1 引言
自20世纪80年代以来,经济全球化是经济地理学理论创新的“孵化器”。北美、欧洲新产业区的发展,拉美地区的发展停滞,以及东亚和东南亚地区的经济腾飞,极大地激发了经济地理学者研究“全球经济景观”的兴趣。经济地理研究从“地方空间”迈向“流空间”,关注跨国公司等主体之间的关系如何引导资本、商品、技术、劳动力在全球范围内的流动,推动全球经济布局的演变,促成了经济地理学的“关系”与“演化”转向,形成了全球生产网络、战略耦合、全球—地方互动等理论创新,发展出了创新地理、金融地理、消费地理、环境经济地理等新兴领域[1]。
2008年世界经济遭遇冲击以来,经济全球化转型初见端倪。由于世界经济复苏乏力,国际关系与地区形势的变数持续增加,英国脱离欧盟、中美关系恶化、俄乌冲突升级等一系列事件深刻地改变经济全球化进程,经济全球化逐渐从原有的“一体化”方向掉头,朝着区域“割据”的方向发展[2-3]。经济全球化叙事开始偏离“国际化”与“自由化”的传统语境:一方面,发达国家和新兴国家之间矛盾加剧,国际合作的制度基础面临挑战[4],各国为规避日益扩大的国际关系风险,寻求不同程度的经济脱钩以维护本国发展安全[5],经济全球化背离“国际化”内涵;另一方面,为应对日益增强的不确定性,各国针对投资和贸易的限制措施在增加,发达国家对国内产业的保护力度在增加,对技术的出口限制在增加[6],“自由化”内涵显著削弱。据此,本文所关注的经济全球化新叙事包括3个方面:变化的经济治理逻辑、变化的经济地理内涵、变化的中国与世界联系。
经济全球化转型改变了全球经济治理的逻辑,表现为全球产业链的重组、价值链的重构、供应链的重塑[7]。经济活动的空间布局特征、空间组织逻辑,以及不同地区的经济发展模式相应发生变化。对此,如何理解经济全球化转型背后的地理内涵变化?经济全球化转型打破了经济地理学自1980年以来形成的惯性思维,即交通通讯技术发展提升了空间相互依存水平,使得全球经济地理具有整体性。自1980年以来经济地理学以此为基础,发展出多主体、多层级、多尺度的立体关系网络刻画全球经济地理的整体性[8]。随着经济全球化的复杂性与不确定性持续提升,全球经济地理的整体性遭受冲击。对此,经济地理学如何适应经济全球化转型的地理内涵变化,形成分析全球经济地理的新理论与新方法?经济全球化转型影响了中国与世界的经济联系。2008年以来,中国转变了作为参与者被动融入经济全球化的角色,开始发挥“变革者”的作用为深化经济全球化贡献中国方案[9]。中国角色的转变影响着世界和中国的经济地理格局,与加快构建以国内大循环为主体、国内国际双循环相互促进的新发展格局密切相关。对此,中国经济地理学研究如何积极响应经济全球化转型和中国角色的变化,为构建新发展格局、推动高质量发展的一系列战略任务实施提供科技支撑?
本文围绕上述3个问题展开讨论,首先分析经济全球化转型的地理内涵变化;其次梳理经济地理学不同“转向”在适应经济全球化转型过程中表现出的融合趋势;最后讨论中国经济地理学在响应经济全球化转型过程中的已有实践基础与理论创新方向。
2 经济全球化转型特征及其地理内涵
2.1 经济全球化从一体化转向区域化
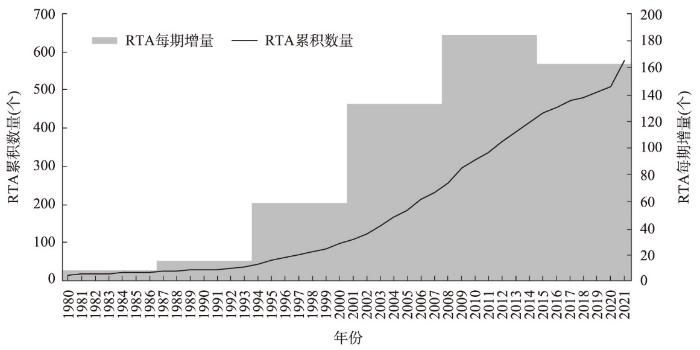
对照经济全球化的时空特征,可以发现当前经济全球化转型正转向区域化,而非朝着具有整体性的方向迈进。根据世界贸易组织(World Trade Organization, WTO)披露数据(图1),区域贸易协定(Regional Trade Agreement, RTA)数量长期维持个位数增量,呈缓慢增长态势。自2000年起,RTA数量开始以两位数的增量上扬,2008年以后增量达到新高峰。截至2021年,全球范围内已正式通告的RTA达578个。其中,由东盟十国与中国、日本、韩国、澳大利亚、新西兰签署的《区域全面经济伙伴关系协定》(RECP)是当前人口最多、经贸规模最大的区域集团;全球第一个自由贸易协定——《北美自由贸易协定》(NAFTA)被新签订的《美墨加三国协议》(USMCA)取代,强化了战略同盟属性;欧盟(EU)则在英国脱离后面临着离心力加剧和内部集团化的新风险[13]。加上南方共同市场(MERCOSUR)、欧亚经济联盟(EAEU)、海湾阿拉伯国家合作委员会(GCC)、南亚区域合作联盟(SAARC)、非洲大陆自由贸易区(AFCFTA),形成了全球最大的8个区域集团,基本覆盖了世界经济的主要经济体。区域贸易协定的签订和区域集团的形成产生了显著的贸易转移效应和贸易创造效应,在强化区域内部经济联系的同时,提升了区域之间经济联系的不确定性[14]。
图1
图1
1980—2021年全球范围内区域贸易协定累积数量
注:数据来源世界贸易组织区域贸易协定数据集(
Fig. 1
Numbers of Regional Trade Agreements, 1980-2021
经济全球化朝着区域化的方向发展,带来了新的地理内涵,表现在两方面:一方面,经济全球化转型迫使各国希望缩短对外经济联系的地理距离,抵御日益增加的外部风险[15]。在全球经济面临冲击的情况下RTA数量显著增加,2008—2009年增量达到39个,2012—2013年增量达到26个,2020—2021年增量高达67个(图1),反映出各国更倾向于将经济联系局限于有限的地理范围之内,以减少局部风险发生和波及所造成的损失。另一方面,经济全球化转型使得各国(特别是发达国家)希望保护本土市场,改善本土利益严重失衡带来的困境[16]。区域化使得各国能够通过政府间合作引导涉外经济的发展方向,选择合作伙伴国组成区域集团,在促进经济发展的同时,还带有平衡政治、社会等不同方面的发展目标[17-18]。根据裕利安怡集团(Euler Hermes)2019年全球贸易报告显示,全球主要贸易经济体自2008年以来为保护本土市场而设置的贸易限制数量并不少。即便是号称贸易自由化拥趸的美、德、英、法等国家,贸易限制数量同样居于全球前列。2017年中美贸易发生争端以来,美国进口平均关税水平从原有的3.5%增长至8%。2020年正式签署的《美加墨三国协定》为了促进制造业回流美国,限制跨国公司将墨西哥作为生产基地,甚至增加了孤立中国的“毒丸条款”。
整体而言,经济全球化朝向区域化方向发展,既是对地缘关系风险的响应,同时在区域集团竞争的过程中产生新的风险。在此过程中,地理距离对经济全球化进程的制约重新提高,而国家力量对经济全球化的干预能力重新增强。
2.2 经济全球化从成本驱动转向创新驱动
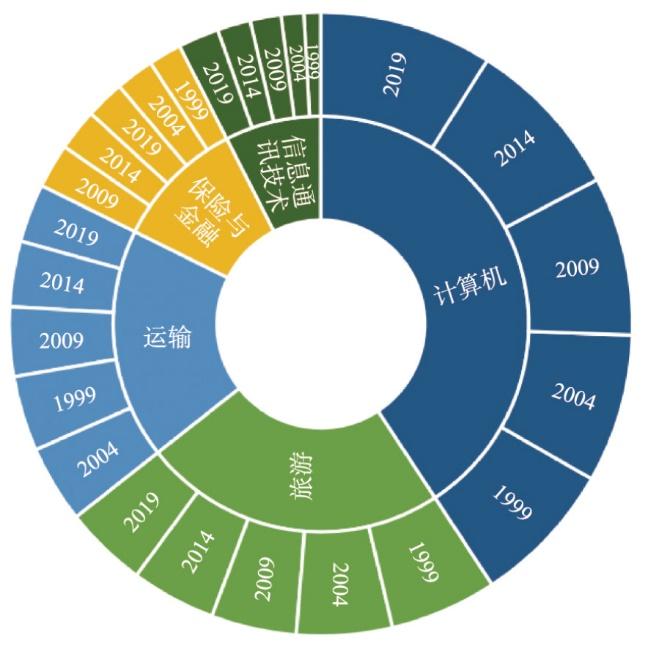
一方面,资源要素更多地流向知识和信息密集型行业、流向价值链中的研发环节,从支持低成本重复生产转向支持产品改进、新产品研发与创新体系建设[25]。与此同时,专业服务企业成为经济全球化的主导者之一,在专业领域具有支配地位,在全球生产网络中占据重要地位[26]。另一方面,服务贸易发展快速,对全球经济生产总值(GDP)的贡献稳步提升,而商品贸易对全球GDP的贡献则有所下降。分类结果表明(图2),服务贸易以计算机、信息通讯技术服务为主且稳步提升;保险与金融服务在上一轮全球化增长迅猛,2008年之后有所回落;传统的运输与旅游服务则持续下降且降幅明显。服务贸易的结构变动反映出数字信息在经济全球化进程中日益重要的作用。
图2
图2
1999—2019年全球各类服务贸易出口占服务贸易出口额的比例
注:数据来源世界银行公开数据库(
Fig. 2
The ratio of global service exports by sectors, 1999-2019
综上,经济全球化正逐步转变通过优化空间布局实现降本增效的传统逻辑,信息、技术、服务等与研发创新密切相关的内容正成为经济全球化寻求地理整合的目标,反映出经济全球化向创新驱动转型的趋势。
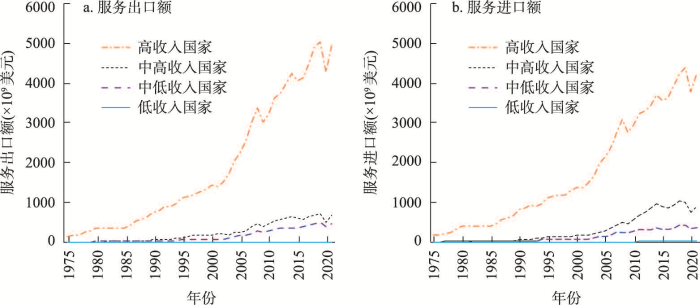
经济全球化从成本驱动朝着创新驱动的方向发展,带来了新的地理内涵,表现在以下两方面:一方面,参与经济全球化的基础优势将从要素禀赋供给与成本节约的挖潜,转向创新资源组织与创新效益的竞争。发达国家在创新资源、创新效益等方面都具有明显优势。当经济全球化转向创新驱动,发达国家的基础优势使其在全球价值链和全球生产网络中占据支配地位。已有实证研究发现,发达国家更有能力通过参与全球价值链实现技术升级并达到行业顶尖水平,发展中国家却大多只能依靠后向联系获得一定收益[27]。另一方面,尽管服务贸易对GDP的贡献不断提升,并为发展中国家获取先进技术提供重要渠道,但是服务贸易同样受制于各国的创新基础而呈现出显著的地理不均衡性。根据世界银行披露数据(图3),全球服务贸易的进口与出口高度集中于高收入国家,高收入国家的服务贸易出口额和进口额甚至大于其他国家之和。服务贸易整体上集中于高收入国家之间,对于发展中国家的拉动作用相对有限。
图3
图3
1975—2021年不同收入水平国家服务出口额与进口额
注:数据来源世界银行公开数据库(
Fig. 3
The service exports (a) and imports (b) of countries by income groups, 1975-2021
整体上,经济全球化朝着创新驱动的方向发展,可能导致经济全球化的红利在发达国家与发展中国家之间重新分配,导致发达国家和发展中国家之间陷入新的争论,给经济全球化的前景带来更多的不确定性。在此过程中,经济全球化转型可能加剧经济发展的地理不均衡性,强化已有的核心—边缘结构。
2.3 经济全球化陷入提升效率与抵御风险的权衡
全球价值链分工延展了经济活动的地理边界,改变了本地化生产所面临的基础约束,强化了各经济体的相互依存,是驱动经济全球化朝向一体化发展的前提[28]。不过,全球价值链分工的趋势自2008年起有所放缓。尤其自2011年以来,跨国固定资产投资停止增长,中间产品贸易对产出的贡献在下降[29],全球价值链的长度有所缩短[30]。跨国公司在东道国面临的“外来者劣势”增强,削弱了跨国公司远距离组织供应链的能力[31]。全球价值链分工在地理空间上呈现出从离岸外包向在岸外包、近岸外包等方式转变[32]。在岸外包促使制造业回流至本土,使得经济全球化转向本地化,而近岸外包和友岸外包则将价值链分工限制在符合地缘战略目标的地区,使得经济全球化转向区域化。尽管各行各业的全球价值链调整难度不同,但地理延展性整体表现出收缩倾向[33]。
导致全球价值链在地理上收缩的原因是多方面的,涉及经济治理、技术革新、企业责任、外部风险等[34]。其中,技术革新、企业责任等内生因素的作用大体上遵循全球价值链降本、增效、提质的组织逻辑。但是经济治理、外部风险等外生因素则反映出全球价值链面临的冲击、限制与干预[33]。当前经济治理从原有全球范围内的多边关系朝着区域关系和双边关系的方向退缩,保护主义抬头,区域集团之间的竞争加剧,全球价值链分工的收益下降而成本上升[35],既造成经济效率损失,又增加了地缘风险。与此同时,地缘关系、环境变化、公共健康、金融危机等一系列风险将从根本上改变经济主体的风险偏好,导致产业链供应链管理从原有的即时响应变成有备无患,产业链空间配置中再次表现出地理边界(本地化)和缓冲区(区域化)[36]。
综上,经济全球化转型迫使经济活动空间布局面临提升效率与抵御风险之间的权衡,隐含的地理问题是:应对经济全球化转型,经济活动是否应当回归本地化?对此,现有研究整体持负面观点,即回归本地化可能得不偿失。关键点在于如何评估并比较本地化生产的收益与损失。现有观点大体从4个方面出发:① 经济全球化转型是短期波动,但长期趋势并不会变,各国在现有基础上寻求经济脱钩要付出极大的代价[37];② 不同全球供应链的调整难度存在明显差异。不考虑本地化程度在经济全球化进程中已经较高的供应链,单就原有空间配置范围较广的全球价值链而言,回归本地化可能面临比较严峻的生产能力限制[33];③ 本地化生产不一定是应对不确定性的有效手段。发展中国家的本地化生产可能导致经济波动水平增加,而发达国家的本地化生产则导致成本大幅提升[38];④ 本地化生产本身也是经济全球化诸多过程的一部分,能够提升经济韧性的不是本地化生产,而是向着高技术、高附加值环节的本地化转型。这一过程仍然需要推进全球价值链分工的深化与多元化[39]。
整体而言,经济全球化不确定性的提升迫使经济活动空间布局面临着提升效率与抵御风险的权衡,国际劳动分工的格局发生转变,全球价值链的长度缩短、空间配置范围缩小,由此引发了回归本地化生产的争论。
3 应对经济全球化转型的经济地理学
自1980年以来经济全球化改变了劳动空间分工,重塑了世界经济地理格局,强化了国家和地区之间的经济联系,丰富了区域与城市的发展模式,推动经济地理学先后出现了制度、文化、关系、演化等转向,取得了理论创新[40]:① 在经济全球化削弱距离摩擦的背景下,经济地理学通过制度与文化转向,凸显了地方的重要性,论证了地方制度环境、文化基础塑造独特的经济社会关系,在降低交易成本、提升经济效率、鼓励研发创新等方面具有不可替代的作用[41];② 在经济全球化朝着自由化、一体化方向发展时,经济地理学通过关系转向,有意识地突破了传统社会科学以国家为中心的全球化分析方法,提出了从企业跨国经济活动的特征着手,通过关系网络考察经济活动的空间配置及其对涉及地区发展的影响,发展出了全球生产网络、战略耦合、全球—地方互动等一系列理论[21,42];③ 在经济全球化带来的外部冲击逐渐增多的背景下,经济地理学通过演化转向,强调了区域的经济社会结构不是一种均衡状态,而是处于持续变化的过程中,论证了区域经济结构变化既是对外部冲击的响应,也是历史累积的结果,形成了区域产业分化、路径创造、区域韧性等理论[43⇓-45]。自2008年起,经济全球化的转型趋势愈发明显,经济地理学发展的现实基础相应发生变化。适应经济全球化转型的新特征,经济地理学理论与实践表现出新的趋势。
3.1 国家力量兴起与再认识
当经济全球化更多表现出国际化、自由化、一体化的内涵时,经济地理学的全球化研究更关注的经济主体是跨国公司,考察企业之间的关系;更关注的地理尺度是全球和地方,考察全球与地方之间的关联。国家作为一个经济主体、作为一类地理尺度的作用在一定程度上被弱化。
随着经济全球化转型,地缘关系、国家治理对经济发展及其布局的影响变大,经济地理学近年来的研究逐渐从“全球—地方”转向“全球—国家—地方”的关系尺度。在关系经济地理研究中,研究强调了国家是企业参与全球生产网络的促进者,同时也是调节者、生产者(国有企业)、消费者(政府采购)[46]。资源要素在全球生产网络中的稀缺性和流动性同样受制于其领土性[47]。在演化经济地理研究中,研究开始强调国家是驱动路径突破的关键力量。例如,随着生命科学技术越来越多地被生物科技和制药公司垄断,发展中国家在生物医药行业的生产和消费均处于被动地位。Zhou等的研究[48]揭示了在国家力量资助下,国内公共研究机构是生物医药产业核心技术供给者,减少了产业发展对跨国公司的依赖;同时积极参与到全球生物医药监管体系当中,为产业发展突破全球生物资本主义起到关键作用。
3.2 关系网络从扁平化到立体化
当经济全球化极大强化不同个体、不同地区之间的相互依存程度时,经济地理学研究大量地应用网络方法开展研究,以适应解析“流空间”的研究需求。其中包含了两类截然不同的网络:一类是作为隐喻存在的,以行动者网络理论为基础的社会分析方法;另一类是以拓扑关系为基础的,针对社会关系网络开展的结构分析[8]。但无论是哪一类网络,都面临着空间性与尺度关系不明确的问题。
随着经济全球化转型,多类型的经济主体、多层级的制度联系、多尺度的地理现象相互纠缠。原有空间性、尺度特征不明确的扁平化网络难以充分展示新现象与新矛盾。为此,经济地理学近年来的研究普遍趋向于“多主体、多层级、多尺度”的理论框架建构。例如,在关系经济地理研究中,Verbeek等[49]通过多尺度的公司网络分析,发现石化行业存在西方主导企业的一体化网络、亚洲和其他新兴市场企业的孤立网络。尽管二者在宏观层面上表现为高度分隔,但在微观层面上仍通过不同组织渠道存在联系。因此,全球石化行业格局仍朝着多极化但一体化的方向发展。在演化经济地理研究中,不同层级制度、不同层次知识在本地经济布局与发展过程中被证实存在复杂的关联关系[50]。例如,跨国公司推动本地集群创新存在两类作用机制:吸引新外国企业进入、对本土企业知识溢出。但Crescenzi等[51]研究发现并非水平越高的企业越能产生知识溢出,恰恰相反,技术水平越高的外国企业越少参与本地技术协作,对本地企业的知识溢出也比较弱。
3.3 解析经济地理与经济全球化转型的互反馈关系
经济全球化转型过程中产生了大量的“变数”有待经济地理学研究。经济地理学近来重视以反映地缘关系的重大事件、重点地区为切入点,解析经济地理与经济全球化转型的互反馈关系,判断世界经济格局的未来走向。
3.4 多元“转向”的交叉融合
经济全球化转型进程中,制度对经济布局与经济联系的影响不断增强,为经济地理学制度、文化、关系、演化转向的交叉融合提供了“接口”。传统的制度转向、文化转向专注于本地,忽视了其他尺度和层级的制度与文化影响;关系转向强调了企业和政府主体在多尺度制度环境中的关系[63],但是空间性不够明确;演化转向以企业为主体,对其他主体的作用考虑不足,对制度的认识过于简化[64]。近年来,以全球生产网络为代表的关系经济地理研究、以路径创造为代表演化经济地理研究,逐步呈现出交叉融合的倾向。其中,关系经济地理通过拓展全球生产网络理论,力求解释经济组织结构与区域不均衡发展之间的因果关系,朝着与经济全球化转型密切相关的国家、金融、劳动力、环境、发展等议题延展[65]。演化经济地理以区域多样化、技术关联、路径创造理论为基础,与经济转型、可持续发展、发展韧性等议题深度融合,为经济全球化新叙事下的区域发展路径提供分类依据、过程机制、施策基础[66-67]。
在此基础上,经济地理学面向经济全球化转型的经济布局、结构转型与区域发展研究,逐步融合地理政治经济方法、战略耦合理论、路径创造理论,形成一个综合的理论分析框架,用于解析有能力的行动者如何在不同层级的制度环境中行动,通过本地和非本地资产之间的战略耦合,实现区域发展的路径创造[68-69]。在此基础上,研究得以考察地方差异所隐含的制度环境差异性,不同层级制度的一致性与互补性,地方制度演化与企业、产业组织演化的关联,以及经济与非经济主体互动过程对制度与政策的相应[70]。以此为基础,经济地理研究能够更好地适应当前对全球治理的研究需求,围绕全球价值链、创新、环境、转型等关键议题,系统地建立经济地理与经济全球化转型的复杂关系[71]。
3.5 发展趋势
经济全球化转型反映出阶段性的外部条件变化,对经济地理学理论建设的守正创新提出新的要求。基于上述分析,本文试归纳为3点:① 提升理论解析复杂系统的能力。以上一阶段全球化条件下兴起的局部模式归纳为基础,探索“多元”转向融合的操作化路径,实现全局与局部之间互反馈关系的有效推断,以适应经济全球化转型条件下不确定性快速提升的挑战。② 加强非经济因素的有机引入与有效表达。经济全球化转型条件下,非经济因素对于经济活动的扰动显著增强,原有理论中视为外生条件的因素具备越来越强的内生性。当前经济地理学理论愈发重视制度、金融、资源环境等要素的内生化,更广义的社会、文化因素也开始以不同的形式纳入经济地理的理论视野[65,68 -69]。③ 重视人地关系在全球尺度的新变化,及其跨区域、跨尺度关联的新路径。全球变化和全球化是人地关系在全球层面交互的两大关键背景。但在上一阶段全球化条件下,“经济—环境”关系在国际经济地理学理论发展过程中日益边缘化。伴随着全球化转型,经济治理与环境治理的逻辑势必协同变化,经济发展与资源环境的耦合机理(特别是在局地与全局之间的相互作用)势必发生改变。经济地理学理论需要借此契机,提升人地关系在学科理论建设中(特别是国际语境下)的解释力与影响力。
4 探索支撑新发展格局的中国经济地理学
中国对经济全球化转型的基本判断是“百年未有之大变局”,包含来自经济复苏乏力、国际局势动荡、治理体系缺位、大国博弈加剧、人口结构失衡、科技范式变革等方面的变数与风险[72]。应对世界百年未有之大变局,中国共产党“二十大”报告提出“坚持高水平对外开放,加快构建以国内大循环为主体、国内国际双循环相互促进的新发展格局”,要求“增强国内大循环内生动力和可靠性,提升国际循环质量和水平,加快建设现代化经济体系,着力提高全要素生产率,着力提升产业链供应链韧性和安全水平,着力推进城乡融合和区域协调发展,推动经济实现质的有效提升和量的合理增长”。应对经济全球化转型的复杂形势,面向国家提出的战略任务,中国经济地理学势必需要为构建新发展格局、实现高质量发展提供创新的理论与方法支撑。
(1)共建“一带一路”高质量发展的案例比较与模式研究
“一带一路”倡议是中国超越地缘博弈旧思维、开创国际合作新范式的探索。在经济全球化的多边关系退缩、区域集团竞争加剧的新形势下,“一带一路”所倡导的包容性全球化重申了发展多边关系的价值,并在实践中探索经济治理与国际合作的新模式[73]。从经济地理视角看,新模式的形成需要关注两方面问题:一是充分认识各国家和地区的发展基础差异,为建立优势互补的经济联系提供基本的“地情”;二是充分揭示沿线国家和地区的竞合关系,归纳已有实践经验,求解整体发展的“最大公约数”。
(2)“双循环”新发展格局的经济地理模式与过程研究
经济全球化转型过程中,发达国家试图重新平衡本土和海外的利益关系,经济脱钩风险迅速上升,发展中国家在发展转型和外部风险提升的双重压力下,也开始重新调整本土和海外经济联系。中国提出加快构建“双循环”新发展格局,正是在坚持高水平开放前提下所进行的调整,充分发挥本土市场规模优势,通过内循环降本增效,通过内外循环衔接提档升级[76]。从经济地理视角看,“双循环”新发展格局既涉及到中国深度参与全球产业分工与合作,也涉及到中国如何构建优势互补的区域经济布局,是一个“全球—国家—地方”相互耦合的经济地理格局与过程。
(3)全球生产网络重组下的区域转型与韧性研究
经济全球化转型背景下,全球生产网络重组与中国经济结构调整同步,对中国经济发展既是机遇也是挑战。一方面,中国凭借初级产品、劳动力价格优势和规模化生产能力被动嵌入全球生产网络的模式不可持续,转型压力显著提升。全球生产网络重组为打破原有的发展惯性、调整结构性矛盾创造了外部条件[80]。另一方面,经济全球化转型同样创造了一个不确定性显著提升的发展环境,经济结构调整面临的风险类型增加,地方保护主义抬头,技术壁垒提升。中国企业在全球生产网络中遭受严峻冲击,特别是处于转型升级地位的企业及其网络面临有组织的针对与围堵,给转型升级带来挑战。
(4)产业集群演化与国际竞争力提升路径研究
(5)全球、国家、区域创新体系建设与布局研究
从全球层面看,随着经济全球化从成本驱动向创新驱动转型,创新资源与创新能力决定了未来继续从经济全球化获益的空间。中国坚持高水平对外开放,势必需要积极融入全球创新网络,包括建立稳定的科技合作关系、深度参与国际大科学计划与科学工程、参与标准规范的制定等。从本国层面看,中国经济当前同样朝着创新驱动发展的方向演进。传统生产要素对区域发展的贡献在减少,而知识与技术的贡献持续增大,创新能力的差异逐渐成为塑造国内经济地理格局的重要力量[86]。
对此,经济地理关注两个基本问题:一是中国如何提升在全球创新网络中的地位?二是中国如何布局全球创新中心建设,形成全球创新人才与资源的汇源地?回答这两个问题,不仅涉及到中国与世界的创新联系,同样涉及到中国本土的创新资源配置与协同创新,既要考虑核心地区打造全球创新中心的路径,也涉及周边地区的协同与整合[87]。这一过程仅凭借传统的多尺度创新网络研究难以充分解释[88],仍需要系统地解析全球、国家、区域的创新体系建设,以及三者之间关联。当前多样化的创新体系类型和协同创新模式不断涌现,特别是京津冀、长三角、粤港澳大湾区等重点地区的实践基础丰富且背景差异显著[89⇓-91],值得进一步比较、归纳,形成中国经济地理学的理论化成果。
(6)全球环境治理与区域可持续发展互动关系研究
已有研究通过资源环境承载建立了区域可持续发展基本的“经济—空间”关系认知,透过隐含污染和虚拟资源流动建立了跨尺度、跨区域的“经济—空间”关系认知[94]。但是对此过程中,全球治理体系的制度基础与关系结构,各级经济主体的类型、关系与作用,经济—空间的供需关系形成与演变等尚缺少系统认识。对此,经济地理学应深化两方面的探索:一是战略性资源保障供应的空间策略,尤其是不同尺度地域单元的战略性资源保障应当有差异化策略;二是价值链治理、环境治理与空间治理的协同,支撑优化经济布局与国土空间体系的现实需求,及其对产业绿色化转型与发展绿色产业的影响。
(7)地缘经济格局变化对国家安全和发展利益的影响研究
地缘经济格局的变化是经济全球化转型的直观表现。自20世纪90年代美国和苏联“冷战”结束之后,地缘经济的竞争逻辑取代地缘政治的冲突逻辑[95],主导了上一阶段以自由化为内核的经济全球化。当前大国博弈、区域集团竞争、国际治理缺位等问题则重新突出了地缘经济的政治内涵[96]。重新理解地缘政治与地域经济的逻辑是理解经济全球化转型的基础,也是在维护好国家安全和发展利益的前提。经济地理学自2012年以来对地缘经济的重视程度快速提升,针对东亚、东南亚、南亚、中亚、西亚、东欧、非洲、北美、拉丁美洲等地区的研究都在复苏[97],“一带一路”是研究的热点地区,极地等新兴议题亦开始出现[98]。国内层面,东北、西南、海南等边境地区的地缘经济关注较多,南海的地缘战略地位亦颇受关注[99]。
已有研究聚焦于地缘经济的格局及其变化特征分析,尤以能源流动、经贸联系为主。在此基础上,经济地理学可进一步关注以下两方面问题:① 中国地缘环境的发展风险评估与应对策略研究。从地缘经济格局分析朝着地缘环境的系统解析[100],为维护经贸格局稳定和战略资源保障提供决策支持;② 地缘经济与区域发展的关系研究。处于不同地缘经济关系的边境地区如何塑造经济联系方向,打开机会窗口,应对发展风险?需要系统性、体系化的区域研究作为支撑。
5 结论
经济全球化转型重塑了世界经济地理格局。当前经济全球化的地理整合范围逐渐缩小,形成交错层叠的区域集团;经济全球化的驱动力逐渐从成本驱动转向创新驱动,全球化红利可能在发达国家和发展中国家重新分配;全球价值链分工面临效率与安全的权衡,原有的离岸外包可能逐渐转向在岸、近岸、友岸。经济全球化转型过程中,距离、制度、韧性3个变量的重要性在提升,在不同地理尺度下加剧经济发展的不均衡性。
经济全球化转型改变了经济地理学理论创新的土壤。自1980年以来的经济全球化浪潮先后催生了经济地理学的制度、文化、关系、演化转向,随着北美和欧洲的新产业区发展、拉美地区经历繁荣后陷入中等收入陷阱、东亚地区出现经济增长奇迹,经济地理学揭示了经济全球化的空间性,建立了全球产业分工与区域发展的互动关系,建构了全球化与地方化并存的尺度关联关系,揭示了区域在开放发展过程中复杂的时空关联。随着经济全球化转型,经济地理学理论发展需要摆脱一体化的思维惯性。当前经济地理学研究逐渐从“全球—地方”转向“全球—国家—地方”的关系尺度,关系网络的表达愈发重视突出其多尺度、多层级、多主体的特征,国家力量的重要性被重新强调,反映国际与地区形势的重大事件、重点地区成为新的热点。在此基础上,多元转向呈现出交叉融合的趋势,集成了地理政治经济、战略耦合、路径创造等理论的综合框架正愈发广泛地应用于创新、环境、转型等全球议题的研究中。
应对经济全球化转型,国家奠定了“坚持高水平对外开放”的发展基调,提出了加快构建“双循环”新发展格局的战略任务。对此,中国经济地理学研究需要在国际前沿与国家战略之间寻得新的平衡。在已有研究基础上,应特别重视“一带一路”高质量发展的实践案例,推动包容性全球化的理论化与模式化;深入解析“双循环”新发展格局的经济地理格局与过程,为经济布局与空间治理提供科学支撑;关注全球生产网络重组下的区域转型路径及其韧性,突破既有的路径模式和韧性理论框架;关注产业集群演化与国际竞争力提升的路径,支撑培育世界级产业集群的战略要求;深化全球、国家、区域创新体系建设的研究,为建设国家和区域创新中心、提升国家创新体系整体效能提供决策支持;理解全球环境治理与区域可持续发展的互动关系,实现价值链治理、环境治理、空间治理相协同的理论创新,支撑优化经济布局与国土空间体系的现实需求;揭示地缘经济格局变化对国家安全和发展利益的影响,形成全球、国家、地区相融合的地缘环境系统认知。
参考文献
From globalization to regionalization: The United States, China, and the post-Covid-19 world economic order
DOI:10.1007/s11366-020-09706-3 [本文引用: 1]
Causes and consequences of the war in eastern Ukraine: An economic geography perspective
DOI:10.1080/09668136.2019.1684447 URL [本文引用: 1]
Transformation of global economic governance
全球经济治理变革的三个判断
From Global to Local: The Making of Things and the End of Globalization
Research on the influence of US trade protection policy on globalization
美国贸易保护政策对全球化的影响探究
The new trend of economic globalization and the reform of global economic governance
经济全球化的新态势与全球经济治理的变革
Economic globalization research based on scale-construction in Western human geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.09.001
[本文引用: 2]

Time-space compression in the context of globalization leads to declining costs of communication and transportation and increasing transnational activities. The emergence of multi-national firms and international organizations, in accordance with increasing boundary-crossing activities, has simultaneously weaken the power of state on economic, political, and cultural processes within its territory. Under such circumstances, some researchers assert globalization as "the end of geography", which sounds like an argument of hyper-globalist. In light of scale construction, human geographers are engaged in reconstructing the global scale and relating it to other scales. It turns out that space matters in the process of globalization. Two key points emerge: (1) Scale construction is not necessarily with hierarchical structures. Relation-based scales provide a better model for globalization, which is featured with horizontal communication rather than vertical regulation. (2) Global shifting exhibits trends both towards globalization and localization simultaneously, much of which appears to be global-local nexus rather than simplex globalizing process. These findings introduce new perspectives into globalization research in human geography: framework based on relational network makes it possible to conduct a trans-territorial analysis and to depict a big picture of the reshaping pattern of global economic landscape. On the other hand, in light of localized globalization, researchers set out to refer regional development to global-local interactions other than local embeddedness and endogenous factors, which offers insight into urban and regional governance in the context of globalization.
尺度重构视角下的经济全球化研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.09.001
[本文引用: 2]

全球化的“时空压缩”特征降低了要素流动的空间成本,而为组织和协调跨国经济活动而出现的跨国公司与国际组织,导致象征权利范畴的领土边界对经济、文化和政治的影响力不断削弱,进而引发了极端全球主义式的“地理终结”论调。人文地理学者结合全球化的特征,通过改变尺度结构,明确了全球尺度涉及的主体与内容,凸显出地域单元的意义,避免了全球尺度的抽象理解,从而反驳了地理终结论,形成了两个关键认识:①尺度建构不一定建立在相对性的基础上并构成垂直体系,基于关系建构的全球尺度更契合不同主体和空间联系日趋紧密的特征;②全球化与地方化过程是并存的。全球化并不意味着尺度的垂直叠加,而是全球与地方之间的复杂联系。这两个关键认识为人文地理学参与全球化研究形成了独特的视角:一方面,学者们运用立体网络思维,以关键主体与空间为节点、以关系为纽带,实现“超越边界”式的分析;另一方面,全球化与地方化并存的理念也促使城市与区域发展研究从单纯强调区域差异转向探讨区域内外相互作用,为城市与区域治理提供了新思路。
The dynamics of world economy geography and the role of China in economic globalization
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202004
[本文引用: 2]

From the perspective of economic geography, this paper studies the changing spatial pattern of world economy and China's role in different waves of economic globalization. Firstly, this study finds that the geographical pattern of world economy changes from "core-periphery" to "chain-reconfiguration", and to current "network-imbalance". Meanwhile the driving force of economic globalization shifts from "trade globalization" to "manufacturing globalization". At present, "multiple globalization" is involving into a new engine to driving the development of economic globalization. We then discuss that how China changes its role in economic globalization by changing modes of strategic coupling. We argue that the role transition of China breaks the traditional developing path which developed countries set for developing countries and theoretical spatial order put forward by classical industry gradient transfer, bringing new restructuring power and possibility for changing pattern of globalization. Finally, we discuss the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the development of economic globalization and the development trend of economic globalization in the post-pandemic era. Based on the analysis, we come up with some suggestions regarding to the potential development paths of China under the background of economic globalization.
经济全球化变革下的世界经济地理与中国角色
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202004
[本文引用: 2]

经济全球化浪潮下的世界经济地理格局和中国角色演变一直以来都是学术界关注的热点问题,然而当前学界偏重从国家经济模式和国际贸易角度来解释这种格局的变化,而较为缺乏基于生产组织视角的经济地理解释。因此,本文从经济地理视角出发,解析经济全球化浪潮下世界经济地理格局变动与中国角色的演变。本文揭示了在三次全球化浪潮的冲击下,世界经济地理格局从“核心—边缘”到“链式重构”再到“网络不均衡”的演变过程,以及经济全球化的驱动力如何从“贸易全球化”转变为“生产全球化”,继而朝“多元全球化”演进。本文还论述了中国如何通过战略耦合模式的动态调整实现从经济全球化的参与者到变革者的转变。本文认为这种角色转变,改变了西方发达经济体对后发经济体的预设发展路径,以及经典的产业梯度转移理论所预测的空间秩序,为全球化格局的变动带来新的重构动力与可能。最后,本文结合此次新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情全球爆发带来的影响对未来经济全球化发展存在的可能路径进行分析,并从经济地理学视角为中国未来经济全球化发展道路选择提供了参考建议。
Theoretical progress and future trend of globalization
全球化的理论进展与未来趋势
Brexit: A reflection of the social and political divisions in Europe
从英国脱欧透视欧洲的社会与政治分裂
A new examination of the impacts of regional trade agreements on international trade patterns
DOI:10.11130/jei.2019.34.2.236 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tasks, occupations and slowbalisation: On the limits of fragmentation
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsac014
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Following the trade collapse in 2009, Globalisation has recovered but the growth rate slowed down compared to the preceding period of Hyper Globalisation. The persistence of this slowdown is remarkable. We argue that increased awareness of firms for the costs of involvement in global supply chains can explain the recent developments in trade flows. We formalise the existence, length and consequences of changes in fragmentation cost along global supply chains. From a theoretical point of view, we allow tasks to be a combination of different occupations while the model endogenises production fragmentation, allowing for multiple production stages in multiple countries, while remaining tractable. From an empirical point of view, the model explains both the period of Hyper Globalisation and the subsequent Slowbalisation in terms of changing fragmentation costs along global supply chains. The model is also consistent with developments regarding labour market polarisation associated with modern globalisation: the labour market position of medium-skilled workers in advanced countries has deteriorated relative to high- and low-skilled workers, which can be understood by changing global supply chains. Our model implies, however, that even with zero fragmentation costs the demand for certain occupations does not fall to zero for any country.
Reconstructing globalization: The reform orientation of global economic governance
<div class="page"> <div class="layoutArea"> <div class="column"> <p style="text-align:justify;"> The dialectical relationship between economic globalization and the global economic governancesystem is basically in line with Marx’s theory of“economic foundation and superstructure”. Economicglobalization plays a fundamentally decisive role, while the global economic governance system has the oppositeeffect of promoting or hindering on it, and the two are closely related. The expansion of the global value chainsrequires timely and effective changes to the WTO multilateral trade rules system. Due to the stagnation of theDoha Round, the spread of regional trade agreements has departed from the normal approach of global economicgovernance. In 2018, the United States initiated the reconstruction of international economic and trade rules,attempting to reshape the world economy through the counteraction of superstructures, but further dragged globaleconomic governance into an“exclusive”regional approach, which not only caused an“anti-globalization”trend,but also harmed the common interests of countries around the world. The current global public health crisis hasbrought the issue of supply chain security to the level of national security and may exacerbate the dilemma ofglobal economic governance. As a major economy that is deeply integrated into economic globalization, Chinashould strengthen its advocate and actively promote the improvement of the global economic governance system,to make sure that the global economic governance can return to the normal approach and form a dynamic virtuous <span>circle with the development of the world economy.</span> </p> </div> </div></div>
重构全球化: 全球经济治理的改革取向
经济全球化与全球经济治理体系的关系符合马克思“经济基础与上层建筑关系”理论,即经济全球化起着基础性决定作用,而全球经济治理体系对其有着促进或阻碍的反作用。全球价值链扩展和深化,需要对WTO多边贸易规则体系进行变革,但多哈回合的停滞、区域贸易协定的蔓延等,已经背离了全球价值链对全球经济治理的要求。近年来,美国启动的国际经贸规则重构,企图通过全球经济治理体系的反作用来重塑世界经济,正在将全球经济治理拖入“排他性”区域化模式,不仅造成“逆全球化”趋势,也损害了世界各国的共同利益。而全球公共卫生危机进一步将供应链问题提到国家经济安全的高度,并可能加剧全球经济治理的区域化困境,疫后世界经济联系的修补极可能是一个“重构全球化”的过程,而不是简单地恢复此前的全球价值链。本质上而言,对于未来国际经贸规则的构建,美国大选后仍将在相当长的一段时间内采取“排他性”的区域化模式,世界上层建筑和经济基础之间的不协调将呈现新的形态。作为高度融入经济全球化的贸易大国,中国应当坚定自身主张,积极推动全球经济治理体系的改革与完善,使全球经济治理符合世界经济发展的客观要求。
From success to failure: Under what conditions did mercosur integrate?
DOI:10.11130/jei.2016.31.4.855 URL [本文引用: 1]
Eurasian Economic Union: Present and future perspectives
DOI:10.1007/s10644-016-9182-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Asian economic integration: A perspective on South Asia
DOI:10.1016/S1049-0078(02)00184-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
Global production networks and the analysis of economic development
DOI:10.1080/09692290210150842 URL [本文引用: 1]
Toward a dynamic theory of global production networks
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2015.91.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 2]
Global production networks and uneven development: Exploring geographies of devaluation, disinvestment, and exclusion
DOI:10.1111/gec3.v10.11 URL [本文引用: 1]
Trend and path of digitalized transformation of the traditional industries
传统产业数字化转型的趋向与路径
The fourth industrial revolution, changing global value chains and industrial upgrading in emerging economies
DOI:10.1080/17487870.2020.1735386 URL [本文引用: 1]
The next innovation opportunities in China. Multinationals are shifting their R&D focus from cost savings to knowledge-based research
Professional service firms as agents of economic globalization: A political perspective
DOI:10.1093/jpo/joy014 URL [本文引用: 1]
How important is GVC participation to export upgrading?
DOI:10.1111/twec.v44.10 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mainly inner circulation, outer circulation empowerment and higher level double circulation: International experience and Chinese practice
内循环为主、外循环赋能与更高水平双循环: 国际经验与中国实践
Made in the world? Global value chains in the midst of rising protectionism
DOI:10.1007/s11151-020-09781-z [本文引用: 1]
Springboard MNEs under de-globalization
DOI:10.1057/s41267-021-00423-4 [本文引用: 1]
Security of industrial chain: Internal logics, practical challenges, and strategic priorities
产业链安全: 内在逻辑、实践挑战与战略取向
GVC transformation and a new investment landscape in the 2020s: Driving forces, directions, and a forward-looking research and policy agenda
DOI:10.1057/s42214-020-00088-0
[本文引用: 1]

Global value chains (GVCs) will undergo substantive transformation in the decade ahead, reshaping the global trade and investment landscape. The change will be driven by five major forces: economic governance realignment, the new industrial revolution, the sustainability endeavor, corporate accountability, and resilience-oriented restructuring. All of this will present challenges and opportunities for firms and states alike, leading to an investment-development paradigm shift. This article discusses the five driving forces for the GVC transformation, projects ten broad trends in the evolution of the global trade and investment landscape, and also presents a forward-looking agenda for multi-dimensional research and policy in the decade ahead. It aims at providing a framework for future research that encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration as well as a structured dialogue between academia and policymakers.
China's opening up during the past 70 years: Empowering growth and reform
新中国对外开放70年: 赋能增长与改革
The turn from just-in-time to just-in-case globalization in and after times of COVID-19: An essay on the risk re-appraisal of borders and buffers
The impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the development of economic globalization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200514
[本文引用: 1]

The COVID-19 pandemic is considered the biggest crisis confronted with the world after the Second World War, which has brought huge impacts on people’s health and daily life, economic growth and employment as well as national and international governance. Increasing pessimism is buzzing among scholars, critics, entrepreneurs, the mass and even government officials, and views like the end of economic globalization, large-scale spatial restructuring of global supply chains and fundamental change of the world economic governance structure are becoming prevailing on the media. This paper tries to address the issue of the development trend of economic globalization in the post-pandemic era by developing a framework of globalization’s Triangle Structure to understand its dynamics in addition to a summary of the on-going impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. We argue that the spatial fix of capital accumulation, time-space compression led by technological advance and openness of nations are the three major drivers of economic globalization, and the changes and interactions of these three drivers decide the development trend of economic globalization. From such a dynamic viewpoint, economic globalization is an ever-changing integration process without an end but constant fluctuations. The cost of decoupling of nations from globalization would be very huge because they have been highly integrated by global production networks and trade networks and no nation can afford a complete decoupling. The so-called de-globalization phenomena are just short-term adjusting strategies of nations to cope with power reconfigurations brought by economic globalization. The pandemic will have little impacts, or probably nothing, on the spatial fix of capital accumulation and time-space compression led by technological advance, but may temporarily influence some nations' openness. If the pandemic does not last long, economic globalization will resume from the shock soon after the world goes back to normal, and develop and restructure according to its own dynamics. Thus, we tend to believe the pandemic at most slams the brake of globalization and would not be able to put it into reverse. Economic globalization will not stop or reverse, but develop towards a more inclusive stage.
新冠肺炎疫情对经济全球化的影响分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200514
[本文引用: 1]

新冠肺炎疫情是第二次世界大战以来世界面临的最大危机,给世界带来巨大的冲击,包括人们的心理和生活、经济增长与就业、国家治理及世界治理等。这些影响使很多学者、评论家、大众、企业家乃至政府官员产生了非常悲观的情绪,舆论中不乏经济全球化将终结、全球供应链将大规模调整、世界治理格局将彻底改变等言论。本文通过建立“全球化的三角结构”剖析了经济全球化的动力机制,并结合疫情对世界的主要影响,试图揭示后疫情时代经济全球化的走势。我们认为,资本的“空间出路”、技术的“时空压缩”和国家的开放程度是驱动经济全球化的三个基本力量,这三者的变化及其相互作用结果影响着全球化进程。从动力机制看,全球化是一个没有终点且不断变化的历史过程,它不会倒退,而是波动。过去半个世纪以来,世界各国已经被全球化紧密地联系在一起,相互脱钩的代价极其昂贵,没有国家会选择完全脱钩。所谓的逆全球化现象,是全球化发展过程中世界格局变化及各国应对策略调整的结果。新冠肺炎疫情并不能影响全球化的资本和技术驱动力,但是可能影响国家的开放程度。如果疫情持续时间不是很长,经济全球化将很快会回归原有的发展轨迹,继续进行调整。各国也将继续围绕经济全球化进行斗争、妥协、再斗争,直至形成一个相对稳定的状态。因此,经济全球化可能因为应对疫情而踩下急刹车,甚至暂退半步,但很快将继续前行,向着“包容性全球化”的方向发展。
Global value chains: Efficiency and risks in the context of COVID-19
Restructuring the global value chain and promoting the stability of industrial supply chain
全球价值链重构与提高产业链供应链稳定性
Recent developments in western economic geographies and theoretical thinking for China's counterpart
西方经济地理学新进展及其启示
Progress of economic geography in the West: A literature review
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408014
[本文引用: 2]

Since the 1980s, the western countries have developed into the postindustrial society with the dominance of knowledge based economies and services. The societal economic transformations make the space-economy relations more complex. Economic actors are embedded in the complex global-local system. Economic geography starts to go beyond economics and widely borrows theories and methods from sociology, management, institutional economics, anthropology, and cultural studies. This paper provides a comprehensive literature review about the progress in the western economic geography in the last three decades, documenting the changes of research perspectives, progresses in hot research areas and policy relevance. The mainstream economic geography has experienced a number of turns in research perspectives, including new regionalism, institutional turn, cultural turn, relational turn and evolutionary turn. Political economy remains one of the influential perspectives in the research of economic geography, especially in the global financial crisis. Based on the analysis of knowledge network of economic geography built with key words, this paper identifies eight hot research areas in the western economic geography and reviews their progresses in research. Those areas include region and local development, industrial geography, economic globalization, labor geography, innovation geography, consumption geography, financial geography and environmental economic geography. Finally, this paper summarizes the key features of economic geography in the west and proposes some implications for economic geographers in China.
西方经济地理学研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408014
[本文引用: 2]

20世纪80年代以来,西方经济地理学与经济学、政治学、社会学、管理学等社会科学广泛融合,呈现出空前繁荣的局面。本文对这一时期西方经济地理学的思潮演变、热点研究领域以及政策研究等方面进行梳理。西方经济地理学在经历了地理学的“新经济地理学”和经济学的“新经济地理学”两个影响深远的变革后,研究领域和主题逐步走向多样化与复杂化。本文综述了8个热点研究领域,包括区域与地方发展、经济全球化、产业地理、劳动力地理、创新与创意地理、消费地理、环境经济地理和金融地理的研究进展,并讨论了经济地理学与政策研究的关系,最后总结了西方经济地理学的特点。
Global production networks and the analysis of economic development
DOI:10.1080/09692290210150842 URL [本文引用: 1]
Towards an evolutionary perspective on regional resilience
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.959481 URL [本文引用: 1]
Editorial: Constructing an evolutionary economic geography
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbm021 URL [本文引用: 1]
Editorial: Evolutionary economic geography: Theoretical and empirical progress
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2015.1033178 URL [本文引用: 1]
State roles in global value chains and global production networks
Designed to break with state‐centric approaches to understanding economic development, global commodity chain, global value chain (GVC), and global production network (GPN) analyses have deepened our understanding of the corporate governance of global lead firms and associated development outcomes in an era of globalisation. Although this research field is recognised to have provided considerable insight into private governance, a rapidly emerging body of research has given greater attention to the role of the state in GVCs and GPN. Although the state playing a role as facilitator towards firms participating in GPNs has often been an emphasis, this article argues that a variety of other roles are of increasing prominence, including as regulator, producer (state‐owned enterprises), and buyer (public procurement). A major challenge for both policymakers and researchers is to understand how a range of state initiatives not just shape but also are shaped by their positioning in GVCs and GPNs.
Geographies of energy transition: Space, place, and the low-carbon economy
DOI:10.1016/j.enpol.2012.10.066 URL [本文引用: 1]
Creating knowledge assets under biocapitalism: Analyzing China's biomedical industry and its patent networks
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2022.2070471 URL [本文引用: 1]
Integration and isolation in the global petrochemical industry: A multiscalar corporate network analysis
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2020.1794809 URL [本文引用: 1]
The geography of technology legitimation: How multiscalar institutional dynamics matter for path creation in emerging industries
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2020.1842189 URL [本文引用: 1]
Innovation catalysts: How multinationals reshape the global geography of innovation
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2022.2026766 URL [本文引用: 1]
Economic geography, politics, and policy
DOI:10.1146/polisci.2020.23.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
The changing landscape of international financial centers in the twenty-first century: Cross-border mergers and acquisitions in the global financial network
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2021.2010535 URL [本文引用: 1]
How does de-globalization affect location decisions? A study of managerial perceptions of risk and return
DOI:10.1002/gsj.v10.1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relocation decisions in uncertain times: Brexit and financial services
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2021.2009336 URL [本文引用: 1]
The implications of brexit for UK and EU regional competitiveness
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2020.1820862 URL [本文引用: 1]
People or places that don't matter? Individual and contextual determinants of the geography of discontent
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2021.1973419 URL [本文引用: 1]
The development of COVID-19 in China: Spatial diffusion and geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200329
[本文引用: 1]

The study of the spatial diffusion and geographical mode of COVID-19 is of great significance for the rational allocation of health resources, the management and response of public health emergencies, and the improvement of public health system in the future. Based on multiple spatio-temporal scale, this paper studied the spatial spreading process of COVID-19 between cities and its evolution characteristics in China, and then explored its influencing factors. The results are shown in the following: the inter-city spreading process of COVID-19 in China mainly experienced six stages, namely, stage I: diffusion in Wuhan, stage II: rapid multi-point diffusion in space, stage III: rapid increase of confirmed cases, stage IV : gradual decrease of new confirmed cases, stage V: the epidemic under control, and stage VI: cases imported from overseas. In the context of globalization and open regional system, the social and economic development of regions are closely related to each other. With the development of fast and convenient high-speed railway network, the spatial characteristic of population migration shows a cross-regional and hierarchical pattern, and forms a certain spatial cascade structure along the transport corridor. Accordingly, the spatial spread of COVID-19 mainly showsthe characteristics of adjacent diffusion, relocation diffusion, hierarchical diffusion, and corridor diffusion. The study found that geographical proximity, population migration and population size, traffic network, epidemic prevention and control measures have significant influence on the spatial diffusion process of COVID-19. Among different modes of transportation, airplanes play agreater role than others in the early stage of the epidemic. In addition, the population flow during the Spring Festival had a certain impact on the spread of the epidemic. In conclusion, to some extent, the spatial spread process and pattern of COVID-19 epidemic reflects the spatial organization pattern of social and economic activities under the "space of flows" network, which is closely related to the geographical proximity, the social and economic linkages between regions, and the spatial an temporal patterns of human activities. From the perspective of geography, this paper analyzed the inter-city spread pattern of COVID-19 epidemic and provided some implications for prevention and control measures against the epidemic in other countries, and also offered some suggestions for China to deal with public health emergency risks in the future.
新冠肺炎疫情的空间扩散过程与模式研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200329
[本文引用: 1]

研究新冠肺炎疫情的空间扩散过程与模式对于防疫抗疫资源的合理配置、突发公共卫生事件的管理与应对以及未来公共卫生体系的完善具有重要意义。本文综合时间和空间尺度,从地理学视角研究了新冠肺炎疫情的城际空间扩散过程,归纳总结扩散模式,并揭示了其影响因素。研究发现:新冠肺炎疫情在中国的发展主要经历了6个阶段,并在空间上表现出邻近扩散、迁移扩散、等级扩散和廊道扩散等地理模式;地理邻近性、人口流动、人口规模、交通网络、疫情防控管理等因素对疫情的空间扩散具有显著影响。新冠肺炎疫情的空间扩散过程和模式一定程度上是“流空间”网络下人类社会经济活动空间组织模式的一种反映,与地理邻近性、社会经济联系的跨区域性及人类活动的时空规律等密切相关。本研究以期为世界各国的疫情防控措施制定提供参考,也为中国未来应对公共卫生应急风险提供经验借鉴。
Economic globalization and the COVID-19 pandemic: Global spread and inequalities
DOI:10.1007/s10708-022-10607-6 [本文引用: 1]
Analysing the socio-economic impacts of COVID-19: A new regional geography or pandemic enhanced inequalities?
DOI:10.1080/21681376.2022.2084447 URL [本文引用: 1]
COVID-19 and alternative: Conceptualisations of value and risk in GPN research
DOI:10.1111/tesg.v111.3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Necrocapitalist networks: COVID-19 and the 'dark side' of economic geography
DOI:10.1177/2043820620934927
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The economic fallout from COVID-19 has precipitated a crisis in global supply chains. The lockdown of consumers worldwide has triggered a fall in demand that has so far led to the dismissal of up to one-third of Cambodia’s garment sector workforce. Though the pandemic is exceptional, this is a crisis rooted in the exemplary rather than extraordinary hyper-precarity of workers in global industry. Here, I argue that COVID-19 spotlights the elusive ‘dark sides’ of global production in economic geography, revealing the necrocapitalist logics of supply chains.
Progress of relational economic geography: Whether theorizing China's experiences
关系经济地理的研究脉络与中国实践理论创新
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020191002
[本文引用: 1]

关系经济地理学是当前经济地理学界的主要流派之一,当前国内研究对该流派中的全球生产网络分析框架较为熟悉,但是对流派本身的认识不足。本文全面回顾了该流派的缘起、孕育、成型和深化拓展的历程,对存在问题展开评述。主要得到三个结论:① 关系经济地理有鲜明的地理学科特色,是全球化研究不可或缺的中坚力量,是提升经济地理学科地位的重要支撑。② 关系经济地理当前的理论模型存在体系复杂、变量过多的问题,同时核心解释变量缺乏完整的理论推导逻辑,依然需要靠案例来完善实证,而无法定量测度。③ 当前学者已经在国际期刊上基于中国实践进行理论修补与创新,为我们提供了良好的示范。本文为此评述了两个系列的研究,评述基于中国实践进行理论创新的方法和路径。本文有助于推动中国经济地理研究的国际化,对探讨中国经济发展实践经验的理论创新,有着积极的科学意义。
Evolution in economic geography: Institutions, political economy, and adaptation
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2009.85.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Global production networks: Mapping recent conceptual developments
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbz018
[本文引用: 2]

In this framing paper for the special issue, we map significant research on global production networks during the past decade in economic geography and adjacent fields. In line with the core aim of the special issue to push for new conceptual advances, the paper focuses on the central elements of GPN theory to showcase recent rethinking related to the delimiting of global production networks, underlying political-economic drivers, actor-specific strategies and regional/national development outcomes. We suggest that the analytical purchase of this recent work is greater in research that has continued to keep a tight focus on the causal links between the organizational configurations of global production networks and uneven development. Concomitantly, considerable effort in the literature has gone into expanding the remit of GPN research in different directions, and we thus engage with five domains or 'constituent outsides' that relate to the state, finance, labour, environment and development. We believe such cross-domain fertilisation can help realize GPN 2.0's potential for explaining uneven development in an interconnected world economy.
Towards a theory of regional diversification: Combining insights from Evolutionary Economic Geography and Transition Studies
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2016.1258460 URL [本文引用: 1]
Green industry development in different types of regions
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2019.1648385
[本文引用: 1]

At the regional level, the imperative of sustainable development often manifests itself in an emphasis on developing green industries. However, regions vary in their preconditions for achieving this. In this paper we link regional preconditions to various pathways for green industry development. This provides the foundation for identifying place-based policy implications for growing green industries in different types of regions, grounded in the emerging perspective in innovation studies on transformative innovation policy. The paper thereby helps to understand the pathways for greening the economy in different regional contexts and how such green pathways can be promoted through policy.
Rethinking path creation: A geographical political economy approach
DOI:10.1080/00130095.2018.1498294 URL [本文引用: 2]
A review of global-local interactions for regional development
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.10.001
[本文引用: 3]

Extra-regional linkages can benefit regional development by introducing supplement resources and technologies. They also enrich the local knowledge base, keeping regions away from depression due to lock-in effects. Global-local interaction (GLI) research represents the academic effort to theorize this process by examining the interplay between a wide array of actors at multi-scales within particular territorial confines. It raises four critical questions regarding the conditions, regional differences, channels, and actors for interaction. The literature has documented that the relatedness between local and nonlocal inputs determines the probability of GLI. Local capabilities determine the extent of GLI. The literature also reveals that the leading and most lagging behind regions tend to benefit from GLI. Knowledge diffusion, foreign investment, and international trade are primary elements that support GLI. As one region continues to develop, the immigrants and nonlocal institutions may enrich the GLI. Conventionally, the literature on GLI is firm-centric. Recent advances highlight the role of individuals, such as entrepreneurs and employees. There is also increasing awareness of the non-economic agency, especially the institutional agency. Overall, an in-depth examination is still required for understanding the scales, dynamics, and agencies of GLI for regional development. Grounded in the context of China's regional restructuring and opening-up, this study proposes a framework to model GLI in China and discusses its potential for future studies.
区域发展的“全球—地方”互动机制研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.10.001
[本文引用: 3]

建立对外联系、利用外部资源有助于弥补区域发展新经济活动所面临的资源与技术缺口,为区域发展注入新活力,避免陷入路径锁定导致发展停滞甚至衰退。对外联系的建立势必与本地已有联系相互作用,表现为“全球-地方”之间多类型行为主体在特定空间支持与约束下的互动,涉及4个基本问题:发生条件、区域差异、互动内容与行为主体。梳理现有研究发现:① 本地与非本地要素的相似性或互补性决定了互动发生的可能性,本地能力则进一步决定互动发生的程度;② 互动对于优势地区和后进地区2类极端类型地区更为有效;③ 互动内容以知识、贸易、资本等要素为主,日益强调非本地劳动力和非本地制度的影响;④ 互动主体以企业为中心。近年来研究一方面强调企业家等个体作用,另一方面关注非经济主体的作用。整体而言,既有研究在区域发展中“全球-地方”互动的尺度结构、动态变化和行为主体等方面仍面临挑战。结合中国当前区域经济转型与主动全球化并行的发展现状,论文提出理解中国区域发展“全球-地方”互动的关键问题与潜在方向。
Co-evolution in contemporary economic geography: Towards a theoretical framework
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2018.1494824 URL [本文引用: 1]
Globalisation in reverse? Reconfiguring the geographies of value chains and production networks
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsac012
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Standing at a crossroads, where ongoing ‘slowbalisation’ coincides with new forces such as the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, heightened geopolitical tensions, the emergence of disruptive technologies and the increasing urgency of addressing environmental challenges, many important questions remain unsolved regarding the nature and impact of the current economic globalisation. This special issue on ‘Globalisation in Reverse? Reconfiguring the Geographies of Value Chains and Production Networks’ aims at showcasing recent work that seeks to contribute to, and advance, the debates on economic globalisation and the reconfiguration of global value chains and production networks. This introductory article has three objectives: first, based on a broad literature review, we aim to identify four key forces, as well as the fundamental relatively stable capitalist logics contributing to the complex reconfiguration of global economic activities. Second, we will position the papers included in this special issue against the four main forces identified and discuss the contributions of each article to capture some emerging cross-paper patterns among them. Finally, we outline the contours of a research agenda that suggests promising avenues for further investigation of the phenomenon of value chain and production network reconfigurations in times of uncertainty.
Understanding the "Great transformations once in a century"
理解百年未有之大变局
A discursive construction of the Belt and Road Initiative: From neo-liberal to inclusive globalization
DOI:10.1007/s11442-018-1520-y
[本文引用: 1]

An international consensus is emerging around the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) proposed by the Chinese government, with a growing number of countries seeing it as a way of jointly exploring new international economic governance mechanisms. Meanwhile, with the crisis of neo-liberalism, economic globalization has arrived at a crossroad. In particular, incessant voices speak out against globalization, making the quest for a new way of promoting global development a major challenge. In this context, more and more political elites and scholars consider that the BRI opens up a possible new globalization path, amongst which inclusive globalization warrants exploration. On the basis of a brief analysis of the course and mechanism of global economic expansion and the limitations of neo-liberal globalization, along with the putting into practice of the BRI, this paper outlines some of the core features of inclusive globalization, i.e., inclusive growth with effective and efficient government regulation; inclusive infrastructure development; inclusive development paths chosen nationally that suit national conditions; inclusive participation; and cultural inclusiveness. Although these features are not sufficient to characterize fully inclusive globalization, they do identify some directions for future research, and provide elements of a discursive construction of the BRI.
Progress in research on the Belt and Road Initiative
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804003
[本文引用: 1]

The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has changed from a China-based initiative to an international consensus, and is becoming a platform for a growing number of countries in the world to explore new international economic governance mechanisms. Such a great change along with impressive achievements of BRI development has attracted academic attention from almost all disciplines except basic sciences, giving rise to huge literature. This paper will first explore data from China Knowledge Resource Integrated Database to summarize the characteristics of literature on BRI in general, and then review progress in research on major BRI topics related to geography. The paper finds: (1) the number of Chinese papers on BRI increased by 21 times in three years, from 1012 in 2014 to 21216 in 2017; (2) these papers cover various BRI-related topics but most of them are macroscopic and very general studies of BRI with a taste of public voices, implying that quality papers with deep academic studies are demanded to support the BRI development; (3) more frequently discussed topics are China's outward foreign direct investment, facilities connection, "going out", globalization, global economic governance, community of shared destiny and internationalization of Renminbi; and (4) specific topics that are more deeply studied by geographers are connotation and discourse of BRI, geopolitical analysis of BRI, China-Europe Express Train, global strategic shipping pivot, model of China's outward foreign direct investment and overseas industrial parks, trade pattern and its impacts on economic growth of both China and its trade partners. Lastly, the paper suggests enhancing the discursive construction of BRI and studies of new BRI mechanisms as well as studies of countries involved in BRI, and promoting dialogues and collaborations between Chinese scholars and foreign scholars on BRI studies.
“一带一路”建设研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804003
[本文引用: 1]

“一带一路”经历了从中国倡议到国际共识的巨大转变,正在成为世界上越来越多国家和政治领袖们探索全球经济治理新模式的平台。伴随这种转变以及“一带一路”建设所取得的成就,“一带一路”研究已经深入到除了基础科学领域外的几乎所有学科。本文根据中国知网(CNKI)数据分析了4年多来“一带一路”研究文献的特征,而后总结了与地理学密切相关的“一带一路”核心议题的研究进展。研究发现:① 自2014年以来“一带一路”研究发文量迅速上升,由2014年的1000多篇飙升到2017年的20000多篇;② 文献比较庞杂,以宏观性、战略性和一般性文献为主,舆论性很高,基于深入研究的高水平学术文献少,还不能很好地支撑“一带一路”建设;③ 对外直接投资、互联互通、“走出去”、全球化、全球治理、命运共同体、人民币国际化等得到的关注较多;④ 地理学在“一带一路”的战略内涵和理论构建、地缘政治经济分析、“中欧班列”、海上航运战略支点、海外投资模式、经贸格局及其经济影响、资源环境问题等方面研究较为深入。最后,本文呼吁加强“一带一路”的理论建构以及建设机制和国别研究,并积极开展中外学者之间“一带一路”研究对话以及合作研究。
Geography and international development studies: China's opportunity
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202212010
[本文引用: 1]

International Development Studies refers to the study of the localization process of development experience and knowledge of relatively developed countries in developing countries, and is a classic topic of Western geographic research. This paper reviews and summarizes the disciplinary development of International Development Studies since the mid-20th century, including the background and process of its emergence, and its current disciplinary pattern. It also systematically discusses four phases of evolution in international development knowledge, including the modernization theory phase (1950s-1970s), the neoliberal phase (1980s-1990s), the neo-structural phase (2000s), and the new modernization theory phase (2010s-present). Drawing on the Western experience and considering the current rise of China, we suggest that China has reached a new stage when it needs to provide international development knowledge to developing countries and should actively promote the study of International Development Geography. In relation to the requirement of constructing the Belt and Road Initiative towards a new stage of high-quality development, and based on the disciplinary advantages of geographic research, we propose four directions of future research in International Development Geography, including China's regional development experience and spatial governance model, the modernization geography of developing countries, case studies of major overseas projects of the Belt and Road construction, and the geography of international development financing.
地理学与国际发展研究及中国的机遇
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202212010
[本文引用: 1]

国际发展研究指相对发达国家的发展经验和知识在发展中国家本地化的研究,是西方地理学的经典议题。本文梳理和总结了20世纪中叶以来国际发展研究的发展历程,包括其出现背景、兴起过程和学科格局,系统评述了国际发展知识演变的4个阶段,即现代化理论阶段(20世纪50—70年代)、新自由主义阶段(20世纪80—90年代)、新结构主义阶段(21世纪初10年),以及新现代化理论阶段(21世纪10年代至今)。借鉴西方经验,对照当前中国崛起的过程,提出中国已经到了需要为发展中国家提供国际发展知识的新阶段,应积极推动国际发展地理学。结合高质量共建“一带一路”的必然要求,立足学科优势,建议了中国开展国际发展地理学研究的4个方向,包括基于中国的区域发展经验和空间治理模式研究,针对发展中国家现代化地理研究,“一带一路”建设海外重大项目案例研究和国际发展融资地理研究。
New globalization and China's regional development strategy optimization
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.01.2020799
[本文引用: 1]

After the global financial crisis in 2008, especially the new global epidemic COVID-19 outbreak at the beginning of 2020 has deeply impacted the whole world, and the world is entering a century of unprecedented changes. In the post-crisis era, the development orientation and strategy of globalization have already undergone a subversive change, the development of globalization has entered a new cycle and stage, with the decoupling of globalization, regionalization and localization, trade protectionism, geopolitical friction and conflict having becoming a prominent feature of new globalization. In order to fully deal with the uncertain risks bring by the new globalization, it is necessary to objectively summarize the main features and overall trends of the new globalization, deeply analysis the impact and main challenges of the new globalization both to the world economic landscape and China's regional development, conform to the global restructuring trend of 5th global industrial transfer, build regional value chains and production networks on the basis of BRI, take efficiency and fairness into account of China's regional development strategy from the perspective of top-level strategic planning, build a new development pattern both focus on domestic big cycle and dual cycle of internal and external. This is a responsible performance of highlighting China's status as a global development power and daring to shoulder the burden of leading global development. And it is also a necessary measure to effectively control and deal with various uncertainties and conflicts caused by structural weaknesses of new globalization.
新全球化与中国区域发展战略优化对策
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.01.2020799
[本文引用: 1]

2008年全球金融危机后,特别是2020年伊始全球新冠疫情深度冲击全球,世界面临百年未有之大变局。本文分析了“后危机时期”的全球化发展导向和策略转变,以及全球化脱钩、区域化与本土化、贸易保护主义、地缘摩擦与冲突等新全球化的显著表征,认为全球化发展已发生转折并进入新的周期与阶段。为充分应对新全球化带来的不确定性风险挑战,中国需要客观总结新全球化的主要表征与整体趋势,准确把握新全球化对于全球经济地理和中国区域发展的影响与挑战,顺应全球第五次产业转移深度影响全球经济地理演变的总体趋势,以“一带一路”倡议为契机构建以中国为核心的区域价值链和生产-贸易网络,在顶层战略谋划中兼顾中国区域协调发展的效率与公平,构建以国内大循环为主体,国内、国际双循环相互促进的发展新格局,这既是有效管控和妥善应对新全球化阶段性转折和结构性弱点的必然举措,更是有效统筹国内、国际两个大局,彰显中国全球性大国地位、勇于承担引领全球发展重担的负责任表现。
"Dual circulation" and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei high-quality coordinated development: From the division in the value chain and factor mobility perspective
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206004
[本文引用: 1]

The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region has experienced a path from competition and cooperation to high-quality coordinated development. Under the new development pattern of "dual circulation", the coordinated development of the BTH region is facing new challenges and new development goals, and it is urgent for the region to achieve innovation-driven economic transformation. This paper starts from the aspects of division in the value chain, technology and capital element flow, systematically combs the status in value chain and radiation capabilities of the BTH region in the "international circulation" and "national circulation", and coordinated development status of the BTH region expressed by "internal circulation". It was found that the BTH did not form the capacity corresponding to the world-class urban agglomeration in the "international circulation", and occupies the low value-added link of the value chain. In the "national circulation", the BTH has played a role of R&D service center, so it occupies the high value-added link of the value chain. It also exports technology and capital and becomes a highland of domestic innovation and capital, but its attraction and radiation are limited. Further exploration found that the BTH is relatively marginalized in the "international circulation", which is one of the important reasons that they have not been complementary to each other in "internal circulation". Moreover, Tianjin and Hebei are less attractive to Beijing's capital and technology, so Beijing's patents are difficult to transform within the BTH urban agglomeration. Therefore, the BTH region failed to achieve innovation-driven economic growth. In the next stage, the BTH urban agglomeration should be driven by the horizontal knowledge chain and gradient innovation chain to build a vertical industrial chain. Specifically, in the "national circulation", efforts should be made to create a collaborative pattern, that is, Beijing specializes in research and develop, Tianjin specializes in high-end manufacturing, and Hebei specializes in logistics service. "International circulation" builds a model of "Beijing innovation cluster, Hebei integrated manufacturing, Tianjin R&D and shipping" mode, gradually realize the "national circulation" to feed back the "international circulation".
“双循环”新格局与京津冀高质量协同发展: 基于价值链分工和要素流动视角
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206004
[本文引用: 1]

京津冀地区经历了从竞争、合作到迈向高质量协同发展的过程,在“双循环”新发展格局下,京津冀协同发展面临着新挑战和新目标,亟需实现创新驱动经济转型。本文从价值链分工和要素流动等方面入手,系统梳理了京津冀在“外循环”和“国内大循环”中的价值链地位和辐射能力,以及以“京津冀小循环”为表现的京津冀协同发展现状。结果发现,京津冀在“外循环”中没有形成世界级城市群相对应的技术分工和知识生产能力,处于价值链较低附加值环节;在“国内大循环”中,京津冀占据价值链高附加值环节,并向外输出技术和资本,但吸引和辐射力有限。进一步探究发现,京津冀在“外循环”中相对边缘化的重要原因之一是“京津冀小循环”尚未打通,创新成果难以在城市群内部转化,从而未能实现“创新驱动经济增长新引擎”的城市群定位目标。下一阶段京津冀城市群应以水平知识链、梯度创新链为驱动,构建城市群垂直产业链。具体来说,“内循环”中应着力打造“北京研发—天津高端制造—河北物流服务”协同格局,“外循环”中构建以知识转移和市场突破为核心的“北京创新集聚溢出—河北综合制造—天津研发、航运”分工模式,逐步实现“内循环”反哺“外循环”。
The evolution process and growth mechanism of global cross-border M&A network
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110014
[本文引用: 1]

Cross-border M&A (mergers and acquisitions) is an important way for enterprises to carry out overseas strategic layout, which has a significant impact on the pattern evolution of world economic geography. Based on record data of global cross-border M&A transactions from 2001 to 2017, a national-based network for the global scales is established to explore the evolution process and growth mechanism of global cross-border M&A network via the complex network analysis, the GIS method, and the spatial gravity model. Several conclusions can be drawn as follows. (1) The scale, density, and scope of the global cross-border M&A network have increased slightly, while there exists a trend of decentralization. (2) There is a sign that the center of gravity has been shifting from Western Europe and North America to the Asia-Pacific region for global cross-border M&A network, which is mainly driven by China. However, Chinese import and export of cross-border M&A largely rely on Hong Kong, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands and so on. (3) There is a process of division and integration for condensing subgroup of global cross-border M&A network. Among them, the scope of condensing subgroup led by the UK and the US has been narrowed, while that led by China has been expanded, and the European condensing subgroup has been further integrated. (4) The evolution of global cross-border M&A network to varying degrees was influenced by the indicator attributes for each country (region), which was in turn related to the science and technology level, offshore financial center, as well as proximity indicators, which were related to geographical conditions, language and history. However, natural resource endowment and economic market size for cross-border M&A linkages only have one-way (receiving or output) effect, and economic proximity index is not significant in 2009 to 2017.
全球跨境并购网络的空间格局演化及形成机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110014
[本文引用: 1]

跨境并购是企业实施全球化战略的重要途径,对世界经济地理格局演化具有重大影响。本文基于2001—2017年全球跨境并购交易记录数据建构网络,借助复杂网络分析、GIS空间技术以及引力模型等方法,对全球跨境并购网络的空间格局演化及其形成机制进行探讨。研究发现:① 全球跨境并购网络的规模、密度、范围均有小幅度增长,并存有去中心化趋势。② 全球跨境并购方和标的方的空间分布重心出现由西(欧美)向东(亚太)转移的迹象,其首要推动者为中国,但中国跨境并购联系的出入口依赖于中国香港、英属维京群岛、开曼群岛等地区。③ 全球跨境并购网络社团的空间组织范围总体与世界大区的范围保持吻合,其中全球最大的社团由英美主导但其凝聚范围出现收缩,中国主导的亚太社团凝聚范围得到扩大,德法主导的社团对欧洲进一步整合。④ 研究期内国家(地区)科技发展水平和离岸金融中心等属性要素,以及国家(地区)间地理、语言以及历史的邻近性要素始终是驱动网络形成的重要动力,而自然资源禀赋、经济市场规模指标在2009—2017年对跨境并购联系的形成只产生了单向(接收或发出)影响,经济邻近性作用失效。
Functional differentiation of Chinese cities participating in the dual circulation: Chinese companies' global expansion perspective
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211056
[本文引用: 1]

The expansion of leading Chinese companies facilitates the circulation of production factors, and endows cities with the dual role of participating in the internal and external dual circulation. The dual circulation strategy implies that China should "rely on the internal circulation of domestic demand and innovation as the main driver of the economy, and balance emphases on both internationalization and self-sufficiency". In this context, recognizing the functional differentiation of cities participating in the dual circulation is of great significance. Drawing on the organizational network of Chinese companies in the Forbes Global 2000 and Fortune Global 500 list in 2018, this research applies the interlocking network model to map the domestic and international connectivities of Chinese cities. In doing so, it uncovers cities′ different roles in participating in the internal and external circulations, as well as their intermediary functions in the dual circulation. Based on their major business activities, we further divide companies into four sectors: advanced producer service, consumer service, manufacturing, as well as mining and construction. This allows us to examine the sectoral differentiation of cities′ functions. We find that, administrative ranking and level of economic development have a significant impact on Chinese cities′ ability to participate in dual circulations. Our results also suggest hierarchical characteristics: national-level industrial centers have extensive global connections, and they are able to provide high-level products and services. Industrial centers at a regional level, by contrast, have stronger domestic connections, providing lower-level products and services to surrounding areas. Besides, different sectors shape various network structures and city functions. In the network shaped by advanced producer services, cities with high administrative rankings are able to participate the dual circulation; for the general service sector, the ability to participate in dual circulation is more affected by the level of economic development. By contrast, in the case of the manufacturing industry, a larger number of cities are involved in the dual circulation process, with a more scattered spatial distribution; in terms of the mining and construction industries, cities with resource advantages can widely participate in the dual circulation.
中国城市链接国内国际双循环的职能分异: 基于中资企业海内外扩展的视角
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211056
[本文引用: 1]

重要中资企业的海内外拓展布局,促进了生产要素的循环流动,也赋予了作为空间载体的城市参与链接国内国际循环的双重角色和职能分工。在“加快构建以国内大循环为主体、国内国际双循环相互促进”的新发展格局背景下,认清城市参与双循环的职能分异,对于科学评估城市融入双循环的能级水平具有重要意义。研究从福布斯全球企业2000强和《财富》世界500强中资企业的全球组织网络出发,利用链锁模型映射了企业视角下中国城市的国内国际联系网络,解析了城市参与链接国内国际循环和担任中介节点的职能分异,并分高级生产性服务业、一般服务业、制造业和采矿建筑等四种行业解析了职能分异的行业异质性。研究发现,中国城市链接国内国际循环的职能分异受行政等级和经济发展水平的影响显著,具有明显的层级性。其中,国家级产业中心城市,具有明显的对外服务职能;区域级中心城市,则具有更强的对内服务职能。不同类别行业塑造的网络格局和城市职能分工具有明显差异。
The restructuring of global industrial chain and the upgrading of China's industrial chain
全球产业链重构趋势与中国产业链升级研究
An analytical framework on regional economic resilience from the perspective of evolutionary strategic coupling
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210293
[本文引用: 1]

In the contexts of on-going global political-economic shifting and shocks of multi-scalar crises, regional economic resilience has become one of the key themes in economic geography for exploring regional development dynamics. Regional economic resilience is not only about local economic configurations and adaptability, but also related to extra-regional dynamics. Thus, it paradigmatically requires adopting a geographically multi-scalar and dynamic network perspective. This paper attempts to integrate the concept of strategic coupling from the GPN theory into the EEG-based regional economic resilience thinking, and to comparatively review the literature related to the two parts by bibliometric methods. Based on that, by focusing on different modes of evolutionary strategic coupling (including coupling, decoupling, and recoupling), the paper constructs an analytical framework of regional economic resilience from the perspective of strategic coupling in evolution. The paper concludes that: (1) any mode of strategic coupling is an agency-based process of strategic change and context-responding, which can be regarded as the core to understand the scalarity and the source of ability for regional economic resilience. (2) The two concepts come across several epistemological similarities on “connectedness”, “contextual sensitivity” and “path development”, and their integration can help to advance the understanding of regional economic resilience. (3) The agent's agency, motives, the degree of embeddedness and modes of strategic coupling are the keys to understand the ability and mechanism of regional economic resilience. This can also help to form a “local-global relational interaction” perspective to comprehensively explore the structural properties (regional advantages), processes (recovery, renewal, and reorientation), ability (recoverability, transformability, and renewal ability), and consequences (multiple development paths) of regional economic resilience. This paper argues that the perspective of strategic coupling in evolution can deconstruct the conventional “regionalism” wisdom of regional economic resilience, which can systematically help explore the causal mechanism of multi-scalarity, multi-agentic processes and multi-factor involved impacts in regional economic resilience. Moreover, this study fosters the integrative innovation between the relational and evolutionary paradigm and makes a practical contribution to corporation decision-making and regional economic development in China under the current “Double Circulation” strategy.
战略耦合演化视角下的区域经济韧性分析框架
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210293
[本文引用: 1]

在全球政治经济变局和多尺度危机冲击语境下,区域经济韧性已成为当下经济地理学探究区域发展动态的核心议题。区域经济韧性不仅有关本地经济属性和适应力,更受到外部联系动态的影响,在范式上需融入多尺度网络动态观。本文将全球生产网络理论中的战略耦合概念纳入到演化经济地理学的区域经济韧性思想中,对两部分文献进行计量分析和梳理对比。在此基础上,以战略耦合不同模式(即耦合、去耦合、再耦合)为切入点,构建了一套基于“战略耦合演化”的区域经济韧性分析框架。研究结论:① 任何一种战略耦合模式,均是一种“战略性求变”和“语境应对”的能动行为过程,是理解区域经济韧性尺度性与能力来源的核心。② 两者在“连接度”“语境敏感性”“路径发展”概念上有较高的思想共性,相互融合可提升区域经济韧性的理论内涵。③ 战略耦合的能动主体、目的、嵌入性程度及方式是理解区域经济韧性特征和机制的关键,有助于从“地方-全球连接互动”的视角来综合分析区域经济韧性的初始属性(区域优势)、过程(恢复、更新和转型)、能力(恢复力、转型力和更新力)和结果(多元路径发展趋势)。本文认为战略耦合演化视角有利于破除以往“区域主义”韧性思想,能更科学地剖析区域经济韧性的多尺度语境依赖、多主体能动过程和多要素互动机制。此外,有利于推动关系与演化经济地理范式的融合创新,对“双循环”战略下中国企业决策和区域经济发展有重要现实意义。
Research progress of regional economic resilience and exploration of its application in China
DOI:10.2307/142031 URL [本文引用: 1]
区域经济韧性研究进展和在中国应用的探索
Economic resilience and spatial divergence in the Guangdong-Hongkong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China
粤港澳大湾区经济韧性的特征与空间差异研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200418
[本文引用: 1]

当前区域经济韧性的测度研究的测度维度较为单一地聚焦在GDP之上,缺乏揭示韧性在其它经济指标上的表现;同时过于注重区域内因素,忽略了外向联系的影响。因此,本研究以粤港澳大湾区为例,选择5个经济指标对大湾区的经济韧性进行多维度测算,并借助关系经济地理学理论视角,对区域内部差异的形成原因给予解释。主要得到三个结论:第一,区域的经济韧性难以从单一维度来判定,多维度指标所揭示的经济韧性存在显著差异,其中GDP所表现出来的区域经济韧性较为保守,而就业指标所表现出来的经济韧性变动较大。第二,大湾区内部各城市的经济韧性存在显著差异,这些差异与区位和GDP规模无显著关系,而与其产业经济结构和嵌入全球生产网络方式有显著关系。第三,湾区城市在经济韧性表现的差异可以用战略耦合来进行初步解释,深圳因自主耦合而经济韧性表现最佳,佛山和广州次之,香港和澳门因以依附耦合的方式嵌入全球金融和酒店网络,因而经济韧性相对较差。本文为经济韧性研究提供了大湾区案例和新的分析视角,推动了关系经济地理学在经济韧性研究中的应用。本文建议未来要重视基于定性方法的经济韧性研究。
Regional industrial development and evolution: Path dependence or path creation?
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 1]

Regional development is a process in which industries develop, transform and upgrade constantly. Evolutionary economic geography understands the spatial evolution of firm, industry, cluster, network, city and region through the lens of firm entry, growth and exit, and argues that regional industrial evolution is path dependent and determined by inter-industrial technological relatedness. However, path dependence theory overemphasizes the endogenous factors in regional industrial development and ignores the critical role of external linkages and institutional factors, which would bring path creation for regional development. In China, there has been dramatic transformation in regional industrial structure since the economic reform. Empirical studies indicate that technological relatedness has indeed significantly determined regional industrial evolution, suggesting a path dependent process. Meanwhile, marketization, globalization and regional decentralization provide great opportunities to create new industries for regional development. In particular, external linkage, institutional factors and purposeful and strategic actions of local actors would stimulate path creation.
区域产业发展演化: 路径依赖还是路径创造?
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 1]

区域发展是区域产业不断演化、转型与升级的过程。近年来发展起来的演化经济地理学旨在通过分析企业进入、成长、衰退和退出等动态过程阐释企业、产业、集群、网络、城市和区域的空间演化,认为区域产业发展演化遵循路径依赖,并决定于产业技术关联。然而路径依赖式演化理论过于强调内生发展过程,忽视了外生因素和制度变革带来的路径创造机会。中国处于经济转型时期,区域产业结构变动剧烈。技术关联推动了区域产业演化,显示中国区域产业演化具有路径依赖性,同时市场化、全球化和分权化的经济转型过程为区域产业发展创造了新路径。外部联系、制度安排、行为主体的战略性行为等促进了路径创造。
The principle of relatedness in China's regional industrial development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012010
[本文引用: 1]

Geographical distribution and agglomeration of industries have been a long lasting concern of economic geographers. Some studies have stressed geographical proximity and industrial agglomeration as the key driving force of uneven distribution of industries. Recently, evolutionary economic geography, based on evolutionary economics, has adopted a dynamic and historic perspective to study the evolution of regional industrial dynamics. It argues that geographical proximity is neither sufficient nor necessary for efficient knowledge spillovers; instead, it calls for more attention to the idea of cognitive proximity as well as its importance in regional industrial dynamics. The idea is that for knowledge spillovers to take place effectively, some kind of cognitive proximity in terms of shared competencies must be in place. Inspired by this, we examine China's regional industrial development through the lens of cognitive proximity, and propose the "principle of relatedness", that is, the probability of a region to enter/exit one specific economic activity is heavily dependent on regional pre-existing economic profile and local knowledge base. This paper first introduces some key, relevant concepts, and then reviews empirical studies that are underpinned by the "principle of relatedness". Furthermore, it discusses the applicability of "principle of relatedness" in the Chinese context. Our main findings are as follows: (1) theories on resource base view and knowledge spillovers both support the existence of the "principle of relatedness"; (2) the "principle of relatedness" enables us to better understand China's regional economic development, innovation and resilience; however, (3) the effectiveness of the "principle of relatedness" may be compromised by external shocks and internal institutions. One policy implication from the "principle of relatedness" as well as our empirical research is that Chinese regions should seek to diversify related industries and enhance related variety of their regional profiles. In doing so, they are able to become more economically resilient and achieve more sustainable economic development.
中国产业发展与布局的关联法则
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012010
[本文引用: 1]

产业地理学研究产业空间分布及其动态演化规律。基于地理邻近性的集聚理论揭示了产业地理不平衡分布的内在机制。演化经济地理学借鉴演化经济学的历史视角,从历史角度考察经济活动空间分布的渐进演化机制,认为地理邻近性不是产业地理格局演化的充分必要条件,以认知邻近性为核心的多维邻近性能够提供更好的解释。本文从认知邻近视角系统地分析了中国区域产业发展与布局动态演化规律,总结出中国产业发展与布局的“关联法则”,即一个企业或区域进入(或退出)某项经济活动的概率是该企业或地区拥有的基于相关知识基础的经济活动的函数。本文全面地回顾了关联法则涉及的关键概念,梳理企业和区域尺度的实证研究成果,讨论关联法则在中国的适用性及其补充和拓展。本文指出:① 在认知邻近视角下,基于资源转换和组织学习等理论基础,关联法则研究了企业或区域发展新产业与现有产业之间的关系。② 关联法则不仅适用于中国企业和区域尺度,还会影响区域经济发展、创新和韧性等。③ 外部联系、冲击以及内部制度环境等可能会降低区域产业动态对本地产业基础的依赖性。关联法则指出中国区域需培育内生发展模式,围绕现有区域能力、技术和知识积累发展区域产业和实现区际产业优化布局与分工,逐步建立相关多样化的产业体系,增强区域韧性,支撑国内经济循环。
Spatial evolution process of China's regional development pattern in big changes unseen in a century
百年未有之大变局下中国区域发展格局演变
Research progress of glocal innovation networks
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.05.007
[本文引用: 1]

Against the background of economic globalization and technological development, innovation network has been a heated topic in the field of economic geography research. However, the scale of research of innovation network remains debatable. Among the global, nation, and local scales, which one is important? The concept of “glocalization” provides a new perspective to this research. Glocalization refers to the twin process whereby, firstly, institutional arrangements shift from the national scale both upwards to the global scale and downwards to local configurations and, secondly, economic activities and inter firm networks are becoming simultaneously more localized/ regionalized and transnational. Based on solid theoretical reviews, this article defines the concept of glocal innovation network and then discusses the main issues and research methods of glocal innovation networks. In this article, glocal innovation network is defined as the sum of knowledge network channels of various innovators, for example, firms, universities, and research institutes, which increasingly connect globally scattered innovation resources together. Local innovation networks, which are the sub-networks of global innovation networks, are connected by trans-local knowledge flows. Glocal innovation networks are organized by the negotiation among industrial associations and technology alliances and their members. Network knowledge measurement is the suitable method to analyze the structure, evolution, and mechanism of glocal innovation network. The concept of glocal innovation networks provides a new perspective to analyze the approaches of local/regional innovation capabilities promotion and economic development by utilizing global and local knowledge. We conclude that existing research remains at the stage of conceptual discussion and case studies. Therefore, the following issues should be further studied: (1) glocal innovation network evolution dynamics and its connection with economic development; (2) comparative study of glocal networks of different industries and technologies; (3) characteristics of Chinese glocal innovation networks, which can provide empirical evidence of latecomer regions in the catching-up process for further theoretical discussion.
基于全球—地方视角的创新网络研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.05.007
[本文引用: 1]

全球化、创新驱动是新时代的重要特征之一,创新网络成为经济地理学者关注的热点领域之一。在评述现有创新网络研究成果的基础上,本文界定了全球—地方创新网络的内涵和特征,论述了其类型、结构、作用机理和分析方法,并得出结论:全球创新网络与地方创新网络是不可分割的有机体,地方创新网络是全球创新网络的子系统,知识流是创新网络各主体之间联系的重要纽带,行业协会、技术联盟与成员之间的多次协商是全球—地方创新网络的重要组织方式,而网络知识测量方法则能较好地实现定性分析结论与统计计算结论的融合,能较好地刻画、模拟全球—地方创新网络的形态、结构、演变和机理。从服务国家建设和推动中国创新地理学发展的目标出发,有必要开展基于中国国情和视角的全球—地方创新网络机理与区域经济增长之间互动关系的研究,启动不同产业领域的全球—地方创新网络的比较分析,检验网络知识测量方法的可靠性和准确性。
Literature review and prospect on innovation network
创新网络研究进展述评与展望
Evolutionary characteristics of science and technology cooperation network of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its influencing factors
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206005
[本文引用: 1]

Building a hierarchical and reasonable structured science and technology cooperation network plays a very important role in promoting collaborative innovation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (BTH). This paper analyzes the evolutionary characteristics of the science and technology cooperation network between cities in the BTH during 2013-2018 from two perspectives: the research cooperation network based on knowledge innovation and the technology cooperation network based on technology innovation. This paper uses micro data of collaborative papers and collaborative patents and applies social network analysis to examine the evolutionary characteristics of the science and technology cooperation network between cities in the BTH from 2013-2018, and empirically tests the influence of 78 pairs of city in the study area on the science and technology cooperation based on panel econometric model factors. The main conclusions can be drawn as follows. First of all, the rapid growth of the research cooperation network of the BTH presents a spatial structure characterized as the twin cores of Beijing and Tianjin, with Beijing-Tianjin as the main axis and Beijing-Baoding-Shijiazhuang as the secondary axis. Second, the BTH gradually formed a technical cooperation network structure with Beijing as the main center, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang as secondary centers, Langfang, Baoding and Cangzhou as tertiary hubs, and other cities as nodes. Finally, small distance plays a positive role in science and technology cooperation between cities, and the compression of spatial and temporal distance brought by the operation of high-speed rail can weaken the spatial attenuation coefficient of science and technology cooperation. Compared with research cooperation, technical cooperation is more sensitive to spatial distance. Technological proximity is the main driving factor for promoting science and technology cooperation between cities, especially the promoting effect on technological cooperation is more obvious. The smaller the gap of economic development, the easier it is to generate science and technology cooperation cooperation between cities.
京津冀科技合作网络的演变特征及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206005
[本文引用: 1]

构建层次分明、结构合理的科技合作网络对于推动京津冀协同创新具有非常重要的作用。本文从基于知识创新的科研合作网络和基于技术创新的技术合作网络的角度,使用合作论文和合作专利数据,采用社会网络分析法对2013—2018年京津冀地区地级及以上城市之间科技合作网络的演变特征进行了分析,并基于半参数估计和面板计量模型实证检验了影响京津冀78个城市对之间科技合作的主要因素。主要结论为:① 京津冀科研合作网络快速成长,呈现北京与天津双核引领,以京津为主轴、京保石为次轴的空间结构。② 京津冀逐渐形成了以北京为主中心,天津、石家庄为次中心,廊坊、保定、沧州为三级枢纽,其他城市为节点的技术合作网络结构。③ 空间距离越近的城市之间越容易产生科技合作,高铁开通带来的时空距离压缩可以减弱科技合作的空间衰减系数;相对于科研合作,技术合作对于空间距离更为敏感;技术邻近性是促进城市间科技合作的主要驱动因子,尤其是对技术合作的促进效应更为明显;经济发展差距越小的城市之间相对容易产生技术合作。
The study of regional innovation network patterns: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration
区域创新网络模式研究: 以长三角城市群为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.07.002
[本文引用: 1]

网络范式的兴起赋予城市创新模式新的内涵,引起了经济地理学者对不同空间尺度知识流动和创新联系的关注。基于网络视角,以中国知识产权局2014年长三角城市群26个地级市合作发明专利信息为原始数据,借助Ucinet、ArcGIS等分析工具,从本地和跨界多维空间尺度,刻画长三角城市群创新网络结构,测度城市创新网络地位,评价城市创新能力,进而对城市创新模式进行划分。研究表明:①研发密集的大型国有企业、中外合资企业和知名的理工科院校具有较高的知识生产能力,成为长三角城市群创新合作优先链接主体;②长三角城市群重视外部知识获取,跨界网络成为重要的创新合作途径,地理距离对创新合作空间载体选择的制约减弱;③创新网络位置影响知识获取和城市创新,网络视角下的长三角城市群呈现四类创新模式,密集的“本地—跨界”创新网络有助于城市创新。研究结论对长三角城市群不同类型创新模式的优化升级具有一定的参考价值。
Progress, problems, and strategies of innovation and development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.09.001
[本文引用: 1]

Building an international science and innovation center is the strategic direction for the sustainable development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA), and it is also an important spatial carrier for China to cope with future global competitions. On the occasion of the third anniversary of the promulgation and implementation of the "Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Development Plan Outline", by reviewing the main progress and problems of the innovation and development of the region, this article presents the strategic re-thinking of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area international science and technology innovation center under the new situation. The GBA has initially entered the stage of "innovative economy" development. Platform construction, talent agglomeration, and policy support have continued to be strengthened. Diversified cross-regional innovation collaboration models have emerged, but real challenges also exist in the areas of R&D output quality, resource allocation, and structure of talents. On the basis of continuing to consolidate the progress made in the construction of an international science and technology innovation center in the region, it is necessary to focus on the acquisition of innovation resources and improvement of innovation capabilities and the coordination and redistribution of innovation resources in the future, with continuous strategic optimization and adjustment.
粤港澳大湾区创新发展的进展、问题与战略思考
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.09.001
[本文引用: 1]

建设国际科技创新中心是粤港澳大湾区打造国际一流湾区的战略方向,也是中国应对未来全球竞争的重要空间载体。值《粤港澳大湾区发展规划纲要》颁布实施3周年之际,论文通过梳理粤港澳大湾区创新发展的主要进展、问题,对新形势下建设粤港澳大湾区国际科技创新中心进行战略再思考。粤港澳大湾区已初步进入“创新经济”发展阶段,平台建设、人才集聚与政策配套持续强化,多样化的跨区域创新协同模式不断涌现,但是在成果质量、资源配置、人才结构等方面存在现实挑战。在继续巩固粤港澳大湾区国际科技创新中心建设已有的基础上,未来应从“创新资源的获取与创新能力的提升”“创新资源的协同与再分配”等方面持续进行战略优化与调整。
Progress of environmental effects of international trade: A global-local perspective
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.08.012
[本文引用: 1]

Trade-environment relationship is one of the major manifestations of the coupled human-environment system, exhibiting significant complexity and uncertainty. Studies on the environmental effects of trade (EET) seek to explore the complementary or competing relationship between free trade and environment conservation, and give birth to a series of theories and hypotheses. Since globalization has witnessed increasing global-local interactions, this article outlines a framework of global connection, national power, and regional development to review existing studies on EET. It highlights how the process (flows) and the outcome (stocks) of trade work together to generate EET. Based on neo-classical international trade theory, this study identifies three types of stocks, namely location, growth, and regulation. In contrast, the integration of international trade and investment indicates the importance of intra-industry trade. This study shows that existing literature on EET is primarily based on the global and national scale, showing a "top-down" trend, where the role of environmental regulation stands at the center. However, these studies failed to incorporate the localized factors and neglected the interaction between trade policy and environmental regulation. They are also confined to the "north-south" trade and cease to follow the changing geography of trade. Accordingly, this article argues that EET studies should pay closer attention to regional development from a "glocalization" perspective to: (1) consider the expanding trade-induced regional inequality; (2) adapt to the coexistence of intra-and inter-industry trade; and (3) produce a proper scale for the coordination between trade policy and environmental regulation.
“全球—国家—地方”尺度下的国际贸易环境效应研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.08.012
[本文引用: 1]

贸易与环境关系是理解人地关系的重要方面,是“人—地”相互作用复杂性与不确定性的集中体现。国际贸易环境效应研究旨在探究自由贸易和环境保护之间的互补或互斥关系,由此催生了一系列具有关联性和竞争性的理论假说。本文结合全球化过程中全球联系强化、地方力量崛起和国家力量变革等特征,分别从全球联系、国家力量和地方发展3个层面梳理了现有贸易环境效应理论假说和实证研究,指出贸易环境效应是贸易过程(流量变化)与贸易影响(存量累积)共同作用下的结果。建立在比较优势基础上的存量因素包括经济增长、环境规制与地理区位,而贸易与投资一体化的特征则揭示了产业内贸易的重要性。由此,本文发现既有研究更多地建立在比较优势的基础上探讨全球与国家层面的贸易环境效应,表现出“自上而下”的特征,强调环境规制的作用。同时,也存在局限于南北国家关系、对地方化特征关注较少、对贸易政策与环境规制协调机制的理解有待深化等不足。据此,本文提出全球地方化进程中的区域发展分析将为贸易环境效应研究提供有益补充,其作用为:①实现对贸易引致的区域不均衡性的考量;②满足产业内与产业间贸易并存的分析需要;③为协调环境规制与贸易政策提供合宜的尺度。
A review of China's natural resource flows in response to the evolution of globalization
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211204
[本文引用: 1]

In response to the changing globalization process and its uncertainty, we should get a better understanding of China's exchanges of natural resources with the world, which lays the foundation of national resource security and promotes sustainable development. The international division of labor has experienced development from inter-industrial trade, intra-industrial trade, to global value chains. These phases offer quite different insights into the natural resource flows of China. Recent advances primarily focus on the direct exchanges of natural resources between nations as well as the indirect flows of resources embodied in trading goods. The literature demonstrates four mismatches of China's natural resource flows: the mismatch between steady ramping demand and highly concentrated supply, between high intensity and low efficiency of resource utilization, between endowment differences and flow directions of resources, and between global improvement and local deterioration. Future efforts should be made to extend the theoretical perspective and respond to the rising uncertainties. Regarding the extension of theoretical perspectives, the introduction of global production network theory provides a holistic framework to investigate how firm linkages shape the routes of resource flows. Such an investigation represents the changing strategy of China's globalization from bringing-in to going-global. It can also contribute to the emerging research agenda of natural resource governance in China. In response to the rising uncertainties of globalization, we should deepen the understanding of the resilience of the network of natural resource flows and the dual circulation development pattern of natural resources.
全球化变革下的中国对外自然资源流动及其关键研究问题
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211204
[本文引用: 1]

应对全球化变革及其不确定性,认识中国对外自然资源流动的特征与问题,是保障国家资源安全的基础,对实现高质量、可持续发展有重要意义。对应国际劳动分工从产业间贸易、产业内贸易到全球价值链的不同阶段,理解中国对外自然资源流动有不同的理论视角。现有研究主要关注自然资源以原始形态和制成品中的隐含形态在国家之间的流动,讨论了中国对外自然资源流动在供给与需求、利用强度与效率、资源禀赋与流向,以及全局与局部影响之间的矛盾。未来研究仍面临理论和现实的挑战。在理论方面,适应全球价值链分工发展,引入全球生产网络理论探讨企业间互动关系如何塑造自然资源流动路径,能更好地适应中国从“引进来”向“走出去”的转变,以及当下自然资源综合治理的研究需求。在现实方面,应对日益增强的不确定性,亟需深化对自然资源流动网络韧性,以及“双循环”互促关系的认识。
Environmental economic geography: Recent advances and future challenges
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210667
[本文引用: 1]

Environmental economic geography emerges as a reflection of the marginalization of the environment within the discipline of economic geography. It seeks to re-establish the linkage between economic geography and the environment. After almost two decades of development, environmental economic geography is still suffering from its poly-vocal, fragmented, and marginalized issues. This study scrutinizes the debates over the research agenda on environmental economic geography and reviews two primary strands of the literature. On this basis, this study discusses challenges for the future development of environmental economic geography. This study comes to four conclusions. Firstly, the development of environmental economic geography follows the theoretical advances in economic geography. It explore how environmental changes modify the spatial patterns of economic development. It also investigate how the spatial configuration of economic activities responds to the rising environmental risks and intensifying resource scarcity. Two research themes emerge, namely environmental governance and green transition. Secondly, environmental economic geography uses the theoretical framework of the Global Value Chain (GVC) and Global Production Network (GPN) to investigate how firms and regions can simultaneously upgrade in environmental and economic terms. It also seeks to establish the linkages between GVC/GPN governance and environmental governance. On the other hand, environmental economic geography identifies environmental regulation as a locational factor and examines its role in the location choice model. The empirical result offers various counter-examples for classical hypotheses, such as the Pollution Haven Hypothesis, the Porter Hypothesis, and the Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis. Thirdly, environmental economic geography combines its theoretical interests with the theoretical advances in evolutionary economic geography. Particularly, the regional diversification theory and the path creation theory are incorporated into the empirical studies of environmental economic geography, which seek to unravel the conditions and processes of green transitions. Based on these theories, recent studies also offer some predictors for the regional green transition. Lastly, this study proposes that environmental economic geography is still suffering from the divergence between natural science and social science on research paradigm. Besides, the theoretical development of environmental economic geography is subject to a late-comer disadvantage. In this regard, it requires environmental economic geography to become more problem-oriented in the future, embracing the opportunities embedded in the issues for China’s sustainable development.
环境经济地理学的研究现状与挑战
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210667
[本文引用: 1]

环境经济地理学是经济地理学反思资源环境在学科内部边缘化的产物,旨在重建经济地理学理论与资源环境之间的联系。历经近20年的发展,环境经济地理学研究片段化、地位边缘化的问题无明显改观。为此,本文回溯了环境经济地理学的发展思路,归纳了以环境经济地理学名义开展的研究工作,探讨了环境经济地理学发展面临的挑战与应对。研究发现:① 环境经济地理学过去20年的发展思路是以经济地理学理论为基础,探讨适应资源环境变化的经济发展与空间布局模式,凝练了环境治理和绿色转型两个研究主题。② 面向环境治理,环境经济地理学应用全球价值链和全球生产网络理论,探讨企业和地方如何实现环境和经济效益的共同提升;同时,借助区位分析评估作为区位因子的环境规制如何影响经济布局,发现了诸多“经典假说”的反例。③ 面向绿色转型,环境经济地理学与演化经济地理学结合,应用区域多样化和路径创造理论,分析了区域绿色转型的条件和过程。④ 环境经济地理学的未来发展需要克服范式差异、加强问题导向、推动理论创新,挖掘中国丰富的环境经济地理问题所蕴含的机遇。
Some thoughts on the strengthening of geopolitical and geo-economic studies
The rise and fall of the great powers undoubtedly is not dominated by geo-political and geo-economic rules. Since the end of the Cold War, with the rapid economic development of China and other emerging countries, the international power structure is undergoing profound restructuring and the world is entering the new geo-political and geo-economic era. At present, China's geopolitical environment has become increasingly complex and its peaceful development urgently needs geopolitical and geo-economic theoretical support. Based on analysis of the current world geopolitical and geo-economic development trend, this paper discusses the ideological origins on the fundamental role of geography in the development of geopolitics and geo-economics; analyzes the deficiencies of the Chinese geographers in the field of geopolitics and geo-economics; and then puts forward some suggestions how to strengthen the geopolitical geo-economic studies.
关于加强地缘政治地缘经济研究的思考
大国间的争霸与兴衰更替,无疑不受地缘政治和地缘经济法则的支配。冷战结束以来,随着中国等新兴国家经济的迅速发展,国际权力结构正发生深刻重组,世界正在进入新的地缘政治、地缘经济大时代,中国和平发展亟需地缘政治学、地缘经济学的理论支撑。本文在总结世界地缘政治和地缘经济发展态势的基础上,从思想渊源上论述了地理学在地缘政治学和地缘经济学发展中的基础性作用,剖析了当前中国地理学在地缘政治地缘经济领域研究中的不足,进而提出了地理学界如何加强地缘政治地缘经济研究的几点建议。
The progress and prospect of geo-economic research in China and the West
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2022.05.2021393
[本文引用: 1]

Under the reshaping of the world political and economic map, regional grouping promoting the adjustment of global governance, and the change of international system brought about by the game of great powers, it is relevant to sort out the historical context of geo-economics. Based on the clarification of the geo-economic academic thought, this paper selected WOS and CNKI as the literature retrieval library, and used CiteSpace to sketch out the knowledge map of geo-economic research. The results of this study are as follows. Firstly, the geo-economic academic trend of China and the West has experienced the "greening period -development period - backtracking period". The budding period still exists in realistic political logic. The development period is liberal. The backtracking period re-emerged the national political connotation. Secondly, in recent years, the intensity of geo-economic research in the West is much higher than in China. The western authors are mainly distributed in the US, Russia, UK and Italy. The domestic scholars are mainly concentrated in the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yunnan Normal University and East China Normal University. Thirdly, geo-economic literatures have a clear knowledge base and knowledge network, and the highly cited literatures are derived from the works of geography or political science. Geo-economics forms a knowledge structure based on power, and space as the logical starting point, economy as the logical spindle. The evolution process of hot topics is highly coupled with the development of academic thought. Competition in science and technology will become the focus of geo-economics research in the future. This paper suggests that geo-economic research should build a geo-economic theory with win-win cooperation and open development, and strengthen empirical research.
中西方地缘经济研究的进展与展望
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2022.05.2021393
[本文引用: 1]

在科技革命重塑世界政经版图、区域集团化推动全球治理调整、大国博弈带来国际体系变革的背景下,梳理地缘经济研究脉络对于提升地缘经济理论品质具有重大意义。本文在厘清地缘经济思潮发展的基础上,借助Web of Science和CNKI数据库,运用知识可视化工具探究中西方地缘经济知识图谱的演进过程,研究结果如下:①在学术思潮发展层面,中西方地缘经济思潮经历了“萌芽期—发展期—回溯期”,萌芽期存在现实政治逻辑,发展期转向自由主义思潮,回溯期再度涌现国家政治内涵。②在时空演进层面,近年来西方地缘经济研究强度远高于国内,西方作者主要分布在美国、俄罗斯、英国和意大利,国内学者主要集中在中国科学院、云南师范大学、复旦大学等高校和科研机构。③在知识网络层面,地缘经济存在较强的学科交叉属性,拥有明确的知识基础,高被引文献源于政治学或地理学,形成以权力为逻辑基础、空间为逻辑起点、经济为逻辑主轴的知识架构,热点议题演进与学术思潮发展高度耦合,科技竞争将成为当前乃至未来很长一段时间的研究重点。最后,本文认为国内地缘经济研究应突破西方的理论桎梏,构建以合作共赢、开放发展为核心的理论体系,在方法论上应强化定量分析和实证研究。
Study on the spatial-temporal evolution and internal mechanism of geo-economic connections of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201606005
[本文引用: 1]

The interdependence of economics among countries has been distinctly enhanced due to the end of the Cold War and the intensification of globalization. In terms of its content and form, geo-politics has shifted from a "high political area", which focuses on safety, to a "low political area", which emphasizes economics, making geo-economics the focus of the researches. Using tools including Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA), Fragmentation Index and Revealed Comparative Advantage Index, this paper revealed China's evolutionary characteristics of geo-economic connections at the global scale, and explored its internal mechanism by grey relational analysis. The results show: (1) China's geo-economic connections have undergone 4 periods of "Inoculating - Sprouting - Rising - Flourishing", which were significantly correlated to economic development and the industrial restructuring. (2) Labor-intensive industry is currently dominant in China, but capital-intensive and technology-intensive industries are gradually developing, and the disadvantages of primary goods is prominent. (3) China's economic power is heterogeneous across space. The geo-economic connections could be identified as global powers' agglomeration and geographical proximity, but it became homogeneous through time and the diameter of economic power has continuously expanded. China has not only maintained stable geo-economic connections with developed countries like the United States of America, Japan and some European countries, but also strengthened connections with developing countries in Africa and South America. (4) Capital, technology and labor endowments are the main internal driving forces behind the spatial-temporal evolution of China's geo-economic connections, among which capital endowment is the key driving force, technology endowment is the important impetus and labor endowment is the fundamental advantage.
中国地缘经济联系的时空演化特征及其内部机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201606005
[本文引用: 1]

随着冷战结束以及全球化深入发展,国家之间经济相互依存明显加强,地缘政治在内容和形式上从以安全为主的高政治向以经济为主的低政治转变,地缘经济成为研究焦点。本文运用空间探索性方法、碎化指数和显性比较优势指数等工具,揭示中国在全球经济空间中地缘经济联系的演化特征;借助灰色关联度分析方法探索中国地缘经济联系演化的内部机制。结论为:① 中国地缘经济联系经历了“孕育—萌芽—兴起—繁荣”四个阶段,与经济发展以及产业结构调整存在显著的相关性;② 中国的优势部门仍以劳动密集型产业为主,逐步形成资金和技术密集型产业的竞争优势,初级产品劣势日益显现;③ 中国经济权力空间的异质化特征明显,地缘经济联系呈现大国集聚效应和地理临近效应。随着时间推移,地缘经济联系空间趋于均质化,经济权力半径不断向外围拓展,不仅同美日欧等发达国家保持稳定的地缘经济联系,与非洲、拉丁美洲等发展中国家和地区的联系也不断加强;④ 资本禀赋、科技禀赋和人力禀赋是中国地缘经济联系时空演化的主要内在动力,资本禀赋是中国地缘经济发展的核心驱动力,科技禀赋是重要的推动力,人力禀赋是主要的基础优势。
The geo-economics relationship in the Arctic Region
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.02.2018582
[本文引用: 1]

With the impact of climate change,Arctic Region has aroused extensive concerns worldwide. Based on the GDP and trade value (US$) data in 2001, 2006, 2011, 2016, this paper used economic interdependence index, trade status and social network analysis including network density, centrality and PageRank to analyze the geo-economics relationship of Arctic States and regions, considering influence of 13 observers of Arctic Council. Results show that trade flows among Arctic States and regions increased first and decreased afterwards during 2001-2016.The status and influence significantly varied from economy to economy with the unequal relationship in bilateral trade.Geo-economics relationship showed the core-periphery-edge pattern in past few years.Bilateral trade flow between USA and Canada is particularly significant, accounting for more than 70% of inter-Arctic trade flows.In terms of bilateral relations,USA has prominent dominance as Canada is highly dependent on USA economy.Sweden, Denmark, Norway and Finland have important geo-economics influence in the Arctic Region, while Iceland and Greenland have been at the edge positions all the time, however their important geographical locations play a significant role in Arctic affairs, which cannot be ignored. In the geo-economics relationship, performance of Russian Federation doesn't match with its status as a significant international political power, but it has huge potential in economic trade.German, the United Kingdom, France, Japan, Italy, Netherlands and China are countries with significant influence on geo-economics relationship in Arctic Region.Influence of emerging economies represented by China have been enhanced in Arctic Region. In contrast, some traditional economic powers such as United Kingdom, France, Japan, Italy, Canada and Spain were weakening in some degrees. The geo-economics pattern, however, has not been fundamentally changed yet.
北极地区地缘经济关系演变研究
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.02.2018582
[本文引用: 1]

在气候变化的背景下,北极地区的战略地位不断提升,北极事务正深刻地影响着世界格局的演变。以北极8国为基础,进一步考虑北极理事会13个观察员国的影响,基于2001、2006、2011和2016年的GDP和贸易额数据,采用社会网络分析方法,结合贸易依存度和进出口位次分析,全面地揭示北极地区地缘经济关系的演变特征。研究表明:2001—2016年北极地区地缘经济关系先走向紧密,而后有所减弱;不同国家的地缘经济地位和影响力存在显著差异,双边存在不对等的贸易关系,具有明显的“核心-外围-边缘”的特征。美加双边贸易流尤为显著,占到北极国家间贸易流的70%以上;在美加双边关系上,加拿大对美国经济高度依赖,美国拥有充分的主导权;瑞典、丹麦、挪威和芬兰在地区内具有重要的地缘经济影响力,而冰岛和格陵兰地区则长期处于贸易网络的边缘地带,但二者都具有极其重要的地理位置,应引起重视;在北极地区地缘经济关系中,俄罗斯的经济影响力并未与其国际政治地位相匹配,拥有巨大的经贸潜力。德国、英国、法国、日本、意大利、荷兰和中国都是对北极地区地缘经济有显著影响的国家。以中国为代表的新兴经济体的地缘影响力在不断扩大,而一些传统经济大国的地缘经济优势呈不同程度的减弱趋势。总体来说,近年来北极地区的地缘经济关系基本格局并未发生本质变化。
Geopolitical and geoeconomic situation in the surrounding areas and China's strategies
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the introduction of representative Western geopolitical and geoeconomic theories of the late nineteenth century and the twentieth century, this paper analyzes the characteristics of historical and contemporary geopolitics and geoeconomics in China's surrounding areas. It also discusses the basic patterns and trends of geopolitical and geoeconomic situations in the area. The main patterns and characteristics are as follows. China's geopolitical relationship is close and geoeconomic relationship develops at a relatively rapid pace with northern neighboring countries. Its geopolitical relationship continuously develops and prospect of geoeconomic cooperation is very promising with neighboring countries to the west. On the other hand, China's geopolitical relationship with countries to the southwest is very fragile but the geoeconomic relationship has great potential to develop. In the south, China's geopolitical and geoeconomic relationship with neighboring countries is overall healthy, but the issue of South China Sea can be a potential cause of instability. Last but not the least, the geopolitical situation in the area to the east has sensitive and complex hotspots, whereas the structure of geoeconomics maintains relatively stable. This paper puts forward strategies and countermeasures in order to improve the geopolitical and geoeconomic situations, which can be summarized as "Uniting in the North, Advancing in the West, Cooperating in the South, and Extending in the East". More specifically, "Uniting in the North" focuses on building a stable zone geopolitically based on mutual trust, economic and trade ties, science and technology, culture and other fields of cooperation with countries including Russia and Mongolia. "Advancing in the West" means expanding the economic and trade cooperation and cultural exchanges with five Central Asian countries, Russia and West Asia, Eastern Europe and the European Union countries through the development of the "Silk Road Economic Belt", which vigorously promotes the vast development of geoeconomics and creates a favorable geopolitical environment for Western China. "Cooperating in the South" aims at further strengthening traditional cooperative relations with South Asia and Southeast Asia countries by means of negotiation and dialogue, gradually resolving the Sino-Indian border dispute and territorial disputes in South China Sea. It also means promoting regional cooperation between China and ASEAN countries and countries located in the South Asia subcontinent, deepening the strategic friendship relations. All goals under "Cooperating in the South" cannot be accomplished without the development of the China-ASEAN Free Trade Area, the China-Burma-India-Bangladesh economic corridor and the twenty-first century maritime Silk Road. At last, "Extending in the East" places emphasis on breaking the first and second island chain encircled China set by USA and Japan and makes an ambitious plan that captures the mastery of the seas in 2020.
中国周边地缘政治与地缘经济格局和对策
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

在对19 世纪末和20 世纪西方代表性地缘政治与地缘经济理论进行重点介绍的基础上,分析了中国周边地缘政治与地缘经济的历史和现状特点,阐述了中国周边地缘政治与地缘经济的基本格局与发展态势,即:北部地缘政治关系紧密,地缘经济发展较快;西部地缘政治关系持续发展,地缘经济合作前景广阔;西南部为地缘政治破碎带,地缘经济极具潜力;南部地缘政治与地缘经济关系总体良好,但南海问题是不稳定因素;东部地缘政治热点问题敏感复杂,地缘经济结构相对稳定。最后提出了改善提升中国周边地缘政治关系与发展地缘经济的“北联、西进、南合、东拓”地缘战略及对策建议。
Key research direction of China's geopolitics in the next decade
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201702001
[本文引用: 1]

Rise and fall in strength along with changes in the balance of power are most likely to happen among world powers in the next decade and beyond. Consequently, both world and regional patterns will change accordingly, and the importance of geopolitical researches will become increasingly significant. China's geopolitics has obtained satisfying achievements in the past several decades. However, China's geopolitics is still now in a developmental stage. A focused direction and unification of force are the top priority of China's geopolitics. Literature research methods and expert consulting methods have been adopted in this paper to conclude and summarize five key research directions of China's geopolitics. They are geo-setting analysis theory and method, geo-structure and future changes of global geo-setting, regional response to co-construction of "One Belt and One Road" and geo-setting faced by China, national geo-strategies of a peacefully rising China, and big data integration and service platform construction of a geo-setting. Also, the current research status and future research ideas of each key research direction are demonstrated. Finally, the internal relations among these five key research directions as well as the insufficiencies in development ideas of domestic and foreign geopolitics are discussed.
未来十年中国地缘政治学重点研究方向
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201702001
[本文引用: 1]

未来十年乃至更长时间,世界大国之间最有可能发生实力盛衰,权力转换,世界格局和区域格局发生相应变化,地缘政治研究的重要性将会日益凸显。中国地缘政治学在过去的几十年发展中取得了可喜的成绩,但是仍然处于发展阶段,凝练方向、汇聚合力才是当前中国地缘政治学当务之急。采用文献研究法和专家咨询法,归纳了未来十年中国地缘政治学重点研究的五个方向,即地缘环境解析理论与方法、地缘结构与未来全球地缘环境变化、共建“一带一路”的区域响应与中国面临的地缘环境、和平崛起的中国国家地缘战略和地缘环境大数据集成与服务平台建设,并对每一个重点研究方向阐明了其原因和各研究方向的当前研究现状、未来研究思路。最后对五个重点研究方向之间的内在联系以及国内外地缘政治学发展思路的不足进行了探讨。