1 引言
绿色技术的协同开发和全球共享被认为是应对全球气候变化、降低环境污染和生态破坏的关键举措[1-2]。全球绿色技术扩散和共享机制也在不断探索中建构,如由几个大型跨国公司IBM、诺基亚、索尼等,于2008年发起的生态专利共享项目(Eco-Patent Commons)[3-4],以及联合国气候变化框架公约中的技术需求评估计划(Technology Needs Assessment Program)等。同样,在强调以减污降碳、推动绿色发展、促进人与自然和谐共生为目标的中国经济高质量发展关键期,构建以市场为导向的绿色技术创新体系从而加速绿色技术在区域、城市、机构间的扩散,已上升为国家战略决策[5]。2019年国家发展改革委和科技部联合颁布了《关于构建市场导向的绿色技术创新体系的指导意见》,提出要建立健全绿色技术转移转化市场交易体系,完善绿色技术创新成果转化机制,选择绿色技术创新基础较好的城市建设绿色技术创新综合示范区。2020年国家发展改革委、科技部、工业和信息化部、自然资源部组织编制了《绿色技术推广目录(2020年)》,涉及节能环保产业、清洁生产产业、清洁能源产业、生态环境产业和基础设施绿色升级5个领域的116项绿色技术。
绿色技术扩散作为一般技术扩散形式中的一类,不仅在全球气候变化和环境生态压力下获得了极大的关注,而且在产业转型升级和企业绿色技术创新实践中扮演关键角色。与一般技术扩散不同的是,绿色技术扩散无论是对国家、区域、城市还是对于企业而言,其不仅能够带来技术溢出的经济效益,还能够带来技术溢出的环境效益。综观当前绿色技术扩散研究,集中于以下几个议题:① 绿色技术扩散过程的仿真模拟研究。创新扩散理论的“S”型曲线规律激发了大量学者对绿色技术扩散过程(包括扩散时间和接纳者数量)进行研究,学者们采用了多种模型(如S型模型、Logistic模型、Bass模型、网络动力学模型等)对企业绿色技术扩散过程进行仿真模拟和曲线拟合[6⇓-8];② 绿色技术扩散的驱动因素研究。绿色技术扩散的驱动因素研究是当前绿色技术扩散研究最主要、最集中的领域[9-10]。知识基础理论、吸收能力理论、技术差距理论、知识粘性理论、多维邻近性理论、利益相关者理论、社会网络理论等理论模型被广泛应用于揭示驱动绿色技术扩散的主要因素[11⇓-13],其中多维邻近性理论及技术差距理论是最常见的分析理论框架,普遍发现环境规制、地理距离、企业自身属性、预期收益、技术复杂性和相关性、公众消费需求等因素影响着绿色技术扩散的效率[14-15];③ 加快绿色技术扩散的对策研究。绿色技术扩散存在多重外部性,加速绿色技术扩散会产生多重收益,如企业个体绿色经济增长、行业群体绿色经济增长,城市或区域绿色经济增长等,因而众多学者将研究视角放置在如何加速绿色技术扩散上来,并展开了一系列的对策探索研究[16⇓-18]。相关研究发现,稳定的绿色技术扩散途径(合作伙伴关系)、专业化的中介机构、有力的政策支持(补贴、减税、知识产权保护等)等措施能够显著加速企业间或区域间的绿色技术扩散[19-20]。
综上可知,当前绿色技术扩散研究主要集中于某一绿色技术领域(绿色制造技术、绿色建筑技术、绿色交通技术、绿色照明技术、节能技术、节水技术等)下企业绿色技术扩散过程模拟、驱动因素和加速对策探索[21⇓-23],研究方法多采用基于案例分析的计量经济学模型和系统动力学模型,鲜有从空间层面开展城市、区域绿色技术扩散的时空过程研究[14],也鲜有开展多技术领域下的绿色技术扩散比较研究。虽然近年来在响应创新驱动发展战略下,创新经济地理学中围绕知识流动、技术转移、科技成果转化、创新扩散的研究屡见不鲜[24⇓⇓-27],但呼应“绿色技术创新支撑绿色发展”的研究才刚刚起步[28-29],而关于绿色技术的空间扩散研究则更是不多见[30-31]。基于此,本文以绿色专利转让刻画绿色技术扩散,将企业绿色技术扩散拓展至空间层面,从城市尺度分析了2001—2020年中国绿色技术扩散的时续发展动态以及空间分布格局,揭示了中国城市绿色技术扩散活动中的热门技术、行为主体和城市类型,并探讨了驱动中国城市绿色技术扩散的主要因素,一方面试图丰富当前创新和环境经济地理学的研究内容,另一方面试图为建设市场导向的绿色技术创新体系提供案例支撑。
2 数据和方法
2.1 绿色技术扩散数据获取与处理
本文在测度城市绿色技术扩散时,采用世界知识产权组织(World Intellectual Property Organization, WIPO)测度绿色技术扩散的惯例做法,以绿色专利转让来衡量绿色技术扩散。首先,借鉴段德忠等构建的基于IPC专利分类号的绿色专利识别体系(包括清洁能源技术、温室气体处理技术、绿色交通技术、绿色建筑技术、环境治理技术和绿色水技术)[32],以知识产权出版社专利信息服务平台(
2.2 城市绿色技术扩散类型划分
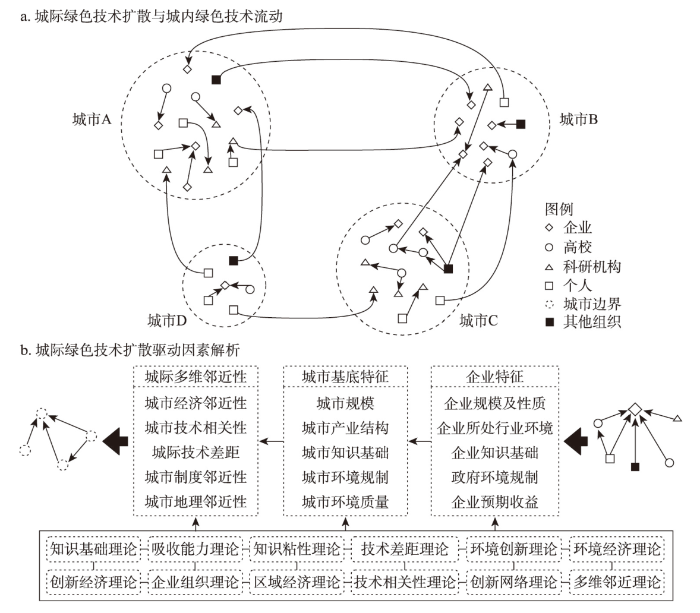
将主体间的绿色技术扩散映射至城市尺度,就必然面临将原组织内部或组织间的绿色技术扩散重构为城市内部或城市间的绿色技术扩散。根据城市城内绿色技术转移量、城际绿色技术转移量的相对大小,可将城市绿色扩散类型划分为3大类,城内集散型、城际集散型和混合型(表1):① 城内集散型即城市绿色技术扩散活动完全或主要发生在城市边界以内,根据其活跃程度又可划分为完全自给自足型和主要城内集散型两种细分小类;② 城际集散型即城市绿色技术扩散活动完全或主要呈现于跨越城市边界形态,根据城际绿色技术扩散量、城际绿色技术集聚量的相对大小,城际集散型又可划分为完全外销型、完全外源型、主要外源型、主要外销型和外源外销兼顾型;③ 混合型城市意味着城内绿色技术转移和城际绿色技术转移对其都很重要,由于在城内绿色技术转移维度,集聚量即是扩散量,因而在混合型大类下,继续依照城际绿色技术扩散量和城际绿色技术集聚量对其进行细分,可细分为混合集聚型、混合扩散型和混合集散型。
表1 城市绿色技术扩散类型划分
Tab 1.
| 大类 | 小类 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 城内集散型 | 完全自给自足型 | 仅存在城内绿色技术流动现象 |
| 主要城内集散型 | 同时存在城内绿色技术流动和城际绿色技术流动现象,但以城内绿色技术流动为主 | |
| 城际集散型 | 完全外销型 | 仅存在向其他城市扩散绿色技术现象 |
| 完全外源型 | 仅存在从其他城市获取绿色技术现象 | |
| 外源外销兼顾型 | 同时存在向其他城市扩散绿色技术和从其他城市获取绿色技术现象,且两者所占比例基本持平 | |
| 主要外源型 | 同时存在向其他城市扩散绿色技术和从其他城市获取绿色技术现象,但以从其他城市获取绿色技术为主 | |
| 主要外销型 | 同时存在向其他城市扩散绿色技术和从其他城市获取绿色技术现象,但以从其他城市获取绿色技术为主 | |
| 混合型 | 混合集聚型 | 城内绿色技术转移和城际绿色技术转移量基本持平,但以绿色技术集聚活动为主 |
| 混合扩散型 | 城内绿色技术转移和城际绿色技术转移量基本持平,但以绿色技术扩散活动为主 | |
| 混合集散型 | 城内绿色技术转移和城际绿色技术转移量基本持平,且绿色技术集聚和扩散量也基本持平 |
2.3 城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素分析
(1)理论框架建构。无论是城内绿色技术流动还是城际绿色技术扩散,其依托的核心主体还是企业,因而驱动城内绿色技术流动和城际绿色技术扩散演化发展的因素在本质上是内在相通的。但由于本文重在探讨城市尺度的中国绿色技术扩散特征,因而本文聚焦解析绿色技术跨城流动的驱动因素(图1)。
图1
图1
城市绿色技术扩散研究分析框架
Fig. 1
Analysis framework of city green technology diffusion
企业绿色技术扩散驱动因素的研究积累为本文探讨城际绿色技术扩散的影响因素提供了很好的借鉴[14-15]。知识基础理论、吸收能力理论和知识粘性理论认为,主体或区域的知识基础在很大程度上决定了其知识创新的演化路径,以及其获取外部知识的能力[33⇓-35]。在企业绿色技术扩散上,以企业现有绿色技术创新能力衡量的知识基础通常作为基本变量,一方面决定企业绿色技术创新的演化路径,另一方面决定企业在绿色技术扩散上的扩散能力和吸收能力。在城际绿色技术扩散上,城市绿色技术创新能力(知识基础)越强,代表其拥有的绿色技术数量越多,也代表其从外部获取绿色技术的能力越强。同时,技术差距理论认为技术差距能够诱导技术转移或技术扩散发生[36-37],且过往中国城际技术扩散研究也证明,技术差距是中国城际技术扩散体系演化的动力与拓扑连接机制。
环境创新理论认为,政府环境规制对企业、城市、区域绿色技术创新在长期视角来看存在显著的正向影响[5]。在绿色技术扩散研究中,地方、区域或国家环境规制强度同样被作为一个核心驱动因素被广泛考量。如领先市场的环境规制强度一方面会对发展中国家或地区的生产者施加增加绿色技术投入的影响,另一方面也会迫使本地落后产能向环境规制强度较弱的地方转移,并带来绿色技术扩散的溢出效应。在城际绿色技术扩散上,环境规制较强的城市不仅会刺激本地绿色技术的生产,也会加大城市对外部绿色技术获取的力度;而环境规制较弱的城市由于其本地绿色技术需求较低,也会促使本地绿色技术向环境规制较强的城市流动。
环境经济学、创新经济学和区域经济学理论认为,企业属性影响着企业绿色技术创新能力。在绿色技术扩散上,企业属性同样起着重要作用,在企业规模层面表现出企业规模越大,其扩散和获取绿色技术的能力就越强;在企业性质层面表现出民营企业相对国有企业而言更具有绿色技术扩散的主观意愿[38-39]。在城际绿色技术扩散上,固然会存在因城市基底特征的不同而形成城市间绿色技术扩散行为差异,如大城市或者高等级城市往往在绿色技术创新和绿色技术扩散上更具主动性。企业组织理论还认为,不同产业、不同行业的企业对绿色技术需求的量存在差异,对绿色技术需求的领域存在差异[21⇓-23]。在城市层面,城市主导产业既决定了城市哪类绿色技术产出量较大,也决定了城市对哪类绿色技术需求量较大。
多维邻近性分析框架下的创新网络演化理论也为解析技术扩散的驱动机制提供了有效的分析框架,认为地理邻近性、认知邻近性、制度邻近性、文化邻近性、组织邻近性等能够有效地促进机构间、城市间、区域间以及国家间的技术扩散[40⇓-42]。在企业绿色技术扩散中,技术相关性影响着企业所吸收的绿色技术领域和规模,即企业间如果在绿色技术创新领域存在高度同构性,则相互之前进行绿色技术扩散的意愿和规模就越大。放置在城市层面,城市间的绿色技术创新结构如果高度相关,则被认为具有共同的知识基础,则更容易扩散和吸收绿色技术。另外,城市绿色技术扩散本质上就是知识或技术的空间扩散,虽然不断升级变革的信息通讯和交通运输技术大大缩小了地理距离对技术空间扩散的约束,但创新经济时代仍然重要的“面对面的交流”依然凸显了地理邻近性在交流沟通、技术扩散以及科技合作上的重要性。同时,已有研究也揭示出城市间经济发展水平相似性对城际技术扩散体系演化有着显著正向促进作用,即经济发展水平相近的城市间,其技术扩散活动越活跃。
(2)模型建构。基于上述理论框架建构过程,本文借鉴多维邻近性分析框架[42],通过建构城市多维邻近性指标,分析影响城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素:
式中:α为常数项;
式中:
3 中国绿色技术扩散的时序动态
3.1 环境治理热情快速冷却,面向消费端的绿色建筑和清洁能源技术快速崛起
2001—2020年中国绿色技术交易市场中流行技术由环境治理技术转变为绿色建筑技术和清洁能源技术。具体来看:2001—2005年环境治理技术主导中国绿色技术扩散,该领域的专利转移量占整体绿色专利转移量的比重由2001年的28.6%增长至2005年的34.4%。根据绿色专利识别体系,环境治理技术包括空气污染减排、水污染治理、废物管理、土壤修复和环境监测五小类,即主要涉及污染物排放总量控制和污染物排放治理达标这两个层面的“末端治理”技术。1978年改革开放至20世纪末,中国快速经济增长和工业化、城镇化进程给生态环境带来了前所未有的压力。在1996年《国务院关于环境保护若干问题的决定》提出的污染物排放总量控制制度指导下,“一控双达标”(控制主要污染物排放总量,工业污染源达标和重点城市的环境质量按功能区达标)成为“九五”(1996—2000年)至“十一五”(2006—2010年)期间中国环境保护和治理政策的核心,国家先后颁布实施《全国主要污染物排放总量控制计划》和《跨世纪绿色工程规划》,并在“十一五”期间将“总量控制”提升到国家环境保护战略的高度[43]。
2006年绿色建筑技术的转移量超过环境治理技术,以及2007年清洁能源技术的转移量也超过环境治理技术,从而形成持续至今的中国绿色技术交易市场主要特征,即绿色建筑技术和清洁能源技术主导中国绿色技术扩散,并根据其发展态势(年均增长率分别达到44.5%和46.2%),这两大技术仍将在未来一段时间继续主导中国绿色技术扩散。这一方面是由于从“两型社会”、生态文明建设和美丽中国建设,到推动绿色发展、促进人与自然和谐共生,从《清洁生产促进法》《循环经济促进法》到新一轮《环境保护法》重大修订,中国环境保护和污染治理模式已由末端治理转向全过程控制,中国的绿色技术创新也由偏重于环境治理技术转向偏重于绿色生产技术。另一方面也源于中国高速增长的房地产经济对绿色建筑技术的需求持续增大和快速崛起的新能源汽车产业对清洁能源生产、能源储备和电池技术的需求持续增大。
3.2 城市边界的“栅栏”效应开始减弱,绿色技术跨城流动成为新常态
在地方政府的强力监管下和专利技术流动的地理距离约束性,中国绿色技术的空间流动严重受到城市边界的“限制”,呈现出“自产自销”式的自给化特征。2001—2018年中国绿色专利转移始终以城内转移为主导,其中2003年城内转移的比重更是达到84.7%。但随着市场经济体制的持续深入改革,专利流动的行政壁垒和地区封锁逐渐被打破,以专利为主的创新要素的自由流动和充分竞争得到保证。同时在本地技术创新路径依赖下,本地绿色技术愈发无法满足城市产业结构转型和可持续发展的需求,地方绿色技术创新网络逐渐跨越城市边界,融于区域创新网络和国家创新体系,城市边界对于专利技术的“栅栏”效应减弱,城际绿色技术流动愈发繁,绿色技术跨城流动成为常态。2001—2020年中国绿色专利转移中城际转移的比重由18.2%快速增长至57.5%,尤其2019年城际绿色专利转移量首次超过城内绿色专利转移量,并在2020年迅速拉大两者间的差距。
依据中国绿色专利转移的时续发展特征,将中国绿色技术扩散划分为3个阶段,即2001—2007年的缓慢发展阶段(转移5001件绿色专利)、2008—2014年的初步增长阶段(转移45251件绿色专利)和2015—2020年的快速增长阶段(转移156876件绿色专利)。通过梳理每个阶段内不同技术领域的城内专利量和城际转移量发现,3个阶段内唯有环境治理技术的城际转移量在第3阶段超过其城内转移量,而其他5类绿色技术的城际转移量虽快速增长,但在3个阶段内皆少于其城内转移量。这表明,在技术创新路径依赖、以及环境治理技术开发成本较高的前提下,再加上环境治理技术市场交易“冷却”行情,本地的环境治理技术愈发无法满足本地的污染物总量控制目标,需要进行跨城技术交易来弥补本地的供给不足。
3.3 企业不仅是中国绿色技术的主要出让者,也是集成吸纳者
根据创新主体的分类以及绿色技术转移前后权利人信息,中国绿色技术扩散的行为主体可以划分为4个类别:企业、大学及科研机构、个体、其他(无法识别其主体的具体类别,故归为“其他”)。2001—2020年企业始终主导中国绿色技术扩散,即企业既是中国绿色技术的主要出让方,也是中国绿色技术的主要购买方,且主导的力度在持续加强。在技术出让维度,中国绿色技术交易市场中来源于企业的绿色技术占比由2002年的40.7%波动增长至2020年的67.2%;在技术购买维度,企业作为消费者购买的绿色技术占比由2002年的66.1%波动增长至2020年的85.9%。个体在中国绿色技术扩散中也扮演着至关重要的角色,但主要体现在技术出让维度。2001—2020年中国绿色技术交易市场中来源于个体的绿色技术占比基本维持在20%以上,其中在2004年和2010年更是分别达到41.7%和41.9%。大学和科研机构在中国绿色技术扩散中的作用较小,无论是在技术出让维度还是在技术购买维度,其所占的比重皆较小。
从主体间技术扩散来看,企业不仅通过“自我消化”耗散掉中国绿色技术交易市场中的大部分绿色技术,还广泛吸收来自大学和科研机构、个体出让的绿色技术。即对于大学和科研机构、个体而言,企业是其绿色技术的主要消费者,但在不同阶段也有所差异。2001—2007年大学和科研机构出让的195件绿色专利中有161件流向企业,占比达82.6%。个体出让的802件绿色专利中有445件流向企业,占比达55.5%。2008—2014年大学和科研机构出让的2110件绿色专利中有1213件流向企业,占比下降至57.5%。个体出让的11104件绿色专利中有8116件流向企业,占比升至73.1%。2015—2020年大学和科研机构出让的10437件绿色专利中有7130件流向企业,占比上升至68.3%。个体出让的32733件绿色专利中有27413件流向企业,占比继续升至83.7%。
4 中国绿色技术扩散的空间格局
4.1 城内流动:京津—长三角—珠三角与长江经济带构成的“T”型格局显现
2001—2020年中国城内绿色技术流动活动高度集聚在以京津、长三角和珠三角为增长极的东部沿海地区,以及以长三角、长江中游和成渝城市群为核心枢纽的长江经济带,中国国土开发与经济布局的“T”型架构在城内绿色技术扩散上显得尤为明显。
2001—2007年,1662件绿色专利(占整体73.8%)在127个城市内部发生了专利权的转移,实现了绿色技术的流动。虽东部沿海城市居多,但中西部地区也广泛分布,整体较为均衡。其中仅有28个城市的城内绿色专利转移量超过10件,北京、深圳和上海分别以309件、125件和119件的城内绿色专利转移量分列全国1~3位。2008—2014年城内绿色专利转移量增至24717件,但占整体的比重稍有下降,降至70.5%。有城内绿色技术转移活动的城市数量也增至278个,但城内绿色专利转移量超过100件的城市也仅有47个,其中北京、上海和深圳3个城市的城内绿色专利转移量超过1000件,分别达到3870件、2504件和1985件。这一阶段,除北京、上海和深圳外,长三角和珠三角地区其他城市的城内绿色专利转移量也快速增长,如长三角的杭州(877件)、南京(724件)、宁波(589件)、苏州(563件)、无锡(477件)等,珠三角的佛山(719件)、广州(541件)、东莞(428件)等。2015—2020年,64923件绿色专利在319个城市内部发生专利权转移,但其占整体的比重下降较快,至49.9%,城际绿色技术转移量已经超过城内绿色技术转移量。这一阶段,城内绿色专利转移量超过100件的城市增至73个,超过1000件的城市也有15个,北京继续以7834件绿色专利转移量位列第1,深圳和上海分别以5893件和4123件绿色专利转移量位列第2和第3。此外,除了长三角和珠三角地区城市城内绿色专利转移量普遍性增长外,长江经济带沿线的省会城市在这一阶段也上升较快,如成都、武汉、重庆、长沙分别以1876件、1472件、1339件和830件城内绿色专利转移量位列第6、第10、第12和第19位。至此,由京津—长三角—珠三角与长江经济带构成的中国城内绿色技术转移“T”型格局初步显现。
4.2 城际扩散:由随机分散格局经三角格局向菱形格局演化
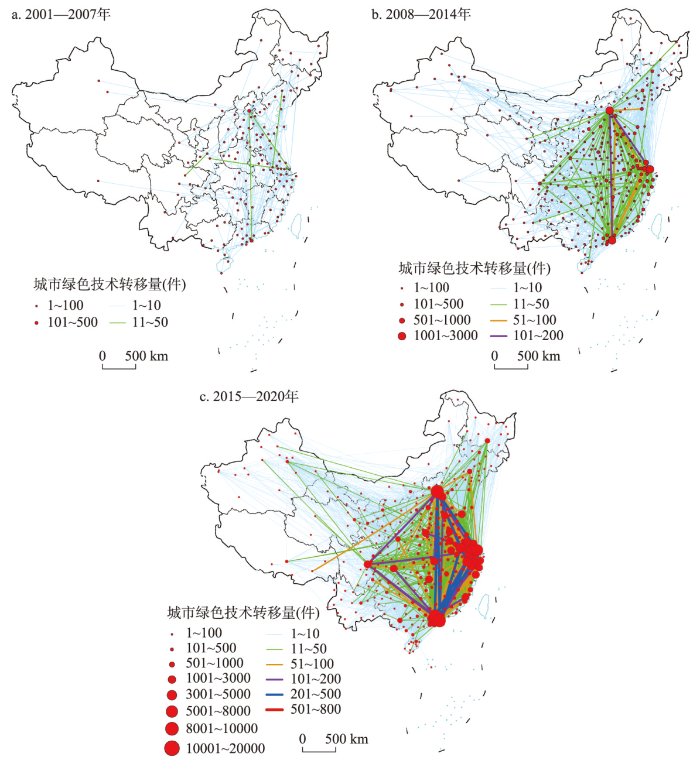
2001—2020年,随着参与城际绿色技术扩散的城市数量不断增多和扩散的绿色专利数量急剧增加,中国城际绿色技术扩散网络呈现出由随机分散格局经三角格局向菱形格局演化,京津、长三角、珠三角和成渝地区成长为中国城际绿色技术扩散网络的枢纽(图2)。
图2
图2
2001—2020年3个阶段中国城际绿色技术转移的空间演化特征
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统审图号为GS(2016)1554号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Spatial evolution characteristics of China's intercity green technology transfer in three stages from 2001 to 2020
(1)中国绿色技术城际扩散由扩散经济向集聚经济转变。2001—2020年,参与中国城际绿色技术扩散网络中的城市数量由第一阶段的137个增长至第三阶段的352个,其中从其他城市集聚绿色技术的城市数量由第一阶段的82个快速增长至第三阶段的345个,由第一阶段的少于向其他城市扩散绿色技术的城市数量(101个),发展至第二(268个)和第三阶段(337个)的超过向其他城市扩散绿色技术的城市数量。由此可见,随着对绿色经济发展的“觉醒”,越来越多的城市表现出对绿色技术的强烈需求,而在此方面率先行动的城市通过促进本城绿色技术创新,逐渐从早期的绿色技术购买者发展为后期的绿色技术出售者。如2001—2007年北京和深圳分别从44个、14城市吸收107件和70件绿色专利,成为这一阶段中国绿色技术的两个最大购买者;而到了2015—2020年,深圳和北京分别向230个、235个城市扩散5229件、4984件绿色专利,成为了这一阶段中国绿色技术的两个最大出售者。
(2)中国绿色技术城际扩散由随机分散性向空间集聚性转变。2001—2007年中国绿色技术城际转移关系表现出一定的随机性和分散性,在250对城际转移关系中,有139对仅转移1件绿色专利,转移绿色专利超过10件的仅有8对(占比为3.2%),最大的城际转移关系发生在北京和深圳之间,即北京向深圳转移41件绿色专利。2008—2014年中国绿色技术城际转移网络在第一阶段的随机性和分散性的基础上,逐渐发育出有序性和集聚性,以京津、长三角和珠三角为节点的城际绿色技术转移“三角”结构初步形成。在2378对城际转移关系中,虽也有1111对仅扩散1件绿色专利,但扩散绿色专利超过10件的已达221对(占比为9.3%)。这一阶段,绿色技术在京津、长三角和珠三角地区间以及地区内频繁流动,如深圳向北京扩散134件绿色专利位居第一位,北京向深圳扩散110件绿色专利位居第2位,北京向上海扩散106件绿色专利位居第3位,上海向北京扩散103件绿色专利位居第4位。2015—2020年中国绿色技术城际扩散网络的有序性和集聚性继续发育,以京津、长三角和珠三角为节点的城际绿色技术扩散“三角”结构稳定形成,并在此基础上发育出以成渝地区为节点的“菱形”结构。在11460对城际扩散关系中,扩散绿色专利超过10件的关系对达到1319对,占比升至11.5%。其中,深圳向东莞扩散696件绿色专利,北京和广州皆向杭州扩散435件专利,深圳向广州扩散340件专利,北京向上海扩散340件绿色专利。
4.3 城市类型:由自给自足向开放创新发展,全国统一的绿色技术交易大市场正在逐渐形成
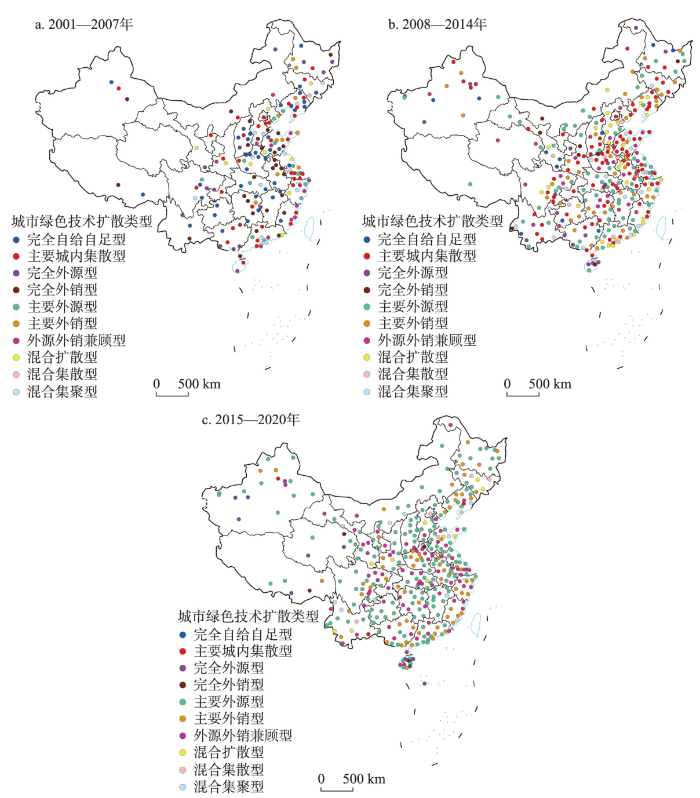
根据城市绿色技术扩散类型划分体系,对2001—2020年融入中国城市绿色技术扩散网络中的城市类型进行了3个阶段的识别(图3)。
图3
图3
2001—2020年3个阶段中国城市绿色技术扩散类型演化
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务系统审图号为GS(2016)1554号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig 3.
The evolution of city green technology diffusion types in China in three stages from 2001 to 2020
(1)绿色技术转移量较大的城市逐渐由“城内集散型”向“城际集散型”,特别是向“外销型”转型,这表明绿色技术创新“先行者”城市在满足自身需求的基础上,逐渐打开“城门”,开展绿色技术的对外服务。2001—2007年绿色技术转移量(城内转移与城际转移之和)排名前10的城市中有7个城市的类型为“主要城内集散型”,如北京(518件,第1)、上海(207件,第3)、咸阳(127件,第4)、杭州(109件,第5)等;2008—2014年,绿色技术转移量排名前10的城市中依然有7个城市的类型为“主要城内集散型”,如北京(6838件,第1)、上海(3823件,第2)、杭州(1356件,第4)、南京(1190件,第6)等;2015—2020年绿色技术转移量排名前10的城市中,除北京属于“混合集散型”外(14809件,第1),其余9个城市全部为“城际集散型”,且其中更是有8个城市为“外销型”,如深圳(14809件,第2,主要外销型)、广州(10142件,第3,外源外销兼顾型)、上海(9973件,第4,外源外销兼顾型)、苏州(7046件,第5,外源外销兼顾型)等。
(2)也正是因为上述这些“先行者”城市逐渐扩大的城际绿色技术扩散活动,才使得更多的城市能够通过城际集聚来获取绿色技术,以及加入到中国绿色技术扩散网络中。2001—2007年,有177个城市通过城内集散或城际集散融入中国绿色技术扩散网络中,而到2008—2014年,融入中国绿色技术扩散网络中的城市数量增加至319个,相较于前一阶段(2001—2007年),新增143个城市,其中有57个城市是完全(15个城市为“完全外源型”)或者主要(42个城市为“主要外源型”)通过城际技术集聚来加入至绿色技术扩散网络中,还有15个城市则部分通过(为“外源外销兼顾型”)城市技术集聚来加入至绿色技术扩散网络中。2015—2020年,中国绿色技术扩散网络中城市数量增至353个,相较于前一阶段(2008—2014年)新增34个城市,其中16个城市是完全(6个城市为“完全外源型”)或者主要(10个城市为“主要外源型”)通过城际技术集聚加入至绿色技术扩散网络中,还有3个城市则部分通过(为“外源外销兼顾型”)城市技术集聚来加入至绿色技术扩散网络中。
(3)愈发频繁的绿色技术跨城流动促使全国统一的绿色技术交易大市场正在逐渐形成。2001—2007年中国绿色技术扩散网络中177个城市中有77个属于“城内集散型”,占比达43.5%。其中更是有40个城市属于“完全自给自主型”,在网络中属于孤立的节点,与其他城市不产生任何联系。2008—2014年,虽然中国绿色技术扩散网络中“城内集散型”的城市数量增至99个,但占比下降至31.0%,其中孤立节点——“完全自给自足型”城市数量减少至12个。至2015—2020年,中国绿色技术扩散网络中“城内集散型”的城市数量锐减至4个,仅占整体的1.1%,其中“完全自给自足型”城市仅有1个(海南省万宁市)。也就是说,353个城市构成的中国绿色技术扩散网络中有349个城市通过强城际绿色技术转移关系架构了全国绿色技术交易市场体系,同时随着核心城市(深圳、北京、广州和上海)的对外辐射能力增强,这一绿色市场交易体系逐渐由区域性向全国统一性演化。如2015—2020年,由深圳、北京、广州和上海4个城市架构的城际绿色技术转移关系对就达到1624对,占比达17.2%,覆盖除万宁市以外融入中国绿色城际扩散网络中的所有城市。这4个城市参与的城际绿色技术转移量达28054件,占这一阶段城际转移量的43.0%。
5 中国城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素
5.1 偏好性:新加入城市倾向于从网络中枢纽城市获取绿色技术
复杂网络或社会网络生长机理中的偏好连接法则从动态视角揭示了现实生活中大部分真实网络生长过程中遵循的一般规律,即网络中新加入的节点总是先寻求与现有网络中的枢纽节点建立联系。偏好连接法则既揭示了网络中新成员如何能够快速“站稳脚跟”并得以发展的“生存法则”,也揭示了网络中已有核心成员如何快速地开辟新市场和扩大其腹地范围从而巩固其枢纽地位的“垄断法则”。从创新扩散理论的视角,偏好连接法则还印证了技术差距论的存在价值,即“距离产生美”。上文已经分析了后两个阶段相较于前一阶段新加入中国绿色技术扩散网络中城市的类型特征,揭示了新加入的城市中有50%左右是通过城际技术集聚来补充本城的绿色技术供给,那么这些绿色技术是来源于网络中的已有城市节点,还是来源于新加入的其他城市,是来源于网络中的枢纽城市,还是来源于网络中与其地位相同的城市?这些问题的答案正是偏好连接法则验证所得的结果。通过分析2008—2014年相对于2001—2007年新加入的城市特征以及2015—2020年相对于2008—2014年新加入的城市特征发现,偏好连接现象在中国绿色技术扩散体系(网络)中同样存在。在2001—2007年中国绿色技术扩散体系中,北京、深圳和上海无疑是网络的枢纽。2008—2014年中国绿色技术扩散体系中新加入的143个城市中,仅8个城市为“完全自给自足型”,其余135个城市皆与其他城市进行绿色技术转移活动,共转移了1841件绿色专利,其中有543件绿色专利的转移活动有北京、上海和深圳这3个城市参与,占比达29.5%。在2008—2014年中国绿色技术扩散体系中,北京、深圳和上海同样是网络的枢纽。2015—2020年中国绿色技术扩散体系中新加入的34个城市中,仅2个城市为“完全自给自足型”,其余32个城市皆与其他城市进行绿色技术转移活动,共转移了479件绿色专利,其中有155件绿色专利的转移活动有北京、上海和深圳这3个城市参与,占比升至32.4%。
5.2 同配性:网络中枢纽城市间的绿色技术流动更加频繁
相较于偏好连接从动态的视角阐释网络的生长过程,度相关性则从相对静态的视角解构网络的架构骨架。同样地,在大量现实生活的真实网络(如互联网、科学家合作网络)中,强劲的度相关性特征被普遍发现,即网络中的枢纽节点总是倾向于与其他枢纽节点相连,当然也存在异配性。网络科学将具有正相关特性的网络称之为同配网络,负相关特性的网络称之为异配网络,而不显著(即随机性)的网络称之为中性网络。通过分析3个阶段中国城际绿色技术扩散网络的加权度相关性特征(中国绿色技术扩散网络是典型的加权有向网络,故而分析其加权度相关性特征),中国城际绿色技术扩散网络也遵循度相关性规律,呈现出同配网络的特性,即绿色技术流动更加活跃于枢纽节点之间。在前两个阶段的中国城际绿色技术扩散网络中,网络中最大的技术流动始终发生在北京和深圳这两个城市间,而这两个城市的加权度值(即绿色技术转移量)皆为前两个阶段最大的两个城市。在2001—2007年250对城际绿色技术扩散关系中,扩散量前30对(占整体46.2%)中有20对(占整体40.1%)发生于加权度值前10的城市之间。在2008—2014年2378对城际绿色技术扩散关系中,扩散量前30对(占整体18.8%)中有23对(占整体16.9%)发生于加权度值前10的城市之间。虽然在2015—2020年的城际绿色技术扩散网络中,网络中最大的技术流动,甚至是扩散量前8对中没有一对发生在加权度值最大的两个城市,即北京和深圳之间,但扩散量前30对(占整体12.6%)中有29对(占整体12.4%)发生于加权度值前10的城市之间。
5.3 城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素分析
鉴于城际绿色技术扩散为非负整数,且被解释变量的方差明显大于期望。因此,本文采用负二项式回归方法来分析中国城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素。模型检验发现,Alpha的置信区间在5%的显著性水平上拒绝“过度分散”参数“Alpha=0”的原假设,即本文使用负二项回归方法正确,模型的回归结果如表2所示,基本佐证了本文在理论框架建构中的推论。
表2 城际绿色技术扩散驱动因素的负二项回归模型估计结果
Tab. 2
| 变量 | 2001—2007年 | 2008—2014年 | 2015—2020年 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.021* | 0.036** | 0.048*** | |
| 0.015* | 0.023** | 0.037*** | |
| 0.023** | 0.041** | 0.052** | |
| -0.002* | -0.003** | -0.015*** | |
| -0.231* | -0.324** | -3.568*** | |
| 0.421* | -0.714** | -1.124*** | |
| -0.824* | 6.321** | 7.214*** | |
| 常数 | 2.314 | -1.245 | -3.541 |
| 样本量 | 250 | 2378 | 11460 |
注:*、**、***分别表示10%、5%和1%的水平显著。
① 城市绿色专利申请量是影响城际绿色技术扩散网络生长的重要影响因素,且影响程度呈持续强化趋势。城市间绿色技术扩散规模与各自的绿色专利申请规模成正比,即申请的绿色专利越多,两城之间存在绿色技术扩散的可能性及扩散量越大,表明城际绿色技术扩散存在显著的强强联合、合作共赢特征,这也与上文发现的“同配性”特征相互佐证。② 城市间绿色技术专利申请量的差距越大,城市间绿色技术扩散规模也就越大,这不仅证实了本文在理论框架建构部分的技术差距理论的推论一致,也与已有关于城市一般技术扩散研究的结论相一致[6]。③ 城市间的地理距离对城际绿色技术扩散的阻抗作用愈发凸显,即城市之间的地理距离与城际绿色技术扩散的数量呈显著的负相关。在地理距离约束这一点,城内绿色专利转移的活跃就已经表征城市边界和地理距离在绿色技术扩散中扮演中非常重要的作用。实际上,2001—2020年,虽然中国城际绿色技术扩散的平均距离不断增长,由2001—2007年的805.60 km增长至2015—2020年的927.03 km,但高于这一平均距离的城际绿色技术扩散量所占比重则逐渐降低,由50.1%下降至41.8%。
由于本文采用的是城市GDP比值(高/低)和环境规制比值(高/低)来分别衡量城市经济邻近性和城市制度邻近性,因而这两个指标实则为负向指标。2001—2020年城市经济邻近性对城际绿色技术扩散的影响系数为负,这意味着城市经济邻近性对城际绿色技术扩散的影响显著为正,且影响程度呈持续强化趋势,突显出中国城市绿色技术流动越来越多的发生在经济发展水平相近的城市之间,城市间的经济发展水平越接近,相应的绿色技术需求越一致,越能促进绿色技术扩散规模,这一研究发现与已有城际技术流动网络的驱动因素研究一致[12]。然而,城市制度邻近性的影响系数在2001—2007年为正,在2008—2014年和2015—2020年为负,这表明城市制度邻近性对城际绿色技术扩散的作用机制呈现出由负转正的发展过程。这一变化态势在城市认知邻近性上同样得到验证。2001—2007年城市制度邻近性系数为正,城市认知邻近性的系数为负,表现出城市间环境规制强度差异越大或技术关联性越小,则城市间绿色技术扩散规模越大。在环境规制层面似乎印证了本文上述假设,但在技术关联性层面则与本文上述假设相悖,究其原因可能是2001—2007年中国绿色技术城际扩散体系尚处于初始阶段,且城市绿色技术创新活动也高度集聚于少数城市,城市间的绿色技术创新技术领域差异较大。2008—2014年和2015—2020年城市制度邻近性系数为负,而认知邻近性的系数为正,且正向影响作用显著增强,呈现出城市间环境规制强度差异越小或技术关联性越大,则城市间绿色技术扩散规模越大。在技术关联性层面似乎印证了本文上述假设,但在环境规制层面又发展为与本文上述假设相悖。这一结果也可以理解,随着城市绿色技术创新的发展以及城市经济发展水平的提升,尤其是城市工业化的不断发展,大多数城市已具备一定的绿色技术产出和转化能力,愈发强化的环境规制强度不仅能促使绿色技术供给过剩的城市向外扩散技术,也激发绿色技术供给不足的城市不断从外部寻求技术,进而呈现出城市环境规制强度越相似,城市间绿色技术扩散规模越大的现象。
6 结论与讨论
6.1 结论
促进绿色技术自由流动是构建以市场为导向的绿色技术创新体系的核心内涵,也是新时期中国推动绿色发展、促进人与自然和谐共生,从而实现中国经济高质量发展和提升国家创新体系整体效能的关键。以绿色专利转让刻画绿色技术扩散,本文从城内和城际两个视角探讨了2001—2020年中国绿色技术扩散活动的时空特征及其驱动因素,得出以下结论:
(1)随着中国环境保护和污染治理模式由末端治理转向全过程控制,2001—2020年中国绿色技术交易市场中的热门技术由环境治理技术快速转变为绿色建筑技术和清洁能源技术,企业不仅是中国绿色技术的主要出让者,也是集成吸纳者,广泛吸收来自大学和科研机构、个体出让的绿色技术。环境治理技术转移量的下降、绿色建筑技术和清洁能源技术转移量的上升,也从侧面说明了作为中国绿色技术扩散的行为主体,企业的绿色技术创新的战略导向也从“成本控制”转向了“效益追求”。环境治理技术的开发大大增加了企业的生产成本,而绿色建筑技术和清洁能源技术却能够让企业快速地得到因政府环境规制和消费者绿色产品偏好带来的“收益”。
(2)中国城内绿色技术流动活动高度集聚在以京津、长三角和珠三角为增长极的东部沿海地区,以及以长三角、长江中游和成渝城市群为核心枢纽的长江经济带。城际绿色技术扩散网络呈现出由随机分散格局经三角格局向菱形格局演化,京津、长三角、珠三角和成渝地区成长为中国城际绿色技术扩散网络的枢纽。随着市场经济体制改革的持续深入和开放创新的迫切需求,中国绿色技术的空间流动受到城市行政边界的约束作用开始减弱,绿色技术跨城流动成为新常态。中国城市在绿色技术扩散网络中的角色逐渐由自给自足式的城内集散型向开放创新式的城际集散型发展,尤其是绿色技术转移量较大的城市逐渐由“城内集散型”向“城际集散型”转型,越来越多的城市,特别是新加入绿色技术扩散网络的城市主要通过城际技术集聚来补充本城的绿色技术供给,因而在愈发频繁的绿色技术跨城流动下,全国统一的绿色技术交易大市场正在逐渐形成。
(3)在城际绿色技术扩散的形成机制上,复杂网络生长机理中的偏好连接法则和同配性法则分别从动态视角和静态视角揭示了中国城际绿色技术扩散体系生长过程中遵循的一般规律,即中国城际绿色技术扩散网络中,新加入城市倾向于从网络中枢纽城市获取绿色技术,且枢纽城市间的绿色技术流动更加频繁。多维邻近性分析框架下的模型回归结果也验证了上述规律,即中国城际绿色技术扩散存在显著的强强联合、合作共赢特征,并呈现出强劲的“技术差距”链接机制。此外,城市间地理邻近性、经济邻近性也对城际绿色技术扩散起着显著的正向促进作用,而制度邻近性和认知邻近性对城际绿色技术扩散的作用机制皆呈现出由负转正的发展过程。
(4)挖掘绿色技术扩散的空间特征及分析城际绿色技术扩散的驱动因素,是探索构建以市场为导向的绿色技术创新体系和建构全国统一绿色技术交易大市场的基础研究工作。基于上述实证研究发现,为建构全国绿色技术转移转化市场交易体系提出以下几点对策:① 鉴于城内绿色技术流动仍占较大比重,应继续打破各级行政壁垒,加速绿色技术的跨省、跨区域和跨城流动;② 强化绿色技术转移转化交易体系中企业的主体地位,通过设立绿色技术转移转化示范试点企业,来加强主体间的绿色技术流动;③ 以北京、上海、深圳、武汉、成都(重庆)等为枢纽城市,建立国家级绿色技术银行或绿色技术转移转化中心,并依托长三角、粤港澳、京津冀等区域,建立绿色技术转移转化综合示范区,借助区域一体化国家战略强化区域内部的绿色技术流动。
6.2 讨论
以绿色专利转让衡量绿色技术扩散,将企业尺度的绿色技术扩散拓展至城市尺度,本文在建构城市绿色技术扩散研究分析框架的基础上,对中国绿色技术扩散的热门技术、行为主体和城市类型等进行了详细的研究,不仅将当前创新地理学中一般技术扩散(无技术领域之分)的研究细化至绿色技术领域,还将当前环境经济地理学集中于城市绿色发展差异研究拓展至城市绿色发展空间联系研究,有益地丰富了创新和环境经济地理的研究内容。但无论是在绿色技术扩散的衡量指标上,还是在城市尺度绿色技术扩散抽象过程中,都无法忽视片面化导致本文存在诸多尚待改进的地方:
(1)以绿色专利转让衡量绿色技术扩散虽是国际惯例,但仅仅涉及绿色技术扩散规模这一维度,绿色专利转让实际包含诸多信息,如转让价格表征的绿色技术质量,转让时间表征的绿色技术扩散速度等[31],这些维度本文并没有涉及。同时,绿色技术扩散的形式和途径多种多样,除绿色专利转让外,如何进行其他扩散形式相关数据的获取从而进行多途径下的绿色技术扩散综合研究以及多途径的绿色技术扩散比较研究是下一步需要攻克的方向。
(2)本文虽然通过绿色技术领域分类识别了2001—2020年间中国绿色技术交易市场上的热门技术,但并未分析每一类绿色技术扩散的详细特征。实际上,无论是从绿色技术创新的视角还是从绿色技术扩散的视角,技术领域不同,其创新主体、空间分布和时序发展特征差异显著。同时,中国绿色技术扩散体系的建构也应当充分考虑技术领域不同带来的差异性。因此,不同技术领域、甚至不同行业领域的绿色技术扩散比较研究是未来需要研究的问题。
参考文献
Greening Global Value Chains:Innovation and the International Diffusion of Technologies and Knowledge
Innovation and diffusion of clean/green technology: Can patent commons help?
DOI:10.1016/j.jeem.2012.12.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Green technology diffusion: A post-mortem analysis of the Eco-Patent Commons
Evolution pattern and impact factors of environmental innovation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.07.006
[本文引用: 3]

The “T” structures in China’s territorial development and economic layout remain to be the two areas with the greatest potential for economic growth in China, among which the Yangtze River Economic Belt is the only first-class development axis across the three plates of East, Central and West. Over the years, in the excessive pursuit of rapid economic growth, the Yangtze River and its two sides of the great lakes and major tributaries have suffered serious environmental pollution, ecosystem imbalance, and frequent water security problems. To pay attention to the great protection together and not to engage in the great development is the guideline for the construction of the green Yangtze River Economic Belt, and the environmental innovation is the core support of the green development of the economic belt of the Yangtze River. In this paper, the spatial and temporal characteristics of environmental innovation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt are explored by taking the number of green patent applications as the evaluation index, and the influencing factors are also revealed. The results are as follows. First, from 2007 to 2017, the number of green patent applications in the Yangtze River Economic Belt increased from 35422 to 47563, among which the number of patent applications in the field of green building technology always ranked first. In addition, the environmental innovation of Yangtze River Economic Belt has significant spatial correlation effect. Second, in terms of spatial pattern, the environmental innovation of the Yangtze River Economic Belt was dominated by the eastern region, and shows the characteristics of development from the East to the West. Third, environmental innovation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt has significant spatial spillover effects. The intensity of environmental regulations, technological innovation level, city scale, the proportion of tertiary industry, and urban air quality all have a significant positive role in promoting the urban environmental innovation capacity of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. The intensity of environmental regulation does not have obvious spatial spillover effects, and the level of urban technological innovation has significant negative spillover effects.
长江经济带环境创新的时空特征及其影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.07.006
[本文引用: 3]

以绿色专利申请量为评价指标对长江经济带环境创新的时空特征进行了多维度挖掘,并揭示了其影响因素,研究发现:① 时序发展上,长江经济带环境创新空间集聚特征显著,绿色建筑技术始终主导长江经济带环境创新演化发展;② 空间演化上,长江经济带环境创新格局整体表现为由东部地区主导,并呈现出由东向西的阶梯推进的发展特征,且呈现出显著的空间关联性;③ 长江经济带环境创新具有显著的空间溢出效应,环境规制强度、技术创新水平、城市规模、第三产业比重和环境质量皆对长江经济带城市环境创新能力有着显著的正向促进作用,但环境规制强度不具有明显的空间溢出效应,且技术创新水平具有显著的负向溢出效应。
Evolutionary game analysis of the diffusion of green technological innovation of enterprises
企业绿色技术创新扩散的演化博弈分析
Two-stage evolution analysis of green technology innovation diffusion based on complex market network
基于复杂市场网络绿色技术创新扩散的两阶段演化分析
The spatio-temporal pattern of environmentally-friendly agricultural technology diffusion and its influencing factors: From the social network perspective
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210463
[本文引用: 1]

Facing the severe problem of agricultural non-point source pollution, the diffusion and adoption of environmentally-friendly agricultural technology is of decisive significance to the modernization and the revitalization of ecology in rural China. However, environmentally-friendly agricultural technology is currently hard to promote and with a low acceptance in rural areas. Previous studies have proved that social network is an effective way and foundation for technology diffusion. Correspondingly, this paper constructs a theoretical framework of environmentally-friendly agricultural technology innovation diffusion from the perspective of social networks. Through the quantitative analysis of questionnaire data of 3015 households in 10 counties and cities of Guangdong Province from 2018 to 2020 and the fieldwork observation of non-point source agricultural pollution control in this province, this paper concludes that there are four stages of environment-friendly agricultural technology diffusion: (1) Initial stage: discrete and simple technical interaction among rural households emerges. (2) Single-core stage: single core such as elite farmer has formed and technology starts to diffuse through kinship network. (3) Multi-core stage: there have been several elite farmers and the diffusion goes through occupational network rather than kinship. (4) High-level interaction stage: agricultural economic organization and agricultural entrepreneur have been established; functional network has been formed. Behind the four stages, individual farmers keep on accumulating their own material, human and social capital to achieve the upgrade of their node level, also known as the process of technology diffusion, from disorder to formalization. Correspondingly, there are four main influencing factors of the diffusion of environmentally-friendly agricultural technology: individual resource endowment, technology effectiveness and perception, technology diffusion channels and external environment. These factors play different roles in different stages. The results of this study can be beneficial to the understanding of the underlying mechanism of environmentally-friendly agricultural technology diffusion in rural China, and are of policy significance for the diffusion and adoption of similar technologies. According to the stage characteristics of the diffusion of new technology, the government needs to guide and promote the mode of communication in accordance with local conditions.
环境友好型农业技术扩散的时空演化与影响因素: 基于社会网络视角
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210463
[本文引用: 1]

面对严峻的农业面源污染问题,环境友好型农业技术的推广和落地对于中国实现乡村生态振兴和农业农村现代化具有重要意义。但现实中,该类型技术在乡村地区一直面临推广难,采纳度低的问题。以往众多研究证明,社会网络是技术扩散的有效途径和支撑。基于此,本文从社会网络的视角构建了农业技术创新扩散的理论框架,通过2016—2020年广东省农业面源污染治理的实践调研及10个县市3015份问卷数据的定量分析,总结出环境友好型农业技术扩散的四个阶段:① 初始阶段:农户间简单离散的技术互动。② 单核阶段:精英农户的点式嵌入与拟亲缘网络扩散。③ 多核阶段:多个精英农户形成与业缘关系网络扩散。④ 高水平互动阶段:农业经济组织的形成与功能性网络扩散。个体资源禀赋、技术有效性及感知度、技术传播方式和外部环境作为技术扩散的四个主要影响因素,在不同的阶段发挥着不同的作用。本研究成果有助于理解中国农业技术扩散的实践逻辑和底层机制,对同类技术推广有重要的政策意义。
Local implementation for green-manufacturing technology diffusion policy in China: From the user firms' perspectives
DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.112 URL [本文引用: 1]
Inverted U-shaped relationship between socio-economic status differences and the diffusion of agricultural green control technologies: Mediating effect of social learning
社会经济地位差异与农业绿色防控技术扩散倒U型关系: 社会学习的中介效应
Energy performance contract models for the diffusion of green-manufacturing technologies in China: A stakeholder analysis from SMEs' perspective
DOI:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.03.040 URL [本文引用: 1]
Dissecting diffusion: Tracing the plurality of factors that shape knowledge diffusion
Research on the diffusion network of green technology in the context of professional virtual community
专业虚拟社区情境下的绿色技术扩散网络研究
'License to green': Regional patent licensing networks and green technology diffusion in China
Research on the influencing factors of green technology innovation diffusion based on multi-agent model
基于多智能体模型的绿色技术创新扩散影响因素研究
How to accelerate green technology diffusion? Directed technological change in the presence of coevolving absorptive capacity
Intra-firm diffusion of green energy technologies and the choice of policy instruments
DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.144 URL [本文引用: 1]
Diffusion intermediaries: A taxonomy based on renewable electricity technology in Sweden
DOI:10.1016/j.eist.2019.11.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Green technology transfer under the global environment facility: Approaches and implication
全球环境基金促进绿色技术转移的路径及启示
Promoting green manufacturing technology diffusion using an innovative policy implementation method
促进绿色制造技术扩散的政策模式创新研究
Green technology diffusion: The case of GIVEWATTS green lanterns
Green technology diffusion: The case of Arivi paraffin cookstoves
Green technology diffusion: The case of Ecosan waterless toilets
Technology transfer in China's city system: Process, pattern and influencing factor
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804011
[本文引用: 1]

<p>Based on the records of patent transfer from the patent retrieval and analysis platform in the State Intellectual Property Office of China, this research built an assessment index and model for technology transfer in China's city system in terms of agglomeration and dispersion, using big data mining technology, geo-coding technology, spatial autocorrelation model and multiple linear regression model. Then we studied the spatial-temporal pattern, agglomeration model and influencing factors of technology transfer in China's city system from 2001 to 2015, and obtained the following results. Firstly, with the increasing capability of city's technology transfer and the growing number of cities involved in transferring technology, the polarization and strong agglomeration of technology transfer in China's city system have been intensified. Secondly, technology transfer in China's city system has experienced a process of constant spatial polarization, the three-pole pattern led by the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta region and the Pearl River Delta region has been gradually prominent. Thirdly, technology transfer system from global to local scale in China's city system has initially taken shape. Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen have become the three global centers of China in technology transfer. Fourthly, technology transfer in China's city system has produced an obvious spatial correlation and agglomeration effect. The four types are mainly in the cluster, and the geographical proximity of technology transfer in China's city system is significant. Last but not least, the influencing factors of technology transfer in China's city system were also verified by multiple linear regression model. We found that the demand and supply capacity respectively represented by the scale of tertiary industry and the number of patent applications has a great influence on the growth of technology transfer capability. In addition, the number of R & D employees is an important factor, but its correlation is low. The findings further confirm that the scale of primary industry has a significant impedance effect on city's technology transfer capability.</p>
中国城市创新技术转移格局与影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804011
[本文引用: 1]

以国家知识产权局专利检索及分析平台中历年专利转让记录为数据源,采用大数据挖掘技术、地理信息编码技术、空间自相关模型和多元线性回归模型,并从集聚和扩散两个方面构建城市创新技术转移能力评价指标体系及评估模型,对2001-2015年中国城市技术转移的时空格局、集聚模式及影响因素进行了研究。结果发现:① 2001-2015年,随着城市创新技术转移能力的不断上升,且在参与创新技术转移的城市数量不断增加情境下,中国城市创新技术转移能力的两极分化及强集聚特征持续发育;② 中国城市创新技术转移格局经历着空间不断极化的历程,由京津冀、长三角和珠三角主导的三极格局逐渐凸显;③ 中国城市创新技术集散体系不断完善,从全球至地方的中国创新技术集散体系已初步形成;④ 中国城市创新技术转移呈现出显著的空间关联与集聚效应,4种类型基本呈“抱团”分布,城市创新技术转移的地理邻近性显著;⑤ 多元线性回归模型发现,城市创新技术的需求能力和供给能力决定其转移能力,第三产业产值规模和专利申请量对城市创新技术转移能力影响较大。另外,研发人员数量也是影响城市技术转移能力的重要因素,但是相关性较低,而城市第一产值规模对城市创新技术转移能力具有显著的阻抗作用。(注:①考虑到专利技术从申请至授权以及转移的期限较长,因此本文城市吸收、转出的专利速度主要基于1年转移量、2年转移量和5年转移量来综合评定。)
The theoretical construction and network simulation of intercity innovative relationships in knowledge flow space
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004004
[本文引用: 1]

The interactive relationships between cities in the knowledge economy era have attracted much attention. Researchers have applied a range of methods to explore intercity innovative relationships and associated network characteristics. It nevertheless remains unclear just how intercity innovative relationships can be theoretically constructed based on knowledge flow space and how further scientific simulation methods can be designed. Research questions in this area have rarely been explored in detail, an issue which has inevitably placed obstacles on further exploration. A framework for the theoretical construction of intercity innovative relationships is presented in this study; the basis for this research is that an intercity innovation network is essentially a 'soft network', distinct from a 'hard network'. These interconnections are founded on a subjective relationship construction process and therefore necessitate scale transformation from 'point-point' connections between innovative subjects in different cities with respect to 'city-city' interactions. At the same time, this transformation process is prone to exaggerations and deviations from objective intercity innovative relationships and therefore exerts considerable influence on the accuracy of results such that constructions must be entirely theoretical. Four construction methods for intercity innovative relationships and network simulation are summarized in this study, including an intercity undirected network based on cross-city co-operations between scientific and technological achievements, an intercity directed network based on the cross-city transfer of scientific and technological achievements, an intercity innovation network based on the cross-city flow of high-end talents, and an intercity innovation network based on the multi-city distribution of innovative enterprises and institutions. Simulation tests were then undertaken using relevant data to reflect aspects of these relationships. The results of this analysis are conducive to further exploration of global and regional innovative spatial patterns from the perspective of urban geography and intercity relationships and provide a theoretical and methodological foundation for further research on intercity innovation networks.
知识流动空间的城市关系建构与创新网络模拟
Embedded technology transfer from an institutional and cultural perspective: A case study of Mombasa-Nairobi standard gauge railway
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006004
[本文引用: 1]

Since the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was proposed, the pace of projects investment and construction has been accelerated, which accumulated much experience in the going-out strategy in the context of BRI. Modern railway projects are characterized by "natural monopoly", as well as huge investment and extensive geographical coverage. Moreover, their construction is a typical transformative project, which embedded the necessary institution and culture. The countries along the Silk Road are characterized by weak institutional construction, lack of regulatory system, and underdeveloped industrial civilization, therefore they cannot operate and manage the railway system. In this context, all links, including financing, design, construction, and operation, should be considered in the going-out process of China's railway system. The transfer subject is the technology-institution-culture nexus which takes railway technology as the core. In other words, to achieve railway technology transfer successfully, the host countries should offer rational institutional guarantee and cultural adaptation. Besides, the technical standard of railway construction, management mode, and industry chain in the process of railway operation and maintenance need to be localized. Mombasa-Nairobi standard gauge railway is a successful going-out case of China's railway technology. Learning from the case, this paper proposed the concept of "embedded technology transfer" and constructed the theoretical model of technology-institution-culture nexus transfer. The results can provide references for the transfer of transformative projects or technologies between countries with different institutions and cultures.
制度与文化对嵌入式技术海外转移的影响: 以蒙内铁路为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006004
[本文引用: 1]

中国与东道国之间制度与文化上的差异,已经成为中国企业“走出去”关注的重点,也是推动“一带一路”建设向高质量发展转变必须考虑的重要因素。现代化铁路项目具有“自然垄断”、投资大、涉及地域广的特点,其建设对运营制度与文化的依赖性强,属于一种典型的变革性项目和嵌入式技术转移。“一带一路”沿线国家制度建设相对薄弱,与中国文化差异较大,且往往不具备铁路运营技术与能力,因此中国铁路在“走出去”的过程中,必须从设计—建设—运营乃至投融资进行全链条考虑,并将铁路项目作为“技术—制度—文化”复合体进行培育,即通过制度保障、文化相互适应以及技术标准、管理模式、产业链条的属地化管理,来保障项目的成功运营。蒙内铁路是中国铁路“走出去”较为成功的案例,本文通过实地调研,总结了“技术—制度—文化”复合体海外发展模式,从而为推动海外项目建设与运营成功、“一带一路”建设向高质量发展提供借鉴意义。
Institutional-economic-cultural adaptability of overseas railway construction: A case study of Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006006
[本文引用: 1]

The development of a country at a certain stage is an outcome of a long-term historical accumulation process, which forms a mutually adaptive state of development among the main national factors such as institution, economic, cultural and technological systems. And the technology transfer breaking through the original level will cause a disorder among the institutional-economic-cultural-technological systems (IECT system), and produce the frictional effect of technology-environment. This paper constructed a conceptual model on the complex system among the institution, economy, culture and technology, and analyzed its major features. Then, we simplified the above model into railway-institution-economic-cultural model (RIEC system) and probed the adaptive mechanism between railway and institutional-economic-cultural system. Furthermore, we explored the institutional-economic-cultural adaptability of the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway. This article insists that Ethiopia and Djibouti had not experienced the large-scale industrialization. As an electrified railway, the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway is a "spanning transfer" of the technology and there is a misplacement between this railway and the developing stage of Ethiopia and Djibouti. And the construction and operation of this railway brought out an obvious challenge for the institutional-economic-cultural development of these two countries, which resulted in the inadaptability of local institutional, economic and cultural system, and the unbalance of RIEC system. This study can provide a scientific guidance for China's enterprises to construct railways and spread China's railway standard in the world especially in the less-developed countries.
铁路技术跨越式转移的制度—经济—文化适应性: 基于亚吉铁路的实证分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006006
[本文引用: 1]

国家在制度、经济、文化、技术等要素之间组成相互支撑、制衡、嵌套的平衡系统,而技术的跨越式转移将会引起系统的失衡,造成“技术—环境”摩擦效应。本文试图构建技术与制度、经济、文化平衡系统概念模型,进而凝练铁路—制度—经济—文化平衡系统模型,并以亚吉铁路为例,分析铁路技术跨越式转移与属地国制度—经济—文化系统的适应性。研究表明,埃塞俄比亚和吉布提仍处于农牧业阶段,而亚吉铁路作为电气化铁路技术,属于“跨越式”的技术转移,脱离了属地国的既有发展基础,造成铁路技术与制度、经济、文化的不适应性。本文的研究结论可以为中国企业在全球尤其是欠发达国家承担铁路建设运维与推广中国铁路技术标准提供理论指导。
Does environmental regulation promote environmental innovation? An empirical study of cities in China
Promoting environmental innovation through environmental regulation is a key measure for cities to reduce environmental pressure; however, the role of environmental regulation in environmental innovation is controversial. This study used the number of environmental patent applications to measure urban environmental innovation and analyzed the role of urban environmental regulation on urban environmental innovation with the help of the spatial Durbin model (SDM). The results showed that: (1) From 2007 to 2017, the number of environmental patent applications in China has grown rapidly, and technologies related to buildings dominated the development of China’s environmental innovation. (2) Although the number of cities participating in environmental innovation was increasing, China’s environmental innovation activities were highly concentrated in a few cities (Beijing, Shenzhen, and Shanghai), showing significant spatial correlation and spatial agglomeration characteristics. (3) Urban environmental regulation had a positive U-shaped relationship with urban environmental innovation capability, which was consistent with what the Porter hypothesis advocates.
The spatio-temporal evolutionary pattern and driving forces mechanism of green technology innovation efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta region
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210102
[本文引用: 2]

