

快速升温下的北极径流变化及其驱动机制综述
|
王平(1979-), 男, 安徽人, 研究员, 研究方向为水文水资源。E-mail: wangping@igsnrr.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-06-30
修回日期: 2023-10-16
网络出版日期: 2023-11-29
基金资助
国家自然科学基金中俄合作研究项目(42061134017)
中国科学院特别交流计划
Arctic runoff changes and their driving mechanisms under rapid warming: A review
Received date: 2023-06-30
Revised date: 2023-10-16
Online published: 2023-11-29
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China-Russian Science Foundation(42061134017)
Special Exchange Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
全球快速升温背景下,多年冻土广泛发育的北极流域水文情势发生显著变化,不仅改变了该地区的生态环境,也对全球气候系统和社会经济带来了深远影响。因此,北极流域水文过程研究已成为当前国际科学界关注的前沿热点问题。本文通过梳理国内外相关文献,系统回顾并总结了北极主要流域的径流时空变化及其驱动机制的研究成果与最新进展;详细分析了欧亚大陆和北美地区的径流变化规律与时空差异;深入探讨了快速升温下降水变化(降水量、雨/雪组分比例)和冻土退化对北极流域径流的直接与间接作用机制。尽管当前北极水文研究在数据积累和科学认识方面取得了重要进展,但仍面临地面观测站点稀少以及气候、积雪/冻土、水文之间响应难以定量等挑战。因此,建立完善的北极流域观测网络并发展具有北极特色的寒区水文模型,是深入理解北极水系统快速变化的基础,也是应对北极地区水灾害风险和提升水资源管理能力的关键所在。
王平 , 黄其威 , 刘诗奇 , 于静洁 , 张一驰 , 王田野 , 白冰 , POZDNIAKOV Sergey P , FROLOVA Natalia L , 刘昌明 . 快速升温下的北极径流变化及其驱动机制综述[J]. 地理学报, 2023 , 78(11) : 2718 -2734 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202311005
Under the background of rapid global warming, the hydrological regime in the Arctic river basins, where permafrost is widely developed, has changed significantly. These changes not only altered the local ecological environment, but also had far-reaching impacts on the global climate system and socio-economy. Therefore, the study of hydrological processes in Arctic river basins has become a hot-spot issue at the forefront of the international scientific community. Based on a thorough review and critical analysis of domestic and international literature, this paper systematically summarizes the research findings and latest progress on the spatial and temporal changes of the runoff of major Arctic rivers, as well as the driving mechanisms behind these variations. In addition, the patterns and spatiotemporal differences in runoff changes between Eurasia and North America were analyzed in detail. Furthermore, the direct and indirect effects of precipitation changes (e.g., precipitation amount, rain/snowfall fractions) and permafrost degradation on Arctic runoff are thoroughly examined. Despite significant progress in data accumulation and scientific understanding in current Arctic hydrological research, considerable challenges persist, such as the scarcity of ground observations and the difficulty of quantitatively assessing the interactions among climate, snow/permafrost, and hydrological processes. Thus, establishing a robust observation network in the Arctic river basins and developing cold region hydrological models with account for the Arctic specifics are fundamental for gaining in-depth insights into the rapid changes occurring in the Arctic hydrological system. This is also crucial for addressing the risks of water-related disasters and enhancing water resource management in the Arctic region.

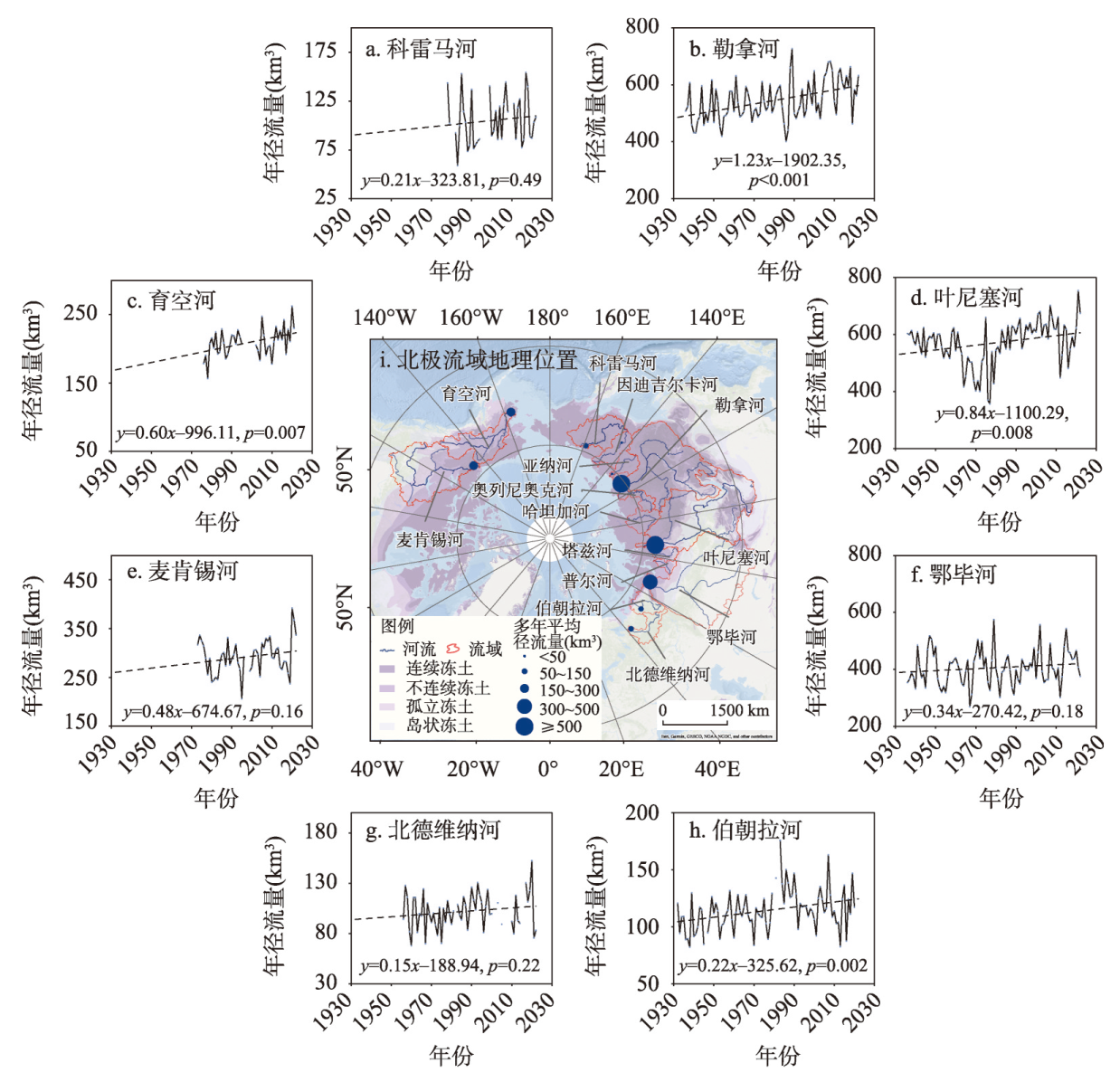
| 河流 | 水文站纬度 (°N) | 水文站经度 (°) | 多年平均径流量 (km3) | 流域面积 (106 km2) | 径流观测时段 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鄂毕河 | 66.63 | 66.60 E | 405 | 2.95 | 1936—2022年 |
| 叶尼塞河 | 67.43 | 86.48 E | 570 | 2.44 | 1936—2022年 |
| 勒拿河 | 70.68 | 127.39 E | 544 | 2.43 | 1936—2022年 |
| 科雷马河 | 67.47 | 153.69 E | 105 | 0.65 | 1978—2022年 |
| 育空河 | 61.93 | 162.88 W | 209 | 0.83 | 1976—2021年 |
| 麦肯锡河 | 67.45 | 133.74 W | 292 | 1.75 | 1973—2022年 |
| 北德维纳河 | 64.13 | 41.92 E | 102 | 0.35 | 1956—2022年 |
| 伯朝拉河 | 65.42 | 52.28 E | 114 | 0.25 | 1932—2020年 |
| 普尔河 | 67.01 | 78.22 E | 168 | 0.11 | 2018—2022年5—10月 |
| 奥列尼奥克河 | 71.85 | 123.65 E | 42 | 0.22 | 1991—2022年 |
| 亚纳河 | 70.77 | 136.08 E | 33 | 0.24 | 1978—2022年 |
表2 北极地区地表径流量评估汇总表Tab. 2 Summary of various assessment values of surface river runoff in the Arctic region |
| 序号 | 汇流面积 (106 km2) | 多年平均径流量 (km3) | 多年平均径流深 (mm) | 研究时段 | 研究方法 | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.9 | 2603 | 202 | 1912—1995年 | 观测 | [57] |
| 2 | 24.2 | 4749 | 212 | 1960—1989年 | 观测+分析 | [55] |
| 3 | 9.1 | 1932 | 212 | 1936—1999年 | 观测 | [31] |
| 4 | 16.9 | 3658 | 216 | - | 观测+模型 | [58] |
| 5 | 18.9 | 4314 | 228 | 1921—1999年 | 观测+分析 | [44] |
| 6 | 23.7 | 5250 | 222 | 1921—1999年 | 观测+分析 | [44] |
| 7 | 11.4 | 2310 | 203 | 1940—1990年 | 观测 | [59] |
| 8 | 16.4 | 3596 | 219 | 1979—1999年 | 模型 | [54] |
| 9 | 8.8 | 1796 | 204 | 1936—2006年 | 观测 | [60] |
| 10 | 12.1 | 2420 | 200 | 1964—2000年 | 观测 | [61] |
| 11 | 15.8 | 3162 | 200 | 1980—1999年 | 模型 | [62] |
| 12 | 16.7 | 3730 | 223 | 2003—2005年 | GRACE卫星 | [56] |
| 13 | 19.0 | 4300 | 226 | 1936—2006年 | 观测+模型 | [63] |
| 14 | 5.26 | 1154 | 219 | 1964—2013年 | 观测 | [64] |
| 15 | 11.3 | 2310 | 204 | 1970—2017年 | 观测 | [65] |
| 16 | 13.5 | 2996 | 221 | 1975—2015年 | 观测+分析 | [66] |
| 17 | 22.1 | 5169 | 234 | 1984—2018年 | 模型 | [30] |
