1 引言
21世纪以来,伴随全球化、信息化、网络化交互作用的深化发展,旅游资源要素的空间模式与空间关系发生深刻变革[1]。从供给侧来看,快速交通网络与移动通信技术形成的时空压缩效应[2-3],导致旅游要素的高度动态化和关系化,旅游目的地的空间关联效应与空间组合关系日益显著[4]。从需求侧来看,流动性作为现代社会的基本原则[5],重新定义了人类旅游活动[6],旅游活动的空间范围与空间选择不断拓宽[7]。旅游目的地作为一定空间范围内旅游资源、基础配套设施、旅游专用设施以及其他相关条件的有机结合[8-9],是一个明确的地理区域[10],本质上是由各类旅游要素相互作用形成的综合性旅游产品。伴随旅游要素空间关系的日益强化,旅游目的地依托山脉、河流、道路、古道、运河等跨越不同地理单元、文化板块的线状自然、文化、交通要素为关联轴线[11],由特定空间范围向连续空间范围“线性”整合的空间趋势日益显著[12],绿道、风景道、遗产廊道、文化线路、旅游公路、线型旅游体验空间等旅游目的地空间供给形式与空间消费形式逐渐涌现。
旅游目的地空间形态、空间规模、空间关系的“线性”发展,需要我们超越结构主义静态化的研究范式,针对旅游目的地的新型空间关系与新型空间结构进行动态开放的整体性审视,并在认识论、方法论层面形成新的阐释。后结构主义对结构主义“解构”的学术转向,推动了地理学研究的关系转向[13],尤其是后结构主义对事物发展过程中相互影响的异质性关系的关注,为地理学的空间研究带来了实质性的理论和实践启发[14-15]。后结构主义强调空间的开放性与关系性[16],注重不同要素间的关联互动关系[17],理论视角由封闭性、决定性的结构研究转向动态、开放的关系研究[18-19],为流动性背景下旅游目的地的空间关系研究提供了理论指引。因此,本文尝试基于后结构主义的理论视角,针对旅游目的地空间关系的“线性”发展,建立概念框架,并从过程、机制和尺度层面构建整体性的认知体系,以期为旅游目的地的发展研究提供新的理论视角与研究视域。
2 理论基础与概念界定
2.1 后结构主义
2.1.1 理论转向:从本质主义到关系主义
后结构主义是对结构主义的批判检视形成的新型思维模式与方法论革命[20]。结构主义强调基于二元对立的思维模式寻求固定的规则结构以揭示事物本质[21⇓-23],对时间、空间、人类主体的概念排斥使其忽略了事物的动态性、开放性及其自身的生产性[24]。20世纪60年代后期,Barthes、Derrida、Foucault等开启了批判结构主义的“解构”思潮——后结构主义。后结构主义强调事物是联系的产物而非本质自我的产物[25-26],事物皆存在内在的规则结构,但更为重要的是事物在形成发展过程中的连通性[13]。这种连通性并非固化的存在,纵向上表现为事物本身与过去、现在和未来的联系,横向上表现为事物与特定社会条件、社会关系的联系[19]。关系主义的理论转向推动了社会学领域对空间概念的系统关注[17],空间意识的复兴以及社会学研究的“空间转向”推动了地理学者对空间、场所的内涵进行重新解构与定义[27⇓-29],空间和场所被解读为“关系场中的节点”。
2.1.2 空间转向:从空间到关系空间
关系主义的理论转向推动地理学领域形成新的空间理念——关系空间[16]。空间由传统社会文化地理学中客观静态的活动容器转化为社会经济发展的重要组分与能动因子[30]。从空间特征来看,关系空间由竞争、并存的各类关系所构成[31],伴随关系的流动与展开,空间处于永恒的生成之中,竞争关系不断分割空间主权,并存关系则在特定空间中形成协同,驱动关系在地方、区域、全球尺度之间的整合、流动和跃迁[32-33]。从空间意义来看,关系空间推动地理学关注的社会空间现象更为复合多元,信息空间、流空间等空间理论的涌现更新了地理学传统的空间认知范畴[34],各类要素相互依存、相互生产、相互建构的辩证关系引起广泛关注[35-36]。Massey[31]、Doel[33]、Cresswell[37]等学者开始通过连通性、开放性来解读空间,认为空间是被不断生成的异质关系塑造而成的流动性场域,创新网络演化、全球生产网络、全球旅游系统等跨越地理空间界限的研究议题受到地理学者的广泛关注[38⇓-40]。
2.1.3 视角转向:旅游目的地概念内涵的再认识
后结构主义关系主义的理论转向、关系空间的空间转向,为旅游目的地空间组织结构线性发展的现象梳理和概念界定提供了认识论基础与方法论启示。在认识论层面,关系主义对连通性的解读,能够以关联性、开放性、生成性的理论视角透视旅游要素空间互动、空间扩张以及旅游目的地空间形式线性发展的组织特征,为旅游目的地向线性旅游目的地的概念延伸提供了组织层面的理论启示。在方法论层面,关系空间对尺度有界性的弱化,为旅游目的地由特定空间地域向连续空间地域动态扩张的空间形态、空间尺度分析提供了多类型、多层次的立体化研究体系。关系的流动、展开与生成,为点、线、面等不同空间形态目的地以及地方、区域、国家、国际等不同空间尺度目的地关联互动的空间实践建构了普遍的探索路径与方法逻辑。总的来说,后结构主义为旅游目的地向线性旅游目的地的概念延伸与建构提供了基本的理论依托与分析逻辑,是基于新的社会现实基础展开旅游目的地概念内涵再认识、再理解、再创新的重要理论视角。
2.2 线性旅游目的地
2.2.1 主题与关系建构:从旅游目的地到线性旅游目的地
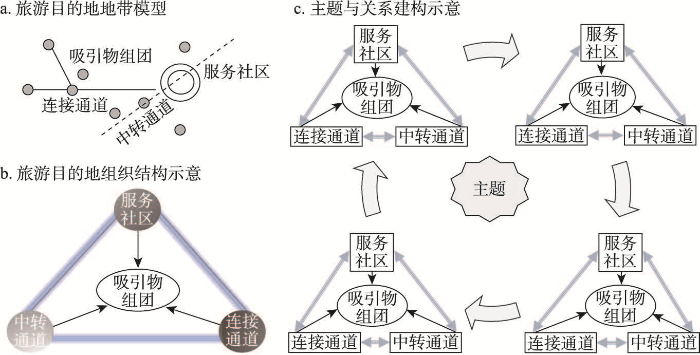
旅游目的地的概念研究始于20世纪70年代,Gunn基于对旅游地域系统的微观研究提出旅游目的地地带的概念模型[9],认为吸引物综合体、服务社区、中转通道和区内连接通道等旅游要素共同构成一个完整的目的地地域系统(图1)。国内学者在此基础之上突出强调地理空间的逻辑[41-42],认为旅游目的地是一定地理空间范围内旅游资源、基础配套设施、专用设备及其他条件的有机结合[43]。伴随全球化、信息技术革命以及交通运输技术的推进,旅游目的地的可进入性、连通性发生深刻变革,相关学者围绕旅游目的地在次区域、区域、全球等不同空间尺度上的空间组织模式与形成发展机制展开广泛讨论[35,44]。伴随旅游目的地由特定地理空间向动态关系空间的特征转向,目的地被视为涉及行动者个体层面、目的地层面、区域层面等多层次合作生产网络的组成部分,对于独立的目的地个体来说,与其他目的地以及更广泛的地理区域之间建立联系变得十分重要[45]。Baggio等在此基础之上进一步强化了旅游目的地的关系属性与网络逻辑,认为旅游目的地是包含旅游资源、旅游服务、旅游产品及其相互作用关系的复杂网络系统[46]。
图1
旅游要素空间关系的交织深化,不仅重塑了旅游目的地的概念内涵,也重构了传统的旅游目的地发展模式。其中,线路旅游被认为是强化旅游目的地空间关系、实现旅游地可持续发展的有效形式[47-48]。线路旅游是指基于统一主题,将特定区域的目的地和旅游活动联系在一起,通过开发配套产品和服务而获得更多发展机会的旅游组织形式[49]。跨越地理距离和文化多样性的主题,往往能够与更大尺度的发展愿景相契合[50],汇集更为广泛的资产和活动[51-52]。同时,主题不是刻意迎合旅游市场的产物,而是与区域历史、文化、景观、生活方式密切相关、对地方发展具有意义潜力,并能够反映区域旅游产品核心价值、本质属性的特定要素或符号[53],这些要素能够驱动旅游者、旅游活动、旅游消费由单一目的地节点向多个目的地节点动态扩散[54]。在线路旅游的组织形式下,新型旅游目的地发展模式逐渐形成,并取得了较为显著的社会经济效应[55⇓-57]。欧洲圣地亚哥·德·孔波斯特拉之路(Routes of Santiago de Compostela)、丝绸之路(Silk Road)、南非花园大道(The Garden Route)、美国66号公路(Route 66)、澳大利亚大洋路(Great Ocean Road)等地均基于线路旅游的组织形式,凭借特定主题的关系建构,形成沿一定方向关联互动的目的地集合体系——线性旅游目的地。
2.2.2 线性旅游目的地:概念依据、基本特征与概念界定
(1)概念依据。从学理依据上来看,旅游目的地是旅游地理学的核心研究对象[58]。在高速流动的当今社会,旅游目的地空间形态、空间规模、空间关系“线性”发展的趋势特征日益显著,逐渐成为旅游目的地建设发展的重要形式与展开路径。相关学者基于不同的学科视角与研究侧重,提出了绿道、风景道、遗产廊道、文化线路、旅游廊道、旅游公路、线型旅游空间等概念范畴,多侧重于静态的概念阐释与碎片化的现象分析,在学理层面尚未形成完整的理论建构和系统性深入研究。因此,本文尝试厘清“线性旅游目的地”的概念内涵,回归旅游地理学基本概念、基本对象的理论探讨,基于新的社会历史条件形成对旅游目的地这一基本概念的再认识与再思考,完善已有的目的地认知体系,建立完整的“理论指导实践、实践完善理论”的旅游目的地反馈机制。
从现实依据上来看,伴随现代交通体系与网络通信技术的日益完善,以旅游者为引领的旅游要素的空间传导速率不断提升,区域旅游边界效应逐渐弱化,旅游目的地的空间组织结构逐渐由点状向轴线状、网络状动态演变[59],空间结构的连通性不断增强。其中线路旅游作为有效的组织形式与工作方法,在世界各地的遗产保护、经济发展、区域合作、文化传承中发挥了重要作用,受到国际组织的广泛关注。基于此,本文尝试通过线性旅游目的地的概念界定,在现实层面回应新一轮科技革命所引发的旅游目的地空间组织形式的实践变革。线性旅游目的地并非是对旅游目的地概念内涵的学理否定,而是基于新的社会条件和实践态势形成对旅游目的地概念内涵的补充阐释与深入认识。
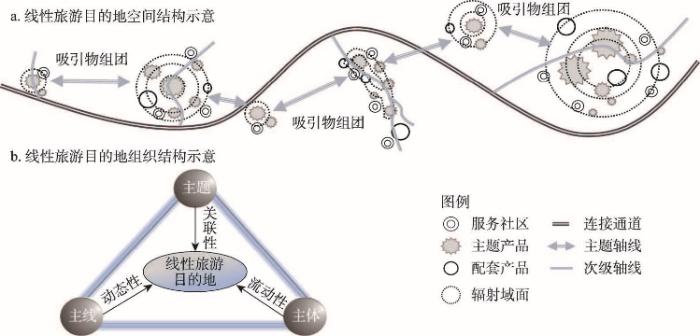
(2)基本特征。线性旅游目的地的概念虽尚未统一提出,但已有研究针对其关联性、流动性、动态性的空间组织特征已形成基本认同(表1)。其中,关联性是线性旅游目的地空间组织的基础特征,主要指旅游目的地之间自然、社会、文化关系的建构与发展;流动性是线性旅游目的地的要素特征,主要指旅游目的地在稳定的自然、社会、文化关系基础上形成的以旅游者为引领的各类旅游要素的流动;动态性是线性旅游目的地的结构特征,指线性旅游目的地在旅游要素流动速率、流动规模不断强化的背景下空间组织结构所发生的动态变化。
表1 相关概念内涵与基本特征
Tab. 1
| 概念内涵 | 基本特征 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 绿道 | 为实现多种用途(可持续土地利用、生态、休闲、文化、美学)而规划、设计、管理的线性要素组成的土地网络,是具有生态、游憩、文化、审美等多功能的,可持续发展的绿色开敞空间 | 线性的空间结构,关联性,多功能性,可持续性,整体性 | [60-62] |
| 沿河滨、溪谷、山脊、风景道路等自然、人工廊道建立的线形绿色开放空间 | |||
| 风景道 | 具有交通运输和景观欣赏双重功能的通道 | 多功能性(价值混合体),节点、线路、域面的联合发展 | [63-65] |
| 旅游和交通功能相结合的、在路旁或视域之内具备景观、游憩、历史、文化、自然、文物等多重价值的景观道路 | |||
| 遗产 廊道 | 拥有特殊文化资源集合的线性景观 | 景观的连续性、整体性、互动性,潜在的连接元素;多尺度类型 | [66-67] |
| 遗产廊道是特殊类型的遗产区域,其保护主体包括连续的河流、峡谷、道路、铁路线等,也涉及把遗产点串联形成的具有历史意义的线性廊道 | |||
| 文化 线路 | 基于陆路、水道或者混合类型通道的、能够反映人类互动和跨越较长历史时期的民族、国家、地区间交流的线路 | 主题,多尺度类型,多元价值,流动性,关联性 | [68-70] |
| 基于特定历史路线、文化概念、人物或现象建立的旅行线路,以具有代表性与普遍性的主题为发展基础。该主题能够阐释区域记忆、历史和遗产,并且在与旅游机构或经营者合作的过程中,能够促进旅游产品的发展 | |||
| 旅游 公路 | 以旅游交通通行为主要功能并连接旅游景点或路侧具有旅游价值的带状公路廊道 | 主线、支线、服务节点的基本空间构成 | [71] |
| 线型旅 游体验 空间 | 以交通功能为基础、以满足旅游者体验需求为根本目的,在风景道及其辐射范围之内具备多元功能的一种线型旅游目的地形象 | 旅游资源的串联,空间的连续与外推,网状的空间开发模式,协调沿线的竞合关系 | [72] |
首先,就关联性而言,线性旅游目的地通常以特定主题为引领,以交通基础设施等实际通道载体为依托,建构沿线目的地节点的组织关系[73⇓-75],形成主题引领、主线明确、主体联系通道顺畅的关联性组织结构(图2)。如Snowball等在南非的文化遗产路线研究中指出,特定主题能够将区域性的目的地节点、活动联系在一起,实现旅游吸引力的强化整合,并带来更为高效统一的目的地管理与营销[47]。Meyer认为文化线路建构了孤立城镇、城市、旅游历史城市之间的历史、经济、文化联系,使多样化、分散化的欧洲遗产具备相对一致的表现形式,丰富旅游者体验的同时也能够驱动旅游需求、旅游消费的外溢与扩散,是建立区域合作伙伴关系、刺激区域经济发展的有效工具[73]。
图2
图2
线性旅游目的地的空间组织特征
Fig. 2
Spatial structure of model for route tourism destinations
其次,就流动性而言,线性旅游目的地超越了旅游目的地固有的空间范畴[76],主题轴线、交通干线将吸引物综合体、连接通道、中转通道、服务社区吸纳进一个流动性更高、连通性更强的高维目的地体系之中,跨区域的空间地理特征明显[77],较点状、团块状目的地空间形态更为有机连续和多维自由。Ward-Perkins等认为线路旅游能够驱动旅游者沿特定方向的流动扩散,而这种流动性也是传播经济效益、缓解过度旅游的重要力量[53]。此外,张圆刚等在线型旅游体验空间的特征研究中指出,风景道内旅游者高度的定向流动能够带来旅游生产要素的空间集聚与扩散,促进目的地空间地域的连续与外推[72]。杨效忠等发展了对已有研究的认识,在线型旅游空间吸引力模型研究中指出,线性旅游目的地的动态景观具备显著的流动性特征,流动景观是线型旅游空间最重要、最基本的旅游吸引物[78]。
最后,就动态性而言,组织结构的关联性、空间结构的流动性使线性旅游目的地能够实现以旅游者为引领的各类要素主体的高效流动与跨地方聚合,不断创造、强化目的地的空间关系,以点、线、面等形式塑造新的目的地节点[79-80]。邱海莲等在哥伦比亚河历史公路的研究中指出,风景道旅游目的地具备线型空间的连续性与外推性、空间系统的开放性与整合性,作为一个开放的空间系统,其辐射区没有明确界限,不断动态变化[74]。前约旦步道协会主席Haddad进一步指出,线性旅游目的地是持续动态变化的,在发展中国家尤为明显,伴随宏观社会经济环境的变化,旅游基础设施不断完善,线性旅游目的地空间组织结构的变化一直在发生,处于动态的涌现与生成之中[53]。
(3)概念界定。“性”多指事物本身所具有的作用、性质及属性,“形”多用于表示形象、形体、形状等外部形态,“型”多指模型、类型[81]。因此本文采用“线性”对旅游目的地空间关联的连通性思维进行指代,既包括外在空间形态的连通性,也涵盖内在组织结构的连通性,以突破“线型旅游空间”“线形旅游产品”等已有表述对线性旅游目的地外在空间形态、功能结构的表层关注,深入线性旅游目的地空间组织结构的关系本质。
关联性、流动性、动态性的空间组织特征决定了线性旅游目的地区别于其他目的地形式的产品结构与体验特征。从旅游产品构成来看,线性旅游目的地能够通过特定主题的关系渗透与价值引领,在不同旅游产品与产品生产者之间建立有机联系。Meyer在线路旅游发展的关键问题研究中指出,主题不仅是线性旅游目的地的组织基础,住宿、餐饮、服务、购物等各类基础旅游要素的发生发展也均基于统一主题而展开[73]。从旅游体验特征来看,特定主题能够提供一个统一的体验框架,使旅游者沉浸在由整体叙事联系起来的事件、人物、景观、符号的连续序列中,形成连贯、强烈的情感体验,激发旅游者的深刻认知[82]。Hsu在台湾长途步道的旅游研究中指出,特定主题能够赋予旅游者探索、游览沿线相关目的地节点的动机与使命[56]。基于线性旅游目的地概念提出的学理依据与现实依据,结合已有研究对其空间组织特征、产品结构、体验特征的剖析,本研究认为线性旅游目的地是以特定的自然、文化主题为引领,以旅游基础要素的线性延展为基础,以旅游者、旅游经营者、旅游产品、旅游信息、旅游服务等各类要素主体的流动关系为根本,形成的沿特定方向关联互动的目的地组织共同体与空间连续体,具备关联性、流动性、动态性的空间组织特征。
3 理论适用性论证与分析框架
3.1 理论适用论证
关系主义的连通性与关系空间的开放性、动态性、生成性既体现在线性旅游目的地以主题为引领的组织结构的构成与演化上,也体现在其空间结构的形态变化与尺度转换上。因此,本部分主要从线性旅游目的地的内在组织结构与外在空间结构出发,充分考察关系主义与关系空间在其中的具体表征。
从组织结构来看,关系主义与线性旅游目的地的组织结构过程具有高度的内在耦合性。一方面,从组织结构的构成来看,主题作为潜在的连接要素,是线性旅游目的地的组织关联核心。主题通常与目的地的文化、生产生活方式密切相关,无论主题是“莱茵河的城堡”还是“印度的民间节日”,都可以直接与潜在的消费者建立对话,传达共同的理解[11]。另一方面,从组织结构的演化来看,关联性的组织结构决定线性旅游目的地组织结构的发展演化并非是固化在特定空间地域的静态关系体系。Stoffelen认为线性旅游目的地具备强大的扩散效应与外溢潜力,旅游活动的社会经济效应能够通过旅游者的经济足迹扩散到边缘地区,形成区域性的利益主体网络[83],刺激沿线社区、目的地节点基于更广泛的经济发展目标建立紧密联系[84]。因此,关系主义连通性、历时性的研究视角与研究方法,为线性旅游目的地的组织结构研究提供了理论透视视角与过程性分析框架。
从空间结构来看,关系空间与线性旅游目的地的空间结构特征具有显著的逻辑关联性。一方面,从空间形态特征来看,线性旅游目的地融合了点状、团块状旅游目的地“点轴”驱动、“多中心”驱动的空间优势,形成高效多向的要素流动与主体互动。Schuhber等认为线性旅游目的地能够有选择地连接阶段性地区、停留节点和目的地节点,建构商品、服务的空间通道以及思想、知识的交流通道,实现“区域—部门”集群的空间串联[85],壮大区域旅游供给主体之间的关系规模[86]。另一方面,从空间尺度特征来看,线性旅游目的地在不同的空间尺度下基于不同的主题而运行,主题不同,旅游产品结构与旅游体验特征不同。同时,“点轴—多中心”的空间扩张模式也为线性旅游目的地在不同尺度之间的流动关联提供空间可能。MacLeod认为线性旅游目的地秩序化的旅游空间生产方式能够创造统一的体验框架,使旅游者充分体验目的地的多样性[87]。同时,线性旅游目的地也通常涉及不同尺度上的竞争与合作,具备多层次的旅游生态系统构成[88]。因此,关系空间中非嵌套、动态的尺度认识为线性旅游目的地的空间发展提供了认知基础与方法指导。
3.2 分析框架
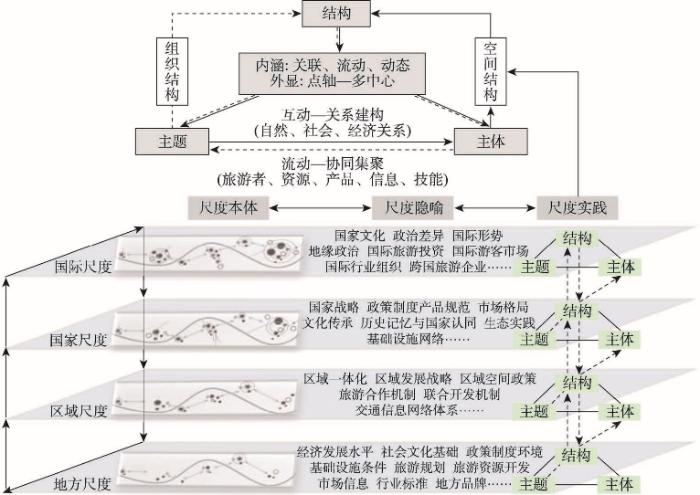
线性旅游目的地的发生发展具备多元空间形态与多尺度空间特征。尺度是地理学的核心概念[89],最初与制图学密切相关[90]。20世纪80年代,Taylor基于结构主义的视角,将尺度的概念引入人文地理学研究[91],通过权力关系等级与空间结构层次的对应关系,建立社会、政治、经济过程的分析层次[92]。20世纪90年代,伴随后结构主义的兴起,尺度等级化的结构主义倾向逐渐受到批判,后结构主义秉持更加开放、关联的尺度观,认为“全球—国家—地方”的嵌套层级结构应当被“连通性”所替代[93]。后结构主义视域下,尺度不再是社会关系的封闭容器,更加关注尺度被社会行动者及其实践活动塑造和转换的过程[94]。这一转变的实质在于从关注尺度本体转向关注行动者为实现特定目标或发展优势所采取的表达手段或政治策略[95],即尺度隐喻和尺度实践。然而,尽管“连通性”日益重要,人类主体及其社会经济过程仍然存在于由地方、区域、国家等组成的现实世界[96],单纯地关注尺度隐喻与尺度实践缺乏实体尺度支撑[97],难以厘清线性旅游目的地的尺度变化过程。因此,本文结合后结构主义对尺度的非物质理解,综合尺度本体、尺度隐喻与尺度实践,关注不同尺度线性旅游目的地行动主体、制度逻辑及其结构变迁的实践过程,建立线性旅游目的地空间组织结构的综合性分析框架(图3)。
图3
具体而言,在内在的组织结构上,明确主题引领、主体协同的旅游目的地组织结构过程。主题是线性旅游目的地的组织基础,主题不同,旅游目的地各类要素主体的关系建构方式与关联程度存在差异,并作用于目的地整体空间组织结构的线性整合。Ward-Perkins等在针对线性旅游目的地的理论实践研究中指出,线性旅游目的地是在强有力的主题基础上发展起来的,除了旅游吸引物,目的地在内的住宿、餐饮、服务、购物等配套产品和服务均围绕特定主题而展开[53,73]。因此,需要将旅游目的地主题、旅游目的地的各类要素主体作为核心,探索主题关系建构的过程差异与阶段特征。在旅游目的地主题上,考察不同主题的社会建构过程,分析不同类型主题在旅游目的地关系生产中的过程特征与一般规律,明确区域旅游目的地自然、社会、文化关系形成发展的主题驱动与建构路径。在旅游目的地的要素主体上,探索政府组织、行业协会、旅游企业、社区居民以及旅游者等权力主体与社会组织的关系生产过程,归纳总结线性旅游目的地基础旅游要素、核心旅游要素以及创新旅游要素的流动过程和关系效应。
其次,在外在的空间结构上,构建多尺度、多中心的目的地空间连续体。Lourens 在圣地亚哥·德·孔波斯特拉之路与南非米德兰兹线路(Midlands Meander)的案例研究中指出,线性旅游目的地的长度、规模、主题存在较大差异,涉及地方、区域、国际等不同尺度,并在不同的空间尺度上吸引不同类型、不同规模的旅游者[49]。因此,需要遴选地方、区域、国家、国际等不同空间规模的线性旅游目的地,分析总结线性旅游目的地的空间形态特征与空间关联机制。在空间形态上,基于特定空间尺度的线性旅游目的地,分析目的地节点、轴线、网络的空间优化过程,剖析旅游者、旅游资源、旅游企业、旅游信息等旅游要素集聚扩散的空间特征。在空间尺度上,深入刻画不同空间尺度上线性旅游目的地空间组织结构的特征差异与尺度效应,结合不同空间尺度的发展环境与行动主体,探索线性旅游目的地尺度关联、尺度转换的行动机制,总结目的地空间关联的内源动力与外源拉动路径,建立多尺度、综合性的空间分析体系。
4 研究展望
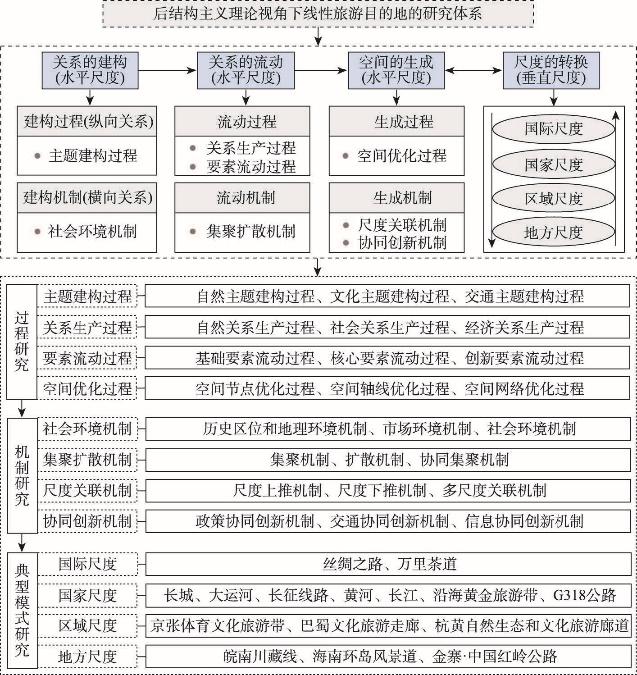
后结构主义的关系思维溶解了事物的空间边界[98]。Amin认为地方不存在禁止边界,通过多样性节点的并列集聚,能够形成在时间和空间上延伸更远的关系实体,并由此产生不断动态变化的组织特征和空间形态[99]。Jones基于后结构主义的尺度认知提出平面本体论,认为我们对尺度的认知不仅包括向上向下的垂直想象,还包括辐射水平空间性,这种水平和垂直的结合也许能提供认知世界的框架[100]。因此,本文进一步基于后结构主义的关系思维及尺度认知,从关系的建构、关系的流动、空间的生成以及尺度的转换出发,将线性旅游目的地置于水平和垂直相结合的尺度框架内进行综合考察,从过程、机制和不同尺度空间模式3个层面进行研究展望的归纳与讨论(图4),以期形成关于线性旅游目的地多层次、多维度、多视角的综合性认知体系。
图4
4.1 线性旅游目的地发展演化的过程研究
4.1.1 主题建构过程
主题作为定位和识别旅游产品的有效方式,能够整合和推广一系列旅游景点与活动,并进行连贯营销。Benur等在旅游产品集中度和多元化的研究框架中指出,主题能够有效降低区域旅游发展的协调成本和不确定性,形成效率与经济性的综合优势[101]。因此,主题是线性旅游目的地发展演化过程的核心与基础。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 自然主题的建构研究。从综合人地关系、社会建构视角出发,遴选依托山脉、河流、海岸线等自然生态景观进行关系建构的线性旅游目的地,分析自然景观系统、自然符号系统的价值内涵与传播路径,梳理自然主题引领下线性旅游目的地的符号体系及发展历程。② 文化主题的建构研究。围绕文化线路、线性文化遗产、历史线路以及重大文化工程等文化主题,基于社会认同理论、社会网络理论、文化记忆理论、符号互动理论探索文化主题形成发展的资源基础与要素体系,分析文化主题要素在区域旅游产品发展中的价值渗透路径与意义关联特征。③ 交通主题的建构研究。围绕自驾、骑行、徒步等交通、户外、冒险主题的线性旅游目的地,分析交通主题在目的地关系建构中的塑造力量、行动主体与响应过程,基于对比分析的视角总结交通主题建构的关键环节与特征差异。
4.1.2 关系生产过程
Weidenfeld等通过对旅游目的地特定主题和空间关系的评估,认为基于特定主题的关系生产为旅游地提供了创新和增强竞争力的机会[102-103]。关系生产作为主题建构的结果表征,是线性旅游目的地发生发展的重要过程。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 自然关系的生产过程研究。分析生态伦理、环境正义、公平与效率以及可持续发展等自然环境理念在线性旅游目的地发展演化中的传播过程与组织路径,总结线性旅游目的地自然关系的关联路径与价值转化模式。② 社会关系的生产过程研究。基于社会关系网络视角,分析线性旅游目的地不同利益主体社会观念、行为方式与社会关系的变化过程及其空间影响,考察目的地内外交互社会关系的稳定变量与连续变量,总结社会关系演变在目的地空间组织结构发展演化中的作用特征。③ 经济关系的生产过程研究。分析线性旅游目的地旅游市场规模、资源配置以及经济组织模式的特殊性,识别其经济活动的核心主体、合作模式与整合路径,根据耦合协调模型、旅游吸引力模型、旅游经济联系强度模型分析线性旅游目的地旅游经济发展的空间格局、空间溢出效应与空间收敛性。
4.1.3 要素流动过程
主题的关系建构实现旅游要素在更广泛时空尺度上的关联流动,如Murray等在西班牙圣地亚哥·德·孔波斯特拉之路的旅游研究中指出文化线路的旅游消费、旅游需求是动态扩散的[55],并非集中在特定的目的地节点,叠加现代交通信息技术带来的时空压缩效应,线性旅游目的地的流动性特征更为突出。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 基础要素的流动过程研究。旅游者是旅游目的地要素流动的基础构成,分析旅游者消费行为的时空动态模式,构建线性旅游目的地关联性、流动性、动态性的空间体验模型。② 核心要素的流动过程研究。旅游产品作为目的地发展演化的核心要素,包括正在利用的旅游吸引物、旅游服务、旅游设施以及旅游购物品等要素[104],分析线性旅游目的地旅游产品要素的空间配置与功能布局特征,总结旅游服务、旅游设施以及旅游商品线性整合的空间特征与流动规律。③ 创新要素的流动过程研究。分析服务技能、管理经验、营销策略等技术创新要素的关联互动过程,剖析市场信息、游客信息、政策信息等信息创新要素的一体化发展模式,识别线性旅游目的地创新要素的集散节点及其与旅游创新活动、创新能力的空间耦合。
4.1.4 空间优化过程
线性旅游目的地的空间优化涉及旅游目的地节点、轴线以及网络等多元目的地空间形态优化与生成的关联集成分析[85]。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 空间节点优化过程研究。分析不同层级目的地节点的空间辐射范围与空间拓展方式,根据复杂网络理论构建目的地节点旅游要素空间传输、空间集聚、空间匹配的指标与评价体系,分析目的地节点空间优化的资源策略、区位策略、交通策略与制度策略。② 空间轴线优化过程研究。遴选典型的目的地集聚轴线,基于区域空间结构理论探索目的地轴线联动的经济、交通、资源、技术基础,分析不同规模层级目的地轴线集聚的空间格局特征与空间战略意义。③ 空间网络优化过程研究。分析整体网络节点的联系密度以及网络关系构建的关键因子,总结线性旅游目的地空间网络优化的重心移动过程与关系扩张规律及其与域内城市、城镇节点的整合发展历程。
4.2 线性旅游目的地发展演化的机制研究
4.2.1 社会环境机制
线性旅游目的地作为旅游目的地时空关系交替演化的结果,在时间上依赖于特定主题的关系建构,而主题又往往与区域自然环境、社会文化特征紧密相关[105]。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 历史区位和地理环境机制。区域历史文化资源、自然地理景观的集聚程度与集聚方式是线性旅游目的地形成发展的资源禀赋基础。因此,需要归纳总结区域历史地理环境特征,探索历史区位要素、自然环境要素对线性旅游目的地空间组织结构的影响机制。② 市场环境机制。市场需求的阶段性转型不断推动旅游产品的组织联动与空间协同,这就需要我们剖析当代旅游者旅游体验需求的特征趋势,探究线性旅游目的地发展演化的需求牵引机制、资本整合机制、要素配置机制与资源流动机制。③ 社会环境机制。基于高质量发展的时代主题,总结线性旅游目的地的价值体系与意义功能,分析线性旅游目的地在区域政治经济发展、文化传承、社会公平以及生态文明建设中的正向促进机制与价值输出机制。
4.2.2 集聚扩散机制
Flognfeldt与Asero等指出线性旅游目的地整体的功能效应取决于目的地节点或集群之间集聚扩散的作用水平及关系程度[106-107]。因此,集聚扩散机制是线性旅游目的地关系生产与要素流动的重要机制形式。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 集聚机制。分析线性旅游目的地旅游要素节点集聚、轴线集聚与多中心网络集聚的空间关系特征,探究线性旅游目的地旅游要素、旅游产业空间集聚的主题引领机制、关系建构机制与设施联通机制。② 扩散机制。研究线性旅游目的地旅游要素流动扩散的全新组合、全新路径与全新比较优势,总结线性旅游目的地要素扩散的关系结构机制、地理邻近机制、产业辐射机制与政策网络机制,剖析旅游要素扩散过程中旅游者、旅游地居民、旅游企业以及相关政府部门等利益主体的参与互动机制。③ 协同集聚机制。基于线性旅游目的地的组织关联特征分析不同要素、不同主体的空间诉求,梳理线性旅游目的地旅游要素协同集聚的产业关联机制、辐射带动机制、知识溢出机制与制度匹配机制。
4.2.3 尺度关联机制
旅游目的地通常会在特定主题的基础之上展开合作以提升市场份额[49],因此,线性旅游目的地通常会突破固定、独立的层次,以线路的形式或目的地网络的形式延伸到广阔的地理区域[11]。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 尺度上推机制。结合线性旅游目的地在不同空间尺度上的发展环境特征,厘清各类环境因子间的综合作用与互动机制,识别空间组织关系向上流动的主控因子与抵抗力量,探索跨尺度合作组织、基础设施网络的建设机制与促进机制。② 尺度下推机制。分析不同尺度线性旅游目的地发展演化的尺度环境与尺度冲突,探究线性旅游目的地强化地方特色、品牌形象与旅游吸引力的逻辑控制机制与空间限定机制,分析上级尺度线性旅游目的地向下级尺度旅游目的地尺度转换的边界条件和环境诉求。③ 多尺度关联机制。分析不同尺度上线性旅游目的地动态演化与时空耦合的互馈机制,总结目的地关联关系尺度推进与空间拓展的突破路径和关键因子,梳理不同尺度线性旅游目的地演化发展的过程耦合机制与尺度协调机制。
4.2.4 协同创新机制
线性旅游目的地是“人—信息—交通—地”耦合的体验系统[78],需要制度化力量激活、强化旅游业及相关产业之间的协同关系,以促进目的地关系网络的价值创造。相关研究可以从以下方面展开:① 政策协同创新机制。基于线性旅游目的地的制度政策网络,分析政策促进目的地关联关系的作用机制与阶段演进的时空特性,识别线性旅游目的地一体化建设发展的政策需求与制度需要。② 交通协同创新机制。分析线性旅游目的地产品空间网络与区域综合交通网络的空间耦合与空间差异,探索跨区域旅游交通的协同联动对目的地组织结构、空间结构的整合机制、联通机制与集体行动机制。③ 信息协同创新机制。分析市场信息、游客信息、技术信息以及政策信息的传播特征与创新传播路径,探究线性旅游目的地综合信息数据库及其传播媒介空间建设发展的行动创新机制与监管创新机制,考察线性旅游目的地空间关联、资源共享与产业融合发展中的信息交换机制。
4.3 线性旅游目的地发展演化的不同尺度空间模式研究
后结构主义推动空间研究视角由存在与结构性研究转向生成与关系性研究[108],强调空间在地方、区域、全球不同尺度之间的变动、演绎与联结,这需要我们在关注线性旅游目的地在同一尺度上关系建构、关系流动与空间生成的同时,也要关注不同尺度上线性旅游目的地组织作用关系及其外在环境的尺度特征差异。
4.3.1 国际尺度的典型模式研究
在国际尺度,线性旅游目的地的发展演化涉及多层主体力量与多元要素互动[109],相关研究应重点关注国际形势、国家文化、政治差异、地缘政治环境等国际性要素对目的地关系拓展的促进与制约,基于对全球—地方权力网络关系的认知,以国际—国家—区域—地方的多尺度关系思维进行目的地空间组织模型的构建与实践。在今后的研究中,可以以丝绸之路旅游带、万里茶道为典型区域,剖析国际尺度线性旅游目的地的主题建构过程以及自然、社会、经济关系的生产特征,探究跨国企业、跨国投资、跨国服务设施、高端国际人才等国际旅游要素的流动过程与集聚扩散特征,考察目的地建设发展过程中国际主体、国家主体以及地方主体的多元合作机制、政策协调机制与应急管理机制。
4.3.2 国家尺度的典型模式研究
国家尺度是线性旅游目的地融入国家战略、贯彻国家战略政策的先行尺度,是线性旅游目的地发挥历史记忆与国家认同、文化传承创新、生态文明建设等意义功能的主要阵地[110-111]。国家层面统一的政策制度、产品规范、市场引导以及基础设施网络的综合建设,为线性旅游目的地的发展提供了强有力的政策保障与科学指引。在今后的研究中,可以重点关注长城、大运河、长征线路、黄河、长江、珠江旅游带、沿海黄金旅游带以及G318公路等目的地,分析国家尺度线性旅游目的地发展的核心要素特征及其空间组织的关联机制,总结国家尺度线性旅游目的地的建设发展对新时代文化繁荣发展重大工程的促进机制,研究国家尺度线性旅游目的地经济功能、社会功能、文化功能、生态功能、教育功能等多元功能与多重价值的释放整合模式。
4.3.3 区域尺度的典型模式研究
区域一体化、区域协调发展驱动线性旅游目的地向区域间的空间关联与组织联动,区域尺度是线性旅游目的地发展演化的关键尺度[112]。区域旅游合作通道、资源联合开发以及区域间交通信息网络体系是区域尺度上线性旅游目的地发展演化的核心要素,是目的地关系联动与空间关联的重要基础。在今后的研究中,应聚焦区域尺度线性旅游目的地节点、轴线之间的组合特征与支配关系,识别旅游要素流动扩散的机制障碍与政策堵点,总结线性旅游目的地经营管理体制机制优化创新的突破路径,选取京张体育文化旅游带、巴蜀文化旅游走廊、杭黄自然生态和文化旅游廊道等区域尺度的线性旅游目的地,分析区域尺度线性旅游目的地产业融合、业态创新以及资源整合的空间组织中心,分析区域间目的地关联关系的文化整合机制与文化认同机制。
4.3.4 地方尺度的典型模式研究
地方尺度是线性旅游目的地发展演化研究的基础尺度,是旅游目的地关联发展的创新实验区[113]。在地方尺度上,线性旅游目的地的形成发展与地方经济发展水平、政策制度环境、基础设施条件、社会文化基础等要素密切相关,自下而上的自主发展特征明显。在今后的研究中,可以以皖南川藏线、海南环岛风景道、金寨中国红岭公路为例,研究线性旅游目的地在地方尺度上的关联强度、关联密度与关联形态,探索地方主题符号系统与地方品牌形象的塑造机制与强化路径,总结目的地以及各类旅游要素关联关系在地方尺度的生产组织模式,探索地方旅游交通及其关联性设施的发展完善机制、旅游资源综合开发与保护的政策促进机制、交通联动机制与信息共享机制。
5 结论讨论
5.1 结论
本文从后结构主义的理论视角出发,针对旅游目的地“线性”发展的空间现象,提出线性旅游目的地的概念框架与研究体系,主要得出以下结论:
(1)旅游目的地是旅游地理学的核心概念,旅游目的地空间形态、空间规模、空间关系的“线性”发展需要我们立足本学科视角,形成关于线性旅游目的地相对独立、统一的概念界定,完善已有的旅游目的地认知体系,建立完整的“理论指导实践、实践完善理论”的旅游目的地反馈机制。
(2)线性旅游目的地是以特定的自然、文化主题为引领,以旅游基础要素的线性延展为基础,以旅游者、旅游经营者、旅游产品、旅游信息、旅游服务等各类要素主体的流动关系为根本,形成的沿特定方向关联互动的目的地组织共同体与空间连续体,具备关联性、流动性、动态性的空间组织特征,是现代化背景下旅游产品的重要供给形式与空间消费形式。
(3)后结构主义与线性旅游目的地的空间组织研究之间具有良好的理论适用性,线性旅游目的地发生发展的演化过程既包括时间维度上组织结构线性整合的过程演化,也包括空间维度上各类要素主体集聚扩散的空间优化。后结构主义的关系思维与尺度认知为线性旅游目的地关系的建构、关系的流动、空间的生成以及尺度的转换等时空演化研究提供了关联、流动、动态的综合认知框架。
5.2 讨论
旅游目的地空间组织结构的演变往往基于一定的社会背景与实际土壤,研究范式和理论概念的发生过程也表现出一定的历史传承性与时代创新性[16]。从旅游目的地到线性旅游目的地,是不同社会历史条件下对旅游目的地认知思维、认知理论转变的体现。旅游目的地是旅游地理学的核心概念,核心概念是学科发展的基础和根本,针对核心基础概念展开宏观的、哲学层面的探讨对学科发展具有重要意义[114]。基于此,旅游地理学需要立足本学科视角,针对旅游目的地线性发展的空间现象,展开哲学层面的认识论、方法论的探讨,明晰线性旅游目的地的学术内涵与实践价值,以促进学科发展。同时,线性旅游目的地作为关联性的目的地空间体系,是后结构主义的关系思维及关系空间在旅游地理学领域的理论实践。因此,后结构主义理论视角下线性旅游目的地概念框架与研究体系的确立,不仅推动了后结构主义向旅游地理学研究领域的理论拓展,也促进了后结构主义关系思维、关系空间在实体空间地域上的实践检验。
近年来,国土空间规划体系、国家文化公园体系、国家风景道体系等国家战略体系对“线性”自然、文化资源空间价值的发掘与优化日益突出[115],赋予线性旅游目的地新的时代任务与时代价值。同时,从环境资源本底来看,中国兼具广阔的自然地理环境与深厚的历史文化底蕴,山脉、河流、谷地、海岸线形成自然要素的带状延伸,迁移路线、商品交易路线、文明交流路线形成文化要素的线状遗存,为线性旅游目的地的形成发展提供优良的历史区位与地理环境。因此,本文基于新的社会、经济、技术、制度条件,初步构建线性旅游目的地的概念框架与研究体系,以期为国内外旅游目的地理论实践的创新研究提供新视角、新思路与新借鉴。
需要指出的是,后结构主义视域下线性旅游目的地的建设发展仍存在一定的挑战。首先,在方法实践层面,空间的开放性与旅游目的地管理的有界性往往存在一定的矛盾,而线性旅游目的地的关系建构与流动是一个复杂的多层次过程,对旅游基础设施、旅游信息、旅游服务、旅游政策之间的连通性、协调性要求较高。未来应将更多的社会、经济、文化、制度、信息数据纳入线性旅游目的地的实践研究当中,基于大数据驱动的方法论,建立线性旅游目的地的信息收集与测量系统,丰富线性旅游目的地的科学研究案例,提炼不同类型、不同阶段线性旅游目的地创新转型的关键举措,厘清线性旅游目的地建设发展的实践条件与范围。其次,在理论认识层面,线性旅游目的地关联性、流动性、动态性的基本特征是“象思维”这一中国传统哲学思维在旅游目的地研究中的延伸与投射,“象思维”强调事物在同一层次或不同层次的流动与转化[116],侧重“生”,现有的旅游目的地研究受西方“体思维”的影响显著,注重“分”,侧重空间结构、功能结构的静态解剖与分割,未来线性旅游目的地的空间组织关系研究需要整合国内外的思维认知模式,加强“生”与“分”的辩证分析,针对线性旅游目的地的动态关系与静态秩序形成整体性的思考与认识。
参考文献
Research framework of tourism resources from a new perspective of tourism resources
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220301
[本文引用: 1]

Tourism resources, the basic elements of tourism activities, determine the benefits of the development and utilization of tourism resources. The relationship between tourism resources and major national strategies has become increasingly close. Establishing a new viewpoint of tourism resources is a re-understanding and re-practice of regional development practices, which can put forward a new topic for tourism resources research. We sorted out and summarized the development context of tourism resources research under the traditional view of tourism resources. The results showed that: (1) The research contents of tourism resources are constantly enriched, and the research directions are becoming more and more diversified. Basic research actively makes great contributions to serve the national major strategies, as well as regional economic and social development. To a certain extent, the positive interaction between "theory guides practice" and "practice enriches theory" has been realized. (2) The new concept of tourism resources refers to the dynamic process of people integrating, configuring, reorganizing and optimizing tourism resources from different sources, levels, structures, and contents under the background of scientific and technological progress, changes in value concepts, increased tourism demand, and per capita income. It is regarded as an active response of people's cognition to the changes of tourism resource characteristics. The new outlook on tourism resources is a fundamental breakthrough to the traditional view of tourism resources, presenting new viewpoints on resource value, new resource utilization, new resource development, new resource benefits and new resource space. (3) This paper constructs a "five-dimensional integration" tourism resources research system from a new perspective of tourism resources, especially the value conversion of tourism resources, the sustainable use of tourism resources, the integrated development of tourism resources, the regional benefits of tourism resources, and the spatial reconstruction of tourism resources. It aims to strengthen the cross-regional aggregation, competition and integration of tourism resources, and to reveal the interaction mechanism of the development and utilization of cross-regional tourism resources. (4) There are some new problems and topics in the development and utilization of tourism resources in the new perspective of tourism resources. The integration of multiple disciplines and the introduction of new methods is an inevitable trend for comprehensive, dynamic, regional and systematic research on the development and utilization of tourism resources.
新旅游资源观视角下旅游资源研究框架
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20220301
[本文引用: 1]

旅游资源是旅游活动的基本要素,决定着旅游资源开发利用的综合效益。旅游资源与国家重大战略的关系日益密切,树立新旅游资源观是对区域发展实践的再认识和再实践,能够为旅游资源研究提出新的课题。梳理与总结传统旅游资源观视角下旅游资源研究成果的发展脉络,研究发现:(1)旅游资源研究内容不断丰富,研究方向日益多元,在开展基础研究的同时,积极为服务国家重大战略和区域经济社会发展做出重要贡献,一定程度上实现了“理论指导实践”与“实践完善理论”的良性互动局面。(2)新旅游资源观是指在科学技术进步、价值观念变革、旅游需求提升、人均收入提高等背景下,人们对不同来源、不同结构、不同层次的旅游资源进行整合、配置、重组和优化的动态过程,表现为人们的思维认知对旅游资源性状改变的一种能动响应。新旅游资源观是对传统旅游资源观的根本突破,呈现出新旅游资源价值观、新旅游资源利用观、新旅游资源发展观、新旅游资源效益观和新旅游资源空间观等特征。(3)从旅游资源价值转化、旅游资源可持续利用、旅游资源融合发展、旅游资源区域效益、旅游资源空间重构等方面构建新旅游资源观视角下的“五维一体”的旅游资源研究内容体系,强化旅游资源的跨区域聚合、竞合与融合,揭示跨区域旅游资源开发利用的相互作用机理。(4)面对新旅游资源观视角下旅游资源开发利用过程中出现的新问题和新课题,多学科交叉融合与新方法引进是开展旅游资源开发利用综合性、动态性、区域性和系统性研究的必然趋势。
The intercity space of flow influenced by high-speed rail: A case study for the rail transit passenger behavior between Beijing and Tianjin
DOI:10.11821/xb201302002
[本文引用: 1]

In the perspective of space of flows, the passenger flow of high-speed rail has become an important representation of functional linkage between the city-regions. Based on the interviews and questionnaires from the passengers of high-speed rail of Beijing and Tianjin, this paper analyzes the intercity space of flows and the spatial integration indicated by the individual micro behavior choice. The findings include: (1) Both of the metropolitan areas of Beijing and Tianjin are the dense areas of intercity passenger flow while suburban counties and districts are the sparse areas, which indicates the spatial polarization of HSR in the aspect of passengers' characteristics; The central city of Beijing-Tianjin is the dominant spatial association, while Beijing-Tanggu, Beijing-Wuqing and Tianjin-Wuqing corridors are the secondary spatial association axes, which presents a hub-and-spoke pattern. (2) Leisure activities, such as tourism, shopping, enhance the cross-city flows. Although intercity high-speed rail reduces the temporal and spatial distance to a certain extent, the effects on changing place of housing or work to another city are not obvious. (3) The frequency of cross-city activities is not very high, commuters across cities generally take 7 days as a cycle; Currently, passenger flows of intercity by HSR are mainly business travel and leisure tourism, which reflects HSR as the material foundation for the spaces of flows; the respondents who take the HSR are mostly male, business people with high education and prospective occupation, and the business travelers who have a higher cross-city frequency are more sensitive to travel time, which demonstrates the intercity space of flow has represented some of the elite space characteristics. (4) There is spatial asymmetry in the cross-city space of flow between Beijing and Tianjin, which could be found from the uneven distribution of O-D passenger flows, the differences on the proportion of the business travel flows and the unbalanced function linkage directions.
京津城际高速铁路影响下的跨城流动空间特征
Mapping the terrain of time-space compression: Power networks in everyday life
DOI:10.1068/d150611
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper I seek a more comprehensive mapping of the experience of time—space in late modernity. I develop Massey's critique of the work of Harvey and Jameson in their reading of time space compression as a socially uniform experience of disorientation. Building on Massey's notion of ‘power geometry’ I integrate discussions of time—space with an application of different understandings of power (from traditional political philosophy, Marxism, and poststructuralism) and their manifestations—in latent-power conditions, socioeconomic networks, actor networks, ‘local’ interpersonal relations, and the network spaces of subjectivity. Rather than being posited as irreconcilable conceptions, these versions of power and their articulations can be seen as initial coordinates in the mapping of the complexities of the experiences of time and space in late modernity.
Spatial coupling between rapid traffic superiority degree and tourist flow intensity in tourist destinations
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181347
[本文引用: 1]

Rapid transportation is a convenient channel for connecting space elements in the new era, as well as for increasing the vitality of regional development. Tourist flow is a phenomenon of collective spatial movement of tourists, which relies on traffic due to the similarity of tourist demand. Due to the non-transferability of tourism products and the rapid traffic dependence of tourism flow space displacement, rapid traffic has a major impact on the transfer flow, scale and spatial distribution of tourism flows. Therefore, revealing the spatial coupling relationship between rapid traffic and tourist flow has become an important issue. In this study, taking a typical tourist destination, Yunnan Province, as a research case, and based on multi-data such as Gaode traffic big data and statistical data, according to the thought process of “road network and site density + traffic size + traffic function + location superiority + transfer convenience”, a rapid traffic superiority model is constructed. In addition, based on the diachronic dimension of “scale → consumption → benefit →effect” of the tourist flow, a tourist flow intensity model is built. The weighted TOPSIS method is then used to measure the two evaluation values, and the coupling four-quadrant model is used to divide the coupling types. The results showed the following: (1) There is a significant spatial difference between the rapid traffic and tourist flow coupling. Kunming, Honghe and Lijiang showed strong coupling and coordination. The coupling type is “high tourist flow - high rapid traffic superiority”, while at the fringe region with a low level of tourism, away from the transportation hub and main traffic arteries, the coupling effect of tourist flow and rapid traffic is characterized by “low tourist flow - low rapid traffic superiority”. (2) There is a positive correlation between rapid traffic superiority and tourist flow intensity, and the goodness of fit between different rapid traffic modes and tourist flow intensities showed the characteristics of “air transport > highway > high speed railway”. (3) The coupling level of rapid traffic superiority and tourist flow intensity in Yunnan Province is generally low, and the dominant mode of rapid traffic development is coordinated and complementary mode. In addition, due to the “time-space convergence” effect and “organization-space synergy” effect of rapid traffic, there is a positive correlation between the rapid traffic combination type diversification and the tourist flow intensity. The contribution effect of different rapid traffic development modes to the intensity of tourist flow showed the characteristics of “multiple symbiosis mode > coordination complementary mode > single class isolation mode > low speed traffic maintenance mode”. From a spatial perspective, this paper explores the coupling and coordination situation between rapid traffic dominance and tourism flow intensity, and the results can be used to identify the bottleneck of regional tourism development. It is important for the promotion of regional rapid transit facilities construction and improvement of tourism performance level to achieve synergy between rapid traffic and tourism flow intensity. At the same time, the results also provide references for other similar areas.
旅游地快速交通优势度与旅游流强度的空间耦合分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020181347
[本文引用: 1]

以典型旅游地—云南省为研究案例,以高德交通大数据、统计数据等多源数据为基础,依据“路网及站点密度+通行规模+通行功能+区位优势度+换乘便捷度”的思路,构建快速交通优势度模型;基于旅游流“规模→消费→效益→效应”的历时性维度构建旅游流强度模型;采用加权TOPSIS法对二者评价值进行测算,并运用耦合四象限模型对两者耦合类型进行划分。结果发现:① 快速交通与旅游流耦合存在显著空间差异性。昆明、红河和丽江呈现良性耦合协调,耦合类型表现为“高旅游流-高快速交通优势”,而旅游化水平低、远离交通枢纽和主要交通干线的边缘地区,旅游流与快速交通耦合效应则表现为“低旅游流-低快速交通优势”。② 快速交通优势度与旅游流强度呈正相关关系,不同快速交通方式与旅游流强度的拟合优度表现为“航空运输>高速公路>高速铁路”的特征。③ 云南省快速交通优势度与旅游流强度耦合水平总体偏低,快速交通发展的主导模式为协调互补模式,且缘于快速交通的“时间-空间收敛”效应和“组织-空间协同”效应,快速交通组合类型多样化与旅游流强度存在正相关关系。不同快速交通发展模式对旅游流强度的贡献效应表现出“多元共生模式>协调互补模式>单类孤立模式>低速交通维持模式”的特征。
Immobility under the new flow paradigm: Research progress and future prospect
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210908
[本文引用: 1]

The interruption and immobility under the Covid-19 are changing the narrative logic of the new mobility paradigm. Mobility as a basic principle of modern society has been challenged and questioned, and a correct understanding of immobility is related to the future shift and change of the new mobility paradigm. To this end, this study summarizes the static research under the new mobility paradigm, considers the dialectical relationship between liquidity and static, and provides a new path for the transformation of the new mobility paradigm. We found that the study of immobility under the new mobility paradigm has four important turns. Firstly, there has been a shift from criticism of immobility to the understanding of the relationship of immobility. Geographers formed the thought of dialectical relationship (e.g., infrastructure and power geometries) between mobility and immobility based on criticizing the theory of sedentarism metaphysics. Secondly, previous research has opened space for an ontology and epistemology of immobility in and of itself. Traditional mobility research has viewed immobility as passive, othered, and utilized objects, while recent research has endowed immobility with activity, selfness, and subjectivity. Thirdly, much research has clearly shifted in favor of the microscopic interpretation (e.g., daily life) not just macroscopic view (e.g., locals and cosmopolitans). Fourthly, methodology has transformed from the duality of methods to the balance of methods. At the same time, there are four important issues in the study of immobility: (1) the antecedences of immobile regular population including factors that retain, repel, and adjust internal constraints; (2) the significant impact of anchoring space on mobility, such as supporting role; (3) the embodied experiences of non-representational silent body, such as the practices and emotions; (4) the node subject across time and space which has proved the immobile mobility. Overall, the research of immobility under the new flow paradigm has become a topic full of postmodernism and posthumanism color. Finally, we propose relevant prospects for the future research of immobility: to focus on the population heterogeneity of immobility, to pay attention to diversified immobility spaces, to understand post-human technology and immobility bodies, and to explore the mobility of sustainable development. This research has crucial value and significance for the new flow paradigm to enter a new historical development stage.
新流动范式下非流动性的研究进展与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210908
[本文引用: 1]

新冠疫情下的中断与非流动性改变新流动性范式的叙事逻辑,作为现代社会基本原则的流动性受到挑战与质疑,而正确认识非流动性事关新流动范式的未来转向与变革。为此,本研究对新流动范式下的非流动性研究进行综述,思考流动性与非流动性的辩证关系,为新流动范式的转型提供新的路径。本研究发现,新流动范式下非流动性的研究领域具有四个重要转向:从批判解构到辩证关系的认识;从本体不可能到有可能的思考;从宏观视野到微观解释的叙述;从方法二元到方法平衡的转变。同时,非流动性研究中存在四大重要议题:地方性非流动人口;支撑性的停泊空间;非表征的静默身体;跨时空的节点主体。最后,本研究为非流动性的未来研究提出相关展望:关注非流动性的人口异质性;关注多样化的非流动性空间;认识后人类技术与非流动性身体;探讨可持续发展的流动性。
Sociology Beyond Societies: Mobilities for the Twenty-first Century
Mobility in geographical research: Time, space and society
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201610001
[本文引用: 1]

With the profound impact of globalization on society, the connotation and denotation of mobility have become three-dimensional and multi-faceted today. Various types of mobilities are representing and reshaping our social structure and values. How to analyze and understand mobility has important implications on our cognition of social culture, local structure and contextual significance, as well as all kinds of socio-cultural phenomena which are currently measured by multiple spatial scales. On the one hand, mobility is an unprecedented enhancement of movement. This process not only occurs in the global and regional scales, but also in the scale of daily life and commuting within the urban areas. On the other hand, mobility overturns our understanding of the basic conceptions in humanities and social sciences in a revolutionary way. For example we need to rethink these crucial issues like space and identity with a perspective of mobility. Under the new paradigm—taking time and space as a basic judgement of mobility, the multi-layered and three-dimensional sociocultural meaning of mobility is thus to be discussed in terms of regions, cities, immigration, tourism, identity, policy, regulation and so on. This practice offers a field for interdisciplinary dialogue and communication which carries the expectation of providing references and prospects for lifting the discussion on movement to mobility.
跨学科聚焦的新领域: 流动的时间、空间与社会
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201610001
[本文引用: 1]

在全球化对社会产生深刻影响的当下,流动获得了内涵和外延的立体化与多面性,各种类型的流动正表征并重塑地方、社会结构和价值观念。如何认识流动、分析流动对理解当前世界多重空间尺度的各类社会文化现象、理解空间及附加其上的意义具有重要影响。一方面,流动性是流动实践空前增强的过程,这个过程既发生在全球与区域的尺度上,也发生在城市内部日常生活与通勤的尺度上。另一方面,流动性对于人文社会科学中基本概念的阐释具有革命性的作用,例如地方,认同这些话题都需要从流动性的视角进行重新思考。以时间和空间作为刻画流动性的基础尺标,在新流动性范式下,从地方、城市、移民、旅游、身份认同、政策与管制等方面探讨流动性多层次的社会文化意义,期于在流动性这一场域进行跨学科的对话,并促使国内学界对流动现象的关注上升为对流动性理论本身的解读。
Marketing the competitive destination of the future
DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(99)00095-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research on tourism resources in the new era: Protection, utilization and innovative development: Comments of young tourism geographers
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200419
[本文引用: 1]

Nowadays, China has fully come into the massive tourism era. Tourism continuously occupies one most quickly growing industry in the macro-economy and becomes a strategic pillar industry in regional economic development. Since China is rich in tourism resources, which are the foundation of conventional tourism development, it is crucial to deal with the relationship between property protection and utilization of tourism resources, meanwhile, achieving innovative development. In this issue, 16 young tourism geographers discuss tourism resources protection and utilization in the new era. They clarify a set of key points about tourism resources research, including new knowledge of value, new ways to protect and use, and new discussions for special resources. The main points state as follows. (1) Massive tourism mode changing bring the industry innovation, as well as resources' meaning expansion. In the new era, by embracing a perspective of construction, generalization, and a combination of tourism resources, we need to rethink how to define, classify and evaluate these resources. In the future, resources will still be the basis of tourism development, which should capture more reasonable recognition of their new characteristics and values. (2) Under the constraints of ecological reserves, controls in exploitation of traditional resources will be more severe. From the supply-side, considering the transformation from resources to products, we should take more measures such as complying with the market rules, meeting tourists' new needs, excavating cultural senses, creating new developing paths amid new technologies support, and forming popular products. These measures will be beneficial to stimulate the marketing values, upgrade the regional industry, and realize to coordinate resources, capital, and assets in a sustainable way. (3) From the demand-side, we should be aware of the common changes of tourists, lead to new behavioral norms in civilized tourism, and guide the tourists to protect resources spontaneously, which will rewardingly balance environmental protection and industrial development. (4) Abundant resources require diverse approaches to protect and rationally use. In light of rural tourism resources, we should assess their new value, follow the strategy of rural vitalization, suit measures to local conditions, pay main concerns on tourism agglomerations, consider local communities' interests, and innovatively promote sustainable development. Based primarily on sustainability, agricultural heritages re-use needs to be concerned about novel multi-participation machinery dynamically. For human tourism resources, it is necessary to maintain authenticity with traditional culture integration, and coordinate cultural inheritance and tourism growth. Mentioned with ethnic tourism resources in mountainous region, we suggest paying attention to the uniqueness of regional system, taking account of the contemporary value and human-land relationship, and then adopting appropriate measures. Besides, owing to homestay's role in activating rural stacks, it is recommended to enhance ecological protection, and boost the homestay cluster.
新时代的旅游资源研究: 保护利用与创新发展: 旅游地理青年学者笔谈
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200419
[本文引用: 1]

当前,我国已经全面进入大众旅游时代,旅游业持续领跑宏观经济,并成为带动区域发展的支柱产业。旅游资源是传统旅游业的发展基础,我国是旅游资源大国,处理好旅游资源保护与利用的关系、实现创新发展是旅游资源研究的关键。来自旅游地理研究领域的16位青年学者,以笔谈方式探讨了新时期、新阶段下旅游资源保护与利用的基本思路,从旅游发展的新特征、资源价值的新认知、开发与保护的新方式以及针对专项资源的保护开发的新对策等方面重新定义新时代旅游资源研究的重点,核心观点整理如下:(1)随着旅游业的发展,大众旅游方式变化推动旅游产业革新,旅游资源的内涵也相应不断丰富。新时代旅游资源的重构、泛化和组合的变化需要重新对旅游资源进行识别、划分和评价,未来资源仍是旅游产业发展的基础,需要合理认知旅游资源的新特征和新价值。(2)新时代,传统资源开发的条件趋严,坚守生态底线是发展的基础。从供给端看,资源转化为产品的过程中,要尊重市场规律,面向游客新需求,以深入挖掘文化内涵为重点,借助科技新手段,创新资源开发新模式,推出受游客欢迎的旅游产品,从而激发旅游资源的市场价值属性,推动区域旅游产业升级,实现资源、资本、资产的可持续发展。(3)从需求端看,捕捉客群变化特征,构建社会规范和文明旅游新方式,从多方面引导游客主动保护旅游资源的行为,从而形成推动旅游资源保护和开发协调的新思路。(4)旅游资源的类型丰富,决定了旅游资源保护与开发方式的多样化:针对乡村旅游资源,要在资源评估的基础上,重新认识其新价值,在乡村振兴战略的引领下,因地制宜,以产业集聚为突破,重视乡村社区利益,推动乡村旅游资源的创新利用和可持续发展;针对农业文化遗产资源,在可持续发展的基础上,活态利用,构建多方参与的新机制;针对人文旅游资源,需要挖掘人文旅游资源本真性,融入传统文化,促进文化传承与旅游产业的互动发展;针对山地民族旅游资源,在时代价值重新认知的基础上要重视其地域系统的独特性,基于人地关系整体化保护与开发;针对民宿旅游,重视其转化农村闲置资源的重要功能,强化生态保护,构建民宿旅游集聚区。
The application and prospect of assemblage theory in human geography research
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202210014
[本文引用: 1]

Against the background of the French "May Wave" and the postmodernist, the theory of assemblage as a research perspective starts to gain momentum. This paper proposes a philosophical view of "becoming" based on rhizome thinking, which critically exposes ignorance of the spatial topology in the current research based on network structure and opens up a new field of the knowledge for human geography. On the one hand, the assemblage theory forms a "heterogeneous generated space" on the basis of spatial theories such as "spatial production theory", "heterotopia" and "third space", emphasizing the interactions of the heterogeneous elements while also paying attention to the logic of the continuous generation and spatio-temporal change; on the other hand, the assemblage theory reconstructs the concept of relations, emphasizes the "object agency" and "relations of exteriority", which generates the "post-relational ontology" and acknowledges that all things are assembled through relations. With the application of the assemblage theory in the field of human geography, the existing empirical research mainly focuses on political assemblage and mobility, urban assemblage and critical urbanism, daily life assemblage and non-human agency, and compared with other related theories such as Complexity Theory and Actor Network Theory. In order to expound the connotation of the assemblage theory and enhance the applicability of the theory, the article analyzes the assemblage logic through border assemblage. In addition, based on the new research framework and theoretical paradigm constructed by the assemblage theory for human geography, as well as the coupling of the theoretical characteristics and the transitional period of Chinese society, it is expected that Chinese geographers can critically engage into the assemblage theory to explain the Chinese situation, as well as promoting the diversities of the Chinese geography theory and philosophical methodology.
拼装理论在人文地理学研究中的应用与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202210014
[本文引用: 1]

在法国“五月风潮”和后现代主义思潮的影响下,拼装理论应运而生。该理论提出了以根茎思维为基础的动态生成哲学观,批判地揭露了现有研究以网络结构为主,忽视空间拓扑的局限,为人文地理学开辟了新的知识空间。一方面,拼装理论在“空间生产理论”“异托邦”和“第三空间”等空间理论的基础上形成“异质生成空间”,强调属性不同的元素互动的同时,更关注时空不断生成、变化的逻辑;另一方面,拼装理论重构了关系,强调“客体的能动性”和“外部联系”,生成“后关系本体论”,承认所有事物都是通过关系进行拼装的。随着拼装理论在人文地理领域的运用,现有的实证研究主要聚焦于政治拼装与流动性、城市拼装与批判城市化、日常生活拼装与非人的能动性,以及与行动者网络理论、复杂性理论的比较研究。为了阐述拼装理论的内涵,增强理论的应用性,本文以案例的形式详细解析了边界拼装蕴含的拼装逻辑。此外,基于拼装理论为人文地理学注入的过程逻辑与克服人类中心主义的理念,以及该理论特征与中国社会转型期的耦合性,期望国内地理学者能批判地运用拼装理论解释中国情境,以便推动中国人文地理学理论与哲学方法论的多元发展。
The reasons, connotations and significance of the new paradigm of western social and cultural geography
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190097
[本文引用: 3]

In recent years, the new paradigm of Western social and cultural geography has become a research hotspot in the domestic geographic circles, but some scholars have different opinions and argue that the new paradigm lacks the professional characteristics of geography and deviates from the traditional research paradigm. On the basis of combing the thoughts of Western humanistic geography school and the evolution of its paradigm, this paper analyses the background, basic issues, connotation and significance of the new paradigm of the new paradigm of Western social and cultural geography. The results show that the new paradigm of Western social and cultural geography advocates subjective ideas in geography, the turn of social and cultural theory, in addition, it also includes issues of "interrelationships" and "ethics, morality and ontogenesis". It is not only a reflection on positivism and space science characterized by the metrological revolution, as well as the "cultural superorganism" of the Berkeley School, but also a new interpretation paradigm of complex social space and cultural cognition caused by the growing globalization and global localization that have become increasingly prominent since the Second World War. In terms of research perspectives and objects, the new paradigm incorporates "human" into the study of geography and establishes the position of "human" in geography. The new paradigm predicts the possibility of social space as well as the significance and value of social culture through the filter of "theoretical turn". It guides people's attention to various spaces, especially spatial relations through the filter of "interrelationships", and strengthens the moral practice of social cultural geography and the promotion of human nature, reconstructs the harmonious coexistence of human and self, human and society and human and the natural environment through the filter of "ethics, morality and ontogenesis". The new paradigm uses a unique way to explain the geographic environment and the social, economic and cultural causes of the spatial process and interaction of human activities, which is a major change in the evolution of human cognition of natural and social environment practice and represents a new philosophy and thinking of geography. One of the reasons why there are different opinions on the new paradigm in Chinese academic circles is that researchers lack in-depth dialogue on the philosophical cognition of the old and new human geography paradigms, and the other reason is that the academic circles' theoretical interpretation of the new paradigm is insufficient. In the future, the Chinese school of social and cultural geography needs to actively embrace and absorb the reasonable contents of the western frontier theories, and construct a new discipline paradigm to actively respond to major issues reflecting China and the world on the basis of careful reference to the Western theories.
西方社会文化地理学新范式的缘由、内涵及意义
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190097
[本文引用: 3]

近年来,西方社会文化地理学新范式在中国地理学界受到“热捧”,但也有学者对此存有分歧、质疑、困惑和焦虑,认为新范式“缺少地理味”“跑偏了”。在梳理西方人文地理学派思想及其范式演变的基础上,对新范式的出场背景、基本议题和内涵及意义进行了剖析。研究认为:① 西方社会文化地理学新范式倡导的“人之主观意念”“理论转向”“空间间性关联”“伦理道德及本体生成”,既是对以计量革命为特征的实证主义和空间科学,以及伯克利学派“文化超有机体”的反思,也是对第二次世界大战以来日益凸显的增长全球化和全球本土化,引致的复杂社会空间和文化认知的新阐释。② 在研究视角和对象上,新范式倡导“人之主观意念”,并确立“人”在地理学中的位置和对“地”的人文主义说明;通过社会文化等“理论转向”滤镜,预见社会空间的可能性,以及社会文化的意义和价值;通过“空间间性关联”滤镜,引导人们对多种空间,尤其是空间关系的关注;通过“伦理道德及本体生成”滤镜,强化社会文化地理的道德实践和人性提升,重构人与自我、人与社会、人与自然环境的和谐共生;③ 新范式用一种独特的方式,阐释地理环境和人类活动空间进程和交织的社会经济及文化发生动因,是人类对社会文化和自然环境实践认知演变中的一次重大变革,代表一种新的地理学哲学观和思维观。④ 中国学术界对新范式之所以存在不同声音,原因之一是研究者对新旧人文地理学范式的哲学认知缺乏深度对话,另一原因是学术界针对新范式的理论阐释不足。未来社会文化地理学的中国学派,需要主动拥抱并吸收西方前沿理论的合理内容,在此基础上参与建构新的学科范式,积极回应反映时代中国和世界的重大问题。
Post-structuralist Geography: A Guide to Relational Space
Research progress of relational geography under the background of post-structuralism
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908014
[本文引用: 2]

The relational geography is conceived with the development of post-structuralism and "relational turn". From the perspective of relational geography, the world is understood as a topological structure of flowing while things are not considered as products of eidos ego but products of the relations. Relational thinking is counter-essentialized, it stresses on the dynamic, inter-dependent interactions between things. Through literature review, we find out the development relational geography is strong influenced by the social network and non-representational theory. The appearance of relational geography reconstructs the connotations of space, place, scale and subjectivity. We put forward the concept of relational space, place relations, multi-scale or the end of scale and the geographical inter-subjectivity. We construct the networking, relational and the flow of topological geography. The current empirical studies of the relational geography focus on the spatial diffusion and expansion, subject development, socio-cultural, bodily, tourist, health issues. Besides, we hope to offer new perspectives for Chinese human geographers based on the concepts of "human", "more-than-human", "things" and "re-materialization".
后结构主义背景下关系地理学的研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201908014
[本文引用: 2]

随着后结构主义思潮和“关系转向”的兴起,关系地理学(relational geography)应运而生。关系地理学把世界理解为流动的拓扑结构以及相互关联的产物,主张关系思维,强调事物在发展过程中相互影响与依存的动态关系。通过对关系地理学相关著作和期刊论文的分析发现,关系地理学的产生受到社会网络分析理论与非表征理论的深刻影响,其重构了空间、地方、尺度与主体性的内涵,提出关系空间、地方关系、多尺度或尺度终结,以及主体间性的地理学概念,建构了新的关于网络、关系和流的拓扑地理。关系地理学现有的实证研究主要聚焦于空间扩散与空间发展、主体发展与社会文化问题、身体与健康旅游/地理等内容。此外,基于“人”与“超越人类”,“物”与“重返物质”4个方面的内容提出关系地理学可能的研究展望,并对“关系”的内涵与外延进行了延伸讨论,以期为中国人文地理学研究提供新的学术视角。
Poststructuralism and Educational Research
Educational research: From structuralism to poststructuralism
教育研究: 从结构主义到后结构主义
The theory of contextual identity: A solution to the problem of scientific representation
语境同一论: 科学表征问题的一种解答
Social Structure: From "form" to "deconstruction"
社会结构: 由“形构”到“解构”: 结构功能主义、结构主义和后结构主义理论之走向
The basics and problems of western constructivist sociology
西方建构主义社会学的基本脉络与问题
The socio-spatial dialectic
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1980.tb01308.x URL [本文引用: 1]
The concept of geography as a science of space, from Kant and Humboldt to Hettner
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8306.1958.tb01562.x URL [本文引用: 1]
Post-structuralist discourses and social theories: Michel Foucault and Henri Lefebvre
后结构主义语境下的社会理论: 米歇尔·福柯与亨利·列斐伏尔
Power-geometrics and the Politics of Space-time
Landscape as a provocation-reflections on moving mountains
DOI:10.1177/1359183506062991
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This article opens with a story of the mobility and varied temporalities of a particular landscape and uses this to reflect on a range of issues that revolve around the different kinds of ‘grounding’ that are appealed to in sociocultural, political and academic life. It reflects upon the relations between human and natural sciences, the nature of appeals between them, and the important, but often questionable, place within this of particular political positions. It goes on to query the role of ‘Nature’ as a grounding to place and landscape and stresses the potentially differential effectivities of contrasting temporalities – between, for example, the temporalities of the taskspace and the temporalities of tectonics. Nonetheless, the argument continues, there are indeed provocations from the moving rocks to the nature of scientific discourse and to debates within political philosophy. It concludes with a conceptualization of both landscape and place as events.
Post-structuralist geography: A guide to relational space by Jonathan Murdoch
DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8306.2007.00587.x URL [本文引用: 2]
Grassrooting the space of flows
DOI:10.2747/0272-3638.20.4.294 URL [本文引用: 1]
The translocal practices of intangible cultural heritage in the perspective of geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202015
[本文引用: 1]

Intangible cultural heritage (ICH) encompasses not only local traditional practice derived from the past, but also future-oriented modern cultural political and economic processes generated due to globalization. Therefore, this paper uses translocal theory as an entry point to move beyond the paradigm of localities in analyzing the socio-spatial processes of intangible cultural heritage, with a specific focus on the processes of formation, operation, and identity. Accordingly, this paper reconceptualizes the practice of ICH. Different from the prevailing rigid, intrinsically stable, and human-centered approach, this paper adopts the idea of translocal assemblage to consider ICH practices as rhizomatic networks. The network binds heterogeneous elements together by power mediation to form temporarily stabilized systems. The translocal assemblage of ICH practices firstly connects human and non-human components as well as tangible and intangible components in different localities. Second, due to the openness of the deep structure, a translocal assemblage is a complex, multifarious, non-linear, and unstable whole with exteriority. Lastly, the structural linkages woven by power relations improve the current flat understanding of the world and emphasize the need to distinguish the intensity and criticality of different connections. Case studies of Heqing silver-forging technology and Mosuo textile technology use the three aspects above to identify when and where heterogeneous elements are linked and influence local development. This paper further argues that for better safeguarding of ICH as well as promotion of local development by heritage practices, attention should be given to elements and processes beyond the local, including their interrelation mechanisms with the local place. In valuing the potential of intangible cultural heritage to support development strategies such as rural revitalization, the article calls for consideration of the impact of trans-localism on heritage authenticity and cultural values together with the enhanced linkages between intangible cultural heritage and local identities and livelihoods in the light of global production and consumption of heritages.
地理学视角下非物质文化遗产的跨地方实践
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202015
[本文引用: 1]

非物质文化遗产不仅是来源于过去的特定区域的传统实践,更是生成于全球化体系中面向未来的现代文化政治和文化经济过程。因此,本文尝试以跨地方性理论为切入点,架构非遗的形成、运作和认同的社会—空间过程,在此基础上使用跨地方聚合的思想重新概念化非遗实践,将其解读为多元主体权力关系中介下,由跨地方异质性要素聚合而成的不稳定的开放系统,以区别于固有对非遗实践“稳定”“以人为中心”和“边界化”的认知。通过分析云南鹤庆银器锻制技艺和摩梭纺织技艺两个案例来呈现非遗实践作为跨地方聚合的过程及特性,以及非遗传承和保护由此所面对的机遇和挑战,呼吁在重视非遗服务于乡村振兴等发展战略的潜力时,要进一步认识非遗实践的跨地方性对本土社区的影响,反思遗产原真性和文化价值与当前非遗实践的关系,强调在非遗全球化生产和消费中保持其与本土认同和本土生计之间的关联。
Geographic Thought: A Critical Introduction
Structural features and driving factors of the evolution of the global interurban knowledge collaboration network
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210165
[本文引用: 1]

Based on data drawn from the Web of Science and a selection of 526 major world cities in line with the world city network research related with advanced producer services, this paper performed multiple spatial and network analyses to examine the evolution of structural features and driving factors of the global interurban knowledge collaboration network. The results show that: (1) the spatial structure of the top cities of the network, which are mostly in Europe and US, has remained stable. The spatial configurations of the centers of global innovation and global production services are different. The connectivity of cities is unevenly distributed across different geographical scales, with a clear west-to-east and north-to-south shift. (2) In terms of topological structures, the scale, density, and connectedness of the network have increased over time. The network exhibits small-world and scale-free features, and presents significant “core-periphery” and “community” structures. Cities differ in their national and global functions. (3) The evolution of the global interurban knowledge collaboration network is influenced by both endogenous and exogenous driving factors. Endogenous driving factors include the shifting paradigm of contemporary knowledge innovation, the non-linear development paths of knowledge innovation, the unique modes of knowledge combination, the “preferential attachment”, and the social interdependence of maintaining knowledge collaboration. Exogenous driving mechanisms include geographical proximity, country borders, regional agreements, and colonial histories.
全球城市知识合作网络演化的结构特征与驱动因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210165
[本文引用: 1]

以Web of Science合著论文数据为基础,参照以高端生产性服务业为对象的世界城市网络系列研究选取全球526个主要城市,借助空间分析和网络分析,分析全球城市知识合作网络演化的结构特征和驱动因素。结果显示:① 空间结构方面,“头部”城市格局稳定,欧美城市垄断明显;城市在全球知识合作网络与全球高端生产性服务网络中的空间分布存在差异;全球城市知识合作网络在不同地理尺度上均呈现出非均衡特征,网络重心有显著的东移和南移趋势。② 拓扑特征方面,全球城市知识合作网络的规模、密度和连通性不断增强;网络呈现出显著的“小世界性”和“无标度性”、“核心-边缘”结构和“社群”结构;不同城市在网络中发挥着不同的“全球功能”和“国家功能”。③ 驱动因素方面,全球城市知识合作网络的演化由内生和外生驱动因素共同作用。其中,内生驱动因素包括当代知识创新范式的转变、知识创新过程的非线性演进、知识组合的特定方式、合作对象择取的“偏好依附”以及维持合作关系的“社会纽带”;外生驱动因素包括地理邻近、国家边界、区域协定以及殖民历史。
Explaining the structure of inter-organizational networks using exponential random graph models
Tourism as an ordering: Towards a new ontology of tourism
DOI:10.1177/1468797604057328
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This article offers an entirely different way of understanding the origins, significance and relational materialism of tourism. Borrowing from the emergent sociology of ordering, which combines aspects of Foucault’s notion of governance with ‘post-ANT’ insistence on relational materialism, it shows how tourism came to be a heterogenous assemblage ‘at large’ in the world, remaking the world anew as a touristic world; a world to be seen, felt, interpellated and travelled. In doing so it underlines the paradoxical significance of nationalism as an ordering with clear implications for the emergence of the tourism ordering. It also, at last, invites research on the relationality of technologies and objects of tourism as well as key individuals whose dreams of tourism were essential to the history of the tourism ordering. Seen as an ordering this conception of tourism offers an alternative to structuralist accounts that have long influenced and inhibited tourist studies. It also explains why tourism was so hard to define, until now.
An empirical research on the factors that affect tourism destination brand loyalty and overall impression: Evidence from Changji region in Xinjiang
旅游目的地品牌忠诚度与整体印象影响因素研究: 以新疆昌吉州为例
On "tourism destination" and "tourism transit venue"
论“旅游目的地”与“旅游过境地”
Rethinking the tourism system from a post-structuralist perspective and its theoretical prospect
后结构主义视角下的旅游系统及新议题展望
Development of tourism destinations: An integrated multilevel perspective
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2010.08.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Mapping time series into networks as a tool to assess the complex dynamics of tourism systems
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2015.10.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Cultural heritage routes in South Africa: Effective tools for heritage conservation and local economic development?
DOI:10.1080/0376835X.2010.508589 URL [本文引用: 2]
Tourism routes: A scoping review
DOI:10.54055/ejtr.v32i.2575
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This scoping review provides an overview of the literature on tourism routes, concerning 1) the categorization of tourism routes, 2) how the research has been conducted, in terms of methodologies and main research themes, and 3) future research paths. The review includes documents from four databases, written in English, published until May 2020 and focused on tourism routes as organisations of stakeholders under a unified theme to achieve common goals. Based on 194 documents, regional-scale routes under the theme of food and drink are identified as the commonest. The main research theme is route development. Empirical studies, qualitative approaches, primary data usage, and data collection triangulation techniques predominate. Lastly, future research should focus mainly on route planning and management.
Route tourism: A roadmap for successful destinations and local economic development
DOI:10.1080/03768350701445574 URL [本文引用: 3]
Tourism routes as vehicles for local economic development in South Africa: The example of the magaliesberg meander
DOI:10.1007/s12132-007-9006-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Rural tourism and the small country town
DOI:10.1080/02508281.1991.11014600 URL [本文引用: 1]
Scenic roads and rural development in the U.S
DOI:10.1080/02508281.1991.11014623 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tourism routes, local economic promotion and pro-poor development: The case of the crocodile ramble
Exploring the dialectics of route-based tourism: The Camino de Santiago
DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(97)00075-7 URL [本文引用: 2]
Across the administrative boundaries: The first mile of the long-distance trail collaboration in Taiwan
Tourism routes as a tool for the economic development of rural areas: Vibrant hope or impossible dream?
DOI:10.1016/S0261-5177(03)00063-3 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research progress of foreign tourism geography based on Tourism Geographies in recent years
基于《Tourism Geographies》的近十年国外旅游地理研究进展
Spatial and temporal differentiation characteristics of transportation service function and tourism intensity coordination: A case study of Yunnan province
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200615
[本文引用: 1]

Taking the typical tourist destination-Yunnan province as a research case, and based on the multi-source data such as Gaode traffic big data and electronic map POI, this study uses the improved TOPSIS method, coupled coordination model and Tobit model to construct the comprehensive traffic service function and tourism intensity conceptual model. From the perspective of time and space, this paper examines the spatial differentiation characteristics of transportation service function and tourism intensity coordination and the contribution of different transportation service functions to tourism intensity. The results show that: (1) From 2006 to 2016, the synergy effect of comprehensive transportation service functions and tourism intensity in various cities of Yunnan province became more prominent, and the type of coordination leading has changed from "official disorder" to "primary coordination type". (2) The overall pattern of comprehensive transportation service functions and tourism intensity coordination degree shows a pattern of "high in the middle, but low in the east and west as well as in the north and south", and the east and west are greatly divided, and the north-south changes are relatively stable. The regional differences within the province are characterized by "Central part > Southeast > Southwest > West > Northwest > Northeast". There is a significant difference in the spatial differentiation characteristics of different types of transportation modes and tourism intensity coordination. (3) The contribution of roads, railways and aviation lines to tourism intensity is characterized by the unbalance of "air transportation > road traffic > railway traffic". The income of tourism residents, the endowment of tourism resources and the degree of marketization all have positive effects on tourism intensity. However, the lower level of opening up has restricted the improvement of regional tourism intensity to a certain extent.
旅游地交通服务功能与旅游强度协调时空分异特征: 以云南省为例
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200615
[本文引用: 1]

以典型旅游地云南省为研究案例地,基于高德交通大数据、电子地图POI等多源数据,通过构建综合交通服务功能与旅游强度概念模型,采用改进的TOPSIS法、耦合协调模型和Tobit模型,从时空视角审视交通服务功能与旅游强度协调空间分异特征及不同交通服务功能对旅游强度的贡献效应。结果表明:(1)2006—2016年,云南省各州市综合交通服务功能与旅游强度协同效应逐渐凸显,协调主导类型由“濒临失调型”跃迁为“初级协调型”。(2)综合交通服务功能与旅游强度协调度总体格局呈“中部高,东西两侧和南北两翼低”的空间布局态势,且东西分异剧烈,南北变化相对平稳;区域差异特征呈现“滇中>滇东南>滇西南>滇西>滇西北>滇东北”俱乐部趋同空间态势;不同交通方式与旅游强度协调度空间分异特征存在显著差异。(3)公路、铁路、航空对旅游强度的贡献效应表现为“航空运输>公路交通>铁路交通”的不均衡特征;旅游地居民收入、旅游资源禀赋、市场化程度均对旅游强度呈现正向促进效应,但对外开放水平较低一定程度上制约了区域旅游强度提升。
Greenways as a planning strategy
DOI:10.1016/0169-2046(95)02039-V URL [本文引用: 1]
Overall plan for the construction of greenway network in Guangdong Province
.http://www.gdgreenway.net/.
广东省绿道网建设总体规划
.http://www.gdgreenway.net/.
On the principle and applications of scenic byways abroad
国外风景道的理论与实践
Literature review on scenic byway research and planning practice
DOI:10.11821/yj2007060021
[本文引用: 1]

This paper firstly reviews the theoretical study abroad on scenic byway, and discusses the development of practical work in foreign countries from the prospective of American national scenic byway plan and national scenic byway system. Secondly, according to the feature that our research on scenic byway is accompanied by local planning, the paper analyzes the practice of scenic byway in China through several cases of scenic byway planning. The preliminary theoretical research of different subjects on scenic byway, greenway and heritage corridor from respective point of disciplines background is also discussed, be combining mostly with the production tasks. Finally, this paper points out that both theoretical research and practice in China is still at the initial stage, management organization should be established, research and practice in this field should be actively carried out, and construction of national scenic byway system should be also discussed and concluded.
风景道研究与规划实践综述
The need for a transnational approach to the material heritage of migration: The China-Australia corridor
DOI:10.1177/1469605316673005
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Currently, a unilinear, nation-bounded approach is taken to the recording and interpretation of the material heritage of immigration in settler nations, largely ignoring the transnational social fields to which the immigrants who created the heritage places and buildings belonged. Focusing on Chinese migration to Australia in the 19th and 20th centuries, I offer the ‘heritage corridor’ concept as better representing the transnationally ‘stretched’ or ‘distributed’ built environment emerging from the cross-border flows of people, objects, ideas and money to which migration typically gives rise. I argue that intensities of affect and emotion have acted to entangle migrants and their relatives remaining at home in this environment. Remittance payments from Chinese migrants in Australia are shown to have been instrumental in the building of houses, temples, schools, shops, roads and bridges in the emigrant villages of Pearl River Delta region of Guangdong Province, many of which are now regarded as heritage items.
The new trend of world cultural heritage protection: Cultural route
世界文化遗产保护的新动向: 文化线路
The Baku Cultural Routes Declaration-Council of Europe cultural routes: Cultural tourism for intercultural dialogue and social stability
Concept, attributes and classification of tourism highway development in China
旅游公路概念、属性及分类
The logic transformation of the scenic byway system to the linear experience space transformation
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200204
[本文引用: 2]

From the perspective of traveling experience, the scenic byway is no longer the only tourist transit or tourism passage as experiencing scenic byways has become a new travel motive, which reflects the spatial mobility of tourism industry elements. Regarding "on the road" traveling experience as the major travel motivation of tourists, this paper believes that the scenic byway system performs the function of direct expression of tourists traveling experience rather than the traditional tourism highway system that transits tourist flow. Recognizing the scenic byway system as a special derived form of tourism destination, the paper analyzes the rationality of scenic byway system as a new linear experience space and expounds the theoretical analysis of this derived form of tourist destination. Their characteristics are summarized using relevant domestic and international case studies. Taking the Tongling- Huangshan section of the Beijing-Taiwan Expressway in southern Anhui as an example, this paper explores the necessity and importance of developing the scenic byway in the region, proposes the construction components of linear tourism experience space and summarizes the differences in development connotation. The introduction of the linear experience space profoundly expands the existing tourism research on the scenic byway system and provides a new direction for tourist destinations development.
线型旅游体验空间: 风景道的体验性逻理嬗变
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200204
[本文引用: 2]

在体验视角下,风景道不仅只是旅游系统中的旅游过境地或旅游通道,旅游者逐渐将体验特色风景道作为出游动机,同时也折射出旅游产业要素在沿线空间范围上的流向扩散。在将“在路上”这一旅游体验作为旅游者出游的主要动机,使传统意义上仅以交通功能承载旅游流的风景道转向为旅游者体验最直接的表现形式,并将其整体视为一种特殊类型的旅游目的地衍生形态,不仅可以串联各自区隔的旅游空间,还是我国建立国家公园体系的有效支撑,同时也符合全域旅游发展的内在需求。通过对风景道作为新型线性体验空间的合理性进行分析,阐述这种旅游目的地衍生形态的理论解析,并结合国内外相关案例对其特点特征进行总结。以安徽南部京台高速铜黄段为例,探讨打造该区域的必然性与重要性,提出线型旅游体验空间构建内容,并总结发展内涵上的差异性。线型旅游体验空间的提出,在理论上深化拓展了现有关于风景道的旅游研究,为现实中旅游目的地发展提供一个新的发展方向。
Tourism routes and gateways: Key issues for the development of tourism routes and gateways and their potential for pro-poor tourism
Product pedigrees of scenic byway based on wording frequency: A case study of blue ridge road
基于词频的风景道产品谱系: 以美国蓝岭风景道为例
Study on the tourism image strategies of cross-regional linear cultural heritage based on geographical characteristics
基于地理特征的跨区域线性文化遗产旅游形象策略研究
On value evaluation of tourism resource of cross-regional linear cultural heritage: Taking the routes network of Chang'an-Tianshan corridor in China as an example
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.10.013
[本文引用: 1]

The cross-regional linear cultural heritage is a kind of important tourism resource, as well as a special kind of tourism resource. But the whole value of the heritage tourism resource is difficult to evaluation, and hard to avoid fuzzy, so that the evaluation is lack of practical significance, because of the scattered resources, internal differences, and relatively loose connection between the heritage sites. Based on the particularity of cross-regional linear cultural heritage and the core resource meaning of its heritage sites, this article regards the value of its heritage sites as the value of the entire heritage from a certain extent. That is to say, “the Cultural Route recognizes and emphasizes the value of all of its elements as substantive parts of a whole”. The Chang’an-Tianshan Corridor Routes Network of Silk Road formed in the 2nd century BC ( Some people think that it had formed before Shang Dynasty ), and still in use to the 16th century. The Routes Network, span nearly 5 000 km, had played a very important role in business trade and cultural exchanges, and leaves a large number of cultural relics and remains. In June 2014, the heritage of the Routs Network with a total of 33 heritage sites, including 22 heritage sites in China, was included in the World Heritage List, as one of the longest linear cultural heritages in the world. Therefore, it is typical significance in exploring the value evaluation of tourism resource of cross-regional linear cultural heritage. The value evaluation of resource is the evaluation of connotation value, application value, social impact and so on from the feature, function of the resource itself and so on, not the comprehensive evaluation including resource environment and development condition. The article, with Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Fishbein M- Rosenberg M Model, builds a model, which sets the score standards and evaluation grades, for the value evaluation of tourism resource of cross-regional linear cultural heritage. The empirical analysis shows that the proposed research method and evaluation model can more accurately evaluate the resource value. The value of heritage sites of Chang’an-Tianshan Corridor Routs Network in China is in good grade and above. The 5th grade resource, also known as special grade resource, accounts for 27.3% of the all resources, the 4th grade and 3rd grade resource account for 59.1% and 13.6% respectively. Those strategies, such as leading development, key project development and strengthening the historical culture mining and popularization of heritage sites, should be taken in tourism development of the Routs Network of Chang’an-Tianshan Corridor in China.
跨区域线性文化遗产类旅游资源价值评价: 以长安—天山廊道路网中国段为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2017.10.013
[本文引用: 1]

跨区域线性文化遗产是一类特殊的旅游资源。基于其特殊性,以其各遗产点的价值评价作为整个遗产的价值评价;借助层次分析法、菲什拜因-罗森伯格模型,通过设定评分标准与评价等级,构建跨区域线性文化遗产旅游资源价值评价模型;实证分析认为提出的方法与模型能较准确地评价资源价值,长安-天山廊道路网中国段各遗产点价值均在优良等级及以上,其中27.3%为五级(特品级)资源,59.1%为四级资源,13.6%为三级资源,在旅游开发中应采取领先开发或重点开发、分区开发及加强遗产点历史文化挖掘与宣传普及等策略。
Attractiveness model of linear tourism space based on the new mobilities paradigm
游客移动性视角下线型旅游空间吸引力模型研究
The evolution progress and mechanism of Guilin-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism destination system
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2012.09.1066
[本文引用: 1]

By constructing the basic mode of tourism spatial evolution, this article analyzes the evolution progress of Guilin-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism destination system. The evolution progress of tourism destination system is divided into 3 stages (the embryonic stage, the polarization stage and the optimization stage), which shows different characteristics (homogeneous development, polarization development, proliferation development) respectively, and tends to plate development stage. Before 1978, the tourism destination was in the stage of homogeneous development when the destination system was in the embryonic statement. The original landscape provided a good foundation for tourism development, but during this period, tourism space structure was in the low homogeneous disordered state, and the scenic spots have not been effectively developed. The following 20 years has experienced the polarization process, which can be divided into the early polarization evolution marked by the formation of the tourism growth pole of Guilin City and late polarization evolution stage marked by the formation of Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism destination system. In the early polarization evolution stage, with the driving of tourism demand, Guilin City had a rapid development as the tourism growth pole, and provided a good infrastructure and service facilities for the tourism of Lijiang River. It played a role of the organization for the regional tourist development. During the late polarization evolution stage, Yangshuo County had a good development as the new growth pole, Guilin City further strengthened tourism function, Lijiang River was developed as tourism corridor. Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism spatial system was formed basically. During the 11th Five-Year Plan, the tourism destination was in the proliferation stage. The tourism impact diffused at this stage and pushed the transformational development of the tourism destination. Meanwhile, the shape of regional tourism plate was initially formed. Travel city and scenic sites were increasingly interconnected, and a more coordinated Guilin City-Lijiang River-Yangshuo tourism system promoted the formation and development of a higher level of tourism spatial system, which can be called the tourism spatial system, or North Guangxi tourism board. This article analyzed the dynamic mechanism of the evolution and considered that there were varies leading dynamic mechanisms at different times. In the homogeneous development stage, the tourism resources endowment had played a decisive role. The dominating dynamic factor in the development stage of polarization was affected by circulation accumulation, and different types of demand had become the main power for construction. In the proliferation stage, the pursuit of overall efficiency has become the dominant force.
桂林—漓江—阳朔旅游地系统空间演化模式及机制研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2012.09.1066
[本文引用: 1]

通过构建旅游地空间演化基本模式,阐释了以漓江为主导的桂林-漓江-阳朔旅游地系统演化过程,归纳其经历了萌芽期、极化期和优化期,3个阶段分别体现出均质发展、极化发展、扩散发展的特征,并有向板块发展阶段演化的趋势。20世纪70年代以前,旅游地处于均质发展为特征的萌芽期,原赋景观为旅游发展提供了良好的基础,但是这一时期的旅游地在空间结构上处于低位的均质无序状态,各景区点未得到有效地开发;20世纪70年代末至 2000年代中期,旅游地进入极化期,其中又分为以桂林城区旅游增长极形成为标志的初期极化发展阶段和以桂林城区-漓江-阳朔县城旅游地系统形成为标志的后期极化增长阶段;初期极化发展阶段,在旅游需求的推动下,桂林城区作为旅游增长极得到较快发展,为漓江旅游提供良好的基础设施和服务设施,对区域旅游发展起到组织作用。后期极化增长阶段,阳朔县城作为新的增长极发展起来,桂林城区旅游功能进一步强化,漓江作为旅游廊道功能也日益强化,桂林-漓江-阳朔旅游地空间系统基本形成;“十一五”期间为扩散发展时期。在此期间旅游影响对外扩散,区域旅游板块逐渐形成,并推动旅游地转型发展。桂林-漓江-阳朔旅游系统的旅游城镇、景区点间相互联系日益紧密,功能上更加协调,推动了更高一级的旅游地空间系统的形成和发展,因此可称其为桂北旅游地空间系统,或桂北旅游板块。探讨了旅游地系统演化机制,认为在不同时期,起主导的机制不同:在萌芽期,资源禀赋起着决定性作用;在极化发展期,受循环积累因果效应的推动,不同类型的需求成为建构的主要动力;在扩散发展期,对综合效益的追求成为主导力量。
The discrimination of linearity
“线形”“线性”与“线型”辨析
Applying the Hollywood scriptwriting formula to destination branding
DOI:10.1080/13683500.2020.1739005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tourism trails as tools for cross-border integration: A best practice case study of the Vennbahn cycling route
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2018.09.008 URL [本文引用: 1]
Sustainable cycle tourism along the Danube cycle route in Austria
Cultural tourism routes as incubators for innovation and economic diversification: A potential analysis in the framework of the new silk road initiative in Azerbaijan
Towards a model of destination innovation process: An integrative review
DOI:10.1080/02642069.2018.1491970 URL [本文引用: 1]
The role of trails in the creation of tourist space
DOI:10.1080/1743873X.2016.1242590 URL [本文引用: 1]
Drivers and emerging innovations in knowledge-based destinations: Towards a research agenda
The social construction of scale
DOI:10.1191/030913200674086272
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Over the last ten years, scholars in human geography have been paying increasing theoretical and empirical attention to understanding the ways in which the production of scale is implicated in the production of space. Overwhelmingly, this work reflects a social constructionist approach, which situates capitalist production (and the role of the state, capital, labor and nonstate political actors) as of central concern. What is missing from this discussion about the social construction of scale is serious attention to the relevance of social reproduction and consumption. In this article I review the important literature on scale construction and argue for enlarging our scope for understanding scale to include the complex processes of social reproduction and consumption. I base my critique on a short case study which illustrates that attention to other processes besides production and other systems of domination besides capitalism can enhance our theorizing and improve our attempts to effect real social change.
Rescaling and politics of scale in China's city-regional governance
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

This article aims to systematically demonstrate the evolution and development of scale theory and its features in different periods. The perspective of scale theory is then used to elaborate the formation of city-regional governance in China. A conceptual framework is proposed in this article. Four major conclusions are presented as follows. First, the geographical scale of China’s city-region consists of two modalities, namely, metropolitan area and urban agglomeration. The governing scale of China’s city-region is essentially constituted by administrative powers, all of which made up a top-down power matrix. The restructuring of governing scale oriented geographical scale of city-region is the nature of rescaling of China’s city-regional governance. This restructuring process is central to understand the rationale of China’s city regional governance. Second, the macro socioeconomic development in China has manifested as the dynamic adjustment process between decentralization and recentralization. The rise of city-regional governance in China is the outcome of state spatial selectivity oriented city-regions to overcome the crises brought by the conventional city-based accumulation regime. Third, the governance of urban agglomeration is featured by the soft rescaling. Correspondingly, the governance of metropolitan area is characterized by rigid rescaling. This rigid rescaling has embodied as the reconfiguration of various jurisdictions oriented a new administrative relation. Last but not the least, there are complicated games between multiple actors at the city-region scale. To sum up, China’s city-regional governance reflects the changing political economy of regional development in post-reform era.
中国城市区域治理的尺度重构与尺度政治
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.011
[本文引用: 1]

系统回顾西方尺度理论,尤其是尺度生产(尺度重构与尺度政治)理论,借此阐释中国城市区域治理形成的尺度逻辑。研究发现,中国城市区域包括城市群与都市区2个地理尺度;治理尺度是以行政权力为核心,形成自上而下的行政权力金字塔;治理尺度的动态重配并与地理尺度相耦合的过程是中国城市区域治理的尺度建构的本质;改革开放后,中国宏观政治经济在“去中心化-再中心化”过程中持续动态调整;中国城市区域的产生是国家空间选择性的结果,来克服以城市为基础的资本积累模式的体制危机;城市群治理以柔性尺度重构为主,都市区治理以刚性尺度重构为主;城市区域内部产生复杂的多主体间的尺度博弈。
A materialist framework for political geography
DOI:10.2307/621909 URL [本文引用: 1]
The production and restructuring of interurban cooperative space: From the perspective of territory, network and scale
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.12.006
[本文引用: 1]

Space-based cooperation is an important form of interurban cooperation and a multidimensional sociospatial process concerning reterritorialization, network building, and rescaling. Based on the case study of the Shenzhen-Shanwei Special Cooperation Zone and considering three sociospatial dimensions including territory, network, and scale, the production and restructuring of interurban cooperative space is analyzed. This research suggests that the reterritorialization involved both capital and regulatory power; the network that link actors together serves as tools for political mobilization and information sharing; the key factor for rescaling is the mobilization of actors at higher scales. Common interests of relevant actors are fundamental factors of space-based interurban cooperation. Specifically, the actors at higher scales tend to embed their own interests into the political strategies crossing scales. Moreover, a complex interaction is found among the three sociospatial dimensions, with four major types of combination including identical, parallel, substitution, and realization, which could be of significance in future studies aiming to further examining the production of multidimensional space.
城际合作空间的生产与重构: 基于领域、网络与尺度的视角
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.12.006
[本文引用: 1]

空间合作是城市合作的重要形式,同时又是一个涉及领域、网络和尺度等多维度的社会空间过程。本文以深汕特别合作区为例,从领域、网络和尺度3个社会空间维度分析城市间合作空间的生产与重构。研究表明,在这种合作形式中,再领域化涉及资本和管制权力2个方面,联系网络具有政治动员、信息共享等功能,而尺度重组的关键则是对高尺度行动者的动员。此外,共同利益是城市空间合作中最核心的要素,高尺度行动者在合作过程中也可能将自身利益嵌入合作空间。最后,这些维度之间存在复杂的相互作用,并具体表现为同一、并行、替代和实现4种组合关系。这4种组合关系对更细致地分析多维度的空间生产具有一定借鉴意义。
Intensities of feeling: Towards a spatial politics of affect. Geografiska Annaler: Series B
Concept of scale in human geography and politics of scale: Based on anglophone human geography since 1980s
尺度的人文地理内涵与尺度政治: 基于1980年代以来英语圈人文地理学的尺度研究
Reconstructing scale: Towards a new scalar politic
DOI:10.1177/0309132510367841
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, the dominant political-economic approach to scale has been subject to critique from poststructuralist perspectives. In this paper, I argue that the charge of ‘reification’ has been accepted too readily, masking areas of conceptual overlap between political-economic and poststructural approaches, particularly in terms of their shared concern with the construction of scale. On this basis, I propose to replace the established concept of ‘the politics of scale’ with ‘scalar politics’, arguing that it is often not scale per se that is the prime object of contention, but rather specific processes and institutionalized practices that are themselves differentially scaled.
Retheorising the scale of globalisation: Topologies, actor-networks and cosmopolitanism//Herod A, Wright M K. Geographies of Power: Placing Scale
The limits to scale? Methodo logical reflections on scalar structuration
DOI:10.1191/030913201682688959
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Fruitful new avenues of theorization and research have been opened by recent writings on the production of geographical scale. However, this outpouring of research on scale production and on rescaling processes has been accompanied by a notable analytical blunting of the concept of geographical scale as it has been blended unreflexively into other core geographical concepts such as place, locality, territory and space. This essay explores this methodological danger: first, through a critical reading of Sallie Marston's (2000) recent article in this journal on ‘The social construction of scale’; second, through a critical examination of the influential notion of a politics ‘of ‘ scale. A concluding section suggests that our theoretical grasp of geographical scale could be significantly advanced if scaling processes are distinguished more precisely from other major dimensions of sociospatial structuration under capitalism. Eleven methodological hypotheses for confronting this task are then proposed.
Book Review: Post-structuralist geography: A guide to relational space
DOI:10.1177/147309520700600108 URL [本文引用: 1]
Regions unbound: Towards a new politics of place
DOI:10.1111/j.0435-3684.2004.00152.x URL [本文引用: 1]
Phase space: Geography, relational thinking, and beyond
DOI:10.1177/0309132508101599
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Recent years have witnessed a burgeoning of work on `thinking space relationally'. According to its advocates, relational thinking challenges human geography by insisting on an open-ended, mobile, networked, and actor-centred geographic becoming. The paper discusses the importance of this `relational turn' by positioning it within the lineage of philosophical approaches to space in geography. Following this, it highlights some silences and limits, namely factors that constrain, structure, and connect space. The paper then offers a moderate relationalism by discussing the notion of `phase space'. This acknowledges relationality but insists on the confined, sometimes inertial, and always context-specific nature of geography. Some challenges for this approach are discussed.
Tourism product development and product diversification in destinations
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2015.02.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Clustering and compatibility between tourism attractions
Cumulative attraction or compatibility is a powerful factor in locational decisions of retail outlets, but it has received little attention in the tourism literature. Existing studies largely ignore the impact of spatial and thematic clustering on compatibility between tourism businesses. This research questions whether and how spatial and thematic clustering are related to tourist movements between visitor attractions. The study in Cornwall, England, is based on in‐depth interviews with tourist attraction managers and key informants, complemented by a survey of 435 tourists. It provides insights into the relationship between the nature of the tourism product, spatial clustering and tourism behaviour. Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
The role of clustering, cooperation and complementarities in the visitor attraction sector
DOI:10.1080/13683500.2010.517312 URL [本文引用: 1]
On the economic nature of tourism scenic area, tourism product, tourism resource and several related concepts
论旅游景区、旅游产品、旅游资源及若干相关概念的经济性质
Heritage tourism, thematic routes and possibilities for innovation
The tourist route system-models of travelling patterns
Building tourism networks through tourist mobility
DOI:10.1177/0047287515569777
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This article aims to define tourism networks analyzing tourist mobility between destinations. The study adopts network analysis methods, testing a data processing strategy that combines descriptive measurements and clustering tools. A segmentation approach has been employed to investigate differences or similarities between the trip-related attributes of tourists within networks. Data are from a sampling survey carried out on tourists’ visit in Sicily. The results show that the tourist choice defined the role of a destination as “central” or “peripheral” within a network. Tourists build their own networks around nodal destinations, even if they are geographically distant. Thus, tourist mobility affects the shape, the dimension, and the structure of the networks, where tourists are different for characteristics, trip-related behaviors, and type of holiday chosen. The study provides some evidence that can be useful for planning tourism facilities, managing tourism routes, and defining destination management strategies.
Local service industry and tourism development through the global trade and infrastructure project of the New Silk Road: The example of Georgia
DOI:10.1080/02642069.2019.1623204 URL [本文引用: 1]
International tourists' value perception of the Grand Canal heritage: From the perspective of translocal subjectivity
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220908
[本文引用: 1]

The stance and criteria of assessing heritage value reflect the competition for heritage discourse power and the dissemination of values. At present, China's world heritage value assessment is subject to the universal values promoted by the West, and is faced with serious challenges of heritage discourse power. Especially in inbound heritage tourism, namely the frontier of cultural diplomacy, the current heritage practice presents Chinese cultural traditions according to the Western standards, which may presuppose the positions and standards of international tourists to judge the value of heritage, and lose the home field advantage of Chinese cultural diplomacy. With the CPC Central Committee vigorously promoting common values which provide guidelines for heritage value assessment, how to make use of inbound heritage tourism to confirm and disseminate common value positions and standards has become an important issue in heritage practice. In view of this, this paper explores the interaction process between international tourists and the Grand Canal heritage site and the specific paths of international tourists' perceptions and judgments of heritage value based on the theoretical perspective of translocal subjectivity. Suzhou Ancient Canal section of the Grand Canal is taken as the research site. The results show that international tourists interact with the heritage sites at both micro and meso levels, and realize intercultural dialogue and negotiation through two specific paths, including empathic understanding and self-reflexive construction. In this process, international tourists actively perceive and judge the value of the Grand Canal heritage, crossing the narrow, rigid Western-centric cultural value positions presupposed by the universal values, and reaching an open and inclusive civilizational interaction practice, which further promote greater international recognition of the positions and standards of common values. The article attempts to break the hegemonic practices behind the Western universal value theory by introducing the common values' positions and standards. It offers important practical implications for China to strive for the discourse power of world heritage, promote equal interactions among civilizations, and improve Chinese cultural identity.
国际游客对大运河遗产价值的感知: 基于跨地方主体性的视角
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220908
[本文引用: 1]

遗产价值评判的立场与标准隐含了遗产话语权的角逐以及价值观传播的问题。目前,中国世界遗产的价值评定受制于西方所谓的“普遍价值”;特别是在入境遗产旅游这一文化外交的前沿阵地,现行遗产实践按照西方标准来展示中国文化传统,有可能预设了国际游客的遗产价值评判立场与标准,反而丧失了中国文化外交的主场优势。“共同价值”为遗产价值评判提供了指引,如何借力入境遗产旅游的现实情境,证实并传播共同价值立场与标准,是遗产实践的重要议题。鉴于此,本文以大运河苏州段遗产地为例,基于跨地方主体性的理论视角,解析国际游客与大运河遗产地的互动过程及其感知评判遗产价值的具体路径。研究发现:国际游客从微观与中观两个层面来与遗产地互动,并通过移情性理解与自反性建构两种具体路径,实现了不同文化间的对话与协商;这一过程中,国际游客能动地感知评判着大运河遗产的价值,跨越了所谓“普遍价值”所预设的狭隘僵化的、西方中心主义的文化价值立场,达成了开放包容、交融互鉴的文明交往实践,成为共同价值立场与标准的国际群众基础。文章引入共同价值立场与标准来尝试破除西方普遍价值论背后的霸权主义行径,对争取世界遗产话语权、推进文明间平等交往、弘扬中华文化自信具有重要的实践意义。
Pedigree identification and spatial differentiation of the "Millennium Canal" brand genes
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210313
[本文引用: 1]

In February 2019, the General Office of the CPC Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council issued the Planning Outline for the Protection, Inheritance and Utilization of the Grand Canal Culture. The Outline proposes to build the cultural tourism brand of the "Millennium Canal" and promote the national image of China. However, the brand positioning lacks diverse and divergent perspectives and the core theme of the brand is not prominent. The existing research mainly focuses on the overall brand of the Canal and a brand of a canal city but lacks attention to the regional brand of the Canal. The "Millennium Canal" brand genes are the soul of the national cultural tourism branding and development of the "Millennium Canal". This paper identifies and extracts the "Millennium Canal" brand genes from the online travelogues related to the Grand Canal by using the co-word analysis method in 35 cities at the prefecture-level and above along the Grand Canal. The geographic regionalization based on machine learning was also applied to further analyze the spatial differentiation of the "Millennium Canal" brand genes. The results show that: (1) A gene identification framework for the "Millennium Canal" brand is constructed, which consists of 2 gene categories, 4 gene dimensions, and 14 gene sub-dimensions. (2) The canal core genes and canal-derived genes are mainly distributed along the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal, and there are more canal-associated genes distributed in cities along the Sui-Tang Grand Canal, especially along the Weihe River section. (3) According to the distribution characteristics of the brand genes of the "Millennium Canal", the cities along the canal can be divided into six types of geographical areas, each with different dominant genes and functional positioning. The Grand Canal brand genes, which have been accumulated from thousands of years of history and multiple cultures, are the soul of the building and development of the "Millennium Canal" national cultural tourism brand. The "Millennium Canal" branding relying on the brand genes has positive significance for the integrity preservation of the Grand Canal heritage, the deep integration of culture and tourism industries, and the economic and social development of the regions along the Grand Canal.
“千年运河”品牌基因谱系识别与空间分异研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210313
[本文引用: 1]

“千年运河”品牌基因是“千年运河”国家文化旅游品牌塑造和发展的灵魂。本文以中国大运河沿线35个地级及以上城市为研究对象,运用共词分析法,从与大运河相关的网络游记中识别和提取“千年运河”品牌基因谱系。并运用基于机器学习的地理分区方法,进一步分析了“千年运河”品牌基因的空间分异特征。研究结果: ① 构建了由2个基因类别、4个基因维度和14个基因子维度组成的“千年运河”品牌基因识别框架。② 运河核心基因和运河衍生基因主要分布在京杭大运河沿线,隋唐大运河尤其是卫河河段沿线城市的边缘关联基因分布较多。③ 根据“千年运河”品牌基因的分布特征,可将运河沿线城市划分为6类地理区域,每类地理分区中的主导基因、功能定位不同。研究结果为“千年运河”国家文旅品牌塑造与发展提供参考,也为大运河文化遗产完整性保护与传承提供了新的切入点。
Tourism themed routes: A Queensland perspective
DOI:10.1177/135676670300900403
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper examines the potential role of tourism themed routes, not only as drive tourism products to increase visitation to regional Australia, but also as potential contributors to road network efficiency and improving road safety. The paper is based on extensive research undertaken by Tourism Queensland since the late 1990s into the potential role of themed routes within the tourism framework. These interactive visitor road corridors have demonstrated their ability to affect visitor dispersion, but rely heavily on cross-sector (tourism and transport) cooperation. This paper explores the market for themed routes, examines the potential contribution of tourism themed routes to ‘win-win’ tourism and transport outcomes and highlights the need for greater national coordination.
Inter-sectorial collaboration in networks: A boundary object approach to wine route
Leading the research innovation of Danxia landform and tourism geography by synthetic thinking: The geographical thoughts and academic contribution of Peng Hua.
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812004
[本文引用: 1]

Peng Hua was a professor at Sun Yat-sen University who was long devoted to Danxia Landform research and geographic tourism. In retrospect, Peng's achievements can be introduced from three aspects. First, through seeking overseas collaboration and applying for nomination of world natural heritage sites, he made a great practical contribution in promoting Danxia Landform as an internationally known heritage. Second, concerning his academic contribution, Peng produced a wealth of nuanced insights in multiple aspects of Danxia Landform, including, but by no means confined to, its typology and evolution and the distribution of red beds. Equally, he systematically compared Danxia landform with many others, both in and outside China. Additionally, in recent years, he made benchmark progress by successfully extending the scope of research on red beds, including its underground and above ground surfaces, such as geological structure, rock properties, geomorphological evolution, natural hazards, soil erosion, land degradation, and its socioeconomic development. Also, Peng Hua initiated the national survey of Danxia Landform and constructed its data platform. Third, in addition to research on Danxia Landform, he devised multiple significant concepts in the fields of tourism planning, tourism culture, urban tourism and regional tourism development. Particularly, the concept of 'Broad Tourism', which was proposed by Peng Hua, has had a massive impact on the academic community of Chinese tourism studies. Based on this concept, he proposed a number of innovative theories and research methods, such as the system and mechanism of tourism, development stages of tourism destinations, integration of tourism exploitation and city construction, market classification analysis, and correspondence analysis of products and demands. To a considerable extent, there is no exaggeration in arguing that these theories provide a bird's-eye view of the tourism development, clarify the differences and inter-connections among the direct, involved, and supportive systems and mobilize the role of tourism in regional development. All in all, Peng's achievements reflect his openness, overall awareness, and optimal portfolio, which helps researchers keep a comprehensive view in dealing with more subtle research of geography.
以综合思维引领丹霞地貌与旅游地理研究创新: 彭华先生的地理学思想与学术贡献
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201812004
[本文引用: 1]

彭华先生长期从事丹霞地貌和旅游地理研究,为中国丹霞事业和旅游发展做出了突出贡献,是“把论文写在祖国大地上”的科学家的典范。作为中国丹霞地貌研究国际化阶段的代表人物,彭华先生在丹霞地貌分类系统、丹霞地貌发育过程、国内外红层分布及其地貌发育的对比等方面开展了系列研究,同时,针对中国南方湿润环境下红层区严重的地貌灾害和荒漠化问题,用跨学科的思维和方法,开展了红层区地质构造—岩石特性—地貌发育—自然灾害—水土流失—生态退化—综合景观—社会经济发展之间相互关系的综合地理学研究实践,将原来的红层地表研究拓展为“地下+地表+地上”(红层的地质问题+地貌与土地问题+生态问题)的一体化研究,为丹霞地貌的未来研究指明了方向。彭华先生在旅游开发实践中不断总结新思想、新方法和新理论,在旅游地开发、旅游文化、城市旅游、区域旅游发展和旅游规划理论研究方面取得了大量成果,所提出的“大旅游”理念在学界有重要影响。在“大旅游”理念基础上提出的旅游系统及动力机制、旅游地发展阶段论、旅游开发与城市建设一体化、市场分类研究法、产品—需求对应分析法等理论,创新意义显著。彭华先生的学术研究典型体现了地理学的综合性思维和系统性思维。
Notice on printing and distributing the tourism development plan of the 14th Five-year Plan
[2022-01-20].http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-01/20/content_5669468.htm.
关于印发“十四五”旅游业发展规划的通知
[2022-01-20].http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-01/20/content_5669468.htm.]