

“双碳”目标下国土空间减排增汇路径研究
|
郑欢(1998-), 女, 辽宁沈阳人, 博士生, 研究方向为陆地生态系统碳循环。E-mail: zhenghuan@mail.bnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-07-23
修回日期: 2025-04-23
网络出版日期: 2025-05-23
基金资助
北京师范大学地理科学学部“全球环境变化”学科发展专项(2023-GC-ZYTS-01)
Carbon emission reduction and carbon sink enhancement pathway for national spatial planning under the "dual carbon" goals
Received date: 2024-07-23
Revised date: 2025-04-23
Online published: 2025-05-23
Supported by
BNU-FGS Global Environmental Change Program(2023-GC-ZYTS-01)
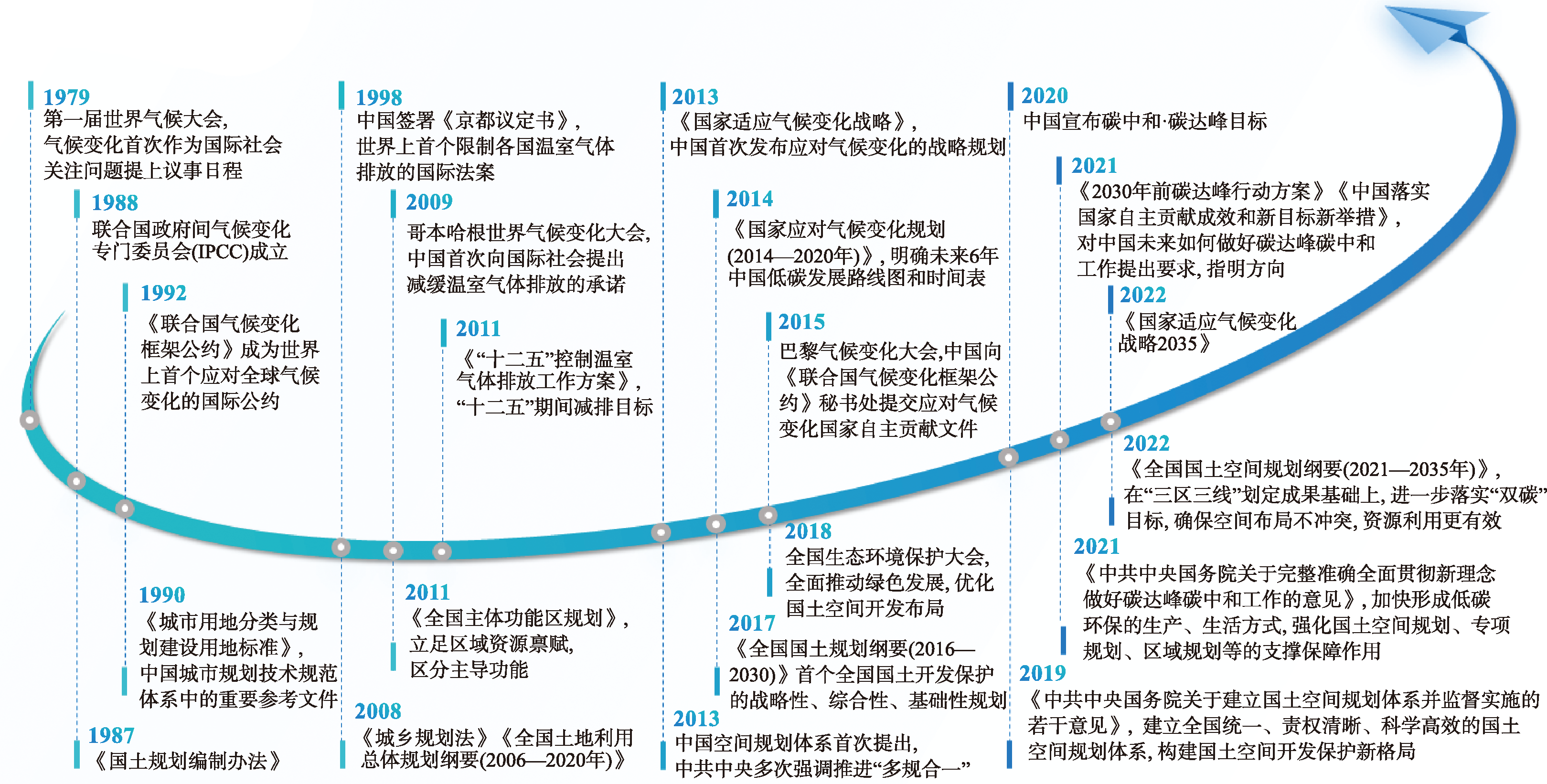
为实现“双碳”目标,需要在中国现有国情和制度框架下,积极探索国土空间的“双碳”响应战略,创新发展国土空间减排增汇路径研究。目前关于助力碳中和的讨论重点聚焦单一空间、单个部门的减碳维度,缺少面向“双碳”目标的多空间、多部门的整体统筹以及具体路径的论证研究,导致不同国土空间减排增汇的目标定位和权责关系不清,总体任务无法针对性分解并具体落实。对此,本文在统筹考虑生态、农业和城镇“三类空间”功能属性和交互作用的基础上,首先建立了“三类空间”碳收支效应的认知框架,提出“三类空间”减排增汇路径的设计原则。其次,结合“三类空间”承担的减碳份额,根据各路径的应用现状、历史贡献、适用范围及未来潜力,进一步总结提炼生态空间固碳增汇、农业空间减排增汇和城镇空间减排降碳的多空间协调行动路径,来助力实现可持续的生态修复、农田管理和城镇管控,促进形成未来国土空间一体化下的减排增汇优化策略和绿色转型应对方法。
郑欢 , 何斌 , 张文新 , 郭兰兰 , 黄大全 , 郑龙飞 , 李铁威 , 褚阳 . “双碳”目标下国土空间减排增汇路径研究[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(5) : 1183 -1211 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202505003
To realize the "dual carbon" goals, it is necessary to actively explore the "dual carbon" response strategy in the national spaces and innovate the research on carbon emission reduction and carbon sink enhancement pathways within the existing Chinese national conditions and institutional framework. Currently, discussions centered around supporting carbon neutrality predominantly emphasize the carbon reduction dimensions of a single space or department, lacking comprehensive coordination and specific pathways demonstration research across multiple spaces and departments. This has led to unclear goal positioning and accountability relationships for carbon emission reduction and carbon sequestration in different national spaces, making it challenging to decompose the overall tasks and implement them concretely. On the basis of considering the spatial functional attributes and interactions of ecological space, agricultural space, and urban space, this study first establishes a cognitive framework for carbon balance effects of three types of space (ecological, agricultural, and urban spaces) and proposes design principles for carbon emission reduction and carbon sink enhancement pathways. Then, based on the share of carbon reduction undertaken by the three types of space, as well as the current application status, historical contributions, scope of application, and future potential of each pathway, this study further summarizes and proposes a multi-spatial coordinated pathway for enhancing carbon sinks within ecological spaces, reducing carbon emissions and increasing sinks in agricultural spaces, and decreasing emissions in urban spaces. This initiative not only contributes to achieving sustainable ecological restoration, efficient cropland management, and effective urban control, but also fosters the formation of climate mitigation optimization strategies and green transformation response methods under the integration of future national space.

表1 生态空间固碳增汇路径的历史贡献及未来潜力(亿t CO2 a-1)Tab. 1 Historical contributions and future potential of the pathway for carbon sink enhancement in ecological space (100 million t CO2 a-1) |
| 生态空间 | 类型 | 路径 | 应用现状 | 历史贡献 | 参考文献 | 未来潜力 | 参考文献 | 合计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生态保护 | 森林系统 | 1避免森林退化 | *** | - | - | 0.90~1.20 | [18] | 1.87~2.47 |
| 草地系统 | 2避免草地退化 | *** | - | - | 0.20~0.50 | [18] | ||
| 湿地系统 | 3湿地保育 | *** | - | - | 0.02 | [18] | ||
| 4泥炭地保护 | *** | - | - | 0.75 | [18] | |||
| 生态修复 | 森林系统 | 1森林恢复 | *** | 1.60~1.70 | [45, 79] | 4.30~5.90 | [18, 80] | 4.49~6.11 |
| 草地系统 | 2草地恢复 | *** | 0.20 | [45-46] | 0.04~0.06 | [46] | ||
| 湿地系统 | 3滨海湿地恢复 | *** | - | - | 0.02 | [81] | ||
| 4泥炭地恢复 | *** | - | - | 0.13 | [18] | |||
| 可持续管理 | 森林系统 | 1天然林管理 | *** | 0.85 | [86] | 1.10~1.80 | [18] | 2.20~3.51 |
| 2人工林管理 | *** | - | - | 0.17~0.49 | [46] | |||
| 3森林火灾管理 | ** | 0.10 | [46] | 0.10~0.27 | [47] | |||
| 4城市绿化 | ** | - | - | 0.18~0.30 | [40] | |||
| 草地系统 | 5放牧优化 | *** | 0.29~0.59 | [18, 46] | 0.65 | [95] | ||
| 生态技术 | - | 1土壤增汇技术 | * | - | - | - | - | > 8.60 |
| 2 BECCS | * | - | - | 8.60 | [104] |
注:应用现状分3级,星号数量表示应用程度,星号越多该路径目前的应用越广泛;合计为各路径未来潜力的汇总。 |
表2 农业空间减排增汇路径历史贡献及未来潜力(亿t CO2 a-1)Tab. 2 Historical contributions and future potential of the pathway for carbon emission reduction and carbon sink enhancement in agricultural space (100 million t CO2 a-1) |
| 农业空间 | 类型 | 路径 | 应用现状 | 历史贡献 | 参考文献 | 未来潜力 | 参考文献 | 合计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农田管理 | 增汇型 | 1保护性耕作 | *** | 0.66 | [111] | 2.10 | [53] | 3.44 |
| 2覆盖性种植 | *** | 0.06 | [18] | 0.24 | [54, 115] | |||
| 3农林复合系统 | ** | - | - | 1.10 | [18] | |||
| 减排型 | 4农田养分管理 | *** | 0.48 | [46] | 0.19~0.21 | [47, 117] | 0.48~0.71 | |
| 5稻田耕作管理 | ** | - | - | 0.29~0.50 | [46] | |||
| 农业技术 | 增汇型 | 1农光互补 | ** | - | - | - | - | 2.20~5.30 |
| 2生物炭 | * | 0.01 | [46] | 2.20~5.30 | [47] | |||
| 减排型 | 3畜种改良 | ** | - | - | 0.19 | [18, 119] | > 2.42 | |
| 4饲料改良 | *** | - | - | 0.73 | [18, 119] | |||
| 5秸秆能源化利用 | ** | 0.14 | [129] | 1.50 | [129] | |||
| 6沼气综合利用 | ** | 0.02 | [130] | - | - |
注:应用现状分3级,星号数量表示应用程度,星号越多该路径目前的应用越广泛;合计为各路径未来潜力的汇总。 |
表3 城镇空间减排降碳路径历史贡献及未来潜力(亿t CO2 a-1)Tab. 3 Historical contributions and future potential of the pathway for carbon emission reduction in urban space (100 million t CO2 a-1) |
| 城镇空间 | 类型 | 路径 | 应用现状 | 历史贡献 | 参考文献 | 未来潜力 | 参考文献 | 合计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城镇管理 | 供应端 | 1低碳电力转型 | *** | 22.60 | 本文 | - | - | >22.60 |
| 2调控油气消费 | ** | - | - | - | - | |||
| 消费端 | 3优化交通运输结构 | ** | - | - | 1.90~3.10 | [134-135] | 4.83~6.21 | |
| 4调整城市空间布局 | ** | - | - | 0.98~1.10 | [134, 139] | |||
| 5优化工业生产结构 | *** | - | - | 1.76 | [141] | |||
| 6废弃物资源化利用 | ** | 0.05 | [142, 145] | 0.19~0.25 | [143, 145] | |||
| 替代性技术 | 供应端 | 1新型智能电网 | ** | 4.83 | [147, 152] | - | - | 4.83 |
| 消费端 | 2新能源汽车消费 | *** | 0.80 | 本文 | 3.40 | [134] | 39.70~40.70 | |
| 3智慧交通系统 | * | - | - | 2.20 | [134] | |||
| 4工业电气化 | ** | 0.80 | 本文 | 2.70 | 本文 | |||
| 5建筑电气化 | ** | - | - | 3.00~4.00 | [165-166] | |||
| 6超低能耗建筑 | ** | - | - | 28.40 | [168-169] | |||
| 负碳技术 | 固碳端 | 1碳捕集利用与封存 | * | 0.04 | [171] | 16.00 | [174] | 16.00 |
注:应用现状分3级,星号数量表示应用程度,星号越多该路径目前的应用越广泛;合计为各路径未来潜力的汇总。 |
| [1] |
IPCC. Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021.
|
| [2] |
[赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 回顾IPCC 30年(1988—2018年). 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 540-546.]
|
| [3] |
IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 ℃: IPCC Special Report on Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 ℃ above Pre-industrial Levels in Context of Strengthening Response to Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022.
|
| [4] |
[王田雨, 岳文泽. 面向碳增汇的国土空间格局优化:理论框架与行动逻辑. 自然资源学报, 2024, 39(5): 1008-1021.]
|
| [5] |
The General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Comprehensively Promoting the Construction of a Beautiful China. 2024. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202401/content_6925405.htm
[中国共产党中央委员会办公厅, 中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 中共中央/国务院关于全面推进美丽中国建设的意见. 2024. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202401/content_6925405.htm
|
| [6] |
[王艳. “双碳”目标下中国碳排放规模情景预测[D]. 济南: 山东财经大学, 2022.]
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
[熊健, 卢柯, 姜紫莹, 等. “碳达峰、碳中和”目标下国土空间规划编制研究与思考. 城市规划学刊, 2021(4): 74-80.]
|
| [9] |
The General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Fully, Accurately, and Comprehensively Implementing the New Development Philosophy and Doing a Good Job in Peak Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Carbon Neutrality. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/ zhengce/2021-10/24/content_5644613.htm
[中国共产党中央委员会办公厅, 中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 中共中央/国务院关于完整准确全面贯彻新发展理念做好碳达峰碳中和工作的意见. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/ zhengce/2021-10/24/content_5644613.htm
|
| [10] |
The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. Notice of the State Council on Issuing the Action Plan for Carbon Peak before 2030. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm
[中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 国务院关于印发2030年前碳达峰行动方案的通知. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm
|
| [11] |
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Notice of the Ministry of Natural Resources on Further Strengthening the Compilation and Implementation Management of National Land Spatial Planning. 2022. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202210/t20221026_2763118.html
[中华人民共和国自然资源部. 自然资源部关于进一步加强国土空间规划编制和实施管理的通知. 2022. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202210/t20221026_2763118.html
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
[于贵瑞, 郝天象, 朱剑兴. 中国碳达峰、碳中和行动方略之探讨. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(4): 423-434.]
|
| [29] |
[刘强, 陈怡, 滕飞, 等. 中国深度脱碳路径及政策分析. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2017, 27(9): 162-170.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
[刘俊伶, 项启昕, 王克, 等. 中国建筑部门中长期低碳发展路径. 资源科学, 2019, 41(3): 509-520.]
|
| [32] |
[杨璐, 杨秀, 刘惠, 等. 中国建筑部门二氧化碳减排技术及成本研究. 环境工程, 2021, 39(10): 41-49.]
|
| [33] |
[罗仕华, 胡维昊, 刘雯, 等. 中国2060碳中和能源系统转型路径研究. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2024, 54(1): 43-64.]
|
| [34] |
[林坚, 赵晔. “双碳”目标下的国土空间规划及用途管控. 科技导报, 2022, 40(6): 12-19.]
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
[谭显春, 郭雯, 樊杰, 等. 碳达峰、碳中和政策框架与技术创新政策研究. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(4): 435-443.]
|
| [37] |
[宋晓聪, 杜帅, 邓陈宁, 等. 钢铁行业生命周期碳排放核算及减排潜力评估. 环境科学, 2023, 44(12): 6630-6642.]
|
| [38] |
[庄贵阳, 魏鸣昕. 城市引领碳达峰、碳中和的理论和路径. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2021, 31(9): 114-121.]
|
| [39] |
[谷树忠, 谢美娥. 基于生态文明建设视角的农业资源与区划创新思维. 中国农业资源与区划, 2013, 34(1): 5-12.]
|
| [40] |
[于贵瑞, 朱剑兴, 徐丽, 等. 中国生态系统碳汇功能提升的技术途径: 基于自然解决方案. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(4): 490-501.]
|
| [41] |
[刘洋. “双碳”目标下我国农业增汇减排的路径与潜力. 农业经济, 2023(11): 120-122.]
|
| [42] |
[李寒冰, 金晓斌, 韩博, 等. “双碳”目标下全域土地综合整治的学理研究与实践路径. 地理研究, 2022, 41(12): 3164-3182.]
|
| [43] |
[陈可欣, 陶韦华, 方晓丽, 等. 国土空间规划中碳中和评估及规划应用路径研究. 规划师, 2022, 38(5): 134-141.]
|
| [44] |
The General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. The General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China/the General Office of the State Council has issued the "Opinions on Delineating and Strictly Observing the Ecological Protection Red Line". 2017. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2017-02/07/content_5166291.htm
[中国共产党中央委员会办公厅, 中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 中共中央办公厅/国务院办公厅印发《关于划定并严守生态保护红线的若干意见》. 2017. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2017-02/07/content_5166291.htm
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
[黄季焜. 新时期的中国农业发展: 机遇、挑战和战略选择. 中国科学院院刊, 2013, 28(3): 295-300.]
|
| [49] |
[刘静萍, 金晓斌, 韩博, 等. 农业空间半自然生境内涵、特征与识别. 生态学报, 2022, 42(22): 9199-9212.]
|
| [50] |
[
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
[平晓燕, 王铁梅, 卢欣石. 农林复合系统固碳潜力研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2013, 37(1): 80-92.]
|
| [53] |
[薛彩霞, 李园园, 胡超, 等. 中国保护性耕作净碳汇的时空格局. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(5): 1164-1182.]
|
| [54] |
[巴晓博, 隋鑫, 刘鸣达, 等. 东北黑土区覆盖作物—玉米间作保护性耕作的生态系统服务价值. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(7): 1883-1891.]
|
| [55] |
[高秀秀, 张晓彤. “双碳”背景下低碳宜居城镇可持续发展的技术策略. 可持续发展经济导刊, 2021(11): 31-33.]
|
| [56] |
[于婷婷, 冷红, 袁青. “双碳”目标下县域城镇空间低碳规划技术研究. 城市规划, 2023, 47(6): 110-120.]
|
| [57] |
[丁仲礼. 中国碳中和框架路线图研究. 中国工业和信息化, 2021(8): 54-61.]
|
| [58] |
[董寅, 金贵, 邓祥征. 中国国土空间布局优化研究. 地理学报, 2024, 79(3): 672-687.]
|
| [59] |
[谈明洪, 吕昌河. 城市用地扩展与耕地保护. 自然资源学报, 2005, 20(1): 52-58.]
|
| [60] |
[赖力. 中国土地利用的碳排放效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2010.]
|
| [61] |
[柯新利, 杨银玲, 朱梦珂. 耕地位移的演进, 挑战与对策建议. 中国土地科学动态, 2022(4): 1-4.]
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
[林辰辉, 朱雯娟, 张永波, 等. “双碳”目标下的国土空间规划方法研究与实践: 以天津市为例. 城市规划学刊, 2022(Suppl.2): 229-234.]
|
| [65] |
[张兵兵, 王捷, 闫志俊. 中国城市碳达峰路径及其驱动因素的结构分解. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2023, 33(9): 38-44.]
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. The General Plan for the Major Projects of Conservation and Restoration of National Important Ecosystems (2021-2035). 2020. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-06/12/content_5518982.htm
[中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会, 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 全国重要生态系统保护和修复重大工程总体规划(2021—2035年). 2020. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-06/12/content_5518982.htm
|
| [68] |
OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2024-2033. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2024.
|
| [69] |
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China. Implementation Plan for Agricultural and Rural Carbon Reduction and Fixation. 2022. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-07/01/content_5698717.htm
[中华人民共和国农业农村部. 农业农村减排固碳实施方案. 2022. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-07/01/content_5698717.htm
|
| [70] |
WEF. Net Zero Carbon Cities: An Integrated Approach. Geneva: World Economic Forum, 2021.
|
| [71] |
[丁仲礼. 碳中和对中国的挑战和机遇. 中国新闻发布(实务版), 2022(1): 16-23.]
|
| [72] |
[彭云峰, 常锦峰, 赵霞, 等. 中国草地生态系统固碳能力及其提升途径. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(4): 587-602.]
|
| [73] |
[张瑶, 赵美训, 崔球, 等. 近海生态系统碳汇过程、调控机制及增汇模式. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(4): 438-449.]
|
| [74] |
[唐剑武, 叶属峰, 陈雪初, 等. 海岸带蓝碳的科学概念、研究方法以及在生态恢复中的应用. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(6): 661-670.]
|
| [75] |
The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. State Council General Office's Opinions on Strengthening Grassland Protection and Restoration. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-03/30/content_5596791.htm
[中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于加强草原保护修复的若干意见. 2021. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-03/30/content_5596791.htm
|
| [76] |
[张骁栋, 朱建华, 张小全, 等. 中国湿地碳汇功能的提升途径. 自然保护地, 2022, 2(3): 17-23.]
|
| [77] |
[刘子刚, 王铭, 马学慧. 中国泥炭地有机碳储量与储存特征分析. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(10): 1814-1819.]
|
| [78] |
[王法明, 唐剑武, 叶思源, 等. 中国滨海湿地的蓝色碳汇功能及碳中和对策. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(3): 241-251.]
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
[马学慧. 中国泥炭地碳储量与碳排放. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013.]
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
[孟佶贤, 梁晨, 陈文汇. 异质性环境规制对我国森林碳汇增长的影响机制研究. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 23(2): 42-51.]
|
| [85] |
[姜霞, 黄祖辉. 经济新常态下中国林业碳汇潜力分析. 中国农村经济, 2016(11): 57-67.]
|
| [86] |
[张逸如, 刘晓彤, 高文强, 等. 天然林保护工程区近20年森林植被碳储量动态及碳汇(源)特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(13): 5093-5105.]
|
| [87] |
[刘晓曼, 王超, 高吉喜, 等. 服务双碳目标的中国人工林生态系统碳增汇途径. 生态学报, 2023, 43(14): 5662-5673.]
|
| [88] |
[张颖, 张子璇. 中国森林碳汇生产总值核算及分析. 中国国土资源经济, 2023, 36(8): 28-34.]
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
[赵彩君, 刘晓明. 城市绿地系统对于低碳城市的作用. 中国园林, 2010, 26(6): 23-26.]
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
[唐芳林, 杨智, 王卓然, 等. 生态文明视域下草原治理体系构建研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2381-2390.]
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
[王绍强, 周成虎, 李克让, 等. 中国土壤有机碳库及空间分布特征分析. 地理学报, 2000, 55(5): 533-544.]
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
[钱壮壮, 朱孔鑫, 王会利, 等. 菌剂添加对人工林土壤呼吸和有机质含量及细菌群落影响. 南方林业科学, 2021, 49(2): 37-41, 78.]
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
IPCC. Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 ℃ above Pre-industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. Geneva: World Meteorological Organization, 2018.
|
| [103] |
[樊静丽, 李佳, 晏水平, 等. 我国生物质能—碳捕集与封存技术应用潜力分析. 热力发电, 2021, 50(1): 7-17.]
|
| [104] |
[李洪深, 楚洁璞, 徐伟涛, 等. 干法生物天然气BECCS工程碳负排效益分析. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(5): 158-164.]
|
| [105] |
IPCC. Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change, Report of Working Group Ⅰ. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
[张文艳, 张武斌, 陈玉梅. “双碳”目标下农业绿色低碳发展现状与措施. 农业工程, 2022, 12(Suppl.1): 48-51.]
|
| [111] |
[张雄智, 李帅帅, 刘冰洋, 等. 免耕与秸秆还田对中国农田固碳和作物产量的影响. 中国农业大学学报, 2020, 25(5): 1-12.]
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
[曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3.]
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
[王丽宏, 胡跃高, 杨光立, 等. 农田冬季覆盖作物对土壤有机碳含量和主作物产量的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2006, 24(6): 64-67.]
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
[巨晓棠, 谷保静. 我国农田氮肥施用现状、问题及趋势. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4): 783-795.]
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
[刘祥照, 王桦, 吴学涛, 等. 农村新能源转型下的“光伏+”模式探讨. 光源与照明, 2023(12): 86-88.]
|
| [121] |
[刘小磊. 我国农光互补产业发展现状与展望. 产业创新研究, 2023(22): 65-67.]
|
| [122] |
[周子莜. 中国不同农光互补系统“能源—环境—经济”综合影响分析及发电潜力评估[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023.]
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
[陈温福, 张伟明, 孟军. 农用生物炭研究进展与前景. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(16): 3324-3333.]
|
| [126] |
[彭华, 纪雄辉, 吴家梅, 等. 生物黑炭还田对晚稻CH4和N2O综合减排影响研究. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(11): 1620-1625.]
|
| [127] |
[何可, 李凡略, 刘颖. “双碳”目标下的畜禽养殖业绿色发展. 环境保护, 2022, 50(16): 28-33.]
|
| [128] |
[许梓荣, 汪以真, 邹晓庭, 等. 高效转化、肉质改良、资源开发型全价饲料的研发与产业化. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2018, 44(2): 198.]
|
| [129] |
[霍丽丽, 赵立欣, 孟海波, 等. 中国农作物秸秆综合利用潜力研究. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(13): 218-224.]
|
| [130] |
[李劼, 徐晋涛. 我国农业低碳技术的减排潜力分析. 农业经济问题, 2022, 43(3): 117-135.]
|
| [131] |
[朱民,
|
| [132] |
[刘淳森, 曲建升, 葛钰洁, 等. 基于LSTM模型的中国交通运输业碳排放预测. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(5): 2574-2582.]
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
[张红军. 促进可再生能源发展的多种能源利用协同机制与路径[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2023.]
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
[肖华斌, 盛硕, 刘嘉. 低碳生态城市空间规划途径研究综述与展望. 城市发展研究, 2015, 22(12): 8-12.]
|
| [137] |
[潘海啸. 面向低碳的城市空间结构:城市交通与土地使用的新模式. 城市发展研究, 2010, 17(1): 40-45.]
|
| [138] |
[陈飞, 诸大建. 低碳城市研究的理论方法与上海实证分析. 城市发展研究, 2009, 16(10): 71-79.]
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. The Chinese government submitted the "New Measures,Goals and Achievements of China's Implementation of National Independent Contributions". 2022. https://wzq1.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/hjywnews/202110/t20211029_958240.shtml
[中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中国政府提交《中国落实国家自主贡献成效和新目标新举措》. 2021. https://wzq1.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/hjywnews/202110/t20211029_958240.shtml
|
| [141] |
The General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. Notice of the State Council on Issuing the Action Plan for Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction from 2024 to 2025. 2024. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202405/content_6954323.htm
[中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 国务院关于印发《2024—2025年节能降碳行动方案》的通知. 2024. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202405/content_6954323.htm
|
| [142] |
[王航, 王先恺, 陈祥, 等. 城市有机固体废弃物协同处置碳排放分析. 环境工程, 2024, 42(2): 66-72.]
|
| [143] |
[张晨怡, 董会娟, 耿涌. 中国城市生活垃圾处理碳排放时空分布特征及减排潜力. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2024, 34(4): 23-35.]
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
[李秋虹, 孙晓杰, 胡心悦, 等. 中国城市生活垃圾处理的碳排放变化趋势研究. 环境污染与防治, 2023, 45(7): 952-958.]
|
| [146] |
[徐建中. 科学用能与分布式能源系统. 中国能源, 2005, 27(8): 10-13.]
|
| [147] |
China Industry Research Network. Annual Research and Consultation Report of Panorama Survey and Investment Strategy on China Industry. 2022. https://www.chinairn.com/yjbg/
[中国行业研究网. 2024—2029年分布式能源产业现状及未来发展趋势分析报告. 2022. https://www.chinairn.com/yjbg/
|
| [148] |
[肖百霞. 碳达峰、碳中和背景下国土空间规划响应路径思考. 智能城市, 2022, 8(8): 84-86.]
|
| [149] |
[秋慈. 中国特高压点亮千家万户. 科学之友, 2023(11): 42-43.]
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
[江亿. 光储直柔: 助力实现零碳电力的新型建筑配电系统. 暖通空调, 2021, 51(10): 1-12.]
|
| [152] |
[刘雅静, 王宁. 清洁能源助力“绿色办奥”张家口绿色能源点亮冬奥之光. 环境与生活, 2022(1): 30-31.]
|
| [153] |
[顾庆康, 林乐芬. “双碳”目标下制造业碳减排成效、影响因素与达峰路径: 基于制造业大省的面板数据分析. 经济问题, 2024(2): 57-63.]
|
| [154] |
[王伟, 邹伟, 张国彪, 等. “双碳”目标下的城市群国土空间规划路径与治理机制. 环境保护, 2022, 50(Suppl.1): 64-69.]
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
[李文竹, 梁佳宁. 新兴技术作用下未来城市空间的碳减排效益研究综述. 城市与区域规划研究, 2023, 15(1): 111-128.]
|
| [157] |
|
| [158] |
[汪旭颖, 李冰, 吕晨, 等. 中国钢铁行业二氧化碳排放达峰路径研究. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(2): 339-346.]
|
| [159] |
|
| [160] |
|
| [161] |
|
| [162] |
[李惠民, 童晶晶. 中国建筑部门碳排放的区域差异及其碳中和路径选择. 环境保护, 2021, 49(Suppl.2): 23-29.]
|
| [163] |
[王明涛, 刘焕卫, 张百浩. 燃气机热泵供热性能规律的理论和实验研究. 化工学报, 2015, 66(10): 3834-3840.]
|
| [164] |
[姚春妮, 马欣伯, 罗多. 碳达峰目标下太阳能光电建筑应用发展规模预测研究. 建设科技, 2021(11): 33-35.]
|
| [165] |
[徐伟, 张时聪, 王珂, 等. 建筑部门“碳达峰”“碳中和”实施路径比对研究. 江苏建筑, 2022(2): 1-6.]
|
| [166] |
|
| [167] |
[罗晓予, 曹星煜, 宋志茜. 中日建筑全生命周期碳排放比较. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 220-230.]
|
| [168] |
[吴泽洲, 黄浩全, 陈湘生, 等. “双碳”目标下建筑业低碳转型对策研究. 中国工程科学, 2023, 25(5): 202-209.]
|
| [169] |
[常莎莎, 冯国会, 崔航, 等. 建筑行业碳排放特征及减排潜力预测分析. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 39(1): 139-146.]
|
| [170] |
[张贤, 李凯, 马乔, 等. 碳中和目标下CCUS技术发展定位与展望. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2021, 31(9): 29-33.]
|
| [171] |
[罗海中, 曾少雁, 吴大卫. 双碳背景下CCUS技术发展现状及展望. 山东化工, 2023, 52(23): 101-106.]
|
| [172] |
Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China. Annual Report on Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage in China (2023). 2023. https://www.most.gov.cn/kjbgz/202307/t20230714_187011.html
[中华人民共和国科学技术部. 中国碳捕集利用与封存年度报告(2023). 2023. https://www.most.gov.cn/kjbgz/202307/t20230714_187011.html
|
| [173] |
[陈婉. CCUS是实现《巴黎协定》温控目标的必要技术手段. 环境经济, 2023(18): 36-39.]
|
| [174] |
[张贤, 李阳, 马乔, 等. 我国碳捕集利用与封存技术发展研究. 中国工程科学, 2021, 23(6): 70-80.]
|
| [175] |
[徐一剑, 李潭峰, 徐丽丽. 国土空间总体规划温室气体核算模型. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 355-365.]
|
| [176] |
[赵荣钦, 黄贤金, 郧文聚, 等. 碳达峰碳中和目标下自然资源管理领域的关键问题. 自然资源学报, 2022, 37(5): 1123-1136.]
|
| [177] |
|
| [178] |
|
| [179] |
[王震坡, 詹炜鹏, 孙逢春, 等. 新能源汽车碳减排潜力分析. 北京理工大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 111-122.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |