1 引言
当今世界正处于大发展大变革大调整时期,科技水平的发展变化深入影响着世界政治经济力量格局的发展变化,甚至影响着各国各民族的前途命运。在世界面临百年未有之大变局的背景下,科技霸权、民粹主义、贸易保护主义思潮明显抬头,科技竞争越来越成为国际竞争的焦点[1-2]。科技全球化和科技网络化深刻的改变着国家创新模式并重塑世界科技格局,新兴国家在全球科技格局中的地位越来越凸显[3-4]。军事科技作为国家科技体系中重要而独特的部分其实力的变化更为显著的影响着世界局势的走向。目前,从地缘经济和政治探讨世界权力格局演化成果已较为丰富,世界地缘经济与政治格局“东升西降”和主要大国力量对比“南升北降”的格局已得到广泛认同[5],但对地缘军事科技的权力演化格局还缺乏探讨。因此,探讨全球军事科技权力的时空演化规律,准确把握世界政治军事格局的变化对深刻认识和有效应对百年未有大变局具有重要的现实意义。
军事科技贸易是军事学、经济学、政治学和国际关系学等学科关注的重要内容,这些学科对军事科技贸易的研究主要集中在军事科技转移与武装冲突[6⇓-8]、军事科技贸易与产业发展[9-10]、军事贸易与国际政治格局的交互影响[11⇓-13]等方面,往往缺乏地理空间思维,对军事科技贸易时空格局、空间演化效应和规律等地理特征有所忽视。军事科技贸易在地理学研究中属于地缘军事科技范畴,并兼具地缘经济、地缘政治和地缘战略多重属性。目前,关于地缘军事科技的研究主要集中于地缘科技相关概念、内涵、框架和理论体系的初步探讨[14⇓-16],对地缘军事科技国际转移和空间流动的量化研究方面,仅部分学者基于知识产权和商品贸易对地缘科技格局演化进行探讨[17-18],对全球军事科技资源转移和科技要素空间流动等地缘军事科技问题的研究仍有待完善[19]。知识经济时代科技实力作为国家核心软实力将重塑国际体系结构并促使国家权力结构分配格局不断调整[20],加强地缘军事科技的空间流动研究有助于从军事科技实力视角识别国际权力体系的时空格局和演化规律。
军事科技作为具有军事和科技双重属性的独特科技产品,在全球范围内的流动不仅仅是产品贸易的流通过程,更是世界军事科技实力动态演变的过程,并深刻影响全球政治经济和地缘军事战略格局的变化[21]。军事武器产品的国际进出口贸易是最直接最典型最主要的军事科技转移手段,其流通过程不仅是经济学意义上的产品贸易,更蕴含着深刻的政治学、军事学和国际关系学内涵。大国间的强权竞争和国际社会的持续冲突使军事科技贸易成为世界关注的焦点,伴随着俄罗斯和乌克兰爆发冲突,军事武器的支援及背后的大国利益和地缘军事关系引发世界各国的广泛关注。因此,从全球尺度厘清军事科技贸易的全局特征,揭示全球军事科技贸易背后的大国战略和地缘军事权力格局演变,对准确把握地缘军事格局和权力演化具有重要的意义和现实价值。基于此,采用全球武器贸易数据来探讨全球军事科技贸易时空格局演化、网络格局特征和贸易的动力机制,以丰富地缘科技要素流动和地缘军事权力演变研究,从军事科技视角深刻认识地缘军事科技格局演化,并为深刻认识百年未有之大变局,科学制定地缘军事科技战略制定提供有益参考。
2 研究方法与数据来源
2.1 研究方法
2.1.1 区位商
区位商是地理学和经济学中用来衡量某一产业部门专业化程度或某区域功能和作用的常见计量模型[22]。本文借鉴区位商模型来反映不同国家和地区在军事科技贸易中的比较优势和依赖程度,通常区位商大于1则表示该产品在出口贸易中具有比较优势或在进口中具有依赖性。其公式如下:
式中:
2.1.2 网络分析
网络密度。该指标用来反映网络发育状况,网络密度越大表明网络发育程度越高。其公式为:
式中:m为网络间贸易联系数;n为节点总数。
网络中心势。该指标反映网络联系的集中程度,军事科技贸易网络中的网络中心势可分为出度网络中心势和入度网络中心势。出度网络中心势越高,贸易网络的出口越集中;入度网络中心势越高,贸易网络的进口越集中。公式为:
式中:S为网络的中心势;Smax为网络各节点出度/入度的最大值;Si为节点i的出度/入度。
网络社团。该指标用来度量贸易网络中国家(地区)组成的社团,同社团内贸易联系较紧密,不同社团贸易联系相对稀疏。公式为:
式中:Q代表网络模块度;wij为矩阵中节点i与节点j的联系状况,若有联系为1,否则为0;Si、Sj分别是节点i、j的度值;δ(Ci, Cj)用以判别节点i和节点j是否为相社团,若是则为1,否则为0。
2.2 数据来源
军事科技贸易数据来源于斯德哥尔摩国际和平研究所(SIPRI),SIPRI是世界上致力于研究和平与安全等重要问题的著名权威学术机构,其武器转让数据库包含所有主要常规武器转让的信息。为比较国家(地区)武器贸易中不同军事科技资源转移趋势,SIPRI开发了趋势指标值(TIV)来衡量主要常规武器的国际转让量,TIV有效地代表军事科技资源的转移而非武器贸易的财务价值。国家间地理距离,共同语言和历史殖民等数据来源于CEPII数据库,GDP、专利申请、军费强度等数据来源于世界银行数据库,政治稳定性指数来源于世界政治治理指标数据库。
3 全球军事科技贸易产品结构演化
3.1 贸易整体规模演变
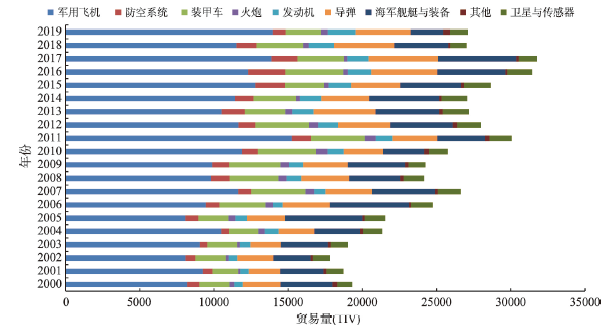
全球军事科技贸易规模整体呈波动上升的趋势,贸易产品结构表现出一极三核主导的特征。具体来看,2000—2019年全球军事科技贸易规模虽有波动,但总体呈上升态势,总贸易量从19307 TIV上升至27105 TIV,各类军事科技产品除海军舰艇与装备由3508 TIV下降至2183 TIV外,均呈上升趋势(图1)。其中,发动机、军用飞机和导弹成为贸易额增幅最大的产品,发动机的贸易增幅年均增长更是达到6.7%,反映了21世纪以来,区别于以往军事科技贸易以清理库存而出口过时的、技术落后的产品,市场的激烈争夺使科技含量高的核心产品成为贸易重要商品。2007年、2011年和2017年是典型的阶段性贸易增长峰值,在遭受经济危机后全球军事科技贸易却逆势上扬,其原因在于军事产品的贸易受经济危机的影响小,其高额利润在经济低迷时成为众多军事大国提振经济的方式之一,加上中东欧、南海、中东和北非等地区争端或局部性战争以及沙特阿拉伯、卡塔尔等石油大国为保障国家安全大幅进口军事科技产品最终在2017年形成贸易峰值。
图1
图1
2000—2019年全球军事科技产品贸易结构变化
Fig. 1
Changes in the global trade structure of arms products from 2000 to 2019
在产品结构方面,军用飞机、海军舰艇与装备、导弹和装甲车是全球军事科技贸易的主要产品,历年贸易比重均超过80%。军用飞机一直是全球军事科技贸易的主体,贸易量均在8084 TIV以上,但2011年后其所占的比例开始下降;海军舰艇与装备、导弹和装甲车,3类产品的贸易比重整体差别不大,贸易比重基本上位于[0.24]的极值区间之内。发动机、防空系统、卫星传感器、火炮等军事科技的贸易比重均在10%以下。总体上看,全球军事科技贸易主要集中在军用飞机、海军舰艇与装备、导弹和装甲车等实战型产品上,该产品的杀伤力和威慑力对提升国防实力和改变地区局势具有重要作用,因而成为贸易需求最旺盛的产品;发动机、防空系统和卫星传感器等功能性和模块化的产品主要特点在于辅助性、防御型和功能性,对军事科技产品升级、提升军事综合实力具有重要作用,但技术门槛较高且缺乏直接有效的威慑力和战斗力,因此,在全球市场的贸易量较少,主要的进口国为突破军事技术瓶颈或弥补军事短板并具有较强经济、科技和军事实力的大国。
3.2 主要贸易国家(地区)出口结构演变
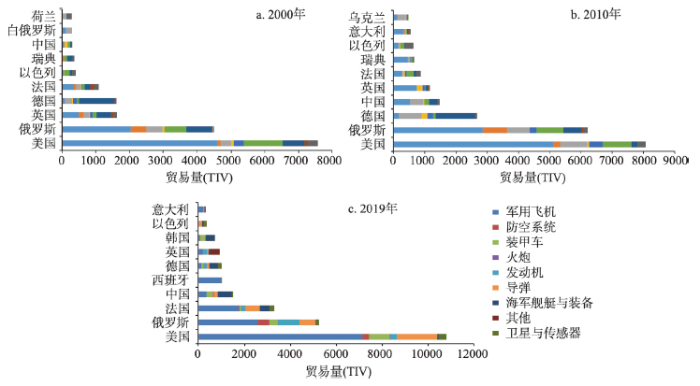
从产品出口规模看,美国和俄罗斯是世界上最主要的军事科技产品出口国,军用飞机是大部分国家(地区)最主要的出口产品。2000年超过17个国家的军用飞机出口比重占全部军事科技产品30%以上,2019年更是有20个国家的军用飞机出口占比超过30%。美国是历年来军用飞机出口规模最大的国家,出口规模由4584 TIV增长至7147 TIV,占全球军用飞机出口的51.2%和美国军事科技产品出口总量的66.2%。俄罗斯是世界第二大军用飞机出口国,出口额保持在2000~3000 TIV之间,但出口占全球的比重从24.9%下降至18.3%,市场占有率持续下降并与美国的差距扩大。俄罗斯原是装甲车和导弹的最大出口国,但美国分别在2003年和2006年超越俄罗斯成为全球的最大出口国,产品的市场占有率被美国持续挤压。在研究期内海军舰艇与装备的最大出口在出现多次交迭,德国、美国、俄罗斯、中国多次交替领先,2019年中国的海军舰艇与装备出口规模达到622 TIV,成为最大的出口国,也反映了中国在发展海军和海上军事力量建设上取得的巨大成就;法国、韩国在海军舰艇和装备上也具有较大的出口规模。
图2
图2
2000年、2010年和2019年全球前10国家(地区)军事科技出口结构
Fig. 2
Export structure of arms products from 10 countries (regions) in 2000, 2010 and 2019
基于区位商对全球军事科技出口进行测度,结果发现:美国和俄罗斯的大部分军事科技产品在贸易中居于绝对优势地位并具有极高的比较优势,中国、法国、德国、韩国等国依托自身的比较优势专注于少数几类军事科技研发和出口占据着一定的军事科技市场份额,从而形成错位发展的贸易格局。装甲车是全球多国最具相对比较优势的出口产品,2019年有18个国家的出口优势产品是装甲车,主要为德国、中国、白俄罗斯、土耳其、乌克兰、奥地利等陆军强国或内陆型国家;发动机和卫星与传感器等极具科技含量的产品上,具有比较优势的国家则以西欧和北美等发达国家为主,包括英国、美国、加拿大、德国、法国、意大利、以色列、瑞士和芬兰等,体现着欧美发达国家在航空航天技术领域的主导和垄断地位。有趣的是,美国比较优势最大的产品为军用飞机,而俄罗斯比较优势最大的产品为防空系统,导弹则是两国共同的比较优势产品,这也从侧面反映了美国和俄罗斯目前军事竞争中的攻守地位。
3.3 主要贸易国家(地区)进口结构演变
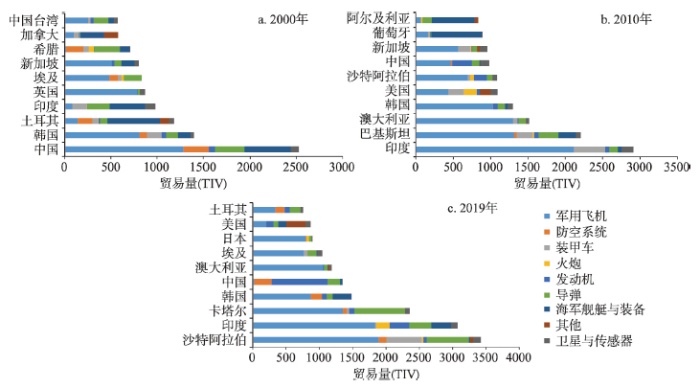
从产品进口规模上看,军用飞机是全球需求最大的军事科技产品,进口国家(地区)从71个增长至的84个,进口比重也相对呈增长趋势,装甲车、导弹、发动机和卫星与传感器的进口国(地区)也在40家以上。受卡特尔外交危机事件影响,沙特阿拉伯是2017年成为世界上最大的军事科技产品进口国,军用飞机、装甲车、卫星与传感器的最大进口国和导弹的第二大进口国,并由此引发卡塔尔大幅进口武器从而在2019年成为第三大军事科技产品进口国。在有较大军事科技产品进口规模的国家(地区)中,以海军舰艇和装备为主要进口产品的国家(地区)则比例相对减少,主要为新西兰、孟加拉国、马来西亚、希腊、波兰、葡萄牙、以色列、阿尔及尼亚和阿根廷等少数滨海国家,也体现其增强海军实力的军事力量发展意愿。防空系统是军事科技贸易中的冷门产品,历年进口国家(地区)仅保持在10个左右,主要包括中国、埃及、土耳其、韩国和沙特阿拉伯等。
图3
图3
2000年、2010年和2019年全球前10国家(地区)高科技产品进口结构
Fig. 3
Import structure of arms products from 10 countries (regions) in 2000, 2010 and 2019
基于区位商的进口依赖产品进行识别发现,军用飞机仍是大部分国家(地区)的进口依赖产品,2019年有58个国家(地区)的进口依赖产品为军用飞机。印度、卡塔尔、沙塔阿拉伯、埃及等南亚、中东和非洲等地区的发展中国家主要的进口依赖产品为军用飞机、装甲车和导弹等实战型产品;丹麦、法国、德国、比利时、加拿大、英国、意大利等西欧北美发达国家的进口依赖产品主要为发动机和卫星与传感器等高精尖的功能型产品,这也反映发达国家和发展中国家在现代战备方向和战争理念上的巨大差异。滨海和海陆复合型大国则是海军舰艇与装备的进口产品依赖国,如日本、英国、法国、印度等,体现了地理环境对国家军事发展方向的影响。中国主要的进口依赖产品经历了军用飞机、防空系统、发动机、海军舰艇与装备到发动机、海军舰艇与装备到发动机的演变历程,发动机一直是中国最重要且依赖程度最深的进口产品,表明中国在防空系统和海军力量建设上取得了一定的成绩,但发动机依赖进口的情况仍未得到有效缓解,集中力量在发动机领域取得突破性进展,改变发动机受制于人的状况是实现军事科技强国的必经之路。
4 全球军事科技贸易网络空间格局演化
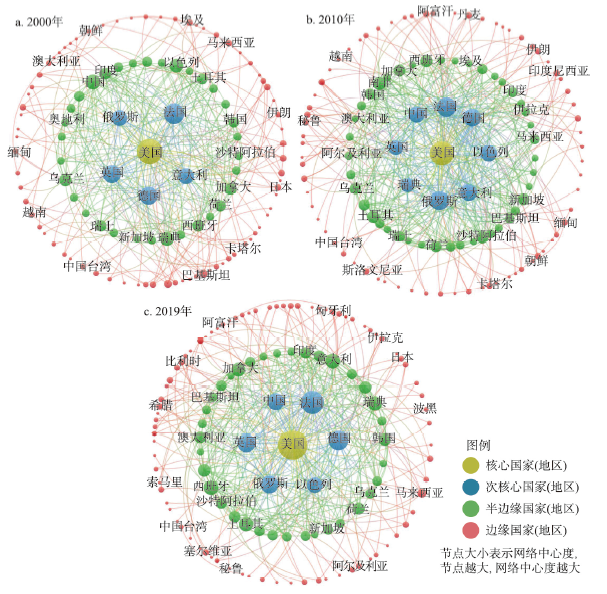
4.1 全球军事科技贸易空间分布特征
4.1.1 全球军事科技出口重心朝东南方向移动,美国、俄罗斯、西欧三极分布格局显著
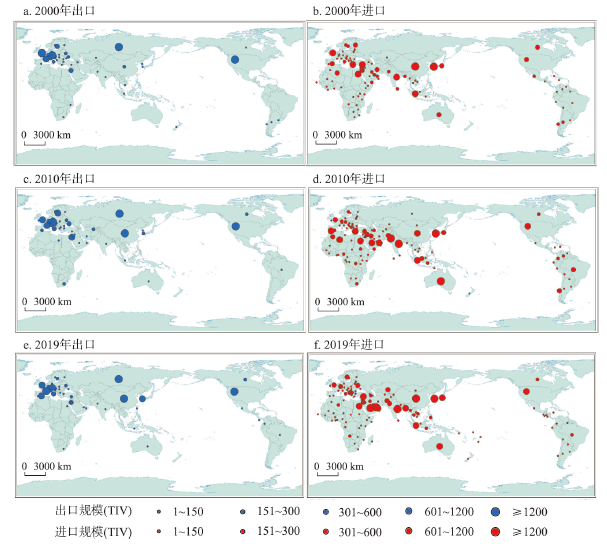
2000 年全球军事科技贸易网络出口主要由美国、俄罗斯和西欧主导,贸易出口联系占全球的84.54%,三极分布特征明显;美国是世界上最大的军事科技贸易出口国,与美国产生贸易联系国家(地区)达到48个,占全球总数的15.24%;其后分别为法国31个、德国27个、英国25个、俄罗斯22个。受到以色列、中国和韩国等亚洲国家军事科技实力不断崛起的影响,2010年美国、俄罗斯、西欧在全球贸易网络中比重下降至77.19%,中国、以色列和韩国等亚洲国家在贸易网络中的地位也呈上升趋势,比重由8.57%上升至12.21%,军事科技出口的重心向东南方向转移,标准差椭圆中心点坐标由16°20′44″W、50°43′56″N向东南方向至转移至0°16′12″W、48°52′12″N,表明亚洲国家军事实力的提升正使军事贸易重心向东转移,并成为重构世界军贸出口格局的重要力量。2019年美国、俄罗斯、西欧在贸易网络仍具有先发优势,虽然全球贸易联系比重进一步下降至75.93%,但美国的军事科技贸易出口国(地区)进一步扩张至66个,重心开始向西南方向回移,标准差椭圆中心点坐标变为14°39′53″W、47°37′53″。虽然亚洲的以色列、中国和韩国等国在贸易网络中产生的联系占比达进一步上升到12.9%,但军事科技出口以美国主导的格局还未发生根本性改变。整体上,全球军事科技贸易表现出十分显著的美国、俄罗斯和西欧三极主导格局,中国、以色列和韩国等亚洲国家在贸易网络中贸易规模和贸易比重均呈较大幅度的提升,全球军事科技贸易出口的重心向东南方向移动,世界军事科技贸易存在一定程度的东移和重构趋势,地缘军事科技出口格局东升西降、南升北降明显,但美国在全球军事科技贸易体系中仍具有绝对的影响力和控制力。
4.1.2 全球军事科技进口重心朝东南方向移动,空间分布与边缘地带相吻合
全球军事科技贸易进口国(地区)集中分布于东亚—东南亚—南亚—中东—南欧—北非一带,空间分布的范围大致与斯皮克曼边缘地带理论中的边缘地带相吻合。2000年亚洲国家(地区)进口总规模为9505 TIV,占比为49.9%。贸易量上,中国、韩国、土耳其、印度和英国是最大的5个进口国;印度向10个国家进口军事科技,成为贡献贸易联系最多的进口国家;2010年亚洲国家(地区)进口总规模上升至13319 TIV,印度和巴基斯坦成为全球进口军事科技规模最大的两个国家,澳大利亚、韩国、美国和沙特阿拉伯紧随其后的进口规模也有所扩大,而中国的贸易量则下降至981 TIV,促使军事科技进口的重心由46°17′41″E、30°39′50″N向西南方向至转移至45°34′9″E、23°50′36″N,方向角增长至95.23°表明军事科技进口分布的西北—东南格局有强化趋势(表1)。2019年沙特阿拉伯、印度、卡塔尔和韩国军事科技进口规模扩大,泰国、新加坡、印度尼西亚、阿联酋等国军事科技贸易伙伴数量的增加,亚洲国家(地区)进口总规模已达19170 TIV,占比达到全球70.7%,进而使军事科技贸易的进口重心向东北方向转移,标准差椭圆中心点坐标变为57°47′6″E、27°10′40″N。总体上看,由于印度、沙特阿拉伯等南亚和中东国家军事科技进口规模和贸易伙伴的增加,贸易出口的重心朝东南方向移动,地缘军事科技进口格局亦呈现出东升西降、南升北降态势。进口国(地区)的空间分布主要集中在欧亚大陆边缘地带,与斯皮克曼描述的边缘地带和麦金德提出的新月形地带具有极高的一致性,而美国军事科技出口的重点地带依旧是欧洲、东亚和中东等地缘政治敏感区,与斯皮克曼擘画的需要经略的边缘地带极为吻合,体现扼制欧亚大陆出现全球性大国以保持美国世界霸主地位的战略意图[27],这也表明经典地缘政治理论对深刻理解目前的世界政治军事格局具有重要的指导意义。
表1 2000年、2010年和2019年全球军事科技贸易重心分布空间演化
Tab. 1
| 参数 | 出口 | 进口 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000年 | 2010年 | 2019年 | 2000年 | 2010年 | 2019年 | ||
| 中心经度 | 16°20′44″W | 0°16′12″W | 14°39′53″W | 46°17′41″E | 45°34′9″E | 57°47′6″E | |
| 中心纬度 | 50°43′56″N | 48°52′12″N | 47°37′53″N | 30°39′50″N | 23°50′36″N | 27°10′40″N | |
| 方向角度(°) | 86.63 | 87.98 | 88.67 | 92.66 | 95.23 | 97.92 | |
| 扁率 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.69 | |
图4
图4
2000年、2010年和2019年全球军事科技出口和进口国(地区)的时空分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS2016(1666)号的标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 4
Distribution of global arms trade export and import countries (regions) in 2000, 2010 and 2019
4.2 全球军事科技贸易网络整体特征
4.2.1 全球军事科技贸易网络规模呈扩大趋势,欧美国家(地区)具有极强的市场垄断能力
2000—2019年全球军事科技贸易网络节点和规模呈扩大趋势,军事科技贸易国家(地区)从114个增长至130个(表2),表明随着时间的演化越来越多的国家(地区)参与到军事科技贸易中来,但贸易网络的密度却相对稳定的保持在0.024左右,军事科技贸易网络的规模持续扩大,网络间的整体联系却并未得到明显增强。对比全球各类产品贸易、科技合作、人才流动和交通运输[28⇓⇓⇓-32]等网络的全面增长态势,军事科技贸易网络增长趋势不够显著,反映了军事科技的政治、经济和军事多重属性使全球军事科技贸易网络演变具有明显的特殊性。深入研究发现,全球军事科技贸易网络的出口国(地区)数量相对稳定,基本保持在40个左右,美国和俄罗斯一直以来都保持全球军事科技出口规模前两位的垄断地位,2000年的出口前10强中有6个在2020年依然保持在前10地位,占据市场规模超过80%,军事科技高额的利润、天然的技术门槛、激烈的市场竞争和敏感的地缘政治关系使军事科技出口对市场具有极强的垄断地位。同时,由于军事科技并非国家生产生活的必需品,进口规模具有波动性特征并存在较多的偶发性进口,如缅甸、阿富汗、索马里、阿尔巴尼亚等,这些国家出于增强国家实力、维护国家稳定或其他某种需要,往往在某些特殊的时刻进口军事科技产品,但实际上却可能并未完全镶嵌到贸易网络中,更难以实现网络地位的提升和转变。
表2 全球军事科技贸易网络的统计特征量
Tab. 2
| 特征量统计 | 2000年 | 2010年 | 2019年 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 节点数 | 114 | 123 | 130 |
| 网络密度 | 0.024 | 0.029 | 0.024 |
| 平均聚集系数 | 0.232 | 0.299 | 0.302 |
| 出度网络中心势 | 0.0297 | 0.0283 | 0.0287 |
| 入度网络中心势 | 0.0094 | 0.0094 | 0.0088 |
4.2.2 军事科技贸易网络存在去中心化趋势,亚洲国家(地区)成为重塑贸易格局的重要力量
2000—2019年全球军事科技贸易网络平均聚集系数增长趋势明显,由2000年的0.232增长至2019年的0.302,贸易网络扩大且贸易联系更为多样。出度网络中心势显著高于入度网络中心势表明军事科技贸易网络处于明显的卖方市场,出口集中于少数国家和地区,亦印证着出口国(地区)的主导和垄断地位,而进口国家(地区)规模相对较大,在全球的空间分布也趋于扩散。出度网络中心势和入度网络中心势均表现出下降趋势,表明全球军事科技贸易网络存在去中心化趋势,核心出口和进口国(地区)的网络联系扁平化特征明显,等级化的贸易层级特征开始逐步瓦解,具体到贸易网络看,美国的军事科技贸易伙伴和贸易规模不断增长直接推动网络向扁平化发展,英国、德国、意大利等次核心地位的西欧国家贸易伙伴数量减少,市场份额不断收缩,中国、韩国、以色列等亚洲国家贸易规模进入前列并成长成为贸易出口大国,出口规模和贸易伙伴日益扩大,成为重塑军事科技贸易格局和等级体系的重要力量,并在较大程度上改变着世界地缘政治军事格局。
4.3 全球军事科技贸易网络空间联系特征
4.3.1 全球军事科技贸易网络呈一超多强格局,欧亚大陆是全球军事科技贸易的主要舞台
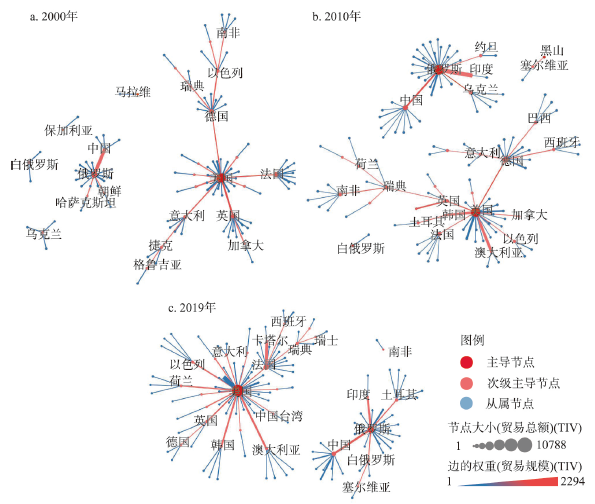
美国在全球军事科技贸易网络中占据绝对核心的地位,研究期内贸易规模从7571 TIV增长到10788 TIV,占比达到全球总额的39.8%,出口国家更是由50个扩大到68个,新增出口国主要分布在东欧、中东、亚太和非洲等地区(图5),如2003年北约东扩后,美国开始向拉脱维亚、立陶宛等中东欧国家转移军事武器,2017年黑山加入北约后,美国首次向黑山转移军事武器;美国提出重返亚太战略后又开始加大对东南亚、东亚等亚太地区增加军事科技出口,并扩张了科威特、卡塔尔等中东地区市场,在一定程度上反映了美国北约东扩、重返亚太和经营中东等政治和军事意图。俄罗斯、法国、德国、英国等作为传统军事强国居于次核心地位,出口国家(地区)超过均超过20个,俄罗斯的出口市场主要分布在亚太、南亚、中亚和中东欧等地区,与美国的新增和扩大出口的市场具有较高的重叠度,受到美国的市场竞争和冲击较为明显。中国和以色列由于科技水平的不断进步和市场规模的不断扩大在全球军事科技贸易网络中的地位明显提升,由半边缘国家转变成为次核心国家,中国军事科技贸易差值从-2227 TIV转变为125 TIV,成为唯一实现从入超到出超转变的军事大国。
图5
图5
2000年、2010年和2019年全球军事科技贸易网络的核心—边缘结构
Fig. 5
Multicore-periphery structures in the global arms trade network in 2000, 2010 and 2019
从军事科技出口目的地分布看,欧亚大陆是全球军事科技出口的主要目的地,超过60%的进口国(地区)位于欧亚大陆,超过80%的军事科技贸易流向欧亚大陆。美国和俄罗斯主导的前10条最大贸易流中就有7条以上流向欧亚大陆,主要分布在亚太和中东等地缘政治敏感区,贸易规模约占全球的1/3,且增长的趋势较为明显,反映了该区域潜在并日益激烈的大国博弈,欧亚大陆越来越成为全球军事科技贸易最主要的舞台。
整体上看,全球军事科技贸易网络呈现出以美国为核心的一超多强格局,欧亚大陆是全球贸易最主要的舞台,中东、亚太和东欧等地缘敏感区是军事科技贸易的主要流向地。美国凭借军事科技贸易对国际事务和地缘格局产生全球性的影响远超其他国家(地区),这与当前国际政治经济和军事格局具有较高的一致性。
4.3.2 以美国和俄罗斯为核心军事科技贸易竞争格局凸显
通过最大流分析贸易网络的等级层次结构发现,全球军事科技贸易网络存在明显的断裂特征,形成以美国和俄罗斯为核心的两个主体网络和多个从属网络(图6)。以美国为核心的主体贸易网络规模较大,基本覆盖60%以上的国家(地区),其中,美国的最大军事科技贸易伙伴规模扩张趋势明显,2019年已增长至39个,在网络内的主导能力持续上升;英国、法国、德国和意大利等国家是该主体网络最主要的次级主导国家,但除法国外,各国的最大贸易伙伴均明显减少,最大流贸易网络也显示以美国为主体的网络由层级化网络向扁平化网络转变,反映了在美国网络主导能力提升的同时各国家(地区)的影响力和控制力在不断下降和削弱,并有成为从属节点的趋势。以俄罗斯为核心的主体贸易网络规模相对较小,核心国家俄罗斯的最大军事科技贸易合作伙伴规模呈波动上升的趋势,并先后整合了白俄罗斯和乌克兰两个从属网络扩大了自身网络的影响力,但拉脱维亚、克罗地亚、斯洛伐克等国先后脱离俄罗斯主导的贸易网络,成为美国及其从属节点的最大军事科技贸易合作伙伴,表明俄罗斯的市场空间也在较大程度上受到美国的竞争和挤压。作为次级主导节点,中国的从属节点规模也不断增加,表明中国最大军事科技贸易合作伙伴不断增加,中国还始终是俄罗斯的最大军事科技贸易合作伙伴,两国间的军事科技贸易和交流极为密切,印证着两国的全面战略协作伙伴关系。整体上,全球军事科技贸易最大流显示出美国和俄罗斯相互竞争的格局,反映美苏两极军事对抗格局在全球军事科技贸易网络中的历史惯性。美国、俄罗斯、法国和中国的从属节点规模不断扩大,影响力和控制力持续提升,英国、德国、意大利、瑞典等国的从属节点不断萎缩,影响力和控制力逐渐式微,平均聚类系数不断上升也显示从属节点不断向核心节点靠拢,原有的等级体系开始逐渐瓦解,这也从军事科技贸易的角度反映着全球政治经济军事格局演化的百年之大变局。
图6
图6
2000年、2010年和2019年全球军事科技贸易网络的等级层次性
Fig. 6
The hierarchy of the global arms trade network in 2000, 2010 and 2019
4.4 全球军事科技贸易网络空间组织特征
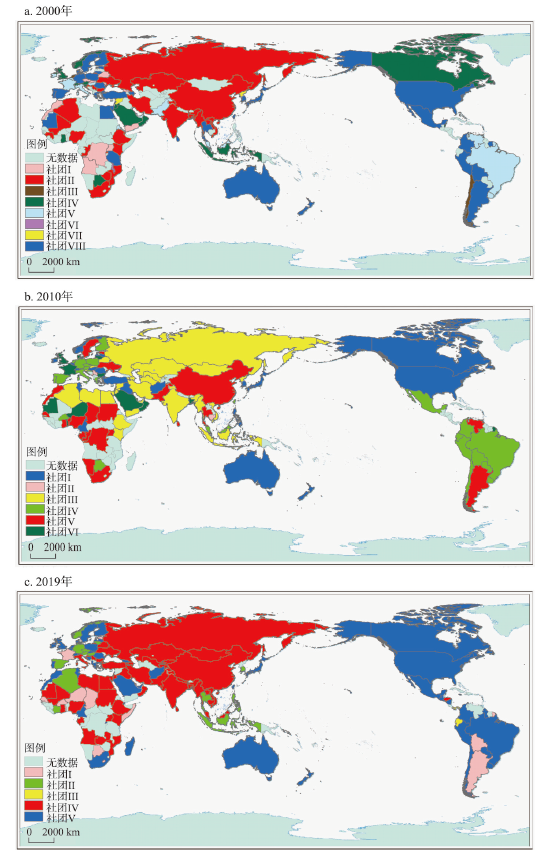
4.4.1 网络空间组织具有空间集聚与空间紊乱并存的特征
全球军事科技贸易网络的社团分布呈现空间集聚和空间紊乱并存的地理分布特征,社团边界相对较为模糊,各大洲和大陆之间的社团构成相对复杂,不同大陆之间的社团混杂度存在差异。西欧、北美和亚洲内陆总体上的社团结构较为一致,边界相对清晰,空间权力整合度高体现出空间集聚的特征;非洲、中东、亚太和南美地区等地缘政治敏感区受到大国博弈和地缘竞争影响,区域国家和地区的社团归属混杂多变,社团边界难以划分,体现出明显的空间紊乱特征。对比文化贸易、人才流动、技术转移和交通网络等社团结构空间组织,发现军事科技贸易网络的空间集聚社团联系特征与文化贸易、技术转移等虚拟的社会流网络相似,但亚太、中东等地区在社团归属上的紊乱特征具有极其突出的独特性,在当地特殊的战略地位、丰富的化石能源导致地区的大国竞争十分激烈,造成了复杂的政治经济军事环境,从而使其在社团归属上表现出极其紊乱的特点。
4.4.2 网络社团分裂整合重组特征明显,美国和俄罗斯社团范围逐渐扩大
全球军事科技贸易网络的社团数量从8个减少至5个,社团分裂整合重组特征明显,美国社团和俄罗斯社团始终是全球军事科技贸易网络中最重要的主导社团,美国社团范围主要包括西欧、美洲、非洲和亚太等国家(地区),俄罗斯主导社团空间集聚于欧亚大陆和非洲等国家和地区。研究期内,美国社团完成了对中东、南美、非洲和西欧等部分国家,俄罗斯社团整合亚洲、中东和非洲部分国家扩大了自身社团的影响力。美国和俄国作为世界上最大的军事科技出口国通过贸易网络分别主导着最大的两个社团,社团边缘成员之间的分裂和转化较多,体现着美国和俄罗斯在军事科技贸易市场上激烈的竞争,也蕴含着两国在敏感地区和地缘政治军事领域的争夺。西欧社团逐渐分化出德国和法国主导的两个社团,两个国家作为欧盟的领导国家不同于英国,未重组进入美国社团,反而整合欧洲和非洲部分国家形成两个新社团,在一定程度上反映了德国和法国相对独立地缘策略和对社团领导地位的追求。有意思的是,不同于德国和英国,法国始终没有融入美国主导的社团,即使在2019年西欧已经基本被美国和德国社团整合的局面下,法国仍然整合非洲等原殖民地国家形成独立的社团。总体上,全球军事科技贸易网络的社团结构存在不断分裂整合重组的特征,以美国和俄罗斯为主导的两个社团是全球主要的两个社团,其空间范围相对固定且边界不断分裂重组并向外围扩张,英国、法国、德国等国家主导的社团范围明显收缩,社团空间组织的稳定性较差,受美国和俄罗斯社团扩张的挤压严重。
5 全球军事科技贸易网络的影响因素
5.1 指标选取
(2)国家发展水平。经济发展水平是国际贸易发生的重要基础,前已述及,军事科技的进口以发展中国家为主而出口主要为发达国家,段德忠等通过对高科技产品的贸易研究也发现武器等军事科技产品出口集中于发达国家[42]。因此,采用人均国民收入指标表示国家(地区)的发展水平,分析国家发展水平与军事科技进出口的关系。
图7
图7
2000年、2010年和2019年全球军事科技贸易网络社团的空间组织格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS2016(1666)号的标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 7
The spatial organization pattern of the global arms trade network community in 2000, 2010 and 2019
(3)科技发展水平。现有理论普遍认为技术创新是影响国际贸易的重要因素,技术创新能有效提升产品科技含量和市场竞争力,形成国家(地区)间的技术势差驱动国际贸易。同时,军事科技产品的生产、维护和贸易也高度依赖于国家(地区)高科技产业制造和创新体系的完整程度。故采用专利申请量指代科技发展水平检验其对贸易结网机制的影响。
(4)军费支出强度。资金投入是保持科技领先地位和市场竞争力的必要条件,军费是国防、军品研发和贸易等方面最重要的资金来源,军费开支直接作用于军事科技产品的贸易从而触发国家(地区)间的贸易连接。故采用军费支出占GDP的比重来表征军费支出强度分析贸易网络的演化。
(5)自然资源禀赋。古典和新古典国际分工理论均认为资源禀赋会对产品结构和国际贸易产生影响,国家贸易也具有寻求东道国自然资源和技术市场等目标,Yang认为军事科技贸易具有强烈地寻求能源和自然资源动机[43]。因此,通过世界银行的国家自然资源指数表征资源禀赋,测度资源禀赋与贸易间的关系。
(6)政治稳定程度。国际贸易理论认为国家政体、关税制度、贸易政策的变化对国际贸易具有显著的影响,军事科技贸易中国家的政治稳定使军事科技的贸易政策具有连贯性。因此,采用世界银行数据库中的政治稳定和无暴力指数表征政治稳定程度,对全球军事科技贸易演化机制进行分析。
5.2 模型构建
军事科技贸易规模为非负整数,被解释变量存在“过度离散”现象。考虑军事科技贸易的方向性,本文采用负二项回归方法对模型进行估计:
式中:TIVij表示国家(地区)i与国家(地区)j之间的军事科技贸易量,是本文的被解释变量,α是常数项,GEORPOij表示国家(地区)i与国家(地区)j之间的地理邻近性,以国家首都之间的球面距离衡量;HISRPOij表示国家(地区)i与国家(地区)j之间的历史邻近性,以国家间具有共同宗主国为1,否则为0;LANRPOij表示国家(地区)i与国家(地区)j之间的语言邻近性,国家间有相似语言为1,否则为0;ECORPOij表示国家(地区)i与国家(地区)j之间的经济邻近性,国家间同属世界银行的收入水平分组为1,否则为0;GNIi、GNIj分别表示国家(地区)i和国家(地区)j的人均国民收入;PCTi、PCTj分别表示国家(地区)i和国家(地区)j的专利申请总量;PMEi、PMEj分别表示国家(地区)i和国家(地区)j的军费支出占GDP的比重;NRIi、NRIj分别表示国家(地区)i和国家(地区)j的自然资源指数;PSTi、PSTj分别表示国家(地区)i和国家(地区)j的政治稳定和无暴力指数;ε是随机误差项。
5.3 回归结果
为确保模型的准确性对模型变量进行多重共线性检验,结果显示14个自变量中VIF最高值为1.32,模型不存在多重共线性问题,模型构建正确并具有较强的解释力,模型估计结果如表3所示。
表3 全球军事科技贸易网络驱动机制的负二项回归结果
Tab. 3
| 自变量 | 系数 | 标准误 | z | P>|z| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEORPOij | -0.228* | 0.135 | -1.69 | 0.091 |
| HISRPOij | 0.654** | 0.328 | 2.00 | 0.046 |
| LANRPOij | 1.366*** | 0.312 | 4.39 | 0.000 |
| ECORPOij | 1.083*** | 0.219 | 4.95 | 0.000 |
| GNIi | -0.132*** | 0.029 | -4.57 | 0.000 |
| GNIj | 0.149*** | 0.043 | 3.46 | 0.001 |
| PCTi | 0.193*** | 0.029 | 6.73 | 0.000 |
| PCTj | 0.799*** | 0.042 | 19.01 | 0.000 |
| PMEi | 0.147** | 0.069 | 2.15 | 0.032 |
| PMEj | 0.364*** | 0.080 | 4.56 | 0.000 |
| NRIi | 0.023* | 0.013 | 1.77 | 0.077 |
| NRIj | -0.020 | 0.020 | -1.02 | 0.307 |
| PSTi | -0.014*** | 0.004 | -3.64 | 0.000 |
| PSTj | 0.018*** | 0.005 | 3.57 | 0.000 |
| 常数项 | -7.951*** | 1.301 | -6.11 | 0.000 |
注:*、**、***分别表示10%、5%和1%的显著性水平。
多维邻近性方面,地理邻近性、历史邻近性、语言邻近性和经济邻近性都有利于军事科技贸易的产生。其中,地理邻近性显示国家(地区)间的地理距离对军事科技贸易量呈负向关系,地理距离通过作用于贸易双边的联系效率和频率从而对贸易产生影响,地理距离对贸易的阻抗效应和削弱作用仍然十分显著。实际上,现有国际贸易、科技合作等领域研究均发现距离具有显著的负向阻碍作用。历史邻近性、语言邻近性和经济邻近性的测度指标均表现出显著的正向关系,表明历史、语言和经济越相近的国家(地区)军事科技贸易越频繁。历史邻近表明贸易双方具有相同或较为接近的历史文化环境,这大大减少交易双方的社会文化成本从而促进军事科技贸易的完成;语言邻近的双方使用着相同的语言,这能有效降低双方的交流障碍和沟通成本,减少错误信息传递带来的风险从而推动贸易双方交易的达成;经济邻近则表明经济发展水平接近的双方更倾向于发生贸易。
国家属性方面,国家发展水平对军事科技贸易的影响显著,但进口和出口国(地区)双方影响机制相异,出口国(地区)表现出国家发展水平与军事科技贸易呈正向促进作用,反而进口国(地区)随着国家经济的不断发展,军事科技的进口需求反而减弱,甚至向出口转变,这也印证了前文军事科技的出口以发达国家为主,进口以发展中国家为主的观点。科技发展水平和军费支出强度显示出明显的双向积极影响效应,这表明类似于其他产品贸易网络,科技发展水平和经费支出会有效促进全球贸易网络的形成和演化。自然资源禀赋因素对进口和出口国(地区)双边存在相异影响机制,结果显示其仅在进口侧通过显著性检验,出口侧的自然资源禀赋对军事科技贸易起负向作用(未通过显著性检验),而进口侧的自然资源禀赋对军事科技贸易起正向作用,即自然资源越丰富的国家(地区)越倾向于进口而非出口军事科技产品,呈现出以资源换技术的特征,这也与目前国际贸易中关于军品贸易的情况吻合。政治稳定和无暴力指数同样表现出明显的相异影响特征,进口侧政治稳定程度对军事科技贸易起负向作用而出口国侧呈正向促进作用,其原因可能在于政治稳定程度较差的国家(地区)往往面临国际和国内各种政治不稳定性的因素,甚至面临政权的更迭,因此,倾向于通过进口先进的军事科技维持和稳固政权;而政治稳定性高的国家(地区)在地区发展环境、经济水平和军事科技实力等诸多方面具有优势,从而有效促进军事科技产品的生产与贸易。
通过对军事科技贸易的影响机制进行建模、检验和分析,结果发现多维邻近性和国家发展、科技实力、资金投入、政治稳定和资源禀赋等因子对军事科技的贸易具有不同程度和不同作用的影响,最终得到军事科技贸易网络的驱动机制(图8)。
图8
图8
全球军事科技贸易网络驱动机制
Fig. 8
The influencing factors of the global arms trade network
6 结论与讨论
6.1 结论
为深刻认识全球地缘军事科技权力的时空演化规律,探讨全球军事科技转移时空格局演化态势和驱动机制,本文基于斯德哥尔摩国际和平研究所武器贸易数据和世界银行数据库,借鉴区位商、网络分析和负二项回归模型等方法对产品结构、网络特征和演化机制进行探究,研究发现:
(1)全球军事科技贸易规模整体呈波动上升的趋势,贸易产品结构表现出军用飞机为主导,海军舰艇与装备、导弹和装甲车为重要组成的一极三核主导特征,军用飞机一直是最主要的出口产品和进口依赖产品,美俄在大部分军事科技中具有绝对优势,各国(地区)依托比较优势占据一定的市场份额,从而形成错位发展的贸易格局。
(2)全球军事科技出口分布呈现出欧洲、美国和俄罗斯的三核特征,地缘军事格局东升西降、南升北降特征明显,以色列、中国、印度等亚洲国家影响力明显提升并重构着世界军事科技贸易格局,而进口集中分布于东亚—东南亚—南亚—中东—南欧—北非一带,空间分布格局与斯皮克曼边缘地带理论中的边缘地带位置相吻合。
(3)全球军事科技贸易网络一超多强的格局特征明显,网络规模虽呈扩大趋势,但欧美国家一直占据着贸易出口市场主导地位,美国、俄罗斯、法国和中国的网络影响力和控制力持续提升,欧亚大陆始终是全球军事科技贸易的主要舞台,中国和以色列等亚洲国家成为重塑贸易格局的重要力量。
(4)以美国和俄罗斯为核心的军事科技贸易竞争格局凸显,以美国为核心的主体贸易网络由层级化向扁平化转变揭示着美国主导能力的提升和西欧次主导国家的衰退,印证着美国和俄罗斯通过分裂重组整合了相关贸易国家(地区),有效扩大其空间组织范围。
(5)军事科技贸易网络演化是进出口国(地区)属性和双方邻近性共同作用的结果,军事科技贸易遵循距离衰减律,地理距离对全球军事科技贸易起明显负向作用,历史邻近、语言邻近和经济邻近对军事科技贸易网络均具有一定的正向作用;国家发展水平、科技发展水平、军费支出强度和政治稳定程度对军事科技出口具有促进作用,国家发展水平和政治稳定程度在进口侧表现出负向作用,自然资源禀赋仅在进口国(地区)通过显著性检验,以资源谋技术的军事科技进口策略是全球军事科技贸易的动力之一。
6.2 讨论
军事科技的贸易具有多学科交叉属性,本文从地理学视角通过对军事科技贸易网络进行研究揭示了其部分地理规律,类似于世界地缘政治和经济权力格局“东升西降”和主要大国力量对比“南升北降”的格局特点,以中国为代表的亚洲国家的崛起使地缘军事格局同样具有“东升西降”和“南升北降”特点,并一定程度上重塑世界军事科技的等级体系;不同于其他高科技产品贸易的西欧—北美双拱格局,全球军事科技的出口呈现出美国—俄罗斯—西欧三极分布和美国—俄罗斯相互竞争的特点,俄罗斯在全球地缘军事中的地位要显著高于其经济地位。此外,美国实施“亚太战略”和“印太战略”对中国崛起的围堵也将导致大国地缘角逐加剧。
美国和俄罗斯是世界上最大的两个军事科技出口国家,2000年以来美国的出口国(地区)数量和出口规模都经历较大幅度的增长,其军事科技影响力和市场占有率呈明显上升趋势;而俄罗斯虽然贸易总额在全球军事科技贸易出口中占第2,但市场占有率和影响力相对美国的差距呈拉大趋势,对外贸易国家(地区)数量一度被法国超越,这表明俄罗斯的军事科技在全球的影响力有较明显的削弱趋势。从军事科技发展演化角度看,2000年以来中国主要的进口依赖产品经历了从军用飞机、防空系统、发动机、海军舰艇与装备到发动机演变历程,对国外的军事科技进口依赖程度大大降低,但发动机仍然是中国最重要且依赖程度最深的进口产品,未来要注重发动机研发与发动机进口并重的发展策略,防止和摆脱发动机技术的卡脖子现象,实现军事综合实力的全面提升。
古典地缘战略理论仍具有极大全球影响力,军用飞机作为世界各国最主要的出口产品和进口依赖产品从侧面反映了杜黑的空权论对各国制空权战略的影响。军事科技贸易主要由出口国(地区)主导,而出口主要目的地分布与麦金德的内新月形地带和斯皮克曼的边缘地带区域分布极为吻合,这也反映了其地缘战略思想在军事科技贸易出口国家中的体现。如美国出口主要对象包括韩国、日本、印度、中东、埃及等,分布范围与边缘地带极为吻合,反映美国控制边缘地带和围堵欧亚大陆的地缘战略布局[26]。
此外,本文还存在一定的局限,如军事科技的多重复杂属性注定军事科技贸易和转移中的驱动机制具有综合性和复杂性,政治联盟和军事合作都会对军事科技的贸易和转移产生一定程度的影响,但受限于数据的可获取性未能进行分析,未来需要构建更加系统更加合理的定量与定性相结合的理论框架对军事科技贸易的机制进行更为细致全面的探讨。
致谢:
真诚感谢匿名评审专家对论文打磨和可视化表达方面的修改意见,使本文获益匪浅。
参考文献
A comparative study of Sino-US science and technology competitiveness
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.04.2018851
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the elaboration of national scientific competitiveness, this paper builds the national science competitiveness evaluation system from 5 aspects, including scientific human resource competitiveness, scientific and financial resources competitiveness, scientific research competitiveness, technological innovation competitiveness and technology internationalization competitiveness, with specific comparison of science and technology development between China and the United States. Studies show that even though China has enhanced the scientific competitiveness, the United States surpasses China in both overall competitiveness and individual area like scientific investment, scientific research, technical innovation, and globalization of science and technology. For China, there is still a long way to improve scientific competitiveness further. After analyzing the present situation and the development trend of the scientific competitiveness between China and the United States, the paper believes that China should not only learn from the powerful and advanced scientific nations like the United States with new reforming and opening, but also be aware of self-weaknesses. China should stick to the two-wheel driver of scientific innovation and systematic innovation, the organic combination of development speed and the innovation quality, the mutual promotion of individual innovation and the open innovation, the innovation strategy focusing on quality and result, the enhancement of basic scientific research, the breakthrough of critical and core technology, the attraction of advanced scientific and innovative talents, so that the national scientific competitiveness could accelerate rapidly and continuously.
中美科技竞争力比较研究
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2019.04.2018851
[本文引用: 1]

在界定国家科技竞争力内涵的基础上,从科技人力资源竞争力、科技财力资源竞争力、科学研究竞争力、技术创新竞争力和科技国际化竞争力五个方面建构了国家科技竞争力评价指标体系,从而详细对比了中美两国在科技发展上的差异。研究发现,无论是整体竞争力还是科技投入、科学研究、技术创新、科技国际化等单项竞争力,中国都与美国都存在不小差距,中国科技竞争力虽然加速提升,但仍显著落后于美国,中国科技发展任重道远。基于中美两国科技竞争力的现状对比及趋势研判,本文认为:中国进一步提升科技竞争力,加快建设世界科技强国,既需要对标先进、参照一流,进一步深化开放式创新,充分学习和借鉴美国等科技强国的成功经验,更需要立足自身、正视短板,坚持科技创新与制度创新双轮驱动、发展速度和创新质量有机统一、自主创新与开放创新相互促进,着力推动以质量和效益为核心的创新战略,加强基础科学研究,突破关键核心技术,集聚高端科创人才,以实现国家科技竞争力的持续稳步增强。
Study on the spatial-temporal evolution and internal mechanism of geo-economic connections of China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201606005
[本文引用: 1]

The interdependence of economics among countries has been distinctly enhanced due to the end of the Cold War and the intensification of globalization. In terms of its content and form, geo-politics has shifted from a "high political area", which focuses on safety, to a "low political area", which emphasizes economics, making geo-economics the focus of the researches. Using tools including Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA), Fragmentation Index and Revealed Comparative Advantage Index, this paper revealed China's evolutionary characteristics of geo-economic connections at the global scale, and explored its internal mechanism by grey relational analysis. The results show: (1) China's geo-economic connections have undergone 4 periods of "Inoculating - Sprouting - Rising - Flourishing", which were significantly correlated to economic development and the industrial restructuring. (2) Labor-intensive industry is currently dominant in China, but capital-intensive and technology-intensive industries are gradually developing, and the disadvantages of primary goods is prominent. (3) China's economic power is heterogeneous across space. The geo-economic connections could be identified as global powers' agglomeration and geographical proximity, but it became homogeneous through time and the diameter of economic power has continuously expanded. China has not only maintained stable geo-economic connections with developed countries like the United States of America, Japan and some European countries, but also strengthened connections with developing countries in Africa and South America. (4) Capital, technology and labor endowments are the main internal driving forces behind the spatial-temporal evolution of China's geo-economic connections, among which capital endowment is the key driving force, technology endowment is the important impetus and labor endowment is the fundamental advantage.
中国地缘经济联系的时空演化特征及其内部机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201606005
[本文引用: 1]

随着冷战结束以及全球化深入发展,国家之间经济相互依存明显加强,地缘政治在内容和形式上从以安全为主的高政治向以经济为主的低政治转变,地缘经济成为研究焦点。本文运用空间探索性方法、碎化指数和显性比较优势指数等工具,揭示中国在全球经济空间中地缘经济联系的演化特征;借助灰色关联度分析方法探索中国地缘经济联系演化的内部机制。结论为:① 中国地缘经济联系经历了“孕育—萌芽—兴起—繁荣”四个阶段,与经济发展以及产业结构调整存在显著的相关性;② 中国的优势部门仍以劳动密集型产业为主,逐步形成资金和技术密集型产业的竞争优势,初级产品劣势日益显现;③ 中国经济权力空间的异质化特征明显,地缘经济联系呈现大国集聚效应和地理临近效应。随着时间推移,地缘经济联系空间趋于均质化,经济权力半径不断向外围拓展,不仅同美日欧等发达国家保持稳定的地缘经济联系,与非洲、拉丁美洲等发展中国家和地区的联系也不断加强;④ 资本禀赋、科技禀赋和人力禀赋是中国地缘经济联系时空演化的主要内在动力,资本禀赋是中国地缘经济发展的核心驱动力,科技禀赋是重要的推动力,人力禀赋是主要的基础优势。
Spatial and temporal patterns of evolution of global trade networks during 1985-2015 and its enlightenment to China's geostrategy
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201803004
[本文引用: 1]

The paper, from the perspective of social network, explores the spatial patterns and evolutionary characteristics of the global trade network and focuses on the Chinese community ownership and their strategic implications by adopting social network indexes, including centrality, community classification and structure entropy. The results show that: (1) The structure of global trade network evolved towards complexity, specifically shifted from "one super state and more powerful countries" towards"multi-polarization". The collective rise of developing countries has weakened the monopoly position of traditional European and American countries in the network, leading to increasing complexity of the network structure. (2) Community evolution of the global trade network has experienced the dominant stage of the developed countries, the budding stage of the Asian region, the separated stage of the Asian Community and the fourth stages of "ripartite confrontation". During the evolution, China has gradually moved from being dominated to the center of the stage. (3) The diversification of trade market is a common characteristic of foreign trade countries. In the process of global market segmentation, China, the United States, and Germany gradually formed a relationship of "dislocation competition", and their core interests are concentrated around the surrounding areas. (4) The areas of Asia-Pacific Region, Middle East, Africa and Latin America have become the play field of China to compete other powers for local trade markets. Currently, the Asia-Pacific market is the preferred market for China's global trade, and China should extend the market to the Middle East, Africa and Latin America through "Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st Century Maritime Silk Road", In this way, economic advantage can be transformed into global strategic influence. Meanwhile, direct conflicts and confrontations with the core interests of the United States should be avoided.
1985—2015年全球贸易网络格局的时空演化及对中国地缘战略的启示
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201803004
[本文引用: 1]

从社会网络视角,采用中心度、社团划分和结构熵等社会网络指标,探究全球贸易网络的空间格局及演化特征,重点分析中国在网络中的社团归属及其地缘战略启示。研究表明:随着时间推移,发展中国家的群体性崛起使得全球贸易网络结构呈现日益多元化的复杂格局;全球贸易网络的社团演化经历了发达国家主导、亚洲崛起的萌芽、亚洲社团的分离和“三足鼎立”四个阶段,中国从被支配的边缘地位逐步走向“舞台中央”;中、美、德三国在全球市场细分过程中形成一种“错位竞争”关系,亚太、中东、非洲和拉美地区成为大国之间争夺贸易市场的博弈区域。中国应首先立足于亚太地区,通过“一带一路”倡议延伸至中东、非洲和拉美地区,将经济优势转化为全球战略影响力。
Major changes unseen in a century are unfloding
世界“百年未有之大变局”全面展开
Military technology and human loss in intrastate conflict: The conditional impact of arms imports
DOI:10.1177/0022002719893446 URL [本文引用: 1]
DOI:10.1177/0022343302039006003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Foreign military industry trade development experience and its implications to China
国外军工贸易发展经验及其对我国的启示
Arms production, national defense spending and arms trade: Examining supply and demand
DOI:10.1016/j.jce.2014.03.001 URL [本文引用: 1]
Arming in the global economy: The importance of trade with enemies and friends
Middle East upheaval and the development of the arms trades in the Middle East
中东剧变与中东军火贸易的发展
Science and technology and national security: The strategic significance of China's Arctic scientific expedition
地缘科技学与国家安全: 中国北极科考的战略深意
Theory and significance of geo-science and technology
地缘科技学的理论及其意义
Research on attribute and concept of geo-entity
地缘体概念内涵及特征研究
Global geopolitical pattern on science & technology from the perspective of intellectual property trade
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180789
[本文引用: 1]

<p id="C3">The transformation of the global production networks into global innovation networks has made the interdependence of countries gradually shift from the trade investments between countries to the asymmetric dependence formed in knowledge cooperation and technology transfer. The profound changes in the logic of geopolitics have resulted in the fact that the core sources of state power have evolved from military strength in the colonial era to economic strength in the era of trade, and to scientific and technological strength in the era of knowledge. The key to the rise of China lies in the rise of science & technology. Looking back at China’s scientific and technological development, we can find that there has never been a shortage of “containment” and “blockade”, from the “Paris Coordinating Committee” to the “Wassenaar Arrangement”, to today’s “ZTE Incident”. No country can compare the technical blockade faced by China, and China’s technological development path is also more rugged than that of any other country. In the international environment where technology is currently targeted and blocked, how to construct a global innovation network led by China and scientifically formulate geo-scientific strategies for China are the primary topics for research under the future of innovative geography and geopolitics. Based on this, we, taking the imports and exports of intellectual property rights among countries in the world from 2001 to 2015 as the data source, studied the network structure and pattern of the global intellectual property trade, and discussed the space-time evolution pattern of the global science and technology system. The following conclusions were drawn as follows. Firstly, the global intellectual property trading network is markedly polarized. It is a typical small-world network, with a hierarchical hierarchy of pyramid structure. The “central-periphery” pattern with the United States as the core is continuously consolidated. Secondly, the asymmetric dependence of global intellectual property trade based on sensitivity and vulnerability models further verifies that the United States is the core of the global geo-scientific and technological landscape, and its core position is continuously consolidated and strengthened.</p>
知识产权贸易下的全球地缘科技格局及其演化
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180789
[本文引用: 1]

中国崛起,关键在于科技崛起。在当前技术针对与封锁的国际环境中,探讨建构以中国为核心的全球创新网络和科学制定中国未来科技战略是当前创新地理学和地缘政治学交叉之下研究的重点课题,而明晰全球地缘科技格局及其演变过程则是基础所在。本文基于2001—2015年全球国家(地区)间的知识产权进出口数据,在研究全球知识产权贸易格局和网络结构的基础上,探讨了全球地缘科技体系的时空演化特征,得出以下结论:① 全球知识产权贸易网络两极分化显著,是一典型的小世界网络,以美国为核心的金字塔结构不断夯实;② 基于敏感性和脆弱性模型阐释的全球知识产权贸易的非对称依赖性进一步验证了美国是全球地缘科技格局的核心,且其核心地位不断巩固和加强。
The evolutionary properties and functions of the geo-economic system from the perspective of global commodity trade network
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200010
[本文引用: 1]

Since the financial crisis, the world economy has emerged as geo-economy and showed network features. To expand and deepen the research paradigm of geo-economic system, a systematic and dynamic perspective is needed to explore its intrinsic properties and the operating law. Considering the importance of the commodity trade in measuring geo-economic system, this perspective provides an effective path to study the geo-economic system. In this paper, we constructed an analytical framework of geo-economic system on the basis of System Dynamics to examine the evolutionary properties, functional levels and types of the global geo-economic system from 1996 to 2016 from the perspective of global commodity trade network. The result shows that, firstly, in terms of the attribute features, geo-economic system has the small world property. Its evolution is conjugated with the development of the world economy. The scale-free property of degree gradually disappears, and the construction of geo-economic relations is balanced. The scale-free property of weighted degree is significant, and the increase in the number of intermediate-order countries optimizes the weight-degree fractal structure. Geo-economic system belongs to the mismatch network. Geo-economic links follow the selection mechanism and tends to weaken. Secondly, in terms of the functional level, geo-economic system presents a strong relationship-dependent effect and the third-party effect. The association between the weighted degree centrality and eigenvector centrality is the highest and displays a spatial match, both of which gradually form a spatial pattern of East-West parallelism with China and the US acting as two cores. The betweenness centrality and the closeness centrality show spatial homogenization. The quantity distribution of its function type presents a “pyramid” structure, indicating the power of countries in the world economy, while spatially three core-periphery clusters show a “circle” structure. The competitiveness of the central geo-economic zone increased. The network structure of the transformation geo-economic zone is diverse and complicated. The function level of some countries in the general geo-economic zone leaped, while the isolated geo-economic zone remains stable. Natural geospatial separation, national socio-economic development, the interaction and coupling among functional zones are important factors driving the spatial evolution of geo-economic functional zones.
商品贸易网络视角下地缘经济系统的属性与功能演进
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200010
[本文引用: 1]

金融危机以来,世界经济发生了深刻变革。“区域化、集团化、碎片化”逐渐取代经济全球化成为国际社会最为活跃的内容,以“地缘”为基础的经济板块日益涌现。本文结合系统动力学理论构建地缘经济系统的分析框架,从商品贸易网络的研究视角,对1996—2016年地缘经济系统的属性特征、功能等级的演进过程深入分析,得出如下结果。① 在属性特征演进层面,地缘经济系统具备小世界性,其变化趋势与世界经济局势的阶段性发展共轭;商品贸易网络度分布的无标度性逐渐消失,地缘经济关系呈均衡化,而权重度的无标度性显著,中间位序的国家数量增多使权重度分形结构趋于优化;商品贸易网络属于异配型网络,地缘经济系统遵循择优选择机制但趋向弱化。② 在功能等级演进层面,地缘经济系统具有较强的关系依赖性,第三国效应凸显;商品贸易网络的权重度中心性与特征向量中心性的关联度最高且空间同配,逐步形成以中美为核心的东西并立格局,介数中心性和接近中心性呈现空间均质化发展态势;功能类型在数量特征上呈“金字塔”型结构,在空间分布上形成三个“核心-边缘”集聚的“圈层结构”,核心型地缘经济区之间的竞争性强化,中转型地缘经济区的联系网络呈复杂化,一般型地缘经济区的部分国家出现等级跃升,孤立型地缘经济区保持稳定。③ 自然地理空间分异、国家社会经济发展、不同功能区的交互耦合是地缘经济功能区空间演进的重要因素。
Retrospect and prospect of world regional geography in China
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2011.12.008
[本文引用: 1]

Based on a review on works of world regional geography accomplished in China during the past 10 years and an analysis of its current problem, the research orientation for further sustained development of the discipline is discussed in this paper. Accompanied by a rapid rise of China, the fields of world regional geography in China have expanded from pure geography research on regions and countries outside China to including the study of global economy and political geography in its quest to satisfy the need of the national development. The major concerns of world regional geography researchers in China in recent years include: (1) research on world geopolitics and geo-economy, e.g. geopolitics-related theories, changing tendencies of geopolitical situations in given places across the world and some hot spots and impacts that geopolitical situations of the powers and surrounding regions have on China; (2) geographical research on international investment and multinational corporations, focusing on theories and mechanism of outward investment, spatial distribution and location determination of foreign investments in China, and analyses of investing scales, modes and performance; (3) theoretical and empirical research on the development of cities and regions in the world, highlighting the researches on laws of formation and mechanism of megalopolis and urban agglomerations around the world and empirical research on major cities in some countries such as USA, Japan, UK and France. The theoretical and empirical research on foreign regions revolves around the theory and practice of“new regionalism”, new regional division of labor, regional interaction and sustainable regional development; (4) research on global resources and environmental protection and conservation, focusing on the exploitation, development and utilization of global natural resources. The most serious one is the issue of energy, which is the main subject of much related research. On the basis of the above points, the authors point out the problems emerging in the development of world regional geography as a discipline in China, such as ineffective research team, insufficient research funds and poor research abilities, as well as differences between China and other countries in this area. Finally, the paper comes to the conclusion that the golden age of world regional geography research in China has arrived, therefore, it is necessary to enhance special research on critical global issues such as geopolitics and geo-economy. Thus, it is imperative to follow through the world geography research plans, such as the comprehensive research on countries and regions closely related to China in the areas of the developing trends of world economy, politics, science and technology and strictly conform with the objectives to implementing the important strategies for national development.
中国的世界地理研究进展与展望
Geo-military situation analysis based on arms trade data
基于武器贸易数据的地缘军事态势分析
Local cluster networks, information spillover effects and export network expansion of China's ICT products
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020191086
[本文引用: 1]

Exploring the export network expansion of China′s ICT products helps to better understand the global-local interactions, which would shed light on the relationship between international trade and internal geography of industries. We propose that export network expansion of ICT products would condition on local cluster networks and information spillover effects among exporters. Local cluster networks represent effects of cluster specialization and cognitive proximity while information spillovers include export experience spillovers and spillovers from foreign investment. Using Customs Data of China, this study describes the dynamic pattern of export network expansion of China′s ICT products and conducts an empirical analysis to identify the driving forces of export network expansion of China′s ICT products. Since the beginning of the 21st century, China′s ICT export has experienced four stages of development: vigorous and rapid growth (2000-2006), financial crisis response (2007-2009), recovery and adjustment (2010-2013) and the ebb of foreign investment (2014-2016). China′s ICT export is characterized by high proportion of foreign enterprises and large share of processing trade. It is found that although still concentrated in the coastal region, ICT exporters have been increased from the inland provinces such as Sichuan and Chongqing and export markets have been expanded from the traditional markets such as USA, Japan, and western European countries to the emerging markets including Southeast Asia, Latin America and the BRICS. It is further found that significant export expansion has been reported in the following trade flows: from the coastal provinces to East Asia and North America, from the western provinces to North America and Western Europe and from the central provinces to North America and East Asia. Although the market expansion priority differs between two periods of 2000-2008 and 2009-2016, there are some similarities in the major trade flows and the market destinations of ICT export among different provinces. Panel data regressions further show that both local cluster networks and information spillover effects have significant positive effect on the growth and specialization of China′s ICT export and the results are robust with the consideration of labor costs and external transportation linkages.
地方集群网络、信息溢出效应与中国ICT产品出口地理网络扩张
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020191086
[本文引用: 1]

研究中国ICT产品的出口贸易扩张有助于理解“全球-地方”互动视角下国际贸易与国内产业地理的相互作用。本文构建地方集群网络和信息溢出效应促进产品出口扩张的机制分析框架,利用2000—2016年中国海关库数据,探究中国ICT产品出口地理网络扩张机制。研究发现: ①中国ICT产品出口源地从沿海地区向内陆地区扩张,出口目的地扩张重点在不同时间段存在差异。②中东部省份出口到东亚和北美、西部省份出口到北美和西欧的贸易扩张较为显著。③面板Probit模型分析表明,地方集群网络和信息溢出效应能够增加出口源地-目的地层面ICT产品出口额,提升出口专业化程度。
Network analysis of 'urban systems': Potential, challenges, and pitfalls
DOI:10.1111/tesg.12392 URL [本文引用: 1]
Structural characteristics and influencing factors of the global inter-city knowledge flows network
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200443
[本文引用: 1]

In the age of globalizing science and technology, urban economic development increasingly rests on knowledge production and knowledge flows. Inter-city scientific collaborations, as the most potent aspect of modern knowledge production, are more and more frequent, which produces some of the highest quality science. However, there is a paucity of analysis of the world city system from the knowledge flows perspective. Using highly cited papers data from the Web of Science database in 2017, this study applies social network analysis, a Bayesian-inference weighted stochastic block model (WSBM), the dominant flow analysis and spatial interaction model to explore the topological structure, spatial pattern and influencing factors of global inter-city scientific collaboration. Results show that the science hotspots are highly concentrated in three regions: North America, East Asia and Western Europe, and the whole network is dominated by a tri-polar world. The two seemingly paradoxical trends, star-shaped and triangulated structure, coexist in the global inter-city knowledge flows network. The spatial pattern of inter-city collaboration network forms a quadrilateral graph with four vertexes in Western Europe, North America, East Asia and Australia, particularly on the trans-Atlantic axis between North America and Western Europe. The network has a distinctive multicore-periphery structure, which can be divided into five categories: global core, macro-region core, strong semi-periphery, semi-periphery, and periphery, and identifies New York, London, Boston, San Francisco-San Jose, Washington, Los Angeles, Paris and Beijing as eight global core cities and forty-one macro-region cores. The network is characterized as hierarchical “hub-and-spoke” structures, and the hierarchy of the network is obvious, New York, Beijing and Jeddah are dominant nodes in the three subnetworks. In addition, the gravity model indicates the spatial distance impedes inter-city scientific collaboration, while the amount of science output and the number of urban residents, the number of world-class universities, institutional proximity and social proximity have positive and significant effect on inter-city scientific collaboration. In order to further our understanding of world city network, this paper calls for more attention to inter-city knowledge flows.
全球城市知识流动网络的结构特征与影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200443
[本文引用: 1]

在科技全球化时代,城市之间的知识流动日益频繁,成为当代知识生产的重要特征。然而,鲜有从知识流动的视角开展全球城市体系的研究。基于2017年的高被引论文合作数据,采用社会网络分析方法和空间计量模型系统地刻画了全球城际科研合作网络的拓扑结构和空间格局及其影响因素。研究发现:① 拓扑结构呈现出以北美、欧洲和亚太城市的三极格局,轴辐式和分布式结构特征并存。② 世界城市科研合作网络形成以北美、西欧、东亚和澳大利亚为顶点的四边形格局。③ 多核心-边缘结构显现,纽约、伦敦和北京等8个城市为全球核心,芝加哥等41个城市为区域核心。④ 全球城市科研合作网络的等级层次特征显著,纽约、北京和吉达分别是三大子网的主导型城市。⑤ 空间相互作用模型表明地理距离阻碍了城市间的科研合作,城市的科研规模、人口规模、世界一流大学数量、制度邻近性和社会邻近性促进了城际联系。
High-speed rail network spatial structure and organization model in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.010
[本文引用: 1]

High-speed rail is an important part of modern transport infrastructure. It has an important impact on the flow of production factors, the expansion of urban space, and the reconstruction of regional spatial structure. Based on the O-D data of high-speed rail network in 2018, the social network analysis is used to discuss the structural characteristics of high-speed rail network and other organizational modes from HSR network and urban nodes. The results show that: 1) China's high-speed rail network has experienced four stages of germination, start-up, tortuous development and prosperity. China's high-speed rail network is relatively loose overall, the northeast region has the highest network density and western network density is sparse. High-speed rail links between the western region and the northeastern region are sparse. The intermediary role of the central and eastern regions in the overall network is obvious; 2) The “corridor effect” of the important high-speed rail channel is remarkable. The area along the Beijing-Shanghai high-speed railway and the Beijing-Guangzhou high-speed railway has become hot spot with high central value region. On the whole, it has a “triangular flag” composed of Beijing-Guangzhou, Beijing-Shanghai and Shanghai-Kunming high-speed railways. Spatial pattern and the trend of decreasing toward the cities on both sides. The centrality of the intermediary shows that the random distribution of the central hub city can better play a cohesive role; 3) The first-level high-speed rail network shows the high-speed rail corridors closely related to Shanghai-Nanjing Intercity, Beijing-Tianjin Intercity and Wuhan-Guangzhou High-speed Railway. The second-level network basically reveals the road network planning of China's high-speed railways and the provincial cities in the high-speed rail network as a prominent intermediary role; The third level identifies the trend of the high-speed rail network from four horizontal and vertical expand to eight horizontal and eight vertical. The fourth level of China's high-speed rail network shows overall spatial network details; 4) The territorial organization models of high-speed railway network is characterized by point-axis beading mode, dual-core grouping mode and polar core model, the perfection of the high-speed railway networkhas transformed the organizational model from a single core to a network.
中国高铁网络结构特征及其组织模式
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.010
[本文引用: 1]

基于2018年高铁网络OD数据,运用社会网络分析方法从高铁网络、城市节点等方面探讨中国城市高铁网络结构特征及其地域组织模式,结果表明:①中国高铁网络整体较为松散,东北地区网络密度最高,东部和中部地区作为整体网络的中介作用明显;②重要高铁线路的“廊道效应”突出,中心度呈现出以京广、京沪和沪昆高铁组成的“三角旗状”空间格局并向两侧城市呈不规则递减的态势;③多层级网络识别出紧密关联高铁线路和四横四纵向八横八纵格局的转变;④高铁网络的地域组织形式表现为点-轴串珠模式、双核组团模式和极核模式,高铁网络的完善使组织模式由单核趋向于网络化转变。
The evolution process and growth mechanism of global cross-border M&A network
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110014
[本文引用: 2]

Cross-border M&A (mergers and acquisitions) is an important way for enterprises to carry out overseas strategic layout, which has a significant impact on the pattern evolution of world economic geography. Based on record data of global cross-border M&A transactions from 2001 to 2017, a national-based network for the global scales is established to explore the evolution process and growth mechanism of global cross-border M&A network via the complex network analysis, the GIS method, and the spatial gravity model. Several conclusions can be drawn as follows. (1) The scale, density, and scope of the global cross-border M&A network have increased slightly, while there exists a trend of decentralization. (2) There is a sign that the center of gravity has been shifting from Western Europe and North America to the Asia-Pacific region for global cross-border M&A network, which is mainly driven by China. However, Chinese import and export of cross-border M&A largely rely on Hong Kong, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands and so on. (3) There is a process of division and integration for condensing subgroup of global cross-border M&A network. Among them, the scope of condensing subgroup led by the UK and the US has been narrowed, while that led by China has been expanded, and the European condensing subgroup has been further integrated. (4) The evolution of global cross-border M&A network to varying degrees was influenced by the indicator attributes for each country (region), which was in turn related to the science and technology level, offshore financial center, as well as proximity indicators, which were related to geographical conditions, language and history. However, natural resource endowment and economic market size for cross-border M&A linkages only have one-way (receiving or output) effect, and economic proximity index is not significant in 2009 to 2017.
全球跨境并购网络的空间格局演化及形成机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202110014
[本文引用: 2]

跨境并购是企业实施全球化战略的重要途径,对世界经济地理格局演化具有重大影响。本文基于2001—2017年全球跨境并购交易记录数据建构网络,借助复杂网络分析、GIS空间技术以及引力模型等方法,对全球跨境并购网络的空间格局演化及其形成机制进行探讨。研究发现:① 全球跨境并购网络的规模、密度、范围均有小幅度增长,并存有去中心化趋势。② 全球跨境并购方和标的方的空间分布重心出现由西(欧美)向东(亚太)转移的迹象,其首要推动者为中国,但中国跨境并购联系的出入口依赖于中国香港、英属维京群岛、开曼群岛等地区。③ 全球跨境并购网络社团的空间组织范围总体与世界大区的范围保持吻合,其中全球最大的社团由英美主导但其凝聚范围出现收缩,中国主导的亚太社团凝聚范围得到扩大,德法主导的社团对欧洲进一步整合。④ 研究期内国家(地区)科技发展水平和离岸金融中心等属性要素,以及国家(地区)间地理、语言以及历史的邻近性要素始终是驱动网络形成的重要动力,而自然资源禀赋、经济市场规模指标在2009—2017年对跨境并购联系的形成只产生了单向(接收或发出)影响,经济邻近性作用失效。
World geographic structure and U.S. global strategy and military force design
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.04.2020998
[本文引用: 1]

This paper examines the effects of the world geographical structure on national security strategy and military force design of great powers, so as to help understand the geo-security risks and opportunities that China is facing on its global development path. As the most of world's land, population and economic activities are concentrated in the eastern hemisphere, especially in Eurasia, Eurasia has always been the central arena for world powers to compete. As the first non-Eurasian hegemonic power in the human history, the United States has always regarded the prevention of regional hegemony on the Eurasian continent as the supreme goal of its national security. From the perspective of the world geographical structure and its dynamic changes, this paper analyzes the geographical advantages of the eastern hemisphere, especially Eurasia, which gave birth to the world powers and human civilization. It also analyzes the influence of the geographical location of the United States on its early rise, the formation of its global strategy under this geographical condition, particularly, and the global military design of the United States based on preventing the emergence of regional hegemony in Eurasia. Finally, It points out that in the strategic game between China and the United States, China, which is located in the eastern edge of Eurasia, has natural geographical advantages.
世界地理结构与美国的全球战略及军力设计
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.04.2020998
[本文引用: 1]

本文旨在阐明世界地理结构在大国战略制定及军力设计中的基础性作用,以助于认识中国全球发展道路上面临的地缘安全风险和机遇。由于世界陆地、人口和经济活动相对集中于东半球特别是欧亚大陆,欧亚大陆历来是世界大国逐鹿的中心舞台。美国作为人类历史上第一个非欧亚大陆上的霸权国家,一直把防范欧亚大陆上出现区域性霸权作为国家安全的最高目标。本文从世界地理结构及其动态变化的角度,分析东半球尤其是欧亚大陆孕育世界大国和人类文明的地理优势,解析美国的地理区位对其早期崛起的影响,以及在这一地理条件下其全球战略的形成,并重点探讨美国基于防范欧亚大陆出现区域性霸权的全球军力设计。文章最后指出,在中美战略博弈中,位于欧亚大陆东缘的中国具有天然的地缘优势。
The geography of global electric information industry trade network
全球电子信息产业贸易网络演化特征研究
The topology structure and spatial pattern of global city technical cooperation network
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.10.003
[本文引用: 1]

<p id="C3">In the background of economic globalization, the technology globalization has become significant. International technical collaboration and R&D activities are major forms of technology globalization. Cities are the engine of innovation and economic development. Due to the development of transportation technology and telecommunication technology, cities are getting closer and the impact of geography distance is weakened. By providing good entrepreneurial environment, cities attract talents, information and capital from all over the world. As a result, innovation is the major function of cities. Global cities make great efforts to become the global science and technology innovation centers with world influence. These kind of centers are cities with leading innovation abilities and most of them are hubs of innovation activities. Patents are an important indicator of measuring technology development and innovation activities. Exploring cities’ role in the global technical cooperation networks is key to understand global technical cooperation pattern. Meanwhile, it is also meaningful for Chinese researchers to explore what position Chinese cities are in and how to construct Chinese cities as global science and technology innovation centers with world influence. Although plenty of articles have focused on the global technical cooperation network at multiple scales such national, regional, urban and community scales, few research has focused on the global city technical cooperation network. The global city technical cooperation network is constructed based on 2015 public PCT patent data. By complex network analyzing methods and spatial analyzing methods, this article demonstrates the topology structure and spatial pattern of global city technical cooperating activities. The results show that: In terms of the topological structure, the density of the network is relatively low, which means the strength of linkages in the network are unbalanced. The network is scale-free network and has prominent city nodes. The network has significant group structure and there are 11 groups which contain over 50 nodes. In terms of spatial pattern, cities with higher patent output distribute in zonal pattern. Cities with more links with others distribute in the area of Calgary (Canada), Silicon Valley (USA) and Boston-Cambridge-New York-Philadelphia (United States) of North America, Paris metropolitan (France), Greater London (United Kingdom), Randstad (Netherland), Essen (Germany) and Basel (Switzerland) of Europe, Tokyo (Japan), Seoul (South Korea), Beijing (China), the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomerations (China) and the Pearl River Delta (China) of East Asia. Tokyo and Paris are in the leading position in both total patent output and number of linkages. The spatial distribution of degree centrality is similar with the distribution of the patent output. Moreover, the distribution of nodes’ betweenness centrality is more concentrated than nodes’ degree centrality. The ranks of Beijing and Shanghai’s betweenness are higher than Shenzhen’s. The reason is that Beijing is the capital city of china. And Beijing holds a variety of universities, institutes and high-tech companies, which provides Beijing with science and technology innovation. Shanghai has a large number of FDI, and it has close connection with foreign companies to do transnational R&D activities. However, Shenzhen has relatively less links with cities in foreign countries, which means the technology output of Shenzhen still depends on its own market. This phenomenon is due to the special immigration culture, open market mechanism and competitive environment.</p>
全球城市技术合作网络的拓扑结构特征与空间格局
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.10.003
[本文引用: 1]

采用2015年PCT专利数据,构建全球城市技术合作网络。利用复杂网络分析和空间分析方法研究全球城市技术合作网络的拓扑结构与空间分布。研究发现:拓扑结构上,全球城市技术合作网络的密度较低,城市节点对外联系强度极不均衡。网络为无标度网络,社团结构明显。空间格局上,全球技术合作网络中城市节点的专利总量和对外联系次数都呈一定区域性,城市节点主要通过全球知识网络获取知识。巴黎和东京无论是专利产出还是合作数量都具有领先优势,对外联系紧密,枢纽性强。网络中城市节点度中心性的空间分布上与专利产出的分布格局基本相同,而介数中心性的分布格局更为集中。
Spatio-temporal evolution and factors influencing international student mobility networks in the world
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004002
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the data released by UNESCO on international student mobility in tertiary education from 2001 to 2015, this paper draws on network science to construct a multidimensional weighted directed network heterogeneity model. This model combines the GIS spatial analysis method and the negative binomial regression model to study spatiotemporal evolution and factors influencing international student mobility networks. The results are as follows. First, in terms of the evolutionary characteristics of time series, the linkages of international student mobility networks have increased from 4921 to 9137, and its average weighted degree centrality has rapidly increased from 8004 to 20,834, which indicates that both the number of international students and the choices of overseas routines are mounting. Second, in terms of the topological structure, it has evolved from a single core comprising the United States into dual cores comprising the United States and China. Gradually, Asian countries have become the main body of international student mobility networks, while the centrality of European countries has reduced. Thirdly, in terms of spatial structure, the international student mobility network has a significant core-periphery structure and hierarchical characteristics. The countries in the core, strong semi-periphery and semi-periphery alternate with countries from other tiers. The spatial patterns of the international student mobility network "from east to west, and from south to north" are changing. China and Australia have become the new regional centers of international student mobility networks, meaning that regionalization has become an important trend. Finally, regression analysis shows that the flow of international students correlates positively with the quality of higher education in destination countries, the number of students in colleges and universities, the per capita GDP, the historical links connection between the destination country and the country of origin, and the level of globalization. Geographical distance and linguistic proximity have a significant negative correlation with the flow of international students, indicating that the impediment of language is rapidly weakening, while geographical distance still hinders student mobility.
全球留学生留学网络时空演化及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004002
[本文引用: 1]

基于联合国教科文组织公布的全球高等学校留学生流动数据,借鉴网络科学,利用社会网络分析方法和负二项回归模型,对2001—2015年全球留学网络时空演化及其影响因素进行研究。主要结论为:① 时序演化特征上,全球留学网络关系流从4921个增加到9137个,平均加权度从8004迅速增加到20834,表明全球留学网络不仅学生数量在增加,且留学路径数量也在不断增加。② 拓扑结构上,从以美国为单一核心,演变成以美国、中国为双核心的拓扑结构,亚洲国家逐渐成为全球留学网络的主体,欧洲国家的中心性逐渐萎缩。③ 空间结构上,全球留学网络具有明显的等级层次性,美国是全球性主导型节点,德国、捷克是区域性主导型节点,次级主导型节点从25个增加到32个,全球留学网络“东向西、南到北”的地理空间格局正在发生变化,中国、澳大利亚等国成为新的区域性中心,区域化成为全球留学网络一个重要趋势。④ 回归分析发现,留学目的地国高等教育质量、高校在校生数量、人均GDP、留学目的地国与留学生来源国间的历史联系及全球化水平与留学生流量呈显著正相关关系,地理距离、语言临近性与留学生流量呈显著负相关关系,表明语言差异的阻抗作用在迅速减弱,地理距离仍然是阻碍学生流动的一个重要因素。
Spatiotemporal evolution of global talent mobility network based on the data of international student mobility
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181156
[本文引用: 1]

High-quality talents are reshaping the world economic landscape by transcending geographic flows and driving global innovative activities. Based on the data of international student mobility, this paper draws on complex network theory to construct a multidimensional weighted directed network heterogeneity model. This model uses the GIS spatial analysis method to study spatiotemporal evolution of global talent mobility network complexity from 2001 to 2015. The results are as follows. First, the scale of the global talent mobility network is expanding rapidly, and the relationship is becoming closer and closer. In the network, both the number of talents and the choices of overseas routines are mounting. The network development has obvious small-world characteristics. However, the two levels of network differentiation are significant, and the difference is decreasing year by year. Second, the rank-size distributions of network nodes weighted degree of accession and weighted degree of output conform to the law of power distribution, showing a typical "pyramid structure" characteristics, reflecting that the global talent mobility network is controlled by a small number of pivotal node countries. The spatial patterns of the global talent mobility network are basically "from east to west, and from south to north", but the trend of mobile regionalization is gradually emerging, and the role of emerging countries attracting talents has gradually increased. Thirdly, the core-periphery structure of the global talent mobility network is remarkable. The countries in the core, strong semi-periphery and semi-periphery alternate with countries from other tiers. There is a strong mobility of relations between the core countries. The marginal countries are not connected with each other, or have weak links with each other. The talent of the marginal countries mainly flows to the core countries and semi-marginal countries. Finally, the global talent mobility network community has been significantly differentiated. The network has evolved into six associations, including American associations, EU associations, Chinese associations, South American and South African associations, Malaysian associations, and CIS associations. The scale of associations varies widely. Like the overall network, each community has a similar "pyramid structure" feature.
全球人才流动网络复杂性的时空演化: 基于全球高校留学生流动数据
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181156
[本文引用: 1]

高质量的人才跨越地理的流动影响和驱动着全球范围内的创新活动,正在重塑世界经济格局。研究基于全球高校留学生流动数据,构建加权有向网络模型,对2001—2015年全球人才流动网络复杂性时空演化进行全面刻画。主要结论如下:① 全球人才流动网络规模迅速扩大,网络发育具有明显的小世界性,两级分化显著。② 全球人才流动网络呈典型“金字塔结构”特征,基本呈“东向西,南到北”的地理格局,新兴国家作为人才吸纳国的角色逐渐上升。③ 全球人才流动网络核心-边缘结构显著,核心国家间存在较强的关系流,边缘国家间联系较弱,其人才主要流向了核心国家和半边缘国家。④ 全球人才流动网络分化成美国社团、欧盟社团、中国社团、南美和南非社团、马来西亚社团、独联体社团等6个凝聚子群。
Spatio-temporal evolution on connection strength of global city network based on passenger flight data from 2014 to 2018
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.005
[本文引用: 1]

This article analyses the spatio-temporal evolution of connection strength on global city network by using Gephi, which is based on passenger flights data from April 2014 to August 2018. Although Gephi can be used to analyze many topological properties of city network, we mainly used Average Weighted Degree and Betweenness Centrality to depict the basic characteristics of global city network, which reflected the connection strength and spatial differences of network. In order to reinterpret the breakthrough of connection strength to spatial distance constraint on global city network, we propose a model of connection strength-space distance based on concept of definite integral. The study mainly draws the following conclusions: 1) The connection strength of global city network becomes stronger in general from 2014 to 2018 and its backbone is formed by three big urban agglomerations, including West Europe megaregion, North America megaregion and East Asia megaregion. New York and other important nodes play a key role in building a global city network and form a self-centered network framework, bearing the flow of elements of global economic development. The variation coefficient obtained from the Betweenness Centrality of each city reflects that the polarization of the global city network is slightly reduced, but the ‘pyramid’ hierarchical structure does not change fundamentally. In addition, the Average Weighted Degree first increases and then decreases, which indicates that the global city connection strength has been improved and the complexity of the global city network in the evolution process. 2) The fitting curve obtained by the connection strength-space distance model basically conforms to the distance attenuation law, and the distance range of the peak indicates that the global city network has the highest connection strength in the short and medium range. Furthermore, the peak value first rises and then falls, which also proves the complexity and periodical characteristics of the change of global city network on connection strength. The breakthrough value of distance (BVD), obtained by the connection strength-space distance model, reaches a peak in 2016 and then falls with fluctuation, which reflects the complexity and volatility of global city network in its evolution and reconstruction process. On the one hand, this article makes a detailed investigation of the global city network from a spatio-temporal perspective, and on the other hand, it makes a quantitative analysis of the distance decay law.
全球城市网络联系强度的时空演化研究: 基于2014—2018年航空客运数据
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.01.005
[本文引用: 1]

基于2014年4月至2018年8月的全球航空客运数据,运用Gephi网络分析探讨全球城市网络联系强度的时空演化过程,并基于定积分的基本概念构建了“联系强度-空间距离”模型,从新的视角解读全球城市网络联系强度对空间距离的突破,研究得出以下结论:①全球城市网络联系强度在2014~2018年总体呈上升态势,西欧城市群、北美城市群、东亚城市群构筑了全球城市网络骨架;② 全球城市网络对空间距离的突破在2016年达到峰值后又呈现阶段性回落,反映出全球城市网络演化与重构的复杂性和波动性。
Analysis of international transfer and regulation of military: Science and technology evidence from arms trade network
军事科技的国际转移与管制分析: 来自军火贸易网络的证据
International transfer of military technology: Motivation, path and influence
军事技术国际转移: 动因、路径及影响
A review on geographies of international trade
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.012
[本文引用: 1]

It is expected that the world economy would be gradually integrated and interconnected by trade liberalization and progress in technology in globalization era. However, researchers have found that international trade remains significantly affected by geographies. At the same time, economic geographers put little effort on building theories about geographies of international trade and their main contribution in this field is confined to descriptive analysis on the heterogeneous patterns and network structures of international trade. In this article, how geographies affect trade in international economic studies is reviewed from three dimensions—production, circulation, and consumption. Differences on production side promote trade through the intermediation of opportunity cost while differences in circulation process hinder trade by increasing trade cost. Differences on consumption side affect trade through the intermediation of demand level. By summarizing the literature on the relationship between trade and institutional change, trade and urban agglomeration, trade and inequality, trade and innovation, and trade and pollution, we identify three major limitations of these studies. First, few studies dig into the endogeneity of geography systematically. Spatial disparity can be shaped by international trade rather than only determining international trade. Second, there is a dearth of multi-scale and inter-scale perspective despite that gains from trade at the macro level predicted by traditional trade theory are found not evenly distributed at the meso and micro levels, resulting in evident spatial disparity. Third, some of the studies do not fully explore product heterogeneity, thus cannot completely capture the various spatial impacts of trade. Therefore, possible contribution of economic geographers to international trade studies lies in thorough investigation on multi-dimensional heterogeneity and complex interactions between geographies and international trade from multi-scale and inter-scale perspective.
国际贸易地理研究进展
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.10.012
[本文引用: 1]

全球化时代的技术进步和贸易自由化似乎逐渐将世界经济连为一体,但研究发现国际贸易仍然显著地受到地理因素影响。与此同时,经济地理学对国际贸易地理的理论建构存在欠缺,其对国际贸易研究的贡献目前集中于对国际贸易地理格局和贸易网络异质性的描述分析上。在此背景下,论文从生产、流通和消费3个方面归纳国际贸易研究对地理因素作用的理论建构和实证研究:① 生产上的地理差异经由机会成本差异促进贸易;② 流通上的地理差异经由贸易成本而抑制贸易;③ 消费上的地理差异经由市场需求地空间差异而影响贸易。通过总结贸易与制度变迁、贸易与集聚、贸易与不平等、贸易与创新、贸易与污染间的关系相关研究,论文认为当前国际贸易研究存在如下局限:① 并未深入讨论地理变量的内生性,即贸易可能反过来塑造地理差异而非仅由地理变量决定;② 相对缺乏多尺度、跨尺度视角,即贸易理论预测的宏观尺度贸易利得在中观、微观主体上并非均等分配,表现出显著的空间差异;③ 部分研究对产品异质性缺乏探讨,无法全面刻画贸易的差异化地理效应。据此,经济地理学未来对国际贸易研究的贡献可能在于运用多尺度、跨尺度联系的视角深入阐释贸易与地理的多维度异质性和复杂互动。
Global trade network pattern and influencing factors of advanced manufacturing in China
中国高端制造业的全球贸易网络格局及其影响因素分析
Spatial evolution characteristics and influencing factors of trade multidimensional network: A comparative study based on trade in goods, services and value-added
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.08.013
[本文引用: 1]

Under the mode of global value chain division of labor, the focus of global industrial structure has shifted from manufacturing industry to service industry, and service trade has become a new engine to promote world economic growth. The trade value-added accounting method can truly and effectively restore the trade gains and actual status of a country participating in the global value chain, which is a beneficial supplement to the study of trade network under the traditional gross value accounting system. Based on the complex network theory and trade added value accounting, This research focuses on the spatial evolution and its influencing factors of trade in goods, services and value-added of the world’s 64 economies, applying the related technique tools, such as ArcGIS, Ucinet, and MATLAB. The main conclusions are as follows: 1) The tightness and accessibility efficiency of the three kinds of networks are steadily increasing, and the networking trend of service trade is more significant. The global financial crisis has a great impact on network balance and network link, which is shown in the index of network reciprocity and compatibility. 2) There are significant ‘core-edge’ in spatial pattern. At the regional level, there are two ‘cliques’ in the Asia-Pacific region and the European Union region. The United States, China, Japan and Germany are the pivotal nodes of the connection between the two ‘cliques’. 3) Top1 network shows different evolutionary characteristics among goods, services and value-added trade networks, and we found these three types of organizational structure of networks are shown the shape as ‘star’, ‘snowflake’ and ‘star-chain’ respectively. The rise of China is remarkable in three types of networks. In contrast, the development of service trade lags far behind that of goods trade. 4) The QAP analysis shows that traditional factors have strong explanatory power for the formation of the three types of networks, such as GDP, geographical distance, common language. Meanwhile, Disparities of per capita GDP, Economic Integration Agreement lead to their differences, but their significance level is not high and tends to weaken. Finally, combined with the current international situation, this paper gives some policy suggestions on the development of China’s foreign trade under the background of new era of globalization.
多重贸易网络的空间演化特征及其影响因素: 基于货物、服务和增加值贸易的比较
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.08.013
[本文引用: 1]

基于复杂网络分析与贸易增加值核算方法,借助ArcGIS、Ucinet和MATLAB等工具,对全球64个主要经济体货物、服务和增加值多重贸易网络的空间演化及其影响因素进行综合对比分析,结果表明:① 全球货物、服务和增加值贸易网络的紧密性和通达效率均呈现稳步提升趋势,服务贸易的网络化趋势更为显著;金融危机对网络的“互惠性”“异配性”产生较大影响;② 空间格局上均具有显著的“核心-边缘”等级性,区域层面上形成了亚太和欧盟地区两大“派系”,美、中、日、德为两大“派系”联系的枢纽节点;③ Top1网络表现出不同的演化特征,其中货物、服务和增加值贸易网络分别呈现“星型”“雪花型”和“星型+链式”空间组织结构。3类网络演化过程中中国的崛起态势令人瞩目;④ QAP(二次指派程序)分析显示,传统的GDP、地理距离、共同语言等因素对于3类网络的形成具有相似的较强解释力,要素禀赋差异和贸易制度是影响它们之间差异性的主要因素,但其显著性水平不高且趋于弱化。
Research on global grain trade network pattern and its influencing factors
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20210615 URL [本文引用: 1]
全球粮食贸易网络格局及其影响因素
Proximity and innovation: A critical assessment
DOI:10.1080/0034340052000320887 URL [本文引用: 1]
Investment network structure and its impact mechanism of the Belt and Road initiative area
“一带一路”沿线国家投资网络结构及其影响因素: 基于ERGM模型的研究
Structural heterogeneity and proximity mechanism of global scientific collaboration network based on co-authored papers
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704014
[本文引用: 1]

Despite increasing importance of academic papers in global knowledge flows, the structural disparities and proximity mechanism related to international scientific collaboration network attracted little attention. To fill this gap, based on data mining from Thomson Reuters' Web of Science database in 2014, its heterogeneities in topology and space were portrayed using visualizing tools such as Pajek, Gephi, VOSviewer, and ArcGIS. Topologically, 211 countries and 9928 ties are involved in global scientific collaboration network, but the international network of co-authored relations is mono-centricand dominated by the United States. It exhibits some features of a "small-world" network with the smaller average path length of 1.56 and the extremely large cluster coefficient of 0.73 compared to its counterpart, as well as the better-fitting exponential distribution accumulative nodal degree. In addition, the entire network presents a core-periphery structure with hierarchies, which is composed of 13 core countries and the periphery of 198 countries. Spatially, densely-tied and high-output areas are mainly distributed in four regions: West Europe, North America, East Asia and Australia. Moreover, the spatial heterogeneity is also observed in the distributions of three centralities. Amongst these, the countries with greater strength centrality are mainly concentrated in North America (i.e. the US and Canada), Western Europe (i.e. the UK, France, Germany, Italy and Spain), and China, noticeably in the US, which forms the polarizing pattern with one superpower of the US and great powers such as China and the UK. Similarly, the big three regions consisting of West Europe, North America and Asian-Pacific region have the peak betweenness centrality as well. Slightly different from the two above, the distribution of nodal degree centrality is uneven in the world, although regional agglomeration of high-degree countries is still observed. Last but not least, the proximity factors of its structural inequalities were also verified by correlational analysis, negative binomial regression approach and gravity model of STATA. The findings further confirm that geographical distance has weakened cross-country scientific collaboration. Meanwhile, socio-economic proximity has a positive impact on cross-country scientific collaboration, while language proximity plays a negative role.
全球科研论文合作网络的结构异质性及其邻近性机理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704014
[本文引用: 1]

以科研论文为媒介的知识合作网络已成为知识溢出的重要通道,但目前学术界对全球科研合作网络结构的复杂性涌现机制缺乏深入的探讨。基于2014年Web of Science核心合集所收录的科研论文合著数据,借助大数据挖掘技术、复杂网络、空间统计和重力模型分析,刻画了全球科研论文合作网络的拓扑结构、空间格局及其邻近性机理。结果发现:① 拓扑结构上,形成了以美国为核心的层级网络,具有小世界性和等级层次性,发育出典型的等级“核心—边缘”结构。② 空间格局上,以美国、西欧、中国和澳大利亚为顶点的“四边形”成为全球科研论文合作网络的骨架;三大中心性指标值的空间分异明显,强度中心性形成以美国为极核,加拿大、澳大利亚、中国及西欧诸国为次中心的“一超多强”格局,与之类似的介数中心性呈现北美、西欧和东亚“三足鼎立”的形态,度中心性分布则相对均匀,表现出“大分散、小集中”的“多中心—边缘集散”格局。③ 重力回归分析发现,地理距离抑制了国际科研论文合作,不过其影响力较弱;社会与经济邻近性对全球科研论文合作具有明显的促进作用,语言差异不是国际科研合作交流的障碍。
Structural evolution of global high-tech trade system: Products, networks and influencing factors
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012015
[本文引用: 1]

Since 2018, with the major adjustment of the global political and economic structure, Sino-US relations, which take trade friction as the representation and science and technology competition as the essence, have become increasingly tense. Based on this, this paper characterizes the evolution of global high-tech products trade structure from three aspects of product structure, network structure and influencing factors, and draws some conclusions. First of all, in terms of product structure, global high-tech trade is increasingly concentrated on electronic communication products based on telecommunications equipment. However, on the national scale, chemical products and armament products are not only the dependence products of most countries (regions) on imports, but also the superior export products of most countries (regions). Second, in terms of topology, the global high-tech product trade network continues to expand and is closely linked. It is a typical small-world network and develops a stable "core-edge" hierarchical structure. Third, in terms of spatial structure, the global trade pattern of high-tech products has changed from Europe-North America dominated to East Asia dominated, and also the largest trade country has changed from the United States to China. In addition, the spatial structure has changed from the "double arch" structure with the United States as the core to the "multi-arch" pattern with China as the core, but the United States still occupies a central position in the trade network of various high-tech products. Fourth, in terms of influencing factors, trade scale, economic proximity and cultural proximity have positive effects on the evolution of global high-tech products trade network, while geographical distance has an obvious negative effect. The four factors of political stability, openness, infrastructure and technological innovation only pass the significance test on the importing country (region), while the economic scale only passes the significance test on the exporting country (region). The technological gap is one of the driving forces for the evolution of the global high-tech product trade network.
全球高科技产品贸易结构演化及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012015
[本文引用: 1]

为清晰刻画全球高科技产品贸易体系变迁,本文利用世界银行以及联合国商品贸易数据库中2000—2017年高科技产品贸易数据,从产品结构、网络结构和影响因素3个方面探讨了全球高科技产品贸易结构的演化态势。研究发现:① 产品结构上,以电信设备为主的电子通讯产品主导全球高科技贸易发展,但在国家尺度上,化学产品和武器产品是大部分国家(地区)的进口依赖产品或出口优势产品;② 拓扑结构上,全球高科技产品贸易网络持续扩张,联系紧密,是一典型的“小世界”网络,并发育出稳定的“核心—边缘”式的等级层次结构;③ 空间结构上,全球高科技产品贸易格局呈现出由欧洲—北美主导向由东亚主导转变,贸易最大国也由美国转变为中国,网络空间结构也呈现出由以美国为核心的“双拱”格局向以中国为核心的“多拱”格局转变,但美国依然在多种高科技产品贸易网络中占据核心地位;④ 影响因素上,贸易规模、经济邻近性和文化邻近性对全球高科技产品贸易网络演化皆具有一定的正向作用,地理距离对全球高科技产品贸易网络的演化起到明显的负向作用。
Determinants of China's arms exports: A political economy perspective
DOI:10.1080/13547860.2019.1637706 URL [本文引用: 1]