1 引言
产业是影响乡村社会经济发展的核心要素之一,是促进乡村土地利用转型和人口流动的重要推手[1-2]。乡村旅游作为一种新型产业模式,是实现乡村振兴的重要路径,推动乡村旅游发展体现了产业振兴和美丽乡村建设的内在需求[3]。由于深厚的历史底蕴、丰富的多民族文化以及复杂多样的自然地理景观,中国形成了以传统村落[4]、森林乡村[5]、乡村旅游重点村[6]、少数民族特色村寨[7]和历史文化名村[8]为主的一大批特色乡村,它们是乡村产业振兴和城乡休闲旅游的重要载体,是打造休闲农业和乡村旅游精品工程的关键。中国乡村旅游正处于巨大的历史机遇期,挖掘特色乡村旅游发展潜力,构建兼具差异化和特色化的乡村旅游格局,有助于建立具有影响力的乡村旅游品牌,促进乡村旅游可持续发展[9]。
乡村旅游的兴起与全球乡村衰退直接相关,特色乡村在“城市星球”中已然成为稀有资源,是后现代社会城镇居民回归自然的重要载体[12]。国外大量研究探讨了海滨型乡村“3S”(Sun, Sea, Sand)资源的开发利用及其可持续发展模式[13],随着乡村旅游者个性化需求的增长,与农业产品、生态田园、历史文化和传统节事等相关的特色乡村及其旅游发展模式也逐渐引起广泛关注[14⇓-16]。从全球乡村旅游发展来看,特色乡村在推动地方经济发展和文化传承方面发挥了积极作用,但旅游者对特色乡村自然生态的影响和乡村本土文化的冲击也越来越令人担忧[17-18]。国内学者围绕特色乡村生产和生活方式及其与村落环境关系开展了系统深入的研究[19⇓-21],并从生态景观视角探讨了特色乡村文化景观的塑造和旅游开发模式[22-23],其中以传统村落为主的特色乡村研究内容最为丰富,主要集中于景观规划和空间格局两个层面,探讨传统村落价值、文化景观、公共空间、空间形态和保护开发等内容[24⇓-26]。随着生态文明建设和乡村振兴战略的实施,中国各级政府遴选了一批以森林乡村和乡村旅游重点村等为代表的特色乡村,为地方政府发掘特色乡村旅游资源、拓展休闲旅游发展空间和补齐全域旅游短板提供了指引。同时,围绕特色乡村的相关研究内容也持续深化,形成了涵盖特色村庄空间格局、发展模式和演变机理的研究体系[27-28],基于GIS空间分析、社会调查及数理统计的定量模型和实证研究不断涌现[29]。
中国特色乡村建设带来了乡村旅游系统和旅游要素关系的深刻变化,促进了乡村旅游空间结构优化与重组,推动着区域乡村旅游集群化和协同化发展。旅游空间结构可以抽象为节点、通道和面域的要素集合,其中节点是旅游资源最密集和旅游活动最活跃的要素,是旅游空间结构中重要的“磁体”[30]。特色乡村因独特的资源优势而成为乡村旅游系统中的重要节点,并依靠自身吸引力在一定范围内辐射形成一个节点域,在乡村旅游空间结构优化过程中发挥着重要作用。大量研究探讨了不同类型特色乡村的空间分异特征及其影响机制,为区域乡村旅游空间格局优化提供了重要基础[31⇓-33]。旅游空间优化的主要目的是提升旅游资源的空间接触机会,优化交通网络和提升旅游设施供给水平是改善旅游区位条件的主要途径[34]。可见,旅游区位的评估和优化配置应贯穿于旅游地生命周期的全过程,特色乡村仅仅依靠自身吸引力难以发挥乡村旅游的集聚效应,需要在整合不同类型特色乡村资源优势的基础上,依托旅游区位形成发展合力[35]。然而,现有研究多聚焦于单一类型特色乡村的空间格局分析与影响机制识别,忽略了全国尺度不同类型特色乡村的空间关联和区位关系,缺乏基于乡村旅游视角的特色乡村发展潜力评价和空间优化,难以为全国层面不同类型特色乡村旅游集群化和协同化发展提供支撑。
特色乡村旅游需要因地制宜制定差异化和特色化发展战略。系统把握特色乡村旅游资源分布格局和影响因素,科学识别特色乡村旅游潜力区和发展方向,有助于实现区域乡村旅游要素的空间协同优化,从而培育一批国家级特色乡村旅游聚集区和示范基地。基于此,本文以5类国家级特色乡村为研究对象,系统识别特色乡村差异化格局、空间联动与功能互补特征,综合运用耦合协调度模型与地理探测器识别特色乡村集聚区及旅游发展潜力区,结合特色乡村与旅游配套设施的区位匹配度分析,提出中国特色乡村旅游空间协同优化分区方案,为特色乡村旅游空间格局优化和协同发展提供决策依据。
2 研究数据与方法
2.1 研究数据
截至2021年9月,国家部委发布的中国传统村落、国家森林乡村、全国乡村旅游重点村、中国少数民族特色村寨和中国历史文化名村名录中,5类国家级特色乡村共计17743个(表1),具体包括6819个中国传统村落、7586个国家森林乡村、1199个全国乡村旅游重点村、1652个中国少数民族特色村寨和487个中国历史文化名村(暂未含港澳台地区),部分村从属于多个特色乡村名录;本文运用腾讯地图API(Application Programming Interface)工具(
表1 国家级特色乡村名录
Tab. 1
| 序号 | 特色乡村 | 发布部门 | 发布时间 | 发布批次 | 数量(个) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 中国传统村落 | 住房和城乡建设部、文化和旅游部、国家文物局、财政部、自然资源部、农业农村部 | 2012年12月 | 第一批 | 646 |
| 2013年8月 | 第二批 | 915 | |||
| 2014年11月 | 第三批 | 994 | |||
| 2016年12月 | 第四批 | 1598 | |||
| 2019年6月 | 第五批 | 2666 | |||
| 2 | 国家森林乡村 | 国家林业和草原局 | 2019年12月 | 第一批 | 3947 |
| 第二批 | 3639 | ||||
| 3 | 全国乡村旅游重点村 | 文化和旅游部、国家发展改革委员会 | 2019年7月 | 第一批 | 320 |
| 2020年8月 | 第二批 | 680 | |||
| 2021年8月 | 第三批 | 199 | |||
| 4 | 中国少数民族特色村寨 | 国家民族事务委员会、财政部 | 2014年9月 | 第一批 | 340 |
| 2017年3月 | 第二批 | 717 | |||
| 2019年12月 | 第三批 | 595 | |||
| 5 | 中国历史文化名村 | 住房和城乡建设部、国家文物局 | 2003年1月 | 第一批 | 12 |
| 2005年9月 | 第二批 | 24 | |||
| 2007年5月 | 第三批 | 36 | |||
| 2008年1月 | 第四批 | 36 | |||
| 2010年7月 | 第五批 | 61 | |||
| 2014年3月 | 第六批 | 107 | |||
| 2019年1月 | 第七批 | 211 |
土地利用数据、GDP、人口、植被指数、高程、日照和年均降水量等因子空间网格数据均来源于中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(
其他数据包括路网、兴趣点(Point of Interest, POI)、夜间灯光遥感数据和社会经济统计数据等。其中,路网数据基于2018年Open Street Map获取,以县域为单元计算得到路网密度值,并将数据进行空间栅格化。POI点数据为开源网站爬取的2018年全国兴趣点数据,根据兴趣点二级类筛选得到研究所需的22类旅游配套设施兴趣点坐标,主要涉及旅游资源、住宿、饮食、交通和其他旅游服务接待设施5个方面。夜间灯光遥感数据来源于科罗拉多矿业大学地球观测组2018年的全球夜间灯光遥感数据均值(
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 空间格局分析
(1)核密度分析。核密度分析通过平滑的峰值函数模拟真实的概率分布曲线,能够体现地理空间内部差异化分布的点聚焦强度和空间连续性特征[39]。本文采用核密度分析方法测度全国尺度各类特色乡村空间分布的连续性与差异性特征,其计算公式如下:
式中:f(x, y)为位于位置(x, y)的特色乡村密度估计;n为观测数量;h为带宽或平滑参数;k为核函数;di为位置(x, y)距第i个观测位置的距离。
(2)标准差椭圆模型。标准差椭圆模型通过椭圆中心、长轴、短轴、旋转角等基本参数,定量化描述地理要素分布的范围、方向性和延展性[40]。本文运用标准差椭圆识别各类特色乡村的分布趋势和重点方向,其计算公式如下:
式中:SDEx、SDEy分别为长、短轴轴长;xi、yi是i类特色乡村的坐标;
(3)耦合协调度模型。耦合协调度反映了系统或系统内部两个或两个以上要素相互作用的耦合程度和协调发展水平[41]。本文引入耦合协调度模型测度不同类型特色乡村的空间关联和功能互补特征,其计算公式如下:
2.2.2 旅游发展潜力评价
(1)潜在影响因子探测。乡村旅游发展潜力是指乡村利用自身资源实现其旅游发展的综合能力。特色乡村因在产业、生态和历史文化等方面的独特优势而彰显出巨大的旅游发展潜力。尽管各类国家级特色乡村是由政府主导遴选而出,但从区域层面而言,这些特色乡村具有典型的地理环境依赖性或社会经济关联性特征[6⇓-8]。一方面,地形、气候与水源等自然地理条件是乡村形成和发展的基础,对乡村聚落选址、农耕和文化习俗等产生重要影响。另一方面,乡村不是孤立的地理单元,新时期乡村发展需要立足于县域融合发展,乡村所处一定地域范围内的社会经济发展水平是推动乡村旅游发展的重要支撑力,不利的区位条件会增加外地游客的机会成本,稀疏的人口分布又难以形成本地市场的有效供给[44]。此外,旅游发展潜力又与区域旅游市场发展水平及旅游设施完善度息息相关,完善的旅游设施为旅游者提供了多样化选择,是提升乡村旅游品质的重要保障[45]。
基于此,本文综合考虑乡村演变机制和5类特色乡村特点,从环境适宜度、社会发展度和旅游关联度3个维度,构建特色乡村分布的潜在影响因子指标体系(表2)。环境适宜度选取日照、年均降水量、坡度和NDVI等4个指标,表征乡村旅游所必需的光、水、地、植被等乡村旅游的基础条件;社会发展度选取地均GDP、人口密度、离城镇的距离、路网密度、县域城镇化率和夜间灯光指数等6个指标,表征乡村旅游地的区位条件和周边潜在市场的支撑能力;旅游关联度选取旅游设施POI密度和旅游产业规模指数2个指标,其中旅游产业规模指数基于接待国内外游客总数与旅游总收入两个统计指标测算[46],表征乡村旅游地的产业发展水平和服务能力。运用SPSS软件对该指标体系进行共线性诊断,结果显示各因子间的Pearson相关系数均小于0.7,容忍度(Tol)均大于0.1,且方差膨胀因子(VIF)均小于5,表明所选取的因子均通过了多重共线性检验。
表2 特色乡村空间分布的潜在影响因子
Tab. 2
| 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 变量 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 环境适宜度 | 日照 | X1 | h |
| 年均降水量 | X2 | mm | |
| 坡度 | X3 | ° | |
| NDVI | X4 | 无量纲 | |
| 社会发展度 | 地均GDP | X5 | 万元/km2 |
| 人口密度 | X6 | 人/km2 | |
| 离城镇的距离 | X7 | km | |
| 路网密度 | X8 | km/km2 | |
| 县域城镇化率 | X9 | % | |
| 夜间灯光指数 | X10 | 无量纲 | |
| 旅游关联度 | 旅游设施POI密度 | X11 | 个/km2 |
| 旅游产业规模指数 | X12 | 无量纲 |
借助地理探测器的因子探测器模块,探讨具有统计显著性的自变量及其解释力[47]。计算公式如下:
式中:L为因变量或自变量的分层;
考虑到中国特色乡村在空间上分布广泛,存在典型的区域集聚与分散特征。为避免一些区域零散性特色乡村分布的随机性因子影响,本文首先识别中国特色乡村聚集区,在此基础上,以集聚区内每个特色乡村所在区域的核密度值为因变量,识别影响特色乡村分布的关键因子。
(2)潜力评价分级。以地理探测器识别的各关键因子的q值为基础,对其归一化处理后分配各因子的权重,进而测算全国特色乡村旅游发展潜力,计算公式如下:
式中:T为旅游发展潜力;xk是变量因子;wk为第k个变量因子的权重;qk为第k个变量因子的地理探测值;Q为所有主导因子的q加和值;m为因子数量。
2.2.3 旅游空间协同分区
特色乡村旅游发展不仅需考虑其发展潜力,同时需要在区域层面考量其与旅游配套设施的匹配度。区位熵是衡量某一区域要素空间分布及其地位与作用的重要指标[48],本文借鉴区位熵度量方法测算区域旅游配套设施与特色乡村的匹配水平,计算公式如下:
式中:LQi为i单元(栅格)旅游配套设施与特色乡村的区位匹配度;pi为i单元(栅格)的旅游配套设施POI点核密度值;vi为i单元(栅格)特色乡村核密度值;P为i单元(栅格)所在行政区范围内的旅游配套设施POI点核密度值之和;V为i单元(栅格)所在行政区范围内的特色乡村核密度值之和。
为保持全国分区的地域完整性,本文将区位匹配度无意义区看作中低区位匹配度区,再将其与发展潜力进行组合分析,并结合区域实际情况进行分区。综合特色乡村旅游发展潜力和区位匹配度分级结果,基于县级行政单元将全国划分为优先发展区、特色挖掘区、资源整合区、协同提升区和优化引导区5类,进而明确不同分区的优化方向和发展路径。
3 结果与分析
3.1 中国特色乡村空间格局与耦合特征
3.1.1 空间格局特征
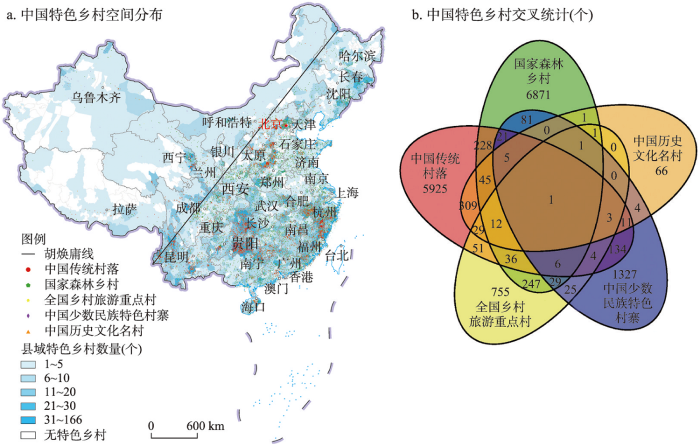
中国5类国家级特色乡村分布具有明显的东密西疏特征(图1a),特色乡村数量超过10个的县域主要分布在“胡焕庸线”东南侧,西北侧大部分县域的特色乡村数量少于5个。在中国第二和第三级阶梯的分界线——太行山脉—巫山—雪峰山沿线特色乡村密布,形成一条鲜明的特色乡村分布带。从区域分布来看,华东地区拥有最多的中国历史文化名村、国家森林乡村和全国乡村旅游重点村,而西南地区拥有最多的中国少数民族特色村寨和中国传统村落,其中国少数民族特色村寨数量占全国的比重高达44.67%;华中地区的各类特色乡村数量均排名前列且数量分布相对均衡。
图1
图1
2021年中国特色乡村空间分布与交叉统计
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站 GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 1
Spatial distribution and cross statistics of characteristic villages in China in 2021
通过对5类特色乡村交叉统计分析可以发现,特色乡村具有显著的复合型特征,即同一乡村出现在两个及以上的特色乡村名录中,这些特色乡村拥有更丰富的乡村旅游资源。如图1b所示,中国传统村落和历史文化名村的个体重合度最高,309个乡村同时出现在以上两个名录中,两者都拥有深厚的历史底蕴且留存着一定的物质、非物质历史文化遗产。247个乡村既属于国家森林乡村又属于全国乡村旅游重点村,这与森林乡村自身优越的生态环境密不可分,乡村旅游发展潜力较大。中国传统村落和国家森林乡村的重合个体有228个,表明部分历史悠久的传统村落仍然保留着良好的自然生态风貌,森林覆盖率高,兼具丰富的自然和人文旅游资源。
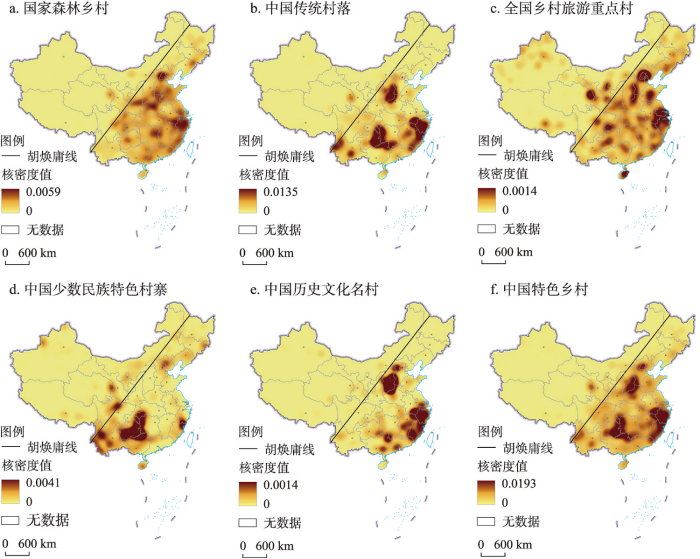
不同类型特色乡村分布直接反映了自然与人文环境的地域分异。国家森林乡村集中分布于“胡焕庸线”东南侧(图2a),这与自然条件及森林景观的分布特征具有高度一致性;“胡焕庸线”以东区域降水相对充沛,自然地理环境适宜植被生长,华北平原、长江中下游平原和东南丘陵等区域都是森林乡村高度聚集区。中国传统村落的分布呈现出显著的区域集聚特征(图2b),全国范围内出现了3个主要的集聚区:一是河北省、河南省和山西省接壤处;二是安徽省、浙江省和福建省的交界处,一直延伸覆盖浙闽两省大部分区域;三是湖南省、广西壮族自治区和贵州省形成的“L”型条带区。全国乡村旅游重点村分布相对较为离散(图2c),呈现出“多点开花”的蓬勃发展态势,尤以京津地区、长江三角洲地区等东部发达区域集聚程度最高,密集且富裕的人口为乡村旅游产业发展带来了巨大的客源市场。
图2
图2
2021年中国特色乡村核密度分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Kernel density distribution of characteristic villages in China in 2021
中国少数民族特色村寨集在贵州省、重庆市东部、湖南省西部和广西壮族自治区北部形成了一个反“L”型聚集区(2d),区域内广泛分布了土家族、苗族、壮族、瑶族、侗族、彝族和布依族等少数民族特色村寨,这与少数民族人口在这些地区的集中分布趋势是一致的[49]。此外,云南省全域分布着大量的少数民族特色村寨,浙闽交界处大量的畲族聚落形成了东南沿海地区的特色村寨聚集区,四川北部和青海东部形成了两个以藏族村落为主的特色村寨分布热点区域。中国历史文化名村的分布呈现出更为显著的东西区域差异(图2e),主要聚集区全部位于“胡焕庸线”东南侧;中国历史文化名村与中国传统村落的空间分布趋势具有相似性,华北和华东的集聚区存在一定范围的重合,但在中部地区有较明显的差异。
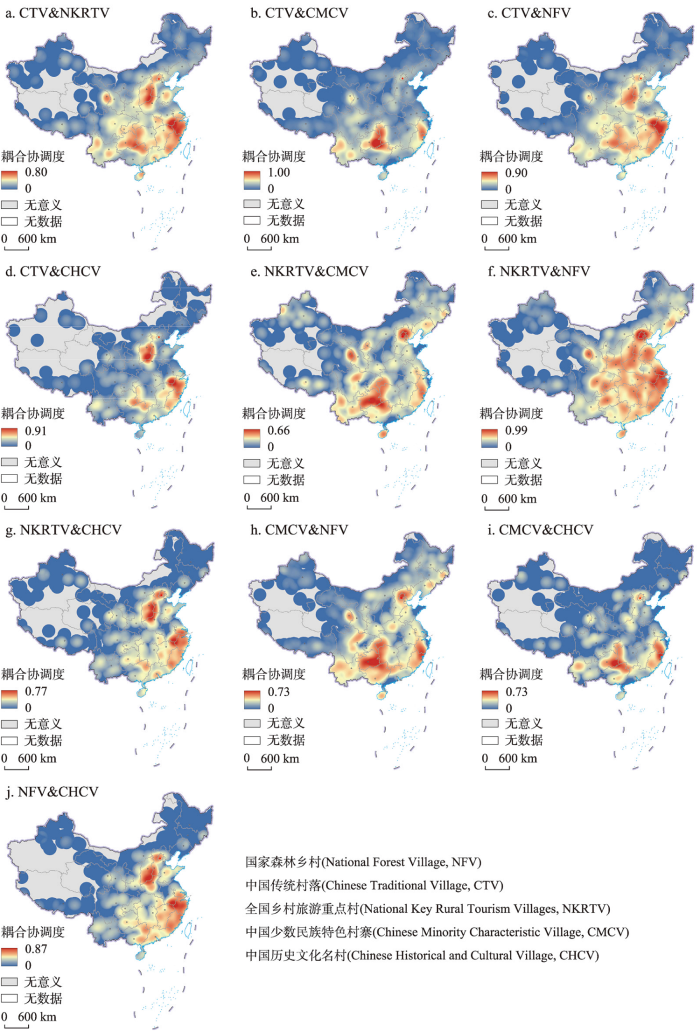
3.1.2 空间耦合关联特征
图3
图3
2021年中国特色乡村耦合协调度分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 3
Spatial distribution of coordination degree of characteristic villages in China in 2021
整体而言,自然条件优越的东南沿海区和乡村人文特色明显的西南区是耦合协调度高值分布区,表明这些区域内不同特色乡村间有良好的空间联动,不同资源特色的乡村在区域内部形成了良好的功能互补,能够提供多样化的乡村旅游产品供给。西北青海东部与甘肃交界处出现一个小范围的耦合协调度高值区,鉴于西北地区特色乡村的耦合协调度整体偏低,未来该区域有望成为该地区特色乡村发展的重要支撑点。
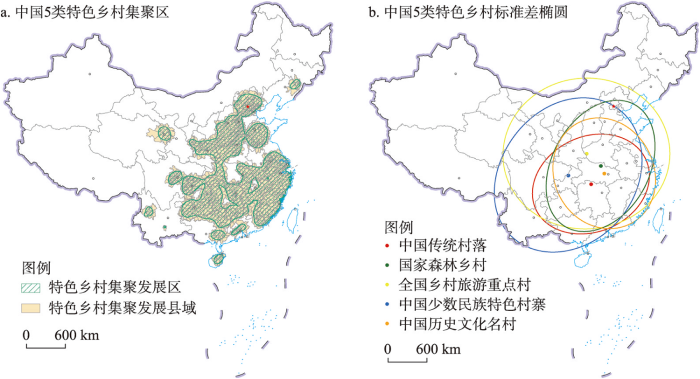
(2)集聚区识别与标准差椭圆分析。将特色乡村两两耦合协调度达到0.5及以上的区域识别为特色乡村聚集区,并将其拓展到相应县域单元(图4a)。中国特色乡村集聚区主要位于中东部的华北、华东、华中和华南地区,与图2f呈现的中国特色乡村核密度高值分布区具有较好的一致性。空间上呈现出典型的沿海(东海)、沿江(长江)和沿河(黄河)特征,反映了乡村发展“渔猎为生、逐水而居”的生活方式和空间依赖性。河北省、河南省和湖南省均拥有上百个集聚县域,特色乡村旅游集聚开发潜力较大。北京市、浙江省和福建省的全部县域及江苏省、山东省的大部分县域均处于集聚区,这些区域相对发达的社会经济发展水平和密集的人口为乡村旅游发展提供了重要支撑,区内特色乡村在一定程度上能够实现空间联动和功能互补。
图4
图4
2021年中国特色乡村集聚区及标准差椭圆分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站 GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 4
Agglomeration areas and standard deviation elliptic distribution of characteristic villages in China in 2021
基于ArcGIS空间分布标准差椭圆工具,进一步分析中国5类特色乡村的整体分布态势和差异化分布特征(图4b)。全国乡村旅游重点村的椭圆面积最大,表明其分布范围最广,离散程度较高;中国传统村落的椭圆面积最小,分布范围最小,空间上更为集中。少数民族特色村寨的标准差椭圆呈现明显的向西扩展的态势,覆盖了中国西南地区。椭圆的长轴表征着特色乡村分布方向,国家森林乡村和中国少数民族特色村寨整体呈东北—西南方向分布,全国乡村旅游重点村则整体呈现东西走向分布,长短轴的长度接近,空间分布的方向性和向心力较不明显;中国传统村落椭圆的长轴同样为东北—西南走向,但空间范围更为集中;中国历史文化名村是唯一一个呈现沿西北—东南方向分布的特色乡村。从圆心位置来看,除中国少数民族特色村寨的椭圆圆心位于重庆市外,其余4类特色乡村的椭圆圆心均位于华中地区,这与特色乡村集聚区分布基本一致。
3.2 中国特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价
3.2.1 影响因子识别
区域一定范围内特色乡村核密度大小反映了区域整体特色乡村建设条件和发展水平。因此,提取每个特色乡村所在区域核密度值作为因变量,将表2中的X1~X12因子作为自变量,自变量分类处理成类型量,采用地理探测器识别因子关联性和作用强度,各因子分层异质性q值介于0.01~0.14之间,均通过显著性检验(表3);其中,县域城镇化率、年均降水量、人口密度和旅游产业规模指数的影响显著(q ≥ 0.10)。城镇化率较高的县域乡村旅游需求往往较大,乡村旅游设施建设水平一般也较高;降水是乡村耕作和发展的基础,南北降水的差异造成中国特色乡村“南多北少、东聚西散”的格局;人口是经济社会发展的第一要素,在驱动特色乡村发展的同时,为特色乡村旅游发展提供了重要市场;旅游产业规模指数越高,地区旅游接待水平和服务能力也越高,为特色乡村旅游发展提供了良好的支撑条件。各因子对特色乡村形成和发展具有明显的差异化作用,而双因子共同作用明显强于单因子,如人口密度与县域城镇化率以及年均降水量与坡度的两两共同作用的q值分别达到0.21和0.19,远高于各单因子的作用大小,说明特色乡村是多重因子交互作用的综合结果。
表3 中国特色乡村分布的交互作用因子探测
Tab. 3
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.17 |
| X2 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.26 | |
| X3 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.17 | ||
| X4 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.17 | |||
| X5 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.12 | ||||
| X6 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.23 | |||||
| X7 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.11 | ||||||
| X8 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.12 | |||||||
| X9 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.32 | ||||||||
| X10 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 | |||||||||
| X11 | 0.07 | 0.18 | ||||||||||
| X12 | 0.10 |
注:深灰色为双因子增强,浅灰色为非线性增强,所有因子在1%水平上显著。
3.2.2 乡村旅游发展潜力
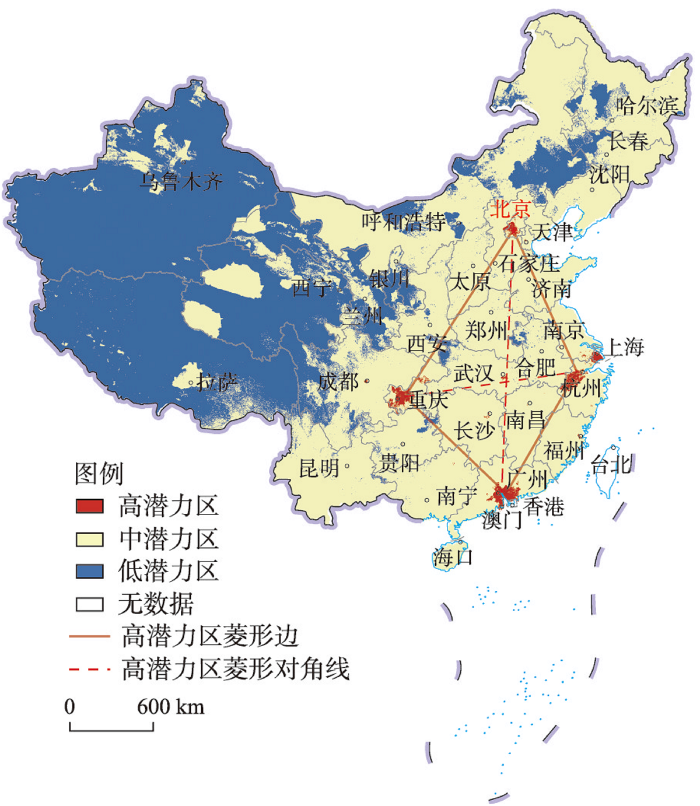
基于地理探测器的因子探测结果,选取q ≥ 0.05的因子,并将其q值归一化作为确定指标权重的基础,最终确定特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价的8个因子及其权重值,即日照(0.066)、年均降水量(0.175)、坡度(0.095)、NDVI(0.085)、人口密度(0.162)、县域城镇化率(0.194)、旅游设施POI密度(0.089)和旅游产业规模指数(0.134),根据式(8)计算潜力值。中国特色乡村旅游发展潜力值介于0.09~0.75之间,采用等分法将全国划分为特色乡村建设低潜力区(0.09~0.31)、中潜力区(0.32~0.53)、高潜力区(0.54~0.75),该分类方法具有简单、直观和容易理解的特点,其分类结果很好地体现了3类潜力的地域分异,整体形成高潜力点状集聚、中低潜力连片分布特征(图5),与已有特色乡村分布格局基本一致。高潜力区形成以长三角城市群、京津冀城市群、粤港澳大湾区以及成渝城市群的中心城市为战略支点的菱形分布格局,有效体现了大城市周边巨大的乡村旅游市场需求和地域丰富的特色乡村旅游资源供给。中潜力区基本覆盖了东中部大片范围及西部部分区域,东中部良好的自然地理环境和经济发展水平为区内特色乡村发展创造了条件,西部巴音郭楞蒙古自治州、拉萨市、格尔木市和内蒙古自治区等地,因独特的地方文化与自然景观而具有一定的特色乡村建设潜力。低潜力区在西部地区集中连片分布,这与区内相对恶劣的自然地理环境直接相关。由此可见,评价结果既能反映现有特色乡村旅游发展水平,又能有效识别具有高潜力特色乡村旅游发展潜力的重点区域,能够为区域层面的特色乡村统筹规划提供依据,一定程度上验证了本文特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价方法的有效性。
图5
图5
中国特色乡村旅游发展潜力图
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 5
Tourism development potential of characteristic villages in China
3.3 中国特色乡村旅游空间协同分区优化
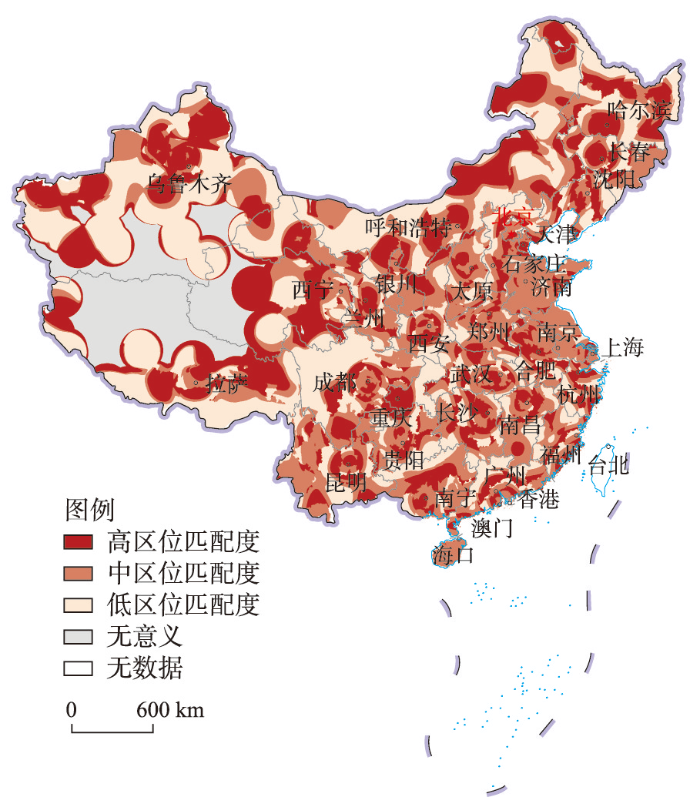
3.3.1 特色乡村与旅游配套设施的区位匹配度
图6
图6
中国特色乡村与旅游配套设施的区位匹配度分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 6
Location matching degree distribution between characteristic villages and tourism facilities in China
与中国特色乡村分布相比,3类区位匹配度在全国的空间分布较为离散化,尤以高区位匹配度的分布更为明显,说明一些区域特色乡村分布与旅游配套设施的不匹配状态。整体而言,广西壮族自治区、湖南省和贵州省等省份分布着大量的特色乡村,但与之相关的旅游配套设施需要加强;而西部青海省、西藏自治区和新疆维吾尔自治区等地的高区位匹配度更多偏向一种低水平的高匹配,即特色乡村和旅游配套设施分布均较稀疏,但两者之间有较好的一致性,能够满足低密度乡村旅游的供需匹配需求。
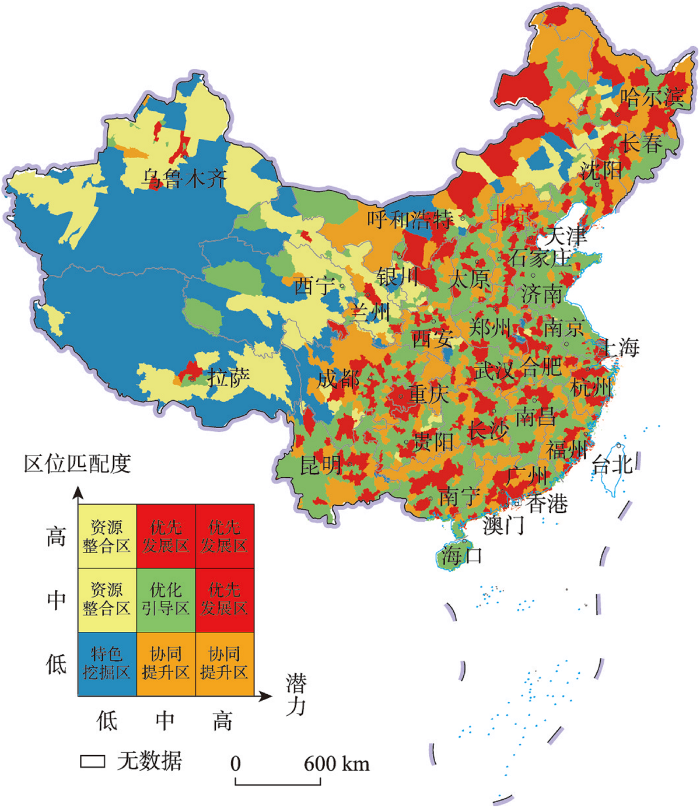
3.3.2 特色乡村旅游空间协同优化分区
图7
图7
中国特色乡村旅游空间协同优化分区图
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站 GS(2019)1815号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 7
Coordinated optimization zoning of tourism space of characteristic villages in China
表4 中国特色乡村旅游空间分区特征与优化方向
Tab. 4
| 类型 | 空间分布 | 主要特征 | 限制因素 | 优化方向与路径 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优先发展区 | 主要分布于直辖市、省会城市周边以及东北和西南地区乡村资源丰富的区域 | 自然地理环境优越、县域经济支撑力强、乡村旅游规模化和产业化程度高、乡村旅游配套设施完善 | 乡村旅游同质化竞争明显 | 方向:差异化与精品化发展 路径:因地制宜实施特色乡村旅游精品工程,以全国乡村旅游重点村为抓手,打造深度体验乡村旅游产品;以乡村民宿体验为核心,提供多样化配套服务和差异化旅游产品;搭建跨区域旅游协作平台,推进特色乡村旅游精品路线建设 |
| 特色挖掘区 | 集中分布于新疆维吾尔自治区、西藏自治区和青海省等地 | 乡村地域地理环境特色鲜明、乡村特色文化元素丰富 | 可达性不高、乡村旅游配套设施薄弱 | 方向:品牌化与特色化挖掘 路径:大力支持发展戈壁农业、山地康养、沙漠越野等西部特色乡村旅游项目,构建全方位、多层次的特色乡村旅游品牌体系;充分挖掘西域文化和藏族文化,增强特色乡村品牌影响力和标识度;完善对外交通和旅游配套设施,加强乡村环境综合整治 |
| 资源整合区 | “胡焕庸线”东南侧零散分布,西北侧相对集聚分布 | 自然条件差异性较大、乡村旅游配套设施相对较完善 | 乡村旅游资源分割零散、县域经济支撑不足 | 方向:融合化与市场化运作 路径:整合区内特色乡村文旅资源,以县域为单元,将农业、文化、康养等元素进行深度融合包装;招商引资,通过市场化运作,促进特色乡村文化和休闲旅游深度融合 |
| 协同提升区 | 主要分布于东中部和“胡焕庸线”沿线地区 | 特色乡村集聚程度较高、自然地理环境优越 | 协同效应不明显、乡村旅游市场竞争大 | 方向:协同化与均等化服务 路径:发挥区内特色乡村协同效应,串珠成链,打通特色乡村旅游关键节点和廊道,打造“特色旅游点”和“流动风景线”;构建优质均衡的旅游供给体系,建设1~2 h特色乡村自驾旅游圈 |
| 优化引导区 | 主要分布于东中部和西部青海省、内蒙古自治区等地 | 乡村地域文化丰富多元、自然生态环境相对脆弱 | 乡村旅游产品粗放发展、县域经济支撑不力 | 方向:品质化与规范化引导 路径:以红色文化、绿色文化和农耕文化为主线,丰富乡村旅游产品体系,提升旅游体验品质;完善利益联结机制,有序引导集中连片特困区村集体和村民入股乡村旅游合作社、旅游企业,实现旅游脱贫致富 |
(1)优先发展区。该区是旅游发展潜力和区位匹配度中一项达到高水平且另一项处于中高水平的区域,主要分布于直辖市、省会城市周边以及东北和西南地区乡村资源丰富的区域。该区是中国美丽乡村建设的前沿阵地,区内乡村旅游市场需求较大,特色乡村类型多样,乡村旅游规模化和产业化程度高,但乡村旅游同质化竞争明显。该区应以差异化与精品化发展为优化方向,因地制宜实施特色乡村旅游精品工程,如北上广大都市周边乡村“微度假”、呼伦贝尔乡村草原生态游、西南村寨少数民族风情游和传统村落文化体验游等[51]。以国家乡村旅游重点村为抓手,打造深度体验乡村旅游产品;以乡村民宿体验为核心,提供多样化配套服务和差异化旅游产品;搭建跨区域旅游协作平台,推进特色乡村旅游精品路线建设。
(2)特色挖掘区。该区是旅游发展潜力和区位匹配度均低的区域,主要分布于西部新疆维吾尔自治区、西藏自治区和青海省等地。区内乡村地域地理环境特色鲜明、乡村特色文化元素丰富,但特色乡村分布稀疏。该区应以品牌化与特色化挖掘为优化方向,在提升对外交通和完善相关旅游配套设施的基础上,充分挖掘区域内独特的自然风貌和风土人情,发展戈壁农业、山地康养、沙漠越野等西部特色乡村旅游项目,构建全方位、多层次的特色乡村旅游品牌体系;充分挖掘西域文化和藏族文化,增强特色乡村品牌影响力和标识度;同时,积极运用云旅游、云直播等多种网络宣传营销渠道,塑造特色乡村旅游品牌,培育西部“网红打卡”乡村旅游目的地。
(3)资源整合区。该区是区位匹配度处于中高水平但旅游发展潜力低的区域,主要分布于西部和东北地区,在“胡焕庸线”东南侧和西北侧分别呈现零散与集聚分布特征。区内自然条件差异性较大、乡村旅游配套设施较完善;但乡村旅游资源分割零散,孤立化发展特征明显。该区应以融合化与市场化运作为优化方向,打破特色乡村旅游资源分割和孤立化发展局面,以县域为单元,整合区内特色乡村文旅资源,将农业、文化、康养等元素进行深度融合包装,如西南地区加大森林乡村建设与民族文化资源的整合[31];借鉴西安市依托华清池骊山大景区和华山风景区的乡村旅游发展模式,将乡村旅游资源融入到周边城市、景区等旅游产品设计中,拓展特色乡村旅游产品供给链;同时加强市场化运作,探索乡村旅游运营体系和模式,促进特色乡村文化和休闲旅游深度融合[52]。
(4)协同提升区。该区是区位匹配度低但旅游发展潜力处于中高水平的区域,空间上多与优先发展区毗邻,主要分布于东中部和“胡焕庸线”沿线地区。区内特色乡村集聚程度较高、自然地理环境相对优越;但相对其丰富的特色乡村资源而言,乡村旅游配套设施供需匹配度有待进一步提升,特色乡村的高密度分布易导致内部恶性竞争。该区应以协同化与均等化服务为优化方向,充分发挥区内不同类型特色乡村空间关联与功能互补优势,形成特色乡村协同化效应,串珠成链、扩线成面,打通特色乡村旅游关键节点和廊道,打造“特色旅游点”和“流动风景线”;同时完善局部旅游配套设施,构建优质均衡的旅游供给体系,建设1~2 h特色乡村自驾旅游圈;加强区内乡村旅游相关从业者职业化教育和培训,综合提升区内乡村旅游软实力。
(5)优化引导区。该区是旅游发展潜力和区位匹配度均处于中水平的区域,主要分布于东中部和西部青海省、内蒙古自治区等地。区内乡村地域文化丰富多元,但大多地区自然生态环境相对脆弱,存在乡村旅游产品粗放发展和县域经济支撑不力的问题。该区东部应以品质化与规范化引导为优化方向,以红色文化、绿色文化和农耕文化为主线,挖掘乡村教育、传承、生态和康养等多功能[53],丰富乡村旅游产品体系,提升旅游体验品质;该区中西部应积极开展资源环境承载力评价和乡村旅游供需评估,科学编制乡村旅游发展规划;同时有序引导社会资本投资,完善利益联结机制,引导集中连片特困区村集体和村民入股乡村旅游合作社、旅游企业,在赋予乡村旅游发展活力的同时,实现旅游扶贫和产业振兴。
4 讨论
中国独特的地理环境、悠久的历史文化和传统农耕文明孕育了大量特色乡村,在快速城镇化的浪潮下,一些特色乡村正面临衰退甚至消亡的困境。当前,国家政府部门出台了多个权威性特色乡村名录,为中国特色乡村保护和历史文化传承创造了良好条件,同时为地区特色乡村旅游发展和产业振兴提供了政策指引。大量研究证实了不同类型特色乡村与旅游发展的相互促进关系,但乡村旅游发展对特色乡村文化和村民生活方式也带来了不可逆转的影响。寻求一种原生态、沉浸式的乡村独特体验是乡村旅游者的最根本动机,当特色乡村失去原真性和本土性,也就失去了核心吸引力和竞争力。如何保护和传承中国特色乡村的原真性与本土性,实现特色乡村转型发展与价值提升,已成为乡村振兴亟待解决的现实问题[54]。在信息化时代,特色乡村建设必然与乡村旅游密不可分,保护和传承是各类特色乡村建设的根本目的,两者缺一不可[55]。相关研究发现中国传统村落分布与贫困村分布存在显著相关性[56],许多特色乡村因为无人问津的原始型保护而陷入发展危机,使得乡村民俗、技艺和文化等面临几乎无人传承的境地。由此可见,为了发展而保护才能真正体现特色乡村建设的核心价值,乡村旅游通过激活地方经济活力为特色乡村保护留住人才和提供资金,从而更好地传承乡村历史文化。但建设特色乡村并不等同于发展乡村旅游,应避免特色乡村建设过程中过度旅游产业化倾向,把握乡村旅游开发的合理度,是真正实现特色乡村保护和传承的关键。惟有保存特色乡村的原真性和乡土性,才能真正实现乡村旅游的可持续性。
本文在甄别特色乡村关键作用因子的基础上,开展中国特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价,这是基于乡村旅游者共性需求的假设,即在不考虑旅游产品供给差异的条件下,理性的乡村旅游者会选择环境适宜、交通便捷和设施完善的乡村旅游目的地。然而,不同类型特色乡村形成机制和旅游吸引力具有明显差异,这种差异性如何更客观地融入到特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价指标体系中,是需要进一步深入探讨的问题。相关研究表明,降水是国家森林乡村、中国传统村落和中国少数民族特色村寨等形成的重要因素[7,31,57],人口和城镇化率等对各类特色乡村空间分布均有重要影响,而旅游产业规模指数与中国乡村旅游重点村分布高度相关[6]。本文识别出县域城镇化率、年均降水量、人口密度和旅游产业规模指数是影响中国特色乡村旅游发展潜力的关键因子,这与已有研究结论基本一致。但特色乡村与旅游产业发展存在互为因果的相互作用,自然因素是孕育特色乡村的基础,社会经济因素是特色乡村发展的保障,特色乡村因资源禀赋的独特性而吸引旅游者,而乡村旅游的兴起又促进了地方旅游产业发展,从而为特色乡村发展创造良好条件。本文立足于既有特色乡村分布格局,挖掘未来特色乡村旅游发展潜力,即在承认自然和社会经济等因素内在动因的基础上,进一步识别与特色乡村旅游发展关联的核心指标。此外,各类特色乡村名录是政策产物,在遴选过程中不可避免存在一定的政策导向,如指标分配和地区倾斜等,对未来特色乡村旅游发展格局会产生不确定性影响。
就全国尺度而言,现有上万个国家级特色乡村基本反映了中国乡村地域自然与人文要素的分异特征,塑造了中国乡村旅游的基本格局。但除了本文研究的5类国家级特色乡村外,还存在地方遴选的各类特色乡村,以及大量正通过全域国土空间综合整治与乡村规划发展建设的新兴美丽乡村,这必然对全国乡村旅游格局及其优化重构产生直接影响。本文提出的特色乡村旅游发展潜力评价是基于国家级特色乡村分布格局的演绎推导,其评价结果在一定程度上能够为地方特色乡村建设和管理提供决策参考。但需要说明的是,乡村旅游发展对于交通、餐饮、住宿、购物等具有不同的配置需求,本研究将旅游配套设施作为一个研究主体要素,并未进一步细化讨论各类旅游配套设施的结构配比关系。同时,不同乡村地域存在差异化旅游市场和产品供需关系,如何在顾及地域分异性的基础上精准量化特色乡村的旅游供需关系,是后续研究值得深入探讨的问题。
5 结论
本文在构建5类中国特色乡村基础地理数据库的基础上,运用空间探索性数据空间分析方法探讨了特色乡村数量特征与空间格局,分别运用耦合度模型和地理探测器识别了特色乡村集聚区及旅游发展潜力区,分析了特色乡村与旅游配套设施的区位匹配度,明确了中国特色乡村旅游空间协同优化分区及其优化方向。主要结论包括:
(1)全国特色乡村分布呈现明显的东密西疏特征,在中国第二和第三级阶梯的分界线形成一条鲜明的特色乡村分布带。5类特色乡村之间具有交叉重合特征,以中国传统村落和中国历史文化名村的个体重合度最高。特色乡村集聚区主要位于中国中东部的华北、华东、华中和华南地区,空间上呈现出典型的沿海(东海)、沿江(长江)和沿河(黄河)特征,反映了乡村发展“渔猎为生、逐水而居”的生活方式和空间依赖性。
(2)中国特色乡村的形成和发展是多重因子交互作用的综合结果,其中,县域城镇化率、年均降水量、人口密度和旅游产业规模指数的影响尤为明显。中国特色乡村旅游发展高潜力区形成以长三角城市群、京津冀城市群、粤港澳大湾区以及成渝城市群的中心城市为战略支点的菱形分布格局,有效体现了大城市周边巨大的乡村旅游市场需求和地域丰富的特色乡村旅游资源供给。
(3)基于特色乡村旅游发展潜力和区位匹配度的组合分析,将全国划分为优先发展区、特色挖掘区、资源整合区、协同提升区和优化引导区,为中国特色乡村旅游空间格局优化和协同发展指明方向。优先发展区侧重差异化与精品化发展,特色挖掘区强调品牌化与特色化挖掘,资源整合区突出融合化与市场化运作,协同提升区形成协同化与均等化服务,优化引导区聚焦品质化与规范化引导。
参考文献 (References)
参考文献
Land consolidation and rural vitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810002
[本文引用: 1]

The core objective of rural vitalization is to systemically establish a coupling pattern of various rural development elements including population, land and industry. As one of the prerequisites, land resources is required to be optimally allocated via land consolidation. Consequently, land consolidation contributes greatly in population agglomeration, industry development and resources support under the context of combating rural decline. In light of these facts, this paper conducts an elementary analysis on the connotation of land consolidation and rural vitalization in the new era, as well as their relationships. Furthermore, the issues on the alternative paths for achieving rural vitalization via land consolidation in different regions were also discussed. Main conclusions are drawn as follows: (1) It is manifested that rural vitalization in the new era can be explained as a comprehensive process of tackling the loss and decline of rural development elements through political, economic and cultural means. Most importantly, vitalizing the interior motivation and absorbing the external power are essential for the efficient reconfiguration and utilization of rural population, land and industry, thus achieving the goals of arousing rural vitality, optimizing elements structure, enhancing territorial function and restructuring rural morphology. (2) From the perspective of rural vitalization, land consolidation, which adheres to the path of connotative development, should not only target at stimulating the key elements of rural development, but also place emphasis on the coordination of material space and spirit core, so as to realize the co-prosperity of the urban and the rural areas. (3) Regional natural indigenous factors and the corresponding phases of socio-economic development should be both taken into account in the process of implementing rural land consolidation. Following the principle of adjusting measures to local conditions, appropriate paths or modes are supposed to be chosen in different regions constrained by the territorial development pattern. Finally, focusing on a series of problems and new concepts, which is aimed at achieving urban-rural integration development and boosting socio-economic growth in rural areas, we propose further discussions.
论土地整治与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810002
[本文引用: 1]

乡村振兴的核心目的是系统构建人口、土地、产业等多种发展要素的耦合格局。土地整治在乡村振兴过程中肩负着为人口集聚、产业发展提供资源支撑的基础性作用。本文基于影响乡村发展的关键要素阐释了新时代乡村振兴和土地整治的内涵及其互馈关系,剖析了乡村振兴背景下土地整治的区域实施路径。最后,就未来乡村振兴视角下土地整治的方向进行了展望与讨论。结论如下:① 乡村振兴的内涵在于为应对乡村内部要素的流失与衰退,通过经济、政治及文化建设等手段激发内部动力和吸纳外部资源来重新组合、优化配置和高效利用乡村人口、土地和产业等发展要素,从而优化要素结构、提升地域功能、重塑乡村形态,实现乡村地域经济、社会及生态的全面复兴和城乡融合发展的新格局;② 乡村振兴视角下土地整治要激活乡村人口、土地和产业等关键发展要素,统筹物质空间振兴与精神内核提升;③ 开展农村土地整治要与区域自然本底条件和社会经济发展阶段相适应,按照分区统筹、分类施策的原则在国土空间开发格局的框架下因地制宜地采取相应的模式与路径;④ 未来有必要重塑土地整治的价值取向,在统一空间规划体系下统筹土地整治规划与乡村振兴规划,大力发展土地整治与多功能农业相结合的新模式。
The logic of rural spatial governance and revitalization
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204002
[本文引用: 1]

The rural vitalization in the new era and space development and utilization are closely related. It is meaningful to construct a theoretical system and practical path of rural vitalization based on rural spatial governance. Based on the deconstruction framework of "demand→effect→path→strategy", this paper discusses the internal logic relationship between rural vitalization and spatial governance. The results show the following: (1) The reconstruction of rural value is the key to ensure the realization of rural vitalization; rural spatial governance can be a good way to realize the rights allocation and effective control of rural space; rural spatial governance includes material spatial governance, organization spatial governance, and ownership spatial governance; through spatial governance, the structure and function of physical space can be reconstructed, the organization relationship can be reorganized, and the value distribution can be reshaped. (2) The effect of spatial governance on rural vitalization is presented from the optimization of the urban-rural interaction, as well as the stimulation and strengthening of rural endogenous power, and the capabilities of grassroots organizations. (3) Rural spatial governance is an effective path to implement rural vitalization by promoting the urban-rural integration development, activating rural endogenous development, and ensuring the organizations mechanism. (4) The rural spatial governance system combines "top-down" and "bottom-up" forms to implement rational allocation of spatial development power. The channels, capabilities, and effects of multiple subjects participating in spatial governance will promote the realization of space development and the establishment of a system with equitable rights and interests. The "right-sharing" spatial governance can implement the rural revitalization strategy in urban-rural sharing, subject and regional sharing. In summary, the research will provide references for improving the scientific system of rural spatial governance and implementing the rural revitalization strategy.
论乡村空间治理与乡村振兴战略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204002
[本文引用: 1]

新时期乡村振兴挑战与空间利用问题密不可分,基于空间治理建构乡村振兴的理论体系和实践路径具有现实意义。本文基于“诉求→效应→路径→策略”解构方案,探讨了基于空间治理的乡村振兴可行性和内在逻辑体系。结果表明:① 乡村价值重构是确保乡村振兴目标实现的关键环节,乡村空间管控和发展权利配置可从乡村空间治理寻找突破口;乡村空间治理从物质空间治理、空间组织治理、空间权属治理入手,重构物质空间结构功能,重组空间组织关系,重塑空间价值分配体系;② 空间治理振兴乡村的效应从城乡互动关系优化、乡村内生动力激发、基层组织能力强化等层面加以呈现。③ 乡村空间治理推动城乡融合发展、激活乡村内生发展、保障组织机制,是落实乡村振兴的有效路径。④ “上下结合型”乡村空间治理有利于落实空间开发权利的合理配置;多元主体参与空间治理的渠道、能力与效应,推动空间发展目标落地和公平权益体系建设;“权利共享型”空间治理可在城乡共享、主体共享和区域共享中落实乡村振兴目标。研究结论可为完善乡村空间治理科学体系和落实乡村振兴战略提供参考。
The research framework and prospect of rural revitalization led by rural tourism
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180454
[本文引用: 1]

Socialism with Chinese characteristics has entered the new era. Problems such as unbalanced development between urban and rural and inadequate development in rural areas have become increasingly prominent. The implementation of the rural revitalization strategy is an inevitable requirement for resolving the contradictions between unbalanced and inadequate development and the people's ever-growing needs for a better life. With the rapid advancement of new industrialization and new urbanization, China's rural tourism has entered the era of big tourism instead of small and medium tourism. The development of rural tourism can effectively pursue the development strategy of the country in the new era, promote agricultural quality and efficiency, increase farmers' income, make the countryside prosperous and stable, and speed up the development of urban-rural integration. Therefore, it is an important way to realizing rural revitalization. This paper has reviewed the related research on rural revitalization led by rural tourism at home and abroad. In addition, it has grasped the new characteristics, new missions and new requirements of rural tourism development in the new era. Considering the basic situation of China as a developing economic power, and a large agricultural country with a large population, this paper has constructed a research framework of rural revitalization led by rural tourism in China in the new era, which integrates theories of geography, tourism, economics, sociology, management and other related disciplines. It has summarized the five key research contents of rural revitalization led by rural tourism, which contains study on theory and logic mechanism of rural revitalization led by rural tourism, study on the path of rural economy revitalization led by rural tourism, study on the path of rural ecological livability led by rural tourism, study on the path of reconstruction of rural governance system led by rural tourism and study on the policy system of rural revitalization led by rural tourism. The five key research contents cover the theoretical, practical and safeguard aspects, promote the development of urban-rural integration through interconnection, mutual influence and interaction, and ultimately realize the scientific, sustained, and healthy development of the rural revitalization strategy. In the new era, the key of rural revitalization led by rural tourism is to master and apply scientific methodology, to learn the wisdom and nutrition of scientific methodology, to construct a method system for multi-method comprehensive integration, and to ensure the authenticity of data collection and the scientificalness of data processing.
乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的研究框架与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180454
[本文引用: 1]

中国特色社会主义进入新时代,城乡发展不平衡、乡村发展不充分等问题日益突出,实施乡村振兴战略是解决人民日益增长的美好生活需要和不平衡不充分的发展之间矛盾的必然要求。发展乡村旅游能够有力地契合和服务新时代国家发展战略,促进农业提质增效、农民增收致富、农村繁荣稳定,加快统筹城乡融合发展步伐,是实现乡村振兴的重要途径。系统梳理国内外乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的相关研究成果,针对内容深度相对薄弱、功能拓展比较泛化、时代特征不够显著等问题,把握新时代乡村旅游发展的新特点、新使命、新要求,充分考虑中国是一个发展中的经济大国、人口大国、农业大国的基本国情,构建了融合地理学、旅游学、经济学、社会学、管理学等相关学科理论的新时代中国乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的研究框架,归纳了乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的五个重点研究内容,即乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的学理和逻辑机理研究、乡村旅游引导乡村经济振兴的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村生态宜居的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村治理体系重构的路径研究、乡村旅游引导乡村振兴的政策体系研究。五个重点研究内容包括理论层面、实践层面和保障层面,在相互联系、相互影响、相互作用中共同促进城乡融合发展,实现乡村振兴的科学、持续、健康发展。掌握和运用科学的方法论,汲取科学方法论的智慧和营养,构建多方法综合集成的方法体系,确保数据采集的真实性和数据处理的科学性,是新时代乡村旅游引导乡村振兴研究的关键。
Construction and empirical research on the evaluation system of sustainable development of Chinese traditional villages
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202104010
[本文引用: 1]

As important carriers of Chinese civilization, traditional villages are endowed with rich and diversified values. Although the government and academia have implemented lots of programmes on protections and researches, the sustainable development still has a long way to go. Therefore, it is of profound significance to establish an evaluation system for the sustainable development of Chinese traditional villages and to evaluate the sustainable development level of Chinese traditional villages. Through long-term field survey of traditional villages, this study proposes that understanding the two basic attributes of community and heritage is the key to cognizing the sustainable development of traditional villages. Then it uses the analytic hierarchy process and Delphi method to construct the index system of community development subsystem and heritage protection subsystem, and applies an expert judgment matrix and the Delphi method to determine the index weights of the subsystems at all levels, and constructs the systems of data collection, assignment, and standardization for each secondary index. The comprehensive evaluation index is used to evaluate the development level of traditional villages, and determine the criteria for ranking. In order to better evaluate the sustainable development level of traditional Chinese villages, a coupling coordination model is further introduced to construct an evaluation system. Finally, through the evaluation of 10 traditional Lingnan villages in Guangzhou, Foshan and Zhongshan cities of Guangdong province, the validity of the index system is verified and further revised. This index system can not only promote the research paradigm of traditional villages, coupling degree and sustainable development assessment, but also widely guide and apply to the protection practices of traditional villages in China.
中国传统村落可持续发展评价体系构建与实证
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202104010
[本文引用: 1]

作为中华文明重要载体的传统村落具有丰富多元的价值,虽然政府与学界进行了大量保护与研究工作,但其可持续发展之路仍任重道远。因此建立中国传统村落可持续发展评价体系,准确评估其可持续发展水平具有重要理论与现实意义。通过对传统村落的长期实地调研,本文提出社区和遗产两个基本属性间协调关系是传统村落可持续发展的关键。本文使用层次分析法和德尔菲法构建社区发展和遗产保护子系统指标体系,采用专家判断矩阵和德尔菲法确定子系统指标权重,并构建详细的数据收集、赋分与标准化方法。为了更好的评价中国传统村落可持续发展水平,在采用综合评价指数评估传统村落综合发展水平的基础上,进一步引入耦合协调度模型构建可持续发展类型评价体系。最后,通过测评广东省广州市、佛山市和中山市10个岭南传统村落,检验该套指标体系具有较好效度,并进一步对指标体系进行修正。该评价体系不仅可以推进传统村落、耦合度、可持续发展评估研究范式,也可以广泛指导与应用于中国传统村落保护实践。
Multi-scale differentiation characteristics and optimization zones of forest villages in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210627
[本文引用: 1]

National forest villages construction is an important path to promote the implementation of rural revitalization strategy and the improvement of rural living environment; however, the differentiation characteristics of forest villages at different scales and the optimization directions at the national scale are unclear. This study analyzed the characteristics in spatial pattern, quantitative scale, and internal differentiation of forest villages at national, regional, and administrative scales by using the kernel density estimation, the Lorenz curve, and the Theil index. The coupling degree between forest villages and population, and the spatial accessibility of forest villages were explored based on the coupling model and the Voronoi diagram, which provided important information for optimization zones of forest villages. The results showed that the density of forest villages in China has obvious differentiation characteristics of high density in the east and low density in the west, and the Yangtze River Delta is the largest contiguous area with high density of forest villages. There was a significant difference of provincial Theil index of forest villages based on county units. The distribution of forest villages was relatively balanced in the southeast region, whereas the difference was great in the southwest and northeast regions. Xinjiang, Tibet, Qinghai, and the three provinces of northeast China had high Theil index values, and the forest villages in these regions showed typical characteristics of small agglomeration and large dispersion. The spatial accessibility of forest villages had a high spatial correlation with the Hu Huanyong Line (hereafter Hu Line), presenting a pattern of high in the east and low in the west bounded by the Hu Line. Although the distribution of forest villages and population density showed a similar pattern of high in the east and low in the west, the spatial heterogeneity of the coupling degrees between east and west was obviously stronger. The paper divided the whole country into five types, namely, key development areas, characteristic mining areas, agglomeration and upgrading areas, moderate guidance areas, and functional transformation areas, based on the combination analysis between coupling degree and spatial accessibility. The key optimization directions of different zones were proposed. The results would provide valuable information for the construction of national forest villages and the optimization paths under the rural revitalization strategy in China.
中国森林乡村的多尺度分异特征与分区优化
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210627
[本文引用: 1]

国家森林乡村建设是实施乡村振兴战略和改善农村人居环境的重要措施,但森林乡村在不同尺度的分异特征及优化方向尚不明晰。本文综合运用探索性空间数据分析、耦合度模型和Voronoi图分析等研究方法,从全国、区域和行政尺度分析了国家森林乡村空间格局、数量规模和内部分异特征,并基于森林乡村与人口耦合关系及乡村可达类型识别,分析了全国森林乡村的分区格局及其优化方向。结果表明:全国森林乡村密度具有明显的东高西低分异特征,长江三角洲地区是森林乡村高密度集中分布最大的连片区。基于县域单元的省域森林乡村泰尔指数差异较大,东南区域森林乡村分布相对均衡,西南和东北区域内部差异显著。森林乡村空间可达性呈现自东向西的梯度递减,森林乡村与人口密度的耦合类型分布具有较强的内部分异性。文章基于森林乡村可达类型与耦合分区的组合分析,将全国划分为重点发展区、特色挖掘区、集聚提升区、适度引导区和功能转型区五类,明确了不同类型区森林乡村建设的重点方向,将为面向乡村振兴的全国森林乡村建设与分区优化提供决策依据。
Characteristics and influencing factors of the key villages of rural tourism in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204009
[本文引用: 3]

The key villages of rural tourism are typical demonstrations for promoting the high-quality development of rural tourism, which are of great significance for optimizing rural tourism supply and leading rural tourism development. The article analyzes the spatial distribution pattern and structural characteristics of 1000 key villages of rural tourism nationwide by using Nearest Neighbor Index and Kernel Density Estimation. The study further reveals spatial differentiation of the key villages of rural tourism. The main factors affecting spatial distribution of the key villages of rural tourism are analyzed by using Multiple Linear Regression, Vector Buffer Analysis and Geographic Detectors. The conclusions can be drawn as follows. Firstly, there are more key villages of rural tourism in the eastern region than in the western region of China. The inter-provincial spatial density stratification feature is obvious and the spatial distribution pattern of double core-ring core cluster-ribbon zone is unique. Secondly, the spatial distribution of key villages of rural tourism has significant positive spatial correlation. The key villages of rural tourism are spatially dispersed in cold spots and concentrated in hot spots. Thirdly, kernel density estimation shows that villages of agricultural production type have high spatial distribution density, while the others have low density. Fourthly, the spatial distribution pattern is the result of five factors: natural ecology, social economy, transportation facilities, scenic resources and policy environment. Gross domestic product per capita and household consumption expenditure have a significant positive impact, while the distance from the tourist market and the distance from transportation access are negative influencing factors. Fifthly, the driving factors for the spatial distribution of various types of villages are different and closely related to the village resource endowment and development characteristics.
中国乡村旅游重点村的空间特征与影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204009
[本文引用: 3]

乡村旅游重点村是推进乡村旅游高质量发展的典型示范,对优化乡村旅游供给、引领乡村旅游发展具有重要意义。本文运用最邻近指数、核密度估计等方法分析了中国1000个乡村旅游重点村的空间分布格局和结构特征,揭示了乡村旅游重点村的空间分异规律。运用多元线性回归、矢量缓冲分析、地理探测器等方法剖析了影响乡村旅游重点村空间分布的主要因素。研究发现:① 乡村旅游重点村总体呈“东多西少”的空间分布格局。省际空间密度分层特征明显,“双核心—环核群—带状区”的空间分布规律突出。② 乡村旅游重点村的空间分布具有显著的空间正相关性,地域间呈冷点分散、热点集中的空间分异格局。③ 6类乡村旅游重点村的核密度呈一高五低、分异鲜明的类型特征。④ 乡村旅游重点村空间分布格局的形成是自然生态、社会经济、交通配套、景区资源、政策环境五大因素共同影响的结果。人均GDP和居民消费支出具有显著正向影响,客源市场距离及交通通达距离是负向影响因素。⑤ 各类乡村旅游重点村空间分布的驱动因素各异,与村落资源禀赋和发展特点具有密切关系。
Spatial heterogeneity and the influencing factors of ethnic villages in China
中国少数民族特色村寨空间异质性特征及其影响因素
Temporal-spatial distribution and formation of historic and cultural villages in China
The ancient village possesses unique regional characteristics, integrated building structure, abundant material and intangible cultural heritage, and more importantly, they are still be used today. The rapid development of urbanization brings chances for the ancient villages and also deeply affects transformation of social economic structures of ancient villages. The thesis selects some representative old villages—historical cultural villages to analyze the balanced degree of spatial distribution of ancient villages, then discusses the influencing factors and finally puts forwards strategies to keep spatial balance of ancient villages and further lead simultaneous development of all the old villages in order to promote the progress of urban and rural integration. The study shows: (1) Chinese historic cultural villages have different characteristics in spatial distribution, spatial form, river system distribution, regional culture and transportation system. The majority of these villages are distributed along the river and are cultural centers, traffic hubs and birthplace of civilization in history; the villages form three centers, three sub-centers and four transition diffusion areas, and cultivate six cultural centers. (2) Chinese historic cultural villages mainly built in the Tang, Song, Ming and Qing dynasties, have a long history. Among the villages, the Ming Dynasty dominates the number and spatial distribution. (3) The reasons for their spatial uneven distribution include the resource endowment, limited selection criteria, economic development level and regional policy making.
中国历史文化名村的时空分布特征及成因
古村落是具有文化遗产性质的乡村聚落,选取古村落发展中最具代表性的国家级历史文化名村来分析中国古村落的空间分布特征,探讨其影响因素和分布原因,从而进一步引导中国乡村地区的同步发展,促进城乡一体化进程。研究表明:① 我国历史文化名村主要沿河流分布、多是历史上的经济文化中心、交通要塞和文明的发祥地,并形成了3 大集中区、3 大相对集中区和4 大过渡扩散区,孕育了6 个文化区;② 中国历史文化名村建造时间跨度较大,但多集中在唐宋明清4 个朝代,明朝保留下来的古村落最多,分布范围最广;③ 造成中国历史文化名村分布不均衡的主要原因有资源禀赋特点、评定标准的局限、依托腹地的经济发达程度和区域政策导向。
Construction on evaluation system of sustainable development for rural tourism destinations based on rural revitalization strategy
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020201226
[本文引用: 1]

Rural tourism has become a dazzling focus and breakthrough point in the rural revitalization strategy. Constructing a sustainable development evaluation system for mesoscale rural tourism destinations is of great significance and value. The evaluation system needs to take into consideration both the standards and the flexibility, the theory and the practice. This study uses the "attributive analysis and system integration" logical framework to construct a sustainable development evaluation system for rural tourism destinations based on the rural revitalization strategy and long-term tracking of rural tourism destinations in multiple regions. First, the essence of rural tourism destinations is broken down into three basic attributes: community, heritage, and tourism industry, which are corresponding to the subsystems of community development, heritage protection, and tourism development, respectively. The focus of this study is to construct the tourism development subsystem, while the community development and heritage protection subsystems have been built in a previous study. Based on the tourism geographic system model, the tourism development subsystem is involving four primary indicators, namely the destination system, the source market system, the tourism channel system, and the tourism support system. The analytic hierarchy process, the Delphi method, and the expert judgment matrix are used to make a scientific indicator system, including 31 secondary indicators that focus on rural scale with strong operability. Furthermore, through the integration of basic attributes and the use of the coupling coordination model, the comprehensive evaluation index and coordinated development degree are used to evaluate the sustainable development level of rural tourism destinations. Finally, through the evaluation of 10 rural tourism destinations in Guangzhou, Foshan, and Zhongshan in Guangdong Province, we confirmed that the evaluation system had good reliability, validity, and explanatory power. The sustainable development evaluation system of rural tourism destinations constructed by this research integrates rural revitalization strategy, tourism system theory, and heritage protection policy. It can not only effectively evaluate the sustainable development level of one rural tourism destination both from the whole system or different subsystems, but also assess the level of several villages of different types in different periods, which can enable time-space tracking and comparative research from the micro to the macro, and from static to dynamic perspective.
基于乡村振兴战略的乡村旅游地可持续发展评价体系构建
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020201226
[本文引用: 1]

乡村旅游已成为乡村振兴战略中耀眼的着力点和突破点,因此构建兼顾标准性和灵活性、理论性和实践性的中观尺度乡村旅游地可持续发展评价体系具有重要意义。本研究使用“属性解析-系统整合”逻辑框架构建基于乡村振兴战略的乡村旅游地可持续发展评价体系。首先,将乡村旅游地解析出社区、遗产和旅游3个基本属性,分别对应社区发展、遗产保护和旅游发展子系统。依据旅游系统模型,采用层次分析法、德尔菲法和专家判断矩阵,重点构建旅游发展子系统指标体系,涵盖目的地、客源市场、旅游通道和旅游支持系统4个一级指标和具有较强操作性、聚焦乡村尺度的31个二级指标。进而,将子系统整合并引入耦合协调发展模型,使用综合评价指数和协调发展度进行乡村旅游地可持续发展水平评价。最后,通过测评广东10个乡村旅游地,验证该体系具有较好效度和区分度。
Hybridity: Rethinking rurality
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710005
[本文引用: 1]

Rurality has always been a central topic of rural studies in the West. Discussions on its definitions have been quite complex, contested and even ambivalent, reflecting recent dramatic changes occurring in rural economies, politics and social cultures. In tradition, rurality has been regarded as a given nature that is self-evident, generalized and one-dimensional. However, with the post-modern transformation of social realities and academic trends, the concept of rurality now focuses on dynamic processes through which diversified and heterogeneous meanings are produced and reproduced. Many scholars have called for a 'post-rural' context from which to understand rural reconstruction in a new era. Just as 'post-modernity' refers to the reflexivity of modernity, the concept of the 'post-rural' has been advanced not to partition phases of rural development, but to realize the reflexive turn occurring in rural studies. The 'post-rural' can be regarded as a 'complex', as multiple actors, events, discourses and practices co-exist and interplay. Hybridity refers to a process of recreation based on the integration of heterogeneous elements together with the elimination of borders between systems. Thus, hybridity is considered to be one of the most useful theoretical perspectives for understanding the essence of rurality in an increasingly complex context. Hence, based on interpretations and analyses of previous literature of the West, this paper proposes a framework on hybridity in 'post-rural' settings based on the following three aspects: (1) hybridity produced by human and non-human actors and trends of rematerialization emphasizing performances and practices in post-rural everyday life; (2) hybridity embedded in fluid networks and relations and dialectical relationships between rurality, globality, and urbanity; (3) hybridity stimulated through rural area's integration into processes of modernization and processes of negotiation occurring between the de-alienation of traditional local cultures and the alienation of modernity. Finally, considering the particularities of the context of rural China, this paper discusses ways in which the perspective of hybridity offers new insights into the studies and practices of Chinese rural reconstruction.
混杂性:关于乡村性的再认识
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201710005
[本文引用: 1]

乡村性一直是西方乡村地理研究的核心。传统认识中的乡村性被认为是一种乡村本身既有的平面化和单向度的性质。然而,在社会现实和学术思潮的后现代转向下,乡村性被置于“后乡村”的语境中进行重新理解,强调了一种多元化和异质性意义上的不断生产和再生产的动态过程。当今,“后乡村”的重构牵涉多元主体、跨越多重尺度、交织流动关系,镶嵌于混杂的过程、话语和实践之中,“混杂性”成为理解日益复杂的乡村性的有益视角。从主体混杂与再物质化、网络混杂与关系乡村、意义混杂与融入现代性三个方面,对近年西方研究关于“后乡村”的混杂性视角进行系统评述,重新解读有关乡村性的认识,并探讨其对国内乡村研究的启示。
Rurality and rural tourism development in China
DOI:10.1016/j.tmp.2019.02.006 [本文引用: 1]
Navigating the early stages of a large sustainability-oriented rural tourism development project: Lessons from Træna, Norway
Rural tourism activities in mass tourism destinations: Residents vs non-residents perspectives
DOI:10.1108/TR-05-2022-0225
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper aims to examine rural tourism preferences as an alternative niche market to mass tourism destinations. The analysis discusses the differences in perceptions and willingness to pay (WTP) for various packages of rural tourism activities in Gran Canaria Island among residents and non-residents.
Experiencing agricultural failure: Internal migration, tourism and local perceptions of regional change in the Yucatan
DOI:10.1016/j.geoforum.2010.03.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Contested rural landscapes: Contemporary entanglements of tourism and farming
Not only tourism: Unravelling suburbanization, second-home expansion and "rural" sprawl in Catalonia, Spain
DOI:10.1080/02723638.2015.1113806 URL [本文引用: 1]
Limits to mass tourism's effects in rural peripheries
DOI:10.1016/j.annals.2014.11.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
Tourism wetlands and rural sustainable livelihood: The case from Iran
Process, characteristics and mechanism of spatial transformation in traditional villages from the perspective of spatial production: A case study of Maihuayucun village in Huangshan city
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003425
[本文引用: 1]

Traditional villages are the best witness of the process of agriculture civilization, with rich material and intangible culture heritage. However, under the influence of rapid urbanization, industrialization and globalization, the development of traditional villages is faced with dilemmas such as the decline of material space, the inactivation of cultural space and the hollowing of social space. Scientifically guiding the function renewal and spatial adaptive transformation of traditional villages is not only the practical needs of their protection and development, but also an important topic of rural development and planning research in China. Taking the national traditional village Maihuayucun Village in Huangshan City as an example, on the basis of field investigation, combined with the relevant literature review, and based on the perspective of "ternary dialectics" of space production, this paper analyzes the spatial transformation process, characteristics and driving mechanism of traditional villages from the three dimensions of material space, social space and institutional space. The results show that: (1) Since the reform and opening up, Maihuayucun Village has gradually evolved from a traditional agricultural village to an industrial village characterized with bonsai industry, which has experienced three stages: endogenous slow transformation and development, exogenous space rapid expansion and orderly space quality improvement. (2) The spatial transformation of traditional villages is characterized by the functional differentiation and remodeling of material space, the disintegration and reconstruction of social space, and the gradual improvement of institutional space. The space function has gradually changed from the traditional production and living function to multiple composite functions such as ecological leisure, characteristic bonsai planting, commercial operation and service, and cultural inheritance and display. The livelihood of villagers has been diversified, from the traditional single agricultural planting industry to the diversified livelihood methods such as bonsai management, farmhouse entertainment, and tourism services, and the social relations have changed from closed tradition to open and modern. And the subject of institutional space has changed from the dual subject of village committee and villagers to the multiple subject of government, village committee, villagers, capital and tourists. (3) The changes of social relations, capital investment and power intervention are the main driving forces for the spatial production of Maihuayucun Village. The three forces interact and promote the interactive evolution of social space, material space and institutional space, and jointly promote the spatial transformation. With the disintegration of traditional agricultural economy and the growth of bonsai industry, the growing demand for production and residence of villagers has promoted the continuous expansion and transformation of village material space. Driven by bonsai industry and rural tourism, the exogenous construction of villages has developed rapidly, and the support of a large amount of external capital has provided a strong driving force for the spatial transformation of villages. A series of rural development policies and measures issued by the state, especially the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy, provide strategic guidance and policy guarantee for the protection, development and spatial transformation of traditional villages. In the context of rural revitalization and integrated rural and urban development in the new era, and the increasingly complex relationship between man and land in rural areas, it is particularly important to explore the differentiated and distinctive path of China's rural transformation and development. And the research on the temporal and spatial characteristics and mechanism of rural spatial transformation of different types and different spatial scales needs to be further broken through. This paper can provide reference for relevant researches in terms of research perspective, research ideas and research spatial scale, and provide guidance for the protection, development and planning of traditional villages
空间生产视角下的传统村落空间转型过程、特征与机制: 以黄山市卖花渔村为例
DOI:10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003425
[本文引用: 1]

基于空间生产的“三元辩证法”视角,以黄山市歙县卖花渔村为例,从物质空间、社会空间和制度空间3个维度分析传统村落空间转型过程、特征及驱动机制。结果表明:1)改革开放以来卖花渔村空间转型经历了内生性缓慢转型发展、外源性空间快速扩展、有序化空间品质提升3个阶段。2)随着盆景产业复兴和乡村旅游业兴起,传统村落物质空间分化重塑、社会空间解体重构、制度空间日趋完善,呈现出空间功能复合化、社会关系开放化、空间主体多元化的空间转型特征。3)在社会关系变迁、资本投入、权力干预等共同作用下,社会空间、物质空间及制度空间互动演进,共同推动了传统村落空间转型过程。
The organic renewal of the human settlement environment in traditional villages: Theoretical cognition and practical path
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210368
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of new urbanization, the human settlement environment in Chinese traditional villages is facing a rigorous crisis of the human-land relationship, and the organic renewal of it is particularly important. Based on the scientific connotation of the organic renewal and the evolution characteristics of the human settlement environment in Chinese traditional villages, this paper analyzed the theoretical cognition of the organic renewal of the human settlement environment in traditional villages, and constructed the path mechanism of the organic renewal of the human settlement environment in traditional villages on this basis. The results show that: (1) By summarizing the problems faced by the human settlement environment in traditional villages, the dilemma is classified as material space, cultural space and social space, and the theoretical cognition of the organic renewal is proposed with living-production-ecological space as the spatial carrier, the landscape gene as the cultural core, and the social field as the basic context. (2) Focusing on the renewal and optimization of material space, cultural space and social space, the three-dimensional path mechanism of "material-culture-society" for the organic renewal of the human settlement environment in traditional villages is constructed, including the renewal of the material space: the optimization of dominant functions and the reshaping of living-production-ecological space; the renewal of the cultural space: the repair of recessive genes and the repair of dominant genes; the renewal of the social space: the darning of relationship networks and the reconstruction of social order. In order to realize the sustainable development of the human settlement environment in traditional villages, the theoretical cognition and practical path of the organic renewal are discussed in depth, and have been established as a "multi-dimensional optimization, and multi-objective overall planning" mechanism, to provide scientific and practical reference for the organic renewal of the human settlement environment in Chinese traditional villages.
传统村落人居环境有机更新: 理论认知与实践路径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210368
[本文引用: 1]

新型城镇化背景下,中国传统村落人居环境面临着严重的人地关系危机,对其进行有机更新显得尤为重要。立足于有机更新的科学内涵及传统村落人居环境系统的演变特征,辨析了传统村落人居环境有机更新的理论认知,进而构建了传统村落人居环境有机更新的路径机制。研究结果表明:① 将传统村落人居环境系统的问题困境归类为物质空间、文化空间与社会空间,提出以三生空间为空间载体、景观基因为文化核心、社会场域为基础脉络的传统村落人居环境有机更新理论认知。② 以更新优化物质空间、文化空间与社会空间为着力点,构建了传统村落人居环境有机更新“物质-文化-社会”三维路径机制,包括物质空间更新:主导功能优化与三生空间重塑;文化空间更新:隐性基因修复与显性基因修补;社会空间更新:关系网络织补与社会秩序重构。以实现传统村落人居环境可持续发展为目标,通过建立“多维度优化-多目标统筹”的传统村落人居环境有机更新理论与路径,以期为中国传统村落人居环境有机更新提供科学参考与实践借鉴。
Tourism development and local borders in ancient villages in China
Revitalizing traditional villages through rural tourism: A case study of Yuanjia village, Shaanxi province, China
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2017.04.003 URL [本文引用: 1]
Two activities about village cultural landscape's conservation and sustainable development: Analyzing eco-museum and rural tourism
村落文化景观保护与可持续发展的两种实践: 解读生态博物馆和乡村旅游
Traditional village forest landscapes: Tourists' attitudes and preferences for conservation
DOI:10.1016/j.tourman.2016.09.007 URL [本文引用: 1]
Knowledge map analysis of traditional village landscape research in China
中国传统村落景观研究的知识图谱分析
Recognition of sacred space form, contemporary value and research paradigm of traditional villages
传统村落神圣空间形态、当代价值及其研究范式再认识
Spatial strategy for development of large-scale rural area in cultural context: Based on the development plan for featured rural area of southern Taihu in Huzhou
基于文脉的大尺度乡村地区发展空间对策研究: 以湖州市南太湖特色村庄带发展规划为例
The spatial patterns, generative mechanism and protective strategies of Tibetan village names: A case study in Gannan Tibetan autonomous prefecture
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180465
[本文引用: 1]

Place names refer to proper terms of both physical and human geographic entities in certain spaces. Village names, as an important part of cultural landscape, are carriers of multicultural information and collective memories. The research on the spatial patterns, generative mechanism and protective strategies of village names is of profound significance to inheritance of native culture. Taking villages in Xiahe county, Gannan Tibetan autonomous prefecture as examples and applying to GIS kernel density estimation, this paper describes the spatial patterns of Tibetan village names and interprets their classification and generative mechanism from the perspective of culture landscape. The research suggests the three categories constitute the basic paradigm of Tibetan village name system, with the names of nature as the major part, the names of culture as the minor part and the names of mixed mode as supplements, which reflects some essential features of cultural landscape such as the feature of nature, the feature of topophilia, the feature of description and the feature of interrelationship. It is also shown that the environment orientation, ethnic inheritance, belief identity and interregional blending are the driving forces for the genesis of Tibetan village names. To protect Tibetan village names, the top priorities are making a dictionary of protection and establishing an identification system of place names.
藏族村落地名的空间格局、生成机制与保护策略: 以甘南藏族自治州夏河县为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180465
[本文引用: 1]

地名是特定空间上自然或人文地理实体的专有名称。村落地名作为文化景观的重要组成部分,记录着多元文化信息,也是集体记忆的重要载体。研究村落地名的空间格局、生成机制与保护策略,对于传承乡土文脉具有深远的价值。以甘南州夏河县藏族村落为例,应用GIS核密度估计法刻画了地名的空间格局,从文化景观视角出发解读了藏族村落地名的类型和生成机制。研究表明:以文化型为主、自然型为辅、复合型补充的地名体系是藏族村落命名的基本范式;映射出深厚的自然性基因、恋地性基因、记述性基因和关系性基因等文化景观特质;环境指向、族源沿袭、信仰认同和区际交融是藏族村落地名生成的源发力量。制定地名保护名录、建立地名标识系统是藏族村落地名保护的当务之急。
An empirical study on rank cumulative size model of rural settlements in the Hehuang area
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106012
[本文引用: 1]

Scientific determination of rural settlement system is one of the keys to implement the strategy of rural revitalization and promote the modernization of agriculture and rural areas. Meanwhile, understanding the distribution law of rural settlement size is helpful for the optimization of rural settlements. In order to provide a reliable theoretical basis for the study of rural settlement size distribution and the optimization of rural settlement system, this article took the Hehuang area as an example, and explored a more accurate expression and law of Rank Cumulative Size Model based on the original Rank Cumulative Size Model. Then we examined the applicability and accuracy of the model in rural settlement size distribution compared with the Rural Rank-Size Rule. We also studied the characteristics and evolution law of rural settlement size distribution in the study area. The results show that: (1) Rank Cumulative Size Model is a monotonously increasing concave function (P ≥ 1), and its expression varies with the change of the Pareto coefficient of rural settlements. When 1 ≤ P < 1.20225, Si = aln(Ni) + b, there is a positive correlation between the fitting coefficient a and the size of first settlements. When P ≥ 1.20225, $S_i=be^{aln(N_i)}$ the coefficient of variation of settlement size and the size of the first settlements are negatively correlated with the fitting coefficient a, and positively correlated with the fitting coefficient b. (2) Rank Cumulative Size Model is more suitable for the study of rural settlement size distribution in Hehuang as it has better applicability and accuracy; while the Rural Rank-size Rule is not applicable. (3) The rural settlement size in Hehuang nearly shows the equilibrium distribution pattern of Pareto coefficient 2 and tends to be more concentrated. In the future, the rural settlements should be concentrated in areas with superior natural and socio-economic conditions, and the layout of regional rural settlements and villages should be planned reasonably. Based on this, we can develop a rural revitalization path with the harmonious coexistence between human and nature, as well as between urban and rural development.
河湟地区乡村聚落位序累积规模模型的实证研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106012
[本文引用: 1]

科学确定乡村聚落体系是落实乡村振兴战略和促进农业农村现代化的关键之一,研究乡村聚落规模分布规律有助于乡村聚落体系优化。基于理论假设推导出了位序累计规模模型的准确表达及其规律,在此基础上,比较研究了位序累计规模模型和乡村位序—规模法则在河湟地区的适用性和准确性,厘清了河湟地区乡村聚落规模分布的特征和演变规律。研究显示:① 位序累积规模模型是一个单调递增的凹函数(P ≥ 1),函数表达式随着聚落规模分布的帕累托系数变化而变化。当1 ≤ P<1.20225时,S<sub>i</sub>=aln(N<sub>i</sub>)+b,拟合系数a与首位聚落规模呈正相关;当P ≥ 1.20225时,$S_i=be^{aln(N_i)}$,聚落规模变异系数和首位聚落规模与拟合系数a呈负相关关系,而与拟合系数b则呈正相关关系。② 位序累积规模模型在河湟地区乡村聚落规模分布研究中具有良好的适用性和准确性,而乡村位序—规模法则不适用。③ 河湟地区乡村聚落规模分布为接近于帕累托系数为2的均衡分布且总体趋于集聚。未来河湟地区应有序推进乡村聚落向自然和社会经济条件较为优越区域适度集聚,合理制定区域乡村聚落布点规划和实用性村庄规划,走人与自然和谐共生、城乡融合发展的具有河湟地区特色的乡村振兴道路。
Spatial structures of tourism destinations: A trajectory data mining approach leveraging mobile big data
Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of China national forest villages
中国国家森林乡村的空间分布特征与影响因素
Spatial distribution, type structure and influencing factors of key rural tourism villages in China
中国乡村旅游重点村空间分布、类型结构及影响因素
Temporal-spatial distribution and formation of historic and cultural villages in China
The ancient village possesses unique regional characteristics, integrated building structure, abundant material and intangible cultural heritage, and more importantly, they are still be used today. The rapid development of urbanization brings chances for the ancient villages and also deeply affects transformation of social economic structures of ancient villages. The thesis selects some representative old villages—historical cultural villages to analyze the balanced degree of spatial distribution of ancient villages, then discusses the influencing factors and finally puts forwards strategies to keep spatial balance of ancient villages and further lead simultaneous development of all the old villages in order to promote the progress of urban and rural integration. The study shows: (1) Chinese historic cultural villages have different characteristics in spatial distribution, spatial form, river system distribution, regional culture and transportation system. The majority of these villages are distributed along the river and are cultural centers, traffic hubs and birthplace of civilization in history; the villages form three centers, three sub-centers and four transition diffusion areas, and cultivate six cultural centers. (2) Chinese historic cultural villages mainly built in the Tang, Song, Ming and Qing dynasties, have a long history. Among the villages, the Ming Dynasty dominates the number and spatial distribution. (3) The reasons for their spatial uneven distribution include the resource endowment, limited selection criteria, economic development level and regional policy making.
中国历史文化名村的时空分布特征及成因
古村落是具有文化遗产性质的乡村聚落,选取古村落发展中最具代表性的国家级历史文化名村来分析中国古村落的空间分布特征,探讨其影响因素和分布原因,从而进一步引导中国乡村地区的同步发展,促进城乡一体化进程。研究表明:① 我国历史文化名村主要沿河流分布、多是历史上的经济文化中心、交通要塞和文明的发祥地,并形成了3 大集中区、3 大相对集中区和4 大过渡扩散区,孕育了6 个文化区;② 中国历史文化名村建造时间跨度较大,但多集中在唐宋明清4 个朝代,明朝保留下来的古村落最多,分布范围最广;③ 造成中国历史文化名村分布不均衡的主要原因有资源禀赋特点、评定标准的局限、依托腹地的经济发达程度和区域政策导向。
The importance of location and scale in rural and small town tourism product development: The case of the Canadian Fossil Discovery Centre, Manitoba, Canada
DOI:10.1111/cag.v62.2 URL [本文引用: 1]
Location-based services in tourism: An empirical analysis of factors influencing usage behaviour
DOI:10.54055/ejtr.v23i.386
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This contribution focuses on tourists’ usage behaviour of Location-Based Services (LBS) during their vacation. LBS represents technologies that localise a user’s mobile device (Turowski & Pousttchi 2004: 73) to offer services and content based on the user’s current geographical location (Egger & Jooss 2010: 21; Frey et al. 2015: 124). In vacation spots tourists find themselves in a situation characterised by increased information and service needs (Link & Seidl 2008: 56). Given that, LBS are considered to be promising services in the tourist industry (Egger & Jooss 2010: 21). In order to make use of the entire potential of LBS in tourism, the following key question needs to be answered: Which factors influence tourists’ usage behaviour of LBS and which possibilities can be derived for tourism providers and destinations? To answer its research question, this empirical study follows a deductive approach using UTAUT2, a popular technology acceptance model. The findings show a high usage rate of LBS in vacation and indicate that especially performance expectancy, effort expectancy as well as hedonic motivation influence the rate of usage. Considering these main causes, we derive theoretical implications as well as valuable clues for tourism management in practice.
Remotely sensed mapping and analysis of spatio-temporal patterns of land use change across China in 2015-2020
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202205002
[本文引用: 1]

The continuous remote sensing monitoring of land use/cover change at the national scale is of great scientific significance for land spatial planning and blueprint drawing of "Beautiful China" in the new era. Landsat 8 OLI, GF-2 and other satellite remote sensing data were used to develop the data of land use change across China during 2015-2020 and China Land Use/Cover Dataset in 2020 (CLUD 2020) by integrating remote sensing big data and expert knowledge-assisted human-computer interaction interpretation methods. Long time series land use dynamic database at a 30-m resolution in China was established at 5-year interval in the end of 1980s-2020. On this basis, the general trend, regional differences and main characteristics of land use change in 2015-2020 were revealed from national and regional scales. The research indicated that integrating vegetation cover change at a 30-m resolution and land change information generated by remotely sensed big-data cloud calculation into the expert human-computer interaction interpretation can effectively improve the efficiency of mapping and the accuracy of land use change detection. The overall accuracy of CLUD 2020 first-level type mapping reaches 95%. In general, the intensity of territorial development entered a stable state compared with 2010-2015. During the period, the cropland continued to decrease. Nationwide farmland was encroached by urban development and construction, paddy fields in Northeast China continued to decrease, and cultivated land in Xinjiang was reclaimed in the south and abandoned in the north. The built-up land continued to increase, showing a spatial pattern that "the expansion of built-up land changed from the agglomeration of coastal areas and mega and large cities in 2010-2015 to the surrounding sprawl of large, medium and small towns in the central and western regions in 2015-2020". Although the area of natural ecological land for forest and grass continued to decrease nationwide, the intensity decreased compared with 2010-2015. Under the continuous impact of climate change, the area of water in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau increased significantly. The pattern of land use change is closely related to the national macro strategy for high-quality development during the "13th Five-Year Plan" period (2016-2020) and ecological civilization construction, as well as the impact of climate change.
2015—2020年中国土地利用变化遥感制图及时空特征分析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202205002
[本文引用: 1]

持续地开展国家尺度土地利用/覆盖变化遥感监测对于新时代国土空间规划和“美丽中国”蓝图绘制具有重要的科学价值。本文采用Landsat 8 OLI、GF-2等卫星遥感数据,融合遥感大数据云计算和专家知识辅助人机交互解译方法,研发了中国土地利用变化(2015—2020年)和2020年土地利用现状矢量数据(CLUD 2020),建立了完整的30 a(20世纪80年代末—2020年)每隔5 a的30 m分辨率中国土地利用动态数据库。基于CLUD 2020数据,从全国和区域两个尺度揭示了2015—2020年中国土地利用变化的总体规律、区域分异和主要特征。研究表明:将遥感大数据云计算生成的30 m分辨率植被覆盖变化和地表类型变化检测信息融入到人机交互遥感解译方法,可有效地提高大范围土地利用变化遥感制图的效率和变化图斑辨识的准确性;精度评价表明,CLUD 2020一级类型制图的综合精度达95%。总体上,全国范围内国土空间开发强度与2010—2015年比较进入相对稳定状态。期间全国耕地面积仍保持减少态势,空间分异特征为耕地南减北增,东北松嫩平原及其与三江平原交界区大规模的旱地向水田转移,西北新疆南部开垦和北部退耕/撂荒并存;全国城乡建设用地持续增加,空间分异特征表现为由以往的沿海地区和超大、大城市集聚转向中西部地区的大中小城镇周边蔓延为主。全国范围的林草自然生态用地面积持续减少,但强度与2010—2015年比较有所下降;受气候变化的持续影响,青藏高原地区的河流湖泊等水域面积显著增加。以上土地利用变化格局与“十三五”期间国家高质量发展、生态文明建设宏观战略和气候变化的影响密切相关。
Spatialization approach to 1 km grid GDP supported by remote sensing
基于遥感的全国GDP 1 km格网的空间化表达
Annual time series of global VIIRS nighttime lights derived from monthly averages: 2012 to 2019
A consistently processed annual global nighttime lights time series (2012–2019) was produced using monthly cloud-free radiance averages made from low light imaging day/night band (DNB) data collected by the NASA/NOAA Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS). The processing steps are modified from the original methods developed to produce annual nighttime lights products from nightly data. Only two years of VIIRS nighttime lights (VNL) were produced with the V.1 methods: 2015 and 2016. Here we report on methods used to produce a V.2 VNL time series from the monthly averages with filtering to remove extraneous features such as biomass burning, aurora, and background. In this case, outlier removal is achieved with a twelve-month median, which discards high and low radiance outliers, thus isolating the background to a narrow range of radiances under 1 nW/cm2/sr. Background areas with no detectable lighting are further isolated using a statistical measure of texture, 3 × 3 data range (DR). The DR threshold for zeroing out background rises as the number of cloud-free observations falls. The V.2 method extends the temporal leverage in the noise filtering by developing the DR threshold from a multiyear maximum DR and a multiyear percent cloud-free grid. Additional noise filtering is achieved by zeroing out grid cells that have low average radiances (<0.6 nW/cm2/sr) and detection in only one or two years out of eight. The spatial extent and average radiance levels are compared for the V.1 and V.2 2015 VNL. For the vast majority of grid cells, the average radiances are nearly the same in the two products. However, the V.2 product has more areas of dim lighting detected. The key advantages of the V.2 time series include consistent processing and threshold levels across all years, thus optimizing the set for change detection analyses.
Spatiotemporal evolution of national development zones and their impact on urban land growth in China
DOI:10.1007/s11442-022-2005-6
[本文引用: 1]

Development zones are important growth poles for promoting regional economic development. However, the spatiotemporal relationship between development zone construction and urban land growth is still unclear. This paper analyzes the spatiotemporal changes of national-level development zones (NDZs), approximately 219 national economic development zones, and 156 high-tech development zones during 1990-2018 in China. The impact of development zone establishment on the growth of surrounding urban land was quantitatively explored using circle buffering analysis and time series comparative analysis. The results show that China’s NDZs spread from the southeast coast to the inland area from 1990 to 2018, and the establishment of the development zones has an obvious promoting effect on the surrounding urban land growth. The scope and intensity of influences of the development zone established in different periods present distinct nonstationarity in space and time. Overall, the impact on urban land (IU) of China’s NDZs established in different years was mostly highest at the 100 m buffer zone radius, while the slope of the IU was mostly negative, which meant that the 100 m buffer zone radius of the development zone center was the most efficient scale to promote urban land growth. In the meantime, the curve of IU of NDZs established before 1990, during 1996-2000 and 2001-2005 has a clear inflection point, which indicates that the most efficient scales of NDZs established before 1990, during 1996-2000, and 2001-2005 are 1300 m, 900-1000 m, and 800 m, respectively. NDZs established in other periods do not have the most obvious efficient scale. The development zone played the greatest role in promoting urban land growth from 2000 to 2010. Three association modes, including post-growth, pre-growth and steady-growth, were identified based on the differences in geographical location, establishment time, and type of development zones. We quantitatively identify the impact of the growth pole of NDZs on urban land growth from the perspective of spatiotemporal evolution. The findings would provide decision-making support for optimizing the spatial relationship between development zone construction and urban land growth.
Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviational ellipse
DOI:10.1086/214027 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial differentiation and hierarchical collaborative zoning of rural homestead withdrawal potential: A case study of Yicheng city, Hubei province
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.07.04
[本文引用: 1]

The potential of rural homestead withdrawal, with typical characteristics of regional differentiation and spatial association, is the basis for the stratified implementation of rural homestead system reform. This study analyzed the logical relationship of rural homestead withdrawal based on the theoretical potential, willingness potential, and real potential. A hierarchical collaborative zoning method of potential of rural homestead withdrawal is proposed by combining the analysis of space combination with the coupling model. We took Yicheng City in Hubei Province as an example to carry out the empirical research. The differentiation and coupling relationship of the three types of potentials of rural homestead withdrawal were well revealed in Yicheng City. The zoning of rural homestead withdrawal and the optimization direction for different zones were identified. The results show that: (1) The theoretical potential of rural homestead withdrawal in Yicheng is widely distributed, while the willingness potential and real potential show a typical core-periphery feature, which means that the willingness potential and real potential in the central plain area is significantly higher than those in the surrounding hilly areas. The proportion of migrant workers is an important factor affecting the areal proportion of willingness to withdraw from homesteads. (2) The combination analysis of the three types of potentials shows that more than half of the villages (communities) exhibit hierarchical consistency, while the three types of potentials within the non-consistent areas of the hierarchical combination are mainly low level coupling. (3) The rural homestead withdrawal area of Yicheng City is divided into five zones, including priority withdrawal area, key withdrawal area, general withdrawal area, elastic withdrawal area, and willingness limit area. Among them, the priority withdrawal area is the key site to implement rural homestead withdrawal reform pilot projects. The government should construct a differentiated zoning withdrawal mechanism centered on farmers’ interests and a protection mechanism of farmers’ long-term benefits based on clarifying the direction of rural homestead withdrawal and transformative development.
农村宅基地退出潜力空间分异与分层协同分区: 以湖北宜城市为例
DOI:10.18402/resci.2021.07.04
[本文引用: 1]

农村宅基地退出潜力具有典型的地域分异性和空间关联性特征,是分类实施农村宅基地制度改革的基础。本文基于理论潜力、意愿潜力和现实潜力3个层次,深入探讨农村宅基地退出的内在逻辑关系,运用空间组合分析和耦合度模型,提出一种农村宅基地退出潜力分层协同分区方法,以湖北省宜城市为例揭示3类农村宅基地退出潜力的分异特征和耦合关系,识别农村宅基地退出的分区类型及其优化方向。结果表明:①宜城市农村宅基地退出理论潜力分布广泛,意愿潜力和现实潜力呈现出典型的“中心-边缘”特征,外出务工人数占比是影响农村宅基地退出意愿潜力的重要因子;②3类退出潜力的组合分析显示超过一半的村(社区)具有分级一致性,而分级组合非一致区的3类潜力以低水平耦合为主;③宜城市农村宅基地退出可划分为5个区,包括优先退出区、重点退出区、一般退出区、弹性退出区和意愿限制区;其中,优先退出区是推进农村宅基地退出改革试点的重点。政府应在明确农村宅基地退出与转型发展方向的基础上,构建以农户利益为中心的差异化分区退出机制和农户长久利益保障机制。
The coupling coordination degree and spatial correlation analysis on integrational development of tourism industry and cultural industry in China
中国旅游与文化产业融合发展的耦合协调度及空间相关分析
Quantitative investigation of the interactive coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment
京津冀地区城市化与生态环境交互耦合关系定量测度
Evaluation of China's Plateau ecotourism development potential
中国高原生态旅游发展潜力评价
Spatiotemporal patterns of public service levels in China's rural tourism and their origins
中国乡村旅游公共服务水平时空演化及成因分析
The spatial pattern and driving mechanism of tourism development in border regions of China
中国边境地区旅游发展的空间格局及驱动机制
Geodetector: Principle and prospective
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
地理探测器:原理与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

空间分异是自然和社会经济过程的空间表现,也是自亚里士多德以来人类认识自然的重要途径。地理探测器是探测空间分异性,以及揭示其背后驱动因子的一种新的统计学方法,此方法无线性假设,具有优雅的形式和明确的物理含义。基本思想是:假设研究区分为若干子区域,如果子区域的方差之和小于区域总方差,则存在空间分异性;如果两变量的空间分布趋于一致,则两者存在统计关联性。地理探测器q统计量,可用以度量空间分异性、探测解释因子、分析变量之间交互关系,已经在自然和社会科学多领域应用。本文阐述地理探测器的原理,并对其特点及应用进行了归纳总结,以利于读者方便灵活地使用地理探测器来认识、挖掘和利用空间分异性。
A study on the spatial match of jobs-housing balance and its change over time in the central city of Shanghai
上海中心城区的职住空间匹配及其演化特征研究
Population distribution and its changes of the ethnic minorities
少数民族人口分布及其变动分析
Areal types and their development paths in rural China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 1]

Rural revitalization strategy is the general starting point for China's agriculture, rural areas and farmers in the new era. Because of the significant differences in rural areas in China, it is necessary to promote rural revitalization strategy according to local conditions, regional guidance and classification. Based on the theory of regional system of human-land relationship, this study constructs a comprehensive index system and measurement model to measure the level of rural development from the perspectives of resource endowments, geographical environment, humanistic elements and economic level, divides the areal types in rural China, and suggests the regional development ways. The results show that the level of rural comprehensive development in China varies significantly from east to west and that level in the eastern region is generally higher than that in the central and western regions. China's rural areal types can be divided into 11 first-class zones and 45 second-class zones, and there are distinct regional differences among different types. Geographical environment is the decisive factor for the differentiation of rural areal types, and resource endowment or resource type is the key factor for rural regional differentiation, and human and economic factors play an important role in the transformation and development of rural areal system. The connotation of rural areal differentiation lies in the difference of development level and industrial structure. The difference of rural development level is the comprehensive reflection of the interaction of many factors such as resource endowment, function orientation, location condition, national or regional policy, and historical background. From the perspective of human-land relationship, this study analyzes the characteristics, problems and development strategies in different types of rural areas so as to provide theoretical basis and decision-making guidance for the smooth promotion of the rural revitalization strategy in the new period.
中国乡村地域类型及分区发展途径
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180981
[本文引用: 1]

由于我国乡村地域差异显著,乡村振兴需分类有序推进。本研究立足于人地关系地域系统理论,从资源、环境、人文、经济等维度构建了度量乡村综合发展水平的指标体系和计量模型,划分了乡村地域类型,明确了分区发展途径。结果表明,我国乡村综合发展水平区域差异显著,呈现明显的自东向西递减规律;全国乡村地域类型可以划分为11个一级区和45个二级区,不同类型区制约因子各异;乡村发展水平差异是资源禀赋、功能定位、区位条件、政策文化等因子交互作用的综合体现。地理环境是乡村地域类型分异的决定性因素,资源禀赋状况是乡村地域分异的关键因子,人文和经济因素在乡村系统转型发展中扮演着重要作用。通过对乡村地域类型、特征及其分异机制的研究,为乡村振兴战略的顺利推进提供了理论依据。
Evaluation and influencing factors of regional protection level of traditional villages in Southwest China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202014
[本文引用: 1]

This study constructs a conceptual research framework for the protection of traditional villages, and focuses on the macro perspective of regional protection level and its influencing factors with geographic analysis techniques. The conclusions can be drawn as follows: (1) The conceptual research framework includes models of evaluation system and influencing factors. The evaluation system model includes three levels from macro to micro, namely, the spatial and temporal distribution, the overall protection level, and the single attribute. The evaluation of overall protection level is divided into the macroscopic regional protection and the microscopic community protection. Retention rates and distribution densities are the two important dimensions to evaluate the level of regional protection. The influencing factors model includes two types of basic analysis based on time, space, and the classification. (2) The regional protection levels of traditional villages in Southwest China show significant spatial differences, and five hotspots are formed in the boundary area of administrative divisions. (3) The geographical factors that affect the regional protection level of traditional villages in Southwest China are terrain, river system, central city, and arterial roads. Among the economic and social factors, the scale of intangible cultural heritage is the most important one. There are significant spatial differences in the correlation coefficients of population density, economic development, traffic construction, traffic flow, and the scale of intangible cultural heritage. Urbanization rate and industrial structure have no significant influence on the regional protection level. This research enriches the theoretical system for the protection of traditional villages from individual cases to an integrated study, from micro to macro, from scattered to systematic, from single to multiple methods, which has important theoretical and practical value.
西南地区传统村落区域保护水平评价及影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202014
[本文引用: 1]

本文在理论层面构建传统村落保护研究模型,并以西南地区为例,分析宏观视角下传统村落区域保护水平及影响因素。结论显示:① 传统村落保护研究模型涵盖评价体系和影响因素两个子模型。评价体系模型包含从宏观到微观的传统村落时空分布、整体保护水平和单一属性3个层次,其中整体保护水平分为宏观区域和微观社区两个亚层,保存率和分布密度是评价区域保护水平的简易方法;影响因素模型包含基于时间、空间和类型划分的两类基本分析模型。② 西南地区传统村落区域保护水平呈现显著空间分异,在行政区划边界地区形成5个热点集聚区,丽江市传统村落保存率最高,黔东南州分布密度最高。③ 影响西南地区传统村落宏观保护水平的地理区位因素为海拔、水系、中心城市和交通干道。经济社会因素中,非遗规模是最重要的影响因素,人口密度、经济发展、交通建设、交通流动和非遗规模的相关系数存在显著空间分异,城镇化率、产业结构对于区域保护水平无显著影响。本文是对传统村落保护理论体系由个案向整体、由微观向宏观、由零散向系统、由单一向多元方法的推进,具有重要理论和实践价值。
Evaluation system and influencing paths of the integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202304013
[本文引用: 1]

The integration of culture and tourism is conductive to the realization of the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization. Taking 16 typical traditional villages in Beijing as cases, this study proposes the evaluation system and influencing factor model of the integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages. Based on the TOPSIS model supported by entropy method, it analyzes the level of the integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages. Moreover, we discuss the main influencing factors and their paths of the integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages by using fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fs/QCA). The results can be concluded as follows: (1) The integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages is a dynamic process that continues to promote the comprehensive revitalization by deepening resource integration, advancing product cultivation and strengthening industry functions. (2) There are obvious differences in the development level of the integration of culture and tourism of case villages. Specifically, the level of each village in the four dimensions presents the characteristic of differentiation and imbalance. (3) None of single factors can constitute the necessary and sufficient conditions of the integration development of culture and tourism. (4) There are three influencing paths of the integration of culture and tourism of traditional villages, namely, mature development path, rapid development path and progressive development path, which correspond to their respective combinations of influencing factors. This study could provide theoretical inspiration and scientific guidance for the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization of traditional villages from the perspective of the integration of culture and tourism.
传统村落文旅融合发展水平评价及影响路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202304013
[本文引用: 1]

文旅融合发展有助于推动城乡融合发展与乡村全面振兴。以北京市16个典型传统村落为研究对象,在探讨传统村落文旅融合发展理论框架的基础上,使用层次分析法构建传统村落文旅融合发展水平指标体系,运用加权TOPSIS模型进行传统村落文旅融合发展水平评价分析,采用模糊定性分析法(fs/QCA)解析传统村落文旅融合发展的主要影响因素及其组合路径。结果表明:① 传统村落文旅融合发展是一个沿着“文旅资源深度融合—文旅产品体系培育—文旅产业功能提升”脉络,持续向传统村落地域系统释放综合效益,进而推动传统村落全面振兴的动态过程。② 案例村落的文旅融合发展水平整体差异较大,不同效益维度呈现梯级分化的典型特征,各村自身在4个效益维度上的水平具有非均衡性。③ 单因素必要性分析中,所有单变量因素均无法单独成为传统村落文旅融合发展的必要条件。④ 传统村落文旅融合发展的影响因素组合路径共有3种类型,即成熟发展路径、快速发展路径及渐进发展路径,分别对应着不同的影响要素组合。本文从文旅融合视角为传统村落全面振兴与城乡融合发展提供了理论基础和科技支撑。
Theoretical cognition and application innovation of Chinese rural tourism resources under the goal of common prosperity
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230202
[本文引用: 1]

The creative utilization of resources is an important foundation and key driving force for rural tourism to promote common prosperity, as well as a major scientific issue and practical demand. The interview shows that rural tourism is developing vigorously, but there are still some practical problems such as insufficient understanding, unclear mechanisms and limited promotion effect. Given that the weaknesses and potential of common prosperity are all in the countryside, we should continue to pay attention to them from different perspectives. To solve the above problems, we should clarify the connotation and driving logic of the theory of rural tourism promoting common prosperity, innovate the rural tourism industry system, and build a model and realization mechanism for promoting common prosperity based on the practice of villagers' participation mechanism and endogenous power cultivation, cultural resources protection and inheritance and the promotion mechanism for common prosperity of spiritual life, digital empowerment mechanism and path, tourism income distribution system reform, spatial effect and land use optimization; and we also should promote balanced, coordinated and inclusive development. This paper aims to provide theoretical support and application basis for the creative use of rural tourism resources and the promotion of common prosperity.
共同富裕目标下中国乡村旅游资源的理论认知与应用创新
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20230202
[本文引用: 1]

资源创造性利用是乡村旅游促进共同富裕的重要基础和关键动力,也是重大科学问题和现实需求。访谈表明:乡村旅游蓬勃发展,但仍存在认识不足、机理不清、促进效应有限等现实问题。鉴于共同富裕短板、弱项、潜力均在乡村,要从不同视角持续关注。紧扣这一问题,要厘清乡村旅游促进共同富裕的理论内涵与驱动逻辑、创新乡村旅游产业体系、构建促进共同富裕模式与实现机制等;还要落脚于村民参与机制与内生动力培育、文化资源保护传承及对精神生活共同富裕促进机制、数字赋能机制与路径、旅游收入分配制度改革、空间效应与土地利用优化等实践中,并促进平衡性、协调性、包容性发展等。以便为乡村旅游资源创造性利用、促进共同富裕提供理论支撑和应用依据。
The process of rural development and paths for rural revitalization in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106007
[本文引用: 1]

China is a large agricultural country, and issues concerning agriculture, rural areas and farmers are closely related to national economic and social development. To achieve the "Two Centenary Goals", rural revitalization strategy has become the choice to resolve unbalanced urban-rural development and inadequate rural development in China. Rural development is a comprehensive process of cycle accumulation and dynamic evolution of rural regional system. Thus, it is of great significance to systematically analyze the process and regional pattern of rural development to scientifically promote the implementation of rural revitalization strategy in the new era. Based on the theory of human-earth areal system and human-earth system science, this study examines the process and features of rural development in China from 1978 to 2050, discusses the internal relationship between rural transformation and rural revitalization, reveals the spatial pattern of the level of county rural revitalization in 2017, and finally puts forward the key problems and countermeasures for rural revitalization in the new era. Results show that the evolution of China's rural development in the period of 1978-2050 can be divided into three stages, i.e. solving the problem of food and clothing (1978-2005), building a well-off society (2005-2020) and realizing prosperity (2020-2050). In general, it is a dynamic and continuous process from low-level and basic-type to high-quality and innovation-type. Rural revitalization is a special stage of rural transformation, and a strategic choice to solve the prominent problem in rural development when it has evolved to a certain stage, thus boosting rural development to a higher stage. In 2017, when rural revitalization strategy was initiated, the level of rural revitalization in 57.3% of the counties in China was between 0.40 and 0.50, and there was an obvious gradient differentiation from the east to the west, with significant clustering characteristics and positive correlation. Specifically, the counties featured by "high-high (H-H)" clustering were mainly distributed in the third step of the terrain and the middle of Sichuan Basin; while the counties featured by "low-low (L-L)" clustering were concentrated in western China except Sichuan Basin, the eastern part of Inner Mongolia and the north of Tianshan Mountains. Due to the regionalism, stage and the difference in constraints of rural development, the focuses of rural revitalization in the new era lie in scientifically identifying the targeting areas of rural revitalization, comprehensively judging the trends of rural development, and systematically diagnosing the dominant constraints of different types of rural areas, so as to take targeted measures to make up for the shortcomings of the modernization of agriculture and rural areas. Besides, it is necessary to fully understand the interactions between urban and rural areas, thus promoting urban-rural integrated development.
中国乡村发展进程与乡村振兴路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202106007
[本文引用: 1]

乡村发展是乡村地域系统循环累积与动态演化的结果,全面梳理乡村发展历史脉络与地域分异格局,对于科学推动新时代乡村振兴战略落实具有重要意义。基于人地关系地域系统理论和人地系统科学认知,本文解析了1978—2050年中国乡村发展演化进程,探讨了乡村转型发展与乡村振兴的内在逻辑,揭示了中国县域乡村振兴水平的空间格局,进而提出了新时代乡村振兴的关键问题及其路径对策。研究表明:① 中国1978—2050年的乡村发展可划分为解决温饱、小康建设和实现富裕三个主要阶段,是一个由低水平、基础型向高质量、创新型不断发展的过程;② 乡村振兴本质上是乡村转型发展的一个特殊阶段,是乡村发展演化到一定阶段后,为解决其面临的突出问题以向更高层次迈进的战略选择;③ 2017年中国57.3%的县域乡村振兴综合水平介于0.40~0.50之间,在空间上呈现出明显的东中西地域分异,并具有显著的聚集特征和正相关性;④ 新时代乡村振兴战略的落实重在科学识别乡村振兴的瞄准区域,综合研判乡村发展演化的趋势,系统诊断乡村地域类型的主导制约因素,全面认知城乡耦合互动的逻辑关系,进而采取针对性措施推进农业农村现代化。
A study on the integration and mutual promotion between construction of ethnic villages with characteristics and tourism industry
少数民族特色村寨建设与旅游产业交融互促研究
Study on the spatial correlation between traditional villages and poverty-stricken villages and its influencing factors in China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211211
[本文引用: 1]

Based on the five lists of traditional villages published by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (China) and the poverty-stricken villages in poverty alleviation for a whole village during the 12th Five-Year Plan period (2011-2015), this paper analyzes the distribution pattern and spatial correlation of Chinese traditional villages and poverty-stricken villages, and discusses the relationship between the spatial correlation and regional natural environment and socio-economic factors. The results show that: (1) In terms of the spatial distribution relationship between traditional villages and poor villages, the regions with high-density traditional villages and high-density poor villages are mainly distributed in provincial-level regions of Hubei, Hunan, Guizhou, the border of Guangxi, the north of Shanxi, which are mostly contiguous poverty-stricken mountainous areas. Regions with low-density traditional villages and low-density poor villages (low-low type) are generally located in coastal and border areas, while low-high type areas are generally located in provincial border areas; the villages of high-low type are mainly distributed in Zhejiang and Fujian provinces with high economic development level. (2) Taking the low-low type regions as the reference, the low-high type areas are significantly negatively correlated with transport accessibility and regional economic development, and positively correlated with population, temperature, elevation and slope, which indicates that the risk of poverty is higher in areas with larger population and worse natural conditions (higher temperature, gradient and elevation). (3) Compared with low-low type areas, high-low type areas have a significant positive correlation with urbanization rate, which indicates that areas with higher density of traditional villages tend to have higher urbanization rate, and the urbanization process has no serious impact on the protection of traditional villages. There is a significant negative correlation between transport accessibility, population and high-high type areas. (4) The influence of different slope, temperature and precipitation areas on the spatial correlation of traditional villages and poor villages is different. It is necessary to make strategies for poverty alleviation and development of traditional villages according to local conditions. This paper aims to provide some guidance and support for China's poverty alleviation and rural revitalization based on the protection and development of traditional villages.
中国传统村落与贫困村的空间相关性及其影响因素
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211211
[本文引用: 1]

以住房和城乡建设部公布的五批传统村落及“十二五”期间“整村推进”贫困村为对象,分析中国传统村落和贫困村的空间相关性,并探讨其与区域自然环境和社会经济因素之间的关系。研究发现:(1)传统村落与贫困村的空间相关性方面,传统村落密度高—贫困村密度高的聚类区域主要分布在湖北、湖南、贵州以及广西的交界、山西北部,集中在连片特困山区。低—低类型区域主要集中在东北沿边、西北以及部分沿海地区,低—高类型区域集中在省际边界地区,高—低类型区域则主要分布在经济发展水平较高的浙江和福建。(2)将传统村落密度低—贫困村密度低类作为参照,低—高类区域与交通可达性水平、地区经济发展显著负相关,与人口、气温、高程、坡度这几个变量显著正相关;说明传统村落密度低的区域,人口更多、交通可达性水平差、地区经济发展更差、自然条件更为恶劣(气温变化、坡度和高程增加,降水量少)地区,陷入贫困的风险也更高。(3)相对低—低类型区域,城镇化率与高—低类型区域显著正相关,说明当同时位于低密度贫困村区域时,传统村落密度更好的地区其城镇化率也更高,城镇化进程没有严重冲击传统村落的保护;高—高类区域与交通可达性水平、人口呈显著负相关。(4)不同坡度、气温、降水量对传统村落与贫困村分布空间相关性的影响情况均有所不同,因此有必要因地制宜制定传统村落扶贫开发策略。研究成果可为我国基于传统村落保护和开发的乡村振兴提供一定的对象指引支撑。