1 引言
中国共产党十九届五中全会对增进民生福祉提出明确要求,指出要改善人民生活品质,不断增强人民群众的幸福感,促进人的全面发展和社会全面进步①(① 央广网. 改善人民生活品质 提高社会建设水平.
幸福是一种生活状态[6],幸福研究的科学性不仅是国际学术研究的热点,也是分析中国发展的重要视角[7]。其中,对国民幸福感的分析是幸福研究的重要主题。幸福感是个体基于自身生活经历而产生的对其生活质量的综合评价[8]。因此,幸福感研究关注的是个体在客观环境中的主观感受[9],是人积极的生活体验或生活质量的总体状态感知[10],它不仅取决于物质条件,更取决于主观需求的满足[11-12]。一方面,经济发展是增进幸福感的前提条件;另一方面,在经济发展中实现人的精神满足是实现幸福状态的关键[13]。以往研究多从经济学、社会学和心理学视角出发[14],探索特定群体的幸福感,包括老年群体[15-16]、农民群体[17]、城市移民群体[18]、旅游劳工移民[19-20];分析特定区域内的幸福感[21],包括北京、广州等一线城市[2,6]、环渤海地区[7],以及欠发达地区[22]和更小范围的低收入社区等[23];亦有研究探索特定领域的幸福感,例如休闲中的幸福感[24]。但在此之外,基于大规模地理格局的幸福感研究还有待拓展。
何种因素影响着国民幸福感?影响因素分析也是幸福感研究的重要领域,以往研究基于不同思路进行维度划分,典型方式是宏微观要素的区分,个体微观要素包括性别、年龄、婚姻状况和收入[25]等,宏观要素涉及区域要素[26]、社会和经济状况等宏观指标[27]。另一种划分方式是经济、文化、社会、政策管理等多维区分。经济角度以经济增长水平[28]和城市发展规模[29]为代表;从社会角度出发,常见影响因素包括受教育水平[30-31]、适应于中国特殊国情的户籍制度、公共服务支出水平等要素[29];环境角度包含城市空气[32]、社区环境、健康环境等[33-34];在管理层面,研究发现涵盖政府效率、公共物品供给、财产权利保护等指标的政府质量对幸福感的影响甚至要大于经济增长[35]。研究指标和方法上,早在21世纪初,学者就指出发展的终极目标是人民的幸福,这种幸福与客观衡量指标之间并无直接关联,更多的是一种主观感受[36]。因此,诸多研究验证了满意度对幸福感的重要影响[37]。总体看来,以往研究大多从指标体系探索幸福感,但面对具有整体性的幸福感,传统的测度结果存在局限[38]。因此,亟待探索适用于包含多维度的、涵盖大尺度区域的幸福感研究方法。
要解决上述实践和理论需求,从地理空间角度对幸福感进行规模性分析至关重要。人的幸福感是地理学研究的重要主题,其根源于人地关系是地理学的研究核心[39]。近年来兴起的发展地理学关注人发展水平和生活品质,关注如何提升人类幸福[40]。在城市化建设分析中,“幸福”城市也是建设的重要目标[41]。在此背景下,研究者也逐渐认识到从地理学视角分析幸福差异的重要价值,已有研究基于特定省域对幸福感进行了空间分异研究[38],也指出主体主观幸福感存在地理空间差异[42]。但是在区域分析之外,地理学研究具有综合性和区域性特点[43-44],大尺度研究至关重要,但幸福地理学研究中对尺度问题的讨论仍属空白[45]。基于此,本文基于全国尺度,采用规模数据分析与幸福感密切相关的生活状况感受的空间分异格局;从多维度的影响因素出发,系统性分析中国城市居民生活状况感受的影响机制。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 研究区域与数据来源
本文采用国务院发展研究中心2020年“中国民生调查”课题组的调查数据。数据获取过程中采用多阶段分层设计、PPS系统抽样技术,调查对象为18~74岁的城乡居民。该数据的研究单元是作为行政单元的地级及以上城市,覆盖到全国31个省(自治区、直辖市),共包括164个地级及以上城市。另外,由于本文主要关注城市居民的生活状况感受,因而筛选出数据库中回答居住地为“城镇”的人口样本,并剔除掉遗漏问题或大量问题不予回答而导致数据缺失较多的样本,最终得到样本的数量为26370份。
2.2 生活状况感受及其评估方法
在2020年中国民生调查中,涉及到居民生活状况感受的问题主要有3个:① 与2019年比较,您今年的总体生活状况是否有所改善?② 总体而言,您对自己目前生活状况的评价是什么?③ 您对未来生活信心如何?3个问题均设置5个选项,对应0、25、50、75、100五个等级的评分,其中问题①中“0~100”的评分标准分别对应“明显不如以前”“比以前差一些”“没变化”“有一定改善”和“有明显改善”;问题②中“0~100”的评分标准分别对应“非常不满意”“不太满意”“一般”“比较满意”“非常满意”;问题③中“0~100”的评分标准分别对应“没有信心”“信心不足”“一般”“比较有信心”“非常有信心”。在此基础上,利用主成分分析法对以上3个问题的评分进行权重计算,最终以问题①评分占比为31.78%,问题②评分占比为35.00%,问题③评分占比为33.22%进行加权计算,得到城镇居民生活状况感受的评分。
2.3 研究方法
2.3.1 趋势面分析
本文采用趋势面分析法,衡量中国地级及以上城市居民生活状况感受空间分异格局的趋势,计算公式如下:
式中:
本文采用二阶多项式计算趋势值,计算公式如下:
式中:
2.3.2 冷热点分析
采用冷热点分析(Getis-Ord
式中:Xj是空间要素j的属性值;
2.3.3 主成分分析
主成分分析法可以通过对原始数据变量相关系数矩阵或协方差矩阵相关关系的分析,综合提取原始数据中的信息以代替原始变量,并达到降维的目的。新的综合变量之间能够保留原始变量的绝大部分信息,使问题得到最佳综合[49]。其计算步骤为:① 预处理后的原始数据构造标准化矩阵;② 对标准化矩阵计算相关系数矩阵R = (
式中:rij是变量xi和xj之间的相关系数;
(5)计算主成分载荷矩阵以及主成分得分,其中载荷矩阵表示原始数据的协方差矩阵的特征值。
最后,将原始样本数据带入主成分的表达式中即可计算出主成分得分。
2.3.4 分层模型
本文主要关注中国城市居民的生活状况感受,但是由于不同规模的城市间可能存在较大的差异,在影响因素分析时,不仅要考虑到个体层面因素对居民幸福感的影响,也要考虑到城市层面因素的影响。在涉及到多个层面的影响因素时,一般的多元线性回归模型或者多元Logistic回归模型可能无法准确评估影响变量的结果,而多层回归模型则能有效解决涉及多个层面影响因素分析的问题,同时可用于分析个体层面与城市层面的交互效应对城市居民生活状况感受的影响。
基于城市居民生活状况感受在不同规模等级城市之间可能存在差异的假设,本文将建立具有随机系数的多层模型,其中,个体层面的模型形式如下:
式中:Yij代表城市j中居民i的生活状况感受;β0j表示第j个个体的平均水平;βij表示个体层面中自变量对因变量的效应值,体现了由于个体不同而导致的因变量Y对平均水平的系统性偏离;X1ij表示个体层面因素中能反应不同个体特征的自变量;γij表示个体层面的随机误差项。
在城市层面,进一步将城市规模等级的影响因素纳入模型,以分析城市规模等级差异对城市居民生活状况感受的影响;βij在不同区域可能不同,具体的模型形式如下:
式中:γ00表示全部城市层面的平均水平;γi0系数反应各效应层级变量的效应值;X2ij表示城市层面的变量对于城市居民生活状况感受影响的主效应,而γij则反映城市层面的变量X2与第一层变量的交互效应;μij表示城市层面的随机误差项。
最终得到的混合模型为:
3 城市居民生活状况感受的水平及空间差异
3.1 城市居民生活状况感受的区域分异
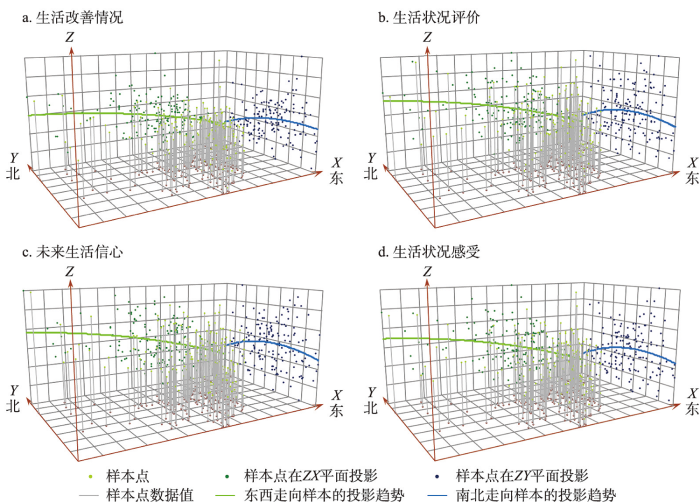
利用趋势面分析法分析中国部分地级及以上城市居民生活改善情况、生活状况评价、未来生活信心以及生活状况感受的分异方向(图1)。中国城市居民生活改善情况整体上呈现出自西向东逐渐下降的趋势,在南北方向上,自北向南生活改善情况逐渐变好,在中部偏南达到高值后趋势放缓,而后趋于定值;城市居民生活评价状况与未来生活信心的区域分异走势具有极大的一致性,即东西方向分异明显,呈现出自西向东下降的趋势,在南北方向上,自北向南先显著上升,而后略有下降趋势,最低值在北方。就城市居民生活状况感受而言,在东西方向上,自西向东呈现出明显的下降趋势,西部城市居民的生活状况感受最高;在南北方向上,自北向南呈现出先上升后轻微下降的变化趋势,在中部偏南达到最高值。可以看出,生活改善情况、生活状况评估、未来生活信心三者的分布格局呈现较高的一致性,一方面说明中国民生调查中3个涉及生活状况感受的问题能够联合描述生活状况感受的区域分异;另一方面,现有研究对生活状况感受调查多为对现状评价,该结论也说明国民在评价生活时采用的是一种具有历史性和过程性的视角,过去的改善与对现状的感知紧密相连,对现状的感知亦与未来信心紧密相关。
图1
图1
城市居民生活状况感受趋势面分析结果
Fig. 1
Results of the trend surface analysis of urban residents' perceptions of living conditions
3.2 城市居民生活状况感受的空间关联特征
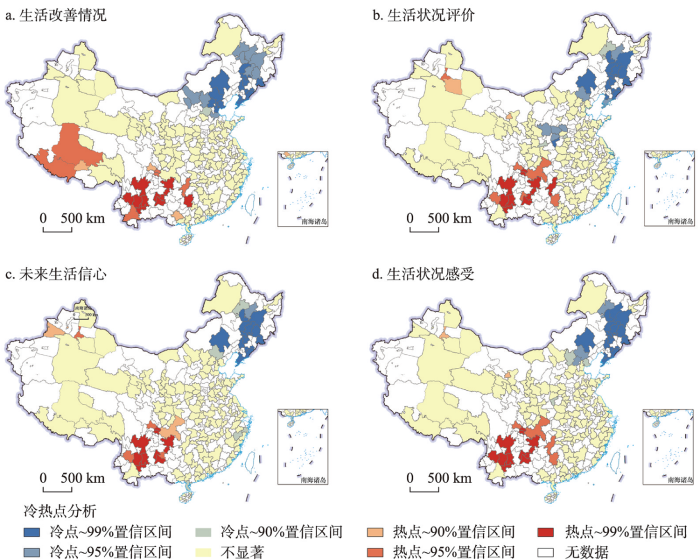
利用冷热点分析法进一步识别中国城市居民生活改善情况、生活状况评价、未来生活信心以及生活状况感受的热点区和冷点区,也即高值集聚区和低值集聚区。由图2可以看出,城市居民人口的生活改善情况在空间上呈现出显著的连块集聚特征,低值集聚区集中在中国的东北地区,主要包括25个城市,平均得分为50.12,高值集聚区位于西南地区,部分分布于中南地区,主要包括20个城市,平均得分为58.55。城市居民的生活状况评价在空间上呈现出“块状集聚与零散分布并存”的空间特征,其中,低值集聚区除了分布于东北地区,在华北地区与中南地区交界处也有分布,主要包括24个城市,平均得分为65.29;高值集聚区主要分布于西南地区和中南地区,在西北地区的青海省和内蒙古自治区也出现零星的高值集聚区,主要包括19个城市,平均得分为70.51。城市居民对于未来生活信心的空间低值集聚区主要分布于东北地区,主要包括20个城市,平均得分为73.50,高值集聚区主要分布于西南地区,新疆维吾尔自治区边境处也形成高值集聚区,该类城市主要有16个,平均得分为79.20。城市居民生活状况感受在空间上与其他3个指标情况相似,低值集聚区集中于东北地区,主要包括21个城市,平均得分为62.79,高值集聚区主要位于西南地区,在与西南地区接壤的中南地区也有分布,主要包括18个城市,平均得分为68.83。
图2
图2
中国城市居民生活状况感受冷热点分析结果
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1825号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Results of the hotspots and coldspots analysis of urban residents' perceptions of living conditions
3.3 城市居民生活状况感受的空间格局特征
利用ArcGIS 10.5软件对中国城市居民生活改善情况、生活状况评价、未来生活信心和生活状况感受4个指标进行空间可视化,并利用自然断点法将各项指标的得分均值划分为5级,在此基础上进一步对比4个指标在不同地理区域分区间的空间分布差异(图3)。西南地区城市居民生活改善情况的得分均值最高,为57.39,但不同城市之间存在一定的分异;华北地区这一数值最低,仅有49.37,其中低值主要集聚在河北省和内蒙古自治区的部分城市。西南地区与西北地区的城市居民生活状况评价相差不大,且显著高于其他地区,其中西南地区这一数值为70.68,西北地区为68.69。城市居民未来生活信心是4项指标中得分均值最高的一项,西南地区这一指标的均值达到78.10,比较而言东北地区最低,为71.64,值得注意的是,按照自然断点法分类后,该地区的大多数城市均处于中下等水平,成为名副其实的“洼地”。就城市居民生活状况感受而言,西南地区得分均值显著高于其他地区,达到68.75,华北地区和东北地区得分均值较低,分别为62.37和62.04,其余地区这一指标的得分均值差距不大。
图3
图3
2020年中国地级及以上城市居民生活状况感受及相关指标的空间分布格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1825号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 3
Spatial distribution pattern of perceptions of living conditions and related indicators of urban residents at the prefecture level and above in China in 2020
4 城市居民生活状况感受的影响因素分析
4.1 自变量选取
本文从城市居民个体和城市两个层面分析城市居民生活状况感受的影响因素,具体的解释变量说明及描述性统计如表1所示。在城市居民个体层面,选取性别、年龄、受教育程度、婚姻状况、工作情况、户口类型等个体特征变量,以及对城市公共服务满意度评价。其中城市公共服务满意度评价具体包括政府部门服务评价、社会保障状况评价、公正执法状况评价、食品安全状况评价、住房状况评价、教育状况评价、医疗服务评价、交通状况评价和环境状况评价这9个细分指标,并利用主成分分析法获得9个具体指标的权重,从而算得城市公共服务满意度评价的结果;在城市层面,选取基于常住人口数量划分的城市规模等级这一解释变量。针对上述自变量进行VIF共线性检验,发现VIF的值均小于3,说明自变量之间不存在多重共线性。
表1 变量名称、赋值及描述
Tab. 1
| 变量名称 | 变量赋值 | 均值/占比(%) | 标准差 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 因变量 | |||
| 生活状况感受 | 连续变量 | 65.11 | 20.44 |
| 自变量 | |||
| 个体层面(N=26257) | |||
| 性别 | 1=男,2=女 | 1(50.4),2(49.6) | 0.500 |
| 年龄(岁) | 1=18~34,2=35~59,3=“≥60” | 1(39.6),2(52.3),3(8.1) | 2.584 |
| 受教育程度 | 1=“初中及以下”,2=“普通高中/职高/中专/技校/大学专科”,3=“大学本科”,4=“研究生及以上” | 1(18.7),2(48.3),3(30.0),4(3.0) | 1.653 |
| 婚姻状况 | 1=“未婚”,2=“已婚”,3=“同居”,4=“离异或丧偶” | 1(20.7),2(73.3),3(1.0),4(5.1) | 0.641 |
| 工作情况 | 1=“有工作”,2=“没有工作” | 1(74.2),2(25.8) | 0.438 |
| 户口类型 | 1=“非农业户口(城镇户口)”,2=“农业户口”, 3=“居民户口” | 1(59.0),2(27.2),3(13.8) | 0.724 |
| 城市公共服务满意度评价 | 连续变量 | 67.91 | 18.93 |
| 政府部门服务评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 72.219 | 24.022 |
| 社会保障状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 70.590 | 24.818 |
| 公正执法状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 71.764 | 24.603 |
| 食品安全状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 68.860 | 23.569 |
| 住房状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 70.527 | 24.819 |
| 教育状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 67.282 | 25.847 |
| 医疗服务评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 65.890 | 25.963 |
| 交通状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 70.965 | 24.849 |
| 环境状况评价 | 0=“非常不满意”,25=“不太满意”,50=“一般”, 75=“比较满意”,100=“非常满意” | 71.980 | 23.969 |
| 城市层面(N=162) | |||
| 城市规模等级 | 1=“中小型城市”,2=“大城市”,3=“特大城市”,4=“超大城市” | 2.600 | 0.893 |
现有研究中对于生活状况感受的研究多为对现状生活的评价,本文中对于生活状况感受的评价综合考虑到生活改善情况、生活状况评价以及未来生活信心,使用主成分分析法降维,最终利用3个指标的综合得分来评价城市居民生活状况感受。
4.2 模型结果及实证分析
本文利用分层模型分析中国城市居民生活状况感受的影响因素。首先,建立空间模型,用以检验多层模型的适用性以及个体和城市两个层面对因变量解释的效果差异。结果显示见表2,组内相关系数(ICC)为0.219,且在给定显著水平α为0.05的前提下,概率p值为0.000,小于给定显著水平,即可以认为不同城市间居民生活状况感受存在显著差异。因此分层模型能够比单一层次的模型更好地解释城市居民生活状况感受的差异。
表2 2020年中国地级及以上城市居民生活状况感受影响因素的回归结果
Tab. 2
| 变量名称 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 个体层面 | 性别(女性) | 1.545** | 0.666** | 0.639** | 0.639** |
| 年龄(18~34岁) | |||||
| 年龄(35~59岁) | -0.941** | -0.027 | -0.051 | -0.056 | |
| 年龄(≥ 60岁) | 5.589** | 5.770** | 5.944** | 5.943** | |
| 受教育程度(初中及以下) | |||||
| 受教育程度(普通高中/职高/中专/技校/大学专科) | 2.517** | 1.750** | 1.863** | 1.854** | |
| 受教育程度(大学本科) | 5.865** | 3.463** | 3.654** | 3.635** | |
| 受教育程度(研究生及以上) | 4.365** | 4.463** | 5.069** | 5.046** | |
| 婚姻状况(未婚) | |||||
| 婚姻状况(已婚) | 0.212 | 0.568* | 0.472 | 0.459 | |
| 婚姻状况(同居) | -1.751 | 0.458 | 0.345 | 0.331 | |
| 婚姻状况(离异或丧偶) | -6.470** | -3.184** | -3.367** | -3.376** | |
| 工作情况(无工作) | -2.864** | -1.315** | -1.245** | -1.235** | |
| 户口类型(城镇户口) | |||||
| 户口类型(农村户口) | -2.223** | -0.699** | -0.773** | -0.768** | |
| 户口类型(居民户口) | -0.477 | -0.059 | 0.031 | 0.018 | |
| 城市公共服务满意度评价 | 5.912** | 5.865** | 5.937** | ||
| 城市层面 | 城市规模等级(大城市) | ||||
| 城市规模等级(中小型城市) | 1.242** | 1.273** | |||
| 城市规模等级(特大城市) | -0.342 | -0.332 | |||
| 城市规模等级(超大城市) | -2.611** | -2.666** | |||
| 交互项 | 城市公共服务满意度评价×中小型城市 | -0.143 | |||
| 城市公共服务满意度评价×特大城市 | -0.051 | ||||
| 城市公共服务满意度评价×超大城市 | -0.251* | ||||
| 样本量 | 26370 | 26370 | 26370 | 26370 | |
| 调整R2 | 0.028 | 0.44 | 0.443 | 0.443 | |
| F值 | F(12, 26357) = 64.710 | F(13, 26356) = 1593.731 | F(16, 26353) = 1310.252, | F(19, 26350) = 1103.701 | |
注:*:p < 0.05,**:p < 0.01;括号内为该变量的说明。
在此基础上,表2构建了4个模型:模型1仅考虑个体特征因素,模型2加入了城市公共服务满意度评价,结果显示2个模型中个体层面的影响因素结果较为一致,主要的发现如下:① 相较于男性,女性的生活状况感受更高。② 年龄对城市居民生活状况感受的影响是非线性的,相较于18~34岁的群体,35~59岁城市居民的生活状况感受显著较低,但当加入城市居民对于城市公共服务满意度评价时,该指标不再显著,而≥ 60岁的城市居民生活状况感受则显著提升。③ 就受教育程度而言,相较于初中及以下学历的城市居民,其他群体生活状况感受普遍较高。④ 是否结婚并不会显著影响城市居民的生活状况感受,但离异或丧偶会导致城市居民生活状况感受下降。当加入城市居民对于城市公共服务满意度评价时,已婚(有配偶)的城市居民生活状况感受显著提升。⑤ 无工作者的生活状况感受更低。⑥ 相较于拥有城镇户口的城市居民,户口类型为农村户口者生活状况感受更低。模型2加入了城市居民对于城市公共服务满意度评价,发现该指标与城市居民的生活状况感受呈显著的正向相关关系,说明城市居民对城市公共服务满意度越高,其生活状况感受越强。传统上看,经济增长是生活状况感受提升的动力[50],但前文发现的“西高东低、南高北低”的空间格局和本部分发现的生活状况感受受到的年龄、性别、工作状况、婚姻、户口状况等要素的综合影响可知,生活状况感受是一项融合个体生活状况的综合感知。例如西部地区的总体经济发展水平虽然低于东部地区,但总体生活状况感受并不低于东部,其原因在于受到地区人口总体年龄、工作状态、婚姻状态等其他要素影响,也是未来可具体探索的方向。
城市层面的结果显示,在控制其他变量影响的基础上,以常住人口规模为100万~500万的大城市作为参照对象,发现中小型城市(常住人口规模< 100万)居民的生活状况感受相对较高,超大城市(常住人口规模≥ 1000万)居民的生活状况感受相对较低,而特大城市(常住人口规模为500万~1000万)居民的生活状况感受与大城市(100万~500万)没有显著差异。在模型3的基础上,模型4进一步考虑个体对城市公共服务满意度评价与城市规模等级的交互效应,用以反映这一因素在不同规模等级城市的差异。结果显示:① 与大城市相比,在中小型城市中,城市居民对城市公共服务满意度评价与其幸福感的关系没有显著差异;② 相较于大城市而言,超大城市中城市公共服务满意度评价这一指标对城市居民生活状况感受的正向影响被削弱。一方面可能是因为相较于其他城市,超大城市的社会公共服务往往更为完善,因而对于超大城市而言,社会公共服务提升居民幸福感的边际效应相对于其他城市更低;另一方面超大城市中城市居民生活状况感受的影响因素会更加多元化。
模型5控制了个体层面变量,将城市公共服务满意度评价进一步细分,发现各指标均会对城市居民生活状况感受产生显著的正向影响。在模型5的基础上,模型6和模型7以其他城市作为参照,进一步考虑各因素与超大城市之间的交互效应,用以反映这些因素在超大城市与其他城市之间的差异。结果显示(表3):与其他城市相比,在超大城市中,城市居民对于医疗服务评价和交通状况评价对其生活状况感受的正向影响作用会相对较弱。可能的原因在于,对于超大城市的居民而言,高质量医疗和便捷的公共交通已经是司空见惯的状况,因此对生活状况感受的边际效益不如其他城市明显。另外,规模等级越低的城市,其公共服务设施往往基础比较薄弱。近年来,随着统一的城乡医疗保险制度、基本公共服务均等化等政策的推动,医疗服务质量的提升以及交通状况的改善对规模等级较低城市的居民生活状况感受产生了较强的边际提升作用。综合前文的生活状况感受总体格局“西高东低”的格局来看,以西部地区的中小规模等级城市为例,相关政策的落实在西部地区人民生活状况感受的总体提升中发挥了较大作用。
表3 2020年中国地级及以上城市公共服务指标对城市居民生活状况感受影响的回归结果
Tab. 3
| 变量名 | 模型5 | 模型6 | 模型7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 个体层面 | 控制 | 控制 | 控制 |
| 政府部门服务评价 | 2.386** | 2.357** | 2.284** |
| 社会保障状况评价 | 4.759** | 4.725** | 4.681** |
| 公正执法状况评价 | 1.619** | 1.598** | 1.600** |
| 食品安全状况评价 | 1.146** | 1.150** | 1.246** |
| 住房状况评价 | 3.895** | 3.816** | 3.777** |
| 教育状况评价 | 1.757** | 1.768** | 1.729** |
| 医疗服务评价 | 1.030** | 1.103** | 1.254** |
| 交通状况评价 | 0.822** | 0.823** | 0.957** |
| 环境状况评价 | 0.553** | 0.518** | 0.490** |
| 城市规模等级(超大城市) | -2.105** | -2.046** | |
| 政府部门服务评价×超大城市 | 0.336 | ||
| 社会保障状况评价×超大城市 | 0.249 | ||
| 公正执法状况评价×超大城市 | -0.036 | ||
| 食品安全状况评价×超大城市 | -0.495 | ||
| 住房状况评价×超大城市 | 0.194 | ||
| 教育状况评价×超大城市 | 0.153 | ||
| 医疗服务评价×超大城市 | -0.817* | ||
| 交通状况评价×超大城市 | -0.623* | ||
| 环境状况评价×超大城市 | 0.139 | ||
| 样本量 | 26370 | 26370 | 26370 |
| 调整R2 | 0.462 | 0.464 | 0.464 |
| F值 | F(21, 26348) = 1080.700, p < 0.001 | F(22, 26347) = 1038.375, p < 0.001 | F(31, 26338) = 737.945, p < 0.001 |
注:*:p < 0.05,**:p < 0.01。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
本文基于全国大尺度区域空间,采用大规模民生调查数据,采用趋势面分析、冷热点分析、主成分分析和分层模型等多维度分析方法,探索中国城市居民生活状况感受空间分异格局和多维度影响因素,为幸福地理学的理论推进提供数据与理论支撑。研究结论为:
(1)中国城市居民生活改善情况、生活状况评价、未来生活信心以及生活状况感受的分异呈现以下特征:① 生活改善情况整体上呈现出自西向东逐渐下降、自北向南逐渐提升的态势;② 生活评价状况与未来生活信心的空间分异具有一致性,即自西向东下降,自北向南先显著上升,而后略有下降趋势,最低值在北方;③ 居民生活状况感受在西部城市最高,自西向东明显下降,自北向南呈现出先上升后轻微下降的变化趋势,在中部偏南达到最高值。
(2)就空间聚集状况看,① 城市居民人口的生活改善情况在空间上呈现出显著的“连块集聚”特征,低值集聚区集中于东北,高值集聚区集中于西南,分散于中南地区;② 城市居民的生活状况评价在空间上呈现“块状集聚与零散分布并存”的特征,其中,低值集聚区集中于东北,零散分布于华北地区与中南地区交界,高值集聚区集中于西南地区和中南地区,零散分布于西北地区的青海省和内蒙古自治区;③ 城市居民对于未来生活信心的空间低值集聚区集中于东北地区,高值集聚区集中于西南地区和新疆维吾尔自治区边境处;④ 城市居民生活状况感受的空间低值集聚区主要集中于东北地区,高值集聚区集中于西南地区和与西南地区接壤的中南地区。
(3)在空间分布差异上,① 城市居民生活改善情况均值最高和最低分别位于西南、华北地区;② 城市居民生活状况评价在西南地区与西北地区相差不大,且显著高于其他地区;③ 城市居民未来生活信心在4项指标中均值最高,区域最高位于西南地区,最低位于东北地区,且东北地区大多数城市处于中下等水平,呈现“洼地”状态;④ 就城市居民生活状况感受而言,西南地区均值显著高于其他地区,华北地区和东北地区均值较低。
(4)在城市居民生活状况感受的影响因素方面,涉及个体层面与城市层面多元要素的共同作用。个体层面,女性相比男性的生活状况感受更高;年龄对城市居民生活状况感受的影响是非线性的,相较于18~34岁的群体,35~59岁城市居民的生活状况感受显著较低,但当加入城市居民对于城市公共服务满意度评价时,该指标不再显著,而≥ 60岁的城市居民生活状况感受则显著提升;初中及以下学历的城市居民生活状况感受相对较低;婚姻状况不显著影响城市居民的生活状况感受,当加入城市居民对于城市公共服务满意度评价时,已婚(有配偶)的城市居民生活状况感受显著提升;无工作者的生活状况感受更低,农村户口者生活状况感受更低;城市居民对城市公共服务满意度评价显著正向影响城市居民的生活状况感受。在城市规模层面,相较于大城市,中小城市的城市居民生活状况感受更高,超大城市居民的生活状况感受相对较低,而特大城市居民的生活状况感受与大城市没有显著差异。此外,相较于大城市,超大城市中居民对城市公共服务满意度评价这一指标对城市居民生活状况感受的正向影响会被削弱。
(5)就城市公共服务满意度评价的具体指标而言,政府部门服务、社会保障状况、公正执法状况、食品安全状况、住房状况、教育状况、医疗服务、交通状况、环境状况评价都显著正向影响生活状况感受;与其他城市相比,在超大城市中,城市居民对于医疗服务评价和交通状况评价对其生活状况感受的正向影响作用会相对被弱化。
5.2 讨论
在中国发展中,促进人民福祉的均衡提升是区域均衡发展的最终目标[51],也是新时代国土空间规划需解决的重要问题。以往研究指出了区域非均衡发展造成的资源空间分配不均衡等格局[52],但实际上除了经济和资源的空间分异,社会空间分异也会对地理格局产生重要影响[53]。在此前提下,本文发现了城市居民生活状况感受的不均衡分布,中国城市居民对生活改善情况、生活状况评价、未来生活信心以及生活状况感受的总体感知呈现出西部高于东部、南部高于北部的态势,空间聚集也呈现西部和南部高于东部和北部的格局。研究结论在一定程度呼应了近10余年来出现在多个国家的“伊斯特林”悖论[22],反映出人民的生活状况感受是一个需要对物质环境和精神体验进行统筹考虑的系统工程。
在治理路径上,需要考虑居民生活状况感受受多层次、多维度要素影响。在个体层面,教育的提升能够带来更高的生活状况感受水平,工作状况和城市户口也会带来更高的生活状况感受。城市层面,政府服务、社会管理、城市环境等多维度要素共同作用,并体现出中国特色。例如,对于社会管理中“强政府”角色来说,政府部门服务、社会保障状况,以及公正执法状况能够对生活状况感受产生重大影响。随着城市化进程的不断完善和公民意识的不断增强,社区公共服务也成为居民生活状况感受的来源。以往研究指出,在传统的劳动力流出地,平等开放的高质量公共服务供给是吸引人口回流的重要途径[54],本文进一步解释了高水平的公共服务带来的人的生活状况感受将成为人才选择留居地的重要参照。交通、环境和教育水平反映的是生活环境和精神需求的满足,也能够影响幸福水平。此外,随着“健康中国”战略的不断推进,国民健康意识增强,食品安全状况、医疗服务日益成为生活状况感受的重要影响因素。
此外,城市规模对不同因素在居民生活状况感受上的作用发挥调节功能。在等级规模越高的城市中,住房状况对人们生活状况感受的正向影响越大。但不同的是,在等级规模越高的超大城市中,医疗状况评价对生活状况感受提升的边际作用越小。前者反映了在社会观念和社会管理中,住房状况通过心理满足、社会地位,以及户籍保障等能够影响居民生活状况感受,后者的原因在于中国城市医疗资源聚集于大规模的城市及中心地区[55],并呈现出东高西低的态势[55⇓-57]。对超大城市医疗状况评价来说,生活较久的本地人已经对本地医疗保障习以为常,相比之下,规模较小的城市或偏远地区医疗水平进步对居民生活状况感受的提升作用更大。这种现象也在其他新兴变量中有所体现,例如研究者发现的数字普惠金融对西部地区主观生活状况感受的提升作用相对更大[58]。这一结论说明不同地区在提升生活状况感受时要注重补充“短板”。此外,随着家庭私家车拥有量的不断飙升,越来越多的城市面临愈加严重的交通问题,而对于超大城市来说,早已开始施行“限行”,提倡公共交通等方式应对这一问题,因而可以理解其他城市中,居民对交通状况的评价会更有力地影响其生活状况感受。对该问题的进一步探索也是未来研究有价值的方向。
综合本文的研究结论可以看出,提升居民生活状况感受是一项综合物质和精神要素、客观环境和主观体验、社会优化,以及政府管理等多维度的系统工程,不仅全国不同区域之间的居民生活状况感受城乡分异格局,甚至在同一区域内的不同群体也会产生不同感知,因此要针对不同地区、不同群体有针对性地制定策略。本文为城市居民总体生活状况感受的理论认识和实践判断提供了基础,为治理维度比较和选择提供了参照。未来研究可进一步针对城市不同群体进行分析,从城市居民拓展至乡村居民的生活状况感受研究,并通过对比和综合研判,不断为地理学视角下的生活状况感受研究提供理论支撑,切实为居民创造美好生活,推进居民生活幸福感的提升。
参考文献
Emotional reconstruction of farmers in poverty-alleviated villages from the perspective of emotional geography: A case study of Shibadong village in Hunan province
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003459
[本文引用: 1]

The aim of rural revitalization is to improve the prosperity of farmers. However, farmers are not purely "economics-driven people." In fact, their behavioral logic is driven by internal emotions, which can affect the external environment. At the same time, changes in the external environment can alter a farmer's emotions toward the place. Therefore, research on the emotional reconstruction of farmers in villages where poverty has been alleviated is not only conducive to guiding the direction of construction and governance of such villages and maintaining their harmonious and stable development but also helpful for retaining "returning" farmers. These farmers make up for the absence of the "main body" of the economic development of the village, all of which is significant for the smooth realization of effective connections between poverty alleviation and rural revitalization. For this article, Shibadong Village in Huayuan County, Hunan Province was chosen as the case study, with the "left behind" farmers and "returning" farmers in the village as the research subjects. From the perspective of emotional geography, we used in-depth interviews and participatory observation methods to explore the emotional reconstruction of the farmers and the related mechanism involved under the influence of the targeted poverty alleviation policy. The research showed that 1) the emotional reconstruction of farmers in poverty-alleviated villages mainly includes the reconstruction of five perceptions sense of belonging, sense of happiness, sense of risk aversion, sense of relative deprivation, and sense of loss. 2) The implementation of the targeted poverty alleviation policy has optimized or improved the material space, industrial structure, economic income, and governance services of poverty-alleviated villages, resulting in increases in the farmers' senses of local belonging and happiness and a decrease in their sense of risk aversion. However, an imbalance in poverty alleviation efforts leads to an enhancement of their sense of relative deprivation. The dissolution of traditional cultures and the reconstruction of social relationships result in the farmers feeling lost. These five senses of emotions affect and restrict one another. 3) In the process of emotional reconstruction of farmers in poverty-alleviated villages, the cognition of the individuals is the core force of the process. However, farmers find it difficult to make long-term and wise decisions because of their low cognitive level, which is not conducive to the positive development of emotions. As the leading force driving the emotional reconstruction of farmers, the government—through various poverty alleviation measures—coordinates the order of other individuals participating in poverty alleviation governance, optimizes the rural regional system in the poverty relief village, and improves the farmers' cognition to reshape their local emotions. Enterprises play an auxiliary role in this process, participating in poverty alleviation in various ways. In addition, they facilitate the market economy in optimizing the allocation of resources and improving both the efficiency of poverty alleviation and the resilience of poverty-alleviated villages to resist risks. To consolidate the achievements of poverty alleviation and realize rural revitalization, poverty-alleviated villages should take relevant measures based on the characteristics of emotional space, time, sociality, and hierarchy to cultivate positive emotions, and reduce negative ones, in the farmers. Use of the "place-emotion-behavior" analysis model is helpful for elucidating the interactive processes between the emotions, behaviors, and social material environments of farmers and the significance of those individuals in the reconstruction of the rural regional system in the context of macro policies. This article provides a useful reference for promoting the effective connection between targeted poverty alleviation and rural revitalization.
情感地理视角下脱贫村农户情感重构: 以湖南省十八洞村为例
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003459
[本文引用: 1]

以湖南省花垣县十八洞村为案例地,以“留守”农户和“返乡”农户为研究对象,基于情感地理视角,通过深度访谈法和参与式观察法探究了精准扶贫政策影响下农户情感重构及其重构机制。结果表明:1)脱贫村农户情感重构主要包括归属感、幸福感、风险厌恶感、相对剥夺感和失落感5个维度的重构,这些维度相互影响、相互制约。2)精准扶贫政策的实施使得脱贫村农户地方归属感上升,幸福感增强,风险厌恶感下降。然而,扶贫力度的不均衡导致农户间的相对剥夺感增强,传统文化的消解和社会关系的重构等使得农户产生失落感。3)在脱贫村农户情感重构过程中,农户认知是核心力量,政府行动起主导作用,企业行动发挥辅助作用。政府和企业行动通过重构乡村地域系统的物质空间、经济空间和社会空间刺激乡村地域主体即农户认知转变,继而引发情感的重构。
Impacts of urban built environments on residents' subjective well-being: An analysis based on 15-minute walking distance
城市建成环境对广州市居民幸福感的影响: 基于15 min步行可达范围的分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.08.003
[本文引用: 2]

人民群众幸福感的提升,是新型城镇化的落脚点,改善人居环境是城镇化质量提升的必然要求。既有的社区环境与居民幸福感关系的研究大多基于行政管辖范围评估社区的建成环境状况,且忽视了城市建成环境影响居民幸福感的中间机制。论文基于广州市23个社区采集的问卷调查数据,利用多层线性回归模型、中介效应分析和分层分析,识别影响居民幸福感的建成环境因素,揭示了居住满意度所起到的中介作用,尤其关注缓冲区的重新划定对分析结果的影响,以及建成环境对幸福感影响的异质性效应。结果表明:① 相较于行政管辖范围和1000 m面要素缓冲区,基于15 min步行可达范围所提取的建成环境指标与居民主观幸福感的关联程度更高;② 人均绿地面积、POI点密度与居民幸福感呈正相关关系,人口密度与幸福感呈负相关关系;③ 居住满意度在POI点密度与居民主观幸福感之间的关系中发挥了完全中介作用;④ 异质性分析结果表明,社区建成环境与个体幸福感的关联程度因居民的户籍、住房产权和就业情况不同而呈现显著差异。
Factor components and differences of the park-based recreational happiness for urban residents: A case study of Hangzhou
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2013.09.1074
[本文引用: 1]

In the process of rapid urbanization, the outdoor recreational resources are becoming scarcely. Although the construction of parks can promote recreational welfare and happiness for urban dwellers, few studies have focused on the recreational happiness of park users and its inherent differences, which carried great significance for urban governments to allocate the recreational facilities and services. Thus, this study, taking Hangzhou as a case, carried out a questionnaire survey on the dwellers in urban parks so as to explore the components, spatial disparities and social differences of recreational happiness for urban residents by using the methods of Principal Component Regression and Multivariate Analysis of Variance. The results show that: firstly, the park-based recreational happiness of urban residents exists three dimensions with emotional happiness as the first principal component which can be interpreted by the variables of enjoyment, relaxation and fullness, perceptional happiness as the second component which can be explained by the variables of ‘increasing efficiency at work’, ‘promoting family harmony’ and ‘enhancing personal health’, and social happiness as the third component which can be illustrated by the variables of ‘making new or old friends’, ‘developing interpersonal relationship’ and ‘improving life quality’; secondly, there exist spatial disparities for the recreational happiness of park users,with the large urban parks mainly undertaking the functions of improving the emotional and perceptional happiness and the community parks raising the social happiness for urban residents; thirdly, the four demographic variables, including income, age, education and occupation have significance influences on park-based recreational happiness, which can be further illustrated by the impact of income on the emotional happiness variable, education on social happiness, age on emotional and social happiness, and occupation on the whole components of recreational happiness. Hence the urban governances should allocate the recreational facilities in parks according to the components of recreational happiness and the characteristics of its social and spatial differences.
城市居民公园游憩幸福感的因素构成与差异分析: 以杭州市为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2013.09.1074
[本文引用: 1]

以杭州市为例,对公园游憩者进行问卷调查,运用主成分回归和方差分析法揭示游憩幸福感的因素构成、空间分异与社会差异。研究发现:城市居民的游憩幸福感主要由情感幸福感、认知幸福感和社会幸福感构成,是具有层次性的主观幸福感;公园游憩幸福感存在空间分异性,居民主要通过城市大公园游憩获取情感幸福感和认知幸福感、通过社区小公园游憩获取社会幸福感;公园游憩幸福感存在社会差异性,收入、年龄、文化程度、职业4个变量对游憩幸福感有显著影响。为此,城市政府应以游憩幸福感为核心,根据居民游憩幸福感的感知现状及其空间、社会差异特征进行公园游憩空间的建构与游憩设施配置。
Research on the spatial structure and complex characteristics of tourism destination network: A case study of Yesanpo tourism destination
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20161212
[本文引用: 1]

<p>Tourism destination is a complex adaptive system including many spatial elements which connect with each other composing tourism destination network. Complexity is the inevitable trend of the development of tourism destination network. Taking the Yesanpo tourism destination in Hebei Province as a case, this paper selects four types of tourism elements as the tourism nodes, which are core scenic spots, central towns, rural communities and characteristic gardens, to build the tourism destination network whose edges are the tourism connection strength. Based on the spatial analysis of TOP network, the paper analyzes the spatial structure of tourism destination network and its complexity characteristics. The results show that: 1) There is a hierarchical agglomeration phenomenon in the tourism destination network, which forms the spatial agglomeration units composed of core scenic spots, central towns, rural communities and characteristic gardens and has the dual characteristics of “adjacent connection” and “preferential connection”. 2) Yesanpo tourism destination network obeys power-law distribution, which shows the scale-free characteristic. 3) Compared with the random network, the Top3 and Top5 networks have smaller average path length and larger agglomeration coefficient, showing typical characteristics of “small world network”. 4) The tourist network is a typical heterogeneous network whose degree has a negative correlation, and it shows hierarchical properties since there is an approximate reciprocal relation between the agglomeration coefficient and the degree of nodes. The study also finds that the development model integrating scenic spots, towns, communities and gardens as basic structural unit is of great significance to guide spatial reconstruction of tourism destinations.</p>
旅游目的地网络空间结构及其复杂性研究: 野三坡旅游地案例实证
DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.20161212
[本文引用: 1]

复杂性是旅游目的地网络化发展的必然趋势,是认识旅游地网络空间结构与组织特征的重要研究手段。论文以河北省野三坡旅游地为例,通过构建旅游联系强度模型,建立旅游地空间网络,并运用TOP网络空间分析以及复杂网络理论,揭示旅游地网络空间结构与组织的复杂性特征。研究发现:1)旅游地网络具有空间集聚性,形成了以核心景区为中心,由中心城镇、乡村社区和特色园区共同构成的空间集聚单元,并体现出“邻近连接”与“择优连接”的双重特性;2)旅游地网络服从幂律分布,具有无标度网络特性;3)每个节点的前三名和前五名旅游联系强度网络(Top3和Top5网络)具有较小的平均路径长度、较大的集聚系数,呈现出典型的“小世界网络”特征;4)旅游地网络是典型的异配型网络,度-度呈负相关,而网络节点的集聚系数与其度值之间存在近似的倒数关系,因此具有层次性。
New-type urbanization, well-being of residents, and the response of land spatial planning
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200602
[本文引用: 1]

The urbanization of China has entered the middle and late stage, and the connotation of the people-centered urbanization needs to be further enriched and refined. The land spatial planning is the key to the practice of the new-type urbanization and ecological civilization construction. This paper proposes that the improvement of well-being of residents is the core of the people-centered urbanization. It sorts out relevant domestic and foreign studies on the connotation of well-being, summarizes the subjective and objective measure index systems and methods of well-being, and examines the factors influencing well-being and happiness of residents. In this study, we draw on the experience of foreign spatial planning and take the improvement of the well-being of urban and rural residents as one of the guiding principles for the compilation of land spatial planning. In the process of the practice of land spatial planning, it is necessary to focus on public health, disaster risk assessment system and construction of urban resilience, optimization of "production-living-ecological" spaces, community living spatial planning, fine-scale management, and big data and intelligent decision-making system. Urbanization is the indispensable important component of national spatial planning, and the establishment of national spatial planning promotes the high-quality development of new-type urbanization and the well-being of urban-rural residents. So, we should show great concern on urban scale hierarchy structure, the pattern of population flow network, peri-urbanization and local urbanization, basic allocation and equalization of public service of urban and rural areas, the impacts of climate change and urban disaster risk management, and the basic research of the new-type urbanization, such as the evolution of man-land relationship in the rapid urbanization.
新型城镇化、居民福祉与国土空间规划应对
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200602
[本文引用: 1]

