

东北区域性城市收缩的地理认知与治理逻辑
|
孙平军(1981-), 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事区域发展与城乡规划、经济地理等方面的研究。E-mail: sunpj031@163.com |
收稿日期: 2023-03-22
修回日期: 2023-06-28
网络出版日期: 2024-08-06
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41501173)
教育部人文社科基金项目(21XJC790010)
Geographical cognition and governance logic of regional urban shrinkage in Northeast China
Received date: 2023-03-22
Revised date: 2023-06-28
Online published: 2024-08-06
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41501173)
Humanities and Social Science Research Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China(21XJC790010)
伴随全球城镇化进程的不断推进,世界范围内涌现了一批又一批的收缩型城市,给传统基于增长情景模拟的城市—区域规划范式带来了极大的冲击与挑战,也赋予了新时期中国地理学者和城乡规划工作实践者新的使命要求和责任担当。东北三省是中国人口流失最为严重、收缩城市最为集中的典型代表区,当前已呈现出十分明显的区域性城市收缩现象,如何理性认知与妥善处理这种区域性城市收缩现象(或问题),成为新时期全面落实区域协调高质量发展、全民共同富裕中国式现代化与全方位东北振兴中拟重点关注的核心科学问题。本文据此对其展开了逻辑思辨与实践探讨,首先,基于城镇化语境对区域性城市收缩本义内涵进行逻辑思辨,同时以国家整体战略目标为导向综合评判东北区域性城市收缩的合理性;其次,从区域空间关联“拉力”作用、区内城市收缩“挤出”作用和交通、通讯技术发展源于降低要素流动成本的“催化剂”作用3个层面探讨了东北区域性城市收缩的生成逻辑;最后,立足市场主导的精明收缩论和政府主导的活力再生论治理逻辑,在“区域协调高质量发展、以人为本新型城镇化、效率与公平、全面安全观”治理目标的导向下,对东北区域性城市收缩的治理模式及其治理策略从尺度异质性、发展语境关联性、要素差异化与多学科交融的视角展开了系统梳理。研究表明,区域性城市收缩是对传统城市收缩研究的延伸与扩展,其治理模式与治理策略的选择更多聚焦国家整体发展目标的落实;东北区域性城市收缩不能再单纯地将其看成是一个人口外迁的市场经济规律,背后夹带的“市场失灵”已经严重影响了习近平总书记对东北提出的“五大安全”重要使命。研究结果可为东北落实高质量发展、推进东北振兴提供参考借鉴。
孙平军 , 张可秋 , 曹乃刚 , 刘菊 . 东北区域性城市收缩的地理认知与治理逻辑[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(8) : 1918 -1939 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202408003
In the wake of unprecedented global urbanization, an alarming trend of shrinking cities has emerged worldwide, presenting a profound challenge to conventional urban-regional planning approaches, primarily centered on growth scenarios. This trend has also bestowed upon Chinese geographers and urban and rural planning practitioners a new mandate in this evolving era. One region that exemplifies this predicament is Northeast China, experiencing the most severe population decline and the highest concentration of shrinking cities in the country. How to rationally recognize and properly deal with this phenomenon (or problem) of regional urban shrinkage has become the core scientific issue to be focused on in the comprehensive implementation of regional coordinated high-quality development, Chinese-style modernization of common prosperity for all and all-round revitalization of Northeast China in the new era. This paper delves into a logical speculation and practical discussion to understand the underlying causes and implications of regional urban shrinkage in Northeast China: Initially, it examines the original concept of regional shrinking cities within the context of urbanization, critically evaluating the rationality of such shrinkage in light of the broader national strategic objectives. Subsequently, the generation logic of regional urban shrinkage in Northeast China is explored through three key factors: the "pull" effect of regional spatial correlation, the "extrusion" effect of urban shrinkage at a regional level, and the "catalyst" effect of transportation and communication technology development in reducing the cost of factor flow. Moreover, this study draws on the market-led shrewd contraction theory and the government-led vitality regeneration governance logic. It takes into account the governance objectives of achieving "regional coordinated high-quality development, people-oriented new urbanization, efficiency and fairness, and comprehensive security concept". With a systematic perspective that considers scale heterogeneity, development context relevance, factor differentiation, and multidisciplinary integration, the paper outlines a governance model and strategy for addressing regional urban shrinkage in Northeast China. By emphasizing the alignment of governance approaches with national development goals, this research underscores that regional urban shrinkage goes beyond a mere outcome of market-driven population migration. The presence of underlying "market failures" severely impacts the vision of the five major securities (national defense, food, ecology, energy, industry) advocated by Chinese President Xi Jinping for the Northeast China region. The findings of this study offer valuable insights to guide Northeast China's pursuit of high-quality development and contribute to the region's revitalization efforts.

表1 2010—2019年东北三省财政情况Tab. 1 Financial situation of three provinces of Northeast China, 2010-2019 |
| 指标 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 公共预算收支比 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.34 |
| 公共预算收入(亿元) | 3363 | 4067 | 4418 | 4434 | 4135 | 3146 | 3115 | 3126 | 3160 | 2961 |
| 公共预算支出(亿元) | 7236 | 8056 | 8483 | 8684 | 8298 | 8139 | 8313 | 8459 | 8414 | 8580 |
| 公共预算收入占全国比重(%) | 4.05 | 4.32 | 4.53 | 4.47 | 4.06 | 2.97 | 2.89 | 2.81 | 2.80 | 2.64 |
| 公共预算支出占全国比重(%) | 8.05 | 8.15 | 8.10 | 8.07 | 7.53 | 6.66 | 6.60 | 6.52 | 6.25 | 6.15 |
注:数据来源于相关年份统计年鉴和统计公报,其中公共预算收入与支出经过平减化处理。 |
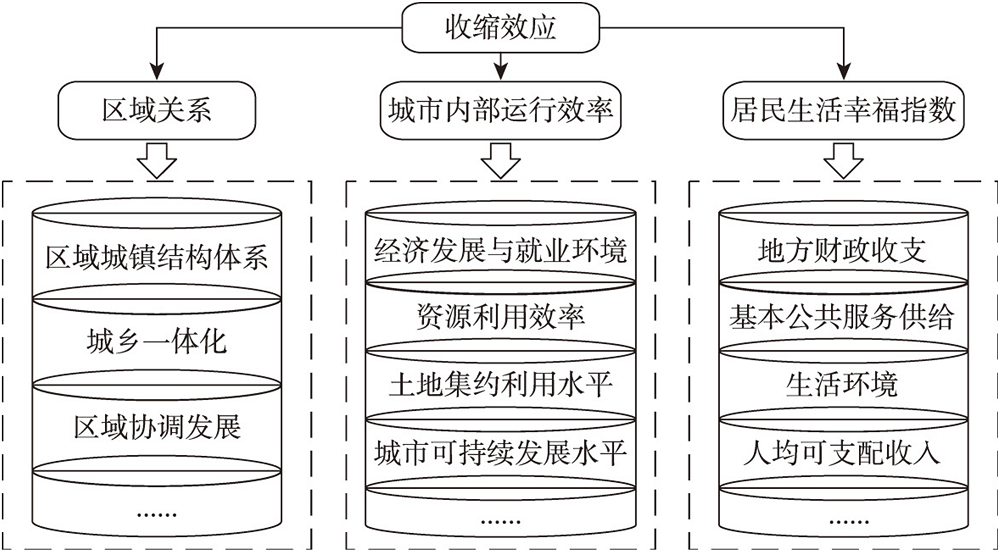
图2 基本公共服务收缩效应生成逻辑Fig. 2 Generation logic of shrinking effect of basic public services |
表2 东北三省与全国人口结构比较Tab. 2 Comparison of population structure between Northeast China and the whole country |
| 指标 | 东北层面 | 全国层面 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第六次人口普查 | 第七次人口普查 | 第六次人口普查 | 第七次人口普查 | ||
| 人口总量(人) | 109513129 | 98514948 | 1339724852 | 1411778724 | |
| 0~14岁占比(%) | 11.78 | 11.05 | 16.60 | 17.95 | |
| 15~59岁占比(%) | 74.33 | 64.95 | 70.14 | 63.35 | |
| 60岁及以上占比(%) | 13.89 | 24.00 | 13.26 | 18.70 | |
| 65岁及以上占比(%) | 6.51 | 16.21 | 8.87 | 13.50 | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
[沈丽珍, 顾朝林. 区域流动空间整合与全球城市网络构建. 地理科学, 2009, 29(6): 787-793.]
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
[吴康, 戚伟. 收缩型城市: 认知误区、统计甄别与测算反思. 地理研究, 2021, 40(1): 213-229.]
|
| [25] |
[陈棋, 薛东前, 马蓓蓓, 等. 黄土高原地区人口收缩格局与驱动力分析. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(1): 258-267.]
|
| [26] |
[杜志威, 李郇. 珠三角快速城镇化地区发展的增长与收缩新现象. 地理学报, 2017, 72(10): 1800-1811.]
|
| [27] |
[黄鹤. 精明收缩: 应对城市衰退的规划策略及其在美国的实践. 城市与区域规划研究, 2011, 4(3): 157-168.]
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[李诚固, 李振泉. “东北现象”特征及形成因素. 经济地理, 1996(1): 34-38.]
|
| [30] |
[刘振, 戚伟, 齐宏纲, 等. 多时期演变视角下中国人口收缩区的识别、空间特征与成因类型分析. 地理科学进展, 2021, 40(3): 357-369.]
|
| [31] |
[宫攀, 张槊, 王文哲. 人口视角下中国城市收缩的演变特征与时空格局: 基于第七次全国人口普查公报数据的分析. 人口与经济, 2022(3): 1-15.]
|
| [32] |
[陈蕊. 中国收缩型城市的综合测度与影响因素分析. 统计与决策, 2021, 37(23): 68-71.]
|
| [33] |
[马佐澎, 李诚固, 张平宇. 东北三省城镇收缩的特征及机制与响应. 地理学报, 2021, 76(4): 767-780.]
|
| [34] |
[孙平军, 王柯文. 中国东北三省城市收缩的识别及其类型划分. 地理学报, 2021, 76(6): 1366-1379.]
|
| [35] |
[刘玉博, 张学良. 武汉城市圈城市收缩现象研究. 规划师, 2017(1): 18-25.]
|
| [36] |
[孙平军. 城市收缩: 内涵·中国化·研究框架. 地理科学进展, 2022, 41(8): 1478-1491.]
|
| [37] |
[刁目林, 胡颖. 基于熵权TOPSIS法中国城市营商环境评价与比较. 北方经贸, 2023(1): 41-46.]
|
| [38] |
[孙平军, 丁四保, 修春亮, 等. 东北地区“人口—经济—空间”城市化协调性研究. 地理科学, 2012, 32(4): 450-457.]
|
| [39] |
[田深圳, 李雪铭, 杨俊, 等. 东北三省城市拟态与现实人居环境时空耦合协调特征与机制. 地理学报, 2021, 76(4): 781-798.]
|
| [40] |
[张倩男. 东北地区城市经济发展差异及影响因素研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.]
|
| [41] |
[孙平军, 彭雅丽, 曹乃刚, 等. 延边朝鲜族自治州城镇收缩: 特征、机理与响应. 地理科学, 2023, 43(5): 796-806.]
|
| [42] |
[赵继涛, 卢小君, 费俊嘉. 东北地区基本公共服务公众获得感提升研究. 合作经济与科技, 2021(16): 185-187.]
|
| [43] |
[霍鹏, 魏剑锋. 城市间高铁开通影响了产业集聚态势吗? 以知识密集型服务业为例. 产业经济研究, 2021(4): 13-26, 84.]
|
| [44] |
[孙威, 王晓楠, 刘艳军. 高速铁路对中国资源型城市区位的影响. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34(1): 1-13.]
|
| [45] |
[孙宏日, 刘艳军, 周国磊. 东北地区交通优势度演变格局及影响机制. 地理学报, 2021, 76(2): 444-458.]
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
[西尔维亚·索萨, 保罗·皮诺, 雷链, 等. 为收缩而规划一种悖论还是新范式. 国际城市规划, 2020, 35(2): 1-11.]
|
| [49] |
[周恺, 刘力銮, 戴燕归. 收缩治理的理论模型、国际比较和关键政策领域研究. 国际城市规划, 2020, 35(2): 12-19, 37.]
|
| [50] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |