1 引言
国内外相关文献多利用国际贸易理论研究边境贸易的具体内容、产生原因、发展阶段与变化、及其对地区经济发展的影响等,涉及到欧美、非洲、亚洲等地区[3]。关于欧美边境贸易的研究对象比较正式和现代化,包括边境电力贸易模型、购物贸易机制、在线电子贸易的影响因素等[4⇓-6]。相比之下,非正式贸易是非洲边境贸易研究的主要内容,常以结构化访谈、问卷调查等方式关注非正式贸易对贸易方式转化、边境安全和治理的影响[7⇓-9]。而有关亚洲及中国边境贸易的研究或以定量测度方法分析边界两侧供需和价格成本差异、边境商品便利化水平等因素对边境贸易发展的作用[10⇓⇓-13],或定性分析边境贸易的研究热点[14]、区位选择[15]、贸易政策转变[16]等。其中,由于西藏边境贸易的数额相对非常小,加之历史原因,相关研究偏少。
在这些有关历史与现实状况的研究中,部分学者对其影响因素与发展瓶颈进行了分析。首先从自然条件看,西藏边境处于喜马拉雅地区,使得边境贸易常受到气象地质灾害的限制。特别是2015年尼泊尔大地震,使得樟木口岸几近被毁,中尼贸易受到沉重打击[28-29]。受自然本底的约束,边境地区交通、电力、通讯等基础设施亦不健全,增加边境贸易商品运输的时间成本,妨碍其进一步扩大[22,30 -31]。此外,中印大国博弈造成的通道关闭与开放建设也影响着边境贸易的发展。总体上,这些研究或侧重大国博弈、地方建设等人类因素的主观驱动,或指出自然条件及其影响下的基础设施建设等非人类因素的客观限制,缺乏对西藏边境贸易发展的多因素整合分析研究。而这些自然地理、基础设施等非人类因素同大国关系、地方交流等人类因素一起,恰恰是推动和分析西藏边境贸易发展的基础。因此,本文拟引入行动者网络理论(Actor-network Theory, ANT)探索边境贸易是如何受各种异质因素(包括人类和非人类)相互作用而产生发展的。
在批判传统哲学自然与社会、主体与客体二分法的不对称分析基础上,ANT提出广义对称性原则,指出对称地看待自然和社会对科学知识的解释功能,并通过经验研究将科学知识视为异质行动者形成的网络借助转译机制进行建构的产物[32-33]。ANT的本质,即异质性、对称性和网络本体,使其成为理解网络构建过程中人类与非人类、物质与符号、阻力与权力动态间复杂关系的有用且独特的工具[34]。将其援引入地理学中的边境贸易情景,可以将大国、地方主体等人类与自然条件、基建设施等非人类结合,将宏观结构与微观行动结合,综合研究边境贸易发展过程中行动者网络的关联产生和稳定的过程,以及网络中各异质行动者的角色和功能,为揭示边境贸易的复杂联系发展提供一种新的理论和方法平台。
本文基于ANT,借助历史地理文献资料及相关研究成果,结合2020年7—8月与2021年7—8月沿中尼、中印边境对边境贸易现状的实地考察,剖析影响西藏自治区边境贸易的人类和非人类因素作用机制,为西藏破解边境贸易的发展瓶颈、培育环喜马拉雅经济合作带和参与中尼印经济走廊建设提供科学依据。
2 地理学中的行动者网络理论
2.1 行动者网络理论
行动者网络理论(ANT)是以Callon、Latour、Law等为代表的巴黎学派于20世纪80年代中后期提出的关于科学技术如何与社会中各异质要素重新融合构建成一个网络的社会学理论,属于科学知识社会学领域,包含行动者(Actor)、转译(Translation)和异质性网络(Heterogeneous Network)3个核心概念[35]。ANT中的行动者指的是所有参与科学实践过程中的异质性元素,包括人类(Humans)与非人类(Non-humans)[36]。人类行动者指代表不同利益的个人、组织、国家或社群,而非人类行动者含有观念、技术、生物、组织、思想等非人的生命、物质或符号,后来也常用行为者(Actant)一词进行指代,以示与人类行动者的区分[34]。基于广义对称性原则,两者处于平等地位,没有主客体之分,而不同的行动者代表了不同的利益取向和行为方式[37]。另外,ANT理论家根据重要程度也将行动者划分为调停者(Mediator)和中介者(Intermediaries)。前者定义了行动者网络中的目的和问题,并试图说服其他行动者在彼此的利益之间建立一致性,往往是关键行动者;中介者是相对稳定的一般行动者,以支持网络存在[33-34]。ANT还强调特定的社会情境和人类行动者如何将这些中介者纳入行动者网络,即为行动者网络中的转移过程[34]。
转译是指调停者(或关键行动者)将中介者(或一般行动者)的利益诉求与问题进行转换,得到他们的认可并建立稳固的联盟以达成共同目标的过程[38]。为解决一般行动者的各自问题,关键行动者建立了必经之点,即实现各方利益的共有问题,使所有行动者达成共识[39]。转译过程包括问题界定(Problematization)、利益赋予(Interessment)、征召(Enrollment)、动员(Mobilization)和异议(Dissidence)等5个环节[40]。在关键行动者的主导作用下,各类行动者之间的连接和相互作用都要通过转译完成,以此连接成行动者网络。该网络既非互联网似的技术型网络,也不是非正式链接的结构化网络,而是一种阐释事物发展的工具,它是行动者界定各自角色的同时形成的动态化扁平网络,其稳定性取决于行动者利益的不断转译。
2.2 ANT在地理学中的应用
作为社会理论“关系转向”的典型代表,ANT最初是为了将科学和技术融入社会过程而提出的,以一种反结构化的扁平方式跟踪和揭示各种人类和非人类之间关联的异构网络来理解事物的复杂性,为各学科研究提供了全新视角。在地理学中,ANT的广义对称性和关系性启发着对地球表面地区差异的描述和解释[41]。在广义对称性的原则下,ANT主张自然物质和人类社会同等重要,认为自然物质本身也具有能动性,将其看作积极塑造行动者网络的重要组成部分,超越传统地理学自然与社会的二元本位[41]。另一方面,ANT从关系的角度将空间视为一种拓扑,认为空间的距离不一定是现实的地理距离,而是网络中行动者的紧密程度,有助于理解远距离行动和网络在空间上的工作方式[42-43]。借鉴ANT的关系性,地理学者能追溯网络中的权力如何嵌入行动者间的关联并跨越空间的约束进行扩展,克服许多地理情景中默认的微观与宏观、地方与全球的二元分析框架[44⇓-46]。由上可知,ANT对地理学的主要关注点——社会和自然的关系、空间和距离的概念、跨越空间的权力行使——产生了深远影响,无疑促成其在地理学大量子领域的普及[47]。
20世纪90年代以来,国外地理学者率先将ANT应用于乡村地理研究,评价自然和社会文化在农业空间建构中的乡村发展模式、农村空间商品化、乡村冲突等问题[48⇓-50]。此后,ANT在城市地理、经济地理、旅游地理等领域有一定使用,如全球城市的行动者网络[51]、全球生产网络与跨国投资[52-53]、旅游景观与旅游区合作[54-55]等。与之相比,ANT自2005年才被引入国内地理研究,多涉及乡村发展与空间转型[40,56 -57]、土地利用冲突与治理[58]、乡村旅游[37,39]等话题。部分研究已开始对ANT进行理论思考与框架改进[35,41],但大多仍停留在ANT分析框架的直接套用,在广度和深度上与国际研究仍有差距。比如,ANT因起源于社会学而常常关注中微观范畴空间网络里人与非人的对等作用,但随着全球—地方联系的日益密切,宏观尺度的国家或区域组织等人类行动者的权力影响需要得到地理学界的重视和补充。同时需要指出的是,现有研究在行文上习惯于重笔人类行动者对行动者网络的能动作用,缺乏对自然地理、社会物质等非人类行动者的有效描述分析。
在21世纪物质性回归的思潮下,地理学界对于这些缺陷有一定的探讨和添补。超越人类的地理学主张重新恢复唯物主义,不是过去的唯物主义和决定论,而是呼吁地理学超越人类自身,回归非人类生命或物质,强调非人本身的能动性与活力[38]。这表示地理空间不是单纯地受人类意志控制的,也不是一味进行的话语建构,同时还有自然环境、动植物等非人类元素的参与和影响,启发地理学加强对ANT中非人作用的研究与表达[59-60]。亦有地理学者认为,ANT在强调对称性的同时,往往忽略了人类主体言语和意识的特殊性,即表达能力、发明创造能力和虚构能力[41,61];但不可否认,人类的意向性是一种特殊的动员力量,在行动者网络构建的初始阶段有关键作用[41]。这要求ANT在描述传统异质关系的基础上,需要重视有意识与动机的人类行动者,特别是超越中小尺度的国家或区域组织。受冷战后经济全球化持续推进的影响,边境地区吸引愈多国家或区域行动者的有意介入,边境贸易中人类和非人类元素日益交流成网,成为地理学界创新ANT研究的合适议题。
3 边境贸易的行动者网络分析
3.1 ANT与边境贸易
相比ANT研究的传统地理话题,边境贸易不仅恰当适用,而且为激发ANT的学理创新和发展潜力提供了强劲动力。首先从概念上讲,边境贸易指相邻国家边境地区边民或企业之间进行的货物贸易或经济联系,符合ANT研究常见的中小尺度范畴[18]。这是因为源于对科学实验、乡村发展等具体事物复杂性研究的ANT常常专注于中微观范畴的话题,与边境贸易这类一般聚焦边界线附近小范围毗邻地区的议题不谋而合。但边境贸易不仅受地方边民或企业主动交流的传统影响,同时还受到相邻国家的权力管控。福柯关于国家权力的统一管理性主张认为,国家可以透过远距离指挥的方式来影响边境网络[56]。例如在中国,根据国务院有关规定,边境贸易一般按照边民互市贸易和边境小额贸易两种形式进行组织管理,限定边民或企业在政府批准的开放点、集市或陆地边境口岸进行商品贸易[18]。这证明边境贸易可以成为探讨ANT中人类能动性、特别是国家权力影响的典型话题,补足其对人类表达或发明创造等特殊动员能力的忽视。
另外,边境贸易往往会受其所处边境地区自然和人文地理空间的先天性作用。传统的国家边界被认为是自然边界,常以山脉、江河、沙漠、峡谷、瀑布、海岸线等差异化地貌进行划分[62]。这些地貌或呈现荒凉、险恶且难以穿越的地理环境,或提供一定程度便利的通道,从非人类物质的角度对边境贸易产生着或阻碍或促进的天然影响。在20世纪末的后现代和后结构主义思潮下,边界不再是预设的国家间分割的自然界线,而是被政治、经济、社会、文化、民族、宗教、情感等日益频繁的跨国流动所建构的[63-64]。这意味着边境被认为是一种多人文社会要素混杂的场所,从人类理念和实践的角度对边境贸易的发展产生着综合作用。由此可知,边境贸易既强调ANT中人类与非人类的基本协同作用,又能有效推动其在国家等人类有意识的能动影响方面的学术创新。因此,基于ANT界定边境贸易的行动者构成,提出边境贸易的行动者网络分析框架,并确定这些行动者网络中大国博弈、地方交流与非人类影响的作用归属,从而填补相应的研究空白。
3.2 边境贸易的行动者构成及分析思路
不同于传统的行动者构成,边境贸易中的人类行动者大致可以分两类:国家或区域行动者、地方行动者(表1)。国家或区域行动者主要指的是主权国家的中央政府以及具有一定权力影响的全球或区域组织,如联合国和欧盟。这类行动者可以凭借自身的权力对边境贸易政策、口岸开通进行宏观决策,对边境贸易发展具有强大的主导力,是其中的调停者或关键行动者。地方行动者则是在边境地区直接参与边境贸易发展的各种人类行动者。比如,地方政府或弱政府国家的边贸协会承担传递政策讯息、制定具体规定与监管措施等职能,辅助中央政府或国际区域组织的领导和决策,可与其一同称为调停者。除此之外,地方行动者中包含大量的中介者,即当地或外地的民众、商户、投资企业、承包公司、施工单位等。除了这些人类行动者,还涉及当地的自然地理环境、社会经济文化现象、基础设施建设、通商政策法律规定等非人类中介者,对边境贸易网络产生着物质性或理念性的影响。
表1 边境贸易的行动者构成
Tab. 1
| 类别 | 行动者 | 具体形式 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 人类 | 国家或区域行动者 | 全球或区域组织 | 调停者或关键行动者 |
| 中央政府 | |||
| 地方行动者 | 当地政府、边贸协会或商会等 | ||
| 民众、投资企业、承包公司等 | 中介者或一般行动者 | ||
| 非人类 | 自然地理环境 | 地形、气候、水文、土壤、植被等 | |
| 人文社会现象 | 经济、文化、民族、宗教等 | ||
| 基础设施建设 | 道路、市场、仓储等 | ||
| 政策法律规定 | 通行、住宿、税收、贸易清单等 |
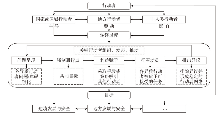
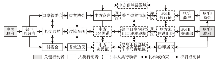
边境贸易的行动者网络主要通过ANT术语中的转译概念进行分析,即分析国家或区域行动者、地方行动者与非人类行动者间的关系谈判与互动过程,以实现利益一致的边境贸易发展(图1)。由前文可知,国家或区域行动者凭借自身的权力优势对边境贸易的转译过程起主导作用,地方行动者主要起直接的驱动作用,而非人类行动者产生基础性的促进或约束影响。受异质行动者的综合作用,分析转译过程常常先在问题界定阶段明确边境贸易中所有行动者面临的问题,并在调停者或关键行动者的组织下识别共同关注的必经之点以促成共同目标的达成。之后,调停者或关键行动者发起并对其他行动者进行利益赋予和分配,并确定其在网络中的角色。然后,进行征召和动员,赋予每一个行动者互相可以接受的任务并进行动员,使所有行动者为边境贸易发展而行动起来。只有达到这个阶段,一个成功的行动者网络才算完成。最后,由调停者或关键行动者排除异议,即排出行动者之间的争议与背离以促进边境贸易网络的顺利形成和稳定运行。倘若异议无法完全排出时,需要在调停者或关键行动者的带领下重新对以往过程进行反思和修正。当异议最终排除后,边境贸易行动者网络便会在所有行动者的共同作用下稳定运行,以实现边境贸易发展的共同目标,以及边境和地方各自的发展和安全目标。借鉴边境贸易的行动者网络分析思路,下文将对西藏边境贸易进行全面解读和印证。
图1
图1
边境贸易的行动者网络分析框架
Fig. 1
The analytical framework of the actor-network of border trade
4 21世纪以来西藏边境贸易发展的行动者网络分析
西藏自治区地处中国的西南边疆,位于青藏高原之上,与印度、不丹、尼泊尔、缅甸及克什米尔等国家和地区相邻,经贸文化往来密切。据统计,西藏超过4000 km的边界线上形成了对外通道312条,其中通向尼泊尔184条、印度93条,在18世纪末期有相对固定的边境贸易市场和贸易点达60多个[18,65]。1978年改革开放以来,受地方发展驱动的影响,西藏边境贸易开始逐渐恢复。但受中印在战略互信及边界争端等问题上的干扰,西藏边境贸易,特别是中印边境贸易,恢复和发展缓慢。此外,地处南北地形差异较大且位于地震带上的喜马拉雅地区,边境贸易的基础设施建设常受到气象地质条件的限制和损害。因此,除地方行动者驱动之外,西藏边境贸易深受国家或区域行动者的主导决策,以及非人类行动者的限制约束,宜引入ANT进行深入分析。
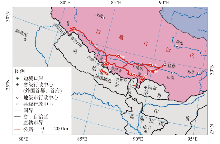
本文重点追溯了21世纪以来西藏边境地区中印和中尼贸易的行动者网络发展建设过程。作为中印边境贸易的典型代表,亚东县乃堆拉互市贸易自2006年恢复开通以来增设边境贸易机构、兴建边境贸易市场,但发展仍受中印关系影响较为缓慢。2015年尼泊尔大地震后,中尼边境贸易的重心逐渐转移到吉隆县吉隆口岸,吉隆边境贸易市场、口岸建设和公铁规划迅速开展。此外,普兰县的边境贸易历史悠久,发展却不温不火,但由于地处中尼印3国交界处,成为同时呈现中印和中尼边境贸易差异的天然选择。本文选择以上3个案例(图2),将重点描述边境贸易发展如何促使相关行动者加入这些网络的。需要补充说明的是,该地区其他的口岸贸易、互市贸易或传统贸易等鉴于代表性不强、信息可获得性弱等因素,不纳入此次的研究范围中。
图2
图2
西藏自治区的主要边境贸易通道示意图
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站下载的审图号为GS(2016)2921号的标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Major trade corridors in Tibet's border
4.1 亚东县中印乃堆拉互市贸易
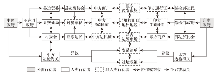
亚东县曾是古代“丝绸之路”南线的主要通道,是中国与南亚诸国陆路贸易的“桥头堡”,具有对外通道45处。20世纪初,亚东成为中印之间的重要通商口岸,边境贸易交易额最高时达到上亿银元,占当时中印贸易总额的80%以上;1962年中印边界战争爆发后,乃堆拉通道一度关闭,直到80年代双方关系逐渐缓和,才再次出现少量的互市贸易[66]。2003年两国签署《关于扩大边境贸易的谅解备忘录》同意增开乃堆拉山口通道,并于2006年正式开通。因此,“扩大边境贸易”成为中印乃堆拉边境贸易行动者网络的发展目标,也就是各方利益交汇的必经之点。
图3
图3
中印乃堆拉互市贸易行动者网络
Fig. 3
The actor-network of China-Indian border trade at NathuLa
但不同地方行动者在实现该目标的过程中面临着不同的问题。比如,中方地方政府主要面临管理不协调、市场规模小等问题;当地边民主要面临参与意识低、经济收入少等问题。对此,在中央政府的主导调停下,地方政府作为边境贸易网的协调者,积极开展部门帮扶征召,赋予交通局、公安局等部门维护道路设施建设、严格入境人员登记等职责。另外,考虑到双方一直未建立官方会晤机制且印方于2006年已成立边贸协会,亚东县边贸委于2016年下设仁青岗边贸协会专门负责对印交流,赋予其贸易沟通、秩序维护等职能。每年5月互市开放前,亚东县边贸委、边贸协会、海关、边检等地方行动者会深入各乡镇对边民进行集中式培训,推行“一站式”边民证办理服务。与此同时,怀有提高生活收入、参与边境建设等利益诉求,双方村组织或边民主要通过当地带头征召和动员,号召边民们积极参与互市贸易,或者加入到边贸协会进行管理工作,是边境贸易网的主要参与者。
除国家和地方行动者,非人类行动者也或多或少地参与塑造着乃堆拉边境贸易网。从自然类行动者看,海拔超过4700 m的乃堆拉山限制着山腰间仁青岗边境贸易市场的空间大小,仅有44间偏老旧的样板房铺面;在交通方面,通往山口的上坡路为双向两车道,仅允许双方过境车辆单行通过,时而还受到地质灾害的阻断[67]。这呼吁着交通基础设施的进一步改善与边境贸易市场的易地建设改造。根据访谈介绍,在国家、自治区等有关行动者的支持下,新市场2016年开工建设于山下的亚东河谷平缓区,2017年正式竣工,总面积超1万m2,提供贸易房铺近200间。通往亚东的204省道也于2016年提升为562国道并进行改造养护,进一步提升边境贸易网的通达性。
开通10余年来,在中印国家权力的主导征召下,亚东地方行动者积极参与并同非人类行动者适应互动,推进乃堆拉边境贸易网的丰富发展,促使边境贸易额从开通时的每年20余万增长至近年的2亿人民币以上。但双方现有的贸易政策已无法满足边境贸易网进一步扩大的发展需求,存在一定异议。一方面,现存的贸易清单仍是2006年旧本,印方出口商品大多以原材料为主且仅限中方出口15项商品;同时印方进口商品只能在甘托克范围销售,而中方则对进口商品完全开放,造成中方巨大的边境贸易逆差[67]。另一方面,印度始终坚持出境边民必须当天往返且不得留宿的过境政策,限制双方商户的经商持续性。对此,中方通过印方边民去信锡金邦政府表示可以允许边民过夜,但印方迟迟不予理会。这些异议都反映出国家行动者对边境贸易网发展的强有力约束,亟待未来进一步协商解决。
4.2 吉隆县中尼吉隆口岸贸易
相比樟木口岸,吉隆口岸位于海拔约1800 m的吉隆藏布河谷,尽管地理距离稍远,但该地非人类行动者的能动参与为其边境贸易网建设提供先天的比较优势。特别是在地质地貌方面,樟木口岸位于聂拉木—措勤断层裂谷这一地壳能量释放通道,谷内山体更破碎;自然纵坡平均约80%,而吉隆口岸的最大值约60%;沿线冰湖分布约17个,远高于吉隆口岸的3个,历史记载约有7次大溃决,地质灾害风险极高[68]。而吉隆口岸附近自然纵坡较小、沿途降雨量小、受构造影响较小,发生地震及次生灾害的风险较低,在2015年震后房屋及边坡的破坏程度也远小于樟木口岸。受此影响,吉隆口岸涉及的道路施工与运营风险偏小,216国道经过乡镇据点较多且工程投资经济,为该地边境贸易网发展奠定了较好的非人类基础。
图4
图4
中尼吉隆口岸贸易行动者网络
Fig. 4
The actor-network of China-Nepal border trade through the Gyirong port
以中方为例,吉隆县政府进行部门帮扶征召,专设口岸管理委员会承担口岸及相关边境贸易事宜,同时建议授予县交通局、公安局、外事办等部门维护道路基建、简化入境登记等职责。其中,口岸管委会积极推动吉隆边境经济合作区规划,监督吉隆边境贸易市场于2016年动工且于2019年10月底正式开放,大约可容纳67家商户;交通局和道班人员全天候监测216国道通行情况,防范地质灾害风险;出入境管理方面,在2019年允许700余名尼方司乘人员办理临时入境许可,便利其跨境参与边境贸易相关商务和运输业务。当地村委会和村民主要通过带头征召和动员,号召边民们或独自或成立边民合作社积极参与互市贸易。尼方商户也可以在吉隆镇范围内直接售卖尼泊尔商品。
地处良好的地理区位,吉隆口岸贸易网在中尼两国的宏观设计推动下,吸引地方行动者积极建设。但其发展仍处于起步阶段,同时受新型冠状病毒肺炎感染的影响,很多规划还未落地,导致边境贸易网建设存在一些异议。一是吉隆边境贸易市场建设开放晚、房租费用高、入驻商户率低,受疫情影响几近关闭,发展非常迟缓。另外,尼方道路交通基建水平较差,尤其是从尼方沙夫鲁比西镇到中尼边境拉苏瓦加蒂的沙拉公路较窄、仅为砂石路面,非常限制物流通行,影响下一步的边境贸易网发展。幸运的是,这些异议已经得到双方国家和地方行动者的重视,有望未来得到一定的解决。
4.3 普兰县中尼、中印边境贸易
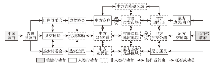
面对普兰边境贸易发展缓慢、停滞不前等主要问题,中尼双方行动者均认同“重点建设普兰口岸”视为普兰边境贸易行动者网络发展的必经之点。同样作为关键行动者,相比中印两国关系的限制性,中尼双方均有深化战略合作伙伴关系的诉求,支持普兰口岸贸易发展(图5)。以中方一侧为例,国务院积极采取行政征召,于2015年明确普兰口岸为沿边国家级公路口岸;2018年普兰口岸正式被列为药材进口边境口岸;2019年普兰海关获批成立。
图5
图5
普兰县中尼、中印边境贸易行动者网络
Fig. 5
The actor-network of China-Nepal/Indian border trade in Burang County
在国家行动者的征召支持下,地方行动者也参与到普兰口岸贸易网的发展中。2014年3月设立普兰口岸管委会专门负责口岸及相关边境贸易事物的管理和协调,并且进行部门帮扶征召,多次邀请县海关、边检、公安局、交通局等相关部门就中草药通关、边民进出口贸易统计、口岸限定区域开放、边民证实施等议题进行讨论交流。地方相关的政策制定也吸引村委会进行当地带头征召和动员,号召边民们积极参与互市贸易,或准许成立边民合作社。从访谈中获悉,部分具有运输资质的边民每年也被征召参与到口岸往返县城的物流运输中。此外,普兰镇区域常年也有印度和尼泊尔的商户在边境贸易市场做生意,其中印度商户10余家,尼泊尔商户300余家,常集中于每年5—11月份;他们在普兰都分别成立商会,用于组织商户在当地的日常运行和纠纷处理。
尽管中尼双方的权力征召推动普兰边境贸易网的地方发展建设,但令人遗憾的是,其还是受到非人类行动者能动性的一定限制。在中方现有边境贸易市场及配套设施老化缺乏,虽然新唐嘎边境贸易市场于2016年4月开工建设,但仍未建好,限制着边境贸易网发展的交易空间[67]。而尼方落后的交通和口岸基础设施页成为制约边境贸易发展的瓶颈。普兰口岸到尼泊尔胡木拉县的超过30 km至今不通公路,货物运输主要依靠人背马驮,游客运输以直升机为主。反观印方,海拔超过5300 m的强拉山口以及贸易清单限制对中印边境贸易本就产生天然或认为的限制作用。因此,受中方与尼、印两国非人类参与的失衡影响,普兰边境贸易网发展水平低、速度慢,是未来需要重点解决的异议。
4.4 对比分析
作为西藏边境贸易发展的典型代表,3个案例均反映出国家行动者的主导决策、地方行动者的驱动协调以及非人类行动者的基础影响。但对比发现,这3个案例代表了互不相同的行动者网络发展历程,特别是在国家行动者和非人类行动者方面(表2)。作为中印边境贸易的典型代表,乃堆拉互市贸易在中印关系好转后迅速起步,但受中印关系长期波动且边境争端时有发生的影响,其网络发展始终受到印方国家权力的约束限制。反观吉隆口岸和普兰口岸贸易,依托于环喜马拉雅经济合作带构想下中尼关系的不断亲密深化,双方国家和地方行动者积极践行建设新边境贸易市场以及跨境经济合作区的未来新目标,推动边境贸易行动者网络的繁荣发展。
表2 西藏边境贸易的案例对比[67]
Tab. 2
| 案例 | 国家行动者 关系 | 非人类行动者特征 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然地理 | 道路交通 | 市场政策 | |||
| 亚东县中印乃堆拉互市贸易 | 中印关系不温不火,时有争端 | 海拔超高,离印度核心区远但距锡金邦首府甘托克约24 km,离拉萨约471 km | 中方为562国道,下亚东乡至乃堆拉山口道路改造,冬季大雪封路 | 新仁青岗边贸市场,贸易清单局限,限当天往返双方市场 | |
| 吉隆县中尼吉隆口岸贸易 | 中尼关系21世纪以来持续升级 | 海拔高,地质地貌条件偏好,离尼泊尔首都加德满都约131 km,离拉萨约830 km | 中方为216国道;尼方公路相对较窄,仅为砂石路面 | 新吉隆边贸市场,可凭边民证享受免税政策并长期往来双方乡镇 | |
| 普兰县 中尼、 中印边 境贸易 | 普兰口 岸通道 | 中尼关系21世纪以来持续升级 | 海拔高,地质地貌条件偏好,离尼泊尔首都加德满都约1200 km,离拉萨约1350 km | 中方为564国道;尼方一侧约30 km道路不通,靠人背马驮或直升机运输 | 老普兰边贸市场,可凭边民证享受免税政策并长期往来双方乡镇 |
| 强拉山 口通道 | 中印关系不温不火,时有争端 | 海拔超高,离印度首都新德里约436 km,离拉萨约1350 km | 中方为564国道,普兰镇至强拉山口道路窄小,冬季大雪封路 | 老普兰边贸市场,贸易清单限制,限短期暂留中方乡镇 | |
与此同时,非人类行动者在这3个案例中的能动性影响则差异显著。受乃堆拉山口海拔超高的影响,边境贸易互市的自然条件先天薄弱。地质灾害偶发、冬季大雪封山等不利条件,增加道路交通与市场基建等物质性行动者参与的难度,即山路仍在改造且新市场不得不建在山下河谷区;同时考虑到该地离印度核心区较远且临近双方地缘文化相近的锡金邦,印度因忌惮边境贸易的繁荣动摇其在锡金邦的统治力,故而采取较为严格的当天往返出行限制和贸易清单约束,导致乃堆拉互市贸易的行动者网络迟迟发展缓慢。在吉隆口岸贸易中,通道海拔高但位于较为宽敞的吉隆藏布河谷,相较于樟木口岸的地质条件偏好且同加德满都距离也近,为口岸贸易提供了优良的自然条件。再加上双方边民亲缘相近,也被允许长期往来双方乡镇,促进了边境贸易行动者网络的深度发展。虽然第3个案例中的普兰边境贸易行动者网络总体体现了中尼与中印的非人类行动者差异,但由于普兰离加德满都偏远而离新德里偏近、尼方道路不通、中方新市场还未建成等地理基建的限制,普兰的中尼口岸贸易相比发展较缓,但中印互市贸易貌似也仅有少许优势,体现在印度边民可短期暂留在普兰镇。
以上分析清楚地反映了西藏边境贸易发展的行动者网络转译过程与比较差异,特别是在国家行动者关系和非人类行动者影响方面的异议显著。因此,着重从国家行动者和非人类行动者两方面提出优化措施。① 在国家行动者方面,积极构建与印度或尼泊尔的友好稳定关系,提出符合双方利益的边境贸易发展策略,服务于南亚大通道建设。在乃堆拉互市贸易中,征召建立中印官方会晤机制,打破边境贸易壁垒,依托国家力量推动双方互市贸易网的新发展。在吉隆口岸贸易中,建议国家有关部门对吉隆边境经济合作区的功能定位与发展方向进行高位谋划与专题研究,指导合作区出台涉及土地、财税、贸易、投资、人员往来、通商便利的政策,发展创造优良的边境贸易行动者网络。② 在非人类行动者方面,加强物流通道与市场建设,形成高效有序的边境贸易发展网。比如在吉隆口岸与普兰口岸通道,对尼方一侧基础设施投资和建设进行一定帮扶,增强与尼基础设施互联互通;同时继续完善边境贸易市场设施条件,提高对人流物流的吸引力和服务能力,推动边境贸易网的物质建设发展[72]。
5 结论与讨论
本文基于ANT构建地理学研究的边境贸易行动者网络分析框架,并以乃堆拉互市贸易、吉隆口岸贸易、普兰边境贸易为例,分析中印、中尼双方(主要为中方一侧)在西藏边境贸易的网络互动中提出问题、界定利益并解决异议的过程,并对边境贸易优化提出建议。主要结论如下:
(1)与传统的行动者网络分析框架不同,边境贸易的行动者网络分析强调边境贸易的发展是由国家或区域行动者的主导决策能力、地方行动者的驱动协调作用与非人类行动者的物质理念影响共同作用推动的。一般来说,在国家或区域行动者的领导下,各异质行动者彼此通过提出问题、界定利益、征召动员、排出异议等转移过程,实现边境贸易的发展。
(2)在21世纪西藏边境贸易的案例分析中,中央政府作为关键行动者统一领导各异质行动者转译互动,但同时重点受到中印、中尼等国家行动者关系亲疏、以及喜马拉雅地区自然地质脆弱和基础设施落后等非人类行动者的共同影响和差异性约束,总体呈现中尼边境贸易行动者网络发展优于中印的特征。具体而言,中印乃堆拉互市贸易网于2006年正式开通建设,但囿于大国权力约束下贸易清单和出行限制等非人类行动者的影响长期发展有限。利用2015年尼泊尔大地震樟木口岸严重受损的契机,中尼各方行动者大力在非人类基础相对较好的吉隆口岸,以及普兰口岸进行征召动员以支持当地边境贸易网发展,但依然受到边境贸易市场发展不成熟、基础设施落后等异议的约束。对此,西藏边境贸易发展应继续在中尼、中印国家友好关系构建、口岸发展定位与专题研究、交通与市场基础设施建设等人类或非人类行动者方面进行优化。
作为将ANT应用于边境贸易话题的一种新尝试,本文初步展示了边境贸易行动者网络建设的复杂分析情形。不同于传统ANT关注人类和非人类行动者的对称性作用,该方法借鉴地理学界的新思想,创新性地将国家或区域行动者从人类行动者中剥离出来,突出体现了国家权力对边境贸易行动者网络的主导塑造影响,一定程度上补充了人类行动者的特殊动员能力对行动者网络作用的空白,也将ANT研究中惯常的中微观尺度拓展到宏观范畴[73]。这种对边境贸易行动者之间复杂权力关系的研究,必将对ANT产生新的学术启发性。
沿着ANT的主张,重新审视并加强人类与非人类之间关系的研究,也有利于应对西藏边境贸易中涌现的新问题、新挑战。比如,伴随着大数据时代的到来,除了传统的物质通道建设,边境地区5G网络建设、基于大数据与人工智能等新技术线上购物云平台、物流智能调度系统等物流运营与管理平台的搭建,也可能成为西藏现代边境贸易物流网发展的引擎。但不可忽视的是,在后疫情时代与百年变局复杂交织下,边境疫情态势、中印、中尼国家关系等人类或非人类行动者对边境贸易网发展和稳定的不利影响依然存在。比如,加勒万河谷事件后中印边境贸易长期封闭;中尼边境贸易的恢复发展与基建政策配套优化。这些都成为接下来值得关注和研究的新问题。
致谢
感谢匿名评审专家和编辑部对本文的学理创新点、案例分析表达等方面的指导建议;感谢中国科学院青藏高原研究所博士黄宇、青海师范大学博士叶帅、北京师范大学硕士冶莉和李娜以及访谈对象的调研信息分享。
参考文献
Silks and the Silk Road in western Tibet
西藏西部的丝绸与丝绸之路
Exploring the evolution process and driving mechanism of traditional trade routes in Himalayan region
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109009
[本文引用: 2]

Traditional trade routes that penetrate the natural barrier of the Himalayas are critical for connecting major Chinese and South Asian markets. Research on these trade routes can contribute significantly to facilitating the construction of the South Asia Channel and enhancing trans-Himalayan connectivity. Combining historical literature, field surveys, and Geographic Information System (GIS) techniques, this study examined the spatial distribution characteristics and dynamic mechanisms driving the formation, development, decline, and restoration of the routes, focusing on transverse valleys of the Himalayan arc. The key findings were as follows. First, there are 21 traditional trade routes traversing the Himalayan region: 6 Sino-Nepalese routes, 4 Sino-Bhutanese routes, and 11 Sino-Indian routes. The routes are arranged in a "one horizontal and multiple vertical" spatial pattern. Second, the evolution of the traditional trade routes has entailed five distinct phases: an incipient period (pre-7th century), formation (7th century-842 AD), development (842-1959), decline (1959-1962) and recovery (1962-present). Third, the incipient and formative developmental phases were prompted by the spread of Buddhism and the exchange of goods. The stability of local governments in Tibet and in the Central China Plains and favorable border trade policies along with Britain's colonial expansion and commercial interests stimulated further development of traditional trade routes. However, India's strategic miscalculation and "Forward Policy" instigated the decline phase, while China's strategic needs are currently the key driver of the restoration and construction phase. Finally, a lack of strategic mutual trust and existing border issues are the main obstacles impeding the restorative and construction phases. Future efforts to support the construction of the South Asia Channel and the stability and development of border regions should focus on strengthening multi-perspectival investigations and research on traditional trade routes, formulating strategies for corridor construction and control, and emphasizing the corridor's commerce, tourism, and cultural exchange functions.
喜马拉雅地区传统贸易通道演变过程及动力机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109009
[本文引用: 2]

喜马拉雅地区传统贸易通道是突破喜马拉雅山脉天然屏障、连接中国与南亚腹地两大市场的关键,对于南亚大通道建设和跨喜马拉雅互联互通建设具有重要的战略意义。本文以喜马拉雅山脉断裂河谷为出发点,综合历史文献、实地调查及GIS技术手段,分析通道的空间分布特征、演变过程及动力机制。研究表明:① 喜马拉雅地区的传统贸易通道主要有21条,其中中尼通道6条,中不通道4条,中印通道11条,在空间上形成了“一横多纵”的空间格局。② 传统贸易通道的发展经历了萌芽期(7世纪以前)、形成期(7世纪—842年)、发展期(842—1959年)、衰落期(1959—1962年)和恢复期(1962年至今)的演变过程。③ 货物交换和佛教传播促进了通道的萌芽和形成,西藏及中原地方政权稳定和边贸政策、英国的殖民扩张和商业利益推动了通道的发展,印度的战略误判和前进政策导致了通道的衰落,中国的战略需求将推动通道的恢复和建设。④ 战略互信和边界问题是通道恢复和建设面临的主要障碍,未来需要加强对通道的多视角调查和研究,制定通道的建设和管控策略,充分发挥通道的商贸、旅游和文化交流功能,积极服务于南亚大通道建设,促进西藏边疆地区的稳定与发展。
The drivers and impediments for cross-border e-commerce in the EU
DOI:10.1016/j.infoecopol.2014.05.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
The EU regulation on cross-border trade of electricity: A two-stage equilibrium model
DOI:10.1016/j.ejor.2005.12.040 URL [本文引用: 1]
North American natural gas model: Impact of cross-border trade with Mexico
DOI:10.1016/j.energy.2016.06.133 URL [本文引用: 1]
The human side of regions: Informal cross-border traders in the Zambia-Malawi-Mozambique Growth Triangle and prospects for integrating Southern Africa
DOI:10.1080/08865655.2017.1390689 URL [本文引用: 1]
The (in)commodities of laissez-faire integration: Trade and mobility in a cross-border market
DOI:10.1080/00020184.2013.776197 URL [本文引用: 1]
Brokerage in the borderlands: The political economy of livestock intermediaries in northern Kenya
DOI:10.1080/17531055.2020.1845041 URL [本文引用: 1]
The Role of Informal Cross-border Trade in Myanmar
Influence of frontier trade facilitation on frontier trade flow: An empirical trade gravity analysis of Xinjiang Province in China
边境贸易便利化水平对中国新疆维吾尔自治区边境贸易流量的影响: 基于贸易引力模型的实证分析
Barriers to cross-border trade and the impact factors in southwest China
我国西南边境地区跨境贸易的阻力及其影响因素
The current status and impact of frontier trade of China and North Korea on the social economy in the frontier region
中朝边境贸易的现状及其对边境地区社会经济的影响
东北亚论坛,
Comment on the hot spot of researches on China's frontier trade
我国边境贸易研究热点述评
A study on location of frontier trade in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.1994.04.297
[本文引用: 1]

With analysing six locational elements of frontier trade: geography, politics econo-my,policies transportation and port fundament, territory differences between open con-ditions and main areas of frontier trade are discussded. The important frontiers are in northeast China,Yunnan-Guangdong and Neimeng-Xinjiang respectively.Six characteristics of frontier trade in China are generalized as follows:(1)The function has changed;(2)Agglomeration and spread are formed simultaneously;(3)Quantitative growth is faster than ever;(4)The structure of import-export goods is special;(5)The territory of trade is enlarged;(6)There are various trade ways.
我国内陆边境贸易的区位研究
Historical exploration on China's border trade policy evolution since reform and opening-up
改革开放以来中国边境贸易政策演变的历史考察
An analysis of the history and current state of Tibet's border trade
西藏边境贸易的历史演进与现实情况分析
On the spatial layout, development and countermeasures of the land border crossings in Tibet from the geo-economic perspective
地缘经济视角下西藏边境陆路口岸空间布局、发展效力及对策研究
Development of border trade in Tibet and customs supervision
西藏地区边境贸易的发展与海关监管
On the trade between Tibet and Nepal
西藏地方与尼泊尔贸易试述
Coupling and coordination of ports trade and cross-border transportation of China and Nepal
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.03.002
[本文引用: 2]

As a window of the Economic Cooperation Belt around the Himalayas, the development of trade and transportation at the Chinese-Nepalese ports is an important support for China's construction of the Grand Opening Channel to South Asia. This study explored the coupling and coordination composite system of ports trade and cross-border transportation of China and Nepal, evaluated the ports trade sustainable development level and the accessibility of cross-border transportation of China and Nepal using an evaluation index and cross-border transportation accessibility model, and analyzed the coupling and coordination relationship between ports trade sustainability and cross-border accessibility from 2010 to 2019 using the coupling and coordination model. The results show that: 1) The composite system of ports trade and cross-border transportation is an organic whole with an interactive coupling relationship. The simultaneous high-level development of ports trade and cross-border transportation is the key to the coupling and coordination of ports trade and cross-border transportation. 2) The overall sustainable development level of China-Nepal ports trade is relatively low, and trade flow is the key for ports trade sustainability. The cross-border transportation accessibility of the Chinese-Nepalese ports has been slowly improved, and the Zhangmu Port has obvious advantages in cross-border transportation. 3) The coupling and coordination of ports trade and cross-border transportation of China and Nepal are moderately out of balance, trade lags behind transportation development, and transportation has a limited role in promoting trade. In order to promote the coupling and coordinated development of ports trade and cross-border transportation, it is necessary to give full play to the cargo transportation function of the Chinese-Nepalese ports, vigorously develop Nepal's re-export trade, and open up the South Asian market. Accelerating the construction of a cross-border economic cooperation zone at Jilong Port, building new channels in the long term to give full play to the cargo transportation function of Zhangmu Port, and using helicopters to develop the "Holy Mountains and Lakes" tourism economy at Pulan (Xie erwa) Port will promote the sustainable development of ports trade.
中尼口岸贸易与跨境交通耦合协调研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.03.002
[本文引用: 2]

中尼口岸作为环喜马拉雅经济合作带的窗口,其贸易和交通发展是中国建设“面向南亚开放大通道”的重要支撑。论文探讨口岸贸易与跨境交通的耦合协调机理,运用评价指标体系法和可达性模型分别评估中尼口岸的贸易可持续发展水平和跨境交通可达性,运用耦合协调模型分析2010—2019年中尼口岸贸易可持续性与跨境交通可达性的耦合协调关系。研究结果表明:① 口岸贸易与跨境交通复合系统是一个具有交互耦合关系的有机整体,口岸贸易与跨境交通高水平同步发展是口岸贸易与跨境交通耦合协调的关键。② 中尼口岸贸易的整体可持续发展水平偏低,贸易流量是中尼口岸贸易可持续发展的关键要素;中尼口岸的跨境交通可达性提升缓慢,樟木口岸的跨境运输优势明显。③ 中尼口岸贸易与交通发展的耦合协调整体处于中度失调状态,贸易滞后于交通发展,交通对贸易的促进作用有限。为了推进口岸贸易与跨境交通的耦合协调发展,应当充分发挥中尼口岸的货运职能,大力发展尼泊尔转口贸易,打通南亚大市场。加快建设吉隆口岸跨境经济合作区;远期打造新通道以发挥樟木口岸大宗货物运输功能;利用直升机发展普兰(斜尔瓦)口岸的“神山圣湖”旅游经济,促进口岸贸易可持续发展。
Small-scale border trade in Tibet and increasing border residents' income: Based on the field investigation in Luozha County
西藏的边境小额贸易与边民增收: 基于洛扎县的田野调查
Three models of traditional trade between Bhutan and Tibet in China
中国西藏与不丹之间传统贸易的三种模式
India-China trade at the borders: Challenges and opportunities
DOI:10.1080/10670564.2013.766387 URL [本文引用: 2]
India-China border trade through Nathu La Pass: Prospects and impediments
Seismic risk of Himalayan region after Nepal earthquake
尼泊尔地震后喜马拉雅地区地震风险浅析
Investigation on the development of border trade of Zhangmu Port in Tibet
西藏樟木口岸边境贸易发展情况调查
On current situation, influence and development path of Sino-Nepal trade
中国—尼泊尔贸易现状、影响及发展路径研究
An analysis of bilateral trade and investment prospects between China and Nepal
中国与尼泊尔双边贸易及投资前景分析
Some elements of a sociology of translation: Domestication of the scallops and the fishermen of St Brieuc Bay
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-954X.1984.tb00113.x
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper outlines a new approach to the study of power, that of the sociology of translation. Starting from three principles, those of agnosticism (impartiality between actors engaged in controversy), generalised symmetry (the commitment to explain conflicting viewpoints in the same terms) and free association (the abandonment of all a priori distinctions between the natural and the social), the paper describes a scientific and economic controversy about the causes for the decline in the population of scallops in St. Brieuc Bay and the attempts by three marine biologists to develop a conservation strategy for that population. Four ‘moments’ of translation are discerned in the attempts by these researchers to impose themselves and their definition of the situation on others: (a) problematisation: the researchers sought to become indispensable to other actors in the drama by denning the nature and the problems of the latter and then suggesting that these would be resolved if the actors negotiated the ‘obligatory passage point’ of the researchers' programme of investigation; (b) interessement: a series of processes by which the researchers sought to lock the other actors into the roles that had been proposed for them in that programme; (c) enrolment: a set of strategies in which the researchers sought to define and interrelate the various roles they had allocated to others; (d) mobilisation: a set of methods used by the researchers to ensure that supposed spokesmen for various relevant collectivities were properly able to represent those collectivities and not betrayed by the latter. In conclusion it is noted that translation is a process, never a completed accomplishment, and it may (as in the empirical case considered) fail.
Case studies on transport infrastructure projects in Belt and Road Initiative: An actor network theory perspective
DOI:10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2018.01.007 URL [本文引用: 4]
Actor network theory and commodification in rural space: A case study of Mayufang Village in Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708006
[本文引用: 2]

Along with the development of facility agriculture, horticultural agriculture and leisure agriculture, nowadays, the functions of agricultural production in rural areas have been weakened but the functions of consumption have been increased in Beijing. This shows that the commodification of rural space in Beijing has been developed in recent years. Rural tourism, as one of the important forms of the commodification of rural space, has played an important role in increasing farmers' income, preventing rural decline and revitalizing rural economy. Therefore, this paper selects rural tourism as the representative of the commodification to examine the formation and evolution of spatial commodification of rural space in Mayufang village as well as to explore farmers' participation in this process based on the actor network theory. In the process of the transformation, the rural areas being the farmers' producing and living spaces have changed to the urban residents' leisure and consumption spaces in Mayufang village and formed a heterogeneous actor-network, in which Tourism Bureau of Changping District and Changling Travel Company and other human actors and non-human actors have played a focal role. Major actors used the policy and the financial support to enroll farmers and other actors by the top-down executive network. Along with development of promotion, training, supervision and infrastructure, some local farmers started to create the physical and non-physical environments for the urban residents' consumption activities. Thus more and more farmers have been engaged in rural tourism, and the commodification of rural spaces in Mayufang village has been developed. As Mayufang village became the consumption space to the urban residents, the commodification of rural space in Mayufang village started its transformation of actor network. However, with the quit of non-human actors, which is Duijiuyu Natural Beauty and reduction of incentives launched by the original major actors, the representative of market has become the focal actor in the new actor network. More and more farmers, who were against the common purpose of the actor network were excluded, quitted the former actor network, thus commodification in rural space in Mayufang village declined. In the process of the formation of commodification of rural space in Mayufang village, the farmers who had the advantages of location, age and profession have much stronger desire to be involved in rural tourism, unemployed farmers prefer to be involved in rural tourism than farmers who make a living on agriculture. The farmers who worked in township enterprises are more willing to participate in rural tourism than self-employed business persons; villagers employed in the government units have less possibility to take part in rural tourism. While commodification of rural space in Mayufang village has declined, farmers began to transfer the labor force to other professions from rural tourism. When interests of major actors are commonly and inextricably linked with actors in actor network in rural areas, its commodification in rural space is strengthened, and vice versa.
行动者网络理论与农村空间商品化: 以北京市麻峪房村乡村旅游为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708006
[本文引用: 2]

乡村旅游作为农村空间商品化的表现形式之一,在增加农民收入、阻止农村衰退、振兴农村经济方面发挥着重要作用。为此本文以北京市昌平区麻峪房村的乡村旅游为例,借助行动者网络理论分析农村空间商品化的形成与演变,并讨论农户在此过程中的参与。麻峪房村在从农民生活空间转变为城市居民消费空间的过程中,形成了以区旅游局、乡旅游公司为关键行动者,并吸纳了多个人类和非人类行动者所构成的行动者网络。在网络形成的过程中农户参与乡村旅游的程度逐渐提高,由此推动了麻峪房村农村空间商品化的发展。麻峪房村演变为城市居民消费空间后,由于行动者网络发生变化使农村空间商品化发生变化,导致麻峪房村农村空间商品化程度降低。同时新的行动者网络中的各行动者的不对等性明显,各行动者之间存在很多异议,使该网络趋于僵化、丧失活力,不足以支撑麻峪房村乡村旅游继续发展。在麻峪房村农村空间商品化的形成过程中,农户的院落区位、年龄与原有工作等对农户参与乡村旅游的意愿产生不同的影响。当农村地区行动者网络中的关键行动者与行动者利益共通且紧密联系时,其空间商品化就得到强化,反之亦然。
Evolution process and mechanism of rural gentrification based on actor-network theory: A case study of Panyang River Basin of Bama County, Guangxi
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204007
[本文引用: 1]

Rural gentrification is a new path for rural transformation and revitalization under the background of two-way flow of urban and rural elements. This paper analyzes the evolution process, type and mechanism of rural gentrification based on actor-network theory (ANT) based on a diachronic field survey of rural gentrification in the Panyang River Basin of Bama County, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. The following results were obtained. (1) The evolution of rural gentrification is a dynamic actor-network jointly established by human and non-human actors, "grass-roots" actors and institutional actors. The evolution of rural gentrification has experienced a transition from initial to development stage, which has brought a series of changes. The key actors are replaced from the "amenity immigrants" pioneer and local elites to local governments and investment developers, while the OPP (obligatory passage point) has changed from "developing 'migratory bird' tourism and building a longevity village" to "developing comprehensive health industry and building a global longevity town". The path succession of rural gentrification changes from "grass-roots" gentrification to institutional gentrification with the replacement of key actors from "amenity immigrants" pioneers, and the rural gentrified industry has changed from receiving amenity migrants and developing tourism to the integrated development of comprehensive health industry. The gentrification type has evolved from "amenity immigration oriented" to "tourism oriented" and "real estate oriented", and finally formed a mixed rural gentrification pattern of "multiple types in one place". (2) Factors such as the replacement of key actors along with their roles and functions, the path succession of rural gentrification, the replacement and integrated development of leading industry, China's macro rural development system, as well as the regional natural and cultural environment, which jointly affect the stage succession and type symbiosis of rural gentrification. The replacement of key actors along with their roles and functions transformation dominates the stage succession of rural gentrification, while the path succession of rural gentrification as well as the replacement and integrated development of leading industry, which jointly promotes the evolution type of rural gentrification, is the general mechanism of rural gentrification evolution. At present, China's rural macro development strategy (Beautiful Countryside Construction, Targeted Poverty Alleviation and Rural Revitalization) and basic institutional arrangements (rural land collective ownership, homestead system, and regional development dominated by the local government) as well as the regional natural and cultural environment (unique healthy geographical environment, and "migratory immigrants" healthy geographical dependence, combined with the actors' power balance under the comprehensive action comprised by "Bama complex", the Zhuang clan power and the rural nostalgia) shapes the symbiotic characteristics of evolution type, which is the regional mechanism of rural gentrification evolution. (3) Actor-network theory (ANT) is a conducive method to show the stage succession context and symbiotic characteristics of evolution type, and reveal the general mechanism and regional mechanism of rural gentrification evolution.
基于行动者网络理论的乡村绅士化演化过程与机制解析: 以广西巴马盘阳河流域为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204007
[本文引用: 1]

乡村绅士化是城乡要素双向流动背景下乡村转型与振兴的新型路径。基于对广西巴马盘阳河流域乡村绅士化现象的历时性田野调查,采用行动者网络理论解析乡村绅士化演化的过程、类型与机制。研究表明:在巴马盘阳河流域乡村人类行动者与非人类行动者、“草根”行动者与机构行动者共同缔结的行动者网络的转换过程中,伴随关键行动者从“候鸟人”先锋、屯社精英向地方政府、投资开发商的更替,乡村绅士化路径从“草根”绅士化向机构绅士化演替,乡村产业从接待“候鸟人”、发展旅游转向大健康产业融合发展,乡村绅士化类型从单一的舒适移民绅士化向舒适移民、旅游和地产共构的“一地多类”绅士化演化。关键行动者更替及其功能角色转换、绅士化路径变迁和主导产业更替与融合发展、宏观乡村发展制度与地域自然人文环境共同作用于乡村绅士化的阶段演替与类型共生。行动者网络理论与方法利于呈现乡村绅士化的阶段演替脉络与共生演化特征,并揭示乡村绅士演化的一般机制与地域机制。
Actor-network-theory (ANT) and paradigm innovation for tourism research
行动者网络理论(ANT)与旅游研究范式创新
The progress of more-than-human geographies in western geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910016
[本文引用: 2]

Along with the growing public awareness of the impossibility of separating nature from society and the difficulty of dividing the world neatly into spaces of 'human' and 'non-human', more-than-human geographies become increasingly popular in exploring the human-nonhuman assemblages in Western countries. However, existing literature demonstrates that the investigation of more-than-human geographies has received insufficient attention from non-Western countries, including China. Based on a systematic analysis of journal papers published in the Core Collection of Web of Science over the last 15 years, this article is dedicated to introduce the more-than-human geographical thoughts and approaches into China. The software Citespace has been used to analyze a total of 298 journal papers published from 2002 to 2017 in the Core Collection of Web of Science, among which the main themes can be generalized into five categories: new animal geographies and natural conservation, urban culture and political ecology, materiality and commodity economy, body and life health, climate change and environmental issues. New animal geographies have usually been understood as comprising the mainstream of more-than-human geographies, while the last two topics have been regarded as new fields. This article first investigates the core views of three philosophical and theoretical ideas which inspired the development of more-than-human geographies and explained how these insights influence the associated thoughts and approaches. Moreover, to show more details about what kinds of assemblages more-than-human geographies are interested in, this article introduces the content of each category with classical case studies. Finally, the primary contributions and critiques of more-than-human geographies are also presented. China's rich natural products and multiple social cultures, as well as the rapid development of science and technology mean that there is a potential for Chinese geographers to provide more interesting and vivid investigations for more-than-human geographies in the Chinese context.
西方超越人类的地理学研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910016
[本文引用: 2]

随着现代科技发展与社会环境变化,人类与非人类的边界日益模糊,这使得以往研究中未能引起足够重视的非人类生命与物质逐渐引起学者们的关注。21世纪以来,在西方地理学界兴起的“回归唯物主义”思潮中,超越人类的地理学(MTHG)应运而生,并成为探索人类与非人类共同构成的世界的重要途径之一。通过对298篇相关期刊论文及著作的分析发现,超越人类的地理学主张“关系本体论”,其产生受到行动者网络理论、生物哲学与非表征理论的深刻影响,现有研究议题聚焦于新动物地理学与自然保护、城市社会文化与生态政治、物质性与商品经济、身体与生命健康、气候变化与环境问题等方面。本文通过梳理超越人类的地理学的理论源起并剖析各议题的经典研究案例,以期为中国地理学研究提供新的视域。
An empirical study of rural tourism endogenous development based on actor-network theory: A case of Xianhuashan Village, Pujiang County, Zhejiang Province
基于行动者网络理论的乡村旅游内生式发展的实证研究: 以浙江浦江仙华山村为例
Rural transformation development mechanism and rural revitalization path from the perspective of actor-network: A case study of Dabian Village in the central mountainous area of Hainan Province
基于行动者网络视角的乡村转型发展机制与优化路径: 以海南中部山区大边村为例
Research on the interaction between actor-network theory and human geography: Reconstruction, debate and reflection
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200270
[本文引用: 5]

The actor-network theory (ANT), originated from the sociology of science, has been widely used in many disciplines. In the field of geography, this theory tends to break through the long-standing dualism between global and local, nature and society, etc. Much of the theoretical work has been done to understand the complex and obscure connotation of ANT. For instance, representative human geography scholars like Jonathan Murdoch and Sarah Whatmore proposed to cancel many dualistic presuppositions in geography, thus rethinking the nature of geographical knowledge through ANT. However, the current empirical studies in Chinese academic world show the trends of oversimplification and misuse of this concept by reason of lacking a sufficient understanding of the relationship between ANT and human geography. Therefore, the paper aims to investigate the interaction between the actor-network theory and human geography. Specifically, it is found that there are overlaps and similarities in the aspect of temporal-spatial view by summarizing and comparing ANT and the related theories of human geography. More importantly, the principle of general symmetry links ANT with human geography, which makes us re-recognize the description methodology, the significance of nature and materiality, and the network in human geography. Nevertheless, the understanding of ANT is still controversial and has been critically discussed, ranging from the aspects of social interpretation and network interpretation, the legitimacy of traditional criticism and the authenticity and validity of human-nonhuman symmetry. To accommodate the neglected and insufficient description of the real world, some geographers bring in assemblage thinking, including concepts like desire, virtual and flux. In addition, as the profound impact of the case study of the scallop experiment on the understanding and application of ANT by human geographers, the article analyzes the latent translation logic contained in this case. Finally, the study points out key issues that need to be reflected in the application of actor-network theory in empirical research, and indicates the possible directions for further research from the perspectives of human and nature, scientific knowledge production and dissemination. In summary, this paper discusses the enlightenment of ANT to human geography, which provides more possibilities of dialogues between different studies based on ANT, enhancing the innovation and geographical knowledge spillovers.
行动者网络理论与人文地理学的交互关系研究: 重构、争辩与反思
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200270
[本文引用: 5]

行动者网络理论(ANT)被用于诸多学科,对突破地理学中的二元思维具有重要意义。通过梳理和比较ANT与人文地理学的相关理论,发现其时空观具有相通之处。广义对称性原则将ANT与人文地理学链接,使得人文地理学中描述的方法论、自然和物质的重要性及网络被重新认识。地理学者对ANT的批判主要围绕社会解释与网络解释、传统批判的合法性、人与非人对称的真实性与有效性等方面展开。一些地理学者试图使用拼装(assemblage)思维来弥补ANT的不足,将欲望、虚拟、流等概念补充进来,使之更为贴近现实世界。由于扇贝实验的案例研究对人文地理学者理解与运用ANT影响较大,文章解析了该案例中蕴含的转译逻辑。最后,阐明ANT在经验研究中需要反思之处,并讨论了可进一步研究的方向及对人文地理学的启示。
The spaces of actor-network theory
DOI:10.1016/S0016-7185(98)00011-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
The where abouts of power: Politics, government and space
DOI:10.1111/j.0435-3684.2004.00151.x URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards a geography of heterogeneous associations
DOI:10.1191/030913297668007261
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Dualisms have been a recurring feature of sociospatial analysis. Micro/macro, local/global, subject/object, particular/universal – one or more of these dualistic frameworks can be discerned in many geographical texts. Dissolving the dualisms, somehow finding a way through the gaps which open up between them, requires the development of an approach which allows the various scales of social life to be treated symmetrically so that we never have to shift to a different register when studying large-scale or ‘big’ (usually termed structural) phenomena. It is proposed in this article that a geography of associations, which traces how actions are embedded in materials and then extended through time and space, provides one means of overcoming the dualisms. Drawing upon actor-network theory it is argued that interactions are both ‘localized’ and ‘globalized’ using nonhuman entities and these permit certain actor-networks to act at a distance on others. Patterns of centrality and marginality thus emerge as particular power geometries are drawn. Tracing these power geometries by following the associations can only be undertaken in a nondualistic fashion.
Urban wild things: A cosmopolitical experiment
DOI:10.1068/d351t
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Cities are inhabited by all manner of things and made up of all manner of practices, many of which are unnoticed by urban politics and disregarded by science. In this paper we do two things. First, we add to the sense that urban living spaces involve much more than human worlds and are often prime sites for human and nonhuman ecologies. Second, we experiment with what is involved in taking these nonhuman worlds and ecologies seriously and in producing a politics for urban wilds. In order to do this we learn how to sense urban wildlife. In learning new engagements we also learn new things and in particular come to see urban wilds as matters of controversy. For this reason we have borrowed and adapted Latour's language to talk of wild things. Wild things become more rather than less real as people learn to engage with them. At the same time, wild things are too disputed, sociable, and uncertain to become constant objects upon which a stable urban politics can be constructed. So a parliament of wild things might be rather different from the house of representatives that we commonly imagine. It may be closer to what Stengers (1997, Power and Invention University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN) has characterised as cosmopolitics, a politics that is worked out without recourse to old binaries of nature and society. Using empirical work with urban wildlife-trust members we muddy the clean lines of representational politics, and start to grapple with issues that a reconvened wild politics might involve.
Assemblage thinking and actor-network theory: Conjunctions, disjunctions, cross-fertilisations
DOI:10.1111/tran.2016.41.issue-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
The spatialization of politics: Local and national actor-spaces in environmental conflict
DOI:10.2307/622657 URL [本文引用: 1]
Researching rural conflicts: Hunting, local politics and actor-networks
DOI:10.1016/S0743-0167(97)00038-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
A review on the application of actor network theory to human geography
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.07.016
[本文引用: 1]

Recently, the actor-network theory (ANT) was widely applied to the field of human geography. ANT approach provides a new perspective by allowing researchers to take into consideration the flow of factors and network interaction. After a brief introduction of ANT, this paper summarizes the progress of ANT applications to human geography by summing up the application topics and methods in different branches, and compares the gap between international and domestic researches. This paper reveals that ANT promotes the progress of human geography in both theory and application. Most theoretic explorations happened in the field of economic geography: the relational economic geography based on ANT provides new angle for the reconstruction of "postmodernism" economic geography theory system. In application, analytical framework of ANT applied to the field of human geography emphasizes actors, translation process, and the result, with special attention to the spatial changes as verification of the effect of actor network. ANT uses a structural way to construct the main actor behaviors, resulting in an effective analysis framework for local development and policy implementation research in every branch of human geography. High citation rates of ANT applied research papers indicate ANT approach is now attracting more and more attention in the field of human geography. However, compared to international researches, domestic researches are relatively lagged and limited. Currently, domestic researches still remain in the stage of applying ANT analysis framework directly with little thinking about theory improvement, while international research is starting to rethink the limitations of ANT approach. Based on recent rethinking of ANT use, this study emphasizes that analytical framework of ANT should be highlighted and the use of ANT should carefully control the size of the network and the list of actors, due to the uncertain research paradigm.
行动者网络理论在人文地理领域应用研究述评
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.07.016
[本文引用: 1]

行动者网络理论以一种结构化的方式来构建行为主体之间的关系, 并将要素流动和网络化互动形态纳入分析范畴, 为各学科研究提供了全新的视角, 在人文地理领域的应用也日渐增多。本文在总结行动者网络理论主要内容的基础上, 分类归纳评述了行动者网络理论在不同分支研究领域的应用主题和方式, 并就研究的深度、广度、影响力进行国内外对比。研究表明, 行动者网络理论对人与非人行动者的一致看待及其通过转译过程解析网络关系的研究模式, 除强化了经济地理等领域的理论建构之外, 也为乡村地理、城市地理、经济地理、旅游地理等领域的地方发展、政策实践研究提供了一种有效的分析方法。引入该理论的人文地理研究引用频次高, 有较大的学术影响。目前国内研究多停留在行动者网络理论分析框架的直接套用, 极少涉及分析框架改进和理论思考, 在广度和深度上与国际研究仍有差距。
Specification of the world city network
DOI:10.1111/gean.2001.33.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Global production networks and the analysis of economic development
DOI:10.1080/09692290210150842 URL [本文引用: 1]
Building trust in economic space
DOI:10.1191/0309132506ph617oa
URL
[本文引用: 1]

While there is widespread recognition of the importance and role of trust in facilitating regional development, technology transfer, and agglomeration economies, the concept remains rather undertheorized within economic geography and regional science. This paper reviews and assesses the literature on the role and constitution of trust for economic and industrial development and presents a conceptualization of the trust building process that accounts for the influences of agency, institutions, materials, and interpersonal expression. In doing so, geographic concerns about the role of space and context are linked to economic and sociological conceptualizations of trust and to scholarship from actor-network theory (ANT) and social psychology regarding the influence of power, non-human intermediaries, and performance on social outcomes and network configurations. The result is a heuristic framework for analyzing trust-building processes as temporally and spatially situated social phenomena shaped by context-specific subjective, intersubjective, and structural factors. The conceptualization’s broader significance lies not in detailing the many factors that influence trust but in its contextualization of the micro-social processes that can strengthen business relationships. In doing so, the framework can facilitate a move beyond solely instrumental conceptualizations of trust and toward a relational understanding of how the means for establishing and sustaining trust influence the development and potential of such ‘ends’ as clusters and production networks.
Actor-network theory and stakeholder collaboration: The case of Cultural Districts
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2010.05.016 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tourismscapes: An actor-network perspective
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2007.05.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
The actor-network perspective on the reconstruction process and internal mechanism of typical Taobao villages in the Pearl River Delta region
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112014
[本文引用: 2]

