

中国植被光学厚度的时空变化及其影响因素
|
石曼青(1999-), 女, 河南洛阳人, 博士生, 研究方向为极端天气变化。E-mail: shimq7@mail2.sysu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-10-31
修回日期: 2025-04-15
网络出版日期: 2025-05-23
Spatio-temporal patterns of vegetation optical depth and its influencing factors over China
Received date: 2023-10-31
Revised date: 2025-04-15
Online published: 2025-05-23
本文基于Ku波段、X波段和C波段微波遥感数据,采用新兴时空热点分析法解析2002—2017年中国植被光学厚度(Vegetation Optical Depth, VOD)的时空演变规律,并探究气候因子与人类活动对其变化的影响。研究发现:① 中国VOD空间分布呈东南向西北递减趋势,中部与南部为VOD热点区,而新疆及内蒙古高原中部为冷点区;三波段分析表明,研究初期全国植被稀疏区普遍呈现“变绿”特征。② 土地利用类型转变对VOD的时空变化具有显著影响,例如草地转为林地与VOD持续和增强的热点区空间一致性高。③ 基于偏最小二乘结构方程模型的归因分析显示:湿润区在热量与水分条件充足时,温度与降水增加会抑制植被生长;干旱区温度抑制作用不显著;青藏高原高寒区的植被生长则受暖湿化协同促进。本文研究成果可为大尺度生态环境评估、驱动机制解析及生态修复政策制定提供方法支撑与数据参考。
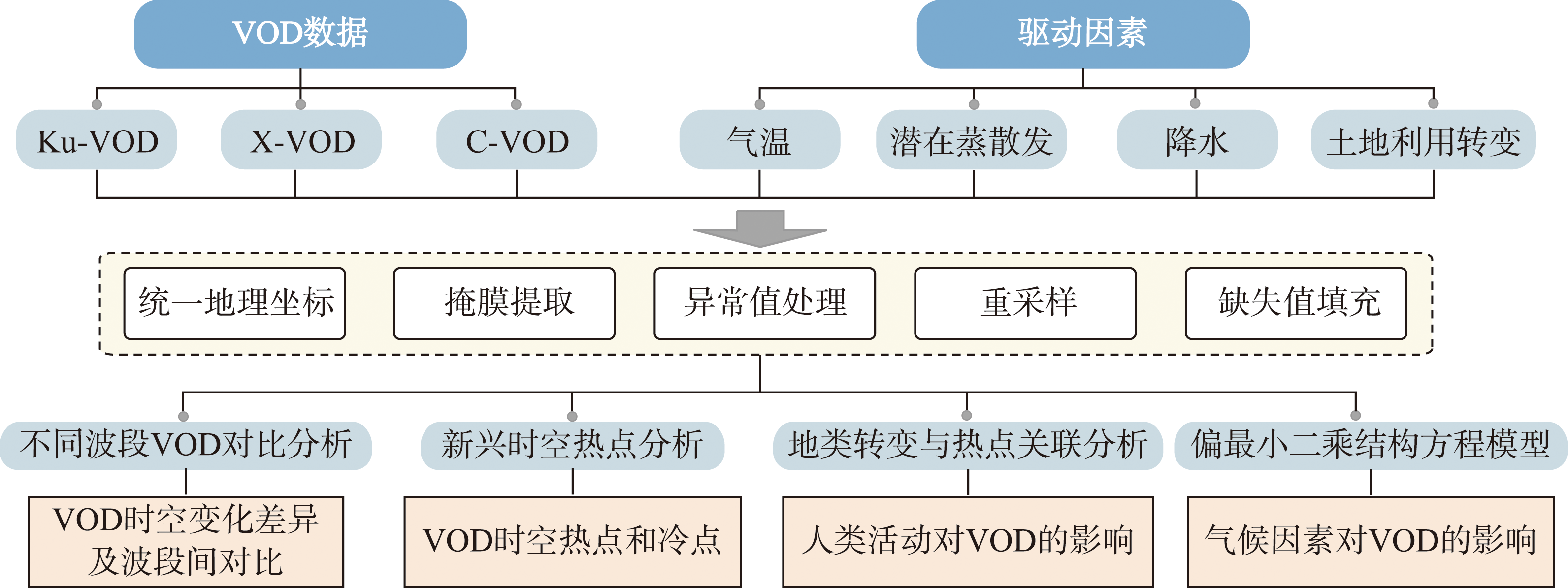
关键词: 植被光学厚度; 新兴时空热点分析; 偏最小二乘结构方程模型
石曼青 , 杨小玉 , 邱建秀 , 罗明 , 王前锋 , 王大刚 . 中国植被光学厚度的时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(5) : 1212 -1225 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202505004
This study utilizes emerging hotspot analysis to explore the spatio-temporal trends of vegetation optical depth (VOD) observed in Ku, X, and C microwave bands over China from 2002 to 2017. Furthermore, it analyzes the impacts of anthropogenic activities, represented by land use change, on the spatial and temporal changes in VOD, and employs Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Model to quantitatively assess the climatic effects on VOD changes. Overall, VOD exhibits a southeast-to-northwest gradient over China, with central and southern regions identified as VOD hotspots, while Xinjiang and the central Inner Mongolia Plateau are identified as VOD cold spots. Regions with consistent emerging hotspot analysis results across the three bands demonstrate a "greening" phenomenon in sparsely-vegetated regions nationwide. Additionally, the association between land use change and emerging hotspots reveals strong impacts of human activities on VOD variations. Specifically, persistent and intensified VOD hotspots predominantly correspond to scenarios where grassland is converted to forest. Attribution of VOD changes using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling indicates that, in the humid zone, where hydrothermal conditions are favorable and soil moisture is abundant, further increases in temperature and precipitation may inhibit vegetation growth. In contrast, in the arid zone, the inhibitory effect of temperature is less prominent. In the Tibetan Plateau, increases in both temperature and precipitation will promote vegetation growth. The insights from this study are expected to provide scientific support for monitoring ecosystem changes, uncovering their driving forces, and assessing the effectiveness of ecological measures.

| [1] |
[赵静, 李静, 穆西晗, 等. 高分一号卫星中国植被覆盖度高时空分辨率产品验证与分析. 遥感学报, 2023, 27(3): 689-699.]
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
[金凯, 王飞, 韩剑桥, 等. 1982—2015年中国气候变化和人类活动对植被NDVI变化的影响. 地理学报, 2020, 75(5): 961-974.]
|
| [8] |
[刘悦, 刘欢欢, 陈印, 等. 2000—2018年中国植被光学厚度时空动态特征及驱动因素. 地理学报, 2023, 78(3): 729-745.]
|
| [9] |
[王琦, 柴琳娜, 赵少杰, 等. 基于多角度微波辐射亮温数据反演冬小麦光学厚度. 遥感技术与应用, 2015, 30(3): 424-430.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[杨绪红, 金晓斌, 杨永可, 等. 1950—2020年东北地区林地时空变化特征分析. 地理科学, 2022, 42(11): 1996-2005.]
|
| [22] |
[白昆立, 陈蕾伊, 邓洪涛, 等. 华南地区不同类型森林生态系统植被碳现状研究. 林业与环境科学, 2022, 38(6): 102-108.]
|
| [23] |
[朱军强. 国家退牧还草工程出台新政策. 中国产业, 2011(10): 18-19.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
[李茂华, 都金康, 李皖彤, 等. 1982—2015年全球植被变化及其与温度和降水的关系. 地理科学, 2020, 40(5): 823-832.]
|
| [27] |
[莫兴国, 刘苏峡, 胡实. 黄河源区气候—植被—水文协同演变及成因辨析. 地理学报, 2022, 77(7): 1730-1744.]
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
[杨天垚, 邱建秀, 肖国安. 华北农业干旱监测与冬小麦估产研究. 生态学报, 2023, 43(5): 1936-1947.]
|
| [37] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |