1 引言
地理大数据实现对区域人地系统的精细刻画,为研究人地关系和区域发展等提供新的数据语境[1-2]。当前,大数据管理机制及实施流程尚未完善,易出现地理位置信息缺失等质量问题,降低数据效率和应用深度[3]。POI数据作为基于位置服务的底层关键数据,记录地理实体所承载的人类活动及与地理位置的相互关联性[4-5],具有一定的扩展性和丰富的应用场景。随着互联网和基于位置服务的发展,POI数据信息纵深和应用场景得到长足发展[4,6],从对地物基本信息记录转向于跨领域属性综合集成,为解决空间格局、人类活动、区域综合等关键地理问题提供数据支撑[6⇓-8],如甄峰等[9]基于POI等数据实现城市内部空间结构及影响因素分析;Wang等[10]基于POI等数据探索可持续通勤模式;浩飞龙等[11]基于POI数据实现城市复合功能检测。
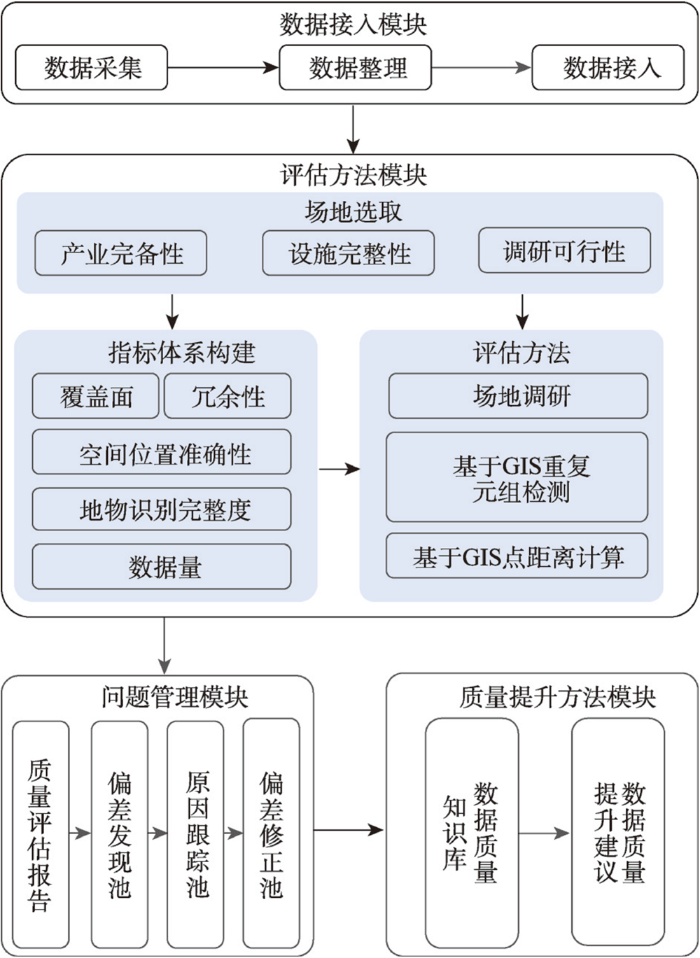
基于此,本文提出POI类地理大数据质量评估与提升方法(图1),基于数据获取与评估、问题发现与管理、质量提升与管理等一系列措施全面评估及提升数据质量。在数据采集和预处理后,根据调研的可行性、产业发展完备度及多样性等选择研究区。基于POI特性及数据质量一般评估准则,构建质量指标体系,包括空间位置准确率、地物识别完整率和数据冗余率,综合场地调研和GIS等手段创建评估方法体系,最终基于生命周期分析偏差原因,提出数据质量提升有效途径,为自然语言、地理音频及视频等多源地理大数据质量评估及提升方案和案例参考,为地理大数据的高效利用提供基础支撑。
图1
图1
POI类地理大数据质量评估与提升方法示意图
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of the quality assessment and enhancement method for POI-type geographic big data
2 数据与方法
2.1 POI数据获取
2021年12月在中国知网以POI数据为数据源的文章数量共计32篇,其中以高德地图为数据源(简称“高德”)文章24篇,占比75%,以百度地图为数据源(简称“百度”)文章5篇,占比15.63%,两者占比90.63%。故选择百度地图和高德地图POI进行质量评估。POI数据基于WEB API接口获取,百度获取方式是“以圆形区域检索”和“以行政区检索”,高德则是“周边检索”和“以行政区检索”,获取时间是2021年12月9日—2021年12月18日。预处理包括清洗和坐标系投影转换等。清洗是删除研究区以外数据,包括:① 地物及POI采集点均位于研究区外;② 地物位于研究区外,POI采集点位于研究区内。坐标系投影转换包括地理坐标系转化投影。本文分别借助百度数据源及高德数据源API接口,将坐标系进行解密,转换为WGS1984,并基于沈阳地理位置,将WGS 1984投影为WGS 1984 UTM ZONE 51N。
2.2 场地选取
2.3 指标体系构建
2.4 评估方法
(1)场地调研
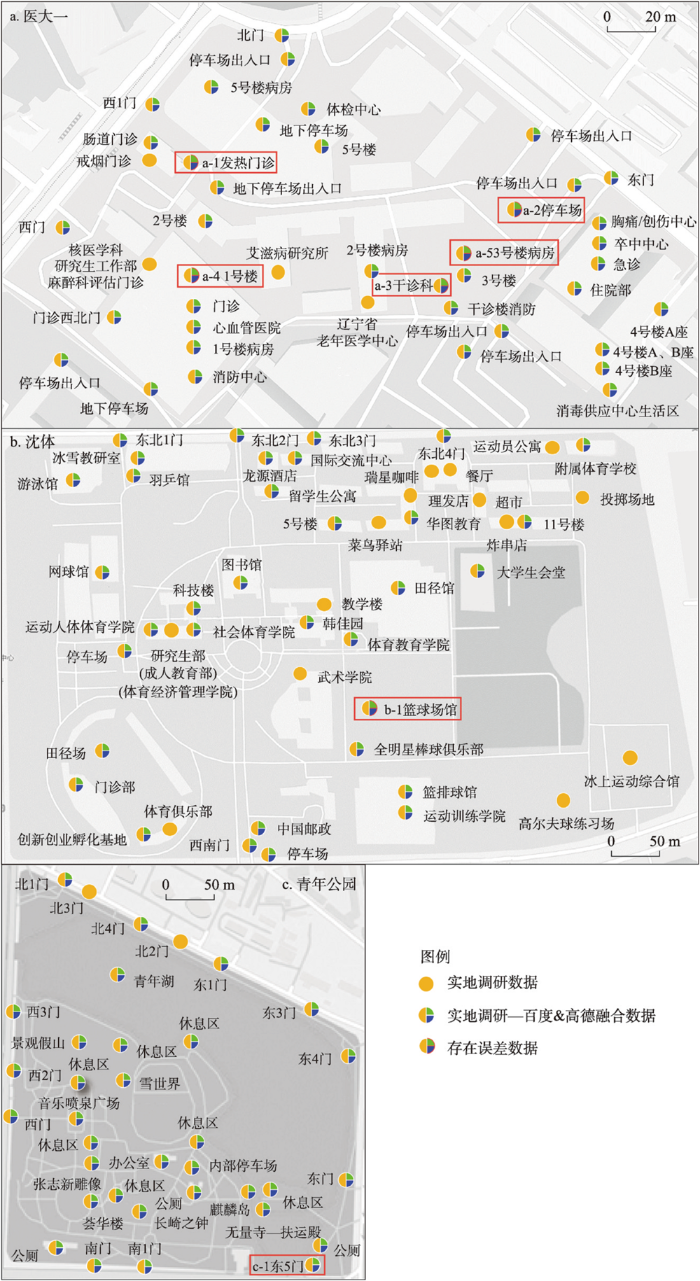
场地调研是了解地物实际空间位置及本质信息,掌握第一手真实资料的有效手段[34]。本文基于观察法和询问法获取地物的数量、地理及非地理属性等,为精准评估数据质量提供支撑。流程为:① 研究区格网化处理。因研究区内建筑物数量较多,为防止调研期间出现遗漏及重复等问题,进行格网化处理,依据研究区面积、地物丰富度和调研执行度等因素,沈体为100 m×100 m,青年公园为50 m×50 m,医大一为25 m×25 m。② 调研信息标记及预处理。调研主要借助GPS等工具记录地物的空间信息,询问法了解地物更新情况。预处理是指数据接入、清洗及数字化。本文基于转换器,将.gpx格式转换为.shp格式,糅合询问所得信息,数字化调研信息。调研时间是2021年12月20—27日。
(2)基于GIS重复元组检测模型
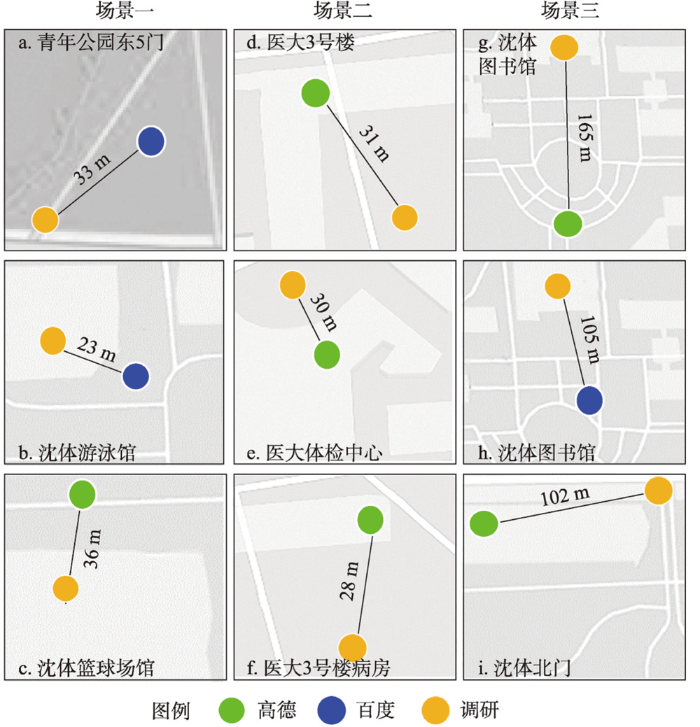
该模型用于测算冗余率。因城市存在相似地物,若仅对比非地理属性相似度,可能提高数据冗余率,因此本文在对比非地理属性基础上,借助GIS邻域分析进行点距离计算,认为一定空间距离内相似POI数据即为重复元组,即“名称”“类别”字段相同,空间位置接近的样点。流程:对样本进行循环遍历,寻找相似元组;计算重复元组间的空间距离;结合场地调研确定重复元组可能性。根据重复元组占比计算冗余率。
式中:
(3)基于GIS点距离计算模型
该模型用于计算偏差点的偏差距离。本文通过计算调研与样本数据间的欧氏距离确定POI数据的偏离距离、区间及特征,为挖掘数据采集阶段产生误差的可能因素提供基础支撑。公式为:
式中:
(4)比值法
本文借助比值法(Count Ratio, CR)辅助计算数据地理及非地理属性准确率:
式中:
3 数据质量评估
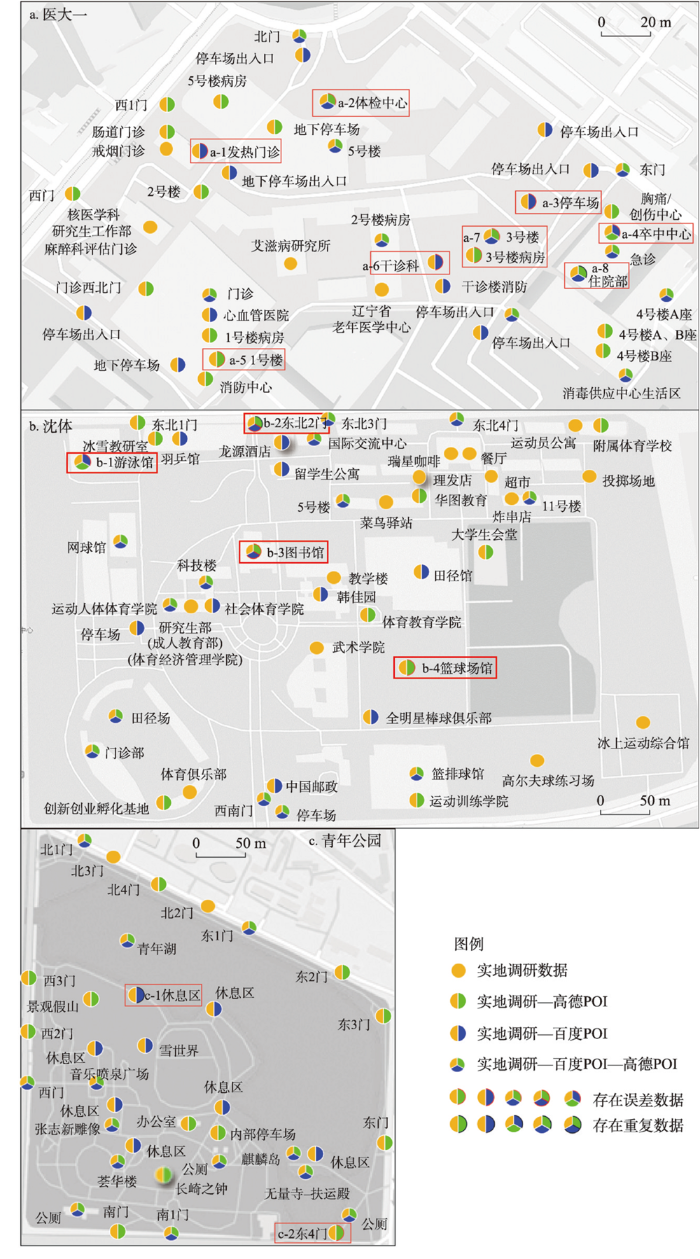
本文基于场地调研获取地物共126个,包括青年公园35个,沈体48个,医大一43个,结合GPS定位器、观察及询问法等记录地物的空间位置及地物建造、翻新、营业及开放等非地理属性。同时基于GIS平台等实现POI与调研数据的对比分析,包括检测元组重复率、计算偏差距离等,发现高德及百度数据源在冗余率、地物识别完整率及空间位置准确率3个维度的特征:
图2
表1 网络地图与调研数据对比
Tab. 1
| 地点 | 来源 | 数据量(条) | 地物识别完整率(%) | 重复数量 | 冗余率(%) | 误差数 | 位置准确率(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青年 公园 | 高德 | 26 | 71.43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 96.15 |
| 百度 | 23 | 62.86 | 1 | 4.30 | 0 | 100.00 | |
| 沈体 | 高德 | 27 | 54.17 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 92.60 |
| 百度 | 26 | 52.08 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 88.46 | |
| 医大一 | 高德 | 29 | 65.17 | 1 | 3.40 | 4 | 86.21 |
| 百度 | 26 | 58.14 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 84.62 |
注:青年公园实地调研的数据量为35条;沈阳体育学院实地调研的数据量为48条;中国医科大学第一附属医院实地调研的数据量为43条。
地物识别完整率特征(图2、表1):① 高德地物识别完整率高于百度。高德数据量大于百度,最大数据差存在于医大一,共3个,最小数据差存在于沈体,共1个。② 高德对地物的入口识别度更高,识别青年公园入口12个,占比85.71%;百度数据源识别青年公园入口4个,占比28.57%。③ 百度数据源对同一地物多种属性识别率更高,百度数据源识别医大一急诊楼4种属性,包括急诊、卒中中心、住院部和消毒供应中心生活区。④ 地物识别完整率与地物对外开放度成正比。3个场地的社会属性与开放程度不同,青年公园、医大一和沈体分别为城市绿地,医疗服务和教育服务,对社会公众开放程度依次从高到低,数据采集难度依次上升,地物识别完整率下降。
图3
数据量特征(图2、表1):① 基于宏观角度,高德数据量远大于百度,是其7.82倍。根据“以行政区划区域检索”,获取高德POI数据411501条,百度POI数据52591条。② 对比“以圆形区域检索或周边搜索”数据获取方式,发现返回的数据量和数据精准度相差较大,以青年公园为例,百度数据“以圆形区域检索”获取数据是以“以行政区划区域检索”获取数据的3.83倍,“以行政区划区域检索”无重复和存在误差数据;高德数据“以周边搜索”获取数据是“以行政区划区域检索”获取数据的1.63倍,“以行政区划区域检索”返回空间位置误差数据2条。此外,对比两种数据源面积较大地物的采集点一般位于地物中心;面积较大场地内商家门店识别率较低,如沈体内存在瑞星咖啡、理发店和菜鸟驿站等商业服务业设施,未能成功识别。
4 数据质量影响因素
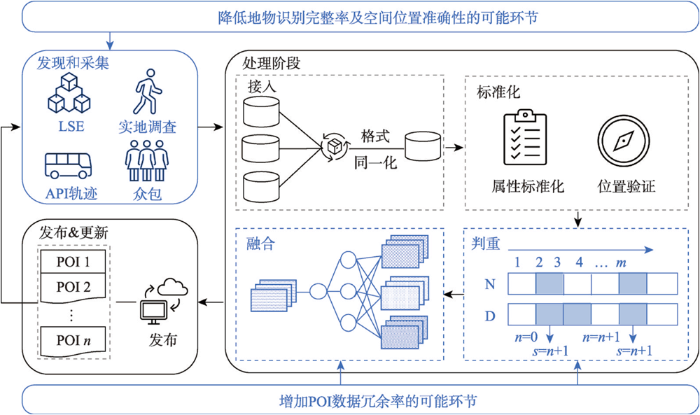
基于质量评估结果,基于API接口返回的数据均存在不同程度的质量问题,如存在重复数据、地物及其属性未能完全识别、空间位置获取有误、数据量受数据获取方式影响等。本文基于数据生命周期,发现并总结影响数据质量环节及因素,为提高数据质量及应用效率提供技术支撑和可行性建议。
生产过程包括发现、采集、处理和发布4个阶段[35]。发现和采集主要有3种方式:采集员实地调查、众包和基于遥感影像等数据的自动识别[36]。实地调查是采集员通过驾驶车辆或步行形式发现地物,借助采集设备对获取地物详细信息并传回数据中心,采集员可能未发现全部地物及其属性,降低地物识别率,亦因采集员记录地物空间位置习惯差异,降低空间位置准确性[37]。众包是通过浮动车或用户发现并向数据中心反馈数据,地物发现率及用户对地物的定位习惯影响地物识别率及空间位置准确性[38]。基于遥感影像等数据的自动识别在一定程度上提高空间位置准确性,却无法识别地物的多种属性[39],如沈体同一栋教学楼设立成人教育部、社会体育学院等多个部门(图2b)。
处理阶段包括数据接入、标准化、判重、融合4个程序[40](图4)。因来源及内容多样性,须先进行规范化处理,将其转化为可处理的格式。在接入后,进行标准化处理,包括标准化属性字段及验证数据行政区划正确性[41]。判重是将新接入数据与原有数据进行对比,构建模型判断相似度,当相似度达到阈值则为重复,进行数据的融合与更新[42];若无重复数据,将新增数据添加至数据库。此过程可能因同一地物多次采集信息有异,无法将其判定为重复数据,提高冗余率。融合是将多源数据合并满足不同业务需求,如与其他平台对接获取扩展属性等[43]。此阶段因多源数据描述不同,提升数据冗余率,如沈体(高德)中的住院部和4号楼住院部(图2a)。数据更新和发布是一个长久且持续过程。电子地图商会根据地物更新进行更新和融合。
图4
图4
影响POI数据质量的可能环节示意
Fig. 4
Schematic diagram of possible links that affect POI data quality
5 数据质量提升方法
多源数据丰富度和信息完善度不同。在数据质量一定的情况下,获取更丰富与完整的数据信息,提升数据质量是研究者的迫切需求之一。基于多种数据源,抽取精准度较高的数据进行融合处理,是提高数据质量的有效途径之一。
图5
表2 网络地图与融合后数据对比
Tab. 2
| 地点 | 来源 | 数据量(条) | 地物识别完整率(%) | 重复数 | 冗余率(%) | 误差数 | 位置准确率(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 青年 公园 | 融合 | 34 | 94.29 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 97.14 |
| 高德 | 26 | 71.43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 96.15 | |
| 百度 | 23 | 62.86 | 1 | 4.30 | 0 | 100.00 | |
| 沈体 | 融合 | 34 | 68.75 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 97.06 |
| 高德 | 27 | 54.17 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 92.60 | |
| 百度 | 26 | 52.08 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 88.46 | |
| 医大一 | 融合 | 40 | 90.70 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 87.50 |
| 高德 | 29 | 65.17 | 1 | 3.40 | 4 | 86.21 | |
| 百度 | 26 | 58.14 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 84.62 |
注:青年公园实地调研的数据量为35条;沈阳体育学院实地调研的数据量为48条;中国医科大学第一附属医院实地调研的数据量为43条。
6 总结与展望
本文基于微观视角构建POI大数据质量评估与提升方法,包括“数据获取与评估→问题发现与总结→质量提升及管理”等多个逐层递进、相辅相成的模块。在数据获取与评估模块,借助场地调研、GIS等方法从地物识别完整率、数据冗余率和空间位置准确率3个维度实现POI数据质量评估,为评价数据质量状态、考察数据在应用层面满足程度提供支撑。在问题发现与总结模块,基于数据生产过程发现和总结数据质量的可能影响因素,为整改生产流程和形成智慧生产提供基础。在质量评估及管理模块,多源数据融合是提升POI数据质量的有效手段,是提高数据高效应用和有效决策的重要支撑。
参考文献
Geographic big-data: A new opportunity for geography complexity study
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808001
[本文引用: 1]

Since 2010, big data has played a significant role in various fields of science, engineering and society. The paper introduces the concepts of geographic big-data, the fourth paradigm and nonlinear complex geographic system, and discusses interactive relationships of these concepts. It is proposed that geographic big-data and the fourth paradigm would become a new opportunity to research on geography complexity. Then the paper discusses how to use the methods of geographic big-data and complexity science to examine geography complexity. For example, based on big-data, a series of indicators of statistical physics fields could be constructed to describe the complex nonlinear characteristics of the real geographic world. Deep learning, complex network and multi-agent methods can be used to model and simulate the complex nonlinear geographic systems. These methods are important for a better understanding of the complexity of geographic phenomena and processes, as well as the analysis, simulation, inversion and prediction of complex geographic systems. Finally, the paper highlights that the combination of geographic big-data and complexity science would be the mainstream scientific method of geography in the 21st century.
地理大数据为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201808001
[本文引用: 1]

大数据之风自2010年席卷全球,已在科学、工程和社会等领域产生深远影响。本文首先从地理大数据、第四范式以及非线性复杂地理系统3组基本概念出发,剖析上述3组概念之间的科学联系与相互支撑作用,提出大数据和第四范式为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇。其后,探讨如何利用大数据和复杂性科学的理论方法开展地理复杂性研究。基于地理大数据,可以通过统计物理学的系列指标描述现实地理世界的复杂非线性特征,同时,还可利用深度学习、复杂网络、多智能体等方法,实现复杂非线性地理系统的推演和模拟。上述方法对认知地理现象和过程的复杂性,对复杂地理系统的分析、模拟、反演与预测有重要作用。最后,提出地理大数据和复杂性科学相互支撑可能成为21世纪地理学的主流科学方法。
From calibration to parameter learning: Harnessing the scaling effects of big data in geoscientific modeling
The behaviors and skills of models in many geosciences (e.g., hydrology and ecosystem sciences) strongly depend on spatially-varying parameters that need calibration. A well-calibrated model can reasonably propagate information from observations to unobserved variables via model physics, but traditional calibration is highly inefficient and results in non-unique solutions. Here we propose a novel differentiable parameter learning (dPL) framework that efficiently learns a global mapping between inputs (and optionally responses) and parameters. Crucially, dPL exhibits beneficial scaling curves not previously demonstrated to geoscientists: as training data increases, dPL achieves better performance, more physical coherence, and better generalizability (across space and uncalibrated variables), all with orders-of-magnitude lower computational cost. We demonstrate examples that learned from soil moisture and streamflow, where dPL drastically outperformed existing evolutionary and regionalization methods, or required only ~12.5% of the training data to achieve similar performance. The generic scheme promotes the integration of deep learning and process-based models, without mandating reimplementation.
Urban complexity studies from the perspective of geography: A review based on the literature in the past 20 years
地理学视角下城市复杂性研究综述: 基于近20年文献回顾
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.01.014
[本文引用: 2]

城市作为组织结构复杂的开放人地地域系统,一直是地理学的研究核心之一。论文以2000—2020年相关文献为数据源,构建一套定量分析与定性认知相结合的文献分析判读体系,基于地理学视角从概念内涵、研究主题、技术方法等方面综述城市复杂性研究成果并开展讨论。过去20 a来,中国的城市复杂性研究逐渐从单尺度的格局、过程和机制研究转向于多尺度下复杂交互过程的集成与综合研究,并逐步形成了城市设施网络、城市人居环境、城市经济活动以及城市空间治理4个主要主题,在数据方法上逐步转向于空间技术及社会计算支持下的全景式全生命周期数据支撑的多维场景化分析。今后及未来一段时期,地理学视角下的城市复杂性研究需要进一步加强城市数字基础设施建设及全周期信息采集能力,加深对城市生态经济体系的综合测度及监控,增强跨区域发展机制影响下的城市流空间研究。
Overview of man-land relationship research based on POI data: Theory, method and application
基于兴趣点(POI)大数据的人地关系研究综述: 理论、方法与应用
Big data driven functional interaction patterns and governance strategy for Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206006
[本文引用: 1]

The coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region and the implementation of the policy of relieving non-capital functions from Beijing are one of hot topics in current academia and the government. The distribution and interaction patterns of urban functions are an important aspect to depict the performance of the coordinated development and governance strategies of the BTH urban agglomeration. Based on the interaction principle of urban functional zones in the BTH region, we introduced the shift-share analysis model, revised land ecological niche model, and coupled a new interactive model by expanding the gravity model for urban functional interaction patterns, supported by GIS technique. We consider the POI as a commonly used big data to analyze urban problems and characteristics, this study takes the BTH urban agglomeration as the study area and uses three periods (2010, 2016, 2019) of POI datasets to identify urban functional zones. Then we apply the new interactive model to reveal the characteristics of the functional interaction patterns from space and time dimensions. Meanwhile, we analyze and evaluate the coordinated development and implementation of the policy of relieving non-capital functions from Beijing, and come up with some suggestions. Our findings are: (1) the total area of urban functional areas increased 1.5 times over the past decade, and the mixed functional areas are the fastest-growing urban functional zone (1.7 times). (2) The industrial and commercial functional zones of Beijing had been dispersing steadily, but the residential, scientific, educational and cultural, and public service functional zones were still aggregated. (3) Langfang, Tangshan, Tianjin, and Baoding, which are located in the center of BTH region, act as "middlemen" in the redistribution process of the relieving policy. They become main cities to drive functional interaction. (4) Shijiazhuang mainly received the functional zones from Tianjin and Langfang, which shows the relay characteristics. (5) The government's decision-making for redistribution of urban functional zones in the BTH region should consider the evolution trend of functional interaction patterns among cities so as to take targeted governance measures. Our findings indicate that the urban functional interactive model could better explain and reveal changing characteristics of the functional interaction patterns in the study region.
京津冀城市群城市功能互动格局与治理策略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206006
[本文引用: 1]

京津冀协同发展和北京市非首都功能疏解政策实施状况是当前学术界和政府关注的热点。城市功能的分布和互动格局是刻画城市群协同发展和治理策略成效的重要内容。本文在阐述城市群内城市功能之间互动原理基础上,引入偏离—份额分析模型、改进土地生态位模型、扩展引力模型和GIS技术,耦合构建了新的城市功能互动模型。以京津冀城市群为研究对象,基于2010年、2016年、2019年3期POI大数据提取不同类别城市功能区,从时空两个维度揭示京津冀城市群功能的互动格局特征,分析协同发展和北京市非首都功能疏解政策实施状况,并有针对性地提出了治理策略。结论显示:① 2010—2019年间城市群建成区城市功能区总面积增加1.5倍,其中混合功能区增长最快,增加1.7倍;② 北京市工业功能、商业功能正在稳步疏解,但是居住功能、科教文化功能、公共服务功能仍在聚集与强化;③ 廊坊市、唐山市、天津市、保定市等中部城市在非首都功能疏解中发挥了“二传手”作用,成为功能互动的主要驱动城市;④ 石家庄市吸纳的疏解功能主要来源于天津市和廊坊市,具有接力特征;⑤ 京津冀城市群城市功能疏解在治理策略上需要关注功能互动格局演化趋势来进行精准施策。上述结论表明本文构建的城市功能互动模型可以较好地揭示和解释京津冀城市群城市功能互动格局的变化特征。
Application and reflection of POI big data from the perspective of geography
地理学视角下POI大数据的应用研究及反思
POI-based spatial correlation of the residences and retail industry in Shenyang city
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.03.010
[本文引用: 1]

It is a crucial research content of human-economic geography to quantitatively research the spatial correlation between urban residences with its price and the regional commercial service. Taking Shenyang City in Liaoning Province as a case study and using the residential and retail points of interest (POI) as a data source, this paper extracted the spatial clustering patterns of various residences based on the spatial kernel density analysis method, and then quantitatively expressed the correlation between commercial and residential spatial distribution. On this basis, this paper used the geo-statistical method to measure the spatial heterogeneity of houses prices and measured the impact of retail format layout on houses prices. Solutions presented in this research can be summarized as follows: The overall spatial aggregation characteristics of retailing are similar to that of dwellings, the distribution pattern of the central urban agglomeration and the multi-centers dispersion in the periphery city is presented. The correlation coefficient between retails’ density and residences’ density is 0.95. There is a strong correlation between residences, and some small-scale retails including supermarkets and convenience stores, the aggregation effect of shopping malls is lagging behind the urban dwellings. Large retail’ should be located in the Tiexi eco-technological development zone and other similar residential areas, in order to provide residents advanced shopping services. The inverted ‘U’ type spatial distribution model that houses prices presented is consistent with the attenuation characteristics of retail space’s density.
基于POI大数据的沈阳市住宅与零售业空间关联分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.03.010
[本文引用: 1]

城市住宅及其价格与区域商服业的空间关联性量化研究是人文-经济地理学的重要研究内容。以辽宁省沈阳市为案例,以住宅和零售业兴趣点(Point of Interest, POI)为数据源,基于空间核密度分析提取住宅和各类零售业的空间聚类形态,量化表达商住空间布局的相关性,并在此基础上运用地统计方法测算房价的空间异质性及其与零售业态空间布局的差异特征。结果表明,零售业的整体空间聚集特征与住宅相似,呈现中心城区块状聚集、外围城区多中心离散的分布格局;零售业与住宅核密度相关系数为0.95,超市、便利店等小规模的零售业与住宅密度相关性较强,商场商厦的聚集效应落后于城市住宅,大型零售业应该在铁西经济技术开发区等住宅密集区规划选址,为居民提供高端购物服务;住宅价格的倒“U”型空间分布模式与零售业空间密度的圈层衰减特征相符。
A note on GeoAI from the perspective of geographical laws
从地理规律到地理空间人工智能
Analysis of urban internal spatial structure characteristics and its influencing factors based on population flow: A case study of Nanjing
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210597
[本文引用: 1]

At present, the research on urban network structure from the perspective of “flow space” is in the ascendant. Compared with the fruitful results at the regional scale, the stable network analysis framework and formation mechanism model of city-group have not yet been built. It is urgent to comprehensively use the urban regional network analysis method and expand it at the microscopic scale. At the same time, more and more attention has been paid to the city hierarchy and assortativity in the network context. In this research context, focusing on two types of directed flow of people: commute and recreation, this paper takes Nanjing as the study area, and uses the methods of centrality and control, community division and improved gravity model to analyze the characteristics and influencing factors of urban network association from the city-local level. The results show that: (1) The decomposition of spatial scale can effectively identify the city-local structure of commute and recreation. Nanjing presents a “unipolar” development trend of the main city to the south of the Yangtze River. The main performance is that the main city to the south of the Yangtze River attracts intensive commute and recreation flows, and it has all types of centers, providing both local and regional service. (2) The results show that the improved gravity model has a good fitting effect on the real flow of people in the whole area, and the number of residents and spatial distance limit affect the flow of residents to a great extent. The occupation residence ratio and per capita POI amount are the direction regulators of commuting flow and leisure flow respectively. The difference of functional energy levels of township streets determines the interpretation of gravity model to local pedestrian network. The gravity model underestimates the distribution capacity of people flows in Pukou district, Gaochun district and other key policy inclined areas.
基于人口流动的城市内部空间结构特征及其影响因素分析: 以南京市为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210597
[本文引用: 1]

当前,“流”空间视角的城市网络结构研究方兴未艾,而城市内部急需寻找到稳定的网络结构分析框架与形成机制模型。在此背景下,本文聚焦通勤和休闲两类有向人流网络,以南京为研究对象,利用中心性与控制力、社区划分、改进重力模型等方法,解析南京内部的人流网络结构特征及其影响因素。结果显示:① 对空间尺度的分解可以有效识别全域-局域两个层次的空间结构。南京江南主城的“单极化”发展态势明显,主要表现为江南主城是通勤流与休闲流的密集流入地,且集中了各类型引力中心,兼具地方服务和区域服务功能。② 改进重力模型对全域人口流动强度的拟合效果较好,人口数量和空间距离在很大程度上影响着人口流动,职住比和人均POI数量分别是通勤流、休闲流的方向调节器。重力模型低估了浦口区、高淳区等政策重点倾斜地区的人流集散能力。
Exploring regional sustainable commuting patterns based on dockless bike-sharing data and POI data
Geographic detection and multifunctional land use from the perspective of urban diversity: A case study of Changchun
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020170705
[本文引用: 1]

Mixed and multifunctional land uses have been identified as an enabling way to promote urban vibrancy and yield socio-economic benefits. As a key strategy in New Urbanism and Smart Growth, mixed use has been widely accepted in urban planning for promoting urban vibrancy and sustainability. This study aims to reveal the differences in the spatial distribution characteristics of different types of mixed use and the influencing factors of their distribution in Changchun central district from the perspective of urban diversity. Based on the POI data in the central district of Changchun, this study focuses on four function categories: Residence, office, commerce, and leisure. Location quotient, entropy index, and Geodetector are used to explore the distribution features and influencing factors of mixed use in Changchun. Serveral conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) Mixed use is the major form of street scale function elements distribution, from the perspective of concentration. All types of elements form a functional gathering area of specialization, but there are large differences between the degrees of specialization. The distribution of concentration of functional elements shows consistent trends with the overall quantity distribution. (2) The degrees of mixed use performance of core-periphery spatial differences reflects that the degree of the core street area a is higher than that of the external zone. The degrees of mixed use of office, commerce, and leisure is stronger than their mixture degree with residence. (3) The main features of mixed use at street scale are the mixed multi-functions compatible with each other. Among the various types of functional elements, leisure and commercial elements have a higher degree of interaction with others, which means that they have a strong compatibility, with the positive effect on mixed use. (4) The spatial heterogeneity of the degrees of mixed use is significant. The primary determinants of the spatial distribution of mixed use include: land price, number of leisure elements and commercial elements. The total number of functional elements, the density of population and the density of road network variables show a weak influence on the differentiation of multifunctional land use. Except that the land price varies, other influencing factors behave differently in the by-type mixed use impact mechanism.
多样性视角下的城市复合功能特征及成因探测: 以长春市为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020170705
[本文引用: 1]

多功能要素的复合化已成为信息时代城市空间发展的重要趋势,而复合功能开发亦被认为是解决城市交通拥堵、低效能源消耗及职住不平衡等问题的重要手段,对促进有活力的、宜居的及可持续的城市环境建设具有重要意义。基于城市多样性的理论框架,在界定城市功能复合内涵的基础上,以长春市中心城区城市功能兴趣点(POI)数据为基础,采用区位熵指数、信息熵指数及地理探测器模型,分析城市居住、办公、商业、休闲四类功能要素的复合特征,并探讨城市功能复合空间分异的驱动因素。结果表明:① 城市功能要素集中度特征显著,各类型功能要素均形成了专业化的功能集聚区,但各区块间功能要素的专业化程度存在较大差异。② 城市功能要素复合度整体表现出核心—边缘的空间差异,核心区街道复合度整体高于外围开发区,办公、商业、休闲三种功能要素间的复合度要整体强于其各自与居住功能的复合。③ 以单一功能为主、多功能兼容的综合型复合是街道尺度功能复合的主要表现形式;各功能要素中,休闲、商业功能具有较强的兼容性。④ 城市功能复合的空间异质性特征显著,土地价格、休闲要素数量是造成多功能复合分异的主要原因;分类型复合中,各解释因子影响力度表现各异。
Data quality and data use in primary health care: A case study from Iran
Opportunities and challenges of geo-spatial information science from the perspective of big data
论大数据视角下的地球空间信息学的机遇与挑战
DOI:10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2022012
[本文引用: 1]

大数据时代已经到来,并且已经深入人类生活的方方面面。作为地球科学与信息科学交叉融合催生出的地球空间信息学,大数据时代的来临在为其提供更丰富的数据保障的同时,也带来数据存储、管理、分析和挖掘方面的新挑战,甚至造成了某种程度上的“数据爆炸”。从大数据视角,梳理了当前地球空间信息学涉及的地理信息系统、智慧城市、遥感大数据和空间数据挖掘4个核心领域的瓶颈和挑战;指出在大数据时代,地球空间信息学可为地球科学研究提供更加精准、实时的空间信息框架和更加智能高效的信息处理手段,从而服务于智慧城市、智慧地球建设和人类社会的可持续发展。而且,大数据时代下,地球空间信息学的发展面临着软件和硬件水平的双重考验。
Big data-driven measurement of the service capacity of public toilet facilities in China
Public health facility planning is one of the important contents of national land planning, which needs to balance geospatial equity and service capacity. However, assessment models and data acquisition methods based on a geosystemic analysis perspective have been lacking for a long time. By focusing on urban public toilets and taking the highly urbanized city of Shenyang, China as the study area, this study developed a new data strategy for urban public facilities with points of interests (POI) big data as the main data source, and subsequently corrected the POI data and analyzed the errors through a field survey, and conducted an empirical assessment oriented toward spatial equity and service capacity to discover the development dynamics of urban facilities over the past ten years and the impacting factors. We found that the integrated population and spatial elements could more accurately evaluate the service capacity of public toilets. Meanwhile, POI data have value in the research of public health facilities, but there are some errors in data quality and data access. The study empirically explores the geographic analysis methods of field research data (small data) and POI data (big data) with empirical contributions.
SparkDQ: Efficient generic big data quality management on distributed data-parallel computation
DOI:10.1016/j.jpdc.2021.05.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
A pragmatic and industry-oriented framework for data quality assessment of environmental footprint tools
A POI data-based study on urban functional areas of the resources-based city: A case study of Benxi
基于POI大数据的资源型城市功能区识别方法与实证: 以辽宁省本溪市为例
Where have you been: Dual spatiotemporal-aware user mobility modeling for missing check-in POI identification
Deep-learning generation of POI data with scene images
DOI:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.04.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research on rural e-commerce and influential factors of product diversification: Based on the field investigation and analysis of Taobao villages in Zhejiang province
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.08.002
[本文引用: 1]

With the rapid development of e-commerce, Taobao village has become one of the most influential economic geography phenomena in China. However, little is known about how to promote product diversification of Taobao villages as yet. Based on the field research data of 282 Taobao villages in Zhejiang Province, this study measured the ability of Taobao villages to apply e-commerce to realize path creation from the aspects of vertical diversification and horizontal diversification of products, and analyzed the improvement of product diversification in Taobao villages after the introduction of e-commerce. This study constructed the influential factor models of product vertical and horizontal diversification improvement in Taobao villages, which include the ordinary least square (OLS) model and spatial econometric models. The mechanisms of the models were also analyzed. We found that: 1) The overall improvement of product diversification in Taobao villages is polarized and the improvements of vertical diversification and horizontal diversification are roughly the same. It was believed that in 40.4% and 42.6% of the villages the degrees of product vertical diversification and horizontal diversification have been improved greatly or very greatly since they became Taobao villages, while in 28.7% and 32.6% of the villages the improvement is small or very small. 2) The spatial agglomeration characteristics of improvement of product diversification in Taobao village of Zhejiang Province are obvious. The high-value gathering points of improvement of product vertical diversification are mainly located in Lin'an, Huzhou, Cixi, Yuyao, and other regions. The high-value gathering points of improvement of horizontal diversification are located in the Hangzhou-Jiaxing-Huzhou area, Cixi, as well as Yuyao. The low-value gathering points of improvement of both horizontal diversification and vertical diversification are mainly located in Yiwu City. 3) The result of OLS model shows that the improvement of vertical diversification of products is significantly positively correlated with product deepening processing and policy support. 4) The result of spatial error model (SEM) shows a significant positive correlation between improvement of product horizontal diversification and mechanized operation level, and a significant negative correlation with the establishment of e-commerce associations.
农村电子商务与产品多样化影响因素探究: 基于浙江淘宝村的实地调研分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.08.002
[本文引用: 1]

论文基于浙江省282个淘宝村的实地调研数据,从产品的垂直多样化和水平多样化2个方面衡量淘宝村抓住电子商务机遇并实现路径创造的能力,分析了电子商务对农村产品多样化的提升程度,并通过普通最小二乘法(ordinary least square, OLS)模型、空间计量模型构建淘宝村产品多样化的影响因素模型并分析其作用机制,以期弥补电子商务产业演化方面理论研究和经验分析的不足,同时为乡村经济发展与转型的实践提供建议与参考。研究表明:① 淘宝村产品多样化的提升情况呈现两极分化的趋势,垂直多样化和水平多样化的提升程度大致相同;② 浙江省淘宝村的产品多样化提升程度的空间集聚特征明显,产品垂直多样化提升程度的高值聚集点主要位于临安、湖州、慈溪、余姚等地,产品水平多样化提升程度的高值聚集点则位于杭嘉湖区域以及慈溪、余姚等县市,水平多样化提升程度和垂直多样化提升程度的低值聚集点都主要位于义乌市;③ OLS模型显示产品垂直多样化提升程度与产品深化加工及政策的支持情况呈显著正相关;④ 空间误差模型显示产品水平多样化的提升与机械化操作水平呈显著正相关,但电商协会的建立却逆向促进了产品水平多样化提升程度。
Residents' sense of urban public security and community environment: Analysis based on a large-scale questionnaire survey of Beijing
居民城市公共安全感知与社区环境: 基于北京大规模调查问卷的分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202108009
[本文引用: 1]

新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情的爆发使得民众对公共安全问题的关注到了前所未有的程度,社区作为社会治理基本单元,在防疫减灾中所发挥的作用尤为突出。本文基于北京2019年城市体检问卷调查数据,采用多层线性模型检验个体属性及社区环境指标对公共安全感知的影响。研究发现,公共安全感知的差异主要来自个体属性的不同,老年人及健康状况一般或较差的群体,以及低收入、低学历、待业人群的安全感相对较低;安全感的社区差异显著,人口稠密、公交线路密集的社区居民安全感较低,道路交叉口较多的社区安全感较高;社区离Ⅰ型应急避难设施和医院的距离越近,居民安全感越高,但中小型设施影响不显著;良好的社区社会环境对居民安全感具有非常明显的正向影响,但租户很难从物业管理水平的提高中获益。据此本文提出了建设安全韧性社区的若干建议。
Complexity, relatedness and urban technology evolutionary path: A comparative study between Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.002
[本文引用: 2]

In the development of science and technology innovation centers, upgrading to complex technologies requires full consideration of the local technology capacities. Evolutionary economic geography emphasizes the impact of technology relatedness with the local technology capacities on technology evolution. This study took three international science and technology innovation center cities, Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen, as examples, and incorporated complexity and relatedness into the research framework to comparatively analyze the technology relatedness and complexity of the three cities and their impact on technological change. It is found that there are significant differences in technology structure, technology relatedness, complexity, and evolutionary paths among the three cities. Shanghai has higher technology relatedness and lower complexity, Shenzhen has the lowest technology relatedness and highest technology complexity, and Beijing is in between. In terms of evolutionary trends, Beijing has experienced an obvious change to complex technologies; Shenzhen has the largest increase in overall technological complexity, but after 2006 there was a trend toward diversification into low-complexity technologies; and Shanghai has the smallest increase in technological complexity. The econometric analysis shows that technologies with stronger local technology linkages are more likely to become the dominant technologies in the next stage of development in the three cities, but technologies with high complexity are more likely to become the dominant technologies in the next stage of development in Beijing, and have no significant impact on the technology change of Shanghai and Shenzhen. The construction of science and technology innovation centers requires cities to fully consider urban technology base and evolutionary characteristics, and formulate targeted technology development strategies.
复杂度、关联度与城市技术演化路径: 基于北京、上海、深圳的对比分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.002
[本文引用: 2]

演化经济地理强调与本地的技术关联对技术演化的影响,在建设科技创新中心的过程中,向复杂技术的升级需要充分考虑本地技术结构及演化特点。论文以北京、上海和深圳3个国际科技创新中心建设城市为例,将复杂性和关联性纳入研究框架,比较分析技术关联和复杂性对城市技术演化的影响。研究发现,北京、上海和深圳的技术结构、技术关联度、复杂性和演化路径存在明显的差异。上海的技术关联度较高,而复杂度偏低;深圳的技术关联度最低,技术复杂度最高;北京居中。从演化趋势看,北京经历了明显的向复杂技术演化的过程;深圳的整体技术复杂度上升幅度最大,但在2006年以后出现向低复杂度技术多元化发展的趋势;上海的技术复杂度上升幅度最小。计量分析表明,与本地技术关联越强的技术越有利于成为3个城市下一阶段的优势技术,但复杂度高的技术更容易成为北京下一阶段的优势技术,对上海和深圳的技术演化没有显著影响。未来国际科技创新中心建设需要充分考虑本地技术基础和演化特征,并制定针对性的技术发展策略。
Characteristics of elderly activity space by public transport and influencing factors: Based on the comparative analysis of daily and occasional activities
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.009
[本文引用: 1]

Public transport is of great significance for maintaining the quality of life of the elderly population. Based on frequency differentiation, this study took the urban area of Wuhu City as the research area and used the Thiessen polygon of bus stations as the spatial unit and smart card data of four months in 2018 to analyze the activity space of the elderly. Based on the identification of the locations of elderly bus card swiping, this study calculated the residential area of the elderly and the bus activity points of different activity frequencies and used the standard deviation ellipse to represent the activity space, and selected the radius and direction as the measurement indicators.The global linear regression analysis model was used to compare and analyze the difference in the impact of the built environment on daily and occasional activity spaces. Furthermore, the geographically weighted regression model was used to analyze the spatial heterogeneity of the impact of built environment factors. The main findings of the study are as follows: 1) The daily and occasional public transport activities of the elderly present similiar typical zonal distribution characteristics, but the specific zonal hierarchical structure and coverage are different. Occasional activities have a more obvious attenuation level from the city center to the periphery, while daily activities are relatively even. 2) There are differences in the mechanism of influence of daily and occasional activity spaces, and the intensity and direction of influence of the built environment in different spaces are clearly different, especially in the outer parts of the city. More factors in the built environment affect daily activities, the intensities of influence are relatively homogeneous; there are clear differences in the coefficient level of the influencing factors of occasional activities. The research results show that in the planning of the layout of urban public transport and public service facilities, it is necessary to consider the regular daily activities of the elderly to meet their high-frequency and basic life needs, as well as their occasional and low-intensity activity requirements. Establishing a structured and heterogeneous public service facility layout system for different spaces in the city can solve the problems of existing public transportation and public service facilities that do not consider the needs of the elderly, which can help provide improved urban services for the elderly.
老年人公交活动空间特征及影响因素研究: 基于日常与偶发活动的对比分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.04.009
[本文引用: 1]

公交出行对保障老年人生活质量具有重要意义。论文以安徽省芜湖市区为研究区域,从频率分异的视角出发研究老年人公交活动空间,利用公交刷卡数据,对比分析日常与偶发活动空间的分布特征,并进一步借助地理加权回归方法探讨建成环境对其影响机制的差异。研究发现:① 老年人日常和偶发公交活动空间呈现出相似的圈层式空间分布特征,但偶发活动的圈层结构层次相对更加明显;② 日常与偶发活动空间的影响机制存在差异,建成环境在不同空间的影响强度和方向存在明显不同,尤其表现在城市外围空间。研究结果有助于更加全面地解读老年人活动空间的结构层次,并为面向不同城市空间、不同类型设施的系统性规划建设提供参考。
Redefining Chinese city system with emerging new data
DOI:10.1016/j.apgeog.2016.08.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Nationwide geospatial analysis of county racial and ethnic composition and public drinking water arsenic and uranium
There is no safe level of exposure to inorganic arsenic or uranium, yet recent studies identified sociodemographic and regional inequalities in concentrations of these frequently detected contaminants in public water systems across the US. We analyze the county-level association between racial/ethnic composition and public water arsenic and uranium concentrations from 2000-2011 using geospatial models. We find that higher proportions of Hispanic/Latino and American Indian/Alaskan Native residents are associated with significantly higher arsenic and uranium concentrations. These associations differ in magnitude and direction across regions; higher proportions of non-Hispanic Black residents are associated with higher arsenic and uranium in regions where concentrations of these contaminants are high. The findings from this nationwide geospatial analysis identifying racial/ethnic inequalities in arsenic and uranium concentrations in public drinking water across the US can advance environmental justice initiatives by informing regulatory action and financial and technical support to protect communities of color.© 2022. The Author(s).
Credibility of the cadastral data on land use and the methodology for their verification and update
Detecting and mapping tree seedlings in UAV imagery using convolutional neural networks and field-verified data
DOI:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.08.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Verifying an ENVI-met simulation of the thermal environment of Yanzhong Square Park in Shanghai
POI-based analysis on the affecting factors of property prices' spatial distribution in the traditional industrial area
基于POI大数据的老工业区房价影响因素空间分异与实证
POI-based analysis on retail's spatial hot blocks at a city level: A case study of Shenyang, China
基于POI大数据的城市零售业空间热点分析: 以辽宁省沈阳市为例
Big earth data promotes assessment of even development
地球大数据助力均衡发展评估
A government data quality management architecture based on multi-classification sub-chain
一种基于多分类子链的政务数据质量管理架构
Modeling hierarchical category transition for next POI recommendation with uncertain check-ins
DOI:10.1016/j.ins.2019.12.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Survey on historic districts of National Historical and Cultural City Research Center in Nanlang Ancient Town, Zhongshan City, Guangdong Province
广东省中山市南朗古镇国家历史文化名城研究中心历史街区调研
A next POI recommendation method for data-poor cities
面向数据匮乏城市的下一个POI推荐方法
POI processing method, device, electronic equipment and computer storage medium
兴趣点POI的处理方法、装置、电子设备及计算机存储介质
Method, device and storage medium for obtaining quality freshness of map data
地图数据质量鲜度获取方法、装置及存储介质
National tax and local tax joint data acquisition system and its operation method
国税地税联合数据采集系统及其操作方法
Application of basic geographic data in digital city data collection
基础地理数据在数字城市数据采集中的应用
Feedback method, terminal and server of geographic element information of navigation electronic map
导航电子地图地理要素信息的反馈方法、终端及服务器
The invention relates to a data processing method and device
一种数据处理方法及装置
Location method, device, device and storage medium based on POI spatial distance
基于POI空间距离的定位方法、装置、设备和存储介质
Research on the integration and update technologies of electronic map based on multi-source vector data
多源矢量数据的电子地图整合更新技术研究
The invention relates to a POI information supplement method and device
一种POI信息补充方法及装置
Multi-source POI data fusion based on the spatial location information
空间位置信息的多源POI数据融合
Study on the method of matching and fusion of multi-source POI
多源异构POI融合方法及应用
Methods and devices for measuring the quality of map POI data
衡量地图POI数据的质量的方法和装置
Analysis of spatial economic structure of Northeast China cities based on points of interest big data
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

Urban spatial structure is the form of interaction among the urban human-land relationship elements. Taking the Northeast 36 cities as the research area, using the more than 4 million Points of Interest (POI) grouped by industry types, the article used the kernel density estimation method, the diversity index method and the standard deviational ellipse method to analyze the urban spatial structure and the agglomeration characteristics of the various industries. This research found that the urban structure of Northeast China is mainly characterized by concentrated mass, dispersed combination, linear and radial types. Some cities have diversified spatial structure. The second industry and real estate industry in Northeast China show the characteristics of suburbanization, the development direction of each industry is consistent with the economic axis of the Northeast region, and most industries have not yet formed a specialized functional area; The centrifugal development of secondary industry and real estate industry is not strong for the shaping of concentrated block cities, but it contributes greatly to the spatial structure of dispersed group cities. Linear cities usually have a multi-center composite characteristics, the various industries of radial city are still biased towards centripetal aggregation. This research deepens the empirical researches of the big data-driven urban spatial structure as well as industry spatial pattern, and also provides scientific cognitive basis for the rational planning of urban space and the coordinated sustainable development in Northeast China during the revitalization period.
基于兴趣点(POI)大数据的东北城市空间结构分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.05.003
[本文引用: 1]

以东北三省36个城市为研究区,利用 400余万条兴趣点行业分类大数据,采用核密度估计、标准差椭圆、区位熵等方法分析城市空间结构及其行业构成机制。研究发现,东北城市要素显著集聚,城市内部空间结构呈现集中团块型、分散组合型、线型、放射型特征以及多元复合类型;第二产业和房地产业呈现郊区化特征,各行业发展方向与东北大区域的经济轴线一致,多数行业尚未形成专业化功能区;第二产业与房地产业的离心发展对集中团块型城市的塑造作用不强,但对分散组合型城市空间结构的贡献较大。线型城市通常兼具多中心特征,放射型城市各行业仍偏向于向心聚集。
Spatial diffusion pattern and mode of local snacks: Based on POI data of four famous local snacks in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.12.011
[本文引用: 1]

The spatial gathering and diffusion of local snacks is the main content of spatial communication of catering culture, and also an important performance of population migration and regional cultural exchange. Taking the four famous local snacks in China as the analyzing examples, this paper analyzes the spatial agglomeration and diffusion pattern of local snacks based on the density, distance and weighted average center method, taking the POI of snack stores as the main data source. Then, the spatial autocorrelation, clustering, outlier analysis and hot spot analysis are used to study the spatial correlation characteristics and spatial diffusion model of local snack clusters. The results show that: 1) There are significant differences in the spatial diffusion pattern of local snacks on different scales. The eastern region and the central and western capital cities are the main gathering places of local snacks. 2) The spatial agglomeration of local snacks shows positive spatial autocorrelation. The spatial diffusion model has the characteristics of neighborhood diffusion, grade diffusion and jump diffusion. 3) There are obvious differences in the cold and hot spots of spatial diffusion of different kinds of local snacks, reflecting the differences in the scope of different snack recognition groups and the spatial differences in the eating habits of different parts of China. 4) The diffusion of food culture and population migration and diffusion have space coincidence. The areas with higher economic development level and net population inflow have stronger inclusiveness to different food culture. The areas with large population have more abundant demand for food consumption, and the distribution density of various snacks and fast food stores is higher. In the eastern coastal areas and the capital cities with large population, the proportion of floating population is relatively high. Local snacks not only maintain the livelihood of snack practitioners, but also meet the consumption needs of a large number of floating population with different eating habits.
地方小吃空间扩散格局与模式: 基于中国四大知名地方小吃POI数据的研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.12.011
[本文引用: 1]

以中国四大知名地方小吃门店兴趣点(POI)大数据为主要数据源,基于密度、距离与加权平均中心方法分析地方小吃空间集聚与扩散格局,采用空间自相关、聚类和异常值分析以及热点分析方法研究地方小吃空间集聚关联特征以及空间扩散模式。结果表明:① 地方小吃在不同尺度上的空间扩散格局存在显著差异,东部地区和中西部省会城市是地方小吃的主要集聚地;② 地方小吃的空间集聚表现出自相关特征,邻域扩散、等级扩散和跳跃式扩散等扩散模式相互融合;③ 地方小吃空间扩散的冷热点集聚区分异明显,反映出不同小吃认可群体范围的差异以及中国各地饮食习惯的空间分异;④ 饮食文化扩散与人口迁移扩散具有空间重合性,经济发展水平较高、人口净流入地区对不同饮食文化的包容性较强。
Modeling and analysis of geographic events supported by multi-source geographic big data
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202111018
[本文引用: 2]

Geographic events, as a basic construct in geographic process description, have become a core content of geographic information system (GIS). Due to the limitation of acquiring human activity data, GIS modeling and analysis of geographic events has long been focused on the event-induced changes of geospatial objects and the interaction between the objects. However, in recent years, with the explosive growth of location-based service data and the rapid development of quantitative depiction of human activities, the impact of geographic events on human activities and online social participation in geographic events have aroused wide concern in many fields, which poses great challenges to the space-time cognition, modeling methods and analysis framework of geographic events. In this regard, this study discussed the conceptualization and categorization of geographic events in the context of big data, and then introduced the space-time semantics and graph-based data model for geographic events. The "node-edge" graph data structure is used to establish event ontology, the secondary or cascading events, the evolution process, and the "cause-effect" interaction. The spatiotemporal data mining approaches for geographical events were also summarized, which are limited to conventional event detection in "physical space". Integrating "virtual space" event discovery and propagation simulation ideas into data mining approaches is essential for recognizing multi-scale spatiotemporal responses and understanding regional difference of human activities under diverse geographic events. Finally, the study used urban rainstorm events as an example to examine the conceptualization and modeling method of geographic events. Social responses to urban rainstorms and regional differences were examined at inter-urban and intra-urban scales. The case study proved the concept and verified the feasibility and practicability of the proposed framework.
多源地理大数据支撑下的地理事件建模与分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202111018
[本文引用: 2]

地理事件作为描述地理过程的基本单元,逐渐成为地理信息科学(GIS)核心研究内容。由于受人类活动数据获取限制,GIS对地理事件的建模和分析主要关注事件所引起的地理空间要素变化及要素之间的相互影响与作用机制。然而,近年来随着基于位置服务数据(LBS)爆炸式的增长和人类活动大数据定量刻画手段的快速发展,地理事件对人类活动的影响以及公众对地理事件的网络参与度都引起了多个领域的广泛关注,对地理事件的时空认知、建模方法和分析框架提出了巨大的挑战。对此,本文首先深入分析了大数据时代地理事件的概念与分类体系;其次,基于地理事件的时空语义给出了基于图模型的事件数据建模,建立了事件本体及其次生或级联事件的“节点—边”表达结构,开展了事件自身时空演化及其前“因”后“果”的形式化描述;第三,从时空数据分析与挖掘的角度,给出了大数据时代地理事件建模与分析的整体框架,拟突破传统“地理实体空间”事件探测与分析方法的局限性,融合“虚拟空间”事件发现与传播模拟思路,实现多源地理大数据支撑下的面向地理事件的人类活动多尺度时空响应与区域差异分析;最后,本文以城市暴雨事件为例诠释了本文所提出的地理事件建模与分析方法,从城市和城市内部两个尺度进行了暴雨事件与人类活动的一致性响应及区域差异分析,得到了明确的结论,验证了前文分析框架的可行性与实用性。
Points of interest synthetic similarity calculation method and its application
兴趣点综合相似度计算方法及应用研究
Deep learning in multimodal remote sensing data fusion: A comprehensive review
Construction and practical application of big data development index in China: From the government data and social data fusion perspective
我国大数据发展指数构建及实践应用: 从政务数据与社会数据融合的视角
DOI:10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2022023
[本文引用: 1]

针对大数据发展指数研究数据源较单一、无法覆盖到各城市的不足,从政务数据、社会数据的全量数据融合视角,在充分融合政务数据、企业数据、互联网数据的基础上,从基础能力、创新应用、综合保障3个维度,构建了政务数据与社会数据相融合、全景式展示各城市大数据画像的大数据发展指数,客观评估我国大数据的发展水平,为政府治理、产业发展及民生服务能力提升提供客观数据参考。
Big data aggregation: Connotation, classification, and framework
地理大数据聚合的内涵、分类与框架
Scientific big data management technology and system
科学大数据管理技术与系统
Principle of big data mining
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201903014
[本文引用: 1]

This paper reveals the principle of geographic big data mining and its significance to geographic research. In this paper, big geodata are first categorized into two domains: earth observation big data and human behavior big data. Then, another five attributes except for "5V", including granularity, scope, density, skewness and precision, are summarized regarding big geodata. Based on this, the essence and effect of big geodata mining are uncovered by the following four aspects. First, as the burst of human behavior big data, flow space, where the OD flow is the basic unit instead of the point in traditional space, will become a new presentation form for big geodata. Second, the target of big geodata mining is defined as revealing the spatial pattern and the spatial relationship. Third, spatio-temporal distributions of big geodata can be seen as the overlay of multiple geographic patterns and the patterns may be changed with scale. Fourth, big geodata mining can be viewed as a tool for discovering geographic patterns while the revealed patterns are finally attributed to the outcome of human-land relationship. Big geodata mining methods are categorized into two types in light of mining target, i.e. classification mining and relationship mining. The future research will be facing the following challenges, namely, the aggregation and connection of big geodata, the effective evaluation of mining result and mining "true and useful" knowledge.
地理大数据挖掘的本质
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201903014
[本文引用: 1]

针对地理大数据的内在本质以及地理大数据挖掘对于地理学研究的意义,本文解释了地理大数据的含义,并在大数据“5V”特征的基础上提出了粒度、广度、密度、偏度和精度等“5度”的特征,揭示了地理大数据的本质特点。在此基础上,从地理大数据的表达方式、地理大数据挖掘的目标、地理模式的叠加与尺度性、地理大数据挖掘与地理学的关系等4个方面阐述了地理大数据挖掘的本质与作用,并从挖掘目标的角度对地理大数据挖掘方法进行分类。未来地理大数据挖掘的研究将面临地理大数据的聚合、挖掘结果的有效性评价以及发现有价值的知识而非常识等几方面的挑战。
Analytical methods and applications of spatial interactions in the era of big data
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202007014
[本文引用: 1]

Spatial interaction is a critical basis of understanding human processes on the land surface. Together with spatial dependence, it embodies the uniqueness and relatedness of geographical space, as well as the impact on the embedded geographical distribution patterns. Spatial interaction also has distinctive space-time attributes, and thus it is significant to geographical research. Big data bring new opportunities for the studies of spatial interaction, which enables us to sense and observe spatial interaction patterns at different spatial scales, and simulate and predict their dynamic evolution. This provides great support for the research of human activity regularities and regional spatial structures. In this article, we first demonstrated the relationship between spatial interaction and geospatial patterns, and introduced how to sense spatial interaction with big geodata. Then, we generalized the progress of relevant models and analytical methods, and introduced the corresponding applications in fields of spatial planning, urban transportation, public health and tourism. Some key issues were also discussed. We hope this review can provide guidance for the studies of spatial interaction supported by big data.
大数据时代的空间交互分析方法和应用再论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202007014
[本文引用: 1]

空间交互是理解地表人文过程的重要基础,与空间依赖一起共同体现了地理空间的独特性、关联性以及对嵌入该空间的地理分布格局的影响,具有鲜明的时空属性,因此对于地理学研究具有重要意义。大数据为空间交互研究带来了新的机遇,能够使我们在不同时空尺度感知和观察空间交互模式并对其动态演化特征进行模拟和预测,从而为揭示人类活动规律及区域空间结构提供有力支持。本文在探讨空间交互与地理空间模式关系的基础上,描述了利用地理大数据感知空间交互的方式和定量模型,介绍了空间交互分析方法的研究进展及其在空间规划与交通、公共卫生、旅游等领域的应用情况,并就一些基本问题进行了讨论,以期为大数据支持下空间交互相关研究提供指导。
Research process on human settlements: From traditional data to big data+
从传统数据到大数据+的人居环境研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.016
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着城市化的快速推进,环境问题日益突出,人居环境研究已成为学术界关注的热点。论文以CNKI和Web of Science数据库中关于人居环境的文献为基础,结合CiteSpace软件分析国内外人居环境研究的热点领域,探讨其数据获取方式、研究方法与技术、研究视角3个方面。结果表明:① 数据获取方式由传统的抽样调查和官方统计向卫星遥感、电子设备感知及互联网等大数据靠拢,实现传统统计数据向网络大数据获取的转变;② 研究方法日趋完善,注重问卷调查、新地理计量模型与GIS相结合,同时引入物联网大数据、人工智能等先进技术,使研究方法更加多样、研究结果更加准确;③ 社会感知、乡村振兴、拟态人居等成为近年来的研究方向。今后,人居环境研究应综合利用传统方式和现代化技术手段获取的数据,深度学习挖掘大数据,加强乡村振兴、虚拟人居环境等方面的研究。
Geographic modeling and simulation systems for geographic research in the new era: Some thoughts on their development and construction
面向新时代地理学特征研究的地理建模与模拟系统发展及构建思考
Disciplinary structure and development strategy of information geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109004
[本文引用: 1]

The arrival of the information era has exceptionally advanced the development of geographic science. The research scope of the discipline has expanded from the space of traditional physical and human geography to the space of information geography. Meanwhile, the discipline gradually formed three subdisciplines, i.e., geographic remote sensing science, geographic information science, and geographic data science. In the context of preparing the disciplinary structure of geographic science of the "Development Strategy of Discipline and Frontier Research in China (2021-2035)", this paper summarized the history, definition, and disciplinary structure of information geography. Additionally, it highlighted the strategic layout of the discipline, as well as the goals and key directions of its priority development fields. We expect this paper to provide insight into the new discipline that could help promote the developments and applications of remote sensing and geographic information within the framework of geographic science, strengthening the synthesis of geographic research and promoting the integrated development of geographic science.
信息地理学学科体系与发展战略要点
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109004
[本文引用: 1]

信息时代的到来极大地促进了地理科学的发展,地理科学的研究已从传统的自然地理空间、人文地理空间拓展到了信息地理空间,催生了信息地理学的发展,并逐渐形成了地理遥感科学、地理信息科学和地理数据科学3个分支学科。在《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划背景下,本文梳理了信息地理学的形成、定义和学科体系,重点阐述了信息地理学的学科发展战略布局、优先领域发展目标和重点方向。以期本文有助于促进遥感、地理信息科学与技术的发展和应用回归地理科学,进一步强化地理科学研究,使其更加系统化、科学化和现代化,促进地理科学的整体发展。