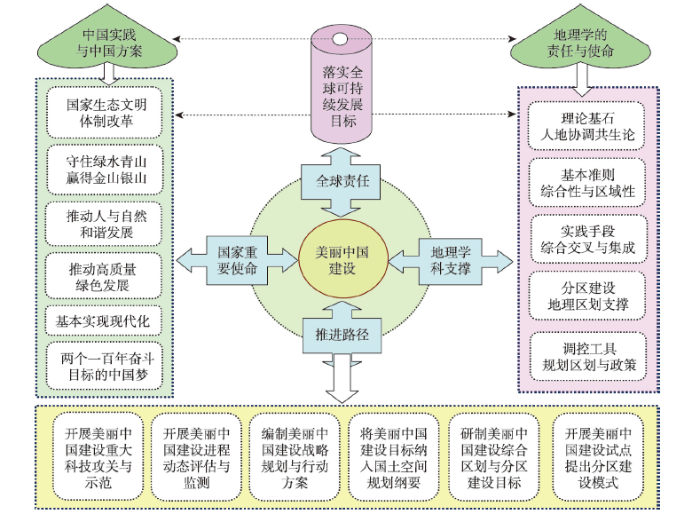
1 美丽中国建设的全球责任和国家战略要义
美丽中国是指在特定时期内,将国家经济建设、社会建设和生态建设落实到具有不同主体功能的国土空间上,实现生态环境有效保护、自然资源永续利用、经济社会绿色发展、人与自然和谐共处的可持续发展目标,形成天蓝地绿、山清水秀、强大富裕、人地和谐的可持续发展强国。建设美丽中国是落实联合国2030年可持续发展目标的中国实践和国家样板,是中国生态文明体制改革创新的战略举措与高质量绿色发展的成果检验,是推进人与自然和谐发展,守住“绿水青山”赢得“金山银山”的重要手段,是国家基本实现现代化和实现两个一百年奋斗目标的中国梦的现实选择,也是贯彻落实美丽中国建设路线图和时间表的具体行动。
1.1 联合国到2030年可持续发展目标在中国的具体实践和国家样板
2016年1月联合国大会第70届会议通过并发布了《2030年可持续发展议程》,成为联合国历史上通过的规模最为宏大和最具雄心的发展议程①(联合国大会. 《2030年可持续发展议程》, 2016-01-01),其目标就是创建一个可持续的方式进行生产、消费和使用自然资源,兼容经济增长、社会发展、环境保护,人类与大自然和谐共处,野生动植物和其他物种得到保护的世界。中国从共建人类命运共同体的全球视野和全球责任担当出发,积极响应并做出了重要战略部署,制定了《中国落实2030年可持续发展议程国别方案》,在中国共产党的“十九大”报告中明确提出将“美丽中国建设”作为落实《2030年可持续发展议程》的重要实践。2018年5月18日中国国家主席习近平在全国生态环境保护大会上进一步提出了美丽中国建设的“时间表”和“路线图”,“确保到2035年,生态环境质量实现根本好转,人与自然和谐共生,美丽中国目标基本实现”,“到本世纪中叶,人与自然和谐共生,生态环境领域国家治理体系和治理能力现代化全面实现,建成美丽中国” ②(新华社. 习近平出席全国生态环境保护大会并发表重要讲话. 中华人民共和国中央人民政府网站, 2018-05-19)。美丽中国建设目标和具体指标与《2030年可持续发展议程》提出的17个可持续发展目标、169个具体目标和300多个技术指标基本一致,涵盖了“天蓝、地绿、水清、人和”等各个维度。可见,建设美丽中国就是实现联合国可持续发展目标的本土化,就是全球可持续发展的中国实践,就是以美丽中国建设为国家样板,共同面对全球性发展问题,共同分享发展经验,从而实现全球可持续发展。
1.2 生态文明体制改革与制度建设成效的定量检验
2015年5月5日,中共中央、国务院印发了《关于加快推进生态文明建设的意见》(中发〔2015〕12号),提出了节约资源、保护环境、自然恢复、绿色发展的总体思路;同年9月21日,又印发了《生态文明体制改革总体方案》(中发〔2015〕25号),提出了尊重自然、顺应自然、保护自然、发展和保护相统一、“绿水青山就是金山银山”、山水林田湖是生命共同体等生态文明建设理念,提出要加快建立系统完整的生态文明制度体系,这是国家对生态文明体制改革创新的顶层部署。2016年12月22日,中央办公厅和国务院办公厅印发了《生态文明建设目标评价考核办法》(厅字〔2016〕45号),国家发展改革委、国家统计局等部门印发了《生态文明建设考核目标体系》(发改环资〔2016〕2635号),包括资源利用、生态环境保护、年度评价结果、公众满意程度、生态环境事件等5类23项考核目标。从指标体系可看出,国家生态文明考核指标体系的理念、目标、指标、重点与美丽中国建设评估的理念、目标、指标和重点高度一致。可见,建设美丽中国是推进生态文明体制改革创新的战略举措,美丽中国评估指标体系更是生态文明建设指标体系在不同视角上对国家可持续发展的定量检验。
1.3 推进人与自然和谐发展,守住“绿水青山”赢得“金山银山”的重要手段
2017年10月18日,习近平总书记在党的“十九大”报告中明确指出,坚持人与自然和谐共生,必须树立和践行“绿水青山就是金山银山”的理念,坚持节约资源和保护环境的基本国策。像对待生命一样对待生态环境,坚定走生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好的文明发展道路,建设美丽中国,为人民创造良好生产生活环境,为全球生态安全做出贡献。2020年4月22日习近平总书记在陕西考察期间,专门视察了秦岭生态环境保护情况,再次强调要牢固树立“绿水青山就是金山银山”的理念,提出“人不负青山,青山定不负人”。可见,建设美丽中国,就是要处理好发展经济和保护生态之间的辩证关系,就是处理好“绿水青山”和“金山银山”的辩证关系,既要“金山银山”,又要“绿水青山”,守住“绿水青山”就能赢得“金山银山”,护美“绿水青山”、做大“金山银山”,这是美丽中国建设的根本目标,也是推进人与自然和谐发展的根本保证。通过美丽中国建设,将生态资本作为区域发展的最大财富和最大资本,通过生态资本积累生产资本,提升生活资本,从靠山吃山转变为养山富山,从浏览美丽风光转变为发展美丽经济、建设美丽城市和美丽乡村,通过生态红利催生发展成效。
2 美丽中国建设的地理学使命与责任
地理学从学科诞生之日起就是为国家经济社会发展持续服务的应用型学科,地理学的综合性和区域性特点决定了地理学家肩负着建设美丽中国、筑造美好家园的历史使命,因而责无旁贷地率先成为美丽中国建设的先行者和实践者,以人地系统近远程耦合论作为美丽中国建设的理论基石,以地理学的学科交叉与综合集成作为美丽中国建设的实践手段,以综合地理区划作为因地制宜地分区建设美丽中国的重要基础(图1)。
图1
图1
美丽中国建设的地理学使命与人地耦合路径框架图
Fig. 1
Framework of geographical missions and ways to advance the Beautiful China Initiative
2.1 地理学家应成为美丽中国建设的先行者和实践者
地理学是研究地球表层自然环境与人类活动之间相互作用及其空间分异规律的科学,研究的最终目标就是推动人与自然和谐发展,这一目标也正是美丽中国建设的最终目标。地理学家应该将人地关系地域系统的理论和人地和谐共生思想贯穿到美丽中国建设的全过程中去,以地理学理论指导美丽中国建设实践,在实践中提升地理学理论,推动地理学学科建设,这是每一位中国地理学家的责任和使命。地理学家可通过编制美丽中国建设总体规划、制定美丽中国综合区划、分析美丽中国建设的资源环境承载力、开展美丽中国建设进程评估、绘制美丽中国建设路线图、提出美丽中国建设的实施方案和行动计划、开展美丽中国建设试点等一系列实践活动,成为美丽中国建设的先行者和实践者。通过理论创新、规划、区划、评估、标准制定、关键技术研发、示范区建设、可视化、智能化等手段,推动美丽中国建设。美丽中国建设的理念提出以后,一系列地理学家率先开展了美丽中国建设的理论与方法研究探索[1],提出了美丽中国建设的基本内涵、理论基础与评估方案[2],构建了美丽中国建设评估指标体系[3,4,5],分析了美丽中国与国土空间管制、国土空间规划、城市规划的关系[6,7,8]、美丽中国与生态文明建设战略[9]等。这些研究均为美丽中国建设提供了重要参考。
2.2 人地系统耦合论是美丽中国建设的理论基石
人地系统是地球表层上人类活动与地理环境相互作用形成的开放的复杂巨系统[10],人地关系地域系统始终被视为人文地理学研究的永恒主题与核心[11,12]。从古代“天人合一”的人地关系到现代人地和谐共生的人地关系,从古代农业文明到近代工业文明,再到现代生态文明,从近程的人地关系到近远程的人地关系,其演进主线基本围绕人地关系和谐这一核心伸展,不同演进阶段的人地系统耦合始终围绕协调人与人、人与地、地与地三者之间的关系进行模拟调控。特别是近年来,伴随全球性人口、资源、经济和环境问题的日益加剧,人地关系矛盾日益突出,人地系统的性质及人地关系内涵在演进中不断深化,从可持续发展、到科学发展观、再到生态文明、进而到美丽中国建设等,都是新形势下人地关系理论的具体实践形式,都是将人地系统协调共生理论作为综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的亘古不变的理论基石,充分体现出人地关系论在指导国家和区域经济社会发展中的重要地位与发挥的重大作用[13]。考虑到人地系统是一个开放系统,系统耦合模拟调控除了充分考虑系统内近程要素的深刻影响外,还要关注系统外的远程要素带来的影响。2020年傅伯杰院士提出发展地理学、促进可持续性研究的五大核心领域,其中第3大领域强调人与环境系统的恢复力和承载边界、人类活动及其环境影响的定量表征、自然和人文因素耦合影响及双向反馈机制、自然—社会系统的多尺度结构匹配与近远程耦合等[14]。这体现出人地系统的近远程耦合是新形势下指导美丽中国建设的重要理论基础,也是美丽中国建设的核心目标。
2.3 综合地理区划为因地制宜地建设美丽中国奠定了分区基础
综合地理区划是从区域角度观察和研究地域综合体,探讨区域单元的形成发展、分异组合、划分合并和相互联系,是揭示某种现象在区域内的共同性和区域之间的差异性的手段,是对过程和类型综合研究的概括和总结[15,16,17]。从古代人们对地球版图的概念划分,到近代德国的洪堡、李希霍芬等根据实地考察对地表系统的分区[18],再到当代在GIS、大数据等支持下各类与国民经济社会密切相关的综合区划、专题区划的蓬勃发展,地理学在其发展历程中的每一次进步都与地理单要素或综合要素的区划密切相关,每一次特定地理要素区划的突破都标志着一个地理学分支的成熟和学科建设迈向了一个全新的发展阶段。1949年中华人民共和国成立以来,一代又一代的地理学家完成了大量具有理论和应用价值的综合地理区划成果,包括了中国自然地理综合区划[19,20,21]、中国生态区划[22]、中国陆地表层系统区划[23]、中国气候区划[24]、中国人文地理综合区划[25]、中国主体功能区划[26]、中国农业区划[27]、中国经济区划[28]、中国新型城镇化区划[29]、中国聚落景观区划[30]等。这些综合地理区划不仅为指导特定时期国家经济社会发展、生态环境保护做出了重要贡献,同时为新形势下美丽中国综合区划方案的制定奠定了坚实的理论、方法和实践基础。
2.4 地理学的综合性与区域差异性分析是美丽中国建设质量诊断的重要手段
地理学的两大基本属性是综合性和区域差异性,也是美丽中国建设遵循的基本准则。从综合性分析,地理学的研究对象涉及到地球表层的人口、经济、社会、生态、环境等自然要素和人文要素的方方面面,这些要素间发生着极为复杂的非线性作用,单独研究某一要素而忽视其他要素的作用,都无法解释地球表层各种要素相互作用的机制和规律,只有采取综合思维,统筹各要素的相互作用,才能得出对特定地理现象全面而系统的认识。借助地理学的空间分析方法,不仅可以科学诊断美丽中国建设过程中生产、生活、生态空间(三生空间)的冲突与问题,还可定量测算空间利用质量的耦合协调程度[31]。以此为基础,可多维度解析美丽中国建设过程中各要素的协同促进关系,分析各子区域耦合协调程度的时空分异特征。从区域差异性分析,地理学的地带性分异规律告诉我们,地球表面复杂多样的自然地理环境和人文地理环境虽然千差万别,但体现出差异之美,锦绣河山各有各的秀美之处。这就要求我们在建设美丽中国、开展美丽中国建设进程评估时,要遵循地理学的差异性原则,充分体现地区差异性,综合考量各地区发展水平、资源环境禀赋等实际,科学合理分解各地区目标,不搞一刀切,针对不同地区的特点,制定差异化指标体系,提出差异化的美丽中国建设目标和行动计划,确保中华大地各展风采,各显其美,共同富裕。
2.5 地理学的综合集成与模拟优化方法为美丽中国发展路径选择提供了科学工具
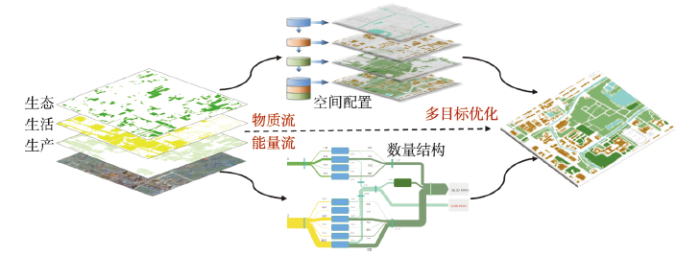
地理学作为自然与人文交叉学科,从地理学视角认识理解地理“耦合”,实现综合集成[32],可以探索出实现美丽中国建设的基本路径。人地系统功能的强弱取决于各组成部分之间的组合与匹配状况,只有相互协调、相互适应,才能顺利地演进[33]。美丽中国建设过程是人地系统的具体实践形式,其子系统之间或系统内外部之间物质能量流动多变,受多方面因素影响,兼具系统性、复杂性和非线性等特征。通过地理学的综合集成和学科交叉,采用人地系统耦合圈图谱和耦合器调控优化方法可推动美丽中国建设由理论认知转化为实践行动[34]。通过地理学的综合集成、学科交叉理念和复杂系统优化方法,可推动美丽中国建设由理论认知转化为实践行动。应用遥感和GIS技术结合资源代谢理论,可分析美丽中国建设过程中的能量流动、物质循环和信息传递过程及其影响因素和驱动机制,包括土地资源的空间配置、水资源和能源在三生空间特别是不同产业之间的流动,以及生产、社会、生态活动过程中的碳流通等,通过数值模拟和定量估算,为其要素整合和结构调整提供目标导向(图2);系统动力学模型能够表达系统复杂关系,在人口分布、经济布局、国土利用以及生态环境保护等多目标规划框架下引入系统动力学模型,能够有效实现以多目标为导向的美丽中国发展要素总量控制,再到资源结构调控、物质能量转换效率提升,落实到空间合理布局的地理复杂巨系统的动态优化过程。以系统功能整体协同演化为目标,自上而下的逐层实现要素的统筹分配和结构调整,用“空间与过程耦合—时空动态统一—复杂系统优化”的思路构筑美丽中国发展的级联优化路径,最终实现合理的资源保护和高效利用。
图2
图2
基于复杂系统优化方法的美丽中国路径选择示意图
Fig. 2
Choosing Beautiful China path by the complex system optimization
3 美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合调控路径
从人地系统耦合角度推进美丽中国建设,需要树立美丽国土观,开展人地系统耦合的重大科技攻关和试验示范,进行美丽中国建设评估的人地系统耦合监测,编制美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合路线图,因地制宜地做好美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合区划,在试点中总结美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合模式。
3.1 开展美丽中国建设的重大科技攻关和人地系统耦合试验示范
建设美丽中国尚且面临一系列亟待突破的关键技术瓶颈,需要开展美丽中国建设的重大科技攻关和人地系统耦合试验示范。在中国科学院战略科技先导专项“美丽中国生态文明建设科技工程”专项支持下,重点开展:重点污染区大气环境与大型复杂场地污染防控关键技术研发与示范、长三角区域生态环境协同管理与综合治理示范、粤港澳大湾区城市群生态建设工程与生态系统智能管理示范、长江经济带干流水环境水生态综合治理与应用、近海与海岸带环境综合治理及生态调控技术和示范、生态脆弱区绿色升级发展途径与示范、绿水青山提质增效与乡村振兴关键技术及示范、自然保护地健康管理与生态廊道设计技术与示范、气候变化条件下山地致灾风险绿色调控关键技术与示范、生态文明建设地理图景技术与应用示范等10大关键技术研发及应用示范,通过实验示范,开展多尺度精准检测和诊断生态文明建设状态,突破研制复合污染防治、生态系统修复及绿色升级核心技术和装备体系,设计支撑生态文明建设供给侧改革的重要技术平台和制度创新的关键技术,科学设计区域环境污染综合治理和生态环境协同管理、自然保护地健康管理、生态智慧城市建设、乡村振兴等发展路线图,提出优化国土空间管控方案,多尺度动态模拟美丽中国建设2035年目标和2050年愿景。为建设美丽中国,打造山水林田湖草生命共同体提供蓝图与实施途径。
3.2 开展美丽中国建设进程的动态评估与人地系统耦合监测
2020年2月28日国家发展改革委印发了《美丽中国建设评估指标体系及实施方案》(发改环资〔2020〕296号),明确了美丽中国建设进程评估体系由空气清新、水体洁净、土壤安全、生态良好、人居整洁5类指标22个具体指标构成,并从2020年起正式启动对美丽中国建设进程评估,规定每5年评估两次,作为国民经济和社会发展五年规划纲要实施中期和末期美丽中国建设目标落实情况的综合评判依据。发挥评估工作对美丽中国建设的引导推动作用,以此引导各地区落实和推动工作,助力实现美丽中国目标。
在美丽中国建设的推进过程中,建设进展程度如何,建设效果如何,综合美丽程度如何考量?回答这些问题需要开展美丽中国建设进程的动态评估与监测。需要在协调好与生态文明建设考核目标体系、绿色发展指标体系、高质量发展指标体系、以及联合国可持续发展指标体系的逻辑关系前提下,按照美丽中国建设评估指标体系及实施方案,开展美丽中国建设进程评估。具体评估的技术流程为:按照评估指标采集评估数据,以省及地级行政单元为空间尺度采集从2000—2020年的各类数据,包括实地调研数据、文字数据、遥感数据、土地利用数据、网络问卷调查数据等;对采集的数据采用无人机等高新技术手段进行数据校验,预处理分析和加工,建立评估数据库;对评估指标量化辨识并计算权系数,提出美丽中国建设的分阶段目标值和阈值,研发美丽中国建设进程动态评估监测系统,编制《美丽中国建设进程评估技术规程》,研制美丽中国建设满意度调查APP系统;提出美丽中国建设的分区方案与差异化评估指标体系;形成美丽中国建设评估总报告,作为指导全国和各省市区美丽中国建设成效的评判依据。通过动态评估和人地系统耦合监测,确保全国和各省市区按照美丽中国建设的时间表和路线图逐步接近目标值,在“比美健美”的竞相建设行动中实现美丽中国建设目标。
3.3 编制美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合路线图与“十四五”规划行动方案
美丽中国建设是一项长期性的重大工程,短期内无法实现所有目标,需要编制全国及各省市区美丽中国建设的中长期战略规划,绘制全国及各省市区美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合路线图,提出全国及各省市区美丽中国建设的时间表和分阶段行动方案。具体到“十四五”期间,需要先行制定出美丽中国建设的5年目标值。在正向指标方面,需要提出到2025年地级及以上城市空气质量优良天数比例、地表水水质优良(达到或好于Ⅲ类)比例、地级及以上城市集中式饮用水水源地水质达标率、受污染耕地安全利用率、污染地块安全利用率、农膜回收率、化肥利用率、农药使用率、森林覆盖率、湿地保护率、水土保持率、自然保护面积占陆域国土面积比例、重点生物物种种数保护率、城镇生活污水集中收集率、城镇生活垃圾无害化处理率、农村生活污水处理和综合利用率、农村生活垃圾无害化处理率、城市公园绿地500 m服务半径覆盖率、农村卫生厕所普及率共19个指标提升的目标值;在负向指标方面,需要提出到2025年地级及以上城市细颗粒物(PM2.5)浓度、地级及以上城市可吸入颗粒物(PM10)浓度、地表水劣Ⅴ类水体比例3个指标降低的目标值。根据美丽中国建设进程评估的22个正负指标的目标值,结合“十四五”期间经济社会高质量发展目标、生态环境高水平保护目标,分类提出“十四五”时期空气清新、水体洁净、土壤安全、生态良好、人居整洁等方面的建设重点和任务,合理确定切实可行的建设方案,构建美丽中国建设政策体系,确保实现“十四五”期间美丽中国建设的阶段性目标。
3.4 树立美丽国土观,在《全国国土空间规划纲要》中充分体现美丽中国建设目标
2019年5月中共中央、国务院下发了《关于建立国土空间规划体系并监督实施的意见》,标志着中国自此终结了长达40多年之久的“多规演义”和各类空间规划“分治”冲突的局面,这是中国空间规划编制与实施从“多规分治”的浅水区进入“多规合一”的深水区的重要里程碑,必将为优化中国国土空间格局、提高国土空间利用质量、为推动美丽中国建设发挥重要作用。回顾中国国土空间走过的开发、破坏、保护、利用的曲折演变历程,在美丽中国建设进程中,必须汲取经验教训,树立美丽国土观,在编制《全国国土空间规划纲要》时,贯彻落实“多规合一”“多审合一”和“多证合一”的“三合一”主线思维,突出生态功能保障基线、环境质量安全底线、自然资源利用上线、生态保护红线“四线”管控的要求,按照统一的测绘基准和测绘系统、统一的规划用地分类体系、统一的规划技术标准体系、统一的规划编制审批体系、统一的规划监督实施体系、统一的规划法规政策体系的“六统一”规划要求,突出美丽中国建设中的“空气清新、水体洁净、土壤安全、生态良好、人居整洁”五个维度的美丽国土建设目标,提出国土空间高水平保护、高质量发展、高品质利用、高效率修复、高强度协同的总体思路,构建美丽国土轴和美丽城市群,形成点线面结合的美丽国土高效利用格局、支撑保障体系和分区管控方案。在编制省市国土空间规划时,把美丽中国建设目标分解到各省市区国土空间优化布局的总体方案中,实现国土空间开发保护向更高质量、更有效率、更加公平、更可持续方向发展,通过规划实施推进美丽中国建设进程。借鉴发达国家美丽国土审计经验,尝试开展美丽国土审计,确保国土安全和美丽中国建设。
3.5 因地制宜地做好美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合区划,建好美丽城市群和美丽公园群
充分考虑全国地域差异,瞄准国家重大战略布局,因时制宜地做好美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合分区。美丽区是在已有的自然、人文、经济、城镇等综合区划基础上,基于ArcGIS空间分析方法,按照综合性、主导性、自然环境与社会经济系统相对一致性、空间分布连续性和行政区划完整性等原则,以自然要素、生态要素、气候要素、经济要素、人口要素、文化要素、主体功能要素、城市群要素、城镇化要素、聚落景观要素等要素为基础,将全国美丽国土划分为美丽东北、美丽华北、美丽华东、美丽华中、美丽华南、美丽西北、美丽西南和美丽西藏等8大美丽区。美丽群是指建设由5个国家级城市群、9个区域性城市群和6个地区性城市构成的20个美丽城市群[35],作为美丽中国建设的战略重点地区,这一区域以占全国29%的面积,集中了全国65%的人口、80%以上的经济总量,同时也产出了全国70%以上的污染,是国家今天和未来经济发展的战略核心区,因而也是美丽中国建设的战略重点区。除此以外,需要在国家重点生态功能区中建设一批国家公园,形成与美丽城市群错位配置的国家公园群,以保护具有国家代表性的大面积自然生态系统,实现自然资源科学保护和合理利用,作为美丽中国建设的另一类保护性战略重点区。
3.6 先行开展美丽中国建设样板试点,总结美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合模式
建设美丽中国是一场涉及经济发展方式、技术创新模式、消费价值观念和生活方式变革的系统工程,建议以美丽中国综合区划方案为基础,分区进行美丽中国样板区建设试点,因地制宜地建立若干个公认的美丽中国建设样板和示范区,进一步总结归纳“美丽”模式与“美丽”路径,为美丽中国建设提供经验与借鉴。2015年杭州成为全国首个省部共建的美丽中国建设试点城市,取得了阶段性试点成效,2019年杭州市印发《美丽城镇建设试点工作方案》,到2020年创建10个以上小城镇率先成为省级美丽城镇示范镇。2019年起住房与城乡建设部在全国启动11个城市体检与美丽城市建设试点,威海市成为全国首个获批“美丽城市”建设试点的城市,聚焦生态宜居、城市特色、交通便捷、生活舒适、多元包容、城市活力、安全韧性等目标,旨在综合提升城市人居环境与建设品质。在开展美丽城市建设试点的同时,农业农村部在全国组织开展了1100个“美丽乡村”创建试点。这些试点样板和试点经验为在全国范围内建设美丽中国提供了典范。根据不同试点美丽城市和乡村建设的实情,可总结美丽中国建设的通用模式和差异化模式,其中通用模式包括生态保护型模式、绿色发展型模式、文化传承型模式、体制机制创新型模式、市场驱动型建设模式、远程推动型建设模式、开放带动型建设模式、综合发展型建设模式等,差异化建设模式基本是千城千策,万村万方,只可借鉴,不可复制,这就是美丽中国建设的空间差异性。
4 结论与讨论
美丽中国建设是落实中国生态文明制度、推进国家可持续发展、提升可持发展能力和质量的阶段性战略部署,是对生态文明长效目标的阶段性落实,也是推动国家实现高质量发展的核心目标。
(1)美丽中国建设有广义和狭义之分。广义内涵的美丽中国是指将国家经济建设、政治建设、文化建设、社会建设和生态建设“五位一体”的总体布局落实到具有不同主体功能的国土空间上,形成山清水秀、强大富裕、人地和谐、文化传承、政体稳定的建设新格局;狭义内涵的美丽中国是指将国家经济建设、社会建设和生态建设落实到具有不同主体功能的国土空间上,形成天蓝地绿、山清水秀、强大富裕、人地和谐的可持续发展新格局。地理学推进美丽中国建设重点立足于狭义内涵的美丽中国建设目标。
(2)建设美丽中国肩负着全球责任和国家使命。是落实联合国2030年可持续发展目标的中国实践和国家样板,是中国生态文明体制改革创新的战略举措与高质量绿色发展的成果检验,是推进人与自然和谐发展,守住“绿水青山”赢得“金山银山”的重要手段,是国家基本实现现代化和实现两个一百年奋斗目标的中国梦的现实选择,也是贯彻落实美丽中国建设路线图和时间表的具体行动。
(3)地理学是美丽中国建设的先行者和实践者。地理学的综合性和区域性特点决定了中国地理学家责无旁贷地率先成为美丽中国建设的先行者和实践者,以人地系统近远程耦合论作为美丽中国建设的理论基石,以地理学的学科交叉与综合集成作为美丽中国建设的实践手段,以综合地理区划作为因地制宜地建设美丽中国的分区基础。
(4)从地理学视角推进美丽中国建设有其独特的人地系统耦合路径。可综合运用地理学的学科交叉和综合集成方法开展美丽中国建设的重大科技攻关和人地系统耦合试验示范;进行美丽中国建设进程的动态评估与人地耦合监测;编制美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合路线图与“十四五”规划行动方案;树立美丽国土观,在《全国国土空间规划纲要》中充分体现美丽中国建设目标;因地制宜地做好美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合区划,建设好美丽城市群和美丽公园群;先行开展美丽中国建设样板试点,总结美丽中国建设的人地系统耦合模式。
(5)建设美丽中国是一个长期的持久过程。是一场涉及经济发展方式、技术创新模式、消费价值观念和生活方式变革的革命性转变过程,需要立足长远,从眼下做起,根据国家经济社会发展所处的不同阶段和生态环境变化的趋势循序渐进,坚持不懈,期间会出现这样那样的问题和挑战。地理学家需要有敏锐的洞察力和高度的责任感,随时发现美丽中国建设中出现的新动向、新要素和新问题,及时提出解决对策,确保美丽中国建设向着更高质量、更高效率和更佳成效方向发展。
参考文献
Research progress and prospect of Beautiful China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Building Beautiful China is an important starting point for accelerating the reform of the ecological civilization system and realizing the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. At present, the country has set the timetable and roadmap of the construction of Beautiful China. It is of great significance to fully understand the current progress of Beautiful China research to guide future study. The current research on Beautiful China is at an exploratory stage, mainly focusing on the background and connotation of Beautiful China, the discussion of the index system, and the construction path. Among them, the connotation and theoretical basis of Beautiful China is the main body and focus of the present research, but a mature system is yet to be developed. The research of evaluation index system is in the exploration stage, and a unified understanding and standards have not been formed. The research content of the construction path is rather vague, and operability is limited. Future research needs to prioritize the following aspects. The first is to clarify the definition and connotation of Beautiful China, to build a theoretical system, and to answer the question of "what is". The second is to build a differential, development-oriented indicator system that is accessible, can be assessed, and can be implemented, to answer the question of "what to build". The third is to sum up local experiences, build a Beautiful China construction path system, and answer the question of "how to build".
美丽中国的研究进展及展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.007
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Building Beautiful China is an important starting point for accelerating the reform of the ecological civilization system and realizing the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. At present, the country has set the timetable and roadmap of the construction of Beautiful China. It is of great significance to fully understand the current progress of Beautiful China research to guide future study. The current research on Beautiful China is at an exploratory stage, mainly focusing on the background and connotation of Beautiful China, the discussion of the index system, and the construction path. Among them, the connotation and theoretical basis of Beautiful China is the main body and focus of the present research, but a mature system is yet to be developed. The research of evaluation index system is in the exploration stage, and a unified understanding and standards have not been formed. The research content of the construction path is rather vague, and operability is limited. Future research needs to prioritize the following aspects. The first is to clarify the definition and connotation of Beautiful China, to build a theoretical system, and to answer the question of "what is". The second is to build a differential, development-oriented indicator system that is accessible, can be assessed, and can be implemented, to answer the question of "what to build". The third is to sum up local experiences, build a Beautiful China construction path system, and answer the question of "how to build".
Exploration on the theoretical basis and evaluation plan of Beautiful China construction
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
美丽中国建设的理论基础与评估方案探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China construction (BCC) is of fundamental importance for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation and a Chinese practice of the 2030 UN sustainable development agenda. The Chinese government has made strategic arrangements for the BCC with a five-pronged approach. President Xi Jinping proposed the schedule and roadmap for the BCC at the National Ecological Environmental Protection Conference. But at present, the theoretical basis, evaluation index system, evaluation criteria and construction effect of the BCC are not clear. This paper puts forward the basic connotation of the BCC from a broad and narrow perspective, regards the theory of man-earth harmony and Five-dimensional integration as the core theoretical basis of the BCC, and further constructs the evaluation index system of the BCC, which includes five dimensions: ecological environment, green development, social harmony, institutional improvement and cultural heritage, and uses the United Nations human development index (HDI) evaluation method to scientifically evaluate the construction effect of 341 prefecture-level cities (states) in China in 2016. The results show that the average value of the BCC Index (Zhongke Beauty Index) is 0.28, which is generally at a low level. The average of the sub-indexes of the ecological environment beauty index, the green development beauty index, the social harmony beauty index, the system perfect beauty index and the cultural heritage beauty index are respectively 0.6, 0.22, 0.29, 0.22, and 0.07. The sub-index values are all low, and the regional development is quite different, which indicates that the construction process of Beautiful China is generally slow and unbalanced. In order to implement the schedule and roadmap for the BCC with high quality and high standards, it is recommended that we construct and publish a general evaluation system for the BCC process, carry out dynamic monitoring and phased comprehensive evaluation of the BCC process, compile and publish the evaluation standards for BCC technology, do a good job in the comprehensive zoning of Beautiful China, carry out pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China's model areas according to local conditions, and incorporate the achievements of Beautiful China into the assessment indicators of all levels of government.
Connotation and evaluation index system of Beautiful China for SDGs
面向SDGs的美丽中国内涵与评价指标体系
The "Beautiful China" evaluation system based on niche theory
基于生态位理论的“美丽中国”评价体系
Reflections on the construction of the system of the Beautiful China
关于美丽中国体系建构的思考
Beautiful China and the land space use control
美丽中国与国土空间用途管制
The construction of Beautiful China calls for landscape management legislation
美丽中国呼唤景观风貌管理立法
Geographical thinking on the relationship between Beautiful China and land spatial planning
美丽中国与国土空间规划关系的地理学思考
Designing a strategic framework for ecological civilization construction towards Beautiful China
迈向美丽中国的生态文明建设战略框架设计
Man areal system: The core of geography study On the geographical thoughts and academic contributions of Academician Wu Chuanjun
DOI:10.11821/xb199802001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Academician Wu Chuanjun is an outstanding geographer of China, well known home and abroad. In his academic career of 60 odd years, Professor Wu has made significant contributions to the development of geographical study and national construction in China, and has been taking a leading role in the process of increasing international recognition of Chinese geography and enhancing international communication of China’s geographical circle with foreign colleagues through his continuous hard efforts and serious commitment. This paper elaborates briefly the profound geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, and gives a concise introduction to his remarkable contributions to the overall development of geography in China, with focus on his significant achievements in the aspects of strengthening agriculture geography and land use study, defining the development orientations of China’s economic geography, opening up new research fields such as territorial planning and sustainable development, initiating and organizing the renewal of China’s human geography, organizing the internal cooperation in China’s geographical society, promoting international academic communication, etc.. This paper also gives insight discussions on the theory of man-earth areal system, the essence of geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, mainly referring to the background, conceptions and its relationship with sustainable development of the theory. Professor Wu creatively put forward the theoretical term of “man earth areal system”, and stresses that man earth relationship remains as the core of geographical study in all developmental stages of the discipline. He proposed that the major contents of geographical study should include following issues: general theories about the formation, functional structure and development of man earth areal system; study on the relationship among sub systems of man earth areal system, such as interaction intensity analysis, potential assessment, effect evaluation and risk analysis; study on the basic rules concerning the material and energy flow and convey in man earth areal system and approaches of overall systematic control; analysis of areal capacity of population; study on the dynamic models; analysis of areal differences and areal categorizing; study on the improved monitoring and modeling of coordinated man earth relationship of various types of regions of different spatial levels and scopes, and so on. Professor Wu has long been paying great efforts in training qualified personnel for the long term prosperity of China’s geographical career, with remarkable results concerning various fields and levels. With his most respected age of eighty approaching, Professor Wu is still on his important career mission with full energy and wisdom, providing strategic support to the development of China’s geographical study towards the 21st century.
地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统——论吴传钧院士的地理学思想与学术贡献
DOI:10.11821/xb199802001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Academician Wu Chuanjun is an outstanding geographer of China, well known home and abroad. In his academic career of 60 odd years, Professor Wu has made significant contributions to the development of geographical study and national construction in China, and has been taking a leading role in the process of increasing international recognition of Chinese geography and enhancing international communication of China’s geographical circle with foreign colleagues through his continuous hard efforts and serious commitment. This paper elaborates briefly the profound geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, and gives a concise introduction to his remarkable contributions to the overall development of geography in China, with focus on his significant achievements in the aspects of strengthening agriculture geography and land use study, defining the development orientations of China’s economic geography, opening up new research fields such as territorial planning and sustainable development, initiating and organizing the renewal of China’s human geography, organizing the internal cooperation in China’s geographical society, promoting international academic communication, etc.. This paper also gives insight discussions on the theory of man-earth areal system, the essence of geographical thoughts of Professor Wu, mainly referring to the background, conceptions and its relationship with sustainable development of the theory. Professor Wu creatively put forward the theoretical term of “man earth areal system”, and stresses that man earth relationship remains as the core of geographical study in all developmental stages of the discipline. He proposed that the major contents of geographical study should include following issues: general theories about the formation, functional structure and development of man earth areal system; study on the relationship among sub systems of man earth areal system, such as interaction intensity analysis, potential assessment, effect evaluation and risk analysis; study on the basic rules concerning the material and energy flow and convey in man earth areal system and approaches of overall systematic control; analysis of areal capacity of population; study on the dynamic models; analysis of areal differences and areal categorizing; study on the improved monitoring and modeling of coordinated man earth relationship of various types of regions of different spatial levels and scopes, and so on. Professor Wu has long been paying great efforts in training qualified personnel for the long term prosperity of China’s geographical career, with remarkable results concerning various fields and levels. With his most respected age of eighty approaching, Professor Wu is still on his important career mission with full energy and wisdom, providing strategic support to the development of China’s geographical study towards the 21st century.
Theoretical studies of man-land system as the core of geographical science
关于地理学的“人—地系统”理论研究
"Territorial system of human-environment interaction": A theoretical cornerstone for comprehensive research on formation and evolution of the geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
“人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
Promoting geography for sustainability
A preliminary study of issues of integrated geographical regionalization
Regional study is an ancient and important tradition, forming the regional school of geography. In view of integrated or unified geography, regional study of sustainable development is an important level for approaching regional system of man-land relationship and effective way for coordinating man-nature relationship. Aimed at sustainable development the integrated geographical regionalization includes natural elements and human factors. Main principles for demarcation are as follows: combining regional differentiation of physical environments and human geography, integrating comprehensive analysis and principal factors, genetic unity, as well as linking regional frameworks with regional types, etc. Criterion and index system of the integrated geographical regionalization consists of environments, resources, economy, society and population, etc. The selected criteria and indices for demarcation should be practical, simplified, comparable, quantified, and reflecting dynamic state and trends of various regions. Regional types of development states may be identified based on the above mentioned results, then proposing a tentative scheme of the integrated geographical regionalization.
关于综合地理区划若干问题的探讨
Regional study is an ancient and important tradition, forming the regional school of geography. In view of integrated or unified geography, regional study of sustainable development is an important level for approaching regional system of man-land relationship and effective way for coordinating man-nature relationship. Aimed at sustainable development the integrated geographical regionalization includes natural elements and human factors. Main principles for demarcation are as follows: combining regional differentiation of physical environments and human geography, integrating comprehensive analysis and principal factors, genetic unity, as well as linking regional frameworks with regional types, etc. Criterion and index system of the integrated geographical regionalization consists of environments, resources, economy, society and population, etc. The selected criteria and indices for demarcation should be practical, simplified, comparable, quantified, and reflecting dynamic state and trends of various regions. Regional types of development states may be identified based on the above mentioned results, then proposing a tentative scheme of the integrated geographical regionalization.
Regionalization in China: Retrospect and prospect
中国区划工作的回顾与展望
All Possible Worlds: A History of Geographical Ideas
Draft of China comprehensive physical regionalization
中国综合自然区划草案
The problem of China physical regionalization
中国自然区划问题
A new scheme for comprehensive physical regionalization in China
中国综合自然地理区划的一个新方案
Scheme of ecological regionalization in China
中国生态区划方案
Study on division of the terrestrial system in China
DOI:10.11821/xb200205002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the idea of Top-down and Bottom-up advocated by Huang Bingwei, five integrated divisions in China, including the physio-geographical division, the ecological division, the potential agro-productivity division, the economic division, and the response to global warming of China, are integrated to divide the terrestrial system of China into nine regions at the first level. Then by evaluating the Pressure, State and Response on 46 components for 344 prefectures in China with the PSR Models, the criteria in seven grades for terrestrial system status in every prefecture are established, and terrestrial system status for nine regions are assessed. The results show: (1) The regional differences in landforms and climate are the dominant priority to the regional terrestrial system status. (2) The socio-economic development dominated by human dimension is the secondary priority to the regional terrestrial system status. (3) For terrestrial system status in nine regions, North China, Southeast China and South China are at better level; Northeast China is at middle level; the Southwest China and Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia-Gansu-Shaanxi are at poor level; Northwest China and Qinghai-Xizang are at the worst level.
中国陆地表层系统分区初探
DOI:10.11821/xb200205002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the idea of Top-down and Bottom-up advocated by Huang Bingwei, five integrated divisions in China, including the physio-geographical division, the ecological division, the potential agro-productivity division, the economic division, and the response to global warming of China, are integrated to divide the terrestrial system of China into nine regions at the first level. Then by evaluating the Pressure, State and Response on 46 components for 344 prefectures in China with the PSR Models, the criteria in seven grades for terrestrial system status in every prefecture are established, and terrestrial system status for nine regions are assessed. The results show: (1) The regional differences in landforms and climate are the dominant priority to the regional terrestrial system status. (2) The socio-economic development dominated by human dimension is the secondary priority to the regional terrestrial system status. (3) For terrestrial system status in nine regions, North China, Southeast China and South China are at better level; Northeast China is at middle level; the Southwest China and Shaanxi-Inner Mongolia-Gansu-Shaanxi are at poor level; Northwest China and Qinghai-Xizang are at the worst level.
The climate regionalization in China for 1981-2010
DOI:10.1007/s11434-013-5948-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
1981—2010年中国气候区划
DOI:10.1007/s11434-013-5948-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comprehensive regionalization of human geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography is based on the rules governing regional differentiation of Chinese physical geography factors. Based on regional differences and similarities in human factors, this study divides the whole country into two levels of relatively independent, complete and organically linked human geographic units. As a fundamental, comprehensive, cutting-edge, practical and important task, the comprehensive regionalization of human geography highlights the characteristics, regional and sub-regional features, complexity and variety of spatial differences between factors of Chinese human geography. It is capable of promoting the development of human geography based on local conditions, providing basic scientific support to national and local development strategies, such as the Belt and Road Strategy, new urbanization and environmental awareness, and creating a sound geopolitical environment in key areas. Using results from existing physical and human geography zoning studies, and in accordance with the principles of synthesis, dominant factors, the relative consistency of the natural environment, the relative consistency of economic and social development, the consistency of the regional cultural landscape, the continuity of spatial distribution and the integrity of county-level administrative divisions, and taking as its basis the division of human geography into 10 major factors (natural condition, the economy, population, culture, ethnicity, agriculture, transportation, urbanization, the settlement landscape and administrative divisions), this paper constructs an index system for the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography through a combination of top-down and bottom-up zoning and spatial clustering analysis. In this study, Chinese human geography is divided into eight regions (first level) and 66 sub-regions (second level). The eight human geography regions are (I) Northeast China, (II) North China, (III) East China, (IV) Central China, (V) South China, (VI) Northwest China, (VII) Southwest China, and (VIII) Qinghai and Tibet. This zoning proposal fills gaps in studies involving the non-comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography. Each human geography region and sub-region has different topographical, climatic, ecological, population, urbanization, economic development, settlement landscape, regional cultural and ethno-religious attributes. This proposal on the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography dovetails closely with previous studies on comprehensive regionalization in Chinese physical geography, Chinese economic zoning, and Chinese agriculture zoning. It shows that, under the dual roles of nature and humans, there are certain rules of regional differentiation that govern the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography.
中国人文地理综合区划
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography is based on the rules governing regional differentiation of Chinese physical geography factors. Based on regional differences and similarities in human factors, this study divides the whole country into two levels of relatively independent, complete and organically linked human geographic units. As a fundamental, comprehensive, cutting-edge, practical and important task, the comprehensive regionalization of human geography highlights the characteristics, regional and sub-regional features, complexity and variety of spatial differences between factors of Chinese human geography. It is capable of promoting the development of human geography based on local conditions, providing basic scientific support to national and local development strategies, such as the Belt and Road Strategy, new urbanization and environmental awareness, and creating a sound geopolitical environment in key areas. Using results from existing physical and human geography zoning studies, and in accordance with the principles of synthesis, dominant factors, the relative consistency of the natural environment, the relative consistency of economic and social development, the consistency of the regional cultural landscape, the continuity of spatial distribution and the integrity of county-level administrative divisions, and taking as its basis the division of human geography into 10 major factors (natural condition, the economy, population, culture, ethnicity, agriculture, transportation, urbanization, the settlement landscape and administrative divisions), this paper constructs an index system for the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography through a combination of top-down and bottom-up zoning and spatial clustering analysis. In this study, Chinese human geography is divided into eight regions (first level) and 66 sub-regions (second level). The eight human geography regions are (I) Northeast China, (II) North China, (III) East China, (IV) Central China, (V) South China, (VI) Northwest China, (VII) Southwest China, and (VIII) Qinghai and Tibet. This zoning proposal fills gaps in studies involving the non-comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography. Each human geography region and sub-region has different topographical, climatic, ecological, population, urbanization, economic development, settlement landscape, regional cultural and ethno-religious attributes. This proposal on the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography dovetails closely with previous studies on comprehensive regionalization in Chinese physical geography, Chinese economic zoning, and Chinese agriculture zoning. It shows that, under the dual roles of nature and humans, there are certain rules of regional differentiation that govern the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography.
Draft of major function oriented zoning of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
中国主体功能区划方案
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Major Function Oriented Zoning (MFOZ) is the blueprint for the future developmnt and protection pattern of China's territory, and has been raised to from major function zones planning to major function zoning strategy and major function zoning institution. From 2004 to 2014, the author organized a series of research projects to compose MFOZ for the country, studied basic theory of regional function and MFOZ technical process, and proposed that space controlling zones of national and provincial scales can be divided into four types: urbanized zones, foodstuff-security zones, ecological safety zones, cultural and natural heritage zones. On this basis, major function zones of county scale should be transferred to optimized, prioritized, restricted, and prohibited zones. In this paper, a regional function identification index system comprising nine quantitative indicators (including water resources, land resources, ecological importance, ecological fragility, environment capacity, disaster risk, economic development level, population concentration and transport superiority) and one qualitative indicator of strategic choice is developed. Based on the single index evaluation, comprehensive evaluation using regional function suitability evaluation index is conducted, aiming at testing several key parameters including lower limit of protection zones and upper limit of development zones at the provincial level. In addition, a planning-oriented zoning method of major function zones is also discussed, which has brought the first MFOZ planning in China. According to the MFOZ caliber, it is forecasted that national spatial development intensity will rise from 3.48% in 2010 to 3.91% in 2020. Furthermore, according to caliber of the provincial integrated MFOZ planning, the area of optimized, prioritized and restricted zones accounts for 1.48%, 13.60% and 84.92%, respectively, and that of urbanized, foodstuff-security and ecological safety zones accounts for 15.08%, 26.11% and 58.81%, respectively. In combination of analyses of development level, resources and environmental carrying status and quality of the people's livelihood, the main characteristics of MFOZ were identified. Through verification, MFOZ draft of national and provincial scales, which is interactively accomplished with "MFOZ Technical Process" put forward by the author, is mostly above 80% identical with what have been forecasted.
Discussion on China's top ten economic zones
中国的十大经济区探讨
Landscape division of traditional settlement and effect elements of landscape gene in China
DOI:10.11821/xb201012006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The landscape division of traditional settlement is the job with a strong concept with theory and practicality. It is one of the most important topics in studies on cultural landscape division. In views of the characteristics of regional, systematic, stable, development, identical, typical and harmonious traditional settlement landscape in China, setting the inner similarity of traditional settlement landscape "Image" as precondition, and taking opposite consistency principle as main principle while considering other principles, this paper divides the nation's settlement landscape into three large-sized landscape regions, 14 landscape regions and 76 landscape subregions. The division, from the practice, are based on the relevant landscape principle, such as the principle of environmental constraints, the principle of cultural guidance, the principle of integrated regions, the principle of relevant identity, the principle of covering and non-continuity, the principle of structures, the principle of comprehensive and landscape identity, etc.Naming principle of landscape area at all levels is area-name plus charecteristic and general name. These large-sized landscape regions, landscape regions and landscape subregions are all different in environmental quality and cultural background, so their integrated settlement and architectural landscapes show strong "identifiability" and "impressionality".The division of China's traditional settlement in this article is from the landscape gene perspective rather than based on cultural characteristics used before. Finally, the paper, in the view of "landscape gene", analyzes the main elements that influence the judges of China's traditional settlement landscape genes, from the elements of psychology, ecology, aesthetics, environment, culture, time and order and so on.
中国传统聚落景观区划及景观基因识别要素研究
DOI:10.11821/xb201012006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The landscape division of traditional settlement is the job with a strong concept with theory and practicality. It is one of the most important topics in studies on cultural landscape division. In views of the characteristics of regional, systematic, stable, development, identical, typical and harmonious traditional settlement landscape in China, setting the inner similarity of traditional settlement landscape "Image" as precondition, and taking opposite consistency principle as main principle while considering other principles, this paper divides the nation's settlement landscape into three large-sized landscape regions, 14 landscape regions and 76 landscape subregions. The division, from the practice, are based on the relevant landscape principle, such as the principle of environmental constraints, the principle of cultural guidance, the principle of integrated regions, the principle of relevant identity, the principle of covering and non-continuity, the principle of structures, the principle of comprehensive and landscape identity, etc.Naming principle of landscape area at all levels is area-name plus charecteristic and general name. These large-sized landscape regions, landscape regions and landscape subregions are all different in environmental quality and cultural background, so their integrated settlement and architectural landscapes show strong "identifiability" and "impressionality".The division of China's traditional settlement in this article is from the landscape gene perspective rather than based on cultural characteristics used before. Finally, the paper, in the view of "landscape gene", analyzes the main elements that influence the judges of China's traditional settlement landscape genes, from the elements of psychology, ecology, aesthetics, environment, culture, time and order and so on.
Comprehensive assessment of production-living-ecological space based on the coupling coordination degree model
Understanding geographic coupling and achieving geographic integration
理解地理“耦合”实现地理“集成”
Theories and methods of optimal control of human-earth system: Commemoration of 100th anniversary of academician Wu Chuanjun's birth
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The optimal control of the human-earth system plays the most important role in the theoretical foundation of human-earth areal system (abbreviated as the "human-earth system") advocated by Academician Wu Chuanjun. Based on the thinking and related discussion of optimal control of human-earth system proposed by Academician Wu, this paper deepened and expanded the theoretical and methodological aspects of structure, nonlinear effects, coupling relationship and evolution of the human-earth system. After that, we focused on the following two aspects. The first is to discuss the optimization of human-earth system and coordinated development of regional PRED (i.e., population, resources, environment, and development), including the relationship between human-earth system optimization and PRED coordinated development, as well as the objectives, key points, theoretical models and quantitative measures of coordinated development of PRED. The second is to explore the path and countermeasures of comprehensive regulation of human-earth system in the new era. First of all, we should promote the continuous and healthy development of human-earth systems through innovation. Secondly, we should optimize the spatial pattern of the human-earth system according to the main function-oriented zoning. Thirdly, we should build a modern economic system through supply-side structural reforms. Fourthly, setting long-term balanced development of population as a goal, we should gradually improve the population policy. Finally, we should follow the market principles to improve the mechanism of paid use of resources and environment and ecological compensation.
人地系统优化调控的理论方法研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The optimal control of the human-earth system plays the most important role in the theoretical foundation of human-earth areal system (abbreviated as the "human-earth system") advocated by Academician Wu Chuanjun. Based on the thinking and related discussion of optimal control of human-earth system proposed by Academician Wu, this paper deepened and expanded the theoretical and methodological aspects of structure, nonlinear effects, coupling relationship and evolution of the human-earth system. After that, we focused on the following two aspects. The first is to discuss the optimization of human-earth system and coordinated development of regional PRED (i.e., population, resources, environment, and development), including the relationship between human-earth system optimization and PRED coordinated development, as well as the objectives, key points, theoretical models and quantitative measures of coordinated development of PRED. The second is to explore the path and countermeasures of comprehensive regulation of human-earth system in the new era. First of all, we should promote the continuous and healthy development of human-earth systems through innovation. Secondly, we should optimize the spatial pattern of the human-earth system according to the main function-oriented zoning. Thirdly, we should build a modern economic system through supply-side structural reforms. Fourthly, setting long-term balanced development of population as a goal, we should gradually improve the population policy. Finally, we should follow the market principles to improve the mechanism of paid use of resources and environment and ecological compensation.
Theoretical analysis of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil and coupler control
城镇化与生态环境耦合圈理论及耦合器调控
Spatiotemporal characteristics of the expansion of an urban agglomeration and its effect on the eco-environment: Case study on the northern slope of the Tianshan mountains
DOI:10.1007/s11430-018-9369-x URL [本文引用: 1]