1 引言
当前城市“网络化”研究范式成为主流[5],城市功能研究也从规模属性导向转变为网络联系导向,企业组织[6]、交通流[7]、信息流[8]、创新合作[9]等多元数据已被广泛用于刻画城市空间结构,进而映射城市在不同类型、不同尺度网络中的功能和地位[10]。随着联系数据及研究尺度的拓展,学者们意识到不同联系数据下的城市网络功能并不相同[11-12],同一联系数据下不同空间尺度的城市网络功能也存在差异[13-14]。不同尺度网络功能之间并非完全独立而是存在互动关联效应[2,15],跨尺度网络功能联系逐渐成为城市网络研究的新方向[15-16],但目前相关研究多探讨城市在单一尺度或多尺度网络中的功能地位,有关城市跨地方、全国、全球等多尺度网络功能关联演变的研究却存在明显不足。
企业网络常被认为是驱动城市网络形成和演变最重要的活动主体[5]。目前企业视角下的城市网络研究主要基于涵盖多种行业的或围绕具有独特价值的某一特定行业的企业内部门组织数据开展[10,12],后者愈加受到重视并拓展至制造业、物流、金融等多个行业[12],但较少关注文化产业。扩大内需是双循环发展格局的战略基点,其中文化消费具有很大的增长潜能,有助于消费升级。电影作为文化消费的重要形式,同时也是文化合作开放的主要载体,有利于提升国内大循环效率和水平,更好联通国内市场和国际市场。另外,企业间基于功能合作互补的产业链分工协作关系日益紧密,相比企业内部联系更具有普遍意义。电影产业作为最具活力的文化创意产业[17],拥有成熟的多尺度网络化生产组织方式,基于临时项目的大规模产业链分工联系正在成为塑造多尺度城市网络的重要力量[18⇓-20]。
总体来看,以电影产业为代表的文化产业,为基于产业链分工的企业间联系探究城市跨尺度网络功能关联提供了良好的切入点。基于产业链分工的城市跨尺度网络功能反映了城市内部集聚互动能力及其在不同尺度的对外联系能力。因此,本文将基于电影产业链分工,辨识城市在地方、全国、全球多尺度网络中的功能分化,并在城市功能演变过程中,重点探究跨尺度功能关联效应演变,明晰城市内部集聚互动能力与城市在不同尺度的对外联系能力之间的动态相互作用关系。研究结果有助于认知多尺度城市网络的空间组织规律,能够为城市提升本地集聚能力以及对外建立多尺度分工协作提供指导建议,助力城市在多尺度区域中的“地位转型”[21]。
2 文献综述与研究思路
2.1 城市跨尺度网络功能内涵与类型划分
随着全球化的推进和劳动分工的深化,城市间经济社会联系愈加密切,表现为人员、产品、资本、信息等要素在不同空间尺度的交换与交流,城市功能逐渐由腹地范围拓展至全国和全球尺度[2]。城市空间结构也由垂直化的规模层级分布向网络化的功能体系转变。在此背景下,“世界城市”假说[22]、“全球城市”概念[23]被相继提出,基于属性视角分别强调城市的世界资本支配和控制功能、高级生产性服务业集聚的全球资本服务功能。Castells提出的“流空间”理论[24]以及Taylor提出的连锁网络模型基于网络联系视角进一步推动了城市网络实证研究的开展[1,10]。网络联系的本质为城市功能联系[3,5],多尺度是其重要特征,即人、物质、信息等复杂多样的流要素作为城市功能要素(制造、物流、贸易、金融等)的联系载体[3],以交通和信息通讯设施为联系通道,通过不同尺度下的城际流动来实现城市功能间的交互联通。网络社会中的城市功能不再局限于其本身的属性要素,城市在多尺度网络联系中的地位与角色愈加深刻地影响着其跨尺度功能的形成与演变[3,25]。城市的跨尺度网络功能可理解为,城市在层级嵌套的多尺度网络中对不同类型流要素的集聚、扩散、流通和控制能力[25⇓-27]。其中地方功能体现了城市内部集聚和互动能力,全国和全球功能体现了城市在不同尺度的辐射影响力和竞争优势。因此,研究跨尺度功能关联有助于探清城市内部互动能力与城市在不同尺度对外联系能力之间的相互作用[2],更好地认知多尺度城市网络组织规律。
城市在不同类型和不同尺度网络中均存在功能分异。已有研究在单一或多个尺度下基于不同视角进行了城市网络功能类型划分。① 全国尺度下基于价值链功能分工进行公司总部、商务服务、研究开发、传统制造、现代制造、物流仓储和批发零售等城市类型划分[28];全国或省域尺度下基于转变中心性和转变控制力进行典型城市、枢纽城市、门户城市和边缘城市划分[21,26];区域尺度下基于多元流要素联系进行城市功能定位[29]。② 全国和区域尺度下基于区域内外网络联系的参与程度进行枢纽城市、普通城市、门户城市和边缘城市划分[27];全国和全球尺度下分析城市参与国内国际双循环及承担中介节点的职能分异[30];城市、省域、跨省城市群和全国尺度下,基于基本功能与非基本功能优势程度进行综合功能发展型、基本功能均衡发展型和单一基本功能发展型划分[2]。
2.2 跨尺度网络功能关联效应与作用机制
学术界不乏对城市跨尺度功能联系的讨论。Sassen等认为随着世界城市间的联系增强,它们与国家城市体系的联系将减弱[23]。“本地蜂鸣与全球管道”(Local Buzz and Global Pipeline)模型认为集群的内部互动和对外联系相辅相成[31],共同促进了集群知识创造,实证研究中也拓展至城市和区域尺度[32]。网络外部性(Network Externalities)理论及其实证研究则强调不同尺度的网络联系对于城市经济增长、创新水平、企业生产率等存在正向或负向的外部效应[33-34]。在此基础上,城市跨尺度网络功能关联的实证研究逐渐显现。网络构建方面,企业在区域分工协作中占据核心地位,是城市跨尺度网络功能关联中最重要的行为主体。已有研究多基于企业内部门组织关系构建多尺度功能联系网络。根据关联主体可将研究内容分为两种:① 城市内部功能联系与城市对外功能联系之间的关联[2,15]。主要发现城市内部企业互动和城市在全球网络中的对外联系之间具有相互促进作用;城市/城市群自我经济集聚能力与其对外辐射带动功能之间存在紧密的正向关系[2]。② 不同尺度城市对外功能联系之间的关联。长三角地区“区域—全国—全球”城市网络功能联系之间动态相互作用的案例研究[35],发现在网络外部性的作用下,城市在长三角地区内部的功能联系增强有助于提升其在全国和全球功能联系中的地位,全国和全球功能联系之间能够相互促进。此外,学者们也发现跨尺度功能关联效应具有空间异质性[35]、动态演变性[35]和功能类型差异[2],具有多尺度功能优势的城市比功能单一的城市更显著和密切。
在已有研究基础上,结合网络外部性、“本地蜂鸣与全球管道”和集聚效应理论,本文尝试阐述城市内部(地方功能)和城市对外(全国功能、全球功能)网络功能联系之间关联效应的形成机制。其中地方尺度网络功能联系同时具有企业集中和在其基础上的企业间互动两种效应[36],二者共同反映了城市内部集聚能力[15]。因此,本文也同时阐述企业集中与地方功能联系之间、企业集中与全国和全球功能联系之间的关联机制。① 企业集中与地方功能联系。企业集中一方面为企业间互动提供规模基础,另一方面地理邻近下的集聚优势能够降低交易成本[37],促进信任关系的建立和隐性知识的交流传播[38],增加企业间合作机会,有助于提高城市内集聚互动能力。城市内互动是“本地蜂鸣”的重要体现,蜂鸣能够促进知识流动和创新产生[31-32],增强城市的企业吸引力,有助于企业集中。② 企业集中与全国、全球功能联系。企业集中增加了管道建立的机会[31],有助于城市融入全国和全球联系网络。全国和全球功能联系通过网络外部性和“声誉溢出”(Reputational Spill-overs)[39]效应影响企业集中。一方面,全国和全球网络外部性可以使城市依托协同效应和规模借用效应享受知识、技术和创新的空间溢出[37-38,40],有助于提高城市在网络中的竞争优势[33],促进企业集中。另一方面,通过网络传递的“声誉溢出”[39],城市在全国和全球网络中较强的联系能力可以向网络中其他城市传递可达性优势,能够增加企业集中的机会。③ 地方功能联系与全国、全球功能联系。蜂鸣强度的提高会增加对管道建立的需求[31-32],也可以促进外部知识在城市内的扩散[31],提高管道建立的效率和质量。全国和全球网络外部性能够为城市注入新的思想、技术和知识[31,37 -38],增强企业活力和创新性,促进蜂鸣的自我更新和累积强化[31-32]。需要说明的是,网络的类型、尺度、结构以及城市的网络联系能力均会影响网络外部性的强弱[15,33]。因此,不同功能类型城市通过全国网络外部性和全球网络外部性得到的企业集中效益和城市内互动效益也存在差异[41]。
2.3 基于电影产业的城市网络研究
伴随着劳动分工的深化,基于产业链分工协作的企业间联系成为城市间经济联系的主要形式,并深刻影响着城市跨尺度功能的演变。受限于企业间联系数据获取困难,相关研究数量较少。直到近几年,相关研究才开始显现[42⇓-44],尤其是电影产业的每一部电影都提供了企业跨地理空间的产业链分工信息,为研究基于企业间联系的城市网络尤其是向更大的空间维度拓展提供了可能。相比于制造业等行业以生产这一单一环节为核心且高度固定化的组织方式[18],电影产业具有独特的生产组织逻辑:① 电影产品的数字化程度较高[19],城市(企业)间产业链分工主要基于功能协同,对地理邻近的依赖性相对较低;② 基于临时项目的方式开展出品、制作、发行环节高度网络化的分工联系①(①完整的电影产业链涵盖了出品、制作、发行、营销推广、放映和衍生品开发等环节[17-18],其中营销推广、放映和衍生品开发环节缺少客观、统一的数据来源,故不在本文研究范围内。)[20],各环节联系均跨越地方、全国、全球多个尺度,临时项目的实施对城市内和城市间网络均有较强依赖[12,42,44];③ 除生产制作外,融资出品、推广发行等环节对电影产品的质量和消费也具有重要作用;④ 一个城市(企业)可以同时具备参与多个环节的功能。
出品、制作、发行环节具有差异化的生产特征和要素需求。电影出品要求较高的金融资本投入,同时存在较高的风险[19-20]。电影制作是资本、技术、创意、人才等要素密集的环节,要求较高的集聚生产能力。电影发行则需要有效的影片定位与包装技术、宣传营销策略、档期排映技术[18],以获得更广泛的传播与消费。城市在不同环节的功能是其参与多尺度产业链联系网络能力的综合体现。已有电影产业网络研究中,国内学者主要基于产业链一个或多个环节的联系进行地方、全国、全球等尺度的城市网络结构刻画[17⇓-19,42,44]。国外研究集中在欧美发达国家,多以特定电影产业集群为例[45-46],探究集群内部互动和集群与外部市场的联系在集群知识创造、经济增长中的作用。但城市在多尺度电影产业链联系网络中的功能类型及跨尺度网络功能之间的关联效应还鲜有研究。
2.4 研究思路
综合来看,已有研究多关注城市网络功能识别与类型划分,但对多尺度网络功能关联关注不足,仅少数探究了跨尺度网络功能关联效应,主要发现城市内部集聚能力与城市对外辐射能力之间存在正向关联效应,不同尺度的城市对外功能联系之间也存在一定相互作用。但也存在以下不足:① 需要强化在基于产业链分工的企业间联系下的城市跨尺度网络功能关联效应探究,企业内部联系无法揭示产业链分工联系如何影响跨尺度网络功能关联效应。② 行业类型有待拓展,不同行业企业联系下的城市网络功能存在差异,尤其是以电影产业为代表的文化产业企业联系下的城市跨尺度功能关联是怎样的?
目前中国电影产业正处于黄金发展期,中国也正由电影大国向电影强国转变。电影产业链分工愈加灵活复杂和交易密集,能够较好地识别城市在多尺度分工协作中的功能演变,且有助于进一步明晰产业链不同环节联系下跨尺度功能之间呈现怎样的关联效应。基于以上,本文研究思路为:首先,依据地方、全国、全球多尺度电影产业链网络联系,基于多尺度和产业链相结合的视角划分城市功能类型分析城市功能演变;其次,探究不同功能类型城市的多尺度网络功能关联效应及演变特征,在此基础上探究产业链环节对城市跨尺度网络功能关联效应的影响;最后,为不同功能类型城市提升本地集聚能力以及参与多尺度对外分工协作提供分类指导建议。
3 数据来源与研究方法
3.1 数据来源
中国电影的市场化运营始于2002年6月的电影院线制改革[17],2010年中国电影“走出去”国家战略被提出,此后与其他国家签订的电影合拍协议逐渐增多。2003—2010年和2011—2019年代表了中国电影产业发展的两个典型阶段:产业化初期和市场化快速发展期②(②综合中国电影产业政策的关键时间节点以及中国电影年度票房和中国电影年度产量进行划分。)。因此,本文根据猫眼专业版的电影评分排名选取了2003—2010年和2011—2019年各年度中国(未含港澳台)排名前30、中国香港排名前10、中国台湾排名前10的电影作为研究样本(澳门数据暂缺)。从猫眼专业版官网、1905中国电影网、IMDb等平台获取每部电影的出品企业、制作企业和发行企业名录,结合天眼查平台、百度地图获取电影企业所在城市。剔除信息不完整的电影后,共获得有效电影546部。546部有效电影的猫眼影评大多集中于8.0~9.7,两阶段电影样本票房分别占中国电影总票房的79.43%和78.98%③(③中国电影总票房指中国电影在国内市场的票房,不包括中国电影的国外市场票房以及进口电影的国内市场票房。),一定程度上能较好地反映中国电影市场和电影生产活动的发展。
3.2 研究方法
3.2.1 多尺度网络联系矩阵构建
电影产业链出品、制作、发行环节的分工联系包括联合出品、联合制作、联合发行的横向联系,以及出品—制作、出品—发行、制作—发行的纵向联系[18]。本文基于电影产业链横向联系和纵向联系构建2003—2010年和2011—2019年地方、全国、全球多尺度网络联系矩阵,各尺度联系矩阵构建步骤如下:
(1)地方尺度。根据各部电影的出品企业、制作企业和发行企业名录,汇总得到参与每部电影出品、制作、发行的电影企业,进而构建两时期分别为194×315和352×1086的电影—企业矩阵A1和A2。根据企业所属城市,整理得到每个城市参与每部电影出品、制作、发行的电影企业数量,构建每个城市的电影—企业数量矩阵A1i (A2i)。如果城市i内两家电影企业同时参与了同一部电影出品、制作、发行中的同一环节,则它们之间发生了1次联合出品/联合制作/联合发行的横向联系,如果二者分别参与了出品、制作、发行中的两个不同环节,则它们之间发生了1次纵向联系。由此计算出每部电影生产中城市i内部的横向联系强度与纵向联系强度及二者相加后的总体联系强度,各电影项目生产中总体联系强度累积得到城市i内部总体联系的总强度Pi。
(2)全国尺度。根据企业所属城市,由两时期电影—企业矩阵A1 (A2)整理得到出品、制作、发行环节的电影—城市矩阵分别为B、C、D,由此提取得到参与各部电影出品、制作、发行的电影企业中位于城市i的数量的列矩阵Bi、Ci、Di。如果一部电影生产中,城市i和城市j分别有m家和n家电影企业同时参与了出品、制作、发行环节,则两城市之间发生了m×n次联合出品/联合制作/联合发行的横向联系;如果城市i和城市j分别有p家和q家电影企业参与了出品环节,r家和s家电影企业参与了制作环节,则两城市之间发生了p×s次i出品—j制作和r×q次i制作—j出品的纵向联系,同理可求得i出品—j发行、i发行—j出品、i制作—j发行、i发行—j制作的纵向联系强度。各部电影项目累积得到城市i与国内其他城市之间联合出品、联合制作、联合发行、i出品—其他城市制作、i制作—其他城市出品、i出品—其他城市发行、i发行—其他城市出品、i制作—其他城市发行、i发行—其他城市制作的联系强度的行矩阵Eilc、Eilz、Eilf、Eicz、Eizc、Eicf、Eifc、Eizf、Eifz,各城市以上行矩阵汇总得到国内城市间联合出品、联合制作、联合发行、出品—制作、出品—发行、制作—发行联系矩阵Nlc、Nlz、Nlf、Ncz、Nzc、Ncf、Nfc、Nzf、Nfz,进而相加得到国内城市间总体联系矩阵N。
(3)全球尺度。由两时期电影—企业矩阵A1 (A2)整理得到参与各部电影出品、制作、发行的国外电影企业数量列矩阵X、Y、Z,三者的转置矩阵和B、C、D相乘可得到国内外城市联合出品、联合制作、联合发行及国内城市出品—国外城市制作、国内城市制作—国外城市出品、国内城市出品—国外城市发行、国内城市发行—国外城市出品、国内城市制作—国外城市发行、国内城市发行—国外城市制作的联系矩阵Glc、Glz、Glf、Gcz、Gzc、Gcf、Gfc、Gzf、Gfz,相加得到全球尺度总体联系强度矩阵G。
3.2.2 多尺度网络功能与产业链功能测度
本文以城市在地方、全国、全球尺度网络中的加权度中心度测度其在多尺度网络中的功能[2]。由上述多尺度网络联系矩阵可计算得到城市i在各尺度产业链总体联系网络中以节点间联系强度为权重的加权度中心度Pi、Ni、Gi,以此测度其在总体联系下的地方功能、全国功能和全球功能④(④本文中的全球功能仅代表国内城市在中国电影出品、制作和海外发行中与国外城市所建立的产业链联系。),地方功能反映了城市内产业链互动能力,全国功能和全球功能反映了城市在不同尺度的对外联系能力。由城市i在各尺度联合出品、联合制作、联合发行、出品—制作、制作—出品、出品—发行、发行—出品、制作—发行、发行—制作联系网络中的加权度中心度计算得到出品、制作、发行环节下城市i在各尺度网络中的功能,各尺度累加得到城市i在多尺度网络中的出品、制作和发行功能。地方、全国和全球功能的总和与出品、制作和发行功能的总和大小相等,均为城市总功能。以出品功能为例,计算公式如下:
式中:Ci为城市i的出品功能;Pci、Nci、Gci分别为出品环节下城市i的地方、全国、全球功能;Pilc、Picz、Picf分别为城市i内部联合出品、出品—制作、出品—发行的联系强度;Nilc、Nicz、Nicf /Gilc、Gicz、Gicf分别为全国尺度/全球尺度下城市i在联合出品、出品—制作、出品—发行网络中的加权度中心度,分别代表i在相应尺度下与其他城市联合出品、i出品—其他城市制作、i出品—其他城市发行的总联系强度。制作功能Zi、发行功能Fi的计算方法与出品功能Ci相同。
3.2.3 城市功能类型划分
本文基于多尺度和产业链的综合视角划分城市在多尺度产业链联系网络中的功能类型,划分过程包括3步:首先,借鉴产业多样化计算方法,运用Frenken提出的熵指数法构建尺度功能多样化指数和产业链功能多样化指数[47],测度每个城市的尺度功能多样化程度和产业链功能多样化程度。计算公式如下:
式中:VAR_Scale和VAR_Link分别为尺度功能多样化指数和产业链功能多样化指数,指数越大说明多样化水平越高;Si为地方功能、全国功能和全球功能在城市总功能中的占比;Li为出品功能、制作功能和发行功能在城市总功能中的占比。
其次,运用自组织特征映射网络(Self-Organizing Feature Map, SOFM)模型对城市进行聚类分析。SOFM属于非监督分类的人工神经网络,模拟大脑皮层的竞争(抑制)原理,能够将输入层的高维度数据映射到竞争层的低维度数据[48]。与输入层神经元距离最小的竞争层神经元为获胜单元,通过调整获胜单元及其邻域单元的权值[28],多次迭代后得到最终聚类结果,能够提高分类的客观性和科学性。通过Matlab 2016b中的Neural Net Clustering模块构建SOFM网络,根据尺度功能多样化指数、产业链功能多样化指数、城市总功能大小、尺度细分功能大小(地方功能、全国功能和全球功能)、产业链细分功能大小(出品功能、制作功能和发行功能)9个维度的指标对城市进行聚类分析。2003—2010年和2011—2019年输入层分别为9×30(指标维度×城市数量)和9×58的矩阵,训练次数设置为1000次,经多次试验对比,两阶段聚类数量分别设置为4类和5类。最后,结合聚类时所基于的9个维度指标对聚类类型进行命名。
3.2.4 跨尺度网络功能关联效应测度
地理探测器是一种探测地理现象的空间分异性并揭示其背后驱动力的统计模型[49]。其核心思想基于以下假设:如果某自变量对某因变量有影响,那么自变量与因变量应该具有相似的空间分布。本文运用地理探测器中的因子探测模块来分析城市内企业集中(以城市内电影企业数量测度)和地方功能与全国功能和全球功能之间,以及企业集中与地方功能之间相互影响的解释程度。地理探测器要求自变量为离散变量,因此运用自然间断点分级法将上述变量分为2~3级。因子探测是指探测某一自变量对因变量空间分异性的解释力度,以q值度量,以此测度跨尺度功能关联指数的大小,并结合Pearson相关系数判断关联指数的正负向,表达式如下:
式中:h = 1, 2, …, L为因子X或因变量Y的分层;N和Nh分别为全区和层h的单元数;
4 城市跨尺度网络功能分化及关联效应演变
4.1 基于多尺度产业链联系的城市功能分化
4.1.1 城市功能类型划分
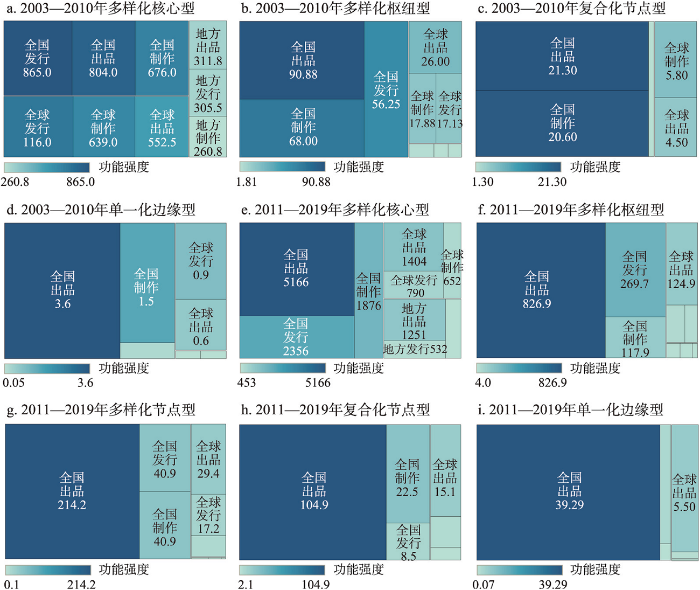
在SOFM聚类基础上,将2003—2010年的4种聚类和2011—2019年的5种聚类均按照城市总功能大小的均值进行降序排列,依次记为类型I1~IV1(表1)和类型I2~V2(表2),结合每种聚类在尺度功能多样化、产业链功能多样化、城市总功能、尺度细分功能和产业链细分功能方面的特征,进行聚类类型的命名(表3)。具体如下:运用自然间断点分级法将功能多样化指数及归一化处理后的总功能和细分功能均划分为5个层级,对应“强”“较强”“一般”“较弱”“弱”5种级别。其中产业链功能多样化指数的级别在“一般”及以上,属于“多样化”型;级别为“较弱”,属于“复合化”型;级别为“弱”,属于“单一化”型。地方功能、全国功能和全球功能的级别均为“强”,属于“核心”型;全国功能和全球功能的级别为“较强”,地方功能的级别为“较强”或“一般”,属于“枢纽”型;全国功能的级别为“一般”,全球功能和地方功能的级别均在“一般”及以下,属于“节点”型;地方功能、全国功能和全球功能的级别均为“弱”,属于“边缘”型。
表1 2003—2010年不同类型城市的功能多样化指数与细分功能均值
Tab. 1
| 聚类类型 | VAR_Scale | VAR_Link | Ti | Pi | Ni | Gi | Ci | Zi | Fi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类型I1 | 0.993 | 1.086 | 5130.5 | 878 | 2345 | 1907.5 | 1668.3 | 1575.8 | 1886.5 |
| 类型II1 | 0.552 | 1.057 | 283.1 | 7 | 215.1 | 61.0 | 120.2 | 87.8 | 75.2 |
| 类型III1 | 0.402 | 0.583 | 51.5 | 0 | 41.6 | 9.9 | 26.4 | 24 | 1.2 |
| 类型IV1 | 0.133 | 0.077 | 4.1 | 0.1 | 3 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.2 |
注:VAR_Scale、VAR_Link、Ti、Pi、Ni、Gi、Ci、Zi、Fi依次为尺度功能多样化指数、产业链功能多样化指数、城市总功能、地方功能、全国功能、全球功能、出品功能、制作功能、发行功能,颜色灰度从深到浅依次表示“强”“较强”“一般”“较弱”“弱”,
表2 2011—2019年不同类型城市的功能多样化指数与细分功能均值
Tab. 2
| 聚类类型 | VAR_Scale | VAR_Link | Ti | Pi | Ni | Gi | Ci | Zi | Fi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类型I2 | 0.741 | 0.988 | 14480.3 | 2236 | 9398.5 | 2845.8 | 7820.8 | 2981.9 | 3677.6 |
| 类型II2 | 0.452 | 0.756 | 1419.4 | 23.2 | 1214.5 | 181.7 | 962.1 | 150 | 307.4 |
| 类型III2 | 0.419 | 0.767 | 345.3 | 0.8 | 290.3 | 54.2 | 240.0 | 44.1 | 61.3 |
| 类型IV2 | 0.406 | 0.485 | 146.5 | 0.1 | 125.9 | 20.5 | 116.8 | 28.7 | 1.1 |
| 类型V2 | 0.227 | 0.080 | 31.4 | 0 | 28.5 | 2.9 | 28.5 | 2.5 | 0.3 |
表3 基于多尺度产业链网络联系的城市功能类型划分
Tab. 3
| 功能类型 | 2003—2010年 | 2011—2019年 |
|---|---|---|
| 多样化核心型 | 北京、香港 | 北京、上海、香港、天津 |
| 多样化枢纽型 | 上海、台北、广州、深圳、金华、西安、杭州、武汉 | 霍尔果斯、金华、杭州、广州、深圳、无锡、青岛、南京、成都、台北 |
| 多样化节点型 | - | 长沙、西安、福州、合肥、重庆、嘉兴、宁波、武汉、乌鲁木齐、石家庄、昆明、郑州、拉萨 |
| 复合化节点型 | 出品—制作型:成都、佛山、南京、天津、太原、长春、银川、绍兴 制作—发行型:长沙、重庆 | 出品—制作型:厦门、廊坊、扬州、济南、珠海、长春、呼和浩特、贵阳、苏州、秦皇岛、南昌、大连、银川、承德 出品—发行型:山南、喀什、沈阳 |
| 单一化边缘型 | 出品型:哈尔滨、呼和浩特、青岛、郑州 制作型:九江、济南、厦门、石家庄 发行型:乌鲁木齐、苏州 | 出品型:佛山、鄂尔多斯、东莞、徐州、海口、盐城、新余、绍兴、中卫、澳门、南平、常州 制作型:芜湖、保定 |
类型I(多样化核心型):包括类型I1和I2,两阶段该类型城市产业链功能多样化指数分别为1.086和0.988,级别均为“强”;地方、全国和全球功能的级别均为“强”,定义为多样化核心型城市。该类型城市拥有强大的金融资本、集聚生产和市场推广能力,以及地方集聚、全国辐射和全球门户功能,是多尺度产业链联系网络中的核心城市。类型II(多样化枢纽型):包括类型II1和II2,两阶段该类型城市产业链功能多样化指数分别为1.057和0.756,级别均为“较强”;全国功能和全球功能的级别均为“较强”,地方功能级别均在“一般”及以上,定义为多样化枢纽型城市。该类型城市数量小幅增长,组成有明显变动。类型III(多样化节点型):包括类型III2,前一阶段未出现该类型,后一阶段该类型城市产业链功能多样化指数为0.767,级别为“较强”;全国功能的级别为“一般”,全球功能和地方功能的级别分别为“一般”和“弱”,定义为多样化节点型城市。该类型城市绝大多数为具有较高行政等级的副省级城市和省会城市,少数为拥有大型影视基地的城市(嘉兴)。
类型IV(复合化节点型):包括类型III1和IV2,两阶段该类型城市产业链功能多样化指数分别为0.583和0.485,级别均为“较弱”;全国功能的级别为“一般”,全球功能和地方功能的级别分别为“较弱”和“弱”,定义为复合化节点型城市。在出品、制作和发行功能中选取级别较高的两个环节,可进一步命名得到出品—制作型、制作—发行型和出品—发行型3小类城市。数量上,出品—制作型城市占比均在80%及以上且增长最快,制作—发行型城市有所减少,少数出品—发行型城市出现于后一阶段。组成上,前一阶段多数为省会城市,后一阶段还包括半数左右具备政策(山南和喀什),区位(位于三大城市群的廊坊、秦皇岛、承德、扬州和珠海)和影视基地资源(苏州)等优势的中小城市。类型V(单一化边缘型):包括类型IV1和V2,两阶段该类型城市产业链功能多样化指数分别为0.077和0.080,级别分别为“较弱”和“弱”,其中类型IV1多数城市仅一个环节的功能大于0;地方功能、全国功能和全球功能的级别均为“弱”,定义为单一化边缘型城市。在出品、制作和发行功能中选取级别较高的一个环节,可进一步命名得到出品型、制作型和发行型3小类城市。数量上,前一阶段3小类城市数量较为均衡,后一阶段出品型城市数量增长明显,占比为85.71%,制作型和发行型城市数量有所减少。组成上,前一阶段除苏州和九江外,均为副省级城市和省会城市,后一阶段除海口和澳门外,均为中东西部的中小城市。
4.1.2 城市功能演变
进一步分析各类型城市在各环节下的地方功能、全国功能和全球功能。各环节下不同尺度功能大小(图1)可以反映电影企业更倾向于开展城市内联系还是不同尺度的城市间联系,也体现了不同尺度功能联系在电影产业链分工协作中的重要性。不同环节的功能大小则反映了城市参与程度的差异。发现:① 各类型城市的全国功能在多尺度功能中均占据主导地位,其次是全球功能,地方功能强度最低,说明城市内联系对产业链分工协作的贡献程度相对低于城市间联系,这与已有研究结果一致[42,44]。城市内联系可以降低交流成本,但不同环节所需的取景地、资金技术、专业人才等互补性资源多需要通过城市间联系来获取。从单一化边缘型到多样化核心型的等级提升过程中,城市在全国功能基础上逐渐具备参与全球联系和地方集聚的能力,一定程度上体现了“全国→全球→地方”的多尺度功能发展规律。② 各类型城市的出品功能明显高于制作和发行功能,且复合化节点型和单一化边缘型城市在出品环节的功能集中度明显高于多样化型城市。一方面,随着中国电影产业商业化和金融化深入,出品环节的高投资和高风险特征增加了其对参与主体的数量需求;另一方面,制作和发行环节对生产要素具有较高要求,同时核心与枢纽型城市向各环节不断扩张,加大了中小城市进入的门槛。因此,出品成为参与的企业和城市数量最多且联系强度最高的环节,也是中小城市嵌入多尺度网络的重要方式,体现了城市网络的“俱乐部”特征。
图1
图1
各类型城市的尺度与产业链细分功能
Fig. 1
Elaboration on subdivisions of scale functions and industrial chain functions of different types of cities
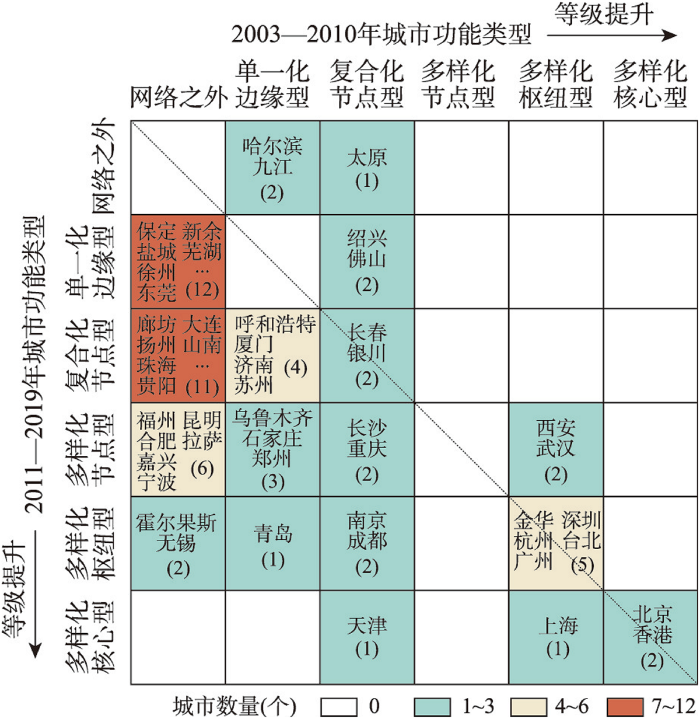
综合来看,城市在多尺度网络中的功能演变分化明显(图2)。① 多数城市(45个,占比73.77%)的功能类型等级有所提升,主要表现在两个方面:一是网络原有城市中单一化边缘型向复合化节点型(4个)、多样化节点型(3个)和多样化枢纽型(1个)转变,复合化节点型向多样化节点型(2个)、多样化枢纽型(2个)和多样化核心型(1个)转变,以及多样化枢纽型向多样化核心型(1个)转变。说明这些城市的尺度功能和产业链功能的大小及多样化程度均逐渐提高。其中上海和天津分别由多样化枢纽型和复合化节点型转变为多样化核心型城市,成为后一阶段多尺度网络的次核心城市。二是前一阶段网络之外的31个城市融入,其中17个中小城市多呈现为复合化节点型中的出品—制作型和单一化边缘型中的出品型。它们多在金融驱动下以联合出品电影的方式嵌入全国网络,但全球功能较弱,企业集中程度很低,也尚未形成地方联系。具有行政等级或税收政策或影视基地优势的福州、合肥、宁波等8个城市,呈现为多样化节点型和多样化枢纽型。其余贵阳、南昌、海口等6个城市呈现为复合化节点型和单一化边缘型。较为特殊的是后一阶段跻身多样化枢纽型城市行列的新疆霍尔果斯口岸,以及复合化节点型城市中的山南和喀什。它们主要基于税收优惠政策吸引了相当数量的电影企业在此注册,但缺少企业实体入驻,也很少参与电影实际生产过程,主要与其他城市进行出品和发行环节的金融联系。因此较高的功能类型等级并不能反映它们在多尺度网络中实际形成的城市内与城市间电影生产联系,也难以有效发挥对当地电影产业发展的促进作用。这类城市的出现反映了金融资本对电影生产网络组织结构及城市网络功能的重要影响。② 少部分城市(9个,占比14.75%)保持原有功能类型,主要为多样化核心型和多样化枢纽型城市,尤其是北京在多尺度网络中占据稳固的主核心地位。③ 另有少部分城市(7个,占比11.48%)的功能类型等级有所下降,其中西安和武汉由多样化枢纽型转变为多样化节点型,哈尔滨、九江和太原则退出多尺度网络。
图2
4.2 不同城市功能类型下的跨尺度网络功能关联效应演变
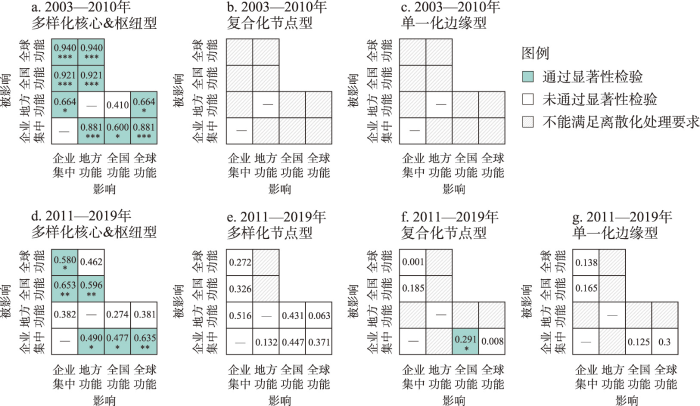
本文运用地理探测器计算两阶段产业链总体联系下,各类型城市的跨尺度网络功能关联指数(图3),结果显示:① 对于多样化核心&枢纽型城市⑤(⑤由于多样化核心型城市数量较少,故将其与多样化枢纽型城市合并为一组进行地理探测,下同。),前一阶段除全国功能对地方功能的影响不显著外,其他关联指数均显著;后一阶段企业集中和地方功能之间由相互促进关系转变为非对称影响,即地方功能对企业集中存在正向影响,而企业集中对地方功能的影响不再显著。企业集中与全国功能和全球功能之间仍具有相互的正向影响。地方功能对全国功能具有促进作用,与全球功能之间的关联不再显著。② 对于多样化节点型城市,后一阶段各关联指数均不显著。③ 对于复合化节点型和单一化边缘型城市,前一阶段两类城市的企业数量较少(多为1~5家),企业间产业链联系也很薄弱(联系强度多为0和1),各关联指数均不显著。后一阶段复合化节点型城市的全国功能对企业集中具有较弱的正向影响(关联指数为0.291),单一化边缘型城市仍未表现出显著的关联效应。
图3
图3
不同城市功能类型下的跨尺度功能关联指数
注:*、**、***分别为0.1、0.05、0.01的显著性水平。
Fig. 3
Cross-scale functional correlation indexes from the perspective of different types of urban functions
对于多样化核心&枢纽型城市,① 企业集中和地方功能之间的关联:在两个阶段城市内密切产业链互动下的“本地蜂鸣”均有助于集群知识生产和创新发展,并吸引更多电影企业集中。企业集中对城市内产业链联系的影响与集群发展阶段有关。前一阶段企业集中的集聚效应一方面通过增加合作伙伴数量来有效支撑企业间结网互动,另一方面地理邻近有助于营造合作氛围(如影视产业园区),刺激电影创意等缄默知识的交流,促进企业间联系。后一阶段集群发展趋于成熟,受组织、社会、技术等其他邻近性影响,企业集中对企业间联系的促进作用不再显著。② 企业集中与全国功能和全球功能之间的关联:电影产业链联系由临时项目联系累积而成,具有较强的可变性和偶然性。因此企业集中水平的提高可以带来更多参与全国和全球联系的机会。同时,全国和全球功能联系的提升也能够反过来促进企业集中。一方面,全国和全球网络外部性带来的知识、技术溢出有助于提高城市竞争力;另一方面,在“声誉溢出”的作用下,城市较强的全国和全球联系能力能够增加电影企业设立于此的可能性,其中全球功能联系的促进作用更强。③ 地方功能与全国功能和全球功能之间的关联:城市内广泛密切的产业链互动能够促进城市间联系中的知识流动和信息传播,提高城市间联系效率和质量;同时也增加了通过全国和全球联系获取新知识的需求,因此对全国辐射力和全球竞争力均具有正向效应。前一阶段全国和全球功能联系对城市内互动的影响分别为不显著和显著。这是由于两种尺度功能联系中的知识复杂性和多样性存在差异,进而影响了网络外部性的效用。多样化核心&枢纽型城市在全国联系中已处于“链主”地位,全球联系能使其吸收学习到更先进、多样的新创作理念、新制片技术和新发行经验,有助于地方互动的有效更新和强化。后一阶段集群发展更为成熟,全国功能联系对城市内互动的影响依然不显著,受企业规模等级、社会关系和已有合作经历等影响,全球功能联系对城市内互动的正向效应转变为不显著。对于复合化节点型城市,依托与多样化核心&枢纽型城市之间的规模借用效应,逐渐增强的全国网络外部性有助于企业集中。
4.3 不同产业链环节联系下的跨尺度网络功能关联效应演变
运用地理探测器计算两阶段各类型城市在出品、制作、发行单个环节的跨尺度网络功能关联指数,结果显示(图4),单个环节的跨尺度功能关联效应差异明显。前一阶段:多样化核心&枢纽型城市在制作和发行环节的关联效应显著情况与总体联系一致,显著的关联指数个数为总体=制作=发行>出品,且出品环节的关联指数也低于制作和发行环节。与总体联系一致,其余类型城市单个环节的关联指数均不显著。后一阶段:多样化核心&枢纽型城市单个环节的关联效应显著情况与总体联系均不一致,显著的关联指数个数为出品>制作=总体>发行,且出品和制作环节的关联指数也高于发行环节。两阶段对比发现,部分关联指数的显著情况未变化,即地方功能和全球功能对企业集中的正向影响,以及地方功能和全国功能之间的非对称影响(仅地方功能对全国功能存在正向影响)在各环节及总体联系下均具有稳定的显著性。显著情况变化的关联指数中,一是企业集中和全球功能在前一阶段制作和发行环节对地方功能具有正向效应,在后一阶段各环节均不显著;二是地方功能在前一阶段各环节对全球功能均具有促进作用,在后一阶段发行环节不再显著;三是全国功能对企业集中的正向影响在前一阶段各环节均显著,后一阶段仅在出品环节显著。企业集中对全国功能和全球功能的影响在后一阶段发行环节不再显著。对于多样化节点型和复合化节点型城市,企业集中于后一阶段在出品环节分别受到全国功能、全国功能和全球功能的促进作用,但均未能反过来显著影响全国功能和全球功能,在制作和发行环节均无显著关联。单一化边缘型城市在单个环节的关联指数均不显著。
图4
图4
不同产业链环节联系下的跨尺度网络功能关联指数
注:*、**、***分别为0.1、0.05、0.01的显著性水平。
Fig. 4
Cross-scale functional correlation indexes from the perspective of different types of film industrial chain connections
对上述跨尺度功能关联结果的解释分析如下:① 对于多样化核心&枢纽型城市,制作和发行环节的知识流动、技术合作和创意交流比出品环节更核心和密集,所产生“蜂鸣”的质量和网络外部性的强度也更高,因此在前一阶段形成了更显著和密切的关联效应。后一阶段,在金融资本驱动下,电影出品逐渐发展为网络规模最大和强度最高的环节,功能关联效应的显著性稳定、强度相对提高且与制作环节相当。制作环节的核心优势稳固,功能关联效应的显著性较为稳定且强度较高。多样化节点型城市的兴起相对减弱了多样化核心&枢纽型城市在发行环节的功能优势程度及关联效应整体显著性。此外,在制作和发行环节,企业集中和全球功能对地方功能的正向影响不再显著,这一变化也受到前述集群发展阶段的影响;全国功能对企业集中的正向影响不再显著,这一变化说明随着集群发展趋于成熟,需要从全球联系中吸收学习多样化的新知识和新资源,以促进企业集中。② 多样化节点型和复合化节点型城市虽具备出品、制作和发行中三个或两个环节的功能,但仅在功能强度最高的出品环节具有逐渐显著的关联效应,表现为从全国和全球网络外部性中受益,进而促进企业集中。而企业集中和城市内产业链互动均较弱,尚未达到显著影响全国功能和全球功能的门槛。制作和发行环节尚未进入网络外部性驱动发展阶段,两类城市在高功能等级城市辐射带动下的受益并不显著。③ 单一化边缘型城市虽大多为出品型,但因功能发育水平较低而未在出品环节形成显著关联效应。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
(1)城市在地方、全国、全球多尺度和电影出品—制作—发行产业链联系网络中的功能分化明显,综合多尺度和产业链视角可划分为多样化核心、多样化枢纽、多样化节点、复合化节点和单一化边缘5种类型。多数城市的功能等级有所提升,少数城市的功能等级保持不变或有所下降,新增城市主要通过金融导向下的出品环节融入网络。
(2)企业集中和城市内产业链互动共同反映的城市内部集聚能力与城市在不同尺度的对外联系能力之间具有动态关联效应,且存在城市功能类型分异和产业链环节分异。多样化核心&枢纽型城市的跨尺度功能动态关联效应较为显著,主要表现为城市内部产业链互动和全球尺度对外联系能力对企业集中的正向影响,以及城市内部产业链互动和企业集中对全国和全球尺度对外联系能力的正向影响,且较为稳定。多样化节点型和复合化节点型城市的跨尺度功能关联效应逐渐显著但较弱,单一化边缘型城市不显著。
(3)多样化核心&枢纽型城市在各环节均具有显著的跨尺度功能关联效应,显著性高低和关联强弱因不同环节联系的网络结构和外部性大小而具有差异。多样化节点型和复合化节点型城市仅在出品环节具有逐渐显著的关联效应,表明中国电影产业正处于金融化和商业化发展阶段,金融资本驱动下的出品环节仍是较低功能等级城市通过网络外部性享受有限效益的主要渠道,而制作和发行环节尚未进入网络外部性驱动发展阶段。
(4)区别于制造业等行业随地方集聚强化而逐渐对外辐射的过程,由边缘型到核心型的等级提升过程中,呈现出全国→全球→地方的多尺度功能发展特征,体现了电影产业链联系更多发生在城市间而非城市内的特点。由于全国网络中节点型和边缘型城市可直接与头部的核心型和枢纽型城市建立联系,而不必先关联其他城市,且核心型城市同时也承担着全球联系的门户功能,故尚未出现门户型城市。区别于制造业网络中城市以生产过程的不同价值环节而呈现出研发、生产、代工服务等类型,同一城市在电影产业链联系中往往参与融资出品、生产制作、推广发行多个环节,产业链功能随不同环节的功能组合而具有多样化、复合化和单一化的特点。相较于企业内部门组织视角下的跨尺度功能关联效应,电影产业链联系网络中不仅同样呈现出具备多尺度功能优势的城市比功能单一的城市更显著的分异特点,还表现出产业链功能多样化的城市整体上比复合化和单一化的城市更显著且环节间显著分异的特征。
5.2 讨论
基于本文研究结果,有针对性地为以下类型城市提供分类指导建议:① 对于多样化核心&枢纽型城市,依托功能完备的产业链条和相对成熟的影视集群,一是应侧重强化电影制作环节的核心竞争力,以电影制作引领带动城市内各环节联系中的资本交汇、技术交互、人才交流和创意交融。二是应积极与国外影视企业开展电影摄制、国际发行和投资出品的合作,并从中吸收学习先进的电影创作知识和技术,提高其在全球网络中的门户功能。三是应基于以上措施来强化企业集中优势和提升全国辐射引领力,尤其是在制作和发行环节,应提高对较低功能等级城市知识、技术、人才和创新溢出的范围与强度。② 对于多样化节点型和复合化节点型城市,一方面,在出品环节基础上,应积极接受多样化核心&枢纽型城市的辐射带动,有序强化制作和发行环节的对外功能联系,进而从中获取更多效益并促进企业集中;另一方面,也应依托行政等级或特殊资源优势来优化自身文化生产环境,吸引更多电影企业集聚。
本文不足之处及研究展望如下:① 限于数据可获性,主要围绕电影产业链上游的出品、制作环节和中游的发行环节展开探究,未能将下游的营销和放映环节纳入研究。未来可拓展至全产业链,同时对综合多尺度和产业链划分城市功能类型的方法进行改进。② 进一步补充完善全球电影数据,更加全面地识别城市在全球尺度电影生产网络中的功能。③ 随着中国电影产业发展,城市群尺度功能联系及其与企业集中和地方功能之间关联效应的研究有待强化。
关联数据信息:本文关联实体数据集已在《全球变化数据仓储电子杂志(中英文)》出版,获取地址:
致谢
真诚感谢3位匿名审稿专家提出的专业细致的宝贵意见,使本文受益匪浅,谨致谢忱!
参考文献
The progress and prospect of research on Chinese city network
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.07.007
[本文引用: 3]

City network is an important perspective to study cities and regions. In recent years, a large number of studies on city networks involving China have emerged. For the one hand, the case study of China has always been attracting the attention of scholars all over the world for the past decades, and remarkable development has been achieved in city network research on China. For the other hand, while the number of publications is growing really fast, some limitations and challenges of this research has also appeared. Therefore, a systematic review to this large body of literature is needed at present. This article summarizes and reviews the progress of city network research on China from four aspects: 1) Data and methods used in city network research on China; 2) The major findings of this research, including network patterns and formation mechanism on different spatial scales; 3) The main contributions of this field; 4) Some limitations of current studies and the prospect for future research. The findings of this article are provided as follows. City network research on China utilizes various data and methods to construct networks, while Social Network Analysis and Complex Network Analysis are applied to the description of city networks. Major findings of city network research on China covers three spatial scales: global scale, national scale and regional scale, which have revealed the characteristics and formation mechanism of city network on China under different spatial scales. Mainly contributions of city network research on China include: 1) Multi-scale studies on city networks of Chinese cities are important inspirations for city network research worldwide; 2) Avoiding Western Centralism views on studying globalization and making up for the major defects in the research of world cities; 3) Using some original perspectives and data to depict inter-city relations, which has promoted the development of world city network research; 4) Bringing the network logic to the studies of Chinese cities as well as helping promote the academic development of urban geography and economic geography in China. Main limitations and challenges include: 1) A large number of empirical studies dedicate to describe and explain the network structure, paying less attention to theoretical innovations; 2) The data sources and network construction methods used are increasingly convergence, leaving no much room for related innovations in future work. Accordingly, we propose that city network research on China should actively expand the research perspective. Deepening the mechanism research and theoretical innovation should also be highlighted. And strengthening policy studying of city networks on China can benefit the further development of this field, which is almost neglected in current stage.
中国城市网络研究评述与展望
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.07.007
[本文引用: 3]

现有研究采用多元化的数据和方法构建并分析城市网络,揭示不同空间尺度下中国城市网络的特征和形成机制。中国城市网络研究的贡献体现在以下4个方面:① 以中国为背景的多尺度城市网络分析对世界城市网络研究具有重要启发;② 强调国家和区域背景,避免了欧美中心论的全球化观点;③ 采用新颖的数据和视角构建城市网络,推动了世界城市网络研究的进展;④ 增强了国内地理学界对城市网络和外部联系视角的重视,促进了学科发展。同时,当前中国城市网络研究也面临挑战。一方面,大量研究主要着力于城市网络的可视化和描述性分析,机制分析薄弱,理论创新不足;另一方面,当前研究的数据和方法日益趋同,迫切需要新的研究视角。未来需要加强方法和理论创新,深化机制和影响研究,并提高研究的政策相关性。
The characteristics of urban network of China: A study based on the Chinese companies in the Fortune Global 500 list
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904006
[本文引用: 9]

Based on the data of Chinese enterprises that entered the Fortune 500 list in 2015, this paper uses the eclectic model to construct the inter-city association network. Using the network analysis method, the spatial connection characteristics of 311 inter-city networks at prefecture level and above and 20 urban agglomerations networks in China are examined respectively. The research found that: (1) The overall connectivity of urban network is poor, the centripetal concentration is strong, and the network is not complete. The urban network connection shows a strong tendency of political center cities directivity, coastal cities directivity as well as resource-based cities directivity. The external economic dependence of each node city in the urban network is high, and the urban network structure has obvious flattening characteristics. The network of urban agglomerations is characterized by decentralization of power, differentiation of status and dependence on external connections. (2) The boundary effect of provinces, urban agglomerations and urban agglomerations clubs in the urban network is significant. The network evolution process is influenced by the provincial administrative district economy, the urban agglomerations economy and the urban agglomerations club economy. The size and number of central cities in the region and its surrounding areas have an impact on the provincial administrative district economy, the city agglomerations economy and the urban agglomerations club economy. (3) The function of cities is obviously divided in a multi-scale network. The large cities and regional central cities have a complete and more balanced function system than the small and medium-sized cities do. The radiation effect of three major urban agglomerations in coastal China is significant, while the dominant function of other urban agglomerations needs to be strengthened. (4) The cross-scale regional functional interaction effect of cities (clusters) is significant. The radiation-driven function of cities (clusters) is positively related to their self-agglomeration capabilities. This study provides support for the understanding of urban network model expansion and the spatial relation of urban network in China.
基于财富500强中国企业网络的城市网络空间联系特征
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904006
[本文引用: 9]

基于2015年世界财富500强中的102家中国企业数据,根据企业组织特征构建了反映企业—城市间关联的折衷网络模型,借助网络分析等多种方法分析了中国地级城市间和典型城市群之间的网络联系。研究发现:① 城市网络总体连通性较差、向心集中性强,发育不够完备;城市网络连接具有明显的行政中心指向、沿海指向和资源指向;网络节点城市对外经济依赖度高,网络结构扁平特征明显。城市群网络存在权力分散、地位分化和外部联系依赖特征。② 城市网络中省域、城市群和俱乐部边界效应明显,区域内外的中心城市规模和数量对省域行政区经济、城市群经济和俱乐部经济的发展产生影响。③ 城市在多尺度网络中的功能分化明显,大城市和区域型中心城市比中小城市拥有更加完备和均衡的功能体系。沿海三大城市群的辐射带动作用明显,其他城市群的优势功能有待突出。④ 城市(群)跨尺度区域功能互动效应显著,城市(群)的自我经济集聚能力与城市(群)的对外辐射带动功能之间存在密切的正向关系。研究为城市网络模型拓展及理解中国城市网络空间联系特征提供了支撑。
City linkage based on city functional network: Taking Zhujiang River Delta as an example
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.03.306
[本文引用: 4]

As an important property of city, city functions in different periods differ in forms, intensity and spatial characteristics from the preindustrial age to the postindustrial age. City function experienced from a single and simple function to various, messy and homogeneous functions and then to the diversified different and complementary networked evolution process. This article tries to open a new view angle of city linkage research based on the evolution of city function by constructing an analytical structure of city functional network. The city functional network in the postindustrial period consists of three components of function elements, linkage channel and role carrier. On the basis of diverse, different and complementary city function and through the tangible or intangible linkage channel and taking the entity or virtual spatial flow as the role carrier, forms spatial network structure of city functional network was formed. Based on the evolution process of city function and the concept and connotation of city function network, the article took the evolution of city function network in the Zhujiang River Delta as an example, and reconstructed the history and space features of city linkage in the region and finally constructed a new analytical perspective of city function network on city linkage researches.
基于城市功能网络视角的城市联系研究: 以珠江三角洲为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2015.03.306
[本文引用: 4]

以城市功能的演进历程为城市联系研究的新视角,构建了城市联系的城市功能网络分析框架。其中,城市功能网络由功能要素、联系通道和作用载体三部分组成,是城市功能在多元、差异和互补的基础上通过有形或无形的联系通道,以实体或虚拟的空间"流"为作用载体形成的城市功能空间网络化结构。基于城市功能网络的概念内涵,以珠江三角洲城市功能网络的演化历程为实例,演示了该地区城市联系的演化历程和空间特征,探索了城市联系的城市功能网络分析视角。
The industry spatial layout optimization in the new pattern of dual circulation in China
“双循环”新发展格局下中国产业空间布局优化
Research progress of networking of urban systems in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904005
[本文引用: 3]

At present, there is a consistency that the focus of urban system research has shifted from the hierarchical to network paradigm. Based on an extensive review of existing studies, this paper investigates the shift of paradigm of China's urban system research since the 1980s, and discusses the development situation, main problems, and key topics of related research on urban network. The results show that: (1) After 2010, the amount of literature about urban network has increased dramatically and become the mainstream of urban system research, while the number of studies on the hierarchy system decreased. And the existing studies mainly focus on the urban system at national level and in the Yangtze River Delta. (2) The attribute data to a certain extent compensate for the lack of data in the early urban network research. Meanwhile, although the gravity model was widely used in these studies, its suitability is gradually decreasing. (3) In contrast, the relationship data have attracted scholars' attention, which is mainly applied to the urban system research from three perspectives: enterprise organization, traffic flow and information flow. However, due to the limitations of different perspectives, a comprehensive research on multiple perspectives has gradually become imperative. (4) The identification analysis has been the dominant theme of urban network research. Visualization analysis and design for urban system is mainly supported by directed unprivileged networks and undirected weighted networks. (5) Five important aspects of urban network research in future include adjusting the research framework of national urban network, examining the physical connections between cities directly without traffic data, measuring the horizontal linkages between the outside enterprises, analyzing and visualizing the directed weighted network research, and intensifying the geospatial characteristics of urban network research.
中国城市体系网络化研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201904005
[本文引用: 3]

当前,学者普遍认同城市体系研究的重心从等级范式向网络范式转向。在大量的文献梳理基础上,阐述20世纪80年代以来中国城市体系研究范式的转向过程,并进一步梳理中国城市网络研究的进展、问题与关注重点。结果表明:2010年之后,网络成为中国城市体系研究的主流范式,等级体系文献数量呈波动递减趋势,全国和长三角成为热点关注区域;属性数据一定程度上弥补了早期城市网络研究中数据匮乏的状况,关系数据应成为未来研究的侧重点;不同研究视角及其所应用的数据存在着一定的局限性,多元视角的综合研究成为趋势。在此基础上,提出城市网络研究未来可能的突破点,包括:调整国家城市网络的研究框架、超越交通数据直接考察城市间的实体联系、测度企业外部的横向联系、有向加权网络分析和可视化、增加研究中的地理“意味”等。
Spatial evolution and growth mechanism of urban networks in western China: A multi-scale perspective
DOI:10.1007/s11442-022-1959-8
[本文引用: 1]

Globalization and informatization promote the evolution of urban spatial organization from a hierarchical structure mode to a network structure mode, forming a complex network system. This study considers the coupling of “space of flows” and “spaces of places” as the core and “embeddedness” as the link and a relevant theoretical basis; then we construct a conceptual model of urban networks and explore the internal logic of enterprise networks and city networks. Using the interlocking-affiliate network model and data from China’s top 500 listed companies, this study constructs a directed multi-valued relational matrix between cities in western China from 2005 to 2015. Using social network analysis and the multiple regression of quadratic assignment program model (MRQAP), this study adopts a “top-down” research perspective to analyze the spatio-temporal evolution and growth mechanism of the city network in western China from three nested spatial scales: large regions, intercity agglomerations, and intracity agglomerations. The results show the following: (1) Under the large regional scale, the city network has good symmetry, obvious characteristics of hierarchical diffusion, neighborhood diffusion, and cross-administrative regional connection, presenting the “core-periphery” structural pattern. (2) The network of intercity agglomerations has the characteristics of centralization, stratification, and geographical proximity. (3) The internal network of each urban agglomeration presents a variety of network structure modes, such as dual-core, single-core, and multicore modes. (4) Administrative subordination and economic system proximity have a significant positive impact on the city network in western China. The differences in internet convenience, investment in science and technology, average time distance, and economic development have negative effects on the growth and development of city networks. (5) The preferential attachment is the internal driving force of the city network development.
Comparison of spatial structure and organization mode of inter-city networks from the perspective of railway and air passenger flow
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708013
[本文引用: 1]

As traffic flow reflects the socio-economic relations between cities, it is widely applied as a key factor in studies on city networks. Based on the inter-city railway and air passenger flow in 2010, this article made a comparison of the spatial structure and passenger flow organization of inter-city networks from the perspective of railway and air passenger flow, in terms of node, linkage, and community. The results are as follows: (1) Both city networks based on railway and air passenger flow present a hierarchical structure with Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou being the top three, while the nodes in the lower classes of two networks are different. (2) The spatial structure of linkages between cities based on railway passenger flow displays strong neighborhood effect. In contrast, the cities' own characteristics play a dominant role in the organization of air passenger flow. (3) Most of the dominant railway passenger flow is directed to the capital city in each province, forming several disperse regional systems separated by the provincial boundaries. In terms of air passenger flow, the regional systems are integrated by vertical linkages between them. (4) Although the community structure is not obvious from the perspective of air passenger flow, there are seven communities of significant geographical characteristics being detected in the railway network. The main differences between two networks are attributed to the management systems and technical characteristics of the modes of transportation.
中国城市网络等级结构特征及组织模式: 基于铁路和航空流的比较
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201708013
[本文引用: 1]

交通流是反映城市间社会经济联系的重要表征,被广泛应用于城市网络研究中。基于2010年中国城际铁路与航空客流OD数据,本文从城市节点、流量、子网络视角对中国城市网络的结构特征与组织模式进行了比较研究,发现:① 铁路与航空流视角下的中国城市网络均呈现出以北上广为顶层节点的空间等级结构体系,但除顶层结构外两种网络结构差异较大。② 城市网络体系中的铁路流联系表现出空间邻近性特征,而航空流联系则主要受到城市节点的规模大小与职能属性的影响。③ 铁路流的首位联系受省级行政区划的制约,航空流的首位联系空间跨度大,形成了若干具有垂直层间联系的地域子系统。④ 铁路网络拥有具有显著地域特征的7个子网络,而航空网络中则不存在明显的子网络。技术经济特征与管理体制是造成铁路与航空两种网络特征差异的主要原因。
China's city network characteristics based on social network space: An empirical analysis of sina micro-blog
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003
[本文引用: 1]

The change of urban regional spatial structure influenced by information technology has become a hotspot of research at home and abroad. This study tries to analyze China's city network characteristics from the social network space perspective by using Sina microblog as an example. The result shows that China's city network based on the micro-blog social space has a clear hierarchical structure and level distinction. Firstly, the result shows the existence of regional characteristics, performance as a visible regional development pattern which contains "Three Main-regions and Four Sub-regions" according to the analysis of the level distinction in the city network and the connection rate between cities. Specifically speaking, the three main regions contain the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region represented by Beijing, Pearl River Delta region represented by Guangzhou and Shenzhen, and the Yangtze River Delta region represented by Shanghai, Hangzhou and Nanjing. The four sub-regions contain Chengdu-Chongqing region, west coast of the Taiwan Straits region represented by Fuzhou and Xiamen, Wuhan region represented by Wuhan and Changsha, Northeast China represented by Shenyang, Harbin and Changchun. Secondly, the result shows there is a significant difference of the network links among Eastern, Central and Western China. Links within Eastern China and the links between Eastern, Central and Western China constitute almost all of the current network systems. It is also found that the high-level cities have an absolute dominance in the city network pattern, and that Beijing is the contact center in China's city network, with an overwhelming advantage. Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are the sub-contact centers in the China's city nework.
基于网络社会空间的中国城市网络特征: 以新浪微博为例
DOI:10.11821/xb201208003
[本文引用: 1]

信息技术影响下的城市区域空间结构变化得到了国内外学者的关注。本文以新浪微博为例, 从网络社会空间的角度入手, 对中国城市网络发展特征进行了研究。研究表明:微博社会空间视角下的中国城市网络存在着明显的等级关系与层级区分, 城市的网络连接度与城市等级表现出了相对一致性。根据城市网络层级与网络联系强度, 东部、中部、西部3 大区域板块的网络联系差异明显, 东部地区内部的联系, 以及东部与中部地区和西部地区的联系几乎构成当前网络体系中的全部。城市网络呈现出分层集聚现象, 具体表现为“三大四小”发展格局, 即京津冀区域、珠三角区域、长三角区域、成渝地区、海西地区、武汉地区、东北地区。高等级城市在整个城市网络中处于绝对支配地位, 北京以突出的优势成为全国性的网络联系中心, 而上海、广州、深圳则成为全国性的网络联系副中心。
The theoretical construction and network simulation of intercity innovative relationships in knowledge flow space
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004004
[本文引用: 1]

The interactive relationships between cities in the knowledge economy era have attracted much attention. Researchers have applied a range of methods to explore intercity innovative relationships and associated network characteristics. It nevertheless remains unclear just how intercity innovative relationships can be theoretically constructed based on knowledge flow space and how further scientific simulation methods can be designed. Research questions in this area have rarely been explored in detail, an issue which has inevitably placed obstacles on further exploration. A framework for the theoretical construction of intercity innovative relationships is presented in this study; the basis for this research is that an intercity innovation network is essentially a 'soft network', distinct from a 'hard network'. These interconnections are founded on a subjective relationship construction process and therefore necessitate scale transformation from 'point-point' connections between innovative subjects in different cities with respect to 'city-city' interactions. At the same time, this transformation process is prone to exaggerations and deviations from objective intercity innovative relationships and therefore exerts considerable influence on the accuracy of results such that constructions must be entirely theoretical. Four construction methods for intercity innovative relationships and network simulation are summarized in this study, including an intercity undirected network based on cross-city co-operations between scientific and technological achievements, an intercity directed network based on the cross-city transfer of scientific and technological achievements, an intercity innovation network based on the cross-city flow of high-end talents, and an intercity innovation network based on the multi-city distribution of innovative enterprises and institutions. Simulation tests were then undertaken using relevant data to reflect aspects of these relationships. The results of this analysis are conducive to further exploration of global and regional innovative spatial patterns from the perspective of urban geography and intercity relationships and provide a theoretical and methodological foundation for further research on intercity innovation networks.
知识流动空间的城市关系建构与创新网络模拟
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202004004
[本文引用: 1]

知识经济时代城市间的创新关系是新时代城市间相互作用关系的新内涵,研究者尝试采用各种方法探索城市间创新关系及其网络特征。然而,如何从理论上建构知识流动空间的城市间创新关系?如何设计更加合理的城市间创新网络模拟方法?这些问题却少有专门探讨。基于相关研究,本文提出了城市间创新关系构建的理论框架,认为城市间创新网络本质上是区别于“硬网络”的“软网络”,是一种主观的关系建构过程,需要经过异城创新主体间的点—点关系向城—城之间关系的尺度转换,这一转换过程容易发生夸大或偏离城市间客观存在的创新关系,对结果的精确度产生很大影响,应对关系建构给予充分理论论证;本文论述了4种城市间创新关系建构和网络模拟方法,包括科技成果异城合作的城市间无向网络构建方法、科技成果转让转移的城市间有向网络构建方法、高端人才跨城移动的城市间创新网络建构方法和创新企业机构多城分布的城市间创新网络建构方法,并运用相关数据进行了模拟试验与结果展示,来反映城市间创新关系的不同方面。本研究有助于推动从城市地理学视角和城市关系的维度探讨全球/区域的创新空间格局,为城市间创新网络研究提供理论和方法支撑。
Progress, thoughts, and prospect of urban network research based on enterprise perspective
基于企业视角的城市网络研究进展、思考和展望
A comparison between airline passenger network and advanced producer service network in the urban system of China
中国城市体系中航空网络与生产性服务业网络的比较
Spatial structure of urban networks in China based on the perspective of cultural industry enterprise networks
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.008
[本文引用: 4]

In recent years, urban networks have become a focus of research in geography, urban studies, and other related disciplines. While previous research has examined the urban networks in China from different perspectives, the networks generated by cultural industries have remained a largely unexplored area. This article aims to fill this gap by presenting a comprehensive analysis of the spatial structures of the cultural industry-generated urban networks in China's mainland and compares the disparities between these networks and the urban networks created by other types of economic activities. Data of the headquarter-affiliation connections of 230 NEEQ (National Equities Exchange and Quotations)-listed cultural firms in 2017 were collected and analyzed using social network analysis method. In addition, the article also explores the economic and social factors that shape the formation of the spatial patterns of China's cultural industry urban networks drawing on the method of multiple linear regression (MLR). The outcomes reveal that: First, shaped by both market mechanisms and the interventions of local governments, the distribution of the NEEQ-listed cultural firms demonstrates a geographically dispersive, but quantitatively concentrated pattern in China. The spatial structure of the cultural industry urban networks is highly uneven, with most inter-city connections concentrated in the eastern part of the country. The cultural industry urban networks do not exhibit the typical diamond-shaped structure that has been observed in many other urban networks in China. Second, the core nodes of the cultural industry urban networks are mainly economically advanced metropolises in the eastern and central areas, as well as a few minor cities that possess some special local assets, including large film and television studios, unque natural or humanistic environment, and preferential tax policies. Most cities are receivers instead of exporters of cultural industry functions. Third, the expansion of the cultural industry urban networks is mainly between the core nodes of different hierarchies instead of between geographically proximate cities. The contribution of local (intra-urban) networks to the formation of intra-firm relationships of cultural industries is weaker than that of trans-local networks, which indicates that, compared with the advantages of geographical proximity, the complementarity of market or resources is the primary factor considered by cultural firms during their expansion. Fourth, the urban networks of different subsets of cultural industries have rather diverse spatial structures, which reflect the varied market demands and development conditions of different cultural industry activities. Fifth, according to the outcome of MLR analysis, the function of local governments and urban industrial structure are two important factors that shape the location strategy of cultural firms and the pattern of cultural industry urban networks in China, whereas the impacts of other economic and social factors are not significant. The article enriches our understanding of the spatial organization of cultural industries and the diversity of modern urban networks. It also sheds light on cultural industry development policies in the Chinese context.
基于文化产业企业网络视角的中国城市网络空间结构研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.01.008
[本文引用: 4]

论文通过对230家“新三板”文化产业挂牌企业总部—分支机构关联数据的收集、整理和分析,对文化产业视角下中国城市网络的空间结构特征进行研究,比较文化产业城市网络与其他类型城市网络的差异性,并探索影响文化产业城市网络空间格局的经济社会因素。结果表明:① 中国文化产业挂牌企业地理分布呈现出地域分散但数量集中的特点,城市网络空间分布高度不均衡,并未表现出常见的“菱形结构”;② 网络核心节点以东中部发达城市以及少数具有特殊资源的城市为主,多数城市的对外输出能力有限;③ 城市网络扩散以核心节点城市间的等级扩散为主,邻近城市间的扩散效应不明显,同时本地网络(即城市内部网络)对文化企业组织结构的贡献度低于跨地域网络;④ 不同类型文化产业在网络结构上表现出较为明显的差异,反映其市场需求和发展条件的不同;⑤ 地方政府作用和城市产业结构是影响中国文化产业企业布局和网络格局形成的重要因素,其他社会经济因素的作用则较为不明显,反映出中国文化产业的独特性。
Application of the interlocking network model to mega-city-regions: Measuring polycentricity within and beyond city-regions
DOI:10.1080/00343400701874214 URL [本文引用: 1]
Connecting the 'workshop of the world': Intra-and extra-service networks of the Pearl River Delta city-region
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.962492 URL [本文引用: 1]
Opening the black box of agglomeration economies for measuring cities' competitiveness through international firm networks
DOI:10.1177/0042098010377369
URL
[本文引用: 5]

The ability of cities to operate in global networks is usually measured according to their central position within multinational firm linkages. These measures are often used at the interurban level and neglect the intraurban processes of multiplier effects. The present study demonstrates that this affects the measurement of city centrality in business networks. Intraurban capabilities of interaction are considered in the measurement of interurban indices. The study is based on hypothetical networks at a micro level between long-range links and it mobilises processes as agglomeration economies, social capital developments and transaction costs. These processes at the intraurban level strengthen the efficiency of interurban linkages. It is suggested that the indices used to measure city centrality should include these local effects. Applied to a small sample of six firm networks, the methodology shows advantages for emerging large metropolises, but insufficient local effects for specialised clusters. The multilevel approach offers improved perspectives for the comparison of city centralities.
A preliminary analysis on urban innovation network of metropolitan region and its characteristics
大都市圈城市创新网络及其发展特征初探
Study on the city network based on value chain division of Chinese film industry
基于中国电影产业价值链分工联系的城市网络研究
China's film production industry based on the network structure
DOI:10.2307/142505 URL [本文引用: 4]
基于网络结构的中国电影制片业研究
Literature review on the network of film industry
As an “industry”, the time of Chinese film is short. So research about Chinese film industry is rare and far behind the actual development of practice. Foreign economic geography scholars research film industry mainly from industrial cluster as the core of the local network and value chain, global production network as the core of the global network. In the theoretical aspect, the research from the network perspective on the film industry is similar with manufacturing, high-tech industries and so on. They pay more attention to the production of whole process. The research about the distribution and exhibition of film industry is less. From the empirical perspective, the case studies are almost about the developed countries. However, the social, cultural and institutional factors have great influence on the development of the network. Therefore, research of the film industry in the developing countries is urgently needed to be carried out.
电影产业网络研究综述
我国电影以“产业”形态发展的时间较短,学者们对电影产业的研究较为匮乏。国外经济地理学者关于电影产业的研究主要从以产业集群为核心的地方网络和价值链、全球生产网络为核心的全球网络视角出发。理论层面,从网络视角出发对电影产业的研究与制造业、高技术产业等一致,核心关注点是生产这一单一环节的网络构建、发展、空间演化特征等,对发行、放映等其他价值链环节的系统性研究不足。案例层面,主要集中在欧美发达国家的电影产业,然而社会、文化和制度因素对网络发展影响较大,因此以我国为代表的发展中国家电影产业的网络研究亟待展开。
Urban positionality in the regional urban network: Through the lens of alter-based centrality and national-local perspectives
Re-cognition of the theoretical connotation of urban agglomeration in the new period
新时期城市群理论内涵的再认知
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.011
[本文引用: 2]

在全球化、信息化背景下,城市之间的竞争已经不再局限于单体城市本身的规模属性,而是越来越取决于城市参与分工协作的地位以及多尺度空间的功能联系,尤其表现在城市网络化、集群化的竞合态势,而城市群已经成为该背景下具有全球意义的空间组合模式。在系统梳理了中西方城市功能地域概念的内在关联基础上,论文认为,中国的城市群概念具有尺度伸缩性,与西方的巨型城市区域、巨型都市区和巨型区域概念是最为接近的。在空间内涵上看,城市群是2个以上城市体系组成的巨型城市地域,是兼具形态连续性和功能内聚力的城市系统,是全球化与本地化显著交互作用的大型经济单元,是当今时代城市与区域分工协作的一种尺度修复。基于此,城市群发育的基本条件主要包括良好的资源环境综合承载能力、大都市区与多个城市系统、地理空间上的邻近性与紧凑性、发达和完善的基础设施网络、深入协调的功能分工与经济联系以及相对一致的社会网络和文化认同。未来,中国城市群研究应更加兼顾形态和功能维度的统一,尤其注重从关系地理与城市网络视角探索城市群的空间集聚效应及其演化规律。
Measurement of directed alternative centricity and power of directed weighted urban network: A case of population flow network of China during "Chunyun" period
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201704004
[本文引用: 2]

With the rapid development of ICTs and big data technology, various "flow" data have become easier to be obtained such as population flows, information flows and capital flows. These data are key material to build the production network, social network, urban network and other types of network, which are becoming very important research subjects of geographical sciences and enrich the research content of this field. So far, researches on the networks in geography are still in their infancy stage. There are a number of methods that have not been utilized effectively, while it is difficult to find a proper abstracted network model to simulate the geographical phenomenon in many occasions. Therefore, to seek more appropriate methods and models for geographical network studies undoubtedly become urgent tasks in this field. In this context, an exploratory research was carried out. First, population flow network of China in the period of "Chunyun", a typical directed-weighted urban network, was built based on the population flow data acquired from “Big data on human migration during the "Chunyun" period from Baidu Map ("Baidu migration data" in short). Sequentially directed alternative centrality and directed alternative power were proposed in predecessor's foundation to evaluate the importance of each node and divide these nodes into different types according to their roles in the urban network. As analysis result, two dimensional spatial characteristic and geographical spatial characteristic was revealed which endowed the methods more practical significances. To validate the effectiveness of the methods, a contrastive analysis of the directed alternative centrality/directed alternative power and centrality/directed alternative power in previous studies was conducted. Based on directed weighted urban network and with the help of this method, this paper classified the cities into quintessential cities, hub cities, gateway cities and periphery cites, and identified the characteristics of agglomeration and diffusion at the mean time. And the result of classification was explained according to the internal structure and external context of the population flow network during the "Chunyun" period. It is found that the regional difference of directed alternative centrality and directed alternative power have certain relationship to economic and social development, national development strategy and administrative division. This explorative process demonstrated that one can effectively extract the information on the hierarchical structure, function divergence and imbalance of the directed weighted urban network via the directed alternative centrality-directed alternative power method. Directed alternative centrality-directed alternative power method is really a feasible approach to analyze the geographical network, and it also demonstrated that directed-weighted urban network can really make a difference from undirected and unweighted network in the geographical network studies.
有向加权城市网络的转变中心性与控制力测度: 以中国春运人口流动网络为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201704004
[本文引用: 2]

目前中国地学领域对网络的研究仍处于起步阶段,大量网络研究方法尚未得到应用的同时,许多地理现象尚未寻找到合适的抽象网络模型,不断拓展和应用有效的网络分析方法成为当务之急。在这一背景下,基于百度迁徙平台获取的春运人口流动大数据,构建中国春运人口流动的有向加权城市网络,在已有研究基础上提出有向转变中心性与控制力测度方法,对该城市网络的节点重要性和功能进行评估和分类,分析其呈现的二维空间特征与地理空间分布特征,并与已有方法进行对比。结果表明:利用有向转变中心性和控制力方法,可有效提取有向加权网络的层级结构、功能分异和非均衡性等特征,不但可区分典型城市、枢纽城市、门户城市与边缘城市等不同的城市类型,还可以识别城市的集聚与扩散特征,从而获得比无权无向网络更为丰富和具有实践意义的信息参考,是一种有效的地理网络分析方法。
The structural characteristics and spatial organization pattern of China's urban network based on the multiple flow
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220731
[本文引用: 2]

Networking of the relation among cities is a momentous trend in the development of urban system structure. The connection between cities is often the superposition of multiple elements rather than a single dimension. The urban system of the spatial network of different factor flows differs from each other in spatial organization. Furthermore, the network based on one single factor has obvious limitations so that it is necessary to make a comparative study on the differences of factor flows under the multi-city network. Therefore, this paper, on the basis of four element networks, which are enterprise connection, scientific research cooperation, population migration and gravity simulation, analyzes respectively the external spatial characteristics and disparities of China's urban networks under the perspective of multiple flow space, to be specific, urban node, path connection, community characteristics and etc; explores the internal pattern and law of inter-city connections; as well as attempts to advance proposals to optimize the development of China's urban system. The results reveal that: (1) The spatial organization of multi-city networks shows that the characteristic of similar stability with a “diamond+cross” spatial structure and a “core-node-edge” hierarchical structure, integrates with the characteristic of multiple diversity from the perspective of multi-dimensional data sources; (2) Mobility of population, circulation of materials and other networks that depended on the operation of infrastructure, to some certain extent, are greatly constrained by geographical distance and at the same time show obvious small group characteristics in adjacent areas and strong community structure. However, the less substantial elements such as capital flow and information flow break through this geographical restriction. The focus of the connection lies in the attraction of the target city to the element flow, and the community structure of this type appears to be weak. (3) At present, China's urban connection has the dual characteristics of hierarchy and flattening in form. Therefore, this paper proposes an urban connection model of the “community buzzer-gatekeeper-regional pipeline” model, compatible with the dual features of vertical structure and network structure, applying well for demonstrating the characteristics of China's urban connection, identifying 10 core gatekeeper cities and 8 types of regions in China. Among them, the goalkeeper city with special resources and regional advantages is the leader of the region, playing a key role in undertaking, transforming and spreading various resource elements. This paper aims to improve the theory of urban network and provide theoretical support for urban network development.
多重流空间视角下的中国城市网络空间结构特征及组织模式
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220731
[本文引用: 2]

城市关系网络化是城市体系结构发展的重要趋势,不同要素流空间网络下的城市体系在空间组织上不尽相同,依托单一要素对网络进行表征的结果具有明显的局限性。本文基于企业联系、科研合作、人口迁徙和引力模拟四类要素网络,从城市节点、路径联系、社区特征等角度剖析多重流空间视角下中国城市网络的外部空间特征与差异,并探究城市间联系的内在模式规律。结果表明:① 多维数据源视角下构建的多重城市网络在空间组织上表现出相似稳定性和多元差异性的统一。② 一定程度上依赖于基础设施运转的人流、物流等网络受到地理距离的约束较大,相邻地区的小团体特征明显,社区结构较强;而资金流、信息流等实体性较弱的要素则突破了这种地理限制,发生联系的重点在于目标城市对于要素流的吸引力,社区结构较弱。③ 目前全国城市联系形态上具有层级性和扁平化的双重特征,据此本文基于“管道-蜂鸣”模型提出“社区蜂鸣-守门员-区域管道”城市空间组织模式,这一模式对于阐述中国的城市联系特征具有较好的适用性,可在全国识别出10个核心守门员城市和8个类型区。
Patterns and determinants of functional division of cities across product value chain in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020191045
[本文引用: 2]

Decreasing spatial transaction and trade costs facilitates the geographical fragmentation of functions, i.e. the stages or activities within product value chain could give rise to functional differentiation of cities. Despite the recent advances in the study of the spatial structure of urban networks, the analysis of functional differentiation of cities across multi-location firms' value chain has been largely neglected. The study sets out to investigate the patterns of functional division of economic activities within China's urban system, and explore the underlying factors with multiple regression models. To this end, data on the corporate networks of China's top 500 public companies in 2018 are collected, and the establishments within the corporate networks are grouped into seven functions: headquarters, business services, research and development, modern manufacturing, standardized production, logistics, and wholesale and retail. The following results are obtained. First, different types of functions within the value chain show different spatial patterns, which leads to the differentiation of urban functions, and promotes the transformation of Chinese cities from sectoral specialization to functional specialization. The three knowledge-rich functions of headquarters, business services and research and development are mainly centralized in the core cities of China's major urban agglomerations, while standardized production has the lowest level of spatial concentration. The second major finding is that functional specialization co-exists with functional diversification within the urban system in China. Overall, large cities are much more functionally diversified, while small and medium-sized cities tend to be specialized in standardized production. Using the clustering algorithm based on self-organizing feature maps, the 334 cities in China can be classified into 9 functional types. Third, location fundamentals play a key role in driving the functional differentiation of cities. Although city size, vital resources, accessibility, urban infrastructure, business environment positively contribute to the presence of all functions, their marginal effects differ across the seven functions. The improvement of economic scale and vital resources will increase the probabilities for cities to develop into headquarter centers, business service centers and R&D centers, while reducing the probabilities of cities is becoming standardized production bases. The traditional urban resource advantages has been transformed into the competitive advantages of urban functional status, suggesting that the development gaps between cities in China will further be enlarged under the network environment.
中国城市价值链功能分工及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020191045
[本文引用: 2]

价值链的空间重组正在深刻的改变着城市体系的经济景观,建立在价值链分工基础上的城市功能结构的研究已经成为经济地理学的重要课题。将中国上市公司500强企业网络划分为公司总部、商务服务、研究开发、传统制造、现代制造、物流仓储和批发零售七种类型功能区块,研究了中国城市价值链功能分工及其影响因素。结果发现:沿着价值链的功能分工已经成为中国城市体系经济景观的显著特征,功能多样化城市和功能专业化城市并存于中国城市体系,东部地区和城市密集地区的城市在价值链分工中占据了更好的地位;中国城市按照价值链中的优势功能可以划分为九种类型,少数城市转变为承载公司总部、研究开发、商务服务等多样化功能的高等级中心城市,而大量中小城市则转变为传统制造专业化基地;市场潜力、关键资源、区位条件、营商环境等城市属性特征是城市功能分工的重要影响因素,城市资源、区位可达性等属性特征的增强将提高城市成为总部基地、商务中心和研究基地的概率,而降低城市成为传统制造基地的概率。
Urban connection and function in Wuhan urban agglomeration based on multi-dimensional urban factor flows
基于多维城市要素流的武汉城市圈城市联系与功能分析
Functional differentiation of Chinese cities participating in the dual circulation: Chinese companies' global expansion perspective
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211056
[本文引用: 1]

The expansion of leading Chinese companies facilitates the circulation of production factors, and endows cities with the dual role of participating in the internal and external dual circulation. The dual circulation strategy implies that China should "rely on the internal circulation of domestic demand and innovation as the main driver of the economy, and balance emphases on both internationalization and self-sufficiency". In this context, recognizing the functional differentiation of cities participating in the dual circulation is of great significance. Drawing on the organizational network of Chinese companies in the Forbes Global 2000 and Fortune Global 500 list in 2018, this research applies the interlocking network model to map the domestic and international connectivities of Chinese cities. In doing so, it uncovers cities′ different roles in participating in the internal and external circulations, as well as their intermediary functions in the dual circulation. Based on their major business activities, we further divide companies into four sectors: advanced producer service, consumer service, manufacturing, as well as mining and construction. This allows us to examine the sectoral differentiation of cities′ functions. We find that, administrative ranking and level of economic development have a significant impact on Chinese cities′ ability to participate in dual circulations. Our results also suggest hierarchical characteristics: national-level industrial centers have extensive global connections, and they are able to provide high-level products and services. Industrial centers at a regional level, by contrast, have stronger domestic connections, providing lower-level products and services to surrounding areas. Besides, different sectors shape various network structures and city functions. In the network shaped by advanced producer services, cities with high administrative rankings are able to participate the dual circulation; for the general service sector, the ability to participate in dual circulation is more affected by the level of economic development. By contrast, in the case of the manufacturing industry, a larger number of cities are involved in the dual circulation process, with a more scattered spatial distribution; in terms of the mining and construction industries, cities with resource advantages can widely participate in the dual circulation.
中国城市链接国内国际双循环的职能分异: 基于中资企业海内外扩展的视角
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211056
[本文引用: 1]

重要中资企业的海内外拓展布局,促进了生产要素的循环流动,也赋予了作为空间载体的城市参与链接国内国际循环的双重角色和职能分工。在“加快构建以国内大循环为主体、国内国际双循环相互促进”的新发展格局背景下,认清城市参与双循环的职能分异,对于科学评估城市融入双循环的能级水平具有重要意义。研究从福布斯全球企业2000强和《财富》世界500强中资企业的全球组织网络出发,利用链锁模型映射了企业视角下中国城市的国内国际联系网络,解析了城市参与链接国内国际循环和担任中介节点的职能分异,并分高级生产性服务业、一般服务业、制造业和采矿建筑等四种行业解析了职能分异的行业异质性。研究发现,中国城市链接国内国际循环的职能分异受行政等级和经济发展水平的影响显著,具有明显的层级性。其中,国家级产业中心城市,具有明显的对外服务职能;区域级中心城市,则具有更强的对内服务职能。不同类别行业塑造的网络格局和城市职能分工具有明显差异。
Clusters and knowledge: Local buzz, global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation
DOI:10.1191/0309132504ph469oa
URL
[本文引用: 7]

The paper is concerned with spatial clustering of economic activity and its relation to the spatiality of knowledge creation in interactive learning processes. It questions the view that tacit knowledge transfer is confined to local milieus whereas codified knowledge may roam the globe almost frictionlessly. The paper highlights the conditions under which both tacit and codified knowledge can be exchanged locally and globally. A distinction is made between, on the one hand, the learning processes taking place among actors embedded in a community by just being there dubbed buzz and, on the other, the knowledge attained by investing in building channels of communication called pipelines to selected providers located outside the local milieu. It is argued that the co-existence of high levels of buzz and many pipelines may provide firms located in outward-looking and lively clusters with a string of particular advantages not available to outsiders. Finally, some policy implications, stemming from this argument, are identified.
Knowledge collaboration patterns of Chinese cities and their impacts on knowledge output:An empirical study based the "buzz-and-pipelines" model
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204013
[本文引用: 4]

With the rise of the knowledge economy and network society, knowledge collaboration networks have become vital to understanding innovation processes. There are two types of collaboration patterns within interurban knowledge collaboration networks, namely "local buzz" and "global pipelines". This study discusses the characteristics of intraregional and interregional collaboration linkages and their impacts on the knowledge output based on the logic and hypotheses of the "buzz-and-pipelines" model. First, the study proposes novel measures of buzz and pipelines. Second, the study constructs knowledge collaboration networks among 215 cities at prefecture-level and above across 20 urban agglomerations in China based on the co-publication data drawn from the Web of Science. An investigation of the evolution paths and combination patterns of buzz and pipelines in the networks identifies different collaboration patterns among Chinese cities. Finally, the impacts of buzz and pipelines on cities' scientific output are examined. The results show that: (1) The evolution of buzz and pipelines in China's interurban collaboration networks presents cumulative and self-reinforced path dependences. (2) Chinese cities can be categorized into four types, namely "networked", "outward-oriented", "inward-oriented" and "isolated" cities. Different kinds of cities present distinct features in terms of collaboration trajectories and knowledge production. (3) There is an inverted U-shaped relation between intraregional linkages and the knowledge output performance of Chinese cities, whereas the relation between interregional linkages and knowledge output is significantly positive. The relationship between intraregional and interregional linkages is complementary in facilitating cities' knowledge production processes.
基于“蜂鸣—管道”模型的中国城市知识合作模式及其对知识产出的影响
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204013
[本文引用: 4]

知识经济与网络社会时代,知识合作网络成为理解城市创新过程的重要视角。在知识合作网络中,存在两种不同类型的合作模式,即“本地蜂鸣”和“全球管道”。本文以“蜂鸣—管道”模型的逻辑思想和理论假设为基础,探讨区域内和跨区域两种不同城市知识合作模式的特征及其对城市知识产出的影响。首先提出了蜂鸣与管道的测度方法;然后以“Web of Science”数据库为基础构建了中国20个城市群的知识合作网络,考察了网络中蜂鸣和管道的演化路径和组合特征,归纳出城市知识合作模式的不同类型;最后,通过计量模型揭示了蜂鸣和管道对城市知识产出的影响。结果显示:① 中国城市知识合作网络中的蜂鸣与管道表现出渐进积累和自我强化的空间演化特征;② 根据蜂鸣和管道的组合特征,可将城市划分为“网络型”“外向型”“孤岛型”“内向型”4类,不同类型的城市在知识网络中的空间分布规律和发展演进路径存在差异;③ 根据负二项回归模型发现,蜂鸣与城市知识产出呈倒“U”型关系;管道与城市知识产出显著正相关;此外,两种合作模式在促进城市知识生产的过程中存在互补效应。
Review on the urban network externalities
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.04.015
[本文引用: 3]

Urban network research has become the frontier academic field of international urban research and has gradually become a hot spot. At present, the related literature on "urban network" mostly focuses on conceptual discussion, dimension analysis, and network structure analysis. Research on the influence of network on regional economic development is relatively weak. Externality, as an essential attribute of urban network, is of great significance to the evolution of urban network and the development of cities and regions. This article starts from a comparison of agglomeration externalities with urban network externalities, focusing on the review and evaluation of the formation mechanism, utility, and measurement methods of urban network externalities. The synergy effect, integration effect, and borrowing size are considered important reasons for the formation of urban network externalities. The research on the effectiveness of urban network externalities focuses on two aspects. The first is the role of factor flow in promoting knowledge diffusion and innovation, and the second is the impact of urban network on competitiveness and economic growth. Based on the existing literature, the research on the measurement of urban network externalities mainly involves identification and estimation, including three common methods: correlation analysis, regression analysis, and spatial econometric analysis. The existing empirical research on externalities is still mostly based on static analysis and lacks dynamic consideration. To a large extent, the existing research has insufficient theoretical framing and insufficient explanatory power, often resulting in the discovery of conditional associations, but not causal relationships. The Western research on urban network externalities is relatively early and mainly focuses on the global and regional dimensions, while Chinese scholars focus on the national and regional dimensions. In terms of empirical methods and objects, Chinese scholars have also made some innovations based on the study of world city network. The issues that need further attention in the future include theoretical understanding of urban network externalities, externality measurement methods, and empirical research.
城市网络外部性研究述评
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.04.015
[本文引用: 3]

城市网络研究已成为国际上城市研究的前沿学术领域并渐成热点,外部性作为城市网络的本质属性,对城市网络的演化及城市与区域的发展均具有重要意义。论文从集聚外部性与网络外部性比较的视角切入,重点对城市网络外部性形成机理、效用和测度方法等方面的研究进展进行梳理和评述。其中,协同效应、整合效应和规模借用被认为是城市网络外部性形成的重要原因。而城市网络外部性的效用研究较多集中在2个方面:一是关注要素流动对知识扩散和创新的促进作用,二是关注城市网络对竞争力提升和经济增长的影响。从已有文献来看,城市网络外部性测度研究主要涉及识别和估算2种类型,包括3种常用方法:关联分析、回归分析和空间计量分析。未来需要进一步关注的问题包括城市网络的外部性理论认识、外部性量度方法以及经验研究问题。
From network description to network performance: Preface to the special issue 'Urban Network Externalities'
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220811
[本文引用: 1]

In recent years, network analysis has been widely used to understand urban and regional organizational patterns and their spatial effects. A single city benefits from the scale economy of 'networking' in the inter-city synergy relationship. Some cities or regions also suffer from the loss of resources or elements due to more convenient connections to other cities. The traditional urban endogenous growth theory emphasizing agglomeration economy is no longer suitable to explain the urban and regional organization shaped by 'spaces of flow' alone. The externality of urban network has become another important factor affecting urban growth and regional integration. At present, the existing research (especially in China) is relatively scarce, and most of the studies focus on the spatial pattern and process of the network, and the effects (externalities) of network connections are relatively ignored, i.e., how the urban network externalities interact with the agglomeration economy, which types of cities will benefit or suffer from urban network externalities, and what are the conditions for generating urban network externalities. The above need to be discussed urgently. In order to call on academia to shift more attention on network research to the scientific exploration of 'what' and 'how' regarding the effects of urban and regional development and its optimization, this special issue has selected 15 related papers which carry out the systematic theoretical discussion and empirical research aiming at the 'urban network externalities'. They outline the research agenda on Chinese experience of urban network externalities, and use this as a starting point to promote the deepening of urban network research from pattern description to network performance.
从网络描述走向网络绩效: “城市网络外部性”专辑序言
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220811
[本文引用: 1]

近年来,网络分析被广泛应用至理解城市与区域组织模式及其空间效应中。单个城市在城际协同关系中借助“网络化”的规模经济而受益,一些城市或地区也因更便捷地连接其他城市从而导致资源或要素的流失。传统强调集聚经济的城市内生增长理论不再适宜用来单独解释“流动空间”塑造下的城市与区域组织,而城市网络的外部性成为影响城市增长、区域一体化的另一重要动因。目前,已有的研究(特别在国内)相对匮乏,多集中在网络的空间格局、过程等方面,针对网络联系的效应(外部性)较为忽视,比如城市网络外部性与集聚经济如何相互作用,哪些类型的城市将从城市网络外部性中获益或受损,城市网络外部性的产生条件如何等问题亟需探讨。为呼吁学术同行将更多对网络研究的关注移向探究城市网络对城市与区域发展有何作用、如何作用、怎样优化的科学探索,本专辑精心遴选了15篇相关论文,针对“城市网络外部性”开展系统的理论探讨与实证研究,勾勒城市网络外部性的研究议程与中国经验,并以此为起点推动城市网络研究从格局描述走向网络绩效的研究深化。
Spatial evolution and interaction effects of multi-scalar urban networks in the Yangtze River Delta
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.10.009
[本文引用: 3]

Based on the cross-national, cross-regional and regional enterprises’ nonlocal investment data in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and applying the social network analysis, panel vector auto regression and geographically weighted regression, this paper reveals the spatial evolution characteristics and interaction effects of the YRD’s multi-scalar urban networks. The results are obtained as follows: Global, national, and regional urban networks in the YRD are in the preliminary, steady, and perfect development stages. Besides, the YRD’s multi-scalar urban networks tend to be regionalized: On a global scale, a dense regional network is gradually forming between the YRD and East Asia, Western Europe, and North America; on a national scale, the connectivity between the YRD and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the Pearl River Delta becomes closer; on a regional scale, there are closer economic ties within the provinces compared with trans-provincial economic ties. Additionally, the network spatial structure dominated by the Shanghai-Nanjing-Hefei-Hangzhou-Ningbo development corridor is forming. When it comes to the interaction effects of the YRD’s multi-scalar urban networks, there is a mutual promotion relationship between the global and national functional connectivity. The improvement of the city’s regional functional connectivity can promote its integration into the global and national urban networks. However, the improvement of the city’s global and national functional connectivity cannot promote its further integration into the YRD’s regional urban network, and its integration into the global urban network even has a significant inhibitory effect on the city’s regional functional connectivity. Furthermore, obvious spatial heterogeneity of interaction effects can be observed, which is coupled with regional economic development patterns.
长三角地区多尺度城市网络空间演化及互馈效应研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.10.009
[本文引用: 3]

基于2003—2018年长三角地区跨国、跨区以及区内企业异地投资数据,融合社会网络分析、面板向量自回归模型和地理加权回归模型等方法,探究长三角地区多尺度城市网络空间演化及其动态互馈效应。结果表明:① 全球、全国和区域尺度城市网络分别处于初步发展、稳步发展和完善发展阶段,各尺度网络均呈现出区域化倾向,以沪宁合杭甬发展廊道为支撑的网络空间结构正在形成。② 城市的全球与全国功能联系之间存在相互促进的关系;城市的区域功能联系提升能够促使其融入全球和全国尺度城市网络,反之,城市的全球与全国功能联系提升却未能促进其进一步融入长三角内部城市网络,融入全球尺度城市网络甚至对城市的区域功能联系产生显著的抑制作用。此外,多尺度城市网络互馈效应具有明显的空间异质性,并与区域经济发展格局相耦合。
Urban network externality modelled through spatial econometric models
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220732
[本文引用: 1]

In the context of economic globalization and regional integration, urban development forces have shifted from geographical agglomeration to external network coordination. The connectivity among cities or city network is increasingly becoming “the second essence of cities”. With bibliometric analysis of urban network externality studies, we find that spatial econometric models have been increasingly employed to quantify whether, and to what extent, urban network externality matters in the developmental process of cities or regions. This study first investigated the mathematical properties of spatial econometric models and in particular, the correspondence of model parameters and various measures of urban network externality. More importantly, we highlighted two essential issues of classic spatial econometric models when being applied to model urban network externality: the asymmetric effect and scale effect of urban network externality. Then, we developed an asymmetric spatial economic model (ASEM) to capture the asymmetric effect of urban network externality and, a hierarchical spatial autoregressive model (HSAR) to deal with the scale effect of urban network externality. A series of Monte Carlo simulation experiments were conducted to assess the benefits of these two proposed methodologies. We found that: (1) Ignoring the potential asymmetric effects in the urban network will significantly reduce the accuracy of model parameter estimation. On the other hand, the proposed ASEM can accurately identify the asymmetric effects of network externalities and yield more accurate parameter estimation. (2) Ignoring multi-scale network effects in real world data and modeling the network effects at a single scale will cause serious estimation distortion. The HSAR model instead can provide a reliable quantitative method for modeling the externalities of multi-scale networks.
基于空间计量模型的城市网络外部性定量测度
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220732
[本文引用: 1]

在经济全球化、区域一体化的背景下,城市发展动力由内部功能集聚转向外部关系协调,城市间的关联作用愈发重要,成为“城市的第二本质”。通过文献计量分析,发现空间计量模型逐渐成为城市网络外部性定量测度的主要方法之一。从研究设计角度,空间计量模型作为城市网络外部性的定量建模工具,存在至少两方面的问题:城市网络外部性的非对称效应和城市网络的多尺度问题。本文结合城市网络外部性测度与建模,首先阐述如何规范地解读空间计量模型参数及其与网络外部性测度的对应关系;其次基于蒙特卡洛模拟实验论证非对称城市网络外部性和多尺度城市网络外部性的建模方法。研究表明:① 忽视城市网络外部性中潜在的非对称效应会显著降低模型参数估计的准确性,本文开发的非对称空间效应模型(Asymmetric Spatial Econometric Model,ASEM)可以准确识别网络外部性的非对称效应,给出更加准确的参数估计;② 忽略现实存在的多尺度网络效应,只在单一尺度对网络效应建模会造成参数估计失真,而空间多尺度统计模型(Hierarchical Spatial Autoregressive model,HSAR)为多尺度网络外部性建模提供了有效的工具,并且通过合理的模型设定,HSAR能准确区分并识别地理集聚效应和网络外部效应。
Agglomeration externalities, network externalities and urban innovation development
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211015
[本文引用: 3]

With the rapid development of high-speed transportation technology and mobile communication infrastructure, urban innovation activities are no longer confined to a specific geographical space, and there is still a lack of empirical evidence on whether synergistic innovation can be achieved between cities that are far from each other but have strong business linkages in cyberspace. Based on the macro panel data of 289 prefecture-level cities and the micro data of listed-companies in China from 2001-2016, this paper portrays the spatial distribution of innovative activities, and then quantitatively analyzes the impact of agglomeration externalities and network externalities on urban innovation development using social network analysis (SNA), instrumental variables approach (IV) and spatial durbin model (SDM). The findings show that innovation factors still tend to be concentrated in the head companies and the central cities, and it is the agglomeration externality brought by this concentration that promotes the innovation development of the head companies and the central cities; moreover, the nodal cities benefit their innovation development from network externalities caused by cooperation with other cities through the corporate affiliate network or the investment network. In terms of different transmission mechanisms between agglomeration and network externalities for urban innovation development, the level of government spending on science and education, the level of urban infrastructure, and the operation of high-speed rail networks are important conditions for the agglomeration externalities and network externalities to improve the urban innovation. However, the agglomeration externalities arising from the increased density of economic activity can also reinforce the innovation effects brought by network externalities, while the advanced technology and management experience brought by foreign direct investment activities help network externalities to break through the limits of geographic space and improve the level of the urban innovation. Based on these findings, the government, in exploring the path of urban innovation development, need not hoard on the spatial agglomeration of innovation factors as the only path, but lead cities to actively participate in the construction of international science and technology innovation centres within city clusters, which can also achieve innovation development with the new knowledge and technology shared in the business network.
集聚外部性、网络外部性与城市创新发展
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211015
[本文引用: 3]

随着高速交通技术和移动基础设施的迅速发展,城市创新活动已经不再局限于特定的地理空间,在网络空间中彼此远离但有着较强经济活动关联的城市之间是否也可以实现协同创新,目前仍缺乏经验证据。基于2001—2016年中国289个地级市宏观面板数据和微观层面上市公司数据,采用社会网络分析法、工具变量法以及空间杜宾模型等方法,定量研究了集聚外部性与网络外部性对于城市创新发展的影响。结果显示:创新要素依旧存在着向头部企业和中心城市集中的趋势,且正是这种集中所带来的集聚外部性促进了城市的创新发展;城市可通过融入经济关联网络,借助于网络外部性来提高自身创新水平;就集聚外部性与网络外部性促进城市创新发展的传导机制来看,虽然政府科教支出水平、城市基础设施状况以及高铁网络的建设是集聚外部性与网络外部性发挥的重要条件,但经济活动密度的提升所带来的集聚外部性还可以强化网络外部性所带来的创新效应,而外商直接投资活动所分享的先进技术和管理经验则帮助网络外部性突破了地理空间的限制。因此,政府在探索城市创新发展路径的过程中,就无需囿于创新要素的空间集聚这一条路径,积极融入城市群内的国际科技创新中心建设,凭借网络外部性所分享的新知识与新技术,同样也能实现创新发展。
The impact of multidimensional proximity on the formation of regional innovative collaboration network: A case study of medical science institutions in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang-Shanghai region
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211005
[本文引用: 3]

Innovation is acknowledged as the main driving force of the sustained growth of regions. In the literature on innovation geography, multidimensional proximity has become an important proposition that helps to understand the structures, processes, and mechanisms of regional innovation and the formation of innovation networks. However, many studies focus on the independent effect of different types of proximity on regional innovation, and much less attention has been paid to their joint effect. Moreover, in terms of methodology, studies on proximity have been dominated by quantitative approach on macro level, and very few cases can be found with in-depth qualitative approach on micro level. Based on the co-publication data from the Web of Science database, the study constructs an interorganizational collaboration network of medical sciences in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang-Shanghai (JZS) region. With combined approaches of quantitative and qualitative methods, the study explores the impacts of, and joint effects (substitutional and complementary effects) between geographical proximity and non-geographical proximity (institutional, social, cognitive and cultural proximity) on the formation of the collaboration networks in this field of the region from both macro and micro perspectives. First, we use the method of the MRQAP regression to quantitatively examine the independent and joint effects of geographical and non-geographical proximity on the formation of scientific collaboration network of the medical sciences in the region. Second, we conduct semi-structured interviews with four selected interorganizational collaborative groups in the region to reveal how these different types of proximity affect the motivation of collaborations. The results of both quantitative and qualitative analyses support each other and show that (1) each form of proximity has a positive impact on regional knowledge collaboration with the exception of cultural proximity. (2) Geographical and institutional proximity can be substituted in their influence on the formation of regional knowledge collaboration network. (3) The relations between geographical and social/cognitive proximity are complementary. (4) There is no significant joint effect between geographical and cultural proximity. This study not only examines the relations between multidimensional proximity and the formation of innovation networks by quantitative methods, but also explains why such interrelations exist through qualitative approach.
多维邻近性对区域创新合作网络形成的影响: 基于江浙沪医学科研机构的实证
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020211005
[本文引用: 3]

本文以Web of Science数据库的合著论文信息为基础构建江浙沪区域医学科研机构合作网络,采用计量分析与半结构化访谈相结合的方式从宏观和微观层面考察多维邻近性(地理邻近性、制度邻近性、社会邻近性、认知邻近性和文化邻近性)对该区域医学领域创新合作网络形成的影响,并进一步讨论了地理邻近性和非地理邻近性之间的交互效应(替代效应或互补效应)。综合定量与定性分析结果,研究发现:① 地理邻近性、制度邻近性、社会邻近性和认知邻近性对该区域医学创新合作网络的形成有促进作用,而文化邻近性的作用不显著;② 地理邻近性与制度邻近性之间存在替代效应;③ 地理邻近性与社会邻近性、认知邻近性之间均存在互补效应;④ 地理邻近性与文化邻近性之间不存在显著的交互效应。
Geography of reputation: The city as the locus of business opportunity
DOI:10.1080/00343400601145194 URL [本文引用: 2]
The rise of urban network externalities: A new mechanism for the high-quality integrated development of regional economy
城市网络外部性的崛起: 区域经济高质量一体化发展的新机制
Spatial heterogeneity of urban network externalities in the Yangtze River Delta
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220172
[本文引用: 1]

Is there is a phenomenon of "low-end locking" in the urban network? Can low-grade cities benefit from the urban network? Have high-grade cities played a leading role in the urban network? These issues are related to the strategic orientation of the development of urban agglomeration, which is still lack of in-depth research. Urban network externalities refer to cities benefited by connecting with other cities, which provides a theory for answering the above questions and has become a new hotspot in urban network research. Existing studies focus on the overall characteristics of urban network externalities, but ignore the differences of urban network externalities between cities. In this paper geographical weighted regression model is used to accurately measure the urban network externalities to each city and reveal the spatial heterogeneity of urban network externalities. Taking 41 cities in the Yangtze River Delta region as case studies, we construct the urban network according to the scale of mutual investment of enterprises between cities. Then we analyze the influence of network connection on urban development, which proves that there exist urban network externalities in the study area. The results are as follows: (1) Although the urban network externalities are not dominant, joining urban networks has played a positive role in the urban development of Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai. (2) There are great regional differences in urban network externalities. The urban network externalities of cities in Jiangsu are generally stronger than those of Zhejiang, while those in Anhui are not strong. Urban development is still mainly determined by the local agglomeration of people, land and capital. (3) The urban network externalities in the Yangtze River Delta are formed mainly under the influence of Shanghai, but the influence of the three provincial capitals — Nanjing, Hefei and Hangzhou — is limited. (4) Although low-grade cities have not benefited from the network, they are not "low-end locking" either. High-grade cities do not form a "cluster shadow" around them. This paper hopes to improve the theory of urban network externalities and provide theoretical support for regional network development.
长三角城市网络外部性的空间异质性
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020220172
[本文引用: 1]

城市网络中是否存在“低端锁定”现象,低等级城市能否从网络中获益,高等级城市是否发挥了辐射带动作用,这些问题关系城市群发展的战略导向,当前仍缺乏深入论证。城市网络外部性是指城市因联系而得到的效益,为回答上述问题提供了理论依据,已成为城市网络研究的新热点。但现有研究主要关注网络外部性的整体特征,忽视区域内城市间的网络外部性差异。本文使用地理加权回归模型将网络外部性测度精确到每个城市,揭示网络外部性的空间异质性特征。研究以长三角地区41个城市为研究对象,按城市汇总企业之间相互投资规模构建城市网络,分析网络联系对城市发展水平的影响,证实了长三角地区存在网络外部性。研究发现:① 虽然网络外部性未成为主导,但嵌入城市网络已经对江浙沪城市发展起到了积极影响。② 网络外部性的地域差异较大,江苏省城市的网络外部性普遍强于浙江省,安徽省的网络外部性不强,城市发展仍主要由人、土地和资本的本地集聚决定。③ 长三角地区的网络外部性主要是在上海的辐射带动作用下形成的,3个省会城市南京、合肥、杭州对周边城市的辐射带动作用有限。④ 低等级城市虽未从网络中获得明显的效益,但也未被“低端锁定”,高等级城市没有在周边形成“集聚阴影”。本文希望能有助于完善城市网络外部性理论,为区域网络化发展提供理论支撑。
Behind the scenes: The evolving urban networks of film production in China
DOI:10.1080/02723638.2018.1477297 URL [本文引用: 4]
The rise of venture capital centres in China: A spatial and network analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.geoforum.2016.07.013 URL [本文引用: 1]
Inter-and intra-city networks: How networks are shaping China's film industry
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2020.1807492 URL [本文引用: 4]
Cluster relations in the media industry: Exploring the 'distanced neighbour' paradox in Leipzig
DOI:10.1080/0034340052000320860 URL [本文引用: 1]
Global-local linkages, spillovers and cultural clusters: Theoretical and empirical insights from an exploratory study of Toronto's Film Cluster
Related variety, unrelated variety and regional economic growth
DOI:10.1080/00343400601120296 URL [本文引用: 1]
An ecological function zoning approach coupling SOFM and SVM: A case study in Ordos
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201903005
[本文引用: 1]

It is of great significance to analyze the main environmental issues, coupled with their spatial heterogeneity, and divide the ecological function zones to achieve ecological security and optimization of territory development in a certain region. In recent years, ecological function zoning, widely concerned by scholars, has played a vital role in regional ecosystem management and sustainable development. There arose a problem that the spatial characteristics of ecological functions were hard to be reflected in the previous studies based on spatial average data over basins or geopolitical regions such as counties, cities and provinces. This paper, using the approaches of coupling self-organizing feature map (SOFM) and support vector machine (SVM), attempts to develop an automatic demarcation and zoning approach, and explores the best possible division of ecological functions in the city of Ordos with the index system of ecological function zoning in mind involving the ecosystem services as well as ecological sensitivity. Ordos, which is located in the transitional zone between temperate grasslands and desserts, has become a key research area of global terrestrial ecosystem. The ecological functional zoning indexes indicate that there appears an obvious spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem functions in Ordos. Accordingly, land grids have been clustered into 7 ecological function types by SOFM with clustering quality index (CQI) in view. Hence, Ordos has been divided into 11 ecological function zones owing to the implementation of SVM to identify the optimal division borders, in which the border demarcation is treated as a classification system in spatial domain. The optimal combination of SVM hyperparameters is determined by grid search method. In this study, machine learning algorithm has been adopted to cope with the situation where the bottom-up physical regionalization might weaken the spatial position attribute of the partition features, and to realize the quantitative conversion from classification to partition. It has turned out that such SOFM-SVM-coupled zoning approach could effectively improve the spatial accuracy of the partition, which can be considered as a new way to realize the automatic ecological zoning.
耦合SOFM与SVM的生态功能分区方法: 以鄂尔多斯市为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201903005
[本文引用: 1]

辨析区域主要生态环境问题及其空间异质性,划定生态功能区,对保障区域生态安全和国土开发优化具有重要指导意义。以往自下而上的分区研究多基于行政区或流域开展,难以体现行政区或流域内部的生态功能分异。以鄂尔多斯市为例,基于生态系统服务与生态敏感性构建区域生态功能分区指标体系,耦合自组织特征映射(SOFM)网络与支持向量机(SVM)划定鄂尔多斯市生态功能分区。结果表明,区域内各生态功能分区指标呈现明显的空间分异特征,通过SOFM网络基于栅格进行指标聚类,构建分类效果指数筛选最佳聚类方案,将区域分为7种不同的生态功能类型。最终,利用SVM识别最优分区界线,将鄂尔多斯市分为11个生态功能区。本文构建分类效果指数实现多分类方案优选,使用机器学习算法解决自下而上的自然分区容易弱化要素空间位置属性的问题,完成了从分类到分区的定量转换,有助于提升分区的空间精度与客观性,为生态功能分区与分区边界划定提供了新的方法途径。
Geodetector: Principle and prospective
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

Spatial stratified heterogeneity is the spatial expression of natural and socio-economic process, which is an important approach for human to recognize nature since Aristotle. Geodetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has elegant form and definite physical meaning. Here is the basic idea behind Geodetector: assuming that the study area is divided into several subareas. The study area is characterized by spatial stratified heterogeneity if the sum of the variance of subareas is less than the regional total variance; and if the spatial distribution of the two variables tends to be consistent, there is statistical correlation between them. Q-statistic in Geodetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences which can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. In this paper, the authors will illustrate the principle of Geodetector and summarize the characteristics and applications in order to facilitate the using of Geodetector and help readers to recognize, mine and utilize spatial stratified heterogeneity.
地理探测器: 原理与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201701010
[本文引用: 1]

空间分异是自然和社会经济过程的空间表现,也是自亚里士多德以来人类认识自然的重要途径。地理探测器是探测空间分异性,以及揭示其背后驱动因子的一种新的统计学方法,此方法无线性假设,具有优雅的形式和明确的物理含义。基本思想是:假设研究区分为若干子区域,如果子区域的方差之和小于区域总方差,则存在空间分异性;如果两变量的空间分布趋于一致,则两者存在统计关联性。地理探测器q统计量,可用以度量空间分异性、探测解释因子、分析变量之间交互关系,已经在自然和社会科学多领域应用。本文阐述地理探测器的原理,并对其特点及应用进行了归纳总结,以利于读者方便灵活地使用地理探测器来认识、挖掘和利用空间分异性。