

黄土高原地下啮齿类动物挖掘对土壤侵蚀的贡献
|
白晓亮(1997-), 女, 甘肃平凉人, 硕士生, 研究方向为生物地貌过程研究。E-mail: 220220949280@lzu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-05-07
修回日期: 2024-12-28
网络出版日期: 2025-05-23
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42322101)
国家自然科学基金项目(42130110)
The contribution of subterranean rodent excavation to soil erosion in the Loess Plateau
Received date: 2024-05-07
Revised date: 2024-12-28
Online published: 2025-05-23
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42322101)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42130110)
白晓亮 , 耿豪鹏 , 刘茹 , 程维明 , 潘保田 . 黄土高原地下啮齿类动物挖掘对土壤侵蚀的贡献[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(5) : 1327 -1338 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202505011
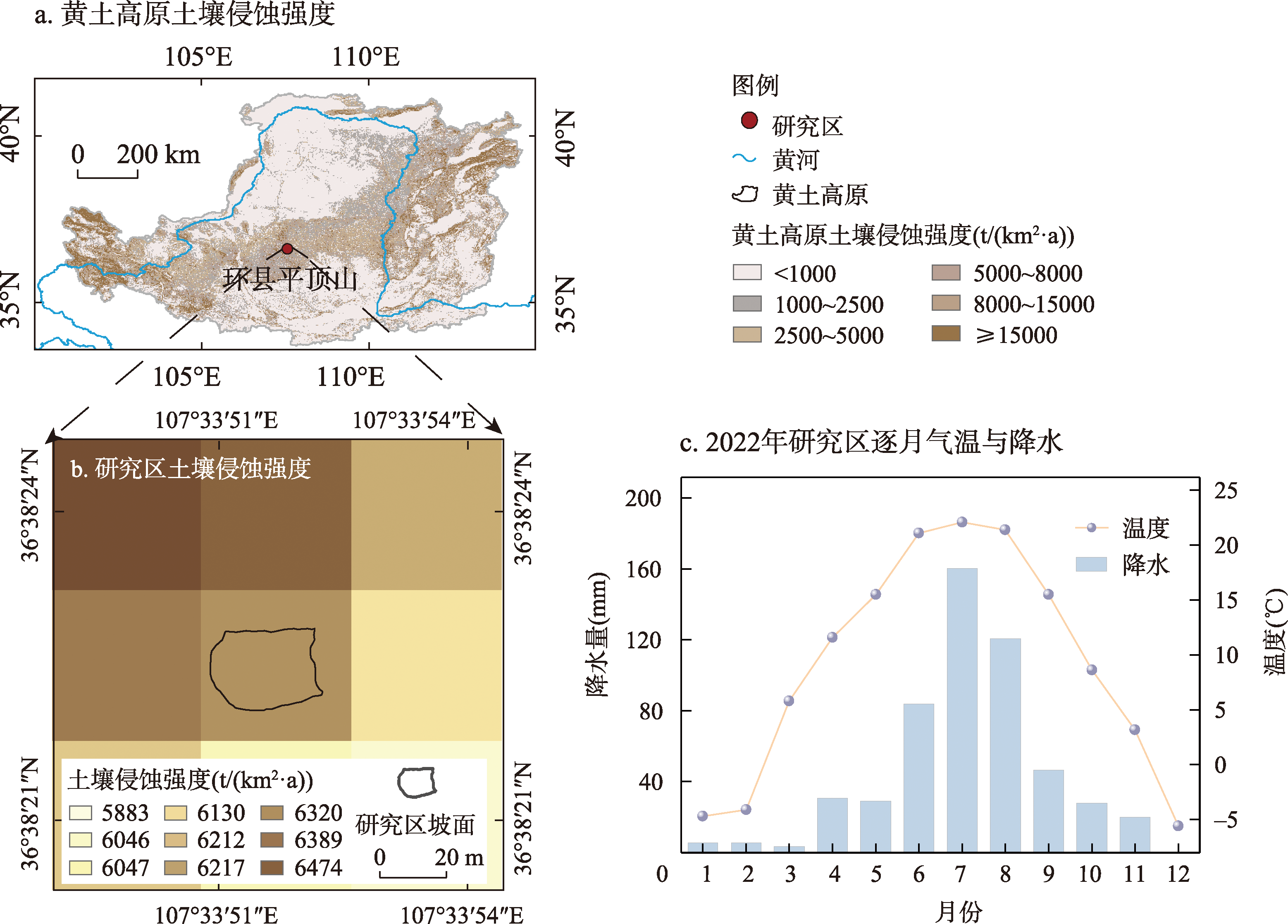
Subterranean rodent excavation activities constitute one of the factors influencing soil redistribution and erosion on hillslopes. Investigating these activities in depth contributes to a better understanding of the complex mechanisms of soil erosion. To explore the spatial distribution characteristics of subterranean rodent excavation activities and their impact on soil erosion in the Loess Plateau, this study conducted six months of fixed-point repeated monitoring on a typical hillslope (665 m2) in Pingdingshan, Huanxian county, located in the central part of the Loess Plateau. Utilizing unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) surveying combined with field investigations, the study tracked the spatial distribution of subterranean rodent excavation activities, analyzed their effects on soil properties, and quantified the soil erosion generated by excavation activities on the study hillslope. The results indicate that: (1) Subterranean rodents exhibit a preference for feeding and burrowing activities in areas with gentle slopes, dispersed flow, and convex slope regions. (2) Excavation activities decrease the bulk density of fresh soil mounds by 14% (P < 0.05) compared to undisturbed soil, while porosity and saturated hydraulic conductivity increase by 11% (P < 0.05). (3) Over the observation period, subterranean rodent excavation activities overturned 0.13 t of soil onto the surface, with an associated slope transport flux of approximately 2.18 cm3/(cm·a). If all these fluxes were converted into soil erosion, the erosion modulus would be approximately 397 t/(km2·a). These results highlight the significant role of excavation activities in soil redistribution on hillslopes of the Loess Plateau, contributing to approximately 10.1% of the total soil erosion, which warrants attention in future assessments and modeling of soil erosion and loss.

Key words: subterranean rodents; excavation activities; soil erosion; Loess Plateau
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
[李相儒, 金钊, 张信宝, 等. 黄土高原近60年生态治理分析及未来发展建议. 地球环境学报, 2015, 6(4): 248-254.]
|
| [7] |
[高海东, 李占斌, 李鹏, 等. 梯田建设和淤地坝淤积对土壤侵蚀影响的定量分析. 地理学报, 2012, 67(5): 599-608.]
|
| [8] |
[刘文超, 刘纪远, 匡文慧. 陕北地区退耕还林还草工程土壤保护效应的时空特征. 地理学报, 2019, 74(9): 1835-1852.]
|
| [9] |
[杨学军, 韩崇选, 李继光, 等. 固原退耕还林区经济林木甘肃鼢鼠防治经济阈值研究. 林业科学, 2006, 42(9): 74-78.]
|
| [10] |
[吴晓民, 刘楚光, 张洪峰, 等. 黄土高原退耕还林(草)区的鼠害治理问题. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(Suppl.1): 133-137.]
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
[宋梓涵, 李希来, 苏晓雪, 等. 高原鼠兔和高原鼢鼠种群暴发区干扰斑块空间分布格局与演替规律. 生态学报, 2023, 43(7): 2949-2958.]
|
| [13] |
[李国荣, 李希来, 李进芳, 等. 黄河源高寒草甸高原鼠兔土丘的土壤风力侵蚀规律. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(2): 110-114, 168.]
|
| [14] |
[王红兰, 蒋舜媛, 崔俊芳, 等. 不同形成时间鼢鼠鼠丘土壤水力学性质的对比. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(3): 180-184, 190.]
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
[白茹茹, 张加琼, 邓鑫欣, 等. 黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错带风蚀对砂质壤土迎风坡水蚀特征的影响. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(3): 30-36, 43.]
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
[耿文广, 诸云强, 陈鹏飞. 黄土高原逐年土壤侵蚀模数1-km栅格数据集(2001—2015). 全球变化数据学报, 2022, 6(1): 85-92.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[鲍根生, 王宏生, 王玉琴, 等. 高原鼢鼠造丘活动对高寒草地土壤养分空间异质性的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 95-103.]
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[吴克宁, 赵瑞. 土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1): 227-241.]
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
[田永亮, 蒋永梅, 王贵珍, 等. 地下啮齿动物栖息环境及其生存策略研究. 四川动物, 2018, 37(3): 343-350.]
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
[杨莹博, 辛小娟, 艾得协措, 等. 鼢鼠土丘植被恢复演替过程中的物种多样性变化. 草业学报, 2010, 19(1): 14-20.]
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
[何俊龄, 张金沙, 杨莹博, 等. 高原鼢鼠土丘空间格局及主要特征研究. 草业学报, 2006, 15(1): 107-112.]
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
[花立民, 柴守权. 中国草原鼠害防治现状、问题及对策. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(1): 415-423.]
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |