1 引言
城乡关系普遍经历城乡分化、隔离、对立,再到融合一体的发展过程[1-2],根据城镇化发展阶段[3-4],城乡融合阶段的城镇化率一般在50%~70%[5]。伴随中国城乡发展政策导向的逐步调整以及城镇化、工业化及全球化进程的推进,城乡地域空间、人口、产业以及经济社会结构等都经历了迅速转型[6⇓⇓-9],2011年末城镇化率首超50%,2019年末达60.60%[10-11],标志着中国城乡关系逐渐由分割对立的二分范式向统筹一体的发展阶段迈进。然而,长期束缚城乡经济社会发展的二元结构仍未从根本上打破,工农关系不协调、城乡要素市场割裂[12],城进村衰的趋势难以扭转[6,13 -14],城乡居民生活水平、基础设施、公共服务和人居环境等存在巨大发展差距。
着眼当前发展阶段与现实矛盾,需要进一步从发展理念和政策实施等方面来推动城乡关系转变,中国共产党“十九大”适时提出“建立健全城乡融合发展体制机制”的重大决策部署,作为两大战略的有效衔接与交叉问题,推动城乡要素平等交换和双向流动,构建新型城乡关系,以城乡融合发展带动乡村振兴不仅成为快速转型阶段党和国家关切的工作重点,也是当今学术界关注的焦点议题[15-16]。理论和实证层面,围绕城乡融合发展的理论脉络[17⇓⇓-20]、概念界定[21⇓⇓-24]、内涵解析[14,20,25 -26]、测度评价[27⇓⇓-30]与影响机理[26,28⇓⇓⇓ -32]、政策路径[33-34]等方面开展了大量研究。综合现有成果来看,在定性分析上,社会学、经济学、管理学、地理学等多学科从特有或交叉视角对城乡融合发展这一多维议题进行了诸多富有意义的探讨,使得城乡融合发展的内涵与外延进一步拓展深化[22];相比之下,囿于城乡融合发展的内涵解读差异以及目前研究方法和数据获取的限制[22-23,35],现阶段定量研究的开展相对不足。其中,系统定量测度城乡融合发展水平是将城乡关系问题及城乡要素相互作用、结构与功能转型由定性分析转向定量研究的前提[23,36]。中国地域广阔,不同区域、不同阶段的城乡发展特征不尽相同,现有研究成果在时间和空间范围的切入视角相对单一,多基于单一年份截面数据的静态评价分析[31,36],缺乏不同时期下城乡融合发展演变动态格局及时空异质性的对比分析与研判;研究视角偏重城乡经济、社会发展差距,而对人文、空间及生态视角的关注相对单薄,缺乏不同维度演进特征的分类探究。研究尺度较为宏观粗放,多以区域、省域或某一特定地市为研究对象[27,36⇓⇓⇓⇓ -41],对更微观和精细尺度下城乡融合的态势、格局及特征的整体刻画分析相对欠缺。因此,亟待对中国城乡融合发展水平进行全面测度,并研判目前城乡融合发展现状与理想样态的现实差距,识别当前城乡融合发展进程中的短板问题,从而为分区分类、因地制宜推进城乡融合发展及后续优化路径研究提供更为精准的科学依据。
地级区域在中国行政管理架构中是央地政府自上而下主导与自下而上协同治理的重要场域,国家方针战略与区域政策落实响应的核心空间载体,重点和中心城市、城市群区对引导和重塑区域发展格局发挥着重要作用。在当前县乡级统计数据和监测手段相对缺乏的情况下,市域尺度的城乡融合发展能够更为精准地识别区域城乡发展短板,为进一步探索面向县域的城乡融合发展提供衔接突破与参考依据。鉴于此,本文在对城乡融合发展内涵简要解析的基础上,结合不同尺度多源数据,构建市域尺度中国城乡融合发展测度指标体系,对全国336个地级单元2000年、2010年和2018年3个阶段城乡融合发展的时空格局及分异特征进行全面测度,并逐步识别出城乡融合发展的优势区域和典型问题区域,以期对城乡发展不平衡不充分的分异格局、演进特征和形成机制提供更为精细的科学认知,为科学合理优化城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的政策与调控建议提供参考。
2 城乡融合发展的内涵解析与评价指标体系构建
2.1 城乡融合发展的内涵解析
2.2 评价指标体系构建
回顾已有的城乡发展和城乡融合评价体系,现有研究多将表明城乡发展状态、城乡子系统各自发展水平及对比类指标形成一套静态指标体系进行耦合测度。由于数据存在内生性等影响,难以避免某一类指标的贡献度较高所引致的偏差。因此,为了保证评价结果的客观性与准确性,构建城乡融合评价体系指标时分别引入区域综合发展指数(Regional Development Index, RDI)和城乡协调互融指数(Rural-urban Coordinate Index, RCI),从反映城乡整体发展阶段与城乡协调互动程度两种态势特征刻画区域城乡融合发展过程。RDI旨在测度区域城乡整体发展水平以评价该区域所处城镇化发展阶段,RCI旨在衡量区域内城乡发展的公平性及城乡互融动力潜能,主要包含测度城乡之间是否遵循协调发展原则的对比性指标以及表征城乡融合发展效率与活力的动态驱动类指标。每一目标层包含经济、社会、人口、生态和空间5个维度,表征各维度融合发展状态的相应代表性指标的具体测算方法如表1所示。
表1 城乡融合发展评价指标体系
Tab. 1
| 决策层 | 目标层 | 指标层 | 属性 | 计算方法 | 权重 | 决策层 | 目标层 | 指标层 | 属性 | 计算方法 | 权重 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 区 域 综 合 发 展 指 数 (RDI) | 经济 发展 | 人均GDP | + | 区域GDP/区域常住人口(元/人) | 0.283 | 城 乡 协 调 互 融 指 数 (RCI) | 经济 协调 共进 | 县域资金外流率 | - | ((本期存款-上期存款)-(本期贷款-上期贷款))/本期存款 | 0.126 | |||||
| 人均可支配收入 | + | 区域人均可支配收入(元) | 0.246 | 土地流转规模 | + | 土地流转面积占行政区域面积比例 | 0.497 | |||||||||
| 人均收支比 | + | 人均可支配收入/人均支出 | 0.164 | 乡城收支比之比 | + | (农村居民人均可支配收入/人均支出)/(城镇居民人均可支配收入/人均支出) | 0.377 | |||||||||
| 人均消费水平 | + | 区域社会消费品零售总额/常住人口(元/人) | 0.307 | 人口 互动 互融 | 乡城人口潜力差距 | - | 县域与市辖区每万人中义务教育阶段在校生数之比-1 | 0.104 | ||||||||
| 人口 发展 | 城镇化率 | + | 城镇常住人口/区域常住人口 | 0.341 | 从事第一产业人员比例 | - | 第一产业从业人员数/区域常住人口 | 0.233 | ||||||||
| 义务教育阶段学生数 | + | 中学和小学在校生数/区域常住人口(人/万人) | 0.218 | 第一产业从业人员人均产值效率 | + | 第一产业从业人员人均产值/人均GDP | 0.396 | |||||||||
| 高校学生比例 | + | 高校在校生数/区域常住人口 | 0.441 | 人口迁移率 | + | (常住人口-户籍人口)/户籍人口 | 0.267 | |||||||||
| 社会 发展 | 生师比 | - | 生师比/教育部规定生师比标准① | 0.102 | 社会 服务 均等 | 教育条件差距 | - | |县域与市辖区中小学生师比之比-1| | 0.191 | |||||||
| 床位数 | + | 医疗机构床位数/常住人口(张/万人) | 0.119 | 医疗条件差距 | - | |县域与市辖区每万人享有医疗机构床位数之比-1| | 0.305 | |||||||||
| 移动电话用户数 | + | 移动电话用户数/常住人口(户/百人) | 0.353 | 教育投入 | + | 人均公共教育支出 | 0.504 | |||||||||
| 互联网用户数 | 互联网用户数/常住人口(户/百人) | 0.425 | 空间 布局 有序 | 乡城人口密度差距③ | - | |乡村与建成区人口密度之比-1| | 0.411 | |||||||||
| 空间 发展 | 路网密度 | + | 区域内国道、省道、高速、铁路长度/区域面积(km/km2) | 0.357 | 耕地与建设用地变化速率比② | + | 0.283 | |||||||||
| 人口密度 | + | 单位土地面积上的常住人口(人/km2) | 0.268 | |||||||||||||
| 建成区占比③ | + | 建成区面积/区域总面积 | 0.375 | 耕地与建筑用地效率比 | + | (第一产业产值/耕地面积)/(二、三产业产值/建筑用地面积) | 0.306 | |||||||||
| 生态 发展 | 建成区绿化覆盖率 | + | 城市建成区的绿化覆盖面积占比 | 0.391 | 生态 环境 共享 | 乡城植被差距③ | - | |乡村与建成区NDVI之比-1| | 0.469 | |||||||
| 空气质量 | - | 单位土地面积PM2.5浓度 | 0.164 | 乡城空气质量差距③ | - | |乡村地区与建成区PM2.5之比-1| | 0.271 | |||||||||
| NDVI | + | 生长季区域NDVI均值 | 0.446 | 热岛效应③ | - | 建成区与乡村地区夏季平均温度之差 | 0.260 | |||||||||
注:① 根据中央编办发[2009]6号等相关文件,将县镇、农村中小学教职工编制标准统一到城市标准,即高中教职工与学生比为1∶12.5、初中为1∶13.5、小学为1∶19;② t1、t2 为研究初期与末期,以10年为一个研究周期,如当t2 = 2000年时,t1 = 1990年,以此类推;③ 此类指标计算范围基于建成区和乡村地区的空间区域划分。
(1)区域综合发展指数。衡量区域内部城乡融合发展程度,不能脱离区域发展的整体水平来单独看待,处于不同城镇化阶段时,城市和乡村地域系统间将存在对应不同发展阶段的互动联系与相互作用模式。城乡融合是城乡关系演化到高级阶段的产物。区域综合发展指数(RDI)旨在测度区域整体发展水平以评价该区域所处城镇化发展阶段,是判断城乡融合发展的前提。当处于城镇化发展前期时,区域综合发展水平较低,城乡差距虽小但其互动性较弱,城市与乡村尚未形成清晰界限与分化特征;而快速城镇化转型发展时期,城乡产业分工和经济活动进一步增强,城乡差距随着城市高速发展而不断扩大;随着城乡地域系统的要素、结构与功能的一系列演化与转型,城乡各部门的形态功能随之产生一系列冲突并在城乡要素动态交织下逐渐缓释达到新的平衡[43],而这一过程将助推乡村潜在发展活力与价值的显化,补齐城乡融合系统中的乡村短板,城乡差距不断缩小并最终促成区域城乡融合与协调一体发展,同时助推区域整体发展水平的进一步提升。因此,判断区域整体发展状态是把握城乡融合发展的前提,也是城乡地域系统能够实现互动互融的基础。其维度构成及内涵如下:① 经济发展:区域人均GDP、可支配收入、收支比和社会消费品零售总额可反映区域生产力和经济实力,并从收入水平与消费水平的综合作用下形成的财富剩余、资本累积与购买力水平反映区域整体的生活水平质量与发展潜力。② 人口发展:人口城镇化率反映了区域所处城镇化阶段,每万人义务教育阶段学生数及高校学生比例则可以衡量区域人口结构中未成年人比例与高素质人力资源储备状况。③ 社会发展:生师比以及每万人床位数、每百人移动电话用户数和每百人移动互联网用户数则反映区域基础设施配置水平与政府对公共产品的供给与投资,同时也是吸引劳动人口流动的重要拉力。④ 空间发展:区域人口密度用以表征空间人口聚集程度与人口分布结构,人口规模的聚集通常将伴随经济在空间的聚集从而形成一定的规模效应,推动地区的整体发展,也可以在一定程度上反映区域发展活力;建成区占比则可以反映城市空间扩展强度与变化,城市用地空间的有序化程度,从土地城镇化的角度透视区域发展水平与协调程度。⑤ 生态发展:生态环境是城乡地域系统其他功能存在发展和有序运行的基础与前提,是衡量区域发展是否可持续的重要指标。选取代表性的绿化覆盖率、植被指数与空气指数来衡量区域生态环境状况与宜居程度。
(2)城乡协调互融指数。城乡协调互融指数(RCI)涉及人口、土地、资本、城乡基础设施与服务等多种测度指标,从多个时间截面刻画了城乡地域系统中关键生产要素流动、聚集与发展状态,以及在要素联动作用下城乡地域系统结构与功能的演化状态,意图衡量区域城乡生活质量、公共服务等多维发展状态差距,更旨在通过城乡内外部要素与资源配置情况反映出城乡系统连通性与流动性及其对促进提升城乡融合发展作用的驱动潜力。同时,为与RDI评价层形成参照与横向对比,同样基于经济、人口、社会、空间、生态5个维度进行构建,各维度内涵如下:① 经济协调共进:城乡融合发展的目标包括实现城乡的回报趋同等值发展,可显化为城乡的劳动生产率、土地价值和劳动力回报的趋同[25]。因此,乡城收入比与收支比之比可以从一定程度上刻画城乡收入差距以及城乡居民财富剩余与资本累计的差距,从而侧面反映城乡发展潜力与相对发展速率;耕地与建筑用地的产值效率及第一产业从业人员劳动生产率则在一定程度上反映城乡人地要素的生产与利用效率的差距,从而衡量城乡人口、土地要素配置效率与回报趋同的程度;② 人口互动互融:通过从业结构、产业劳动力效率及受教育水平可反映出城乡从业结构、人口素质与人力资本差距,以及城乡人口劳动收入与回报差距,根据刘易斯定理可推测城乡人口潜在流动趋向;③ 社会服务均等:教育医疗等公共服务和基础设施的配比分布,反映了城乡居民在社会公共服务福利保障与基础设施享有的差异,是影响城乡人口流动与资源配置的主要因素;④ 空间布局合理:要素在城乡空间的分布与配置将影响城乡空间结构体系与城乡之间互通互连效率及作用,人、土地与交通网络作为要素流动与相互作用的媒介,也是城乡融合发展的驱动因子。城乡人口和路网密度比反映城乡人口分布结构以及城乡空间双向流通的便捷及频繁程度差距,耕地和建设用地变化率则从数量结构角度反映城乡土地利用转型的演变幅度与用地的配置利用差距;⑤ 生态环境共享:生态环境的发展已经成为人口迁移、生产和投资活动等城乡资源配置活动的重要考量因素之一。考虑对居民生活影响的关键环境要素并综合城乡地区数据的可获得性,选取代表性的城乡植被指数、空气污染指数及热环境差距指标来衡量城乡生态环境宜居水平,可表征城乡生态环境协同治理的发展态势。
3 研究数据与方法
3.1 数据来源
本文选择中国336个地级单元作为研究对象(除海南省三沙市外,包括4个直辖市和332个地级市(地区)或自治州、盟以及省直辖单位,因数据的可得性,暂未含港澳台地区)。研究年份为2000年、2010年和2018年。社会经济数据主要来自对应年份的《中国城市统计年鉴》《中国城市建设统计年鉴》《中国县域统计年鉴》以及各省(自治区、直辖市)统计年鉴和公报,极少数地市的个别缺失指标采用邻近年份插值法进行填补。同时,为减少价格变动指数的影响,以2000年为基期,对2010年和2018年的经济数据采用GDP平减指数进行折算。1 km生长季NDVI、30 m土地利用数据、路网数据等基础自然地理数据来源于中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心;PM2.5浓度数据来源于达尔豪斯大学大气成分分析组(V4.GL.02),其数据在中国地区的精度和普适性已得到充分验证[44]。进一步为了消除波动等外界因素影响,将研究时期作为中间年份对PM2.5和NDVI原始数据取3年的平均值以保证研究数据的平稳性。夜间灯光数据来自常用两套夜间灯光数据(DMSP-OLS和NPP-VIIRS)经校正合成的全球500 m类NPP-VIIRS夜间灯光数据集。人口密度数据来自美国能源部橡树岭国家实验室,是最为常用的全球1 km分辨率人口分布动态统计数据集。
3.2 数据处理及分析方法
由于现有长时间跨度的城镇和乡村社会经济统计数据无法满足本文的研究需要,考虑到市辖区内乡村空间范围较小,乡村人口和农业经济活动较少,因此将市辖区近似于城镇地区;县域相对市辖区而言包含的乡村范围较大,从而将县域或县级市近似为乡村地区以便开展后续定量评价与分析研究。土地利用等空间数据的处理单元基于栅格尺度,对建成区与乡村地区进行提取勾画,其具体步骤如下[45]:利用30 m分辨率的土地利用数据,用4 m×4 m的格网将其重采样,提取每个连续格网单元中建筑用地占比超过75%的地区,视为该区域的建成区,其余部分为乡村地区。
为消除量纲及数据级的差异,本文首先对数据进行标准化处理,对于能够通过数据本身增长或减少来反映指数趋于优化或退化的指标分别赋予正指标和负指标属性,继而采取极差法进行标准化处理。同时,因文中的指标体系涉及指标数量较多,时间跨度较大,为避免主观赋权所产生的偏差,本文采用熵值法对各指标的权重系数进行测算,通过加权求和计算得到各维度得分,进一步考虑到各维度存在一定相关性,而采用多边形面积法[46]对经济、人口、社会、空间和生态各子维度进行计算得到RDI和RCI。
进一步,为刻画城乡融合发展的时空动态分异格局以及识别问题区域,对城乡融合发展类型的分类进行划定:采用标准差法,以平均值(mean)为参照,1个标准差(std)为间隔,将3个年份的区域综合发展指数及城乡协调互融指数划分为低值区(小于mean-0.5std)、中值区(mean±0.5std)、较高值区(mean+(0.5~1.5std))和高值区(大于mean+1.5std)4个等级,以保证不同时段的评价指标和分类标准具有可比性。基于此,将RDI(x)与RCI(y)的4个等级“高”“较高”“中”“低”按照由高到低的次序赋予属性值1~4,属性值越大,对应的该维度发展程度越低,在此基础上进行两两耦合得到16种“区域发展—城乡互融”属性特征组合,进一步根据两类指数高低所反映的融合状态与融合动力水平特征对其进行组合归并,最终得到4种耦合类型,分别为“高发展—高融合”的融合发展型,“高发展—低融合”的融合失调型,“中发展—中融合”的趋向融合型以及“低发展—低融合”的融合滞后型(表2)。
表2 城乡融合发展类型划分标准
Tab. 2
| 类型 | 耦合结果 | 特征 |
|---|---|---|
| 融合发展型 | (1, 1) (1, 2) (2, 1) (2, 2) | “高发展—高融合”,城镇化发展步入中后期,城乡经济、社会、空间、生态环境等方面基本协调,融合动力较高 |
| 趋向融合型 | (3, 1) (3, 2) (3, 3) | “中发展—中融合”,城乡差距逐步缩小,存在进一步融合潜力 |
| 融合失调型 | (1, 3) (1, 4) (2, 3) (2, 4) (3, 4) | “高发展—低融合”,快速城镇化发展同时差距明显,融合动力不足 |
| 融合滞后型 | (4, 1) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 4) | “低发展—低融合”,城镇化发展相对滞后,城乡联系和互动较弱,尚未达到融合发展阶段 |
4 结果与分析
4.1 整体时空分布格局
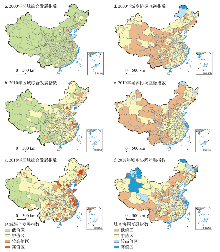
自2000年来中国城市的区域综合发展(RDI)与城乡协调互融(RCI)指数均呈提升态势,整体呈现东部高中西低的空间分布格局(图1);但城乡协调互融指数时空分布具有明显的空间分异特征,且整体增长程度略低于区域综合发展指数。随着生产力的提高与社会经济的发展,RDI整体提升,低值水平地市数量从80.65%下降至27.98%,范围逐渐缩减至“胡焕庸线”以西地区。随着西部大开发以及扶贫开发战略的推进,2018年低RDI的地市数缩减至4.76%,呈面状聚集于青藏地区、南疆三地州以及陇南地区。中RDI地市数量则呈现先上升后持平的变化趋势,由东部沿海发达地区的省会地市或中心城市逐步辐射至其周边地区并逐渐向中西部地区扩散。高值和较高RDI地市显著增加,比例从2000年不足1%逐渐提升至约40%,多数带状聚集于东部沿海地区,并呈团块状分布于珠三角、哈长、辽中南以及中原城市群区,零散位于西部省会及其周边地市。相比而言,RCI的整体提升态势中存在局部衰退与回升,分化出明显的空间聚集分布特征,呈现西北和东部地区的城乡发展趋于协调、互动作用逐渐增强,而“胡焕庸线”沿线及西南地区城乡差距及分化格局趋向固化的空间分布特征。2000—2018年低RCI城市占比逐步降低,由30.36%降至21.13%,主要位于一二级阶梯地区,沿“胡焕庸线”呈带状聚集于内蒙古东部和黄土高原地区,以及藏南地区、横断山脉到滇桂一线,呈倒“T”型分布;新疆、内蒙古西部及四川盆地大部分地市RCI逐渐提升。中RCI地市数量占比约56%,主要分布于新疆至内蒙西部以及华中与华南地带。较高及高RCI地市数量持续提升,占比从7.14%逐渐提升至22.62%。此类地市初期分别聚集于以深圳为中心的珠三角核心城市区,以上海、南京为核心的苏南地区,并零星分布于苏北、鲁南和黑龙江北部部分地市。随着社会经济转型,以长三角地区为辐射中心,城乡协调互融趋势逐渐增强,并向苏北、山东及浙北地区逐步辐射扩散。与之相比,珠三角地区的辐射带动效应较为有限,高RCI地市仍集中于深圳、东莞一带地市。同时,随着政策优惠向西部和中部地区倾斜,城乡发展要素逐步由东南沿海向内陆和西部流动汇集,较高及高RCI地市逐渐在北方及西部地区呈现增长趋势,散见于渤海湾地区、中原、长江中游、成渝城市群区以及新疆北部地市。
图1
图1
2000年、2010年和2018年中国城乡融合发展的时空分布格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2016)2882号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 1
Spatio-temporal pattern of urban-rural integrated development
4.2 城乡融合发展类型格局分布
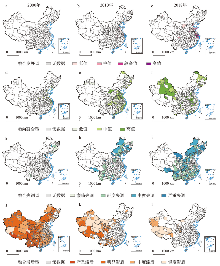
图2
图2
2000—2018年中国城乡融合发展类型转化图
Fig. 2
Transformation of urban-rural integrated development types during 2000-2018
图3
图3
2000—2018年中国不同城乡融合发展类型的时空分布格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2016)2882号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 3
Spatio-temporal pattern of different types of urban-rural integrated development during 2000-2018
(1)融合失调型:2000年乡村发展远落后于区域发展进程而呈现城乡失调发展的地市数量较少,仅有15个。按其成因可以分为两类,其中,一类成团聚集于东北哈长城市群区,该区域工业化与城镇化发端较早,城镇人口和以重工业为主的产业聚集使城市地区有着较好的社会经济基础,但20世纪90年代以来地区发展的持续放缓,结构性矛盾突出,致使区域差距与城乡差距明显扩大而呈现发展失调态势;另一类失调型地市则主要为区域中心城市或省会地市,如北京、南京、昆明、攀枝花等。2000—2010年融合滞后型地市向失调型转化现象较为普遍,集中分布于“胡焕庸线”两侧,如内蒙东北部、华北北部、山西中部、四川中部及滇桂地区,这些地市或对资源具有较强依赖性或自然条件恶劣,产业基础薄弱,创新能力和利用效率较低,对乡村地区的扩散效应及可持续发展动力不足;同时发展过程中对资源禀赋的过度开发进一步对乡村产生掣肘,导致城乡发展愈加不平衡。另一方面,区域中心或省会城市的失调型数量增加,如北京、天津、杭州、合肥、西安、兰州、乌鲁木齐等,这类地市虹吸作用过强而辐射效应不足导致乡村及周边地区劳动力、资金与产业的大幅流失与转移,甚至产生负向溢出效应如环境破坏、空心化等社会问题,导致城乡差距进一步增大,城乡失调态势严重;同时因体制机制尚未健全,转移人口与产业的融入存在壁垒,融合障碍明显。到2018年,城乡失调态势恶化明显的地市增加至181个,多分布于西南、长江—黄河中上游以及长江以南地区;尤其是珠三角核心城市的外围地带,环绕着以江门、肇庆为代表的发展失调型城市,形成与长三角地区高高融合聚集不同的分异格局,可能由于区位、资源与政策背景等因素作用下,深圳、东莞等核心城市存在巨大的虹吸效应,同时低成本导向使其外围城市多承接高能耗或劳动密集型产业的转移,土地开发利用方式粗放、效率低下,人口、基础设施及公共服务等未能与经济要素实现同步聚集,城乡要素流动不畅,产业发展乏力,致使区域与城乡失衡现象日益加重。
(2)融合发展及趋向融合型:2000—2018年城乡呈现融合发展态势的地市数量显著增加,整体趋向良好发展。2000年达到融合发展的地市仅有2个,分别为深圳和广州市,趋向融合型地市69个,集中分布于珠三角、闽西、长江—黄河中下游地区以及环渤海地区,其中,珠三角与长三角地区的融合发展指数相对较高,得益于历史积累以及对外开放的优惠政策,加强了城乡互动与联系,带动了乡镇就地城市化;中部地区乡村主要依托传统农业生产,乡镇企业发展较慢,因而融合程度相对较低。随着快速工业化、城镇化及全球化进程的加快,加之相关政策的推动,2010年融合发展型增长至38个,集中分布于长三角、珠三角、闽西地区,约占70%,其区内融合发展指数显著高于其他区域同类型地市,如上海、无锡、南京、深圳、厦门、泉州等,均处于融合发展阶段前列;中西部地区融合发展程度较高的地市区域包含武汉、长沙、成渝和天山北坡城市群,区位优势、交通便利及政策支持使其具有一定发展基础,城乡转型发展早于区域内其他地区,但与东部地区的政策倾斜力度等优势相比,其发展速度与带动水平相对较弱。2018年融合发展型进一步增加至65个,其中约半数以上呈面状分布于山东、江苏以及浙北,并在长三角和珠三角城市群形成典型高值聚集地带,其余则散布于中原城市群和武汉城市圈;东北和西部地区仅鄂尔多斯、成都和克拉玛依等发展至融合发展状态。相比而言,2000—2018年趋向融合型地市数量减少至73个,各类型之间相互转化较为活跃,提升型主要分布于东部沿海地区,新增型主要集中于甘肃、新疆、青海、四川和贵州等省份,仍保持趋向融合态势的地市主要分布于河南南部、湖北东部与黑龙江北部。
(3)融合滞后型:2000—2018年融合滞后区域缩减明显,从2000年的250个降至2018年的17个地市,滞后型呈现出数量下降、质量提升特征的同时,其空间分异特征进一步强化,东中西部区域差距逐步拉大。2000年,除东北、东部和南部沿海地区以及少数省会或中心城市外,绝大部分区域处于发展相对滞后阶段,比例约占74.40%。此后,随着城镇化的迅速推进,至2010年,“胡焕庸线”以东地区基本已经脱离“低发展—低融合”特征主导的发展滞后阶段,区域的综合实力与城乡互动联系都得到一定程度的提升与改善,融合滞后的地市仅零星分布于黑龙江、山西、陕西、湖南等省份;“胡焕庸线”以西地区则未完全扭转融合滞后的格局,在快速增长背景下区域间差距进一步强化,尤其在黄土高原、西藏及西南地区等与高贫困发生率存在一定重叠的区域,直至2018年仍滞后于中国整体城乡融合发展进程。
4.3 城乡融合分维特征的时空演化格局
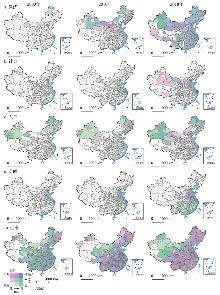
2000—2018年城乡经济融合趋势逐渐增强(图4a)。初期,除东南沿海开放城市外,约90%的地市尚处于城乡经济缓步发展阶段,呈现城乡经济“低发展—低互动”的滞后融合特征。随后在城镇化、工业化及全球化迅猛发展的推动下,以及国家对“三农”问题重视程度的增加,多数地区的城乡经济呈现差距缩小、融合水平提升态势,协调互融指数增加,并以长三角地区的融合水平最为显著,仅在青藏高原、南疆地三州、甘南及云贵地带仍存在少数地市处于城乡经济滞后阶段。
图4
图4
2000—2018年中国城乡融合发展分维属性的时空分布格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2016)2882号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 4
Spatio-temporal pattern of urban-rural integrated development at multi-dimensions during 2000-2018
相比而言,中国城乡社会融合相对缓慢,城乡社会发展差距扩大的现象普遍存在,并具有明显的地带阶梯性及区域内部城市等级分异特征(图4b)。黄淮海与东南沿海地区一直是城乡社会融合高值区,具有较小的城乡差距,同时珠三角和长三角地区的社会融合状态始终处于前列,并形成明显的高值聚集区;而中国第一和第二级阶梯以及东北地区则一直处于城乡社会发展失衡局面。同时,相比于中西部,东部区域特大城市如北京、上海、南京、杭州等地市的城乡社会发展差距要略大于其周边中小城市,这可能与快速城镇化时期乡村以及全国劳动力的持续流入,城市社会公共服务设施配备的增长水平无法匹配转移人口的增长有关,并且优质社会公共资源在城区过于集中也导致城乡社会资源的享有不平等性问题日益尖锐。相比而言,处于相对发达区域腹地的中小城市吸纳人口的潜力尚未充分发掘,因而其城乡社会功能发展不均的问题相对缓和。
中国城乡人口融合演进格局也呈现明显的区域分异特征(图4c),以苏南为主的长三角地区以及东北由于历史因素,人口城镇化程度较高,有着较好的人口融合基础,并随着长三角经济社会水平的提升及户籍政策的不断改革,人口吸纳转化能力逐步提升,进一步促进了城乡人口的互动交流,因此城乡人口融合水平较高;相对而言,中部地区省会或大中城市则由于其经济社会转型与制度供给未能匹配虹吸效应带来的流入人口,多数呈现城乡人口逐渐失衡的发展特征,并与其周边城市形成了分异明显的“失衡—滞后”分布格局。同时,得益于近年来扶贫攻坚力度的加大、西部地区乡村人口结构、素质、自身发展得到明显改善,乡村人口得到更多发展机会,使乡村与城市人口发展的差距逐渐弥补,西北地区的城乡人口趋向互动协调发展,但青藏及西南边陲地区的人口融合过程仍较为缓慢。
城乡空间融合发展在一定程度上会受到地形、植被等地理环境因素的限制,相对经济、社会等其他维度的快速发展,整体水平较低,提升程度相对平缓并存在显著的沿一二三级阶梯梯度递增的空间分异格局(图4d)。地势平坦的平原地区,如黄淮海平原南部、京津唐、珠三角与长三角地区,城乡空间融合起步较早,发展相对迅速。但随着扶贫攻坚与一带一路战略的推进,中央对西部地区基础设施建设的投资增加与政策倾斜,川桂滇黔新大部分城市及城乡间的可达性得到了大幅提升,逐步摆脱贫困锁定效应。
2000—2018年城乡生态环境发展指数在一定时期内呈现总体趋于好转但局部恶化与提升并存的空间分异格局(图4e)。受地理条件、自然气候限制,西部地区气候恶劣,生态承载力较低,生态环境脆弱,其区域生态发展处于低值水平。但随着一系列重点生态保护工程的实施,对地区植被恢复、生态建设起到了一定促进。黄土高原、农牧交错带等区域的生态环境指数呈现不断提升的发展态势。而人口的不断增长导致以城市扩张为特征的土地城镇化加剧并从东南沿海地区、大中城市逐渐向中西部地区、小城镇蔓延[47],致使生态空间不断萎缩;加之城市高能耗、高污染产业也逐渐由发达地区向其郊区及周边中小城市转移,使得城乡生态失衡态势进一步恶化,尤其在人口密集和高度城镇化的中部及东部地区。但得益于生态文明建设要求和可持续发展战略的提出,发达地区对于生态治理和环境保护投入增多,城市污染与乡村人居环境得到一定改善,长三角中心地市、苏北、鲁中地区城乡生态环境融合相对协调;人口分布相对稀疏地区如内蒙古中部以及三江源等地区城乡生态环境差距也相对较小。
4.4 不同城乡融合发展区域的差异化发展建议
中国城乡融合发展整体处于中低水平,不同城乡融合发展类型以及同种类型地市的演化水平、方向及制约因素是不同地理环境、资源禀赋、发展政策等内源外缘因素耦合过程作用的映射,存在明显的地域性差异,从而使其吸引、接收和转化各自城乡生产要素的能力存在差别[48],因此有必要针对不同类型区域,提炼多样化融合发展路径,识别问题区域及其制约因素,并据此提出对应的优化调控措施。
(1)提升区域优化路径。提升区域主要由融合发展型和趋向融合型地市构成,约占整体地市数量的40%,其中,融合发展型集中分布于珠三角及以长三角为中心的东部沿海地区,趋向融合型城市主要分布于华中、新疆、东北城市群区。
未来融合发展型地市首先应注重加强耕地资源及生态环境的保护,确保国土空间开发有序合理;同时推进农村土地制度、社会保障制度和户籍制度改革的多项体制机制协同联动,以实现城市资本要素与乡村土地要素的快速高效结合,为乡村产业化提供资本渠道,实现城乡经济、产业融合;加快城郊及乡镇轨道交通信息网络体系一体化建设,推进城乡基本公共服务均等化高效化;探索创新乡村发展模式,培育兼具生产、游憩、教育、康养、生态为一体的现代农业、休闲旅游、田园社区综合体[52],吸引人口向乡村流动转移。空间布局上,优化城乡空间布局,培育经济聚集带与增长极,发挥中心城市对周边沿线小城镇和乡村地区的辐射带动作用,逐步形成布局合理、联系密切的要素资源流通机制,加强城市间协调联动,推进城乡互促互动,实现融合发展。
趋向融合型城市多由滞后融合或融合失调型逐步改善形成,应控制城镇建设用地规模及城镇空间的扩张,注重耕地保护与生态维护,加强对中小城镇及乡村地区的关注,提升发展的平衡与协调性,防止回落。通过户籍制度、就业机制及社会公共服务保障机制的完善以及财政倾斜等措施对重点城市腹地及周边中小城市、小城镇、县域等在资金、产业、基础设施等方面给予延伸和扶持,完善城乡交通网络体系以促进城乡要素联通流动,引导人口、资源要素在空间上的适度聚集;尤其对于西部和东北地区,注重农业、生态、能源等特色优势产业驱动作用,在集约集群发展基础上,规划建设村镇体系,合理化乡村布局及功能,改善乡村人居环境和基础设施,加大乡村基础公共服务投入,持续改善乡村民生;充分利用区位优势以及“中部崛起”等战略扶持,结合自身资源禀赋,在区内自然资源合理开发利用前提下,加快产业结构转型升级和新兴产业发展,构建高质量发展的产业集群,提升城市区域的辐射带动水平,缩小城乡差距,促进城乡融合。
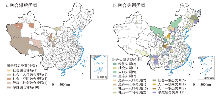
(2)问题区域识别及建议。基于分类结果,将严重和中度融合失调以及融合滞后类型区域作为典型问题区域,并结合分维融合特征,将任意3种及以上维度存在融合失调/滞后的地市定义为多维融合失调/滞后,少于3种维度根据其制约因素进行界定,识别问题区域及其空间分布(图5)。
图5
图5
中国城乡融合发展问题区域识别及其空间分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2016)2882号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 5
The type and pattern of problem regions of urban-rural integrated development
融合失调型数量近年来增加明显,其中严重和中度失调型主要集中于东北、内蒙古及华北平原北部、黄土高原、藏南至横断山区一带,空间分异性明显,制约因素复杂。① 东北区有着较好的城镇化和农业机械化基础,但以资源型产业和重工业为主的发展路径依赖长期制约着东北地区的经济社会转型发展,致使城乡发展内生动力缺失,经济活力不足,开放程度偏低,城乡融合失调态势愈加严峻。未来东北地区的城乡融合发展应注重依托工业基础推动产业结构转型,增加小城镇竞争力。在乡村地区,逐步推进土地制度改革,完善土地流转制度,充分发挥土地增值效用,避免土地的闲置浪费;依托基本农田保护条例、黑土地保护条例等政策,完善耕地生态保护补偿机制,注重农业技术知识和环保意识的普及;利用独特冰雪景观等自然资源以及特有的大规模机械化种植等人文乡土景观资源,开展乡村生态旅游观光,丰富乡村经济业态,提升农业综合发展及可持续发展能力。② 内蒙及华北平原北部地区具有相对较高的城镇化率,但长期资源开发导向下,其经济社会发展与水资源及生态环境的矛盾日益加剧[49-50],中小城市、小城镇建设落后,缺乏城乡融合发展空间载体,导致区域发展不均衡不稳定。未来应完善城镇体系结构,提高城乡建设用地的集约化程度;优化产业内部结构及空间布局,促进能源资源的合理开发利用,加快产业链条的升级、延伸和优化。对于乡村农业发展而言,需在生态保育基础上,优化种植业结构,延长产业链和发展精深加工业,推进现代种养殖业、草牧业、生态农业、草原旅游业等特色产业的发展[50];并在保护具有草原特色的乡村景观的同时改善人居环境,将公共服务及社会福利保障向农区、牧区适度倾斜,缩小城乡差距。③ 黄土高原区是典型的生态脆弱区[51],不合理、高强度的城镇化开发利用叠加脆弱的生态系统条件与资源枯竭、气候变化挑战将会致使人地关系日趋紧张[52]。未来在遵循承载力及生态保育前提,依托现代地理工程技术手段,进行区域生态环境综合治理保护与资源环境要素系统整治的同时,提升耕地质量与潜能[53],改善农业生产条件,优化农业生产结构,推进一二三产融合,并向特色化、绿色化及生态化转型,探索生态产业化与产业生态化发展路径[54];同时,加强乡村地区人才培育,提升乡村主体内生发展动力,吸纳城乡多元主体参与乡村振兴建设。④ 藏南至横断山区受地形及交通条件约束,耕地资源较贫瘠,机械化和规模化难以推广,城乡发展基础薄弱,乡村发展深受贫困化、老弱化、内生动力发展不足等因素困扰[50,55]。未来该区可通过政府引导与政策扶持,鼓励土地适度流转和规模经营以培育多种农业经营主体,基于特色农业资源创新发展特色农产品及加工等特色生态农业,依托其区内乡村自然景观及特有民族乡土文化,延伸产业链条,发展特色乡村旅游业及相关多元农业生产体系,结合电商等互联网经济促进城乡及外界市场的流通;同时应在生态环境承载力基础上,依托人口、交通区位、资源要素及产业基础较好的中心村、重点乡镇及中小城市为辐射中心[56],通过交通路网等基础设施建设、土地整治、村镇体系规划、公共服务均等化、产业培育等措施促进就地城镇化以推动城乡融合与乡村振兴[57]。
融合滞后型主要集中于甘南、南疆三地州、青藏高原地区等西部欠发达地区,地形起伏、气候恶劣、生态环境脆弱等因素是长期制约此类地市发展的客观自然要素,从而导致城乡基础建设薄弱,社会经济文化发展相对迟缓并与其他区域存在较大差距,普遍处于工业化和城镇化早、中期阶段,因而城乡融合发展进程滞后于全国整体水平。未来该区应结合当地发展条件及规律,依托国家减贫政策、“一带一路”倡议等以及自身资源能源优势,通过产业援疆、援藏等政策扶持,承接中东部地区劳动密集型产业转移,促进人口、生产要素等资源的流动集中,从而推动小城镇建设与大中小城市相互协调发展的城镇格局体系构建[48]。农业方面,青藏高原区以河谷农业和畜牧为主,南疆三地州则以绿洲农业为主兼顾畜牧业[58],注重对原有自然生态系统原始性、独特性和多样性维护的同时,进一步挖掘自然生态和乡土民族文化底蕴,改善农牧业生产条件,加快高原特色农牧业产业发展,培育高原特色农牧业品牌体系;创新发展多种经营模式及新型经营主体,通过产业园区、设施农业、特色农业、专业合作社和农户相结合等方式[59],为当地文化和技能相对欠缺的乡村和少数民族劳动力提供生计资本和就业途径的倾斜,促进农业、兼业和非农转移等多种生计方式转型发展,在巩固脱贫攻坚的同时促进城乡融合发展。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
本文从城乡融合发展的概念内涵出发,在市域尺度上基于经济、社会、人口、空间和生态5个维度构建了城乡融合发展耦合评价体系以测度2000—2018年中国市域城乡融合发展的演化过程及阶段特征规律,结果表明:
(1)2000—2018年中国城乡融合发展的程度呈现沿一二三级阶梯地势递增的空间分布格局,其中,东部沿海地区、东北地区和新疆北部地区整体融合水平较高,城乡发展融合态势良好的地市主要集中于珠三角、江浙及山东半岛,融合较为迟缓地区主要位于“胡焕庸线”以西,严重滞后型地市呈面状聚集分布于青藏高原西南部及陇南地区。
(2)进一步将336个市(州)划分为4种城乡融合发展类型,融合滞后型地市缩减明显,但黄土高原、西藏和西南地区呈现显著低值锁定效应;融合失调型增加显著且多由融合滞后型转化形成,主要集聚于“胡焕庸线”两侧地区;趋向融合和融合发展型主要分布于“胡焕庸线”以东地区,东部沿海地区如苏南、浙北和渤海湾地区多呈现融合发展协调共进态势,城乡融合发展程度进一步加深;辽中南及长江中上游、江西及闽西地区城乡差距则逐渐拉大,由趋向融合型衰退为融合失调型。
(3)各维度城乡融合程度存在分异性,城乡经济融合>人口融合>社会融合进程,城乡空间与生态融合发展进程呈现出一定自然地带性特征。
5.2 讨论
本文综合评价了中国城乡融合发展水平,揭示了当前市域尺度下城乡融合的空间格局和区域差异,以希为因地制宜、分区分类推进城乡融合发展提供科学参考,拓展现有城乡融合发展测度评价的定量研究。然而需明确城乡融合发展是一个涉及多维度多层面的复杂动态过程,城乡地域系统的要素、结构与功能在不同发展阶段、空间尺度下具有不同的特征、分布、耦合状态与演化机制。本文在对城乡融合发展宏观整体时空格局与演化过程分析研究中,囿于数据获取与时序问题,研究采用遥感数据提取城市和乡村区域在城乡空间内部土地利用混杂转变剧烈的过渡地带难免存在一定误差,指标体系中城乡功能分工协调以及反映城乡文化、行政治理等非实体要素指标的纳入相对不足,这些都会在一定程度上影响着研究结果的精度,对部分指标评价结果可能存在影响,也是本文需要进一步深化的方向。未来的研究中,需探索挖掘关键指标获取或探寻其他相关代替性指标的方法,如借助手机信令、交通出行等大数据与人工智能数据提取、人地观测网络、站点数据和问卷调查等多源数据,突破统计年鉴数据和行政区划单元边界的限制,借助机器学习、复杂人地系统时空统计模型、大数据分析模型的融合开发与应用,从更精细的空间格网或斑块粒度对城乡内部空间演变特征进行定量刻画与分析,进而全面、系统、科学地揭示城乡融合发展的动态过程与时空分异规律,丰富城乡融合发展的“过程—格局”研究范式,支撑城乡融合发展与乡村振兴战略的实施。
参考文献
Research progress of urban-rural relations and its implications for rural revitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 1]

With the implementation of rural vitalization strategy, China has stepped into a critical period with the dramatic changes of urban-rural relations and the accelerating transformation development of rural territorial system. Scientifically understanding the research progress of urban-rural relation theory and evolution rule is of great significance for boosting rural vitalization, narrowing urban-rural disparity, adjusting urban-rural structure and optimizing urban-rural patterns. This paper elaborates the research progress of urban-rural relations and rural development in China from the dimensions of economy, society, ecology and culture based on the review of foreign urban-rural relations and the characteristics of domestic rural development, as well as the evolution of urban-rural relation. Furthermore, prospect of research focus or key fields in the future were given. Firstly, transforming the development idea from productivism oriented to post-productivism oriented and attaching importance to the multiple values of rural areas should be emphasized. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out intensive studies about the mechanism, regional path selection and development mode of rural vitalization based on the theory of rural multiple function transition. Understanding the relationship of different functions is essential for dealing with rural decline and realizing the comprehensive vitalization. Meanwhile, we should focus on the mechanism and format of rural vitalization based on different territorial types. Against the context of rural-urban integrated development, we should promote the supply-side reform and activate the forces of socio-economic growth in underdeveloped areas. As for the developed rural areas, the “hybridity” should be emphasized and further studies should be conducted. In some rural areas, the phenomenon of the hybridity of development agents, the combination of production space and living space, the mixture of rurality and modernism have emerged. Accordingly, more emphasis should be placed on the heterogeneity and diversity in the process of rural restructuring. Secondly, with the emergence of new factors or new technologies, we should focus on the new morphology of rural development, such as characteristic towns, rural complex and “Taobao village”. In recent years, China's rural areas have undergone intensive restructuring motivated by e-commerce, which has triggered a new wave of rural rejuvenation. But how e-commerce affects rural development and the characteristics of this process are still unclear, and this is important for understanding the urban-rural relations under the context of informatization. Thirdly, the mechanism and format of urban-rural spatial restructuring should be emphasized. From the perspective of urban-rural interaction, the theory of urban-rural network may be practical and meaningful for optimizing the spatial distribution of infrastructure construction and industrial development. Lastly, creating or improving the theory and improving the path of rural vitalization according to the national conditions are meaningful for realizing the strategy.
城乡关系研究进展及其对乡村振兴的启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180880
[本文引用: 1]

随着乡村振兴战略的实施,我国已经进入城乡关系变革及乡村发展快速转型的关键时期。科学认知国内外城乡关系理论发展和演变规律对实施乡村振兴战略、缩小城乡差距、调整城乡结构和优化城乡格局具有重要意义。本文在系统梳理国外城乡关系理论及我国乡村发展与城乡关系演进的阶段性特征的基础上,从经济、社会、生态及文化的视角阐述了我国乡村发展与城乡关系研究的相关进展,并在此基础上探讨了未来重点的研究领域和方向。乡村发展思维应由生产主义导向转向后生产主义,关注乡村多元价值,深化基于乡村多功能转型理论的乡村振兴机制、区域路径与模式研究;在科技迅速发展,新事物新因素大量涌现的新时代,应关注特色小镇、田园综合体、民宿及乡村电子商务等新兴乡村转型发展形态的形成机制;同时,基于不同地域类型的乡村振兴的机制与模式研究也应得到重视,结合国际乡村地理学前沿,深入开展发达地区乡村的混杂性研究。广泛的城乡空间重构进程对乡村地区产生剧烈的影响与挑战,对于乡村振兴视角下城乡空间重构的动力机制与模式的研究仍需持续关注;根据我国的特殊国情,创新适合我国基本国情与发展实际的乡村振兴理论与实现路径,推动城乡融合发展。
China's rural revitalization and development: Theory, technology and management
DOI:10.1007/s11442-020-1819-3 [本文引用: 1]
Urbanization rate and its policy implications: Discussion and development of Northam's curve
DOI:10.11821/yj2011080015
[本文引用: 1]

Northam's curve of urbanization shaping "S" is one of the most important classical theories in urban geography. For common misreading about Northam's curve, this paper compiled original theory contents. The results indicated that the urbanization level can not reach 100% in all the countries; and the urbanization process between 30% and 70% is not always in a state of acceleration. Urbanization rate curve was put forward, which is shaped by an inverted "U". The evolution of urbanization rate was identified into four stages: embryonic stage, acceleration stage, deceleration stage, approaches zero stage. In different stages the changes have different characteristics. There are five important inspirations for policies: first, the urbanization rate of change has its laws, and cannot pluck up a crop to help it grow; second, China has crossed the turning point, "accelerated urbanization" should not be the main theme of the national long-term development strategy; third, China should maintain the steady development orientation for urbanization; fourth, China's urban concept and focus should be in transition; fifth, urbanization, inclusive growth, coordinating urban-rural development, as well as migrant labors becoming city and town dwellers are the primary targets during "the 12th Five-Year Plan" period.
城市化速度曲线及其政策启示: 对诺瑟姆曲线的讨论与发展
The spatial characteristics and formation mechanism of the county urbanization in China
DOI:10.11821/xb201208001
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial and temporal characteristics and the formation mechanism of the county urbanization in China since 1990 were analyzed systematically, using the methods including regional differences, transect and geography detectors. Results show that the temporal and spatial differences of the county urbanization were significant. The "herringbone" shape region pattern of high county urbanization was gradually highlighted, which were made by the counties along the north border and in eastern coastal areas. The county urbanization process of some regions were accelerated and enhanced, including Wuhan metropolitan region, Chengdu-Chongqing region and Guanzhong-Tianshui region. The low county urbanization level was maintained in Southwest China and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau regions. The differences of urbanization and the change rate of county urbanization were converged in China after 2000, but the rate has slowed down since 2000. The county urbanization trend of transects were significantly different, including Lianyungang-Lanzhou railway and Lanzhou-Urumqi railway transects, the Yangtze River transect, the border of north China transect, 106 National Road transect, and the eastern coastal transect. There are many factors affecting county urbanization, mainly including economic development stage, the level of secondary and tertiary industries, rural net income per capita, population density, leading position of grain production, demographic statistics and special arrangements for counties. The high county urbanization in northern border regions was a typical type of statistical unrealistically high urbanization. In the future county urbanization development should follow the geographical differences, highlight its leading function, and adopt multiple urbanization development models such as promoting urbanization intensively in key urban economic development areas, separating urbanization in cropland and grain producing areas, migrating urbanization in ecological and water resource protection areas, suburban areas and urban-based urbanization and other leading county urbanization patterns.
中国县域城镇化的空间特征与形成机理
DOI:10.11821/xb201208001
[本文引用: 1]

本文综合运用样带、地统计、地理探测器等多种研究方法, 分析了1990 年以来中国县域城镇化的时空特征及形成机理。研究表明:①中国县域城镇化水平时空动态的差异特征显著, 北方边境县域高城镇化和东部沿海县域高城镇化形成的“人字形”空间形态逐渐凸显;以武汉都市圈为中心的两湖地区、成渝地区、关中—天水经济区的县域城镇化水平提升较快, 西南地区、青藏高原地区保持较低的城镇化水平;②2000 年以来中国县域城镇化水平及其变化速度的区域差异逐渐缩小, 陇海兰新线、长江沿线、北方边境、106 国道、东部沿海样带县域城镇化差异明显;县域经济发展阶段、固定资产投资、离中心城市距离、二三产业水平、农民人均纯收入、人口密度是影响县域城镇化空间分异的主要因素, 同时粮食生产主导定位、非农业人口统计口径、城镇设置标准等因素也影响县域城镇化水平及发展过程。未来城镇化发展应遵循地域差异, 凸显主导功能, 推进优化与重点发展区的集约型城镇化、耕地与粮食主产区的分流型城镇化、生态与水源保护区的迁移型城镇化, 以及园区与城镇近郊区的融入型城镇化, 实现城乡土地资源集约利用, 促进城镇化进程中人—地—业耦合与协调发展。
Urban-rural development problems and transformation countermeasures in the new period in China
DOI:10.2307/142020 URL [本文引用: 3]
新时期中国城乡发展的主要问题与转型对策
Land use policy in urban-rural integrated development
Differentiation of rural development driven by industrialization and urbanization in eastern coastal China
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2009.03.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
China's new urbanization theory and strategic innovation
中国新型城镇化理论与实践创新
Towards rural-urban integration: Key issues and trends on linking new-type urbanization to rural revitalization
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

It is the key to achieving the aim of rural-urban integration that combine the two national strategies of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, and carry out collaborative governance of urban and rural areas. By analyzing the progresses of the studies on the new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, it is pointed out that the coupling of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategy should clarify the symbiosis effect of two strategies, and scientifically evaluate the coupling degree of urban and rural areas, then discover the spatio-temporal pattern of rural-urban integration. In order to realize rural-urban integration, it is necessary to explore the combination and spatio-temporal differences of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategies. According to conducting interdisciplinary methods to study the relations among the urban and rural administrative management system, the land system, the household registration system as well as the social security system, this article advocates multidimensional system reform from three perspectives of space, economy and society. Reconstructing the theory of rural-urban integration will be based on a whole analysis from the national, provincial, city to community scales. Community-centered governance is significant for rural-urban integration.
迈向城乡融合: 新型城镇化与乡村振兴结合研究的关键与趋势
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴两大国家战略有机结合并进行城乡共治是实现城乡融合的关键。通过分析新型城镇化和乡村振兴研究文献,认为新型城镇化与乡村振兴战略结合应聚焦两大战略的共生效应,科学评价城乡耦合程度,明确城乡融合的时空格局,提炼两大战略的耦合机制。要实现城乡融合,需要深入探究新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的结合点和时空差异,以问题为导向进行学科交叉,从空间、经济、社会3方面入手,厘清城乡在行政管理、土地、户籍和社会保障制度间的关系,倡导多维制度联动改革,从国家、省域、城市、县域、乡镇到社区,通过多尺度整合,重构城乡融合的理论,激发以社区为核心的基层治理活力,进而创新中国城乡共治的模式。
Land use transitions and urban-rural integrated development: Theoretical framework and China's evidence
From native rural China to urban-rural China: The rural transition perspective of China
从乡土中国到城乡中国: 中国转型的乡村变迁视角
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 2]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 2]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Theoretical analysis on the mechanism and evolution law of urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204001
[本文引用: 1]

Urban and rural areas are always an inseparable organic integration, and the high-quality new urbanization is the process of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. "urban disease" and "rural disease" are connected with each other, and are the causes of each other, which are known as "urban and rural diseases". The radical cure of "urban disease" and "rural disease" requires rural revitalization and new urbanization. Based on the review of the research on urban-rural integration development at home and abroad, this study analyzes the pathological roots and opposition pattern of urban and rural areas from the theoretical level, explores the main controlling factors, driving mechanism, sustainability and four-stage regularity of urban-rural integration development, constructs the measurement test system of urban-rural integration development, and puts forward the triangular model of urban-rural multi-integration development. It is known that the urban-rural integration development in China is in the high integration stage of more towns and less villages in the late urbanization, and will enter the deep integration stage of more towns and less villages, namely the final stage of urbanization. This study explores the policy evolution path of urban-rural integration development in China since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949. China has generally experienced the policy evolution process from urban-rural coordinated development to the integration of urban-rural development and then to urban-rural integration development, and played an important guiding role in promoting new urbanization and rural revitalization. From the path level, it is suggested that the Central Urban and Rural Work Conference should be jointly convened, the National Urban-Rural Integration Development Plan should be jointly compiled, and the strategy of deep integration of urban-rural development should be implemented. The new urbanization and rural revitalization should be used as two different means to solve urban and rural diseases and improve the quality of urban and rural development. The theory and method of urban-rural integration development should be innovated, and the evaluation system should be constructed to quantitatively evaluate the depth of urban-rural integration development and build beautiful cities and beautiful villages. We should promote the development of new urbanization and rural revitalization in the direction of high synchronization, deep integration and co-prosperity, as well as improve the quality of urban and rural development and realize urban and rural modernization in a comprehensive way.
城乡融合发展机理与演进规律的理论解析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204001
[本文引用: 1]

城市与乡村始终是一个不可分割的有机融合体,高质量的新型城镇化过程就是城乡融合发展与乡村振兴过程。“城市病”因乡村病而生,“乡村病”也因城市病而生,“城市病”与“乡村病”同病相连,互为病因,复合叠加形成“城乡病”,根治“城市病”必须通过乡村振兴,根治“乡村病”也必须通过新型城镇化。本文在对国内外城乡融合发展研究综述的基础上,从理论层面分析了城乡病理病根及对立格局,解析了城乡融合发展的主控要素、驱动机制、城乡融合发展的规律性和持续性,构建城乡融合发展测度试验系统,提出了城乡多融合发展的三角模式,验证了中国城乡融合发展正处在城镇化后期城多乡少的高度融合阶段,未来将迈入城镇化终期城多乡少的深度融合阶段。从政策层面分析了中华人民共和国成立以来国家有关城乡发展政策的演进路径,总体经历了从城乡二元发展、城乡协调发展、城乡统筹发展、到城乡一体化发展、再到城乡融合发展的政策演进过程,这些政策对推动新型城镇化和乡村振兴发挥了重要指导作用。从路径层面建议合并召开中央城乡工作会议,合并编制《国家城乡融合发展规划》,实施城乡深度融合发展战略,把新型城镇化与乡村振兴同时作为解决城乡病、提升城乡发展质量的两种不同手段,创新城乡融合发展理论与方法,构建评估体系定量评判城乡融合发展程度,建设美丽城市和美丽乡村。推动新型城镇化与乡村振兴向高度同步化、深度融合化和共荣化方向发展,同步提升城市发展质量和乡村发展质量,同步实现城市现代化和乡村现代化。
Research on urban-rural integrated development under the background of new urbanization and rural revitalization
新型城镇化和乡村振兴背景下的城乡融合发展研究
The Evolution of China's urban-rural relations in the past seven decades: From separation to integration
中国城乡关系演变70年: 从分割到融合
From town-country integration to urban-rural integration: New thinking on the relationship between urban and rural areas
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.006
[本文引用: 2]

The in-depth implementation of the new urbanization and rural revitalization strategy has pushed the urban-rural relationship into a new stage of integrated development. Based on Citespace1.0 software analysis and literature induction method, the paper identified the research hotspots of urban-rural relationship, reviewed the research progress of urban-rural relationship. Which included theoretical connotation and influencing factors of urban-rural relationship, measurement and evaluation of urban-rural connection, urban-rural spatial organization and development mode, and coordinated development of urban-rural areas and promotion strategy. Combining with the social economic background of information revolution and the change of urban-rural relationship in China, we points out that the construction of urban-rural relationship in the new period needs to change the traditional urban-rural relationship centered on the city, promote the integration of urban and rural areas and the formation of a new pattern of equal development between urban and rural areas. Based on this, we puts forward and discusses the construction and overall thought of a new urban-rural relationship toward urban-rural integration development. Then we proposes a framework for urban-rural integration analysis based on elements flow, puts forward the general idea of analyzing the characteristics, pattern and mechanism of urban-rural elements flow, which is supported by flow space theory and new mobility paradigm, multi-source data and visual analysis. The paper emphasizes the importance of measurement and evaluation of urban-rural relationship and the flow of urban-rural elements. The characteristics, pattern and mechanism of urban-rural factors flow, and the regulation and control strategy of the integration development of urban-rural areas are discussed in detail. The paper also explores the construction of the urban-rural integration database, the measurement of the flow of urban-rural elements and their spatial-temporal changes, and spatial simulation and visualization expression and other methods and techniques.
从城乡一体化到城乡融合: 新型城乡关系的思考
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.10.006
[本文引用: 2]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的深入实施,推动城乡关系进入了一个融合发展的新阶段。采用Citespace1.0软件分析及文献归纳方法,识别了城乡关系研究热点,梳理了城乡关系研究在理论探索、影响因素、测度与评价、空间组织及推进策略等方面的研究进展。在此基础上,重点对面向城乡融合发展的新型城乡关系研究进行了总结,从理论基础与总体思路、多源数据与方法集成等方面提出了基于要素流动的城乡融合分析框架,指出了城乡融合研究的重点是基于多源数据的城乡关系测度与评价,城乡要素流动的特征、格局与效应,城乡要素融合发展的流动机制,城乡融合发展调控策略等。
The theory of urban-rural integration: Stages, characteristics and enlightenment
城乡融合理论: 阶段、特征与启示
Human geography research based on the new thinking of global rural-urban relationship
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 4]

Sustainable rural development is critical to the achievement of global sustainable development goals. Globalization and urbanization, as the key processes, continuously drive the human-earth system to make adaptive responses, promoting the transformation of urban-rural relations. The rural-urban relationship is essentially a mother-child relationship, which is a comprehensive characterization of the transfer of rural humanistic factors, the transformation of man-land relationship and the transformation of urban-rural development in the process of urbanization. However, the traditional cognition of urban-rural relationship ignores the multi-dimensional connections between the rural and the urban as well as the existence of the rural-urban integration system, resulting in prominent drawbacks of rural regions, negatively affecting the urban-rural development rights, and resulting in urban and rural territorial dysfunction and other problems. The key to solve the problems of socio-economic development in China is to reform the urban-biased development strategy, and to innovate the new cognition of rural-urban relationship based on the thinking of "rural maternal effect", which highlights that rural areas nourish the city. Based on the remote coupling and systematic synthesis of the rural human-earth system, modern human geography urgently needs to strengthen the cross-research with physical geography and information geography, create a coordinated observation system of human-earth system supported by the sky-space-ground integration, reshape the global rural development perspective, rural-urban system perspective, and reorganize the global rural human-earth relationship, the rural-urban integration relationship, and the living and employment relationship. Rural human-earth relationship territorial system is the core of rural geography research. The rural human-earth system research should focus on the coupling of rural natural ecosystem and the socio-economic system and their complex interactive processes and effects. Supported by the intersection of multiple disciplines, the expansion of new fields and the cultivation of new disciplines, it should create the collaborative observation technology of human-earth system and methodology of multi-source data fusion computing, the research idea based on process-mechanism-pattern and the technical path of monitoring-simulation-decision support, and explore the organic connection path between rural human-earth system coupling and rural-urban integrated development, regional sustainable development and global common governance.
全球乡城关系新认知与人文地理学研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 4]

全球化、城镇化作为驱动人地系统不断做出适应性调整和改变的关键过程,持续推动着城乡关系的转型与重塑。本文认为乡村孕育了城市,乡城关系实质上是母子关系,是城镇化进程中乡村人文要素转移、人地关系转变、城乡发展转型的一种综合表征,具体体现在不同发展阶段乡村与城市之间土地非农化、人口城镇化、产业园区化、城乡发展一体化等诸多方面;传统的城乡关系认知忽略了城市与乡村之间的内在关系和多维联系,以及城乡融合系统这一重要地理综合体及其功能价值,成为产生乡村短板效应凸显、城乡发展权能受损、城乡地域功能紊乱等突出问题的根源;转变城市偏向发展观念,基于乡村母体思维,创新全球乡城关系新认知是破解当前全球化特别是中国社会经济发展不平衡、不充分问题的关键所在。现代人文地理学迫切需要强化与自然地理学、信息地理学交叉研究,创建天—空—地一体化人地系统协同观测体系,突出乡村人地系统的远程耦合性和系统综合性,重塑全球乡村观、乡城系统观,探究可持续的全球乡村人地关系、城乡融合关系、村镇居业关系。乡村人地系统研究应聚焦乡村自然生态系统、社会经济系统耦合及其复杂交互过程与效应,以多学科交叉、新领域拓展与新学科培育为支撑,创建人地系统协同观测技术与多源数据融合计算方法论,基于过程—机理—格局的研究思路和监测—模拟—决策支持的技术路径,探寻实现乡村人地系统耦合与乡城融合发展、区域可持续发展及全球共同治理的有机衔接路径。
Toward improved land elements for urban-rural integration: A cell concept of an urban-rural mixed community
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2018.01.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research progress and prospects of urban-rural integrated development based on geographical perspective
基于地理学视角的城乡融合发展研究进展与展望
Review of urban-rural integration evaluation: Connotation identification, theoretical analysis, and system reconstruction
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211013
[本文引用: 3]

The scientific evaluation of urban-rural integration is the core content of urban-rural integration, and it is the foundation for establishing and improving the institutional mechanism of urban-rural integration. Based on the logical line of "connotation identification-theoretical analysis-system reconstruction", this paper carries out the review of urban-rural integration evaluation including concept connotation, theoretical basis, evaluation index, evaluation method, evaluation scale, spatio-temporal differentiation, and mechanism analysis. At present, the academic understanding of the connotation of urban-rural integration is basically the same. The evaluation index selection of urban-rural integration shows multidimensional and multi-attribute characteristics, but the index system construction has not broken through the static characteristics. Quantitative evaluation method is relatively simple. Generally, current research still remains at the macro scale, but lacks quantitative research from a micro perspective and comparative studies of different fusion modes. The spatial and temporal differentiation pattern and its mechanism of urban-rural integration need to be further deepened. Finally, this paper puts forward five prospects: (1) strengthening the construction of basic theory system and perfecting system research framework; (2) optimizing the multidimensional evaluation index system and identifying the development model of urban-rural integration; (3) deepening the flow mechanism of urban and rural elements and promoting the balanced development of urban and rural space; (4) strengthening the exploration of micro-scale details and improving the promoting mechanism of urban-rural integration; (5) strengthening the empowering role of the digital economy and innovating the development mechanism of high-quality urban-rural integration.
城乡融合评价研究综述: 内涵辨识、理论认知与体系重构
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211013
[本文引用: 3]

科学的城乡融合评价是城乡融合工作的重要环节,是建立健全城乡融合体制机制的基础。以“内涵辨识—理论认知—体系重构”为逻辑主线,从城乡融合的概念内涵、基础理论、评价指标、评价方法、评价尺度及演化机理等方面,开展城乡融合评价综述。研究表明:学界对城乡融合概念与内涵的认识基本一致,且已有一定理论基础;城乡融合评价指标选取呈现多维化、多属性化特征,但指标体系构建尚未突破静态性层面;定量评价方法较为单一;研究尺度整体偏向中宏观,缺少微观视角下的量化以及不同融合模式对比研究;城乡融合的时空分异格局及其机理研究亟待进一步深化。对此,提出了以下五点展望:(1)加强基础理论体系建设,完善系统研究框架构建;(2)优化多维评价指标体系,识别城乡融合发展模式;(3)深化城乡要素流动机制,推动城乡空间均衡发展;(4)加强微观尺度细节挖掘,健全城乡融合推进机制;(5)强化数字经济赋能作用,创新城乡高质量融合发展机制。
Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization: Theory, mechanism and implementation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

Rural revitalization and urban-rural integration aim at narrowing the gap between urban and rural areas, promoting balanced development and realizing the equivalent life quality between urban and rural residents. Spatial equilibrium and its quantitative expression provide a new perspective to explain the pattern, process and mechanism of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. Through the analysis of basic theory, this study discusses the scientific content and interaction between urban-rural integration and rural revitalization, sets up the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, defines the urban-rural development isolines, works out the way to implement the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China, and addresses the potential for further research. The results show that: (1) Theory of regional system of man-land relationship and theory of spatial structure are the important theoretical basis for urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. The urban-rural integrated development depends on the all-round development of economy, society and environment with optimized spatial layout and innovative system, and rural revitalization mainly refers to the "pentagon of rural revitalization" and "people-land-capital-industry"; Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization strategy support each other, and the process of urban rural integration and rural revitalization is a dynamic equilibrium process between urban and rural areas. (2) The key issues of implementing rural revitalization and urban-rural integration can be illustrated through the urban-rural spatial equilibrium model, and the overall per capita benefits in rural areas gradually tend to be the same as that in cities by the re-optimization of urban-rural factors and population mobility; the dynamic process and mechanism of urban-rural integration spatial equilibrium is further interpreted via the urban-rural development isolines. (3) Exploring the implementation path of scientific rural revitalization strategy can achieve the goal of urban-rural integration and urban-rural spatial equilibrium development. The scientific path of rural revitalization is discussed from the perspectives of policy system construction, "pole-axis" spatial progressive diffusion, sub-area classification and typical development pattern, and it can provide theoretical reference for the strategy implementation of China's rural revitalization.
城乡融合与乡村振兴: 理论探讨、机理阐释与实现路径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201811001
[本文引用: 1]

缩小城乡差距,促进城乡均衡发展,实现城乡居民生活质量等值,是乡村振兴和城乡融合发展的重要目标。通过基础理论的分析,探讨了城乡融合与乡村振兴科学内涵,剖析了城乡融合与乡村振兴的相互关系,构建了城乡空间均衡模型和定义城乡等值线,提出了中国城乡融合与乡村振兴实现途径及需要深入研究的方向。结果表明:① 城乡融合发展是基于空间布局优化和制度供给创新的经济、社会、环境全面融合发展,“乡村振兴五边形”和“人—地—钱—业”是乡村振兴的核心内涵;城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相互支撑,城乡融合和乡村振兴的过程是城乡空间动态均衡的过程。② 城乡发展的空间均衡模型可以较好地阐释促进城乡融合发展、实施乡村振兴的关键问题,通过城乡要素的重新优化配置和人口的流动,城乡人均综合发展效益逐渐趋于相等;城乡等值线可以进一步解释城乡发展空间均衡的动态过程与传导机理。③ 从政策制度构建、“点轴”渐进扩散、分区分类推进、典型发展模式提炼等方面探讨乡村振兴的科学路径,可以为中国乡村振兴战略实施提供理论参考。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 3]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 3]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Impacts of land market on urban-rural integrated development in China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190201
[本文引用: 3]

The urban-rural integrated development is the key measure to realize rural vitalization and promote new-type urbanization, while the land market is an important channel to realize the flow of urban-rural development elements, also a key link to connect urban-rural development. This paper analyzes the scientific connotation and substantial characteristics of urban-rural integrated development, and then explores the driving mechanism of land market on urban-rural integrated development. Based on these foundation, we quantitatively analyze the evolution law of land market and urban-rural integrated development in 273 cities at prefecture level or above in China. Furthermore, the relationship between land market and urban-rural integrated development was tested based on the panel data model to give a feasible proposal for the integration of urban and rural development from the perspective of land market. Main conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) The urban-rural integrated development is a process of the reconstruction of urban-rural values aiming at removing the obstacles hindering urban-rural development. It helps to promote the free flow and equal exchange of urban-rural elements, and achieve the convergence of returns from urban-rural development elements. The essence is to achieve the overall optimization of urban-rural regional functions through urban-rural integrated development and complementarity. (2) The effect of land market on urban-rural integration is a balance of advantages and disadvantages, and the direction depends on whether the land market is benign. Under the urban-rural dual distribution system and the curtain wall of society, the distorted land market impedes the urban-rural integrated development. (3) From 2005 to 2013, the scale of land market, land market price and land marketization degree increased by 113.66%, 274.09% and 37.07%, respectively, while the level of urban-rural integrated development in 59.34% cities have declined. Steadily developing land market and low level of urban-rural integrated development in China presented stark contrast and obvious spatio-temporal differentiation. (4) Currently, land market is more of a hindrance to urban-rural integrated development, but there is a "low level trap" between land market and urban-rural integrated development. Breaking the suppression inflection point of 88.64%, land market can then play a positive role on promoting urban-rural integration. So, reshaping the healthy value orientation of the land market development, accelerating the land marketization reform and exploring the mechanism of population-land linkage are important parts for follow-up work.
中国土地市场对城乡融合发展的影响
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190201
[本文引用: 3]

城乡融合发展是实现乡村振兴与推进新型城镇化建设的关键举措,土地市场则是实现城乡要素流通的重要渠道,也是连接城乡发展的关键纽带。本文阐释了城乡融合发展的科学内涵与本质特征,探究了土地市场对城乡融合发展的作用机理,在此基础上,量化分析了中国273个地级及以上行政单元土地市场与城乡融合发展的演进规律,并运用面板数据模型对土地市场与城乡融合关系进行了实证检验,以期从土地市场视角为城乡融合发展提供一条可实现路径。结论如下:(1)城乡融合发展是城乡价值重塑的过程,旨在消除阻碍城乡发展的因素,推动城乡要素自由流动与平等交换,实现城乡发展要素回报趋同,本质是通过城乡互动互补实现城乡地域功能的整体优化。(2)土地市场对城乡融合的作用是利弊双轨的权衡,作用方向取决于土地市场是否是良性市场。城乡二元分配体制与社会融入受阻背景下,扭曲土地市场掣肘城乡融合发展。(3)2005-2013年中国土地市场稳步发展,城乡融合发展水平略低,土地市场规模、土地市场价格与土地市场化程度分别提升113.66%、274.09%与37.07%,59.34%城市的城乡融合发展水平下滑,二者反差明显,且均具时空分异特征。(4)现阶段,土地市场对城乡融合发展更多体现为滞碍作用,但土地市场对城乡融合存在“低水平陷阱”,突破88.64%的抑制拐点,即可发挥土地市场对城乡融合的促进作用。重塑土地市场发展价值取向,加快推进土地市场化改革,探索人口—土地挂钩机制是后续工作的重要方向。
Measurement of urban-rural integration level and its spatial differentiation in China in the new century
Study on the influence of factor mismatch on urban-rural integration development: Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data
城乡要素错配与城乡融合发展: 基于中国省级面板数据的实证研究
Coupling coordination and the driving factors of agricultural modernization and urban-rural integration
农业现代化与城乡融合的耦合协调和驱动因素
Spatiatemporal evolution and dynamic mechanism of the urban-rural integration development in China
中国城乡融合发展的时空演变及动力机制
Review of urban-rural multi-dimensional integration and influencing factors in China based on the concept of equivalence
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190572
[本文引用: 2]

Based on the urban-rural equivalence, the Global Principal Component Analysis (GPCA) method is used to measure the China's urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels, and the Global and Local Moran Index, Local Getis-Ord Gi * Index are performed to reveal the spatial distribution of urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels in China during 2000-2016. And finally, the spatial econometric model is introduced to explore the influencing factors of urban-rural integration development from the aspects of labors, land, capitals and industries. Research findings are as follows: (1) the trend of urban-rural integration development in China is well and orderly, but has regional heterogeneity. The agglomeration effect is obvious in Eastern China, and the social and economic coordination level has always occupied the first and the second places. (2) China's urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels often show spatial autocorrelation. The HH values of urban-rural integration overall level are concentrated in Central China and Eastern China, while the LL values are gathered in Western China. The hot and cold spots are located to the southeast and northwest of Heihe-Tengchong Line, respectively. Also the high values of economic integration have always corresponded to those of ecological and environmental integration. Population integration level decreases from Eastern to Western China. Spatial integration level presents the "core-edge" structure such as Beijing, Shanghai and Guangdong. Spatial spillover effect of the economic integration development is obvious in the coastal region of China, while the development of ecological environment integration and economic integration has spatial dislocation. And the clusters of social integration high values are in Central China. (3) The ways of the urban-rural multi-dimensional integration are as follows: Firstly, we should improve the quality of rural labor forces and promote the interaction between urban and rural residents. Secondly, we should stimulate the multi-function of rural land and control the disorderly urban expansion. Thirdly, we should take financial expenditures in a reasonable range and provide a perfect financial support in urban and rural areas. Finally, industrial restructuring is also needed. And moreover, regulating the behavior of the local governments will be benefit to the urban-rural multi-dimensional integration and good governance in China.
等值化理念下中国城乡融合多维审视及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190572
[本文引用: 2]

基于等值化理念采用全局主成分分析(GPCA)和空间自相关分析等方法,测度并审视中国城乡多维融合发展;选取空间计量模型探索推进城乡融合的体制机制。研究发现:① 中国城乡融合发展趋势向好且推进有序。社会和经济融合始终分列第一和第二主导位次,生态环境融合水平亦稳步提升。② 城乡融合热点和冷点区基本分列于“胡焕庸线”东南和西北两侧。人口融合沿东中西递减;空间融合形成“北上广”为主的“核心-边缘”区;东部沿海是经济融合扩散互溢区,而生态环境和经济融合存在空间“错位”;社会融合高值簇集中在中部。③ 破解人才瓶颈、夯实“三权分置”、健全财政体制并创新金融服务、调整产业结构和推动三产融合,打好人、地、钱、业组合拳同时规范政府行为、完善社会服务体系、构建小农户与现代农业有机衔接机制等均利于推进城乡融合。
The impacts of capital deepening on urban housing prices: Empirical evidence from 285 prefecture-level or above cities in China
Development model and effect evaluation of urban-rural integrated in metropolitan fringe areas: A case study of Wangcheng District
大都市边缘区城乡融合发展模式及效应评价: 以长沙市望城区为例
Approaches to rural transformation and sustainable development in the context of urban-rural integration
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

Exploring the evolution rules of rural transformation is significant for systematically understanding stages of rural development, judging trends of rural development, determining paths of rural sustainable development and promoting rural vitalization. Based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, industrial structure evolution theory, and regional spatial structure theory, this paper deduced the evolutionary stages of rural transformation. The evolutionary stages were verified by analysis of the development process of typical villages. Further, this paper explored the implication for rural sustainable development in the new era. The results showed that: (1) Evolutionary process of rural transformation included four stages. The first was the cropland-engineering stage, aiming at realizing the need for food and clothing under the uniform distribution of productivity. The second was the agricultural structure adjustment stage, aiming at increasing income under the intensifying urban-rural relationship status. The third was the industrial restructuring, aiming at improving the quality of life under the strengthening of regional linkages. The fourth was the stage of promoting the equalization of public service facilities with the goal of urban-rural equivalence under the urban-rural integration. (2) The development course of typical developed villages confirmed the evolution rules of rural transformation to some extent. (3) In practice, the evolutionary process of rural development presented skip or parallel phenomena because of regional differentiation of resources, location, market size, and willingness. According to the changes of the roles of different groups in development course, each stage could be subdivided into initial stage, transition stage, and maturation stage. (4) Based on the analysis of evolutionary rules of rural transformation, the paths of rural sustainable development in different types of region included land consolidation and agglomeration path, specialty industrial development path, industrial platform for collection and distribution path, and community function intensification path in the context of urban-rural integration.
城乡融合背景下乡村转型与可持续发展路径探析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912010
[本文引用: 1]

探究乡村转型发展规律对于系统认识乡村发展阶段、研判乡村发展趋势、明确乡村可持续路径、促进乡村转型与振兴具有重要意义。首先基于马斯洛需求层次理论、产业结构演变理论、区域空间结构理论等演绎乡村转型发展阶段,然后结合典型乡村发展历程分析进行实证检验,进而探讨对于新时期乡村可持续发展的启示。研究结果:① 乡村转型发展在理论上可分为4个阶段,一是生产力均匀分布下以实现温饱需求为目标的土地整治促增产阶段,二是城乡联系增强下以改善生活水平为目标的农业结构调整促增收阶段,三是区域联系增强下以提升生活质量为目标的产业结构调整促致富阶段,四是城乡互动融合下以城乡等值为目标的公服设施建设促均等阶段。② 典型发达乡村的发展历程在一定程度上印证了乡村转型发展阶段特征。③ 因资源基础、区位条件、市场规模、发展主动性等因素的差异,乡村实际发展过程可能存在阶段的跃迁或并行的现象。根据发展过程中不同主体发挥作用的变化,每个阶段又可细分为初始阶段、过渡阶段和成熟阶段。④ 基于乡村转型发展规律分析,城乡融合背景下不同类型地区乡村可持续发展路径可分为土地整治集聚路径、特色产业发展路径、产业平台集散路径和社区功能集约路径等4类。
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of high-quality development of China at the prefecture level
中国地级区域高质量发展格局与影响因素
The measurement of the urban-rural integration development level in the Yangtze River Delta region and the analysis of its spatio-temporal characteristics
长三角地区城乡融合发展水平测度及其时空特征分析
Evolution of urban-rural integration in Huaihai Economic Zone from the perspective of spatio-temporal interaction
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200809
[本文引用: 1]

Rural-urban integration is an inevitable trend of the development of rural-urban relations. Studies on urban-rural integration are the requirement for giving play to the comprehensive advantages of geography in order to serve the national strategy. This paper took Huaihai Economic Zone as the research object, constructed multi-dimensional index system, and measured the level of urban-rural integration. The characteristics of spatio-temporal evolution and its driving mechanism were also discussed. Some conclusions were drawn as follows. The difference of urban-rural integration level among cities in Huaihai Economic Zone was relatively small. The level of urban and rural integration showed the characteristics of agglomeration in space. For most cities, local spatial structure of urban-rural integration was more dynamic, and its fluctuation was relatively small. Spatial pattern evolution showed the characteristics of strong integration. Factors of the city itself had more influence on the change of spatial structure of urban-rural integration. It was less affected by the spillover effect of the level of urban-rural integration in neighboring cities. The change of urban-rural integration in the cities was driven by economic development and urbanization. The change of urban-rural integration in the cities, which was at low level, was restrained by urban employment and government action. The change of urban-rural integration in the cities, which was at high level, was restrained by industry and government action. Finally, different countermeasures and suggestions were put forward for different types of cities.
时空交互视角下淮海经济区城乡融合发展水平演化
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200809
[本文引用: 1]

以淮海经济区为研究对象,界定城乡融合内涵,并构建多维指标体系,测度城乡融合发展水平,并探索时空演化特征及驱动机理。(1)在空间集聚方面,淮海经济区城乡融合发展水平集聚较为明显,并且集聚性整体呈现增强趋势。(2)在时空联动方面,具有相对动态的局部空间结构和相对稳定的空间依赖方向,同时空间格局演化方面具有较强的整合性;城市自身因素对城乡融合发展水平空间结构的改变影响较大,受相邻城市城乡融合发展水平的溢出效应的影响较小。(3)要素驱动模式方面,低分位驱动和高分位驱动城市的城乡融合发展水平变化受经济发展—城镇化驱动,低分位制约类型城市的城乡融合发展水平变化受城镇就业—政府行为制约,高分位制约类型城市的城乡融合发展水平变化受产业—政府行为制约。
Spatiotemporal evolution of coupling coordination degree of urban-rural integration system in metropolitan area and its influencing factors: Taking the capital region as an example
大都市区城乡融合系统耦合协调度时空演化及其影响因素: 以环首都地区为例
The development level, evolution and influencing factor of urban-rural integration in the Yangtze River Delta
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220607
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of the growing gap between urban and rural development, this paper takes the Yangtze River Delta region as a research case and uses the Entropy method to calculate the development index for the 2008-2018 urban-rural integration and spatial integration, economic integration, social integration and lifestyle integration. And then it uses the Geographic Detector Model to analyze the main influencing factors and evolution characteristics of the level of urban-rural integration. The results show that the development level of urban-rural integration in the study region is characterized by spatial evolution from the "high-low-high" structure to a "Σ"-shaped pattern; from the perspective of the spatial characteristics of the urban-rural integration subsystem, the high value of the development level of spatial integration and the level of social integration presents the spatial pattern of a "Σ" shape, the economic integration development level is characterized as high and low circle structure, and the life integration development level roughly presents the spatial pattern of high in the west and low in the east. Seen from the results of the geographic detector model, the level of economic development, industrial advancement, the proportion of fiscal expenditures on agricultural support, and fiscal decentralization are conducive to the development of urban-rural integration; while the speed of economic development, the deviation of industrial structure, and the proportion of urban-rural infrastructure expenditures are not conducive to the urban-rural integration. From the temporal perspective, government power is gradually weakening, and market power is gradually intensifying.
长三角地区城乡融合发展水平、演化及影响因素
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220607
[本文引用: 1]

在城乡发展差距日益扩大的背景下,以长三角地区作为研究案例,运用熵值法计算长三角地区2008—2018年城乡融合发展指数,并利用地理探测器模型分析城乡融合水平的主要影响因素及其演变特征。结果表明:长三角地区城乡融合发展水平呈现出“高低高”结构向“Σ”转变的空间演变特征,空间融合发展水平和社会融合发展水平的高值区大致呈现出“Σ”的空间分布特征,经济融合发展水平呈现出“高低高”的圈层结构特征,生活融合发展水平大致呈现出西高东低的空间分布格局;从地理探测器模型结果来看,经济发展水平、产业高级化、财政支农支出比例、财政分权有助于城乡融合的发展,经济发展的速度、产业结构偏离、城乡基本建设支出比例不利于城乡融合的发展;从时间变化上看,政府力量在逐步减弱,市场力量在逐渐增强。
Driving mechanism of urban-rural integration in Huaihai Economic Zone: Based on the space of flow
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200810
[本文引用: 1]

To restructure the evaluation index system of urban and rural integration from population, space, economy, society and ecological environment, the dynamic coupling coordination model was selected to measure the urban and rural multi-dimensional integration level, and the global Moran index and the local indicators of spatial association (LISA) were used to reveal the spatial distribution characteristics of the urban-rural multi-dimensional integration level in Huaihai Economic Zone. And then, the spatial correlation pattern in the study area was analyzed by the spatial structure index (SSI) from the population flow, logistics flow, capital flow and information flow. And finally, the driving mechanisms of urban-rural integration in the study area were explored by the fixed effect spatial error model (SEM-FE) from the perspective of these four types of flow. The results are as follows: (1) The urban-rural multi-dimensional integration levels are low but go well, the overall level in the research area rose from 0.016 in 2003 to 0.028 in 2017, with an annual rate of 0.08%. When the urban-rural multidimensional integration structure maintains stable in the research period, the economic integration is the highest, while the spatial integration is the lowest. (2) The regional interrelation is close in the context of population flow and capital flow, while it shows a "core-periphery" structure under the material flow and information flow. In general, the spatial structure in Huaihai Economic Zone is a decentralized network with multiple central cities, which lays a good foundation for the future development of urban-rural integration and inter-regional coordinated development. (3) In order to achieve the improvement of quantity and quality of urban-rural integration in Huaihai Economic Zone, we should shift the effect of the core area from agglomeration to diffusion, and need reasonable labor distribution and trading to stimulate the regional comparative advantage fully of each city node. Moreover, it is necessary to assist a series of cultural, economic and political systems in the implementation of local and national policies, because urban and rural integration development is a big cycle system of the socio-economy.
“流空间”视域下淮海经济区城乡融合发展驱动机制
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200810
[本文引用: 1]

从要素流动多维重构淮海经济区城乡融合评价体系,以动态耦合协调度模型测度城乡融合水平并分析其时空分异规律,最后从“流空间”视角探索城乡融合发展驱动机制。结果表明:(1)研究区城乡融合水平整体较低但趋势向好,其正向空间关联和局域内向集聚特征明显。(2)流空间视角下区域呈多中心网络结构,且在人流和资金流下相对紧密,而物流和信息流下“核—辐”结构突出。(3)推动核心区集聚效应转向扩散效应,发挥各城市节点比较优势,合理调节要素流动强度、方向和质量,并在实施地方和国家政策时配套相关制度,方能实现淮海经济区城乡融合“量”“质”同升。
Spatial change and correlations of desakota regions in a metropolitan area using NPP/VIIRS nighttime light data: A case study of Wuhan city
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

Research on the spatial-temporal change and intrinsic spatial correlation of metropolitan urban-rural integration zones can help cities to avoid inefficient sprawling development and achieve spatial structure coordination and smart growth. Taking the desakota region in Wuhan City as the case, we used the National Polar-Orbiting Partnership / Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (NPP/VIIRS) nighttime light data to assess urban factor allocation and operational efficiency and effectiveness. This study then detected the spatial correlation intensity, spatial-temporal change of spatial connection potential, and the change of socioeconomic location index of the urban-rural integration areas during 2016-2018 using the gravity model. The results show that: 1) The desakota regions in Wuhan City have expanded by 28.10%, and sprawl most significantly to the northwest during 2016-2018. This process is characterized by the integration of small plaques and the enhancement of regional development continuity. 2) The spatial connection network structure among desakota regions in Wuhan tends to be polycentric, which originates from the changes of economic development levels, urbanization development scale, and traffic accessibility. Wuhan East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Sino-French Wuhan Ecological Demonstration City, Wuhan Airport Economic Zone and so on are the engine of regional development in a decentralized process. 3) The spatial correlation pattern of urban-rural integration areas in Wuhan has been transformed from the "large and small cores" structure consisted of Wuhong District and Jiangxia District to the "peripheral circle" structure composed of Jiangxia-Wuhong-Caihan-Jianghuang-Jiangqiaodong. The spatial connection intensities of desakoda regions have increased year by year, but Wuhong and Jiangxia Districts, as the core areas of Wuhan urban-rural integration area, failed to develop multi-directional spatial radiation and attractiveness, which led to insufficient positive effects to other areas. 4) The changes of socioeconomic location index of each urban-rural integration area show that the impact of existing Wuhan urban planning is more significant in the northern, western, and northeastern parts of urban-rural integration area.
大都市城乡融合区空间演进及内在关联性测度: 基于武汉市夜间灯光数据
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

大都市城乡融合区时空演变及其内在空间关联性研究对避免城市低效蔓延式发展、实现空间结构协同和精明增长有重大意义。论文以武汉市城乡融合区为研究对象,基于NPP/VIIRS夜间灯光强度表征都市要素配置及运行效率和效益,利用引力模型测度2016—2018年各城乡融合区空间关联强度,分析各城乡融合区空间联系势能时空演变趋势和社会经济区位度变化。研究结果表明:① 武汉市城乡融合区面积在2016—2018年间扩大了28.10%,小斑块区域逐渐整合,区域发展连续性增强,总体向西北方向扩展最为显著;② 武汉市城乡融合区之间的空间联系网络结构整体上趋向“多中心”分布,这一过程源于各城乡融合区的经济发展水平、城镇化发展规模和交通通达性变化,东湖新技术开发区、中法武汉生态示范城、武汉临空经济区等在此过程中是各城乡融合区的区域发展引擎;③ 武汉市城乡融合区空间联系强度整体上逐年上升,空间联系整体格局从武洪区和江夏区的“大小中心”结构过渡到江夏区—武洪区—蔡汉区—江黄区—江硚东区的“外围圈层式”结构,但洪山区和江夏区作为武汉市城乡融合区中心区域,未能形成多方向空间辐射力和吸引力,对其他地区的带动明显不足;④ 各城乡融合区社会经济区位度变化显示,现行武汉市都市发展区规划实施成效在北部、西部和东北部城乡融合区较为显著。
The coordination urban growth between rural development, and the reform of the system of the property right of the rural collective land
城乡统筹与农村集体土地产权制度改革
Explanation of land use transitions
土地利用转型的解释
Impact of urban air pollution on surrounding areas in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei provinces
城市空气污染对周边区域空气质量的影响
Divergent trends of urban thermal environmental characteristics in China
Identification and poverty alleviation pathways of multidimensional poverty and relative poverty at county level in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106010
[本文引用: 1]

China has secured a comprehensive victory in its fight against poverty. After 2020, the focus of China's battle against poverty will shift from relative poverty to absolute poverty, and from poverty in terms of income to that in other dimensions. This study applies the county as the basic unit and 31 provinces (autonomous regions/municipalities) of China as the study area. It identifies poverty levels in each county by the average night light index and the county multidimensional development index. Using the multidimensional relative poverty identification method based on the sustainable models, we analyzed the current situation of China's poverty from two aspects—multidimensional poverty and relative poverty. Finally, we explore the poverty alleviation pathways in four aspects, namely, education poverty alleviation, agricultural poverty alleviation, industrial poverty alleviation, and tourism poverty alleviation. The results revealed that nearly 60% of counties in China were primarily in multidimensional relative poverty, most of which were classified as multidimensional relatively light poverty counties. According to the average night light index and the county multidimensional development index, the numbers of poverty counties in China were 602 and 611, respectively; as of 2018, the proportions of national poverty-stricken counties accounted for 63% and 79%, respectively. The result implied that the county multidimensional development index had a more comprehensive poverty identification mechanism. Moreover, the multidimensional poverty counties were concentrated in Gansu, Sichuan, and Yunnan. Meanwhile, the development of Jilin, Liaoning, and Heilongjiang should not be overlooked. From the viewpoint of pathways, 414, 172, 442, and 298 poverty counties were suitable to industrial poverty alleviation, education poverty alleviation, tourism poverty alleviation, and agricultural poverty alleviation, respectively. Some 61% of counties had more poverty-causing factors, implying that multidimensional poverty alleviation is suitable in most of the poverty-stricken counties. These conclusions can provide a crucial scientific basis for ensuring sustainable poverty alleviation.
中国县域多维贫困与相对贫困识别及扶贫路径研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106010
[本文引用: 1]

当前,中国脱贫攻坚任务步入了由绝对贫困转向相对贫困、收入贫困转向多维贫困的新阶段。本文以中国31个省(直辖市)县域为研究对象,采用基于夜间灯光数据的平均夜间灯光指数以及基于脆弱性可持续生计框架的县域多维发展指数和多维相对贫困识别方法,从多维贫困和相对贫困两个层面对中国多维贫困现状进行分析,并基于以上研究筛选出的贫困县,采用耦合协调模型从产业扶贫、教育扶贫、旅游扶贫和农业扶贫分析适宜县域的扶贫路径。结果表明:中国约60%县域处于多维相对贫困状态,其中47%为多维相对轻度贫困县;基于平均夜间灯光指数和县域多维发展指数分别识别出602个和611个多维贫困县,分别包含了63%和79%的国家级贫困县(截至2018年),这表明县域多维发展指数识贫机理更为精准。多维贫困县集中在甘肃、四川和云南等地;而在筛选的贫困县中,适宜产业扶贫、教育扶贫、旅游扶贫和农业扶贫的县域分别有414个、172个、442个和298个,且在4种扶贫方式中,约61%县域适宜采用多种扶贫路径共同扶贫。研究结论将为确保中国扶贫的可持续性提供重要的科学依据。
How cropland losses shaped by unbalanced urbanization process?
Effects of new-type urbanization on poverty alleviation and development and corresponding countermeasures
新型城镇化对扶贫开发的影响与应对研究
Research on the development ideas and promotion strategies of regional integration: A case study of HuBaoE in Inner Mongolia
区域一体化发展思路及推进策略研究: 以内蒙呼包鄂为例
Areal types and their development paths in rural China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 3]

Rural revitalization strategy is the general starting point for China's agriculture, rural areas and farmers in the new era. Because of the significant differences in rural areas in China, it is necessary to promote rural revitalization strategy according to local conditions, regional guidance and classification. Based on the theory of regional system of human-land relationship, this study constructs a comprehensive index system and measurement model to measure the level of rural development from the perspectives of resource endowments, geographical environment, humanistic elements and economic level, divides the areal types in rural China, and suggests the regional development ways. The results show that the level of rural comprehensive development in China varies significantly from east to west and that level in the eastern region is generally higher than that in the central and western regions. China's rural areal types can be divided into 11 first-class zones and 45 second-class zones, and there are distinct regional differences among different types. Geographical environment is the decisive factor for the differentiation of rural areal types, and resource endowment or resource type is the key factor for rural regional differentiation, and human and economic factors play an important role in the transformation and development of rural areal system. The connotation of rural areal differentiation lies in the difference of development level and industrial structure. The difference of rural development level is the comprehensive reflection of the interaction of many factors such as resource endowment, function orientation, location condition, national or regional policy, and historical background. From the perspective of human-land relationship, this study analyzes the characteristics, problems and development strategies in different types of rural areas so as to provide theoretical basis and decision-making guidance for the smooth promotion of the rural revitalization strategy in the new period.
中国乡村地域类型及分区发展途径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 3]

由于我国乡村地域差异显著,乡村振兴需分类有序推进。本研究立足于人地关系地域系统理论,从资源、环境、人文、经济等维度构建了度量乡村综合发展水平的指标体系和计量模型,划分了乡村地域类型,明确了分区发展途径。结果表明,我国乡村综合发展水平区域差异显著,呈现明显的自东向西递减规律;全国乡村地域类型可以划分为11个一级区和45个二级区,不同类型区制约因子各异;乡村发展水平差异是资源禀赋、功能定位、区位条件、政策文化等因子交互作用的综合体现。地理环境是乡村地域类型分异的决定性因素,资源禀赋状况是乡村地域分异的关键因子,人文和经济因素在乡村系统转型发展中扮演着重要作用。通过对乡村地域类型、特征及其分异机制的研究,为乡村振兴战略的顺利推进提供了理论依据。
Ecological and environmental effects of land-use changes in the losses plateau of China
黄土高原土地利用变化的生态环境效应
High-quality development of the Yellow River Basin from a perspective of economic geography: Man-land and spatial coordination
DOI:10.2307/142170 URL [本文引用: 2]
黄河流域高质量发展: 人地协调与空间协调
Land consolidation engineering and modern agriculture: A case study from soil particles to agricultural systems
Coordinated human-earth system and high-quality development in Yellow River Basin
黄河流域人地系统协调与高质量发展
Multifunctional rural development in China: Pattern, process and mechanism
Rural revitalization path under urban-rural integration economic development in karst region of southwest China
西南喀斯特地区城乡融合发展乡村振兴路径研究
Review on the Routledge rural planning guidelines
乡村振兴规划他山之石: 《劳特利奇乡村规划指南》评述
Temporal-spatial characteristics and the driving mechanism of multidimensional comprehensive poverty degree in poverty-stricken counties: A case study of poor counties in deep poverty-stricken areas of southern Xinjiang
DOI:10.2307/142509 URL [本文引用: 1]
贫困县多维综合贫困度时空分异特征及其驱动机制: 以南疆四地州深度贫困地区贫困县为例
The integration of urban and rural development in border areas under the "Belt and Road Initiative": A case study of Kashi prefecture
“一带一路”战略下边疆地区城乡发展一体化研究: 以新疆喀什地区为例