In the strategic background of high quality integration in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), green technology innovation, as the combination of green development and innovation-driven national strategies, has become an important engine of green transformation and development in the region. This paper, by constructing a super-efficiency SBM-DEA model that includes undesired output, measures the efficiency of green technology innovation in core cities of the YRD from 2010 to 2017, and studies its spatio-temporal evolutionary pattern and driving forces mechanism. The results show that, (1) In terms of time series evolution, the green technology innovation efficiency in the study region shows a “W”-shape pattern. (2) In terms of spatial evolution, the green technology innovation efficiency in the southeast of the YRD is relatively stable, while changes in the central and southwestern parts are obvious, showing the characteristics of continuous agglomeration and development as a whole. (3) In terms of spatial correlation, the regional spatial relationship of green technology innovation efficiency in the YRD has gradually changed from the “polarization effect” to the “trickle down effect”. As a whole, Theil index and Gini coefficient show the characteristics of an “M” change opposite to the evolution of time series. (4) Based on the measured results of input, output and efficiency of green technology innovation in the delta region, all cities are identified into six types: high-high-high, high-high-low, high-low-low, low-high-high, low-low-high, and low-low-low This further reveals regional differences in the development path of green technology innovation in the YRD. (5) The research results of driving forces mechanism show that environmental regulation, economic development, industrial structure, opening degree to the outside world, human capital and urbanization all play significant positive roles in promoting the spatio-temporal evolution of green technology innovation efficiency in the YRD, while the innovation support has a significant negative spillover effect. (6) On the whole, the green technology innovation in the study region does have a significant “Porter Hypothesis” effect, but the “pollution paradise” effect mentioned in the literature has not been found.
长三角区域绿色技术创新效率的时空演化格局及驱动因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210102
[本文引用: 2]

在长三角更高质量一体化的战略背景下,绿色技术创新作为绿色发展和创新驱动两大国家战略的结合点,已成为长三角区域绿色转型发展的重要引擎。通过构建包含非期望产出的超效率SBM-DEA模型,对2010—2017年长三角区域核心城市的绿色技术创新效率进行测度,并研究其时空演化格局和驱动因素。结果显示:① 在时序演变上,长三角区域的绿色技术创新效率呈现“W”型变化特征;② 在空间演变上,长三角东南部地区的绿色技术创新效率相对稳定,而中部、西南部变动明显,整体呈现连片集聚发展特征;③ 在空间关联上,长三角区域绿色技术创新效率的区域空间联系逐渐由“极化效应”转变为“涓滴效应”,泰尔指数和基尼系数整体表现为与时序演变相反的“M”型变化特征;④ 基于长三角区域绿色技术创新投入、产出及效率测算结果,将各城市划分为高高高、高高低、高低低、低高高、低低高和低低低六种类型,进一步揭示了长三角区域绿色技术创新发展路径的区域差异;⑤ 驱动因素分析结果表明,环境规制、经济发展、产业结构、对外开放和人力资本皆对长三角区域整体的绿色技术创新效率有着显著的正向促进影响,但创新支持具有显著的负向溢出效应。
Ecological green integration in Yangtze River Delta from perspective of intercity green technology transfer
绿色技术跨城流动下长三角生态绿色一体化发展研究
Environmental regulation and green technology diffusion: A case study of Yangtze River Delta, China
As an important driver of green technology innovation, the impact of environmental regulation on the diffusion of green technology remains controversial. Taking China’s Yangtze River Delta (YRD) urban agglomeration, as an example, and using green patents transfer to measure green technology diffusion, this paper analyzes the effect of environmental regulation on green technology diffusion by revealing the temporal and spatial characteristics of green technology diffusion in the YRD. The results show that: (1) Green technology transfer activities in the YRD mainly take place in Shanghai, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Suzhou, and other cities. (2) Green building technology is the most demanded technology in the green technology transfer market in the YRD. (3) The direction of green technology diffusion in the YRD has changed significantly over time. In the early stage, green technologies mainly flowed to developed cities such as Shanghai, Suzhou, and Nanjing. However, in the later stage, green technologies mainly flowed from developed cities such as Shanghai, Suzhou, and Nanjing to cities with lower economic development levels (mostly located in Anhui Province). (4) The consistency of environmental regulation among cities plays an important role in promoting green technology transfer within the YRD, which is precisely what the YRD ecological green integrated development strategy emphasizes, breaking the administrative barriers between cities in the YRD and accelerating the flow of green technology between cities.
Green technology innovation in China city system: Dynamics and determinants
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202212012
[本文引用: 2]

Green technology innovation is the first driving force to promote green development and harmonious coexistence between human and nature. Green technology innovation is the core issue of environmental economics, innovation economics, innovation management and other research fields. It is also one of the emerging topics in the field of environmental economic geography in recent years. Overall, the research on enterprise level is dominant, while the research on spatial scale is relatively less. In this paper, by deriving green patent applications for measuring green technology innovation from the Wanfang Patent Database, the spatial and temporal characteristics and its determinants of green technology innovation in China's city system from 2007 to 2017 are explored. The results indicate that technologies related to buildings has dominated the development of environmental innovation in China's city system, while technologies in the field of greenhouse gases and water adaptation were quite unpopular throughout China. In 2007, China's environmental innovation was dominated by individuals and enterprises. By 2017, enterprises have become the main body of China's environmental innovation, highlighting the essential characteristics of enterprises as the subject of environmental innovation. In space, the geography of environmental innovation in China's city system presents a strong spatial imbalance feature, a tripolar pattern dominated by the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Beijing-Tianjin region has become increasingly prominent. In terms of determinants, spatial Durbin model regression results reflect that there are significant spatial spillover effects and path dependence characteristics in China's environmental innovation. Environmental regulation intensity, city size, market size, technological innovation level, FDI, and air quality have obvious positive effects on urban environmental innovation, while the industrial structure dominated by secondary industry has obvious inhibitory effect on urban environmental innovation.
中国城市绿色技术创新的时空分布特征及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202212012
[本文引用: 2]

借鉴经济合作与发展组织(OECD)的绿色专利识别方法,本文建构了2007—2017年中国城市尺度的绿色专利申请量时空数据库,从而揭示了2007—2017年中国绿色技术创新活动的时空分布特征,并基于空间杜宾模型探讨了其影响因素。研究发现:① 时序发展上,无论是在专利申请量上还是城市参与度上,绿色建筑技术一直主导中国绿色技术创新发展,11年间绿色建筑技术领域专利申请量占整体的比例一直维持在30%以上;② 创新主体上,中国绿色技术创新由企业主导的特征愈发显著,企业申请的绿色专利占整体的比例由2007年的39.7%增长至2017年的62.6%;③ 空间演化上,中国绿色技术创新空间分布呈现出显著的空间集聚性特征,以长三角、珠三角和京津地区为主导的三极格局日益凸显。个体城市上,11年间北京、深圳相继超越上海,成为中国绿色技术创新最为集聚的两大核心城市;④ 影响因素上,中国城市绿色技术创新具有显著的空间溢出效应和路径依赖性特征,城市环境规制强度、城市经济规模、城市市场规模、城市技术创新水平、城市吸引的FDI以及城市空气质量对城市绿色技术创新具有明显的积极影响,而以第二产业为主的产业结构对城市绿色技术创新具有明显的抑制作用。
The role of inter-sectoral learning in knowledge development and diffusion: Case studies on three clean energy technologies
DOI:10.1016/j.techfore.2019.04.018 URL [本文引用: 1]
Knowledge flows and the absorptive capacity of regions
DOI:10.1016/j.respol.2015.01.016 URL [本文引用: 1]
The innovative performance of firms in heterogeneous environments: The interplay between external knowledge and internal absorptive capacities
DOI:10.1016/j.respol.2018.02.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Does technology gap increase FDI spillovers on productivity growth? Evidence from Chinese outward FDI in Belt and Road host countries
Technology Gap, Reverse technology spillover and domestic innovation performance in outward foreign direct investment: Evidence from China
Does host market regulation induce cross-border environmental innovation?
DOI:10.1111/twec.2019.42.issue-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
How does environmental regulation promote technological innovations in the industrial sector? Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data
Knowledge-relatedness in firm technological diversification
DOI:10.1016/S0048-7333(02)00004-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relatedness and technological change in cities: The rise and fall of technological knowledge in US metropolitan areas from 1981 to 2010
Structural heterogeneity and proximity mechanism of global scientific collaboration network based on co-authored papers
全球科研论文合作网络的结构异质性及其邻近性机理
Historical evolution and reform of China's environmentalstrategy and policy during the past seventy years (1949-2019)
中国环境保护战略政策70年历史变迁与改革方向