1 引言
自然生态系统为人类社会和地球生命系统提供丰富优质的生态产品、稳定永续的生态服务,支撑人类社会经济发展。但随着人类活动方式的多样化和活动强度的持续增加,生态系统结构、过程和功能被改变,影响生态系统服务的可持续供给[1-2],资源不可持续利用及环境污染等问题日益凸显,威胁人类生存与社会经济可持续发展,使自然资本成为限制经济发展的“稀缺条件”[3],生态产品成为人类社会的稀缺品。另一方面,随着人口增加和社会经济的发展,中国社会主要矛盾已转化为人民日益增长的美好生活需要与不平衡不充分的发展之间的矛盾。人民大众的消费提质升级,从传统物质需求逐渐转向自然资源、生态产品、文化服务等方面,对生态系统或生态资源的认识也从“资源供给”逐渐转向“资源供给与环境适宜相结合”,对食品、原材料和能源等生态系统服务的需求日益增大[4-5],尤其是对安全、绿色、健康、多元的农产品和绿色农业、文旅农业、康养农业、智慧农业等农业新业态的诉求逐渐增加[6]。为满足中国日益增长的农产品总量、质量、安全和多功能性需求,功能农业被提出并作为高产农业和绿色农业之后的农业发展新方向[7],面对优质生态产品供给和优质生态服务需求这对新的供需矛盾[8],迫切需要将优质的生态资源及时有效地转化为生态产品和公共服务。
乡村地区是中华民族农耕文明的发源地、农业生产与农民居住的集中地、工业化与城镇消费的原料地、保障生态粮食安全战略高地、现代城市健康发展重要腹地、未来创新创业康养文化兴盛之地[9]。1978年以来,快速工业化和城镇化进程使乡村地域系统发生了根本转变,城乡二元发展体制和城市优先发展战略引发了日益严峻的“乡村病”[10],乡村地区资源利用不当、生产活动加强和生活方式改变,导致土地污损化、水体污染化和空气污浊化[11]。乡村振兴战略是新时代背景下统领农业农村发展、激发农村各类要素潜能和各类主体活力的重要举措,也是释放内需,为农业农村发展注入新动能的必然趋势[10]。乡村振兴不仅要求产业兴旺和生活富裕,更要求生态宜居。因此,乡村产业发展过程中,不仅要充分考虑区域资源环境承载力,充分保障乡村的生态环境,更要依托区域丰富的生态资源,发展生态产业,促进乡村集体经济发展,为农户提供新的生计来源。
乡村地区拥有巨大的绿色生态系统,土地、生态、能源等自然资源开发与利用,能为双循环格局下的中国社会经济发展提供动力源泉[12]。生态优势是一种后发优势,将乡村地区独特的自然资源、美丽乡村以及现代农业景观等生态资源转化为生态产品,发展为生态产业并转化为物质财富,对促进农村社会经济发展具有重要意义[13]。近些年来,在国家相关政策支持和引导下,乡村地区积累了丰富的生态资源,形成了以自然生态资源、现代农业和田园综合体为主的乡村生态产业化模式[14]。例如,脱贫攻坚期的生态工程建设、生态补偿机制及生态资源开发利用等政策促进了贫困人口脱贫,也为乡村地区生态振兴积累了产业形态和典型模式[15];特色经济作物种植促进了典型山地乡村整体自然资源的经济价值与生态价值的耦合,不仅契合了生态文明建设的发展要求[16],也成为破解生态资源富集区域“生态资源诅咒”[17]的有效手段;依托泉河湖溪、森林山地、滨海岛屿等类型多样的自然生态景观,发展乡村旅游[18],通过“湿地公园、湿地农业、湿地小镇”等生态经济区建设[19],充分发挥生态要素的经济功能,可将健康的生态环境转变为强劲的生态经济竞争力。
中国生态系统类型多样,“山水林田湖草沙冰”等资源及各种生物性和文化性资源丰富。生态经济生态产品第四产业的提出[20],将生态资源作为核心生产要素纳入经济体系,使生态红利逐渐释放,成为培育经济高质量发展的新动力。生态产品价值实现能促进生态与经济协同增长,破解发展不平衡不充分的社会矛盾,实现人民物质生活水平和生态产品的双富裕[21]。乡村地区的优良生态环境不仅关系城市的“米袋子”“菜篮子”和“水缸子”,更成为支撑乡村地区特色生态经济发展和生态振兴的关键所在。随着生态文明建设的持续推进,生态产品价值实现的模式和路径不断创新,为绿水青山和自然资源集中的乡村地区提供了生态产品价值实现和乡村振兴的重要理论和实践支撑。叶有华等[22]围绕“市场、政府、公益”视角,提出了乡村振兴视域下的生态产品价值实现路径,梳理归纳了生态保护补偿、生态资源指标和产权交易、绿色金融、生态农业产业化、生态旅游和特色文化产业化、生态修复与保值增值等实践模式。乡村振兴和生态文明战略叠加背景下,为实现乡村经济发展与生态保护的和谐统一,不仅需要发展生态产业,促进乡村地区三产融合,助力乡村振兴,更需要总结提炼生态产业化与乡村振兴的典型案例,阐明生态产业化发展对区域乡村振兴的促进机制与作用路径。因此,本文旨在系统梳理1949年以来中国生态环境政策演变,构建生态系统与人类社会、生态产品与经济发展、生态产业化与乡村振兴的理论框架,并依托陕南地区的典型案例,探索乡村振兴视域下的生态产业化机制与路径,为创新开展乡村振兴实践提供理论和实践支持。
2 中国生态环境政策演变
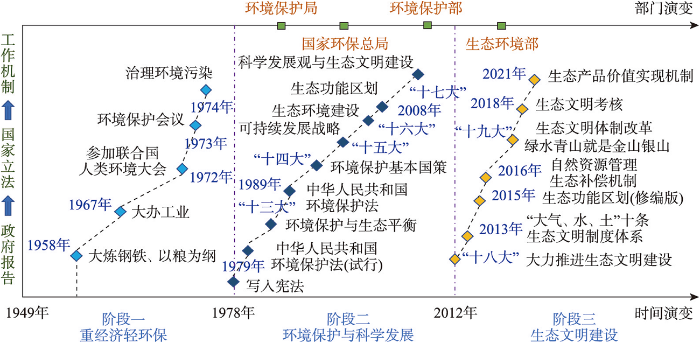
1949年以来,中国生态环境政策演变可划分为3个阶段(图1)。
图1
图1
1949年以来中国生态环境政策演变
Fig. 1
Evolution of ecological environmental policies since the foundation of new China
(1)重经济轻环保阶段(1949—1978年):中华人民共和国成立初期,“大炼钢铁、以粮为纲”和“大办工业”等方针,过度关注解决温饱和促进经济发展,砍伐森林、围湖造田、人造平原、矿山开采等不合理活动和工业废水、废渣、废气等乱排导致部分地区的生态环境遭到破坏和污染。20世纪70年代以来,国家逐渐开始关注环境污染问题,1972年派代表参加联合国第一次人类环境会议,1973年召开第一次全国环境保护会议,1974年提出“五年控制环境污染,十年解决环境污染”目标。
(2)环境保护与科学发展阶段(1979—2012年):1978年改革开放以后,环境保护问题被逐渐重视。从立法来看,1978年环境保护被写入宪法,次年颁布了《中华人民共和国环境保护法》(试行),1989年正式颁布《中华人民共和国环境保护法》;从政府报告来看,中国共产党“十三大”将环境保护和生态平衡与人口控制并列作为关系经济和社会发展的重要问题,中国共产党“十四大”将保护环境作为基本国策,中国共产党“十五大”将可持续发展战略作为国家基本战略,中国共产党“十六大”强调坚持生产发展、生活富裕、生态良好的文明发展道路,建设资源节约型、环境友好型社会,中国共产党“十七大”提出科学发展观与建设生态文明。从管理部门来看,1988年国家成立环境保护局,1998年升级为国家环保总局,2008年成立环境保护部。
(3)生态文明建设阶段(2013年至今):中国共产党“十八大”以来,生态文明建设制度体系日益完善,治理能力明显提升。从立法来看,自2013年以来,国家陆续出台了《大气污染防治行动计划》《水污染防治行动计划》《土壤污染防治行动计划》等,2018年将生态环境和资源保护纳入了党政领导干部考核体系。从政府报告来看,中国共产党“十八大”将“美丽中国”的生态文明建设纳入“五位一体”总体战略布局,中国共产党“十九大”提出了详尽的生态文明建设举措,创造更多物质财富和精神财富以满足人民日益增长的美好生活需要,提供更多优质生态产品以满足人民日益增长的优美生态环境需要;从工作机制来看,生态功能区划、自然资源管理、生态补偿、生态产品价值实现等政策陆续出台,为绿水青山转化为“金山银山”提供了重要的体制机制保障。
3 理论解析
3.1 生态系统与人类社会
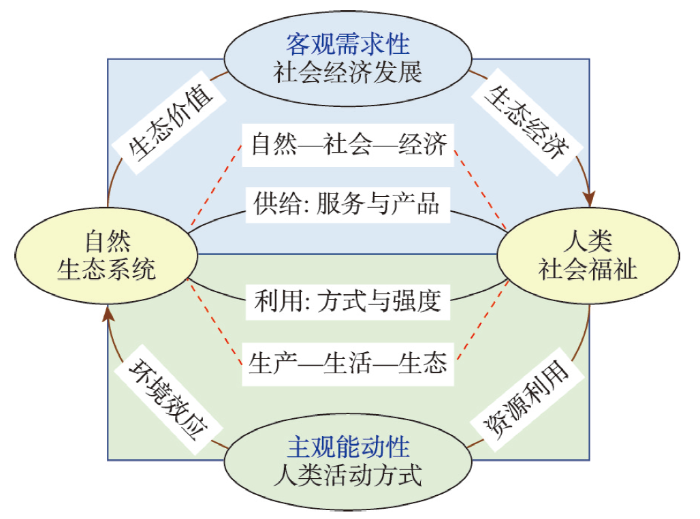
随着当代生态学科学内涵与研究领域的不断扩展,生态系统概念由经典的“生物与环境相互作用的整体系统”[25],扩展为更为普适性的“由生物或生物种群或生物群落与其栖居的资源环境所构成、并通过各个组成部分相互依赖、相互作用形成的生态学系统”[26]。生态系统通过功能和过程供给人类产品和服务,生态系统服务供给和需求使生态系统服务从自然生态系统流向人类社会系统[27],形成和维持人类赖以生存和发展的环境条件与效用[28]。因此,数量充足、品质优良、稳定持续的自然生态系统,能为人类社会经济可持续发展提供产品和服务支持[29]。从供给的角度来看,自然生态系统通过生态价值实现和生态经济建设,促进社会经济发展和“自然—社会—经济”的协调耦合,通过生态系统服务与产品的持续供给,提升人类社会福祉(图2)。
图2
图2
生态系统与人类社会耦合关联框架
Fig. 2
Coupling correlation framework between ecosystem and human society
人类社会及其活动与自然地理环境之间的交互作用形成了人地关系[30],地球上有了人类便形成了人地系统[12]。生态系统服务和功能是客观存在的,生态系统功能和生态产品对人类社会经济发展需求的适用性、适合性及满足程度是主观的,并受需求时间、需求区域、需求对象、需求程度的影响[29]。随着人类活动的逐渐增强,生态系统健康程度逐渐下降,人地关系和人地系统耦合失调,威胁社会经济可持续发展[31],应避免过度利用生态系统导致社会经济发展不可持续问题[32]。从需求角度来看,人类社会福祉的多维性和地域性决定了人类活动方式和强度的差异化,作用于多尺度的人地系统,产生了多样化的资源利用方式和多类型的环境效应,形成了不同的“生产—生活—生态”脉络和空间格局(图2)。
3.2 生态产品与经济发展
经济取决于物质封闭、不可再生、有限的生物圈[33],与“环境”密不可分。生态保护与经济发展协调的途径在于生态产品的产业化,将自然生态系统供给的多样食物、清新空气、洁净淡水、健康土壤、绿色能源、有益生物等生态产品,通过核算、赋值、转化等途径,依托种植、养殖、加工、旅游、康养等产业形式,转化为经济价值。生态产品类型多样,按照来源可以划分为原生产品、衍生产品、融合产品和转化产品[34-35]。原生产品是生态系统直接供给的产品,主要以蓝天、清洁水源、洁净土壤、清新空气、宜人气候、有益生物、天然药材等形式存在,属于公共产品,可以被直接利用;衍生产品是以原生产品为基础而形成的相关产品,主要包括国家公园、自然保护地等自然景观和文化遗址、古村落等文化遗产,是准公共性和经营性产品,可以进行适度的开发利用;融合产品是生态系统与生产、生活结合而形成的产品,如依托生态资源开发的旅游景区、建设的田园综合体和康养小镇等,可以通过“农商文旅融合”等经营方式开发利用;转化产品是运用现代科技手段转化形成的产品,主要包括与人类日常生活息息相关的农林牧渔、手工艺、工业制造等产品,通过种植、养殖、加工等产业发展方式开发利用(表1)。
表1 生态产品类型与利用方式
Tab. 1
| 产品类型 | 产品形式 | 利用方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 原生产品 | 蓝天、清洁水源、洁净土壤、清新空气、宜人气候、有益生物、天然药材等 | 公共性,直接利用 |
| 衍生产品 | 国家公园、自然保护地、自然保护区等自然景观,文化遗址、古村落等文化遗传 | 准公共性和经营性,保护与利用 |
| 融合产品 | 旅游景区、田园综合体、康养小镇等 | 经营性,农商文旅融合发展 |
| 转化产品 | 农林牧渔产品、手工艺品、工业制造品等 | 经营性,种植、养殖、加工等产业发展 |
① 从利用方式来看,生态产品可以被直接利用,也可以通过再加工方式被人类消费;② 从转化路径来看,生态农业、循环农业、有机农业、绿色农业等发展理念,地理标志、地理特色、地理传统等产品认证方式,国家公园、自然保护区、自然公园等自然保护地体系,农商文旅融合发展等新模式均为生态产业化提供了实践参考;③ 从价值实现机制来看,生态系统的“水、粮、碳、生物”等产品库是支撑区域经济发展的“资源银行”,通过重新配置和优化利用,可以转变为资产和资本。
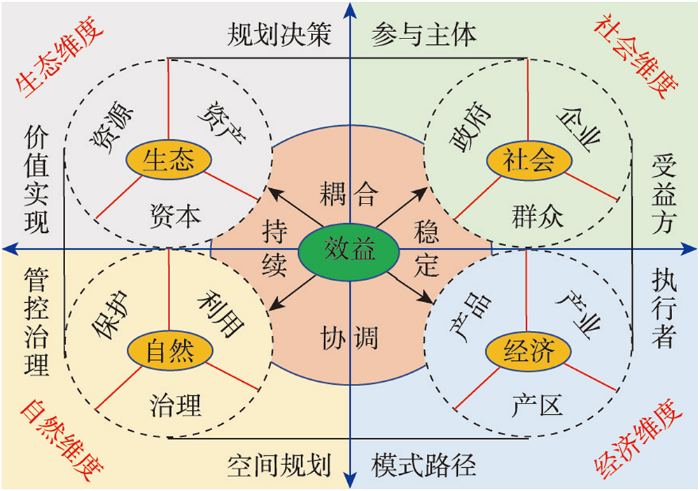
新时代背景下生态产品与经济发展的契合点在于发展新生态经济,重点在于“一核四驱动”的发展方式,目标在于实现区域生态—自然—社会—经济系统的协调发展。围绕“效益”核心,在生态、自然、社会、经济四个维度探明“耦合、协调、持续、稳定”的效益驱动机制(图3)。生态“资源—资产—资本”转化是生态产业形成的基础,通过合理规划决策,在政府主导下,引导企业和群众参与自然资源的保护、治理和利用,形成支撑区域经济发展的产品、产业和产区,促进生态产品的价值实现和社会受益。
图3
图3
区域新生态经济发展框架
Fig. 3
Development framework of regional new ecological economy
3.3 生态产业化与乡村振兴
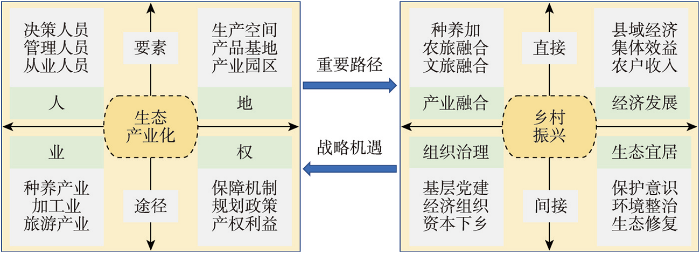
人类、土地、产业、权利是生态产业化的重要保障,共同构成了生态经济发展和生态产品价值实现过程。人是生态产业化的决策者、管理者和执行者,包括政府、企业、群众等各类群体,通过政府引导、企业主体、个体生产的作用,共同推进生态资源市场化和价值实现;土地资源是生态产业化的重要基础,包括山水林田湖草沙冰等不同利用方式,为生态产业化提供生产空间、产品基地和产业园区;生态产业化的形态包括基础的种植业和养殖业、传统的加工业和新兴的旅游业,为满足人类需求和促进经济发展提供新路径;生态产业发展的规划和相关政策及保障机制、生态资源的产权和分配制度、各类权利主体的利益分配等是生态产业化有序推进的重要保障(图4)。
图4
图4
生态产业化发展与乡村振兴的逻辑关系
Fig. 4
Logical relationship between ecological industrialization development and rural revitalization
生态产业化与乡村振兴关系密切,是实现乡村振兴的重要路径之一,直接促进产业融合和经济发展。生态产品生产与综合开发过程中的种养加融合、农旅及文旅融合,可有效促进县域经济发展、壮大集体经济、增加农户收入。其次,生态产业化也间接促进乡村组织治理和生态环境保护(图4)。生态产业化有利于培育家庭农场、龙头企业等农业经营主体,联合科研院所及地方高校,将生态产业发展成产学研政企深度融合的模式[38]。部分生态产品因其亲自然特征和文化多样性,能提供与城市不同的生活方式,成为市民下乡与农民联合创业的作用对象[39]。生态产业化发展使群众享受到保护与发展的利益,促使群众主动转变生态保护意识,开展环境整治和生态修复,积极拓展生态空间,有利于乡村经济价值、生态价值和社会文化价值的协调发展[40]。例如,有机农业依赖于优良的生态环境,是现代农业生产的重要形式之一,有机基地认证、有机品牌打造、有机园区建设等有机化发展是区域生态资源利用和产业化发展的重要途径,绿色健康的有机产品不仅将优良的生态资源转化为经济价值,更是助力乡村经济发展和农户脱贫的重要产业,使环境友好的有机农业成为保障生态系统健康和社会经济可持续发展的重要方式。
4 有机化发展与乡村振兴案例
4.1 生态环境与社会经济发展
陕西洋县地处汉江地区,属北亚热带内陆性季风气候,年平均气温14.5 ℃,年平均降水839.7 mm。洋县是国家南水北调中线工程和陕西省引汉济渭工程的重要水源涵养地,也是陕西省唯一建有朱鹮和长青两个国家级自然保护区的地区,森林覆盖率达到68.6%,汉江干流出境断面水质稳定保持在Ⅱ类,饮用水水源水质达标率100%。2021年全县优良天数达348 d,空气质量综合指数3.04,空气优良率95.3%,PM2.5浓度为27 μg/m3,被誉为地球上同纬度生态最好的地区之一。洋县因朱鹮和大熊猫保护给社会经济发展带来了巨大挑战,朱鹮活动区内禁止使用化肥和农药,禁止开矿、砍伐等活动,导致农户生计和生态保护的矛盾日益凸显,经济发展陷入“绿色贫困”困局。为实现区域生态保护与经济发展双赢,洋县立足优越的生态环境,大力发展有机产业,将生态保护集聚的“绿色能量”转化为“经济增量”,实现了县域经济发展和农户收入增加。尤其是脱贫攻坚以来,全县地区生产总值从2013年的85.05亿元增长至2021年的192.9亿元,人均可支配收入从2013年的9286元增长至2021年的21600元,其中,农村常住居民人均可支配收入从2013年的6618元增长至2021年的13216元,城乡居民可支配收入差距从2013年的3.36降低至2021年的2.80。有机产业成为助力洋县精准脱贫与引领乡村振兴的主要抓手[41-42],因此,选取洋县有机产业作为生产业化与区域乡村振兴的案例研究区域。
4.2 有机产业发展历程与机制
4.2.1 发展历程
2003年洋县提出“生态立县”发展战略,依托生态资源禀赋,推进生态农业、生态旅游和生态文化发展;2005年探索发展有机产业,2010年成立有机产业发展领导小组,编制《优先有机产业发展规划》,有机产业迅速发展。截至2021年,洋县共有有机生产企业38家,其中加工企业12户,认证有机或有机转换产品15大类85种(其中种植类产品39种、养殖类产品7种、加工产品39种)。有机种植面积和产值分别为10066.67 hm2和13.30亿元,比2010年分别增加了28.03倍和31.44倍;有机产值在全县农业总产值和国民生产总值中的占比从2010年的1.86%和0.83%快速增长至2015年的23.61%和9.38%,而后逐渐下降至2021年的19.79%和6.89%。有机示范区内的农民人均纯收入从2010年的4160元持续增长至2021年的14826元,是同时期内全县农民人均纯收入的1.10~1.43倍(表2)。
表2 2010—2021年洋县有机产业发展历程
Tab. 2
| 年份 | 有机面积 (hm2) | 有机产值 (亿元) | 有机产值/农业总产值(%) | 有机产值/全县国民生产总值(%) | 有机示范区农民人均纯收入(元) | 全县农民人均纯收入(元) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 346.67 | 0.41 | 1.86 | 0.83 | 4160 | 3790 |
| 2011 | 3693.33 | 3.20 | 11.43 | 5.13 | 6985 | 4885 |
| 2012 | 5440.00 | 5.73 | 17.36 | 7.73 | 7935 | 5755 |
| 2013 | 6933.33 | 7.52 | 22.79 | 8.84 | 8128 | 6618 |
| 2014 | 8066.67 | 8.82 | 21.74 | 9.34 | 8769 | 7419 |
| 2015 | 8200.00 | 9.41 | 23.61 | 9.38 | 9453 | 8153 |
| 2016 | 8533.33 | 9.66 | 23.00 | 8.78 | 10520 | 9000 |
| 2017 | 8800.00 | 10.14 | 23.24 | 8.39 | 11225 | 9695 |
| 2018 | 9400.00 | 10.68 | 21.07 | 7.62 | 11496 | 10046 |
| 2019 | 9526.67 | 11.07 | 19.80 | 6.78 | 12536 | 11066 |
| 2020 | 9613.33 | 11.79 | 18.27 | 6.84 | 13450 | 11891 |
| 2021 | 10066.67 | 13.30 | 19.79 | 6.89 | 14826 | 13216 |
注:数据来源于洋县有机产业发展办公室。
4.2.2 发展机制
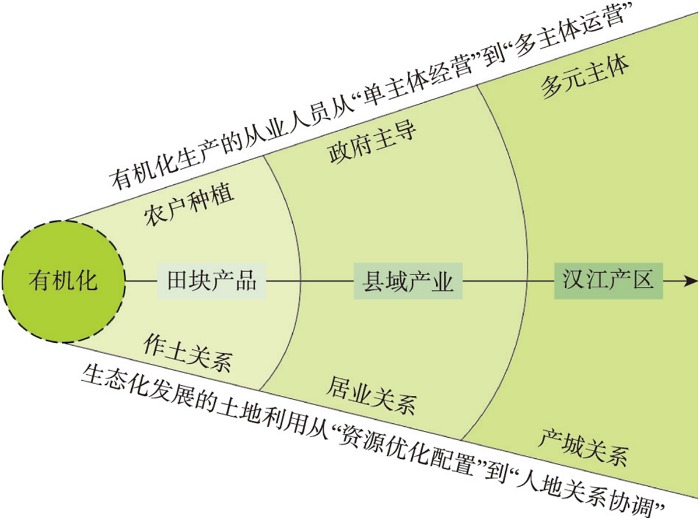
洋县有机化发展已基本建立有机种植、有机养殖和有机加工的产业体系,有机产业链条不断延伸,有机产品附加值显著提升,“朱鹮、有机”品牌化建设和“有机基地+全域旅游”融合发展模式,促进了三产融合和三生结合,将区域生态优势已转化为经济优势。从发展机制来看,洋县有机化生产体系建设是有机农业生产从“田块产品”到“县域产业”和“汉江产区”不断延伸的过程。有机化生产的从业人员从最初的小部分农户种植的“单主体经营”,不断向农户主体、政府主导、社会参与的“多主体运营”发展,生态化发展的土地利用方式从微观作土关系的“水土气生等资源优化配置”,不断向中度居业关系和宏观产城关系的“人地关系协调”发展(图5)。
图5
图5
洋县有机化生产与区域人地关系协调
Fig. 5
Organic production and regional coupling of man-land in Yangxian county
4.3 有机化发展与典型村庄脱贫振兴
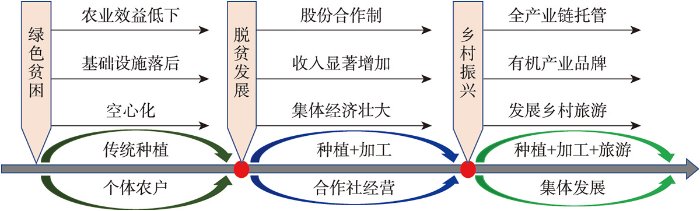
草坝村位于洋县纸坊街道,是朱鹮保护的核心区域,农田土壤肥沃,灌溉水质优良,是洋县有机黑米种植的重要区域之一,但生产经营“散、弱、小”问题突出,青壮年劳动力流失、村庄基础设施落后和空心化等问题日益严重(图6)。朱鹮保护工作造就的优良生态环境,为草坝村有机农业发展提供了重要机遇。2009年草坝村率先成立了洋县首个农民专业合作社—朱鹮湖果业专业合作社,探索推进“每户限一股、每股限一人”和“现金入股、粮食产量入股、联营入股”模式,并对国家财政补贴及社会捐助资金,实行资产量化、资产入股,按照20%现金分红、20%留存集体、60%依据土地所产粮油果产量和合作社整体经营利润进行二次分红模式分配收益。通过“合作社+公司+基地+农户”模式,大力发展有机黑米、油菜和黄金梨等特色有机农业,统筹品种、种植、管理、品牌等环节,提升了产品质量和效益(图6)。例如,有机黑米产量仅为普通黑米的60%,但价格却是普通黑米的6倍,为有机农业提质增效提供了“产量六折、产值六倍”的生产与经营模式[43]。
图6
图6
草坝村有机产业发展与乡村振兴模式
Fig. 6
Model of organic industry development and rural revitalization in Caoba village
2017年以来,合作社持续探索推进全产业链托管土地入股分红的集体发展道路,农户将土地承包经营权入股合作社,实施小块并大块,推行机械化耕作,提升田块质量。其次,整合零散企业与合作社,延伸产业链条,打造“黑米”系列产品,利用“朱鹮”品牌统一化经营与销售,提升产品附加值。此外,整合生态环境资源、历史文化资源,结合交通区位优势,建成有机农业示范区、农耕文化体验区、休闲养生区、梨果采摘区、有机农业观光区、美食文化区和游客服务中心,提升产业融合度(图6)。2021年草坝村已认证有机梨果3800亩(1亩≈ 666.7 m2)、有机水稻油菜4600亩、大樱桃300亩,有机产值6600多万元,集体经济累计210万元,农民人均纯收入1.6万元,实现了产业兴、百姓富、生态美的目标。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
生态产业已经成为乡村地区的新兴产业,生态产业化不仅能满足人民日益增长的生态产品和服务需求,还能持续优化乡村产业结构,增加农民收入,为乡村振兴提供新动能。本文系统梳理了中国生态环境政策的演变过程,并在理论上探讨了生态系统与人类社会、生态产品与经济发展、生态产业与乡村振兴的作用途径与促进机制,基于陕西洋县有机产业与乡村脱贫振兴的典型案例,揭示了生态资源优势转化为产业优势,实现区域人地系统耦合的发展过程与形成机制,探明了“田块产品—县域产业—汉江产区”的现代有机农业与乡村振兴的内在逻辑与典型模式,提出了有机农业“产量六折、产值六倍”的产业融合发展路径,为因地制宜利用生态资源,因势利导发展生态产业,促进区域资源环境保护与社会经济高质量发展,实现乡村振兴提供了科学认知与实践参考。
5.2 讨论
生态农业和循环农业关注物质和能量的多级循环利用,在自然环境承载力范围内,实现发展与环境、资源利用与保护的耦合,是产业生态化的重要途径。有机农业理念除了强调自然循环和生态平衡外,更重视功能提升和价值实现。优良的生态环境可为有机认证提供符合标准的产地环境,为区域有机产业发展提供重要的基础条件。有机产品作为生态产品中的转化产品,应与原生产品、衍生产品和融合产品相结合,通过有机化发展体系,打造区域有机农业与加工业、休闲旅游业的生态产业化融合发展模式,助力现代农业和乡村振兴发展。未来基于陕西汉江流域(洋县)生态保护与社会经济耦合发展的客观需求,应着眼于土地系统的健康化、有机农业的高效化、农业经营的现代化等前沿科学问题,探索现代有机农业特区创建机制和“三生”(生态、生产、生活)结合途径,创建“生态化、智慧化、标准化、品牌化、市场化”的现代有机化工程与区域范式,建成现代有机农业洋县特区[44]、中国乡村振兴汉中模式、全球可持续发展的汉江样板。
具体来说,在区域实践层面上,现代有机农业与乡村振兴发展应重点开展以下内容:① 有机产品“提质增产”的健康土壤、优良品种和精准管理套餐。开展汉江流域生态背景值调查,分析评判现代有机农业立地条件和健康发展路径,开展传统有机肥替代试验与观测研究,科学提出健康土壤的培育方案与可持续利用方式,充分利用优良品种和现代农业管理技术,打造乡村振兴的有机生产体系、现代产业体系、技术标准体系和智慧管理体系。② 有机产业“融合增值”的科学规划、品牌打造和产业融合套餐。基于自然资源、生态环境和地域文化优势,创新“三有(有机种植、有机养殖、有机加工业)三品(农产品、礼品、工艺品)”现代智慧有机农业体系,培植有机种植和有机养殖相结合的生态立体化模式,立足生态本底和汉文化特色,重塑区域人地关系,优化城乡空间布局,构筑“人—地—业—权”四位一体的陕南绿色低碳循环发展经济体系。③ 有机产区“降耗增效”的去同质化、资源利用和生态保护套餐。开展全域视角的整体规划,创新生态产品总值与生态环境导向的开发模式,塑造具有地域特色的“产品—产业—产区”经济链;促进政府和市场、农业与工业、创新与科技的有机结合,延伸有机农产品的产业链条,合理规避有机产业同质化发展问题;创新生态效率,参考集约化经营与生态化生产有机结合的生态高值农业发展理念,转变有机农业生产方式,提高综合生产能力,满足人民大众需求。
参考文献
Land-use history determines ecosystem services and conservation value in tropical agroforestry
Agroforestry is widely promoted as a potential solution to address multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals, including Zero Hunger, Responsible Consumption and Production, Climate Action, and Life on Land. Nonetheless, agroforests in the tropics often result from direct forest conversions, displacing rapidly vanishing and highly biodiverse forests with large carbon stocks, causing undesirable trade‐offs. Scientists thus debate whether the promotion of agroforestry in tropical landscapes is a sensible policy. So far, this debate typically fails to consider land‐use history, that is, whether an agroforest is derived from forest or from open land. Indeed, 57% of papers which we systematically reviewed did not describe the land‐use history of focal agroforestry systems. We further find that forest‐derived agroforestry supports higher biodiversity than open‐land‐derived agroforestry but essentially represents a degradation of forest, whereas open‐land‐derived agroforestry rehabilitates formerly forested open land. Based on a conceptual framework, we recommend to (a) promote agroforestry on suitable open land, (b) maintain tree cover in existing forest‐derived agroforests, and (c) conserve remaining forests. Land‐use history should be incorporated into land‐use policy to avoid incentivizing forest degradation and to harness the potential of agroforestry for ecosystem services and biodiversity.
Spatially non-stationary response of ecosystem service value changes to urbanization in Shanghai, China
DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.04.031 URL [本文引用: 1]
Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: An empirical analysis
Determinants of the ecological footprint: Role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization
Analysis of eco-agriculture construction based on rural revitalization in China
A ten-year overview of functional agriculture from 2008 to 2018
2008—2018年功能农业的理论发展与实践
Industrialized operation of ecology and realizing the value of ecological goods
生态产业化经营与生态产品价值实现
The basic theory and methodology of rural revitalization planning in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

Agricultural and rural modernization is the general goal of the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. The scientific formulation of the rural revitalization planning is related to the implementation effect of the national rural revitalization strategy. How to establish the basic theory of rural revitalization and develop the methods of rural revitalization planning have become important tasks of academic research and government decision-making. This paper constructed the theoretical model and method system of rural revitalization planning, tried to carry out the main function-oriented zoning, dominant type classification and principal purpose classification of rural regional system, and established the spatial system of rural revitalization planning and its optimal adjustment scheme. This system was applied to the overall rural revitalization planning in Yanchi County of Ningxia. By establishing the principle of rural revitalization planning that sticks to ecological priority, adaptation to local condition, industrial support and urban-rural integration, it put forward that the priority should be given to the development of rural professional cooperation organizations and the mixed economy of villages and towns, and the acceleration of the construction of advantageous industrial system characterized by the industrialization of tan-sheep, day lily, and minor cereals, and highlighted by the wisdom of eco-cultural tourism. Moreover, it was encouraged to give prominence to the position of the central town in space, and form the village organism and housing industry coordination body with the county seat and three key towns as the center of integrated industry development. The typical case study of Yanchi County has shown that the main contents and technical points of rural revitalization planning were embodied in the following four aspects: (1) determining the overall orientation of rural revitalization planning, and clarifying the phased development mode, key areas; (2) developing the county area based on the main function-oriented zoning, leading type classification and main purpose classification system, and exploring the territorial pattern and differentiation rules; (3) establishing the county development mode and industrial system, formulating coordination schemes of different main function-oriented zones, and revealing the spatial configuration and structural relationship of different dominant types; (4) exploring the local association and hierarchical system of each dominant type in its scale and level. The main task of implementing the rural revitalization planning is to promote the formation of a new pattern of urban-rural development with factors gathering, reasonable structure and orderly space in accordance with the objective requirements of "industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance and prosperous life". China is facing great differences in rural development and many problems in transformation. Regional disparities and urban-rural differences determine the complexity, diversity and differences of rural governance and rural revitalization planning. China's rural transformation-urban and rural integration-rural revitalization-high quality development will become the major development logic and new normal in the future. The research on rural revitalization planning in the new era should focus on the overall situation of regional coordination and urban-rural integration, and solve the practical problems of "rural disease", so as to serve the national rural revitalization planning and scientific decision-making.
中国乡村振兴规划的基础理论与方法论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

农业农村现代化是实施乡村振兴战略的总目标,科学编制乡村振兴规划事关国家乡村振兴战略的推进及实施成效。《全国乡村振兴战略规划(2018—2022)》提出以来,如何建立符合中国乡村发展基本特点与规律的乡村振兴规划基础理论,研制县域乡村振兴规划方法与方案,成为当前学术研究及政府决策的重要课题和重点任务。基于乡村地域多体系统理论,构建了乡村振兴规划理论模式,提出了“三主三分”乡村振兴规划方法。“三主三分”的基本原理是依据特定区域乡村地域系统结构与格局,进行地域系统主体功能分区、主导类型分类、主要用途分级,确立乡村振兴规划空间体系及其优化调整方案。该体系运用于宁夏回族自治区盐池县乡村振兴总体规划,制定了坚持生态优先、因地制宜、产业支撑、城乡融合的乡村振兴规划原则,提出应重点发展乡村专业合作组织和村镇混合制经济,加快建设以滩羊、黄花、小杂粮产业化为特色、生态文化旅游智慧化为亮点的优势产业体系;在空间上突出中心城镇地位,形成以县城和3个重点镇为中心、“三产”融合发展的村镇有机体、居业协同体。本研究是对创建中国乡村振兴规划体系的有益尝试,可为全国县级乡村振兴规划与乡村发展决策提供参考依据。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 2]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 2]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Pollution and restructuring strategies of rural ecological environment in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.014
[本文引用: 1]

Rural ecological environment issues in the process of rural-urban transition in China have influenced the production and daily living of residents in rural areas. This article reviews the sources and characteristics of rural environmental pollution, and proposes the restructuring strategies of rural ecological environment from the aspects of resources, production, and living. The research shows that unreasonable resource use, intensive production activities, and changed life style resulted in rural land contamination and water and air pollution. Rural environmental pollution is characterized by diversified sources, sporadic discharges, and inefficient management. These problems call for the highly efficient use of resources, cleaning of production processes, and agglomeration of living space to realize the coordination of rural production development, enhancement of quality of living, and ecological environment improvement.
中国乡村生态环境污染现状及重构策略
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.014
[本文引用: 1]

城乡发展转型进程中的乡村生态环境问题日益突出,已经影响到乡村的生产发展和居民的日常生活。本文梳理了乡村生态环境污染的来源和特点,并从资源、生产和生活方面提出了乡村生态环境的重构策略。主要结论为:①资源利用不当、生产活动加强和生活方式改变造成的污染是乡村土地污损化、水体污染化和空气污浊化的主要原因;②乡村生态环境污染具有来源分散多样、排放随机不均和治理局部低效的特点;③通过资源利用的高效化、生产过程的清洁化和生活方式的集聚化进行乡村生态环境的重构,最终实现乡村地区生产发展、生活富裕和生态良好的目标。
Human geography research based on the new thinking of global rural-urban relationship
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 2]

Sustainable rural development is critical to the achievement of global sustainable development goals. Globalization and urbanization, as the key processes, continuously drive the human-earth system to make adaptive responses, promoting the transformation of urban-rural relations. The rural-urban relationship is essentially a mother-child relationship, which is a comprehensive characterization of the transfer of rural humanistic factors, the transformation of man-land relationship and the transformation of urban-rural development in the process of urbanization. However, the traditional cognition of urban-rural relationship ignores the multi-dimensional connections between the rural and the urban as well as the existence of the rural-urban integration system, resulting in prominent drawbacks of rural regions, negatively affecting the urban-rural development rights, and resulting in urban and rural territorial dysfunction and other problems. The key to solve the problems of socio-economic development in China is to reform the urban-biased development strategy, and to innovate the new cognition of rural-urban relationship based on the thinking of "rural maternal effect", which highlights that rural areas nourish the city. Based on the remote coupling and systematic synthesis of the rural human-earth system, modern human geography urgently needs to strengthen the cross-research with physical geography and information geography, create a coordinated observation system of human-earth system supported by the sky-space-ground integration, reshape the global rural development perspective, rural-urban system perspective, and reorganize the global rural human-earth relationship, the rural-urban integration relationship, and the living and employment relationship. Rural human-earth relationship territorial system is the core of rural geography research. The rural human-earth system research should focus on the coupling of rural natural ecosystem and the socio-economic system and their complex interactive processes and effects. Supported by the intersection of multiple disciplines, the expansion of new fields and the cultivation of new disciplines, it should create the collaborative observation technology of human-earth system and methodology of multi-source data fusion computing, the research idea based on process-mechanism-pattern and the technical path of monitoring-simulation-decision support, and explore the organic connection path between rural human-earth system coupling and rural-urban integrated development, regional sustainable development and global common governance.
全球乡城关系新认知与人文地理学研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 2]

全球化、城镇化作为驱动人地系统不断做出适应性调整和改变的关键过程,持续推动着城乡关系的转型与重塑。本文认为乡村孕育了城市,乡城关系实质上是母子关系,是城镇化进程中乡村人文要素转移、人地关系转变、城乡发展转型的一种综合表征,具体体现在不同发展阶段乡村与城市之间土地非农化、人口城镇化、产业园区化、城乡发展一体化等诸多方面;传统的城乡关系认知忽略了城市与乡村之间的内在关系和多维联系,以及城乡融合系统这一重要地理综合体及其功能价值,成为产生乡村短板效应凸显、城乡发展权能受损、城乡地域功能紊乱等突出问题的根源;转变城市偏向发展观念,基于乡村母体思维,创新全球乡城关系新认知是破解当前全球化特别是中国社会经济发展不平衡、不充分问题的关键所在。现代人文地理学迫切需要强化与自然地理学、信息地理学交叉研究,创建天—空—地一体化人地系统协同观测体系,突出乡村人地系统的远程耦合性和系统综合性,重塑全球乡村观、乡城系统观,探究可持续的全球乡村人地关系、城乡融合关系、村镇居业关系。乡村人地系统研究应聚焦乡村自然生态系统、社会经济系统耦合及其复杂交互过程与效应,以多学科交叉、新领域拓展与新学科培育为支撑,创建人地系统协同观测技术与多源数据融合计算方法论,基于过程—机理—格局的研究思路和监测—模拟—决策支持的技术路径,探寻实现乡村人地系统耦合与乡城融合发展、区域可持续发展及全球共同治理的有机衔接路径。
Development path and promotion mechanism of rural eco-industrialization in the new era: Taking Zhejing province as an example
新时代乡村生态产业化的发展路径与促进机制: 以浙江实践为例
Study on the characteristics of development and formation mechanism of industrialization of rural ecology under the strategy of rural revitalization: A case study of Huzhou, Zhejiang Province
乡村振兴战略下乡村生态产业化发展特征与形成机制研究: 以浙江湖州为例
The practical basis and realistic path of the organic connection between ecological poverty alleviation and ecological rejuvenation
DOI:10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00277-9 URL [本文引用: 1]
生态扶贫与生态振兴有机衔接的实践基础及现实路径
The mechanism and comprehensive effect of poverty alleviation with characteristic agriculture in typical mountainous rural areas of Yunnan Province: A case study on the production of special cash crops
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204008
[本文引用: 1]

Agricultural poverty alleviation is one of the most critical and important research contents in rural development and poverty alleviation. The mountainous areas in Southwest China have unique natural ecology and social culture, classic practice of Chinese traditional human-earth interaction, and it is also a place to observe the human-earth relationship transformation under the national development intervention. Taking Maca planting and Pu'er tea production as examples, this paper analyzes and traces the implementation of the agricultural poverty alleviation projections, and presents and compares the development effects of these two projections on typical mountainous villages. The results show that: First, agricultural poverty alleviation projects need to be embedded into the national socio-cultural context and politico-economic governance framework. Various kinds of cash crops are incorporated in the agricultural poverty alleviation projects. This benefits from China's geopolitical strategy, the socio-cultural "centre-periphery" differentiation, and the practices of the complex interaction among multiple actors in Yunnan Province. Second, agricultural poverty alleviation projects have enabled mountainous villages to attract investment and transform land use types, thereby achieving capital accumulation and cultural reconstruction. Local farmers have changed from passive recipients of market competition to active market players. Maca planting and Pu'er tea production have irrevocably tied the natural environment in Yunnan and the life worlds of local people to the commodity economy. Third, in agricultural poverty alleviation, the political logic and market logic represented by "poverty alleviation" and "agriculture industry" are not contradictory and restrictive. The two have been coordinated and compatible in Chinese rural development. However, it is worth pondering that we need to guard against fluctuations in farmers' livelihoods caused by the rise and fall of cash crops in the implementation of agricultural poverty alleviation projects. The research provides a new geographical perspective and reflection for the industrial poverty alleviation research, and provides policy reference for the frontier of southwest China to achieve rural revitalization based on agricultural economy.
云南典型山地乡村农业扶贫的机制与效应研究: 以特色经济作物种植为例
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204008
[本文引用: 1]

农业扶贫是乡村发展与贫困减缓最为关键且重要的研究内容之一。西南山区孕育着独特的自然生态与社会文化,承载了中国传统人地互动的经典实践,同时也是观测国家发展计划实施后人地关系变迁的关键地方。本文以云南丽江高寒山区的玛咖种植与西双版纳热带山地的普洱茶生产为案例,分析并回溯两种特色农业扶贫计划实施的机制与过程,力图呈现并比较特色产业扶贫带来的乡村发展效应。研究发现:① 农业扶贫项目的选择与确立,需要符合“国家—地方”这一对多元尺度层级的社会文化语境与政治经济管治框架。各类经济作物被引进成为山地乡村的产业扶贫项目,得益于中国地缘政治战略、“内地—边疆”的社会文化分异以及地方多元行动者之间的复杂互动;② 农业扶贫使得山地乡村实现了资本下乡、土地利用有效转型,从而达到不同程度的经济资本积累与文化再造,使所在地方农民经历了从市场竞争的被动接受者到主动的市场主体的身份转型;③ 农业扶贫中“扶贫”与“产业”所表征的政治逻辑与市场逻辑之间并非互相矛盾与掣肘,二者在中国乡村发展语境之下得到了有效、协调的互促与兼容。本文为产业扶贫研究提供了来自地理学的新兴视角与反思,对西南边疆地区立足特色产业提振乡村经济亦具有一定的参考价值。
Characteristics and influencing factors of the key villages of rural tourism in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204009
[本文引用: 1]

The key villages of rural tourism are typical demonstrations for promoting the high-quality development of rural tourism, which are of great significance for optimizing rural tourism supply and leading rural tourism development. The article analyzes the spatial distribution pattern and structural characteristics of 1000 key villages of rural tourism nationwide by using Nearest Neighbor Index and Kernel Density Estimation. The study further reveals spatial differentiation of the key villages of rural tourism. The main factors affecting spatial distribution of the key villages of rural tourism are analyzed by using Multiple Linear Regression, Vector Buffer Analysis and Geographic Detectors. The conclusions can be drawn as follows. Firstly, there are more key villages of rural tourism in the eastern region than in the western region of China. The inter-provincial spatial density stratification feature is obvious and the spatial distribution pattern of double core-ring core cluster-ribbon zone is unique. Secondly, the spatial distribution of key villages of rural tourism has significant positive spatial correlation. The key villages of rural tourism are spatially dispersed in cold spots and concentrated in hot spots. Thirdly, kernel density estimation shows that villages of agricultural production type have high spatial distribution density, while the others have low density. Fourthly, the spatial distribution pattern is the result of five factors: natural ecology, social economy, transportation facilities, scenic resources and policy environment. Gross domestic product per capita and household consumption expenditure have a significant positive impact, while the distance from the tourist market and the distance from transportation access are negative influencing factors. Fifthly, the driving factors for the spatial distribution of various types of villages are different and closely related to the village resource endowment and development characteristics.
中国乡村旅游重点村的空间特征与影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202204009
[本文引用: 1]

乡村旅游重点村是推进乡村旅游高质量发展的典型示范,对优化乡村旅游供给、引领乡村旅游发展具有重要意义。本文运用最邻近指数、核密度估计等方法分析了中国1000个乡村旅游重点村的空间分布格局和结构特征,揭示了乡村旅游重点村的空间分异规律。运用多元线性回归、矢量缓冲分析、地理探测器等方法剖析了影响乡村旅游重点村空间分布的主要因素。研究发现:① 乡村旅游重点村总体呈“东多西少”的空间分布格局。省际空间密度分层特征明显,“双核心—环核群—带状区”的空间分布规律突出。② 乡村旅游重点村的空间分布具有显著的空间正相关性,地域间呈冷点分散、热点集中的空间分异格局。③ 6类乡村旅游重点村的核密度呈一高五低、分异鲜明的类型特征。④ 乡村旅游重点村空间分布格局的形成是自然生态、社会经济、交通配套、景区资源、政策环境五大因素共同影响的结果。人均GDP和居民消费支出具有显著正向影响,客源市场距离及交通通达距离是负向影响因素。⑤ 各类乡村旅游重点村空间分布的驱动因素各异,与村落资源禀赋和发展特点具有密切关系。
Conception of construction of wetland ecology economy zone under implementation of rural revitalization strategy
乡村振兴战略实施背景下的湿地生态经济区建设构想
Development path and promotion mechanism of rural eco-industrialization in the new era: Taking Zhejing province as an example
新时代乡村生态产业化的发展路径与促进机制: 以浙江实践为例
Explore the realization path of ecological product value and promote the development of ecological resource asset system
探索生态产品价值实现路径促进生态资源资产协同发展
Researches on the pattern and route of ecological product value realization from the perspective of rural revitalization
乡村振兴视域下的生态产品价值实现模式路径研究
DOI:10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.02.023
[本文引用: 2]

全面推进乡村振兴,加快农业农村现代化建设,已成为中国全面建成小康社会后的重大战略。作为乡村振兴的主战场,也是绿水青山和自然资源的集中分布区域,中国广大农业农村地区蕴含着丰富的生态产品。在乡村振兴和农业农村现代化建设新形势下,如何通过推动生态产品价值的实现,从而促进乡村振兴成为目前的重要课题,尤其是实现模式路径的研究更是重要。文章在系统阐述生态产品概念内涵、基本特征基础上,提出了乡村振兴视域下的市场路径、政府路径、公益路径、“政府+市场”路径、“政府+公益”路径、“市场+公益”路径等6种生态产品价值实现的主要路径。同时,文章提出了生态保护补偿、生态资源指标和产权交易、绿色金融、生态农业产业化、生态旅游和特色文化产业化、生态修复与保值增值等6类实践模式。此外,文章还结合当前工作实际,提出了政府主导、市场需求、科技支撑、公众参与消费等4大类,以及空间分区、产权管理、核算评估等12小类生态产品价值实现机制。研究成果可为生态产品价值实现、乡村振兴和农业农村现代化建设提供参考,也将为继农业、工业、服务业后的“第四产业”——“生态产业”的培育提供参考,助推乡村生态优势真正转化为发展优势,实现区域经济社会发展与资源环境保护的双赢。
The use and abuse of vegetational concepts and terms
DOI:10.2307/1930070 URL [本文引用: 1]
Discussion on the scientific concept of ecology and its evolution and the contemporary ecologi-cal discipline system
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.040
[本文引用: 1]

Ecology is not only a branch of biology, but also an important part of environmental science and earth system science. The results of ecological studies can be directly applied in biodiversity conservation of plant, animal and microbe, biological resource utilization and biological industry management, and other fields. The concept of ecosystem extends classic ecology or basic ecology research to a new stage of ecosystem ecology or ecosystem science, which has laid a theoretical foundation for the scientific research of ecological environment at the global and continental scales, and has promoted the integration of biology, geography, and environmental science, and cross disciplinary of the natural sciences, humanities, and social economic sciences. During the integration processes, together with constantly absorbing nutrition from different disciplines, researches of eco-logy put forward a lot of scientific concepts or theories, and have been applied and developed in the relevant scientific research, formed contemporary ecology and ecosystem science system centered on the cognition of ecosystem, resource environment, and the mutual feedback relation with human society. We comprehensively discussed the scientific concept, basic theory, and discipline system of contemporary ecology from the origin and development of ecological thought, the scientific connotation, and extension of ecological concept, <i>etc</i>., and tried to sort out, investigate, and analyze the scientific connotation, discipline category and discipline system of contemporary ecology, put forward the branch discipline system classification scheme of basic ecology and applied ecology, with the aim to provide references for perfecting and reconstructing the discipline system of contemporary ecology.
生态学的科学概念及其演变与当代生态学学科体系之商榷
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.040
[本文引用: 1]

生态学既是生物学的分支学科,也是环境科学、地球系统科学的重要组成部分,其研究成果可直接服务于植物、动物、微生物的生物多样性保护、生物资源利用及生物产业管理等应用领域。生态系统概念将经典生态学或者基础生态学研究扩展到了生态系统生态学或者生态系统科学的新阶段,奠定了大尺度及全球生态环境科学研究的理论基础,促进了生物学、地理学及环境科学研究的大融合,推动了自然科学与人文科学和社会经济学的学科交叉。在这一大融合的历史过程中,生态学在不断地汲取不同学科营养的同时,提出了许多科学概念或理论学说,并在相关科学研究中得到应用和发展,形成了以认知生态系统与资源环境及人类社会的互馈关系为核心的当代生态学及生态系统科学体系。本文从生态学思想起源与发展、生态学概念的科学内涵及其扩展等方面综合讨论了当代生态学的科学概念、基础理论及其学科体系,并尝试性地对当代生态学的科学内涵、学科范畴、学科体系进行梳理、考察和分析,提出了基础生态学及应用生态学研究的分支学科体系分类方案,期望与学界共同商榷,为完善和重构当代生态学学科体系提供参考。
Spatial dynamics of ecosystem service flows: A comprehensive approach to quantifying actual services
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoser.2012.07.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
The value of the world's ecosystem services and natural capital
DOI:10.1038/387253a0 [本文引用: 1]
Discussion on the ecological theory and assessment methods of ecosystem quality and its evolution
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202204.026
[本文引用: 2]

Ecological civilization construction and ecological environment governance are basic tasks of state gover-nance in China. China has clearly put forward the goal of improving ecosystem quality and stability. However, there are no consensus on the scientific concept of ecosystem quality and the assessment methods of ecosystem quality evolution, which has puzzled the academic community. Based on the summarization of the scientific concept of ecosystem quality and its evolution, we discussed the concept of ecosystem quality and its ecological theory basis by referencing the concept of production quality, quality management and quality assessment of material production. The scientific connotation of ecosystem quality and its evolution was discussed from the perspectives of ecosystem natural attribute-social attribute-economic attribute and the relationships between them, the cascade relations of ecosystem component-structure-process-function-service-efficacy, the feedback of factor-system-environment, and the logic relation of state ecosystem fluctuation-quantity variation-quality alternation. We proposed perspectives and approaches of multi-objective assessment of ecosystem quality alternation from the aspects of natural resource environment system, typical ecosystem, regional macro-ecosystem, and ecological engineering efficacy.
生态系统质量及其状态演变的生态学理论和评估方法之探索
DOI:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202204.026
[本文引用: 2]

生态文明建设和生态环境治理是国家治理的基本任务之一,我国已经明确提出了提升生态系统质量和稳定性的目标。然而,生态系统质量的科学概念及其状态演变的评估理论和方法却是一直困扰学术界且尚未形成广泛共识的难题。本文在梳理生态系统质量的科学概念及其状态演变研究进展基础上,借鉴物质生产的产品质量、质量管理和质量评价概念,论述了生态系统质量概念及生态学理论基础,从生态系统的自然属性-社会属性-经济属性及其相互关系,生态系统组分-结构-过程-功能-服务-功效的级联关系,系统要素-系统-环境互馈关系,以及生态系统的状态波动-数量变化-质量改变的逻辑关系等视角,讨论了生态系统质量及演变的科学内涵,进而从自然资源环境系统、典型生态系统、区域宏观生态系统、生态工程效应/功效等方面,提出了多应用目标的生态系统质量变化评估的视角和方法。
The research core of geography: Human-land area system
DOI:10.2307/140646 URL [本文引用: 1]
论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
A review of ecosystem services supply and demand
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201707012
[本文引用: 1]

Natural ecosystems supply tangible products and intangible services, which are demanded and consumed by human beings. Therefore, supply and demand make up the dynamic process of ecosystem services flowing from natural ecosystems to human society. The process of identifying, measuring, mapping and conducting an equilibrium analysis of the supply and demand of ecosystem services is beneficial for the effective management of natural ecosystems and optimal allocation of natural resources. Moreover, this can provide theoretical support to payments for environmental services and ecological compensation, thus promoting ecological security and sustainable development. Although the study of ecosystem services supply and demand is important, related studies are limited in China and are mainly focused on Europe and North America. Based on the theory and case studies conducted in China and other countries, this paper first presented the definition of ecosystem services supply and demand, including actual supply, potential supply, satisfied demand, and total demand. Second, the classifications of ecosystem services were compared based on their spatial characteristics. Third, the methods of mapping ecosystem services supply and demand were divided as follows: (1) land use estimation, which needs simple operation and limited data, may cause errors due to the loss of internal heterogeneity and boundary effects; (2) ecological process simulation is mostly applied in water-related ecosystem services, showing detailed and reliable results with multi-calculation; (3) spatial data superposition, which is an ideal method for mapping ecosystem services with complete spatial data sets; (4) expert knowledge, where the mapping of ecosystem services supply and demand is decided by a group of experts or is based on the previous related findings; however, the mapping principle followed in a local study may not be applicable to studies conducted at other places; and (5) the use of integrated models InVEST (Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs), which is suitable for supply analysis, and ARIES (ARtificial Intelligence for Ecosystem Services), maps service flow from natural ecosystems to human beings. Finally, we discussed the equilibrium analysis framework for ecosystem services supply and demand from three angles: actual supply and potential supply, satisfied demand and total demand, and the spatial and quantitative relation between supply and demand.
生态系统服务供给和需求研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201707012
[本文引用: 1]

生态系统为人类供给产品与服务,人类对其产品与服务形成需求和消费,供需两者共同构成生态系统服务从自然生态系统流向人类社会系统的动态过程。对生态系统服务的供给和需求进行识别、度量、空间化及均衡分析是生态系统服务研究的重要组成部分,有助于生态系统有效管理以及自然资源合理配置,为生态系统服务付费和生态补偿提供理论支撑。本文基于国内外理论和案例研究成果,首先梳理生态系统服务供给和需求的含义,其次总结和对比从供需空间特征角度对生态系统服务的分类,并归纳生态系统供给和需求的空间化方法,最后从实际供给和潜在供给、实现需求和总量需求、供需数量和空间关系3个方面探讨生态系统服务供需均衡分析框架。
Steady-state economics: Concepts, questions, policies
DOI:10.14512/gaia.1.6.5
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Why should the focus of investment shift from man-made capital to natural capital? How do we invest in something that by definition we are unable to make? Are man-made and natural capital complements or are they substitutes? This paper consists of three parts: First is a discussion\n of the pre-analytic vision or paradigm of steady-state economics, along with its basic magnitudes, idea of efficiency, and relations to the traditional concepts of income and capital. Second are some analytical questions that are immediately suggested by the steady-state vision. Third\n is a discussion of some policy issues of moving toward a steady-state economy.
Understandings on the value realization mechanism of ecological products
对生态产品价值实现机制的几点认识
Analysis of the connotation and realization path of ecological products
生态产品的内涵辨析及价值实现路径
Ecological economization and economic ecologization in succession progress of development
Current production and consumption systems are usually accompanying ecosystem losses. Future progress of economic development cannot be achieved without fully evaluating and reflecting ecosystem service value. Facing increasingly acute contradictions between economic development and the degrading environment and exhausted resources, most countries and regions are trying to explore new development ways. The theory of moving from Plan A, business-as-usual, onto a new path-Plan B is not going to work for China because it is inadequate to provide theoretical explanations and decision-making support to China’s development policies. From the perspective of succession progress of development, in the present paper, the authors focus on discussing the connotation and elements of ecological economization and economical ecologization. The ecological economization contains the following aspects: 1) to coordinate regional economical-social development and ecological capital protection; 2) to promote the ecologization of the whole production-consumption processes, and 3) to reconstruct and revitalize ecosystem capital and functions. The key components of ecological economization are comprised of: 1) to value, manage and use ecological resources as assets; 2) to realize the worth of and capitalize the ecological assets; 3) to monetize both production and consumption of ecosystem services. Some suggestions on China’s development and ecological protection in the future are given as follows. The way of coupled development of ecological economization and economical ecologization is suggested to take. This means that the government should actively promote the shift of the development way to a mode of economical ecologization over developed areas with inadequate natural resources and ecosystem services, and to a mode of ecological economization over the undeveloped areas with abundant natural resources and ecosystem services.
发展转型的生态经济化和经济生态化过程
目前的生产-消费体系是造成生态系统损失的主要原因,未来的经济进步依赖于生态服务价值得到充分的评价与应有的体现。面对资源环境困境,世界各国都在探索新的发展途径,“A模式向B模式转变”的理论不足以为我国发展政策提供足够理论解释和决策支持。从发展过程视角,本文系统总结了生态经济化、经济生态化的内涵、内容,其中,经济生态化过程的主要内容包括:①区域经济社会和生态环境配置和谐化;②从生产到消费的全过程生态化;③生态资产再造和功能激活;生态经济化过程的主要内容包括:①生态资源资产化;②生态资产价值化和资本化;③生态服务供给和消费费用化。最后指出,我国应该走经济生态化和现代生态经济化相结合的道路,即在我国经济发展水平较高而生态资源稀缺的区域推进经济生态化进程,在生态资源丰富而经济发展水平较低的欠发达区域推进生态经济化进程。
Industrial ecologicalization and eco-industrialization development: Promoting the way of management and realizing it
产业生态化和生态产业化发展: 推进理路及实现路径
The innovative form of value realization of ecological resources under the background of rural vitalization
乡村振兴背景下生态资源价值实现形式的创新
Endogenous development: The industrial choice of eco-poverty-stricken villages in the post-poverty era
内源式发展: 后脱贫时代生态型脱贫村产业选择
Rural households' poverty and relocation and settlement: Evidence from western China
Based on survey data collected from five counties across southern Shaanxi, China, the present study employs a multinomial logistic model to explore the main factors related to the type of poverty of rural households, particularly focusing on the role of relocation time, reason for relocation, and type of relocation. The results showed that three types of poverty, “voluntary poverty”, “transient poverty”, and “chronic poverty”, are distinguished by combining income and consumption criteria. Moreover, relocation and settlement programs contribute to a certain degree to these three kinds of poverty, and the effects vary according to the relocation characteristics. Specifically, those relocated long-term were more likely to be trapped in “voluntary poverty” and “chronic poverty”, whereas those relocated short-term were less likely to fall into “voluntary poverty” and “transient poverty”. The poverty alleviation and disaster-related resettlers were less likely to be trapped in “chronic poverty”, whereas centralized resettlers were less likely to be trapped in “voluntary poverty” and “chronic poverty”. Additionally, demographic characteristics, capital endowment variables, and geographical features are all important factors affecting rural households’ type of poverty. This study can serve as a reference for further resettlement practice in China and other developing countries.
Regional land ecological security evaluation and ecological poverty alleviation practice: A case study of Yangxian county in Shaanxi province, China
DOI:10.1007/s11442-022-1967-8
[本文引用: 1]

Land ecological security (LES) is an important part of China’s ecological civilization construction, which plays a vital role in ensuring the sustainable development of its society and economy. Based on the Driving force-Pressure-State-Impact-Response (DPSIR) framework, this study quantified the spatiotemporal changes of LES in 28 counties of the southern Shaanxi Province from 2009 to 2018. The influencing factors of LES in Yangxian County were explored to clarify the mechanisms that rely on the land ecological advantages to develop organic agriculture and boost poverty alleviation. Results show that the LES of Yangxian always ranked in the top six in 28 counties of the southern Shaanxi region during 2009-2018. The LES in Yangxian increased from 0.385 in 2009 to 0.533 in 2018, and the LES level changed from relatively unsafe to safe. The indicators of rural per capita net income, grain output per unit area of arable land, and grazing intensity could explain 99.8% of the LES variance in Yangxian. Relying on ecological resources, Yangxian increased farmers’ income and boosted alleviation of poverty through innovative land policies, developing organic agriculture, and rural tourism. These findings will provide theoretical support and model reference for balancing ecological protection and poverty alleviation in restricted development zones.
GIES case dataset on Yangxian black rice crested ibis (Nipponia nippon) habitat in Caoba village, Shaanxi province of China
洋县草坝村黑米朱鹮栖息地生态环境保护与可持续发展案例研究
Regional function transformation and high-quality development path in Qinling-Daba Mountains of Shaanxi province
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211002
[本文引用: 1]

Based on entropy weight-TOPSIS and improved coupling coordination model, the study analyzed the characteristics of regional function transformation and its system coupling coordination degrees in the Qinling-Daba Mountains, and revealed regional function transformation mechanism, and proposed a high-quality development path. The results show that: (1) Since the implementation of China's western development policy, the regional comprehensive functions of the Qinling-Daba Mountains has been optimized. The function index of economic development and social security have been enhanced significantly. However, agricultural production and ecological service function index decreased first and then increased. (2) The coupling and coordination degree between different regional functions presents a progressive evolution rule from low to high level. Regional functions change from agricultural production-oriented to ecological protection-oriented, and then to balanced coordination of various functions. (3) The degree of coupling coordination among different counties has obvious characteristics of "high in the northwest, but low in the southeast". High-value areas are concentrated on the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains and along the Hanshui River. In the future, by innovating regional coordinated development strategy, constructing a green development system, exploring a high-quality development mode, and building a technological platform, we can enhance the coupling coordination degree of regional function and regional innovation capacity to promote high-quality development of Qinling-Daba Mountains.
陕西秦巴山区地域功能转型与高质量发展路径
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20211002
[本文引用: 1]

以高质量发展为导向的地域功能转型是实现区域可持续发展必然要求。采用熵权-TOPSIS法和改进的耦合协调度模型,定量分析了陕西秦巴山区地域功能转型格局演进阶段性及其空间差异性,探究了地域功能转型机制及其高质量发展路径。结果表明:西部大开发政策实施以来,秦巴山区地域功能趋向优化,其中经济发展和社会保障功能提升快速,农业生产和生态服务功能经过短暂调整后逐步提升。地域各系统功能耦合协调度呈现从低水平平衡向高水平耦合的递进式演进规律,地域功能经过了由农业生产主导型向生态保护主导型,再向各功能均衡协调渐进转型的过程。不同县域单元地域功能耦合协调度差异明显,呈现“西北高、东南低”的特征,高值区集中在秦岭北麓地带和汉江沿岸。研究认为陕西秦岭山区实现高质量发展路径包括:创新区域协调发展战略,促进地区之间互动,提升地域功能协同度;构筑绿色发展体系,促进各系统功能互补,提升地域功能耦合度;探索高质量发展模式,补齐地区发展短板,积极融入新一轮西部大开发新格局;搭建科技创新智库平台,创建秦岭综合研究示范区,提升区域系统创新能力。