

基于“点—轴系统”理论的海南自由贸易港发展战略探讨
|
刘云刚(1973-), 男, 内蒙古呼和浩特人, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 研究方向为政治地理学、城市地理学、生活空间论。E-mail: ygliu@scnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-07-29
修回日期: 2024-12-10
网络出版日期: 2024-12-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42230705)
国家自然科学基金项目(20VHQ002)
The island-based "pole-axis system" theory and its utilization in the development strategy of Hainan Free Trade Port
Received date: 2024-07-29
Revised date: 2024-12-10
Online published: 2024-12-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42230705)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(20VHQ002)
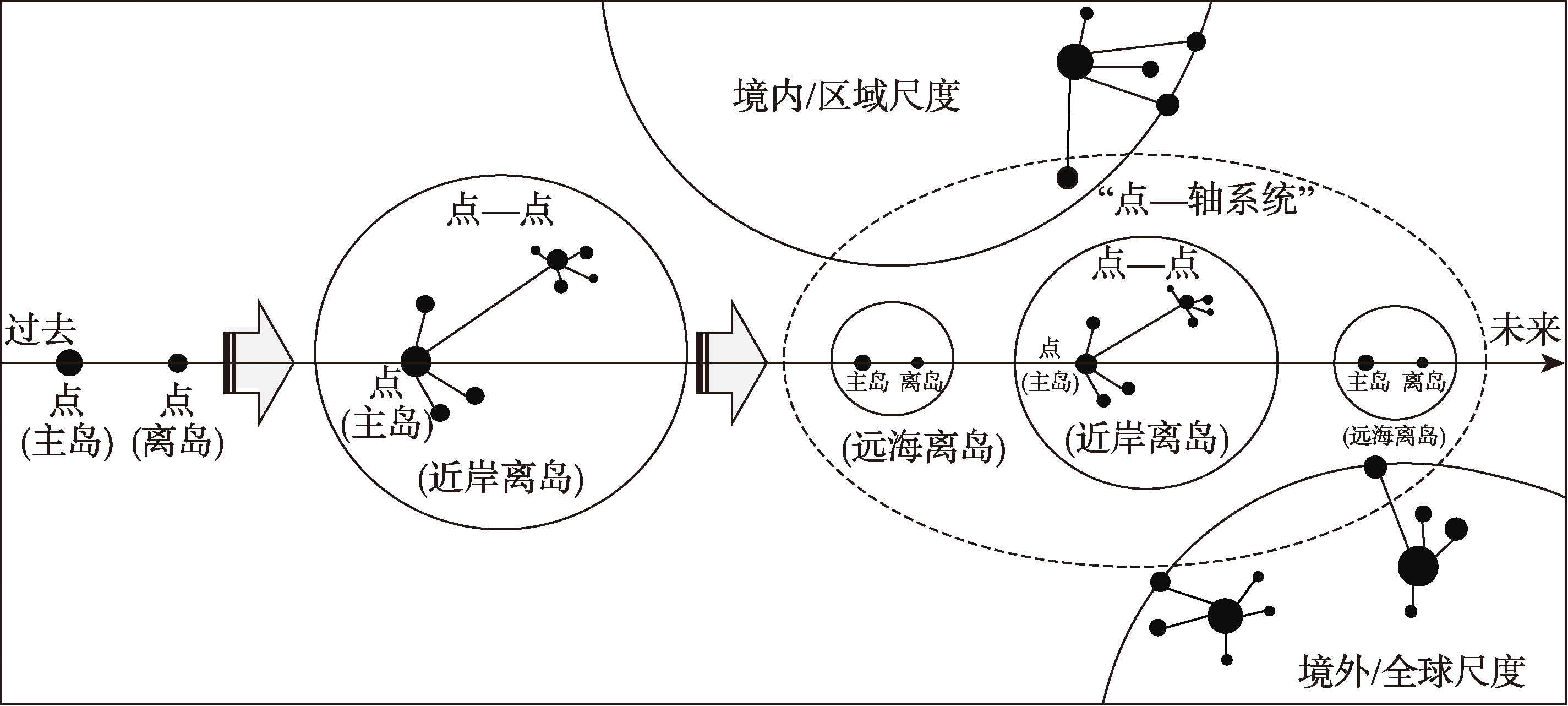
由于长期陆海分治,以“点—轴系统”理论为代表的区域开发理论,对陆海过渡带及海洋空间的发展潜力研究不足。本文在此背景下,梳理“点—轴系统”理论的海洋面向,探讨超越陆域思维的“点—轴系统”及其运用。具体以目前备受关注的海南自由贸易港发展为例,从岛屿经济体的一般规律出发,回溯海南岛的区位关系与发展历程,并基于“点—轴系统”理论的拓展,探讨海南自贸港的发展方向和思路。研究结果:① 海南自贸港的发展需要统筹考虑岛屿区位关系,将“点—轴系统”内置其中,考虑其在全球、国家、区域和地方不同尺度空间的综合作用;② 海南自贸港岛屿“点—轴系统”强调“流”而非地理邻近性对岛屿和岛群增长极的作用,对岛—岛关系关注需从中心性转向节点属性挖掘,对陆—岛关系关注需由等级从属向功能互补转变;③ 海南自贸港需打造兼具陆、岛、海的经济与产业复合“点—轴系统”,通过“以海定陆”和“倚陆向海”双向互动,深化不同地理单元协同发展的内生动力。本文旨在丰富“点—轴系统”理论的海洋面向,为厘清海南自贸港及其他岛屿经济体的发展思路提供助力。
刘云刚 , 刘玄宇 , 王宇渠 . 基于“点—轴系统”理论的海南自由贸易港发展战略探讨[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(12) : 3050 -3062 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202412008
Owing to the long-standing land-sea division, the regional development theory represented by the pole-axis system has conducted insufficient research on the development potential of the land-sea transition zone and even the marine space. In this context, this paper re-explores the marine orientation of the "pole-axis system" theory and investigates the application of the pole-axis system beyond the land-based thinking. Specifically, taking the currently highly-regarded development of the Hainan Free Trade Port (HFTP) as an example, it commences from the general laws of island economies, traces the geographical relationships and development history of Hainan Island, and based on the expansion of the "pole-axis system" theory, deliberates on the development direction and ideas of the HFTP. This paper emphasizes that: (1) The spatial metaphor of isolation and connectivity of islands within the context of the pole-axis system are mutually reinforcing and compatible, and the cultivation and development of the pole-axis system of the HFTP need to take into account the synergetic effects of the island's geographical relationships at different spatial scales, namely the global, national, regional, and local levels. (2) The pole-axis system of HFTP highlights the role of "flow" rather than geographical proximity in the growth of islands and island clusters. The focus on island-island relationships needs to shift from centrality to the exploration of node attributes, while the focus on land-island relationships needs to change from hierarchy to functional complementarity. (3) The HFTP needs to establish an economic and industrial composite pole-axis system that integrates land, island, and sea, and deepen the intrinsic driving force for the coordinated development of different geographic units through the bidirectional interaction of "defining development based on the sea" and "leaning on the land towards the sea". This study hopes to contribute to enriching and enhancing the marine orientation of the "pole-axis system" theory and deepening the study of islands, including the HFTP, other island economies, and the entire island.

| [1] |
[孟广文, 杨开忠, 朱福林, 等. 中国海南: 从经济特区到综合复合型自由贸易港的嬗变. 地理研究, 2018, 37(12): 2363-2382.]
|
| [2] |
[刘卫东, 陆大道. 新时期我国区域空间规划的方法论探讨: 以“西部开发重点区域规划前期研究”为例. 地理学报, 2005, 60(6): 894-902.]
|
| [3] |
[苏昌贵, 孙东琪, 肖林. 点—轴系统理论与国土开发的“T”字型战略架构的探索历程与启示. 长江流域资源与环境, 2023, 32(8): 1620-1627.]
|
| [4] |
[陆大道. 建设经济带是经济发展布局的最佳选择: 长江经济带经济发展的巨大潜力. 地理科学, 2014, 34(7): 769-772.]
|
| [5] |
[陆大道. 国土开发与经济布局的“T”字型构架与长江经济带可持续发展. 宏观经济管理, 2018(11): 43-47, 55.]
|
| [6] |
[王士君, 廉超, 赵梓渝. 从中心地到城市网络: 中国城镇体系研究的理论转变. 地理研究, 2019, 38(1): 64-74.]
|
| [7] |
[段进军, 李雪, 玄泽源. “点—轴系统”理论及“T”字型空间格局的科学性思考. 区域经济评论, 2022(3): 30-36.]
|
| [8] |
[梁进社. 中心地理论中市场原则的再讨论. 地理学报, 2022, 77(8): 1892-1906.]
|
| [9] |
[李满春, 姚梦汝, 汪侠, 等. 基于引文分析法的“点—轴系统”理论研究述评. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(2): 164-174.]
|
| [10] |
[陆玉麒, 董平. 中国主要产业轴线的空间定位与发展态势: 兼论点—轴系统理论与双核结构模式的空间耦合. 地理研究, 2004, 23(4): 521-529.]
|
| [11] |
[高晓路, 许泽宁, 牛方曲. 基于“点—轴系统”理论的城市群边界识别. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(3): 280-289.]
|
| [12] |
[韩增林, 刘伟, 王利. “点—轴系统”理论在中小尺度区域交通经济带规划中的应用: 以大连旅顺北路产业规划为例. 经济地理, 2005, 25(5): 662-666, 676.]
|
| [13] |
[汪德根, 陆林, 陈田, 等. 基于点—轴理论的旅游地系统空间结构演变研究: 以呼伦贝尔—阿尔山旅游区为例. 经济地理, 2005, 25(6): 904-909.]
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
[麻国庆. 人类学视野下的岛屿与世界. 民族研究, 2018(6): 55-65, 124.]
|
| [16] |
[孟广文. 国际经验对海南自由贸易港规划建设的启示. 资源科学, 2021, 43(2): 217-228.]
|
| [17] |
[裴广一, 黄光于. 海南自贸港对接粤港澳大湾区: 理论基础, 战略构想与合作方向. 学术研究, 2020(12): 98-104.]
|
| [18] |
[迟福林, 郭达, 郭文芹. 构建新发展格局下的海南自由贸易港. 行政管理改革, 2022(1): 15-19.]
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
[常路, 符正平, 马咏琪. 岛屿经济体的发展战略、竞争优势及对海南自贸港的启示. 南海学刊, 2022, 8(4): 21-33.]
|
| [21] |
[刘云刚, 刘玄宇. 政治地理学视角下的海南自由贸易港发展解读. 资源科学, 2021, 43(2): 209-216.]
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[秦伟山, 张义丰. 国内外海岛经济研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(9): 1401-1412.]
|
| [24] |
[张耀光. 中国岛屿经济体在国家经济中的作用和地位. 海洋经济, 2013, 3(1): 43-48.]
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
[甄峰, 秦萧, 席广亮. 信息时代的地理学与人文地理学创新. 地理科学, 2015, 35(1): 11-18.]
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |