1 引言
中国共产党“十九大”提出中国特色社会主义进入新时代,中国社会主要矛盾已发生阶段性转换,并将“推进城乡融合发展”和“实施乡村振兴战略”作为引领“三农”发展的行动纲领。中国共产党“二十大”进一步明确提出“中国式现代化”的发展要求,强调“全面推进乡村振兴”和“促进区域协调发展”战略,着力破解乡村发展不充分、城乡发展难融合等现实困境,构建中国式农业农村现代化的全新路径。新时代城乡分治已成为阻碍城乡高质量发展的重要障碍,城乡空间一体化治理将为推进城乡融合发展提供关键动力[1⇓-3]。面向城乡融合发展的多尺度乡村空间特征及其治理仍存在原理不明、机制不清、路径不通等待解难题。面向新时代城乡空间治理现代化的现实诉求,从地理学分析范式出发[4-5],厘清转型期多尺度乡村空间特征的科学机制及其内在逻辑,将为中国城乡治理现代化提供理论依据。
物质性乡村空间特征及其内在机制是开展乡村地理研究的理论基础,也是乡村空间研究的主阵地。社会活动学家Castells认为空间是社会的表现,不是对社会的反映,并将空间界定为共享时间之社会实践的物质支撑[6]。国内外学者针对乡村空间内涵进行了诸多论述,不论是国外学者Halfacree的乡村空间三重模型[7],还是国内学者关于乡村地域(空间)系统的多维乡村空间范畴[8],不断拓展了乡村空间的概念内涵和认知体系。后生产主义主导下的国外乡村地理研究,逐渐将“社会—文化”导向的空间研究应用于乡村空间的界定[9-10],进一步凸显了社会文化活动对乡村物质空间的改造(由生产功能主导到多功能并存)。刘彦随等[8]、张小林[11]、龙花楼[12]从差异化视角解构了乡村空间认知体系。
新时代,面向城乡融合发展和全面乡村振兴目标,从城乡空间结构联动和价值流动视角解析乡村空间特征具有现实意义。文化转型导向下“田园牧歌”式的乡村空间内涵界定是否适用于当前中国乡村转型发展阶段仍待观察[13],基于地理学分析范式剖析物质性乡村空间特征仍具有旺盛的学科生命力[14-15]。中国语境下的乡村空间研究,不能抛开其与城市空间的联系,更不能脱离城乡中国转型的大背景[16⇓-18],城乡空间的联动性和交互性也是中国乡村空间研究区别于欧美发达国家的显著特征之一[19],城乡空间割裂成为建构新型城乡关系亟待破解的空间关系特征。乡村空间特征长期以来是乡村地理学者关注的重要议题,不论是乡村空间结构和功能特征(如聚落集中化和功能复合化等)[20],还是乡村空间转型趋势特征(如宅基地利用空废化和耕地利用边际化等),均主要聚焦于乡村空间自身特征的系统研究[13,20 -21]。面向时代发展新诉求和城乡转型发展新目标,传统地方性乡村空间特征研究难以适应新时代城乡空间融合的需求。
时空压缩的去地域化与乡村空间多尺度交互成为乡村空间流动性的重要特征。Woods研究了全球化背景下的乡村能动性与乡村转型,揭示了乡村空间多尺度特征及其地方性的内在关系[22]。大数据时代,数字孪生、元宇宙等技术变革导致空间运转机制不断转变,乡村空间流动性显著增强,空间网络化趋势不断显现[23],也为跨尺度空间响应提供有效路径[24]。尺度作为地理学的核心概念之一,是表征地理空间规模、层次及其相互关系的量度[5,25]。多尺度乡村空间不断被建构、解构、重构,研判多尺度乡村空间特征及其跨尺度协同逻辑,为理顺多层级空间治理体系,服务城乡空间治理现代化提供理论和技术支撑[25-26]。多尺度视角成为解析新时代乡村空间特征的重要切入点,多尺度乡村空间特征及其治理为打破城乡分治格局创造条件[27⇓-29]。城乡交通扁平化、信息交换网络化、人口流通动态化等新形势下[30-31],乡村空间特征在城乡交互的跨尺度作用下呈现出多样化和复杂化趋势[32]。传统乡村聚落体系和空间用途管制传导体系面临全新的命题和技术挑战,乡村空间多尺度响应特征和尺度适应性治理成为待解难题[33]。国内学者以传统工业化地区、传统农区和大城市郊区为案例地开展乡村空间治理效应和机制探究[13,34 -35],但针对多尺度乡村空间治理尚缺乏系统研究。
因此,本文从物质性乡村空间出发,基于地理学空间分析范式,尝试从综合性、区域性和流动性认知乡村空间的内核特征。面向城乡转型趋势,总结多尺度乡村空间治理困境,探究多尺度乡村空间治理体系及其可行路径。基于此,本文构建了“特征识别—困境解析—治理框架—治理路径”的多尺度乡村空间治理分析体系,深化地理学视角下的乡村空间系统分析,总结面向新时代城乡治理现代化的乡村空间治理逻辑体系。
2 乡村空间特征理论建构
2.1 地理学思维与乡村空间运转逻辑
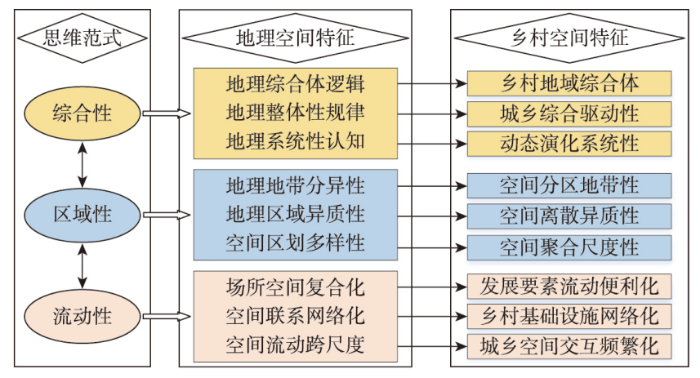
地理学存在的理由在于特征综合,地理综合研究是整体性认知与理解地理系统的重要途径,地理综合甚至成为新时期地理学创新与突破的根本任务[36-37]。区域性一直被认为是地理学的研究核心和基本特征,是地理过程和类型综合的概括和总结。虽然追求区域差异为核心的“区域学派”与崇尚科学规律一致性的“计量学派”经历了广泛的论战,但区域性仍在地理学科体系中占据重要地位[16,38]。地理综合和区域差异已成为地理分析的通识逻辑,综合性和区域性思维范式对人地关系为研究核心的地理学产生了深远影响。随着经济全球化和全球可持续危机的出现,地理流动性日益被学者们重视,并逐渐成为新的分析范式。刘建国提出了“远程耦合”(Telecoupling)分析框架,探讨社会、经济、环境的远距离相互作用机制,用“流”连接不同的耦合系统,系统建构了空间流动性对复杂系统作用的内在逻辑[39-40]。谈明洪等探讨了人地关系思维范式从本地化到全球网络化的转型趋势,揭示了地域开放性和不同地域交互作用对传统人地关系思想带来的冲击,进一步提出应该突破“一方水土养一方人”的传统空间思想[41]。因此,流动的空间相对于静止的空间(场所空间)已广泛影响人类的生产生活,空间的流动性及其与静止空间(场所空间)之间的互动作用逻辑成为未来地理学必须关注的命题[42-43]。空间流动性是区域性和综合性分析范式的有益补充,明晰了地理要素流动带来的空间交互作用,对提升空间分析的适宜性和完善人地关系理论具有重要推动作用。
乡村空间是指城市建成区以外乡村地域上人地关系相互作用的物质载体。乡村空间区别于自然空间的核心特征是其“人”化的空间表征,抽象乡村空间内涵不能脱离“人”与“地理环境”相互作用的内在逻辑,进而形成具有乡村特色的空间表征体系。因为“人”的社会经济属性使得乡村空间兼具自然环境、社会经济、人文文化等综合属性[8]。乡村国土空间内嵌于乡村空间,突出强调空间的自然资源属性和社会经济属性[44-45],乡村国土空间是日常生活接触最密切的空间,土地利用是乡村国土空间最具代表性的空间表征[2]。城乡转型进程中,城市空间与乡村空间交互作用日益频繁,部分地区呈现空间的融合性[35],兼具城市空间和乡村空间的特征,这也导致城市空间与乡村空间难以区分,进而出现“城乡连续体”“城乡有机体”等凸显城乡空间难以分割的空间表征[1]。本文城乡空间是指城市空间和乡村空间的有机整体,突出城乡空间的整体性和交互性。地理学擅长开展区域性的空间异质性分析,空间综合分析强化了地理空间的整体性,空间流动性突出了空间交互作用对传统地理空间的影响。因此,本文从地理学分析范式总结乡村空间的特征体系,从多尺度视角解析乡村空间特征的运转逻辑,为开展乡村空间治理提供理论和实践基础。
2.2 综合性思维与乡村空间特征
地理综合性通常将地理(地域)综合体作为研究对象,关注综合体在多种地理要素相互作用过程中体现的地域结构和功能的整体特征,在此基础上总结地理现象和过程的演化规律[46]。因此,综合性思维强化了地域综合发生规律的科学意义,重点在于揭示地理要素交互作用的内在关系和动力机制,强调地理空间演化过程不是单一要素驱动的结果,指出多要素综合过程是地理规律发生演化的内在逻辑,突出空间综合分析的研究范式[47-48]。为增强地理综合分析的技术和理论支撑,地理系统思维和模型成为地理综合研究的重要抓手,强调自然环境系统与人文经济系统内在的整体性[38],探测自然圈层和社会圈层相互作用规律,突破地理综合的理论与方法难题。面对地理综合分析的理论和实践困境,吴传钧提出的“人地关系地域系统”理论正是地理综合研究的重要理论基石[49-50]。
乡村地域综合性和城乡空间联动性成为乡村空间综合的重要特征。乡村空间的综合性是乡村地理长期研究的主阵地,也是乡村地理的理论前沿。乡村空间综合性主要表现为自然环境系统和人文经济系统交互作用频繁,影响乡村空间演化过程及驱动机制的要素多样性,模拟乡村空间动态的结构体系和技术路径综合,城乡空间联动作用的机制趋于复杂等。《中华人民共和国乡村振兴促进法》中强调“乡村是指城市建成区以外具有自然、社会、经济特征和生产、生活、生态、文化等多重功能的地域综合体”,从法律层面认可了乡村空间的综合性特征,尝试从地域综合体视角解构乡村空间的内在机制。刘彦随基于“人地关系地域系统”思想,提出了乡村地域系统理论,进一步阐述了乡村地域系统由城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体等组成的地域多体系统,利用多体系统建构了乡村空间综合分析的理论和实践路径[1]。乡村空间综合性评价试图探测其发生演化规律,如“乡村性”“乡村活力”“乡村吸引力”“乡村弹性”等评价方案,均尝试从某些侧面揭示驱动乡村空间演化的内在机制[51-52]。由于乡村空间相较于城市空间具有鲜明的“离散性”[53],这也直接导致乡村空间综合性研究的尺度选择特别重要,针对不同尺度的乡村空间开展综合性研究,往往导致研究主体和方案的迥异,这些内容接下来将着重论述。
2.3 区域性思维与乡村空间特征
地理研究的区域性以空间“差异性”与“相似性”作为基本出发点,关注区域间的分异规律、梯度差异、划分体系,以及区域内的时空过程与地理机制[38,54]。因此,区域内部地理要素发生演化规律与区域间地域分异和关联作用规律,成为地理学区域性研究的主导方向。传统单一要素主导的区域性研究已难以满足新时代地理综合的诉求,区域问题分析对多要素驱动、多区域联动、多系统交互提出更高要求。针对“问题区域”的“区域问题”,如何从区域视角提供全局性解决方案,成为新时期区域研究的重要方向。地理区划是地理学的传统工作,也是深化地理区域性研究的有效手段,从区域的“统”“分”方案出发,对地理空间开展区域内和区域间的系统分析,不论是“自上而下”的分类体系还是“自下而上”的聚合方案,区划研究都为区域研究提供重要依据[48,55]。
以乡村发展问题为导向的乡村地理研究长期关注乡村空间的“乡村问题区域”和“区域乡村问题”,并形成了多尺度区域研究传统。乡村空间区域性特征与乡村地域演化规律紧密相关,离散的乡村空间进一步凸显了乡村地域差异性,乡村地域类型划分研究尝试寻找一致性的乡村空间,并进行空间区划,进而建构了“自下而上”的乡村空间划分体系。以农业区划为代表的乡村生产空间区划,突出了分散特征下的乡村空间区域特色[56],乡村空间分区的地带性规律成为揭示乡村空间区域特征的重要手段。乡村空间区域性在多尺度案例选取上呈现显著特色,典型村域成为乡村区域研究的重要载体,村域人地交互作用过程和机制成为解析区域乡村空间演化规律的有效路径。微观乡村空间地域差异性显著,直接导致乡村空间区域间对比研究困难,难以建立统一的测度标准,加之数据获取渠道单一,导致乡村空间区域间对比分析以质性分析为主,空间离散的异质性特征被强化。乡村空间区域研究尚缺乏科学的范式,导致乡村空间区域研究与农村社会经济和土地管理等学科的分析范式区分度不够,乡村地理的区域分析范式仍待完善。此外,乡村空间区划研究深度和广度仍待强化,区域内一致性和区域间对比性研究均需要更科学的评价体系,用以支撑离散空间的聚合研究,推进乡村空间聚合的尺度选择显得尤为重要。新时代,城乡跨尺度交互作用下,乡村空间区域性研究需要在尺度选择和多尺度融合上找到新的突破口。
2.4 流动性思维与乡村空间特征
地理要素流动塑造了空间流动性,成为改变地理空间格局的重要动力,空间流动性成为分析空间演变与地理演化机制不可或缺的重要视角。开放系统、“流”空间、远程耦合成为新时期地理空间研究的新命题[54],面向地球表层自然环境系统和社会经济系统的复杂交互作用,从静止空间分析逻辑向流动空间分析逻辑转型[50],流动性成为复杂地理系统分析的重要思维模式。区域间频繁的物质能量交换提升了人流、物流、信息流、技术流、资金流、能源流等要素的互动频率、流动趋势、流动强度。席广亮等研究发现“流”空间和场所空间的互动作用改变了传统地理空间的关系体系,影响了地理要素的时空弹性,改变了地理空间的组织和布局模式[57]。现代交通(航空航天、高速铁路等)、通讯(互联网、移动通信等)、智能模拟(AI、VR等)等技术的快速发展,突破了自然绝对空间的限制,以空间距离、空间环境、空间演化为基础发展起来的传统地理学理论面临重大挑战[23]。地理要素在多尺度空间的集聚与扩散,改变了传统地理空间综合性和区域性的分析逻辑,本地要素流动的跨尺度效应,进而带来区域地理演化驱动机制的复杂化,改变了地理综合分析的常规模式。
城乡要素流动重塑了乡村空间运转体系和解析方案,数字技术重构了乡村空间的联动特征,乡村空间流动性带来乡村空间的要素混杂化、结构动态化、功能多样化(图1)。社会经济发展要素在城乡空间的频繁流动,突破了城乡之间要素流通壁垒,权利分配障碍、结构功能失衡等问题,发展要素流通便利化成为乡村空间流动的重要特征,为打破城乡空间的不均衡格局创造条件[2]。城乡人口流动是打破城乡要素流通的关键环节,多渠道人口流动与迁移打开了城乡发展要素(技术、信息、资本、人才等)互通的大门[58-59],城乡空间交互的高频度和跨尺度成为可能。城乡市场联动在乡村空间用途管制和权利有序配置过程中得以强化,城乡交通网络体系是市场联通的重要通道,为构建新型城乡关系提供组织保障和资金供给,进而重构城乡空间联通体系,城乡基础设施建设的一体化特征不断增强。城乡土地利用结构与功能联动的动态响应,为揭示乡村空间流动性规律提供重要依据。流动性乡村空间是乡村地域系统转型分析的有利工具,强调系统开放性,突出城乡空间联动的现实逻辑,为分析城乡转型与乡村重构提供全新方案。
图1
图1
地理学思维与乡村空间特征
Fig. 1
Geographical thinking paradigm and rural spatial characteristics
3 新时代多尺度乡村空间特征
乡村空间在城乡快速转型进程中表现出尺度综合、尺度传递、尺度交互等多尺度特征,多尺度乡村空间成为揭示城乡空间演化规律的重要切入点。多尺度乡村空间运转逻辑需要破解尺度综合、尺度分异和尺度流动对乡村空间的作用机制,突出乡村空间多维综合性、强化乡村空间时空异质性、融合乡村空间网络流动性,进而从多尺度视角建构乡村空间的解构方案,也为制定尺度适宜的乡村空间治理体系创造条件。
3.1 多尺度乡村空间综合
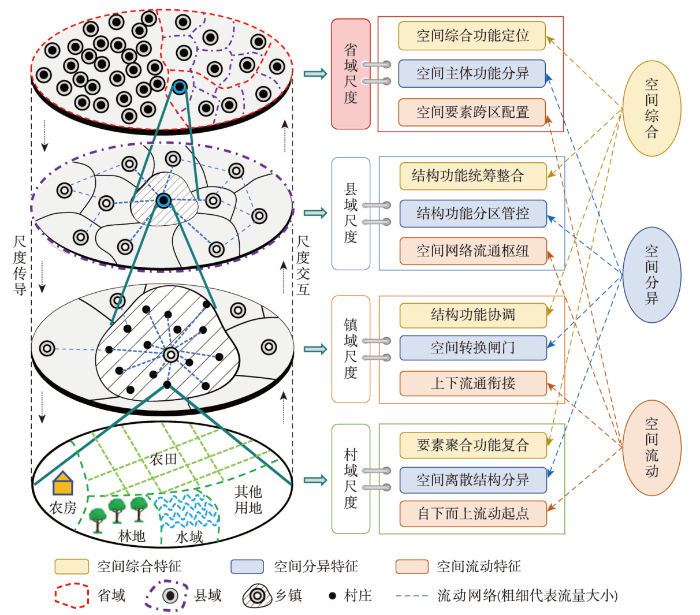
乡村空间多尺度综合是解析乡村地域系统内在机制的重要工具,尺度选择与尺度转换是乡村空间综合研究的关键环节。“国家—省级—县级—乡镇—村庄”等多级行政尺度是划分多尺度乡村空间的常规方案,不同层级乡村空间由于尺度差异,对应的空间综合内容也随之变化,显著的特征是高层级乡村空间内容更宏观,而低层级乡村空间内容更微观,对应的空间综合方案也不同。本文着手从“省域—县域—镇域—村域”4个尺度出发解构多尺度乡村空间治理体系,并没有将国土空间规划体系中的地级市尺度囊括进来。上述选择是由于市域尺度的乡村空间特征处于省域和县域之间,乡村空间尺度特征的典型性不够,因此本文并未将其考虑进来。省域乡村空间综合分析重点是揭示乡村空间要素组成、空间结构与功能等宏观特征,空间综合的解构方案以结构和功能评价为核心手段,突出广域乡村空间的综合特征[48]。随着尺度的下移,乡村空间综合内容逐渐丰富,县域尺度作为长期稳定的治理单元成为乡村空间综合较为成熟的尺度,县域主体功能定位能够较好的阐述中观尺度乡村空间综合的内在机制。县域乡村空间综合分析方案较为成熟,测度县域空间结构功能体系的方法较为完善,评价乡村空间综合特征的指标体系也较为丰富。随着交通通勤半径的扩大,县域尺度逐渐成为乡村空间综合统筹的远景目标尺度。乡镇尺度作为衔接城市与村庄尺度的转换枢纽,随着农民生产生活半径的扩大,乡镇尺度空间统筹协调的潜力和范畴不断拓展,乡镇空间综合在部分地区已全面实现。村庄作为乡村空间的微观载体,包含了丰富的空间信息,空间要素聚合特征和功能复合性得到凸显。然而,由于微观空间的离散性,导致乡村空间综合难度大,典型村庄空间综合在揭示空间演化内在逻辑上提供更多的案例支撑。由此可知,乡村空间综合内容的多样性与尺度选择密切相关,针对乡村空间问题选择合适的尺度开展空间综合至关重要。
多尺度乡村空间交互作用为空间尺度转换与跨尺度作用提供新路径。乡村空间综合研究需要在解构体系和技术方案中找到新的突破,乡村空间多(跨)尺度交互作用为建构空间科学分析体系提供支撑(图2)。新时期数字乡村空间综合分析对多尺度空间综合提出全新要求,面向地理要素交互作用的综合分析方案需要进一步提炼[60]。建构可度量、可模拟、可跟踪的乡村空间信息平台将提升乡村空间的综合分析和模拟能力。传统乡村空间综合分析以“人地关系”“人地作用”“人地关系转型”等作为核心主线,但多尺度乡村空间人地关系交互作用逻辑不清,这也直接导致乡村空间尺度传导与尺度交互机制不明,进一步限制了多尺度乡村空间定量分析和科学模拟。因此,面向多尺度空间交互作用的乡村空间综合分析需要在尺度治理上找到突破口,明确尺度综合要素,找准尺度治理手段,明晰尺度传导机制,突出尺度治理效应,强化尺度交互路径。
图2
图2
多尺度乡村空间内在逻辑关系
Fig. 2
The internal logical relationship of multi-scale rural space
3.2 多尺度乡村空间分异
乡村空间结构的不连续性、功能的多样性、价值的复合性决定了多尺度乡村空间分异,可以基于乡村地域综合体的“要素—结构—功能”分异进行阐述。“城乡分治”的国土空间管控体系、“权利模糊”的空间权属体系、“组织零散”的空间组织体系构成了乡村空间分异的宏观背景,多尺度乡村空间分异需要在区域乡村空间演化中找准合理的分析对象。多尺度乡村空间需要考虑城乡地域系统要素、结构和功能的格局状态,城乡割裂的空间异质性分析难以真正起到“管中窥豹”的作用。多尺度乡村空间要素分异可以将驱动乡村空间转型的自然、环境、经济、社会等要素选择合适的尺度囊括进来。乡村空间结构分异是解析区域空间内在机制的关键环节,有助于完善乡村地域综合体演化的理论逻辑,主要包含空间体系结构、空间关系结构、空间组织结构等。乡村空间功能分异从功能视角展示了区域乡村空间的发生机制,而地域功能类型、主导功能差异、综合功能演化等视角是较为成熟的分析范式。
多尺度乡村空间需要重点分析其“自上而下”和“自下而上”差异化的分异逻辑,进而为建构多尺度乡村空间治理体系提供参考。“自上而下”的乡村空间尺度分异可从空间分异的传导机制上找寻地理踪迹。宏观尺度上(如国家和省域尺度)厘清区域主体功能和综合功能的地域差异是尺度分异及其传导的关键内容,乡村空间地域综合功能分异决定了乡村空间转型趋势。县级尺度上乡村空间分异主要表现为空间结构体系的异构过程,县域作为乡村空间统筹治理的关键尺度,其分异机制是制定空间统筹方案和结构体系优化的基础。而镇域尺度是乡村空间管控和要素统筹的重要尺度,乡村空间分异可以基于土地利用和人口转型趋势,精确测度不同村庄的地域类型,进而填补宏观尺度上乡村空间分异粗糙的裂隙。村域尺度是乡村空间分异的基层单元,地理要素分异是村庄空间分异的底层逻辑,空间离散带来的结构分异需要在数据获取中找到突破口,基于农户调研、多时相高分卫星数据、村庄发展历程访谈,建构村庄尺度乡村空间分异数据库是微观空间分异的数据基础。“自上而下”的乡村空间分异体系核心阐述了国家治理视角下传统尺度传导理念,但尺度传递的地理逻辑仍不明晰,微观尺度空间如何影响宏观尺度空间的地理机制值得深入探讨。新时期如何建构“自下而上”的乡村空间分异体系,引入新的数据和技术方案,将“微观”“分散”“多元”的底层乡村空间分异结果,通过尺度交互逻辑形成全新的空间分异分析范式,将有利于提升乡村空间区域分析精度,推动城乡空间分异研究的底层衔接。
3.3 多尺度乡村空间流动
城乡空间转型是多尺度乡村空间流动的内在动力,进一步推动城乡空间要素流动,将平面城乡空间拓展为立体的多尺度空间。如果说城乡是一个不可分割的有机体,那么城乡空间在空间流动性作用下更具有空间的一致性。长期以来城乡空间的割裂研究已经难以揭示空间联动的内在机制,空间流动性成为衔接多尺度物理空间的纽带,强化了城乡空间的交互作用。空间流动性推动城乡空间结构连通、功能互通、价值流通的内在机制和互动作用逻辑,成为城乡空间综合衔接的科学基础,也是分析多尺度乡村空间流动的前提。多尺度乡村空间要素流动主要有人口流、物流、信息流、资金流、技术流等,人口流动成为解析城乡空间流动的关键信息,城乡人口流动的空间效应,进一步带来其他要素的跨尺度流动(图2)。多尺度乡村空间流动性强化了城乡空间联动作用机制,并强调了“自下而上”底层空间要素流动对城乡空间的重构作用,基于城乡要素流动的空间尺度交互作用,进一步明确多尺度乡村空间流动的尺度嵌套和尺度交互逻辑。
多尺度乡村空间流动完善了城乡空间网络体系,网络化和数字化成为新时期多尺度乡村空间流动的显著特征。空间流动在多尺度乡村空间之间起到了衔接作用,推动乡村空间由尺度割裂转向尺度交互。多尺度乡村空间流动性重构了“自下而上”空间网络的生成机制,进一步强化底层空间流动对顶层空间的影响,空间远程耦合与链接成为可能[37,48],尺度交互强度提升将进一步增强空间网络韧性,也为乡村空间多元发展创造机遇。省域尺度在空间要素跨区域配置上发挥重要作用,县域尺度作为空间流动网络的枢纽作用日渐明晰,镇域尺度的上下衔接作用和村域尺度的流通启动作用得到强化。数字化为代表的乡村发展过程,为多尺度乡村空间信息、物流、资金等流动创造条件,有利于打破城乡数字鸿沟。网络化与数字化叠加后,多尺度乡村空间已具备“自下而上”聚合的现实基础。从底层空间数字信息采集入手,通过信息技术和网络技术,实现多尺度乡村大数据聚合,进而为测度乡村空间多尺度分异提供高精度数据和方法支撑。
4 新时代乡村空间治理困境
4.1 城乡空间综合统筹不足
城乡割裂的空间治理不能适应多尺度空间治理的现实需求,城乡空间综合治理不足成为限制城乡融合发展,导致“城市病”和“乡村病”叠加的重要诱因。城乡空间分治导致城乡空间开发利用政策和空间开发价值流向存在巨大差异,以空间用途管制为核心的空间管制手段,强化了空间治理的城乡撕裂。当前,国土空间规划体系中城镇开发边界内采用“详细规划+规划许可”,城镇开发边界外采用“详细规划+规划许可”和“约束指标+分区准入”的管制方案,城乡空间统筹与综合考虑不足成为空间治理绩效提升、科学有效、公正可行的重要阻力。现有国土空间规划基于“自上而下”开展的层级传导空间治理逻辑,虽然中央空间治理诉求得到了强化,但针对城乡空间有序的统筹治理、“自下而上”和“自上而下”结合的综合治理、多元主体有效参与的公平治理等方面仍存在体制机制障碍。“立足城市看乡村”和“驻足乡村望城市”均脱离空间综合的科学认知。城乡空间既然是难以分割的有机整体,就可以在城乡空间统筹治理上找到突破口。
