1 引言
伴随经济社会发展,城镇化内涵不断丰富。学者们对城镇化认知由一维的城市人口数量变化向城市人口、土地、经济、社会等多维质量目标转型[6],内在逻辑是快速工业化驱动城市扩张的资本积累过程[7]。进入高质量发展阶段,城镇化关注人地关系重塑,重点是面向可持续的“人的市民化进程”。基于此逻辑,新型城镇化的空间价值取向着重平衡“资本”与“人本”的关系,明确“以人为本”的需求导向[8-9]。因此,从人地关系重塑下的城镇化模式转型来看,新时期城镇化的核心是实现人的城镇化与增进居民福祉,本质是从结构主义到人本主义的转变[10]。人本性、协同性、包容性与可持续性成为理解城镇化内涵的新框架[11]。总体而言,上述框架主要聚焦于人地关系转型的供给侧系统目标优化。进一步从要素流动视角来看,各类生产要素由乡村到城市的单向集聚转变为城乡双向流动与溢出[12]。城乡融合[13]、社会融合[14]、居民福祉[15]等重大议题倍受关注。特别是乡村振兴战略实施以来,新型城镇化与乡村振兴共生效应与耦合机制成为热点话题[16]。与此同时,伴随农业转移人口市民化、城市空间重塑与社会发展权利分化的凸显,更多研究转向“自下而上”的城镇化需求侧目标。对空间正义[17]、非正规就业[18]等重要问题的关注,为解析城镇化内涵与特征提供了新的研究视角。
综上所述,现有关于城镇化研究成果丰硕,为本文提供重要参考。但尚有以下问题值得探讨。首先,城镇化内涵认知仍有进一步丰富空间。现有研究注重人口、土地、经济等供给侧系统目标优化,是一种“自上而下”的城镇化方案[24]。而进入新阶段,满足人们需求侧多维目标协同的“自下而上”逻辑,可为丰富城镇化内涵提供新思路。其次,中国城镇化时空分异机制有待进一步丰富。这不仅取决于各地区经济发展水平差异,更与其城镇化道路的结构性分化关系密切。同时,以往研究主要聚焦于影响因素的静态分析,而从动态视角分析城镇化主要驱动力演变相对缺乏。
鉴于此,本文尝试从3个方面丰富相关研究:首先,基于需求侧多维目标协同的“自下而上”视角,从人居生活、人文环境、人城关系等三个维度界定城镇化内涵和评价体系,突出城镇化的新特征;其次,对2010—2020年中国城镇化时空分异进行实证分析,并对比新型城镇化战略实施前后中国城镇化的变化;最后,尝试从直接作用路径和间接作用机制出发,构建城镇化空间分异机制框架,以更好识别城镇化时空分异的驱动力,尤其对新型城镇化战略实施前后的驱动因素进行比较。本文有助于丰富对城镇化的内涵认识,为各地区实行差别化的城镇化发展路径提供参考。
2 需求侧多维目标协同的城镇化内涵
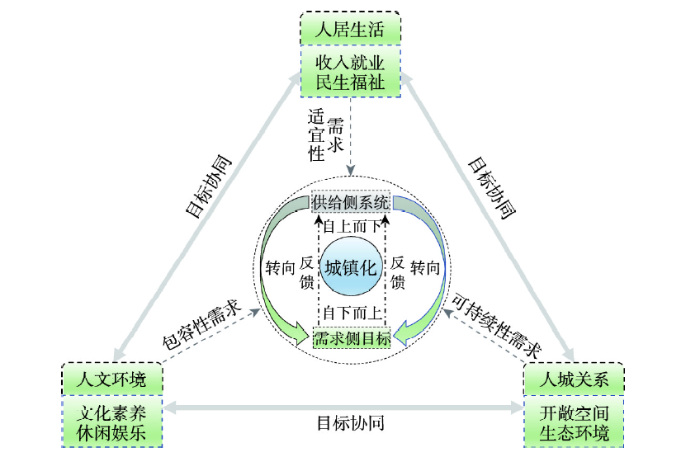
与传统城镇化“自上而下”的供给侧系统目标优化不同,进入新阶段,尤其是新型城镇化战略实施以来,基于“自下而上”的需求侧多维目标协同成为城镇化的逻辑起点,具体是适宜的人居生活、包容的人文环境、可持续的人城关系等三维需求目标集成(图1)。人居生活、人文环境与人城关系均从需求侧出发,以提升居民身份认同、安全保障以及生活激励为目标。缩小人居生活差距、改善人文环境状况、优化人城关系既体现人本性、促进社会公平,又充分体现城镇化的包容性特征。适宜的人居生活、包容的人文环境、可持续的人城关系有机融合发展,可进一步提高经济、人口、社会、生态等协同性,促进城市可持续健康发展。
图1
图1
面向需求侧多维目标协同的城镇化
Fig. 1
Urbanization based on demand-side multi-dimensional goals
其次,包容的人文环境反映了居民的社会文化环境需求,是城镇化的重要保障,主要体现为文化素养提升以及多元包容的休闲娱乐等需求[30]。文化素养提升是人的市民化内在支撑。通过提高受教育年限,促进人力资本积累,可以更好提升文化素养。而关注历史文化遗产与多元现代文化融合,成为维护人与城市情感链接、提升人的归属感与获得感的重要纽带。因此,在城市更新过程中,注重“城市文脉”的保护与延续,同时吸纳与时俱进的现代文化色彩,成为城镇化的必然要求。基于此,本文用平均受教育年限衡量文化素养,用博物馆、公共图书馆和艺术表演场馆等文化场馆总数表征城市文化与娱乐等资源水平。
基于上述分析,本文从人居生活、人文环境、人城关系等需求侧多维目标出发,选取12个典型指标,构建城镇化评价体系(表1)。
表1 城镇化评价指标体系
Tab. 1
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 指标层 | 信息冗余度 | 权重 | 指标属性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人居生活 | 收入就业 | 城镇化率 | 0.0224 | 0.0868 | 正向 |
| 城镇居民人均收入 | 0.0378 | 0.1464 | 正向 | ||
| 城镇登记失业人员 | 0.0079 | 0.0305 | 负向 | ||
| 民生福祉 | 普通小学师生比 | 0.0279 | 0.1080 | 正向 | |
| 平均预期寿命 | 0.0137 | 0.0531 | 正向 | ||
| 房价收入比 | 0.0064 | 0.0248 | 负向 | ||
| 人文环境 | 文化素养 | 平均受教育年限 | 0.0208 | 0.0805 | 正向 |
| 休闲娱乐 | 文化场馆数量 | 0.0361 | 0.1398 | 正向 | |
| 人城关系 | 开敞空间 | 人均城市道路面积 | 0.0171 | 0.0662 | 正向 |
| 人均公园绿地面积 | 0.0206 | 0.0797 | 正向 | ||
| 生态环境 | 森林覆盖率 | 0.0383 | 0.1482 | 正向 | |
| PM2.5浓度 | 0.0093 | 0.0360 | 负向 |
3 研究方法与数据
3.1 改进的熵值法
熵值法是客观赋权法中较常用的一种方法,不仅可以克服人为确定权重的主观随意性,而且不受数据波动干扰,能有效克服指标间的信息叠加[33]。但传统熵值法仅适用于截面数据权重计算,在对面板数据进行分析时不具备可对比性。为此,本文选择改进的熵值法测度城镇化发展水平。计算过程如下:
(1)指标标准化处理:
式中:Xaij与Yaij分别表示第j项指标标准化前和标准化后的指标值;minXj与maxXj分别代表最小值与最大值。
(2)建立概率矩阵Paij:
(3)计算指标的信息熵Ej:
(4)计算各项指标的冗余度Dj:
(5)计算各项指标的权重Wj:
(6)运用权重合成法计算城镇化指数Uai:
3.2 泰尔指数及其分解方法
泰尔指数是荷兰经济学家Theil在测度收入不平等程度时提出的[34]。通过将研究个体划分为多个组群,泰尔指数可以用于分析区域差异产生的原因。与基尼系数相比,泰尔指数除了能够度量区域差异水平外,还可以分解为组内差异与组间差异,由此判断导致区域不均衡的主要原因。为此,本文采用泰尔指数将城镇化区域差异分解为地区间差异与地区内差异。泰尔指数及其分解过程如下:
式中:Tb与Tw分别表示地区间差异和地区内差异;T为城镇化差异程度的总体泰尔指数,是地区间差异与地区内差异之和,其值越大意味着城镇化的整体差异越大;nk代表第k组Gk(
3.3 方差分解方法
方差分解能够探究不同目标维度对地区差异的贡献程度。因此,本文采用方差分解方法,揭示城镇化不同维度差异的贡献度,观测城镇化空间分异的直接作用路径。指标贡献度越高,对城镇化差异的影响越大。具体将城镇化指数(U)分解为人居生活指数(U1)、人文环境指数(U2)与人城关系指数(U3),即U = U1+U2+U3。计算公式为:
两边同时除以
式中:var为方差;cov为协方差。
3.4 地理探测器
探究地理现象影响机制有多种方法,如空间计量模型、地理加权回归模型等,但都不能较好地反映要素在同一区域内的相似性与不同区域之间的差异性。地理探测器是空间数据探索性分析的有力工具[35]。本文使用地理探测器探索中国城镇化空间分异的间接作用机制。利用因子探测识别人居生活、人文环境、人城关系等目标维度空间分异的主要影响因素。因子探测的计算公式为:
式中:q为影响因素对目标维度空间分异的解释力度,其值越大意味着该影响因素对人居生活、人文环境与人城关系空间分异的解释力越大;k代表影响因素的分类;n和nk分别为样本总量和第k层的样本量;
3.5 数据来源及处理
本文以中国省级单元为研究对象(共30个省、自治区、直辖市,受限于数据的可获得性,暂未包含西藏与港澳台地区)。数据来源于2011—2021年《中国统计年鉴》、各省份统计年鉴及EPS(Easy Professional Superior)全球统计数据库。此外,平均预期寿命来源于历次《中国人类发展报告》,缺失数据采用均值差补法补充。平均受教育年限根据不同学历人数及学业年限核算,数据来自于《中国人口和就业统计年鉴》。PM2.5浓度数据来源于加拿大达尔豪斯大学大气成分分析组。
4 中国城镇化时空演变与区域差异
4.1 中国城镇化时间演变趋势
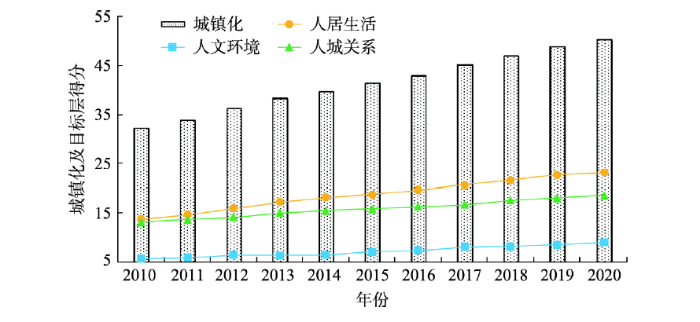
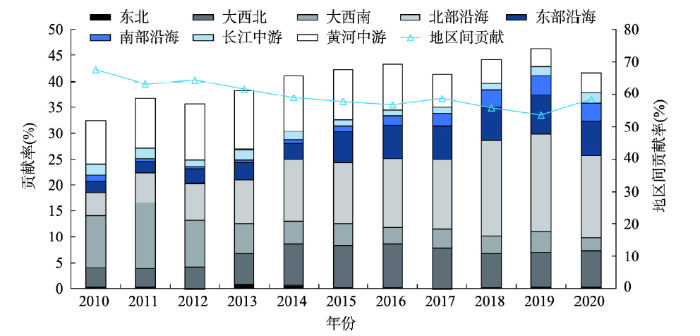
图2展示了2010—2020年中国城镇化的变化趋势。一方面,中国城镇化呈稳步上升态势,城镇化发展水平从2010年的32.279上升至2020年的50.323,均值为41.449,年复合增长率为4.54%。但城镇化增速逐步放缓,2010—2013年与2014—2020年的年复合增长率分别为5.89%和4.00%。另一方面,城镇化的人居生活、人文环境、人城关系等维度表现出一定协同性演进态势,但三者发展水平仍存在一定差距。人居生活与人城关系稳步提升,尤其是2014年新型城镇化战略实施以来,人文环境取得显著进步。但与此同时,人居生活与人文环境、人城关系的差距有所扩大。这表明,未来城镇化发展应更加注重满足人们对包容的人文环境、可持续的人城关系等需求,强化公共资源、生态环境供给,以更好促进城镇化可持续发展。
图2
图2
2010—2020年中国城镇化演变趋势
Fig. 2
The evolution trend of China's urbanization from 2010 to 2020
4.2 中国城镇化空间分布特征
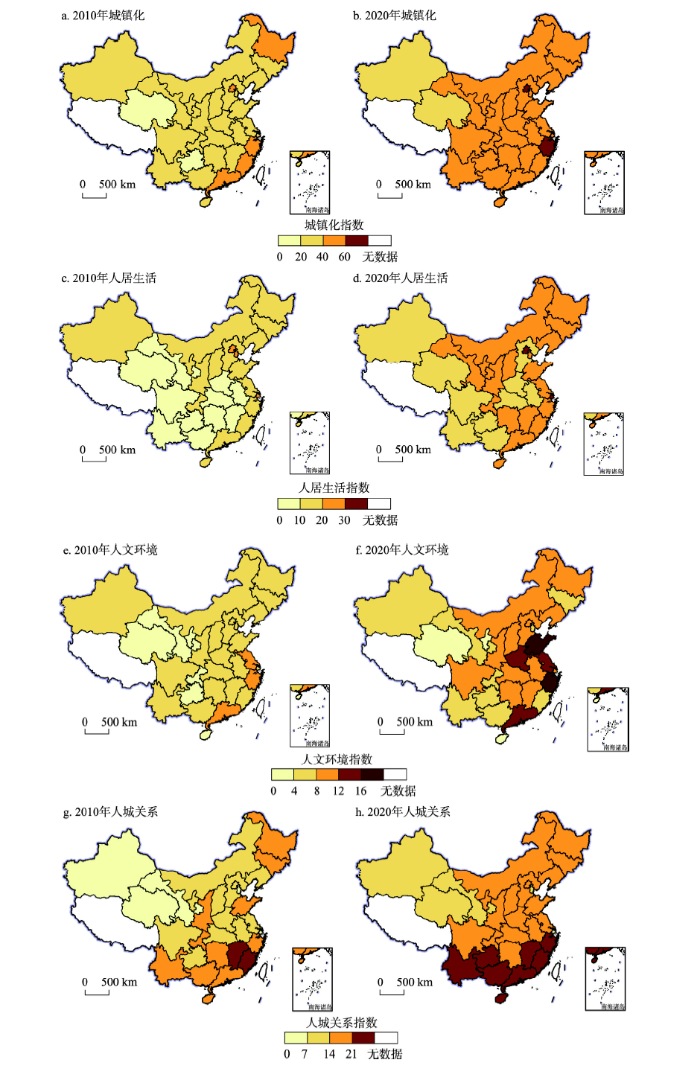
进一步探究中国城镇化空间分布格局变化特征。总体上,中国城镇化呈现出由东向西的空间梯度分异特征。2010年城镇化高值区集中分布于沿海省份。2014年新型城镇化战略实施以后,城镇化高值区域逐渐沿长江流域、黄河流域向内陆地区扩散。但不同需求维度空间分布差异较大,其中人居生活、人文环境整体表现为东、中、西空间分异格局,而人城关系则表现为南北分化特征(图3)。
图3
图3
2010—2020年中国城镇化时空演化
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630标准中国地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 3
The spatio-temporal evolution of China's urbanization from 2010 to 2020
具体来看,2010—2020年间中国北部沿海和东部沿海地区城镇化水平相对较高,但由于不同需求维度差异,上述地区城镇化空间分布呈现分异性特征。其中,北京、浙江城镇化始终处于高值区范围。上述省市收入与就业、民生福祉等发展较好,为城镇化良性发展奠定基础。近年来,伴随新型城镇化战略实施,天津、上海的人城关系显著改善,但由于资源环境承载力矛盾较为突出,导致其人城关系得分有所降低,影响城镇化的可持续进程。而山东、浙江的人文环境始终位于全国前列,尤其是新型城镇化战略实施后,其人文环境取得显著进展。
与上述地区不同,大西北地区的青海、新疆等省份城镇化得分整体偏低。上述省区主要集中于“胡焕庸线”以西,经济发展水平较低。由于城市发展的内生动力不足,物质资本对城镇化发展的支持力度较弱,难以满足人们的多维需求目标。但随着新型城镇化战略实施,尤其是生态文明建设理念逐步贯穿于城镇化建设过程,其人居生活品质逐步提升,人城关系逐步改善,对城镇化建设起到重要推动作用。
一直以来,东北地区城镇化具有较好的“自上而下”工业基础支撑。但在新时期面向需求侧多维目标协同的“自下而上”城镇化,却表现出相对劣势,尤其是人文环境、人城关系维度与沿海地区存在显著差距。此外,8大类型区中,黄河中游地区人文环境得分仅次于东部沿海地区。这意味着黄河中游特别是河南、陕西等省份,作为中华文明重要发源地,其城镇化建设过程中较为注重人文环境建设,取得一定成效。而大西南地区的人城关系仅次于南部沿海地区,较高的森林覆盖率满足了人们的生态环境需求,有利于协调广西、云南等省份的人城关系。
4.3 中国城镇化的区域差异
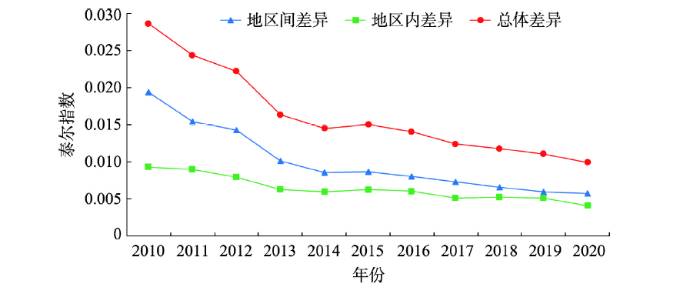
图4为2010—2020年中国城镇化泰尔指数及分解结果的变化趋势。整体上,城镇化泰尔指数呈梯度式下降态势,从2010年的0.029下降至2020年的0.010,城镇化区域差异逐步缩小。分阶段来看,2010—2013年城镇化总体泰尔指数降幅较大;2014年新型城镇化战略实施至2020年,城镇化总体泰尔指数呈现稳步下降趋势。进一步从区域分解来看,地区间差异和地区内差异均有不同程度降低,但地区间差异降幅更大。
图4
图4
2010—2020年中国城镇化区域差异分解
Fig. 4
The decomposition of regional differences of China's urbanization from 2010 to 2020
而从城镇化差异的贡献率变化来看(图5),地区间差异贡献率始终相对较高,平均贡献率达59.74%。但地区内差异贡献率逐步扩大,从2010年的32.47%提升至2020年的41.55%。综合来看,伴随中国城镇化进程深入,地区内开始出现新的分化特征。
图5
图5
2010—2020年中国城镇化区域差异的贡献率变化
Fig. 5
Changes of contribution rate of China's urbanization differences from 2010 to 2020
具体到不同类型区域的地区内差异贡献率,北部沿海、黄河中游与大西北地区贡献率位列前3位,年平均贡献率依次为11.80%、7.92%和6.39%,是中国省际城镇化区域差异的主要空间来源。东北和长江中游地区内差异的年平均贡献率相对较小,分别为0.27%与1.60%。从贡献率变化来看,2010—2020年大西南、长江中游与黄河中游等地区贡献率呈现减小趋势,东北、大西北、北部沿海、东部沿海、南部沿海等地区贡献率逐渐扩大。
总体来看,伴随以经济增长驱动的“自上而下”城镇化转向需求侧多维目标协同的“自下而上”城镇化,中国城镇化逐步形成了新的区域分化趋势。虽然整体上城镇化发展水平与地区经济发展水平相关,但由于各地区人居生活、人文环境、人城关系等需求目标发展差异,导致城镇化在同等经济发展水平地区内部开始出现新的分化特征。
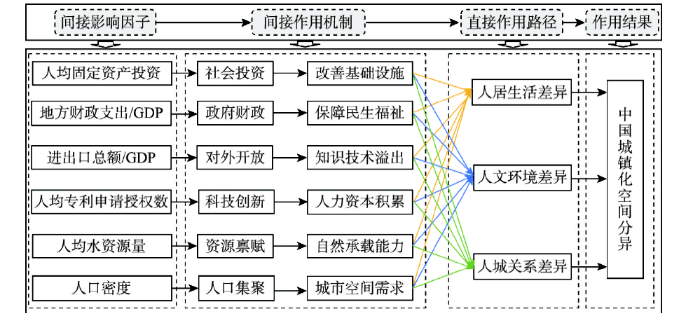
5 中国城镇化空间分异的影响因素
为进一步解析中国城镇化空间分异影响因素,本文从直接作用路径与间接作用机制两方面,构建中国城镇化时空分异机制框架(图6)。直接作用路径主要基于需求侧多维目标的分化对城镇化时空分异带来的影响变化。而间接作用机制是从多要素综合作用视角,探讨不同要素对不同需求侧目标的影响差异。
图6
图6
中国城镇化空间分异的直接与间接作用框架
Fig. 6
The framework for direct and indirect effects of spatial differentiation of China's urbanization
基于此,本文分别选取人均固定资产投资、地方财政支出占GDP比重、进出口总额占GDP比重、人均专利申请授权数、人均水资源量、人口密度作为社会投资、政府财政、对外开放、科技创新、资源禀赋、人口集聚的代理变量。
5.1 中国城镇化空间分异的直接作用路径
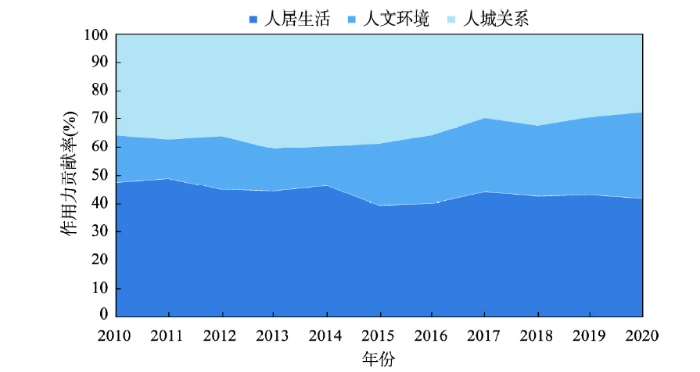
首先运用方差分解方法考察中国城镇化空间分异的直接作用路径。从图7可以看出,人居生活差异和人城关系差异是中国城镇化空间分异的主要原因,平均贡献率分别为44.05%和34.80%。这说明缩小人居生活差异和人城关系差异是中国城镇化区域协调发展的重要支撑。从阶段性变化来看,自2014年新型城镇化战略实施以来,人居生活差异与人城关系差异对中国城镇化空间分异的贡献率逐步降低。尤其人城关系差异贡献率降低幅度最为明显。而与此同时,人文环境差异对城镇化空间分异的作用程度有所增强,改善人文环境成为协调不同区域城镇化的重要方向。
图7
图7
2010—2020年中国城镇化空间分异的直接作用力贡献率
Fig. 7
The direct forces of spatial differentiation of China's urbanization, 2010-2020
由此可见,在城镇化不同发展阶段,其空间分异直接作用力逐步发生变化。在城镇化快速发展阶段,城市以经济发展为主线,追求数量和规模的快速扩张,城镇化发展侧重于提高人居生活水平与改善人城关系。而在城镇化平稳发展向成熟发展转换阶段,城市以宜居宜业的高质量发展为目标,城镇化发展更注重优化人文环境。尤其是2014年后,新型城镇化成为中国经济社会发展的核心主线,这一关键节点对城镇化发展提出更高的要求,城镇化发展的侧重点也有所改变。
5.2 中国城镇化空间分异的间接作用机制
进一步运用地理探测器揭示中国城镇化空间分异的间接作用变化。首先运用自然断点法将各影响因素离散化为3个等级,进而识别各影响因素对人居生活、人文环境与人城关系需求目标的影响程度。因子探测结果表明(图8),各因子主要是通过影响人居生活,进而对中国城镇化空间分异产生影响。而对人文环境、人城关系的影响相对较弱。
图8
图8
2010—2020年中国城镇化空间分异的间接作用力
Fig. 8
The indirect forces of spatial differentiation of China's urbanization from 2010 to 2020
具体来看,对外开放和科技创新是人居生活差异的主要影响因素,2014年新型城镇化战略实施以后,其作用力显著增强。对外开放有助于人居生活水平提升,对中国城镇化起到重要支撑作用。然而,近年来面对复杂的全球化环境变化,不同省区对外开放格局出现一定分化趋势。尤其是“一带一路”倡议提出以来,与沿海地区相比,内陆省区在国内国际双循环中的参与度仍有较大提升空间。科技创新对人居生活作用愈加凸显。2014年以来中国专利授权数飞跃式增长,但各地区差异逐渐扩大。广东、上海、北京、江苏、浙江等沿海地区科技水平位居全国前列,对经济增长与城镇化发展起到重要支持作用。而甘肃、新疆、云南、贵州等西部省区科技产出相对落后。政府财政对人文环境差异起主导作用,但其作用力在2014年以后有所减弱。政府财政支出为优化人文环境,特别是公共服务设施方面,提供重要资金支持,是中国城镇化发展的重要依托。东北、西北等部分省区较低的财政能力对人文环境的改善支撑不足,导致城镇化地区差异较大。但需要注意的是,2014年新型城镇化战略实施后,政府财政作用强度逐渐下降,表明中国城镇化进程中的公共服务均等化状况正逐步改善。而资源禀赋是人城关系差异的主要影响因素,但其作用力有所降低。资源禀赋有助于提升城市承载能力,塑造宜居环境,改善人城关系。尤其福建、江西、广西等地区,自然资源禀赋优势在全国居于前列,未来对城市人口集聚具有较大提升作用。
6 结论与展望
“自下而上”的需求侧多维目标协同可为理解城镇化内涵提供新视角。本文运用改进的熵值法测算2010—2020年中国城镇化发展水平,并采用泰尔指数探究城镇化的区域差异,进一步运用方差分解、地理探测器等方法探究城镇化空间分异的直接作用路径与间接作用机制。研究结论为:2010—2020年中国城镇化发展水平显著提升。其中,人文环境在2014年新型城镇化战略实施以后有显著的改善,但还有较大提升空间。城镇化东中西梯度差异格局仍然突出,虽然地区差异逐步缩小,但2014年以来其趋势正在减缓。地区间差异是中国城镇化差异的主要来源,而地区内差异贡献率逐渐显现。人居生活差异和人城关系差异是中国城镇化空间分异的主要作用力,但人文环境作用在2014年以后逐步增大。而对外开放和科技创新是人居生活差异的主要影响因素,且2014年以后其作用力显著增强。政府财政与资源禀赋分别对人文环境差异与人城关系差异起主导作用。
当前逆全球化、地缘政治扰动以及全球气候变化等对中国经济社会发展带来新的挑战。面对上述不确定性和人文自然风险交织的新形势,推动新时期城镇化高质量发展,满足人们不同层次需求目标,协同优化人居生活、人文环境、人城关系发展成为重要解决途径。首先,从城镇化发展的本底来看,“自下而上”的城镇化为稳定就业、提升居民福祉奠定基础。面对公共卫生等突发事件外部冲击,各地政府积极出台企业纾困举措,既离不开有为政府支持,还得益于新型城镇化带来的全方位保障,稳就业、保民生等经济社会功能不断完善,公共卫生等突发事件应对能力得到极大提升。其次,面向需求侧多维目标协同的城镇化,将“人与自然和谐共生”的生态文明理念贯穿全局,满足人们的精神需求与生态环境需求。通过改善人文环境、协调人城关系,引领区域可持续发展。
本文进一步丰富了城镇化内涵,探索其时空分异规律与机制。未来仍需结合新型城镇化最新实践和发展动态不断深化。① 伴随城镇化进入新阶段,从多尺度视角丰富城镇化内涵具有客观必要性。考虑数据可获取性,本文仅从省级层面进行探讨,未来需要加强对城镇化多尺度时空规律的客观认识、理论挖掘以及发展模式探索。这不仅有助于丰富城镇化理论,亦可为中国及其他发展中国家城镇建设提供理论和决策支撑。② 城镇化是经济社会发展的全过程综合体现。进入后疫情时代,如何通过“自下而上”的城镇化逻辑,应对社会结构转型、社区治理、区域可持续性管理等将成为重要研究议题。③ 在全球气候变化背景下,需要强化城镇化的人城关系维度综合研究。城市是应对全球气候变化尤其是碳减排的空间主体。城镇化基础将从考虑资源环境承载力系统向碳系统转换,未来可深化碳约束下的城镇化过程生态环境适应性研究。
关联数据信息:本文关联实体数据集已在《全球变化数据仓储电子杂志(中英文)》出版,获取地址:
致谢
感谢审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵建议,使文章的理论与实证逐步完善,同时感谢河北师范大学地理科学学院王文刚副教授在论文修改中给予的支持与帮助。
参考文献
Challenges and the way forward in China's new-type urbanization
DOI:10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.07.025 URL [本文引用: 1]
Several viewpoints on the background of compiling the "National New Urbanization Planning (2014-2020)"
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502001
[本文引用: 1]

The "National New Urbanization Planning (2014-2020)" (hereinafter referred to as "Planning") marks a significant transformation in China's urbanization development process, with the core of human urbanization, and the general requirement of seeking advance in stability. This paper elaborates the authors' preliminary thoughts on the formation of the "Planning" mainly from the speed and quality aspects of the urbanization development. Urbanization level should be consistent with industrial restructuring, the amount of new jobs, the actual ability of absorbing rural population, and water-soil resource and environment capacity of the urban area, etc. The large scale and high speed urbanization development in China has resulted in severe environment pollution, great pressures on the infrastructure, and huge challenge to the supporting capacity of natural resources. Urbanization is an important frontier scientific issue with obvious cross disciplinary feature, which is also a complex system. The interdisciplinary human economic geography has outstanding advantages and solid research foundation in the field of urbanization research. Therefore, facing the significant realistic demand of the national new urbanization, we should do some in-depth research and tracking studies in this field.
关于“国家新型城镇化规划(2014—2020)”编制大背景的几点认识
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201502001
[本文引用: 1]

“国家新型城镇化规划(2014-2020)”标志着中国城镇化发展的重大转型,核心是强调了人的城镇化,总体要求是“稳中求进”。本文着重从发展速度和发展质量方面阐述了对这个规划产生背景的初步认识。城镇化发展水平应当与城镇产业结构转型和新增就业岗位、城镇实际吸纳农村人口的能力、以及水土资源和环境承载力等保持一致。中国大规模高速发展的城镇化,付出的环境污染代价巨大,基础设施不堪重负,自然资源的支撑力面临严重的困难。城镇化是具有明显交叉学科特性的重要前沿科学问题,是一个复杂系统。人文经济地理学的跨学科性质在城镇化研究领域具有突出优势和较为扎实的研究基础,面向国家新型城镇化的重大现实需求,还非常需要对这一重大领域进行深入的跟踪和研究。
Perspective of China's new urbanization after 19th CPC National Congress
中国新型城镇化在“十九大”后发展的新态势
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180453
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化建设,关系到城镇化质量提升,关系到中国向高质量发展转型,关系到新时代“两阶段目标”的实现。“十九大”后,中国新型城镇化表现出4个方面新态势:一是走中国特色新型城镇化道路成为广泛共识,从城镇化严重滞后转向新型城镇化,从盲目赶超发达国家转向符合中国实际,从土地城镇化转向人的城镇化;二是新型城镇化是破解新时代不平衡不充分主要矛盾的重要抓手,新型城镇化具有高度综合性,与乡村振兴、“一带一路”等加强协同推进;三是新型城镇化在新时代背景下需要细化和深化,重点是人的城镇化与基本公共服务均等化、生态文明与可持续城镇化、社会治理与制度创新、空间治理与空间规划;四是城市群发展的重要性不断增强,京津冀协同、粤港澳大湾区,长三角城市群、中西部地区重点城市群以及国家级新区等空间载体在新型城镇化中引领作用更加凸显。加强新型城镇化的基础研究,提升地理学服务国家新型城镇化能力。
The new urbanization policy in China: Which way forward?
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.02.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
The theory and practice of new urbanization in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.06.641
[本文引用: 1]

Issue of urbanization is a comphrensive subject which is related to harmonious development of each department of national economy and building a harmonious society. New urbanization is the guarantee of healthy and stable development of urbanization. The research work of the thesis has higher academic meaning and practical value. Urbanization promoted social and economic development of China in the past decades. But some problems arised in the process of urbanization in some areas, such as the rapid pace and disordered state of development, the blind expansion on the edge of cities, degradation of land and water resources, destruction of the ecological environment, and many unsafe, uncomfortable problems in urban environment.From the geographical space and natural resource conservation point of view, this article focuses on three theoretical issues. 1) How to have a good understanding of the basic characteristics and realizing route of new urbanization; 2) How to build a innovation model of new urbanization; 3) In the process of implementing new urbanization, how to understand the development law of China's urbanization, and to take a new road of urbanization with Chinese characteristics.
中国新型城镇化理论与实践问题
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.06.641
[本文引用: 1]

城镇化问题是当代中国社会经济发展的综合性课题,是涉及到国民经济各部门如何协调发展,达到一个新的现代化和谐社会发展的根本问题;新型城镇化是中国城镇化健康稳定发展的基本保证,在当前的新形势下,探索中国新型城镇化理论与实践问题,具有重要的学术价值与实践意义。在过去一阶段,虽然城镇化推动了中国社会经济发展取得了巨大成就,并在城市现代化建设与城乡一体化方面也取得了惊人的发展,但在某个时期或一些地区,城镇化过速发展阶段,出现了无序的发展状态,大中城市边缘盲目扩展,水土资源日渐退化,生态环境遭受破坏,特别是有些政府决策人对城镇化的许多制约因素认识不足,甚至决策失误,导致了城市环境出现许多不安全、不舒适的问题。着重从地理空间与自然资源保护的角度,探索中国新型城镇化3个理论与实践问题:① 如何认知中国新型城镇化的基本特征与新的路径;② 在全球经济一体化形势下,如何构建新型城镇化的创新模式;③ 在新型城镇化实施过程中,如何认识中国城镇化本身的发展规律,走具有中国特色的新型城镇化道路。
Does land transfer promote the development of new-type urbanization? New evidence from urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River
From localization to de-localization and re-localization: Transformation of the human-land relationship in China's urbanization process
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.003
[本文引用: 2]

The relationship between people and land provides an important perspective on urbanization paths. This study analyzed the development context and basic logic of the transformation of human-land relationship in China, and argued that the relationship between people and land has gone through three stages: localization, de-localization, and re-localization. In the stage of localization, the economic form of the country based on agriculture determined people's economic dependence and emotional attachment to the countryside, and the logic of localization is hard to shake. In the de-localization stage, the transformation of industrialization and urbanization in China pushed farmers to leave the agricultural fields and leave the countryside, and structural changes occurred to the value constraint that people cannot be separated from their lands. Under the influence of land use institutions and the household registration system, the passive landless farmers and those leaving the land behind at their own will jointly led the de-localization process of human-land relationship. In the stage of re-localization, the institutional reform led the farmers to become the main agent of urbanization. Nostalgia promotes the coexistence of urban and rural civilizations, which helps reshape the relationship between people and land. Finally, this article maintained that examining the historical context and basic logic of the transformation of human-land relationship can provide a theoretical reference for the institutional adjustment of human-land relationship in the new era and the smooth implementation of new urbanization.
从在地化、去地化到再地化: 中国城镇化进程中的人地关系转型
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.003
[本文引用: 2]

人地关系是透视中国城镇化进路的重要视角。论文在历史向度上分析了城镇化进程中人地关系转型的发展脉络和基本逻辑,认为中国人地关系经历了在地化、去地化和再地化3个阶段。在地化阶段,农本立国的经济形态决定了人们对乡土的经济依附和情感依恋,人地关系的在地化逻辑难以动摇;去地化阶段,中国的工业化、城镇化转型推动农民离土出乡,人不离土的价值观束缚发生了结构性松动,在土地与户籍制度的影响下,被动失地的农民与主动离地的农民共同主导了人地关系的去地化过程;再地化阶段,制度变革引领农民真正成为城镇化的主体,乡愁推动城乡文明走向共生,二者助推中国人地关系重塑。对人地关系变迁的历史脉络和基本逻辑的梳理,可以为适应新时代的人地关系的制度调节和新型城镇化道路的顺利实践提供理论借鉴。
Connotation, logical system and its reflections of production of space on Chinese new urbanization practice
“空间的生产”内涵、逻辑体系及对中国新型城镇化实践的思考
Basic rules and key paths for high-quality development of the new urbanization in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180445
[本文引用: 1]

The high-quality development of the new urbanization in China is focused on man-earth harmony, people-oriented principle, low-carbon, ecology, innovation, wisdom and safety. It is an organic unity of high quality citizenization, infrastructure, living environment, urban construction, public service and urban management. Promoting the new urbanization is an important way for China to build a moderately prosperous society in all respects and achieve modernization basically, and it is an important way to realize the strategy of rural revitalization. To promote the development of China's new urbanization, we need to follow the four stage rule and gradual development rule. To realize the strategy transformation of new urbanization, it is necessary to make more changes: from the quantitative to the quality-oriented, from the "one step" to "step by step" in realizing our goals, from radical to gradual, from inducing "negative effect" to releasing the "positive energy", from passive to active, from "land-oriented" to "people-oriented". The current situation and background conditions of China's urbanization are very different from one place to another. Thus, we should avoid "one-size-fits-all" in promoting the development of new urbanization. Adhering to the principle of adapting local conditions and appropriate conditions, the paper divides the new urbanization area into five major types, including urban agglomeration region (I), major grain-producing region (II), farming, forestry, and animal husbandry region (III), linked poverty alleviation region (IV), and ethnic autonomous region (V), which are further divided into 47 sub-regions. The urbanization development mode between different regions and different subregions cannot be copied from each other, and we need to implement some diversified and differentiated models. According to the main functions of different types of urbanization regions, the different development policies of urbanization should be formulated, and development goals and priorities should be put forward according to local conditions, and the classification guidance should be proposed according to the appropriate conditions. The key paths to promote the high-quality development of China's new urbanization include: enhance the overall synergy of high-quality development and improve the quality of urban agglomeration development; promote the integrated development of industrial and urban areas and the equalization of basic urban public services, and improve the quality of urban development; propel integrated development between urban and rural areas and accelerate the revitalization of rural areas; highlight the main functions of urbanization quality development in different types of areas in accordance with local conditions; innovate institutional mechanisms and ensure that high-quality development is carried out throughout the trial process of new urbanization; standardize small towns with distinctive features and lay a solid foundation for the high-quality development of new urbanization; strengthen the analysis and regulation of the capacity of resources and environment for the high-quality development of new urbanization.
中国新型城镇化高质量发展的规律性与重点方向
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180445
[本文引用: 1]

中国新型城镇化高质量发展是一种人地和谐、高效低碳、生态环保、节约创新、智慧平安的质量提升型城镇化,是高质量的城市建设、高质量的基础设施、高质量的公共服务、高质量的人居环境、高质量的城市管理和高质量的市民化的有机统一。高质量推进新型城镇化发展需要遵循城镇化发展的四阶段性规律和渐进式规律,实现新型城镇化由数量型向质量型、由“一步到位”向“分步到位”、由激进式向渐进式、由诱发“负效应”向释放“正能量”、由被动性向主动型、由“地为本”向“人为本”的战略转型。考虑到中国新型城镇化发展的地域差异显著,新型城镇化高质量发展客观上要因地制宜、因类指导,可将全国新型城镇化高质量发展区域划分为城市群地区(Ⅰ)、粮食主产区(Ⅱ)、农林牧地区(Ⅲ)、连片扶贫区(Ⅳ)、民族自治区(Ⅴ)共5大高质量发展类型区和47个亚区。未来推进中国新型城镇化高质量发展的重点路径包括:增强新型城镇化高质量发展的整体协同性,提高城市群发展质量;推动产城深度融合发展,加快实现基本公共服务均等化,提升城市发展品质与质量;推动城乡深度融合发展,在新型城镇化高质量发展中实现乡村振兴;突出因地制宜,明确不同类型地区城镇化高质量发展的主体功能;创新体制机制,全过程推进城镇化高质量发展;量力而行,以特取胜,规范建设特色小镇,夯实新型城镇化高质量发展的基石;把新型城镇化高质量发展与区域资源环境承载力及高质量保护有机结合起来。
Cognition and construction of the theoretical connotation for new-type urbanization with Chinese characteristics
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904002
[本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening up, China's rapid urbanization has boosted the development of economy and society, but it is also confronted with tremendous challenges. The multidisciplinary research has promoted the issue of National New-type Urbanization Planning, which indicates the transformation of China's urbanization strategy. Further research, however, is needed to explore the theoretical construction of China's new-type urbanization. The paper summarizes the development process of China's urbanization and points out its characteristics, which includes peri-urbanization, special national conditions, complicated factors and governance system. China's urbanization makes a great contribution to the world. Moreover, the literature demonstrates the significance of urbanization to the discipline of human and economic geography and the scientific connotations of new-type urbanization, which refers to peiple-oriented, harmonious, inclusive and sustainable. Under the background of the humanism transformation, new-type urbanization should transform from population urbanization to people-oriented urbanization. There are six crucial scientific issues: people-oriented urbanization and equalization of basic public services, urbanization with integrated and coordinated development of urban and rural, urbanization in the context of resources and environment carrying capability and climate change, diverse regional modes, spatial effect and mechanism, as well as big data and innovation of technical methods. The paper makes efforts to illustrate a framework of China's new-type urbanization connotation, which provides references for theoretical research and policy formulation.
中国特色新型城镇化理论内涵的认知与建构
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904002
[本文引用: 1]

改革开放以来,中国快速城镇化既推动经济社会大发展,也面临巨大挑战。跨学科视野下,围绕城镇化问题的争论和持续研究对国家新型城镇化规划产生重要影响,也标志着中国城镇化方向的重大调整。但对中国特色新型城镇化的科学认知和理论挖掘仍不充分。本文归纳了中国城镇化发展的简要历程,指出半城镇化、特殊国情、复杂因素及治理体系交织的中国城镇化特征,阐明了中国城镇化对世界的巨大贡献,论述作为最显著的人文空间过程的城镇化对人文与经济地理学的学科意义,并解读了新型城镇化认知与建构的4个方面理论内涵:人本性、协同性、包容性和可持续性。伴随结构主义向人本主义发展理念的转变,新型城镇化应逐步实现从“人口城镇化”到“人的城镇化”的转变,其中有6个关键议题:人的城镇化与基本公共服务均等化、城镇化城乡综合过程与协同研究、资源环境承载与气候变化适应下的城镇化、多样化区域模式、城镇化人文社会空间效应及机制、大数据与技术方法创新。本文尝试构建中国特色的新型城镇化理论内涵的认知框架,以期为新型城镇化理论研究和政策实践提供借鉴。
Build a people-oriented urbanization: China's new-type urbanization dream and Anhui model
Re-recognition of precondition and driving mechanism of new-type urbanization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180444
[本文引用: 1]

This paper analyzes the precondition of urbanization, and concludes that the premise that urban area is better than rural area began to change. The result may be the one-way urbanization process from rural to urban area changes into a reverse or two-way process between rural and urban areas. This paper discusses the driving force and evolving mechanism of the new-type urbanization, and believes that the main driving force of urbanization came from the economies of scale under industrialized production in the early period, which gradually expands from industrial sectors to non-agricultural industries, and changes the organization pattern that the bigger the size is, the better the town is. The paper believes that the organization model of the market in "flow" space under the information condition presents the trend of decentralized layout, which will change the scale-hierarchy structure of traditional space. The paper concludes that the new trend of the mutual integration between industries will change the setting of traditional single-use functions, while emphasizing the complex response of function and space. The paper does not believe that the changes in preconditions and driving mechanisms for urbanization means that urbanization is an inevitable process, and that the higher the level of urbanization, the better, and the larger the city size, the better. The paper finds that the goal of urban development has shifted from economic benefits to comprehensive benefits. The paper concludes that the city level depends on its own attraction and the function based on it, instead of size. The paper does not believe that the residents who are engaged in non-agricultural industries and enjoy non-agricultural lifestyle in new type of rural areas be counted as farmers, but as "semi-urbanization" population. The paper believes that the socio-economic patterns are very complex and highly integrated with each other, so it is difficult to rationally distinguish the connotations of cities or villages from the simple definition of urbanization. The paper proposes that in the semi-urbanized areas, local resources should be used as an advantage, and the main employment forms, public service and infrastructure conditions, lifestyle, and community culture should be promoted in close proximity to the urbanization area. The paper believes that in the future, it is necessary to revise and improve the theory and method of urbanization mode, path, planning and regulation, pay attention to urban and rural characteristics, promote urban and rural equivalent development, and realize the integration of urban and rural factors.
新型城镇化前置条件与驱动机制的重新认知
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180444
[本文引用: 1]

本文发现:近年来城市比乡村好的城镇化前提开始出现新变化,以前农村-城市单向的城镇化过程,可能会出现城乡之间的反向或双向的过程。城镇化的主要驱动力逐渐从工业部门拓展到整个非农产业,改变了城镇规模越大越好的组织模式;市场在信息化条件下的“流”空间中开始出现分散化布局的组织模式,改变了传统空间的规模-等级结构;产业之间相互融合的新趋势将改变传统单一用地功能的设置,而更强调功能和空间的复合应对;城市发展由经济利益主导向综合效益转变,城市等级的高低取决于自身的吸引力以及在此基础上所形成的功能。建议未来完善城镇化模式、路径、规划、调控的理论方法,注重城乡特色、推进城乡等值化、实现城乡要素交流融合。
Evolution of rural settlements in the Tongzhou District of Beijing under the new-type urbanization policies
Social integration of rural migrants under the background of new-type urbanization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180460
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of human-oriented new-type urbanization, the citizenization of rural migrants attracted more and more attention from scholars and governments in recent years. On the basis of analyzing the China's urbanization and behavioral agencies, the paper indicated major difficulties facing the rural migrants in the process of social integration. The main findings are as follows: (1) the government, firm and individual are three main behavioral agencies in the process of urbanization in China, and their interaction is the main cause leading to the appearances of social exclusion. (2) The central government is mainly in charge of guiding the overall development of national urbanization by making top-level policies, while local governments play an important part in promoting local urbanization. However, by mean of the household registration system, local governments pay more attention to the economic development, and generally exclude the rural migrants from other administrative units to share the equal welfare together with the local residents. (3) Most China's firms mainly undertake labor-intensive industries, and most of them adopt low-wage and low-social security policies to decrease the productive cost. These measures result in low wages and low social security level for rural migrants and hinder their social integration. (4) The human capital characteristics of individuals also have an important influence on the social integration of floating population. Generally, the rural migrants with more human capitals (well-educated, younger, etc.) are more likely to integrate themselves into local society. Among the three behavioral agencies, the rural migrants are no doubt in the weakest status, and the institutional obstacles hinder them to embed in the urban society. In the end, some suggestions were proposed to promote the social integration of rural migrants. Firstly, we should deepen the reform of the household registration system, build an inclusive city, and promote the equalization of basic public services. Secondly, the government, firms and individuals should share the cost to realize citizenship.
新型城镇化背景下城市外来人口的社会融合
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180460
[本文引用: 1]

促进农业转移人口的市民化、提高城镇化质量,已成为新型城镇化关注的焦点。在考察中国城镇化过程和行为主体的基础上,揭示城市外来人口社会融合面临的主要问题及形成原因,进而提出促进外来人口社会融合的策略。研究发现:政府、企业和个人不仅是推进城镇化的三个行为主体,三者之间的交互影响也导致外来人口社会融合问题的产生。中央政府主要通过政策引导城镇化的健康发展,地方政府在推进地方城镇化中扮演重要的作用,但更多关注自身行政区范围内的经济发展和社会福祉,通过户籍制度排斥外来人口的社会融入。中国企业主要承接劳动密集型的产业,因而大多采取低工资、低社会保障的政策。个人的人力资本等特征对于外来人口的社会融合也具有重要影响。但在三个行为主体中,外来人口处于最弱势的地位,制度性的障碍使他们难以嵌入城市社会。为了更好促进城市外来人口的社会融合,研究认为:需要进一步深化户籍制度改革,建设包容性城市,推进基本公共服务均等化,政府、企业和个人三个行为主体共同承担市民化的成本。
New-type urbanization, well-being of residents, and the response of land spatial planning
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200602
[本文引用: 1]

The urbanization of China has entered the middle and late stage, and the connotation of the people-centered urbanization needs to be further enriched and refined. The land spatial planning is the key to the practice of the new-type urbanization and ecological civilization construction. This paper proposes that the improvement of well-being of residents is the core of the people-centered urbanization. It sorts out relevant domestic and foreign studies on the connotation of well-being, summarizes the subjective and objective measure index systems and methods of well-being, and examines the factors influencing well-being and happiness of residents. In this study, we draw on the experience of foreign spatial planning and take the improvement of the well-being of urban and rural residents as one of the guiding principles for the compilation of land spatial planning. In the process of the practice of land spatial planning, it is necessary to focus on public health, disaster risk assessment system and construction of urban resilience, optimization of "production-living-ecological" spaces, community living spatial planning, fine-scale management, and big data and intelligent decision-making system. Urbanization is the indispensable important component of national spatial planning, and the establishment of national spatial planning promotes the high-quality development of new-type urbanization and the well-being of urban-rural residents. So, we should show great concern on urban scale hierarchy structure, the pattern of population flow network, peri-urbanization and local urbanization, basic allocation and equalization of public service of urban and rural areas, the impacts of climate change and urban disaster risk management, and the basic research of the new-type urbanization, such as the evolution of man-land relationship in the rapid urbanization.
新型城镇化、居民福祉与国土空间规划应对
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200602
[本文引用: 1]

我国城镇化已经步入中后期发展阶段,以人为本的新型城镇化内涵需要进一步丰富和建构。国土空间规划正是新型城镇化建设和生态文明建设落地的关键。本文提出增进居民福祉是以人为本新型城镇化的核心,梳理了居民福祉内涵的国内外相关研究、居民福祉的主客观测度指标体系与方法,归纳了影响居民福祉和幸福感的综合影响因素。借鉴国外空间规划经验,建议把增进城乡居民福祉作为国土空间规划编制的指导思想之一,并在国土空间规划实践中注重公共服务设施优化配置研究、灾害风险评估与韧性城市建设、三生空间优化、社区生活圈规划与精细化管理和大数据与智能决策系统等。城镇化是国土空间规划的重要组成,国土空间规划的科学编制有助于推动新型城镇化的高质量发展和城乡居民福祉提升,需要关注和加强城市合理等级体系、城市人口流动格局网络、半城镇化与就近城镇化模式、城乡基本公共服务配置与均等化、气候变化、城市灾害风险管理以及快速城镇化下人地关系演变等新型城镇化基础研究。
Towards rural-urban integration: Key issues and trends on linking new-type urbanization to rural revitalization
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

It is the key to achieving the aim of rural-urban integration that combine the two national strategies of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, and carry out collaborative governance of urban and rural areas. By analyzing the progresses of the studies on the new-type urbanization and rural revitalization, it is pointed out that the coupling of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategy should clarify the symbiosis effect of two strategies, and scientifically evaluate the coupling degree of urban and rural areas, then discover the spatio-temporal pattern of rural-urban integration. In order to realize rural-urban integration, it is necessary to explore the combination and spatio-temporal differences of new-type urbanization and rural revitalization strategies. According to conducting interdisciplinary methods to study the relations among the urban and rural administrative management system, the land system, the household registration system as well as the social security system, this article advocates multidimensional system reform from three perspectives of space, economy and society. Reconstructing the theory of rural-urban integration will be based on a whole analysis from the national, provincial, city to community scales. Community-centered governance is significant for rural-urban integration.
迈向城乡融合: 新型城镇化与乡村振兴结合研究的关键与趋势
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.04.004
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化和乡村振兴两大国家战略有机结合并进行城乡共治是实现城乡融合的关键。通过分析新型城镇化和乡村振兴研究文献,认为新型城镇化与乡村振兴战略结合应聚焦两大战略的共生效应,科学评价城乡耦合程度,明确城乡融合的时空格局,提炼两大战略的耦合机制。要实现城乡融合,需要深入探究新型城镇化和乡村振兴战略的结合点和时空差异,以问题为导向进行学科交叉,从空间、经济、社会3方面入手,厘清城乡在行政管理、土地、户籍和社会保障制度间的关系,倡导多维制度联动改革,从国家、省域、城市、县域、乡镇到社区,通过多尺度整合,重构城乡融合的理论,激发以社区为核心的基层治理活力,进而创新中国城乡共治的模式。
The methodology on spatial justice and new-type urbanization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180503
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of economic-social transformation and entering the new normal, many spatial injustice problems have emerged due to the previous rapid urbanization mode, which is characterized by emphasis of the quantity, scale expansion and economic benefits. How to achieve the equality of land resource allocation and space development rights are urgently needed to use the theoretical thinking of spatial justice to reflect and reconstruct China's urbanization development mode. The theory of spatial justice has three features: social space, multi-scale and critical construction, which have a significant impact on urbanization research and practice. Western geographers have already had sufficient theoretical discussions on spatial justice with rich practical cases. However, China is still in the initial stage of exploration, lacking the theory that is suitable for China's system and social development needs. Through combining the ideas and the theories of spatial justice, this paper advocates the integrated use of multiple methods to conduct comprehensive analysis and case comparison of multi-scale and multi-agent, explores and summarizes the evolution mechanism and development mode of China's urbanization based on spatial justice. Informed by the socio-spatial dialectic, this paper uses qualitative, multi-scale and multi-agent methods to reveal the evolution mechanism of China's urbanization, seeking for improvement ways so as to realize urban spatial justice. Utilizing the idea of spatial justice to rural-urban development and planning can provide a new perspective for urbanization research and guide the transformation of urbanization to achieve the normal development of economic society and rural-urban areas.
空间正义与新型城镇化研究的方法论
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180503
[本文引用: 1]

在经济社会转型和进入新常态的背景下,以往重数量、规模扩张和经济效益的快速城镇化模式引发的许多空间不公正问题开始突显出来,如何实现土地资源配置、空间发展权利等方面的公平,亟需用空间正义的理论思维去反思和重构中国的城镇化发展模式。空间正义理论具有社会空间、多尺度性、批判建构三个主要特征,它们对城镇化研究和实践产生重要影响。西方地理学界对空间正义已有较充分的理论讨论,实践案例亦很丰富,国内还处在初步了解和探索的阶段,缺少适合中国体制和社会发展需求的理论。通过对空间正义思想与理论的梳理,提倡综合运用多种方法,进行多尺度、多主体综合分析和案例比较,探讨和总结基于空间正义的中国城镇化演化机理与发展模式。在社会空间辩证法的指导下,运用定性、多尺度、多智能体的方法,揭示中国城镇化进程的演变机制,寻找改善途径进而实现城市空间正义。将空间正义思想用于城乡发展与规划,可为城镇化研究提供新视角,并引导城镇化转型,实现经济社会及城乡的常态发展。
New urbanization and informal employment: Scale, pattern, and social integration
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.005
[本文引用: 1]

With the development of urbanization, promoting the citizenization of migrant workers and improving the quality of employment has become an important goal of China's urbanization strategy in the new era. Affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, the problem of informal employment stands out even further. Starting with an examination of the relationship between new urbanization and informal employment, this study draws on the data from population census and the China Labor-force Dynamic Survey (CLDS) to estimate the scale of urban informal employment in China and analyze its spatial and sectoral characteristics. It then identifies the main social integration problems faced by informal workers and discusses some policy options. It is found that urbanization and informal employment are interrelated. Informal employment provides job opportunities for rural migrants with the inability to find formal jobs in cities and urban workers who are unemployed, playing a role in alleviating employment and poverty problems. It is argued that the new urbanization with the principle of putting people first should be concerned with the social integration of informal workers with the aim to promote their citizenization. According to the estimation based on multi-source data, the number of informal workers is 138 million-155 million, accounting for 33.2%-44.7% of urban employment in China. The unobserved/unregistered informal workers are the majority. The distribution of informal employment is characterized by the spatial pattern that the scale of informal employment decreases from the eastern to the central and the western parts of China. In terms of employment types, most informal workers are employed in enterprises. Informal employment in China is mainly concentrated in the sector of wholesale, retail trade, and catering, followed by the sectors of residential service, repair, and other services and manufacturing industry. Informal workers are faced with difficulties in social integration, including job precarity, income instability, social marginalization due to population registration restriction, limited access to public services, and vulnerability to crises. It is recommended that policy intervention should pay attention to improving the quality of informal employment and promoting social integration of informal workers in the future.
新型城镇化与非正规就业: 规模、格局及社会融合
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.005
[本文引用: 1]

中国城镇化由偏重数量转向更加注重质量的新型城镇化,促进农村转移人口市民化、提高就业质量成为城镇化发展的重要目标,疫情影响下非正规就业问题更为突出。论文从新型城镇化与非正规就业的关系出发阐释非正规就业人口的历史产生和发展要求,基于人口普查和《中国劳动力动态调查》测度了中国城镇非正规就业的规模和格局特征,总结了非正规就业者当前面临的社会融合难题,并提出发展思路和路径。结果发现:① 城镇化与非正规就业之间关系密切,非正规就业为城镇化过程中农村转移人口提供大量就业机会,缓解了城镇就业压力。以人为本的新型城镇化需要关注非正规就业模式,以促进农业转移人口市民化和社会融合。② 经多源数据估算,中国城镇非正规就业占城镇总就业的33.2%~44.7%,就业人数达1.38亿~1.55亿,以隐性就业部分为主。在空间分布上总体呈现东、中、西逐渐减少的特征;在雇佣类型上以从事各类非正规工作的被雇型就业为主;行业结构主要集中在批发和零售贸易及餐饮业,居民服务、修理和其他服务业与制造业等。③ 非正规就业者主要面临职业困境、户籍限制、公共服务差距、风险应对能力弱等问题,需要通过完善就业服务体系等改革,提升就业质量,推动市民化和社会融合。
Can new urbanization break through the Hu Huanyong Line? Further discussion on the geographical connotations of the Hu Huanyong Line
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201605002
[本文引用: 1]

The Hu Huanyong Line, which is also called the Aihui-Tengchong Line, is drawn by Hu Huanyong and marks a striking difference in the distribution of China's population. It has been accepted and used for the last 81 years, and has had a considerable influence on Chinese population distribution research at home and abroad. With rapid new urbanization, research on the Hu Huanyong Line has increased sharply. In the context of new urbanization, an urgent question for us is how to understand the Hu Huanyong Line accurately. As a divide between the distribution patterns of the population in China, the Hu Huanyong Line has not changed substantially in the past 81 years. It represents a divide not only for the ecological environment, but also for climate. There are mainly prohibited development areas and restricted development areas in the Major Function Oriented Zones Planning west of the Hu Huanyong Line. It is not only the region east of the Hu Huanyong Line, but also includes some parts of the central and western regions of China. The formation of the line was the result of long-term interactions between the natural environment, economic development and social and historical conditions. Therefore, it would not be changed by what we think and do to break through. New urbanization emphasizes that the rural population migrates to the towns and cities nearby, rather than a large-scale transfer of population. Due to a local transfer of 100 million people in the central and western regions, new urbanization will accelerate the process of the population gathering in these regions. New urbanization has a significant impact on the population structure of different sizes of cities and towns, but little effect on the national spatial pattern. It is healthy urbanization in harmony with nature, therefore, rational thinking is required during the process of new urbanization, in order to optimize the spatial distribution pattern of urbanization. Pushed by the two-child policy issued recently, the population in the eastern and central China is predicted to increase with the western region increasing slowly due to the unbalanced population birth policy. With the implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative, urbanization in the western region will accelerate, opening up and expanding border cities, thus posing new challenges to the population distributed either side of the Hu Huanyong Line.
新型城镇化能否突破“胡焕庸线”: 兼论“胡焕庸线”的地理学内涵
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201605002
[本文引用: 1]

“胡焕庸线”提出80年来,在国际上产生深远影响。随着中国新型城镇化进程的全面推进,对胡焕庸线的研究急剧升温。在新的历史背景下,如何客观看待胡焕庸线成为亟待解决的一个问题。研究认为:胡焕庸线不仅是中国人口分布的分界线,也是重要的自然生态界线,这条界线的形成不以人的意志为转移,不宜人为去“打破”。同时,在新型城镇化背景下,应该树立理性思维,稳妥有序地推进城镇化进程,不断优化城镇化的空间分布格局。在全面放开二孩的新政策推动下,由于中国区域人口政策的差异性,东部和中部地区的人口有望实现较为明显的增长,西部地区增长相对缓慢,由此可能对胡焕庸线两侧的人口空间格局产生一定的影响。
Spatio-temporal coupling of demographic-landscape urbanization and its driving forces in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810004
[本文引用: 2]

Urbanization is an inevitable trend of modernization and the fundamental transition in socioeconomic structure, human production and life style. China is undergoing a rapid and unprecedented urbanization process, and has achieved the short-term goals that European and American countries attained in the past decades or even centuries ago. This kind of rapid expansion has inevitably led to a serious imbalance between urban land expansion and urban population growth. We used the demographic-landscape urbanization coupling relationship index (ratio of the annual average growth rate of demographic permanent population and urban development land) to explore the spatio-temporal characteristics of demographic-landscape urbanization coupling situation, and further explain its driving forces during the past decade in China. All analyses, based on the demographic statistics and landscape dataset of 636 cities in China, aimed to identify and diagnose six coupling types. Furthermore, we made the macro pattern of urbanization development level more visible with the help of Kernel Density spatial analysis tool. Results show that: (1) Over the past decade, the average annual growth rate of urban development land in China was 1.65 times that of the urban population, and demographic-landscape urbanization coupling situation was poorly coordinated. (2) We found that there is a spatial dependency between demographic urbanization and landscape urbanization. Moreover, the spatial agglomeration center of high-density urban population showed a gradual westward moving trend. Meanwhile, urbanization development mode shifted from "land lag" to "population lag". (3) Generally, the area of per capita urban development land has exceeded the standard threshold; and 41.96% of the cities currently have a development land area per capita more than five times of the ideal value. (4) The proportion of three coordination types was 73.25%, which is much higher than that of three incoordination types (26.75%). Among them, "Both Growth and Uncoordinated Type" took the largest proportion of 43.27%, which reflects the uncoordinated relationship between demographic urbanization and landscape urbanization. This situation will continue or even is intensified in the years to come. Additionally, the cities located at the edge of urban agglomeration seemed to be more uncoordinated than cities at the center. This is probably because that the cities at the edge of urban agglomeration, which had a small population and low property price, relied more on the "land finance" to earn their main source of urban economic income. (5) Economic development level, population size, governmental decision-making behaviors, geographical location and regional disparity were all driving factors of demographic-landscape urbanization. In addition, there are few obvious differences in the mechanism and effect of these factors. To sum up, urban population and land use management in the new era should get more attention according to the new trend in system diagnosis and comprehensive analysis, thus to provide a scientific basis in development decision for new urbanization and urban-rural integration strategy as well as the rural revitalization strategy.
中国人口与土地城镇化时空耦合特征及驱动机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810004
[本文引用: 2]

城镇化是现代化的必然趋势,城镇人口与土地利用的合理匹配成为新型城镇化的重要前提。本文以中国636个建制市为研究对象,构建了人口城镇化与土地城镇化耦合发展关系指数,据此划分其耦合类型。借助Kernel Density工具,分析了中国城镇化发展的宏观格局、人口与土地城镇化耦合变化态势,诠释了这些耦合特征形成的原因及其内在驱动机制。结果表明:① 2006-2014年中国城市建设用地年均增长率是城镇常住人口年均增长率的1.65倍,土地城镇化远快于人口城镇化;② 市域人口与土地城镇化发展的空间依赖性较强,人口向城市集聚的密度重心呈现逐渐西移的趋势;③ 城市建成区快速扩展,城市人均建设用地面积普遍超标,其中42%的城市现状人均用地是标准值的5倍以上;④ 人口与土地城镇化耦合失调类型的城市空间分布相对集中,且“同增失调”现象较为普遍,主要城市群外围地区的失调问题较中心地区更为严重;⑤ 人口与土地城镇化耦合发展程度受到经济发展水平、城市性质、人口规模、政府决策行为、地理区位条件和地区内部差距等要素的综合影响,不同要素的作用机理和效应存在明显差异。新时期城镇人口与土地利用管理应当注重新常态、新趋势的系统诊断和动能转化的综合分析,为新型城镇化、城乡融合发展与乡村振兴决策提供科学依据。
Dynamic mechanism of urbanization in China since 2000
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201309010
[本文引用: 1]

In four-dimensional analytical perspective, panel data were used to analyze the dynamic mechanism of urbanization in China since 2000 based on the provincial units.<br> There are three obvious improvements from the previous studies in terms of model building. First, urbanization rate was used to replace the synthetic index system, which helped to eliminate the excessive correlations between synthetic urbanization level and driving forces. Second, the synthetic index system was used to describe the driving force instead of single index. Third, the private economy was integrated into the internal force, while the previous studies only considered the rural economy.<br> In this paper, three analysis methods were employed including panel data analysis, temporal analysis and spatial analysis. The panel data analysis demonstrated that market force, government force, internal force and external force are main forces driving the urbanization of China in the period. Among the four driving forces, the external force was relatively weak, which indicated that the dynamic mechanism was characterized by endogeneity. As an extended analysis, temporal analysis and spatial analysis were used to understand the spatial-temporal process of the mechanism. The temporal analysis revealed that the structure of mechanism was changing all the time and had a clear trend. The internal force was getting stronger, and the government force was getting weaker in overall, if we exclude the interference of the global financial crisis in 2007-2008. The spatial analysis delineated the spatial patterns of the driving forces. From these spatial patterns we found that market force and internal force had certain historical dependences, namely the developed regions will stay ahead of backward regions. Thus, combined with the variation trend of internal force and government force, the inequality of urbanization of China is supposed to be strengthened gradually in the near future. Therefore, we recommend a diversified urbanization dynamic mechanism in order to relief the inequality.
21世纪以来中国城镇化动力机制分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201309010
[本文引用: 1]

以省区为基本单元,借鉴欧向军等人提出的四维分析视角,构建综合指标体系,结合面板数据分析、时序分析、空间分析等方法,对2000年以来我国城镇化发展的动力机制加以考察。面板数据分析发现市场力、行政力以及内源力作用较强,而外向力作用较弱,反映了我国城镇化动力机制的内生性特点。时序分析发现新世纪以来城镇化动力机制具有较强的动态性与趋势性,虽然金融危机会对动力组成结构产生一定的扰动,但是在长时间尺度上,内源力作用逐渐上升而行政力作用逐渐下降将成为必然的趋势。而空间分析显示,市场力与内源力具有一定的历史依赖性,优势地区将继续保持领先,落后地区继续维持落后状态。随着市场力的不断稳固和内源力的持续增长,城镇化不平衡发展的趋势将加剧。增加行政力的宏观调控作用,促进城镇化动力的多元化是缓解这一不平衡的重要策略。
Spatio-temporal pattern and driving forces of urbanization in China's border areas
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008004
[本文引用: 1]

Border area is not only an important gateway for inland opening-up, but also an critical part in the building of a moderately prosperous society and optimizing national urban spatial pattern in China. Due to the location, natural resources endowment, and traffic accessibility, the urbanization development is relatively slow in border areas. Therefore, border area is a special area that should be given close attention, especially under the background of the Belt and Road Initiative and China's regional coordinated development program. Based on the county-level data from 2000 to 2015, this paper tries to analyze the spatio-temporal pattern of urbanization in 134 border counties, and applies the geographical detector method to study the driving forces of urbanization in border areas. Conclusions are as follows: (1) From 2000 to 2015, urbanization rate in border areas was lower than the national average, and the gap was widening. Some border counties in southern Xinjiang, Tibet, northeast of Inner Mongolia, and Yunnan, are even facing the problem of population loss. (2) In the same period, urbanization rate in the northwestern and southwestern borders is low, but it grows relatively fast compared with other border counties; urbanization rate in Tibetan border area is the lowest and grows relatively slowly; urbanization rate in the northeastern and northern border areas is slightly higher, but it grows slowly or even stagnates. (3) Transportation and industry are the important driving forces of urbanization in border areas, while the driving forces of market is relatively weak. And there are obvious mutual reinforcements among the driving forces, while the effort of resource force increases obviously after interaction. (4) Urbanization rate in the northwestern and southwestern border areas grows relatively fast, with industrial power and transportation power, market power and administrative power as the main driving forces. Tibetan border area has the lowest urbanization rate and growth rate, as the driving force of urbanization with strong contribution has not yet formed in Tibet. In the northeastern and northern border areas, the contribution of transportation power to urbanization is greater than that of other forces, and its interaction with market and industry has obvious effects on urbanization.
中国边境地区的城镇化格局及其驱动力
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008004
[本文引用: 1]

边境地区是内陆对外开放重要门户,也是全面建成小康社会、优化城镇空间格局的重要组成。本文深入分析2000—2015年中国134个边境县域的城镇化发展格局,基于边境地区城镇化特征构建驱动力体系,并运用地理探测器探析边境地区城镇化驱动机制。研究发现:① 2000—2015年边境地区城镇化水平长期低于全国平均水平且差距不断拉大,面临城镇化发展滞后、动力不足的困境。② 同期,西北、西南边境的城镇化水平偏低、但增速较快;西藏边境的城镇化水平最低、增速平缓;东北、北部边境的城镇化水平稍高、但城镇化速度缓慢甚至停滞。③ 交通力和产业力对边境地区城镇化贡献最大,市场力作用较小,各种驱动力之间存在明显的相互加强作用。④ 西北、西南边境分别形成了以产业力和交通力、市场力和行政力为主要驱动力的城镇化发展机制;西藏边境的自然、社会、经济条件薄弱,尚未形成具有较强贡献作用的城镇化驱动力;东北、北部边境的交通力对城镇化贡献较大,与市场、产业的交互增强效果明显。
Development model and driving forces of new urbanization in Hainan Province: Qionghai City as a case
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.12.008
[本文引用: 1]

In the process of social and economic transformation in China, the rapid urbanization brought about series of such socio-economic problems as increasing urban population, lag of infrastructure services and deterioration of urban environment. The New Urbanization Strategy provides new train of thought and direction for solving these problems, and also provides a good blueprint for constructing the sustainable city and integrated development of urban and rural areas. Qionghai City, as one of the most important regional central city in the east coast of the Hainan Province. In order to build the international tourism core of the east Hainan Province, the local government of Qionghai City implemented the urbanization development strategy of 'Building a pastoral city and structuring a happiness Qionghai', and emphasized the targets of building particular small towns, constructing agricultural pars and realizing the equalization of public service facility. It sought after a new way of 'in-situ urbanization' of 'no cutting down trees, no occupying fields and no tearing down houses', which has become the typical model of the new urbanization in China. Therefore, this article, under the guidance of the theories of urbanization and urban-rural overall coordination development, analyzed the achievement of new urbanization construction of Qionghai City, and discussed 3 types of development models of new urbanization taking Tanmen town, Boao town and Longshouyang national agricultural park for examples. Moreover, we also analyzed the driving forces of the new urbanization of Qionghai city, aiming at providing reference for the new urbanization construction of Qionghai city and other regions in Hainan province. The findings are as following. Firstly, according to character of the intrinsic terrain, agricultural and ecological resources and cultures, the construction of new urbanization of Qionghai city integrated the rural scenery, folk customs, particular industries and farming culture to build the small style towns with historical memory, regional styles and ethnic characteristics. It formatted a multi-centers and group-style garden city landscape of 'one town one feature, one town one industry, and one town one style'. Secondly, based on the oceanic fishing culture, Tanmen town has built a harbor fishing town with the unique features of garden countryside, fishing village of the South China Sea and particular industry village through the construction of infrastructure and beautiful countryside. Boao town has developed an exhibition tourism town with exhibition of economy and coastal water tourism as the core and local culture as the soul relying on the Boao Forum for Asia, Danjia culture and Yudaitan tourism landscape. And the Longshouyang national agricultural park has constructed a tourism area of modern agriculture and advance demonstration area of rural urbanization integrating such functions as rural sightseeing, tourist attraction and urban leisure relying on its original rural landscape, rural landscape and agricultural ecology. Finally, the pill of industrial transformation, guidance of government policy, impulsion of infrastructure construction, attraction of special culture and propulsion of reverse thinking are the dominate driving forces on the new urbanization of Qionghai city.
海南省新型城镇化发展模式及驱动力分析: 以琼海市为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.12.008
[本文引用: 1]

在中国社会经济转型过程中,快速的城镇化导致城镇人口剧增、基础服务设施滞后、城乡差距拉大等系列问题,新型城镇化战略为解决这些问题提供新的思路和方向,为建设可持续城市和城乡一体化发展提供美好蓝图。以城镇化和城乡统筹发展等理论为指导,分析了海南省琼海市城镇化建设过程及成效,并以潭门镇、博鳌镇和龙寿洋国家农业公园为案例,提炼出3种不同类型区域的新型城镇化发展模式,并分析其特征及驱动力,为海南省其他类似地区新型城镇化建设提供借鉴。
Progress of China's new-type urbanization construction since 2014: A preliminary assessment
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2018.02.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
An analysis of multilevel variables influencing China's land urbanization process
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202001013
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, land urbanization, as a spatial manifestation of China's expanding urbanization, has emerged as a core research field within urban geography and land science. Provincial administrative departments within China's distinctive administrative system significantly influence municipal administrative departments and urbanization levels. Individual-level influencing factors cannot fully explain the Chinese mode of urbanization. Therefore, a multilevel linear model was developed to identify factors influencing China's land urbanization process. The results indicated that in 2005, factor inputs, in particular, and public service critically influenced land urbanization in municipal urban areas. By 2016, economic development levels had superseded factor inputs, public service, and population agglomeration as the key influencing factor. At the provincial level, differences in economic development levels critically influenced land urbanization. The provincial government's prioritization of ecological and agricultural resource conservation had a significant negative impact on city-level factors and urban built-up areas. The relationship between the government's developmental attitude, geographical locations, and city-level factors was complex and varied according to regional development levels. A further finding was that since China's reform and opening-up policy was initiated in 1978, land urbanization has been driven by industrialization and urbanization, gradually shifting from government-led to economy-driven stage. Thus, a multilevel study of land urbanization reveals mechanisms and cross-level relationships among different factors that influence levels of land urbanization. Moreover, it provides a theoretical basis for rational policy formulation.
中国城市土地城镇化多层级影响因素分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202001013
[本文引用: 1]

土地城镇化是地理学与土地科学交叉的核心研究领域。随着中国城镇化水平不断提升,土地城镇化作为城镇化在空间的具体体现,已经成为学者和政府共同关注的焦点。土地城镇化受到省、市多层面因素影响,单一层面的影响因素并不能完全有效解释中国特殊行政体系下的多层级关系。本文采用熵值法对中国省、市两个层面影响因素的不同指标进行客观赋权,建立两层线性模型,对2005年和2016年全国102个具有代表性的城市土地城镇化影响因素进行实证研究。结果表明:① 市级层面,2005年要素投入和公共服务是影响城市土地城镇化的主要因素,其中以要素投入最重要。2016年经济发展水平成为最关键的影响因素,要素投入、公共服务、人口集聚对土地城镇化的影响程度依次降低。② 省级层面,区域经济发展水平差异是土地城镇化的主要影响因素。政府资源保护态度、生态和农业资源与市级因素以及城市建成区面积呈显著负相关。根据区域所处发展水平的不同,政府开发态度、地理区位与市级因素存在复杂的影响关系。③ 1978年改革开放以来,中国土地城镇化是工业化和城镇化共同作用的结果,土地城镇化进程逐步由政府主导转向经济驱动。多层级土地城镇化研究,可以更好地解析不同层面影响因素对土地城镇化水平影响机制和跨级关系,为更合理精准的城镇化政策制定提供理论依据。
The citizenization level and its determinants of the second-generation migrants in China's urbanization process
城镇化进程中二代流动人口市民化水平及影响因素
Measurement and spatio-temporal patterns of urbanization quality in Northeast China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.11.013
[本文引用: 1]

With high-quality development as the starting point, the entropy method is used to determine the weights, and the exploratory spatial data analysis method is used to measure the urbanization quality of 34 cities at the prefecture level and above in Northeast China from 2008 to 2018 and analyze the characteristics of their temporal and spatial patterns. The results showed that: From the overalltrendof change, the urbanization quality of Northeast China showed a significant improvement trend, but the growth curved from 2015 to 2018 showed a ‘U’-shaped fluctuation, and the index scores of ‘urban vitality’ in the criterion-level showed a significant decline trend.From the characteristics of spatial and temporal patterns, the spatial and temporal differentiation of urbanization quality distribution in Northeast China was obvious. Under the overall significant improvement environment, some prefecture-level cities experienced a ‘staged’ decline. Through the analysis of the LISA cluster, it was found that the ‘high-value’ agglomeration areas of urbanization quality were mainly distributed in the ‘Harbin-Changchun’ rban agglomeration and ‘central and southern Liaoning’ urban agglomeration, and the ‘low-value’ agglomeration areas were mainly distributed in the northern of Heilongjiang Province. On the whole, the scores of various cities in northern Heilongjiang appear ‘low level’ agglomeration, and the scores of the ‘Harbin-Changchun’ urban agglomeration andmid-southern Liaoning urban agglomeration appear ‘high’ agglomeration.
东北地区城镇化质量测度及其时空格局特征
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.11.013
[本文引用: 1]

采用熵值法确定权重,运用探索性空间数据分析方法对东北地区34个地级及以上城市2008—2018年城镇化质量进行测度并分析其时空格局特征。结果发现:从整体变化趋势来看,东北地区整体的城镇化质量呈现显著提升趋势,但2015—2018年增长曲线呈现出“U”字型波动特征,各子系统中“城市活力”得分呈现显著下降趋势。从时空格局特征来看,东北地区城镇化质量分布的时空分异明显,整体显著提升趋势下部分城市出现“阶段性”下降,通过LISA集聚图分析发现,东北地区城镇化质量的“高值”集聚区域主要分布在“哈长”城市群和辽中南城市群,“低值”集聚区域主要分布在黑龙江省北部地区。
Assessment and pattern evolvement and comprehensive measures of population urbanization in Northeast China since 2003
2003年以来东北地区人口城镇化水平的综合测度及格局演化
Impact of house price and house price-to-income ratio on urbanization of China: Empirical analysis based on spatial econometric model
DOI:10.2307/141856 URL [本文引用: 1]
房价、房价收入比对中国城镇化的影响与空间效应实证分析
People, recreational facility and physical activity: New-type urbanization planning for the healthy communities in China
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.09.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Impact of land urbanization and population urbanization on economic growth in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.009
[本文引用: 1]

By using the panel data of 331 cities from 2000 to 2017 in China, this article builds an econometric model to analyze the impact of urbanization on economic growth from two aspects of spatial urbanization and population urbanization. The results indicate that: 1) In the overall sample, both land urbanization and population urbanization promote economic growth, but the comprehensive effect and investment effect of population urbanization on economic growth are greater than that of land urbanization; The consumption effect of land urbanization on economic growth is greater than population urbanization. 2) Time difference exists in the impact of urbanization on economic growth. In terms of time effect, the investment effect in land urbanization has a downward trend, while the comprehensive and investment effect in population cities and towns has a strengthening trend. 3) There are regional differences in the effect of urbanization on economic growth. In eastern China, the impact of population urbanization on economic growth lags behind that of land urbanization, and the consumption effect and investment effect are the strongest. Land urbanization in the central region does not play a significant role in driving economic growth. Population urbanization mainly promotes economic growth through consumption effect and investment effect, and consumption effect is greater than investment effect. The impact of land urbanization on economic growth in western China is greater than that of population urbanization. Land urbanization in northeast China significantly promotes economic growth, and the consumption effect of land urbanization is the strongest, followed by investment effect and comprehensive effect. The impact of population urbanization on economic growth is not significant. Land urbanization has the strongest impact on economic growth in the western region, followed by the eastern region, northeast region and central region.
中国土地城镇化和人口城镇化对经济增长影响效应分析
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.10.009
[本文引用: 1]

依据2000—2017年中国331个城市面板数据,借助计量模型从土地城镇化和人口城镇化2个方面分析城镇化对经济增长的影响效应。研究结果表明:① 总体样本上,土地城镇化和人口城镇化均促进经济增长,但人口城镇化对经济增长的综合效应和投资效应大于土地城镇化;土地城镇化对经济增长的消费效应大于人口城镇化。② 城镇化对经济增长的影响存在时间差异。在时间效应上,土地城镇化中的投资效应具有下降趋势,人口城镇中的综合效应和投资效应具有增强趋势。③ 城镇化对经济增长效应存在区域差异性。东部地区人口城镇化对经济增长的影响滞后于土地城镇化的影响,且消费效应和投资效应最强劲;中部地区土地城镇化对经济增长的拉动作用不显著,人口城镇化主要是通过消费效应和投资效应促进经济增长,且消费效应大于投资效应;西部地区土地城镇化对经济增长的影响大于人口城镇化影响。东北地区的土地城镇化显著地促进经济增长,且土地城镇化的消费效应最强,其次是投资效应和综合效应;人口城镇化对经济增长的影响不显著。土地城镇化对经济增长影响最强的区域是西部地区,其次是东部地区、东北地区和中部地区。
Spatio-temporal variation and coupling coordination relationship between urbanisation and habitat quality in the Grand Canal, China
Train timetable stability evaluation based on analysis of interior and exterior factors information entropy
Geodetector: Principle and prospective
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
地理探测器: 原理与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

空间分异是自然和社会经济过程的空间表现,也是自亚里士多德以来人类认识自然的重要途径。地理探测器是探测空间分异性,以及揭示其背后驱动因子的一种新的统计学方法,此方法无线性假设,具有优雅的形式和明确的物理含义。基本思想是:假设研究区分为若干子区域,如果子区域的方差之和小于区域总方差,则存在空间分异性;如果两变量的空间分布趋于一致,则两者存在统计关联性。地理探测器q统计量,可用以度量空间分异性、探测解释因子、分析变量之间交互关系,已经在自然和社会科学多领域应用。本文阐述地理探测器的原理,并对其特点及应用进行了归纳总结,以利于读者方便灵活地使用地理探测器来认识、挖掘和利用空间分异性。
Chinese balanced regional development strategy from the perspective of development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

Large regional differences and uneven regional development is fundamental of China. Regional balanced development is an important topic in the field of development geography. This study reviews the course of regional balanced development in China and summarize the characteristics of regional balanced development in each period. This study suggests that inter- regional development of China shows a state of succession between balanced development and non-balanced development. Each succession brings the quality of social development to a new level and gradually make social development move towards the state of high- quality development and balanced regional development. Then, this study discusses the scientific connotation of regional balanced development. Under the guidance of sustainable development theory, we should pay attention to the resource endowment difference in different area, solve the problem among economy, human and nature and promote spatial balance of regional development and green development of ecological economic coordination. The balanced promotion of regional people's well-being is the ultimate goal of regional balanced development. In the end, based on the thinking of development geography, this study discusses the path of regional balanced development in China from three aspects of society, economy and ecology. Suggestions are put forward for the balanced development of China's regions and the improvement of people's well-being.
发展地理学视角下中国区域均衡发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102002
[本文引用: 1]

区域差异大、发展不平衡是中国的基本国情,研究区域均衡发展问题是发展地理学领域的重大课题。本文首先回顾了中国的区域均衡发展历程,总结了各时期区域均衡发展的特征,研究指出,中国区域间发展呈现出均衡发展与非均衡发展演替的状态,每次演进使得社会的发展质量迈进新的台阶,逐渐走向高质量发展与区域均衡发展的状态。其次,本文探讨了当前区域均衡发展的科学内涵,强调要以可持续发展理论为指引,关注不同地区资源禀赋差异,解决经济、人、自然三者间的矛盾,促进区域发展的空间均衡与生态经济协调的绿色发展,最终落脚到区域人民生活福祉的均衡提升为区域均衡发展的最终目标。最后,本文以发展地理学的思维从社会、经济、生态三个方面探讨中国区域均衡发展的路径,为中国区域均衡发展和国民福祉的提升提出若干建议。
Spatial patterns, formation mechanism and coping strategies of rural vulnerability in China at the county level
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106009
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the essential connotation of rural vulnerability, this study constructs an indicator system for the comprehensive measurement of rural vulnerability in China at the county level. Through the selection of five typical representative transects, we will deepen the analysis of the regional differences in China's rural vulnerability and its formation mechanism and propose targeted coping strategies. The results show that: (1) The rural vulnerability of counties in China is generally within the threshold range of low and medium vulnerability characterized by obvious spatial differences. Along the "Bole-Taipei Line", there is a spatial pattern of north-south differentiation. Villages in southwestern China tends to have higher vulnerability than those in northeastern China. (2) External environmental factors are the leading factors that induce rural vulnerability. The rural ecological subsystem, composed of ecological exposure, ecological sensitivity, and ecological adaptation, is the fundamental influencing factor of rural vulnerability. The rural economic subsystem, which is composed of economic exposure, economic sensitivity, and economic adaptation, is the core influencing factor of rural vulnerability. The social subsystem, composed of social exposure, social sensitivity, and social adaptation, is also an important factor influencing rural vulnerability. (3) On the basis of "geographical location, the dominant driving factors of rural vulnerability and the degree of rural vulnerability", rural vulnerability in China at the county level can be identified into eight categories. According to the principle of adapting measures to local conditions, we should break down the regional embeddedness and path dependence. We should strengthen the prediction and monitoring of the sources of disturbance in the rural-area system and scientifically control the sensitivity of the system itself, then improve the adaptation of the rural system to ensure sustainable development of rural areas.
中国县域乡村脆弱性空间特征与形成机制及对策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106009
[本文引用: 1]

基于乡村脆弱性本质内涵,构建了中国县域乡村脆弱性综合测度的指标体系,对中国县域乡村脆弱性水平进行综合测度;通过遴选具有典型代表性的5条样带,深化分析中国乡村脆弱性的区域差异特征及其形成机制,并提出具有针对性的应对策略。结果表明:① 中国县域乡村脆弱性整体上处于较低脆弱度和中脆弱度阈值区间,并具明显的空间差异性,沿“博台线”呈南北分异的空间格局,东北部乡村脆弱性偏低,西南部乡村脆弱较高。② 外部性环境因素是诱发乡村脆弱性的先导因素,生态暴露、生态敏感和生态适应构成的乡村生态子系统是乡村脆弱性的根本性影响因素;经济暴露、经济敏感和经济适应构成的乡村经济子系统是乡村脆弱性的核心影响因素;社会暴露、社会敏感和社会适应组成的乡村社会子系统也是乡村脆弱性的重要影响因素。③ 以“地理区位、乡村脆弱性主导驱动因素和脆弱性程度”为依据,将中国县域乡村脆弱性划分为8个地域类型区。不同类型区域,遵循因地制宜原则,破除地区根植性和路径依赖,增强乡村地域系统扰动源的预测和监测,并对系统自身敏感性进行科学管制,提升乡村系统的适应能力,促进乡村可持续发展。
Spatial variation of land urbanization in Jiangsu and dominant drivers
江苏省土地城镇化的空间分异及其主导因素探测
Regional disparity and the influencing factors of land urbanization in China at the county level, 2000-2015
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812005
[本文引用: 1]

In the unprecedented urbanization process in China, urbanized land has expanded quickly at the same pace or even faster than the growth of the urban population. Employing both the ordinary least square and geographical weighted regression, we analyzed the spatial patterns and factors influencing land urbanization at the county level in 2000 and 2015. This analysis was assisted by land-use data for China acquired from the resource and environment data cloud platform. The research reveals the following points: (1) The annual growth rate of land urbanization experienced 2.77 percentages on average from 2000 to 2015. About 40% of the counties witnessed an annual increase of 3% or above. Land urbanization was manifested in a pattern of diffusion, which differed from the continued spatial polarization of demographic urbanization in China. (2) Geographically, the north-south differentiation of land urbanization was clearer than the east-west differentiation. And the high-value regions tended to be located to the southeast of "Hu Line". Counties surrounding those metropolitan areas were detected as hotspots of land urbanization. In general, there was a convergent trend of land urbanization among regions in China. (3) The factors of population growth, economic development, industrial structure, city/county features, and geographical location have played significant roles in the spatial disparities of land urbanization at the county level. Besides, the spatio-temporal dependence of their influences were also explored. This study on land urbanization and its influencing factors at the county level advances our theoretical and practical understandings of the new-type urbanization, urban and rural integration, and rural revitalization strategies in contemporary China.
中国县域土地城镇化的区域差异及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812005
[本文引用: 1]

中国经历了史无前例的快速城镇化进程,与之相伴随的是更加迅猛的土地城镇化过程。基于2000年和2015年中国土地利用现状遥感监测数据,综合运用空间分析、多元回归和地理加权回归的方法,深入分析了中国县域土地城镇化的区域特征及其影响因素。结果表明:① 中国县域土地城镇化率年均增长2.77%,其中近40%的区县城镇化率年均增长大于3%;在空间上呈现出不同于人口城镇化的扩散趋势。② 中国县域土地城镇化的南北分异规律较东西分异更为明显。土地城镇化的高值区域始终集中在胡焕庸线的东南半壁,而围绕主要的城市群地区则形成“组团式”增长的热点区,地区间差异趋于收敛。③ 人口集聚、经济发展、产业结构、城市特性与地理区位等要素对县域土地城镇化空间分异格局的影响较为显著、稳定,各要素对土地城镇化的影响均具有明显的时空依赖特征。分析揭示县域土地城镇化的时空特征及其动力机制,对于科学认识新型城镇化和实施城乡融合、乡村振兴战略,具有重要的理论价值与现实意义。