1 引言
2019年2月18日《粤港澳大湾区发展规划纲要》(简称《纲要》)推出,标志着粤港澳大湾区作为中国重要的国家战略正式进入实施与落地阶段,其中涵盖了粤港澳大湾区的发展目标、布局、定位及产业经济发展等多方面的内容。《纲要》中提到要将“协调发展,统筹兼顾”“‘一国两制’,依法办事”作为基本原则,建设成为“内地与港澳深度合作示范区”,强调发展的整体性与粤港澳之间进行分工合作和优势互补,这意味着粤港澳的互动关系的频率与质量是决定粤港澳大湾区发展的关键问题之一。
改革开放以来,粤港澳从工业合作的“前店后厂”模式开始[1,2],到如今三地关系在合作范围、互补层次、经贸投资、政府角色等方面,进入一个全方位合作的新阶段,40年来粤港澳大湾区的空间经济联系逐渐加强,现已具备较强的经济协同发展能力和基 础[3,4,5,6]。《内地与香港关于建立更紧密经贸关系的安排》《内地与澳门关于建立更紧密经贸关系的安排》(简称CEPA)等一系列文件的签署为粤港澳的经济合作做了系统性的制度安排。《粤港澳大湾区发展规划纲要》则通过明确粤港澳大湾区的目标定位、空间布局和产业发展等内容为大湾区的发展指明了方向。总体来看,粤港澳湾区经历了从“孤立”到“共生”[7],从“单向流动”到“双向互动”,从“局部合作”到“多方合作”[8],从“政府主导、民间协同”到“国家级区域发展战略”,从“中国三大城市群之一”到“世界级城市群”的转变,区域联系逐渐紧密,一体化程度不断提高。然而,粤港澳大湾区的代表性和典型性不仅体现在其经济、人口规模上[9],更体现在它是一个存在两种制度、三个关税区、三个法律体系的异质城市群[10]。
粤港澳大湾区实质上是要推动实现异质城市群的一体化协调发展,并促进资源要素在空间上进行重新配置。粤港澳大湾区区域关系的复杂性就在于跨社会制度、跨法律体系、跨行政等级的区域一体化协调过程必然会遭遇一系列的摩擦。学者们针对这一区域的一体化进程进行了广泛的探讨。区域内的流数据是研究区域关系的重要指标,但由于官方发布的香港、澳门与广东九市之间的流数据缺乏,粤港澳大湾区的一体化研究面临着数据可获得性不足的问题。例如由Huh等建立的区域一体化量化指标体系,主要包括贸易投资、资金和金融、区域价值链、基础设施和联通、人民迁移和移民自由度、制度和社会一体化等6个方面26个指标[11],其中的指标设计均体现了区域内的连接与沟通情况,然而在粤港澳大湾区面临着数据统计口径不一,统计内容不一等原因而难以应用。陈秀珍运用贸易、金融、人流等九个指标,编制了一套香港与内地经济一体化程度的综合指数并进行了实证化研究,而香港与珠三角九市的经济一体化程度却无法用此方法衡量[12]。大多数现有的珠三角区域经济一体化研究中,也并未包括香港与澳门两地[13,14,15]。为了解决这一问题,有学者使用引力模型[4, 7]、灯光数据[16]、人口迁移大数据[17,18]、交通基础设施网络[20]等方式观察粤港澳大湾区的一体化发展趋势。还有学者通过梳理粤港澳地区发展的历史地理和空间结构来分析粤港澳的一体化进程[5, 16, 20-21],或是通过粤港澳大湾区与全球三大湾区的比较找出粤港澳一体化发展的差距[22,23]。同时跨境协调等体制机制问题同样得到了相当程度的热议[24,25]。总体来看,目前已有的针对粤港澳大湾区一体化的相关研究更加侧重湾区的经济属性,体制机制协调问题研究尚在起步阶段。然而,这些研究对粤港澳大湾区当前的发展困境的解释能力有限,特别是2019年下半年的香港乱局对粤港澳大湾区造成了较大的负面影响,亟需进行以粤港澳大湾区内部的关系演变与整合过程研究。
全球新闻事件数据库GDELT(The Global Database of Events, Language and Tone)为粤港澳大湾区互动关系研究提供了新的思路,GDELT是一个实时、开源的全球新闻事件数据库,记录了自1979年1月1日以来遍及全球的300多种类型的活动,主要包括骚乱、抗议活动、和平呼吁和外交往来等等。它使用计算机自动编码的方式,每15 min更新一次,从全球各大媒体中持续发掘信息,并将每一个事件的属性进行编码记录在数据库当中。GDELT已逐渐被广泛运用到国际关系的量化模拟和预测研究当中。在全球尺度上,秦昆等利用GDELT数据库进行了国际关系的网络化研究,并通过网络特征分析探测出国家间冲突事件的发生规律[26]。在区域国际关系的时空演变上,陈小强等运用社会网络分析等方法对中国与周边国家的合作与冲突事件所形成的网络对中国周边地缘关系进行了时间和空间维度上的划分与趋势总结[27]。在针对区域的社会发展与风险判断上,马明清等利用GDELT数据库作为数据来源,运用主题模型提取出了“一带一路”沿线25个国家和地区相应的新闻主题词,并相应地对各国的稳定度和社会发展态势进行了量化分析[28]。Zhang等则从GDELT数据库中提取出了“攻击、抗议、压迫、战斗”四类数据,对其进行了核密度分析与莫兰指数分析,并对中国“一带一路”沿线国家和地区的政治风险进行了分析判断[29]。在对国际关系与事件的预测方面,Qiao等利用GDELT建立了一个基于隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)的预测国家不稳定指标的框架,并在对东南亚国家不稳定指标的预测方面进行了实践[30]。此外,GDELT与遥感数据结合还可用于确定受冲突影响的地区的准确范围[31]。可以说,GDELT的时间和空间属性数据为粤港澳三地之间的关系研究提供了新的思路,本文将运用该数据库的合作与冲突数据,结合统计分析与相关时事对粤港澳大湾区三地的关系演变过程进行系统的梳理和探讨,以期对粤港澳互动关系进行解析。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 数据来源
为了量化衡量内地与香港、澳门之间的双边关系,本文选取GDELT数据库提供的全球事件数据,定量衡量粤港澳三地的合作与冲突水平。该数据库将所有事件分为四个大类:言语合作、现实合作、言语冲突和现实冲突,可以方便使用者更好地识别以及归纳整理(表1)。数据库同时列出了事件发生的施动者与被动者,因此GDELT的数据是带有方向指向属性的。为了使关系指数两两比较时具有可比性,本文以1997年1月1日-2019年10月31日作为研究时段,重点关注双边关系中的合作与对抗情况。经过筛选,共得到发生在粤港澳大湾区区域范围内的事件共527项,其中言语合作354项,实际合作90项,言语冲突55项,实际冲突28项。由于粤港澳三地间的关系不能脱离内地与港澳关系发展的大背景,且许多影响粤港澳大湾区发展的事件的发生地不一定在湾区内,因此首先进行内地与港澳之间关系发展的演变分析,然后进一步聚焦到粤港澳之间的互动关系分析。基于此,共筛选出16499条研究区间内内地—香港、内地—澳门、香港—澳门之间的事件记录,其中言语合作12035项,现实合作1728项,言语冲突2043项,现实冲突693项①(①检索发现香港—澳门之间符合条件的事件记录仅有3条,且不是本文的重点,因此本文未做分析)。
表1 GDELT事件类型划分
Tab. 1
| 事件类型 | 具体活动 |
|---|---|
| 言语合作 | 公开声明、呼吁、合作意向、 协商咨询、外交合作 |
| 现实合作 | 参与实际合作、提供援助、产出/收益、投资 |
| 言语冲突 | 要求、不赞成、拒绝、威胁、抗议 |
| 现实冲突 | 展示军力/力量形象、降低/减少关系、 胁迫、攻击、战斗 |
2.2 计算方法
由于GDELT将每个事件的属性归结为合作事件或冲突事件,并基于事件类型进行了赋值(即为GoldsteinScale值),该数值反映了理论上事件对国家稳定性存在的潜在影响,正面事件的赋值为正,最高可达+10,负面事件的赋值为负,最低为-10。值得注意的是,GoldsteinScale是基于事件类型进行赋值而不是事件的烈度,因此在衡量双边关系时,对GoldsteinScale进行相加会相互抵消事件的影响,而在现实中正负两面事件的影响往往同时存在。另外这种方法会隐去两地发生联系的数量,特别是和平时期两地的关系事件发生频繁但都处于较低烈度时,GoldsteinScale分值相加的方法并不能真正体现双边关系水平。也有学者运用GDELT数据库中事件发生的数量进行分析,当合作与冲突事件的数量相减时,其差值可以反映出两地之间的关系水平,但是会随着时间的推移发生“膨胀”,即双方之间事件的总数量随时间增长,造成前后不可比的问题。
相比之下,尽管合作与冲突事件的比值也存在不能完全反映事件数量多少的问题,但其能够较为客观的反映双边关系的状态。如果合作冲突比越高,越能说明两地的合作事件相对冲突事件的发生概率越高,双方关系处于较好的状态当中。池志培等人的研究也证明了GDELT事件比值相比使用其他方法更能把握双边关系趋势[32]。本文构建事件数量Np和合作与冲突的比值C两个指标来反映粤港澳的关系发展的动态变化过程,其中Np表示数据库中记录的事件数量:
式中:p为事件的类别,分别为言语合作(vcoo)、现实合作(mcoo)、言语冲突(vcon)、现实冲突(mcon)四大类;m为变量数,即数据库所记录事件的数量;当事件i被记录在GDELT全球事件数据库当中时
将合作与冲突事件数量的比值设定为C:
式中:Nvcoo、Nmcoo、Nvcon、Nmcon分别对应言语合作、现实合作、言语冲突和现实冲突的事件记录数。
3 结果分析
3.1 内地与香港、澳门关系的演化过程(1997-2019年)
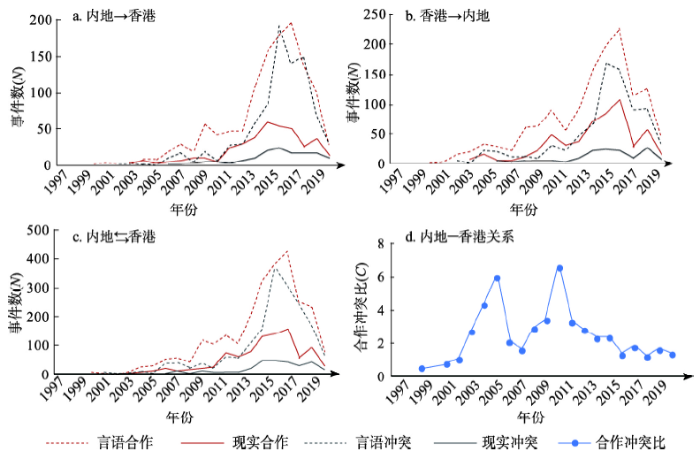
3.1.1 内地与香港的关系图1列出了内地和香港各自作为施动者和被动者合作和冲突事件的相关统计,香港与内地之间最主要的趋势是合作事件远大于冲突事件,并且随着时间的推移,双方的合作与冲突并存并逐渐增多。从2000年开始,双方的合作快速增加,言语上的合作和现实的合作都呈现增长趋势。2008年受金融危机影合作关系出现短暂的下滑,2009年继续高速增长并在2016年达到顶峰,新闻媒体大数据记录双方发生155项实际合作和424项言语合作。2017年、2018年和2019年两地的言语合作关系一般,言语合作逐年下降,现实合作低于之前5年的水平。总体上两地的冲突的事件数量呈现明显的“先涨后降”趋势,2015年是冲突的高峰年,共有363项言语冲突和45项现实冲突。合作与冲突往往相伴相生,2015年、2016年前后合作与冲突事项同时上涨主要源于中国内地企业対港投资的兴起,而内地对港投资加强了双方的经济互动,同时也引起了一定程度的争议。例如2016年中国科技企业的对外投资计划引起了西方媒体的广泛报道,报道既有正面的合作宣传,也有负面的相关评论。
图1
图1
1997年1月-2019年10月内地与香港关系的量化测度
注:图d中删去2005年异常值,将其替换为按照2004年的增长率增长的预测值。
Fig. 1
Quantitative measurement of the relationship between China's mainland and Hong Kong (1997.01-2019.10)
通过合作冲突比来观察两地关系的变化趋势,可以发现除去2005年这个过高的异常值(2005年的对抗与冲突仅有1项,2005年替代为模拟的趋势值),两地的关系曲线呈现“M”型波动:第一个阶段是2005年之前,两地关系自香港回归快速升温,合作开始显现,冲突数量较少,C值从1999年的0.5增长到2005年的5.91;第二阶段是2006-2010年,表现为两地关系先降后升,C值先是降到2008年的2.85,后增长为2010年的6.5;第三个阶段是2011年之后,两地关系出现一些反复和下滑,2015年之后随着双方互动的增多,合作与冲突的发生频率都在增加,双方互动关系处于较低水平的平稳状态,C值维持在1.1~1.7之间。
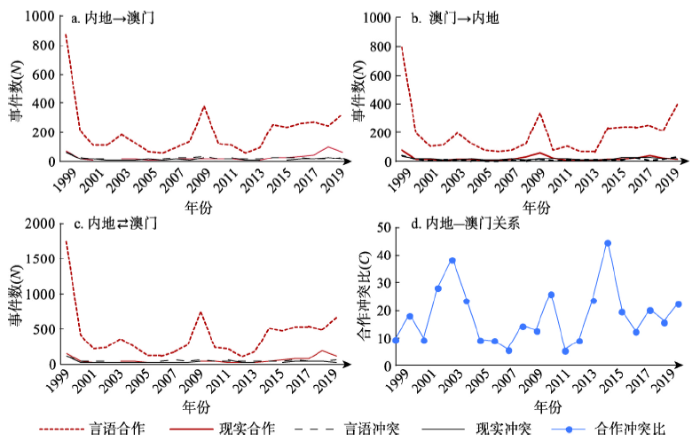
3.1.2 内地与澳门的关系 相比于内地与香港的关系,内地与澳门的互动关系表现为政策与民意的一致性,尤其在言语合作方面内地—澳门和澳门—内地的新闻大数据曲线非常相似(图2)。在现实合作方面,1999年澳门回归之初,即与内地达成130项合作,其中提供援助70项,实际的产出与收益34项,投资9项。随后除2002年(0项)、2005年(4项)、2006年(8项)和2012年(2项)以外,其余年份保持着每年10~30项现实合作的平稳互动状态。2014年快速增长并在2018年猛增到172项合作事件,其中港珠澳大桥成为最受关注的一项合作,媒体普遍正面评价港珠澳大桥对加强区域联系的作用。2018年10月习近平主席对广东进行了考察,并强调推进粤港澳大湾区建设,提振了大湾区发展的信心,对于合作事件的报道显著增多。在冲突方面,在澳门回归之初有110项冲突方面的报道,但随后始终保持较为稳定的状态,最多的现实冲突发生在2011年,共有42项。总体而言,内地与澳门的现实合作远远低于言语合作,仅为言语合作的1/10左右。澳门与内地的言语冲突与现实冲突之比(0.81)远远低于香港与内地对应的指标(6.48),这意味着澳门与内地的主旋律是合作,而香港与内地的冲突关系在新闻媒体的报告中被强化了。在新闻媒体事件中,澳门与内地之间的言语合作是互动关系的主导因素。尤其是,2004年、2014年和2019年在香港发生的严重的社会事件中,澳门在这些节点上均与内地加强了舆论的互信与支持,这3个年份的C值均超过了20。
图2
图2
1999年1月-2019年10月内地与澳门关系的量化测度
Fig. 2
Quantitative measurement of the relationship between China's mainland and Macao (1999.01-2019.10)
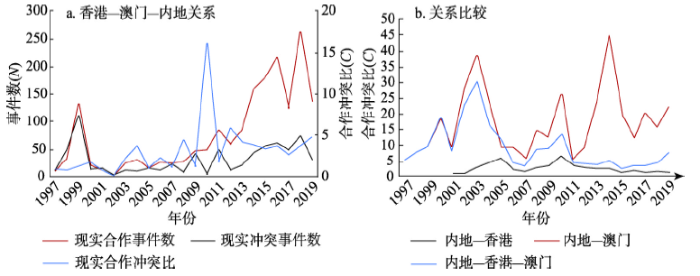
3.1.3 香港、澳门、内地之间的合作与冲突 将内地、香港、澳门之间的双边关系集合为一个数据集合,统计发现合作总体数量迅速上升。2008年以后三地之间的合作呈现明显的增长态势,2017年出现短暂下滑后,到2018年快速增加到262项(图3)。与此同时,冲突事件数量则保持相对平稳,2012年以后有缓慢上升的趋势。从现实的合作冲突比来看,由于近年来合作与冲突的频率都在上涨,导致粤港澳之间的关系改善和提升的速率受到一定影响。通过三者关系的比较可以发展,内地与澳门的关系远远好于内地与香港的关系。内地与澳门之间的言语合作数量相对较多,三者关系受内地与澳门关系的影响更大,而2011年之后,内地—香港—澳门的C值曲线不再随内地—澳门C值曲线一同波动,而更加接近于内地—香港的C值曲线,说明随着近年来粤港澳大湾区内部的关系受内地—香港关系的影响更大,内地—香港的关系在粤港澳中的重要性逐渐凸显出来。
图3
图3
1997年1月-2019年10月香港—澳门—内地关系的量化测度
Fig. 3
Quantitative measurement of the relationship between Hong Kong, Macao, and China's mainland (1997.01-2019.10)
3.2 粤港澳关系的焦点
香港、澳门与珠三角九市之间共有527项记录的新闻事件,其中言语合作354项,现实合作90项,言语冲突55项,现实冲突28项。总体来看合作远远高于冲突,合作冲突比为5.35。粤港澳之间的互动关系存在3个较为明显的频繁互动时期:2000年之前、2009年前后和2015年之后。2000年之前处于香港和澳门回归的初期,粤港形成“前店后厂”的区域协作模式,正在寻求更紧密的经贸联系[8];2009年前后全球金融危机给香港金融业和珠三角地区的出口加工贸易造成了巨大的不利影响,粤港澳的合作意向再一次被激发起来;2015年之后,粤港澳一体化发展成为了国家级的区域发展战略,以港珠澳大桥为代表的基础设施建设再一次拉近了粤港澳之间的联系,以合作为主题的粤港澳大湾区建设再一次引发了热议。
粤港澳三地之间的关系如图4所示,言语合作分别在2000年之前、2009年达到两次高峰,在2014年之后呈现出快速的上升趋势。在现实合作方面,在2014年之后事件的数量大大增加,2015年至2019年这5年间除了2017年合作数量较少以外,每年三地的合作数量都达到了两位数。言语冲突和现实冲突都有偶然性特征,较多的冲突发生在2000年之前、2008年至2009年间和近几年(2017年除外)。可见,粤港澳大湾区合作与冲突的发生具有较高的相关性,近年来随着粤港澳合作与冲突的发生频率同时增长,互动关系的不确定性增强。
图4
图4
1997年1月-2019年10月粤港澳关系变化与比较
注:粤港澳关系中年内冲突为0者,合作冲突比替换为合作总量(即默认冲突为1)。
Fig. 4
Changes and comparison of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao relations (1997.01-2019.10)
粤港澳关系的紧密程度在2014年之前基本低于内地与港澳的关系,但是在2015年后,随着粤港澳大湾区概念的提出与推进,粤港澳的关系超越了内地与港澳的关系,湾区建设得到广泛的关注。
结合粤港澳关系以及内地—香港关系的演化过程,对合作与冲突事件的属性进行统计(表2),发现粤澳之间的关系相比粤港关系更加紧密,在“公开声明”“呼吁”“协商咨询”“外交合作”方面均占到了粤港澳整体较大的份额,在政治立场和对外关系上积极地向内地靠拢。从时间维度来看,粤港澳之间的合作与冲突关系基本上都得到了加强。值得注意的是,随着粤港澳大湾区建设的推进,粤港澳之间以基础设施建设、人才培养和科技合作为代表的产出和收益呈现跳跃式增长,投资项目增多,然而实际的合作却仍然没有大规模地显现出来,说明粤港澳大湾区建设除了投资方面的合作,仍然缺少多元化合作发展的抓手。
表2 1997年1月-2019年10月粤港澳关系事件统计
Tab. 2
| 事件 类型 | 1997-2000年 | 2001-2005年 | 2006-2010年 | 2011-2015年 | 2016-2019年 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粤港澳 | 粤港 | 粤澳 | 粤港澳 | 粤港 | 粤澳 | 粤港澳 | 粤港 | 粤澳 | 粤港澳 | 粤港 | 粤澳 | 粤港澳 | 粤港 | 粤澳 | |||||
| 公开声明 | 18 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 13 | 2 | 32 | 2 | 30 | ||||||
| 呼吁 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 20 | ||||||||
| 合作意向 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 26 | 26 | ||||||||
| 协商咨询 | 30 | 30 | 16 | 2 | 14 | 15 | 3 | 12 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 74 | 6 | 68 | |||||
| 外交合作 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 4 | 16 | |||||||||
| 实际合作 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||
| 提供援助 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 产出/收益 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 40 | 40 | ||||||||||
| 投资 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 6 | ||||||||||
| 要求 | 4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| 不赞成 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 12 | 16 | 4 | 12 | |||||||||
| 拒绝 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 威胁 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 抗议 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 胁迫 | 14 | 14 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 6 | ||||||||||||
| 攻击 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 战斗 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
2015年粤港澳大湾区概念正式提出对粤港澳的互动关系有明显的影响。粤港关系在经济和科技竞争与合作方面受到更多的关注(表3)。中国内地产业升级的加快,科技企业在全球逐渐获得了较大的竞争力,被媒体广泛关注和报道,与此同时内地的科技发展与香港的创新产业形成一定的竞争关系,并对香港科创中心的地位造成了一定压力,例如被称为“中国硅谷”之一的深圳南山区被新华社进行报道后,GoldsteinScale分值却为-2分,这说明世界媒体认为深圳的科技发展会造成一定水平的粤港恶性科技竞争,甚至有西方媒体报道说“中国硅谷恐将香港吞并”。2019年香港乱局成为阻碍粤港澳大湾区发展的一项主要事件,对粤港关系发展造成了很大的不利影响。在粤港关系下降的同时,粤澳关系变得更加紧密,GoldsteinScale分值为2.8。粤澳关系则持续以加强合作为主要趋势,据横琴新区管委会数据显示,截至2019年11月共有2030家企业落户横琴,粤澳合作产业园已落地澳门项目28个,澳门成为粤企业开拓全球市场的一个重要窗口。总体来看,GoldsteinScale分值为负值的事项主要源自粤港关系,粤港的经济和科技竞争与合作关系以及香港局势的发展是影响粤港澳关系发展的主要限制。
表3 2015年1月-2019年10月GDELT数据库粤港澳主要新闻事件统计
Tab. 3
| 年份 | 报道最多的新闻事件 | 参与者 | GoldsteinScale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ① 联想让摩托罗拉重返中国市场 | 粤港 | 3.4 |
| ② 从广州到香港的旅行时间将缩短至45分钟 | 粤港 | 1.9 | |
| ③ 跨境警察合作为中国海外追捕逃犯提供便利 | 粤澳 | 1.9 | |
| ④ 中国发布澳门特区新地图 | 粤澳 | 7 | |
| ⑤ 粤港澳珠江三角洲区域空气质量监测网发布2014年监测结果 | 粤港澳 | 7 | |
| 2016 | ① 新华见解:中国的硅谷充满希望 | 粤港 | -2 |
| ② 澳门将成为“中医药中心” | 粤澳 | 0 | |
| ③ 联想将为香港初创企业提供资金 | 粤港 | 7.4 | |
| ④ Tishman与联想合作开发华南房地产 | 粤港 | 7.4 | |
| ⑤ 华为手机进入高端市场 | 粤港 | -2 | |
| 2017 | ① 横琴将于2017年扩建 | 粤澳 | 5 |
| ② 广东期待与港澳深化合作 | 粤港澳 | 3 | |
| ③ 澳门从台风天鸽灾难中强劲复苏 | 粤澳 | 1.9 | |
| ④ 澳门召开旅游工作会议,商讨区域合作事宜 | 粤澳 | 1.9 | |
| 2018 | ① 中国加强与葡语国家的合作 | 粤澳 | 0 |
| ② 广州将通过澳门开拓全球市场 | 粤澳 | 3.5 | |
| ③ 中国即将公布粤港澳发展规划 | 粤港澳 | 0 | |
| ④ 港珠澳大桥通车后,澳门旅客人数上升 | 粤港澳 | 1.9 | |
| ⑤ 中兴通讯禁令余波蔓延,联想推动中国科技股暴跌 | 粤港 | -5 | |
| 2019 | ① 珠海国际会展中心加快建设成为“粤港澳大湾区高端会展综合体” | 粤澳 | 5 |
| ② 香港抗议活动 | 粤港 | -0.4 | |
| ③ 珠海如何抓住粤港澳大湾区发展的机遇 | 粤澳 | 3.5 | |
| ④ 中国公布粤港澳大湾区发展规划 | 粤港澳 | 0 | |
| ⑤ 中央政府发言人呼吁香港市民反对、抵制暴力 | 粤澳 | 2.8 |
注:统计时间截至2019年10月31日。
4 结论与讨论
粤港澳三地的互动关系的协调一致是粤港澳大湾区共行致远的关键。自港澳回归以来,粤港澳三地的关系经历了较为波折的演变过程。本文利用新闻媒体大数据,对1997年以来粤港澳三地的关系演变过程进行了量化。研究发现:自港澳回归以来,粤港澳之间的关系不断改善,合作成为湾区发展的主流,近年来大湾区区域内合作的项目数量与范围都更加广泛,但是冲突发生的频率也同时在提升。其中,粤澳的关系好于粤港之间的关系,澳门在积极寻求与内地合作,在合作意向的达成,协商协调等方面与珠三角保持着紧密的关系。粤港的关系在基础设施建设、人才培养和科技合作等具体项目的收益与产出方面提升明显,取得了较大的成就,但双方关系的改进受到摩擦与冲突的制约。粤港关系是影响粤港澳关系发展的主要限制,而其中最重要的是粤港的经济和科技竞争与合作关系以及香港局势的发展。
本文利用新闻媒体大数据针对粤港澳大湾区内的互动关系做了一次新的尝试,将粤港澳之间关系发展的演进过程更加直观地呈现了出来,未来需要在经济、社会、政策等更多细节上进行更加系统的分析。新闻媒体大数据,是粤港澳互动关系的投影,也是反映区域一体化不同要素流动、多元主体融合、区域协同发展的一面镜子。应用好这面镜子,对正确认识以及及时矫正粤港澳发展关系,促进粤港澳互动关系健康发展具有重要意义。地理学者擅长复杂综合问题的分析、规划编制与区域发展咨询、经济社会发展战略研究、区域联系与区域功能的设计,在未来大湾区协同发展的理论与实践工作中可以充分发挥学科的优势。在粤港澳复杂的社会制度、法律体系、治理理念、社会融合的互动关系中,不仅要关注这些协同发展策略在空间上的投影,更要关注其在社会舆论与新闻媒体上的投影,才能促进区域一体化协调战略的落实从实体空间建设向虚拟、话语空间的综合引导转变,以强化“硬联通”与“软联通”的互动。
参考文献
Study on regional economic integration of Great Pearl River Delta
大珠三角区域经济一体化研究
Spatio-temporal evolutionary characteristics of the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and its influencing factors
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003011
URL
[本文引用: 1]

To build the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has already become the state development strategy, indicating a new stage of the cooperation among the three places-Guangdong, Hong Kong and Marco. At the same time, the Greater Bay Area has raised the increasing interests of researchers in the fields of all kinds. The existing studies on the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area have been done qualitatively, mainly focusing on the functions, regional relationship and development strategies, while there lacks the research on the regional economy and its spatiotemporal evolutionary structure. In this paper, some quantitative methods have been applied to study the spatiotemporal evolutionary characteristics of the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. First, a comprehensive economic indicator system was established based on the relevant data of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from 1995 to 2015. By means of the Entropy Evaluation Method, the entropy of each indicator was determined. With the comprehensive assessment model of economic development, the level of economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area was calculated. Secondly, the paper used relative development rate (Nich), standard deviation, variable coefficient as well as Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis to analyze the spatiotemporal evolutionary characteristics of the economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area since 1995. Finally, the paper explored the possible influencing factors on the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. The results show that: 1) the economy developed rapidly with some fluctuations as a whole which can be divided into four stages according to its growth rate. Besides, the gross economy has increased and it developed an exported-oriented economy. However, the adjustment of industrial structure was slow. During the study period, Hong Kong and Macao experienced the highest growth rate followed by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, who have already ranked at the first level in the Bay Area; 2) the absolute disparity increased, in the contrary, the relative disparity decreased. Besides, the polarization of economy first experienced a downward trend but then it was strengthened; 3) the spatial characteristic of economy changed from polar central structure composed of Hong Kong and Macao to multi-central structure with Guangzhou and Shenzhen standing out besides Hong Kong and Macao, a reversed “U” type can be seen in the trend analysis; 4) external environment, location and regional policies turned out to be the main influencing factors on the spatiotemporal characteristics of regional economy. After 21 years’ development, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has changed its economic structure from a core-periphery to a network, which indicated the increase of the connection among the cities. In order to improve the international competition of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, this paper gave suggestions from the perspectives of industrial transformation, ecological protection, regional cooperation, cultural innovation and so forth.
粤港澳大湾区经济发展时空演变特征及其影响因素
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003011
URL
[本文引用: 1]

To build the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has already become the state development strategy, indicating a new stage of the cooperation among the three places-Guangdong, Hong Kong and Marco. At the same time, the Greater Bay Area has raised the increasing interests of researchers in the fields of all kinds. The existing studies on the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area have been done qualitatively, mainly focusing on the functions, regional relationship and development strategies, while there lacks the research on the regional economy and its spatiotemporal evolutionary structure. In this paper, some quantitative methods have been applied to study the spatiotemporal evolutionary characteristics of the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. First, a comprehensive economic indicator system was established based on the relevant data of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from 1995 to 2015. By means of the Entropy Evaluation Method, the entropy of each indicator was determined. With the comprehensive assessment model of economic development, the level of economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area was calculated. Secondly, the paper used relative development rate (Nich), standard deviation, variable coefficient as well as Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis to analyze the spatiotemporal evolutionary characteristics of the economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area since 1995. Finally, the paper explored the possible influencing factors on the economic development in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. The results show that: 1) the economy developed rapidly with some fluctuations as a whole which can be divided into four stages according to its growth rate. Besides, the gross economy has increased and it developed an exported-oriented economy. However, the adjustment of industrial structure was slow. During the study period, Hong Kong and Macao experienced the highest growth rate followed by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, who have already ranked at the first level in the Bay Area; 2) the absolute disparity increased, in the contrary, the relative disparity decreased. Besides, the polarization of economy first experienced a downward trend but then it was strengthened; 3) the spatial characteristic of economy changed from polar central structure composed of Hong Kong and Macao to multi-central structure with Guangzhou and Shenzhen standing out besides Hong Kong and Macao, a reversed “U” type can be seen in the trend analysis; 4) external environment, location and regional policies turned out to be the main influencing factors on the spatiotemporal characteristics of regional economy. After 21 years’ development, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has changed its economic structure from a core-periphery to a network, which indicated the increase of the connection among the cities. In order to improve the international competition of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, this paper gave suggestions from the perspectives of industrial transformation, ecological protection, regional cooperation, cultural innovation and so forth.
Economic spatial connection and spatial structure of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay and the surrounding area citie: An empirical analysis based on improved gravity model and social network analysis
粤港澳大湾区及周边城市经济空间联系与空间结构: 基于改进引力模型与社会网络分析的实证分析
Integration process of the Guangdong-Hongkong-Macao Greater Bay Area under the promotion of trade
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003016
URL
[本文引用: 2]

According to the observation of the data of trade between the Pearl River Delta and Hong Kong and Macao after the establishment of the PRC, we can see that the trade scale and structural changes have promoted the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. So, has trade played a role in the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area? If so, how can trade play a role in promoting the process of integration as an integrated link in the development of the Greater Bay Area between Guangdong and Hong Kong and Macao? On the basis of summarizing the existing trade theory and empirical researches, the article develops a long-term dynamic theory of the trade's role in the integration and explains the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. In this article, the process is divided into three phases of natural stage in chronological order since the establishment of the PRC to demonstrate the point above-mentioned. The first stage is the time after the founding of the PRC and before the reform and opening up. In this period, trade of goods dominated by primary commodities was the source of regional cooperation in Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao. Since the reform and opening up, the Guangdong- Hong Kong- Macao regional cooperation has made great progress. The rise of cross-border production and trade with industrial transfer as the mainstay has greatly broken the bias of development between Hong Kong, Macao and the Pearl River Delta. The frequent exchanges between Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao have led to the rapid economic growth of the three regions and the emergence of trade in the east and west of the Pearl River Delta. The phenomenon of industrial clusters has promoted the deepening of infrastructure in the three regions. In the third stage, starting from China's accession to the WTO in 2001, China's economy has been further more open to the world. Hong Kong and Macao, which have extensive experience in international standards, have become the vanguard of the country's active integration with globalization. In 2003, the Mainland and Hong Kong and Macao signed CEPA on the basis of improving the liquidity of commodity trade. Besides, a series of supplementary agreements have also promoted the flow of production trade and service trade from Hong Kong and Macao to the Pearl River Delta cities. With the close trade and service trade, the degree of innovation and knowledge spillover has also been enhanced. The conclusion of this paper is that trade has played a catalytic role in the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. By changing the target of trade from goods to production and finally to service, the main body of trade, from physical goods to intangible goods, is the major process of promoting the integration of the Greater Bay Area of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao, from the primary to the more advanced one. In addition, the process of trade integration has a great spillover effect and it has perfected the regional basic road network. What’s more, the construction of industrial clusters has promoted the emergence of industrial clusters, boosted regional innovation and pushed the integrated area to a new platform for cooperation. The article summarizes the literature on trade and regional integration and would have some theoretical significance. Based on the summary of existing trade theories and empirical studies, the paper develops the conjecture on the dynamic role of trade in regional integration over a long period of time. And through the empirical demonstration of integration of Guangdong, Hong Kong, Macao Bay area, it has laid the foundation for the dynamic role of integration theory in the future study.
贸易促进下的粤港澳大湾区一体化发展
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003016
URL
[本文引用: 2]

According to the observation of the data of trade between the Pearl River Delta and Hong Kong and Macao after the establishment of the PRC, we can see that the trade scale and structural changes have promoted the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area. So, has trade played a role in the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area? If so, how can trade play a role in promoting the process of integration as an integrated link in the development of the Greater Bay Area between Guangdong and Hong Kong and Macao? On the basis of summarizing the existing trade theory and empirical researches, the article develops a long-term dynamic theory of the trade's role in the integration and explains the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. In this article, the process is divided into three phases of natural stage in chronological order since the establishment of the PRC to demonstrate the point above-mentioned. The first stage is the time after the founding of the PRC and before the reform and opening up. In this period, trade of goods dominated by primary commodities was the source of regional cooperation in Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao. Since the reform and opening up, the Guangdong- Hong Kong- Macao regional cooperation has made great progress. The rise of cross-border production and trade with industrial transfer as the mainstay has greatly broken the bias of development between Hong Kong, Macao and the Pearl River Delta. The frequent exchanges between Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao have led to the rapid economic growth of the three regions and the emergence of trade in the east and west of the Pearl River Delta. The phenomenon of industrial clusters has promoted the deepening of infrastructure in the three regions. In the third stage, starting from China's accession to the WTO in 2001, China's economy has been further more open to the world. Hong Kong and Macao, which have extensive experience in international standards, have become the vanguard of the country's active integration with globalization. In 2003, the Mainland and Hong Kong and Macao signed CEPA on the basis of improving the liquidity of commodity trade. Besides, a series of supplementary agreements have also promoted the flow of production trade and service trade from Hong Kong and Macao to the Pearl River Delta cities. With the close trade and service trade, the degree of innovation and knowledge spillover has also been enhanced. The conclusion of this paper is that trade has played a catalytic role in the process of the integration of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. By changing the target of trade from goods to production and finally to service, the main body of trade, from physical goods to intangible goods, is the major process of promoting the integration of the Greater Bay Area of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao, from the primary to the more advanced one. In addition, the process of trade integration has a great spillover effect and it has perfected the regional basic road network. What’s more, the construction of industrial clusters has promoted the emergence of industrial clusters, boosted regional innovation and pushed the integrated area to a new platform for cooperation. The article summarizes the literature on trade and regional integration and would have some theoretical significance. Based on the summary of existing trade theories and empirical studies, the paper develops the conjecture on the dynamic role of trade in regional integration over a long period of time. And through the empirical demonstration of integration of Guangdong, Hong Kong, Macao Bay area, it has laid the foundation for the dynamic role of integration theory in the future study.
The evolution and mechanisms of megalopolitan knowledge polycentricity of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812003
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The concept of megalopolis, since its original inception six decades ago, has inspired many new terms that mainly describe large-scale urbanized forms such as megaregions and polycentric urban regions. However, recent studies have increasingly focused on the two key functions that megalopolises act as an incubator of new ideas and trends and as a hub that articulates knowledge exchange at the megalopolitan, national, and global scales. While the recent studies have mainly analyzed the functional aspects of megalopolis based on China's Yangtze River Delta region, this paper investigates the evolving process and mechanisms of knowledge collaboration within and beyond Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) - one of the most promising and vibrant megalopolises in China. In addition, the GBA megalopolis is unique because it contains Hong Kong and Macao, which have a different political system from China's mainland. Drawing upon a dataset of publications that were indexed in Web of Science Core Collection during the 1990-2016 period, this paper uses the Gini coefficient to measure the degree of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis. Here, knowledge polycentricity is further classified into attribute polycentricity of knowledge production and functional polycentricity of knowledge collaboration within and beyond the GBA megalopolis. Whereas the attribute polycentricity refers to the distribution inequality of the total publications of GBA cities, the functional polycentricity represents the distribution inequality of GBA cities' knowledge collaboration at different geographical scales. Our empirical results show: (1) knowledge production of the GBA megalopolis as a whole has experienced a robust and continuous growth. The degrees of both attribute polycentricity and functional polycentricity have also been on the increase in general, although there are some fluctuations in early years and some deviations in recent years. During the ten years after Hong Kong and Macao returned to China (the 2000-2010 period), the degree of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis especially enjoyed the fastest rise; (2) The degree of functional polycentricity decreased with the expansion in the geographical scales at which it is measured, confirming the findings of previous studies that functional polycentricity is scale-dependent. Moreover, we find that the degree of functional polycentricity becomes more fluctuated at the global scale while it tends to increase continuously at the megalopolitan scale; (3) The evolving process of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis is influenced by institutional proximity, geographical proximity and status proximity between cities. Specifically, the mobility of researchers, the collaboration of universities and research institutes, and the coordination of local governments are three major forces promoting the evolution of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis. Overall, the increasing knowledge polycentricity would be of significance for the GBA megalopolis to form a knowledge-driven region of collective collaboration.
粤港澳大湾区城市群知识多中心的演化过程与机理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812003
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The concept of megalopolis, since its original inception six decades ago, has inspired many new terms that mainly describe large-scale urbanized forms such as megaregions and polycentric urban regions. However, recent studies have increasingly focused on the two key functions that megalopolises act as an incubator of new ideas and trends and as a hub that articulates knowledge exchange at the megalopolitan, national, and global scales. While the recent studies have mainly analyzed the functional aspects of megalopolis based on China's Yangtze River Delta region, this paper investigates the evolving process and mechanisms of knowledge collaboration within and beyond Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) - one of the most promising and vibrant megalopolises in China. In addition, the GBA megalopolis is unique because it contains Hong Kong and Macao, which have a different political system from China's mainland. Drawing upon a dataset of publications that were indexed in Web of Science Core Collection during the 1990-2016 period, this paper uses the Gini coefficient to measure the degree of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis. Here, knowledge polycentricity is further classified into attribute polycentricity of knowledge production and functional polycentricity of knowledge collaboration within and beyond the GBA megalopolis. Whereas the attribute polycentricity refers to the distribution inequality of the total publications of GBA cities, the functional polycentricity represents the distribution inequality of GBA cities' knowledge collaboration at different geographical scales. Our empirical results show: (1) knowledge production of the GBA megalopolis as a whole has experienced a robust and continuous growth. The degrees of both attribute polycentricity and functional polycentricity have also been on the increase in general, although there are some fluctuations in early years and some deviations in recent years. During the ten years after Hong Kong and Macao returned to China (the 2000-2010 period), the degree of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis especially enjoyed the fastest rise; (2) The degree of functional polycentricity decreased with the expansion in the geographical scales at which it is measured, confirming the findings of previous studies that functional polycentricity is scale-dependent. Moreover, we find that the degree of functional polycentricity becomes more fluctuated at the global scale while it tends to increase continuously at the megalopolitan scale; (3) The evolving process of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis is influenced by institutional proximity, geographical proximity and status proximity between cities. Specifically, the mobility of researchers, the collaboration of universities and research institutes, and the coordination of local governments are three major forces promoting the evolution of knowledge polycentricity of the GBA megalopolis. Overall, the increasing knowledge polycentricity would be of significance for the GBA megalopolis to form a knowledge-driven region of collective collaboration.
A study on synergic development of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area
粤港澳大湾区协同发展特征及机制
Reflections on the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: A perspective from political geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.12.005
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Most recently, China has proposed the Belt and Road initiative in an effort to establish a form of multilateral trade cooperation mechanism. This initiative is meaningful for the construction of a healthy global economic structure and the breaking of US-initiated hegemony global economic structure. The notion of "Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area" is a refresh regional concept developed exactly in such a context. In this sense, this notion is inevitably imbued with the meaning of political geography. This article therefore argues that studies related to the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area should not be limited to discussions within segregated practical disciplines, but considered on the macro-level, such as with the perspectives of political geography. In so doing, this article puts forward some suggestions from the lens of modern "vertical-horizontal" spatial management system, the integration of geo-cultures, and geo-economy. First, this article insists that the proposal of the concept of bay economy itself is a type of spatial management thoughts that stresses "upscaling." The development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area is under a rather complex and multi-scale space structure that should pay attention to the competitive and cooperative relations among different cities and regions. It is important to adjust the scale, in particular to the national scale to tackle problems faced in the process of integrating the development of the whole area. Second, this article argues that there is a potential for weakening the integration of various geo-cultures in the process of developing the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. It is very important to discuss how to deal with the "identity crisis" between Hong Kong and the mainland of China, which, to a significant extent, provides stable social environment for the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Third, this article argues that it is important to put the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area into the framework of geo-economy, which underlines the importance of the requirement of the state power on economic development as well as the importance of economic development on power exercises. Finally, this article proposes an agenda to generate suggestions on the scientific development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from multiple perspectives in other disciplines in the future.
政治地理视野下的粤港澳大湾区发展思考
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.12.005
URL
[本文引用: 2]

Most recently, China has proposed the Belt and Road initiative in an effort to establish a form of multilateral trade cooperation mechanism. This initiative is meaningful for the construction of a healthy global economic structure and the breaking of US-initiated hegemony global economic structure. The notion of "Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area" is a refresh regional concept developed exactly in such a context. In this sense, this notion is inevitably imbued with the meaning of political geography. This article therefore argues that studies related to the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area should not be limited to discussions within segregated practical disciplines, but considered on the macro-level, such as with the perspectives of political geography. In so doing, this article puts forward some suggestions from the lens of modern "vertical-horizontal" spatial management system, the integration of geo-cultures, and geo-economy. First, this article insists that the proposal of the concept of bay economy itself is a type of spatial management thoughts that stresses "upscaling." The development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area is under a rather complex and multi-scale space structure that should pay attention to the competitive and cooperative relations among different cities and regions. It is important to adjust the scale, in particular to the national scale to tackle problems faced in the process of integrating the development of the whole area. Second, this article argues that there is a potential for weakening the integration of various geo-cultures in the process of developing the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. It is very important to discuss how to deal with the "identity crisis" between Hong Kong and the mainland of China, which, to a significant extent, provides stable social environment for the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Third, this article argues that it is important to put the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area into the framework of geo-economy, which underlines the importance of the requirement of the state power on economic development as well as the importance of economic development on power exercises. Finally, this article proposes an agenda to generate suggestions on the scientific development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from multiple perspectives in other disciplines in the future.
East Asia's changing urban landscape: Measuring a decade of spatial growth
The building of a world-class city cluster in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: Strategic meanings and challenges
粤港澳大湾区城市群建设的战略意义和现实挑战
Asia-Pacific regional integration index: Construction, interpretation, and comparison
DOI:10.1016/j.asieco.2017.12.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative evaluation of the degree of economic integration between Hong Kong and the mainland: A study on the CDI economic integration index
香港与内地经济一体化程度的量化评价: CDI香港与内地经济一体化指数研究
Measurement and comparison of regional economic integration: Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta
区域经济一体化的测度与比较: 来自京津冀, 长三角和珠三角的证据
Characteristics of regional city connection's spatial pattern based on intercity passenger traffic flow in Pearl River Delta
珠三角城市联系的空间格局特征研究: 基于城际客运交通流的分析
Functional polycentricity of the urban region in the Zhujiang River Delta based on intercity rail traffic flow
Urban region is an important spatial organization form of economic globalization and regional integration trends. Functional polycentricity is the most essential features and the most critical stage of evolution to city region. In the flowing space and urban network theory, functional polycentricity study of urban regions can unfold from intercity functional connection with quantitative measurement and qualitative analysis approaches. In this article, the Zhujiang River Delta urban areas for the study, we carry on the discussion to the functional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta region based on the data of intercity rail traffic flow. Research shows that, intercity rail traffic flow functional relation of the region has a high level of functional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta which include in the middle and upper levels of typical cities or regions in the world. With the measurement and analysis of functional polycentripolycentriccity for the eastern and western wings, it shows that there lacks seffective intercity rail transportation contact between eastern and western wings, which has a serious negative impact on thefunctional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta. The functional polycentricity development of the Zhujiang River Delta has entered the centrifugal stage. Along with the development of the intercity rail transit construction and regional integration, the region of the multifunctional center will tend to be mature.
基于城际轨道交通流的珠三角城市区域功能多中心研究
Urban region is an important spatial organization form of economic globalization and regional integration trends. Functional polycentricity is the most essential features and the most critical stage of evolution to city region. In the flowing space and urban network theory, functional polycentricity study of urban regions can unfold from intercity functional connection with quantitative measurement and qualitative analysis approaches. In this article, the Zhujiang River Delta urban areas for the study, we carry on the discussion to the functional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta region based on the data of intercity rail traffic flow. Research shows that, intercity rail traffic flow functional relation of the region has a high level of functional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta which include in the middle and upper levels of typical cities or regions in the world. With the measurement and analysis of functional polycentripolycentriccity for the eastern and western wings, it shows that there lacks seffective intercity rail transportation contact between eastern and western wings, which has a serious negative impact on thefunctional polycentricity of the Zhujiang River Delta. The functional polycentricity development of the Zhujiang River Delta has entered the centrifugal stage. Along with the development of the intercity rail transit construction and regional integration, the region of the multifunctional center will tend to be mature.
Understanding the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from the perspective of mega-city region
从巨型城市区域视角审视粤港澳大湾区空间结构
Spatial Pattern of population flow among cities in China during the Spring Festival travel rush based on "Tencent Migration" data
基于腾讯迁徙数据的中国“春运”城市间人口流动空间格局
Research on spatial pattern of population mobility among cities: A case study of "Tencent Migration" big data in "National Day-Mid-Autumn Festival" vacation
中国城市间人口流动空间格局的网络分析: 以国庆—中秋长假和腾讯迁徙数据为例
Transport network construction and integrated development of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
交通网络建设与粤港澳大湾区一体化发展
The spatio-temporal evolvement of spatial interaction among cities of Zhujiang River Delta in recent 20 years
From the spatial scale of prefecture-level city and county area, this article establishes an evaluation index system of the urban comprehensive power of Zhujiang River Delta (ZJRD) urban agglomeration to analyze the urban comprehensive power in 1990, 1994, 2000, 2005 and 2009, respectively. Moreover, the spatial interaction level among the ZJRD cities and the potential value of each city are calculated using the improved gravity model and potential model. By these results, some GIS spatial analysis methods such as space thematic map expression method and space interpolation method, etc. are used to analyze the spatio-temporal evolution of the urban space interaction of ZJRD urban agglomeration in recent 20 years. The basic conclusions are obtained as follows: 1) The spatial contact among the ZJRD prefecture-level cities has been gradually strengthened as a whole, and the centrality of Guangzhou in the region is reflected. 2) At county-level scale, the linkage between urban area and counties under the same prefecture-level city, the linkage among urban districts of prefecture-level cities and counties in the Guangzhou-Foshan metropolitan region are strong, while the spatial linkage among other counties and cities is weak. The spatial linkage among most counties at the core region of ZJRD has been gradually strengthened as a whole, however, the spatial linkage among counties out the core region and the spatial linkage between the counties at the inner core region of ZJRD urban agglomeration and counties out the core region go up and down frequently all the way and have no discernible regularity. 3) The city potential values of Guangzhou-Foshan metropolitan region and Shenzhen-Dongguan-Huizhou metropolitan region are all strong and fluctuate pronouncedly. And the diffusivity of these two regions is also stronger than the other. The potential values of other cities are relatively lower and show no obvious fluctuation. 4) There is significant imbalance of the city potential between districts. The features and evolution laws of spatial differentiation and spatial diffusivity of the city potential in ZJRD urban agglomeration are obvious and unrest under stability.
近20年珠三角城市群城市空间相互作用时空演变
From the spatial scale of prefecture-level city and county area, this article establishes an evaluation index system of the urban comprehensive power of Zhujiang River Delta (ZJRD) urban agglomeration to analyze the urban comprehensive power in 1990, 1994, 2000, 2005 and 2009, respectively. Moreover, the spatial interaction level among the ZJRD cities and the potential value of each city are calculated using the improved gravity model and potential model. By these results, some GIS spatial analysis methods such as space thematic map expression method and space interpolation method, etc. are used to analyze the spatio-temporal evolution of the urban space interaction of ZJRD urban agglomeration in recent 20 years. The basic conclusions are obtained as follows: 1) The spatial contact among the ZJRD prefecture-level cities has been gradually strengthened as a whole, and the centrality of Guangzhou in the region is reflected. 2) At county-level scale, the linkage between urban area and counties under the same prefecture-level city, the linkage among urban districts of prefecture-level cities and counties in the Guangzhou-Foshan metropolitan region are strong, while the spatial linkage among other counties and cities is weak. The spatial linkage among most counties at the core region of ZJRD has been gradually strengthened as a whole, however, the spatial linkage among counties out the core region and the spatial linkage between the counties at the inner core region of ZJRD urban agglomeration and counties out the core region go up and down frequently all the way and have no discernible regularity. 3) The city potential values of Guangzhou-Foshan metropolitan region and Shenzhen-Dongguan-Huizhou metropolitan region are all strong and fluctuate pronouncedly. And the diffusivity of these two regions is also stronger than the other. The potential values of other cities are relatively lower and show no obvious fluctuation. 4) There is significant imbalance of the city potential between districts. The features and evolution laws of spatial differentiation and spatial diffusivity of the city potential in ZJRD urban agglomeration are obvious and unrest under stability.
The synergy development between the industrial transfer and the urban space
产业转移与城镇空间协同发展研究: 以珠三角为例
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: Evolution, reference and strategic suggestion
DOI:10.1242/jcs.236737
URL
PMID:31843760
[本文引用: 1]

High-throughput neurotransmission at ribbon synapses of cochlear inner hair cells (IHCs) requires tight coupling of neurotransmitter release and balanced recycling of synaptic vesicles (SVs) as well as rapid restoration of release sites. Here, we examined the role of the adaptor protein AP180 for IHC synaptic transmission in AP180-KO mice using high-pressure freezing and electron tomography, confocal microscopy, patch-clamp membrane-capacitance measurements and systems physiology. AP180 was found predominantly at the synaptic pole of IHCs. AP180-deficient IHCs had severely reduced SV numbers, slowed endocytic membrane retrieval, and accumulated endocytic intermediates near ribbon synapses, indicating that AP180 is required for clathrin-dependent endocytosis and SV reformation in IHCs. Moreover, AP180 deletion led to a high prevalence of SVs in a multi-tethered or docked state after stimulation, a reduced rate of SV replenishment, and a hearing impairment. We conclude that, in addition to its role in clathrin recruitment, AP180 contributes to release site clearance in IHCs.
粤港澳大湾区: 演进发展, 国际镜鉴与战略思考
DOI:10.1242/jcs.236737
URL
PMID:31843760
[本文引用: 1]

High-throughput neurotransmission at ribbon synapses of cochlear inner hair cells (IHCs) requires tight coupling of neurotransmitter release and balanced recycling of synaptic vesicles (SVs) as well as rapid restoration of release sites. Here, we examined the role of the adaptor protein AP180 for IHC synaptic transmission in AP180-KO mice using high-pressure freezing and electron tomography, confocal microscopy, patch-clamp membrane-capacitance measurements and systems physiology. AP180 was found predominantly at the synaptic pole of IHCs. AP180-deficient IHCs had severely reduced SV numbers, slowed endocytic membrane retrieval, and accumulated endocytic intermediates near ribbon synapses, indicating that AP180 is required for clathrin-dependent endocytosis and SV reformation in IHCs. Moreover, AP180 deletion led to a high prevalence of SVs in a multi-tethered or docked state after stimulation, a reduced rate of SV replenishment, and a hearing impairment. We conclude that, in addition to its role in clathrin recruitment, AP180 contributes to release site clearance in IHCs.
Discussion on the developing path and construction strategies of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: Based on the comparative study among three global bay areas
粤港澳大湾区发展路径和建设战略探讨: 基于世界三大湾区的对比分析
Exploration on the governance and cooperation model of Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao Great Bay Area
粤港澳大湾区治理与合作模式探索
Cross-border collaboration in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: Progress, problems and prospect
粤港澳大湾区跨境区域协调: 现状、问题与展望
Networked mining of GDELT and international relations analysis. Journal of Geo-information
GDELT数据网络化挖掘与国际关系分析
Analysis of the geo-relationships between China and its neighboring countries
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Geo-relationships, as an important field of research in geography, have attracted much attention from scholars. Quantitative research on geo-relationships based on big data is an important supplement to traditional geo-relationships study. This paper uses GDELT mass media data to express the geo-relationships between China and its neighboring countries as a global relationship of cooperation and conflict, and identifies the stage division of these relationships using ordered cluster analysis. Social network analysis is conducted for each stage of the cooperation and conflict relationship, and community detection is used to further analyze and interpret the networks of cooperation and conflict. Finally, we highlight bilateral relations in various stages and conduct a China-centered equilibrium analysis. Three main results are presented. First, from 1979 to 2017, the cooperation and conflict relationship between China and its neighboring countries demonstrated an obvious three-stage temporal division. China has gradually become the center of the network, and a broad cooperation pattern centered on China and supported by Russia, Japan, and South Korea has formed. Second, the highlighted bilateral relations in each stage, such as China-Vietnam, China-Japan, China-Russia, and DPRK-ROK, show varied development trends and driving factors. Third, with the process of China's peaceful rise, cooperation between the country and its neighbors is becoming more and more balanced, and conflict between them is expanding.
中国及其周边国家间地缘关系解析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Geo-relationships, as an important field of research in geography, have attracted much attention from scholars. Quantitative research on geo-relationships based on big data is an important supplement to traditional geo-relationships study. This paper uses GDELT mass media data to express the geo-relationships between China and its neighboring countries as a global relationship of cooperation and conflict, and identifies the stage division of these relationships using ordered cluster analysis. Social network analysis is conducted for each stage of the cooperation and conflict relationship, and community detection is used to further analyze and interpret the networks of cooperation and conflict. Finally, we highlight bilateral relations in various stages and conduct a China-centered equilibrium analysis. Three main results are presented. First, from 1979 to 2017, the cooperation and conflict relationship between China and its neighboring countries demonstrated an obvious three-stage temporal division. China has gradually become the center of the network, and a broad cooperation pattern centered on China and supported by Russia, Japan, and South Korea has formed. Second, the highlighted bilateral relations in each stage, such as China-Vietnam, China-Japan, China-Russia, and DPRK-ROK, show varied development trends and driving factors. Third, with the process of China's peaceful rise, cooperation between the country and its neighbors is becoming more and more balanced, and conflict between them is expanding.
Big data analysis of social development situation in regions along the Belt and Road
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The Belt and Road initiative has become China's basic international policy. Keeping abreast of the social development trend of countries along the Belt and Road is crucial to ensuring the steady progress and successful implementation of the initiative. To this end, this study used the Global Data on Events, Location and Tone (GDELT) as a data source to obtain the full-text English news data in 25 countries along the Belt and Road in the past five years, and analyzed the social development trends of various countries by introducing topic models and combining an unsupervised method—the latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and a supervised method—labeled latent Dirichlet allocation (Labeled LDA) to mine the topics contained in the news data, and construct a social stability model. The study found that: 1) The social development trend of the countries along the Belt and Road is uneven, and the countries can be divided into four categories: Stable, such as Oman, Vietnam; Relatively stable, such as Uzbekistan, Iran; Moderate risk, such as Kuwait, Jordan, Pakistan, Myanmar; High risk, such as Syria, Afghanistan. 2) Through the spatiotemporal mining of news topics, hot spots can be effectively identified. For example, this study found that Andijon has an important influence on the social development and stability of Central Asia. 3) The supervised topic model could reveal Uzbekistan's economic and industrial structure, identify major social events, and discover its social security risks and trend. This method can effectively explore the spatiotemporal changes of news events, discover potential risks of countries, support real-time dynamic monitoring of the social development trends of countries along the Belt and Road, and provide auxiliary decision support for the implementation of the Belt and Road initiative, and thus has important application value.
“一带一路”若干区域社会发展态势大数据分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.07.006
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The Belt and Road initiative has become China's basic international policy. Keeping abreast of the social development trend of countries along the Belt and Road is crucial to ensuring the steady progress and successful implementation of the initiative. To this end, this study used the Global Data on Events, Location and Tone (GDELT) as a data source to obtain the full-text English news data in 25 countries along the Belt and Road in the past five years, and analyzed the social development trends of various countries by introducing topic models and combining an unsupervised method—the latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and a supervised method—labeled latent Dirichlet allocation (Labeled LDA) to mine the topics contained in the news data, and construct a social stability model. The study found that: 1) The social development trend of the countries along the Belt and Road is uneven, and the countries can be divided into four categories: Stable, such as Oman, Vietnam; Relatively stable, such as Uzbekistan, Iran; Moderate risk, such as Kuwait, Jordan, Pakistan, Myanmar; High risk, such as Syria, Afghanistan. 2) Through the spatiotemporal mining of news topics, hot spots can be effectively identified. For example, this study found that Andijon has an important influence on the social development and stability of Central Asia. 3) The supervised topic model could reveal Uzbekistan's economic and industrial structure, identify major social events, and discover its social security risks and trend. This method can effectively explore the spatiotemporal changes of news events, discover potential risks of countries, support real-time dynamic monitoring of the social development trends of countries along the Belt and Road, and provide auxiliary decision support for the implementation of the Belt and Road initiative, and thus has important application value.
Spatial big data analysis of political risks along the Belt and Road
DOI:10.3390/su11010001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predicting social unrest events with hidden Markov models using GDELT
DOI:10.1155/2013/720818
URL
PMID:25083120
[本文引用: 1]

In 2001, Friedman et al. conjectured the existence of a "firewall effect" in which individuals who are infected with HIV, but remain in a state of low infectiousness, serve to prevent the virus from spreading. To evaluate this historical conjecture, we develop a new graph-theoretic measure that quantifies the extent to which Friedman's firewall hypothesis(FH)holds in a risk network. We compute this new measure across simulated trajectories of a stochastic discrete dynamical system that models a social network of 25,000 individuals engaging in risk acts over a period of 15 years. The model's parameters are based on analyses of data collected in prior studies of the real-world risk networks of people who inject drugs (PWID) in New York City. Analysis of system trajectories reveals the structural mechanisms by which individuals with mature HIV infections tend to partition the network into homogeneous clusters (with respect to infection status) and how uninfected clusters remain relatively stable (with respect to infection status) over long stretches of time. We confirm the spontaneous emergence of network firewalls in the system and reveal their structural role in the nonspreading of HIV.
World Heritage in danger: Big data and remote sensing can help protect sites in conflict zones
DOI:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2019.02.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Quantitative research on big data and bilateral relations: A case study of GDELT and Sino-U.S. relations
大数据与双边关系的量化研究: 以GDELT与中美关系为例
Key scientific issues and important topics in the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao region
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.12.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Given the modern background of economic globalization, regional economic integration, new global economic development trends caused by modern technological reforms, the Belt and Road initiative, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area development strategy, there is a growing sense of urgency, necessity, and practical significance in achieving the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao region. This requires an in-depth understanding and accurate grasp of the key scientific issues and important topics related to this task. This article argues that research related to the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region must be based on a regionally unified theoretical framework, "global-local" scale theory, and regional spatial interaction theory as its theoretical basis. In this regard, key scientific issues include the study of the theory of regional linkages of scale in Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau under the "One Country, Two Systems" framework, and the exploration of mechanisms, factors, models, and pathways governing linkages in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region. In so doing, this article proposes four important topics that can be considered with regard to the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region: (1) Research and exploration of unification/coordination theory in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region under the "One Country, Two Systems" framework; (2) Research related to the location and role of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region; (3) Research related to the multi-scale and multi-agent impact mechanisms and models for the linkages between Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau; (4) Research related to implementation pathways for the unified development of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau.
粤港澳区域联动发展的关键科学问题与重点议题
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.12.001
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Given the modern background of economic globalization, regional economic integration, new global economic development trends caused by modern technological reforms, the Belt and Road initiative, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area development strategy, there is a growing sense of urgency, necessity, and practical significance in achieving the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao region. This requires an in-depth understanding and accurate grasp of the key scientific issues and important topics related to this task. This article argues that research related to the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region must be based on a regionally unified theoretical framework, "global-local" scale theory, and regional spatial interaction theory as its theoretical basis. In this regard, key scientific issues include the study of the theory of regional linkages of scale in Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau under the "One Country, Two Systems" framework, and the exploration of mechanisms, factors, models, and pathways governing linkages in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region. In so doing, this article proposes four important topics that can be considered with regard to the joint development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region: (1) Research and exploration of unification/coordination theory in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region under the "One Country, Two Systems" framework; (2) Research related to the location and role of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau region; (3) Research related to the multi-scale and multi-agent impact mechanisms and models for the linkages between Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau; (4) Research related to implementation pathways for the unified development of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macau.