城乡空间综合治理需关注多尺度空间结构与功能的联动特征和交互机理,集聚复合的城市空间与离散多样的乡村空间共同构成了国土空间地域特征。新一轮国土空间规划对乡村空间管控力度进一步强化,多尺度乡村空间利用潜力被削弱,城市倾向的空间配置体系恐将进一步固化。如城镇地区的商品房约270亿m2,农村地区房屋约220亿m2,但二者的价值量和资产量差异巨大[61]。宏观尺度的城乡空间近期和远期动态谋划不足,导致大城市无序扩张,进而占用大量乡村空间,城乡空间治理结构性失衡。宏观尺度的城乡空间失衡导致中微观乡村空间被进一步挤压。城乡空间线性界线的区分(如“三区三线”划分方案),缺乏城乡空间弹性调整的科学机制,导致城乡空间统筹的综合治理缺乏实践依据。此外,城乡空间多尺度结构体系缺乏协调机制,如何科学聚合乡村空间,优化城乡空间结构体系,缺乏多尺度城乡空间的动态模拟。
4.2 空间异质性价值不显化
乡村空间价值不显化,异质性空间价值结构不合理,区域性空间价值配置失衡,带来乡村空间开发的无序化和低效化,进一步压缩了原本有限的乡村空间价值。区域乡村空间异质性将带来国土资源开发利用类型的显著差异,空间资源价值形成、分配与流动将导致空间价值的异化,有助于完善区域认知的内在机制。多尺度乡村空间区域异质性价值与空间权属体系和组织关系密不可分,乡村空间权属关系不明晰和空间组织体系不畅通是乡村空间价值难显化的关键限制性因素[2]。当前,多尺度乡村空间异质性价值不显化与价值形成要素不稳定、价值结构体系不适宜、价值流向网络不畅通等因素紧密相关。与之对应,乡村空间权属关系模糊与权利主体不明确,乡村空间集体所有与部分国有(如国有农场)的现实状态导致空间产权实现方式不明朗,直接导致乡村空间价值形成要素不稳定[2,45]。以生产性价值为核心导向的自然资源价值核算体系导致异质性乡村空间价值被严重低估,乡村空间的生态价值、社会价值、文化传承价值没有得到足够的重视,这也导致乡村空间价值结构的不适宜。乡村空间集体化组织实现方式待创新,乡村集体所有的自然资源资产管理制度和法律待完善,精英化集体组织成员和现代乡村经营主体培育待强化,导致乡村空间组织体系不畅通,乡村空间价值流向的组织网络在主体间和尺度间存在堵点。
多尺度乡村空间价值的保值与增值离不开价值配置体系、主体参与机制、空间组织关系的完善。市场配置体系不健全是多尺度乡村空间价值难以显化的关键环节,缺乏市场有序调节的空间价值难以在多尺度空间上形成价值的流通渠道,无法促成空间价值的增值。当前,城乡空间固化的价值传导链、市场供应链、主体参与链,塑造了城乡空间价值分配链,多尺度乡村空间价值传导路径不通与市场的参与程度不高有关,城乡空间价值市场缺乏衔接难以支撑乡村空间价值增值的配置需要。多元主体参与机制不完善与空间组织关系不牢固共同塑造了底层乡村空间价值运转状态,也成为“自下而上”空间价值形成与转化现实障碍的重要表现[13]。乡村空间主体不明确,产权不明晰,交易不明朗,阻碍了自然资源资产化和资本化道路,多元价值培育难以形成社会共识。上述问题造成乡村空间保值与增值的实现方案仍存在理论缺陷,实践方案不足,技术体系不全等现实困境。
4.3 空间流动性网络不畅通
空间网络畅通度与城乡发展要素流通度决定了乡村内生发展动力与乡村振兴潜力。多尺度乡村空间交互作用需要强化城乡发展要素的跨尺度流动,进而推动城乡发展机制联动,破解城乡融合发展困境。当前,多尺度乡村空间在要素流通网络、空间结构网络、功能配置网络均存在流通网络不畅通等现实问题,限制了通讯数字化和交通便捷化给乡村发展带来的巨大机遇。空间流动性网络不畅通既是城乡二元分治遗留的体制弊端,也是多尺度乡村空间治理机制不健全的具体表现。以城乡建设用地指标跨区域流动为例,空间跨区域配置呈现出强烈的行政干预色彩,市场在推动土地要素跨区域流通过程中,交易价格和可交易数量受到严格的行政管控[45]。以城乡聚落体系为代表的空间结构网络不畅通主要表现为规模体系不协调和空间配置不合理,难以支撑城乡空间有序高效开发的目标。功能配置网络不畅通的标志主要有地域主体功能与综合功能配置不均衡,地域功能与空间价值分配不公平,进而阻碍地域功能的流动性配置。
城乡市场流通网络和公共服务网络的不畅通导致空间流动性难以高效配置城乡空间资源,也是多尺度乡村空间治理亟待解决的现实难题。城乡市场链接体系和产业联动体系与多尺度空间流动紧密相关,城乡市场机制难互通,进一步导致城乡统一大市场网络不通畅[62]。城乡市场流通不畅既包含与空间直接相关的空间资源流通也包含与空间权利和价值密切相关的空间资本流通。此外,与城乡市场连通密切相关的劳动力、技术、金融等流通也呈现出显著的空间异质性和尺度分异特征,并且受到多尺度乡村空间流动性的影响。城乡公共服务网络不畅通导致城乡融合发展轨道难疏通,主要表现在城乡教育、医疗、养老、交通等公共服务网络的城乡异构特征,这也成为城乡融合发展急需破解的难题[3]。城乡公共服务网络配置不健全和网络连通不通畅问题,同城乡分异的空间用途管制体系和多尺度连通网络存在密切联系,破解乡村空间多尺度网络的流通性问题,将为解决公共服务城乡不均衡提供有效路径。
5 多尺度乡村空间治理逻辑体系
5.1 多尺度乡村“空间综合—空间分区—空间流动”治理体系建构
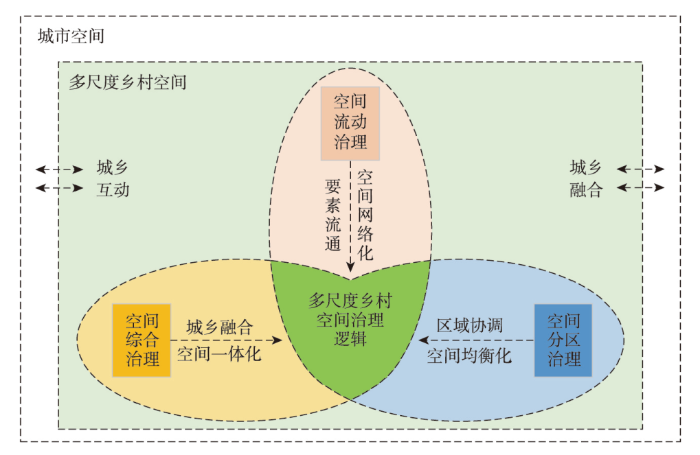
多尺度乡村空间治理核心目标是破解新时代乡村空间开发利用过程中存在的结构性问题,以多尺度思维为牵引,重点突破多尺度空间综合、空间分异和空间流动存在的体制机制障碍,进而提升空间治理水平,完善多尺度乡村空间治理体系。多尺度空间综合治理、空间分区治理和空间流动治理,分别瞄准乡村空间的多尺度分异规律,从多维度视角建构面向城乡空间治理现代化的乡村空间治理逻辑体系。乡村空间多维度和多尺度异质性为开展有针对性的空间治理提供指引,尺度差异与多维度乡村空间建构相结合,进一步明晰多尺度治理主体、治理内容、治理目标、治理路径。通过空间综合性、区域性和流动性的尺度分析,建构面向城乡空间融合、区域配置均衡和空间网络畅通的多尺度乡村空间治理体系(图3)。
图3
城乡转型进程中,乡村空间重构机制存在明显的尺度特征(重构程度、重构效应、重构机制等),“科学、高效、有序”的乡村空间多尺度治理体系有利于推动城乡融合发展,而“紊乱、低效、失序”的乡村空间治理将削弱乡村治理能力,造成系统性治理障碍。因此,面向城乡融合发展的空间综合治理、面向区域协调的空间分区治理、面向要素流通的空间流动性治理成为破解上述问题的有效方案。本文建构了“空间综合—空间分区—空间流动”治理为核心的多尺度乡村空间治理框架,从不同维度建构面向乡村空间治理现代化的多尺度治理内容,重点解决城乡转型期空间难综合、区域空间难协调、空间网络不畅通为核心的多尺度空间治理问题,服务城乡融合发展和乡村振兴战略。
5.2 多尺度乡村空间治理体系设计
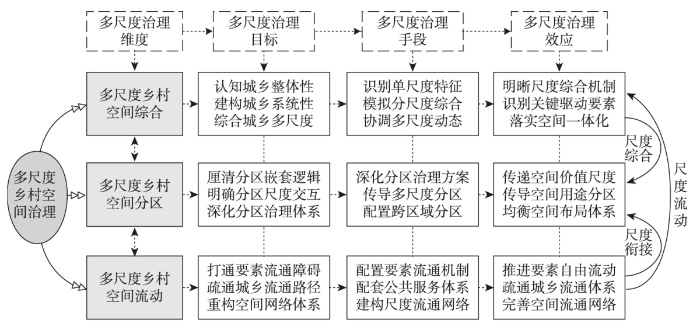
5.2.1 多尺度乡村空间综合治理
现阶段,乡村空间综合治理聚焦于多尺度城乡空间综合,服务城乡空间融合的远景目标,重构城乡空间融合的体制机制,重塑多尺度城乡空间格局,推动城乡空间融合规划落地与统筹治理目标落实。多尺度乡村空间综合在宏观尺度(如国家尺度)应明确城乡空间主体功能定位,落实城乡空间一体化机制建设,从国家治理和城乡治理现代化的愿景出发[59],科学评价和模拟城乡空间动态趋势,尽快实现城乡空间治理在顶层治理层面的一体化布局。省域尺度乡村空间综合治理在明晰地域主体功能和综合功能的基础上科学谋划城乡空间功能定位,以多级城镇体系建构为核心,科学谋划城乡空间战略布局。县域尺度乡村空间综合治理在明确综合地域功能的基础上厘清县域城乡空间的远景定位,统筹推进县域城镇化。镇域尺度乡村空间综合治理在完善城乡空间联动的基础上,推动乡村空间聚合和镇域空间统筹。村域尺度空间综合需要明确乡村地域功能和未来发展导向,服务“上下联动”城乡空间综合治理目标。通过多尺度城乡空间联动治理,推动多尺度乡村在空间统筹治理上实现尺度交互。
基于单尺度特征识别,分尺度综合模拟和多尺度动态协调实现多尺度乡村空间综合治理。通过多尺度乡村空间综合治理,总结乡村地域综合体的运转逻辑,揭示多尺度城乡空间交互的内在规律和分尺度整体特征,形成城乡空间统筹治理的系统性建构和多尺度乡村空间的整体性治理。当前,针对乡村空间底层个案研究和顶层综合评价的研究均较多,但针对乡村空间多尺度综合特征的内在机制及其系统性建构仍需在理论和技术上实现突破[38,50]。面向城乡空间统筹的系统性剖析是破解乡村空间分尺度整体性认知不足和多尺度交互作用机理不清的重要抓手。通过识别决定乡村空间尺度特征的关键地理要素,总结多尺度城乡空间作用的整体性特征,针对关键地理要素的多尺度交互作用机制制定尺度适宜的要素调控方案,形成多尺度城乡空间综合治理可行路径。通过多尺度乡村空间综合治理明晰不同尺度综合的内在机制,识别分尺度的关键驱动要素,进而落实城乡空间一体化综合治理目标。
5.2.2 多尺度乡村空间分区治理
多尺度乡村空间分区及其跨尺度交互作用机制是完善空间治理的重要内容,也是推动乡村空间区域性治理的重要手段。在乡村空间综合认知和多尺度系统解构的基础上,分尺度开展乡村空间分区治理,厘清多尺度分区嵌套逻辑及其转换机制是深化乡村空间多尺度治理的重要内容。当前,以国土空间规划“三区”划定(城镇空间、农业空间、生态空间)为代表的国土空间分区方案基本确立了国土空间用途管制分区的空间治理格局[44-45],进而形成了主导功能和适宜性的分区体系,将国土空间划分为城镇发展区、农业农村发展区和生态保护区,叠加差异化的用途管制方案,形成差异化国土空间分区治理方案。多尺度乡村空间分区治理核心需要界定尺度分区的科学依据,明确跨尺度分区的交互机制,形成分区体系的尺度嵌套,促进分区治理与分尺度治理相衔接。当前,规划分区体系中仍存在多尺度分区传导的理论和技术困境,宏观尺度(如省域)上乡村空间分区在规划分区中难以得到体现,中观尺度(如县域和镇域尺度)上仍存在分区粗糙,难以真实反映底层空间基底问题。微观尺度上(如村域)空间用途如何有效反馈到县域尺度的规划分区方案,进而建立多尺度乡村空间分区治理体系仍待完善。
多尺度乡村空间分区治理效应以优化乡村空间分异格局和突出乡村空间均衡布局为主要价值取向。推动乡村空间分区治理的尺度交互,落实城镇空间高效、农业空间提质和生态空间保育的分区管制目标,强化乡村空间多尺度分区的尺度适应性。多尺度乡村空间分区治理在打通尺度分区衔接和多尺度分区传导的基础上完善空间用途管制体系,创新空间分区治理方案,完善跨区域分区配置体系,服务空间均衡配置目标。针对“三区”划定过程中乡村底层空间管制强度大,空间开发弹性不足等问题,创新多尺度空间分区和跨区域空间调配的用途配置创新方案,以多尺度分区传导和跨区域用途管制衔接为突破,强化空间分区的均衡性和治理强度的伸缩性。省域尺度上以主体功能为依据,在强化乡村空间结构功能协调的基础上(如农业空间与生态空间协调)推动乡村空间功能分区与结构分区的价值均衡,预留乡村空间保护区。县域尺度上识别乡村优势发展区,合理配置镇村聚落体系,推动建设空间分尺度配置,优化农业生产与乡村生活空间结构布局。镇域尺度通过细化乡村空间用途分区及其与县域尺度的协同关系,创新乡村空间价值体系在多尺度分区中的传导逻辑。村域尺度从空间权属关系和组织体系创新入手,上溯乡村空间分区价值,突出多尺度乡村空间分区治理的价值分配导向,落实空间用途分区的有序传导与反馈,实现多尺度空间均衡布局(图4)。
图4
5.2.3 多尺度乡村空间流动治理
多尺度乡村空间流动治理核心是打通地理要素的流动网络和尺度流通路径,在综合治理和分区治理的基础上链接空间尺度分层,推进多尺度空间的网络连通度和尺度交互性,完善数字空间治理与跨尺度空间链接。空间综合和空间分区在强化乡村空间分尺度治理重要性的同时,在空间跨尺度链接上仍待强化,而空间流动性治理为上述问题破解提供有效方案。针对分尺度空间链接和跨尺度交互存在的流通堵点和网络通达度不高等问题,有针对性地引入现代数字信息技术,建设信息网络通道,强化要素流通的数字化运营,基于数字流通带动尺度交互和网络连通。与之对应,多尺度流动治理需要打通乡村流通网络的“最后一公里”困境,从配套基础设施和供给公共服务入手,提升流通网络的基础设施建设水平,夯实底层乡村空间的连通潜力和能力。除数字基础设施建设以外,交通、物流、金融、技术等经济发展核心要素的流通网络建设也至关重要。与多尺度乡村空间流通障碍相对应,在分尺度空间流通系统中预留跨尺度流通接口(或关键要素流通转换接口),分级实施关键要素的尺度配置,提升流通网络的抗扰动能力(图4)。
通过多尺度乡村空间流动治理破解当前城乡空间连通网络不通畅和跨尺度交互不稳定等问题,形成城乡空间价值流通、空间网络跨区域流通、发展要素跨尺度流通的有序空间网络体系,服务乡村空间多尺度治理现代化目标。瞄准新时代数字治理和智能治理趋势,以多尺度乡村空间网络畅通服务城乡要素流通和公共服务设施连通诉求,推进城乡空间要素流通的动态模拟与要素跨尺度交互衔接。省域尺度上突出要素流通与空间价值交互的互动耦合作用,以流通网络搭建为基础推进城乡空间价值流通和区域乡村空间价值交换。县域尺度以畅通基础设施配套体系和完善公共服务供给为突破,推进空间开发价值向乡村底层扩散。镇域尺度以衔接城乡发展要素跨尺度流通为契机,推动创新性乡村产业发展。村域尺度乡村空间流动性治理以“人”的全面发展和跨尺度流通为目标,推动乡村空间人地关系的协调和价值体系的重构,提升村域多尺度要素流通的承载力和和跨尺度交互作用的影响力。
6 多尺度乡村空间治理路径探讨
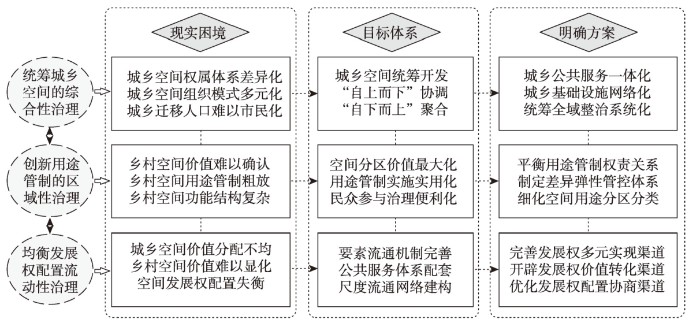
新时代落实多尺度乡村空间治理需要与现有政策体系对接,开辟乡村发展新路径,突出乡村空间创新治理新思路。本文从统筹城乡空间的综合性治理突破城乡割裂的治理困境,从创新用途管制的区域性治理出发强化空间治理的价值取向,从均衡发展权配置的流动性治理突出空间流动性的创新作用。
6.1 统筹城乡空间的综合性治理
统筹城乡空间的多尺度治理有利于突破城乡空间综合瓶颈,打破城乡空间分治带来的城乡融合障碍。城乡市场网络化、信息交互数字化、主体博弈多元化已经成为城乡空间交互常态,城乡空间分治难以适应新时期乡村发展的现实需求,更难以支撑高质量城镇化发展目标。统筹城乡空间的综合性治理在强化乡村空间特征的基础上,从城乡中国的空间联动性入手,强化城乡空间统筹治理的重要性。优化城乡空间互动“强度”和“通道”,重构城乡发展要素流动格局、空间结构特征、空间功能体系,进而建立全新的城乡互动关系。多尺度城乡空间统筹治理需要在平衡国土空间安全的基础上推进城乡关系融合,构建城乡联动高质量发展和城乡共同富裕的新格局。城乡空间多尺度综合治理落实国家发展的安全底线,需要从尺度综合特征出发明确分尺度安全保障支撑体系,进而建构与之对应的城乡空间统筹支撑措施。
通过城乡空间多尺度统筹实现空间治理“自上而下协调,自下而上聚合”,完善空间治理现代化目标。城乡空间统筹需要制定尺度适宜的空间综合方案,进而推动城乡空间的多尺度联动和跨尺度交互。现阶段,推动城乡公共服务和基础设施的一体化将为推动多尺度乡村空间综合创造基础条件。以交通、物流、数字网络等为代表的基础信息网络将成为推动城乡空间统筹的重要基础,也为打通多尺度乡村综合提供网络平台。以数字城乡建设为跳板,推进城乡空间信息化和网络化建设,全面深化城乡空间一体化建设。通过城乡基础设施和公共服务一体化建设,弥合城乡空间统筹的体制机制障碍,打通城乡空间综合治理的基础网络。省域尺度城乡空间统筹需要结合社会经济发展梯度特征,以地域综合功能为指导制定差异化统筹方案。县域尺度作为城乡空间统筹的关键尺度,以全域国土空间整治为核心抓手,面向城乡空间融合目标制定全域空间统筹方案,打破条块化空间治理思路。强化镇域和村域尺度多元主体的能动性,突出主体决策的灵活性和适应性,以空间主体的能动性衔接空间治理的约束性。
6.2 创新用途管制的区域性治理
创新用途管制方案是落实多尺度乡村空间治理的有效手段,也是实现多尺度分区治理的可行路径。多尺度空间治理应以空间分区价值最大化和利益最优解为目标,有效对接国土空间规划指标和规划用途分区传导体系。基于“逐级分解、要素传导、分类管控、分区细化”的乡村空间多尺度用途管制原则,确定分尺度空间管控内容,创新用途分区体系和分区管控方案,在完善刚性管控目标的基础上,寻求乡村空间价值最大化、民众参与便利化、管制实施实用化的可行方案。基于乡村空间的多功能体系,创新乡村空间用途分类体系,以文化保护空间、生态保育空间、社会保障空间等分类突出乡村空间的多元功能,强化乡村空间用途分类的多元价值导向。基于乡村空间复合结构体系,在空间用途分区划定和用途管制规则制定中突出乡村用地结构的混杂性和功能的复合性,强化乡村空间“刚性管控”和“弹性引导”的有机融合。以创新乡村空间价值实现方式为突破,开辟乡村空间权利和价值新领域,培育乡村空间价值交易新渠道,拓展乡村空间价值变现新路径。此外,突出乡村风貌建设和文化传承引导,结合乡村空间分异特征和乡村发展定位,兼顾不同村庄特色和管制诉求进行村庄分区管制。
创新多尺度乡村空间用途管制逻辑,将有利于从尺度分异视角完善乡村空间的区域治理效应。通过多尺度用途分级管控体系,明确管控要素传导逻辑和管控规则,有助于提升乡村空间尺度治理能力。宏观尺度(如省域尺度)结合空间价值重构,明确乡村空间价值体系,重构空间用途管制体系“权”与“责”的对等关系。粮食安全和生态安全贡献越大的区域,越应该创新乡村空间用途管制实施方案,为其提供空间价值转化渠道,平衡“空间贡献”与“空间收益”的巨大差异,推进空间分区价值均衡化。县域尺度在全面评估城乡空间远景变化的基础上,识别乡村空间地域分异特征,制定差异化空间分区管控体系,优先保护稀缺性空间资源,有序开发高价值资源。镇域层面基于土地发展权管制思路明确不同类型村庄差异化管控诉求,统筹分配空间管控指标,引导村庄分区分类,优化用地结构。村域尺度通过整合各类专项规划的用地需求,进一步细化乡村国土空间用途单元,明确各单元承载的用地结构,落实各类控制线和空间管控指标,强化乡村国土空间用途管制的可操作性。
6.3 均衡发展权配置的流动性治理
城乡空间价值分配不均和乡村空间价值难显化已然成为城乡空间治理现代化必须直面的问题,均衡空间发展权配置逻辑是空间治理的重要内容,基于流动性的多尺度乡村空间治理为推动空间发展权均衡配置创造有利条件。推动全面乡村振兴战略核心需要重构乡村空间价值体系和完善价值实现方案,没有城乡空间价值联动和发展权的均衡配置,城乡融合发展和乡村振兴战略的落实均缺乏有效支撑。空间价值的尺度流通性和城乡流动性决定了创新乡村土地发展权的生成、转移和变现渠道,是均衡城乡发展权配置的前提条件,城乡发展权的跨尺度配置将提升空间价值的配置效率,完善配置体系。以城镇开发建设用地指标与乡村发展建设用地指标为博弈核心的发展权配置失衡,与当前乡村空间所有权、财产权、交易权为代表的发展权体系发育不完整和法律保障不完善紧密相关。因此,相信农民用脚投票的合理性[63],给予农民更多的发展选择权和空间配置权,进而以发展要素城乡流动为基础,推动城乡空间发展权实现尺度流动。推动城乡土地市场开放互动,构建城乡一体化土地市场将释放乡村空间巨量经济价值,结合空间价值的跨尺度流动激发乡村地区的发展活力(图5)。
图5
空间发展权的均衡配置需要明确其尺度配置手段,重点包括多尺度发展权多元实现渠道、价值转化渠道和协商沟通渠道的完善,进而落实多尺度乡村空间流动性治理路径。发展权多元实现渠道应结合自然资源产权制度与自然资源配置体系创新契机,引入更多市场化配置元素,完善发展权的市场定价权和打通发展权的市场配置机制,以城乡多尺度流通网络为基础,突破城乡空间发展权的尺度配置障碍。开辟乡村空间发展权的价值转化渠道,以城乡建设用地指标交易为核心,融合3类空间发展权的跨尺度交易网络,以耕地保障效益交易、建设用地指标交易、土地发展权交易、生态空间产品化交易等为基础,培育发展权的价值转化多元渠道。发展要素的多尺度流动网络与发展权配置网络密切相关,基于数字乡村建设和数字乡村治理,培育多元主体参与发展权配置的渠道。新时期,新型农业经营主体、返乡创业者、乡村投资客等为代表的“新农人”,在信息技术支撑下完全有能力通过跨尺度流动网络推动乡村空间价值的变现。因此,鼓励多元主体参与到空间发展权的协商与博弈,为多元发展主体提供更多乡村事务参与权和发展决策权,将有利于疏通城乡空间发展权均衡配置的有机网络。
7 结论与讨论
7.1 结论
新时代乡村空间治理现代化成为国土空间治理能力提升的重要内容,识别乡村空间特征及其内在机制为构建有序的空间治理体系提供科学依据。根植于地理学综合性、区域性和流动性的学科特性,建构多尺度乡村空间特征分析范式,进而从地理学视角搭建多尺度乡村空间治理框架,厘清当前的治理困境并制定有的放矢的治理路径具有时代意义和鲜明的学科特征。研究发现:
(1)地理学综合性、区域性和流动性分析范式为解构新时代乡村空间特征提供理论支撑;多尺度乡村空间运转逻辑需要破解尺度综合、尺度分异和尺度流动对多尺度乡村空间特征的作用机制,突出乡村空间综合性、强化乡村空间异质性、融合乡村空间流动性。
(2)“省域—县域—镇域—村域”是划分中国现代乡村空间治理的主要尺度,城乡空间综合统筹不足和空间流动网络不畅通,叠加乡村空间异质性价值不显化成为新时期乡村空间治理亟待破解的现实困境。
(3)“空间综合—空间分区—空间流动”治理的多尺度乡村空间治理框架,为解决转型期城乡空间难综合、区域空间难协调、空间网络不畅通提供解决方案,为构建“科学、高效、有序”的乡村空间多尺度治理体系创造条件。
(4)统筹城乡空间的综合性治理、创新用途管制的区域性治理、均衡发展权配置的流动性治理,聚焦地理学空间治理特色,以问题破解为核心突破,成为支撑多尺度乡村空间治理的可行路径。
7.2 讨论
本文从地理学分析范式出发,尝试从综合性、区域性和流动性3个维度,全面深化乡村空间的特征剖析,并从“省域—县域—镇域—村域”4个主要尺度出发,结合地理学分析逻辑,深入探讨了多尺度乡村空间内在运转逻辑,尝试建构面向高质量发展的多尺度乡村空间治理体系。新时代,多尺度乡村空间治理路径应与国土空间治理充分对接,基于国土空间规划体系探索乡村空间治理的技术方法和可行方案,完善基层乡村治理手段,深化乡村空间治理的可介入性和可参与性。针对多尺度乡村空间特征的定量测度和可持续模拟是亟待拓展的创新领域,本文虽然从多个尺度出发尝试解析分尺度和分维度的乡村空间特征,但尚缺乏科学的评价体系。因此,面向空间治理现代化,充分吸收多学科创新方法,尤其是大数据等现代数字技术对空间流动带来的显著影响,从多源数据出发建设高精度城乡空间响应的评价体系,从多尺度视角解构乡村空间尺度特征,科学探测城乡空间流动的网络通畅度和拥堵度,评价跨尺度乡村发展要素流通的潜力和能力,为深化多尺度乡村空间治理提供数据支撑。
以国土空间规划为核心的国土空间治理研究成为地理学研究的重要内容,立足物质性国土空间的地理学研究具有学科优势,其中综合性思维和分尺度逻辑在国土空间治理体系建构中得到充分体现。当前人文地理学者对空间的认知已经超出了物质性空间范畴,以社会文化地理学者为代表,对乡村社会空间和文化空间开展了前沿探索,但理论完善度和成熟度有待强化。本文虽然从物质性乡村空间出发分析多尺度乡村空间特征及其治理逻辑,并不排斥对其开展非物质性空间的探索。未来以物质性空间为基础,叠加非物质空间的复合性空间治理体系具有创新空间。
参考文献
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 3]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 3]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 5]

The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
论乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 5]

构建现代乡村治理体系成为推动城乡融合发展和乡村振兴的重要内容。破解乡村空间利用过程中出现的发展空间受限、权属关系不明和组织体系不畅等系统性问题,成为乡村空间治理的首要任务。本文从乡村空间“物质—权属—组织”综合治理的视角出发,尝试解析乡村空间治理在推动乡村空间重构、权属关系重塑和组织体系重建中的作用机制,并进一步探讨乡村空间治理优化城乡格局、改善城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的可行路径。结论如下:物质空间治理可作为乡村空间结构和功能优化的重要手段,空间权属治理有助于保障乡村空间不同参与主体的发展权利,空间组织治理可提升乡村空间的组织效率;乡村空间治理导向的“人口—土地—产业”转型过程为“深化空间治理—活化乡村空间—优化人地关系—改善城乡格局”的分析思路创造条件;乡村空间治理推动城乡发展格局不断演化,城乡互动关系改善成为推动城乡融合发展和破解乡村发展困境的重要依据。最后,本文构建了乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展互动分析框架,并探讨了乡村空间治理与国土空间规划的内在关系及研究趋势。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 2]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 2]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Exploring the integrative development paths of geographic sciences from the perspective of National Natural Science Foundation of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202208001
[本文引用: 1]

