1 引言
经济全球化的不断发展使区域经济系统面临着越来越多的冲击和扰动,从而使更多学者把目光投向区域经济韧性的研究[1⇓-3]。产业结构是影响区域经济韧性的要素[4⇓-6],区域产业结构演化是产业结构研究的主要内容,大量学者通过对区域新产业的分析来考察其产业演化路径依赖与路径突破的特征[7⇓⇓⇓⇓-12]。沿海地区是中国产业活动高度集聚与发达的地区[13],产业门类较为齐全,经济基础较好[14],随着改革开放的不断深化,沿海地区产业结构持续优化升级,率先开始了经济转型的进程[15],其产业演化路径既有普遍的演化规律特点,也有根植于中国国情的个性。中国产业发展具有梯度转移的特征,只有明确沿海地区产业演化路径的现状和特点,以及它们对区域经济韧性的作用机制,才能更好地发挥沿海对内陆的引领和带动作用,为其发展提供物质支撑和宝贵经验。此外,作为中国对外开放的前沿,沿海地区吸引了大量外商投资,对外贸易活跃,也更容易受到外部冲击和扰动的影响。因此,以中国沿海地区为研究对象,探讨较发达地区产业结构演化路径依赖和路径突破对区域经济韧性影响具有典型意义。
区域经济韧性是区域研究的热点和前沿领域之一[16⇓-18],韧性理论及其应用经过工程韧性—生态韧性—演化韧性的发展日趋完善[19-20]。“韧性”最初应用于工程领域,关注系统的单一平衡或者静态平衡。1973年Holling将韧性引入生态学提出“生态韧性”的概念,认为其区别于“工程韧性”,具有多重平衡的特点[2,21]。自Reggiani首次从韧性视角探讨空间经济系统的演化后[22],Martin等进一步提出“演化韧性”是影响区域经济发展的各种要素通过不断调整使区域经济实现持续增长的能力,涵盖抵抗、恢复、重新定位和更新4个维度[5,23 -24]。演化韧性是系统在应对急性冲击或慢性燃烧时表现出来的不断改变、适应和转型的能力和过程[18]。这一定义被普遍接受,运用演化经济地理学的相关理论和概念对区域经济韧性进行研究成为主流[25-26]。
路径依赖是演化经济地理学方法的重要基础[23,27],也是理解区域韧性的关键[4]。“路径依赖”(Path Dependence)一词源于古生物学[28],后被广泛应用于历史学、政治学、经济学等学科,由于不同学科的理解不同,目前仍未形成统一的定义。David于1985年首次将路径依赖概念引入经济学[29],路径依赖作为演化经济地理学的基本特征之一,引起了学者的关注。从路径依赖理论来看,先后涌现出技术“锁定”、动态报酬递增、制度滞后等观点,并就其研究对象、来源、性质和普遍性等问题展开了讨论[30⇓-32]。Martin把路径依赖内涵的关键特征归纳为“非遍历性”,即路径依赖的过程或系统是其自身历史演化的结果,具有一定的历史惯性[11,27]。路径突破与路径依赖是相对应的概念,强调新路径的形成与地方历史发展路径并无密切联系,其概念随着路径依赖理论的完善也不断发展。演化经济地理学在关注区域产业演化的路径依赖与路径突破的基础上对区域新产业及其产业演化路径进行了大量研究[33⇓-35],按照技术关联度的大小将区域新产业划分为路径依赖型和路径突破型[36⇓⇓-39]。
当地发展历史对区域韧性的作用在文献中逐渐得到重视[40],Boschma等学者就产业演化路径与区域经济韧性的作用机制展开了讨论,指出区域经济韧性的概念一直与摆脱路径依赖、实现路径突破密切相关,受到区域经济发展转型的影响,认为已有的经济结构和条件既可能成为区域发展的限制,也能为其提供机会,我们需要构建一个新的体系去重新认识韧性框架下路径依赖与路径突破的作用[4]。由于缺乏定量衡量产业演化路径依赖程度的手段,已有的研究产业演化路径对经济韧性影响的文献相对较少且几乎都是基于相关理论的描述性和探索性分析[4,40 -41]。可见,从实证角度出发,基于区域新产业探讨产业演化路径依赖与路径突破对区域经济韧性的影响,对加深产业演化路径和区域经济韧性的认识与理解有重要意义。
关于产业演化路径依赖与路径突破对区域经济韧性的影响机制,学术界主要有3种观点:① 当地原有的资源、技术、基础设施和人才等条件使路径依赖对区域韧性的提高而言利弊并存,且利大于弊。新产业或新技术往往是在原有的基础上演化而来的,它们之间形成的“相互路径依赖”可以促进产业间的联系,加快知识溢出,提高投资效率,有助于区域经济韧性的提高。② 更多的学者强调路径依赖对于区域经济韧性的消极影响,认为韧性意味着要摆脱当地的历史,发展全新的增长路径从而避免路径依赖。因为产业间过于紧密的联系会导致区域经济结构僵化,陷入“锁定”,限制了多样化的过程,削弱了区域经济系统的适应能力,进而对区域经济韧性产生负向作用。③ 在本地创新、外部条件等因素的作用下,一些区域出现了新产业和新技术,它们与原有产业和技术的关联度很低,有助于区域从“锁定”状态“解锁”,实现路径突破[7,17],这些区域经济系统在遭受冲击或扰动时表现出更强的适应能力。因此,“解锁”能力能够一定程度地反映区域经济韧性的高低。
国内已有研究大多从三次产业结构[25,42 -43]、相关多样化和非相关多样化[14,44]、多样化和专业化[45-46]等角度分析区域在位产业的产业结构对区域经济韧性影响,而从新产业角度研究产业演化路径依赖与路径突破对经济韧性影响的文献屈指可数。沿海地区是中国产业发展相对成熟的地区,2020年以占全国不足14%的国土面积,创造了全国53%的GDP,其产业演化路径具有典型性和代表性。基于此,本文重点研究产业演化路径依赖和路径突破与区域经济韧性的联系,通过对上述指标的测度,深入分析其时空分布特征,并运用一步系统GMM估计探讨了产业演化路径依赖和路径突破对区域经济韧性的作用,为提高较发达地区区域经济韧性,增强其应对冲击并实现经济持续增长的能力提供了参考和依据,对发挥沿海地区在中国其他地区的引领和指导作用也具有重要意义。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 数据来源
中国沿海地区包括辽宁、河北、天津、山东、江苏、上海、浙江、福建、台湾、广东、香港、澳门、广西和海南。由于香港、澳门和台湾的数据存在缺失,暂未列入本文研究范围。出口数据来源于联合国商品贸易数据库(UN Comtrade Database)、国研网对外贸易数据库和中国海关数据库,考虑到数据的可获取性和完整性,整理得到2002—2017年世界各国和中国沿海地区HS4位编码产品层面的数据。HS分类以经济部门、原材料属性和加工程度为依据,对于解释中国出口产业的发展情况具有同等效力。GDP、人均GDP、第三产业比重、规模以上工业企业数、城镇登记失业率、财政支出、地区专利申请数、R&D人员全时当量等数据来源于国家统计局、《中国科技统计年鉴》《中国统计年鉴》《中国城市统计年鉴》和沿海各省市统计年鉴。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 区域经济韧性
式中:
经济韧性为正值表示与全国的经济运行情况相比,该地区的表现更为出色;而韧性为负值则表示该地区的经济运行状况较全国平均水平更差,数值越小相差越大。2001年12月中国正式加入世界贸易组织(WTO)后,对外贸易“井喷式”增长,带动了中国,特别是沿海地区的发展。经历上一阶段的经济快速扩张后,受全球金融危机的影响,全国经济增速开始进入收缩期。期间,全国GDP指数在国家政策的作用下出现了短暂的回升,但总体仍保持下降趋势。2012年以来中国经济发展步入新常态,区域经济结构调整成为发展主流。本文以2002—2017年中国沿海各地区每t年到t+T年的经济运行情况为基础,为更准确地分析不同冲击和扰动下区域经济韧性的特点,同时重点关注到金融危机和新常态下经济转型的大背景,结合经济发展的实际情况和国家相关政策进行了分析。
2.2.2 路径依赖度与路径突破度
考察区域产业演化路径特征的一般思路是计算新产业和原有产业的技术关联度[48]。目前应用最广泛的测度产业间技术关联度的方法是由Hidalgo提出的,通过计算两产品在同一国家同时作为具有显性比较优势的产品出口的条件概率得到产业间的关联度[10]。该方法的优势在于摆脱了投入产出数据在统计口径和获取途径等方面的限制,在全球生产网络不断发展和完善的背景下,通过计算各世界出口国家的相关数据,可以更客观地反映产业之间关联程度的普遍规律,而其局限性在于无法直接判断新产业的演化路径类型。因此,Coniglio在Hidalgo等的研究基础上进一步提出了利用出口数据定量识别新产业路径依赖与路径突破的方法[49]。具体步骤如下:
① 确定新产业,即该产业的显性比较优势指数(RCA)在t时< 0.5,且在t+T时> 1。
② 建立全世界出口国家任意一对产业间的M×M关联度矩阵,计算技术关联度。对于国家c的产业i,在t时的RCA < 1,则记为0,否则记为1:
根据矩阵,计算任意一对产业i和产业j的技术关联度:
③ 用Br, t表示区域r在t时具有显性比较优势的产业集合,然后定义Di, r,一个M×R的矩阵,用于衡量每个区域在t+T时的新产业Nr, t+T和原有优势产业之间的相关性,公式为:
式中:使用代表了技术关联度绝对维度的最大值,因为它可能在探索产业多样化的路径依赖方面发挥更好的作用。
④ 构建基于反事实的最大关联度分布函数。采用蒙特卡罗方法,对每个区域r,从t时不具有比较优势的产业集合中,随机抽取数量等于Nr的新产业并计算其最大技术关联度的平均值,重复2000次得到反事实的技术关联度平均值分布函数。
⑤ 对每个新产业的演化路径进行识别,判断其是否属于路径依赖或路径突破型新产业。对于实际新产业的最大技术关联度,如果落在反事实的最大关联度平均值分布的前5%置信区间内,则认为它是路径突破的;如果落在反事实分布95%以上的置信区间内,则认为它是路径依赖的。否则,认为该产业属于随机型新产业。
根据李伟等关于区域产业演化路径依赖度与突破度的定义[36],产业演化路径依赖度(PD)和路径突破度(PC)分别是指某区域在t到t+T年间产生的新产业中路径依赖型和路径突破型新产业所占的比重,公式分别为:
式中:Nr是区域r在t到t+T年的新产业的总数;Nr, pd和Nr, pc分别是该区域同一时间段内路径依赖型和路径突破型新产业的数量。
2.2.3 产业多样化指数
利用Duranton提出的熵值法计算产业多样化指数[50]是目前学术界认可度较高的方法之一,由于本文的产业演化分析基于HS编码产品的出口情况,因此采用地区各产业产品的出口值代替从业人数进行计算。公式为:
式中:VAR表示产业多样化的熵指数,熵指数越大,地区产业多样化程度越高;k是经济系统中出口产业的数量;pi是该地区某产品出口额占总出口额的比重。
2.2.4 模型设定与变量
产业多样化被认为是可能对区域经济韧性产生影响的重要因素之一,用基于熵值法的产业多样化指数表示地区的产业多样化程度。由于计算产业演化路径依赖度与路径突破度所采用的海关出口数据只涵盖了有形产品,并没有统计服务贸易出口情况,因此选取第三产业比重来控制三次产业结构对区域经济韧性的影响。一般认为,经济发展水平更高的地区往往具有更强的区域经济韧性:在经济收缩期能保持自身发展的相对稳定,在经济扩张期则可以实现更快的经济增长,经济发展水平用人均GDP来表征。用规模以上工业企业中非国有的占比表示市场化水平,用地区专利申请数在全国的占比和R&D人员全时当量表示地区创新和科研水平。固定资产投资是促进经济发展的重要手段,固定资产投资率反映了固定资产投资对经济增长的贡献,人均固定资产反映了地区固定资产投资水平。城镇登记失业率在调查失业率数据缺失时也可以从侧面反映实际就业状况的变化趋势,充分就业对经济系统的稳定运行具有积极意义。考虑到上一期的经济运行情况会对当期的经济运行产生影响,所以将经济韧性滞后一期作为解释变量之一。
基于动态面板数据,模型设定为:
式中:r为地区;τ为时间段,即从t到t+T年;α和β为待估计参数;RESr, τ是地区r在时间段τ的经济韧性;RESr, t-1是经济韧性滞后项,核心解释变量PDr, τ和PCr, τ是路径依赖度和路径突破度;Zr, t是一系列控制变量;vr和μτ分别为地区和时间效应;εr, τ为残差项。
考虑到模型设定中区域经济韧性与产业演化路径可能存在双向因果关系,即经济韧性可能也会对产业演化路径产生影响,以及遗漏变量偏差,本文对由此可能产生的内生性问题及解决方法进行讨论。王宇等基于文献研究系统整理了内生性问题产生的原因及其修正方法,其中,针对双向因果和遗漏变量导致的内生性问题,不同学者都采用了工具变量法、固定效应模型、纳入滞后变量、GMM估计和纳入尽可能多的对自变量和因变量都产生影响的控制变量等方法进行修正[51]。文章综合分析了内生性问题来源及修正方法原理后指出,固定效应模型有助于修正遗漏变量偏差,但用于解决双向因果引起的内生性问题缺乏合理性,一般起到辅助作用。工具变量法是借助外部工具变量把具有内生性问题的解释变量拆分成内生和外生两个部分,但在实际操作中,科学而有效的工具变量往往难以获得。GMM估计不仅可以使用前定变量和内生变量的滞后项作为工具变量,也可以用严格外生的变量作为工具变量,在解决动态面板的内生性问题时十分常见。
综上,本文通过纳入滞后变量和更多的控制变量,分别采用固定效应模型、BCFE估计和一步系统GMM估计进行回归并进行对比分析。各变量的描述性统计见表1。为了保证数据的平稳性,克服异方差影响,将部分指标取其对数。为避免出现伪回归,需要对数据进行平稳性检验,本文所有变量均通过了面板数据单位根检验。通过Hausman检验,发现本文模型的P值小于0.01,因此可以采用固定效应模型。
表1 变量描述性统计
Tab. 1
| 变量 | 具体指标 | 符号 | 形式 | 样本数 | 均值 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 因变量 | 区域经济韧性 | 经济韧性指数 | RES | 132 | -0.050 | 0.180 | -0.680 | 0.320 | |
| 自变量 | 路径依赖 | 路径依赖度 | PD | 132 | 0.590 | 0.110 | 0.210 | 0.850 | |
| 路径突破 | 路径突破度 | PC | 132 | 0.400 | 0.110 | 0.120 | 0.790 | ||
| 控制变量 | 产业多样化 | 产业多样化指数 | VAR | ln | 132 | 1.540 | 0.150 | 0.920 | 1.700 |
| 三次产业结构 | 第三产业比重 | TIS | ln | 132 | -0.860 | 0.130 | -1.150 | -0.450 | |
| 经济发展水平 | 人均GDP | EDL | ln | 132 | 10.210 | 0.640 | 8.620 | 11.480 | |
| 市场化水平 | 规模以上工业企业非国有占比 | ML | ln | 132 | -0.130 | 0.160 | -0.890 | -0.010 | |
| 创新能力 | 专利申请数占全国比重 | PPA | ln | 132 | -3.460 | 1.420 | -6.990 | -1.400 | |
| R&D人员全时当量 | RDP | ln | 132 | 8.490 | 1.000 | 5.310 | 10.270 | ||
| 固定资产投资 | 人均固定资产投资 | PFAI | ln | 132 | 9.500 | 0.790 | 7.350 | 11.080 | |
| 固定资产投资占GDP比重 | FAIR | ln | 132 | -0.690 | 0.370 | -1.430 | 0.270 | ||
| 就业情况 | 城镇登记失业率 | UR | ln | 132 | -3.300 | 0.170 | -3.730 | -2.730 |
3 结果分析
3.1 区域经济韧性特征
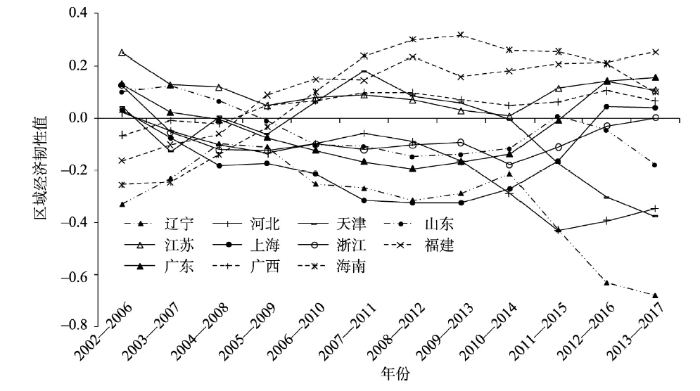
通过计算中国沿海地区2002—2017年的区域经济韧性(图1),发现2007—2008年金融危机发生初期,各地区的经济韧性值大多维持在-0.2~0.1之间,紧接着由于区域间发展特点对经济运行状况产生的不同影响,经济韧性出现了较明显的分异。从长期来看,中国沿海大多地区的经济韧性都维持或恢复到在全国平均水平之上,但也有部分地区经济韧性出现明显的下降趋势且远低于全国平均水平。
图1
图1
2002—2017年中国沿海地区区域经济韧性
Fig. 1
The regional economic resilience of China's coastal areas, 2002-2017
上海和广东作为中国对外开放的重要窗口以及经济发展前沿地区,经济韧性变化趋势有较为一致的表现:遭受金融危机的冲击后持续走低,并在2008—2012年前后达到最低值,相当长的一段时间内都为负值,直到2012—2016年经济韧性才高于全国平均水平。特别是上海作为中国的金融中心,在沿海地区中遭受的冲击最大,2008—2012年经济韧性达到历年最低(-0.324)。在金融危机和新常态下经济发展减速提质等多重压力叠加下,上海和广东受到长时间和较深程度的影响,经济韧性曲线呈“U”型分布。福建、广西和海南的经济韧性不断提高,并较长时间保持在全国平均水平之上。长期以来海南和广西的经济总量在沿海地区中处于较低水平,总体发展落后于其他省市,但随着经济增长速度相对加快,经济韧性得到普遍提升。江苏和浙江在金融危机前保持了较快的发展速度,然而在金融危机和新常态初期新挑战的冲击下,区域经济韧性出现两次下降趋势,在2014年后才逐步回升。尽管两省区域经济韧性的变化趋势十分相似,但与浙江的经济韧性在较长时间内都为负值不同,江苏的经济运行情况始终优于全国平均水平。
从空间差异角度分析,长三角沿海地区和泛珠三角沿海地区内部的经济韧性均存在较大的差异,并没有一致的表现,而以发展传统工业为主的环渤海地区则呈现出波动下降的特征,整体的经济运行状况差于全国平均水平。其中,辽宁的经济韧性在研究期内一直为负数,2013—2017年仅为-0.679,主要是由于长期以来产业发展和转型等问题日益突出导致经济增速放缓,同时也与其GDP“注水”和“挤水”的现象有关。
3.2 产业演化路径特征
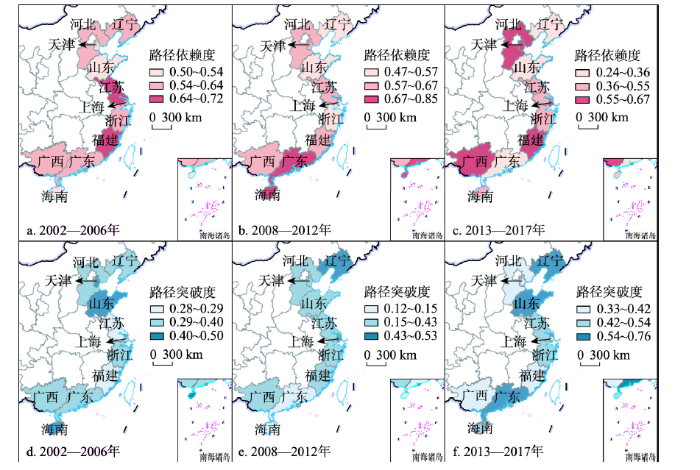
根据定义,产业演化路径依赖度与突破度存在较大程度上此消彼长的关系。图2展示了中国沿海地区产业演化路径依赖度与路径突破度①(①除起止年份外,考虑到2008年全球金融危机的影响,增加2008—2012年作为中间观测年份。),可以看出两者整体分别呈现出波动下降和波动上升的态势。各地区的产业演化处于动态变化过程中,从更大范围的时空格局演变来看,环渤海、长三角和泛珠三角的沿海地区内部并不存在一致的表现。
图2
图2
2002—2017年中国沿海地区产业演化路径依赖度与路径突破度
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Path-dependence and path-creation of China's coastal areas, 2002-2017
研究发现,大多地区从2002—2006年到2008—2012年依赖度的变化趋势与其经济韧性变化保持一致,而同期依赖度较高的地区经济韧性也相对较高,表明在应对金融危机带来的冲击时,路径依赖型新产业的发展对维持区域经济的相对稳定具有积极意义。而对比从2008—2012年到2013—2017年产业演化路径与经济韧性变化的关系,与路径依赖或路径突破变化趋势相似的地区数量相当,则表明金融危机发生较长时间后,以供给侧结构性改革为主基调的新常态时期,在地区差异和不同经济背景的共同作用下,产业演化路径依赖与路径突破都对区域经济韧性产生了重要影响。
对个别表现特殊的省份进一步分析,发现3个时段山东的路径依赖度均在沿海地区的中下水平,路径突破度较高,作为人口人才大省,山东高校数量自2002年的75所增加到2013年的140所,并且十分重视科技研发投入。与此同时,辽宁的依赖度也逐步下降且突破度逐步上升,尽管在经济转型和培育发展新动能方面做出了大量努力并取得一定成果,但面对来自多方面的压力,辽宁的经济仍持续下行,区域经济韧性表现不尽人意。此外,广西的产业演化路径突破度在较长时间内都保持在中高水平,直到2011—2015年以后大幅度降低至沿海地区的平均水平之下,其前期和中期的重要发展动力来源之一是承接东部产业转移,包括大量被政策、地理区位等优势吸引但与原有产业结构相关性不大的路径突破型新产业,新的产业结构逐渐形成后进入的产业,出现依赖度上升和突破度下降的特征。2008—2012年广东和海南的路径依赖度出现大幅上涨,这些地区的外向型经济占有重要地位,在低迷的经济环境下,外商投资和外贸订单更倾向于流入已有的优势产业,新进入产业数量较少。但两者同期的经济韧性形成强烈反差,相比于成功依靠固定资产投资拉动经济发展的海南,以对外贸易为经济发展主要驱动力的广东产业发展受影响的范围更广、程度更深。
综合来看,在研究时段内中国沿海地区产业演化路径依赖度普遍高于路径突破度,表明沿海地区产业结构演化以路径依赖为主,但其优势逐渐减弱,路径突破越来越成为产业演化的新方向。
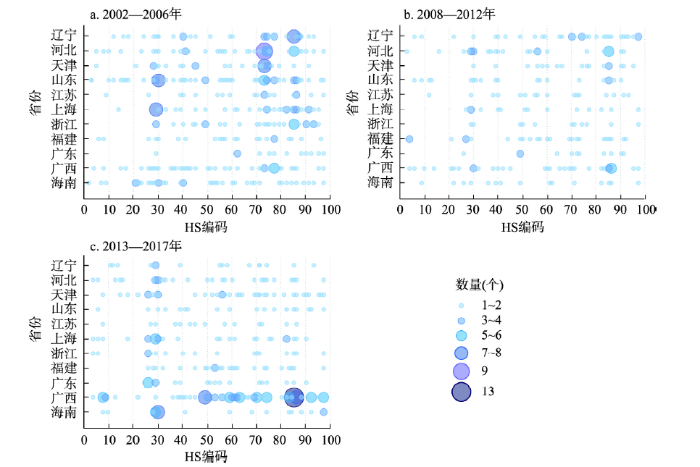
为更直观考察在不同时间内中国沿海各地区新产业的发展情况,本文绘制了2002年、2008年和2013年新进入产品2位HS编码的散点气泡图(图3)。根据《商品名称及编码协调制度》(Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System),2位的HS编码分为98章。可以看出,2002—2006年新产品数量较多,主要集中分布在第72、73章钢铁及其制品,第76章钼及其制品和第84、85章的机械器具类产品、电机和电气设备。到2008—2012年,几乎所有地区新产品的数量都有不同程度的减少,河北、天津、山东和广西在第84章同比保持稍高的进入率,此外,广西在第85章的也有较多新产品进入。2013—2017年大多地区的新产品数量有所增加,产业演化的步伐再度加快。广西新产业数量的增加尤为迅速,多达11章有超过5个产品进入,涵盖纸制品、陶瓷制品、机械器具和电气设备等,经过前期发展初步形成了一定的产业基础,新进入的产业与原有产业关系密切,路径依赖度高于突破度。另外,20章之前农副产品的新产品进入数量在3个年份都较少;第28、29章的无机、有机化学品的新产品数量在2002年和2013年都有较为明显的优势,在2008年也有微弱的聚集。随着钢铁行业去产能等任务的不断深入开展,钢铁及其制品的新产品进入数量大量减少,进而转向发展化学工业、机械制造等技术含量更高的资金密集型产业。
图3
图3
2002—2017年中国沿海地区新产品分布
Fig. 3
Distribution of new products in China's coastal areas, 2002-2017
3.3 产业演化路径依赖与路径突破对区域经济韧性影响
表2分别是固定效应、偏差修正的固定效应和一步系统GMM的估计结果,根据前文关于估计方法的讨论,固定效应和偏差修正的固定效应的结果因存在较明显缺陷,仅作为一步系统GMM结果的参考,起辅助作用。模型1至模型3的结果表明,核心变量路径依赖和路径突破都在5%的水平上显著,回归系数均大于0,且路径突破对于经济韧性提高的促进作用更加明显。
表2 回归分析结果
Tab. 2
| 变量 | 模型1固定效应(FE) | 模型2偏差修正的固定效应(BCFE) | 模型3一步系统GMM |
|---|---|---|---|
| L.RES | 0.774***(10.32) | 1.001***(7.58) | 0.721***(9.33) |
| PD | 0.508**(2.30) | 0.706**(2.09) | 0.959**(1.98) |
| PC | 0.585**(2.37) | 0.811**(2.29) | 1.027**(2.12) |
| VAR | 0.048(0.30) | -0.054(-0.16) | 0.347*(1.97) |
| TIS | -0.575**(-2.57) | -0.832**(-2.24) | -0.266(-1.43) |
| EDL | 0.876(1.05) | 0.275(0.25) | 2.057**(2.10) |
| ML | 0.222(0.88) | 0.077(0.21) | -0.285(-1.66) |
| PPA | 0.098**(3.12) | 0.129**(2.51) | -0.063***(-2.72) |
| RDP | 0.126**(2.71) | 0.158**(2.16) | -0.051(-1.24) |
| PFAI | -1.155(-1.43) | -0.606(-0.55) | -1.994**(-2.10) |
| FAIR | 0.921(1.17) | 0.360(0.33) | 1.847*(1.86) |
| UR | 0.090(0.88) | 0.155(0.88) | -0.326**(-2.01) |
| 样本数 | 121 | 121 | 121 |
| R2 | 0.801 | ||
| AB test for AR(2) | 0.403 | ||
| Sargan test | 0.118 |
注:***、**、*分别表示在1%、5%、10%水平下显著;括号内为t值。
根据模型3,路径依赖(PD)在5%的水平下显著为正,表明产业演化路径依赖对区域经济韧性的提高起到积极作用。在其他条件相同的情况下,路径依赖每增加1%,则区域经济韧性增加0.959%。区域经济韧性受到当地产业发展历程的影响,且有相关实证研究表明,新产业更倾向于在与当地产业相关的产业中产生,由此发展新的增长路径。区域内与现有产业结构相匹配的制度政策、基础设施、生产性服务业、熟练劳动力和组织机构等有利于技术关联性更强的新产业进入与发展,路径依赖型新产业与原有产业之间形成紧密的相互联系,有利于节约成本、促进技术交流和知识溢出,对区域经济韧性的提高起到积极作用。尽管不能否认路径依赖对于区域经济韧性的消极影响,过于紧密的联系会使区域经济结构陷入“锁定”,缺少适应和创新的能力,沉没成本也会让一个区域迈向新增长路径的步伐更加艰难。尤其是在遭受一些特定类型的产业危机(如石油、钢铁危机等)时,更容易造成大范围的衰退,并且更难摆脱危机带来的影响。但就目前中国沿海地区产业演化路径依赖对区域经济韧性的影响来看,路径依赖可能带来的负向作用远不及其产生的积极影响。
而产业演化路径突破(PC)在同样的显著性水平下每提升1%,可以拉动区域经济韧性提升1.027%。路径突破型新产业与原有产业之间的技术关联度较低,在遭受内外部冲击和扰动时,能够有效分散负面影响,起到缓冲器的作用。并且随着突破型新产业的发展,与之配套的设施和服务也逐步完善,为区域经济增长提供了新的动力。此外,路径突破型的新产业和新技术也有助于区域“解锁”,打破由于长期自我强化的路径依赖而僵化的政治、经济和社会关系,使区域经济系统表现出更强的适应能力,提高区域经济韧性。从长远来看,产业演化的路径突破对于区域经济结构调整、要素重新组合也有重要意义。值得注意的是,与当地产业无关的新产业的进入门槛更高,它们需要在劳动力的技能培训、组织咨询等方面付出更多的代价,与其他产业更加松散的联系也让这些新产业更有可能失败和破产。基于路径依赖产生的相关多样性保证了区域在相关领域内的适应性,而产业演化路径突破表现出来的不相关多样性则拓展了已有知识和技能领域的适应能力。这两种情形都有助于提高区域经济韧性,而如何权衡路径依赖与路径突破的关系是未来需要关注的问题。
关于控制变量,模型3中,产业多样化(VAR)和经济发展水平(EDL)对区域经济韧性都有正向效应。产业多样化增加1%,则会使经济韧性增加0.347%,产业多样的地区可以分散外来风险,利用知识和技术的溢出效应,克服由于专业化发展导致的产业结构单一,为区域在冲击和慢性燃烧中适应、改变和转型提供了更多可能性,对区域经济韧性产生积极影响。而经济发展水平每提升1%,将使区域经济韧性提升2.057%,即区域经济发展水平越高则区域经济韧性越高。这与前人研究的结论一致,表明区域产业多样化发展和经济发展水平的提高对经济韧性具有十分积极的作用。地区专利申请数占全国比重(PPA)通过了显著性检验且回归系数为负,但影响作用很小,即专利申请占比的增加会轻微削弱区域经济韧性。这与一般认知不符,结合实际情况分析,其原因可能在于:发明专利占比小,根据《中国科技统计年鉴》,沿海地区专利申请中发明专利的占比在2002年和2017年仅分别为14.9%和32.0%,而同期国外的占比分别达到85.9%和84.1%;专利转化率低,大量科研投入所产出的专利并没有完成转化、实现收益。固定资产投资占GDP比重表示固定资产投资拉动经济增长的能力,其回归系数在10%的水平下显著为正,表明主要依靠投资拉动经济增长的模式对经济韧性的提高具有积极意义,特别在应对冲击时能起到重要作用,比如2008年金融危机背景下的“四万亿计划”对稳定经济发展取得了一定成效。但是,人均固定资产投资表征的固定资产投资水平对经济韧性影响的结果截然相反,作为经济发展基础较好的沿海地区,依旧采取加大投资而不是扩大需求来促进经济增长的方式造成了产能过剩等潜在问题的不断累积,反而降低了区域经济韧性。另外,城镇登记失业率(UR)的上升也会造成经济韧性的降低。
3.4 稳健性检验
为进一步确保回归结果的稳健性,本文通过以下两个方面进行检验:① 替换变量。非国有经济的发展和政府与市场的关系都是衡量市场化水平的重要指标,能从不同的角度反映一个地区市场化的特征。GDP与财政支出的比值体现了在经济发展中政府作用的强弱,可以从侧面体现在政府调控下的市场化水平,政府主导作用的减弱有利于市场更充分发展,因而用GDP与财政支出的比值代替规模以上工业非国有占比表征市场化水平。② 选取长三角核心城市①(①长三角核心城市包括上海、南京、无锡、常州、苏州、南通、扬州、镇江、台州、杭州、宁波、嘉兴、湖州、绍兴、舟山和台州。)2002—2016年市级层面数据,使用地理探测器的因子探测检验产业演化路径依赖与路径突破是否对区域经济韧性产生了影响。受数据获取限制,对部分具体指标也进行了替换:用GDP与财政支出的比值表示市场化水平,用科研综合技术服务业从业人员数表示创新能力。地理探测器不受多重共线性影响,可以有效避免双向因果的内生性问题[56],可以测度各变量对经济韧性的解释力。
表3的模型4至模型6汇报了替换变量后固定效应、偏差修正的固定效应和一步系统GMM的估计结果。其中,核心解释变量路径依赖和路径突破的系数和显著性差异不大,控制变量中经济发展水平、人均固定资产投资、固定资产投资占GDP比重和就业情况的作用方向和显著性也没有发生根本性变化。所以,“产业演化路径依赖和路径突破对提高区域经济韧性都有显著的促进作用,且路径突破的作用更为突出”这一结论是稳健的。模型7因子探测结果表明,路径依赖与路径突破对经济韧性都有显著的解释力,且路径突破的解释力更强,所以,产业演化路径依赖和路径突破会影响经济韧性的结论在市级层面也是稳健的。此外,因子探测结果中控制变量均有不同程度的解释力,也证明了本文控制变量选择的合理性。
表3 稳健性检验结果
Tab. 3
| 变量 | 模型4固定效应(FE) | 模型5偏差修正的固定效应(BCFE) | 模型6一步系统GMM | 模型7因子探测 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.RES | 0.810***(12.31) | 1.031***(7.65) | 0.657***(5.72) | |
| PD | 0.439**(2.24) | 0.664*(1.88) | 1.030*(1.95) | 0.044* |
| PC | 0.506**(0.221) | 0.765**(0.378) | 1.055**(1.98) | 0.071*** |
| VAR | 0.060(-0.38) | -0.164(-0.50) | 0.313(1.15) | 0.085* |
| TIS | -0.585**(-2.29) | -0.796**(-2.05) | -0.423(-1.38) | 0.056* |
| EDL | 0.417(0.49) | 0.009(0.01) | 3.168**(2.32) | 0.122*** |
| ML | 0.027(0.14) | 0.124(0.52) | -0.260(-1.06) | 0.132*** |
| PPA | 0.103**(2.87) | 0.140***(2.67) | -0.022(-0.32) | 0.124*** |
| RDP | 0.157***(3.22) | 0.183**(2.26) | -0.108(-1.18) | |
| PFAI | -0.0266(-0.14) | -0.382(-0.30) | -3.131**(-2.28) | 0.101*** |
| FAIR | -0.750(-0.89) | 0.192(0.15) | 2.895**(2.11) | 0.182*** |
| UR | 0.557(0.65) | 0.150(0.82) | -0.366*(-1.77) | 0.148*** |
| 样本数 | 121 | 121 | 121 | 176 |
| R2 | 0.798 | |||
| AB test for AR(2) | 0.336 | |||
| Sargan test | 0.295 |
注:***、**、*分别表示在1%、5%、10%水平下显著;括号内为t值,模型7的数值为q值。
4 结论和讨论
针对2002—2017年间中国沿海地区经济运行情况所表现出来的区域经济韧性,本文重点研究了产业结构演化路径依赖和路径突破与区域经济韧性的关系,通过对区域经济韧性、路径突破和路径依赖进行测度,探讨了上述指标的时空分布特征,并利用基于动态面板数据的一步系统GMM估计分析了区域经济韧性的主要影响因素,加深了对中国沿海地区经济韧性的认识,为较发达地区区域经济韧性的研究提供了理论和实证支撑。本文得出以下主要结论:
① 受经济、社会和环境等区域差异以及不同类型冲击的影响,中国沿海地区经济韧性的表现各不相同。上海和广东的经济韧性在金融危机与新旧动能转换等多重压力下,呈“U”型分布;福建、广西和海南的经济韧性不断提高并能持续保持在全国平均水平之上;江苏和浙江的经济韧性在金融危机时期和新常态初期分别出现两次下降,而后较快回升,其中,江苏的韧性值始终为正,浙江则普遍为负;环渤海沿海各地区的经济韧性大多时间内均小于0,经济发展速度低于全国平均水平。② 2002—2017年中国沿海地区整体产业演化路径依赖度处于波动下降的态势,而突破度则相应地出现波动上升,且各地区路径依赖度普遍高于路径突破度,说明目前中国沿海地区产业结构演化以路径依赖为主,但其优势逐渐减弱,路径突破越来越成为产业演化的主要方向。从新产业的数量和类型来看,金融危机冲击下各地区新产品的数量明显减少,而随着以钢铁产业为主的去产能等任务的贯彻落实,新产业在钢铁及其制品的进入优势迅速下降,转而集中出现在化工、机械制造等高技术含量的资金密集型产业。③ 产业演化路径依赖和路径突破对区域经济韧性的影响是趋同的,即都存在显著正向效应,其中,路径突破对于区域经济韧性的影响比路径依赖更为突出。此外,区域经济发展水平、人均固定资产投资、固定资产投资占GDP比重和就业情况也是影响经济韧性的重要因素。
我们不仅要承认历史的重要性,更要把产业的演化路径作为分析区域经济发展的关键切入点。本文研究结果与Boschma提出的适应性与适应能力,即路径依赖与路径突破的产业演化过程,均可作为提升区域韧性的重要途径[4],以及Martin把路径依赖与过度限制地区发展的锁定效应区分开的观点一致[27],认为路径依赖和路径突破都可以提高区域在应对冲击和缓慢燃烧时表现出来的经济韧性,部分学者过分地强调路径突破的积极意义而否认路径依赖对区域发展的贡献存在一定的误导性。与此同时,研究结果也证实了辩证地看待不同演化路径,特别是路径依赖的重要性。路径突破对于提高经济韧性有显著的效果,但也要承担更大的风险并付出更高的代价。虽然路径依赖对经济韧性的提高效果不如路径突破,可能存在“锁定”的倾向,但已有的设施、技术和组织机构等基础条件也为相关产业的产生和发展提供了机会。因此,科学地认识产业路径依赖与路径突破对区域经济韧性的影响,为决策者制定产业发展规划提供了参考。
对比以往关于区域经济韧性的研究成果,本文在理论与实证上具有一定的意义:① 区域产业演化路径依赖和路径突破被认为是探讨演化经济地理学视角下区域经济韧性的关键,但已有研究大多仅停留在理论探索的初步阶段,本文在简要梳理相关理论的基础上,以中国沿海地区为例,通过定量方法进一步分析产业演化路径依赖与路径突破对区域经济韧性的影响,弥补了实证研究上的不足。② 利用出口数据计算两产业间的关联度,进而得出中国沿海地区产业演化路径依赖度和路径突破度,摆脱了传统投入产出数据的限制,在经济全球化的背景下可以更客观地反映产业关联和区域产业演化的规律。③ 证实了区域经济发展水平对区域经济韧性的影响是显著且正向的。此外,总结本文的研究还可以得到以下启示:由于路径依赖型和路径突破型新产业在进入门槛、知识溢出等方面具有不同的特征,要在保证路径依赖型新产业充分发展的同时,积极引导路径突破型新产业的进入与扩展,进而使地区经济系统在产业演化过程中变得更有韧性。
本文也存在不足:演化韧性和路径依赖理论的研究仍处于起步阶段,在概念、研究方法等方面尚未形成统一的观点,理论支撑仍有欠缺;制度、文化、社会关系等可能对区域经济韧性产生影响的因素由于缺乏科学合理的量化手段并没有纳入本文模型中。随着获取数据的渠道和手段的增加,未来的研究可以从更全面、准确和客观的角度进行区域经济韧性测度及其影响因素分析。同时,本文研究主要对象是在经济周期内进入的新产业,而经济结构演替涵盖了新产业进入与旧产业退出的过程,未来的研究可以结合产业进入与退出的特征进行分析,更全面地揭示区域产业演化对于经济韧性的影响。
关联数据信息:本文关联实体数据集已在《全球变化数据仓储电子杂志(中英文)》出版,获取地址:
参考文献
Research hotspots of regional resilience and the visualization of research frontiers
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003298
[本文引用: 1]

As a hot regional research realm, regional resilience provides a new research perspective toward regional sustainable development. At the same time, regional resilience is also an important research paradigm of sustainability science. Based on literature from a core database (Web of Science) launched between 1991 and 2019 on the topic of "regional resilience," this study presents a knowledge graph analysis of regional resilience research. The citation visualization analysis software (CiteSpace5.0) was applied. Keywords co-occurrence network analysis, co-citation clustering analysis, social network co-occurrence analysis, and other analytical methods were adopted. This research drew the following three conclusions: 1) The quantity of regional resilience research shows an upward trend, and it mainly focuses on ecosystem, regional economy, social ecosystem, and social well-being. Five countries—including the U.S., Australia, Britain, Canada, China—and research institutes such as the University of Stockholm, University of Queensland, James Cook University, Chinese Academy of Sciences, U.S. Geological Survey, and University of Cambridge are strongly competitive in terms of research on resilience. 2) The representative works of scholars such as Ron Martin, Carl Folke, Angeler D. G., Craig R. Allen, and Gillian Bristow laid a solid knowledge foundation for regional resilience studies. Furthermore, their collaboration deepened the research on regional resilience. Ron Martin is a significant scholar in the field of the theory of regional resilience evolution, and his research reflects how regional resilience evolves from equilibrium theory to evolution theory. 3) Regional economy, social ecosystem, social well-being, and method exploration are hot topics in regional resilience research. According to keyword classification and citation clustering analysis, the research hotspots of regional resilience are mainly concentrated in the following four categories: 1) Due to global warming and increases in human activities, ecosystem disturbances have increased, and the protection of ecosystem diversity has become a long-term research topic. In addition, biodiversity and ecosystem services and management have become new growth points and strategic development directions of geography. 2) Recently, the world economy has been gloomy; global climate is continuously deteriorating, while regional unrest and frictional issues are increasing. At present, with increasing uncertainties in the global economy, how regions maintain long-term development under external strikes has become the core focus of regional resilience research. Not only should the economic structure be adjusted and optimized, but the stable supply of regional food and energy as well as a stable political and social environment should also be emphasized in regional resilience research. 3) Methodological breakthroughs are key points in regional resilience research. Regional resilience is an interdisciplinary concept that requires comprehensive interdisciplinary research, social-economic scenario analysis, and the construction of multilevel models. Exploration of interdisciplinary and multi-level methods is conducive to promoting the standardization and rationalization of regional resilience research. 4) Empirical research is the trend of regional resilience research. Combining resilience research with specific situations is beneficial in solving scientific problems, providing scientific guidance in relevant policies, and boosting the significance of regional resilience in the process of policymaking. With the deepening of the internationalization process, combining specific problems of certain regions and conducting theoretical and empirical research on regional resilience have become an inevitable path for researchers.
区域弹性研究热点与前沿的可视化
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003298
[本文引用: 1]

基于Web of science核心数据库中1991—2019年收录主题为“regional resilience”的文献数据,利用CiteSpace5.0软件,采取关键词共现网络分析、共被引文献聚类分析、社会网络共现分析等方法对区域弹性研究现状进行知识图谱可视化。结果发现:1)区域弹性相关研究文献发表数量总体呈上升趋势,主要集中在生态环境、区域经济、社会生态系统以及社会福祉等领域;美、澳、英、加、中5国以及斯德哥尔摩大学、昆士兰大学、詹姆斯·库克大学、中国科学院、美国地质勘探局、剑桥大学等研究机构在弹性领域具有雄厚的科研实力。2)Ron Martin、Carl Folke、Angeler DG、Craig R Allen以及Gillian Bristow等学者及其代表文章是区域弹性研究的知识基础。3)区域经济、社会生态系统、社会福祉以及方法突破是区域弹性研究的热点内容。未来研究中应结合中国高质量发展背景,构建具有本土特色的区域弹性理论框架和多学科融合的研究范式,为社会高质量、安全发展提供政策建议和实践方案。
New progress in study on resilient cities
DOI:10.22217/upi URL [本文引用: 2]
韧性城市研究新进展
Progress and prospect of urban resilience research
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.011
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of global environmental change and urbanization, various risks and uncertainties have posed an important obstacle on urban security and urban sustainable development. As a potential new approach of urban risk management, urban resilience can improve the ability to resist, dissolve, and adapt when facing risks and uncertainties, and expound the adaptive scheme of risks in the process of rapid urbanization. Urban resilience has been a new topic in geography and related disciplines. Based on the origin and concept of urban resilience research, from the perspective of the impact of various factors (human, environmental, disaster) on urban resilience, this study constructed a theoretical framework of urban resilience, including evaluation and scenario simulation, and discussed the status of urban resilience research, pointing out that there are still many weak links in the theoretical framework, mechanism, practical application, and difference analysis of urban resilience research. Finally, the key directions of urban resilience research were also discussed. The theoretical framework should be used as a guide to promote multi-objective, multi-level, and multi-perspective systematic evaluation research. With the analysis of mechanism as support, studies should aim to achieve a new breakthrough in process simulation of urban resilience and decision making and early warning. Oriented by empirical research, studies should continue to strengthen the application model of multidisciplinary integration and exploration of urban resilience. Considering regional differences, further work should try to achieve a change in urban planning from the unified "one policy for multi-city" approach to the flexible "one policy for one city" approach.
城市韧性研究进展与展望
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.011
[本文引用: 1]

在全球环境变化和快速城市化的背景下,各种不确定风险成为制约城市安全和可持续发展的重要障碍。城市韧性作为一种城市风险治理的新思路,如何提高城市抵御、消解、适应不确定风险的能力,建设有韧性能力的城市,正成为当前地理学及其相关学科领域亟待探索的新课题。论文在概述城市韧性的研究缘起与概念内涵的基础上,从多种要素(人文要素、环境要素、灾害扰动)对城市韧性的影响、城市韧性框架、城市韧性评价及模拟研究等方面出发,对可持续发展视角的城市韧性研究现状进行探讨,并指出当前城市韧性研究在理论框架、作用机理、实证研究、差异性分析等方面仍存在诸多薄弱环节。最后,对城市韧性重点研究方向进行展望,即应以理论框架为引领,推动多目标、多层次、多视角的系统评价研究;以机理解析为支撑,实现城市韧性的动态模拟与决策预警的新突破;以实证研究为导向,继续加强多学科融合和探索城市韧性的应用模式;遵循差异性规律,实现城市规划治理从统一的“多城一策”向灵活的“一城一策”转变。
Towards an evolutionary perspective on regional resilience
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.959481 URL [本文引用: 5]
How regions react to recessions: Resilience and the role of economic structure
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2015.1136410 URL [本文引用: 3]
On the notion of regional economic resilience: Conceptualization and explanation
Path creation in China's industrial evolution
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.006
[本文引用: 2]

In evolutionary economics, the notion of path creation has attracted much attention in recent years. Previous research has expounded the possibility of path dependence and path creation in the process of regional industrial evolution, but it remains unknown that who changes the existing production capacity and accomplishes path creation. This article focuses on regional production capacity, and applies the indicator of density defined by Hidalgo. Based on the data of 424 four-digit industry of 337 prefecture-level cities in China from 1999 to 2012, this article discusses the path creation of China's industrial evolution. It is found that the entry and exit of an industry would break the original production structure of a region and become the creator of a new path. Governmental subsidies, on the one hand, can promote the development of a region's existing production capacity to enhance the regional's path dependence trend, but also can influence industry dynamics and accelerate the process of path creation. The selection of evolutionary path has significant regional differences. This study will help deepen the understanding of the change of China's industrial structure and its regional differentiation, and provides new evidence from developing countries for the development of evolutionary economic geography.
中国区域产业结构演化的路径突破
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.08.006
[本文引用: 2]

在经济转型新阶段,如何突破已有资源条件的束缚,创造新的产业发展路径是区域经济增长的突破口。路径依赖和路径突破是区域创造产业发展路径的两种途径,已有演化经济地理学研究证实区域生产结构的演化依赖地区已有生产能力,是一种路径依赖的结果,而谁是突破区域现有生产能力实现新路径创造的开拓者却尚未得知。本文基于1999-2012年中国337个地级城市的424个四位数产业数据,沿用Hidalgo等人对生产能力的定义,研究中国产业演化过程中路径突破的可能,结果发现:地区新产业的进入以及已有产业的退出有助于地区突破对原有生产结构的依赖,是区域产业发展新路径的创造者。政府补贴一方面有利于地区现有生产能力的提升,增强地区路径依赖趋势;另一方面可为地区带来新的路径,实现路径突破并为区域创造新的发展机会。此外,政府补贴影响产业演化路径选择的效用受地方财政能力限制,并在空间上存在显著差异。
Evolutionary economic geography and regional development
演化经济地理学与区域发展
Regional new industrial development paths: A literature review and future development
区域新产业发展路径: 研究述评与展望
The product space conditions the development of nations
Economies grow by upgrading the products they produce and export. The technology, capital, institutions, and skills needed to make newer products are more easily adapted from some products than from others. Here, we study this network of relatedness between products, or "product space," finding that more-sophisticated products are located in a densely connected core whereas less-sophisticated products occupy a less-connected periphery. Empirically, countries move through the product space by developing goods close to those they currently produce. Most countries can reach the core only by traversing empirically infrequent distances, which may help explain why poor countries have trouble developing more competitive exports and fail to converge to the income levels of rich countries.
Path dependence and regional economic evolution
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbl012 URL [本文引用: 2]
Related variety, trade linkages, and regional growth in Italy
DOI:10.1111/ecge.2009.85.issue-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Green industrial transformation path of Chinese coastal areas based on coupling types of industrial development with environment
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201808009
[本文引用: 1]

<p>As the Chinese population and industrial highly concentrated area, eastern coastal areas accepted a large volume of foreign and domestic investment and became one of the global factories. However, this industrial development process was at the cost of high resources input, environmental pollution, ecological damage and land resource shortage. Taking prefecture-level cities as research units, this paper defined the industrial green transformation coefficient and environmental pressure change coefficient, analyzed the spatial patterns of evolution of industrial structure and efficient and environmental pressure. Further, 114 prefecture-level administrative units were classified into four types of zones with a two-dimensional four-quadrant division method. Also, corresponding suggestions for green transformation routes and environmental regulation were proposed to different zones were proposed. </p><p>As for pressure reduction & industries green transformation zones, they are mainly composed of two types of area, one is the core cities of Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta urban agglomerations and the other is the inland cities taking ecological conservation as the regional main function. We should encourage the former to develop smart and high-level manufacturing, and limit the entering and layout of high-pollution industries for the latter. As for pressure reduction & industries non-green transformation zones, they are only located in several core cities of urban agglomeration, such as Beijing, Tianjin, Hangzhou and Dalian, which have some heavy chemical industrial projects, and some cities in eastern Guangdong and eastern Guangxi. We should strengthen the function of "command and control" at the heart of the urban agglomeration for those core cities, develop modern service industries, limit the development of heavy and chemical industries and drop out low-level manufactures based on the strict environmental standard. Given the environmental problems caused by industrial spatial transfer in some cities of western Guangdong and eastern Guangxi, attention should be given to increasing technical level of transferring products producing and pollutants processing. As for pressure intensification & industries green transformation zones, they mainly include some traditional old industrial base cities. Hence, their industrial restructuring should focus on improving industrial technical level, cultivating and developing new materials, energy-saving and environmental protection industries, and cut backward and excessive production capacity based on strict environmental regulation standards. As for pressure intensification & industries non-green transformation zones, they are mainly distributed in the coastal cities with heavy chemical industry projects or the peripheral cities that undertake the industrial spatial transfer, where the environmental criteria of industrial and space access should be upgraded.</p>
基于产业环境耦合类型的沿海地区产业绿色转型路径研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201808009
[本文引用: 1]

沿海地区高速和高度集聚的产业发展导致其面临严峻的环境污染问题,切实需要在综合考虑地区产业转型特征和环境压力变化规律及其耦合关系的基础上制定科学的产业绿色转型路径和环境管制政策。以沿海地区地级市为空间单元,构建了产业绿色化转型系数,从结构转型和效率转型两个方面对沿海地区2005-2013年产业转型的空间格局进行了刻画,并以产业绿色化转型系数和环境压力系数为指标进行二维四象限划分,将沿海地区114个地级行政单元划分为压力降低产业绿色化转型区、压力降低产业非绿色化转型区、压力加大产业绿色化转型区和压力加大产业非绿色化转型区四种类型区,并针对不同类型区产业发展和环境压力特点,提出对应的产业绿色转型和环境管制建议。
Spatial pattern of urban economic resilience in eastern coastal China and industrial explanation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200486
[本文引用: 2]

Since the global financial crisis in 2008, regional economic resilience has been attracting increasing attention across the world. When facing economic shocks, some regions suffer less and could manage to get through crisis in a short period, while some might be mired in economic stagnation, which mainly depends on the economic resilience of the country. Existing research usually classifies economic resilience into resistance and recovery resilience based on the analysis of a specific economic shock. It is simple and operable in empirical works though, which aims to unravel the economic resilience in a relatively short period and neglects the impacts of longstanding “slow burn” in the urban economy. Thus, this paper divided urban economic resilience into long-term and short-term economic resilience, and further analyzed the features of spatiotemporal distributions of industrial structures (including economic complexity and industrial variety) and urban economic resilience, and explored the impacts of industrial structures on urban economic resilience in different economic development stages with eastern coastal China as a study case. The conclusions are as follows. (1) The economic complexity in the study area is higher in the south and lower in the north, and the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta are the most prominent areas. The distribution of industrial variety is more balanced, while the related variety of center cities is generally higher than that of surrounding cities. Distribution patterns of short-term economic resilience in different periods show great differences, and the long-term economic resilience of the Yangtze River Delta is higher than that in other areas. (2) The elevation of economic complexity and related industrial variety could improve urban long-term economic resilience significantly, while the unrelated variety has no evident impacts, which verifies the importance of knowledge spillover and technology links in the promotion of urban long-term economic resilience. (3) Factors influencing short-term economic resilience vary in different periods. Cities with enormous financial industries were vulnerable to economic shocks in 2008. Comparatively, cities predominated by heavy industries had the lowest economic resilience in the structural adjustment period after 2011. (4) Factors influencing the resistance and recovery resilience on the same shock are different. A higher level of related variety could help cities resist the crisis in 2008, but have no distinct impacts on their recovery, while an elevated level of unrelated variety might harm the recovery from the crisis of 2008. Thus, extending the industrial value chain, establishing local industrial clusters, and upgrading the industrial level are possible ways to raise urban economic resilience.
中国东部沿海地区城市经济韧性的空间差异及其产业结构解释
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200486
[本文引用: 2]

经济韧性的强弱决定着城市在面对冲击时可以快速度过危机还是陷入长期经济发展停滞。本文将城市经济韧性区分为长期经济韧性和短期经济韧性,分析中国东部沿海地级及以上城市的经济韧性和产业结构的时空分异特征,探讨产业结构在不同时期对城市经济韧性的影响。研究发现,东部沿海地区城市不同时期的短期经济韧性及长期经济韧性存在明显的空间差异;长期经济韧性和短期经济韧性的影响因素不同,表征产业整体技术含量的经济复杂度和表征产业关联程度的相关多样化指数能显著提升城市长期经济韧性,短期经济韧性的影响因素则因时期不同而存在差别。延长产业价值链、构建地方产业集群、提升产业层次水平,有助于城市提高经济韧性。
Paths of high-quality development in China's coastal areas
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102003
[本文引用: 1]

High-quality development is the key measure to overcome the middle-income trap and join the advanced economy. With the deepening of reform and opening up, coastal areas have increasingly become the ballast of the economic growth, the center of national manufacturing, the frontier zone for building an innovative country, the pacesetter for constructing an open economy, and the demonstration window for green development. With typical characteristics of high-quality development, coastal areas will effectively drive the hinterland areas to the right track of high-quality development in order to form a strong support for the country's high-quality development, shaping a new pattern of coordinated regional development. According to the status quo and characteristics of high-quality development in coastal areas, this paper focuses on exploring outstanding problems of coastal areas as a whole and the northern, central and southern coastal areas in the process of high-quality development from five aspects of economic growth, industrial strength, innovation ability, opening up and green development. By analyzing realistic reasons for these problems, valuable references for the design of targeted high-quality development paths are designed. In the new era, coastal areas should grasp the historical opportunity of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei coordinated development, Yangtze river delta integration, Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area construction, follow to improve industry core competitiveness, mobilize the vitality of innovation, build high-standard open economy, deepen ecological conservation by combining strategies of industrial upgrading, independent innovation, opening up and ecological civilization. By the method of working in concert to promote high-quality development in the northern, central and southern coastal areas, the leading role of coastal areas can be consolidated.
中国沿海地区高质量发展的路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102003
[本文引用: 1]

高质量发展是跨越中等收入陷阱、跻身发达经济体的关键举措。随着改革开放的深入,沿海地区正日益成为经济增长的压舱石、国家制造业中心、打造创新型国家的前沿地带、开放型经济建设的排头兵、绿色发展的示范窗口,具备高质量发展的典型特征,将有效带动内陆地区步入高质量发展的正轨,形成对整个国家高质量发展的有力支撑,塑造区域协调发展新格局。结合沿海地区高质量发展的现状与特征,本文从经济增长、产业实力、创新能力、对外开放、绿色发展五方面入手,重点探究沿海地区整体以及沿海北部、中部、南部地区在高质量发展进程中的突出问题,分析其背后的现实原因,为设计具有针对性的高质量发展路径提供价值参考。新时代背景下,沿海地区高质量发展需把握京津冀协同发展、长三角一体化、粤港澳大湾区建设的历史性机遇,产业升级战略、自主创新战略、对外开放战略、生态文明战略并济,遵循提升产业核心竞争力、激发创新活力、发展高水平开放型经济、深化生态文明建设等路径,协同推进沿海北部、中部、南部地区高质量发展,巩固沿海地区的引领地位。
Economic resilience characteristics of Shenyang city based on a perspective of industry-enterprise-space
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102012
[本文引用: 1]

In the era of China's New Normal, compared with other regions in China, the Northeast region has been in obvious economic downturn featured by its weak adaption, or in other words, weak regional economic resilience. However, there is a lack of study on how middle or micro economic sectors, particularly industries and enterprises could shape the resilience level of regional macro economy. This paper, therefore, tries to fill this gap by analyzing the multi-level characteristics of Shenyang's economic resilience since 1978, with regard to its economic growth, industrial restructuring, and enterprise spatial dynamics. We found that affected by China's development status, resilience level of Shenyang's economy shows a weak-strong-weak cycle, driven by the fluctuation of its secondary industry. There are obvious differences in the resilience level of old and new paths in Shenyang. In particular, due to its low competitiveness, the resilience level of mechanical industry in old paths has weakened and imposed greater impacts on secondary industry. Meanwhile, the survival rate of old and new enterprises indicates that the resilience level of old paths enterprises is stronger than that of the new paths ones under the context of national economy slowing down; except for enterprises in food industry, the resilience level of old enterprises is stronger than that of the new ones. Moreover, this research indicates that new enterprises of technology-intensive industry such as the old paths and the electronic industry in new paths show a spatial path dependence of city center, and spatial agglomeration has positive effects on enterprises' survival.
基于“产业—企业—空间”的沈阳市经济韧性特征
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102012
[本文引用: 1]

新常态背景下,东北地区与其他区域相比经济下行明显,适应能力较差,即区域经济韧性较弱。产业和企业是区域宏观经济的中微观载体,有助于揭示区域宏观经济韧性的中微观特征,却鲜少有研究。本文从宏观经济增量、中观产业增量及结构变化和微观企业空间动态,分析了1978年以来沈阳市经济韧性的特征。研究发现:① 在全国经济周期影响下,沈阳市经济韧性的变化呈现出“弱—强—弱”的周期性特征,主要是受第二产业韧性的波动变化影响。以支柱产业演替为代表的新老路径产业的韧性变化差异明显,其中老路径产业中机械产业韧性的“强—弱”变化对第二产业的韧性变化影响较大,其韧性减弱主要是由自身竞争力不足造成的。② 在全国经济“增速换挡”放缓的影响下,企业存活率的结果表明,老路径产业企业的韧性强于新路径产业企业的韧性;除食品产业外,其余产业老企业的韧性都强于新企业的韧性。另外初步发现,老路径产业和新路径产业中的电子等技术密集型制造业的新进入企业表现出对中心城区的“空间”路径依赖性,“空间集聚”对企业存活存在正向积极作用。
Review on the evolution of resilience concept and research progress on regional economic resilience
韧性概念演变与区域经济韧性研究进展
Research progress of regional economic resilience and exploration of its application in China
DOI:10.2307/142031 URL [本文引用: 2]
区域经济韧性研究进展和在中国应用的探索
An international literature review of regional economic resilience: Theories and practices based on the evolutionary perspective
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.012
[本文引用: 1]

Regional resilience has become a trendy research branch. However, traditional Chinese research of resilience had been limited within the equilibrium-based epistemology. This article, based on a review of international literature, clarifies different definitions of economic resilience: engineering resilience, ecological resilience, and evolutionary resilience. The article rejects equilibrium-based epistemology of resilience and argues instead the evolutionary perspective. Then, it introduces the formation mechanism of economic resilience from macro and micro aspects; and introduces quantitative measurement of network analysis. This article concludes that resilience should be extended to the economic field and evolutionary-based perspective. Chinese researchers should notice connections between three research branches — namely evolutionary economic geography, innovation geography, and regional resilience. Future research should focus on case studies of urban and regional economies. They should also explore the existing open patent data source to establish the quantitative database of industry space.
国际区域经济韧性研究进展: 基于演化论的理论分析框架介绍
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.012
[本文引用: 1]

区域韧性在中国已成为新兴研究热点,然而国内学者依然将韧性研究局限于均衡论的认识论范畴内。本文首先通过回顾国际最新研究动态从认识论层面辨析均衡论和演化论这两种韧性认知视角的本质区别,由此介绍西方经济韧性的演化论转向。然后从宏观和微观角度阐述演化论视角下区域韧性的形成机制,介绍相关定量测度方法;在此基础上形成系统的西方最新有关研究经济韧性的理论分析框架。未来研究应该在演化论视角基础上强化演化经济地理、创新地理(区域知识网络)和区域韧性这三个研究分支的联系,还应该加强产业历史演化过程的案例研究,并利用专利数据等开放数据源构建产业空间基础数据库。
Understanding urban resilience: A conceptual analysis based on integrated international literature review
城市韧性: 基于国际文献综述的概念解析
Resilience: An evolutionary approach to spatial economic systems
DOI:10.1023/A:1015377515690 URL [本文引用: 1]
Constructing an evolutionary economic geography
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbm021 URL [本文引用: 2]
Regional economic resilience, hysteresis and recessionary shocks
A regional economic resilience approach to the economic revitalization process in Liaoning old industrial base, China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.013
[本文引用: 2]

The concept of regional economic resilience has unique theoretical value for analyzing the evolution of old industrial bases. The article divided the economic cycle of Liaoning old industrial base in 1990-2015 according to the economic growth rate, and constructed a counterfactual function to measure the economic resistance and recoverability of the urban and sub-industry in different stages, revealed the evolution characteristics of regional economic resilience, and reflected the economic revitalization process of Liaoning old industrial base. There were three main findings. First, there was a negative correlation between resistance and recoverability in the same economic cycle, the cities with low resistance were recovering well in the course of subsequent economic revitalization, and there was a 'creative destruction' process. Second, the regional economic resilience was an evolving process, the level of regional resistance to shock was influenced by the recoverability of the previous economic cycle, the shock and the process of recovery itself may lead to change in the region’s economic structure and functions, and these in turn will influence the region’s resistance to subsequent shocks, in other words, resilience both influenced the evolution of regional economies and itself evolved. Third, the economic revitalization process of the Liaoning old industrial base experienced a recession-recovery-decline process, and the process presents an inverted 'N' type, the level of resistance to disturbance was low in Liaoning old industrial base, the secondary industry was more vulnerable to shocks and the tertiary industry had relatively high resistance. Liaoning old industrial base had path dependence and institution locking phenomenon, and the structural-system problem was serious. Liaoning’s economic development relied excessively on traditional heavy-chemical industry, and the development of new strategic industries and modern service industry was slow. Aiming at the regular characteristics of the evolution process of the old industrial base, the paper put forward some suggestions for the economic revitalization of Liaoning old industrial base.
区域经济弹性视角下辽宁老工业基地经济振兴过程分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.013
[本文引用: 2]

区域经济弹性概念对分析老工业基地演变过程有独特的理论价值。依据经济增速划分1990~2015年辽宁老工业基地经济周期,通过构建反事实函数测度不同阶段城市和分产业经济抵抗力和恢复力,揭示了区域经济弹性的演化特征,反映了辽宁老工业基地经济振兴过程,结果发现:同一经济周期中抵抗力和恢复力之间存在负相关关系,抵抗力低受冲击影响严重的城市在随后的经济振兴过程中经济恢复发展好,存在“创造性破坏”过程;区域经济弹性是一个不断演化的过程,区域对冲击的抵抗力水平受前一经济周期恢复力的影响,区域经济弹性在引起区域应对冲击能力的变化同时其自身也因此而发生改变;辽宁老工业基地的经济振兴经历了衰退-恢复-下滑的波动历程,呈现倒“N”型,其面对冲击扰动的抵抗力较低,第二产业更易受到冲击影响,第三产业抵抗力相对较高,老工业基地长期存在路径依赖、制度锁定现象,结构性体制性问题严重,突破能力弱,过度依赖传统重化工业,新兴产业发展缓慢,现代服务业发展严重滞后。针对老工业基地演变过程的规律特征,提出了辽宁老工业基地经济振兴的对策建议。
Review and future prospect of regional economic elasticity research
区域经济弹性研究述评及未来展望
Roepke lecture in economic geography-Rethinking regional path dependence: Beyond lock-in to evolution
Punctuated equilibria: An alternative to phyletic gradualism
Clio and the economics of QWERTY
Path dependence: A foundational concept for historical social science
DOI:10.1007/s11698-006-0005-x URL [本文引用: 1]
A summary of path dependence research
路径依赖研究综述
Why is economic geography not an evolutionary science? Towards an evolutionary economic geography
DOI:10.1093/jeg/lbi022 URL [本文引用: 1]
Relatedness and diversification in the European Union (EU-27) and European Neighbourhood Policy countries
DOI:10.1177/0263774X15614729
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper analyzes the process of industrial diversification in the countries that were part of the European Union (EU-27) and those that were the target of the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) in the period 1995–2010 by means of world trade data derived from the BACI database (elaborated UN Comtrade data). Our results show that in both the EU-27 and the ENP countries, the evolution of the productive structure—as proxied by the export mix—is strongly path-dependent: countries tend to keep a comparative advantage in products that are strongly related to their current productive structure, and they also diversify in nearby products. However, this effect is much stronger for ENP countries, signalling their lower resources and capabilities to diversify in products that are not very related to their productive structure. We also show that the future export structures of countries are affected by their imports: both the EU-27 and ENP countries keep a comparative advantage in products that are strongly related to their imports, but only EU countries show a strong capability to diversify in new products from related import sectors. Our results also hold when controlling for geographical and institutional proximity.
Towards a theory of regional diversification
New industries and urban economic growth: Perspective from evolutionary economic geography
城市新产业与城市经济增长: 演化经济地理学视角
Regional industrial diversification of China: Based on technological relatedness and complexity
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.04.007
[本文引用: 1]

Using export data of the China Customs Database from 2000 to 2016 and methods measuring path-dependent and path-creation new industries and technological complexity of industries, this study analyzed the regional industrial development paths of China. Four types of regional industrial development paths were identified based on technological relatedness and technological complexity dimensions. The results show that, first, Chinese exports have an increasing trend in spatial dispersion, moving from the core cities of the Pearl River Delta to the core cities of the Yangtze River Delta and Shandong Province, and then to the peripheral areas of the Yangtze River Delta, the provincial capital cities of the central and western regions, and Jiangxi Province. Second, regional industrial diversification shows a high level of path dependence. From 2000 to 2016, path-dependent new industries accounted for about 70% of the total, while the figure for path-creation new industries was about 30%. Developed areas in coastal regions and capital cities in the central and western regions showed more path-creation characteristics. Third, in terms of path-dependent new industries, a half of them have a higher technological complexity than their parent incumbent industries. Regarding path-creation new industries, roughly two thirds of them have a higher technological complexity than their corresponding city average. Fourth, coastal regions have more path-creation new industries with a higher technological complexity, while the central and western regions have more path-dependent new industries with lower technological complexity. The results indicate that the Chinese government should take measures to promote the development of path-creation new industries with a higher technological complexity in the central and western regions.
中国区域产业演化路径: 基于技术关联性与技术复杂性的研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.04.007
[本文引用: 1]

论文基于技术关联性与技术复杂性划分出4类区域产业演化路径,利用2000—2016年中国海关进出口贸易数据库,集成不同类型新产业识别方法,在分析中国出口产业空间格局演变基础上重点研究了不同地区产业演化路径存在的差异及变化趋势。研究发现:① 中国出口产业经历了空间分散化过程。2000—2016年中国出口产业首先由粤闽地区向长三角核心城市和山东省等地转移,再向长三角外围城市、中西部省会城市和江西省等地转移。② 中国区域产业演化以路径依赖型为主,但发达地区有更强路径突破性。2000—2016年路径依赖型新产业占新产业总数的70%左右,路径突破型新产业占30%左右。中国东部沿海发达城市和中西部省会城市产业演化更具路径突破性,中西部普通地级市更具路径依赖性。③ 不论是路径依赖型产业分化还是路径突破型产业创生,新产业不必然具有更高技术复杂度。在路径依赖型新产业中,约一半的技术复杂度高于其在位母产业。在路径突破型新产业中,约2/3的技术复杂度高于城市平均水平。④ 不同地区产业演化路径存在较大差异,东部发达地区发展出更多路径突破型新产业,并且新产业技术复杂度高于城市平均水平;中西部普通地级市多充分利用现有知识与技术发展技术复杂度更低的新产业。从变化趋势来看,东部沿海地区路径突破且技术复杂度提高型新产业逐步增多,中西部普通地级市路径依赖且技术复杂度降低型新产业一直占有较高比重。因此,中国政府亟需制定政策推动中西部普通地级市产业发展的路径突破。
Regional industrial development and evolution: Path dependence or path creation?
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 1]

Regional development is a process in which industries develop, transform and upgrade constantly. Evolutionary economic geography understands the spatial evolution of firm, industry, cluster, network, city and region through the lens of firm entry, growth and exit, and argues that regional industrial evolution is path dependent and determined by inter-industrial technological relatedness. However, path dependence theory overemphasizes the endogenous factors in regional industrial development and ignores the critical role of external linkages and institutional factors, which would bring path creation for regional development. In China, there has been dramatic transformation in regional industrial structure since the economic reform. Empirical studies indicate that technological relatedness has indeed significantly determined regional industrial evolution, suggesting a path dependent process. Meanwhile, marketization, globalization and regional decentralization provide great opportunities to create new industries for regional development. In particular, external linkage, institutional factors and purposeful and strategic actions of local actors would stimulate path creation.
区域产业发展演化: 路径依赖还是路径创造?
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 1]

区域发展是区域产业不断演化、转型与升级的过程。近年来发展起来的演化经济地理学旨在通过分析企业进入、成长、衰退和退出等动态过程阐释企业、产业、集群、网络、城市和区域的空间演化,认为区域产业发展演化遵循路径依赖,并决定于产业技术关联。然而路径依赖式演化理论过于强调内生发展过程,忽视了外生因素和制度变革带来的路径创造机会。中国处于经济转型时期,区域产业结构变动剧烈。技术关联推动了区域产业演化,显示中国区域产业演化具有路径依赖性,同时市场化、全球化和分权化的经济转型过程为区域产业发展创造了新路径。外部联系、制度安排、行为主体的战略性行为等促进了路径创造。
Evolution of export product space in China: Path-dependent or path-breaking?
中国对外贸易产品空间路径演化
The role of path-dependence in the resilience of EU regions
DOI:10.1080/09654313.2018.1458284 URL [本文引用: 2]
Exploring regional economic resilience
A comparative analysis of the economic transition process of China's old industrial cities based on evolutionary resilience theory
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804013
[本文引用: 1]

The 2008 international financial crisis had a severe impact on urban economic development globally, which stimulated a new wave of discussion on the importance of urban economic transformation. Compared to the past, Chinese cities are facing tougher challenges in sustaining economic development through transformation because of the slowdown in economic growth nationally. Previous studies mainly focused on the strategies and countermeasures of urban economic transformation, and ignored how local economies develop, adapt, and transform over time. Moreover, there have been no comparative studies among cities in eastern, central and western China. Drawing on the theory of evolutionary resilience, this study examined three typical old industrial cities (Shenyang, Chongqing and Wuhan) to compare and contrast their transformations since 1978 using economic cycle modeling and shift-share methods. Results showed that: (1) economic growth in Chongqing and Wuhan has been above national average since the mid-1990s, whereas that of Shenyang has fluctuated periodically and shown a periodic oscillation phenomenon. (2) Since the 1990s, the shift of industrial structure in Shenyang has been volatile, and the increase in the relative share of the tertiary industry has been mainly the result of the deceleration of growth in the secondary industry. Chongqing and Wuhan, on the other hand, are more stable in industrial restructuring. (3) Since the end of the 1990s, the transformation of the manufacturing industry of Shenyang and Wuhan has been affected mainly by the upgrading of an old path, whilst the transformation of manufacturing industry of Chongqing has been the result of both old and new paths, which contributes to the higher growth rate. (4) Since the beginning of the 21st century, the evolution of the new path in Shenyang has featured a low-end trend, in contrast the evolution of the new path in Chongqing and Wuhan has shown a high-end trend. In conclusion, this paper illustrates the value of applying the resilience theory to the study of urban economic transition and enriches the practical value of the theory.
基于演化弹性理论的中国老工业城市经济转型过程比较
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804013
[本文引用: 1]

运用演化弹性理论(evolutionary resilience)采用经济周期模型法和偏离—份额法,从增长和结构两个方面,比较分析沈阳市、重庆市和武汉市3个典型老工业城市改革开放以来经济发展和转型过程。结果发现:① 重庆市和武汉市经济增长能力水平具有显著地以20世纪90年代中期为分界的阶段性特征;沈阳市经济发展过程呈现出适应循环周期特征,目前处于由维持向释放过渡的阶段。② 20世纪90年代以来,沈阳市3次产业结构转换方向具有较大的波动性,第三产业份额的增加主要是第二产业增长放慢的结果。重庆市和武汉市3次产业结构转换方向具有较强的稳定性。③ 20世纪90年代末以后,沈阳市和武汉市制造业结构演替受老路径增长能力变化影响较大,重庆市制造业结构演替是在新老路径都保持较高增长能力背景下稳步推进的。④ 21世纪初以来,沈阳市新路径的演化呈现出低端化特征,而重庆市和武汉市新路径的演化呈现出高端化特征。本文将弹性理论应用到城市经济转型研究,实证了弹性理论的实践应用价值。
Analysis of the regional economic resilience characteristics based on Shift-Share method in Liaoning old industrial base
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180245
[本文引用: 1]

It is of great significance to study the economic resilience characteristics of old industrial bases to promote the revitalization of these decayed old industrial areas and to enhance their capacity on resisting against domestic and global disruptions. This paper uses the concept of regional economic resilience to show the mechanisms underlying the economic development of Liaoning Province. First, it divides the economic growth rate of Liaoning Province from 1990-2015 into different economic cycles. Then, this paper characterizes the regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province by measuring its urban economic resistance and recovery feature in different periods. Meanwhile, the paper explores the mechanism underlying regional economic resilience by decomposing regional economic resilience into two aspects through the Shift-Share method: the industrial structure and the regional competitiveness. We obtained the following three main findings. First, regional economic resilience displays different characteristics which are dynamically changing across different periods. Compared with the whole nation, urban economy of Liaoning Province shows a lower resistance capacity against various disturbance, and it is more vulnerable to these disruptions. Second, both urban industrial structure and regional competitiveness can affect the capacity of regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province. We found that the regional competitiveness plays a more significant role, as the capacity of Liaoning’s regional economic resilience is constrained by its industrial structure and competitiveness. Third, “path dependence” has affected the development of service industry in the province for a long time, which is featured by the low level of industry structure and weak competitiveness. We also discovered that there exists a serious mismatch between the industrial structure level and the competitiveness in the secondary industry. Influenced by the phenomenon of institutional locking under the path dependence, the state-owned economy, which is often of poor management, accounts for a large proportion in the secondary industry. These all restrict the regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province. Aiming at exploring the characteristics and internal mechanism of regional economic resilience, the paper put forward some suggestions for the economic revitalization of Liaoning old industrial base.
基于Shift-Share的辽宁老工业基地区域经济弹性特征分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180245
[本文引用: 1]

研究老工业基地经济弹性特征对于增强其应对国内外扰动,促进落后的老工业基地全面振兴具有重要意义。本文采用区域经济弹性概念,在对1990—2015年辽宁老工业基地经济周期划分的基础上,测度各城市不同周期中经济抵抗力和恢复力表征区域经济弹性,借助shift-share分析法将区域经济弹性分解为产业结构分量和区域竞争力分量,揭示区域经济弹性的作用机制,结果发现:在不同时段内的区域经济弹性具有动态差异性特征,辽宁省对冲击扰动的抵抗力较低,容易遭受冲击影响;城市产业结构和区域竞争力均对区域经济弹性产生重要作用,且区域竞争力起主导作用,当前辽宁区域经济弹性受产业结构素质低和竞争力弱双重约束;服务业受老工业基地“路径依赖”影响,长期存在结构水平低和竞争力弱问题,第二产业结构素质和竞争力不匹配问题严重,路径依赖下的制度锁定现象仍旧存在,这都限制了辽宁的区域经济弹性水平。针对区域经济弹性特征和内部机制,提出了促进辽宁老工业基地经济振兴的对策建议。
Industrial diversity, innovation, and economic resilience: Empirical analysis of the Pearl River Delta in the post-financial crisis era.
产业多样化、创新与经济韧性: 基于后危机时期珠三角的实证
Influence of industrial agglomeration on the industrial resilience of the Yellow River Basin
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.05.010
[本文引用: 1]

Economic resilience is a hotspot in the field of economic geography, and regional industrial structure is considered to be the most important factor affecting economic resilience. At present, the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin has become a national strategy. It is of great theoretical and practical significance to scientifically evaluate the industrial toughness of the Yellow River Basin and to investigate the impact of industrial agglomeration on the industrial resilience. In this article, 90 cities in the Yellow River Basin are taken as research areas. The industrial resilience level of the region is measured from two levels of resistance and recoverability. An econometric model is constructed to examine the impact of different cluster types of industrial clusters, such as specialization, diversity, related diversity, and unrelated diversity, on the industrial resilience of the region. The main conclusions are as follows: 1) The industrial resilience level of the Yellow River Basin is relatively high as a whole. Most cities have strong resistance to external shocks and strong resilience after external disturbances recedes. 2) There are significant spatial differences in industrial resilience in the Yellow River Basin. The areas with high recoverability level are mainly concentrated in Inner Mongolia, Shandong and some cities of Qinghai, while the resilience of Gansu and Qinghai is relatively low. The spatial distribution of resistance level is higher in the west and lower in the east. 3) Industrial development in a single industrial structure area is easier to recover from the impact of external disturbances. A high concentration of a certain industry will increase the risk of regional industry being subjected to external shocks. Diversified and related industrial structures are more conducive to improving the resistance of regional industry to adverse disturbances, and also to achieving faster regional recovery from the impact of the crisis. 4) In order to improve the industrial resilience of the Yellow River Basin, we should avoid over-specialization and concentration of an industry. While promoting the diversification of industries, we should also pay attention to improving the forward-backward linkages and linkages between industries.
产业集聚对黄河流域工业韧性的影响研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.05.010
[本文引用: 1]

经济韧性是经济地理学领域的研究热点,区域产业结构被认为是影响经济韧性的最重要因素。2019年以来,黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展已上升为国家战略,对黄河流域工业韧性进行系统评价并考察产业集聚对工业韧性的影响具有重要的理论和现实意义。以黄河流域为研究区域,从抵抗力和恢复力2个层面刻画区域工业韧性,构建计量模型考察专业化、多样性、相关多样性、非相关多样性等不同产业集聚类型对工业韧性的影响,研究发现:① 黄河流域工业韧性水平整体较高,绝大多数城市对外部冲击有着较强的抵抗力,同时在外部扰动退去后有着较强的恢复力;② 黄河流域工业韧性的空间差异显著:恢复力水平较高的地区主要集中在内蒙古、山东,甘肃和青海的恢复力相对较低;抵抗力水平在空间上呈西高东低的分布特征;③ 产业结构单一地区的工业发展更容易从外部扰动的影响中恢复,对某一产业的高度集中会增大区域工业受到外部冲击的风险,多样且关联的产业结构更有利于提高区域工业应对不利扰动的抵抗力,也有利于区域从危机影响中实现更快的恢复;④ 提高黄河流域的工业韧性,要避免对某一个产业的过度专业化集中,在推动产业多样化发展的同时,要注意提高产业的前后向联系和关联水平。
Specialization, variety and economic resilience of specialized towns in Foshan
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.011
[本文引用: 1]

Since the economic reforms and opening-up, the process of rural industrialization has led to the development of a large number of specialized towns which have significant implications for the Chinese economy. However, due to their labor-intensive, export-oriented and low-tech industrial structure, the economies of the specialized towns became fragile when the financial crisis in 2008 gave rise to a turbulent global market. Specialization of the towns, which used to generate significant effects of localization economies, shows its weakness in coping with the recession after the economic crisis. The sustainable development of the specialized towns in China emerges as an important issue requiring further scholarly enquiry. The newly developed economic resilience theory has provided a valuable and useful framework to explore the development path of the specialized towns, and the article has in turn served as an important empirical study for the theory at the town level. Economic resilience is associated with the capacity to withstand or recover from economic, social, and environmental shocks to its developmental growth path, or to transit to a new, sustainable one. One of the critical factors to shape economic resilience is the attribute of the industrial structure which can define a region’s ability to adjust and adapt to shocks. Despite an ongoing debate on the role played by specialization and variety, it is increasingly agreed that a greater economic diversity is related to a greater resilience of the economies. Based on the panel data of 32 specialized towns in Foshan City and a detailed case study of Xiqiao, a town specialized in textile, this article investigates the relationship between specialization, related/unrelated variety and economic resilience. The regression results suggest that specialization and related variety exert negative effects on economic resilience, whereas unrelated variety plays an active role. Our study supports the argument, which is well-documented in the existing literature, that specialization is more likely to be stuck in negative “lock-in” with adaptation. However, the effect of related variety is not as positive as expected. For low-level labor-intensive industries, their low technology level and weak cooperation among firms have seriously prevented efficient and effective knowledge exchange which is crucial for innovation and resilient ability. The Xiqiao case further indicates that effects of specialization and related variety on economic resilience are limited even the local government has actively intervened in promoting industrial upgrading through a series of approaches such as industrial park construction, labor training, subsidies and other preferential policies. Unrelated variety is conducive to foster the development of new industries, which can help to absorb unemployed labors caused by the shocks and maintain the resilience level. Thus, the specialized towns should consider an industrial structure of greater unrelated variety to boost necessary restructuring process and to engage in new growth paths.
佛山市产业专业化、多样化与经济韧性的关系研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.011
[本文引用: 1]

以2008年和2013年佛山市30个专业镇的数据为基础,分析其在经济冲击抵抗期的经济韧性。分析结果显示,佛山市专业镇在经济危机之后整体经济韧性恢复缓慢,专业化和相关多样化产业的发展不再有助于经济韧性的提升,而非相关多样化则相反。传统专业化的集聚优势式微,以低水平劳动密集型产业为主的专业化易于导致经济的脆弱性;相关多样化因技术含量低和协作关系弱的限制也无法发挥作用,虽然地方政府采取积极干预的手段,但效果并不明显;非相关多样化的发展则有利于培育新的产业结构,弥补受危机影响而流失的劳动力,维持地区的经济韧性。与既往研究相比,研究结果同样支持高度专业化区域经济脆弱性更大、稳健性更低的主流观点,但是传统观点一是多侧重于某个视角,并未将专业化与多样化进行对比分析;二是在多样化研究中并不区分相关多样化和非相关多样化的对经济韧性作用。结论认为,在专业镇持续转型的背景下,发展相关多样化产业不利于提高其经济韧性,而非相关多样化产业则是积极有利的,应该予以大力鼓励。专业镇作为珠三角经济发展的成功经验,其传统发展模式正面临着严峻的挑战,应积极探索建立新的多样化发展模式。
Economic resilience and spatial divergence in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200418
[本文引用: 1]

The contemporary research of measuring regional economic resilience tends to focus on GDP index, while lacks of considering the other dimensions. Meanwhile, it overlooks the impacts from extra-regional linkage. Therefore, this study takes the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) as an example to measure the economic resilience based on five selected economic indicators, namely, GDP, gross export value, industrial added value, total retail sales of consumer goods, and number of the unemployed. Drawing upon the Resis index proposed by Martin and Gardiner in 2019, this paper calculated the relative resilience of cities in GBA. The result showed that Shenzhen has the best resilience, Guangzhou and Foshan ranked second, followed by Dongguan and Zhuhai. In contrast, Hong Kong and Macao have the worst resilience. This paper then explains the causes of regional divergence through the perspective of relational economic geography. It is argued that strategic coupling plays an important role in shaping the intra-regional divergence of resilience in the GBA. The main conclusions are as follows: First, single dimension shows limitations in depicting regional economic resilience, while multi-dimensional indicators reveals a distinctive divergence among different types of regional economic resilience. Second, intra-regional divergence of economic resilience in the GBA has been developed, which is not relevant to location and the GDP scale, but is more related to industrial economic structure and modes of embeddedness in global production networks. Third, strategic coupling can explain the intra-regional divergence. Shenzhen has been benefited from absorptive coupling with the best resilience, while Guangzhou and Foshan cities are in the medium, and Hong Kong and Macao have the worst resilience due to captive coupling with global financial and hotel networks. This paper contributes the literature with a fresh empirical case of regional resilience in the GBA and also provides an alternative theoretical framework that involves extra-regional linkages into analysis. This paper calls for more attentions of qualitative research on regional economic resilience in future, in terms of the variety of resilience from economic to social dimensions and causal mechanism of how resilience is fostered and exerts power in resistance of the shock, particularly in relation to extra-regional linkage in the contemporary global economy.
粤港澳大湾区经济韧性的特征与空间差异研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200418
[本文引用: 1]

当前区域经济韧性的测度研究的测度维度较为单一地聚焦在GDP之上,缺乏揭示韧性在其它经济指标上的表现;同时过于注重区域内因素,忽略了外向联系的影响。因此,本研究以粤港澳大湾区为例,选择5个经济指标对大湾区的经济韧性进行多维度测算,并借助关系经济地理学理论视角,对区域内部差异的形成原因给予解释。主要得到三个结论:第一,区域的经济韧性难以从单一维度来判定,多维度指标所揭示的经济韧性存在显著差异,其中GDP所表现出来的区域经济韧性较为保守,而就业指标所表现出来的经济韧性变动较大。第二,大湾区内部各城市的经济韧性存在显著差异,这些差异与区位和GDP规模无显著关系,而与其产业经济结构和嵌入全球生产网络方式有显著关系。第三,湾区城市在经济韧性表现的差异可以用战略耦合来进行初步解释,深圳因自主耦合而经济韧性表现最佳,佛山和广州次之,香港和澳门因以依附耦合的方式嵌入全球金融和酒店网络,因而经济韧性相对较差。本文为经济韧性研究提供了大湾区案例和新的分析视角,推动了关系经济地理学在经济韧性研究中的应用。本文建议未来要重视基于定性方法的经济韧性研究。
Progress of research on technological relatedness in the perspective of evolutionary economic geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

Technological relatedness as a key concept at present in evolutionary economic geography (EEG) is of great significance for the development of EEG and studies on economic growth path. This article explores the definition and measurement of technological relatedness and its micro-mechanism, and reviews the literature on how technological relatedness influences product evolution on different scales, including country, regional, and firm level product evolution. Even though the mechanisms differ slightly by scale, most studies confirm the existence of path dependence. In other words, product evolution path is dependent of technological relatedness. However, several studies find that some countries, regions, and firms do not follow their existing technological relatedness but break the path. They investigate the source of path breaking, finding that path breaking derives from some internal or external forces. China's special development path is not only a supplement for Western evolutionary economic geography theories but also an important opportunity for the development of the emerging Chinese evolutionary economic geography.
演化经济地理视角下的技术关联研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.02.006
[本文引用: 1]

技术关联是现阶段演化经济地理学的重要概念,对演化经济地理学的发展和现实经济增长路径的探索具有重要意义。本文在演化经济地理学的背景下,探讨技术关联的概念和测度方法,从静态和动态2个视角探究技术关联影响产品演化的微观作用机制,并在国家、区域和企业等不同尺度上梳理了相关研究成果,绝大多数研究证明了产品演化路径显著依赖技术关联,即遵循路径依赖过程。近年来一些研究成果发现,有些区域通过向技术不相关产品进行演化从而实现了路径突破,并对其原因进行剖析,发现金融危机与扶持政策等外生力量和地方环境与制度等内生变量都会导致路径突破。中国发展路径的特殊性为西方演化经济地理学研究提供很好的案例,同时也为中国演化经济地理学的发展创造重要契机。
The pattern of structural change: Testing the product space framework
DOI:10.1093/icc/dty009 URL [本文引用: 1]
Diversity and specialisation in cities: Why, where and when does it matter?
Dealing with endogenity issues in managenment research: A review and solutions
管理学研究中的内生性问题及修正方法
A finite sample correction for the variance of linear efficient two-step GMM estimators
DOI:10.1016/j.jeconom.2004.02.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Inflection point of inverted U-curve for urbanization and the urban-rural inequality in China: An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data
中国城镇化与城乡收入差距的“倒U型”拐点测度: 基于东、中、西部地区省际面板数据的实证研究
A comparative study on dynamic panel parameter estimation
动态面板模型参数估计方法的比较研究
Bootstrap-based bias correction and inference for dynamic panels with fixed effects
DOI:10.1177/1536867X1501500404
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this article, we describe a new command, xtbcfe, that performs the iterative bootstrap-based bias correction for the fixed-effects estimator in dynamic panels proposed by Everaert and Pozzi (2007, Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 31: 1160–1184). We first simplify the core of their algorithm by using the invariance principle and subsequently extend it to allow for unbalanced and higher-order dynamic panels. We implement various bootstrap error resampling schemes to account for general heteroskedasticity and contemporaneous cross-sectional dependence. Inference can be performed using a bootstrapped variance–covariance matrix or percentile intervals. Monte Carlo simulations show that the simplification of the original algorithm results in a further bias reduction for very small T. The Monte Carlo results also support the bootstrap-based bias correction in higher-order dynamic panels and panels with cross-sectional dependence. We illustrate the command with an empirical example estimating a dynamic labor–demand function.
Research on the spatial-temporal differentiation and driving force of green economic efficiency based on the geographic detector model
基于地理探测器的绿色经济效率时空分异及驱动力研究