1 引言
改革开放以来,中国旅游业蓬勃发展,已成为促进国民经济发展和民生福祉改善的战略性支柱产业。然而,在旅游经济飞速增长的繁荣现象背后,也潜藏着规模失调、结构失衡和资源配置低效等现实矛盾[1⇓⇓-4],严重阻滞着区域旅游产业高质量发展目标的实现。早在2014年,《国务院关于促进旅游业改革发展的若干意见》明确指出要以“转型升级,提质增效”为主线来发展旅游业。《“十四五”文化和旅游发展规划》再次强调要深化旅游业供给侧结构性改革,努力实现旅游业高质量发展,加速结构转型与提质增效愈发受到重视。纵观国际国内经济发展历程可知,产业结构变迁与经济发展效率及规模密不可分[5⇓-7]。经济增长是产业结构不断调整优化的动态转型过程,也是伴随产业结构转型的效率提升过程[7],实质上更是产业规模、结构与效率间有序匹配和交互协调的多维耦合过程。可见,探究在加速结构转型以促进动能转换[3]过程中规模、结构与效率的耦合机制与交互影响,是政府部门与国内外学术界普遍关注和亟待解决的重难点问题,尤其是当前中国旅游产业正处于转型升级与创新发展的关键期,推动转型发展过程中规模、结构与效率的交互协调演进显得更加至关紧要,是产业结构转型背景下推动中国旅游产业高质量发展的重要路径。因此,构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架,从时空动态视角开展耦合旅游产业多维发展过程及其影响因素的综合集成研究尤其紧迫和必要,对推动转型升级背景下旅游产业总量优化、集约生产与提质增效的协调共进,助力区域旅游产业高质量发展具有重要的理论价值与现实意义。
区域旅游产业发展日益成为国内外旅游地理学者普遍关注的热点焦点问题,目前研究主要集中在两个方面:① 旅游业单一系统研究。学界多站在整体旅游业发展层面,从产出角度[8]量化评价旅游产业规模[9],或从投入产出角度[10-11]开展旅游产业效率[12]的时空演化过程[4]及其驱动因素[13]研究。② 旅游业耦合系统研究。地理学者在区域旅游产业研究中借鉴并发展物理学中的“耦合”概念,解译旅游地理关系复杂系统间交互协调的现象、过程及机制[2,4,14⇓⇓⇓ -18],代表性的研究主要集中在旅游业与区域经济[14]、城镇化[15]、生态环境[16]、交通发展[17]等外部耦合协调系统方面,涵盖全国[18]、区域[15]、省域[14,16]、市域[17]等空间尺度,涉及时空格局[14-15]演变和政府调控、人力资本、科技创新等影响因素[19]分析,呈现出地理学、经济学、生态学等多学科领域交互的复杂特征,有助于促进旅游学科与外部学科知识的叠加与融通;创新性的研究从旅游业内部耦合协调角度出发,将旅游产业发展视为产业规模与产业效率的交互耦合过程[2,4],扩展了旅游业耦合协调系统的分析框架,但仅限于运用探索性空间数据分析、重心模型等经典空间分析方法[20]考察区域、城市群等尺度下旅游产业规模与效率耦合协调的时空格局演变,也暂未涉及影响因素层面的深度考量[2,4]。
通过梳理文献及综合评述发现:区域旅游产业研究内容逐渐由单一系统向耦合协调系统转变,与旅游发展实践的综合性及复杂性相契合。在产业结构转型的关键期,区域旅游产业研究对象应由“规模与效率”向“规模、结构与效率”发展,研究内容也应由简单测度向交互耦合协调关系转变。然而,目前鲜有学者构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架并推至实证研究,有效结合时间属性与空间属性来剖析其时空动态特征及影响因素的成果则更为匮乏。
鉴于此,本文尝试作出以下边际贡献:① 构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架,回应产业结构转型背景下规模、结构与效率的交互耦合关系的学术关切,以期为旅游产业转型升级与高质量发展,以及当前地理学多要素耦合协调研究框架[21]的丰富扩展提供有益理论探索。② 借助LISA时间路径与时空跃迁等方法,从时空动态视角解读全国省区宏观尺度下旅游产业规模、结构与效率的交互耦合过程,弥补既有研究仅注重考察区域、城市群等中微观尺度下时间维度或空间维度演变过程的不足,扩展旅游地理学的研究视野。③ 使用时空地理加权回归,从局部动态视角刻画影响中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调关键因素的时空图景,弥补以往研究忽略影响因素考察的缺陷,继而探索出推动区域旅游产业总量优化、集约生产与提质增效协调并进的合理路径,以期为区域旅游产业高质量发展提供研究指引与理论依据。
2 研究设计
2.1 理论基础
国际国内经济发展实践表明,古典经济增长理论与新古典经济学理论难以完全解释产业结构转型过程中中国旅游产业发展的动力源泉[22],推动旅游产业结构的转型升级,从而加速资源要素由低效率的部门向高效率的部门流动与扩散,持续激发新动能与迸发新活力,才是破解当前“结构扭曲”困境和实现动能转换的根本路径[23]。实质而言,产业结构理论与经济发展史均证实产业结构与经济发展效率及规模密切相关[7,23],中国共产党“十九大”报告也明确强调要加速结构转型并注重提质增效,应推动动力变革、效率变革及质量变革,实现高质量发展[24]。可见,区域旅游产业发展实质应表现为资源要素规模数量在结构转型驱动下逐渐由配置低效转变为配置高效的多维动态质变过程,至少涉及规模、结构与效率3个关键维度的交互耦合与有序协调,这是实现旅游产业高质量发展的重要基础与必然要求。
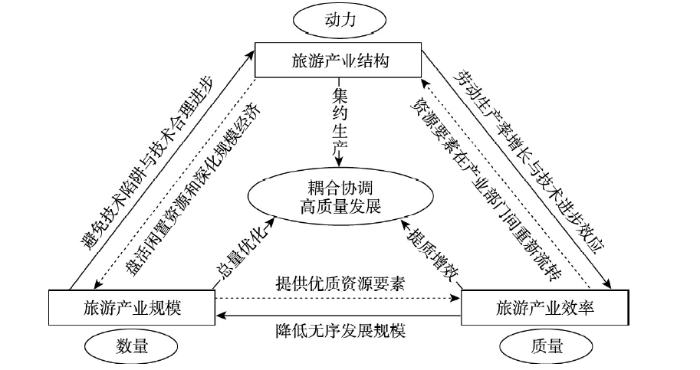
本文紧扣转型发展背景并结合产业结构理论及相关成果[3-4,23,25 -26],构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架,其内在耦合协调互动关系为:① 规模是数量维,以总量优化为主要特征。总量优化反映在旅游产业规模的横向扩大,有助于引发单位成本的降低来形成规模经济,从而依托规模优势来为旅游产业效率改善提供优质的劳动力和技术等资源要素[23],同时可以改善规模纵向扩大所引致的资源闲置与产能不足现象,一定程度上避免“技术陷阱”问题和缓解要素重置带来的风险,进而推动技术水平合理进步,实现旅游产业结构有序转型升级[4]。② 结构是动力维,以集约生产为主要特征。产业结构可通过结构升级来推动资金、技术和劳动力等资源要素在部门间的有序流动与合理扩散[25-26],从而盘活闲置资源和实现集约生产,并驱动着规模经济进一步深化为集聚经济,促进劳动生产率增长和技术进步,从而稳步提升旅游产业效率[3]。③ 效率是质量维,以提质增效为主要特征。效率提升以更高效的投入产出转化率降低无序发展规模,并导致劳动力、资金和技术等资源要素在产业部门间的重新流转,从而引起旅游产业结构的再度调整优化[4]。
可见,旅游产业规模、旅游产业结构与旅游产业效率3个系统在遵循自身演化规律的同时,凭据不断的物质循环、信息传递和能量流动,形成一个密切关联的复杂耦合巨系统,共同决定着旅游产业发展的演化方向(图1)。
图1
图1
旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架
Fig. 1
Analytical framework regarding the coupling coordination of the scale, structure, and efficiency of the tourism industry
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 修正耦合协调模型
耦合协调模型作为识别不同系统间多元耦合关系的有效工具,广泛应用于经济、生态、交通和旅游等领域。传统耦合度模型测算的耦合度非均衡性明显,导致耦合度的信度降低,继而结合协调度模型测算的耦合协调值也存在偏差。王淑佳等[28]修正的耦合协调模型使得耦合度更具离散化,区分度明显增强且效度更佳,测度所得耦合协调值更具合理性。公式为:
式中:D为耦合协调水平;n为系统数;Ti为系统i的观测值;αi为系统i的待定系数,考虑到3个系统同等重要,均取1/3;
2.2.2 全局空间自相关
全局空间自相关能精准勾勒出评析对象的总体空间集聚程度,可从全局视角刻画中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的空间关联图景。公式为:
式中:N为研究单元数;S0为标准化要素;Xi为区域i的观测值;Wij为空间权重矩阵,采用邻接原则[29],并为避免孤岛效应,定义广东、广西与海南相邻。
2.2.3 LISA时间路径
LISA时间路径可借助局部空间关联指数在莫兰散点图中的时空迁移态势来有效结合时间属性与空间属性,使得静态的LISA实现动态呈现[30]。LISA时间路径的几何特征包括LISA时间路径相对长度、弯曲度及移动方向。LISA时间路径相对长度有助于揭示研究单元局部空间结构的动态特征,弯曲度反映出局部空间依赖方向的波动性,移动方向则映射出研究单元的空间整合性的动态变化。相对长度与弯曲度的公式为:
式中:
2.2.4 时空跃迁
表1 时空跃迁类型划分
Tab. 1
| 跃迁类型 | 跃迁形式 | 符号表示 |
|---|---|---|
| I型 | 自身跃迁、邻域稳定 | HH→LH、LH→HH、LL→HL、HL→LL |
| II型 | 自身稳定、邻域跃迁 | HH→HL、LH→LL、LL→LH、HL→HH |
| III型 | 自身跃迁、邻域跃迁 | HH→LL、LH→HL、LL→HH、HL→LH |
| IV型 | 自身稳定、邻域稳定 | HH→HH、LH→LH、LL→LL、HL→HL |
2.2.5 时空地理加权回归
相较于传统计量模型,时空地理加权回归(GTWR)将时间非平稳性与空间非平稳性共同纳入到分析框架,使得局部参数在时空维度上的方向与强度皆得到有效解读,有助于洞悉影响因素系数的时空动态特征,具备更好的解释能力[32]。鉴于此,本文借助时空地理加权回归模型,用以呈现中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展驱动因素的时空动态演化图景。模型设定如下:
式中:
2.3 指标体系
本文充分结合相关成果[1-2,4,13,16,26,33⇓⇓ -36]及数据可得性,构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调评价指标体系(表2)。旅游产业作为多重发展要素共同交融所构成的复杂系统,采用旅游总人次或旅游总收入等单一指标无法准确度量发展规模。因此,本文结合已有的研究成果[2,33 -34],构建涵盖旅游资源本底、旅游接待能力与旅游产出规模3个维度的旅游产业规模集成评价指标体系。学界普遍从合理化与高级化角度诠释旅游产业结构的动态演化过程[1,26],结构合理化是旅游产业部门(旅行社、星级酒店与旅游景区)[3]间协调程度的反映,以往研究多用结构偏离度或泰尔指数度量,但其忽略了部门的相对重要程度,会造成“伪合理化”现象[26],因而本文使用修正泰尔指数[1]表征,可以克服上述局限[26];结构高级化是依托技术进步不断提升要素资源利用效率的过程,突出表现为劳动生产率提升与创新能力增强[26],采用旅行社劳动生产率、旅游景区劳动生产率、星级酒店劳动生产率与旅游专利申请数量表征[26,35]。旅游产业效率投入指标方面,甄选旅游业从业人员数量作为劳动力指标[16],旅游用地无法准确度量,同时对旅游业的约束有限[13],因而暂未纳入;考虑到旅游业固定资产投资数据获取困难,借鉴相关研究做法[2,4,36],从旅游发展吸引力角度选择旅游服务要素与旅游资源要素替代,旅游服务要素为星级酒店与旅行社的数量和[2,4],旅游资源要素借鉴方叶林等[36]的做法,使用熵值法测度3A级以上旅游景区、国家历史文化名城、国家级森林公园、国家级自然保护区、国家级风景名胜区、世界地质公园、世界文化遗产、世界自然遗产及中国历史文化名镇名村的综合值来度量;产出指标选取当前使用广泛且成效较好的旅游总人次与旅游总收入度量[4,13]。需要说明的是,旅游产业规模与旅游产业结构均采用熵值法与线性加权法测算,旅游产业效率借助数据包络分析中的产出导向BCC模型[2,4]测度,但为避免篇幅过多,暂未详细说明。
表2 旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调评价指标体系
Tab. 2
| 系统层 | 一级指标 | 二级指标 |
|---|---|---|
| 旅游产业规模 | 旅游资源本底 | 旅游资源丰富度 |
| 旅游资源品位度 | ||
| 旅游接待能力 | 旅游业从业人员占比 | |
| 星级酒店数量 | ||
| 旅行社数量 | ||
| 旅游产出规模 | 旅游总收入 | |
| 旅游总人次 | ||
| 旅游产业结构 | 结构合理化 | 修正泰尔指数 |
| 结构高级化 | 旅行社劳动生产率 | |
| 旅游景区劳动生产率 | ||
| 星级酒店劳动生产率 | ||
| 旅游专利申请数量 | ||
| 旅游产业效率 | 投入指标 | 旅游业从业人员数量 |
| 旅游服务要素 | ||
| 旅游资源要素 | ||
| 产出指标 | 旅游总收入 | |
| 旅游总人次 |
2.4 数据来源
囿于2011年以前的旅游景区、旅行社及星级酒店相关数据暂未得到全面统计,本文选取2011—2019年中国31省(自治区、直辖市)(暂未含港澳台地区)年度数据为基础数据,并结合国家统计局方案(
3 中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调的时空演化特征
3.1 时序演化特征
借助熵值与线性加权法及BCC模型测算旅游产业规模与旅游产业结构的综合水平及旅游产业效率值,继而使用修正耦合协调模型测度得到2011—2019年中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平(图2)。
图2
图2
中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平
Fig. 2
The level of coupling coordination of the scale, structure, and efficiency of tourism industry in China
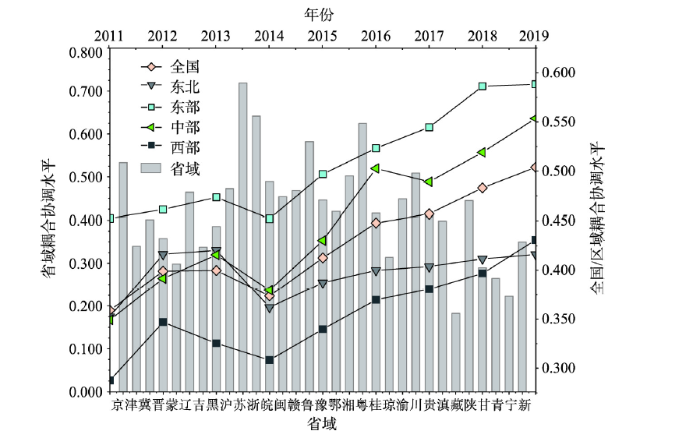
从全国尺度来看,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展水平除在2014年有所下降外总体明显提升,耦合协调值由2011年的0.358抬升到2019年的0.503。可见,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的有序协调关系随时间推移逐渐增强,尤其是在2014年以后增速明显。这与《国务院关于促进旅游业改革发展的若干意见》(2014)所提出的“转型升级,提质增效”发展要求密切相关,其加速着旅游产业结构的转型升级,从而引发人才和技术等要素资源由低生产率的部门向高生产率的部门有序流动与扩散[23],有助于减少无序规模,实现总量优化并提升资源利用效率,进而明显增强旅游产业规模、结构与效率的有序协调关系,充分映射出中国旅游产业发展的政策导向特征。
从区域尺度来看,四大区域与全国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的演变轨迹较为相似,均在2014年下降后明显提升,存在东部(0.508)>中部(0.447)>东北(0.396)>西部(0.353)的区域分异。究其原因,东部地区在经济实力、地理区位与基础设施等方面更具优势,更易于引发技术和人才等关键要素集聚来推动旅游产业结构转型升级,并依托高效灵活的资源配置模式来改善无序规模和提升旅游产业效率[1],可在旅游发展过程中实现结构转型驱动下以效率提升为特征的规模优化,从而导致规模、结构与效率的交互协调关系更强。中部地区尽管能通过吸收东部地区先进技术与管理模式来深化资源配置效率,但受经济实力与地理区位等的制约,无法在要素规模层面为旅游产业结构转型升级及其提质增效提供强有力的支撑,导致有序协调水平未能企及东部地区。东北地区和西部地区的旅游发展基础则更为薄弱,旅游产业规模、旅游产业结构及旅游产业效率与东部地区和中部地区存在较大差距[1,37],因而无法在较高水平上形成有序协调关系。
从省域尺度来看,位居前3位的省份分别为江苏(0.719)、浙江(0.642)与广东(0.625);处于倒数后3位的省份分别为西藏(0.182)、宁夏(0.223)与青海(0.269)。处于末位的西藏与位居首位的江苏的均值相差0.537(极差)。可见,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平存在明显的省际差异。原因在于区域产业结构、基础设施及宏观政策的不同,导致旅游发展环境与资源要素存在明显的空间分异,在一定程度上致使旅游产业规模、旅游产业结构与旅游产业效率及其耦合协调关系存有明显差异。
3.2 空间演化特征
借助全局空间自相关考察2011—2019年中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的总体空间集聚特征(表3)。总体来看,全局莫兰指数值介于0.217~0.407之间,至少在5%显著水平通过显著性检验,存在显著的空间正相关性,说明中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平较高(低)省区在空间上趋于集聚分布。从变化趋势来看,全局莫兰指数在2012—2014年明显提升后缓慢下降,总体表现为弱集聚—强集聚—弱集聚的类周期性特征。结果表明中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平在2012—2014年呈增长极模式,高(低)水平均快速集聚,但集聚态势随时间推移逐渐减弱,空间扩散效应有所增强。
表3 中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的空间集聚特征
Tab. 3
| 年份 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全局莫兰指数值 | 0.280 | 0.217 | 0.379 | 0.407 | 0.395 | 0.370 | 0.320 | 0.369 | 0.295 |
| P值 | 0.012 | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
3.3 时空动态演化特征
图3
图3
2011—2019年LISA时间路径相对长度
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网址GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 3
The relative length of the Local Indicators of Spatial Auto-correlation (LISA) time path
图4
图4
2011—2019年LISA时间路径弯曲度
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网址GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 4
The tortuosity of the Local Indicators of Spatial Auto-correlation (LISA) time path
图5
图5
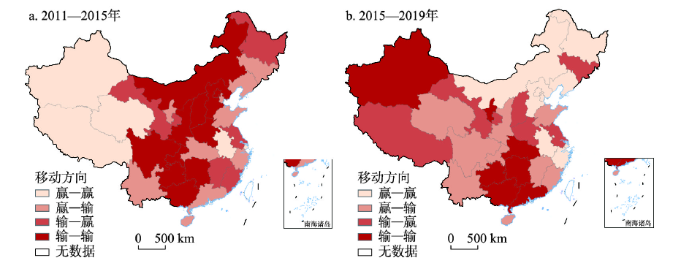
2011—2019年LISA时间路径移动方向
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网址GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 5
The movement direction of the Local Indicators of Spatial Auto-correlation (LISA) time path
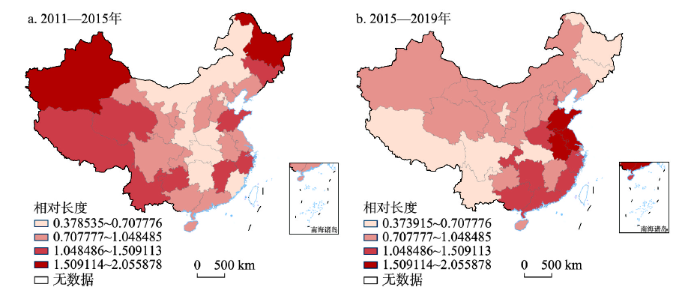
3.3.1 LISA时间路径相对长度
由图3可知,旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的LISA时间路径相对长度在前后阶段小于均值(均为1)的省区数量分别为18个(58.06%)和19个(61.29%),局部空间结构较为稳定。2011—2015年四大区域相对长度均值排序为东北(1.459)>西部(1.087)>东部(0.892)>中部(0.777),最高与最低分别为新疆(2.056)与陕西(0.379),说明此阶段东北地区和西部地区具有更为动态的局部空间结构,而东部地区和中部地区局部空间结构较为稳定。到2015—2019年,相对长度呈现明显的东南与沿海经济带高值集聚,东北与西北地区低值集聚的空间分异,四大区域均值排序为东部(1.259)>中部(1.084)>西部(0.826)>东北(0.663),最高与最低分别为江苏(2.039)与四川(0.374)。可见,LISA时间路径相对长度随时间推移有所缩减,高值区逐渐由东北地区和西部地区向中部地区和东部沿海经济带转移。原因在于,东北地区与西部地区旅游发展基础薄弱、进步空间较大,集约与转型发展前期过程中的规模、结构与效率可在较高改善速度下实现交互耦合协调,致使前阶段局部空间结构较为波动,但囿于区域社会经济发展制约,可用于结构转型与效率提升的技术、资金和人力等资源要素终究有限,从而导致后阶段增速乏力并引发局部空间结构波动有所减弱。尤其是东北地区在后阶段位居末位,这与东北的资源要素短缺及粗放式发展密切相关[37]。相较而言,东部地区旅游发展基础雄厚、进步空间较小,前期的规模、结构与效率无法在较高改善速度下形成有序协调关系,导致局部空间结构波动稍显较弱;但随着转型发展的深入推进,东部地区依托自身优势产业与旅游深度融合来完善与延伸旅游产业链,引发更强的关联效应与协同效应,为规模、结构与效率的全新突破注入新要素与新活力,较大程度上实现结构转型驱动下以高效发展为特征的规模优化,从而导致局部空间结构较为波动。此外,中部地区受东部地区辐射效应的影响,导致其局部空间结构的演变趋势与东部地区较为相似。
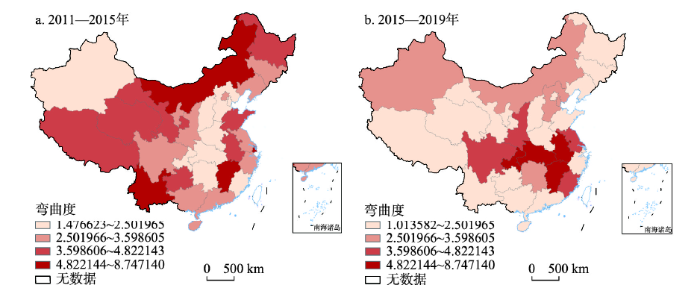
3.3.2 LISA时间路径弯曲度
由图4可知,旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的LISA时间路径弯曲度在前后阶段低于均值(3.750和2.898)的省区数量均为20个(64.52%),局部空间依赖方向较为稳定。2011—2015年四大区域弯曲度均值排序依次为西部(4.163)>东北(3.900)>东部(3.422)>中部(3.393),最高与最低分别为内蒙古(8.747)与湖南(1.477),说明西部地区和东北地区具有更动态的局部空间依赖方向,而东部地区和中部地区局部空间依赖方向较为稳定。2015—2019年LISA时间路径弯曲度呈现明显的以重庆、湖北、江西与安徽为高值中心的“中部凸起”的空间格局,四大区域弯曲度均值排序为中部(4.700)>西部(2.769)>东部(2.455)>东北(1.287),最高与最低分别为湖北(7.261)与海南(1.014)。可见,LISA时间路径弯曲度高值区随时间推移逐渐由东北地区和西部地区向中部地区转移。这与局部空间结构的演化趋势较为相似,符合中国旅游发展存在区域分异的国情,再度凸显旅游发展与地理区域密切相关的基本特征。
3.3.3 LISA时间路径移动方向
LISA时间路径移动方向可揭示区域旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平局部空间结构的空间整合性特征(图5)。通过比较分析中国31省区在局部莫兰散点图中的坐标迁移轨迹,可划分为4种迁移类型:赢—赢(0°~90°),表示省域自身与相邻省份协同高增长;输—赢(90°~180°),表示省域自身低增长,而相邻省份高增长;输—输(180°~270°),表示省域自身与相邻省份协同低增长;赢—输(270°~360°),表示省域自身高增长,而相邻省份低增长。
由图5可知,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的LISA时间路径移动方向在前后阶段反向增长的省区数量均为15个(48.39%),协同增长的省区数量均为16个(51.61%)。可见,区域局部空间结构协作态势强于竞争态势,空间整合性较强。分区域来看,东北地区与东部地区移动方向反向增长的省区数量随着阶段转移分别减少到4个与1个,局部结构竞争态势减弱;而中部地区与西部地区反向增长的省区数量则分别增加到3个和7个,局部结构竞争态势增强。此外,需要注意的是,协同低增长的省市数量明显增多,由前阶段的新疆、西藏、青海、安徽与上海5个省市增加为内蒙古、浙江、安徽、上海、天津、河北、北京、黑龙江与辽宁9个省市,这是区域旅游合作成效不足导致的,应加速完善区域旅游合作手段与方式,推动区域旅游协同高速发展。
3.3.4 时空跃迁分析
囿于LISA时间路径相对长度、弯曲度及移动方向仅能反映LISA坐标的演变轨迹,无法揭示局部空间关联类型的相互转移特征。因此,本文采用时空跃迁分析进一步描绘中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平局部空间关联类型的演变趋势(表4)。
表4 Local Moran's I转移概率矩阵
Tab. 4
| 时间段 | t/t+1 | HH | LH | LL | HL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011—2015 | HH | IV(8, 0.2580) | I(1, 0.0323) | III(0, 0.0000) | II(0, 0.0000) |
| LH | I(2, 0.0645) | IV(4, 0.1290) | II(0, 0.0000) | III(0, 0.0000) | |
| LL | III(0, 0.0000) | II(1, 0.0323) | IV(9, 0.2903) | I(0, 0.0000) | |
| HL | II(1, 0.0323) | III(0, 0.0000) | I(1, 0.0323) | IV(4, 0.1290) | |
| 2015—2019 | HH | IV(9, 0.2903) | I(1, 0.0323) | III(0, 0.0000) | II(1, 0.0323) |
| LH | I(4, 0.1290) | IV(2, 0.0645) | II(0, 0.0000) | III(0, 0.0000) | |
| LL | III(0, 0.0000) | II(1, 0.0323) | IV(8, 0.2581) | I(1, 0.0323) | |
| HL | II(0, 0.0000) | III(0, 0.0000) | I(1, 0.0323) | IV(3, 0.0968) |
由表4可知,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平在研究期内存在明显的转移惰性与路径锁定。2011—2015年发生跃迁的省区数量为6个,占全部省区的19.35%,只存在HH-LH(0.0323)、LH-HH(0.0645)、LL-LH(0.0323)、HL-HH(0.0323)与HL-LL(0.0323)5种类型,暂未出现协调跃迁的省份(III型);未发生时空跃迁的IV型省份有25个,占全部省区的80.65%,呈现明显的路径依赖特征。2015—2019年发生I型时空跃迁的省区数量增至7个,发生II型时空跃迁的省区数量则维持稳定,仍未出现协调跃迁的省份(III型);而未发生时空跃迁的IV型省份为22个,占据总体的70.97%,局部莫兰指数在类型间的转移依旧不活跃,局部空间关联结构较为稳定,省域单元要改变自身相对位置较为困难。综合来看,前后阶段LL型省区数量分别为10个(32.26%)和9个(29.03%),说明中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平较低的省域的总体集聚程度有所减弱;而HH型省份由11个增加至13个,说明中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平较高的省域的总体集聚程度有所提升。但绝大多数省份在评价期内尚未发生时空跃迁,存在显著的路径依赖和空间锁定,空间关联结构较为稳定。
4 中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调的影响因素
4.1 影响因素选取
由时空分析可知,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平存在显著的时空分异和转移惰性。从局部动态视角研究揭示影响中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的关键因素,以提供更具针对性的建议,对推动产业结构转型背景下旅游产业总量优化、集约生产与提质增效协调共进,助力区域旅游产业高质量发展具有重要意义。为合理甄选影响中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的关键因素,综合考虑社会、政治与经济等方面,结合相关成果[13,26,39⇓ -41]及可得数据,选取人口城镇化率表征城镇化(UL)[13,37],中高等旅游院校学生数量表征人力资本(HR)[26,38],科学教育占财政支出比重表征科技创新(KX)[39],具有普适性的公路网密度表征交通设施(TRA)[40],人均财政支出表征政府调控(GMR)[41],产业结构升级系数(三次产业)表征地区产业结构(IS)[40],共6个因素,并均采取对数化形式以弱化异方差影响。
4.2 回归模型评估
中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平存在明显的空间关联,无法满足传统计量模型中变量相互独立的古典假设,会导致OLS估计结果存在偏差[32],而考虑时空非平稳性的GTWR模型更为合理和有效。为评估模型选取的合理性,借助赤池信息准则(AICc)、残差平方和(RSS)与调整拟合优度(R2 Adj)等标准对GTWR模型与OLS模型进行综合研判[32]。由表5可知,变量不存在严重的多重共线性问题(VIF小于10),GTWR模型的调整拟合优度(0.901)明显优于OLS模型(0.788),赤池信息准则与残差平方和也均低于OLS模型,充分证实GTWR模型更为合理和有效[32]。但考虑到篇幅限制,仅以研究初期2011年与研究末期2019年为时间截面,勾勒出中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调发展影响因素的时空动态图景(图6)。
表5 GTWR模型与OLS模型估计参数的描述性统计
Tab. 5
| 变量 | GTWR | OLS | VIF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 下四分位数 | 中位数 | 上四分位数 | 最大值 | |||
| LNGMR | -0.404 | 0.011 | 0.121 | 0.202 | 0.383 | 0.206*** | 2.31 |
| LNHR | -0.211 | 0.005 | 0.056 | 0.083 | 0.221 | 0.087*** | 3.25 |
| LNIS | -0.194 | 0.133 | 0.197 | 0.259 | 0.670 | 0.124*** | 9.04 |
| LNKX | -2.363 | 0.253 | 0.343 | 0.483 | 0.935 | 0.497*** | 2.61 |
| LNTRA | -0.330 | 0.061 | 0.127 | 0.176 | 0.327 | 0.110*** | 4.77 |
| LNUL | -0.892 | 0.211 | 0.393 | 0.700 | 2.186 | 0.322*** | 5.89 |
| R2 | 0.903 | 0.793 | |||||
| R2 Adj | 0.901 | 0.788 | |||||
| RSS | 3.132 | 6.671 | |||||
| AICc | -308.203 | -235.837 | |||||
注:*、**、***分别表示在10%、5%、1%水平上显著;R2为拟合优度;R2Adj为调整拟合优度;AICc为赤池信息准则,RSS为残差平方和,越低越好。
图6
图6
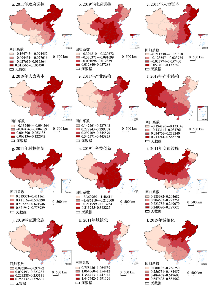
中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调发展影响因素的时空格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网址GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 6
The spatiotemporal patterns of the factors driving the coordinated development of the scale, structure, and efficiency of tourism industry in China
4.3 回归结果分析
(1)政府调控。2011年政府调控回归系数正值区主要分布在东北、华北及东部沿海部分省区(图6a),表现为自东北向西南递减的趋势,到2019年政府调控系数正值区的数量虽有所上升(图6b),但并非是经济发展水平高的区域,而是集聚成簇分布于中部与西部的部分省区,呈现明显的圈层分异。原因在于,适度财政支出能为旅游公共服务体系建设、基础设施完善和人才引进等提供物质保障[37],使得旅游产业自身资金更多地转移到旅游创新中,从而为旅游产业结构升级与效率改善提供关键技术要素[1],并引发资源要素在部门间的有序流转来弱化无序规模,进而有效增强规模、结构与效率的交互耦合协调关系。中部地区与西部地区经济实力较弱,财政支出无法企及东部地区,导致初期的促进效应并不明显;但随着财政支出的增加,政府调控的正向效应逐渐显现。需要注意的是,东部地区政府调控效应由正转负,说明过度政府干预会致使旅游发展效率损失和加深资源闲置现象[42],同时无法妥善维持产业结构的均衡协调,从而产生负向效应。这符合政府规模理论[43],侧面印证中国共产党“十八大”提出的“使市场在资源配置中起决定性作用”的科学性与合理性。因此,未来各省区应制定合理财政方案来实现适度调控,寻求最佳支撑点。
(2)人力资本。2011年人力资本回归系数正值区主要分布在东部地区和中部地区,并表现为自东向西的梯度递减趋势(图6c),到2019年人力资本系数正值区向西部地区扩散(图6d)。可见,人力资本在增强区域旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调关系中的正向效应愈发明显。这主要是缘于人力资本能为旅游产业结构升级提供重要的人才要素[26,38],可依托其带来的先进管理理念与技术水平来提升资源配置效率和减少无序发展规模,实现产业结构转型下以效率改善为重要特征的规模扩张,从而致使规模、结构与效率的交互耦合协调关系得到有效增强。东部地区具有明显的区位优势且经济体制更为活跃,人才数量多、流动性强,旅游产业较早发生追求优质人才的知识密集型趋势,人力资本得到有效利用,从而表现为明显的正向效应。相较而言,西部地区在初期多滞留于依靠数量的劳动密集型阶段,其后在集约转型发展过程中才逐渐向知识密集型转变,从而导致人力资本的正向效应显现较晚。但总体映射出旅游产业存在知识密集型的发展趋势,这是旅游业创新发展与转型发展的重要方向,与生延超等[30]的研究结论相似。
(3)产业结构。2011年产业结构回归系数均为正值,高值区主要分布在东北地区和东部沿海经济带,并表现为自东向西的递减趋势(图6e),2019年则呈现明显的东北与东部地区负值集聚、中部与西部地区正值集聚的空间分异(图6f)。毋庸置疑,产业结构的转型升级有助于加速人才和技术等资源要素在部门间的有序流动和合理扩散,以此可推动区域产业的业态创新与实践,从而为旅游发展提供更坚实的产业基础和更丰富的资源要素,尤其是通过旅游产业与三次产业的融合创新[4],可为旅游产业结构转型升级与效率改善提供更多的资源配置模式和关键技术要素,有效改善无序发展规模,从而明显增强规模、结构与效率的交互协调关系。但东部等旅游发达地区受以往“门票经济”的影响,导致旅游产业与一二三产业融合的广度、深度不够,由此致使旅游产业与相关产业的竞争态势强于协作态势,从而导致负向效应随时间堆积逐渐显现。中部地区和西部地区的产业结构虽无法比拟东部地区但调整潜力大,因而具备相对持续长久的“结构效应”来增强规模、结构与效率的交互耦合协调关系。但结合东部地区来看,未来中西部地区也应注重依托旅游产业与相关产业的深度融合创新来实现协调可持续发展。
(4)科技创新。2011年科技创新的回归系数均为正值,表现为自南向北的递增趋势(图6g),2019年仅新疆、西藏与青海跌落为负值区,总体呈现自东向西的梯度递减趋势(图6h)。可见,科技创新对旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调产生了显著正向影响,尤其是东部地区。究其原因,科技进步是引领旅游产业结构升级的关键因素[39],并可依托技术效应来降低无序规模和提升旅游产业效率[23],实现结构转型驱动的以效率提升为特征的规模优化,从而有效增强规模、结构与效率的耦合协调关系。新疆、西藏与青海等西部省区的科技水平较为滞后,无法为旅游产业的结构升级与提质增效提供强力支撑,甚至受区域自身有限资源要素消耗过多的影响,反而制约规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展。相较而言,东部地区和中部地区的科技实力更强,可更好地推动结构转型过程中的效率提升与规模优化,并实现规模、结构与效率的良性交互耦合协调。总体印证科技实力是旅游产业转型发展与协调发展的有力支撑,符合区域旅游发展对科技创新的现实需要[39]。
(5)交通设施。2011年与2019年交通设施的回归系数均为正值,初期高值区主要分布在西北地区,末期高值区则主要集聚在东北地区(图6i、6j)。交通设施所产生的时空压缩效应有助于加速信息、技术和劳动力等资源要素在区域间的扩散与传递,使得不同地区在转移部分资源要素过程中实现规模优化,从而适当避免“技术陷阱”现象和助力产业结构升级[4],继而可依托“结构红利”引致的技术效应来提升旅游产业效率[23],有效增强区域旅游发展过程中规模、结构与效率的交互耦合协调关系。对于西北等交通滞后的地区而言,交通设施改善空间大,导致其在初期产生相对较强的促进效应,但随时间推移逐渐减弱,说明单纯的交通设施并不能持续性高强度地促进西北等地区的旅游产业发展。这主要在于经济薄弱地区具备的集聚优势较弱,从而导致交通设施的资源要素扩散效果也较弱,在一定程度上制约着旅游产业的创新发展与转型发展。未来更多地应依托重要交通枢纽来引领经济集聚中心的培育与形成,以此吸引更多资金、人力和技术等资源要素的持续注入来巩固旅游创新与转型发展基础,从而稳固交通设施的高强度效应。
(6)城镇化。2011年与2019年城镇化的回归系数均为正值,初期高值区主要分布在西部地区,末期高值区则主要集聚在东部地区(图6k、6l),说明城镇化对旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展产生显著的正向影响。原因在于,城镇化作为人口结构与产业结构等社会经济结构转变的过程,能产生显著的资金、信息、技术与人才等资源要素的集聚效应与外溢效应,并加速推动着旅游产业与文化产业、金融产业和农业等相关产业的深度创新融合发展,有力支撑旅游产业结构的转型升级[42],继而依托“结构效应”降低无序发展规模和提升旅游产业效率[23],从而助力旅游产业在较高发展水平上实现规模、结构与效率的交互耦合协调。西部地区城镇化水平较低、改善空间较大,初期城镇化的推进能产生较强的促进效应,但囿于自身产业基础和经济实力等的制约,城镇化引发的集聚效应终究有限,无法为旅游产业发展提供持续稳定的资金和技术等资源要素支撑,导致正向效应在末期有所降低。相较而言,东部地区与中部地区产业基础和经济实力更具优势,具有更为雄厚和稳定的资金、技术与劳动力等资源要素,城镇化引发的集聚效应更为明显,从而导致正向效应也较为稳定。可见,未来巩固夯实城镇的产业基础来吸引资源要素的流入,是西部等落后地区加强城镇化集聚效应,进而助力旅游产业发展的有效途径。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
本文尝试构建旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调分析框架,从时空动态视角洞悉2011—2019年中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展水平的演变特征及影响因素,主要结论为:
(1)从总体演变特征来看,研究期内中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展水平随时间推移明显提升,始终表现为相对集聚的空间分布态势,但空间正相关性有所降低,空间扩散态势有所加强,并呈现东部>中部>东北>西部的区域分异。
(2)从时空动态特征来看,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的局部空间结构与空间依赖方向的整体波动幅度小,东部地区与中部地区随时间推移更为动态,而东北地区与西部地区逐渐趋向稳定。区域旅游协作态势强于竞争,空间整合性较强,但内蒙古、安徽与黑龙江等多数省份均呈协同低速增长特征,区域协作方式有待转变。绝大多数省份在评价期内未发生时空跃迁,存在明显的路径依赖和空间锁定特征。
(3)从影响因素效应来看,政府调控对中部地区和西部地区旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调发展的正向效应随时间推移逐渐显现,而对东部地区产生负向影响;人力资本对东部的正向效应较强,并存在向中部和西部扩散的趋势;产业结构在调整潜力大的中西部地区的正向效应明显较强,而对东部地区产生负向影响;科技创新、城镇化与交通设施均产生显著正向影响,其中,科技创新对东部地区的促进效应始终强于西部,城镇化和交通设施对西部地区的正向效应在初期较强,但随时间推移有所减弱。
5.2 讨论
结合中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的时空演化趋势与影响因素分析,可为区域旅游产业发展提供针对性建议。① 结合区域分异分析,东部地区旅游产业进步空间相对有限,应加快产业结构转型与旅游技术创新,同时适当转移或分散部分优势要素来辐射带动周边地区发展,缓解自身资源要素过度集聚的压力;中部地区应不断学习和吸收东部地区的管理理念与先进技术,深度挖掘自身资源潜力,从而激活旅游发展动力;东北地区和西部地区旅游发展基础薄弱,改善空间较大,提升旅游规模的同时也应注重技术创新与结构调整,寻求协调发展。② 结合时空动态分析,中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平存在明显的空间依赖,尤其是东北地区和西部地区,应构建无障碍区域协调发展机制来突破行政区划壁垒,加深区域内及区域间的旅游交流与合作,促进资源要素在区域内或区域间的流动与扩散,从而推动区域旅游产业规模、结构与效率的协同发展。③ 结合影响因素分析,应充分把握影响区域旅游产业规模、结构与效率的耦合协调水平的关键要素,寻求合理发展路径。中部与西部等地区应适当加大财政支出力度,为旅游发展提供更为完善的公共服务设施,而东部地区可适度减少财政支付转移,重视和发挥自身的市场优势;同时,中部与西部等地区应注重培育创新能力强的高素质人才队伍,推动旅游产业由劳动密集型向知识密集型转变,东部地区应加速旅游产业与一二三产业的深度融合创新,推动区域产业结构转型升级;此外,四大区域均应加大技术创新力度来促进结构转型与提质增效,并持续完善综合交通网络来为城镇旅游产业发展传递关键资源要素,深化城镇的集聚效应,从而推动区域旅游产业总量优化、集约生产与提质增效的协调并进。
区别于既往多数研究的单一系统视角[1,3]和外部耦合系统视角[14⇓-16],本文创新性地引入转型关键期不可忽视的结构维度,构建旅游产业规模、旅游产业结构与旅游产业效率的内部耦合协调分析框架,扩展旅游业耦合系统的研究思路[4,18]和丰富地理学多要素耦合协调的研究内容[21],也是从旅游产业层面对产业结构变迁与经济效率及规模间关系研究领域的回应与延伸[7]。本文借助LISA时间路径和时空跃迁等方法客观系统的揭示了中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的时空耦合关系,相较于传统的探索性空间数据分析,LISA时间路径和时空跃迁有效结合个体的时间属性与空间属性,从而描绘出地理关系的时空动态演变状况[4],更符合区域旅游发展实际;采用时空地理加权回归,从局部动态视角识别影响旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调的关键因素,弥补了既有研究忽略旅游业内部耦合协调关系影响因素分析的缺陷,为制定因地制宜的旅游调控政策提供依据与借鉴。
但需要指出的是,本文仍存在一定的不足,需后续深化研究:① 拘囿于旅游统计数据的匮乏,本文选取替代性指标表征部分影响因素,研究结果在一定程度上真实客观地反映了影响中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调的相关因素情况,但如若待旅游统计数据逐渐完善,均采用直接指标分析其影响机理,或能使研究结果更具精细化。② 囿于数据限制,本文仅分析了2011—2019年中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率的时空耦合关系,缺少更长时间序列的纵向对比,未来应尝试对数据进行时序追踪并向市域和县域下沉,并关注尺度转换下的尺度关联或尺度传递等尺度效应,更精细地考察其时空动态特征。③ 考虑到区域异质性,本文从局部动态视角展开影响因素实证研究,而在区域关联背景下,驱动因素是否存在空间效应也是亟待探讨的重要方面,未来研究可尝试采用面板空间计量模型分析影响中国旅游产业规模、结构与效率耦合协调的因素的空间溢出效应,以此丰富研究内容。
参考文献
Evolution of tourism industrial structure and spatial network in China
中国旅游产业结构变迁及空间网络演进
Spatial and temporal dynamic evolution and coupling relationship of regional tourism development scale and efficiency: A case study of 14 cities and municipalities in Hunan province
区域旅游发展规模与效率时空动态演化及耦合研究: 以湖南省14地市(州)为例
Changes in the structure of the tourism industry and their effect on the growth of the tourism economy in China
中国旅游产业结构变迁对旅游经济增长的影响
Spatio-temporal evolutions and coordination of tourism efficiency and scale in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008014
[本文引用: 18]

The spatial difference between regional tourism efficiency and tourism scale is evident. It is of great theoretical and practical value to dynamically grasp the spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and the coupling coordination relationship of them to promote the high-quality sustainable development of tourism. This paper measures the tourism scale of 126 city units in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2001 to 2018. The DEA-MI model was introduced to measure and decompose tourism efficiency, while the exploratory spatio-temporal data analysis method was used to explore the spatial and temporal characteristics of regional tourism differences and spatial structure. In addition, the coupling coordination degree model of tourism efficiency and scale was established to examine the coupling superiority and synergy consistency of the two. The results demonstrated the following: (1) the spatial difference in comprehensive tourism efficiency of the study area was recognizable. The average situation exhibited the spatial distribution characteristics of "high in the east and west and low in the middle", and inter-annual changes decline in fluctuations. Scale efficiency played a supporting role in overall efficiency, and technical efficiency played a restrictive role. (2) The fluctuation range with the local spatial structure of tourism efficiency and tourism scale was relatively small, and the direction of dependence was relatively stable. The volatility of the latter is slightly stronger than that of the former, and the change of spatial dependence direction is comparable. The competitive situation of local spatial structure of tourism efficiency was stronger than that of cooperation, and the integration of tourism scale cooperation was strong. (3) The local spatial structure of tourism scale was relatively stable as it was was difficult to change the relative position of the city unit. However, the local spatial structure of tourism efficiency was still unstable, and it was likely to change the possibility within the city unit. (4) The overall coupling degree and coupling coordination degree of tourism efficiency and scale were gradually improved with similar spatial and temporal differentiation characteristics. There was spatial heterogeneity and volatility in local evolution, and the high value region of the degree of coupling coordination generated a broader range and slower diffusion.
长江经济带旅游效率与规模的时空演化及耦合协调
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008014
[本文引用: 18]

区域旅游效率和旅游规模的空间差异明显,动态把握两者时空演化特征和耦合协调关系对推动旅游高质量可持续发展具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。测度长江经济带126个市域单元2001—2018年的旅游规模,引入DEA-MI模型对旅游效率进行测算和分解,运用探索性时空数据分析方法探讨区域旅游差异和空间结构的时空动态特征,构建旅游效率与规模的耦合协调度模型,分析两者的耦合优良性和协同一致性。结果表明:① 长江经济带旅游综合效率空间差异明显,平均情况呈现东西高中间低的分布特征,年际变动呈现波动下降态势,规模效率对综合效率起支撑作用,技术效率起影响和制约作用;② 旅游效率和旅游规模局部空间结构波动幅度较小,依赖方向较为稳定,后者波动性稍强于前者,且空间依赖方向变化相似,旅游效率局部结构竞争态势强于协作,旅游规模协作整合性较强;③ 旅游规模局部空间结构较稳定,市域单元相对位置变动较困难,旅游效率局部空间结构尚不稳定,市域单元存在较大的变动可能性;④ 旅游效率与规模的整体耦合度和耦合协调度逐渐提高,具有相似的时空分异特征,局部演进存在空间异质性和波动性,耦合协调度高值区扩散范围更广、速度较缓。
Evolution of economic efficiency and its influencing factors in the industrial structure changes in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201712005
[本文引用: 4]

The process of modern economic growth shows a close relationship between the industrial structure changes and the evolution of economic efficiency, which is specifically reflected in the stages and heterogeneity of regional development. This paper employs the DEA-BCC model and the Malmquist productivity index to analyze the static efficiency and the TFP changes of three industries at sectional and regional levels. Then, based on the DEA-Tobit two-stage analyzing framework, this paper establishes a panel data model to analyze the factors affecting the economic efficiency of three industries. The results show that, three industries are equipped with certain static scale efficiencies, but they still need to be optimized. The TFP of three industries have all improved from 1978 to 2014, but their contributions to the economic growth of three industries show a decreasing sequence, featured by apparent extension. The technical progress has significantly propelled the TFP growth, and the technical efficiency improvements have gradually shifted from pure technical efficiency to scale efficiency. The TFP changes can be divided into four stages. The dividends of institution, structure, factors and policies have all contributed to the TFP growth, while during the industrial structure adjustment stage, the institutional and structural dividends give way to the technical progress. Three industrial TFP changes present obvious regional differences. In general, Eastern China has comparative advantages, while Central China becomes the "concave area", and the TFP changes of the secondary and tertiary industries in Northeast China reflect serious issues of the structural transformation and upgrading. Due to the differences of the internal development laws of different industries, the factors influencing the economic efficiency show the relatively regional consistency and the sectional differences. The primary and tertiary industries changing effect, the non-agricultural level, the opening degree and the human resource endowment have significant positive effects on the economic efficiency of the primary, and the opening degree largely promotes the economic efficiency of the secondary industry, while the opening degree, the human resources endowment have significant negative impacts on the economic efficiency of the tertiary industry. Finally, this paper concludes with suggestions to the future policy-making.
中国产业结构变迁中的经济效率演进及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201712005
[本文引用: 4]

现代经济增长过程表明,产业结构变迁与经济效率演进关系密不可分,具体反映在区域发展的阶段性与异质性上。运用DEA-BCC模型、Malmquist生产率指数分析中国三次产业静态综合效率与动态全要素生产率(TFP)的部门与区域变动情况,并基于DEA-Tobit两阶段分析框架构建面板计量模型,探究中国不同地区三次产业经济效率变动影响因素。研究表明:中国三次产业具备一定的静态规模效率,但仍有待优化;1978-2014年间,中国三次产业TFP均有提升,但一、二、三产业TFP增长对其部门经济贡献率依次递减,经济增长粗放型特征仍很明显;TFP增长主要源于技术进步,技术效率改进开始由以纯技术效率为主转向以规模效率为主;将三次产业TFP变动划分为四个阶段,制度、结构、要素、政策等红利对经济增长均有贡献,但在结构调整阶段,制度与结构红利让位于技术进步;三次产业TFP变动表现出显著的区域差异特征,总体上东部地区具有相对优势,中部地区表现为经济效率“凹地”,东北地区二、三产业TFP变动反映出严峻的结构转型升级问题。由于不同产业内在发展规律差异,其经济效率影响因素表现出区内相对一致性及部门差异性特征,其中一、三产业结构变动、非农化水平、对外开放程度、人力资源禀赋等对第一产业经济效率产生显著正向作用,对外开放程度显著促进第二产业经济效率提升,而对外开放程度、人力资源禀赋对第三产业经济效率产生显著的负面影响。最后讨论了结论的主要政策启示。
The effects of UNESCO World Heritage List inscription on tourism destinations performance in Italian regions
DOI:10.1016/j.econmod.2015.10.049 URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis on the time-space evolution of the domestic tourism flow to China
国内旅游流流量与流质的时空演化分析
Trade facilitation promoted the inbound tourism efficiency in Japan
Benchmarking and tourism efficiency in France
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2015.05.006 URL [本文引用: 1]
Evaluating the perceived social impacts of hosting large-scale sport tourism events: Scale development and validation
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2014.10.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Temporal and spatial dynamic evolution and influencing factors of tourism efficiency in Hunan Province based on DEA-Malmquist model
基于DEA-Malmquist模型的湖南省旅游产业效率时空动态演化及影响因素
Coordination degree among the tourism-economy-society-ecology system of Jilin Province under the background of all-for-one tourism
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.06.010
[本文引用: 5]

All-for-one tourism is an idea which centers on tourism to boost industrial development, improvement of the urban and rural, residents' well-being, and environmental protection. As a novel concept and pattern of synthesized development within a specific region, all-for-one tourism highlights the match of tourism with economy, society, and ecosystem. Therefore, how to manage the match is an important question for local governments and academia. The research on the tourism-economy-society-ecology system coordination helps evaluate the infrastructure to promote all-for-one tourism in China, enrich the literature on all-for-one tourism, and achieve a balance between tourism, economy, society, and ecosystem. Jilin Province has the most (i.e., 15) exemplars of all-for-one tourist attractions on the list consisting of 262 all-for-one tourism attractions recognized by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism of the People's Republic of China. The great number indicates the hope of Chinese government on tourism industry of Jilin Province. Meantime, Jilin Province showcases great determinations to develop all-for-one tourism and formulates the policy of ‘All-for-one tourism navigates all-for-one Jilin’. Because of both external and internal factors, local government and stakeholders in Jilin have paid plenty of attention to all-for-one tourism. Therefore, Jilin is an appropriate and representative setting to investigate all-for-one tourism. This study takes a lens of all-for-one tourism and applies contrastive analysis to identify status of tourism-economy-society-ecology system of Jilin Province in the entire China. In addition, the present study uses obstacle diagnosis method to examine the system and determinants of all-for-one tourism. The results show that the infrastructure of all-for-one tourism in China is insufficient, and the degree of coordination of tourism-economy-society-ecology system varies significantly across provinces. Specifically, the degree of coordination decreases gradually from the southeast to the northwest. The economical development, societal development, and the tourism system of Jilin is below the national average, and the ecosystem is slightly above the national average. More importantly, the coordination of tourism-economy-society-ecology system is below the national average. Moreover, our results show that the tourism and economic system significantly hinder the coordination of tourism-economy-society-ecology system, and ecosystem is the slightest hinderance. Other hinderances include growth rate of population and GDP, domestic tourism revenue, total tourism revenue, and the number of A-star tourist attractions.
全域旅游背景下吉林省旅游业—经济—社会—生态环境协调性研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.06.010
[本文引用: 5]

以全域旅游为研究视角,借助对比分析确定吉林省旅游业?经济?社会?生态环境间协调性在中国的地位,运用障碍度诊断法分析影响协调发展的主要因素。研究发现,中国全域旅游省域间旅游业?经济?社会?生态环境协调水平差异显著,由东部沿海向中部、西北部梯度递减;与全国平均水平相比,吉林省经济和社会发展水平较为落后,旅游业系统发展水平略低,生态环境系统略高,系统间协调性处于全国中下游水平;旅游业系统和经济系统对协调发展的障碍度较大,生态环境系统最小,人口增长率、GDP增长率、国内旅游收入、旅游总收入和A级景区数量是阻碍吉林省旅游业?经济?社会?生态环境协调发展的主要因素。
Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factor of coupling coordination of tourism urbanization system in the Dongting Lake Region
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.015
[本文引用: 5]

The internal coordination of tourism urbanization is the key to sustainable development. Based on coupling coordinative interactive mechanism, the coupling coordination model is used to analyze the spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factor of tourism urbanization of 17 counties in the Dongting Lake region from 2000 to 2018. The results showed that: 1) The temporal features of coupling degree and coordination degree had increased synchronously for 20 years, both presenting the characteristics of fluctuating ups and downs. The average coupling degree reaches 0.526 2 that was in the high coupling phase, and the average coordination degree reaches 0.434 4 that was in the intermediate coordination stage. In the phase characteristics, coupling degree went through 2 phases of middle coupling and high coupling; coordination degree went through 3 phases of low coordination, middle coordination and high coordination. While the change of coordination degree lagged behind the change of coupling degree, which indicated that there was still room for the increase of coordination degree. 2) The spatial pattern of coordination degree and coupling degree both presented the characteristics of low in the middle and high around. In the past 20 years, there were 4 coupling type with low coupling, medium coupling, high coupling, and 3 coordination type with low coordination, medium coordination and high coordination. In the 2 typical years, the coordination degree and coupling degree of 17 counties showed different types of transformation. The counties of high-level coupling type and coordination type were concentrated in the periphery area of the Dongting Lake, represented by Yueyang City, Changde City and Yiyang City. While the counties of low-level were concentrated in the central area of the Dongting Lake, represented by Yuanjiang City and Nanxian City. 3) The spatial combination had a great difference between coupling and coordination types, there were 5 and 6 types respectively of spatial combination of coupling and coordination types in 17 counties in 2000 and 2018, and the number of counties transformed from low level to high level had reached 9. The spatial distribution pattern of combination types was basically similar to that of coupling degree and coordination degree. 4) Relative researches indicated that the main affecting factor of this kind of spatial differential distribution was the strong relationship between the coordination degree and the characterization of the development level of tourism, urbanization and environment. Therefore, the development of tourism urbanization in the Dongting Lake region should optimize a coordinative developmental mechanism for tourism, urbanization and environment, which plays the driving role of tourism, and consolidate the guarantee foundation for urbanization, and improve the supporting function of ecological environment. A series of corresponding measures will be used to promote internal coordination level of tourism urbanization, and achieve the synchronous development of coupling degree and coordination degree.
洞庭湖区旅游城镇化系统耦合协调性时空格局及影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.015
[本文引用: 5]

基于旅游产业、城镇化和生态环境耦合协调作用机理,运用耦合协调模型分析洞庭湖区2000—2018年17个县域旅游城镇化系统耦合协调性的时空格局及影响因素。结果表明:① 时序特征上,近20 a来耦合度和协调度呈现同步上升态势,两者均出现“一波三折”过程变化特点。耦合度增强的同时,协调度也随之增强,但滞后于耦合度的变化,协调水平有待提升。② 空间格局上,协调度与耦合度均呈现出“中部低、四周高”的分布特点。17个县域2个典型年份的耦合度和协调度出现了不同类型的转变,高层次耦合类型和协调类型的县域集中分布在洞庭湖外围地区,低层次的县域则集中分布在洞庭湖中部地区。③ 耦合协调类型的空间组合差异明显,由低层次向高层次转变的县域达到9个,组合类型的空间分布格局与耦合度和协调度的分异特征基本相似。④ 相关分析表明,协调度与表征旅游产业发展水平、城镇化发展水平和生态环境治理水平因子的较强相关性是形成这种时空分异格局的主要影响因素。
Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and obstacle factors of coordinated development of tourism resources and ecological security in Yunnan Province
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.03.014
[本文引用: 6]

The complex ecosystem composed of nature, economy and society provides conditions for the existence and development of tourism resources. At the same time, rich tourism resources can not only promote the development of tourism, but also provide an important force for promoting economic development and natural environment protection. Using the methods of linear weight, coupling coordination degree model and trend analysis, this paper explores the current situation and obstacle factors of the coupling coordination development of tourism resources and ecological security in the sixteen areas of Yunnan Province. The results show that: ① Although 87.50% of the states and cities are in the stage of moderate coupling coordinated development of tourism resources and ecological security, the overall coupling coordinated development tends to be stable and presents a “core-periphery” structure with Kunming as the core. Thus, the coupling coordinated development needs to be improved. ② Except for the tourism areas in central and southeast Yunnan, the spatial differences of coupling coordinated development of the other four tourism areas are gradually narrowing from the local evolution characteristics, and the tourism development shows a certain “diffusion effect”. ③ The obstacle degree of 50% of the states and cities’ tourism resources have the characteristics of “combination degree > grade degree > type > abundance”. On the aspect of ecological security obstacle degree, the main factors that affect the coupling coordination development of the two systems are the low quality of tourism development and ecological environment, the insufficient driving force of tourism and socio-economic development, and the imperfect response mechanism of ecological security.
云南省旅游资源与生态安全协调发展的时空演化特征及障碍因子分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.03.014
[本文引用: 6]

自然、经济和社会构成的复合生态系统为旅游资源的赋存和开发提供条件,而丰富的旅游资源不仅能够促进旅游业发展,也为推动社会经济发展和自然环境保护提供了重要力量。运用线性加权法、耦合协调度模型和趋势分析等方法探究了云南省16个州市旅游资源与生态安全耦合协调发展现状及其障碍因子,研究发现:① 尽管云南87.50%的州市旅游资源与生态安全处于中度耦合协调发展阶段,两系统具有明显的耦合互动关系,但整体耦合协调发展趋于稳定,且呈现以昆明市为核心的“核心?边缘”结构,耦合协调发展水平仍需增强,空间分布格局有待完善。② 从局部演化特征来看,除滇中和滇东南旅游区,其余四大旅游区耦合协调度空间差异逐渐缩小,旅游业发展具有一定的“扩散效应”。③ 50%的州市旅游资源障碍度具有“组合度>品位度>类型>丰度”的特征,而生态安全障碍度层面,旅游发展和生态环境质量不高,旅游业和社会经济发展驱动力不足,生态安全响应机制不健全是影响两者耦合协调发展的主要因素。
A study on the coupling of traffic-tourism industry-ecological environment in the middle of the Yangtze River
长江中游城市群交通—旅游产业—生态环境的耦合协调评价研究
Coordination relationship between tourism development and regional development with improvement of people's livelihood in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.012
[本文引用: 3]

This article establishes tourism system and regional development and improve people’s livelihood system, and applies the coupled coordination degree model to doing a quantitative evaluation about the relation of tourism with area development and improvement of people’s livelihood in Chinese 31 province in 2000-2013, and analyzes the evolution rules of coupling coordination degree from the view of space-time. The results show that: the comprehensive evaluation value of tourism and the value of regional development and improvement of people’s livelihood are both rising. The former grows slowly, and the latter grows relatively fast. The coupling coordination coefficient continues to increase, but the overall level of coupling coordination is not high, only 2 provinces achieving a high degree of coordination and having not yet appeared extremely coordinated area in 2013. The distribution of coupling degrees basically conforms to the rules that the eastern > the central > the west, the southeast > the northeast, and the southwest > the northwest. To further explore the coupling coordination role of indices of tourism system to the regional development and improvement of people’s livelihood, grey correlation degree analysis method is applied, concluding that the indexes of inbound tourism income, inbound tourists, and tourism college students number are the main factors influencing the regional development and the improvement of people’s livelihood and the teir coordinated development.
中国旅游业与地区发展及民生改善协调关系研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.012
[本文引用: 3]

以中国(未包括港澳台地区)31个省域为实证分析对象,运用耦合协调模型和灰色关联度分析法,从时空角度对旅游业同地区发展与民生改善的耦合协调关系及其演变规律进行分析,探知旅游业同地区发展与民生改善的协调关系和影响二者协调发展的主要因素。研究表明:考察期内,旅游业、地区发展与民生改善的综合评价值持续上升,前者增长较慢,后者相对较快,旅游业发展滞后于地区发展与民生改善,二者耦合协调系数稳步增加,但整体水平不高;旅游业同地区发展与民生改善的耦合协调度在空间分布上,呈现东部、中部、西部梯级递减,南方优于北方的空间分异规律;旅游业系统对于地区经济与民生协调发展起着关键作用,其中入境旅游收入、入境旅游人次、旅游专业化程度和旅游院校学生数是影响地区发展与民生改善和二者协调发展的主要因素。
Spatial-temporal coordination and driving forces of provincial culture industry and tourism industry in China
中国文化产业与旅游产业协调态势及其驱动力
Spatio-temporal dynamics and coupling relationship of regional tourism development pattern from the perspective of performance: A case study of Pan-Yangtze River Delta
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201805011
[本文引用: 1]

It is paramount to hold the trends of regional tourism development pattern from the perspective of performance, which plays a fundamental role for understanding the spatial structure of regional tourism, distributing production factors in tourism industry and improving quality and efficiency of tourism industry. Taking the Pan-Yangtze River Delta as a study case, this paper used the methods of exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA), LISA Time Path and Centre-of-Gravity Path to analyze the space-time dynamism and spatial coupling of regional tourism cities' development pattern from the perspective of performance and efficiency from 2000 to 2015. Results showed that: (1) significant positive spatial correlation and spatial agglomeration in regional tourism development achievement were identified, showing strong stability in its partial spatial structure and spatial dependence direction, while the spatial correlation and agglomeration increased gradually which showed significant volatility in its partial spatial structure; (2) the differentiation of spatial dynamic pattern between the regional tourism development performance and efficiency resulted from the fact that the spatial pattern had transfer inertia, reflecting path dependence and spatial locking characteristics. Local spatial structure of regional tourism development efficiency was unstable - the changes between different types were active and frequent; (3) significant spatial coupling characteristics between the regional tourism development performance and efficiency were detected in this study. In this spatial distribution results of coupling type, Shanghai, South Jiangsu, North Zhejiang and South Anhui belonged to the High achievement-High efficiency cities, while the High achievement-Low efficiency cities gathered around regional central cities and regional central cities' surrounding areas, and North Jiangsu, Central Jiangsu, North and Central Anhui were classified into Low achievement-High efficiency or Low achievement-Low efficiency cities.
绩效视角下区域旅游发展格局的时空动态及耦合关系: 以泛长江三角洲为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201805011
[本文引用: 1]

从绩效视角下对区域旅游发展格局的动态把握是认识区域旅游空间结构、配置旅游业生产要素和实现旅游业提质增效的重要依据。以泛长江三角洲为研究对象,运用ESDA、LISA时间路径和重心轨迹等研究方法,从业绩和效率二维视角对2000-2015年区域城市旅游发展 格局的时空动态及其耦合关系进行分析。研究发现:① 区域旅游发展业绩和效率的时空格局动态变迁路径差异明显,旅游发展业绩总体空间格局呈现显著的正向空间相关性,局部空间结构和空间依赖方向上都具有较强的稳定性,并以协同增长为主;旅游发展效率虽然总体空间格局的相关性不断增强,但其局部空间结构和空间依赖方向上的波动性较强,协同与竞争并存。② 这种空间格局动态的分异是由于区域旅游发展业绩的空间格局具有较强的转移惰性,存在路径依赖和空间锁定,而区域旅游发展效率的局部空间结构极不稳定,类型切换较为活跃、频繁。③ 区域旅游发展业绩和效率的重心趋于集聚,空间耦合关系不断增强。其耦合分布上,上海、苏南、浙东北和皖南地区城市多属于高绩高效型城市,高绩低效型城市多集中在区域中心城市及其周边地区,苏北、苏中、皖北和皖中等地区多为低绩高效型或低绩低效型城市。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 2]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 2]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
On the evolution of the optimization of tourism industrial structure to the contribution of economic growth of regional tourism
旅游产业结构优化对区域旅游经济增长贡献的演变
China's tourism industry, industrial structure and economic growth
产业结构变迁、旅游业与经济增长: 来自中国的经验证据
DOI:10.18402/resci.2017.10.11
[本文引用: 8]

既有关于旅游业导向型经济增长假说的经验研究,由于忽视了产业结构变迁的动态性,从而会导致对旅游业影响经济增长效应的估计偏误。因此,本文在定量测度中国各省产业结构变迁基础上,将旅游业、产业结构变迁与经济增长纳入到统一分析框架进行实证考察,以拓展旅游业导向型经济增长假说的研究体系。研究结果表明:①以泰尔指数反向度量的产业结构合理化对经济增长具有抑制作用,而产业结构高级化则对经济增长具有积极作用,并且产业结构高级化对经济增长的“结构效应”要大于产业结构合理化对经济增长的“失衡效应”;②中国旅游业对经济增长具有显著的正向影响,与此同时,产业结构欠缺合理化抑制了旅游业对经济增长的影响效应,而产业结构高级化可正向调节旅游业对经济增长的影响效应。本文认为,政府在进行产业结构调整时,除应着重强调产业结构高级化的同时,还需高度关注产业结构合理化,从而为发挥产业结构变迁对旅游业影响经济增长的正向调节作用创造条件。
Does the inbound tourism increase the city's green total factor productivity? Based on nonlinear perspective
入境旅游提升了城市绿色全要素生产率吗? 基于非线性视角
Factor structure, institutional environment and high-quality development of the tourism economy in China
要素结构变动、制度环境与旅游经济高质量发展
Departmental contribution and driving forces analysis of tourism industry structure optimization in Shandong Province
山东省旅游产业结构优化的部门贡献与动能分析
Research on misuses and modification of coupling coordination degree model in China
With the deepening understanding of the Scientific Outlook on Development, the coupling coordination degree model has become an effective evaluation and research tool for the regional overall balanced development. However, for this model, there are four types of misuses, including writing errors, coefficients loss, weight misuses and model failures, which have significantly affected the scientific nature of academic research. Therefore, this study firstly clarified the normative formula of the traditional coupling coordination degree model. On the basis of discussing the validity of the traditional model in the field of social science research, this study further proposed a modified model of coupling degree. In addition, the coupling coordination degree model has three reliability issues: the subjectivity of index construction, and the volatility and incomparability of coupling results. Taking the ecological and economic system of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region as an example, we proved that the modified coupling coordination degree model has better validity, and the spatial and temporal changes of the research object will affect the reliability of the coupled coordination model.
国内耦合协调度模型的误区及修正
随着对科学发展观认识的深入,耦合协调度模型成为研究区域整体均衡发展程度的有效评价与研究工具。但在该模型使用中,存在书写错误、丢失系数、错用权重和模型不成立四类误区,已经显著影响到学术研究的科学性。因此首先明确传统耦合协调度模型的规范公式,在探讨该传统模型在社会科学领域研究中效度问题基础上,进一步提出耦合度的修正模型。此外耦合协调度模型还存在指标构建的主观性、耦合结果的波动性和无可比性的信度问题。以京津冀生态与经济系统为例,验证修正后的耦合协调度模型具有较好的效度,研究对象的时空变化会显著影响耦合协调度模型的信度。
Constructing the spatial weights matrix using a local statistic
DOI:10.1111/gean.2004.36.issue-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatio-temporal evolution and trend prediction of urban carbon emission performance in China based on super-efficiency SBM model
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006016
[本文引用: 1]

Climate change caused by CO2 emissions has become an environmental issue globally in recent years, and improving carbon emission performance is an important way to reduce carbon emissions. Although some scholars have discussed the carbon emission performance at the national scale and industry level, literature lacks studies at the city- level due to a limited availability of statistics on energy consumptions. In this study, based on China's city-level remote sensing carbon emissions from 1992 to 2013, we used the super-efficiency SBM model to measure the urban carbon emission performance, and the traditional Markov probability transfer matrix and spatial Markov probability transfer matrix are constructed to explore the spatio-temporal dynamic evolution characteristics of urban carbon emission performance in China for the first time and to predict its long-term evolution trend. The study shows that urban carbon emission performance in China presents a trend of steady increase in the fluctuation, but the overall level is still at a low level, so there is still a great improvement space in urban carbon emission performance, with huge potential for energy conservation and emission reduction. The spatial pattern of national urban carbon emission performance shows the characteristics of "high in the south and low in the north", and there is a significant difference in the level of carbon emission performance between cities. The spatial Markov probabilistic transfer matrix results show that the transfer of carbon emission performance type in Chinese cities is stable, thus it forms the "club convergence" phenomenon, and the geographical background plays an important role in the process of the transfer. From the perspective of long-term trend prediction, the future evolution of urban carbon emission performance in China is relatively optimistic. The carbon emission performance will gradually improve over time, and the distribution of carbon emission performance presents a trend of high concentration. Therefore, in the future, China should continue to strengthen research and development to improve the performance level of urban carbon emissions and achieve the national target of energy conservation and emission reduction. At the same time, neighboring cities with different geographical backgrounds should establish a sound linkage mechanism of economic cooperation to pursue coordinated development between economic growth, energy conservation and emission reduction, so as to realize low-carbon city construction and sustainable development.
基于超效率SBM模型的中国城市碳排放绩效时空演变格局及预测
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006016
[本文引用: 1]

由CO<sub>2</sub>排放所引起的气候变化是当今社会所关注的热点话题,提高碳排放绩效是碳减排的重要途径。目前关于碳排放绩效的研究多从国家尺度和行业尺度进行探讨,由于能源消耗统计数据有限,缺乏城市尺度的研究。基于遥感模拟反演的1992—2013年中国各城市碳排放数据,采用超效率SBM模型对城市碳排放绩效进行测定,构建马尔可夫和空间马尔可夫概率转移矩阵,首次从城市尺度探讨了中国碳排放绩效的时空动态演变特征,并预测其长期演变的趋势。研究表明,中国城市碳排放绩效均值呈现波动中稳定上升的趋势,但整体仍处于较低的水平,未来城市碳排放绩效仍具有较大的提升空间,节能减排潜力大;全国城市碳排放绩效空间格局呈现“南高北低”特征,城市间碳排放绩效水平的差异性显著;空间马尔科夫概率转移矩阵结果显示,中国城市碳排放绩效类型转移具有稳定性,且存在“俱乐部收敛”现象,地理背景在中国城市碳排放绩效类型转移过程中发挥重要作用;从长期演变的趋势预测来看,中国碳排放绩效未来演变较为乐观,碳排放绩效随时间的推移而逐步提升,碳排放绩效分布呈现向高值集中的趋势。因此未来中国应继续加大节能减排力度以提高城市碳排放绩效,实现国家节能减排目标;同时不同地理背景的邻域城市之间应建立完善的经济合作联动机制,以此提升城市碳排放绩效水平并追求经济增长与节能减排之间协调发展,从而实现低碳城市建设和可持续发展。
Spatial empirics for economic growth and convergence
DOI:10.1111/gean.2001.33.issue-3 URL [本文引用: 2]
STARS: Space-time analysis of regional systems
DOI:10.1111/gean.2006.38.issue-1 URL [本文引用: 1]
Multi-dimensional analysis of urban expansion patterns and their driving forces based on the center of gravity-GTWR model: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201806007
[本文引用: 4]

Research into urban expansion patterns and their driving forces is of great significance. Under the background of the integrated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (Jing-Jin-Ji) urban agglomeration, it is important to study the temporal and spatial patterns of urban land expansion and the driving forces development. This paper uses land-use data of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration from 1990 to 2015 and reveals the multi-dimensional characteristics of the urban land expansion patterns. We then combine the urban spatial interaction and the spatial and temporal nonstationarity of the urban land expansion process and build the center of gravity-geographically and temporally weighted regression (GTWR) model by coupling the center of gravity model with the GTWR model. Using the center of gravity-GTWR model, we analyze the driving forces of urban land expansion at the city scale, and summarize the dominant mode and core driving forces of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration. The results show that: (1) Between 1990 and 2015, the expansion intensity of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration showed a down-up-down trend, and the peak period of expansion was in 2005-2010. Before 2005, high-speed development was seen in Beijing, Tianjin, Baoding, and Langfang, which were then followed by rapid development in Xingtai and Handan. (2) Although the center of gravity of cities in the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration showed a divergent trend, the local interaction between cities was enhanced, and the driving forces of urban land expansion showed a characteristic of spatial spillover. (3) The spatial development mode of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration changed from a dual-core development mode to a multi-core development mode, which was made up of three function cores: the transportation core in the northern part, the economic development core in the central part, and the investment core in the southern part. The integrated development between functional cores led to the multi-core development mode. (4) The center of gravity-GTWR model analyzes urban land expansion as a space-time dynamic system. The model proved to be feasible in the analysis of the driving forces of urban land expansion.
基于重心-GTWR模型的京津冀城市群城镇扩展格局与驱动力多维解析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201806007
[本文引用: 4]

城镇用地扩展格局及驱动力研究对城市群发展规划与决策具有重要意义。以京津冀地区为例,基于城镇用地扩展强度指数、城镇用地扩展差异指数、分形维数、土地城镇化率和重心转移模型,多维解析了城市群城镇用地扩展格局特征,并耦合重心转移模型和时空地理加权回归(GTWR)模型构建重心-GTWR模型,在对空间格局进行长时间序列多维度指标分析的基础上,运用该模型依序对其特征进行驱动力解读,进而总结凝练京津冀区域发展的主导模式与城市核心驱动力。主要结论为:① 1990-2015年,京津冀城市群城镇用地扩展强度呈现“下降—上升—下降”的趋势,高峰时期在2005-2010年,在2005年之前高速发展城市集中在北京、天津、保定和廊坊,2005年之后集中在邢台和邯郸;② 城市群城镇用地重心虽呈现出发散态势,但城市之间的局部相互作用力逐渐增强,城镇用地扩展驱动力表现出空间溢出特征;③ 京津冀城市群空间发展模式由以北京和天津为中心的双核发展模式向多核发展模式转变,并出现北部资源运输核心、中部经济发展核心和南部投资发展核心三大功能核心组团,城市群趋向于多核功能协同发展模式;④ 重心-GTWR模型结合了时空非平稳性和城市空间相互作用,将城市群城镇用地扩展作为一个时空变化系统进行分析,经验证,该模型在城镇用地扩展格局驱动力分析研究中具有可行性。
Study on the spatio-temporal evolution of coastal city tourism of China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201410015
[本文引用: 2]

The study on the regional tourism development patterns has become a hotspot in the field of tourism geographies. In recent years, domestic and foreign scholars have mainly focused on the tourism strength, tourism development efficiency, tourism competitiveness, tourism development spatial difference, tourism development spatial patterns and etc. The spatio-temporal evolution of city tourism is the hot-spot of tourism geographies research. This article, choosing China's eastern coastal cities as the research objective, analyzes the temporal and spatial evolution patterns of tourism development. First, it comes to the analysis of the spatio-temporal evolution of coastal city tourism development strength, and then it analyses the spatio-temporal evolution of coastal city tourism development efficiency by DEA data envelopment method.Results show that in the aspect of tourism development strength, there is great difference among the eastern coastal cities. The tourism development strength in the cities of Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone, Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, Liaodong Peninsula and Shandong Peninsula in Bohai Economic Circle is strong, but that on the west side of the Straits Economic Zone and Beibu Gulf Economic Zone is weak. During the ten years, the comprehensive efficiency of tourism development basically maintained unchanged; however, the pure technical efficiency is remarkably enhanced, and the scale efficiency is reduced significantly, which indicates that the development of the coastal city tourism has gradually changed from scale efficiency to technical efficiency. Moreover, through the data analysis of the years of 2002, 2006 and 2011, it is found that as time goes by, the polarization efficiency of tourism development comprehensive efficiency has also increased.
中国东部沿海城市旅游发展的时空演变
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201410015
[本文引用: 2]

城市旅游时空演变是旅游地理学研究的热点领域。以中国东部沿海城市为研究区,分析城市旅游发展的时空演变格局。首先分析沿海城市旅游发展强度的时空演变,进而采用DEA数据包络分析法计算沿海城市旅游发展效率的时空演变。研究表明:① 在旅游发展强度方面,东部沿海城市之间的旅游发展强度差异较大,长三角、珠三角以及环渤海的辽东半岛和山东半岛地区的旅游发展强度较强,海峡西岸经济区和环北部湾地区的旅游发展强度较弱。② 10年间在旅游发展综合效率方面基本维持不变,而旅游发展纯技术效率显著增强,旅游发展的规模效率则显著减弱。说明沿海城市的旅游发展已经逐渐由规模效率向技术效率转变。③ 综合旅游发展强度和旅游发展效率两个方面看,将东部沿海城市旅游发展类型分为“高—有效型”、“低—有效型”、“高—无效型”和“低—无效型”四种类型。其中“高—有效型”城市旅游发展较为成熟,“低—有效型”和“高—无效型”城市旅游发展一般,“低—无效”城市旅游发展相对较差。整体来看,珠三角和海峡西岸地区旅游发展强度和旅游发展效率均出现一定程度下滑,长三角、环渤海和北部湾地区的旅游发展强度和旅游发展效率均呈现不同程度增加。
The coupling coordination degree and spatial correlation analysis on integrational development of tourism industry and cultural industry in China
中国旅游与文化产业融合发展的耦合协调度及空间相关分析
Space network structure and formation mechanism of green innovation efficiency of tourism industry in China
中国旅游产业绿色创新效率的空间网络结构与形成机制
Spatiotemporal evolution of provincial tourism efficiency and its club convergence in the Chinese mainland
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.10.009
[本文引用: 3]

The improvement of quality and efficiency of tourism industry is one of the most important tourism issues under China's new normal economy. Based on the data of tourism development and related data of the Chinese mainland from 1997 to 2015, and comprehensively using the methods of modified data envelopment analysis (DEA) model, spatial Markov chain, impulse response model, and club convergence theory and quantitative calculation of tourism efficiency, this study analyzed the spatiotemporal evolution and mechanism of tourism efficiency in the Chinese mainland. The results indicate that: provincial tourism efficiency showed strong regional characteristics. The tourism economy growth was highly intensive in the eastern area, while it was highly extensive in the western region. The transfer of tourism efficiency is always affected by the tourism efficiency of neighboring regions. The spatial transfer of tourism efficiency is more active, but the basic pattern has not changed after considering the spatial factors. Item efficiency showed high stability, especially the scale efficiency. The spatiotemporal evolution of tourism efficiency led to the effect of club convergence to some degree—a phenomenon of "one takes the behavior of one's company." Club convergence of provincial tourism efficiency objectively makes the tourism development "stable"; however, it is not conducive to efficiency improvement. Tourism development cooperation must break through the geographical restrictions in the future.
中国大陆省际旅游效率时空演化及其俱乐部趋同研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.10.009
[本文引用: 3]

旅游产业的提质增效是新常态下旅游学科研究的重要问题之一。利用中国大陆1997-2015年省际旅游发展相关数据,综合修正的DEA模型、空间马尔科夫链、脉冲响应模型,以及俱乐部趋同理论,在对省际旅游效率进行定量测算的基础上,分析其时空演化趋势及机理。主要结论为:1997-2015年中国大陆省际旅游效率演化具有显著的地带特征:东部地区旅游经济增长的集约化程度较高,西部地区旅游经济增长的粗放型程度较高;各项旅游效率水平转移在地理空间上往往受到邻域地区旅游效率的影响。考虑空间因素后,各项旅游效率的空间转移更加活跃,但基本格局没有发生变化:各项效率均具有较高的稳定性,尤其是规模效率;空间马尔科夫链分析结果表明:旅游效率的时空演化一定程度上导致了俱乐部趋同效应,中国大陆省际旅游发展效率存在着“近朱者赤、近墨者黑”现象。省际旅游效率的俱乐部趋同客观上使得旅游发展维持着一种“稳定”状态,不利于旅游效率的提升,未来的旅游合作必须进一步突破地理区位的限制。
The evolution and influencing factors of spatial network structure of China's provincial tourism efficiency
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.03.004
[本文引用: 4]

This article explored the evolution characteristics and its causes regarding spatial network structure of China’s provincial tourism efficiency from 2011 to 2016 by applying Super-DEA model and social network analysis method comprehensively. The results show that: 1) From 2011 to 2016, the average value of China’s provincial tourism efficiency is 0.739, showing a slight decline as a whole, and the spatial distribution characteristic of ‘Eastern region>Central region>Northeastern region>Western region’ is roughly presented. 2) During the research period, the spatial correlation network of China’s provincial tourism efficiency is presented to be multi-threaded, dense and complicated, and the spatial network structure is not stable yet. The network density of tourism efficiency has decreased, but it still presents a rigid and hierarchical network structure. 3) Guangdong, Jiangsu and Shandong Provinces have the highest priority and play the role of leaders in the spatial network structure. However, Hainan Province is partial to a corner, which is at the end of the transmission of tourism production factors, and its connectivity with other provinces is weak. The core-periphery structure of the whole spatial network tends to be cohesive group. 4) Tourism investment level, the distance among capitals and informatization development level jointly drive the evolution and optimization of spatial network structure of China’s provincial tourism efficiency.
中国省域旅游效率空间网络结构演化及其影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.03.004
[本文引用: 4]

综合运用Super-DEA模型和社会网络分析法探究2011—2016年中国省域旅游效率空间网络结构演化特征及其成因。结果表明:① 2011—2016年中国省域旅游效率均值为0.739,总体呈现轻微下降态势,空间上大致呈现“东部>中部>东北部>西部”的分布特征。② 研究期内,中国省域旅游效率的空间关联网络呈现多线程、稠密化和复杂化的特征,空间网络结构尚不稳定;旅游效率网络密度有所下降,但仍呈现较为森严的网络等级结构。③ 广东、江苏和山东等省份在空间网络结构中掌控的优先权最大,扮演着领导者的角色;而海南省“偏居一隅”处在旅游生产要素传输的末端区位,与其他省份互联互通的能力孱弱;整体空间网络的“核心?边缘”结构趋向于组团式发展。④ 旅游投资水平、各省会间距离和信息化发展水平共同驱动着中国省域旅游效率空间网络结构的演进与优化。
Spatial difference of Human capital promoting regional tourism economic efficiency: Empirical research based on "Hu Line"
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.015
[本文引用: 2]

In this article, based on DEA-MI model, the relationship between human capital and regional tourism economic efficiency and the contribution of human capital to regional tourism economic efficiency are explored by using spatial econometric model. The research results show that the tourism economic efficiency has the typical spatial characteristics of “Hu Line”, and the regional tourism economic efficiency of tourism and its sub-sectors fluctuates up and down with 1 as the standard line; the spatial relationship of Human capital and the regional tourism economic efficiency also basically have the spatial characteristics of “Hu Line”. Meanwhile, the economic efficiency of northwest regions such as Ningxia is higher than other northwestern regions, although the stock of human capital in Ningxia is insufficient, the contribution rate of its human capital is larger than other northwestern regions. There is a phenomenon of “mismatch of human capital” in tourism along the southeast regions such as Fujian province, and along the lines of Sichuan province and Yunnan province and so on. The southeastern region is rich in human capital, yet its contribution rate is low than other provinces in the northwestern regions and along the “Hu Line” regions. In the meantime, star hotel industry and travel agency industry break the regional characteristics of “Hu Line”; Medium human capital can positively promote the regional tourism economic efficiency in tourism and its sub-sectors, while high-level human capital can promote the growth of economic efficiency in tourism sub-sectors. However, high-level human capital can inhibit the tourism economic efficiency as a whole, which shows that tourism as a whole is still a typical labor-intensive industry. And that also shows star-rated hotels and travel agencies have initially possessed the characteristics of knowledge-intensive industries; Regional geography, opening to the outside world and infrastructure and so on, are the main influencing factors of human capital efficiency, which restrict the promotion of regional tourism economic efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary to establish and improve the matching system of tourism talents, play maximum extent efficiency in human capital, and scientifically construct the synergy mechanism between human capital and regional tourism economic efficiency.
人力资本促进区域旅游经济效率的空间差异研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.015
[本文引用: 2]

在DEA-MI模型的基础上,采用空间计量模型就人力资本与区域旅游经济效率的关系进行分析,探究人力资本对区域旅游经济效率的贡献。结果发现:旅游经济效率具有典型的“胡焕庸线”空间特征,旅游业及其子行业的区域旅游经济效率以1为标准线上下波动;人力资本与区域旅游经济效率空间关系也基本具备“胡焕庸线”空间特征。宁夏等西北地区区域经济效率较高,虽然人力资本存量不足,但其贡献率较大。福建等东南地区、四川和云南等沿线地区旅游业存在“人力资本错配”现象,东南地区虽然人力资本富集,但其贡献率较低,星级饭店业和旅行社业打破“胡焕庸线”的区域特征;中等人力资本在旅游业及其子行业中能正向促进区域旅游经济效率,高水平人力资本在旅游子行业中能推进经济效率的增长,但在旅游业整体中反而抑制旅游经济效率,这说明旅游业整体上还是一个典型的劳动密集型行业,而星级饭店和旅行社业已经初步具备知识密集型行业特征;区域地理性、对外开放度、基础设施等是人力资本效能发挥的主要影响因素,制约着区域旅游经济效率的提升。因此需要健全旅游人才匹配体系,最大程度地发挥人力资本效能,科学构建人力资本与区域旅游经济效率协同机制。
Spatial effects of knowledge-intensive business services clustering on tourism innovation in urban aggolomerations
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106014
[本文引用: 4]

Knowledge-intensive business services (KIBS), as a key component of the national innovation system (NIS), has become a crucial driving factor for the regional tourism innovation. Despite ever-increasing overlapping and interaction between tourism and KIBS, there was little literature on the relations of KIBS clustering and regional tourism innovation. In this paper, the authors measured the clustering level of KIBS and total factor productivity (TFP) of regional tourism innovation in China's three mega-city regions (MCR), namely, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Pearl River Delta (PRD), and the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) urban agglomeration, using the methods of location quotient and data envelopment analysis. Then, the authors examined the spatial distribution and cluster mode of regional tourism innovation TFP in the three MCRs using the spatial data analysis method (ESDA). Finally, the authors evaluated the impact and spatial effect of KIBS clustering, among other factors, on regional tourism innovation on the basis of the panel data (from 2005 to 2015) and Spatial Panel Durbin Model (SPDM). The results show that: (1) KIBS in all the three MCRs show high levels of clustering, though the intensity of clustering exhibits a descending pattern from the PRD, to the YRD, and to the BTH. KIBS clustering mainly takes place in municipalities directly under the central government and first-tier cities to the provincial capitals, with significant regional differences among different cities in these MCRs. (2) The regional tourism innovation TFPs in the three MCRs from high to low are the YRD (1.006), the PRD (0.978), and the BTH (0.960), and the changes in TFP are mainly due to technological advancement. (3) Among the three MCRs, only the YRD shows a significant level of spatial clustering of regional tourism innovation on a global scale, while there have been certain signs of spatial clustering in each of the three MCRs on a local scale. However, different MCRs show different spatial clustering patterns: spatial clustering in most cities in the YRD is in the high-low type, while that in most cities in the PRD and BTH region is in the high-low and low-high types. (4) Despite variations from region to region, KIBS clustering has a positive effect on the level of regional tourism innovation. There have been effects of spatial spillover in all the three MCRs, however, it is necessary to set good examples and create favorable conditions for neighbouring cities. (5) An open policy system and well-paced marketization have a promoting effect on regional tourism innovation TFP. The optimization of industrial structure and improvement in digitalization also plays a positive role in regional tourism innovation, which is the result of multiple innovation factors.
知识密集型服务业集聚对城市群旅游创新影响的空间效应
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106014
[本文引用: 4]

知识密集型服务业作为国家创新体系的重要组成部分,已经成为促进区域旅游创新发展的关键因素。以中国长三角、珠三角和京津冀城市群为例,运用区位商、数据包络分析法、探索性空间数据分析法和空间计量模型等方法,对知识密集型服务业集聚和旅游创新的时空演变特征与两者之间的空间关联性深入分析。结果表明:① 三大城市群知识密集型服务业集聚特征明显,集聚程度由强到弱依次为珠三角、长三角和京津冀,且城市群内部各城市间的集聚存在不均衡特征。② 三大城市群旅游创新的生产效率变化主要由技术进步推动,旅游创新均表现出一定的空间集聚特征,长三角城市群具有明显空间集聚性,但空间集聚模式存在差异,珠三角和京津冀旅游创新集聚不明显。长三角城市群内部各城市大多属于高高和低低空间集聚模式,珠三角和京津冀城市群内部各城市大多属于高低和低高的空间集聚模式。③ 知识密集型服务业集聚对城市群旅游创新水平的提高具有一定的促进作用但存在地区差异性,三大城市群旅游创新水平呈现空间溢出效应,但其对周边城市的辐射带动作用有待加强。
Temporal and spatial pattern characteristics and spatial effect of tourism financial efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt
长江经济带旅游金融效率时空格局特征及空间效应
The spatio-temporal evolution and impact mechanism of county tourism poverty alleviation efficiency from the perspective of multidimensional poverty: A case study of 25 border counties(cities)in Yunnan Province
多维贫困视角下县域旅游扶贫效率时空演化及影响机理: 以云南25个边境县(市)为例
Study on the threshold effect of urbanization on the competitiveness of tourism industry
城镇化进程对旅游产业竞争力的门槛效应研究
Growth effects of government expenditure and taxation in rich countries
DOI:10.1016/S0014-2921(00)00083-0 URL [本文引用: 1]