图2 北极流域年径流量和冬季径流量对气温与降水变化的响应Fig. 2 Schematic diagram illustrating the response of annual runoff and winter runoff in the Arctic basin to changes in temperature and precipitation |
感谢课题组研究生于宗绪、张家玲和王睿欣在文献与数据查找方面提供的帮助。特别感谢两位匿名审稿人对本文的修改与完善所给予的宝贵建议。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
[赵进平, 史久新, 王召民, 等. 北极海冰减退引起的北极放大机理与全球气候效应. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(9): 985-995.]
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
[效存德, 苏勃, 窦挺峰, 等. 极地系统变化及其影响与适应新认识. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2): 153-162.]
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
[刘诗奇, 王平, 王田野, 等. 西伯利亚北极河流有机碳输出特征及影响要素. 地理学报, 2021, 76(5): 1065-1077.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[赵涔良, 朱文泉, 郭红翔, 等. 北极气候和陆地环境变化对第一产业影响研究进展. 地理学报, 2022, 77(11): 2838-2861.]
|
| [22] |
[秦大河, 姚檀栋, 丁永建, 等. 冰冻圈科学体系的建立及其意义. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(4): 394-406.]
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
[田霏, 王召民,
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
[郭敬辉, 刘昌明. 水文学的地理研究方向与发展趋势. 地理学报, 1984, 39(2): 206-212.]
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
[王冠, 陈涵如, 王平, 等. 俄罗斯环北极地区地表径流变化及其原因. 资源科学, 2020, 42(2): 346-357.]
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
[陈晓龙, 王平. 1979—2017年北极陆地气候变化趋势. 资源科学, 2021, 43(6): 1260-1274.]
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
[丁永建, 效存德. 冰冻圈变化及其影响研究的主要科学问题概论. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(10): 1067-1076.]
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
[赵林, 胡国杰, 邹德富, 等. 青藏高原多年冻土变化对水文过程的影响. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34(11): 1233-1246.]
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] |
|
| [158] |
|
| [159] |
|
| [160] |
|
| [161] |
|
| [162] |
|
| [163] |
|
| [164] |
|
| [165] |
|
| [166] |
|
| [167] |
|
| [168] |
|
| [169] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |