1 健康中国战略的由来、内涵与意义
1.1 健康中国战略的由来
人民健康是民族昌盛和国家富强的重要标志。20世纪90年代以来,美国[1]、新加坡[2]、日本[3]、英国[4]、加拿大[5]、欧盟[6]等发达国家先后制定了健康国家战略,其健康战略均强调全生命周期健康的促进,但各国的具体实施目标因国情不同而略有差异,同一国家不同阶段的战略目标也有变化。以美国为例,“Healthy People 2010”旨在提高国民健康质量和寿命,并尽可能消除健康差距,包括“营养和超重”“口腔健康”等28个重点领域,467个目标;“Healthy People 2030”总共提出355个可测度公共卫生核心目标(core objectives),其中高度优先的先导健康指标(leading health indicators)23个,涉及全年龄(all ages)、婴儿(infants)、儿童与青少年(children and adolescents)、成年人与老年人(adults and older adults)等4个生命阶段人群①(① 参见:
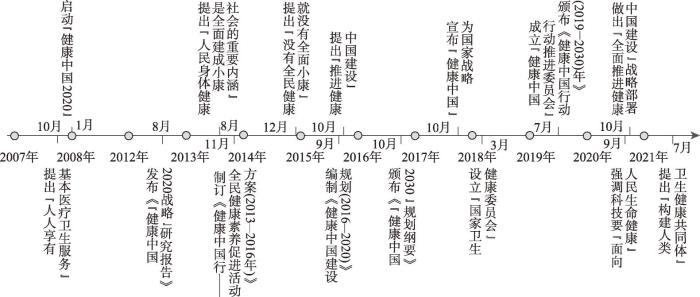
中国的健康战略从理念雏形到实践推进已有十余年。2008年国家卫生部启动“健康中国2020”战略研究。2012年《健康中国2020战略研究报告》正式颁布,提出了2020年“主要健康指标基本达到中等发达国家水平”的战略目标[7]。2013年国家卫生和计划生育委员会出台《健康中国行—全民健康素养促进活动方案(2013—2016)》;2015年国家卫计委启动《健康中国建设规划(2016—2020年)》,“推进健康中国建设”写进中共十八届五中全会报告。2016年中共中央、国务院颁布《“健康中国2030”规划纲要》,提出“普及健康生活、优化健康服务、完善健康保障、建设健康环境、发展健康产业”五大战略任务。2017年“实施健康中国战略”写进中共“十九大”报告,“健康中国”正式成为国家战略。2018年国务院设立“国家卫生健康委员会”,负责“健康中国”战略推进。2019年国务院颁布《关于实施健康中国行动的意见》和《健康中国行动(2019—2030年)》。2020年习近平总书记提出科技发展要“面向人民生命健康”;中共十九届五中全会做出“全面推进健康中国建设”战略部署。2021年十三届人大四次会议通过《中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和二〇三五年远景目标规划纲要》,制定“全面推进健康中国建设”行动指南;习近平总书记在世界政党领导人峰会上提出“推动构建人类卫生健康共同体”(图1)。短短12年,“健康中国”战略从提出到形成到实践,如今与“美丽中国”战略一道,已成为中华民族伟大复兴和现代化强国建设的双翼。
图1
1.2 健康中国战略的内涵
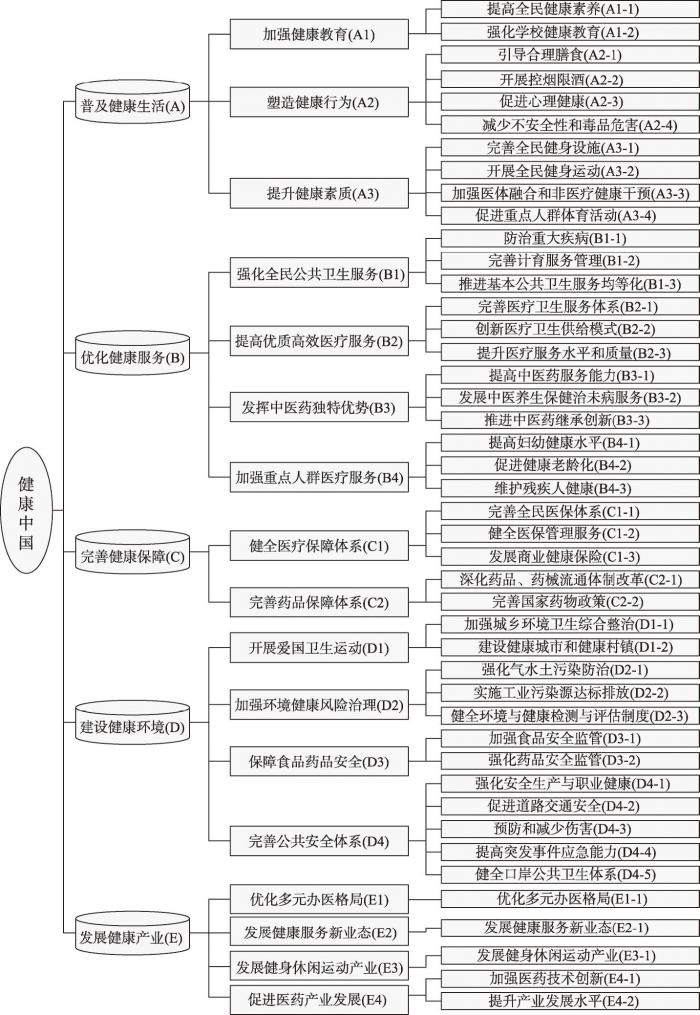
从《健康中国2020战略研究报告》到《健康中国2030规划纲要》,“健康中国”战略内涵不断深化和提升。健康中国战略“是全面建成小康社会、基本实现社会主义现代化的重要基础,是全面提升中华民族健康素质、实现人民健康与经济社会协调发展的国家战略” ②(② 参见:
图2
1.3 健康中国战略的意义
个人健康是立身之本,全民健康是强国之基。实施健康中国战略之重要意义:① 建设“现代化强国”的重要支撑。人力资本是国家最大财富,人民健康是最持久生产力,无论是小康社会建设还是现代化强国建设,都有赖于国民健康水平的提高。② 建设“美丽中国”的重要基石。良好生态环境是人类生存与健康的基础。个人因身体健康而美丽,国家因国民健康而富强,生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好的现代文明发展道路,必须统一于生命健康的进程中。没有“健康中国”的支撑,就不可能有“美丽中国”的绽放。③ 实现“民族复兴”的重要保障。健康是个人幸福的源泉,健康是国家财富的储蓄。“国家的强弱和社会事业的发达与否,首先要看国民是否有健全的体格”[9]。半封建半殖民地时期“病夫之国”的称号如同一面历史的镜子,警示我们民族的复兴和国家的强盛,都离不开国民的健康。④ 构建“和谐社会”的基础工程。健康权是最基本的人权,社会和谐需要健康公平支撑,良好社会秩序是健康公平的重要保障,只有人人都有“小我”的健康才能促成“大我”众人的和谐。⑤ 建设“命运共同体”的必由路径。一方面,全球化的深入,使得世界发展成为一个不可分割的“命运共同体”[10];另一方面,中国的崛起,使得中国力量、中国智慧、中国精神、中国方案在世界舞台发挥的作用日益重要,“中国好,世界才更好”,新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)疫情的全球大流行也表明,构建全球“生命共同体”,首先要建设全球“健康共同体”。
2 地理学参与健康中国建设的重要作用
2.1 地理学能为健康中国建设提供路径指引
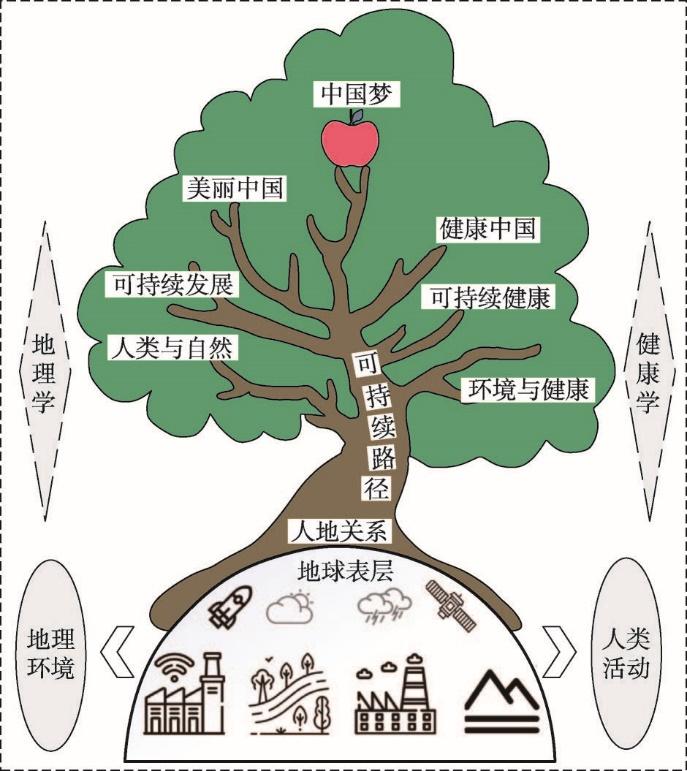
(1)为健康中国建设提供发展战略指引。可持续发展战略是20世纪90年代中国确立的面向21世纪的国家长期发展战略。可持续发展的最高宗旨是协调人与自然以及人与人的关系[16],在地理学领域,主要是协调人地关系、区际关系、代际关系三大关系,可持续发展理论是优化人地关系地域系统、建设美好人居环境的重要理论。在可持续发展系统中,生态可持续发展是物质基础,经济可持续发展是动力支撑,社会可持续发展是根本目的[17],而由人类群体构成的社会要实现可持续发展,其前提是实现人的健康的可持续,因此健康中国建设必须走可持续健康之路。历史已经证明,环境对人类社会深层次系统的影响,首先都是通过对人群健康的影响来实现的[18],因此,任何一个社会的可持续都必须建立在其人群健康的可持续基础之上[19]。这也是中国在实施“美丽中国”战略之后必然实施“健康中国”战略的内在原因。“美丽中国”是着重于生态可持续发展的基础工程,“健康中国”则是着重于社会可持续发展的目标工程,两者均以可持续发展为战略路径,在绿色发展、高质量发展、新发展格局等经济可持续发展的动力工程支撑下,共同托起中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦(图3)。
图3
图3
地理学与健康学支撑的中国梦建设路径示意图
Fig. 3
The construction path of Chinese Dream supported by geography and health-related sciences
(2)为健康中国建设提供过程评价指引。健康中国战略实施过程中,国家是否走在可持续发展道路上,人民是否朝着可持续健康方向进化,都必须及时进行科学的评价和纠偏。如果说战略指引是一种方向指引,那么评价指引就是一种纠偏校正。地理学是研究地理要素/地理综合体的空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,可持续发展系统评价是地理学从科学到决策的重要手段[13],健康中国建设要确保行进在可持续健康之路上,需要地理学提供评价指引。因为健康中国建设评价需要整合特定区域环境、经济、社会各方面指标,需要观照特定区域健康风险/压力、健康水平/状态、健康保障/响应的关系,需要将健康生活普及、健康服务优化、健康环境建设、健康保障完善、健康产业发展的要求因地制宜、因时制宜地落实到具体的地理空间,需要解决健康发展空间不均衡、医疗卫生资源优化配置、环境污染健康风险防治、重大疾病精准防控等有关环境与健康关系、健康时空格局优化的重大问题,在这些方面,以人地关系研究为核心、具有综合性、交叉性、区域性的地理学有着得天独厚的优势,发挥着不可替代的作用。无论是可持续发展评价的指标体系,生态文明评价的指标体系,还是“美丽中国”评价的指标体系[20],基本都是以地理学者为主体建立起来的。目前,虽然“健康中国建设监测评估指标体系”已经初步建立[21],但仍然需要地理学的完善,比如将联合国《2030可持续发展目标》中关于“确保健康的生活方式、促进各年龄段所有人的福祉”的各项指标以及世界卫生组织(WHO)提出的100项核心健康指标[22],把符合中国地理国情实际的指标遴选进去,这就需要地理学者的参与。
(3)为健康中国建设提供政策导向指引。健康问题既是民生问题,也是环境问题和人地关系问题,地理学至少可在3个方面为健康中国建设提供政策指引:①“全民健康”和“健康强国”一体的政策指引。中国是社会主义国家,健康中国建设秉承人民至上、生命至上的原则,体现全民健康、城乡均等、区域均衡的公平正义,地理学能在个体与社会、区域与国家、区际与代际的关系协调[17],在生命全周期、全年龄段人群、全行政区域健康服务的全覆盖,以及基本健康服务均等化和可持续健康等方面提供政策指引。②“美丽中国”和“健康中国”一体的政策指引。环境系统与人体系统平衡是健康的前提,生命健康需要生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好的支撑,健康中国建设需要美丽中国建设的支撑,地理学能为生产空间、生活空间、生态空间一体的“三生空间”规划,为生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好、生命健康的“四生关系”建设,为“美丽中国”和“健康中国”的相互促进与融合等方面提供政策指引。③“人类与自然命运共同体”和“人类卫生健康共同体”一体的政策指引。自然系统与人类系统是人与自然命运共同体,人类卫生健康共同体是建立在这个命运共同体基础之上的全球性健康安全的统一体。由于地球表层的不均衡性、发展的不同步性和健康的空间异质性[23],这两个共同体的建设都需要以人地关系为研究核心的地理学[24]的参与。地理学能在自然系统与人类系统协同进化、促进人与自然关系和谐协调发展、强化健康服务与健康保障的公平正义、共同应对全球性疫情风险、因时因地制宜推进各层次共同体建设等方面提供政策指引。
2.2 地理学能为健康中国建设提供理论指导
(1)人地关系和谐理论的指导。人是环境的产物,环境是影响人体健康的基础因素,健康是人与环境相互作用的良性结果。地理学以人地关系研究为核心,发展了一套人地关系的协同理论(地理区域论、地理综合论、地理系统论等)[25]。环境与健康关系是最基本的人地关系,人类生存繁衍所必需的营养物质大都来自于自然界[26],人体中的元素丰度与地壳中的元素丰度高度一致[27]。地理学探究人地关系,环境与健康关系本身就是地理学的研究范畴,并且已经发展成为一个独立的地理学分支——研究人群疾病/健康状况的地理分布规律、环境机理与健康资源配置的医学地理学[28]。自20世纪90年代以来,国际医学地理学从关注疾病分布和医疗保健服务等内容向研究福祉与更广泛的健康和社会模式的健康地理学转变[29];中国的医学地理学研究也从化学地理转变到环境地理,从传统的医学地理转向为以环境、发展与健康关系为核心的健康地理[30]。环境地理学和健康地理学是地理学参与健康中国建设最紧密的学科,在构建“人与自然生命共同体”、推进健康中国建设的进程中,地理学的人地关系理论都能提供理论指导。
(2)空间系统优化理论的指导。健康不仅是一个人生理上、心理上和社会上的完好状态,也是一种地理现象,具有显著的空间分异特征。地理学作为一门空间科学,“空间”是地理学最基本的概念,“区域性”是地理学最本质的特性,地理学发展出了空间结构理论(如区位论)、空间发展理论(如点轴理论、梯度理论)、空间作用理论(如核心—边缘理论、引力场理论)、空间生产理论等一系列理论,具有庞大的空间系统理论体系。这种种的空间理论都能为健康中国建设提供理论指导。如不同空间尺度上健康状况(如疾病、寿命等)、人体医学指标(如心肺指标、血液指标)、健康影响因素(如环境、收入等)、健康风险因子(如污染暴露、生活方式、不良行为等)、健康服务保障(如卫生投入、保险制度、医疗资源等)、健康环境建设(如城市蓝绿空间生产)、健康产业设施(如医院、养老院、健身中心等)的空间分布、空间差异、空间优化、空间均衡等。
(3)区域可持续发展理论的指导。地理科学是实现可持续发展的基础学科[13],区域可持续发展理论是地理科学调控与优化人地关系的重要理论。环境和人体都是复杂系统,其系统功能的最佳发挥都有赖于结构的优化。地理学研究地理环境及其人地关系,不止在于揭示其空间分异和时间演化的规律,更在于通过环境系统的优化和人地关系的协调来创造更宜居、更舒适、更美丽、更有益于人群健康的人居环境。环境系统和人体系统统一于人地关系地域系统,地理学对地域系统的优化,是以区域可持续发展理论为基本理论,以规划为工具,以自然与社会协同进化为目标的优化。区域人群的健康,不仅是人体内部五脏六腑之间的脏腑关系的协调平衡,而且是人体系统与外部环境系统之间的人地关系的协调平衡,而这两种关系的协调平衡,又有赖于区域内当代人与后代人之间代际关系的平衡和区域间当代人与当代人之间的区际关系的平衡。健康中国建设必须遵循可持续健康的路径,地理学藉以优化人文世界的区域可持续发展理论(如健康可持续发展理念)当然也能为健康中国建设提供理论指导[19]。
2.3 地理学能为健康中国建设提供实践指南
地理学存在的依据是“服务社会”[31],自诞生以来它便是一门具有极强社会功能的、应用性很强的经世致用之学。自1949年中华人民共和国成立以来,中国地理学积极服务国家需求,在自然地理区划、土地类型划分、统筹城乡发展、区域可持续发展等方面,做出了系列重要成果,起到了不可或缺的作用[32]。环境与健康关系为地理学研究的最基本的人地关系,健康促进是地理学研究的重要社会目标,在健康中国建设进程中,地理学在健康生活、健康服务、健康环境、健康保障、健康产业诸方面都可以提供视角独特的实践指南。在参与健康中国建设过程中,地理学区别于其他学科的独特优势在于:地理学能以多尺度时空嵌套方式对健康促进的分布格局(重大疾病、健康资源、重点人群、重大健康风险等),关系机理(自然环境与健康、社会环境与健康、建成环境与健康、环境污染与健康、人类生活方式及其时空行为与健康),优化配置(医疗卫生资源、健身设施与健康服务的配置优化,健康资源的开发利用和保护、健康产业的布局等),环境营造(健康社区、健康乡村、健康城市的建设,健康风险的检测、评估、区划等)等进行实践探索和决策咨询。
(1)健康生活引导。地理教育是国民素质教育的基础科目,环境是影响人体健康最广泛最重要的因子,地理学阐释地理环境与人类健康的关系,探索环境要素对不同地区、不同人群、不同生理健康指标的影响[33],揭示气候、土壤、水质、动物、植物、微生物和自然生态综合体,以及政治、经济、文化、科技、教育和社会综合体对人类疾病、健康、寿命等的影响机制,能为人类规避环境健康风险、探寻健康生活方式、提升公共卫生意识提供实践指南。
(2)健康服务优化。重点人群(老人、妇女、儿童、残疾人)、重大疾病(传染病、地方病、慢性病)、重要区域(地方病区、自然疫源区、贫病区)是健康中国建设的主要服务对象,地理学尤其是人文地理学以人类活动为研究对象,擅长观测、分析各种人类群体的时空行为,擅长总结、提炼出各种人类活动的时空模式,做到健康服务在时间、空间和对象上的精准供给,从而为优化健康服务提供实践指南。
(3)健康环境营造。人体健康不仅取决于人体内部各脏器之间的精细平衡,而且取决于人体系统与外部环境之间的精细平衡。人体的外部环境,大至生态环境、社会环境、人居环境等,小至建成环境、工作环境、生活环境等,均是地理学的用武之地。环境是人类活动的空间,地理学不仅重视“空间”的生产,而且也擅长规划和生产合乎人类健康的“空间”,特别是在健康生态环境、健康建成环境、健康休闲环境、健康邻里环境等的建设与营造方面,没有什么其他科学比地理学更适合、更能够担当此责任。
(4)健康保障决策。健康中国建设需要针对国民的健康压力与风险、健康素养与水平,做出健康服务和健康制度两个方面的响应,即提供强有力的卫生资源保障和卫生制度保障。“分布—关系—配置”是地理学研究的基本范式[11],地理学能为医疗卫生资源(包括医疗机构、医护人员、医疗设施、药品器械等)的精准投入、优化配置和动态调整提供科学依据;能为重大健康风险项目(如易燃易爆、危重污染等)的规划、选址、投资提供决策咨询;能为国民健康安全和公众健康促进提供立法的依据和政策的建议。如突发重大疫情时应急医疗中心的选址和布局、城市供水水质标准的完善、“碧水、蓝天、净土”污染防治计划的制定等,地理学都能施展其特长。
(5)健康产业布局。发展壮大健康产业是健康中国建设的重大战略任务,经济现象是地理学研究的重大空间现象,产业布局是经济地理学传统的和基础的研究领域。在健康中国推进过程中,地理学能发挥其综合性和区域性优势,为各类健康产业的合理布局和空间组合提供科学规划和效益评估。如在中药产业方面,地理学能为道地药材、特色药材的生境调查、产区划定、格局优化提供科学服务;在老龄产业方面,地理学能为养老院选址布局、老人康养环境打造、老人邻里环境治理等提供实践指导;此外,地理学在健康旅游开展、保健产品开发(国家地理标志产品)、健身产业发展、托育中心布局等方面,也能发挥独特的实践指南作用。
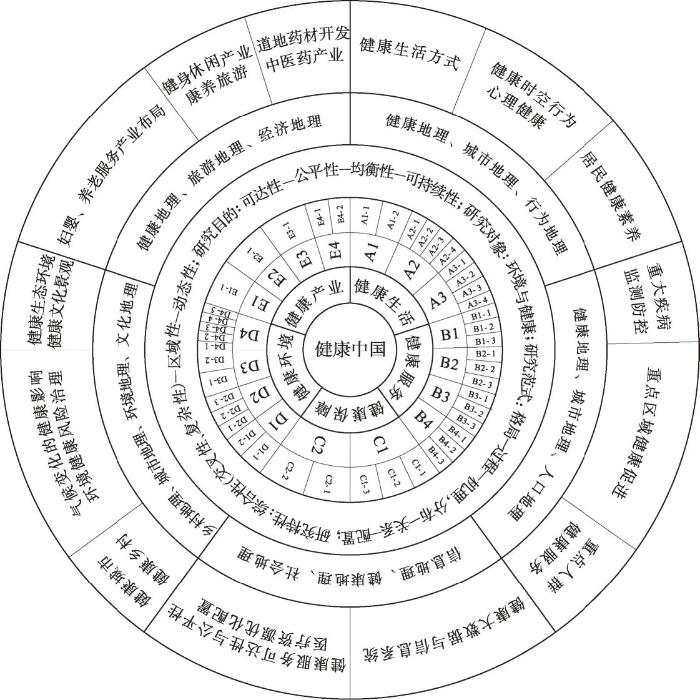
3 地理学参与健康中国建设的重点领域
图4
图4
地理学参与健康中国建设的概念框架
Fig. 4
A conceptual framework for geography participation in the construction of Healthy China
3.1 地理学与普及健康生活
(1)区域居民健康素养研究。健康素养是健康生活的基础,实施国民健康素养行动计划,是普及健康生活的有力抓手。2017年中国居民健康素养水平仅为14.18%③(③ 参见:
3.2 地理学与优化健康服务
(1)重点人群健康服务研究。老龄人口慢性病高发,是健康服务的重点人群。中国自2000年就步入了老龄化社会,并且存在快速老龄化伴随少子化、农村老龄化高于城镇老龄化[49]、老年人健康不平等和城乡差异大[50]等问题,老年人健康服务的需求和压力十分巨大。老年地理学已经成为人口地理学的重要研究分支[51],人口地理学要勇担优化老年人群健康服务的重担,在人口老龄化的时空特征与空间效应[52]、老年人健康与建成环境的关系[53-54]、老年人的空间行为、养老服务空间组织和规划[55]等方面开展研究。除老年人外,妇女儿童[56]、青少年、残疾人等也是健康服务的重点人群,与之相关的健康服务机构(如月子中心、特殊学校、医疗中心等)的优化配置、健康服务效能(如可达性、精准性、时效性等)的优化提升[57],都需要健康地理学、人口地理学、社会地理学的参与才能完成。
(2)重大疾病监测防控的研究。中国是发展中国家,但死亡谱已具备发达国家特征:一方面,重大传染病(如艾滋病、手足口病、血吸虫病等)和地方病(如克山病、大骨节病、地氟病等)的威胁并未解除;另一方面,心脑血管疾病、恶性肿瘤和其他慢性病迅速成为城乡居民最主要的死因。众所周知,人的疾病,无论直接或者间接,都与地理环境有着密切关联。因此,传统的医学地理学一般将疾病分为环境物理性疾病(如高原病、中暑、冻伤等)、环境化学性疾病(如碘缺乏病、硒缺乏病、氟中毒、砷中毒、水俣病等)、环境生物性疾病(如血吸虫、疟疾、鼠疫、霍乱等)和环境综合性疾病(如癌症、心脑血管疾病等),并且认为受地理环境影响,每一种、每一类疾病都有其独特的空间分布模式。过去几十年来,中国地理学对血吸虫病[58]、克山病[59]、地甲病[60]、鼠疫[61-62]、“非典(SARS)”[63]、癌症[64]等的研究取得了重大成果,特别是中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所的环境地理与人类健康研究团队,自20世纪60年代开展地方病环境病因与防治的研究工作,在青藏高原大骨节病、内蒙古饮水型砷中毒、陕南和贵州燃煤型砷中毒和氟中毒、西部少数民族地区饮茶型氟中毒等方面做出了许多开创性研究[65],并且编制出版了《中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集》[60]《中华人民共和国鼠疫与环境图集》[61],系统揭示了中国地方病、鼠疫流行演变与地理环境的关系,为地方病的稳定控制奠定了坚实基础[65]。2020年面对突如其来的COVID-19疫情,地理学者也积极行动起来,在疫情监测、应急防控、趋势预测、信息系统、决策支撑等方面做出突出贡献[66-67]。未来,地理学者应在重大传染病(如艾滋病、手足口病、新冠肺炎等)的时空扩散模拟预测和小尺度精准防控、重大地方病(如地甲病、地氟病、克山病等)的病情监控与土壤化学环境改良、重大疫源性和虫媒性疾病的致病媒介(如引发血吸虫病的钉螺、引发鼠疫的啮齿类动物、引发疟疾和登革热的蚊类等)监测及气候变化对其活动的影响等,继续开展深入研究,将重大疾病监测与环境变化监测有机统一起来,为重大疾病监测防控提供地理学方案。在这方面,国家合作和学科交叉十分重要,健康地理、世界地理、信息地理、气候地理、生物地理等都可以发挥作用。
(3)重点区域健康促进的研究。中国幅员辽阔,不同地区因其所处自然地理环境不同和社会经济发展阶段不同,其人口卫生意识、疾病防控能力和区域健康水平也明显不同。健康服务的目的是实现人的健康可持续,健康中国建设不仅要关注重点人群、重大疾病,更应关注重点区域。由于人群结构、健康风险以及社会经济、生活习俗的不同,不同地区有着不同的健康挑战问题和健康服务需求。贫困地区、自然疫源区、地方病流行区、口岸城市地区比其他地区有着更高的疾病流行风险,是健康中国建设应该重点关注的区域。比如,贫困与疾病是一对孪生姐妹,“因病致贫”与“因病返贫”是贫困地区普遍存在的现象,地理学对贫困区域的研究成果甚多[68-69],但从健康中国战略视角开展的研究还没有,亟待健康地理学、乡村地理学的参与。还有,鼠疫、血吸虫病等自然疫源区,克山病、大骨节病、氟中毒、砷中毒等地方病流行区,其区域环境如何改造,其健康风险如何规避,都是健康地理学值得探究的问题。
3.3 地理学与完善健康保障
(1)健康大数据与信息系统研究。健康保障是健康服务和健康体系对健康风险、健康状态的应对与响应,健康大数据是明晰区域人群健康风险和健康状态,提供精准健康服务和科学政策建议的基础。不同人群、不同区域、不同时段健康服务需求与供给的精准匹配,既是完善健康保障的重要抓手,也是健康地理学研究的重要任务。健康地理学在完善健康保障方面,① 开发健康地理信息技术如地理信息系统(GIS),整合全国重大普查数据(如人口普查、农业普查、经济普查、污染源普查等)和健康调查、健康统计数据,构建健康大数据平台,为大卫生、大健康、大医药的建设提供数据保障。② 采用遥感技术(RS),对疫源地的生态环境和媒介活动进行动态监测和数据采集,为病原体监控和疫病防控提供数据保障。③ 利用空间定位技术(GPS),对个体和群体的时空行为的健康风险进行监测,为卫生资源优化配置和疫情精准防控提供数据保障。④ 发挥地理学制图优势,对疾病/健康现象、影响因素、卫生资源的时空变化开展多时空尺度的可视化表达,为政府施行健康干预决策和百姓实施健康风险规避提供数据支撑。
(2)医疗卫生资源优化配置研究。医疗卫生资源是健康保障的物质条件,优化医疗卫生资源配置,是提高健康服务可达性、解决“看病难”问题的关键。目前,中国医疗卫生资源集中于“胡焕庸线”以东地区[70],西部地区明显不足[71],近年来虽趋向均衡化发展,但东西差异依然偏大[72-73]。资源优化配置是经济地理学研究的重要任务,优化医疗卫生资源(医卫人员、医院病床、医疗机构、卫生经费投入等)的时空配置,科学精准地解决人群、区域、时段健康服务的供需矛盾,这是健康中国建设的完善健康保障的必由路径,也是经济地理学参与健康中国建设的使命担当,经济地理学要加强医疗卫生服务公平性、有效性、均等化的研究,为健康服务机构合理布局、医疗卫生资源优化配置、医疗卫生经费精准投入等提供决策咨询。
(3)健康服务可达性与公平性研究。健康保障首在健康服务的可达性和公平性,而健康服务的可达性和公平性,存在人群的和地区的差异。一般而言,富人的健康服务可达性比穷人高,城市居民的健康服务可达性比农村居民高。如城镇老年人的健康服务,无论是地理可达性还是经济可达性,都显著高于农村老年人[74]。利用空间分析理论和方法,从不同地理尺度分析不同类型人群的医疗卫生服务可达性,并提出健康服务均等化、公平性的政策建议,也是地理学服务健康中国建设的重要方面。
3.4 地理学与建设健康环境
(1)气候变化的健康应对研究。工业革命以来,全球气候显著变暖[75-76],中国气候变暖速率明显高于同期全球平均水平,1951—2020年间中国地表年均气温每10年升高0.26 ℃[77]。气候变暖对人群健康具有重大影响[78],不仅可能导致与热相关的死亡人数大幅增加[79],而且可能抵消过去半个世纪来人类在公共卫生方面取得的成就[80]。气候变暖对健康中国建设也带来巨大挑战,如导致旱涝、高温、热浪、强降水等极端天气事件增多增强,造成额外人员伤亡[78];导致室内空气质量改变,造成致病微生物异常繁殖[81];导致气候敏感型传染病(如虫媒传染病)[82]和心血管病[83]的发病率增加。中国幅员辽阔,气候类型多样,识别不同气候类型区人群健康风险[84]、模拟气候敏感性疾病传播过程[85]、预测气候变化对人群健康的影响[86],响应健康中国战略“实施以环境治理为主的病媒生物综合预防控制策略”等,都是地理学特别是气候地理、生物地理的重要研究任务。
(2)健康生态环境建设研究。良好生态环境是最普惠的民生福祉,健康中国建设需要美丽中国支撑,绿水青山不仅是金山银山,更是人们获取健康的环境基础。一方面,地理学可通过“环境本底”和“环境背景”的健康效应的研究来认识自然、利用自然、适应自然,选择美丽宜居的自然生态来获取健康,如森林康养、海滨疗养、仙山休养等;另一方面,地理学也可通过“环境异化”和“环境变迁”的健康效应研究来改造自然、完善自然、创造自然,协调人类活动与地理环境的关系来获取健康,如防治水土流失、平衡环境污染、创造舒适的人居环境等。环境地理学是地理学的新兴分支学科,应把健康生态环境建设作为重点研究领域。
(3)环境健康风险治理研究。环境污染给人类健康造成巨大威胁,世界上约70%的疾病和40%的死亡人数与环境污染有关[87],中国每年因空气污染导致约100万~200万人的过早死亡和2500万的伤残调整寿命年损失[88]。环境污染健康风险有的来自重金属污染,如铅、砷[89]、汞、锡、镉[90]、铬等[91-92];有的来自有机物污染,如多环芳烃(PAHs)[93]、多氯联苯(PCBs)[94]、挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)[95]等;有的来自空气中的悬浮颗粒(PM2.5)[96];有的来自环境噪音污染[97]。健康地理学者建立了环境砷氟暴露与地方性砷氟中毒的剂量与效应关系[98-99],揭示了人类活动影响下典型区域重金属、稀土元素污染的健康风险及其消减规律[65],为国家生态文明建设、美丽中国建设和健康中国建设提供了科技支撑。目前,地理学者虽然开始探讨污染物健康风险的时空格局、影响机理和应对机制,但研究的区域范围都较小(如农田污灌区、制药化工厂、垃圾填埋场等),亟需环境地理学者和医学地理学者联合开展流域性、全国性的不同污染物质的健康风险及其空间分异规律的研究。
(4)健康城市(环境)建设研究。城市是人口集中区,中国已有超过60%的人口居住在城市,城市健康环境建设是健康中国建设的重中之重。城市地理学至少可在以下3个方面开展研究:① 健康城市时空智能决策支持。采集城市居民高时空分辨率的时空行为信息、生命健康信息、人居环境信息等,构建城市健康地理大数据平台,开展居民健康与地理环境关系模拟,构建城市健康时空智能决策支持系统和突发公共卫生事件应急响应系统,为政府健康风险管控和居民健康风险规避提供决策支持。② 健康城市规划与空间生产。将环境与健康关系、健康风险防控及健康环境建设理念融入城市规划概念框架,通过科学布局“蓝”“绿”空间,塑造舒适邻里环境,打造亲和公共空间,使城市“空间生产”朝着有益人们健康生活普及和健康水平提升的方向转变,提高对居民健康风险的提前干预能力和对突发公共安全事件的精准处理能力。③ 城市建成环境对健康的影响。城市人口膨胀、高密度建筑、交通拥堵等对城市居民身心健康会产生不良影响,研究表明,城市绿地和开敞空间的缺乏,以及长距离的通勤可能导致居民体力活动减少,从而引起健康状况恶化[100]。因此,今后城市规划应以健康促进为目标,以减少污染和促进锻炼为原则[101]。
(5)健康乡村(环境)建设研究。中国虽然只有不到40%的人口居住在乡村,乡村的生态环境也总体上优于城市,但乡村地域远较城市地域广阔,乡村居民在建成环境和居住环境方面也远不如城市居民,农业面源污染、农村医卫条件、农民卫生意识等,都尚未达到促进健康的良好状态,乡村健康环境建设可以说任重道远。比如,因为城市污染的转移,有些乡村癌症高发,形成“癌症村”[64],又如社会经济水平的差异导致的城乡健康不均等问题[102]。与城市规划与建设一样,乡村规划与建设也要融入健康促进理念,着力营造乡村健康环境和生产乡村健康空间,斩断贫困与疾病的恶性链条。正如“美丽中国”建设必须推进“美丽乡村”建设,“健康中国”也必须推进“健康乡村”建设,这为乡村地理学和健康地理学的研究提出了新的要求,也提供了广阔的用武之地。
(6)健康文化景观建设研究。文化景观是生活环境的重要组成部分,对居民身体和心理健康有着重要影响。发展健康文化,移风易俗,是形成健康生活方式的必要途径。文化具有精神层面的特质,身份认同、景观表征、情感归属与空间、地方关系等文化地理学研究热点[103⇓-105],本质上也是文化地理学对环境与健康关系的探讨。“地方认同”“在地经历”“故土情结”“地方依恋”等地方感可对个体的心理健康产生影响,比如,“家”这个空间承载着老年人许多记忆、归属、依恋等情感。营造“家”的文化景观,增加邻里“蓝”“绿”空间暴露,对于老年人的健康维护和促进十分重要[106-107]。因此,在消除环境健康风险的同时,推进健康文化景观建设,也是健康环境建设不可或缺的重要组成部分,而健康文化景观的营造,或者说文化景观的健康促进,应成为文化地理学和旅游地理学参与健康中国建设的新领域。
3.5 地理学与发展健康产业
(1)道地药材开发与中医药产业布局研究。“推进中医药继承创新”是健康中国战略发展健康产业的重要任务。中医药文化是中华民族优秀传统文化的重要组成部分,中医理论强调人与自然和谐以及人与自然一体,其独特之处不仅在于其“上知天文,下知地理,中晓人事”的系统诊疗,而且在于其对天然动、植、矿物药材的单独或组合运用。早在2000多年前的先秦时代就有了丰富的医学地理学思想,《山海经》是中国现存最早的自然地理学著作,里面记载了大量防病、治病的本草药物,堪称第一部药物地理学著作[108-109]。中医用药讲究“道地药材”,道地药材开发必然成为中医药产业发展的抓手,这为健康地理学分支的药物地理学的发展提供了重要机遇。生境严格、有环境指示意义的道地植物药(如人参、虫草等)和道地动物药(如麝香、牛黄等),其地理分布、生境条件、产地布局等,都值得深入研究。道地药材是个历史范畴,历史医学地理也要加强药物地理的研究,为中医药产业的发展提供历史依据[110]。几乎所有的道地药材都是生物体,其地理分布和适生环境都与生物区系有关,生物地理学也要积极参与到中医药产业发展中来。
(2)康养旅游产业与健身休闲产业布局研究。随着人们生活水平的提高,求新、求奇、求知之外,求健康也已经成为旅游的重要动机之一。康养旅游是健康中国建设所需的“健康服务新业态”,近年来,康养旅游需求不断增强[111],生态旅游、养生旅游、医疗旅游等健康旅游形式深受旅游者青睐。旅游地理学要把健康促进理念融入吃住行游购娱的旅游活动环节中,加强各种疗养资源类型(如海滨型、森林型、湖泊型等)标准的制定,加强康养旅游目的地的规划与开发,加强康养旅游活动的策划与营销,推动康养旅游产业的发展。健身休闲产业也是健康中国建设所需的“健康服务新业态”,行为地理学、旅游地理学、城市地理学都可以开展生存环境与居民休闲关系、居民休闲行为与健康、健康休闲空间规划等研究,推动健身休闲运动产业因地制宜的发展,推进健身休闲产业科学合理的布局。
(3)养老服务与妇婴服务产业布局研究。老年人、妇女、儿童是健康中国战略优化健康服务的重点人群。养老服务产业和妇婴服务产业作为“健康服务新业态”,其发展尚未引起地理学界的重视。中国是一个老龄化日趋严重的国家,如何让老年人有尊严地、优雅地老去,不仅是一个人文关怀问题,更是一个产业发展问题,预计5~10年内养老服务业必将成为中国重要的服务产业,而养老服务机构(如养老院)的空间配置优化、养老社区的健康环境建设、养老服务设施的可达性和公平性,都将成为保健地理学的重要研究内容。还有,随着生活节奏的加快,家庭结构的趋简,以妇女、儿童为对象的妇婴服务也悄然兴起,妇婴服务机构(如月子中心)的空间配置优化、妇婴健康环境建设、妇婴服务的客户覆盖度及可获得性等,也将成为保健地理学的重要研究内容。
4 地理学参与健康中国建设的主要问题与对策建议
4.1 地理学参与健康中国建设面临的主要问题
健康是自然、人文和社会多要素综合作用的结果,也是空间上的一种地理现象。地理学有服务国家战略和社会需求的特殊优势,地理学者积极投身健康中国建设责无旁贷。半个世纪以来,中国地理学者在疾病地理研究、疾病图集编制、健康风险评估、健康地理信息技术开发等方面做出了突出贡献[23],近20年来,更在污染物健康风险、传染病预警防控、城市健康地理、旅游健康促进等方面进行了创新探索。不过,就健康中国战略建设而言,地理学的参与还存在一些亟待解决的问题。
(1)地理科学的健康基础薄弱。地理科学本来与健康学有着天然的不解之缘,但对健康问题的研究还没有引起足够的重视,参与健康中国建设的理论框架尚待构建。从时间维度看,中国文明历史悠久,中医药文化源远流长,历史文献中保存的丰富的健康地理学思想亟待系统整理和发掘,但目前中国医学地理学思想的发掘还处于起步阶段[108,112];从空间维度看,中国健康地理学研究的开放性还不够,国外先进的健康地理学理论和方法引入不够,相关研究大多还停留在对国外健康地理学发展转向的介绍和述评上[113-114]。不但如此,中国健康地理学还存在研究队伍分散的问题,从事城市健康/健康城市、旅游健康/健康旅游、人口健康/健康人口、地方病防治/流行病防控等研究的健康地理学力量融合不够,队伍整合不够。这种状况持续下去,虽然一定程度上有利于学科领域专业化发展,促进新的学科生长点形成,但在健康地理学尚未发展成熟的时候就去“各起炉灶”“画地为圈”,其发展必定是畸形的和不可持续的。因此,整合健康地理学力量,壮大健康地理学队伍,是地理学参与健康中国建设的当务之急。
(2)地理学者的参与意识不强。地理学与健康学貌似关系疏远,实则它们之间有着天然的不解之缘:其一,地理学研究的核心——人地关系的最基础部分就是健康学研究的核心——环境与健康关系;其二,健康现象、健康因素、健康效应等,都具有地理空间的差异,健康资源的配置、健康政策的实施也都需要地理工具的帮助。但是,许多健康地理学者尚没有认识到地理学的这些用武之地,参与健康中国建设的意识不强,实践也不多。理论上,在健康中国战略实施过程中,地理学在健康地理信息、健康产业促进、健康环境建设、健康资源配置、健康政策制定等方面都具有其他学科不可替代的优势。目前“健康中国”概念已提出10多年,“健康中国”成为国家战略亦有5年之久,但地理学者的行动相当迟缓,在健康中国战略实施过程中的发声不多,影响不大。“美丽中国”和“健康中国”是中国梦的两翼,地理学者在积极参与“美丽中国”建设的同时,也要积极参与“健康中国”的建设。
(3)地理组织的政策支持不够。一个学科服务国家重大战略的需求,必须要有组织发动和经费支持。地理学参与健康中国建设,中国地理学会(尤其是健康地理专业委员会)的组织发动、国家自然科学基金委员会(尤其是地球科学部地理处)和国家科技部(尤其是国家重点研发计划)的项目支持、地理学术期刊的论文发表至关重要。但是,中国地理学会及其所属健康地理专业委员会迄今尚未号召和组织地理学者参与健康中国的建设,国家自然科学基金委也未将“健康地理”纳入资助专业代码,地理学术期刊还没有专门针对“健康中国建设”开辟专栏和组织征文。以最有代表性的《地理学报》《地理研究》《地理科学》为例,自2012年“健康中国”战略报告发布以来,截至2021年10月未发表“健康中国”主题论文,与健康相关的地理学论文(主题与关键词限定为“健康/疾病/传染病/地方病+地理/区域/空间”)仅96篇,平均每年每刊仅3.2篇,这种状况亟待改变。
4.2 地理学参与健康中国建设的对策建议
(1)强化问题导向和目标导向的健康地理学的理论与实践研究。“追求理论是学科发展最重要的事”[14]。针对理论基础薄弱、研究队伍分散的问题,中国健康地理学应加强理论建设,围绕健康中国建设的五大战略任务,深入开展地理实证研究和政策对策研究。人不是经济学上的“理性人”,在社会文化环境和自然环境的交互背景下,人与人之间的行为模式、人与环境的相互关系都不是理性状态下的最优解,往往受到多种复杂因素的综合影响。环境污染、疾病暴发、气候变化、健康老龄困境等现实问题往往需要将其置身于更宏大的视角中去透视人与环境的互动关系,反省以往及当前人地关系中存在的问题,以应对当前及未来环境与健康关系所面临的挑战。在理论研究中,应以马克思主义哲学观为基础,从人民利益出发,科学解析当下健康与环境、健康与贫困、健康与公平之关系,妥善解决重点人群、重大疾病、重点区域之健康问题,构建具有中国特色的健康地理学理论与方法体系。在实证研究中,应立足健康中国建设亟需解决的实际问题,聚焦健康生活、健康服务、健康环境、健康保障、健康产业的战略任务,全领域、多尺度、动态地揭示疾病/健康现象与自然/人文环境的互动关系与演化规律。在政策研究中,应以“紧贴国家需求和社会需要,符合人民群众最广大根本利益”为宗旨,坚持“生命至上、人民至上”的战略理念,坚持“共建共享、全民健康”的战略原则,坚持“生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好、生命健康”的文明发展,为促进“全民健康、全周期健康、可持续健康”出谋划策,贡献智慧。
(2)强化地理应用技术与地理科学思维深度融合的健康促进研究。国家强盛以国民健康为基础,基础地理教育是壮大地理学科发展、培养健康公民的重要环节,因此,基础地理教育应对中小学生进行健康地理常识科普,培养他们关心环境、关心健康的自觉;同时增加健康地理知识的网络科普途径和社区宣传力度,增强网络时代健康地理学的公众影响力,提升公众的健康地理学知晓率。地理应用技术(如GIS、RS、GPS技术等)是地理学服务健康中国战略的重要工具,地理科学思维(如空间格局思维、系统优化思维、人地协调思维等)是地理学辅助解决健康社会不平等和健康区域不均衡的重要法宝,地理学应强化地理应用技术和地理科学思维的深度融合,拓宽参与健康中国建设的领域,提升参与健康中国建设的能力,特别是要在环境污染与重大工程的健康风险评估、健康大数据与信息系统的建设、医疗卫生资源的优化配置、健康服务新业态的科学合理布局、环境因子与疾病/健康关系的作用机理、重大疾病的监测预警与模拟、健康城乡环境和文化景观的规划与建设、中医药产业和康养旅游产业的发展等重点领域发挥优势作用,提升学科地位。
(3)强化地理组织对地理学者参与健康中国建设的系统引领与政策支持。广大地理学者要努力为健康中国建设献计出力。① 中国地理学会做好参与健康中国建设的顶层设计,包括:制定“地理学参与健康中国建设行动计划”,向全体会员发出参与健康中国建设倡议;部署专业委员会、分会、区域代表处举办地理学与健康中国建设的学术研讨会;主办以健康国家建设和健康可持续为主题的国际地理大会;表彰为健康中国建设做出突出贡献的地理学者和学会组织;针对类似COVID-19这样的重大疫情,组织地理单位进行疫情时空格局的实时监测和科研攻关,为国家对疫情的精准防控和疫后的复工复产提供决策支持。② 国家自然科学基金委地球科学部地理处做好参与健康中国建设的项目支持,包括:将“健康地理学”纳入地理学资助专业目录;将环境—发展—健康关系列入优先资助领域。③ 地理科技期刊做好参与健康中国建设的成果推介,包括:中国地理编辑出版委员会召开系列专题会,专门研究地理期刊如何支持地理学参与健康中国建设;地理期刊根据各自办刊宗旨,围绕健康中国战略重点,开设健康地理学专栏,推介健康中国建设研究成果。④ 高等地理教育做好参与健康中国建设的人才培养,如将健康知识教育和健康生活技能融入地理类和规划类课程,开设环境与健康、健康地理学、环境健康学、健康规划学等课程。⑤ 健康地理专业委员会做好参与健康中国建设的主阵地建设,包括:协助中国地理学会制定“地理学参与健康中国建设行动计划”;推动国家自然科学基金委将“健康地理学”列入专业资助目录;整合健康地理学研究力量,加强地理、规划、城市、环境、旅游、医学、营养等关注健康的学者间的学术交流;与其他相关专委会联合举办健康中国建设主题学术会议,提升委员会的学术与社会影响。
5 结论
健康与环境关系是最基本的人地关系,地理学与健康学有着天然的不解之缘。“健康中国”建设和“美丽中国”建设是实现中华民族伟大复兴“中国梦”的两翼。和参与“美丽中国”建设一样,地理学参与“健康中国”建设,不仅责无旁贷,而且大有作为。
地理学以人地关系为研究核心,区域人群健康有赖于人与自然关系的和谐,在健康中国建设过程中,地理学具有其他学科不可替代的作用:地理学完备的理论—技术—应用体系和知识—科学—决策体系,可为健康中国战略的实施提供路径指引;地理学丰富的人地关系理论、空间系统理论和区域可持续发展理论,可为健康中国战略的实施提供理论指导;地理学独特的格局—过程—机理—优化研究范式,可为健康中国战略的实施提供实践指南。
地理学参与健康中国建设,至少可在18个领域发挥独特作用。在普及健康生活方面,可以开展区域居民健康素养、健康生活方式与时空行为、区域人群心理健康的研究与实践;在优化健康服务方面,可以开展重点人群健康服务、重大疾病监测防控、重点区域健康促进的研究与实践;在建设健康环境方面,可以开展健康生态环境建设、气候变化的健康响应、环境健康风险监测评估、城乡健康环境建设、健康文化景观建设的研究与实践;在完善健康保障方面,可以开展健康大数据与信息系统建设、医疗卫生资源优化配置、健康服务可达性与公平性的研究与实践;在发展健康产业方面,可以开展道地药材开发与中医药产业、康养旅游与健身休闲产业、养老服务与妇婴产业的科学规划与布局。
地理学参与健康中国建设,未来要强化健康中国建设的地理学理论、实证和政策研究;强化地理应用技术与地理科学思维深度融合的健康促进研究;强化地理组织对地理学者参与健康中国建设的系统引领。
致谢
感谢匿名审稿专家和武汉大学城市设计学院谢波教授对论文提出的宝贵修改意见。
参考文献
Healthcare in Singapore: The present and future
Healthy Japan 21
健康日本21
Building on Values: The Future of Health Care in Canada
Together for Health: A Strategic Approach for the EU 2008-2013
"Sick man of East Asia"
“东亚病夫”
Nature and basic issues of geography
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 3]

A discipline has typically the following four key features, namely independent research objects, independent research questions, unique characteristics, and unique social services. This paper first discusses the nature of Geography from three aspects, to reveal the characteristics of modern Geography. First, the research object of Geography is changing from simple to complex evolution. In performing geographic research, we should well recognize the complexity of geographic systems. Second, the framework of geographic research questions is structured by the fusion among geographic features, space, and time. This paper explains the essential distinction between different geographic research questions, which promotes the development of the methods and technologies for answering these questions. Third, the philosophy of combining reductionism and holism is growing continuously. A new pattern of research has been formed based on new disciplines and technologies, which is the parallel development of the research on geographic features and that on systems. This paper then identifies the essential characteristics of geographic research, summarizes the key research questions in Geography, and discusses the multiple effects of driving mechanisms on the laws of Geography. An understanding of the fundamental characteristics and the modern value of Geography illustrated in this paper will be contribute to the societal development of Geography.
论地理学的特性与基本问题
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 3]

学科通常都具有独立的研究对象、独立的学科问题、独特的学科特征以及独特的社会服务功能。本文从3个方面论述了地理学的属性,进而认识现代地理学的时代特征。①地理学研究对象的演化经历了由简单向复杂的变化过程。在研究实践过程中,应充分认识地理系统的复杂属性。②地理的要素、空间与时间相互融合构成了独特的学科问题体系,阐述了不同地理问题的本质区别,进而促进解决不同地理问题的技术与方法体系建设。③“还原论”与“整体论”并举的地理学哲学思维方兴未艾。地理学强调的综合研究在当今时代受到了前所未有的重视。在新兴学科和新兴技术的支撑下,出现了地理要素和地理系统并行研究的新格局。本文从地理学研究的基本特征出发,总结了地理学研究的核心问题,探讨地理学驱动机制对地理规律的组合效应。理解地理学关键特征和时代价值,有助于探索地理学的社会发展契机。
Geographic big-data: A new opportunity for geography complexity study
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808001
[本文引用: 1]

Since 2010, big data has played a significant role in various fields of science, engineering and society. The paper introduces the concepts of geographic big-data, the fourth paradigm and nonlinear complex geographic system, and discusses interactive relationships of these concepts. It is proposed that geographic big-data and the fourth paradigm would become a new opportunity to research on geography complexity. Then the paper discusses how to use the methods of geographic big-data and complexity science to examine geography complexity. For example, based on big-data, a series of indicators of statistical physics fields could be constructed to describe the complex nonlinear characteristics of the real geographic world. Deep learning, complex network and multi-agent methods can be used to model and simulate the complex nonlinear geographic systems. These methods are important for a better understanding of the complexity of geographic phenomena and processes, as well as the analysis, simulation, inversion and prediction of complex geographic systems. Finally, the paper highlights that the combination of geographic big-data and complexity science would be the mainstream scientific method of geography in the 21st century.
地理大数据为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808001
[本文引用: 1]

大数据之风自2010年席卷全球,已在科学、工程和社会等领域产生深远影响。本文首先从地理大数据、第四范式以及非线性复杂地理系统3组基本概念出发,剖析上述3组概念之间的科学联系与相互支撑作用,提出大数据和第四范式为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇。其后,探讨如何利用大数据和复杂性科学的理论方法开展地理复杂性研究。基于地理大数据,可以通过统计物理学的系列指标描述现实地理世界的复杂非线性特征,同时,还可利用深度学习、复杂网络、多智能体等方法,实现复杂非线性地理系统的推演和模拟。上述方法对认知地理现象和过程的复杂性,对复杂地理系统的分析、模拟、反演与预测有重要作用。最后,提出地理大数据和复杂性科学相互支撑可能成为21世纪地理学的主流科学方法。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 3]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 3]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
A preliminary study on variations of the distribution of Zhang-Disease for the past 2000 years in China
DOI:10.11821/xb199304002
[本文引用: 1]

Zhang一disease(瘴),which is an epidemic in the southern part of China in the historical pe-rinds,is a kind of pernicious malarias.This paper discusses preliminarily the links between this disease and geographical environment。the variations of its distribution and its influence on the so-ciety and economy in the region affected by Zhang一disease. The followings conclusions have been obtained: (1) Zhang一disease is an epidemic which occurs under hot and wet climatic conditions in summer and autumn. (2)In the past 2000 years,the disease was moved slowly to the South. The Northern bound-ary of the region affected by Zhang一disease was Qinlin Mountain and Huaihe River in the War-ring States Period and in the Western Han Dynasty(770BC一AD23),Daiba Mountain and Changjing River in the sui and Tang Dynasties (AD581一960),and Nanlin Mountain in the Ming and Qing Dynasties (AD1368一1911).At the present time. Zhang一disease is an epidemic only in the Yunnan Province. One of the main causes the movement of Zhang一desease is the population migration from North to south.Another reason is the change of climate to colder and drier. (3)Zhang一disease influences the society in the region affected in three aspects:population growth,production mode and economic development. These influences resulted in the fact that the northern parts of ancient China were exploited prior to the southern parts.
2000年来中国瘴病分布变迁的初步研究
DOI:10.11821/xb199304002
[本文引用: 1]

中国古籍里所说的瘴病主要是指恶性疟疾一类的传染病,它主要发生在热湿的气候环境和夏秋季节。2000年来,由于人为的作用和气候的变迁,其主要分布范围具有逐渐南移的趋势:战国西汉时期以秦岭淮河为北界;隋唐五代时期以大巴山长江为北界;明清时期则以南岭为北界。历史时期瘴病的流行,是导致瘴病分布区域社会经济发展相对缓慢的重要因素之一。
On human health sustainable development
论人类健康可持续发展
Exploration on the theoretical basis and evaluation plan of Beautiful China construction
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001
[本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
美丽中国建设的理论基础与评估方案探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001
[本文引用: 1]

美丽中国建设是关系中华民族永续发展的根本大计,也是落实到2030年联合国可持续发展议程的中国实践。党和国家针对“五位一体”的总体布局对建设美丽中国做出了战略部署,国家主席习近平在全国生态环境保护大会上进一步提出了美丽中国建设的“时间表”和“路线图”。但目前对美丽中国建设的理论基础、评估指标体系、评估标准及建设成效等问题并不清晰。本文从广义和狭义视角提出了美丽中国建设的基本内涵,将人地和谐共生论、五维一体美丽论作为美丽中国建设的核心理论基础,进一步构建了包括生态环境、绿色发展、社会和谐、体制完善、文化传承等5个维度的美丽中国建设评估指标体系,运用联合国人类发展指数(HDI)测评方法,对2016年中国341个地级市(州)的美丽中国建设成效进行了科学评估。结果显示,美丽中国建设的综合美丽指数(中科美丽指数)平均值为0.28,总体处于偏低水平,生态环境美丽指数、绿色发展美丽指数、社会和谐美丽指数、体制完善美丽指数和文化传承美丽指数分别为0.6、0.22、0.29、0.22和0.07,分项指数值均较低,且地域发展差异较大,说明美丽中国建设进程总体缓慢且不平衡。为了高质量、高标准地贯彻落实美丽中国建设的“时间表”和“路线图”,建议构建并发布通用的美丽中国建设进程评估体系,对美丽中国建设进程开展动态监测与阶段性综合评估,编制并发布美丽中国建设评估技术标准,做好美丽中国建设综合区划,分区域因地制宜地开展美丽中国样板区建设试点,并把美丽中国建设成效纳入各级政府考核指标。
Research on the monitoring and evaluation framework and indicator system of "Healthy China"
“健康中国”建设监测评估框架和指标体系研究
2018 Global reference list of 100 core health indicators (plus health-related SDGs)
Research progress in man-land relationship evolution and its resource-environment base in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201612001
[本文引用: 1]

Man-land relationship research, as the core of geographical research, runs through each development stage of Geography. Based on extensive literature review, this paper systematically generalizes the connotations, research development and contents of man-land relationship in China. (1) It explores the connotations and evolvement rules of man-land relationship in different social development stages in China, and finds that the core role of man-land relationship in geographical research has been strengthened continuously. Changing with times, its connotations have been considerably enriched by sustainable development and other notions, and so does its theoretical system. (2) It applies the bibliometric method to sketch out the basic research status of man-land relationship in China. Specifically, it quantitatively identifies the funding sources, major research teams and journals for publication. It finds that the funding sources show a diversification trend with national funding being the primary source of research grants. The most competitive research teams are mainly concentrated in the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and normal universities. Journals sponsored by the Geographical Society of China are most influential in publishing man-land relationship research. (3) As resources and environment are the fundamental carriers of man-land relationship, this study focuses further on the research on resource-environmental base of man-land relationship, and finds that the resource-environmental base research in China has gone through an evolution process from single factor perspective research to comprehensive multiple perspective research gradually. Research themes have also experienced similar changes from land, water, energy minerals or other single factor research to comprehensive factor research of resources and environment. Empirical studies on national and regional development strategies are the feature of man-land relationship in China. More emphasis should be put on considering and following the changes in features of "man" and "land" and research on the impacts of new factors on man-land relationship in a developing and dynamic manner in the future. Particularly, we should pay more attention to research on the impacts of spatio-temporal changes in resource-environment absolute location on modes of man-land interaction, and to strengthening interdisciplinary research and systematic research on comprehensive integrated techniques so as to advance the development of application of man-land relationship theories and practices.
中国人地关系演进及其资源环境基础研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201612001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系研究始终贯彻在地理学发展的各个阶段,是地理学研究的核心。本文在大量的文献梳理基础上,对中国人地关系的内涵特征、研究概况和主要研究内容进行了系统综述。① 阐述了中国人地关系在不同社会发展阶段的内涵及演进规律,发现人地关系作为地理学研究核心的地位不断强化,其内涵随时代不断演变,尤其是可持续发展等理念的提出极大地丰富了人地关系的内涵及理论体系。② 运用文献计量方法概述中国人地关系的基本研究状况,对1980年以来人地关系研究的经费来源、主要研究团队和主要传播期刊等进行了定量识别,研究经费以国家级基金支持为主,并呈现多元化趋势;研究的优势团队主要集中在中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所及师范类院校;中国地理学会主办的期刊对人地关系研究传播具有重要影响力。③ 资源环境是人地关系的基本载体,本文进一步聚焦到人地关系的资源环境基础研究,发现中国资源环境基础研究经历了从单要素视角逐步向多要素综合视角演变的历程,研究主题从土地资源、水资源、能源矿产资源等单一要素逐步向资源环境综合要素转变。服务于国家和区域发展战略的实证研究是中国人地关系研究的特色,未来要更加注重以发展、动态的思路关注“人”、“地”特征的变化以及新因素对人地关系的影响研究,尤其要注重资源环境绝对区位的时空变化对人地相互作用的模式影响研究,加强学科交叉以及综合集成技术的系统性研究,以推进人地关系理论与实践应用的发展。
Geographical synergetics: From understanding human-environment relationship to designing human-environment synergy
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201901001
[本文引用: 1]

From the perspective of achieving sustainable development in the world and building a community with a shared future for humankind in the "Anthropocene", and considering the complexity of the Earth's surface system, various disasters facing humanity, and future challenges of resource shortages and environmental risks, we proposed the development of "geographical synergy"—the mechanism, process and dynamics of the Earth's surface system and regional sustainability—in order to realize the transformation of geographical research from the explanation of human-environment relationship to the design of human-environment synergy. We discussed the scientific and technological questions of modern geography from the perspectives of integrating natural and social units, natural resources and natural disasters, achievements and faults of humans, and coupling of dynamic and non-dynamic processes and systems. We proposed the metrics of "consilience degree" as a measure of the complexity of integrated disaster reduction system based on the understanding of disaster system and the mechanism, process and dynamics of hazard and disaster formation. Using the principles of synergetic tolerance, synergetic constraint, synergetic amplification and synergetic diversification, we proposed to build an integrated disaster risk governance consilience model under the leadership of governments and with enterprises as the main body and the full participation of communities, with multiple optimization objectives of social consent maximization, cost minimization, welfare maximization, and risk minimization. Finally, we elaborated on the synergy of human and nature through "changing nature appropriately", with a case study on the Dujiangyan irrigation system, which enabled the win-win pattern of disaster reduction and benefit making.
地理协同论: 从理解“人—地关系”到设计“人—地协同”
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201901001
[本文引用: 1]

本文从地球进入“人类世”(Anthropocene)之后,实现世界可持续发展、建设人类命运共同体的角度出发,就地表系统的复杂性、人类面临的各种灾难以及将要面临的各种资源短缺和环境风险等问题,提出发展“地理协同论”,即:地球表层系统与区域可持续性机理、过程与动力学,以实现地理学研究从理解“人—地关系”到设计“人—地协同”的转变。着眼于“人类世”时代地球表层系统由多尺度、多过程等组成的复杂性,回顾了区域论、综合论、系统论等经典地理学理论,从自然单元与社会单元的结合、自然资源利用与自然灾害防御、人类功与过的评价、自然地图与行政地图间的关系、动力学与非动力学的耦合等主题入手,深入讨论了现代地理科学与技术问题。通过理解灾害系统及其致灾成害机理、过程和动力学,构建凝聚度指标,量化综合减灾系统的复杂性。利用协同宽容、约束、放大和分散原理,以灾害风险防范共识最高、成本最低、福利最大、风险最小化为目标,构建以政府为主导、企业为主体和社区全面参与的综合灾害风险防范凝聚力模式。在分析都江堰工程如何实现除害与兴利并举的基础上,综合阐释了“人类世”时代“适度改造自然”,以实现人与自然的协同。
Innovative development of medical geology: A one health perspective
“同一健康”视角下医学地质学的创新发展
Control the environmental and health risks to promote the construction of "Healthy China"
控制环境与健康风险, 推进“健康中国”建设
Progress of medical geography and environmental health studies
医学地理和环境健康研究的主要领域与进展
From medical to health geography: Novelty, place and theory after a decade of change
DOI:10.1191/0309132502ph389oa URL [本文引用: 1]
The value of geographical science and the feelings of geographers
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201510001
[本文引用: 1]

This paper focuses on the viewpoint proposed by predecessors of geography and they believed that geography is interdiscipline subject between natural science and social science. From the perspective of national demand and development trend of international geography, this paper explains the objects and nature of geographical science and characters of region as well as comprehensive characteristics and knowledge structure. Besides, it elaborates the differences among geography, natural science and social science and advocates that geographers should concentrate on the China's environmental changes and the issues of sustainable development and further fulfil the advantages of interdiscipline and comprehensive subject. Finally, this paper proposes that China's geographical science is faced with the significant opportunities and some deep-seated crises.
地理科学的价值与地理学者的情怀
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201510001
[本文引用: 1]

本文强调了前辈地理学家提出的关于地理学是介于自然科学和社会科学之间的交叉学科的观点。从中国国家需求及当代国际地理学的发展趋势,从理论与实践的结合上论述了地理科学的学科对象、学科性质及区域性、综合性、知识结构等方面的特点,特别突出地阐述了地理科学与纯自然科学或纯社会科学的诸多不同点。提倡地理学家要十分关注中国的环境变化及带来的严重的可持续发展问题,并发挥综合和交叉研究的优势。此外还指出中国地理学面临着重要的发展机遇,也出现了深刻的危机。
The spatial distribution of the normal reference values of the activated partial thromboplastin time based on ArcGIS and GeoDA
DOI:10.1007/s00484-020-01868-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Health, environment and development: The theme of contemporary medical geography
健康, 环境, 发展: 当代医学地理的主题
Status and influencing factors of adequate health literacy among occupational populations in rural areas of China
中国农村职业人群健康素养现状及影响因素分析
Understanding healthy lifestyles for urban residents from the perspective of space-time behaviours
城市居民健康生活方式研究的时空行为视角
Regional differences of drug abuse behavior and its influencing factors among middle school students
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201806014
[本文引用: 1]

The research on adolescents' health is one of the main topics in the field of health geography. The health problems in one's teen age tend to have some potential influence in his adulthood, especially the health behaviors. Compared to adult, drug abuse of a teenager is more harmful to one's brain and more likely to lead to addiction. The study of factors that affect drug abuse among middle school students, will contribute to interventions introducing and health risks reducing. Previous researches focused on the factors that lead to drug abuse, including individual, neighborhood and regional factors. But less literature focused on the surrounding built environment of schools or studied the mechanism leading to the differences in the health behavior of different regions. This paper tries to fill in the gaps by a case study of 124 middle schools in Guangdong province, China. Using the factorial ecological analysis and cluster analysis to explore the social spatial structure of the districts in which sample schools located, as well as the multiple stepwise regression models, this paper explores the situation and factors that affect middle school students' drug abuse in different social areas. The results reveal that there are differences in the incidence of drug abuse among middle school students in different social areas. The incidence of young floating population gathering areas is the highest, followed by the aging areas. And the local business practitioners gathering areas have the lowest incidence. In the young floating population gathering areas, built and social environments such as the high proportion of students who would go to internet bars, game centers, and billiard parlors in their free time, as well as the high density of internet bars and game centers within 1000 m around the school, will cause a high incidence of drug abuse among school students. In the aging areas, characterizing good social supervision, the built environment such as the high density of intersections helps to reduce the risk of drug abuse among students. In the local business practitioners gathering areas, family factors such as harmonious family relationship help to reduce drug abuse among students. Meanwhile, if middle school students have more pocket money, they have more chances to buy drugs, and are more likely to suffer from the drug abuse.
中学生药物滥用行为及其影响因素的地域差异
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201806014
[本文引用: 1]

青少年的健康状况尤其是健康行为,往往会延续至成年时期,同时,相比于成年人,青少年的药物滥用对其大脑的危害更大,更易导致成瘾。中学生是青少年的主要群体,研究其药物滥用行为的影响因素及机制,有助于实施干预措施,减少其健康风险。以往文献对中学生药物滥用行为的研究较为全面,但对学校周边的建成环境以及地域差异引起个体健康行为差异背后的原因关注不足。以随机抽取的广东省124所初级中学为研究对象,并基于2010年各区县的人口普查数据,通过因子生态分析方法划分抽样学校所在区县的社会区类型,分析位于不同社会区的中学生药物滥用情况,而后运用多元逐步回归模型,探究中学生药物滥用行为影响因素的地域差异。结果表明,不同社会区的中学生药物滥用行为发生率存在差异,年轻化的外来人口集聚地区中学生药物滥用发生率最高,其次为人口老龄化地区,社会环境相对稳定的本地商业从业人员集聚地区最低。在年轻化的外来人口聚集地区中,课外到网吧、游戏厅、台球室活动学生的高比例与学校1000 m范围内的网吧、游艺室的高密度等外部环境容易导致学校中学生药物滥用的高发;在人口老龄化地区中,道路交叉口的高密度等建成环境表征了良好的社会监督,有助于降低学生滥用药物的风险;在本地商业从业人员聚集地区中,融洽的家庭关系有利于制约中学生滥用药物,同时零花钱越高,中学生购买药物的机会越大,因而越容易发生药物滥用行为。
Health hierarchy: The study on the cause of "diseases of affluence" in the context of ubiquitous obesity
健康的阶层差异: 肥胖流行背景下“富贵病”成因研究
The prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents in China
我国儿童青少年超重、肥胖流行现状调查
Promoting physical activity among older adults: From ecology to the individual
DOI:10.1016/S0749-3797(03)00183-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Geographical association between dietary tastes and chronic diseases in China: An exploratory study using crowdsourcing data mining techniques
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908011
[本文引用: 1]

Chronic diseases are the main cause for death in the world. Among all risk factors concerning chronic diseases, those related to an unhealthy diet are most important. Although much research was done on dietary behavior, there are only few quantitative studies on the relationship between dietary taste and chronic diseases. In this article, a taste dataset of the major categories of Chinese cuisine is established based on crowdsourced data from Chinese recipe websites. For a quantitative analysis of people's taste in different regions, additionally the locations of restaurants by category (using their respective points of interest) are integrated. Using the software Geodetector, these regional taste preferences are then correlated with the three chronic diseases, hemorrhagic stroke, pancreatic cancer, and upper respiratory tract infection. For all the three diseases, the results indicate very salty, moderate sweet and very spicy food as the primary risk factors. Also, the degree of sweetness is not linear with the risk of pancreatic cancer. These results are statistically significant. In this study, a quantitative method on discovering potential health risk factors based on mining of crowdsourced data is proposed for the first time. This method can be applied before disease-related experiments to filter potential factors, and it is helpful for the public health department to make quick corresponding intervention policies.
基于众源数据挖掘的中国饮食口味与慢性病的空间关联
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908011
[本文引用: 1]

慢性病是全球最主要的死亡原因,在所有慢性病风险因素中,不健康饮食因素居于首位,也是影响最广泛的风险因素。尽管已有许多关于饮食行为的研究,但在饮食口味与慢性病关联方面尚缺乏定量研究。鉴于此,利用众源网络菜谱数据,提取菜系中多维口味信息,结合不同地区分类的餐饮类兴趣地点(POI)数据,定量分析不同地区人群口味偏好;使用地理探测器方法,从空间分异性角度建立7种口味与出血性卒中、胰腺癌、上呼吸道感染3种慢性病的关联,得到饮食口味对慢性病空间分布的解释能力度量值。结果表明:在7种口味中,过咸是出血性卒中的首要口味风险因子;一定程度的甜是胰腺癌的首要口味风险因子,且甜的程度与胰腺癌风险并非呈简单线性关系;过辛是上呼吸道感染的首要口味风险因子,三者在统计上均表现显著。本文首次提出了基于众源数据挖掘的潜在健康风险因素定量研究方法,可以应用于病因的探索性分析,并有助于公共卫生部门制定相应的干预措施。
Neighbourhood blue space, health and wellbeing: The mediating role of different types of physical activity
An ecological study investigating the association between access to urban green space and mental health
DOI:10.1016/j.puhe.2013.08.016
PMID:24262442
[本文引用: 1]

This study aims to find whether proximity to urban green spaces is associated with human mental health.A cross-sectional examination of the relationship between access to urban green spaces and counts of anxiety/mood disorder treatments amongst residents (aged 15 years and over) in Auckland City, New Zealand.Anxiety/mood disorder treatment counts by three age groups were aggregated to 3149 small area units in Auckland. Six measures of green space access were derived using GIS techniques involving total green spaces and useable green spaces. Negative binomial regression models have been fitted to test the relationship between access to green space and area-level anxiety/mood disorder treatment counts, adjusted for age and area-level deprivation.Anxiety/mood disorder treatment counts were associated with three green space measures. The proportion of both total and useable green space within 3 km and distance to nearest useable green space all indicated a protective effect of increased access to green space against anxiety/mood disorder treatment counts. Access to total and useable green space within 300 m did not exhibit significant associations.This study found that decreased distance to useable green space and increased proportion of green space within the larger neighbourhood were associated with decreased anxiety/mood disorder treatment counts in an urban environment. This suggests the benefits of green space on mental health may relate both to active participation in useable green spaces near to the home and observable green space in the neighbourhood environment.© 2013 The Royal Society for Public Health. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Therapeutic landscapes: Medical issues in light of the new cultural geography
DOI:10.1016/0277-9536(92)90360-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
From therapeutic landscapes to healthy spaces, places and practices: A scoping review
DOI:10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.11.035 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relationship between long-term residential green exposure and individuals' mental health: Moderated by income differences and residential location in urban China
Geographic Ecological Momentary Assessment (GEMA) of environmental noise annoyance: The influence of activity context and the daily acoustic environment
Noise annoyance is considered to be the most widespread and recognized health effect of environmental noise. Previous research is mostly based on the static study of residential environmental noise, but few studies have focused on the effects of noise exposure in different activity contexts on real-time annoyance. The two deficiency are that they neglect the influence of activity context besides residence and fail to reflect the difference of time-scale effect of noise influence.Using portable noise and air sensors, GPS-equipped mobile phones, questionnaire survey, and geographic ecological momentary assessment (GEMA), this paper measured the environmental noise and real-time noise annoyance of participants at different activity places. Hierarchical logistic regression models were used to examine the effects of environmental noise on people's real-time annoyance. The paper further considered the influence of the geographic context of the activity places and daily acoustic environment on participants' real-time annoyance. Further, a nonlinear regression model was constructed using Random Forest to further examine the nonlinear relationship between environmental noise and real-time annoyance.The results showed that: (1) the average cumulative equivalent sound level during was 55 dB (A) when the participants responded to the EMA surveys; (2) Only the temperature of activity places had an influence on momentary annoyance and the higher the temperature, the more likely participants were annoyed; (3) Participants with higher perception of noise pollution in residential communities were more likely to be annoyed. However, participants with higher daily exposure to noise were less likely to feel annoyed; (4) The threshold value of the effect of noise on real-time annoyance was 58 dB (A) to 78 dB (A).These findings can guide the development of urban planning and environmental noise standards and also provide a reference for noise barrier requirements for different activity places.
Gender differences in the impact of residential mobility on subjective well-being in later life: Evidence from Guangzhou, China
A review on health inequality and related factors of the global elderly
国内外老年人健康不平等影响因素研究综述
Decomposition of income-related inequalities in health among Chinese elderly: Based on the data from Beijing
中国老年人与收入相关的健康不平等及其分解: 以北京市为例
Research progress and prospects of Chinese geriatric geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.10.011
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of China's comprehensive entry into an aging society, the problem of aging has gradually become the new normal and the focus of attention of scholars. This study combineed knowledge map analysis with traditional literature research method. Based on the CiteSpace V software and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database, we analyzed the hot spots in the study of geriatric geography in the past 15 years. The main perspectives of the geography of gerontology in China were summarized by keywords. The results as follows: (1) Spatiotemporal patterns and driving mechanism of population aging and spatial organization and satisfaction of elderly care facilities become the hot fields in the study of geriatric geography in recent years. But future study should focus on broader geographic scope and smaller scale, as well as in-depth examination of driving mechanisms. The spatial allocation of elderly care facilities lacks consideration of the special needs of the elderly. A multi-dimensional integration of elderly resident social life, emotional belongingness, and social resources into the local community is the key direction of community construction and elderly care in the future. A theoretical framework and policies on home-based elderly care with Chinese characteristics are yet to be developed to guide practice. (2) Health and environment of the elderly has become a new research area. Examining the relationship between the health and environment of the elderly at the macro level and the emotional experience and local dependence of the elderly at the micro level, exploring the spatial relationship between health and environment, and identifying and quantifying human factors of this relationship have become the main direction of research. (3) Quantitative and qualitative studies on spatial behavior of the elderly need to be complementary and integrated. Exploring the integration of behaviorist geography that emphasizes individual cognition and behavior preference and time-geography that emphasizes the integrity and restriction of time and space will become the future development direction. The purpose of this study is to provide some insights for the development of Chinese geriatric geography.
中国老年地理学研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.10.011
[本文引用: 1]

在中国全面进入老龄化社会的大背景下,老龄问题逐渐成为新常态和学者关注的焦点。本文采用知识图谱分析和传统文献研究相结合的方法,借助Citespace软件分析了2003-2017年国内老年地理学研究的热点领域,通过关键词共现归纳出中国老年地理学研究的特点为:①人口老龄化时空格局及驱动机制和养老设施空间配置成为近年来老年地理学研究的热点领域,但大区域小尺度、更深层次驱动机制有待进一步研究;如何将老年居民的社会交往、情感归属、社会资源与社区多维度结合,是未来社区建设与养老重点关注的方向;居家养老理论探索与实践总结尚未形成理论突破并推动政策实践,亟待学者对其进行本土化的理论构建。②老年人健康与环境研究成为新兴研究领域和主导方向,如何由宏观层面关注老年人健康与环境关系到微观层面关注老年个体情感体验、地方依赖,空间化健康与环境关系,选择和量化人文因素将是今后研究的重点难点。③对老年人空间行为研究有待实现定量和质性研究的互补融合,探索强调个体认知、行为偏好的行为主义地理学与强调时空整体性与制约的时间地理学的有机结合成为未来发展方向。
Understanding the spatial disparities and vulnerability of population aging in China
Aging, ealth and place in residential care facilities in Beijing, China
DOI:10.1016/j.socscimed.2010.10.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Practice of health aging in place
健康老龄化的“地方”实践
Spatial optimization of residential care facility locations in 2020 in Beijing: Maximum equity in accessibility
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.12.009
[本文引用: 1]

Beijing is facing rapid population aging. Residential care plays an increasingly important role in the care for the elderly people. It is of great importance to optimize the layout of residential care facilities to ensure equal and reasonable access, which has scientific and practical implications. This study first forecasted the spatial distribution of the elderly population under natural growth in 2020 in Beijing. Second, a spatial optimization model was established to maximize equity in access to residential care facilities. The Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm was used to solve the optimization model. As the results show, the elderly population aged 60 or older will reach 4.37 million in 2020 in Beijing, among which 7.9%, 50.2%, 30.1%, and 11.8% of the total elderly population will be located in the Capital Core Functional Area, Urban Functional Extension Area, Urban New Developing Area, and Ecological Protection Area, respectively. By contrast, 2.7%, 32.7%, 48.5%, and 16.1% of the total residential care facility (RCF) beds will be located in the Capital Core Functional Area, Urban Functional Extension Area, Urban New Developing Area, and Ecological Protection Area, respectively when optimized. The optimized RCF layouts improve spatially equal access to residential care resources with very low accessibility standard variation (0.0026), while the accessibility standard variation of actual layouts is 8 times (0.0207) that of the optimized results. In the layouts with maximum equity in access, only a portion of the demands for residential care in the Capital Core Functional Area and Urban Functional Extension Area will be met locally. The residential care resources in the Urban New Developing Area will meet both the local demands and the demands from the two functional areas in the central city. The Ecological Protection Area, however, mainly provides residential care services for the local elderly population. The optimized results of this study correspond to the “Special Plan for the Development of Residential Care Facilities in Beijing,” which also conforms to the reality that the land resources are in shortage in the central city and the physical environment in the suburb is more pleasant for the elderly people. The results of this study will support knowledge-based policy-making and planning of residential care facilities. The methods introduced in this study can also be applied to the spatial optimization of other types of public service facilities.
基于公平最大化目标的2020年北京市养老设施布局优化
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.12.009
[本文引用: 1]

北京市正快速步入老龄化社会,机构养老作为一种重要的养老模式,对其布局公平性和合理性的研究具有重要的科学和现实意义。本文首先预测了自然增长状态下2020年北京市老龄人口的空间分布,然后建立设施布局优化模型,该模型以各需求点到养老设施的可达性差异最小化为目标;并采用粒子群优化算法求解,对北京市养老设施进行以公平最大化为目标的布局优化。研究结果表明,在公平最大化的目标下,首都功能核心区和城市功能拓展区(即中心城区)所提供的机构养老资源不能完全满足本地需求。城市发展新区在满足当地的机构养老需求之外,还将为中心城区提供大量机构养老服务,生态涵养发展区在满足本地需求的基础上还可为其他地区提供少量机构养老服务。该布局导向与《北京市养老设施专项规划》提出的布局建议相一致,且符合中心城区用地紧张、郊区自然环境较舒适的现实情况。研究结果能为养老政策的制定提供科学建议,所采用的方法也能为其他类型公共服务设施的布局优化提供借鉴。
Accessibility to delivery care in Hubei Province, China
Modelling the spatial accessibility of the elderly to healthcare services in Beijing, China
The temporal and spatial distribution of the plague foci since 1840 in China
DOI:10.11821/yj2000030003
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial distribution of plague foci and plague affected areas in China are studied by GIS spatial analysis methods. The results show that there are two uncontinuous plague foci belts in South and North China. The total plague foci cover an area of about 126 km<SUP>2</SUP>, but the plague-affected areas are doubled. Due to the impact of natural environment and human socio-economic activities, the ratio of the plague foci covered area to the plague affected areas is significantly higher in South China than in North China. Then using the historical data of plague and 10-year-interval data, the 150 years spread history of the plague epidemics in China is rebuilt.
1840年以来我国鼠疫的时空分布规律
DOI:10.11821/yj2000030003
[本文引用: 1]

利用GIS空间统计工具分析了中国鼠疫疫源地的分布状况,结果表明我国鼠疫疫源地明显呈现南、北两个不连续的带状分布,北方鼠疫疫源地类型多,面积大;南方鼠疫疫源地类型少,面积小,并计算出我国鼠疫疫源地的面积为126万km2。在此基础上,利用我国人间鼠疫流行资料,分析了鼠疫空间分布规律。两者的对比表明,鼠疫病区面积在鼠疫疫源地基础上扩大一倍。由于受自然条件、人类社会经济因素和鼠疫流行规律影响,南方鼠疫病区在鼠疫疫源地的基础上扩展范围比北方明显。最后作者利用历史病情资料从1840~1990按十年段,重建了150年来中国鼠疫流行扩散简史。
Understanding the spatial clustering of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Hong Kong
We applied cartographic and geostatistical methods in analyzing the patterns of disease spread during the 2003 severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak in Hong Kong using geographic information system (GIS) technology. We analyzed an integrated database that contained clinical and personal details on all 1,755 patients confirmed to have SARS from 15 February to 22 June 2003. Elementary mapping of disease occurrences in space and time simultaneously revealed the geographic extent of spread throughout the territory. Statistical surfaces created by the kernel method confirmed that SARS cases were highly clustered and identified distinct disease "hot spots." Contextual analysis of mean and standard deviation of different density classes indicated that the period from day 1 (18 February) through day 16 (6 March) was the prodrome of the epidemic, whereas days 86 (15 May) to 106 (4 June) marked the declining phase of the outbreak. Origin-and-destination plots showed the directional bias and radius of spread of superspreading events. Integration of GIS technology into routine field epidemiologic surveillance can offer a real-time quantitative method for identifying and tracking the geospatial spread of infectious diseases, as our experience with SARS has demonstrated.
Temporal-spatial distribution changes of cancer villages in China
中国“癌症村”时空分布变迁研究
Innovative development and prospect of physical geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012002
[本文引用: 3]

Physical geography (PG) has always been the core discipline of the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGSNRR, CAS) since its establishment in 1940. It aims to serve the grand needs of national development. PG has made significant scientific and technological achievements and progress in the fields of comprehensive physical geography, climatology, geomorphology, hydrology, soil geography, biogeography, chemical geography, etc. These achievements have set up the worldwide priority status of PG, and made great contributions to the scientific and technological innovation, regional sustainable economic and social development. This paper reviews the innovative development of PG in the IGSNRR, summarizes the academic achievements and landmark progress, and looks forward to the future development strategy. Four key points are presented including the interaction mechanism of land surface elements-process, the dynamics of land surface pattern, the comprehensive integration and simulation of process of land surface system, and the sustainable paradigm and regulation mechanism of orderly human activities of land surface system.
自然地理学创新发展与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012002
[本文引用: 3]

自然地理学自中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所建立以来一直是立所的核心学科,长期以服务国家重大需求为使命,在综合自然地理、气候、地貌、水文、土壤地理、生物地理、化学地理等各学科领域取得一批重要科技成果和进展,奠定了自然地理各分支学科在国内外的优势,为国家科技创新、区域经济社会可持续发展做出了重要贡献。本文回顾了中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所自然地理学的创新发展历程,总结了自然地理学取得的学术成就与标志性进展,并展望了中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所自然地理学未来发展,提出以陆地表层要素—过程交互作用机制,陆地表层格局动态研究,陆地表层系统过程的综合集成与模拟,陆地表层系统有序人类活动的可持续范式和调控机制为核心的发展战略。
The positive impact of lockdown in Wuhan on containing the COVID-19 outbreak in China
Evaluating the effect of city lock-down on controlling COVID-19 propagation through deep learning and network science models
Theoretical system and its application of national targeted poverty alleviation assessment
国家精准扶贫评估理论体系及其实践应用
Geographic detection and optimizing decision of the differentiation mechanism of rural poverty in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701013
[本文引用: 1]

Rural poverty has long aroused attention from countries around the world, and eliminating poverty and achieving realize common prosperity is an important mission to build the well-off society in an all-round way. Scientifically revealing the regional differentiation mechanism of rural poverty has become an important issue of implementation of national poverty alleviation strategy. This paper, taking Fuping County of Hebei Province as a typical case, diagnoses the dominant factors of differentiation of rural poverty and reveals the dynamic mechanism of rural poverty differentiation by using the Geodetector model and multiple linear regressions, and puts forward the poverty alleviation policies and models for different poverty regions. The result shows that the dominant factors affecting rural poverty differentiation include slope, elevation, per capita arable land resources, distance to the main roads and distance to the center of county, and their power determinant value to poverty incidence differentiation are 0.14, 0.15, 0.15, and 0.17. These factors affect the occurrence of poverty from different aspects and their dynamic mechanism is also different. Among various factors, the slope and per capita arable land resources affect the structure and mode of agricultural production, while distance to the main roads and distance to the center of county have influence on the relationship between the interior and exterior of the region. There are significant differences in the four types identified of regional rural poverty, namely, environment constrained region mainly affected by slope (seven towns), resource oriented region mainly affected by per capita arable land (seven towns), area dominated by traffic location affected by distance to the main roads (three towns), and economic development leading area mainly affected by distance to the center of county (four towns). Then, Fuping County is divided into single core, dual core and multi-core area according to the number of core elements of the township. The county has shown a multi differentiation of rural poverty with a horizontal center of dual core area, and both sides have a single core and multi-core, which are affected by different dominant factors. Finally, this paper suggests that policy of targeted poverty alleviation should take science and technology as the foundation and form innovation of targeted poverty alleviation according to the core dominant factors of the differentiation mechanism of rural poverty. The county's poverty alleviation and development under different driving mechanisms need orderly promotion of poverty alleviation and integration of urban and rural development strategy with adjusting measures to local conditions, respecting for science, and stressing practical results.
中国县域农村贫困化分异机制的地理探测与优化决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701013
[本文引用: 1]

农村贫困化是长期以来备受世界各国关注的焦点问题,消除贫困,实现共同富裕是中国全面建设小康社会的重大任务,科学揭示农村贫困化地域分异机制,成为实施国家精准扶贫战略的重要课题。论文以河北省阜平县为典型案例,运用地理探测器、多元线性回归等模型方法,诊断出县域农村贫困化分异的主导因素,揭示了农村贫困化分异的动力机制,提出了不同贫困化地域类型的扶贫政策与模式。结果表明:① 影响农村贫困化分异的主导因素包括地面坡度、人均耕地资源、到主要干道距离、到县城中心距离等,各因素对贫困发生率分异的决定力分别为0.14、0.15、0.15、0.17;② 不同类型区域农村贫困化的分异机制存在明显差异,可归纳为自然环境约束型、资源丰度约束型、交通区位约束型、经济区位约束型等四大类型;③ 根据阜平县各乡镇核心主导因素,进一步划分出单因素、双因素和多因素影响区域,县域整体呈现出以横向中心为双因素影响区,两侧为单因素与多因素并存的多极核心主导因素影响的农村贫困发生分异区;④ 不同驱动机制下的县域扶贫开发亟需因地制宜、尊重科学、讲求实效,有序推进精准扶贫与城乡发展一体化战略。
Regional differences of quality medical resources in China based on different scales
基于不同尺度的中国优质医疗资源区域差异研究
Evaluation of the status quo of medical resource allocation and service utilization in China
中国医疗资源配置与服务利用现状评价
Spatial equilibrium state and its time evolution of medical health resource supply level in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.06.005
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of the national efforts to promote the equalization of medical and health services, to get a correct understanding of the status quo of equalization of medical and health resources and a scientific evaluation of the country to promote the equalization of medical and health services, this article discusses spatial equilibrium of medical and health resources and its time evolution, using the data of 338 cities in China as the research sample, using the medical resources supply level as a measure index of the health service. Based on the methods of kernel density estimation, Gini coefficient and its decomposition and LISA time path analysis, the spatial equilibrium analysis framework of state-region-city domain is constructed, and the spatial equilibrium state of medical and health resources and its temporal evolution are quantitatively described. The results show that: the spatial distribution of medical and health resources is moving towards equilibrium, and the crossed level of medical and health resources is higher between three regions. The high concentration area is mainly maintained in western Xinjiang, Tibet and Sichuan Region, the low and low agglomeration areas are scattered in the provinces such as Henan Province, Jiangxi Province and Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. In particular, there is a concentrated distribution area in the transitional zone between the eastern coast and the central region, the level of medical and health resources supply exists “Beijing-Shantou low belt”, which is an underdeveloped area between two developed areas in Chinese eastern costal and Beijing-Guangzhou railway, and located in “Beijing-Kowloon line”(Beijing to Jiujiang) and the south extension of the “Jiu Shan line” (Jiujiang to Shantou) along the railway. Compared to economic developmentof “Beijing-Shantou low belt”, the medical and health resourcesin “Beijing-Shantou low belt” have a small span between the north and south, and a small east-west span. At the same time, the spatial and temporal path analysis of medical and health resources supply level indicates that the spatial pattern shows a strong stability. The relative length of the time route in the central and eastern regions is relatively small, and the supply level of medical and health resources is relatively slow. In particular, the “Beijing-Shantou Troughs” are basically in the areas with the lowest relative length. Time course curvature is generally small, indicating that the development of medical and health resources supply level has a relatively stable spatial dependence and spatial change direction, that is, strong spatial locking effect. The degree of equalization of medical and health resources has been significantly improved on the national scale, while the supply level of medical and health resources in the region begins to appear. This requires the government to change the support of medical and health services to achieve the full coverage from the basic public health support to the health care services behind the focus of support; at the same time, perfecting the transfer payment system, improving the ability of backward areas to provide medical and health services, and achieve health care resources reasonable allocation in the regions, which is also the connotation of “everyone enjoys basic medical and health services”.
中国医疗卫生资源供给水平的空间均衡状态及其时间演变
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.06.005
[本文引用: 1]

为正确认识医疗卫生资源空间分布的现状,以医疗卫生资源空间均衡状态及其时间演变趋势为研究内容,采用中国338个地级市为研究样本,运用核密度估计、基尼系数及其分解和LISA时间路径分析等方法,构建国家-区域-市域3个层次的空间均衡分析框架,定量刻画医疗卫生资源空间均衡状态及其时间演变特征。研究结果表明,医疗卫生资源的空间分布正在走向均衡;医疗卫生资源供给水平在三大区域之间的交错程度较高且呈现逐渐增高的趋势;在东部沿海到中部地区的过渡地带存在集中分布的低低集聚区,即医疗卫生资源供给水平同样存在“京汕低谷带”。
Temporal-spatial relationship between health resources and residents' health in Southern China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181028
[本文引用: 1]

<p id="C3">Health is not only the basic human right, but also the foundation of personal happiness and national prosperity. Over the past 40 years of reform and opening up, Chinese residents' health has continued to improve. Health resources are the material basis for maintaining residents' health, and residents' health level is closely related to health resources level. At present, there are significant regional differences in health resources and residents' health in China. Promoting equalization level of health resources and reducing regional differences in residents' health are an important goal of "Healthy China" construction and also a vital task of health geography research. Therefore, it is of great academic value and practical significance to study the relationship between health resources and residents' health in China. Based on the coefficient of variation, geographic mapping and GWR, this paper analyzed the temporal and spatial variations of health resources and residents' health in Southern China from 2000 to 2015, and the temporal-spatial relationship between health resources and residents' health. The results showed that:</p> <p id="C3-1">(1) In the past 15 years, the health resources level of most of municipalities in Southern China (96.02%) has been continuously improving. Meanwhile, the spatial difference of health resources level gradually decreases, and the equalization level continues to increase, which is reflected as the continuous expansion of high-value region, the shrinking of low-value region and the decline of the coefficient of variation of municipalities by 23.29%. Furthermore, the western Sichuan Plateau, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta are the high value-region of health resources. </p> <p id="C3-2">(2) In the past 15 years, the residents' health level of all municipalities in southern China has been continuously improving. The spatial difference of residents' health level from east to west is obvious, but the high-value region expands continuously, the low-value region shrinks continuously, the spatial difference decreases greatly and the coefficient of variation of municipalities decreased by 64.62%.</p> <p id="C3-3">(3) In Southern China, residents' health level is moderately positively correlated with the health resources level (r=0.49), but in different cities, the contributions of health resources level to residents' health level are different, which shows significant spatial heterogeneity effects.</p>
中国南方地区卫生资源与居民健康的时空关系
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181028
[本文引用: 1]

卫生资源是维护居民健康的物质基础,居民健康水平与卫生资源水平密切相关。采用空间变异系数、GIS空间分析、地理加权回归等分析方法,对2000—2015年中国南方地区的卫生资源与居民健康的时空关系进行研究,结果表明:① 过去15年间,中国南方地区绝大多数地市(96.02%)的卫生资源水平都是持续提高的;卫生资源水平的空间差异逐渐减小,均等化程度不断提升,表现为最高区不断扩大,最低区不断缩小,空间变异系数下降23.29%;川西高原、长江三角洲、珠江三角洲为卫生资源水平最高区。② 过去15年间,中国南方地区所有地市的居民健康水平都是持续提高的;居民健康水平呈现出自东向西梯度降低的空间分异,最高区不断扩张,最低区不断收缩,空间差异大幅减小,空间变异系数下降了64.62%。③ 中国南方地区的居民健康水平与卫生资源水平呈中度显著正相关(r=0.49),但在不同的地市,卫生资源水平对居民健康水平的贡献是不一样的,呈现出显著的空间异质性影响。
Disparities of medical care access between rural and urban seniors: Based on the data from 2011 CLHLS
我国城乡老年人口医疗服务可及性差异研究: 基于2011年中国老年健康影响因素跟踪调查数据
WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2019
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.13705.19046.
Health and climate change: Policy responses to protect public health
Quantitative risk assessment of the effects of climate change on selected causes of death, 2030s and 2050s
China's challenges and policy recommendations for addressing climate change and improving public health
中国应对气候变化和改善公众健康的挑战与政策建议
Evaluation of microbial content of indoor air in hot arid climate
DOI:10.1007/s13762-018-2068-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Climate and dengue transmission: Evidence and implications
DOI:10.1289/ehp.1306556
PMID:24058050
[本文引用: 1]

Climate influences dengue ecology by affecting vector dynamics, agent development, and mosquito/human interactions. Although these relationships are known, the impact climate change will have on transmission is unclear. Climate-driven statistical and process-based models are being used to refine our knowledge of these relationships and predict the effects of projected climate change on dengue fever occurrence, but results have been inconsistent.We sought to identify major climatic influences on dengue virus ecology and to evaluate the ability of climate-based dengue models to describe associations between climate and dengue, simulate outbreaks, and project the impacts of climate change.We reviewed the evidence for direct and indirect relationships between climate and dengue generated from laboratory studies, field studies, and statistical analyses of associations between vectors, dengue fever incidence, and climate conditions. We assessed the potential contribution of climate-driven, process-based dengue models and provide suggestions to improve their performance.Relationships between climate variables and factors that influence dengue transmission are complex. A climate variable may increase dengue transmission potential through one aspect of the system while simultaneously decreasing transmission potential through another. This complexity may at least partly explain inconsistencies in statistical associations between dengue and climate. Process-based models can account for the complex dynamics but often omit important aspects of dengue ecology, notably virus development and host-species interactions.Synthesizing and applying current knowledge of climatic effects on all aspects of dengue virus ecology will help direct future research and enable better projections of climate change effects on dengue incidence.
Heat-related mortality projections for cardiovascular and respiratory disease under the changing climate in Beijing, China
Health effects of hot weather: From awareness of risk factors to effective health protection
DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61711-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
Identifying spatio-temporal dynamics of Ebola in Sierra Leone using virus genomes
Environmental health in China: Progress towards clean air and safe water
DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60062-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Strengthen environmental and health research capacity to build a beautiful China
加强环境与健康研究助力美丽中国建设
(Barely) living in smog: China and air pollution
Blood pressure associated with arsenic methylation and arsenic metabolism caused by chronic exposure to arsenic in tube well water
Environmental contamination and health hazard of lead and cadmium around Chatian mercury mining deposit in western Hunan Province, China
DOI:10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60139-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Approaches of health risk assessment for heavy metals applied in China and advance in exposure assessment models: A review
健康风险评估方法在中国重金属污染中的应用及暴露评估模型的研究进展
Overview on the research works in the field of environmental geography and human health
DOI:10.11821/yj2010090004
[本文引用: 1]

In the 1960s, the Institute of Geography called for chemical process research in physical geography and set up the first department on chemical geography in China. The department has participated in all earlier national programmes on environment, which has promoted the development of environmental sciences and technologies in China. The department also has led other institutes in the Chinese Academy of Sciences to conduct the studies on the geographic pathogeny and controlling of Keshan disease, Kaschin-Beck disease and other endemics, which has enhanced the initiation and development of medical geography in China. In 2000, the institute redistributed the department from chemical geography to environmental geography, as well as from medical geography to health geography. The expanding research works include the ecological and health risk assessment of pollutants such as heavy metals, the health risks of global environmental change, the biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen and their relationships with greenhouse gas emissions. Sets of technologies on site pollution treatment and health protection have been developed. Further research into environmental geography and human health will focus on the chemical property of geographic environment, so as to probe into the interactions among environment, human health and socio-economic development, for human safety and sustainable development.
环境地理与人类健康研究成果与展望
DOI:10.11821/yj2010090004
[本文引用: 1]

中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所倡导和建立了化学地理研究机构,是我国最早从事环境科学研究的单位之一,推动了环境质量调查、环境质量评价、环境背景、环境容量和环境治理等理论和技术的建立和发展;长期进行克山病、大骨节病等地方病的调查及其环境病因与防治的研究,为上述疾病的控制做出了重大贡献;创立和发展了中国的医学地理学研究体系。2000年以后,在持续开展西部地方病地理流行规律和稀土元素生物地球化学循环研究基础上,重点开展了重金属等污染物及全球环境变化的健康风险评价研究,拓展了区域碳、氮、磷等生命元素的生物地球化学循环与温室气体排放的关系研究,强化了环境污染治理和健康保护的技术研究。实现了从化学地理到环境地理、从医学地理到健康地理的转变。未来的环境地理与人类健康研究将以地理环境的化学属性为重点,以人口健康保护为核心,探讨环境保护、社会经济发展和人类健康安全在整体上协调的机制与途径。
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban surface dust of Guangzhou, China: Status, sources and human health risk assessment
DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.030 URL [本文引用: 1]
Bioaccumulation and human health risks of OCPs and PCBs in freshwater products of Northeast China
DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.046 URL [本文引用: 1]
Pollution profiles, health risk of VOCs and biohazards emitted from municipal solid waste transfer station and elimination by an integrated biological-photocatalytic flow system: A pilot-scale investigation
A 10-year observation of PM2.5-bound nickel in Xi'an, China: Effects of source control on its trend and associated health risks
Understanding the relationships among individual-based momentary measured noise, perceived noise, and psychological stress: A geographic ecological momentary assessment (GEMA) approach
Associations of arsenic metabolites, methylation capacity, and skin lesions caused by chronic exposure to high arsenic in tube well water
DOI:10.1002/tox.22209 URL [本文引用: 1]
Environmental dose-effects of fluoride in endemic fluorosis of drinking type areas
饮水型氟中毒病区氟的环境剂量—效应研究
The combined effects of healthy lifestyle behaviors on all cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.ypmed.2012.06.017 URL [本文引用: 1]
Exploration of approaches and factors of healthy city planning
健康城市规划路径与要素辨析
Child health inequities in developing countries: Differences across urban and rural areas
'Countless acts of recognition': Young men, ethnicity and the messiness of identities in everyday life
Cultural Geographies:An Introduction
Technological trajectories: Old and new dialogues in geography and technology studies
Location or dis-location? Towards a conceptualization of people and place in the care-giving experience
The neighborhood effect of exposure to green and blue space on the elderly's health: A case study of Guangzhou, China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.012
[本文引用: 1]

Exposure to green and blue space refers to the surrounding green and blue space exposed in residence and activity place in daily life, which can bring about health benefits for residents. The neighborhood green and blue space is related to the elderly’s health. Based on questionnaire data in Guangzhou in 2018, remote sensing image, street scape and so on, we extracted various green and blue space indicators, etc. From the perspective of reducing harm, restoring capacities and restoring capacities, we also constructed research framework including five mediating pathway. This research employed multilevel linear regression model and mediating effect model and propensity score matching method to examine biopsychosocial pathways and mechanism linking exposure to green and blue space to the elderly’s health. According to this empirical analysis, firstly, neighborhood exposure to green and blue space is significantly associated with the elderly’s self-reported health and mental health; Secondly, physical activity encouragement and reduction in stress and social cohesion facilitation play a separate role in mediating the effect of green and blue space exposure on the elderly’s health, while reducing environmental harm and improving aesthetic pleasure did not perform significant role on the elderly’s health; Thirdly, the impact of exposure to green and blue space on the elderly's health differs significantly among different social strata. According to our findings and conclusions, we suggest the necessity of achieving 'Healthy city' and 'Health aging' construction, such as increasing the proportion of water body in public space, optimizing the layout of urban green space and improving vertical green space view, which provide new references for relevant public policies for the elderly.
蓝绿空间暴露对老年人健康的邻里影响: 以广州市为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.012
[本文引用: 1]

利用2018年广州社区问卷数据、遥感影像、城市街景、环境污染等多元数据,提取多种蓝绿空间指标,并使用多层模型、中介效应模型和倾向值匹配法,探讨中国城市背景下蓝绿空间暴露影响老年人健康的“生物?心理?社会”邻里影响路径和机制,以及对不同社会阶层间的差异。研究发现,社区层面的蓝绿空间暴露与老年人的身心健康均存在显著相关;周围蓝绿空间程度通过促进体育锻炼、缓解压力提升老年人的身体健康,可达性通过促进社会交往提升老年人的心理健康;蓝绿空间暴露对老年人健康的影响在不同阶层间存在差异。为健康老龄化、健康城市建设提供科学参考。
Medical geography thought in pre-Qin and Han dynasties in China
中国先秦两汉时期的医学地理学思想
The medical geographical value of the classic book Shan Hai Jing
《山海经》的医学地理学价值
The overview and prospects of Chinese historical medical geography in the past 30 years
近30年中国历史医学地理学研究的成就与展望
Health and wellness tourism: Literature review and research prospects
国内外康养旅游研究评述与展望
My humble opinion on medical geography
历史医学地理学刍议
Progress and prospects of geography in public health: A review of literature abroad
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020201058
[本文引用: 1]

World Health Organization defines health as ‘a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity’. Therefore, public health, the art and science of promoting health, is an interdisciplinary field which benefits from communication of different research perspectives. Of these perspectives, geography has a unique advantage in that space and health are intrinsically linked. The geographical context of places and the connectedness between places together play a major role in shaping public health. These features allow geography to theorize the associations between different variables and health from a unique angle of view and tackle public health challenges around the world. Many core geographical research themes in recent years, including inequalities, urbanization, and globalization, are directly related to public health. However, with the definition of health and public management constantly evolving, public health and geography research starting stressing emphasis on socio-economic factors, and crises like climate change and COVID-19 pandemic bringing external pressure, the geographical dimension of public health research has become much more complex and experienced many changes in connotation, theory, content and methodology. This paper starts with a brief review which shows relevant literatures at home and abroad have both experienced a slow rise, an accelerated rise, and the current rapid rise, but are divided in perspectives and topics concerned. It is worth noting that numbers of both reached a maximum in 2020. Then the paper is organized in a set of theories, methods and topics which have dominated much of the recent literature abroad: neighborhood effect, therapeutic landscapes, post-humanist thoughts, evolving quantitative and qualitative methods, healthy aging, health inequalities, and urban planning measures aimed at promoting residents’ health. In particular, it points out current opportunities in which global crises such as climate change and COVID-19 pandemic opened up for geographical research. The purpose of this paper is twofold: first, to examine recent research in the geographical dimension of public health research abroad; second, to introduce relevant theories, methods, and topics which might prove valuable to support future quests and build in-depth research on domestic public health problems.
国外地理学对公共卫生问题的研究与启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020201058
[本文引用: 1]

在工业化、城镇化、信息化持续发展,全球变化和全球事件轮番冲击的背景下,公共卫生研究不断深化,已发展为全球性的跨学科议程及研究热点。回顾相关文献发现,国内外地理学对公共卫生问题的研究在数量上均经历了缓慢上升、加速上升和当前的快速上升阶段,但切入角度和关注议题存在差异。本文通过梳理国外地理学对公共卫生问题的研究,对这一领域概念、理论、方法的发展及热点进行归纳总结和综合评述,探讨健康老龄化、健康不平等、融合健康考量的城市规划等议题下现有研究的主要争议、前景及其对国内研究的启示,尤其指出气候变化和传染病大流行等外部压力下暴露出的地理学研究契机,以期拓展视野、聚焦问题,为国内地理学者参与公共卫生研究提供参考。