1 引言
城市功能空间是城市地理学关注的重点研究领域。近年来,随着中国经济高速增长和城市空间快速扩展,“大城市病”凸显越发要求并策动城市功能空间合理布局与科学重构,加速呈现出多样性、动态性、复杂性的空间景观[1]。城市功能空间主要运用土地利用与遥感影像等进行判定。随着位置服务技术的发展,城市多源地理信息以及社会文化数据的获取和收集能力提升,地理空间大数据的挖掘已成为重要创新方向,Liu等[2]与Wang等[3]分别利用兴趣点(POI)数据与出租车轨迹以及OSM(Open Street Map)数据耦合以实现精细化的城市功能识别,也可根据人类活动密集程度细化功能区[4]以及更新类型[5]。基于GloVe的POI类型嵌套模型[6]、Word2vec算法[7]、Space2vec算法[8]被应用于甄别城市空间功能分类以及交互关系。城市功能复合有利于住宅与就业均衡分布,从而减少钟摆式交通和能耗污染[9]。阚长城等[10]通过TF-IDF算法和信息熵算法提出了基于多源时空大数据的城市功能空间混合评估新方法,Xia等[11]基于信息熵衡量城市功能空间的混合程度。信息熵指数已得到学者的广泛应用[12],通过建立空间信息熵模型,定量评价城市功能空间的混合程度[13]。
2 研究区域与方案
2.1 研究区域与数据来源
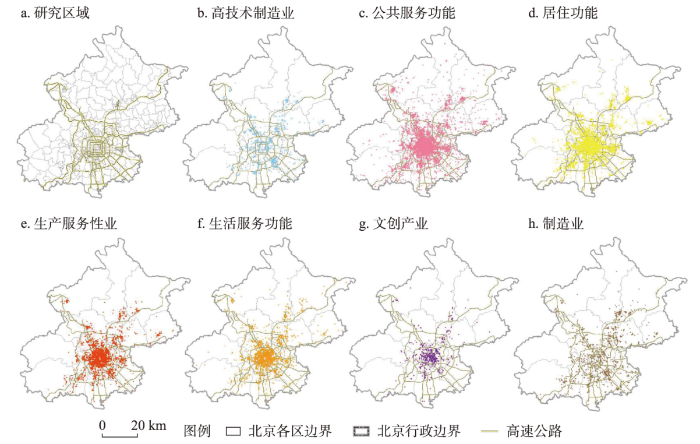
以北京市域为研究区,建立基于住建委发布的工程施工许可证信息的属性空间一体化数据库,共包括2006—2020年间功能项目点,并结合《城市用地分类与规划建设标准》的划分原则,将其规整为7类功能类型,即高技术制造业,公共服务功能,居住功能,生产性服务业,生活服务功能,文创产业,制造业。北京各类城市功能分布如图1所示。高技术制造业包括电子及通信设备制造、计算机及办公设备制造等;公共服务功能包括科教文卫、体育、基础配套设施、公共空间及绿地;居住功能包括商品房、保障房、混住房、社区更新等;生产性服务业包括信息与通讯服务业、科技服务业与金融及其服务业等;生活服务业包括商服娱乐,餐饮服务,物流服务;文创产业即文化与创意产业;制造业包括涵盖农副食品加工业、食品制造业和原材料加工等一般制造业。
图1
2.2 研究方案
首先,对城市功能进行空间计量分析,识别城市功能演化的空间格局及其分异特征;其次,根据频数密度和自然断点法结合识别城市功能演进的结构模式,同时以近邻分析城市各功能之间的邻近关系,判定功能间的聚合规律。
(1)城市功能空间演化格局。针对城市功能演化集进行空间分析,判定城市功能总体以及分类型演化特征,根据自然间断点分级法将核密度分为低、较低、中、较高、高5级,识别北京城市功能演化的空间格局及其变化规律,公式如下:
式中:h为密度计算的搜索半径;n为总项目个数;K(x)为建设规模的核密度函数。
(2)城市功能演进的结构模式。根据自然断点法分别确定各年份不同类型功能的中高等级街道数量,按照四环内、四环至六环和六环外分圈层统计中高等级街道数量占比,并综合考虑其长时间序列平均值、极值和分位值以体现城市功能演进的结构模式。
式中:Fi,j,s为s圈层第j年i类型的中高等级街道数量占比;ni,j,s为s圈层第j年i类型的中高等级街道数量;Ni,j为第j年i类型的中高等级街道总数。
(3)城市功能演进的聚合规律。通过近邻分析,计算某一类型中高等级街道与其他类型中高等级街道中的最近距离以及邻近信息。
式中:DA-B是指A类型的中高等级街道与B类型的中高等级街道之间的平均距离;d1, d2, …, dn为通过近邻分析获取的A类型的中高等级街道与其最邻近的B类型的中高等级街道的距离。
3 功能空间演化格局
3.1 总体特征
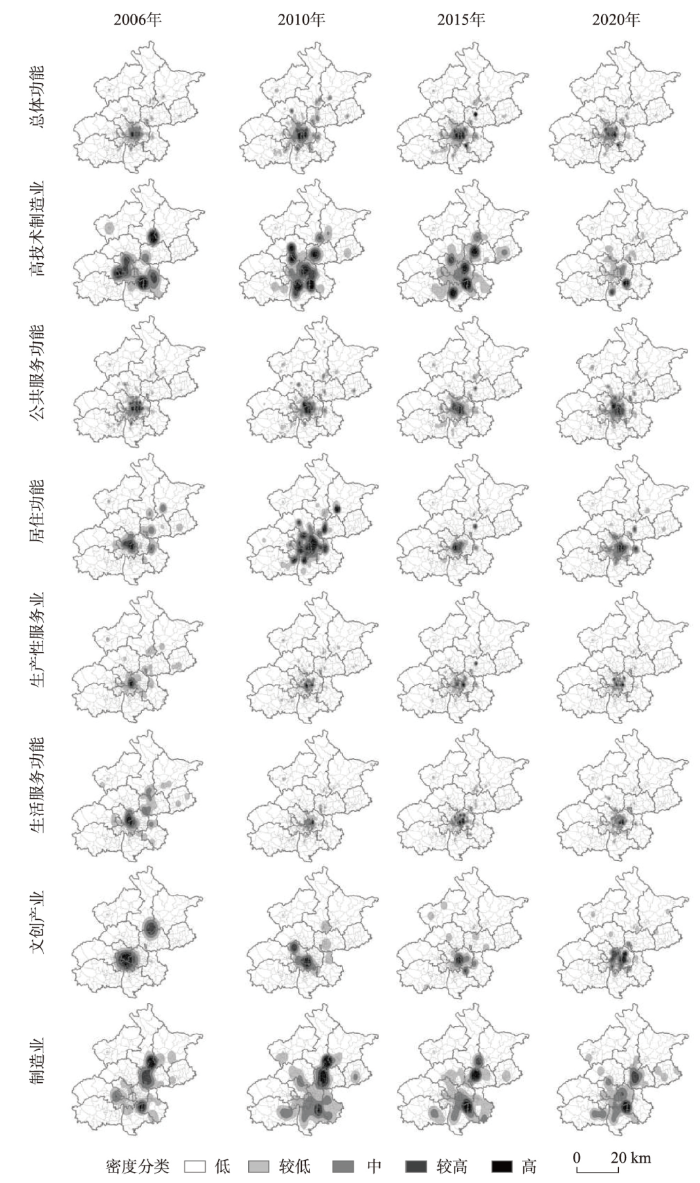
北京城市功能演化主中心位于核心区,并由东西双区组团逐步向东城转移;次中心与城郊区的功能聚集态势先极化后平稳。对2006年、2010年、2015年以及2020年北京的功能点分别进行集聚识别(图2),功能演化的高密度核心始终为东城区和西城区;并且功能演化强度环绕主中心呈向外扩散、依序衰减的圈层结构,延展至朝阳区、海淀区、石景山区、丰台区,并在大兴、顺义、通州、昌平等区中心街道形成功能演化次中心,以及位于生态涵养区的延庆、怀柔、密云和平谷远郊中心。这与《北京城市总体规划(2004年—2020年)》确定的“两轴、两带、多中心”的城市空间结构以及“中心城、新城、镇”的市域城镇体系相契合。与2015年对比发现,2020年北京市各级中心的高密度空间范围逐渐缩小,但功能演替强度仍在不断增加。例如,东西城区的演化强度增加约6倍,朝阳区与海淀区增加约2倍。
图2
3.2 功能类型分异
(2)公共服务与生活服务功能呈现单中心结构,两类功能主要配置于居住人口密度高或区位优势显著的区域。两类功能在核心区及西城—海淀和东城—朝阳交接处形成高密度聚集区。海淀区的中关村街道等公共服务资源丰富齐全;朝阳区的望京、国贸—朝外—三里屯组团的大型居住区和商贸区形成公共服务功能演化聚集区。生活服务功能聚集在核心区以及朝阳区,约78.5%分布在距离城市中心15 km以内的区域,彰显出强中心的服务功能结构。早期生活服务中心位于西单、王府井、新街口等,尔后中央商务区拓展区与国贸商圈成为生活服务功能的高聚集区[6]。随着城市发展逐渐在望京、亚运村、天通苑等大型居住区,海淀区中关村、经济技术开发区等产业区以及国家奥林匹克体育中心、五棵松文化体育中心等文体中心加速建成了生活服务集聚区。
(3)居住功能表现为建成区聚集,并向外部多中心延展,演化内涵由新建向功能改造提升转变。居住功能演化的高密度区域主要位于建成区,随着规划引导以及交通通达性的提高,居住功能空间快速扩张,在近郊和远郊区县形成居住演化的次中心。近几年,城市居住功能演化主要归因于提升中心城区人居环境以及公共服务能力、改善居民生活品质所高强度开展的老旧小区整治、棚户区改造等社区更新。由2006—2010年间占比24%转化为2016—2020年占比46%,由此核心区的演化内涵由新建向功能改造提升转变。
4 空间结构模式
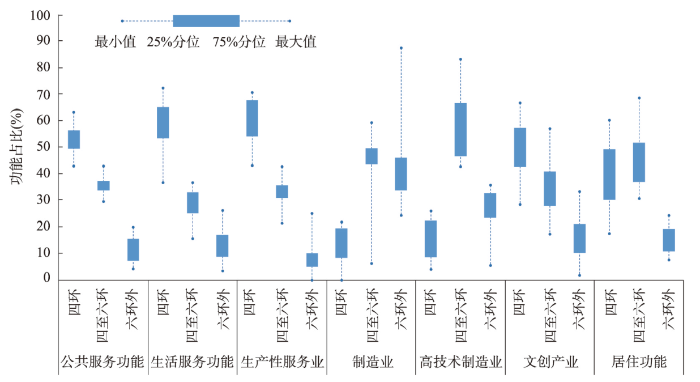
(1)服务功能中心极化。由图3可以发现,北京公共服务功能、生活服务功能、生产性服务业在四环内占比始终处于高位,其各年份占比中位数均超过50%,同时3类服务型功能类数量由四环内至六环外逐圈层递减,总体表现出中心高度极化特征。公共服务功能的快速演化源于核心区始终相对完善的公共服务设施配备,同时得益于夏冬两季奥运会举办的筹备机遇全域开展环境美化及公共设施修缮工程,重大事件加速了城市公共功能补强与提质。此外,生产性服务在中心城区集聚经济的强吸引下不断汇集,生活服务功能也由于人口高密度与区位优势度持续向心汇聚。
图3
(2)产业功能梯序外溢。制造业在北京四环内,四六环之间,六环外3个圈层中高低值范围分别是0~21.88%、6.25%~59.46%、24.32%~87.5%,呈现出明显的制造业梯序外溢特征,由内圈层至外圈层演化数量依次递增。《北京城市总体规划(2004年—2020年)》强调积极引导制造业向新城地区集聚,同时交通通达度、市场竞租、集聚经济等因素均对制造业外溢具有加速影响[39]。高技术制造业各圈层中位数分别为16.98%、57.69%、28.00%,外溢集聚呈现倒“V”型。主要因为高技术制造业由中心城区向外部圈层转移[40],也需顾及对中心城区生产性服务业具有较高的依赖性[41],故而引导其在北京经济技术开发区、中关村产业分园等第二圈层形成聚集。文创产业各圈层占比中位数分别为54.17%、33.3%、12.5%。文创产业的中心集聚态势源于制造业腾退的产业空间转型[42]。近年来,随着以国家文化产业创新实验区为主轴的多类文化创意产业园区兴起[38],其存在显著的圈层外溢趋势。
(3)居住功能圈层分异。北京居住功能演化在四环、四六环、六环的占比中位数分别为33.3%、49.0%、15.8%。在住房体制改革促动与内城空间资源紧缺现实推动以及规划与交通路网引导下居住功能迅速外溢,四六环区域成为吸纳核心区人口疏解的住房建设聚集区。六环外以住房新建为主,但是相较于四环与四六环区域,其演化强度较弱,演化集中在轨道交通站点沿线以及远郊区的中心街道[43]。在居住功能外迁的同时,四环内部居住功能演化内涵也在逐渐改变,社区更新改造成为主要活动,包括建筑老化所引致的加固节能改造和功能退化所引致的综合整治和功能提升。因此,居住功能在各圈层呈现明显的分异特征。
5 聚合规律
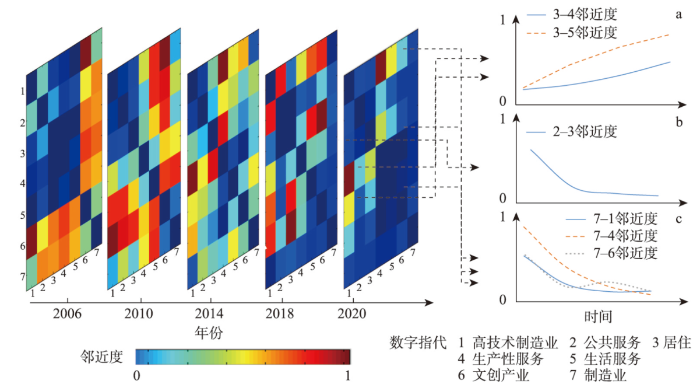
(1)职住分离是首都服务型单中心结构的空间响应。如图4a所示,分析居住功能与生产性服务业以及生活服务功能的空间距离发现,随着时间的推移两组距离均逐渐远离,呈现出职住分离的态势。北京中心城具有极高交通便利度、人文资源丰富度与发展要素汇聚度,虹吸效应明显[44];同时,市场竞租以及非首都功能疏解的驱使下中心城高端产业持续集聚,产业加速转型升级,以金融服务、技术服务、商务办公等高附加值的生产性服务业在中心城迅速演化。而居住功能随着规划引导以及交通通达度的提高快速扩张,逐渐远离生活服务与生产性服务高度聚集的核心区域[45]。首都生活服务与生产服务功能的单中心结构加速了居住空间郊区化,并塑造了职住分离的空间响应。
图4
(2)公共服务均等是城市居住空间品质升级的重要支撑。通过关注居住空间与公共服务功能之间的空间距离,由图4b可以看出,两类功能随着时间的演变越发接近。根据北京市新建改建居住区公共服务设施配置的要求,配套公建应与新建住房同步规划、建设、投入使用,保障居住区合理半径内公共服务供给[46-47]。同时,公共服务功能越完善的区域对于居住功能的吸引效应越强,居住功能更倾向于建设在公服配套完善区域[48]。近年来,居住功能演化热点区域回缩至内部圈层,中心城区富集的公共服务加速城市高强度更新。因此,公共服务功能与居住功能在内外圈层均相互促进,新建与更新都伴随着公共服务功能的强化与提质,公共服务均等是城市居住空间品质升级的重要支撑。
(3)产业集聚与跃迁是城市产业空间迭代的关键路径。由图4c中可以看到,制造业与高技术制造业、生产性服务业、文创产业的空间距离在不断缩小,呈现明显的产业集聚融合趋势。北京实施增量控制与“腾笼换鸟”,中心城劳动密集型制造业基本退出,又大力疏解非首都核心功能[49],产业体系向高精尖方向极化,呈现出产业的跃迁趋势。同时,传统制造业在向外迁移且与高技术制造业共同向工业园区集聚。随着制造业、高技术制造业的不断发展,其对于生产性服务业需求不断增加[35],一同向北京经济技术开发区、中关村科技园区以及临空经济区等重要产业基地集聚[50]。制造业的“腾龙换鸟”以及与文创功能互动为城市产业发展带来新机,使得两者趋于空间邻近。
6 结论与讨论
本文依据长时间序列的北京城市功能变化数据集,探究不同功能类型演变规律及其时空差异,进而分环线圈层认识空间演进的结构模式。在此基础上,以邻近距离为依据探讨功能类间的聚合规律。为城市功能空间的科学重构与精细化治理提供决策支撑与判据。同时,北京是最具有典型意义的特大城市,长期以来形成的城市功能空间具有历史沿袭性、类型完整性和规律代表性。科学认识北京城市功能空间的时空分异格局、结构模式以及聚合规律,可以为特大城市、大城市及其不同功能更新需求城市的优化调控提供指导和借鉴。
后续研究可通过把握功能面积或容积率等空间信息将功能规模纳入考虑。同时,运用多类型空间计量与数据挖掘方法丰富模式与规律的定量阐释方案,并采用综合模拟模型强化演进过程和机理的定量解构、情景仿真与优化调控策略研究。
参考文献
Crowdsourcing urban form and function
DOI:10.1080/13658816.2014.977905 URL [本文引用: 2]
Recognizing urban functional zones by a hierarchical fusion method considering landscape features and human activities
DOI:10.1111/tgis.v24.5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Identification and analysis of urban functional area in Hangzhou based on OSM and POI data
Identifying urban functional zones using bus smart card data and points of interest in Beijing
基于北京公交刷卡数据和兴趣点的功能区识别
Dynamic and drivers of spatial change in rapid urban renewal within Beijing inner city
A glove-based POI type embedding model for extracting and identifying urban functional regions
Points-of-interest (POIs) are an important carriers of location text information in smart cities and have been widely used to extract and identify urban functional regions. However, it is difficult to model the relationship between POIs and urban functional types using existing methods due to insufficient POIs information mining. In this study, we propose a Global Vectors (GloVe)-based, POI type embedding model (GPTEM) to extract and identify urban functional regions at the scale of traffic analysis zones (TAZs) by integrating the co-occurrence information and spatial context of POIs. This method has three main steps. First, we utilize buffer zones centered on each POI to construct the urban functional corpus. Second, we use the constructed corpus and GPTEM to train POI type vectors. Third, we cluster the TAZs and annotate the urban functional types in clustered regions by calculating enrichment factors. The results are evaluated by comparing them against manual annotations and food takeout delivery data, showing that the overall identification accuracy of the proposed method (78.44%) is significantly higher than that of a baseline method based on word2vec. Our work can assist urban planners to efficiently evaluate the development of and changes in the functions of various urban regions.
Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality
From ITDL to Place2Vec:Reasoning about place type similarity and relatedness by learning embeddings from augmented spatial contexts
Mixed land use for urban development: Models and strategies
城市功能复合:模式与策略
The evaluation method and planning strategies of urban function mix of Beijing based on spatiotemporal big data
基于时空大数据的北京城市功能混合评估方法及规划策略
Research on the coupling coordination relationships between urban function mixing degree and urbanization development level based on information entropy
With the rapid development of urbanization, the blind expansion of urban space has led to a series of social problems. In this process, the degree of urban function mixing affects the urbanization development level, making it particularly important to study the degree of coupling coordination between the two aspects. In this paper, taking Beijing as an example, we use urban point of interest (POI) data and taxi GPS trajectory data to calculate the urban POIs’ spatial entropy and taxis’ temporal entropy, based on the information entropy. We use the POIs’ spatial entropy and taxis’ temporal entropy to measure the urban function mixing degree. Also, the model of coupling coordination degree is used to measure the degree of coupling coordination between the urban function mixing degree and the urbanization development level. The results indicate the following: First, the POIs’ spatial entropy and taxis’ temporal entropy have significant regional imbalances. On the whole, both show a declining pattern when moving from the central urban area to the outer suburbs. The urban function mixing degree and urbanization development level are also higher in the central urban area than in the outer suburbs. Second, the coupling coordination among the urbanization development level, POIs’ spatial entropy, and taxis’ temporal entropy is distributed unevenly across various regions, which means that the three types of coupling coordination are in balanced development in the central urban area, but in unbalanced development in the outer suburbs. Third, from the perspective of spatial correlation characteristics, the higher is the degree of spatial agglomeration, the higher are the urban function mixing degree and urbanization development level, and the higher is the coupling coordination degree among the urbanization development level, POIs’ spatial entropy, and taxis’ temporal entropy. Therefore, relevant departments should plan the construction of urban functional areas reasonably, according to the degree of coupling coordination between the urban function mixing degree and the urbanization development level in different regions, so as to realize the healthy and sustainable development of a city.
Spatial differentiation of multi-functional mixed use of construction land based on points of interest
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.02.005
[本文引用: 1]

Mixed land use is of great significance for improving the efficiency of use of regional land and territorial space. A framework for analyzing and optimizing multi-functional mixed use of construction land based on production-living-ecological space was developed in this study. Based on the point of interest (POI) data, entropy model, landscape pattern analysis, and association rules mining were applied to explore the spatial differentiation of mixed land use, taking Jinan City as the study area. The results show that the main types of mixed use of construction land in the city are production space, production-living space, and living space. The degree of mixed utilization of the core urban area is high, the production and living spaces are concertrated and connected, however, the ecological space is not embedded enough. The landscape fragmentation in the rural areas is obvious, and the mixed use led by production and living space is weak. The living-ecological space in the industrial parks is in a very marginal position in the network. Strengthening the internal planning of the parks or forming a complementary living and ecological space with the surrounding areas is the key to realize the sustainable development of the parks. The research of association rules shows that reasonable production space planning is an important way to guide and optimize the mixed land use. At the same time, strengthening the rational use of ecological space plays an important role in promoting mixed land use. Based on the POI data, this study explored the patterns of multi-functional combination of construction land from the perspective of behavioral spatial interaction theory, which enriches the existing land mixed use theory and methods and provides a theoretical basis for land use policy making and spatial pattern optimization.
基于POI数据的建设用地多功能混合利用空间分异研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.02.005
[本文引用: 1]

建设用地多功能混合利用对提升区域用地效率、增进国土空间效能具有重要意义。论文构建基于生产—生活—生态空间(即三生空间)的建设用地多功能混合利用分析框架,以济南市为研究区,采用POI数据,利用熵模型、景观格局分析和关联规则挖掘方法,探究土地混合利用的空间分异特征。结果显示,研究区建设用地混合利用以生产空间、生产—生活空间和生活空间为主;核心城区的建设用地混合利用度较高,而生产、生活空间集中连片,生态空间嵌入不足;乡村地区景观的破碎化特征明显,以生产—生活空间引领的建设用地混合利用度较低;产业园区的生活—生态空间在网络中处于边缘位置,加强园区内部规划与周边区域形成互补的生活、生态空间,是实现园区土地可持续利用的关键。关联规则的分析结果表明,科学的生产空间规划是优化混合利用的重要抓手,而合理的生态空间布局对带动区域建设用地混合利用起着关键作用。研究基于POI数据,从行为空间互动理论视角探究建设用地多功能混合规律,丰富了现有土地混合利用理论与方法体系,也为土地利用政策制定及城市空间格局优化提供了科学依据。
Impact of the mixed degree of urban functions on the taxi travel demand
As an important service industry in cities, taxis provide people with an all-weather travel mode. And its demand is greatly affected by the internal functions of the city. It is very important to understand the relationship between the mixed degree of urban internal functions and the residents’ taxi travel demand to alleviate traffic congestion and formulate corresponding urban traffic strategies. This paper combined two heterogeneous data in the main urban area of Xi’an, urban points of interest (POIs) and taxi GPS. Firstly, a spatial information entropy model was constructed to quantitatively evaluate the mixed degree of functions in different spaces within the city. Secondly, the kernel density estimation method was used to analyze the spatial distribution evolution characteristics of residents’ taxi travel demand. A geographically weighted regression (GWR) model was further used to study the spatial and temporal influences of the mixed degree of urban internal functions on taxi travel demand. Results indicate that there is an obvious spatiotemporal pattern in the impact of the mixed degree of urban functions on taxi travel demand. And the GWR model is used to study the impact is superior to the ordinary least squares (OLS). In more developed areas, improving the mixed degree of urban functions will be more attractive than backward areas. It is also found that although the single function of the city has an impact on the taxi travel demand, the result of the single function is not ideal. This study can provide a reference for the optimal combination of basic units of urban space in urban planning, promote the balance of supply and demand of urban taxis, rationalize urban taxis’ operation and allocation, and solve the problems of urban transportation systems.
Transition of urban functional land in Changchun from 2003 to 2012
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201504003
[本文引用: 1]

The growth of urban space occurs not only through urban land expansion, but also from the transition of urban functional land. The transition of urban functional land can profoundly reveal the internal features of horizontal expansion of urban space, and is the spatial reflection of urban functional agglomeration and diffusion. The paper takes the central city of Changchun as a case study. ArcGIS, AutoCAD and GIS analysis methods are used in the article. Based on remote sensing images, topographic maps and land use maps covering the years of 2003, 2007, 2010 and 2012, the study analyzes the external expansion and internal renewal of urban functional land. First, the paper analyzes the overall pattern of urban spatial expansion and the change of urban land structure. Second, the external expansion and internal renewal of urban functional land are used to express the transition of urban functional land. Finally, the paper explains the internal features of urban spatial expansion and urban functional agglomeration and diffusion. The goal of this work is to provide a new and effective way to study urban spatial expansion, enriching the theoretical foundation of urban space studies. The research reveals the following points: (1) Overall, a continuous urban sprawl is still the main mode of urban spatial expansion. (2) The direction of urban spatial expansion of Changchun has phased characteristics. (3) Residential land and industrial land are the major urban functional land types in Changchun. (4) Examining three study periods reveals that external expansion and internal renewal occur in different time intervals. (5) Internal renewal and external expansion of urban functional land are important indicators of urban spatial expansion.
2003年以来长春市城市功能用地演替
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201504003
[本文引用: 1]

城市空间的增长不仅仅表现在城市用地的扩张,还表现在城市功能用地的演替。城市功能用地的演替可以更加深刻地揭示城市空间外延式水平扩展的内在特征,是城市功能集聚与扩散的空间反映。以长春市中心城区为例,利用2003、2007、2010、2012年4个年份的遥感影像图、地形图及城市用地现状图等数据资源,借助ArcGIS、AutoCAD等软件,运用GIS分析方法,在分析中心城区城市空间扩展的总体格局及城市用地结构变化的基础上,提出以外部扩展与内部更替来表达城市功能用地的演替,进而阐释城市空间扩展及城市功能集聚与扩散的内在特征,为城市空间扩展的研究提供一种新的、有效的手段,以丰富城市空间研究的理论成果体系。
Research on Beijing urban expansion based on information entropy principle
基于信息熵原理的北京城市扩展研究
Evolution characteristics and motivation analysis of main functional land in Zhangye city
张掖城市主要功能用地演变特征及其动因分析
The influence of spatial grid division on the layout analysis of urban functional areas
The identification of urban functional areas is essential for urban planning and sustainable development. Spatial grids are the basic units for the implementation of urban plans and management by cities or development zones. The emergence of internet “big data” provides new ideas for the identification of urban functional areas. Based on point of interest (POI) data from Baidu Maps, the Xicheng District of Beijing was divided into grids with side lengths of 200, 500, and 1000 m in this study. The kernel density method was used to analyze the spatial structure of POI data. Two indicators, that is, the frequency density and category ratio, were then used to identify single- and mixed-functional areas. The results show that (1) commercial and financial areas are concentrated in the city center and multiple business centers have not developed; (2) scenic areas account for the largest proportion of single-functional areas in the Xicheng District of Beijing, followed by education and training, residence, and party and government organizations areas; and (3) the 200 × 200 m and 500 × 500 m grids are the most suitable for the identification of single- and mixed-functional areas, respectively.
Temporal-spatial pattern and contributing factors of urban RBDs in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201508003
[本文引用: 1]

Urban RBD (Recreational Business District), a place where local residents and tourists go for leisure, tourism and consumption, is widely accepted as an indispensable component of urban recreation system in recent years. However, existing research in urban RBD puts an emphasis on its conceptual aspects (i.e., classification, influence, spatial structure), and empirical and quantitative studies have been largely ignored. Firstly, a summary about urban RBDs’ characteristics from the perspectives of location, scale, users, function, and culture was made. Based on previous literature and RBDs’ characteristics and attributes, this study divides urban RBD into three groups, namely: Large Shopping Center (LSC), Commercial Pedestrian Street (CPS), and Urban Leisure Area (ULA). Quantitative methods, such as Gini Coefficient, Spatial Interpolation, Kernel Density Estimation, and Geographical Detector, were employed to collect and analyse data of three types of urban RBDs in Beijing in 1990, 2000, and 2014, respectively, and the spatial-temporal evolution pattern as well as distribution characteristics of urban RBDs were analyzed with the aid of ArcGIS software. The results show: (1) The total number and scale of urban RBDs in Beijing have been expanding, with urban RBDs increasing by 8.20% and 7.26% per year in 1990-2000, and 2000-2014, respectively; (2) spatial agglomeration of urban RBD in Beijing keeps strengthening, and the trend that all types of urban RBDs in Beijing are spatially agglomerated is continuing; However, there exist some variances in terms of their growth speed and degree; (3) the spatial structure evolution model of urban RBDs in Beijing is as one core concentration—two cores development—multi-core diffusion; (4) According to the statistics from database concerning traffic, resident and tourist density, tourism attractions and land price in Beijing, the results showed that urban RBDs were generally located in areas with low traffic density, tourist attractions, high resident and tourist population density, and relatively high land valuations; (5) tourists density strongly influenced the scale of each urban RBD type, compared with other factors.
北京城市休闲商务区的时空分布特征与成因
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201508003
[本文引用: 1]

城市休闲商务区(Recreational Business District, RBD)作为城市重要的游憩空间,为外来游客和城市居民提供休闲消费的场所,逐渐受到学界和业界重视。目前大多数研究还停留在概念层面,在分类、空间结构、分布规律、分异成因等方面上还缺乏一定的实证和定量研究。结合前人研究经验,重新定义RBD,并依据城市RBD的特征和属性将其分为大型购物中心、休闲商业街、城市休闲区三类。选取1990年、2000年、2014年三个时间截面对北京各类城市RBD点进行统计,采用基尼系数、空间插值、核密度分析、地理探测器等方法,结合ArcGIS软件,对北京城市RBD的时空分布特征和成因进行分析,得出以下结论:① 时序上看,北京城市RBD的数量和规模不断增加,增速变快,不同类型的RBD出现不同幅度的空间扩张;② 北京城市RBD的空间集聚程度不断加强,不同类型的RBD,存在一定的增幅和增速差异;③ 北京城市RBD的整体空间结构呈“单核聚集—双核发展—网状扩散”的发展模式;④ 城市RBD多选址在交通便利、临近旅游景区、居民和游客密度较高、地价相对较高的地区。⑤ 游客密度对各类型的城市RBD规模均有较大影响;对于不同类型的城市RBD,各因素对其规模的影响也有所不同。
Spatial pattern of urban functions in the Beijing metropolitan region
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2009.09.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimization of industrial spatial circle structure and layout in Beijing
北京市产业空间圈层结构与布局优化
Impact factors of location choice and spatial pattern evolution of wholesale enterprises in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201802002
[本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening up, Chinese cities have experienced a period of rapid transformation and reconstruction against the background of economic globalization. Industrial development is one of the main driving forces of urban spatial expansion; therefore, urban spatial reconstruction in China is first reflected in the reconstruction of industrial space during the transition period. Alongside rapid urbanization, urban industrial construction has gradually shifted from the secondary industry to the tertiary industry, which has an increasing impact on residents' production and living. Thus, paying attention to the spatial distribution of the service industry and its location selection factors has become an important way to explore urban spatial reconstruction. The wholesale industry is an important part of a city's service industry, which has an important influence on commercial production, circulation and consumption. Because wholesale enterprises involve a great number of employees, and its spatial distribution pattern caused traffic congestion, environmental pollution and a series of urban problems, the location of wholesale enterprises has become a hot topic amongst scholars. This paper uses Beijing as a typical example, takes wholesale enterprises as the research object, and analyzes the spatial pattern evolution and agglomeration characteristics of wholesale enterprises in Beijing using kernel density estimation and Ripley's K(d) function. It then explores the influencing factors of the wholesale enterprise location selection by means of Conditional Logit model. The results show that: (1) In the perspective of spatial distribution, wholesale enterprises are mainly concentrated within the Fifth Ring Road, and present obvious spatial agglomeration characteristics; the scale of agglomeration is mainly concentrated in a range of 0-28 km. (2) Seen from the spatial agglomeration strength, the agglomeration peak distance is constantly expanding, the concentration decreased within the Second Ring Road, and three core groupings are formed in a peripheral area. (3) Local economy, city economy, land price, labor cost, infrastructure and spatial distance have a significant influence on the location choice of wholesale enterprises, and land price and agglomeration is the most prominent of all. (4) According to different types of enterprises, foreign enterprises have a great demand for better traffic conditions and innovation environment, but the impact of commercial benchmark land price on the location choice is not significant.
北京批发企业空间格局演化与区位选择因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201802002
[本文引用: 1]

随着服务业对居民生产、生活影响程度逐渐增强,其企业区位选择已成为从微观视角解析城市空间结构的重要途径。以北京为典型案例地,将批发企业作为研究对象,运用核密度估计方法、Ripley's K(d)函数以及条件Logit模型,分析了北京批发企业空间格局演变规律与集聚特征,在此基础上探究了批发企业区位选择的影响因素。结果表明:① 从空间分布特征来看,批发企业主要集中在北京五环以内,且呈现明显的空间集聚特征,集聚规模主要集中在0~28 km范围内;② 从空间集聚强度看,集聚峰值出现的距离不断向外扩张,二环内集聚强度有所下降,并在外围形成了3个核心集聚区;③ 地方化经济、城市化经济、土地价格、集聚效益、劳动力成本等因素对批发企业区位选择具有显著影响,其中土地价格和集聚效益的影响最大,新企业在区位选择中都存在明显的集聚效益;④ 从不同类型批发企业来看,外资批发企业通过检验的影响因素较少,受已有该企业空间分布的影响显著且对交通区位条件、创新环境要求更高,但商业基准地价在外资企业区位选择中影响不显著。
A study on the process, characteristics and influencing factors of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration
DOI:10.11821/xb200306016
[本文引用: 1]

Beijing has become one of the most important hi-tech industrial agglomeration areas of China now. Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration has its particular developing process and characteristics. Based on the European and American industrial agglomeration theories, using statistics data, and through questionnaire investigation and enterprise interview, this paper summarizes the process and characteristics of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration, and also analyzes its industrial types, spatial evolvement process, driving power, driving factors of the cluster, supporting system, developing performance and other important influencing factors. Besides, based on the Diamond Theory of Michael Porter, the paper summarizes the factors influencing Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration and analyses the interaction among them. The particular historic background and original status decides the formation of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration in some way. While, during the development of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration, policies and foreign investment play key roles. Policies helping build cooperative network among the government, enterprises and research institutes and regional innovation environment accelerate the development of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration greatly. And MNCs have also been the most important driving power of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration these years. Finally, the paper puts forward that the formation of Beijing's hi-tech industrial agglomeration must be analyzed with a comprehensive view, and we should analyze the composition and specific functions of the influencing factors combined with Beijing's peculiarities.
北京高科技产业集聚过程及其影响因素
Location characteristics and differentiation mechanism of logistics industry based on points of interest: A case study of Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706011
[本文引用: 1]

The logistics nodes and logistics enterprises are the core carriers and organizational subjects of the logistics space, and their location characteristics and spatial differentiation have significant impacts on the urban logistics space distribution and logistics resources allocation. Based on Tencent Online Maps Platform from December 2014, 4396 logistics points of interest (POI) were collected in Beijing, China. Adopting the methods of industrial concentration evaluation and kernel density analysis, the spatial distribution pattern of logistics in Beijing are explored, the interaction mechanism among the type difference, supplydemand factors and location choice behavior are clarified, and the internal mechanism of spatial differentiation under the combined influence of transportation, land rent and assets are revealed. The following conclusions are drawn in the paper. (1) Logistics enterprises and logistics nodes exhibit the characteristic of both co-agglomeration and spatial separation in location, and logistics activities display the spatial pattern of "marginal area of downtown area, suburbs and exurban area", which have a low coupling degree with logistics employment space. (2) The public logistics space, namely, logistics parks and logistics centers, is produced under the guidance of the government, and the terminal logistics space consisting of logistics distribution centers serving for the specific industries and terminal users is dominated by enterprises. They have obvious differentiation in location. (3) In the formation of the logistics spatial location, the government can change the traffic condition by re-planning the transport routes and freight station locations, and control the land rent and availability of different areas by increasing or decreasing the land use of logistics, to impact the enterprise behavior and form different types of logistics space and function differentiation. In comparison, logistics enterprises meet the diverse demands of service objects through differentiation of asset allocation to promote the specialization of division and form the object differentiation of logistics space.
基于POI的北京物流业区位特征与分异机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706011
[本文引用: 1]

物流节点和物流企业作为物流空间的核心载体和组织主体,其区位特征和分异机制识别对优化城市物流空间布局、合理配置物流资源有重要意义。2014年12月基于腾讯在线地图平台,采集了北京市4396个物流POI。采用产业集中度评价、核密度分析等方法,刻画了北京物流空间格局,阐明了类型差异、供需侧因素与区位选择行为的微观作用机理,揭示了交通、地租、资产对空间分异形成的内在机制。研究表明:① 物流企业和物流节点呈现协同集聚和空间分离相结合的区位特征;物流活动总体呈现“中心边缘、近郊和远郊交错”的空间格局,与物流就业空间耦合度低。② 由物流园区和物流中心构成的公共物流空间是政府引导的结果,由服务于特定行业和终端用户的配送中心构成的末端物流空间多为企业主导,两者区位分异显著。③ 在物流区位形成过程中,政府通过规划交通线路和货运场站改变交通区位条件,配置物流仓储用地影响不同区域物流地租和可得性,进而调控企业行为并形成物流空间的类型与职能分异;企业则通过资产配置的差异化来满足不同服务对象的多样化需求,促进专业化分工并形成物流空间的对象分异。
Industrial distribution and clusters of urban office space in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/xb201110001
[本文引用: 1]

The study on the industrial structure of urban office space helps to understand the formation of spatial structure of economic activities. We select 594 office buildings as the study samples. The location data of the samples are selected from 1921 office buildings that the research group gathered for two consecutive years by using Trimble Juno SB handheld GPS in six districts of Beijing. Most of the industrial attribute data came from e-Buy Data Information Company, and the rest of them came from the questionnaire and telephone interviews done by the research group. Using spatial analysis methods such as buffer analysis and Ripley's K (d) functions, we analyze the distribution of office industries and spatial clusters in which the office activities have gradually replaced the manufacturing activities in urban economic transformation. Furthermore, the study tries to reveal the spatial structure of economic activities in inner city of Beijing as follows. (1) Generally speaking, the choice of office industry location has obvious centrality in Beijing. Its company and employment density show a decreasing trend from inside to outside, which accords to the circle structure with Tiananmen Square as the center as well as 5 km, 10 km and 15 km as the radius buffer zones. (2) There is a significant difference in the spatial distribution of the industry, featured by "east higher and west lower". The high function area in the city has strong ability to attract employees. The spatial distribution patterns are generally identified in three modes of concentration. Wholesale and retail, social services and technology services present a "large scatter, large cluster" mode, namely, many companies cluster in the hotspots and the range is wide. Transportation and financial sectors have a "small scatter, large cluster" mode, that is, spatial distribution of the large companies show relative concentration and form a wider range of concentration hotspots. The construction, real estate, education and culture industries have a "large scatter, small cluster" mode. (3) The trend of spatial industrial concentration is similar, showing the way of increasing first and then decreasing as an inverted "U"-shaped structure. Owing to the different spatial scales, the office location of social services and wholesale and retail have the largest range of options; the financial industries gather in a specific area, and their location range options are small; transportation, storage and postal industries have a trend to a significant traffic location. The companies with higher absorptive capacity of employment in various office buildings tend to be located along the lines of communication. Thus, transportation condition is still an important factor affecting office location choice. In addition, different concentration features of the office sectors at various scales reflect the differences of selected range of office location.
北京城市办公空间的行业分布及集聚特征
Research on identification and spatial patterns of commercial centers in Beijing based on POI data
基于POI数据的北京市商业中心识别与空间格局探究
Study on the evolution of B&Bs spatial distribution based on exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) and its influencing factors: With Yangtze River Delta as an example
Understanding the spatial organization of urban functions based on co-location patterns mining: A comparative analysis for 25 Chinese cities
The spatial organization of the separation between jobs and residential locations in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/xb200912006
[本文引用: 1]

This study chose Beijing as a case. It was based on the questionnaire answered by nearly 10000 people in 2005. The Geographic Information System (GIS) and spatial analysis were used to analyze the characteristics of the separation between jobs and residential locations in Beijing. Based on the case study, we found that the separation between jobs and residential locations has become a serious phenomenon in Beijing. The average commuter time is 38.0 minutes, and more than 43.7% of the workers spend more than 40 minutes on commuting. The spatial analyses show that there are spatial differences, which may be caused by the spatial structure of Beijing. The problem of the separation is not too serious in the urban central areas. However, as some suburban areas were designed to be large living communities, the residents in these areas faced a more serious problem of the separation between jobs and residential locations. On the other hand, people living in satellite towns have more chances to find jobs, so the problem of the separation between working places and home is not serious. The cluster analysis shows that there are several visible clusters of employment concentration in Beijing. The locations of these clusters are "Spatial Mis-match" with the population concentration. This "Spatial Mis-match" is decided by the rent price of the land in the city. The flow of the commuters is another index of the separation between jobs and residential locations. In Beijing, the "To Center" flows are the main commuter flow now, although there are "Out of Center" flows at the same time. This suggests that the spatial organization of the separation between jobs and residential locations is changing gradually in Beijing.
北京城市居民职住分离的空间组织特征
DOI:10.11821/xb200912006
[本文引用: 1]

利用地理信息系统和空间分析技术,选择北京市为实证研究对象,在近万份实际调查问卷数据基础上,从城市空间结构变迁的角度审视北京城市居民职住分离的空间组织特征和职住分离的影响因素。研究发现北京城市居民单程通勤时间为38分钟,其中通勤时间超过40分钟的人群比例为43.7%,可见北京市居民职住分离程度比较严重;同时,从居住地和工作地的角度都可以发现北京居民职住分离现象在区县尺度和街道尺度存在着明显的空间差异;总体而言城市中心区域职住分离情况好于郊区,在郊区中重点开发的卫星城镇工作机会较多,在这些区域就业者的职住分离问题并不严重;而一些重点建设的大型居住社区由于功能过于单一,这些区域的居民职住分离问题十分突出。集聚分析表明,北京市存在明显的就业和居住集聚区,并且两者在空间上的错位比较明显;对城市居民的通勤流向的分析表明,向心流还是主体通勤方向,但也存在一定比例的逆向通勤,表明北京城市化过程中居民职住分离的空间组织特征正在逐渐演变。
Spatial restructuring of manufacturing industries in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201808008
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial restructuring of industries is usually accompanied with the upgrade of industrial structure. This study analyzes the changes in the industrial composition and the spatial distribution of manufacturing employment in Beijing from 2008 to 2013 based on the economic census data of Beijing. The analysis shows that during the period from 2008 to 2013, the adjustment of manufacturing employment structure of Beijing has speeded up. We categorize the manufacturing industries of Beijing into two groups, namely declining and growing industries, according to the changes in their employment shares to the total manufacturing employment of Beijing. Although the spatial changes of declining industries were more significant than those of growing industries, the redistribution of manufacturing industries from 2008 to 2013 was still mainly driven by growing industries. Since growing industries have become more concentrated, the overall spatial change of manufacturing industries in Beijing was also characterized by the increase of industrial agglomeration. The analysis also shows that growing industries tended to be concentrated in a few sub-districts along the Sixth Ring Road, especially those areas that intersect with major highways. Through analyzing the industrial composition of each sub-district by the Herfindahl index, we find that the areas with more manufacturing industries, especially those with more growing industries, have become more specialized. We identify the specialized industries of each sub-district based on the location quotient of each industry in the sub-district, and the analysis shows that the areas with more declining industries usually have a larger number of specialized industries, while the areas with more growing industries tend to have fewer but more significant specialized industries. This may imply that with the industrial restructuring and the spatial agglomeration of manufacturing activities in Beijing, growing industries are inclined to be specialized in certain areas and form more distinct geographical functional divisions. The south part of Beijing is worthy of attention, since it may face more adjustments and challenges with the dramatic industrial restructuring of Beijing's economy.
北京市域制造业的空间演化特征
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201808008
[本文引用: 1]

北京市域制造业在结构调整的同时也在不断发生空间格局的变动。在京津冀协同发展战略的推进下,北京非首都功能疏解不断加速,将进一步加剧北京制造业产业结构的调整,进而影响空间格局的演化。利用2008年和2013年北京市经济普查数据中街道、镇乡的制造业大类的就业数据,从街乡的尺度,分析探讨北京市域内制造业的空间演化特征与趋势。研究显示:2008-2013年北京市制造业的产业结构和空间结构均趋向集聚,增长产业是制造业空间集聚的主导力量,在引导制造业空间进一步集聚的同时,形成了明晰的空间分异,增长产业更加趋向于在专门化程度更高的地区集聚,就重点街乡来看,北部地区的空间发展趋势将较为稳定,南部地区可能成为未来需要重点关注的高变动区域。
Review of Beijing's urban renewal practice
北京城市更新实践历程回顾
Changing intra-metropolitan spatial distribution of employment with economic restructuring in Beijing metropolitan area
北京都市区就业结构升级与空间格局演化
A study on suburbanization of office and its stages of development in Beijing urban area
北京城市办公郊区化及其发展阶段研究
Spatial-temporal evolution mode of urban innovation spatial structure: A case study of Shanghai and Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201512005
[本文引用: 1]

In today's world, the innovation of science and technology has become the key support for improving comprehensive national strength, also the strong lead for changing the mode of social production and lifestyle. Which country has world-class scientific and technological innovation cities maximizes the attraction to global innovation factors. Which country maximizes the attraction to global innovation factors wins strategic initiative in international competition. Based on urban ZIP code spatial database, the evaluation system of urban innovation was established in the perspective of innovation output, and the spatial evolutionary mode, which is concerning the structure of innovation space of Shanghai and Beijing from 1991 to 2014, was discussed. The results of the research indicated that ZIP districts provided a fresh perspective to study the growth of spatial structure of urban innovation. And the result, which is of the evaluation of spacial structure of urban innovation using urban ZIP code spatial database established by connecting random edge points and Voronoi, was relatively ideal. So the promotional value exists. During the 25 years, the growth of spatial structure of innovation of Shanghai and Beijing demonstrated a lot of common features: with the increase of urban space units participated in innovation year by year, although the overall gap of regional innovation output has narrowed, the trend of spatial agglomeration has strengthened. The growth of spatial structure of innovation of Shanghai and Beijing demonstrated the differences among common features during the 25 years as well: in the trend of the suburbanization of innovation resources, the spatial structure of innovation of Shanghai indicated that the driver has evolved from the single-core driver to the multi-core resonance evolution. Radiation effect using traffic arteries as spatial diffusion corridors was prominent. Accordingly, the spatial correlation effect of its innovation output also indicated the city center hollowness; the spatial structure of innovation of Beijing was single-core (the city center) oriented structure all the way. In the trend that innovation resources were agglomerated in the center, the spatial correlation effect of innovation output indicated the characteristics of the evolutionary feature where "rural area encircles cities". The spatial structure of innovation of Shanghai and Beijing has intrinsic consistency with the spatial structure of their respective regions (Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration), which suggested that the principle of proportional and disproportional distribution of city-scale pattern of technological and innovational activities is closely related to its regional innovation pattern.
上海和北京城市创新空间结构的时空演化模式
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201512005
[本文引用: 1]

基于城市邮编区划空间数据库,从创新产出的视角建构城市创新评价指标体系,对1991-2014年上海市和北京市的创新空间结构的空间演化模式进行了探讨。研究发现:① 邮政区划为研究城市创新空间结构的生长提供了全新的视角,基于随机边缘点连线以及泰森多边形法构建的城市邮编空间数据库评价城市创新空间结构的结果较为理想,因此具有推广价值;② 25年间,上海市和北京市的创新空间结构生长体现出了诸多的共性特征:随着参与创新的城市空间单元逐年增加,区域创新产出虽总体差距在缩小,但空间集聚趋势在加剧;③ 25年间,上海市和北京市的创新空间结构生长也体现出了共性上的差异性,其中上海市创新空间结构在创新资源郊区化转移的趋势下,呈现出由单核驱动向多核共振演进,以交通干道为空间扩散廊道的辐射效应凸显,相应的,其创新产出空间关联效应也显现出了市中心空心化现象;而北京市创新空间结构始终为市中心单核主导型,并在创新资源不断向中心集聚趋势下,其创新产出空间关联效应呈现出“农村包围城市”的演化特征;④ 上海市和北京市创新空间结构与其所在的区域创新空间结构(长三角城市群和京津冀城市群)具有内在的一致性,表明城内尺度科技创新活动空间分布的均衡与非均衡规律与其所处的区域创新格局密切相关。
Spatial distribution of producer services and manufacturing enterprises around the airport area: The case of Beijing Capital International Airport
机场周边地区生产性服务业与制造业空间布局特征: 以首都机场为例
Research on identification and spatial patterns of commercial centers in Beijing based on POI data
基于POI数据的北京市商业中心识别与空间格局探究
Industrial relevancy and spatial distribution between producer services and manufacturing in Beijing city
DOI:10.11821/xb200812007
[本文引用: 1]

Interactive development between producer services and manufacturing was not only a trend of global economic development, but a path of new industrialization in China. As a case study of Beijing city, this paper conducted an empirical study on industrial relevancy and spatial distribution of the interaction between producer services and manufacturing, applying correlative analysis, input-output model, spatial autocorrelation model and so on. The results could be concluded as follows. Firstly, there was a significant positive correlation between intermediate input of producer services and efficiency of manufacturing. But the share of manufacturing on total intermediate demand was low in Beijing. Secondly, there was an uptrend of the intermediate demand structure by manufacturing from 1997 to 2002. The structure of intermediate demand by different types of manufacturing was quite different. Thirdly, the intermediate input of producer services to resources-intensive manufacturing tended to reduce and the technology-intensive manufacturing tended to rise from 1997 to 2002. The structure of intermediate input by different types of producer services was quite dissimilar. Finally, the disparity of spatial distribution between electronic and telecommunication equipment (ETE) and professional, scientific and technical services (PSTS) was remarkable. An exploratory spatial data analysis of employment density of ETE and PSTS revealed strong evidence of spatial autocorrelation as well as significant patterns of local spatial association. Although spatial agglomeration existed significantly at the level of block, the convergence of ETE and PSTS was distinct in spatial pattern, which proved the spatial-disjoin between producer services and manufacturing.
北京生产性服务业与制造业的关联及空间分布
Spatial agglomeration and evolution of cultural and creative industries
文化创意产业空间集聚及演化
Manufacture restructuring and main determinants in Beijing metropolitan area
DOI:10.11821/xb201210002
[本文引用: 1]

At the transformation stage to post-industrialization process, the spatial distribution of economic activities in metropolitan areas tends to change greatly. As one of the key driving forces for urban restructuring, the agglomeration of manufacturing industry has important influence on urban functional optimization. Based on the manufacturing enterprises databases, this paper discussed the relationship between spatial shift of manufacturing agglomeration and the urban function restructuring in Beijing. By contrasting spatial shift of manufacturing density in Beijing metropolitan area in 1996, 2001 and 2010 respectively, the coupling relationship between the manufacturing diffusion and urban function optimization is explored. With the negative binomial models, factors affecting the location of manufacturing enterprises as well as its influence variation among sectors in Beijing are examined. The results indicated that factors such as locational accessibility, agglomeration economy, and development zones are the key determinants for manufacturing enterprises diffusing and re-agglomeration in Beijing metropolitan area. It was also explored that during the process of suburbanization, firms in different sectors can lead to different locational decisions. The high-tech manufacturing enterprises are more likely to agglomerate in central urban area compared to the resource-intensive manufacturing firms. It was concluded that both the market-oriented factors and the government planning factors have great significance on the spatial restructuring and urban function improvement of Beijing.
北京市制造业空间格局演化及影响因子分析
Research on spatial layout optimization of high-end manufacturing industry in Beijing
北京高端制造业的空间布局优化研究
Co-agglomeration of producer services and manufacturing industry in Beijing
北京生产性服务业和制造业共同集聚研究
Characteristics of spatial distribution of the cultural and creative industry agglomeration areas in Beijing
北京市文化创意产业集聚区空间特征探析
Spatial pattern of residential land parcels and determinants of residential land price in Beijing since 2004
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706008
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we take Beijing as a case study and employ the residential leasing parcel data from 2004 to 2015 within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing metropolitan area. Also, we use the GIS data of Beijing's public facilities, such as bus stations, railway stations, park, hospital, primary school and so on. With the help of ArcGIS, GS+, Surfer and Geoda Software, we explore the spatial pattern of residential land parcels, residential land price and determinants of residential land price in Beijing. In the first place, we use the methods of Spatial Trend Analysis, Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI), Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) to explore the spatial pattern of residential land parcels and their price in Beijing. In the second place, we compare the spatial econometric models (SLM and SEM) with traditional OLS model to further explore the determinants of residential land price in Beijing. Based on the analysis, the main conclusions are drawn as follows. (1) The number of residential land leasing parcels is not balanced among years and ring roads. The residential land leasing parcels in the last 20 years are mainly concentrated between the fifth and the sixth ring roads in Beijing. (2) Residential land parcels are generally distributed along the main roads (such as Beijing-Shijiazhuang Expressway, Beijing-Kaifeng Expressway, Beijing-Shanghai Expressway and Beijing-Tibet Expressway) and the subway lines (such as Line 1, Line 5, Line 6, Line 15, Fangshan Line, Daxing Line and Yizhuang Line), which is more obvious in outer suburban areas. (3) Generally, there exists an inverted U-shaped curve trend, indicating that residential land price declines gradually from the city center to the city fringes as a whole, and spatial pattern of residential land price has turned from mono-centric structure to poly-centric structure. (4) Residential land price demonstrates a spatial cluster distribution pattern. There exists obvious spatial autocorrelation in residential land price and it is easy to distinguish "cold spots" from "hot spots". (5) In the model selection, we compare the spatial econometric model (SLM and SEM) with the traditional OLS model. The result shows that SLM is the best, followed by SEM, indicating that there indeed exist spatial spillover effects and spatial dependence in residential land price rather than error dependence. The residential land price is mainly affected by the surrounding residential land price, distance to bus station, distance to subway station, distance to key primary school, area of land parcel, FAR and the type of land leasing. However, in this paper, one drawback is that we fail to take macroeconomic policy factors into consideration, which may play a key role in the formation of residential land price. Also, we have not considered the subway's impact in different periods such as planning period, construction period and operation period on residential land price, which needs to be further studied.
北京市居住用地出让价格的空间格局及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706008
[本文引用: 1]

以2004-2015年北京市六环内居住用地的交易样本为基本数据,借助ArcGIS、GS+、Surfer和Geoda软件,采用空间趋势面分析、最近邻指数(NNI)、探索性空间分析(ESDA)探讨居住用地出让和居住地价的空间格局特征,并对比OLS和空间回归模型(SLM和SEM)进一步探讨居住地价的影响因素。结果表明:① 北京市居住用地出让数量和出让面积不均衡,五六环间出让的居住用地最多。② 出让地块沿主要道路(如京石高速、京开高速、京沪高速及京藏高速)、地铁线(如地铁1号线、5号线、6号线、15号线、房山线、大兴线及亦庄线)呈轴线扩散,其中远郊区域这一特征更加明显。③ 居住地价从中心向外围总体表现“倒U型”趋势,且呈多中心圈层递减结构。④ 呈集聚分布模式,存在空间自相关,低值集聚区和高值集聚区明显。⑤ 模型对比方面,SLM>SEM>OLS,说明北京市居住地价存在实质性的空间依赖,而非干扰性的空间依赖。周边居住地块的价格、公交站、地铁站、重点小学、占地面积、容积率和出让方式对居住地价有显著影响。
Evolution characteristics of industrial layout of Beijing
北京市产业空间布局演变特征
Housing suburbanization and employment spatial mismatch in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/xb200704005
[本文引用: 1]

Along with the social economic development, urbanization has speeded up in China. Suburbanization has been taking place in large and super-large cities. In Beijing, suburbanization (mainly led by housing suburbanization) started from the late 1980s and early 1990s. By now suburbanization in Beijing has experienced three stages: beginning, inner suburbanization and rapid development. Housing suburbanization has been characterized by concentric outward expansion along ring roads, leading to rapid urban sprawl. But urban sprawl in Beijing differs from low-density sprawl in Western countries. New housings are mainly located along arterial roads. Distinct regional variations exist in housing types, showing some similarities to housing segregation in Western cities. This paper argues that housing suburbanization in Beijing and that in Western cities share both similarities and differences. Suburbanization in both settings is a necessary result of improving urbanization and establishment of an urban land market, and guided by urban planning. In Beijing, however, housing suburbanization is "passive" suburbanization, as most residents do not really want to leave the central areas but urban renewal and extremely high housing prices force them to purchase housing in suburban areas. Along with housing suburbanization, the issue of spatial mismatch between housing and employment has emerged in Beijing. Despite all the differences, this spatial mismatch shares similarities to that in American cities in several aspects: spatial separation of residences from jobs, social segregation, leading to increasing costs (in terms of both time and money) for low-income commuters and many social problems such as traffic congestion and social segregation.
北京住宅郊区化与就业空间错位
Retrospection and research on the development process of Beijing residential public service supporting facilities configuration standards//Urban Planning Society of China
北京居住公共服务配套设施配置标准发展历程回溯与研究//中国城市规划学会
Public service facility accessibility as influenced by public transportation in Beijing
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.10.006
[本文引用: 1]

This study evaluated Beijing metropolitan public service facility accessibility, use efficiency, and supply and demand mismatch using a massive amount of spatial data. Ratio and shortest time distance methods were applied to calculate public service facility accessibility. By employing the rank correlation and spatial overlay methods, this study analyzed the mismatch between supply and demand of accessibility. The results show that the overall facility accessibility is good in Beijing. Accessibility of all types of facilities is best within the 4th ring road, where the average shortest travel time from residential areas to facilities is lowest. Facility accessibility is worst between the 5th and the 6th ring roads, where the average shortest travel time is the longest among all zones. Residential communities with high demand and high accessibility account for the highest proportion. Residential communities with high demand and low accessibility are mainly located in the eastern and northern parts of the city between the 5th and the 6th ring roads, where facility accessibility needs to be improved. Among the four types of facilities, primary schools have the highest accessibility because primary and middle schools attached greater importance to equity in access. However, hospitals and shopping malls emphasized more on spatial efficiency. For the residential communities with high demand and low accessibility, measures should be taken to improve travel modes and public transportation routes and construct new facilities in order to solve the accessibility problem and address the imbalance between supply and demand.
公共交通影响下的北京公共服务设施可达性
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.10.006
[本文引用: 1]

本文尝试利用大量微观空间数据从供需角度评价北京公共交通影响下的公共服务设施可达性及其空间效率和供需匹配情况,分别采用比例法与最短时间距离法测算公共服务设施的可达性,运用定序变量相关法与因子空间叠置法分析公共设施可达性的供需匹配程度。结果表明:北京居住小区公共设施总体可达性水平较高。其中,4环以内各类公共设施可达性水平最高,居住小区到公共设施的平均时间20分钟内的小区占比高达90%以上;5-6环可达性水平最差,平均时间20分钟内的小区占比在50%以下。高需求高可达性街道比重相对较高,而高需求低可达性街道主要分布于5-6环的东部和北部地区。在公共设施中,小学可达性最好,而医院和购物中心则更强调空间效率。针对识别出的公共设施的高需求低可达性街道,应从出行方式、公共交通线路与公共服务设施建设等方面采取对策,化解公共设施的供需矛盾问题。
On location advantage value of residential environment (LAVRE) in the urban and suburban areas of Beijing
DOI:10.11821/xb200501013
[本文引用: 1]

Firstly, this paper selects 7 factors such as service facility, natural environment, traffic situation and location condition to evaluate Location Advantage Value of Residential Environment (LAVRE) in the urban and suburban areas of Beijing. Secondly, it constructs a LAVRE model to evaluate LAVRE of different parts of in Beijing and analyze its spatial characteristics. Thirdly, based on data of average prices of lots of commercial housings, this paper sets up GIS-based spatial distribution of prices to analyze spatial relationship between LAVRE and housing prices, and the relationship between LAVRE and residential location selecting behaviors. Lastly, it draws conclusions as follows: (1) Integrated LAVRE has a trend of decreasing from the center of the city to its periphery, and shows the feature of circle configuration. This trend is similar to the spatial change of the commercial housing prices, which shows a fact that the spatial distribution of commercial housing prices is directly influenced by the residential environment. (2) As a whole, the difference of commercial housing prices between northern and southern Beijing is similar to that of LAVRE. (3) Spatial preferences of residential location selecting are affected by the location advantage of residential environment. That is, northern Beijing where LAVRE is relatively high is the concentrated area of residential location selecting, and the rate of residents who choose southern Beijing, where LAVRE is low relatively, is lower than other parts of Beijing.
北京市区居住环境的区位优势度分析
Analysis on the development and evolution of high-tech industries in Beijing and its countermeasures
北京高精尖产业发展演变分析与对策研究
Spatial pattern and evolution of manufacturing industry in Beijing city
北京市制造业空间格局及演变分析
Characteristics of jobs-housing spatial distribution in Beijing based on mobile phone signaling data
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.12.006
[本文引用: 1]

As the most important parts of urban systems, jobs and housing spaces and their balance directly affect the spatial structure of cities, the behavior and experience of the residents, and the harmony and livability of the society. This study used more than 100 million records of mobile phone signaling data, covering the whole city of Beijing and over a period of one month, to identify the jobs-housing spaces by targeting the origin-destination (OD) oriented connections applying the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) method. Furthermore, this study explored the spatial distribution pattern and matching characteristics of Beijing's jobs and housing spaces from different spatial scales by using various measurement methods of jobs-housing balance. The spatial scales for analysis cover the whole city, ring roads, districts, and residential community and town and townships, and the methods applied include the spatial mismatch index, deviation degree, commuting flow rate, and so on. The results show that: 1) Mainly influenced by the spatial layout of the Beijing Master Plan, Beijing's housing space is characterized by dispersion at the large scale and agglomeration at the small scale, showing a pattern of scattered groupings. In contrast, its working space presents features of agglomeration at the large scale and dispersion at the small scale, retaining a significant single-centered layout. 2) Although working in local areas is the first choice for people at both the ring road scale and the district scale, there are still a great number of people works outside their residential areas. The degree of jobs-housing mismatch gradually decreases from the central city to the periphery no matter which method was adopted or at which scale. At the residential community and town and township scale, however, a more detailed feature of three-zones, with job agglomeration inside, housing agglomeration in between, and balanced distribution outside, was observed. 3) Both the general lack of jobs in certain areas caused by the high concentration of working space and the two-way commuting phenomenon in the majority of the areas caused by the high spatial concentration of jobs indicate the necessity of spatial reorganization of residential function and employment function. Specifically, for the regions with a high proportion of two-way commuting flow between them, such as Chaoyang-Changping, Tongzhou-Daxing, Haidian-Changping, Mentougou-Shijingshan, and Chaoyang-Tongzhou, further in-depth investigation should be conducted to find out the reasons for its formation and then possible industrial adjustment or functional reconstruction from the city level should be coordinated. Relying on big data, on the one hand, the job preference and demand of local residents can be identified, so the types and number of jobs in each region could be adjusted accordingly; on the other hand, the proper locations for new job and residential centers may be identified to help rearrange the land use of the whole city.
基于手机信令数据的北京市职住空间分布格局及匹配特征
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.12.006
[本文引用: 1]

职住空间作为城市系统最重要的组成部分,直接影响了城市的形态结构、居民的行为体验以及社会的和谐宜居,长期以来受到城市研究者的关注和重视。论文利用覆盖北京全市域并持续1个月的1亿多条手机信令数据,基于DBSCAN的聚类方法,通过OD定向联系,识别出同时具备居住—就业关系特征的职住空间。在此基础上,针对北京市辖区、环路、街道乡镇等不同空间尺度,综合运用空间错位指数、职住偏离度、职住分离率、通勤流动率等计算方法,研究北京职住空间分布格局及匹配特征。研究发现:① 北京市居住空间呈现大分散、小集聚特征,就业空间呈现大集聚、小分散特征;② 基于各个空间尺度、不同测度方法的分析结果均表明,职住空间的不匹配程度呈现出由中心城区向外围逐渐降低的态势,但基于街道乡镇尺度呈现出由内向外更细化的就业集聚—居住集聚—二者均衡的三段式变化特征;③ 无论是就业空间高度集聚导致的非集聚区就业岗位数量不足,还是包括就业高集聚区在内大量区域出现的双向通勤现象,均说明居住功能和就业功能空间重组的必要性。
Research on spatial development difference and influencing factors of cultural and creative industry in Beijing
北京文化创意产业空间发展差异及影响因素研究