

非洲大陆区域一体化背景下国家边境森林变化及其主要因素贡献
|
唐梦雅(2000-), 女, 新疆巴州人, 硕士生, 研究方向为边境土地利用变化。E-mail: 2022135009@chd.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-06-24
修回日期: 2025-01-08
网络出版日期: 2025-05-23
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42371282)
国家自然科学基金项目(42130508)
Forest change and the contributions of major influencing factors along international borders in the context of regional integration of African continent
Received date: 2024-06-24
Revised date: 2025-01-08
Online published: 2025-05-23
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42371282)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42130508)
唐梦雅 , 李鹏 , 李霞 , 陈生媚 , Jeffrey Chiwuikem CHIAKA . 非洲大陆区域一体化背景下国家边境森林变化及其主要因素贡献[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(5) : 1226 -1243 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202505005
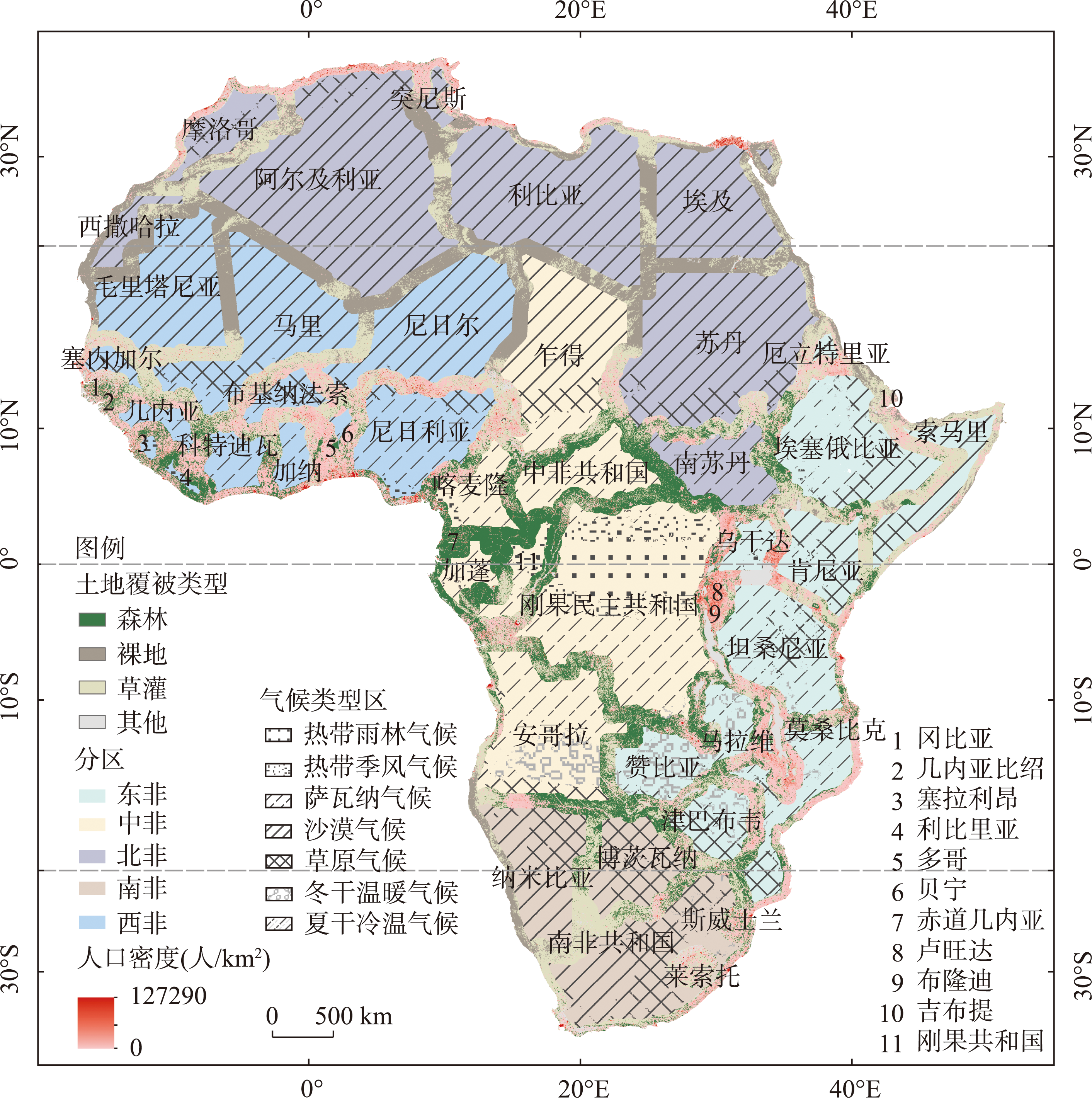
Economic globalization and regional integration have pushed international borders from closure to opening-up, making them a hot spot for studying human-environment relations. The promotion of African integration has lasted for decades and has also affected cross-border landscape and land use. Since the signing of the African Continental Free Trade Area Agreement, the processes of forest loss and gain and other land cover change within international borders of continental Africa and its main influencing factors (e.g., active fire) as well as their contribution remain understudied. With the Sentinel-2 10-m land use/land cover products, Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) active fires, LandScan population density, and armed conflict records during 2017-2022, we first examined the inter-annual dynamics and cross-transformations between forest (trees), rangeland (grass and shrub), and bare ground within a total of 146 international borders of the African continent, covering 49 countries. We then determined the major influencing factors and quantified their contribution using Random Forest Regression and correlation analysis. The results show that: (1) the international borders of continental Africa are characterized by a general distribution pattern of forest, rangeland, and bare ground in a sequential order in both the northern and southern parts, divided by the equator. The three land cover types account for nearly 90% of all borders, and dominate (>80%) the change in land cover at the borders with an average annual rate of 2%. Forest loss due to the transformation into rangeland remains a major trend albeit short-term forest gain in 2020. (2) Active fire and population density are the primary and secondary respectively causes of forest cover change along national borders in Africa. The relationship between forest changes and the frequency of active fire or population density is initially weak and then strong during the study period. (3) Nearly 90% of interannual forest loss is strongly and positively correlated with the occurrence of active fires along the international borders of continental Africa, showing a gradual increase on both the northern and southern sides of the equator due to the seasonal dynamics of active fires. (4) Active fires have a more pronounced impact on forest decline within African borders during dry seasons. This study contributes to providing a methodological reference for exploring the causal factors of tropical forest change and the extent to which land-use change at the borders responds to regional integration.

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
[李鹏, 祁月基, 封志明, 等. 地缘合作背景下柬老越发展三角区农进林退动态特征. 资源科学, 2021, 43(12): 2416-2427.]
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[陈生媚, 李鹏, 封志明, 等. 中南半岛及其毗邻国家边境农用地/建设用地扩张所致森林扰动过程. 地理科学进展, 2024, 43(4): 741-754.]
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
[李鹏, 刘颖, 施冬, 等. 三种活跃火遥感产品(MODIS C6、VIIRS V1和VIIRS J1)一致性与差异性对比. 地理研究, 2022, 41(5): 1481-1495.]
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
[方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平, 等. 随机森林方法研究综述. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(3): 32-38.]
|
| [40] |
[杜树坤, 张晶, 韩志军, 等. 基于随机森林模型的“网格—月”尺度武装冲突风险预测及影响因素分析: 以中南半岛为例. 地球信息科学学报, 2023, 25(10): 2026-2038.]
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
[刘颖, 李鹏, 肖池伟, 等. 中南半岛旱季VIIRS活跃火的空间特征与国别差异. 地理科学进展, 2021, 40(8): 1406-1418.]
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
[李霞, 金相皓, 李鹏. 中南半岛近20年农林转换及其活跃火贡献. 农业工程学报, 2024, 40(24): 256-265.]
|
| [50] |
[胡涛, 彭建, 董建权, 等. 基于全球遥感产品的森林概念协同. 地理学报, 2024, 79(5): 1115-1128.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |