181026
[本文引用: 3]

China’s agricultural competitiveness is weak and agricultural development is hence related to agricultural and rural modernization. The research applies the ‘element-structure-function’ analysis framework to discuss the theoretical basis of China’s agricultural development and industrial prosperity, and to analyze the characteristics, influencing factors and development paths of China’s agricultural development. The results indicate that: (1) Agriculture and rural areas have shifted from emphasizing on agricultural production and social stability to incorporating many functions including product supply, social stability, cultural heritage and ecological conservation. The multi-functional nature of agriculture supports the foundation and the broad space for agricultural development of China. (2) The main theoretical options to promote agricultural development are division of labor based on comparative advantage, increasing agricultural added value by product differentiation, resolving market failures by strengthening government support, and promoting the coordinated relationship among “people”, “land” and “industry”. (3) During the development process of China’s agriculture, the sense of gaining of indirect stakeholder is stronger than that of farmers, and meanwhile, it faces bottlenecks such as low agricultural labor productivity. (4) Considering the multi-functional nature and reality of agriculture, we provide some recommendations to improve China’s agricultural development and industrial prosperity. These includes practically shifting the focus of China’s agricultural development from production increase to quality and efficiency improvement, promoting the integrations between production and towns as well as production and villages, establishing a functional mechanism of agricultural factors and a “accessible, retainable, and beneficial” distribution mechanism of production factors, and increasing the pertinence, coordination and linkage of supportive agricultural policies.
中国乡村振兴背景下的农业发展状态与产业兴旺途径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181026
[本文引用: 3]

中国农业竞争力偏弱,农业发展关乎农业农村现代化目标的实现。本文引入“要素-结构-功能”分析框架,探讨了乡村振兴背景下中国农业发展与产业兴旺的理论基础,解析了中国农业发展特征、影响因素与兴旺路径。结果表明:① 农业乡村已由特别强调农产品生产与社会稳定,转向兼顾产品供应、社会稳定、文化传承、生态涵养等诸多功能。农业的多功能属性,支撑了中国农业的基础地位与广阔的发展空间。② 基于比较优势进行分工、通过产品差异化以提高农业附加值、加强政府支持以化解市场失灵、促进“人”“地”“业”协调耦合,是推动农业发展的主要理论选项。③ 中国农业发展过程中,间接利益相关者的获得感要强于农民群体,同时还面临农业劳动生产效率偏低等瓶颈问题。④ 考虑农业的多功能属性与现实问题,建议切实推动中国农业发展由增产导向转向提质增效,促进产镇融合、产村融合,建立农业要素功能显化增殖机制与“进得来、留得住、能受益”的生产要素配置机制,提高农业支持政策的针对性、协同性与联动性,推动中国农业发展与产业兴旺。
Spatial patterns, formation mechanism and coping strategies of rural vulnerability in China at the county level
中国县域乡村脆弱性空间特征与形成机制及对策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106009
[本文引用: 2]

基于乡村脆弱性本质内涵,构建了中国县域乡村脆弱性综合测度的指标体系,对中国县域乡村脆弱性水平进行综合测度;通过遴选具有典型代表性的5条样带,深化分析中国乡村脆弱性的区域差异特征及其形成机制,并提出具有针对性的应对策略。结果表明:① 中国县域乡村脆弱性整体上处于较低脆弱度和中脆弱度阈值区间,并具明显的空间差异性,沿“博台线”呈南北分异的空间格局,东北部乡村脆弱性偏低,西南部乡村脆弱较高。② 外部性环境因素是诱发乡村脆弱性的先导因素,生态暴露、生态敏感和生态适应构成的乡村生态子系统是乡村脆弱性的根本性影响因素;经济暴露、经济敏感和经济适应构成的乡村经济子系统是乡村脆弱性的核心影响因素;社会暴露、社会敏感和社会适应组成的乡村社会子系统也是乡村脆弱性的重要影响因素。③ 以“地理区位、乡村脆弱性主导驱动因素和脆弱性程度”为依据,将中国县域乡村脆弱性划分为8个地域类型区。不同类型区域,遵循因地制宜原则,破除地区根植性和路径依赖,增强乡村地域系统扰动源的预测和监测,并对系统自身敏感性进行科学管制,提升乡村系统的适应能力,促进乡村可持续发展。
On the analysis of rural space
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

Influenced by the interaction of various internal and external factors including urbanization, informatization, and globalization, rural areas in China are experiencing socioeconomic restructuring, regional function upgrading, and a series of transformations and reconstructions. Rural areas face a range of unprecedented opportunities and challenges, and the proposal of "rural revitalization strategy" puts forward new requirements for rural development and rural geography. Therefore, a comprehensive and systematic understanding of rural space system and accurate depiction of rural space are necessary prerequisites for further studies. Existing Chinese research focused more on the material space and to some extent placed less focus on the study of social-cultural space. Using a single material space view is very difficult to understand and interpret a large number of increasingly complex rural geographical problems. Based on a systematic analysis of the thinking on rural space and development in China and abroad, this article points out the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture. This article preliminarily expounds the complexity of rural territorial system and argues that the rural space system that is derived from the rural territorial system should not be limited within the range of rural material space but be understood through the multi-dimensional perspective of space. According to the human-environment system theory, this study tried to construct a rural space system that consists of three progressive layers including material space-social space-cultural space and clarify the connotations of every layer and the logical relations between them to fully understand the increasingly complex rural area. This article also highlights the necessity that multi-dimensional rural spatial restructuring should be developed. Based on the construction of multi-dimensional rural space system, forming an overview of the historical process and realistic situation of rural spatial restructuring and predicting the future path of rural development are very important research tasks to carry out in the future. In the end, this article appeals that Chinese geographers should continue to discuss and analyze concepts of rural issues in order to constantly improve our understanding about the changing countryside, and deepen the studies of rural spatial restructuring by using the theories and methods of related subjects from the perspective of multi-dimensional space. Finally, for the comprehensive empirical research of rural geographical issues, Chinese rural geographers should strengthen micro scale studies, actively devote themselves to field study, be observant of rural daily life, and understand the rural society and culture to make up for the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture.
乡村空间辨析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着城镇化、信息化、全球化等多种内外因素的交互作用,中国的乡村正经历着社会经济形态重组、地域功能提升等一系列转型与重构的过程,乡村地域面临着前所未有的机遇与挑战,而“乡村振兴战略”的提出也给乡村发展及乡村地理学的研究提出了新要求,全面系统地认识乡村空间系统,准确把握乡村空间是开展进一步研究的必要前提。本文在系统梳理国内外对乡村空间的认知与发展基础上,指出国内乡村地理学在乡村社会—文化空间研究上的不足。本文以人地关系地域系统为理论基础,尝试建构了由“物质空间—社会空间—文化空间”组成的乡村空间系统,以期为全面认识日益复杂的乡村地域提供理论指导。
Land use transition and rural spatial governance: Mechanism, framework and perspectives
DOI:10.1007/s11442-020-1784-x URL [本文引用: 2]
Land consolidation and rural spatial restructuring
Currently, the implementation of new type industrialization, new type urbanization and agricultural modernization strategy lacks of a major hand grip and spatial sustain platform, due to long-term existed "dual-track" structure of rural-urban development in China as well as unstable rural development institution and mechanism and backward rural and agricultural infrastructures, which greatly affects the advancement of urban-rural integration development. It is necessary to restructure rural production, living and ecological space by carrying out land consolidation, so as to establish a new platform for building new countryside and realize urban-rural integration development in China. This paper develops the concept and connotation of rural spatial restructuring, i.e., an optimization and adjustment even utterly changing process of rural production, living and ecological space accompanied by rural socio-economic structure reshaping under the pressure of rapid industrialization and urbanization. The connotations of rural spatial restructuring involve three aspects of assembling industrial development, centralizing farmers' living and intensive resources utilization. Based on the effects analysis of industrialization and urbanization on rural production, living and ecological space, this paper also probes the mechanism which push forward rural spatial restructuring by carrying out land consolidation, an important approach to supplying cultivated land, revitalizing the stock land, optimizing rural-urban land, utilizing land intensively, and increasing land productivity. A conceptualization of the models of rural production, living and ecological environment spatial restructuring is analyzed in combination with agricultural land consolidation, hollowed villages consolidation and industrial and mining land consolidation. Finally, the author argues that a "bottom-up" restructuring strategy accompanied by a few "top-down" elements is helpful for smoothly pushing forward current rural spatial restructuring in China. The optimization and restructuring of rural intensive and high-efficient production space, suitable living space with amenity and ecological space with beautiful mountain and clean water will rely on the innovation of regional engineering technology, policy mechanism and mode of rural land consolidation, and more attentions should be paid to rural space, the foundation base and platform for realizing urban-rural integration development.
论土地整治与乡村空间重构
目前,中国新型工业化、城镇化和农业现代化的推进仍缺乏重要抓手和空间支撑平台,严重影响了城乡一体化发展进程。亟需通过开展农村土地综合整治,重构乡村生产、生活和生态空间,为推进新农村建设和城乡一体化发展搭建新平台。本文在界定了乡村空间重构,即在快速工业化和城镇化进程中,伴随乡村内生发展需求和外源驱动力综合作用下导致的农村地区社会经济结构重新塑造,乡村地域上生产空间、生活空间和生态空间的优化调整乃至根本性变革的过程,及其产业发展集聚、农民居住集中和资源利用集约3 个方面内涵的基础上,分析了工业化和城镇化进程对乡村生产、生活和生态空间的影响;探讨了乡村空间重构的土地整治类型及助推机制;结合农用地整治、"空心村"整治和工矿用地整治提出了乡村生产、生活和生态空间重构的模式与途径,以及依托土地整治的以"自下而上"为主、"自上而下"为辅的乡村空间重构战略。作为城乡一体化发展根基的乡村空间其重要性和基础平台作用应受到足够重视,乡村集约高效的生产空间、宜居适度的生活空间和山清水秀的生态空间的优化重构,有赖于区域农村土地整治工程技术、政策机制与模式的创新。
Progress and prospects of the coupling research on land use transitions and rural transformation development
土地利用转型与乡村转型发展耦合研究进展及展望
The research on optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

This paper introduces the "life quality theory". Based on the two-way interactive mechanism between space of rural settlements and the life quality, the paper researches the optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements in three aspects, which are the integration of rural settlement spatial functions, the optimization of spatial structure and the regulation of spatial scale, so as to build optimization mode and framework of spatial organization of rural settlements with high quality life. The study suggests that: (1) The settlement is the spatial carrier of life quality and the life quality is the essential content of settlements. The two mentioned above influence and improve each other. So, the reasonable rural settlement space is the important precondition for higher life quality. (2) The type of spatial function of rural settlements can be divided into livelihood maintaining, industrial developing and quality optimizing, and the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality requires promotion of livelihood maintaining, integration of industrial developing and engagement of quality optimizing. (3) There are two important aspects in the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements. The one is to promote the organic concentration of living space, agricultural space and industrial space, the organic evacuation of social intercourse space, recreational space and services space, and the organic balance of living space, production space and ecological space, in order to realize the reasonable proportion and optimized combination of internal spatial type in settlements. And the other one is to form a functional structure level of "comprehensive village - featured village" and build spatial organization mode of settlements connected by rural roads by switching the location and adjusting the function, with the destruction of underdeveloped villages, the saving of normal villages, the enlargement of important villages, and the construction of new villages. (4) As an ideal mode of rural settlements space optimization oriented by life quality, RROD mode should be built at a rational scale of unit settlement and distance between settlements, leading to an RROD and RROD system with rational structure, auxiliary facility, fully function and well-organized distribution.
基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

引入“生活质量理论”,基于乡村聚落空间与生活质量的双向循环互动机理,从乡村聚落空间功能整合、空间结构优化、空间尺度调控等三个方面研究乡村聚落空间优化问题,试图构建有效提高生活质量的乡村聚落空间优化框架与模式。研究认为:① 聚落是生活质量的空间载体,生活质量是聚落的本质内容,乡村聚落与生活质量相互促进、相互影响,构建科学合理的乡村聚落空间是提高农民生活质量的重要前提。② 乡村聚落空间功能类型可以划分为生计维持型功能、产业发展型功能与品质提升型功能,生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间功能优化,重点在于提升生计维持型功能,整合产业发展型功能,植入品质提升型功能。③ 乡村聚落空间结构优化的重点有两个方面,一是要促进居住空间、农业空间、工业空间有机集聚,社会交往空间、休闲空间、服务空间有机疏散,生活空间、生产空间、生态空间有机均衡,以实现聚落内部空间类型比例合理化与组合最优化;二是要通过聚居区位转换与聚落职能调整,移拆部分衰落村落,保留部分一般村落,扩大部分重点村落,新建部分新型村落,形成“综合村—特色村”的功能结构等级,构建以乡村公路为链接的聚落体系空间组织模式。④ RROD模式是基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化的理想模式,该模式的构建要合理确定聚落单体的规模尺度与聚落之间的距离尺度,引导形成结构合理、设施配套、功能完备、分布有序的RROD和RROD体系。
Research on dynamic model of urban-rural interface
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201612008
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial location of the urban-rural interface (URI) is at the junction of urban and rural areas. In function, URI is the spatial carrier of communication for urban and rural elements. The development of URI is of great significance to the coordination of urban and rural areas. First, from the perspective of elements flow, this research established a theoretical framework of URI, which is based on system dynamics, to extend the urban and rural system to a three-body framework: urban area-URI-rural area. In this framework, the structure of urban and rural system is composed of three subsystems including urban system, URI system and rural system. And among them, URI system has its unique structure and function. From this meaning, URI consists of three parts including boundary wall, interface and boundary gate. For its function, it mainly plays the role of defense and exchange in the urban and rural system. The formation mechanism of URI reflects the forces of urban and rural systems to URI, and the interaction mechanism reflects the reaction of URI to urban and rural systems. Second, on the basis of the theoretical model, we built a quantitative model to characterize the dynamic evolution mechanism of URI by using methods of quantitative geography. The model solution shows that: (1) In different stages of development, URI is affected by these different degrees of endogenous and exogenous dynamic power. In early stage of URI's formation, the development power is mainly derived from endogenous dynamics. With the development of URI, exogenous dynamics increased gradually, and functioned with endogenous dynamics. Moreover, the gap between two dynamics is narrowed and the development of URI is accelerated. After URI achieves the equilibrium, exogenous dynamics reduce gradually and endogenous dynamics become the main driving force. (2) With the development of URI, the effects transited from negative to positive. The value of effects depends on the cyclic accumulation capacity of URI itself. In early stage of URI's formation, the ability of cyclic accumulation is weak, so the effect of URI is minor, and may even be negative. With the increasing ability of the cyclic accumulation, the negative effect transfer to positive one and increase gradually. (3) The balancing condition of URI is mutually affected by the exchange rate, endogenous dynamics and cyclic accumulation ability of urban-rural elements. The equilibrium of a certain URI is stable and has spatial scale effects. According to the research on the stochastic dynamic model, we found that the random noise term would influence the speed of equilibrium state of certain URI, instead of the equilibrium state itself, which proved the argument that the equilibrium state of a certain URI is stable. Equilibrium solutions of the dynamic model further characterize that its equilibrium state is not exactly equal at different spatial scales. (4) The switch model depicts the function of boundary gate, and the interface equilibrium is the critical point to decide whether we switch the gate open or closed. When the boundary gate is open or closed depends on whether URI reaches the critical value of its equilibrium state. According to the above conclusions, the paper puts forward policy recommendations respectively from temporal and spatial scales. From the temporal perspective, because of the impetus, the effect of URI and the role of boundary gate are different in different development stages of URI, we should take discretionary measures. From the spatial perspective, the equilibrium of URI is different at different spatial scales, so different development policies should be implemented at different spatial scales of URI.
城乡界面动态模型研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201612008
[本文引用: 1]

城乡界面在地域上处于城市和乡村交界处,在功能上起到城乡要素交流的空间载体作用,其发展对城乡协调意义重大。基于系统动力学,从要素流的角度构建城乡界面的理论框架,通过构建数量模型来刻画城乡界面动态演化机制。模型求解结果显示:① 在不同发展阶段,城乡界面受到内生动力和外生动力不同程度的影响。② 随着城乡界面的发展,其效应由负效应向正效应过渡,效应大小取决于其循环积累能力大小。③ 平衡态受城乡要素交换率、自身内生动力和循环积累能力的共同影响;城乡界面的平衡态是恒定的,但具有空间尺度效应。④ 开关模型刻画了界门对城市系统和乡村系统的作用机制。据此,分别从时间尺度和空间尺度对中国城乡系统的发展提出政策建议。
The change and reconstruction of spatial planning system under the goal of modern national governance
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20191002 URL [本文引用: 2]
治理现代化目标下国家空间规划体系的变迁与重构
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of quality of life in rural areas of Hunan province
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812009
[本文引用: 1]

Understanding the regional differentiation regularities and causes of quality of life in rural areas is not only the new content of rural geography for a new era, but also the inherent requirement of the scientific implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. Taking 101 counties (cities, districts) of Hunan province as the research unit, this paper proposes a assessment indicator system of quality of life in rural areas consisting of six dimensions. Then, using the entropy method, exploratory spatial data analysis and geo-detector, we elaborate spatial pattern characteristics and influencing factors of quality of life in rural areas of the province. Our results suggest the following: (1) The spatial distribution pattern of quality of life indicates that the overall feature is high to low from the east to west and descends from east to west. (2) From the perspective of the spatial correlation pattern, obviously, the spatial pattern of High-High area and Low-Low area present a pattern of agglomeration. High-High area is mainly located in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration and its adjacent counties, while Low-Low area is mainly in western Hunan. (3) The primary factors influencing quality of life are per capita GDP, urbanization level, distance from provincial capital, and elevation. The secondary factors are the slope, the proportion of secondary and tertiary industries, the proportion of non-agricultural labor in rural areas, and total power of agricultural machinery. To realize rural revitalization and improve the quality of life in rural areas, we should give priority to rural industrial and economic revitalization based on eco-environmental protection, actively strengthen the interconnection between regions and enhance the modernization of infrastructure and public service facilities in rural areas.
湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812009
[本文引用: 1]

认知乡村生活质量的地域分异规律及形成原因,既是新时代乡村地理学研究的新内容,也是科学实施“乡村振兴”战略的内在要求。以湖南省101个县(市、区)为研究单元,构建由6个维度组成的乡村生活质量评价指标体系,运用熵权法、探索性空间数据分析(ESDA)及地理探测器等研究方法,研究湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局特征及其影响因素。结果表明:湖南乡村生活质量总体上呈现出东高西低并由东向西依次递减的空间分布态势;从空间关联格局来看,HH区和LL区在空间上集聚格局明显,显著HH区主要分布在长株潭城市群地区和周边临近县域,显著LL区主要分布在大湘西地区;影响湖南乡村生活质量空间格局的重要因素为人均GDP、城镇化水平、离省会城市距离、海拔,次重要因素为坡度、第二第三产业占比、农村非农劳动力占比、农业机械总动力。振兴乡村,提高乡村生活质量应在充分保护乡村生态环境的基础上,把乡村产业振兴和经济振兴放在优先的位置,应积极改善广大乡村地区的互联互通条件,促进乡村地区基础设施和公共服务设施的现代化。
Themes evolution of rural revitalization and its research prospect in China from 1949 to 2019
1949—2019年中国乡村振兴主题演化过程与研究展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.09.001
[本文引用: 1]