Owing to the multiple influences of globalization, urbanization, industrialization, and informatization, rural regional space has experienced the process of reconstruction. Focusing on the analysis of the internal mechanism of rural reconstruction driven by the internet economy, this study selected Lirendong Village in Panyu District of Guangzhou, the most active Taobao trading village in the Pearl River Delta, as a typical case. We had an in-depth analysis of the process and internal mechanism of the reconstruction of typical Taobao villages in the Pearl River Delta metropolitan area through semi-structured interviews and the actor-network theory analysis framework. The study demonstrated that the key actors, such as local government, clothing workshop, village committee, e-commerce entrepreneurs, and social networks of fellow villagers, participate in the pursuit and realization of land value in the village according to their goal vision and action logic. Furthermore, these actors jointly evolve and construct the actor-network process of periodic industrial succession and spatial value accumulation in Taobao villages. The process has gone through the stage of agricultural decentralization led by the government, the industrialization stage dominated by the market, and the stage of e-commerce dominated by the social network of fellow towns people. Government subject, market subject, and social subject constitute the core driving force. They are linked together by providing benefits, and rural reconstruction practice is carried out according to the political, market, and elite logic. The reconstruction results in the change in spatial-social relations related to the changes in the dynamic mechanism. The reconstruction is realized through the reshaping of space and the change of value, from exogenous driving force leading to endogenous driving force exhibition, thus initiating a new cycle of the space reconstruction process.
珠三角地区典型淘宝村重构过程及其内在逻辑机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112014
[本文引用: 2]

在全球化、城市化、工业化和信息化的多重影响下,乡村地域空间普遍经历空间重构过程。着眼于互联网经济驱动下的乡村重构内在机制剖析,本文选择珠三角地区淘宝交易活跃度居全国之首的淘宝村——广州市番禺区里仁洞村为典型案例,通过半结构式访谈,以行动者网络理论为分析框架,剖析珠三角大都市地区典型淘宝村重构过程及其内在逻辑机制。研究表明:地方政府、制衣作坊、村委会、电商创业能人、同乡社会网络等关键行动者依其目标愿景和行动逻辑参与村里土地价值的追逐和获取实现,共同演进和建构起淘宝村产业阶段性演替和空间价值积累的行动者网络过程,其历经政府主导的农业去中心化阶段、市场主导的工业化阶段,以及同乡社会网络主导的电子商务化阶段。政府主体、市场主体和社会主体构成核心驱动力,通过利益赋予联结到一起,依据政治逻辑、市场逻辑和精英逻辑推动乡村空间重构实践,重构结果引发空间社会关系的变化,触动动力机制的转变,并通过空间的重新塑造和价值改变来实现,从外源动力主导向内生发展动力转变,带来新一轮空间重构过程。
A study on the application of actor network theory to rural development: A case study on the development of Chiu-Fen settlement from 1895 to 1945
行动者网络理论应用于乡村发展之研究: 以九份聚落1895—1945年发展为例
Land use conflicts and their governance mechanics on actors network theory: A case of fruit tree protection zone of Haizhu District, Guangzhou City
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2010.01.80
[本文引用: 1]

Rapid industrialization and urbanization process makes the functional value of urban ecology space even more remarkable. The green land protection policy on public interest results in barriers to develop rural community economy and promote residents’ income, which lead to more and more social conflicts originated from urban and rural land use. On the basis of urban spatial political-economy theory, and actors network theory, in a case of Fruit Tree Protection Zone of Haizhu District in Guangzhou City(HZFTPZ) the article investigated the evolution process, origins, types and governance mechanics of land use conflicts. The article found that, the evolution process of land use conflicts could be divided into 4 stages according to the intensity and levels of significance, i.e., latent period, obvious period, transformation period and conglutination period. But Nondeterminacy still exists in the further evolution of land use conflicts because of the role of conflict circle. During the evolution of land use conflicts, land use conflicts subjects spread from the core of land use conflicts to the periphery, social actors involved emerged ceaselessly, and conflict issues, standpoints and attitudes of conflict subjects and approaches to resolve conflicts were sequentially changed. In addition, land use conflicts were divided into procedure conflicts, value conflicts, interest conflicts and structure conflicts from appearance to nature, based on their origins and differentiation display. And all types of land use conflicts were logically related, because of the organically interaction and integration of social actors’ factors and social and economic regimes structure factors. Many land use conflicts registered as procedure destination differences among social actors, and the even deeper reasons displayed as the value judgment differences on the priority of protection-development and public interest-individual-interest among parties to a conflict, and the subjective understanding differences on land use interest distribution and risk exposure among parties to a conflict, but the final origins of conflict expansion or continuous agglutination existed in policy defects and regime cruxes in procedure design standard, values guidelines and interest distribution balance. During the governance process of land use conflicts, various sorts and varieties of social actors centered on some issues, established interlaced networks by consultation and negotiation and made up mechanics of recourse sharing and mutual benefit and collaboration, thus gained the ends of collaborative governance. The concrete measures including to establish the participation and communication networks based on communicating and participating of stakeholders, the collaborative governance network based on the networking cooperation of social actors, the community co-management network based on the appeal of community participation, the interest coordination network based on interest balance and coordination of stakeholders, and the land use conflict prevention and mediation network based on the prevention and mediation of land use conflicts.
基于行动者网络的土地利用冲突及其治理机制研究: 以广州市海珠区果林保护区为例
Research progress of relational geography under the background of post-structuralism
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908014
[本文引用: 1]

The relational geography is conceived with the development of post-structuralism and "relational turn". From the perspective of relational geography, the world is understood as a topological structure of flowing while things are not considered as products of eidos ego but products of the relations. Relational thinking is counter-essentialized, it stresses on the dynamic, inter-dependent interactions between things. Through literature review, we find out the development relational geography is strong influenced by the social network and non-representational theory. The appearance of relational geography reconstructs the connotations of space, place, scale and subjectivity. We put forward the concept of relational space, place relations, multi-scale or the end of scale and the geographical inter-subjectivity. We construct the networking, relational and the flow of topological geography. The current empirical studies of the relational geography focus on the spatial diffusion and expansion, subject development, socio-cultural, bodily, tourist, health issues. Besides, we hope to offer new perspectives for Chinese human geographers based on the concepts of "human", "more-than-human", "things" and "re-materialization".
后结构主义背景下关系地理学的研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908014
[本文引用: 1]

随着后结构主义思潮和“关系转向”的兴起,关系地理学(relational geography)应运而生。关系地理学把世界理解为流动的拓扑结构以及相互关联的产物,主张关系思维,强调事物在发展过程中相互影响与依存的动态关系。通过对关系地理学相关著作和期刊论文的分析发现,关系地理学的产生受到社会网络分析理论与非表征理论的深刻影响,其重构了空间、地方、尺度与主体性的内涵,提出关系空间、地方关系、多尺度或尺度终结,以及主体间性的地理学概念,建构了新的关于网络、关系和流的拓扑地理。关系地理学现有的实证研究主要聚焦于空间扩散与空间发展、主体发展与社会文化问题、身体与健康旅游/地理等内容。此外,基于“人”与“超越人类”,“物”与“重返物质”4个方面的内容提出关系地理学可能的研究展望,并对“关系”的内涵与外延进行了延伸讨论,以期为中国人文地理学研究提供新的学术视角。
"Non-representational", "re-materializing" and the research methods of new cultural geography
新文化地理学中的非表征与再物质化研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.02.001
[本文引用: 1]

文化地理学以往对表征和话语的过度重视,引起了部分学者对“非表征”和“再物质化”的思考,呼吁关注日常生活中即时的、动态和无法被表征捕捉的实践和情绪,并重视物质实体的展演性、流动性、情绪塑造和符号交换的意义,引发和促进了新文化地理学对于情感、身体、实践、展演和日常生活等议题的关注。论文对“非表征”和“再物质化”的概念和核心理论进行了梳理,并对“身份、认同及空间的构建”“情感与空间氛围”“身体与展演及意义”以及“权力与网络”4个相关议题进行了讨论,以期促进国内文化地理学对感知的、即时的和物质性的空间要素进行关注,并对新文化地理研究方法进行创新。
Afterwords
DOI:10.1068/d214t
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Gradually, then, it has become clear to me what I am trying to do. I want to provide a body of work which values creative praxis. This will not be easy as—with a few exceptions—most academics nowadays still tend towards impoverished views of praxis which leave remarkably little room for creative exorbitance. Thus, for example, many modern social and cultural theorists would find it difficult to understand the import of Wittgenstein's famous question, “what remains over from the fact that I raise my arm when I subtract the fact that my arm goes up?” In effect, what I attempt to provide is the beginnings of an answer to this question. In the first part of the paper I am therefore concerned with an account of a style of thinking which I call nonrepresentationalist. In the second part of the paper I then broaden the discourse by considering the ways in which this style of work might be linked to other developments in the social sciences and humanities grouped around the notion and the motion of performance. In the third part I consider one particular mode of performance—dance—as illustration of some of the steps I have traced out. Some tentative conclusions follow.
International rivers as border infrastructures: En/forcing borders in South Asia
The multiscalar production of borders
DOI:10.1080/14650045.2016.1195132 URL [本文引用: 1]
Locating the territoriality of territory in border studies
Research on the changes of border port in Shigatse, Tibet from the perspective of the Belt and Road Initiative
基于“一带一路”视角下的西藏日喀则边境口岸变迁研究
The trade relation between Yadong in Tibet and India in modern history
近代西藏亚东与印度的贸易往来
Yadong corridor and "the Belt and Road Initiative"
西藏参与“一带一路”建设不应轻视亚东通道
Study on the selection of cross-border routes of China-Nepal railway
中尼铁路跨境通道线路方案选择研究
Trans-Himalayan power corridors: Infrastructural politics and China's Belt and Road Initiative in Nepal
Historical tracing of border trade in Tibet
关于西藏边境贸易情况的历史追朔
On the development of contemporary Sino-Nepal trade
当代中尼贸易发展述论
On the commodity structure and trade potential of Tibet's border trade in the context of "the Belt One Road" Initiative
“一带一路”背景下西藏边境贸易商品结构与贸易潜力分析