With the progress of holistic science and human society, development of geographical sciences has entered a new stage of interdisciplinary integration. Under this context, geographical sciences urgently needs to seek new paths through the deep integration of disciplines to better improve the knowledge system and contribute to the country and society development effectively. Based on the perspective of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), this paper firstly deeply analyzes the current status and problems of the integration and development of geographical sciences in China, and points out that it is not fully integrated with the frontier of international geographical sciences, and the global political, economic and cultural influence of geographical research in China needs to be strengthened; considers that the ability of Geographic Sciences integrating national major practical needs for theoretical and technological innovation should be improved; suggests that the internal discipline system of geographical sciences in China should be further optimized according to the needs of knowledge integration. Then, this paper proposes three paths for the integrated development of geographical sciences under the guidance of funding policies, that is, the interdisciplinary integration facing the frontiers of science and technology in the world, the multiple fields integration facing the major national development strategies, and inner-discipline integration facing the optimized application codes of NSFC. In future, based on maintaining the continuity and stability of the development of disciplines, the NSFC will encourage the integration of geographical sciences with other disciplines and fields through the improvement and innovation, so as to promote and build a healthier and more innovative system.
国家自然科学基金视角下地理科学融合发展路径探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202208001
[本文引用: 1]

随着整体科学的进步和国家社会的发展,地理科学已迈入跨学科交叉融合发展的新阶段。通过学科间和领域间的深度融合寻求新发展路径,完善知识体系,充分发挥服务国家社会之功能,是当前地理科学发展的当务之急。本文基于自然科学基金视角,分析了中国地理科学融合发展的现状与问题,认为其与国际前沿未充分接轨,研究的全球政治、经济、文化影响力有待加强,认为地理科学融合国家重大需求进行理论与技术创新的能力有待提升,认为学科内部体系要根据知识融合需求进一步优化。在此基础上,提出了资助政策引导下地理科学面向世界科技前沿的学科交叉融合、面向国家重大战略的多领域交叉融合和面向申请代码优化布局的分支学科交叉三大融合发展路径与相应政策工具。未来国家自然科学基金委员会将立足于保持学科发展的持续性和稳定性,通过政策创新来激励地理科学与其它学科、领域的交叉融合,以建设更具有活力与创新性的学术生态系统。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 2]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 2]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
Trial by space for a 'radical rural': Introducing alternative localities, representations and lives
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2006.10.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rural regional system and rural revitalization strategy in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 3]

Rural regional system is a spatial system with certain structure, function and inter-regional relationship, which is composed of humanity, economy, resources and environment that are connected and interacted with each other. It is a regional multi-body system, including urban-rural integrity, rural synthesis, village-town organism, and housing-industry synergy. Targeting the rural regional system and supporting the rural revitalization strategy provides new opportunities and challenges for innovation of Chinese geography in the new era. Guided by the theory of regional system of human-land system and the science of human-land system, the research on rural revitalization geography should serve national strategy by finding solutions to problems hindering rural sustainable development, and make contribution to the comprehensive study of rural regional system structure, transformation process, evolution mechanism, differentiation pattern, regional function, and rural revitalization path and model under the interaction of surface's human-land system. There is an urgent requirement to better understand and reveal differences in the types of rural regional system and their differentiation law. Taking 39164 townships in China as research object, this paper used quantitative and qualitative methods to detect and identify the dominant factors that restrict the sustainable development of rural regional systems in China. Then we divided the types of Chinese rural regional systems, revealed the pattern of rural regional differentiation and further proposed scientific approaches to rural revitalization in different areas. Results demonstrate that topographic conditions, climate conditions, ruralization level, land resources endowment, population mobility and aging level are the dominant factors restricting the sustainable development of rural regional system, of which reflects the level of resource endowment, endogenous power and external aid of rural development. Through cluster analysis and spatial overlay of dominant factors, China's rural regional system can be divided into 12 first-class zones and 43 second-class zones. The first-class zones are named by means of 'geographical location + driving force of dominant factors', and the second-class zones are named by means of 'regional scope + driving force of dominant factors + economic development level'. The driving force of rural sustainable development in different regional types are varied. The regional pattern and path of rural revitalization in different types of areas are varied, and promoting the rural revitalization strategy should be based on local conditions to realize the coordination and sustainable development of rural economy, society, culture and ecosystem.
中国乡村地域系统与乡村振兴战略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 3]

乡村地域系统是由人文、经济、资源与环境相互联系、相互作用下构成的、具有一定结构、功能和区际联系的乡村空间体系,是一个由城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体等组成的地域多体系统。以乡村地域系统为对象,服务支撑国家乡村振兴战略,为新时期地理学创新研究提供了新机遇和新挑战。乡村振兴地理学研究,亟需以问题为导向、战略为指向,以人地关系地域系统理论和人地系统科学为指导,致力于地表人地系统交互作用下乡村地域系统结构、转型过程、演变机理、分异格局、地域功能,以及乡村振兴途径与模式综合研究,科学把握乡村地域系统类型及其分异规律。本文以全国39164个乡镇为基本单元,采用定量和定性相结合的研究方法,诊断识别了制约中国乡村地域系统可持续发展的主导因子,划分了中国乡村地域系统类型,揭示了乡村地域系统分异格局,探明了不同类型区乡村振兴科学途径。结果表明:① 地理环境、村镇化水平、资源禀赋、人口流动程度和老龄化水平等是乡村地域系统分异的主导因子,反映了乡村发展自然本底特征以及外援动力、内生动力的大小。② 通过主导要素聚类和空间叠加分析,将中国乡村地域系统划分为12个一级区、43个二级区。一级区采用“地理区位+主导要素驱动力/约束力”的方法命名,二级区采用“地域范围+主导要素驱动力/约束力+乡村经济发展水平”命名。③ 不同类型区乡村振兴地域模式和路径不同,乡村振兴战略与规划的落地要因地制宜、分类施策。
Progress and implications of international rural space research
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.12.014
[本文引用: 1]

Space is a product of society. Driven by industrialization, urbanization, informationization, and government policies, China's rural space is going through drastic reconstructions. As one of the core contents of international rural geography research, rural space studies are multi-disciplinary, multi-perspective, multi-dimensional, and multi-methods, forming a rich research field. In order to grasp the progress of rural space research more comprehensively, this study reviewed international rural space research literature in recent 40 years. The study found that international researchers described the connotation of rural space from the perspectives of material, imagination, and practice. The three-fold architecture was established to emphasize the practice of everyday life. It introduced living space to build the systematic research framework of rural space. With regard to the theoretical perspective, international research of rural space has gone through functionalism, political economy, and social constructivism; it transformed from productivism to post productivism; the research included settlement space, economic space, social space, and cultural space. As a whole, international research of rural space realized the change from material level to social representation, from object space to subject space, and from static one-dimensional space to dynamic multi-dimensional space, which revealed the importance of interdisciplinary and sociocultural approaches in rural space studies. The construction of rural space in China needs to pay attention to the subject status of farmers and multifunction of rural space, respect the role of locality and difference of various places, and recover the function of production of meaning of rural space.
国外乡村空间研究的进展与启示
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.12.014
[本文引用: 1]

任何空间都是社会的产物。在工业化、城镇化、信息化和政策的驱动下,中国乡村空间正在发生剧烈重构。乡村空间研究作为国外乡村地理学研究的核心内容之一,具有多学科、多视角、多维度、多方法的特点,形成了一个丰富的研究图景。为了更全面地把握国外乡村空间研究的进展,论文对国外近40 a的乡村空间研究文献进行了梳理。研究发现,国外学者从物质、想象和实践等层面诠释了乡村空间的内涵,并通过建立“乡村空间的三重模型”,强调了日常生活实践的重要性,引入了生活空间,构建了较为系统的乡村空间研究架构。在理论视角上,国外乡村空间研究经历了功能主义、政治经济学和社会建构主义3个阶段;在时间的演进上,实现了由生产主义空间研究到后生产主义空间研究的转换;在空间维度上,实现了聚落空间、经济空间、社会空间和文化空间的多重叠加。国外乡村空间研究实现了从物质层面到社会表征、从客体性空间到主体性空间、从静态单维空间到动态多维空间的转变,启示我们对乡村空间进行跨学科研究以及“社会-文化”研究的重要性。中国乡村空间建设要重视农民的主体性地位、强调乡村空间的多功能性、尊重乡村空间的“地域性”和“差异性”、恢复乡村空间的意义生产功能。
The local politics of the global countryside: Boosterism, aspirational ruralism and the contested reconstitution of Queenstown, New Zealand
DOI:10.1007/s10708-009-9268-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
On discrimination of rural definitions
DOI:10.11821/xb199804009
[本文引用: 1]

Rural Geography is a weak branch of Human Geography in China, especially with regard to its theoretical development and some basic concepts. First of all, this paper analyses rural definitions systematically from a multi dimention point of view (occupational、ecological、socio cultural). As an occupational definition, “rural” means an area where farming is the main mode of production. As far as ecological definitions are concerned, it means a settlement whose population scale is smaller, outside urban area, with rural landscapes showing unmistakable signs of being dominated by extensive use of land, and with discrete spatial units isolated from the outside world. Socio cultural definitions are in terms of clear differences in behavior and attitude between people in rural and urban area, such as ways of life, spatial behavior and aspirations. The author thinks that all the definitions are lack of delimitations of rural totally and essentially. Rural can not be summarized by a simple definition, because it is a complicated and indistinct conception. Difficulties of defining rural lie in dynamic evolution of the whole rural, unconformity among rural elements, relativity between rural and urban, and relevant rural urban continuum, which makes the boundary between rural and urban more indefinite. To a certain extent rural is regarded as areas differing from urban greatly and the difference can be compared in many aspects such as production activities, ways of life, etc. The close extent between urban and rural represents different stages of rural development. The author suggests rurality should take place of rural definitions under the background of urbanization in the world of today. Rurality refers to the manifestation of rural characters which take urban as criteria of reference within a specified area. The author draws his conclusions. First, every region can be looked on as a unity of urbanity and rurality. The more urbanity a region is, the less rurality it will have. Urban and rural are continuous and there is not any broken locality between them. Second, the size of rurality index takes urban as unit of reference. Using different urban criteria can reflect difference of rurality and stages of its development. Finally, rurality is concerned with scale, index and method which are used in our research. We can weaken some rural characteristics and improve regional urbanity in practice such as village town planning and regional planning by estimating rurality index of different areas. In order to be favourable to urban rural planning and management we also need to put forward rural countermeasures concerned correctly.
乡村概念辨析
Land consolidation and rural spatial restructuring
Currently, the implementation of new type industrialization, new type urbanization and agricultural modernization strategy lacks of a major hand grip and spatial sustain platform, due to long-term existed "dual-track" structure of rural-urban development in China as well as unstable rural development institution and mechanism and backward rural and agricultural infrastructures, which greatly affects the advancement of urban-rural integration development. It is necessary to restructure rural production, living and ecological space by carrying out land consolidation, so as to establish a new platform for building new countryside and realize urban-rural integration development in China. This paper develops the concept and connotation of rural spatial restructuring, i.e., an optimization and adjustment even utterly changing process of rural production, living and ecological space accompanied by rural socio-economic structure reshaping under the pressure of rapid industrialization and urbanization. The connotations of rural spatial restructuring involve three aspects of assembling industrial development, centralizing farmers' living and intensive resources utilization. Based on the effects analysis of industrialization and urbanization on rural production, living and ecological space, this paper also probes the mechanism which push forward rural spatial restructuring by carrying out land consolidation, an important approach to supplying cultivated land, revitalizing the stock land, optimizing rural-urban land, utilizing land intensively, and increasing land productivity. A conceptualization of the models of rural production, living and ecological environment spatial restructuring is analyzed in combination with agricultural land consolidation, hollowed villages consolidation and industrial and mining land consolidation. Finally, the author argues that a "bottom-up" restructuring strategy accompanied by a few "top-down" elements is helpful for smoothly pushing forward current rural spatial restructuring in China. The optimization and restructuring of rural intensive and high-efficient production space, suitable living space with amenity and ecological space with beautiful mountain and clean water will rely on the innovation of regional engineering technology, policy mechanism and mode of rural land consolidation, and more attentions should be paid to rural space, the foundation base and platform for realizing urban-rural integration development.
论土地整治与乡村空间重构
目前,中国新型工业化、城镇化和农业现代化的推进仍缺乏重要抓手和空间支撑平台,严重影响了城乡一体化发展进程。亟需通过开展农村土地综合整治,重构乡村生产、生活和生态空间,为推进新农村建设和城乡一体化发展搭建新平台。本文在界定了乡村空间重构,即在快速工业化和城镇化进程中,伴随乡村内生发展需求和外源驱动力综合作用下导致的农村地区社会经济结构重新塑造,乡村地域上生产空间、生活空间和生态空间的优化调整乃至根本性变革的过程,及其产业发展集聚、农民居住集中和资源利用集约3 个方面内涵的基础上,分析了工业化和城镇化进程对乡村生产、生活和生态空间的影响;探讨了乡村空间重构的土地整治类型及助推机制;结合农用地整治、"空心村"整治和工矿用地整治提出了乡村生产、生活和生态空间重构的模式与途径,以及依托土地整治的以"自下而上"为主、"自上而下"为辅的乡村空间重构战略。作为城乡一体化发展根基的乡村空间其重要性和基础平台作用应受到足够重视,乡村集约高效的生产空间、宜居适度的生活空间和山清水秀的生态空间的优化重构,有赖于区域农村土地整治工程技术、政策机制与模式的创新。
The logic of rural spatial governance and revitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204002
[本文引用: 4]

The rural vitalization in the new era and space development and utilization are closely related. It is meaningful to construct a theoretical system and practical path of rural vitalization based on rural spatial governance. Based on the deconstruction framework of "demand→effect→path→strategy", this paper discusses the internal logic relationship between rural vitalization and spatial governance. The results show the following: (1) The reconstruction of rural value is the key to ensure the realization of rural vitalization; rural spatial governance can be a good way to realize the rights allocation and effective control of rural space; rural spatial governance includes material spatial governance, organization spatial governance, and ownership spatial governance; through spatial governance, the structure and function of physical space can be reconstructed, the organization relationship can be reorganized, and the value distribution can be reshaped. (2) The effect of spatial governance on rural vitalization is presented from the optimization of the urban-rural interaction, as well as the stimulation and strengthening of rural endogenous power, and the capabilities of grassroots organizations. (3) Rural spatial governance is an effective path to implement rural vitalization by promoting the urban-rural integration development, activating rural endogenous development, and ensuring the organizations mechanism. (4) The rural spatial governance system combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" forms to implement rational allocation of spatial development power. The channels, capabilities, and effects of multiple subjects participating in spatial governance will promote the realization of space development and the establishment of a system with equitable rights and interests. The "right-sharing" spatial governance can implement the rural revitalization strategy in urban-rural sharing, subject and regional sharing. In summary, the research will provide references for improving the scientific system of rural spatial governance and implementing the rural revitalization strategy.
论乡村空间治理与乡村振兴战略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204002
[本文引用: 4]

新时期乡村振兴挑战与空间利用问题密不可分,基于空间治理建构乡村振兴的理论体系和实践路径具有现实意义。本文基于“诉求→效应→路径→策略”解构方案,探讨了基于空间治理的乡村振兴可行性和内在逻辑体系。结果表明:① 乡村价值重构是确保乡村振兴目标实现的关键环节,乡村空间管控和发展权利配置可从乡村空间治理寻找突破口;乡村空间治理从物质空间治理、空间组织治理、空间权属治理入手,重构物质空间结构功能,重组空间组织关系,重塑空间价值分配体系;② 空间治理振兴乡村的效应从城乡互动关系优化、乡村内生动力激发、基层组织能力强化等层面加以呈现。③ 乡村空间治理推动城乡融合发展、激活乡村内生发展、保障组织机制,是落实乡村振兴的有效路径。④ “上下结合型”乡村空间治理有利于落实空间开发权利的合理配置;多元主体参与空间治理的渠道、能力与效应,推动空间发展目标落地和公平权益体系建设;“权利共享型”空间治理可在城乡共享、主体共享和区域共享中落实乡村振兴目标。研究结论可为完善乡村空间治理科学体系和落实乡村振兴战略提供参考。
The methodology of human-economic geography and its characteristics
DOI:10.11821/yj2011030001
[本文引用: 2]

Based on the analysis of the background of geographical development, this paper expounds the basic methodology of human-economic geography and the characteristics of man-land system, and proposes studies on "man-land system dynamics". The paper is an effort to develop a comprehensive theory system and to improve academic research of human-economic geography by expatiating its methodology and characteristics. It can also contribute to forging a consensus that human-economic geography and sustainable development research have had a significant position for academia, especially for physical science; meanwhile, to promoting formation of research framework on resource-environment (including ecological)-sustainable development study in earth surface system.Being dead against the prejudice of a few scholars, it emphasizes and analyzes the uncertainty and scientific characteristics of human-economic geography.
人文—经济地理学的方法论及其特点
Some key issues concerning development of geographical science in China
DOI:10.11821/xb200301001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 20 years, outstanding progress has been made in the development of China's geographical science which consists of both applied aspect and talents training. It also played an essential role in the nation's major research projects. There were more than 200,000 people engaging in geographical education and research in institutions, universities and colleges as well as middle schools in China in 2002. There were 565 professors and 1,001 associate professors working in the major 42 geographical institutions, of which 8 have the power to confer Ph.D degree of primary disciplines and 65 to confer Ph.D degree of secondary disciplines. In the 42 institutions, there are 340 doctoral tutors. Since the second half of 1999, 586 PhD students and 1,579 master students have graduated. Some 1,006 PhD students and 2,563 master students were enrolled in the academic year of 2001-2002. Since 1999, the following projects have been managed: one national major project, and 20 key projects under the National Natural Science Foundation of China; 8 for National 863 Program; 6 special topics and 13 projects for National Brainstorm Program; 4 projects and 8 subjects for National 973 Program; foundation items for outstanding youth and 16 excellent research groups supported by foundations; one major knowledge innovation project and 7 key projects of CAS. In spite of the achievements mentioned above, certain fields in geographical research also face challenges and opportunities. In light with the existing problems, this paper discusses the development direction of the geographical sciences in the 21st century and puts forward suggestions on strengthening theoretical research and integrated research of geography.
中国地理学发展若干值得思考的问题
On the analysis of rural space
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

Influenced by the interaction of various internal and external factors including urbanization, informatization, and globalization, rural areas in China are experiencing socioeconomic restructuring, regional function upgrading, and a series of transformations and reconstructions. Rural areas face a range of unprecedented opportunities and challenges, and the proposal of "rural revitalization strategy" puts forward new requirements for rural development and rural geography. Therefore, a comprehensive and systematic understanding of rural space system and accurate depiction of rural space are necessary prerequisites for further studies. Existing Chinese research focused more on the material space and to some extent placed less focus on the study of social-cultural space. Using a single material space view is very difficult to understand and interpret a large number of increasingly complex rural geographical problems. Based on a systematic analysis of the thinking on rural space and development in China and abroad, this article points out the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture. This article preliminarily expounds the complexity of rural territorial system and argues that the rural space system that is derived from the rural territorial system should not be limited within the range of rural material space but be understood through the multi-dimensional perspective of space. According to the human-environment system theory, this study tried to construct a rural space system that consists of three progressive layers including material space-social space-cultural space and clarify the connotations of every layer and the logical relations between them to fully understand the increasingly complex rural area. This article also highlights the necessity that multi-dimensional rural spatial restructuring should be developed. Based on the construction of multi-dimensional rural space system, forming an overview of the historical process and realistic situation of rural spatial restructuring and predicting the future path of rural development are very important research tasks to carry out in the future. In the end, this article appeals that Chinese geographers should continue to discuss and analyze concepts of rural issues in order to constantly improve our understanding about the changing countryside, and deepen the studies of rural spatial restructuring by using the theories and methods of related subjects from the perspective of multi-dimensional space. Finally, for the comprehensive empirical research of rural geographical issues, Chinese rural geographers should strengthen micro scale studies, actively devote themselves to field study, be observant of rural daily life, and understand the rural society and culture to make up for the deficiency of Chinese rural geographical research about rural society and culture.
乡村空间辨析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着城镇化、信息化、全球化等多种内外因素的交互作用,中国的乡村正经历着社会经济形态重组、地域功能提升等一系列转型与重构的过程,乡村地域面临着前所未有的机遇与挑战,而“乡村振兴战略”的提出也给乡村发展及乡村地理学的研究提出了新要求,全面系统地认识乡村空间系统,准确把握乡村空间是开展进一步研究的必要前提。本文在系统梳理国内外对乡村空间的认知与发展基础上,指出国内乡村地理学在乡村社会—文化空间研究上的不足。本文以人地关系地域系统为理论基础,尝试建构了由“物质空间—社会空间—文化空间”组成的乡村空间系统,以期为全面认识日益复杂的乡村地域提供理论指导。
Rural futures: The consumption countryside and its regulation
DOI:10.1111/soru.1999.39.issue-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of quality of life in rural areas of Hunan province
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812009
[本文引用: 2]

Understanding the regional differentiation regularities and causes of quality of life in rural areas is not only the new content of rural geography for a new era, but also the inherent requirement of the scientific implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. Taking 101 counties (cities, districts) of Hunan province as the research unit, this paper proposes a assessment indicator system of quality of life in rural areas consisting of six dimensions. Then, using the entropy method, exploratory spatial data analysis and geo-detector, we elaborate spatial pattern characteristics and influencing factors of quality of life in rural areas of the province. Our results suggest the following: (1) The spatial distribution pattern of quality of life indicates that the overall feature is high to low from the east to west and descends from east to west. (2) From the perspective of the spatial correlation pattern, obviously, the spatial pattern of High-High area and Low-Low area present a pattern of agglomeration. High-High area is mainly located in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration and its adjacent counties, while Low-Low area is mainly in western Hunan. (3) The primary factors influencing quality of life are per capita GDP, urbanization level, distance from provincial capital, and elevation. The secondary factors are the slope, the proportion of secondary and tertiary industries, the proportion of non-agricultural labor in rural areas, and total power of agricultural machinery. To realize rural revitalization and improve the quality of life in rural areas, we should give priority to rural industrial and economic revitalization based on eco-environmental protection, actively strengthen the interconnection between regions and enhance the modernization of infrastructure and public service facilities in rural areas.
湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812009
[本文引用: 2]

认知乡村生活质量的地域分异规律及形成原因,既是新时代乡村地理学研究的新内容,也是科学实施“乡村振兴”战略的内在要求。以湖南省101个县(市、区)为研究单元,构建由6个维度组成的乡村生活质量评价指标体系,运用熵权法、探索性空间数据分析(ESDA)及地理探测器等研究方法,研究湖南乡村生活质量的空间格局特征及其影响因素。结果表明:湖南乡村生活质量总体上呈现出东高西低并由东向西依次递减的空间分布态势;从空间关联格局来看,HH区和LL区在空间上集聚格局明显,显著HH区主要分布在长株潭城市群地区和周边临近县域,显著LL区主要分布在大湘西地区;影响湖南乡村生活质量空间格局的重要因素为人均GDP、城镇化水平、离省会城市距离、海拔,次重要因素为坡度、第二第三产业占比、农村非农劳动力占比、农业机械总动力。振兴乡村,提高乡村生活质量应在充分保护乡村生态环境的基础上,把乡村产业振兴和经济振兴放在优先的位置,应积极改善广大乡村地区的互联互通条件,促进乡村地区基础设施和公共服务设施的现代化。
Spatial differentiation and mechanisms of typical rural areas in the suburbs of a metropolis: A case study of Beicun Village, Baiyun District, Guangzhou
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908010
[本文引用: 1]

The reforms of global production modes and social systems have accelerated the process of urbanization, and the urban-rural flow speeds up spatial differentiation in the rural suburbs. Based on spatial production theory and game theory, this paper analyzes the spatial differentiation and its influence mechanism in Beicun in the suburbs of Guangzhou. The results are as follows: (1) Since the 1980s, Beicun has experienced three stages: agricultural development, industrial development, and service industry development. The industry has changed from single to diversified, and the transformation from agricultural decentralization to rural community has been realized. (2) In the transformation of rural economic development, the land use type and structure of Beicun tended to be diversified, and the spatial relationship of various types of land use was complicated, emerging in new characteristics of land for mixed commercial and residential use, and mixed industrial and commercial use, gradually forming a circle-type spatial layout structure model of "public service facilities-traditional and modern residential areas-commercial areas-agricultural and industrial areas". (3)The diversification of the rural material space was mainly due to the intervention of new industries and the transformation of leading industries. Both endogenous land-transferring mechanisms and exogenous urban capital promoted the industrialization process, and market power promoted the transformation of manufacturing industry into a service industry. (4) The industrialization process promoted the functional replacement of historical buildings by village organizations; changed the social relationship of the village to the blood clan and made it more geographically oriented; and produced an occupational relationship between migrant workers and urban low-income groups. (5) The multi-differentiation of suburban rural space followed the game logic of capital and land interests. The rural community played a key mediation role in the competition for space and in the game interests among local villagers, farmers, cooperative economy, industrial operators, and service owners.
广州市城郊典型乡村空间分化过程及机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908010
[本文引用: 1]

全球生产方式变革和社会制度改革加速了城市化进程,城乡要素流动加快了城郊乡村空间分化,以空间生产和博弈论为理论基础,针对广州市城郊北村的空间分化过程及机制进行解析,以期丰富乡村空间分化和治理的理论。结果表明:① 20世纪80年代以来,北村的发展经历了农业发展、工业发展和服务业发展等3个阶段,业态结构从单一的农业逐渐转向为多元,兼有农业去中心化向农村社区化发展转变过程。② 伴随村域经济发展转型,北村土地利用类型和结构趋向多元分化,各类用地空间关系变得更加复杂化,呈现出商住混合和工商混合的用地新特征,空间上逐渐形成“公共服务设施—传统居住区和现代居住区—商业区—农业区和工业区”的圈层式布局模式。③ 乡村物质空间的多元分化动力主要源于新产业介入和主导产业的更替转变。内生的土地流转方式和外生的城市资本共同推动乡村工业化进程,市场力推动了产业发展向服务业转型。④ 乡村工业化驱动了村社组织对历史建筑功能的置换,改变了乡村以宗族血缘和地缘为主的社会关系,产生了由外来务工人员和城市低收入阶层组成的业缘关系,乡村社会关系逐渐多元化。⑤ 城郊乡村空间多元分化遵循着资本和土地利益博弈逻辑。本地村民、代耕农民、经济合作社、工业经营主体和服务业经营主体等行为主体对空间进行争夺和利益博弈,村社组织起着关键的中介作用。
Performing rurality and practising rural geography
DOI:10.1177/0309132509357356
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Recent research in rural geography has shown increasing interest in the ways in which rurality is performed and enacted by diverse actors. Rural geographers have also demonstrated increasing awareness of their own ‘performances’ as researchers, including their enactment of multiple roles in engaging with research subjects, funders and users. This progress report for rural geography discusses recent contributions on these two related themes, briefly summarizing research on the performance and enactment of rurality and rural identities before proceeding to review publications that have reflected on methodological developments, positionality in rural research and political and policy engagement in rural geography.
Digital twin space and its applications: Concurrent discussion on the space reconstruction of geographical research
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202203001
[本文引用: 2]

The past two years have witnessed an explosive growth of digital twin research and its increasing application in a wide range of fields and scales. This urgently calls for a methodological framework to guide and consolidate the research and application of digital twin in various fields and with different structures and scales. In this paper, we first summarized and analyzed the development patterns of digital twin research in various fields, and then coined a term "digital twin space" (with definition and characteristics) as a framework to generalize and consolidate digital twins of various scales. Taking digital twin city as an example, we briefly elaborated the application of twin space. Space, as the carrier of the research object or the research object itself in geography, consists of natural geographical space, social space, and cyberspace. These three types of spaces, however, have not been fully integrated in different branches of geography. In order to boost comprehensive geography research, we propose to reconstruct geographical space research by integrating the three types of geographical spaces with the twin space. Digital twin space can interact with the physical space bilaterally in real time and thus break the barriers among the three types of geographical spaces from inside, which further helps realize the tasks of simulating realities, predicting changes, and regulating processes in integrated geography research.
孪生空间及其应用: 兼论地理研究空间的重构
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202203001
[本文引用: 2]

数字孪生研究呈现由平稳发展到爆发态势,应用领域迅速增加,规模不断扩大,亟需发展用于指导各个领域和不同结构与规模的数字孪生研究与应用的方法论体系。本文在总结分析各个领域数字孪生发展过程和趋势的基础上,提出以孪生空间作为概括和统摄各尺度数字孪生体的框架,并给出了孪生空间的定义和一般特征。然后,以目前已有初步实践基础的孪生城市为例简要阐述了其应用。作为地理学研究对象的载体抑或研究对象本身的空间,由自然地理空间、人文社会空间和地理信息空间三元空间构成,彼此整合度不高。为更有效地开展地理学综合研究,我们提出以孪生空间整合三元空间,重构地理研究空间。孪生空间具有与物理空间的双向实时互馈特征,能够打破地理三元空间内部的壁垒,进而实现模拟现实、预测变化和调控过程的地理综合研究任务。
Charisma and agrarian crisis: Authority and legitimacy at multiple scales for rural development
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.10.010 URL [本文引用: 1]
Global crisis and the systems of spatial governance and planning: A European comparison
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2017.1296110 URL [本文引用: 2]
Rural governance and local involvement: Assessing state community relations in the Scottish Highlands
DOI:10.1016/S0743-0167(01)00048-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rural-urban co-governance: Multi-scale practice
DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2020.02.021 PMID:36659192 [本文引用: 1]
Spatial heterogeneity of multidimensional poverty at the village level: Loess Plateau
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810003
[本文引用: 1]

Targeted poverty alleviation is a pillar of China's new and innovative anti-poverty and development strategy. China is an agricultural country with a large but poor rural population. At the village level, poverty alleviation has the potential to affect millions of citizens. The Loess Plateau is a composite of fragile ecological environment and rural poverty communities. As a backward economy often twins with fragile ecology, studying poverty from a multidimensional perspective in tandem with spatial heterogeneity and its influencing factors can provide an effective analysis of poverty in regions with characteristics similar to those of the Loess Plateau. This study features Pengyang, which is a poverty-stricken county located on the Loess Plateau, and relies on the approach by Alkire and Foster to measure multidimensional poverty, using spatial autocorrelation, Geodetector, OLSR and quantile regression (QR) analysis. Results from our investigation show that the study area has a deep level of multidimensional poverty, with a Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) score of 0.045. The rates of health, housing, and education dimensions were 0.263, 0.245, and 0.227, respectively. Moran's I of MPI was 0.2, which indicates that multidimensional poverty was positively correlated with a spatial pattern of "north, south, middle; high, high, low". Using Geodetector, the mean distance between villages and the center of town, as well as the mean elevation of the villages and mean distance to a river, were found to be the main factors of spatial heterogeneity within the MPI. The q-values of them were 0.552, 0.396, and 0.326, respectively, and the result of regression analysis conforms to the Geodetector. The interaction of the above factors enabled the creation of a multidimensional poverty spatial heterogeneity mechanism at village level for the Loess Plateau, revealing a lack in welfare of farmers, the poor of infrastructure, the congenital deficiency and stalled development of industry, and weak government functioning at the township level. Our results suggest that new strategies regarding urbanization should be investigated in order to improve and ensure the quality of public services in areas with similar characteristic as the Loess Plateau. These new strategies could enable the resolution of problems from the root, such as designing public goods and services that fill gaps in current health care and housing options, as well as the operation of transport facilities at the village level. This could help to mitigate welfare loss of farmers as well as reduce the negative impact of health, housing, education, and other dimensions of poverty.
黄土高原村域多维贫困空间异质性研究: 以宁夏彭阳县为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810003
[本文引用: 1]

黄土高原属于生态环境脆弱与农村经济贫困的复合区域,研究其村域多维贫困及空间异质性有助揭示乡村贫困原因及空间格局。以宁夏彭阳县为研究区,运用A-F法对村域多维贫困进行测度,并结合空间自相关、地理探测器和回归分析方法对其空间异质性进行了系统分析。结果表明:① 研究区农户多维贫困程度较深,K = 3时,多维贫困指数(MPI)为0.045,平均剥夺份额0.361,主要致贫维度是住房、健康和教育,贡献率分别为0.263、0.245、0.227,收入维度贡献率仅占0.130;② MPI空间自相关Moran's I值为0.2,即存在正相关,呈现“南北高,中部低”的格局;③ 地理探测器结果显示行政村到镇中心的距离、村平均高程、村委会到主要河流的距离是影响MPI空间异质性的主要因子,其决定力q值分别为0.552、0.396、0.326,且在最小二乘线性回归(OLSR)和分位数回归(QR)中均通过了1%的显著性检验;④ 各因子间的相互作用形成了黄土高原农户福利缺失、基础设施落后与产业发展受阻、乡镇政府职能被削弱的村域多维贫困空间分异机制。⑤ 最后提出推进新型城镇化建设,实现公共服务均等化,从根源上解决农村医疗、住房、交通设施落后等难题的建议。
Diversified agriculture and rural development in China based on multifunction theory: Beyond modernization paradigm
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

There is a big gap between general rural modernization paradigm and huge empirical rural geography studies. This gap results in impotent development strategies on regionally differentiated countryside. Based on multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory which emerged in Western World as a new paradigm, this paper discusses the multiple objectives, differentiated pathways and policies of agriculture and rural development in China. Firstly, this paper reflects the problems and challenges caused by modernization paradigm in rural China on economic, social, and environmental aspects, as well as that of western developed countries. It can be concluded that conventional agricultural and rural modernization is developed largely at the expense of rural environment, social fabric and economic viabilities. Obviously, "modernization development paradigm" alone is not enough for healthy agricultural and rural development in such booming economy as China. A better paradigm should be developed which takes economic development, social justice and environmental sustainability into account at the same time. After a brief review of multifunctional agriculture theory and multifunctional rural theory overseas, the multiple objectives of agriculture and rural development in China are put forward. These multiple objectives, however, should not and could not be a burden on rural space indiscriminatingly due to the enormous differentiation of natural and socio-economic conditions. Thus, the final but main part of this paper envisions the differentiated pathways and policy portfolios of agricultural and rural development in China from the perspective of territorial division.
基于多功能理论的中国乡村发展多元化探讨: 超越“现代化”发展范式
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502007
[本文引用: 1]

传统的乡村现代化发展范式和地理学关于乡村的区域差异研究之间存在缝隙,不足以为快速演化分异的乡村地域发展提供直接理论支撑。本文引入西方近20年来逐渐兴起的多功能农业与多功能乡村理论,从新的视角观察思考中国乡村多元化发展的目标、路径及对策。首先从经济、社会和环境三个方面反思中国乡村现代化的基本历程与得失,以及西方国家乡村现代化产生的问题,指出传统的农业农村现代化发展在很大程度是以牺牲乡村环境和乡村社会机理脆弱化为代价的,也造成了乡村经济对外部支持的过度依赖,仅仅强调“现代化”发展范式显然是不够的;然后简要介绍了国外多功能农业与多功能乡村理论;在此基础上,从功能角度提出中国农业农村发展的多元目标,推演探讨农业农村发展的区域差异化路径及对策。
Rural spatial governance for territorial spatial planning in China: Mechanisms and path
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of unified management of urban and rural space, rural spatial governance has become an important part of the spatial governance system. Conducting in-depth theoretical and practical research on rural spatial governance and analyzing the mechanisms and path of rural spatial governance in national spatial planning will be conducive to improving the planning and control system of rural space. Starting from the connotation rural spatial governance, this paper constructs a theoretical analysis framework of rural spatial governance based on the comprehensive perspective of spatial governance, discusses the internal mechanism and feasible paths of rural spatial governance in territorial spatial planning, and then realizes the theoretical and practical research of rural spatial governance. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Rural spatial governance starts from the coordination theory of human-land relations in the rural regional system. Through planning and negotiation, it realizes effective control of rural space usage, and orderly allocation of space rights. Rural spatial governance highlights the comprehensive governance process that combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" participation by multiple subjects. (2) Through the "action-efficiency-target" system, the comprehensive governance analysis framework of "matter-organization-ownership" in rural space provides an effective scheme for the construction of multiple rural spatial governance that combines rigidity and flexibility, interaction between material space and space relationship, and superposition of spatial ownership and spatial organization. (3) The rural spatial governance features of interconnecting various scales (region-village-plot) are conducive to improving the rural spatial governance system. (4) The multiple governance means, participation modes and value-sharing mechanisms of rural spatial governance are conducive to enriching the territorial spatial planning system, promoting the integration of multiple regulations, refining the control of territorial space use, and ensuring good rural governance and ecological governance. (5) Rural spatial governance uses mobilization strategies of "top-down" and "bottom-up", and creates conditions for the implementation of practical village planning and revitalization strategies through the construction of new village operation models and reconstruction of organizational mechanisms.
面向国土空间规划的乡村空间治理机制与路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106008
[本文引用: 1]

城乡国土空间统一用途管制背景下,乡村空间治理成为国土空间治理体系的重要组成部分。从乡村空间治理的理论内涵出发,构建了乡村空间治理理论分析框架,探讨了乡村空间治理作用于国土空间规划的内在机制和可行路径。结论如下:① 乡村空间治理是以乡村空间为治理对象,通过规划和协商等方式,实现乡村空间用途有效管制,空间权利有序配置,凸显多元主体参与的“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的综合治理过程;② 通过“举措—效能—目标”体系,构建了刚性与弹性结合、物质空间与空间关系交互、空间权属与空间组织叠加的乡村空间“物质—组织—权属”综合治理分析框架;③ 多级尺度互联互通(区域—村域—地块)的乡村空间治理特征有利于完善乡村空间治理体系;④ 乡村空间治理通过多种手段并施、多元主体参与、多重价值共享,完善国土空间规划体系,推进多规融合,细化国土空间用途管制,促进乡村善治和生态治理;⑤ 乡村空间治理通过“自上而下”和“自下而上”相结合的动员和行动策略,构建新型村庄运营模式和组织机制,为落实实用性村庄规划和乡村振兴战略创造条件。
European cross-scale spatial planning and territorial frames in the Italian Median Macroregion
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2019.1581729
[本文引用: 1]

This article describes the preliminary outcome of interdisciplinary research that arises from a study by the Italian Ministry of Infrastructures and Transport and the Abruzzo Region (IT) on local development processes in central Italy, and specifically in the Median Macroregion, whose results have been extended to European context. It concerns the European spatial planning, specifically the study of an original interpretative model of European space, called Territorial Frames - TFs, a particular multi-scale infrastructural mesh that connects the 'local' territories with 'global' ones and that can represent the activating element of processes and policies of spatial development of settlements, of processes of valorization of the productive, naturalistic and landscape sectors. This new model interfaces with the territorial reticular component through the concept of polycentrism, also projecting evolution, and with that of the governance of development projects, using the potential of European Macroregions. The main objective of the research is to feed the topic of spatial planning, oriented to the integration between territories through a cross-scale approach, and to the activation of new processes of sustainable territorial development, with reference to the economically disadvantaged inner areas in a context of Macroregional governance.
Modelling food security: Bridging the gap between the micro and the macro scale
The hierarchical scheme and the vertical transmission of village planning within the national territorial spatial planning system
国土空间规划体系下村庄规划编制的分级谋划与纵向传导研究
Spatio-temporal differentiation and differentiated regulation of the vulnerability of rural production space system in Chongqing
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008009
[本文引用: 1]

Vulnerability, one of the major properties of rural production space system (RPSS), is an effective measure in how system will be susceptible to negative effects or damage, as well as the way to achieving sustainable development of the system. This study establishes an evaluation index system and model of the vulnerability of RPSS and quantitatively measures the RPSS vulnerability of Chongqing from 2007 to 2017 to reveal its spatio-temporal differentiation. Accordingly it identifies vulnerability types and proposes targeted regulation strategies. The results are shown as follows. (1) The vulnerability of the RPSS is a comprehensive measure of the operating state of the system consisting of exposure, sensitivity and adaptability. It embodies the balance relationship of mutual influence and interaction that lies between rural diversified subjects centered on "human" and the rural production space centered on "land". (2) On the whole, the exposure of the RPSS shows an upward trend and a spatial pattern of "partly prominent, high in the north and low in the south"; the sensitivity shows a downward trend of fluctuation and a spatial pattern of "high in the east and low in the west"; the adaptability shows a rapidly increasing trend and a spatial pattern of "high in the west and low in the east". The overall vulnerability of RPSS presents a downward trend and the spatial pattern of "high in the east and low in the west". (3) After dividing the vulnerability of the RPSS into four types, namely, including adaptability type, exposure-sensitivity type, sensitivity-adaptation type, and strong comprehensive type, and based on the principle of "ecological priority - classified regulation - highlight emphasis - local adaptation", this study proposes differentiated "vulnerability reduction" strategies for different types, so as to guide the sustainable development of RPSS.
重庆市乡村生产空间系统脆弱性时空分异与差异化调控
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008009
[本文引用: 1]

脆弱性作为乡村生产空间系统的重要属性,是探讨系统易受负面影响或损害程度的有效度量、解析系统可持续发展趋势的有效途径。以重庆市为研究区,以2007—2017年为研究时段,建立乡村生产空间系统脆弱性评价指标体系和评价模型,以定量测度乡村生产空间系统脆弱性,揭示其时空分异特征,进而划分脆弱性类型并提出差异化调控策略。结果表明:① 乡村生产空间系统脆弱性是系统运行状态的综合度量,包含暴露度、敏感性和适应能力3个要素,其体现了以“人”为核心的乡村多元主体与以“地”为核心的乡村生产空间之间相互影响、相互作用的互动制衡关系。② 乡村生产空间系统暴露度总体呈上升趋势及“局部突出、北高南低”的空间格局特征;敏感性总体呈波动下降趋势及“东高西低”的空间格局特征;适应能力总体呈快速上升趋势及“西高东低”的空间格局特征;脆弱性总体呈下降趋势及“东高西低”的空间格局特征。③ 将重庆市乡村生产空间系统脆弱性划分为适应能力脆弱型、暴露—敏感脆弱型、敏感—适应脆弱型和强综合脆弱型4种类型,并按照“生态优先—分类调控—重点突出—因地施策”原则针对不同类型提出差异化“降脆”策略,以引导乡村生产空间系统可持续发展。
The characteristics and tasks of geography in the new era
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.08.939
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject of "exploring the laws of nature, declaring the human essence", with characteristics of comprehensiveness and interactiveness. Since the 1980s, Geography plays an important role in global environmental change research programs. Theories, methods and techniques of Geography have become the basis for solving the problems of the sustainable development of human society is facing. Originated in the global environment change research, and combined with the social science research, The " Future Earth" research plan represents the direction of the development of Geography in the new period. In contemporary, Geography research methods have shift from survey, observation, and records, drawings and other traditional research methods to the modern scientific methods such as spatial statistics, earth observation, GIS, indoor and outdoor simulation and modeling, decision-making system, etc., and are gradually tend to comprehensive and quantitative. As the problems that Geography is facing are more complex and more comprehensive, the Geography research issues become more comprehensive and diverse, and attract more extensive subjects to participate in. In more and more field, the angle of Geography are considered. The discipline boundary that concepts and tools belonging to is blurring. In the new era, the geography, is heading for geographical science. China is an ideal geography test sites of studying the problem of the sustainable development of human society. The future development of Chinese Geography needs to deepen the comprehensive and integrated understanding of the complex man-land system, and strengthen the research of global problems. To achieve the goal of geographical science and social service value, the internationalization level of Chinese geographical science needs to be promoted, and the ability of using advanced technology to parse geographical phenomenon needs to be improved.
新时期地理学的特征与任务
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.08.939
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是“探索自然规律,昭示人文精华”的一门学科,具有综合性、交叉性特点。20世纪80年代以来,地理学在全球环境变化研究计划中扮演了重要角色,地理学的理论、方法和技术已经成为解决人类社会面临的可持续发展问题的基础。起源于全球环境变化研究,并结合了社会科学研究的“未来地球”研究计划,代表了新时期地理学发展的方向。当代地理学研究方法已经从勘察、观测、记录、制图等传统的研究方法向空间统计、对地观测、GIS、室内外模拟、建模、决策系统等现代科学方法转变,逐渐走向综合性、定量化;随着地理学面临的问题更加复杂、更加综合,地理学研究议题变得更为综合和多元,吸引了更为广泛的学科参与,地理学视角在越来越多的领域得到重视,概念和工具所属的学科边界正变得模糊。新时期的地理学正在走向地理科学。中国是研究人类社会的可持续发展问题的一个理想的地理科学试验场所,中国地理科学未来的发展需要以综合的角度加深对人地复杂系统全面而综合的理解,需要加强全球性问题的研究,全面提升中国地理科学国际化水平,普遍提高先进技术解析地理现象的能力,系统实现地理科学的社会服务价值,促进中国从地理学大国走向地理学强国。
Geography complexity: New connotations of geography in the new era.
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201807002
[本文引用: 2]

Since the 20th century, geography came into being with distinctive disciplinary characteristics by sustained effort of geographers. This paper puts forward predicament from cognitive and thought in the new era, and depicts new geographic characteristics from five aspects: new technology, new orders, new data, new approaches and new driving factors. According to new content of geo-regionality and new approaches of geo-comprehensiveness, the paper proposes that complexity research would be a successful new path in geography, and the complexity would be the third characteristic of geography. Then, the paper details some complex spatial patterns, complex time processes and complex spatio-temporal mechanisms in geography research. Based on the concept of a geographic complex system, this paper presents core issues and corresponding complex research tools. Finally, the paper puts forward new challenges and new requirements for geography in the new era.
新时代地理复杂性的内涵
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201807002
[本文引用: 2]

20世纪以来,经地理学者不断探索和努力,地理学已经形成了其特有的学科特征。首先从认知方法和思维角度,阐述了新时代地理学所面临的困境;从新技术、新秩序、新数据、新方法以及新动因等方面,诠释了地理学的新时代特征。其次,针对地理区域性的新内涵和地理综合性研究所需的新方法,提出了复杂性研究是地理学成功的新路径,并认为复杂性是地理学研究的第三特征。再次,重点讨论了地理研究存在的空间复杂格局、时间复杂过程和时空复杂机制,进而解释了地理复杂系统的基本概念,并就地理复杂系统的核心问题提供了相应的研究方法。最后,提出了新时代地理学面临的新挑战和新要求。
Thinking on the development and construction of geographic modeling and simulation system for the study of geographical characteristics in the new era
DOI:10.1360/SSTe-2020-0264 URL [本文引用: 4]
面向新时代地理学特征研究的地理建模与模拟系统发展及构建思考
Complexity of coupled human and natural systems
DOI:10.1126/science.1144004
PMID:17872436
[本文引用: 1]

Integrated studies of coupled human and natural systems reveal new and complex patterns and processes not evident when studied by social or natural scientists separately. Synthesis of six case studies from around the world shows that couplings between human and natural systems vary across space, time, and organizational units. They also exhibit nonlinear dynamics with thresholds, reciprocal feedback loops, time lags, resilience, heterogeneity, and surprises. Furthermore, past couplings have legacy effects on present conditions and future possibilities.
Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world
Paradigm transformation in the study of man-land relations: From local thinking to global network thinking modes
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110001
[本文引用: 1]

The early studies on the relationships between man and land in geography mostly focused on local regions and held the idea that "the land and water resources in a region feed the person in the region". In the traditional agricultural society, which relies heavily on natural resources, the idea, and regional geographic research and management practice under its guidance play a positive role in promoting the development between man and nature, and sustainable resource use. With the continuous increase in openness of man and land system resulted from development of science and technology and transport improvement, regional systems on different scales and at different economic development levels have formed an interdependent and coupled geographic network. Every region becomes a node in this network, and the formation and solution of regional problems are closely related to other nodes in the network, and are related to internal and external factors of the regional system. In some cases, external factors even play a more important role. The introduction of some concepts and methods marks the paradigm transformation of man-land relationship research from local thinking paradigm to global networked thinking paradigm, such as virtual water, ecological footprint, carbon emissions due to goods trade, resource link and tele-coupling of man-land relationship. This study discusses the paradigm transformation from three aspects: the evolution characteristics of man-land system, the changes of thinking paradigm and study methods in man-land relationships, and the realization paths and practical significances of the transformation of thinking paradigm in man-land relationship research. According to new ideas and thinking paradigms, traditional local thinking modes and related research themes such as regional carrying capacity can not fully express the new characteristics of man-land relationships. At present, studies related to regional carrying capacity have become an important issue in land use planning and urban planning in China. In the development of land use planning at different levels, "evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity" has become the premise and basis of planning. In the implementation of this concept, we usually simply uses population size as the control index. In the context of an increasingly open system, studies in the carrying capacity of resources and environment may be re-examined. This is especially necessary in smaller scale regional systems (e.g., at a county level).
从本土到全球网络化的人地关系思维范式转型
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110001
[本文引用: 1]

早期地理学关于人地关系的研究多基于本土思维,秉持“一方水土养育一方人”的理念。在严重依赖自然资源的传统农业社会,这一理念及其指导下的区域地理研究和区域管理实践,对于促进人与自然的协调发展起到积极作用。随着系统开放程度的增加,规模不等、层级不同的地域系统形成了一个相互依赖、相互耦合的地理网络。每个地域都是这个网络上的节点,地域问题的产生与解决与网络上其他节点有密切关联、与地域系统内外因素紧密相关,地域外因素有时甚至起主导作用。虚拟水、生态足迹、贸易隐含碳排放、资源纽带关系及人地关系远程耦合等概念和方法的提出,标志着人地关系研究范式从本土思维向全球网络化思维转型。依照新的理念和研究范式,传统的本土思维范式及建立在此范式上的相关研究主题(如区域承载力)应该受到重新审视。
Country backwater to virtual village? Rural studies and the 'cultural' turn
DOI:10.1016/S0743-0167(97)00053-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Cascading regime shifts within and across scales
DOI:10.1126/science.aat7850
PMID:30573623
[本文引用: 1]

Regime shifts are large, abrupt, and persistent critical transitions in the function and structure of ecosystems. Yet, it is unknown how these transitions will interact, whether the occurrence of one will increase the likelihood of another or simply correlate at distant places. We explored two types of cascading effects: Domino effects create one-way dependencies, whereas hidden feedbacks produce two-way interactions. We compare them with the control case of driver sharing, which can induce correlations. Using 30 regime shifts described as networks, we show that 45% of regime shift pairwise combinations present at least one plausible structural interdependence. The likelihood of cascading effects depends on cross-scale interactions but differs for each type. Management of regime shifts should account for potential connections.Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
The connotation of territory and the suggestions of drawing up spatial planning in the New Era
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210905
[本文引用: 2]

A better understanding of the connotation of "territory" is a prerequisite for developing the theoretical system and advancing the practical work of spatial planning. It is necessary to constantly update the understanding of "territory" in accordance with the development of disciplines and the changes in the real needs of spatial governance. Therefore, this journal invited 15 young scholars to discuss the connotation of "territory". The main points of view are as follows: (1) Territory is a complex coupled human and natural systems, with the characteristics of pluralism on elements and nesting on spatial and temporal scales. It is necessary to use the thinking of "landscape, forest, field, lake and grass" as a life community to carry out the comprehensive development and utilization and systematic restoration and protection of territory, so that it can become a natural governance platform. (2) Territory is a network space constructed by "flow" and a relational space composed of different stakeholders. It is necessary to integrate the territory through the "space of flows" to promote the sharing of resources and elements between regions to achieve coordinated development; it is also necessary to pay attention to the reconstruction of human and natural relationships and interpersonal relationships, coordinate the interests of multiple subjects, and achieve harmonious development. (3) Territory is a human space. It is necessary to fully perceive the risks, suitability, constraints, and accessibility of the territory. We need compile people-oriented spatial planning to enhance the ecological value, aesthetic value and humanistic care of territory. (4) Territory is the object of spatial planning and governance. It is a specific spatial carrier with marine space, rural space and cultural space, etc. It has attributes such as rights and assets. It is necessary to realize the unified management of resources and assets in the spatial planning, and highlight its economic value, social value and ecological value to achieve the diversified needs of high-quality development and high-quality life for territory.
“国土空间”内涵辨析与国土空间规划编制建议
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210905
[本文引用: 2]

科学辨析“国土空间”概念内涵是推进国土空间规划编制、完善国土空间规划理论的前提。应根据国土空间治理需求变化和学科理论发展需要,及时更新完善对“国土空间”的理解。本刊邀请15位青年学者研讨“国土空间”的概念内涵及国土空间规划编制建议,主要观点如下:(1)国土空间是复杂的人地耦合系统,具有构成要素多元性、时空尺度嵌套性等特征。需要用山水林田湖草沙是一个生命共同体的思维,进行国土空间的综合开发利用与系统修复保护,提出基于自然的空间治理方案。(2)国土空间是“流”所构建的网络空间,是不同利益主体组成的关系空间和为精细化治理服务的可计算领域。需要通过“流空间”进行国土空间的整合,推动区域之间资源和要素的共享,实现协同发展;也需要重视人地关系和人际关系的重构,协调多元主体的利益诉求,实现和谐发展;还需要完善国土空间开发管控的技术手段,平衡国土空间规划中的灵活性与统一性矛盾。(3)国土空间是有温度的空间。需要充分感知国土空间的风险性、适宜性、约束性、可达性,编制“以人民为中心”的国土空间规划,提升国土空间的人文关怀、生态功能和美学价值。(4)国土空间是国土空间规划和空间治理的对象,是具体的海洋空间、乡村空间、文化空间等,具有载体属性、资产属性、权利属性等,需要在国土空间规划中实现资源资产统一管理,彰显其经济价值、社会价值和生态价值,满足高质量发展和高品质生活对国土空间的多样化需求。
Rethinking on the basic issues of territorial and spatial use control in China
中国国土空间用途管制的基础性问题思考
Development overview and some thoughts on geographic synthesis
地理综合研究方法的发展与思考
Comprehensive regionalization of human geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702001
[本文引用: 1]

The comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography is based on the rules governing regional differentiation of Chinese physical geography factors. Based on regional differences and similarities in human factors, this study divides the whole country into two levels of relatively independent, complete and organically linked human geographic units. As a fundamental, comprehensive, cutting-edge, practical and important task, the comprehensive regionalization of human geography highlights the characteristics, regional and sub-regional features, complexity and variety of spatial differences between factors of Chinese human geography. It is capable of promoting the development of human geography based on local conditions, providing basic scientific support to national and local development strategies, such as the Belt and Road Strategy, new urbanization and environmental awareness, and creating a sound geopolitical environment in key areas. Using results from existing physical and human geography zoning studies, and in accordance with the principles of synthesis, dominant factors, the relative consistency of the natural environment, the relative consistency of economic and social development, the consistency of the regional cultural landscape, the continuity of spatial distribution and the integrity of county-level administrative divisions, and taking as its basis the division of human geography into 10 major factors (natural condition, the economy, population, culture, ethnicity, agriculture, transportation, urbanization, the settlement landscape and administrative divisions), this paper constructs an index system for the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography through a combination of top-down and bottom-up zoning and spatial clustering analysis. In this study, Chinese human geography is divided into eight regions (first level) and 66 sub-regions (second level). The eight human geography regions are (I) Northeast China, (II) North China, (III) East China, (IV) Central China, (V) South China, (VI) Northwest China, (VII) Southwest China, and (VIII) Qinghai and Tibet. This zoning proposal fills gaps in studies involving the non-comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography. Each human geography region and sub-region has different topographical, climatic, ecological, population, urbanization, economic development, settlement landscape, regional cultural and ethno-religious attributes. This proposal on the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography dovetails closely with previous studies on comprehensive regionalization in Chinese physical geography, Chinese economic zoning, and Chinese agriculture zoning. It shows that, under the dual roles of nature and humans, there are certain rules of regional differentiation that govern the comprehensive regionalization of Chinese human geography.
中国人文地理综合区划
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201702001
[本文引用: 1]

中国人文地理综合区划是以中国自然地理要素的地域分异规律为基础,充分考虑全国人文要素的地域分异性和相似性,将全国划分为不同空间层级、相对独立完整、并具有有机联系的特色人文地理单元。是一项基础性、综合性、前沿性与实用性的重要工作。通过人文地理综合区划,将突出中国人文地理要素的地域分异性、地方特色性和复杂多样性,因地制宜地推动人文地理学科发展,为面向国家和地方发展战略需求推动“一带一路”建设、新型城镇化和生态文明建设、为营造重点地区良好的地缘政治环境提供基础性的科学支撑。本文在吸纳已有的各类自然和人文地理区划成果的基础上,按照综合性、主导性、自然环境相对一致性、经济社会发展相对一致性、地域文化景观一致性、空间分布连续性与县级行政区划完整性等原则,以自然、经济、人口、文化、民族、农业、交通、城镇化、聚落景观和行政区划10大要素为基础划分依据,构建中国人文地理综合区划指标体系,采用自上而下与自下而上相结合的区划思路和空间聚类分析方法,将中国人文地理划分为东北人文地理大区Ⅰ、华北人文地理大区Ⅱ、华东人文地理大区Ⅲ、华中人文地理大区Ⅳ、华南人文地理大区Ⅴ、西北人文地理大区Ⅵ、西南人文地理大区Ⅶ和青藏人文地理大区Ⅷ共8个人文地理大区和66个人文地理区。该区划方案填补了中国人文地理没有综合区划的空白。各个人文地理大区和各个人文地理区之间呈现出不同的地形地貌属性、气候属性、生态属性、人口属性、城镇化属性、经济发展属性、聚落景观属性、地域文化属性和民族宗教属性。中国人文地理综合区划方案与已经划出的中国自然地理综合区划、中国经济区划、中国农业区划等有较大程度的吻合性,体现出在自然与人文要素双重作用下的中国人文地理综合区划的地域分异规律。
Study on China's land comprehensive functional zone and its division scheme
DOI:10.1360/SSTe-2022-0022 URL [本文引用: 4]
中国陆域综合功能区及其划分方案研究
On the research core of geography-the regional system of man-land relationship
DOI:10.2307/140646 URL [本文引用: 1]
论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统
"Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction": A theoretical cornerstone for comprehensive research on formation and evolution of the geographical pattern
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 3]

Compared with the increasingly obvious humanistic tendency in foreign human geography, China's human and economic geography still follows Academician Wu Chuanjun's theory, with human and economic geography as an interdisciplinary subject which is the study of the formation and evolution of the distribution pattern of human activities under the interaction of natural circle and human circle. And China's mainstream school on human and economic geography has been formed with studies on spatio-temporal rule of sustainable development on territories with different space scales, territories with important production and living, and territories with typical geospatial patterns as the main research points. "Territorial System of Human-environment Interaction", developed by Academician Wu Chuanjun, is the important theoretical foundation not only for human and economic geography, but also for the comprehensive research on geography. The essence of the theory, which includes territorial functional, system structured, orderly process for spatio-temporal variation, and the difference and controllability of human-environment interaction system effect, is entirely harmonious with the forefront of thought of the "Future Earth" studies program. In recent decade, with scientific mode of urbanization, major function oriented zoning, road map for the Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, rural hollowing and targeted poverty alleviation, revitalization of Northeast China and transformation of resource-based cities, and administrative area optimization as the main research objects, theoretical methods have been developed in the aspects of important sustainable process of human and economic geography, territorial function formation and ordering rules for comprehensive geographical pattern, formation and evolution mechanism of urban agglomeration and its resources and environmental effects, sustainable life cycle and the revitalization of the path for problem areas, the interaction between geopolitics, geo-economy and regions, and effect of cultural boundaries on sustainable development. China's human and economic geography has made great progress in discipline development, and the application results have produced profound influences on the ecological civilization construction and sustainable development in recent years. With decades of hard work, China's human and economic geography has reached a world-class advanced level, so as to console the soul and spirit of Wu Chuanjun on the occasion of commemoration of the centenary of his birth.
“人地关系地域系统”是综合研究地理格局形成与演变规律的理论基石
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804001
[本文引用: 3]

同近年国外人文地理学呈现人文化趋势相比,中国人文与经济地理学秉承吴传钧先生关于人文与经济地理学是研究自然圈与人文圈相互作用下、人类活动分布格局形成和演变规律的一门交叉学科的定位,形成了以不同空间尺度的地域、重要的生产生活领域、以及典型的地域空间类型的可持续发展时空规律作为研究指向的中国人文与经济地理学主流学派。吴先生提出的“人地关系地域系统”理论不仅为人文与经济地理学,而且是为整个地理学的综合研究提供了重要的理论基石。地域功能性、系统结构化、时空变异有序过程、以及人地系统效应的差异性及可调控性,是该理论的精髓,这与“未来地球”研究计划的前沿思想完全契合。近10年来,以城镇化科学模式、主体功能区划、一带一路路线图、京津冀城市群、农村空心化和精准扶贫、东北振兴与资源型城市转型、行政区划优化等为研究对象,发展了人文与经济地理重要的可持续过程、地域功能形成和综合地理格局有序化规律、城市群形成演化机理及其资源环境效应、问题地区可持续生命周期与振兴路径、地缘政治地缘经济和区域间相互作用关系、人文界线对可持续发展的影响等理论方法。人文与经济地理学科建设取得重要进展,应用成果对近年来中国生态文明建设和可持续发展产生了重要影响。中国人文与经济地理学在全球范围内发展态势最佳、总体水平领先,以此告慰吴传钧先生,并以此纪念吴传钧先生百年诞辰。
The research on optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

This paper introduces the "life quality theory". Based on the two-way interactive mechanism between space of rural settlements and the life quality, the paper researches the optimization mode of spatial organization of rural settlements in three aspects, which are the integration of rural settlement spatial functions, the optimization of spatial structure and the regulation of spatial scale, so as to build optimization mode and framework of spatial organization of rural settlements with high quality life. The study suggests that: (1) The settlement is the spatial carrier of life quality and the life quality is the essential content of settlements. The two mentioned above influence and improve each other. So, the reasonable rural settlement space is the important precondition for higher life quality. (2) The type of spatial function of rural settlements can be divided into livelihood maintaining, industrial developing and quality optimizing, and the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements oriented by life quality requires promotion of livelihood maintaining, integration of industrial developing and engagement of quality optimizing. (3) There are two important aspects in the optimization of spatial organization of rural settlements. The one is to promote the organic concentration of living space, agricultural space and industrial space, the organic evacuation of social intercourse space, recreational space and services space, and the organic balance of living space, production space and ecological space, in order to realize the reasonable proportion and optimized combination of internal spatial type in settlements. And the other one is to form a functional structure level of "comprehensive village - featured village" and build spatial organization mode of settlements connected by rural roads by switching the location and adjusting the function, with the destruction of underdeveloped villages, the saving of normal villages, the enlargement of important villages, and the construction of new villages. (4) As an ideal mode of rural settlements space optimization oriented by life quality, RROD mode should be built at a rational scale of unit settlement and distance between settlements, leading to an RROD and RROD system with rational structure, auxiliary facility, fully function and well-organized distribution.
基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201410006
[本文引用: 1]

引入“生活质量理论”,基于乡村聚落空间与生活质量的双向循环互动机理,从乡村聚落空间功能整合、空间结构优化、空间尺度调控等三个方面研究乡村聚落空间优化问题,试图构建有效提高生活质量的乡村聚落空间优化框架与模式。研究认为:① 聚落是生活质量的空间载体,生活质量是聚落的本质内容,乡村聚落与生活质量相互促进、相互影响,构建科学合理的乡村聚落空间是提高农民生活质量的重要前提。② 乡村聚落空间功能类型可以划分为生计维持型功能、产业发展型功能与品质提升型功能,生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间功能优化,重点在于提升生计维持型功能,整合产业发展型功能,植入品质提升型功能。③ 乡村聚落空间结构优化的重点有两个方面,一是要促进居住空间、农业空间、工业空间有机集聚,社会交往空间、休闲空间、服务空间有机疏散,生活空间、生产空间、生态空间有机均衡,以实现聚落内部空间类型比例合理化与组合最优化;二是要通过聚居区位转换与聚落职能调整,移拆部分衰落村落,保留部分一般村落,扩大部分重点村落,新建部分新型村落,形成“综合村—特色村”的功能结构等级,构建以乡村公路为链接的聚落体系空间组织模式。④ RROD模式是基于生活质量导向的乡村聚落空间优化的理想模式,该模式的构建要合理确定聚落单体的规模尺度与聚落之间的距离尺度,引导形成结构合理、设施配套、功能完备、分布有序的RROD和RROD体系。
Why some rural areas decline while some others not: An overview of rural evolution in the world
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.03.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Reconceptualising the rural through planetary thinking: A field experiment of sustainable approaches to rural revitalisation in China
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.10.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Nature and basic issues of geography
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

A discipline has typically the following four key features, namely independent research objects, independent research questions, unique characteristics, and unique social services. This paper first discusses the nature of Geography from three aspects, to reveal the characteristics of modern Geography. First, the research object of Geography is changing from simple to complex evolution. In performing geographic research, we should well recognize the complexity of geographic systems. Second, the framework of geographic research questions is structured by the fusion among geographic features, space, and time. This paper explains the essential distinction between different geographic research questions, which promotes the development of the methods and technologies for answering these questions. Third, the philosophy of combining reductionism and holism is growing continuously. A new pattern of research has been formed based on new disciplines and technologies, which is the parallel development of the research on geographic features and that on systems. This paper then identifies the essential characteristics of geographic research, summarizes the key research questions in Geography, and discusses the multiple effects of driving mechanisms on the laws of Geography. An understanding of the fundamental characteristics and the modern value of Geography illustrated in this paper will be contribute to the societal development of Geography.
论地理学的特性与基本问题
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

学科通常都具有独立的研究对象、独立的学科问题、独特的学科特征以及独特的社会服务功能。本文从3个方面论述了地理学的属性,进而认识现代地理学的时代特征。①地理学研究对象的演化经历了由简单向复杂的变化过程。在研究实践过程中,应充分认识地理系统的复杂属性。②地理的要素、空间与时间相互融合构成了独特的学科问题体系,阐述了不同地理问题的本质区别,进而促进解决不同地理问题的技术与方法体系建设。③“还原论”与“整体论”并举的地理学哲学思维方兴未艾。地理学强调的综合研究在当今时代受到了前所未有的重视。在新兴学科和新兴技术的支撑下,出现了地理要素和地理系统并行研究的新格局。本文从地理学研究的基本特征出发,总结了地理学研究的核心问题,探讨地理学驱动机制对地理规律的组合效应。理解地理学关键特征和时代价值,有助于探索地理学的社会发展契机。
From natural regionalization, land change to landscape service: The development of integrated physical geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710001
[本文引用: 1]

The rise of integrated physical geography in China is not an accidental event. It was closely connected with the construction of the related theory system, the fostering of domestic professional scholars, the inheritance of academic history both at home and abroad, and the demand of social development in China. Specifically speaking, it was influenced by the spread of Western modern geography in the early 20th century, and the traditional harmony theory of Chinese ancient geography; it was also associated with the geographical intensive Sino-Soviet academic communications in the 1950s, as well as the needs of economic development in China. All in all, as a branch of physical geography, the integrated physical geography is a practice-oriented subject, focusing on comprehensive perspectives of natural regionalization, land change, and landscape service. The main contents of integrated physical geography studies in China have developed from agricultural regionalization and ecological regionalization to integrated regionalization; from land type, land source to land system; from landscape pattern research to landscape function and service research. Along with the change of the study theme, this subject kept on improving and deepening. Faced with the growing challenges such as rapid urban expansion, serious environmental pollution, and the natural resource exhaustion, the integrated physical geography in China is trying to explore new integrated approaches in accordance with the transformation of the time background. It chooses coupled human and natural systems as its study object, considers the synthesis of processes interaction at different regional scales, makes landscape sustainability as its key research field, and uses big data and high technology as its methodology.
从自然区划、土地变化到景观服务: 发展中的中国综合自然地理学
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710001
[本文引用: 1]

综合自然地理学作为自然地理学的一个独立分支在中国的兴起并非“伊萨钦科讲学”的偶然,而是与之相关的理论体系构建、专业人员培养、中外历史传承及社会实践需求的综合结果。中国综合自然地理学发展一直以实践性为宗旨,围绕着自然区划、土地变化、景观服务等不同的综合视角,经历了从农业区划、生态区划到综合区划研究,从土地类型、土地资源到土地系统研究,从景观格局到景观功能与服务研究等主题的演进,学科体系不断完善和深化。新形势下,综合自然地理学将以人地耦合系统为研究对象,以过程耦合、区域集成为综合方向,以景观可持续性为重点领域,以大数据及高新技术为方法支撑,探索新的综合途径。
The integrated studies of geography: Coupling of patterns and processes
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408002
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject which perceptibly reveals integration and regionalism. The integration means that the diversiform subjects in which geography is involved, and that the regionalism of geography is reflected by the regional differentiation. Through the comprehensive study of the interrelationships among the constituent elements of earth system and the relationship between natural and human systems, it helps us understand the variations of the past, present and future of earth system, and grasp the essence of these changes. Pattern helps us to understand the external features of the world and the process is conducive to the understanding of the internal biophysical mechanism of the world. On the basis of field observations and long-term comprehensive surveys, coupling of patterns and processes at different spatiotemporal scales is an effective way to understand and solve the problems in the field of geography. By analysis of the case studies in the Loess Plateau, the methods of coupling the patterns and processes in the integrated research of geography are discussed and explored.
地理学综合研究的途径与方法: 格局与过程耦合
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408002
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是一门以综合性和区域性见长的学科。地理学的综合性通过要素多样化来体现,区域性则表现为区域分异或区域差异。地理学综合研究是对地球表层各要素的相互作用以及人地关系的研究,帮助我们认识地球表层系统的过去、现状和未来的趋势,把握其变化的脉搏。格局是认识世界的表观,过程是理解事物变化的机理,基于长期的野外观测和综合调查以及模型模拟,对不同时空尺度下的地理格局与过程进行耦合研究,是从机理上理解与解决地理学综合研究的有效途径与方法。文章结合在黄土高原地区的相关研究案例,探讨了将格局与过程耦合研究的地理学综合研究的途径与方法。
Territory spatial security and planning strategies from the perspective of mobility
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220801
[本文引用: 1]

Security is an important aspect for sustainable development of territorial space. It is also a crucial issue in planning, implementing, and supervision of territorial space. With the rapid development of urbanization and industrialization, people, goods, energy, resources and other factors flow more frequently in different regions, between urban and rural areas, and within urban spaces. The coupling relationships between human activities and natural resources have become more and more unstable, which exacerbates the risk of human survival. It is urgent to establish the territory spatial security framework faced with the uncertainty of human activity and elemental flows. This paper explores the security of territorial space from the perspective of mobility. On the basis of the safety of activities in different spaces and the safety of resources and ecology, we should consider the coupling of elemental flows, human activities, and resources and environment, as well as potential risks. The relationships between mobility and territory spatial security can be characterized from three aspects: the coupling of space of flows and space of places, the coordination among resource supply-flow-demand and the reconfiguration of resource, and elemental flows and the resilience of the territory spatial system. Towards safety goals of ecology, water, food, economy, society, and other elements, it is crucial to explore the uncertain impacts of various elemental flows on the man-land system and the mobility risks under extreme conditions such as natural disasters and sudden public safety incidents. It is also important to lead the self-adaptation and benign feedback adjustment between human activities and natural environmental systems through optimizing resource allocation and territory spatial layout. Thus, we proposed a framework of territory spatial security. In territory spatial planning, it is necessary to carry out the coupling coordination analysis with elemental flows and territorial spatial development and protection, to establish new analysis methods of territory spatial structure combining spatial forms and flows, and to enhance the functional flexibility of different spaces to adapt to the uncertainty of elemental flows and activity agglomeration, as well as to construct territory spatial supporting systems that synergize supply and demand. This study is of great significance for improving the sustainable development of territorial space and ensuring the safety of human survival.
流动性视角下的国土空间安全及规划应对策略
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220801
[本文引用: 1]

人员、物资、能源资源等要素在不同层级空间的频繁流动,持续重构人类活动与自然环境关系,并对国土空间安全产生影响。从流动性视角进行国土空间安全探讨,提出在活动承载安全、资源与生态安全基础上,应考虑要素流动与人类活动、资源环境的耦合性及其潜在风险。流动性与国土空间安全的关系可以从“流”空间与场所空间耦合、“供—流—需”协调与资源配置安全、要素流与国土空间系统韧性三个方面来表征。以生态、水、粮食、经济、社会等安全塑造为目标,立足于各类要素流对人地关系系统影响的不确定性,以及自然灾害、突发公共安全事件等极端条件下的流动性风险,通过合理引导资源配置、科学布局国土空间要素等手段,实现人类活动、自然环境系统之间的自适应与良性反馈调节,形成安全韧性的国土空间格局与框架。在国土空间规划中,需要进行要素流与国土空间开发保护的耦合协调性分析评价,建立“形”与“流”结合的国土空间结构优化分析方法,增强不同空间的功能弹性以适应要素流动和活动集聚的不确定性,建立供需协同的国土空间支撑体系。研究对提升国土空间可持续发展水平以及保障人类生存安全具有重要意义。
Rural restructuring: Theory, approach and research prospect
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 1]

For the sake of adapting to the changes of elements in both kernel system and external system of rural development, rural restructuring is a process of optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements affecting rural development, reshaping social and economic structures in rural areas and optimizing spatial pattern in rural territory, and approaching the structure optimization and function promotion of rural territorial system as well as the structure coordination and function complementation of urban-rural territorial system. Based on elaborating the concept and connotations of rural restructuring and the mechanism of promoting rural restructuring due to the evolution of "elements-structure-function", the paper probed the approaches of rural restructuring from the aspects of spatial restructuring, economic restructuring and social restructuring. In order to meet the current national strategic demands and meet the challenges of rural development in the process of urban-rural development transformation, it is in great urgency to strengthen the study on the patterns and processes, dynamic mechanism, differentiated development models, rural planning technology systems, strategies and policies for rural development, and the impacts of globalization on China's rural restructuring in the future. Finally, focusing on a series of problems in the implementation of some important government intervention policies, which is aimed at boosting the social and economic development of rural areas in recent years, a critical analysis and discussion is carried out.
论乡村重构
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 1]

快速城镇化进程驱动中国乡村地域发生巨大变化。乡村重构,即为适应乡村内部要素和外部调控的变化,通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局,以实现乡村地域系统内部结构优化、功能提升以及城乡地域系统之间结构协调、功能互补的过程。本文在界定乡村重构的概念内涵,构建基于“要素—结构—功能”演变助推乡村重构的理论框架基础上,从空间重构、经济重构、社会重构视角探讨了乡村重构的实现路径,并着眼于服务当前国家重大战略需求和解决城乡转型发展进程中乡村地域系统面临的现实困境,提出了未来中国乡村重构研究需重点关注的内容。最后,就现有旨在促进乡村社会经济发展的重大引导性战略和政府干预性政策及其在实践操作中引发的一系列问题,展开批判性分析和讨论。
From governance to rural-urban co-governance: Research frontiers, trends, and the Chinese paths
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

Governance has become an important theoretical and practical issue of multi-disciplinary concern. In the context of rapid urbanization and wide rural-urban disparity, rural-urban governance is particularly important for China. Based on the Chinese and international governance theories, the key aspects of governance include: an open system, self-organization, and the interactive relationship between power and rights. Internationally the research frontier focuses on the governance of social-ecological systems, while urban governance has grown significantly, and rural governance has also risen in recent years. The research trend and policy evolution of governance in China indicate that China has undergone a comprehensive transformation from management to governance by top-level design, and rural-urban governance is becoming a key issue. The main path of China's rural-urban governance in the future lies in three aspects. First, it is necessary to shift from power-oriented to rights-oriented governance. Second, equal attention needs to be paid to both ecological environment and social governance instead of focusing only on social, single-dimensional, and urban governance systems, and form a rural-urban co-governance system with the participation of multiple subjects. Third, it should be launched to assist rural and urban vulnerable groups actively. Rural-urban co-governance will become a new growth point for theories, and multi-disciplinary, multi-subject, and multi-department collaboration is much needed.
从治理到城乡治理: 国际前沿、发展态势与中国路径
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

治理已经成为多学科关注的重要理论与现实问题。在快速城镇化和城乡差距居高不下的背景下,城乡治理对中国而言尤为重要。论文通过梳理国内外治理理论,概括治理的要点为开放系统、自组织、权力与权利的交织3个方面。国际研究强调社会生态系统的治理,城市治理增势显著,乡村治理研究开始兴起。中国在顶层设计上经历了从管理到治理的全面转型,城乡治理逐渐成为研究和政策实践的关键议题。未来中国城乡治理的主要路径在于:从权力导向转向权利导向;从只注重社会维度、一元化的、城市偏向的治理模式转向生态环境与社会治理并重,形成多元主体参与的城乡共治体系;积极开展城乡弱势群体的扶持救助工作。城乡共治将会成为新的理论增长点,需要进行多学科、多主体、多部门的协同工作。
Research on dynamic model of urban-rural interface
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201612008
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial location of the urban-rural interface (URI) is at the junction of urban and rural areas. In function, URI is the spatial carrier of communication for urban and rural elements. The development of URI is of great significance to the coordination of urban and rural areas. First, from the perspective of elements flow, this research established a theoretical framework of URI, which is based on system dynamics, to extend the urban and rural system to a three-body framework: urban area-URI-rural area. In this framework, the structure of urban and rural system is composed of three subsystems including urban system, URI system and rural system. And among them, URI system has its unique structure and function. From this meaning, URI consists of three parts including boundary wall, interface and boundary gate. For its function, it mainly plays the role of defense and exchange in the urban and rural system. The formation mechanism of URI reflects the forces of urban and rural systems to URI, and the interaction mechanism reflects the reaction of URI to urban and rural systems. Second, on the basis of the theoretical model, we built a quantitative model to characterize the dynamic evolution mechanism of URI by using methods of quantitative geography. The model solution shows that: (1) In different stages of development, URI is affected by these different degrees of endogenous and exogenous dynamic power. In early stage of URI's formation, the development power is mainly derived from endogenous dynamics. With the development of URI, exogenous dynamics increased gradually, and functioned with endogenous dynamics. Moreover, the gap between two dynamics is narrowed and the development of URI is accelerated. After URI achieves the equilibrium, exogenous dynamics reduce gradually and endogenous dynamics become the main driving force. (2) With the development of URI, the effects transited from negative to positive. The value of effects depends on the cyclic accumulation capacity of URI itself. In early stage of URI's formation, the ability of cyclic accumulation is weak, so the effect of URI is minor, and may even be negative. With the increasing ability of the cyclic accumulation, the negative effect transfer to positive one and increase gradually. (3) The balancing condition of URI is mutually affected by the exchange rate, endogenous dynamics and cyclic accumulation ability of urban-rural elements. The equilibrium of a certain URI is stable and has spatial scale effects. According to the research on the stochastic dynamic model, we found that the random noise term would influence the speed of equilibrium state of certain URI, instead of the equilibrium state itself, which proved the argument that the equilibrium state of a certain URI is stable. Equilibrium solutions of the dynamic model further characterize that its equilibrium state is not exactly equal at different spatial scales. (4) The switch model depicts the function of boundary gate, and the interface equilibrium is the critical point to decide whether we switch the gate open or closed. When the boundary gate is open or closed depends on whether URI reaches the critical value of its equilibrium state. According to the above conclusions, the paper puts forward policy recommendations respectively from temporal and spatial scales. From the temporal perspective, because of the impetus, the effect of URI and the role of boundary gate are different in different development stages of URI, we should take discretionary measures. From the spatial perspective, the equilibrium of URI is different at different spatial scales, so different development policies should be implemented at different spatial scales of URI.
城乡界面动态模型研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201612008
[本文引用: 1]

城乡界面在地域上处于城市和乡村交界处,在功能上起到城乡要素交流的空间载体作用,其发展对城乡协调意义重大。基于系统动力学,从要素流的角度构建城乡界面的理论框架,通过构建数量模型来刻画城乡界面动态演化机制。模型求解结果显示:① 在不同发展阶段,城乡界面受到内生动力和外生动力不同程度的影响。② 随着城乡界面的发展,其效应由负效应向正效应过渡,效应大小取决于其循环积累能力大小。③ 平衡态受城乡要素交换率、自身内生动力和循环积累能力的共同影响;城乡界面的平衡态是恒定的,但具有空间尺度效应。④ 开关模型刻画了界门对城市系统和乡村系统的作用机制。据此,分别从时间尺度和空间尺度对中国城乡系统的发展提出政策建议。
The logic and path of supporting urban-rural integrated development through territorial space planning
国土空间规划支撑城乡融合发展的逻辑与路径
Realizing common prosperity in building a unified big market
在构建统一大市场中实现共同富裕
共同富裕是社会主义的本质要求,但当前我国发展不平衡不充分问题仍然突出,区域间、城乡间的经济发展及居民收入差距依然较大,如何在高质量发展中促进共同富裕成为新发展阶段的重要目标。国际和国内经验显示,在构建统一大市场的进程中,经济活动和人口将不断向少数地区集聚,这是经济发展的客观趋势,也将促使地区间的人均差距不断缩小,从而走上“在集聚中走向平衡”的共同富裕之路。在空间政治经济学的统一框架下,如果不畅通统一大市场,则有可能导致欠发达地区对转移支付的过度依赖或者地方政府债务问题,即使在短期内能缩小地区差距,但将带来整个国家经济效率的巨大损失,反而不利于实现共同富裕。面向未来,中国需要进一步打破商品和要素流动的体制和观念障碍,不断推进和完善统一大市场,最终实现在高质量发展中促进共同富裕的目标。
A pure theory of local expenditures
DOI:10.1086/257839 URL [本文引用: 1]