实施乡村振兴战略是坚持农业农村优先发展、实现农业农村现代化总体目标、建立健全城乡融合发展体制机制和政策体系的重要途径。论文系统回顾了乡村发展的历程,将1949年以来中国乡村发展分为:人民公社为主体的城乡二元结构阶段、小农经济为主体的家庭联产承包责任制阶段、城市反哺农村的城乡统筹发展阶段、城乡融合发展与乡村振兴阶段4个发展时段。从时间序列深入刻画了乡村振兴的主体分化、产业演变、环境整治、文化重构、乡村治理5个振兴主题及乡村规划的演化过程与研究趋势。最后,着眼于新时代乡村振兴战略需求与研究热点,从学科交叉融合的理论与实践研究、城乡一体化与城乡融合发展研究、乡村产业融合发展与提质增效研究、乡村“三生”空间融合发展研究、乡村跨区域协作与联动研究5个方面对乡村振兴未来研究趋势展开了讨论。
The role of rural settlements in rural revitalization: Perspective of economic geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

This article started with an analysis of the background of rural decline, and the content and logic of the national strategy of rural revitalization from the perspective of human-land relationship. We proposed that rural recession is the result of the adjustment of human-land relationship lagging behind the process of social and economic development. The ultimate purpose of rural revitalization is to adjust the relationship between human and land to adapt to the change of the value of production factors in the new stage of social and economic development. Then, the review of the literature on rural revitalization found that the existing research has paid more attention to the implementation of its strategic content, but not enough attention to rural settlements that have been the important carrier of rural population. There is a close relationship between rural settlement and rural revitalization. Rural settlements are the focus of human social and economic activities in rural areas, and are the core and starting point of rural human-land relationship adjustment. But in the existing literature on rural settlements, emphasis is placed on development cases and neglecting mechanisms, especially the mechanism of change of rural settlements, which is closely associated with rural revitalization. Therefore, bearing in mind the key role of rural settlements in rural revitalization, this article finally put forward five focus areas of future research: the theory of rural settlement evolution, changing trend of spatial structure in rural settlements, specialization transformation of rural settlements, optimization of rural settlements, and landscape of rural settlements.
乡村振兴下的聚落研究: 来自经济地理学视角
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

论文首先从人地关系视角分析了乡村问题的背景及乡村振兴的内容逻辑,提出乡村衰退是人地关系调整滞后于社会经济发展进程的结果,乡村振兴最终目的就是调整人地关系以适应社会经济发展新阶段的生产要素价值变化。对乡村振兴地理研究的评述发现,多数关注其战略内容的实施,而对乡村人口重要载体的乡村聚落重视不够。事实上,乡村聚落与乡村振兴的关系密切,乡村聚落是乡村地区人类社会经济活动的集中场所,是乡村人地关系调整的核心和关键抓手,在乡村振兴中起关键作用。而已有的乡村聚落地理研究多聚焦空间变化,并且重实证轻机理,尤其是与乡村振兴相关联的聚落演变机理研究尚无成果问世。最后,基于乡村聚落在乡村振兴中关键作用,提出从人地关系协调出发,加强乡村聚落演变理论、乡村聚落空间结构变化趋势、乡村聚落专业化转型、乡村聚落整治优化及乡村聚落风貌景观等5个方面的研究。