我国城镇化已经步入中后期发展阶段,以人为本的新型城镇化内涵需要进一步丰富和建构。国土空间规划正是新型城镇化建设和生态文明建设落地的关键。本文提出增进居民福祉是以人为本新型城镇化的核心,梳理了居民福祉内涵的国内外相关研究、居民福祉的主客观测度指标体系与方法,归纳了影响居民福祉和幸福感的综合影响因素。借鉴国外空间规划经验,建议把增进城乡居民福祉作为国土空间规划编制的指导思想之一,并在国土空间规划实践中注重公共服务设施优化配置研究、灾害风险评估与韧性城市建设、三生空间优化、社区生活圈规划与精细化管理和大数据与智能决策系统等。城镇化是国土空间规划的重要组成,国土空间规划的科学编制有助于推动新型城镇化的高质量发展和城乡居民福祉提升,需要关注和加强城市合理等级体系、城市人口流动格局网络、半城镇化与就近城镇化模式、城乡基本公共服务配置与均等化、气候变化、城市灾害风险管理以及快速城镇化下人地关系演变等新型城镇化基础研究。
Residents' subjective well-being and influencing factors in Beijing
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.10.003
[本文引用: 2]

Residents in urban China are paying increasingly more attention to the quality of life and personal well-being with the improvement of living standards. Improving residents' quality of life is also an important target of urban development. Scholars have conducted research on subjective well-being from the perspective of psychology, sociology, and economics for a long time. However, only few geographic studies in China have addressed this topic. Among these studies, some were concerned with the evaluation method of happy city or happy region by building an evaluation index system, others focused on small scale case studies that examine the influencing factors of individuals' subjective well-being. These studies show that individual social attributes have significant impact on subjective well-being; subjective well-being is also influenced by socioeconomic factors such as crime rate and employment of a city or region. On the other hand, by reviewing the literature we found that geographers in western countries have conducted much research on the measurement, index system, and influencing factors of subjective well-being. Given the Chinese socioeconomic, policy, and institutional context of the past decades, it is important to examine the unique factors that affect subjective well-being of citizens in China, which has not been adequately covered by existing research. Based on the data from a large survey of 5732 participants conducted in 2013 in Beijing, this article develops an indicator system of individual subjective well-being; it also analyzes the subjective well-being of individuals with different social attributes and estimates the impact of relevant factors on subjective well-being with a multivariate linear regression model. Several conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) Individuals with diverse social attributes are significantly different in subjective well-being. The young and the old are happier than the middle-aged group of respondents. Family income has positive impact on subject well-being. However, people with highest family income are not the happiest. Individuals who are highly educated or have a big family are happier. Household heads, pensioners, high-rank managers of companies, and employees of state-owned enterprises are more satisfied with their lives. (2) The majority of the survey participants gave higher scores on life satisfaction but lower scores on happiness. (3) Policy and institutional factors have significant impact on individual's subjective well-being. Respondents with Beijing hukou feel happier and those living in commercial housing are happier than those living in residence provided by workplace or in affordable housing. (4) Increase of working or commuting time leads to lower happiness. (5) Respondents who changed residence once or twice in the last five years feels happier, but this is not the case with those who changed housing more than three times. Similarly, changing job makes people unhappy. (6) Individuals feel happier if they feel good about the living environment, national policy, personal health, and relative income.
北京居民主观幸福感评价及影响因素研究
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2014.10.003
[本文引用: 2]

随着生活水平的提高,越来越多的居民开始重视自身生活的幸福程度。学术界对个体主观幸福感的关注虽然由来已久,但是鲜见从地理学角度出发的研究,尤其是评价影响主观幸福感的因素。本文以北京为例,基于大规模问卷调查,构建了个体主观幸福感影响因素框架,分析了不同社会属性人群的主观幸福感差异,并利用多元线性回归模型测度了制度与政策等因素对个体主观幸福感的影响。结果发现:不同社会经济属性个体的主观幸福感差异明显;制度因素对个体幸福感有显著影响,拥有本地户口居民的主观幸福感显著高于外地户口居民;工作时间和通勤时间的增加都能降低个体的主观幸福感;迁居能提高个体的生活满意度,然而频繁迁居和更换工作却会降低个体的生活满意度。
How can Chinese people have a higher level of happiness: Based on the survey of China's livelihood index
中国人如何能有更高水平的幸福感: 基于中国民生指数调查
How can public services affect residents' happiness: Empirical tests based on the income-happiness analytical framework
公共服务何以影响居民幸福: 基于“收入—幸福”分析框架的实证检验
From economic to social factors: The changing influence on Chinese urban residents' subjective well-being: 2003-2017
从经济到社会: 中国城镇居民主观幸福感影响因素的变迁: 2003—2017
Measures of subjective well-being: A review
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.010
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, subjective well-being has attracted increasing attention in psychology, economics, and sociology. Geographical studies on the topic in English language is also growing rapidly. Since measurement is the foundation of empirical studies, this article reviews the major approaches to measuring subjective well-being. We first provide a theoretical framework of subjective well-being, in which two major components are identified: the cognitive component which is mainly known as life satisfaction; and the affective well-being which is usually termed as positive affect and negative affect. Each component can be further divided according to its temporal span. Previous studies mainly adopt self-reported scales to measure different components of subjective well-being, while some facial or ecological indicators are also developed to measure short-term emotions. The self-reported scales are quite flexible and probably provide the most proper insights into individuals' subjectively experienced well-being. These scales can be classified into two types: while the reflective scales select items based on a latent model, the formative scales consider the items as different facets which can be aggregated within an aggregate model or profile model. In general, more reflective scales of subjective well-being have been developed as compared to formative scales. The most widely used scales to measure life satisfaction include the single-item self-anchoring scale and the 5-item Satisfaction with Life Scale. Some formative scales such as the 8-item Personal Well-Being Index (PWI) were also developed to assess one's global life satisfaction. The most often applied measures of affective well-being include the single-item Gurin scale, the multi-item core affect model, and PANAS. Special methods such as the Experience Sampling Method and Day Reconstruction Method and artificial indicators such as U-index were also developed to measure emotional experiences in activity episodes. The current article also reviews the strengths and weakness of those measures. In order to reduce the biases and errors of measurement caused by respondents'cognitive process and the artificially assigned weights for various sub-domains, the multi-item reflective scales are recommended. However, future studies should develop better understanding of the convergence among various measures of subjective well-being. It is also necessary to pay more attention to the cognitive mechanism of evaluating global well-being and select proper models in empirical analysis. Based on the review of measures of subjective well-being and empirical studies in English literature, this article proposes some important topics and issues for future studies in Chinese human geography. This review article mainly contributes to existing literature by providing a framework to understand and design measures of subjective well-being and introducing some widely adopted scales which are readily available for the Chinese geographers to collect data in future studies. This article also points out that existing studies about smart cities mainly focus on the application of information technologies in the analysis of urban built environment and human activities. However, not many studies have investigated the question to what extent smart cities may promote people's subjective well-being. Therefore, the measures of subjective well-being summarized in this article may provide a pool of indicators to monitor national well-being and facilitate the development of smarter cities.
主观幸福感度量研究进展及其对智慧城市建设的启示
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.04.010
[本文引用: 1]

智慧城市在学术研究和政策制定中日益受到关注,已有研究侧重于将信息技术用于城市建成环境和人的行为分析,但鲜有研究关注城市居民的主观幸福感。为此,本文对现有关于主观幸福感的量表进行了系统梳理,并对不同形式量表的误差等问题进行了总结。目前的研究大多对生命满意度和情感幸福感分别加以度量。对生命满意度的度量主要采取单条或多条的反映性量表,以Cantril的自我标定梯形量表和Diener等的生命满意度量表为代表;对情感幸福感的度量也以反映性量表为主,包括单条的Gurin量表与多维度的核心情绪量表和PANAS量表。针对短期情感体验的调查,还发展了诸如经验取样法和日重建法等专门的方法。目前主观幸福感的量表仍以自陈量表居多,其中存在很多测量偏差。基于目前主观幸福感的量表体系和西方地理学中关于主观幸福感的研究进展,本文提出了值得未来国内人文地理学研究的几个话题和需要注意的问题。最后,探讨了主观幸福感的量表和相关研究对于智慧城市建设的启示。
Discussion on the structural model of social indicators and quality of life: A study on the life of Shanghai urban residents
社会指标与生活质量的结构模型探讨: 关于上海城市居民生活的一项研究
The research on optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

This paper introduces the "life quality theory". Based on the two-way interactive mechanism between space of rural settlements and the life quality, the paper researches the optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements in three aspects, which are the integration of rural settlement spatial functions, the optimization of spatial structure and the regulation of spatial scale, so as to build optimization mode and framework of spatial organization of rural settlements with high quality life. The study suggests that: (1) The settlement is the spatial carrier of life quality and the life quality is the essential content of settlements. The two mentioned above influence and improve each other. So, the reasonable rural settlement space is the important precondition for higher life quality. (2) The type of spatial function of rural settlements can be divided into livelihood maintaining, industrial developing and quality optimizing, and the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality requires promotion of livelihood maintaining, integration of industrial developing and engagement of quality optimizing. (3) There are two important aspects in the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements. The one is to promote the organic concentration of living space, agricultural space and industrial space, the organic evacuation of social intercourse space, recreational space and services space, and the organic balance of living space, production space and ecological space, in order to realize the reasonable proportion and optimized combination of internal spatial type in settlements. And the other one is to form a functional structure level of "comprehensive village - featured village" and build spatial organization mode of settlements connected by rural roads by switching the location and adjusting the function, with the destruction of underdeveloped villages, the saving of normal villages, the enlargement of important villages, and the construction of new villages. (4) As an ideal mode of rural settlements space optimization oriented by life quality, RROD mode should be built at a rational scale of unit settlement and distance between settlements, leading to an RROD and RROD system with rational structure, auxiliary facility, fully function and well-organized distribution.
基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

引入“生活质量理论”,基于乡村聚落空间与生活质量的双向循环互动机理,从乡村聚落空间功能整合、空间结构优化、空间尺度调控等三个方面研究乡村聚落空间优化问题,试图构建有效提高生活质量的乡村聚落空间优化框架与模式。研究认为:① 聚落是生活质量的空间载体,生活质量是聚落的本质内容,乡村聚落与生活质量相互促进、相互影响,构建科学合理的乡村聚落空间是提高农民生活质量的重要前提。② 乡村聚落空间功能类型可以划分为生计维持型功能、产业发展型功能与品质提升型功能,生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间功能优化,重点在于提升生计维持型功能,整合产业发展型功能,植入品质提升型功能。③ 乡村聚落空间结构优化的重点有两个方面,一是要促进居住空间、农业空间、工业空间有机集聚,社会交往空间、休闲空间、服务空间有机疏散,生活空间、生产空间、生态空间有机均衡,以实现聚落内部空间类型比例合理化与组合最优化;二是要通过聚居区位转换与聚落职能调整,移拆部分衰落村落,保留部分一般村落,扩大部分重点村落,新建部分新型村落,形成“综合村—特色村”的功能结构等级,构建以乡村公路为链接的聚落体系空间组织模式。④ RROD模式是基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化的理想模式,该模式的构建要合理确定聚落单体的规模尺度与聚落之间的距离尺度,引导形成结构合理、设施配套、功能完备、分布有序的RROD和RROD体系。
Enhancing farmers' happiness in common prosperity: Analysis based on economic income-social network-ecological welfare framework
在促进共同富裕中增进农民幸福感: 基于经济收入—社会网络—生态环境框架的分析
The influence of multidimensional deconstruction of stressors on enhancing urban residents' well-being: From the perspective of rural tourism and leisure involvement
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180660
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, the well-being of residents has attracted increasing attention from the public. Previous studies have focused on the impact of large-scale space environment on urban residents' well-being by analyzing the natural environment, social and humanistic environment and the process of urbanization. Few studies have conducted research on the mechanism of urban residents' well-being from the perspective of rural tourism. Based on SEM, this study explores how rural tourism and leisure involvement enhance well-being of urban residents who are under multidimensional stress. SEM shows that: (1) Stressor has a significant positive impact on the adjustment strategy, but not significant to leisure involvement. The impact on different groups is significant. Stress adjustment has a significant positive effect on leisure involvement. (2) Leisure involvement has a significant positive relationship with flow experience and well-being. Flow experience has a significant positive impact on wellbeing. (3) Flow experience has a significant positive impact on leisure benefits, which then have a positive impact on well-being. (4) Flow experience has a significant mediating effect on leisure involvement and well-being. Leisure benefits have a significant mediating effect on flow experience and well-being. (5) There are significant differences in stress adjustment, leisure involvement and well-being among different tourist groups.
城市居民压力源对幸福感的影响研究: 基于乡村旅游休闲参与的角度
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180660
[本文引用: 1]

居民幸福感研究日益受到重视,以往研究多是从自然环境、社会人文环境和城市化进程等方面探讨大尺度空间环境因素对城市居民幸福感的影响。结合乡村旅游的角度探讨城市居民幸福感的影响研究,目前还较少。运用SEM分析方法,探究处于多维压力之下的城市居民旅游者如何通过前往乡村进行旅游休闲活动提升幸福感,进行模型构建与分析,结果显示:① 压力源对调适策略有显著正向影响,对休闲参与不显著,但不同群体影响差异显著,压力调适对休闲参与有显著正向影响;② 休闲参与对心流体验和幸福感具有显著正向关系,且心流体验对幸福感具有显著正向影响;③ 心流体验对休闲效益具有正向显著影响,且休闲效益对幸福感具有正向显著影响;④ 心流体验在休闲参与对幸福感、休闲效益在心流体验对幸福感均具有显著中介效应;⑤ 旅游者不同背景变项在压力调适、休闲参与及幸福感等分别呈现不同程度的显著差异。
The smartphone use and eudaimonic well-being of urban elderly: Based on intergenerational support and TAM
城市老年人的智能手机使用与实现幸福感: 基于代际支持理论和技术接受模型
本研究以城市老年人为研究对象,探讨其智能手机使用行为对幸福感的影响。本研 究整合了幸福感理论和代际支持理论,基于技术接受模型(TAM),建构了一个扩展 的技术接受结构方程模型。研究发现:老年人的感知有用性显著影响智能手机的使用态 度,感知易用性通过中介感知有用性显著影响智能手机的使用态度;代际技术支持显著 影响老年人智能手机使用态度、使用意愿、实际使用和实现幸福感;而感知趣味性对使 用态度无显著影响。本研究提出在信息技术程序开发设计上应考虑惠老,方便老年人使 用;社会应倡导年轻一代对老年群体的代际技术支持以提升其幸福感。本研究的“代际 技术支持”对老年人幸福感影响研究和技术接受模型建构有拓展和贡献。
The impact of built environment on well-being of older adults under different geographic contexts
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180292
[本文引用: 1]

Impact of built environment on older adults’ health has become a hot topic in aging geography research field. As a kind of subjective perception, well-being is influenced much by environment factors. However, bias exists when built environment’s impact on well-being is analysed only under the context of residential neighbourhood. According to the theory of uncertain geographic context problem, the built environment in daily activity space also affects individual’s well-being, not only environment around neighbourhood. For further understanding of the relationship of built environment and well-being, the article discusses the spatial temporal pattern of older people’s daily activity and the characteristic of built environment in different geographic contexts using 2016 survey of Guangzhou older adults. It is indicated that daily trajectories differ among older adults in different health statuses. What’s more, the environment they exposed are totally different as well. Therefore, Logistic regression model is used to analyse different health effects of built environment under separating geographic contexts. It is indicated that built environment affects well-being under all kinds of the geographic contexts, while the built environment of residential neighbourhood and daily activity space influences well-being to the largest extent. Besides, built environment factors in the place of maintenance activity and the place of recreation activity daily activity space have relation with well-being as well. To be more specific, the health effect of built environment like the density of bus stops, the density of green space and the density of intersections varies with geography contexts due to different activity durations, frequencies and purposes under different geographic contexts. The research verifies that built environment influences well-being not only in residential neighbourhood and reveals that geographic context difference exists while we analyse the health effect of built environment. What’s more, the relationship of built environment factors and older adults’ well-being under different geography contexts is also summarized. The conclusion supplements the research of spatial temporal behaviour from the perspective of daily activity and helps to enhance the understanding of built environment’s health effect. It offers a scientific support to the construction of aging liveable city and the provision of active aging health service.
日常活动地建成环境对老年人主观幸福感的影响
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180292
[本文引用: 1]

建成环境对老年人主观幸福感的影响是老龄化地理学的热点话题,仅从居住地视角探讨建成环境影响可能导致研究结果偏差。为更精确揭示老年人日常活动所处场所建成环境与主观幸福感的关系,利用问卷调查等数据,基于老年人日常活动的时空模式及活动地建成环境特征,采用逻辑回归模型对比不同日常活动地建成环境要素对广州市老年人主观幸福感的影响。研究发现:老年人的主观幸福感受到不同活动地建成环境的共同影响,其中,居住地与日常活动空间建成环境对老年人主观幸福感影响的模型伪R<sup>2</sup>最大,而维护性活动地与休闲性活动地能反映出仅考虑居住地视角下忽略的部分建成环境变量。由于老年人在不同活动地的停驻时长、频率和目的不同,日常活动地建成环境对老年人主观幸福感的影响机制也存在差异,主要通过影响不同活动地相应的活动机会和出行环境产生作用。结论从老年人群日常活动的角度补充了时空间行为研究,有助于为老年主动健康服务供给与老龄宜居城市建设提供科学支撑。
Meta-analysis of the influencing factors of Chinese farmers' subjective well-being
中国农民主观幸福感影响因素的Meta分析
Census register discrimination and the loss of urban migrants' happiness: An extended analysis with non-income factors
户籍歧视与城市移民的幸福感缺失: 包含非收入因素的扩展分析
Social integration on the subjective well-being of seasonal tourism immigrants in Sanya
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.12.013
[本文引用: 1]

At present, the theory of Mobility has become a popular research topic in tourism, but there are rarely researches on tourism consumption immigrants among local scholars. This article takes the representative group of tourism consumption immigrants, which is the seasonal tourism immigrants as the research object, constructs the conceptual model of the influence of the social integration of seasonal tourism immigrants on subjective happiness, and proposes relevant hypotheses; Sanya is taken as the case, and the structural equation model is used to verify the hypothesis. The results are shown as follows: 1) The social integration of seasonal tourism immigrants consists of cultural integration, identity integration and psychological integration. This article developed the scale of social integration of seasonal tourism immigrants and tested its dimensions, reliability and validity through exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. 2) The cultural integration of seasonal tourism immigrants has the least impact on subjective well-being, and has only a significant positive impact on positive emotion; while psychological integration and identity integration are positively used for life satisfaction and positive emotion, and have a significant inhibitory effect on negative emotion.3) Sanya has created a superior living space for seasonal tourism immigrants, which not only satisfies the needs of happy life of seasonal tourism immigrants, but also greatly enhances the subjective happiness of them. In addition, the diversity and inclusiveness of Sanya as a tourist city can eliminate the role of cultural integration in promoting subjective happiness. However, conflicts and misunderstandings caused by obvious identity boundaries have greatly reduced the happiness of seasonal tourism immigrants. Therefore, there is an urgent need to improve the identity integration of the seasonal tourism immigrants. Finally, based on empirical analysis, the promotion strategy of subjective happiness of the seasonal tourism immigrants is proposed from the aspects of cultural integration, identity integration and psychological integration.
三亚市季节性旅游移民社会融合对主观幸福感的影响
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.12.013
[本文引用: 1]

以旅游消费移民的代表性群体——季节性旅游移民为对象,构建季节性旅游移民社会融合对主观幸福感影响的概念模型,并提出相关假设;以典型的旅居城市三亚为案例地,运用结构方程模型对假设进行验证。研究表明:季节性旅游移民的文化融合对主观幸福感的影响较小,仅对正面情绪有显著的正向影响;而心理融合和身份融合均正向显著作用于主观幸福感的生活满意和正面情绪2个维度,且对负面情绪有显著抑制作用。基于实证分析,从文化融合、身份融合、心理融合等层面提出季节性旅游移民主观幸福感的提升策略。
The place attachment and subjective well-being of tourism labor migrants in Xi'an Hui community
西安回坊旅游劳工移民的地方依恋与幸福感
The influences of neighborhood environment on residents' subjective well-being: The effects of time dimension
社区环境对居民主观幸福感的影响: 时间维度的作用
Identification and measurement of the response of urban residents' happiness to tourism urbanization agglomeration in Zhangjiajie
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200710
[本文引用: 2]

This paper takes the response of the happiness level of urban residents in less-developed areas to tourism urbanization agglomeration as the research objective. It constructs a model to identify and measure the response intensity of the happiness level of urban residents to tourism urbanization agglomeration. The results show that: (1) The agglomeration of tourism urbanization is a one-way Granger causality of the happiness level of urban residents. (2) Due to the influence of tourism urbanization agglomeration level, the happiness level is affected by different external factors of happiness in different periods, and the grey correlation changes from spiritual cultural environment, natural ecological environment and other non-economic factors to social security environment, life quality environment and other economic factors. (3) The effect of tourism urbanization agglomeration on the happiness level of urban residents is different from the traditional path of improving the happiness level which meeting people's material needs first and then meeting their non-material needs. Instead, it passively improves the "non-material" needs and then drives the "material" needs to improve the happiness level. The research results can provide theoretical support and reference for similar underdeveloped regions to improve the happiness level of residents through the development of tourism urbanization.
张家界城镇居民幸福水平对旅游城镇化集聚的响应识别及测度
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200710
[本文引用: 2]

以欠发达地区城镇居民幸福水平对旅游城镇化集聚的响应为研究目标,构建二者的响应模型,识别和测度了城镇居民幸福水平对旅游城镇化集聚的响应强度。结果表明:(1)通过对张家界旅游城镇化集聚水平与城镇居民幸福水平进行格兰杰因果检验发现:旅游城镇化集聚是城镇居民幸福水平的单向格兰杰因果关系,即旅游城镇化集聚对城镇居民幸福水平具有正向促进作用。(2)由于受旅游城镇化集聚水平的影响,幸福水平在不同时期也受不同幸福外在因素的影响,关联度从精神文化环境、自然生态环境等非经济因素向社会安全环境、生活质量环境等经济因素转变。(3)旅游城镇化集聚对城镇居民幸福水平的作用路径区别于满足人们物质需求后,再满足非物质需求的传统幸福水平提升路径,而是先被动地改善“非物质”需求后继而带动“物质”需求改善以提升幸福水平。研究成果可为同类欠发达地区通过发展旅游城镇化提升居民幸福水平提供理论支撑及借鉴。
Influence of neighborhood social environment on residents' well-being: A case study of typical low-income communities in Beijing city
邻里社会环境对居民幸福感的影响: 以北京典型低收入社区为例
Urban residents' leisure and subjective well-being: Evidences from Guangzhou, China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180710
[本文引用: 1]

With the development of social economy, leisure behavior of urban residents is changing. It is necessary to discuss the issue on urban residents’ leisure and well-being in modern China. Previous studies have explored the relationship between leisure and subject well-being from the perspectives of leisure participation and leisure satisfaction, but discussions on the mechanism between leisure and well-being have not reached a consensus conclusion, and should be further investigated. Leisure activities will inevitably involve leisure time and leisure space, however, most of the existing literature overlooked the influence of the objective factors. This paper expands the study of leisure and subjective well-being with the dimensions of time and space by establishing a structural equation model of “leisure and well-being”. Based on the structural equation model, this study analyzes the impacts of leisure time, leisure space, leisure participation and leisure satisfaction on the subjective well-being, by using the data of questionnaire survey in Guangzhou. The results show that both leisure participation and leisure satisfaction have significantly positive impacts on subjective well-being, which verifies both the activity theory and the need theory. Compared with leisure participation, leisure satisfaction has a greater impact on subjective well-being with a coefficient of 0.394. The results also show that both leisure time and leisure space are exogenous and have positive effects on leisure participation. More concentrated time and less time pressure will significantly improve leisure satisfaction and promote subjective well-being. Leisure space, including leisure places, facilities, environment and atmosphere are also important in leisure activities; however, leisure space does not show any direct impacts, but only indirect impacts on subjective well-being through leisure participation and leisure satisfaction. Thus, leisure participation and leisure satisfaction play intermediary roles in the relationship between leisure and well-being. The findings have important implications for promoting urban residents’ leisure behaviors and subjective well-being. First, considering the importance of leisure time, the government should implement the paid vacation system to improve leisure quality and subjective well-being of urban residents. Second, leisure space is greatly affected by the local culture and the unique characteristics of a city, and local government should emphasize its own leisure culture to enhance residents’ leisure participation. Last but not least, leisure is not equal to well-being, but can meet the individual’s needs in psychological, physical, social, aesthetic and other aspects. Thus, leisure industry should be further developed to improve residents’ leisure satisfaction and subjective well-being.
城市居民休闲与主观幸福感研究: 以广州市为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180710
[本文引用: 1]

社会经济的发展与生活方式的转变使城市居民的休闲行为面临转型,探讨当代中国城市居民的休闲与幸福感是新时代城市地理研究中的重要议题。结合休闲的时间与空间要素,构建“休闲-幸福感”理论模型,以广州市为例,在访谈和问卷调查的基础上,运用结构方程模型对城市居民休闲行为和主观幸福感进行研究。结果显示:休闲时间和休闲空间均会对城市居民的休闲参与产生正向的促进作用,但休闲时间的影响更大;休闲时间、休闲参与和休闲满意度会对主观幸福感产生显著的正向影响,其中,休闲满意度对主观幸福感的影响最大;而休闲满意度则受到休闲时间、休闲空间和休闲参与的影响;休闲参与和休闲满意度是建立休闲与幸福感内在联系的重要中介机制。
The geography of well-being
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbr041 URL [本文引用: 1]
The status of women and its influence on children's well-being: Do geography, religion and income matter? A comparative study
DOI:10.1111/dpr.v38.6 URL [本文引用: 1]
Urbanization, environmental pollution and subjective well-being: An empirical study on China
城市化、环境污染与居民主观幸福感: 来自中国的经验证据
Does economic growth improve human happiness? A review of the influencing factors of SWB
经济增长为什么没有带来幸福感提高? 对主观幸福感影响因素的综述
City size, happiness and spatial optimization of migration
城市规模、幸福感与移民空间优化
Impact of urban educational attainment on residents' subjective well-being: A study based on multilevel modelling
城市人均受教育水平对居民主观幸福感的影响: 基于多尺度模型的研究
Social-economic status, social security, ecological environment and residents' sense of happiness in urban and rural areas: Based on the empirical analysis of CGSS (2013) data
社会经济地位、社会保障、生态环境与城乡居民幸福感: 基于CGSS(2013)数据的实证分析
Impact of PM2.5 pollution on urban residents' happiness and willingness-to-pay: A case study of urban China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.12.003
[本文引用: 1]

China’s rapid industrialization and urbanization are not necessarily accompanied by the corresponding improvement of living standards. As the largest developing country in the world, the rapid economic growth has been confronted with problems such as inadequate public services, soaring housing prices, environmental degradation and food safety, which have seriously restricted the happiness of Chinese urban residents. In recent years, PM2.5 pollution imposes serious impacts on the health and life quality of residents and restricts the improvement of urban residents’ happiness. Exploring the influential mechanism of air pollution on residents’ happiness and the economic value brought by the improvement environmental quality provide a scientific basis for the construction of livable cities in the new era. Based on the theoretical analysis framework of the impact of meso-and micro-scale air pollution on residents’ happiness and willingness to pay, we select 40 cities in China as the cases for empirical analysis. By employing the large-scale questionnaire survey data of 40 cities in 2015, this article adopts a Bayesian multi-level ordinal categorical response model to empirically explore the impact of PM2.5 pollution on residents’ subjective well-being, and evaluates residents’ willingness to pay to alleviate PM2.5 pollution by using happiness evaluation model. The empirical results are presented in the following aspects. First, PM2.5 pollution exerts a significant negative influence on residents’ subjective well-being, that is, the more serious the PM2.5 pollution is, the lower the residents’ subjective well-being. Specially, for every unit increase in the number of days of haze pollution, the subjective well-being of residents will significantly decrease by 0.040. Household monthly income has a significant positive impact on residents’ subjective well-being, meaning that the increase of household income is accompanied by the increase of residents’ happiness. For every unit increase in monthly household income, residents’ happiness will significantly increase by 0.026 percentage points. Second, willingness to pay is affected not only by household income level, but also by the air quality of the city where residents live. Third, residents in 40 cities were willing to pay 226 yuan, or 2.274 percent of their monthly income in order to improve air quality. Residents in Beijing were the most willing to pay 582 yuan to reduce PM2.5 pollution, accounting for 3.535 percent of their average monthly income. In addition, residents have the highest willingness to pay at the initial stage of reducing PM2.5 pollution and improving air quality. The conclusions of this article not only enriches the relevant research results of environmental pollution and residents’ happiness, but also provides an empirical basis for the policy making of environmental pollution improvement in Chinese cities.
中国城市PM2.5污染对居民主观幸福感的影响及支付意愿研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.12.003
[本文引用: 1]

利用2015年中国40个城市大规模问卷调查数据,采用贝叶斯多层级有序分类响应模型探讨了PM<sub>2.5</sub>污染对居民主观幸福感的影响,进而核算居民为减轻PM<sub>2.5</sub>污染的支付意愿。研究发现:PM<sub>2.5</sub>污染对主观幸福感具有显著的负向影响,PM<sub>2.5</sub>污染每增加1个单位,主观幸福感将下降0.040个百分点;家庭月收入对主观幸福感具有显著的正向影响,家庭月收入每增加1个单位,主观幸福感将提升0.026个百分点。支付意愿不仅受到家庭收入水平的影响,还受到居民所处城市空气质量的影响;在承受PM<sub>2.5</sub>污染的最初阶段,居民为改善空气质量的支付意愿最高。居民为改善空气质量愿意支付的金额平均为226元,占家庭月总收入的2.274%。
Factors influencing residents' emotional well-being in the affordable housing communities of China's big city: A case study of Guangzhou
中国大城市保障房居民情绪幸福感影响因素: 以广州市为例
Environmental justice, capabilities, and the theorization of well-being
DOI:10.1177/0309132515620850
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Environmental justice (EJ) scholarship is increasingly framing justice in terms of capabilities. This paper argues that capabilities are fundamentally about well-being and as such there is a need to more explicitly theorize well-being. We explore how capabilities have come to be influential in EJ and how well-being has been approached so far in EJ specifically and human geography more broadly. We then introduce a body of literature from social psychology which has grappled theoretically with questions about well-being, using the insights we gain from it to reflect on some possible trajectories and challenges for EJ as it engages with well-being.
How can the government make people happy? An empirical study on the influence of government quality on residents' well-being
政府如何能够让人幸福? 政府质量影响居民幸福感的实证研究
Vision of integrated happiness accounting system in China
DOI:10.11821/xb200506001
[本文引用: 1]

Enhancing and sustaining the happiness life or the quality of life (QOL) is a primary and ultimate goal of national policy. First, the evolvement tendency and characteristic of national accounting system have been identified. The fundamental characteristic of GDP, green accounting and ISEW is that these accounting systems are still based on measuring how much is being consumed, with the assumption that more consumption leads to more welfare. Happiness or quality of life as a completely different approach shall be taken to look directly at actual well-being achieved, which will separate the means (consumption) from the ends (happiness or QOL) without assuming one is correlated with the other. Secondly, the theoretical implications of human development have been discussed and three constraints have been identified as environmental constraint, equality and efficiency. Based on brief introduction of environmental and social constraints faced by China's human development, we analysed the relationship between economic growth and environmental pressure from the view of consumption and production in China. The overall findings don't support the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis, and our theoretical analysis can not support the claim that technological progress cannot reconcile the conflict between economic growth and environmental conservation. China should replace much of their faith in technological progress with the pursuit of other forms of cultural progress. Thirdly, The concept of happiness or QOL and its measurement approach have been introduced. If improving gross national happiness (GNH) is indeed the goal of social policies and programs, it follows that appropriate national aggregate accounting system should attempt to measure the extent to which policies actually improve GNH. GNH can be the measurement components of an overall plan to maximize social well-being. The first step in the process would be to identify the constitutive components of a preferred society in the greatest detail possible through a stakeholder dialogue process. This information would be used to identify the relevant instrumental components. The second step would be to identify the metrics of GNH's instrumental components. Direct measurement, indirect measurement and social choice have been recommended as alternative instruments to resolve the complex measurement. A specific action plan for maximizing GNH can be developed based on the above identifying process. Once these are established, the following four guidelines such as focusing on poor people, developing cyclic economy, considering cultural development and harmonizing the equality and efficiency may be useful in developing a successful plan.
建立中国国民幸福生活核算体系的构想
Study on the dual-path mechanism of community business ecological allocation on People's livelihood acquisition and happiness
社区商业生态配置对民生获得感和幸福感的双路径作用机制研究
Spatial-temporal differentiation characteristics and formation mechanism of coordinated development of "four modernizations" and residents' happiness in Zhejiang province
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.10.012
[本文引用: 2]

The study takes 69 counties in Zhejiang Province as the analysis object and selects the panel data from 2005 to 2015 as the research sample. Through the construction of "Four modernizations" level and residents’ happiness comprehensive evaluation index system, the entropy method, coupled coordination model, ESDA and geo-weighted regression model and other methods are used to measure the degree of coupling and coordination between the "Four modernizations" and the residents' happiness in Zhejiang Province, and the spatial features and formation mechanism are analyzed by using spatial visualization method. The following conclusions are drawn: From 2005 to 2015, the level of development of "Four Modernizations", the comprehensive index of happiness of residents, the degree of coupling and coordination all show a rising trend. On the whole, the degree of coordination is a spatial development trend of "northeast high, southwest low", and the distribution of spatial agglomeration shows the characteristics of inverted "V" type spatial evolution. The general trend has formed a significant hotspots that spread from Hangzhou which is the core area to the surrounding areas, and a significant cold spot areas which are the border areas of Zhejiang Province southwestern areas. The influential factors of the coordinated development of "Four modernizations" and residents' well-being have obvious geographical differences, self-awareness, open sharing, social opportunities, cultural values, living environment and economic opportunities are decreasing in turn.
浙江县域“四化同步”与居民幸福协调发展的时空分异特征及其形成机制
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.10.012
[本文引用: 2]

以浙江省69个县域为分析对象,选取了2005~2015年的面板数据作为研究样本,重构“四化同步”和居民幸福的综合评价指标体系,运用熵值法、ESDA、耦合协调模型和GWR模型等方法,对浙江省区域“四化同步”与居民幸福之间的耦合协调度进行了测度,并分析了其空间演化特征以及形成机制。得到了以下结论:2005~2015年,“四化同步”发展水平、居民幸福综合指数、耦合度以及耦合协调度均呈上升趋势,耦合协调度展现了“东北高,西南低”的空间演进趋势,空间集聚的强度以倒“V”型变迁。已形成由杭州湾为核心的连绵区域,不断向外扩散最终以杭州市区-宁波市区双核心分布的热点区域,浙西南散点分布的冷点区域。“四化同步”演进与居民幸福协调发展的影响因子具有明显的地域特征,其影响因子作用强度自信息意识、市场机会、居住环境、经济机会、文化价值和开放共享依次递减。
Basic theories and frontiers of poverty geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110006
[本文引用: 1]

China's poverty alleviation practice has proved that geography has played an extremely important role in supporting anti-poverty targeting and poverty reduction decision-making. However, due to vague basic concepts, lagging basic theories, and an imperfect discipline system, "theoretical poverty" has become the biggest shortcoming restricting the innovation and development of poverty geography. Based on the analysis of the core concept of poverty, this paper systematically analyzed the nature, basic theory, research object, research content, and framework of poverty geography as a branch of the discipline, and put forward the frontier areas of future research on poverty geography. The results show that firstly, poverty refers to the state of inferiority, lack, or insufficiency of various welfares enjoyed by people compared to a certain standard, which has multidimensional, regional, and dynamic characteristics. In terms of measurement standards, absolute poverty emphasizes the minimum value, and relative poverty emphasizes the average value. In terms of target objects, poverty can be divided into individual poverty and regional poverty. The former focuses on the lack and deficiency of individual welfare or capability, while the latter focuses on the regional welfare behind individual welfare from the perspective of space. Secondly, poverty geography is a discipline that studies the formation, distribution, geographic characteristics of poverty-stricken areas, their relationship with the environment, and anti-poverty measures. It takes the impoverished areal system (IAS) as the research object and the poverty-environment nexus as the research core. It has comprehensive, cross-cutting, and regional characteristics, focusing on the study of regional poverty. The basic theories of poverty geography include spatial poverty theory, regional poverty theory, multidimensional poverty theory, and sustainable development theory. Its research content and framework include three dimensions (economic, social, and environmental poverty), two elements (nature and human), two types of objects (regional poverty and individual poverty), and two standards (absolute poverty and relative poverty). Thirdly, there is an urgent need to strengthen the basic research of poverty geography in terms of the evolution of IAS, regional poverty measurement, relative poverty targeting, poverty dynamic monitoring and simulation prediction, urban poverty and rural poverty, poverty alleviation effectiveness evaluation, transformation and development and revitalization path of poor areas. In the situation that we face new challenges of poverty reduction and development at home and abroad, there is an urgent need to constantly innovate and develop the fundamental theory of poverty geography, promote the globalization of China's poverty research, and contribute China's anti-poverty project to the eradication of global extreme poverty.
贫困地理学的基础理论与学科前沿
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110006
[本文引用: 1]

中国的减贫实践证明,地理学在服务国民经济建设和支撑减贫瞄准与扶贫决策中发挥着重要学科价值。然而,由于基本概念模糊、基础理论滞后、学科体系不健全,“理论贫困”成为制约贫困地理学创新发展的最大短板。本文在解析贫困核心概念的基础上,系统剖析了贫困地理学作为一门分支学科的学科性质、基础理论、研究对象、研究内容与框架,提出了未来贫困地理研究中的前沿领域。结果表明:① 贫困是指与一定标准相比,人们所享受的各种福利处于劣势、缺少或不足的状态,具有多维性、区域性和动态性特征。在测量标准上,绝对贫困强调“极小值”,相对贫困强调“平均值”。在瞄准对象上,个体贫困关注个人福利或能力的缺失与不足,区域贫困则是从空间视角关注个体福利背后的“区域福利”。② 贫困地理学是一门研究贫困地区的形成、分布、地理特征及其与环境的关系和反贫困措施的学科,以贫困地域系统为研究对象,以“贫困—环境”关系为研究核心,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性特点。贫困地理学的基础性理论包括空间贫困理论、区域贫困理论和多维贫困理论,其研究内容与框架包括3个维度、2大要素、2类对象、2大标准。③ 贫困地理学需要进一步强化贫困地域系统演化、区域贫困测度、相对贫困瞄准、贫困监测模拟、减贫效应评估、区域可持续发展模式等方面的基础研究。
Research progress and prospect on development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002002
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we review and sort out research progress on development geography since the 20th century, involving its connotation and theory, fields and methods, and development trends in this paper. Specifically, we systematically reviewed the research and application of development geography in the fields such as in the convergence of underdeveloped countries or regions, the convergence in the process of improving the quality of life in developed countries or regions. Then, in line with the analysis of the research progress on development geography in foreign countries, we indicate the development conditions and disciplinary advantages of development geography in China. Further, we pointed that future development geography research in China should focus more on the latest international academic frontier research and national macro-strategic needs. The future research of development geography should be guided by the theory of sustainable development, with the core of improving the sustainable livelihood capacity and regional green development level in underdeveloped areas, and aiming at constructing industrial policy and development geography theory and interdisciplinary integrated research system, and focusing on research on the spatial pattern, diffusion characteristics and convergence mechanism of regional development, to explore the regulatory policies and scientific paths that serve regional economic construction and industrial development.
发展地理学研究进展与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002002
[本文引用: 1]

本文回顾和总结了20世纪以来发展地理学的研究进展,涉及发展地理学内涵和理论、领域和方法及其发展趋势。系统梳理了发展地理学在欠发达国家或地区发展收敛、发达地区或国家生活品质提升过程中的收敛及其路径等研究内容。通过分析国外研究进展,指出了发展地理学在中国的发展条件与学科优势,并着眼于国际学术前沿最新动向与国家宏观战略需求,提出了今后中国发展地理学研究需重点关注的领域。未来发展地理学研究应以可持续发展理论为指引,以提升欠发达地区可持续生计能力与区域绿色发展水平为核心,以构建发展地理学理论和跨学科综合集成研究体系为目标,聚焦区域发展的空间格局、扩散特征与收敛研究,探索出服务于区域经济建设与产业发展的调控政策与科学路径。
A review of the national happiness statistical research in China in the past 10 years
中国国民幸福统计研究十年简史
Towards a beautiful life in the new era: An introduction to the issue of "everyday life geography and urban-rural leisure"
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190497
[本文引用: 1]

With the rise and the turn of “everyday life” study in Western Academia, “going back to the world of everyday practice” and the ontology of life become the new academic perspective. The major conflict in Chinese society triggers the shift of the relations between people and place - from a static and homogenous to a more dynamic and heterogeneous interaction. “People” and “place” is endowed with the connotation and extension of everyday life. In the new era of pursuing a better life, geographers need to find out the geographical characteristics of everyday life practice, and how different subjects exhibit the dynamic relations between people and place, people and people, people and self through everyday practice and leisure; at the same time, they have to concentrate on the life practice and place meaning in different geographical scales. This special issue focuses on the subjective initiative of everyday life and leisure, spatial heterogeneity and the complexities between people and place. Specifically, the article discusses the relations between the leisure the well-being of the residents, between the evaluation of dynamics of urban public space and the ways of leisure, and between the sense of place and the settlement intentions. Future work should firstly focus on the everyday life and the leisure of marginal population. Secondly, there is a lack of study of everyday life practice on the “rural” scale, the study of rural population can be a complement for the research of rules and mechanisms of the everyday life and the leisure. Last but not least, we hope this special issue can be a good start to the promotion of constructing the theoretical debates of everyday life geography in China, meanwhile, a contribution to the geographical wisdom on how to pursue a beautiful life in practice in this new era.
新时代面向美好生活的日常生活地理与城乡休闲: “生活地理与城乡休闲”专栏解读
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190497
[本文引用: 1]

随着西方学界“日常生活”的兴起与转向,“回归生活世界”与生活本体论成为人文地理学研究的新视角。新时代背景下,中国社会主要矛盾的转化催生地理学人地关系的转变,由静止的、同质的人地关系转变为动态的、异质的人地互动关系,“人”与“地”被赋予日常生活的内涵与外延,“闲暇处才是生活”。在追求美好生活的新时代,地理学需要回答日常生活地理以及休闲具有哪些地理特征,不同主体如何通过日常生活及休闲展演人与地、人与人、人与自我的动态关系,从而建构不同空间尺度的生活实践与地方意义等问题。本专栏主要探讨日常生活及休闲中所展演的主体能动性、空间异质性以及人地互动的复杂性,涉及城市居民的生活休闲与主观幸福感、城市公共空间活力评价以及休闲方式、日常生活中的地方情感与定居意愿等内容,以期尝试用中国本土的实证来回应西方日常生活地理学的研究。期待未来的相关研究能够更加关注边缘群体的日常生活及其休闲,能够弥补城乡休闲中“乡”尺度的不足,能够全面系统地阐述日常生活与休闲在时间演变过程中的变化规律及其机制。专栏旨在推动中国情境的日常生活地理学的理论建构,在实践上以期为新时代美好生活的具体践行贡献地理智慧。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
Theory and measurement of regional multidimensional poverty
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004007
[本文引用: 1]

Poverty includes regional poverty and individual poverty, both of which are featured by multidimensional concept. Regional multidimensional poverty (RMP) is a major theme and content in poverty geography. Because of harsh natural environment, vulnerable economy and inadequate public services, severely impoverished areas (SIAs) are typical and highlighted areas of RMP, which have been the biggest obstacle to poverty alleviation in China. Based on the theory of spatial poverty, this paper defines the notion of impoverished areal system (IAS) and regional multidimensional poverty (RMP), explores their internal connections and proposes the evaluation indictors and measurement method for RMP. Taking 334 severely impoverished counties as research samples, we analyze the multidimensional poverty patterns of SIAs in 2016 by BP neural network model and exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA). Results show that: (1) RMP is an external manifestation of the coupling imbalance of "human", "environment" and "industry" in the evolution of IAS. It reveals regional disadvantages in natural environment, economic development and social welfare, corresponding to natural poverty, economic poverty and welfare poverty, respectively. (2) The most severely impoverished county, with the poorest services and infrastructure, is found in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. From a single dimension of regional poverty, the Welfare Poverty Index (WPI) > Economic Poverty Index (EPI) > Natural Poverty Index (NPI) in the SIAs, whose average is 2.77, 2.66 and 1.89, respectively, indicating that the lack of social welfare and public services for the poor has become the prominent problem in the SIAs. From the perspective of multidimensional poverty, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is a high agglomeration region or "hot spot" of RMP, which is significantly higher than other areas in terms of natural poverty, economic poverty and welfare poverty. (3) Both RMP and individual multidimensional poverty are effective measures of poverty targeting. Their matching coefficient (M) can help us to judge the poverty status of some specific areas, e.g., RMP is superior to individual multidimensional poverty in the remote areas, extremely fragile ecological environment and obvious regional disadvantage, where the matching coefficient (M) is higher. RMP can more objectively reflect the true level of geographical capitals, effectively target poor areas and identify determinant impoverishing factors.
区域多维贫困测量的理论与方法
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004007
[本文引用: 1]

贫困包括区域贫困和个体贫困,两者均具有多维属性。区域多维贫困是贫困地理学研究的重要内容,深度贫困地区是区域多维贫困的集中表现,是当前和未来脱贫攻坚的贫中之贫、困中之困、坚中之坚。本文以空间贫困理论为基础,界定了贫困地域系统和区域多维贫困的概念,并探究了区域多维贫困测度指标体系与评估方法。据此,以中国334个深度贫困县为研究对象,运用BP神经网络模型和ESDA技术刻画了中国深度贫困地区的多维贫困空间格局。结果表明:① 区域多维贫困是贫困地域系统发展演化过程中“人”“地”“业”三个核心要素耦合失调的一种外在表现形式,是特定地域在生态环境劣势、经济劣势、社会福利劣势上的综合表现,包括生态贫困、经济贫困和福利贫困3个维度。② 深度贫困地区最“深”的地方在青藏高原,最“深”的短板在公共服务和基础设施。从单一维度的贫困指数来看,深度贫困地区的福利贫困指数(WPI)>经济贫困指数(EPI)>生态贫困指数(NPI),三者平均值分别为2.77、2.66、1.89,贫困人口社会福利供给不足和公共服务短缺是深度贫困地区最突出的问题;从多维贫困指数来看,青藏高原是区域多维贫困指数(RMP)的高集聚区或热点区,生态贫困、经济贫困和福利贫困程度均显著高于其他地区。③ 区域多维贫困指数能较好地揭示特定区域的贫困状况。在地理位置偏远、生态环境极其脆弱、区域劣势突出的地区,区域贫困和个体贫困在空间上高度重叠。
Spatio-temporal scalar traps in geographical studies of subjective well-being
幸福地理学研究中的时空间尺度陷阱
Spatial variation and its determinants of migrants' Hukou transfer intention of China's prefecture-and provincial-level cities: Evidence from the 2012 national migrant population dynamic monitoring survey
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201610003
[本文引用: 1]

Based on data from the 2012 national migrant population dynamic monitoring survey and related statistics, this article examines the spatial pattern and its determinants of migrants' intention of hukou transfer of China's 276 prefecture- and provincial-level cities, using GIS spatial analysis and statistical modelling. The results show that the overall level of migrants' hukou transfer intention of the cities is not high, and varies significantly among different cities. The intention of migrants' hukou transfer increases as the administrative level and/or the size of their destination cities increase. Meanwhile, migrants' hukou transfer intention is generally higher in coastal mega-city regions than in other cities, but it is also relatively high in some provincial capital cities and small and medium-sized cities in some inland regions with good transport location and resource endowment. The spatial pattern of migrants' intention of hukou transfer is shaped jointly by both the characteristics of the destination cities and migrants themselves characteristics, with the former exerting more influence than the latter. High level of socioeconomic development and good location of the destination cities can effectively promote their migrants' intention of hukou transfer; however, their level of basic public services does not have the same effect. The degree of migrants' social integration in the destination cities also exerts positive effects on their hukou transfer intention. However, having medical insurance, the concentration in the secondary labor market and higher household income are negatively related to such intention; furthermore, the individual and family characteristics of migrants do not have a significant impact on it. Finally, on the basis of the above findings, we put forward some suggestions for relevant policy making.
中国城市流动人口户籍迁移意愿的空间格局及影响因素: 基于2012年全国流动人口动态监测调查数据
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201610003
[本文引用: 1]

基于2012年全国流动人口动态监测调查数据和相关统计年鉴数据,对中国地级以上城市流动人口的户籍迁移意愿、空间格局及影响因素进行了系统分析。研究发现,中国城市流动人口户籍迁移意愿的整体水平并不高;等级高、规模大的城市流动人口的户籍迁移意愿高,而等级低、规模小的城市流动人口的户籍迁移意愿低;沿海城市群流动人口的户籍迁移意愿高,其他城市流动人口的户籍迁移意愿低,但内陆部分省会城市和交通区位与资源禀赋较好的中小城市也已经形成了一批流动人口的户籍迁移意愿高值区。中国城市流动人口户籍迁移意愿的空间分布特征受到流入城市和流动人口自身双重力量的影响,流入城市因素的正向影响作用大于流动人口自身因素。其中,流入城市的社会、经济发展水平和流动人口在流入城市的社会融合程度是核心要素,对城市流动人口户籍迁移意愿的提升具有正向的促进作用,而流动人口过于集中在次级劳动力市场的就业特征和较高的家庭财富与收入对户籍迁移意愿的提升却具有显著的抑制作用。最后,提出了相关政策启示。
Spatial difference and influencing factors of floating population's settlement intention in the three provinces of Northeast China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.02.011
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, the three provinces of Northeast China (Liaoning, Heilongjiang, and Jilin) have suffered from economic decline and labor force loss. Supported by the China migrants dynamic survey in 2015, the present study aims to examine the spatial pattern and driving forces of the settlement intention of the floating migrants in the three provinces of Northeast China. Spatial autocorrelation analysis and trend analysis methods are applied to characterize the spatial pattern of the settlement intention at the city level, and a binary logistic model is constructed to detect the drivers of the settlement intention at the micro-level. According to the aboveanalyses, the main findings of our research are as follows: 1) The spatial distribution of the settlement intention of the floating population in three northeastern provinces presents a characteristic of “higher in the north and lower in the south”. Besides, the settlement intention has a more significant spatial variation in the north-south direction, yet the spatial variation degree is weaker in the east-west direction. 2) The spatial autocorrelation is insignificant in the spatial pattern of floating migrants’ settlement intention in the three provinces of Northeast China. Qiqihar City and Heihe City are detected as the High-Low cluster areas, while Haerbin City is detected as the High-High cluster area. With the increase in the size of cities, the settlement intention of the floating population shows the trend of first rising and then declining. From the perspective of the city level, the settlement intention of the floating population in sub-provincial cities is higher than that of ordinary prefecture-level cities in the three provinces of Northeast China. 3) Individual, economic, and social factors show significant effects on the settlement intention of floating migrants in the three provinces of Northeast China. In terms of individual factors, the model results indicate that migrants with agricultural hukou, migrants who are married, highly educated migrants, and ‘80s’ migrants have a stronger willingness to stay in destination cities. 4) For economic factors, income level has a significantly positive relationship with the settlement intention of the floating population, while housing expenditure has a negative effect. 5) Considering social factors, the results show that migrants with longer duration of staying, migrants whose occupation categories are professional or technical personnel and business service personnel, migrants whose employment status is the employer, and migrants participating in urban employee medical insurance have a stronger settlement intention.
东北三省流动人口居留意愿的空间差异及影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.02.011
[本文引用: 1]

基于2015年流动人口动态监测数据,综合运用空间自相关分析,趋势面分析等技术,结合二元Logistic回归模型,对东北三省流动人口居留意愿的空间分布和影响因素特征展开研究。主要发现:① 东北三省流动人口居留意愿呈现出“北高南低,东高西低”的空间格局特征,南北方向上的分异比东西方向大;② 流动人口居留意愿在空间上属于随机分布,齐齐哈尔市和黑河市位于高-高集聚区,哈尔滨市位于低-高集聚区。随着城市规模的增加,流动人口居留意愿呈现出先升后降的特征;③ 个体因素方面,农业户口流动人口、在婚流动人口、高学历流动人口、“80后”流动人口的居留意愿更强;④ 经济特征方面,收入与住房支出分别对居留意愿产生正向和负向影响;⑤ 社会因素方面,流入时间越长、职业类别为“专业技术及办事人员”与“商业服务人员”、就业身份为雇主、参加城镇职工医疗保险的流动人口居留意愿更强。
Spatial pattern of residential land parcels and determinants of residential land price in Beijing since 2004
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706008
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we take Beijing as a case study and employ the residential leasing parcel data from 2004 to 2015 within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing metropolitan area. Also, we use the GIS data of Beijing's public facilities, such as bus stations, railway stations, park, hospital, primary school and so on. With the help of ArcGIS, GS+, Surfer and Geoda Software, we explore the spatial pattern of residential land parcels, residential land price and determinants of residential land price in Beijing. In the first place, we use the methods of Spatial Trend Analysis, Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI), Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) to explore the spatial pattern of residential land parcels and their price in Beijing. In the second place, we compare the spatial econometric models (SLM and SEM) with traditional OLS model to further explore the determinants of residential land price in Beijing. Based on the analysis, the main conclusions are drawn as follows. (1) The number of residential land leasing parcels is not balanced among years and ring roads. The residential land leasing parcels in the last 20 years are mainly concentrated between the fifth and the sixth ring roads in Beijing. (2) Residential land parcels are generally distributed along the main roads (such as Beijing-Shijiazhuang Expressway, Beijing-Kaifeng Expressway, Beijing-Shanghai Expressway and Beijing-Tibet Expressway) and the subway lines (such as Line 1, Line 5, Line 6, Line 15, Fangshan Line, Daxing Line and Yizhuang Line), which is more obvious in outer suburban areas. (3) Generally, there exists an inverted U-shaped curve trend, indicating that residential land price declines gradually from the city center to the city fringes as a whole, and spatial pattern of residential land price has turned from mono-centric structure to poly-centric structure. (4) Residential land price demonstrates a spatial cluster distribution pattern. There exists obvious spatial autocorrelation in residential land price and it is easy to distinguish "cold spots" from "hot spots". (5) In the model selection, we compare the spatial econometric model (SLM and SEM) with the traditional OLS model. The result shows that SLM is the best, followed by SEM, indicating that there indeed exist spatial spillover effects and spatial dependence in residential land price rather than error dependence. The residential land price is mainly affected by the surrounding residential land price, distance to bus station, distance to subway station, distance to key primary school, area of land parcel, FAR and the type of land leasing. However, in this paper, one drawback is that we fail to take macroeconomic policy factors into consideration, which may play a key role in the formation of residential land price. Also, we have not considered the subway's impact in different periods such as planning period, construction period and operation period on residential land price, which needs to be further studied.
北京市居住用地出让价格的空间格局及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706008
[本文引用: 1]

以2004-2015年北京市六环内居住用地的交易样本为基本数据,借助ArcGIS、GS+、Surfer和Geoda软件,采用空间趋势面分析、最近邻指数(NNI)、探索性空间分析(ESDA)探讨居住用地出让和居住地价的空间格局特征,并对比OLS和空间回归模型(SLM和SEM)进一步探讨居住地价的影响因素。结果表明:① 北京市居住用地出让数量和出让面积不均衡,五六环间出让的居住用地最多。② 出让地块沿主要道路(如京石高速、京开高速、京沪高速及京藏高速)、地铁线(如地铁1号线、5号线、6号线、15号线、房山线、大兴线及亦庄线)呈轴线扩散,其中远郊区域这一特征更加明显。③ 居住地价从中心向外围总体表现“倒U型”趋势,且呈多中心圈层递减结构。④ 呈集聚分布模式,存在空间自相关,低值集聚区和高值集聚区明显。⑤ 模型对比方面,SLM>SEM>OLS,说明北京市居住地价存在实质性的空间依赖,而非干扰性的空间依赖。周边居住地块的价格、公交站、地铁站、重点小学、占地面积、容积率和出让方式对居住地价有显著影响。
Principal component analysis and long short-term memory neural network for predicting dissolved oxygen in water for aquaculture
主成分分析和长短时记忆神经网络预测水产养殖水体溶解氧
National sense of happiness in the economic growth period: A study based on CGSS data
经济增长时期的国民幸福感: 基于CGSS数据的追踪研究
Chinese balanced regional development strategy from the perspective of development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

Large regional differences and uneven regional development is fundamental of China. Regional balanced development is an important topic in the field of development geography. This study reviews the course of regional balanced development in China and summarize the characteristics of regional balanced development in each period. This study suggests that inter- regional development of China shows a state of succession between balanced development and non-balanced development. Each succession brings the quality of social development to a new level and gradually make social development move towards the state of high- quality development and balanced regional development. Then, this study discusses the scientific connotation of regional balanced development. Under the guidance of sustainable development theory, we should pay attention to the resource endowment difference in different area, solve the problem among economy, human and nature and promote spatial balance of regional development and green development of ecological economic coordination. The balanced promotion of regional people's well-being is the ultimate goal of regional balanced development. In the end, based on the thinking of development geography, this study discusses the path of regional balanced development in China from three aspects of society, economy and ecology. Suggestions are put forward for the balanced development of China's regions and the improvement of people's well-being.
发展地理学视角下中国区域均衡发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

区域差异大、发展不平衡是中国的基本国情,研究区域均衡发展问题是发展地理学领域的重大课题。本文首先回顾了中国的区域均衡发展历程,总结了各时期区域均衡发展的特征,研究指出,中国区域间发展呈现出均衡发展与非均衡发展演替的状态,每次演进使得社会的发展质量迈进新的台阶,逐渐走向高质量发展与区域均衡发展的状态。其次,本文探讨了当前区域均衡发展的科学内涵,强调要以可持续发展理论为指引,关注不同地区资源禀赋差异,解决经济、人、自然三者间的矛盾,促进区域发展的空间均衡与生态经济协调的绿色发展,最终落脚到区域人民生活福祉的均衡提升为区域均衡发展的最终目标。最后,本文以发展地理学的思维从社会、经济、生态三个方面探讨中国区域均衡发展的路径,为中国区域均衡发展和国民福祉的提升提出若干建议。
Patterns and driving mechanism of spatial agglomeration during the urbanization process in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201602003
[本文引用: 1]

Establishing a scientific and reasonable spatial pattern of urbanization, which has a significant meaning in improving the quality of urbanization and promoting the healthy development of urbanization, is the inherent requirement to advance a new type of urbanization. Based on statistical data and geographic information technology, the paper profoundly reveals the situation on spatial agglomeration during the urbanization process in China as well as the corresponding prominent contradiction, comprehensively examines the mechanism of the spatial agglomeration from the theoretical aspect, and briefly discusses the policy and suggestion of optimizing the spatial layout of urbanization. This paper argues that the spatial agglomeration during the urbanization process in China has been significant since the economic reforms and opening up policy initiated in 1978. Population, resources, elements and industries agglomerated in the eastern coastal area in large scale, forming several city clusters and densely inhabited regions. The spatial agglomeration of various elements was found to be related to many factors. To be specific, the regional difference in the natural background conditions and resources endowment is the fundamental condition while the east-oriented national development strategy and the agglomeration effect of the resource elements are the external conditions. However, the underlying impetus is increasingly widening development gap between regions. It should be noted that there is a certain historical inevitability for the agglomeration of population and industry in the eastern region. However, the scale and speed of the spatial agglomeration in relation to population and industry failed to be consistent, which result in two unharmonious problems—the mismatch of the spatial distribution of population and industry as well as the mismatch of the spatial distribution of population, industry, resources and environment. These two inharmonious problems have caused several prominent problems such as the transfer of hundreds of millions of "amphibious migratory" type of migrant workers, the cross-regional flow of energy and bulk commodities, the tremendous pressure of resources and environment in the eastern region, and the increasingly intensified instability factors and social contradictions. The essence to establish an efficient, balanced and safe spatial pattern of urbanization is to realize a regional harmonious development, not only emphasizing people's prosperity, but also highlighting the regional prosperity. There are two core strategies—"industry shift to the west" and "population shift to the east"—launched to optimize the spatial layout of urbanization.
中国城镇化进程中的空间集聚、机理及其科学问题
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201602003
[本文引用: 1]

构建科学合理的城镇化空间格局,是推进新型城镇化的内在要求,对提升城镇化质量和推动城镇化健康发展具有重要意义。基于统计数据和地理信息技术,深刻揭示了中国城镇化进程中的空间集聚态势及其造成的突出矛盾,从理论视角综合考察了城镇化进程中的空间集聚形成机理,并简要探讨了优化城镇化空间格局的政策建议。研究表明,改革开放以来中国城镇化进程中的空间集聚态势十分明显,人口、资源、要素和产业大规模向东部沿海地区集聚,并在空间上形成了若干个城市和人口密集区。造成这种空间集聚态势的因素是多方面的,自然本底条件和资源禀赋的地带性差异起到基础性作用,国家发展战略的东部偏向及资源要素的空间集聚效应是外部条件,而更深层次的基本动力源于区域之间日益拉大的发展差距。应该看到,改革开放以来中国人口与产业向东部地区集聚具有一定的历史必然性,但二者的空间集聚未能协同一致,由此导致两个“不协调”,即人口分布与产业及就业岗位分布的不协调及人口、经济分布与资源环境承载能力的不协调。这两个“不协调”造成了数以亿计的“两栖”农民工跨区域迁移、能源与大宗商品的跨区域流动、局部地区资源环境面临巨大压力、不稳定因素和社会矛盾日益激化等突出问题。要构建高效、均衡、安全的城镇化空间格局,其本质就是要实现区域协调发展,即不单纯要强调人的繁荣,还要强调地域的繁荣。“产业西进”和“人口东移”是优化中国城镇化空间格局和形态的战略重点。
"Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction": A theoretical cornerstone for comprehensive research on formation and evolution of the geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
“人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 1]

同近年国外人文地理学呈现人文化趋势相比,中国人文与经济地理学秉承吴传钧先生关于人文与经济地理学是研究自然圈与人文圈相互作用下、人类活动分布格局形成和演变规律的一门交叉学科的定位,形成了以不同空间尺度的地域、重要的生产生活领域、以及典型的地域空间类型的可持续发展时空规律作为研究指向的中国人文与经济地理学主流学派。吴先生提出的“人地关系地域系统”理论不仅为人文与经济地理学,而且是为整个地理学的综合研究提供了重要的理论基石。地域功能性、系统结构化、时空变异有序过程、以及人地系统效应的差异性及可调控性,是该理论的精髓,这与“未来地球”研究计划的前沿思想完全契合。近10年来,以城镇化科学模式、主体功能区划、一带一路路线图、京津冀城市群、农村空心化和精准扶贫、东北振兴与资源型城市转型、行政区划优化等为研究对象,发展了人文与经济地理重要的可持续过程、地域功能形成和综合地理格局有序化规律、城市群形成演化机理及其资源环境效应、问题地区可持续生命周期与振兴路径、地缘政治地缘经济和区域间相互作用关系、人文界线对可持续发展的影响等理论方法。人文与经济地理学科建设取得重要进展,应用成果对近年来中国生态文明建设和可持续发展产生了重要影响。中国人文与经济地理学在全球范围内发展态势最佳、总体水平领先,以此告慰吴传钧先生,并以此纪念吴传钧先生百年诞辰。
Changing spatial patterns of internal migration to five major urban agglomerations in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106002
[本文引用: 1]

Internal migration in China has presented a series of new characteristics recently. The secondary migration and spatial redistribution of existing migrants become increasingly important in determining the future patterns of urbanization. Urban agglomerations (UAs) have long been the major destination of China's internal migration. They are also appointed as the main form of future urbanization in the recently released national planning of new-type urbanization. Five major UAs were selected as a case study, including three coastal ones, namely the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Pearl River Delta (PRD), and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region (BTH), and two inland ones, namely the Middle Yangtze River (MYR) and the Chengdu-Chongqing (CC) region. Based on data of the latest population census and the dynamic monitoring survey of floating population in the five major UAs, this paper first examined the spatial patterns of in-migrants from multiple dimensions of destination, origin, and distance of migration. The trends and urbanization effects of migration on the destination and origin were then assessed by comparing the settlement and hukou transfer intentions of migrants with different origins and destinations. The results showed the coexistence of common and distinct features in these mega regions. Although the continuous attractiveness of central cities for migrants was observed in all regions, peripheral cities in the YRD and PRD have become increasingly attractive as well, leading to a moderately dispersing trend in these two pioneering coastal UAs. Moreover, the concentration level and spatial distribution of migrants among cities were generally stable in the YRD and PRD but continuously adjusting in the BTH and two inland UAs. The fastest growth was found in inter-county migration within province and the slowest in intra-county migration. The coastal UAs were strongly preferred by inter-provincial migrants, while the inland ones could only attract migrants from the same or surrounding provinces. Despite this, significant distance attenuation was found in all of them. In terms of the origins of migrants, those from central provinces had flowed mainly to the YRD and PRD, whereas those from the northeast showed a high preference for the BTH region. We can anticipate the future patterns of migration and urbanization from the settlement intentions of migrants from and to different cities. From the destination view, the advantage in public services made central cities considerably more attractive than other cities. Hence, they are expected to be continuously faced with severe contradiction between supply and demand of public services. In the inland UAs, however, central cities and ordinary ones are able to share the pressure of public service provision. From the original view, the high-quality and equally accessible public services are important for inland regions to attract return migrants, and providing high possibility for the return-migration-induced urbanization. However, the population loss in the northeast may become a long-term trend that can hardly be reversed in the visible future.
中国五大城市群人口流入的空间模式及变动趋势
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106002
[本文引用: 1]

城市群在中国城镇化格局中占有重要地位,也是快速城市化时期的主要人口流入地。本文关注京津冀、长三角、珠三角、长江中游和成渝五大城市群,利用人口普查和流动人口动态监测调查数据,从流入人口分布格局、流动范围和来源地等多维度剖析城市群人口流入的空间模式,并从居留和落户意愿空间差异的视角探讨空间模式的发展趋势及其对流入地和流出地的影响。研究发现,各城市群流入人口向中心城市持续集中,等级和空间分布格局总体稳定;流动范围有所扩大,省内流动增速普遍高于省际;沿海城市群人口吸引范围大但仍服从距离衰减律,不同来源地流入人口的城市群偏好存在差异。在流入地,沿海城市群中心城市面临流动人口管理服务的持续挑战,内陆城市群中心城市和一般城市吸引力并存;在流出地,平等开放的高质量公共服务供给是吸引人口回流的重要途径,少数地区的人口流失可能成为较长期的现象。
Spatial equity and influences of two-level public healthcare resources: A background to hierarchical diagnosis and treatment reform in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906008
[本文引用: 2]

In present-day China, the unequal distribution of public healthcare resources across different levels and regions is problematic. Hierarchical diagnosis and treatment (HDT) reform is of great significance for optimising the distribution of healthcare resources and promoting fairness across health services. In this study, exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) was applied to evaluate spatial patterns at the lower and upper levels of healthcare resources. The Geodetector model was used to analyse the influences of the healthcare system at the municipal and county levels during 2015. The results show that there is significant spatial clustering in the distribution of the two-level healthcare resources. Influences on upper-level healthcare resources are more significant than those on lower levels. The dominant influencing factors of the two-level healthcare resources differ across spatial scales and regions. In terms of upper-level healthcare resources, urbanisation, population density and the level of economic development are the dominant global factors, in addition to the regional factors of population aging, topography and the morbidity of epidemic and endemic diseases. In the case of lower-level healthcare resources, urbanisation is an important influencing factor, while economic development, population aging and morbidity have local effects. Ultimately, population density was the dominant factor. Finally, this paper suggests that, aiming for HDT reform, decision makers should allocate healthcare resources among different regions and levels in consideration of relevant global and local factors, united and targeted policies, and top-down and bottom-up decision-making mechanisms. This could promote the overall function of the healthcare system and enhance the equity and coordination of multi-level healthcare resources.
两层级公共医疗资源空间均衡性及其影响机制: 以分级诊疗改革为背景
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201906008
[本文引用: 2]

中国公共医疗资源在层级间和地区间配置不合理的问题较为突出。分级诊疗改革对优化医疗资源配置、实现供需均衡具有重要意义。运用探索性空间分析法和地理探测器分别从全国地级市域和四川县域两个尺度分析了2015年两层级医疗资源的空间配置特征与影响机制。结果表明:基层和上层医疗资源均呈显著空间聚集特征,而层级间空间配置格局具有差异性。不同尺度和区域两层级医疗资源配置的决定力及其影响强度不同,上层医疗资源对外部影响因素响应强度大于基层。对上层级医疗资源配置而言,城镇化率、人口密度、经济发展水平是全局性因素,老龄化、地形条件和发病率为地方性因素;对基层医疗资源配置而言,人口密度是较为显著的全局性影响因素,城镇化率是重要的地方性影响因素,地形、经济发展水平、人口老龄化和发病率在部分尺度和区域有局部影响。为实现分级诊疗改革的目标,各级决策部门需以“全局性和地域性因素相结合,统一性和地方性政策相结合,自上而下与自下而上决策机制相结合”为思路,统筹不同区域和层级医疗资源配置,以提高医疗卫生服务体系的整体功能,促进其均衡、协同发展。
Local financial health investment and urban medical and public services: Double test based on "scale effect" and "quality effect"
Based on the urban administrative hierarchy and the heterogeneity of economic regions, this paper conducts research on the scale and quality effects of the local financial and health investment on the supply of urban medical and public services. Results of the empirical tests are as follows: (1) The local financial health input significantly improves both the supply and the demand of urban public health services in terms of the scale and the quality through the development of the local economy and the improvement of the efficiency of medical input and output; (2) When the administrative hierarchy of cities and the heterogeneity of economic regions are introduced, the local financial health investment shows a significant feature of “helping the disadvantaged”, and both the low-level urban agglomerations and the urban agglomerations in economically underdeveloped regions show a tendency of “scale effect prevailing”, and solve the problem of mismatch of resources in the medical and health field according to the logic of “quantitative change causing qualitative change”; (3) In the current situation where the supply and the demand of medical and public services in China are severely misaligned, the local fiscal and health investment is still at the “increasing marginal effect” stage, but the existence of the “ceiling” effect of the active fiscal policy should not be ignored; (4) Unexpected public health incidents cannot quickly improve the ability to respond to urban public health crises, but the timely increase of the local fiscal health investment can effectively reduce the response time lag.
地方财政卫生投入与城市医疗卫生公共服务: 基于“规模效应”与“质量效应”的双检验
本文基于城市行政等级与经济区域异质性,围绕地方财政卫生投入对城市医疗卫生公共服务供给规模效应与质量效应展开研究。实证检验发现:(1)地方财政卫生投入通过发展地方经济和提升医疗卫生投入产出效能两个渠道,从规模和质量层面显著改善城市医疗卫生公共服务供求状况;(2)地方财政卫生投入具有显著的“帮扶弱者”特征,低行政等级城市群和经济欠发达区域城市群均表现出规模效应占优的态势,按照“量变引起质变”的逻辑解决医疗卫生领域资源错配问题;(3)在当前我国医疗卫生公共服务供求错位较为严重的背景下,地方财政卫生投入仍处于“边际效应递增”阶段,但也不应忽视积极财政政策“天花板”的存在性;(4)突发性公共卫生事件并不能够迅速改善城市公共卫生危机应对能力,但及时增强地方财政卫生投入力度能够有效缩短反应时滞。
Regional inequalities of residents' health level in China: 2003-2013
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704010
[本文引用: 1]

As one of the core problems clsoely related with human development, health inequality has aroused an increasing concern in the world. Through an integration of the coefficient of variation, Theil index, exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) and spatial panel econometric model, we examine the regional inequality, spatial-temporal dynamic patterns and the key factors of the residents' health level (RHL) in China from 2003 to 2013. The aim is to provide scientific basis for policy making on regional health inequality reduction in China. The results are shown as follows: (1) China's RHL index decreased from 0.404 to 0.295 in 2003-2013, with an annual rate of 2.698%. Specifically speaking, the growing rate in the western region was higher than that in the eastern and central regions, but the there is no change in RHL in terms of the basic pattern which decreases from the east to central part then to the west. (2) The regional inequality of RHL presented an extending trend in 2003-2013. Among this, the RHL inequality between regions presented a reducing trend, but that within a region presented an expanding trend. And the growing rate of inequalities of RHL in the western region was higher than that of the eastern and central regions. (3) The spatial distribution of RHL has tended into the letter "T" shape, and the RHL presented a stepped decrease from the east to the central part then to the west and a symmetric decrease from the north to the central part then to the south. (4) By observing the change of Moran's I in 2003, 2008 and 2013, we found that the spatial agglomeration range of RHL presented a narrowing trend. All the hot spots and cold spots presented a shrinking tendency, the RHL in the west formed a stable cold spot, including Xinjiang, Qinghai and Xizang, but that in the east coastal area formed a stable hot spot, including Shandong, Henan, Qinghai, Hubei, Anhui, Jiangsu and Shanghai. (5) The selected explanatory variables, such as per capita GDP, per capita spending on health, urbanization level and environment quality, have significant direct impacts on the RHL in China. With the increase of per capita GDP, per capita spending on health and urbanization level and the improvement of environment quality, the RHL will be raised. Finally, this paper points out the attention should be focused on the research of the regional inequality of RHL, such as the problems of the residents' multi-time-domain, multi-scale and multi-influencing mechanism.
中国居民健康水平的区域差异: 2003—2013
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704010
[本文引用: 1]

健康不公平作为影响人类发展的核心问题,已引起世界各国的广泛关注。基于变异系数、泰勒指数、空间自相关分析和空间面板计量模型,本文探讨了2003年以来中国居民健康水平的区域差异、时空变化及其关键影响因素,旨在为政府制定全民健康政策提供科学依据。结果发现:① 2003-2013年,中国居民健康水平提高26.98%,西部增幅高于东、中部,但始终保持着“东—中—西”阶梯式递减态势;② 中国居民健康水平的区域差异总体呈扩大趋势,其中地带间差异趋于缩小,地带内差异趋于扩大,西部地带内差异扩大尤为显著;③ 居民健康水平的空间分布转为明显的“T”字型格局,并呈“东—中—西”阶梯式及“北—中—南”对称式递减;④ 居民健康水平的空间集聚程度趋于减小,热点区与冷点区均呈收缩态势,且西部形成规模显著的稳定性冷点,东部沿海形成规模显著的稳定性热点;⑤ 人均GDP、人均公共医疗卫生支出、城市化水平及环境质量等因素对居民健康水平时空变化具有显著影响,随着人均GDP与人均公共医疗卫生支出的增加、城市化水平的提高及环境质量的改善,居民健康水平随之提高。未来,还需对居民健康水平的多时域、多尺度及多影响机制等问题开展深入研究。