1 引言
区域经济韧性通常与其发展路径及其所处的阶段密切相关。经济韧性强调区域应对外部冲击和干扰并确保经济可持续发展的能力[1],表征为应对外部冲击的能力,而这一能力又受制于自身发展路径的演化[5-6]。在区域发展路径中表现为“适应力”和“适应性”,前者体现在区域经济系统对原有增长路径的突破,后者则强调区域经济系统维持原有的发展路径[7-8]。另外,区域经济韧性一方面表现为经济增长指标的变化,另一方面与产业结构存在内在关联。一般来说,适应力较强的区域受系统的约束较弱,具有产业多样化及创新发展路径的潜力,会进一步增强区域经济韧性[9]。适应性较强的区域经济韧性高,产业报酬递增效应产生积极的路径依赖,但随着时间的推移,积极的路径依赖可能转化为消极的路径锁定[10],资源型老工业区的发展通常处于消极的路径锁定中,经济韧性较低[11]。由此,地区经济韧性与发展路径可由其产业结构及其特征进行表征,产业结构演变是区域发展路径嬗变的体现,也伴随着或推动了区域经济韧性的演变。
产业结构对区域经济韧性的影响正逐步得到学界的关注,产业专业化、多样化以及基于产业结构的网络分析是研究区域经济韧性影响因素的重要维度[12]。产业专业化方面,对资源型城市以及专业化城市的研究表明,产业专业化水平较高的区域受到外部冲击时,会迅速扩散至整个区域,区域应对外部冲击的抵抗力和恢复力较差,稳健性较低,韧性水平低[9,13]。产业多样化方面,一般地相关产业多样化能够提升地区应对外部冲击的转换能力和调整能力,地区经济韧性较强[14⇓-16];但也有研究表明过度的相关多样化的产业结构会形成产业冗余,降低产业转换效率,不利于区域经济韧性的提高[15,17 -18]。同时,区域产业结构是演进的,区域经济韧性会随之发生变化,产业结构演替既是区域经济韧性演变的动力也是其重要体现[12,19 -20]。由此,产业结构对区域经济韧性的影响仍存在争议,其效应方向的临界性及不同产业组分的影响力仍有待探究。其次,产业结构对经济韧性的影响存在地区差异以及区域内部的异质性,需置于特定的语境和背景中进行探究。
区域发展路径和产业结构演变是解析区域经济韧性形成机理的重要视角。区域经济增长实际上是产业不断出现和消亡的过程,产业结构不仅影响区域产业结构的演变路径,还会影响区域未来的发展路径[21]。既有研究基于特定行业和产业分析了产业结构对区域经济韧性的影响。以企业为研究对象,借助技术关联性、复杂度等指标揭示了区域产业结构演变路径并预测未来发展趋势[22];以特定产业为例,发现其异质性、开放性与动态性以及龙头企业的影响力对区域经济韧性的提高具有正向作用,并影响区域经济的增长路径[4];以更为宏观的三次产业结构视角研究发现,区域产业结构和区域产业竞争力影响区域经济韧性水平[23]。前人研究对认识产业结构演变对区域经济韧性的影响具有重要意义,然而一定程度上割裂了从企业到行业再到产业的尺度联系。从微观个体企业进入与退出的动态变化到中观尺度细分行业再到宏观产业结构变化的视角开展研究,不仅有利于廓清区域发展路径,而且能够呈现产业结构与区域经济韧性演变的耦合关联过程,进而认识不同阶段影响区域经济韧性的主要产业及经济韧性形成的内在机理。
京津冀地区适于开展经济韧性与产业结构演变的关联研究,并具有理论和现实意义。① 北京、天津是中国北方乃至全国重要的对外联系的战略门户[24],京津冀地区在参与国际分工与合作的过程中,势必受到经济危机、贸易摩擦等事件的影响,触发并形成地区经济韧性。其次,京津冀地区为典型的中心—外围结构,各地区不仅经济发展水平和产业结构差异较大[25],而且部分地区处于“慢性燃烧”的状态,路径依赖限制了发展路径的突破[26],有必要开展适应性经济韧性的研究。② 1949年以来,国家对京津冀地区生产力布局进行过多次统一规划和部署,地区内部形成了密切的经济社会联系[27]和复杂的产业协作网络[28],各地区经济韧性与产业结构联系紧密。③ 诸如1998年亚洲金融危机、2000年中国加入世界贸易组织(WTO)、2008年全球金融危机以及2014年以后陆续实施的非首都功能疏解和京津冀协同发展等事件,进一步密切了京津冀地区的整体性和协同性[29],为地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的关联研究提供了理论和现实基础。
因此,本文以京津冀地区为案例地开展区域经济韧性与产业结构的耦合关联研究具有典型的适宜性、理论和现实意义。本文以县域行政单元和企业为基本研究对象,在测度地区经济周期经济韧性水平和产业结构状态特征的基础上,回答区域经济韧性与产业结构是否存在时空关联;并从区域产业结构和区域竞争力两个维度定量分析不同行业产业对区域经济韧性作用的方向和大小,从产业构成的视角揭示区域经济韧性与产业结构演变耦合关联的机理。
2 方法与数据
2.1 研究框架
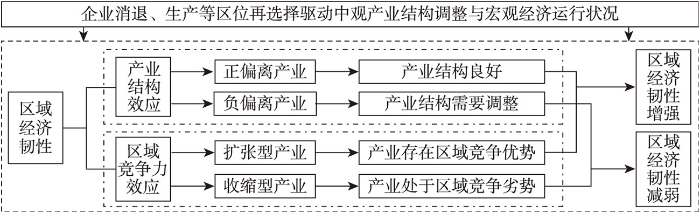
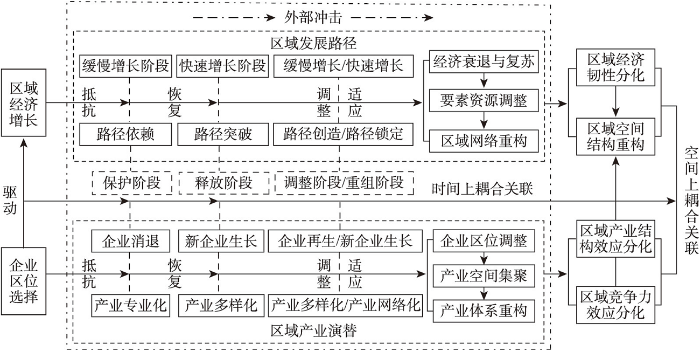
区域经济韧性是指地区在环境、市场、竞争等因素的冲击下,通过必要的经济结构、社会组织及体制的适应性变革,恢复冲击前的发展路径,或转入一个能够更加全面有效利用自然、人文和环境资源的新路径的能力[1]。区域经济韧性具有两个特征:① 区域经济韧性是一个过程且是演化的。从应对外部冲击到自身调整和适应,区域经济韧性可解构为抵抗力、恢复力、调整力和适应力等维度[6]。在区域经济韧性演变的不断阶段,其经济增长的态势会表现出不同的特征,在抵抗外部冲击后,通过恢复、调整以及自身结构性变化从而具有较好的适应性,地区经济会表现为增长的态势。② 区域经济韧性可以由经济发展显性指标以及潜在的结构性变化进行表征。显性的指标可以体现为经济增速的变化,虽然长期来看,区域经济增长是普遍的趋势,但在韧性演化过程中,韧性水平及各阶段可以体现为GDP增速的变化及特征[3,20]。产业结构是认识区域经济韧性演化过程中潜在结构性变化中的重要维度,企业及其形成的行业和产业在区域内的异质性、动态性影响地方产业生命周期的演化[4,21],进而形成区域经济应对冲击的抵抗力和恢复力。由此,藉由经济增速的变化廓清区域经济韧性水平,进而通过产业结构的变化探讨其成因是认识区域经济韧性形成机理的有效逻辑。
企业作为区域经济活动的微观主体,其退出、进入与生长的动态变化构成了中观尺度的行业、产业以及宏观经济运行的结果[30-31]。由众多企业构成的行业及产业是区域宏观经济运行的中观载体,能够有效反映区域经济结构的状况,其组合形态进而可以反映区域产业结构演变的路径。以企业为基本单位,将产业结构对区域经济增长的影响进行分解可以认识区域经济韧性以及产业结构与区域经济韧性的关系。区域经济增长可分为分享增长和转移增长,分享增长是指地区按区域总体增长率所得到的增长量,而转移增长可分为产业结构的结构性和差异性偏离增长,分别对应产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应,这是阐释产业结构对区域经济韧性影响的两个维度[32]。借鉴相关研究[33],使用偏离—份额分析实现产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应的定量化,体现产业结构对区域发展路径及状态的影响。由此,区域发展路径及状态即是其经济韧性的体现,依此逻辑,区域经济韧性可表征为区域产业结构效应和产业竞争力效应。
区域产业结构效应和产业竞争力效应能够分析细分产业对区域发展路径演化的影响,即对区域经济韧性的贡献[23]。产业结构效应是各产业增长率与区域整体增长率的差值,可将区域产业分为结构良好的正偏离产业以及亟需调整的负偏离产业。区域竞争力效应反映区域某产业高于区域其他产业竞争优势的程度,并依次可将区域产业分为具有区域竞争优势的扩张型产业与处于竞争劣势的收缩型产业[37,39]。当地区产业处于由正偏离产业和区域竞争力较强的扩张型产业构成的组合结构时,区域经济韧性较强;相反,由负偏离产业和区域竞争劣势的收缩型产业形成的组合不利于经济韧性的提升[32-33]。由此,本文基于企业营业状态数据,实现区域经济韧性与产业结构演变的关联,从产业视角揭示地区在外部冲击下经济发展不同时期所表现的韧性水平差异,进而探究细分产业对区域经济韧性演化的影响(图1)。
图1
图1
区域经济韧性的产业结构影响分解研究框架
Fig. 1
Methodology framework for the decomposition of industrial structure impacts on the regional economic resilience
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 经济周期模型法
式中:t表示阶段初始时间;t+k表示阶段结束时间;u表示不同地区;
2.2.2 产业结构多样化指数
多样化的产业结构有利于分散风险,增强区域经济韧性,在研究区域经济韧性中常将产业结构多样化指数作为重要指标。借鉴相关研究[36],采用熵测度的方法计算多样化指数(VAR)来表征,指标值越大相对多样化程度越高。计算式为:
式中:n指产业的种类;pi为地区某产业企业统计量所占比重。
2.2.3 格兰杰因果检验法
格兰杰因果检验用来判定两个时间序列变量间是否存在因果关系和变化的一致性。当前,区域经济韧性与产业结构演变间存在关联性仅局限于理论和经验推理,二者间的因果关系及其方向尚有待使用科学的方法进行检验。本文借助格兰杰因果检验方法判定二者间在统计学上是否具有因果关系,亦即二者在时间尺度上演变的一致性和关联性,也是分析二者协同演变机理的前提和基础。为保证统计学意义,在进行格兰杰检验之前要确保时间序列具有平稳性,需先进行单位根检验。本文运用ADF检验,若ADF检验统计量小于临界值,即可拒绝原假设,从而确保时间序列具有平稳性。在进行格兰杰因果关系检验时,假设存在X与Y两个变量,如果对X的过去使用后预测出来的Y比不使用X的过去预测出来的结果更理想,那么即可判定X是Y的格兰杰原因。X为反映产业结构变动的Lilien指数,Y为区域经济韧性。借鉴既有相关研究[19,37],使用修正后Lilien指数表征产业结构变动的速度,具体计算式为:
式中:t为经济增长阶段;eis是产业s在地区i的企业统计量;ei是地区i所有行业产业中企业统计量。
2.2.4 偏离—份额分析法
式中:
将计算式(7)两边同时除
式中:计算式(x)与韧性测度计算式一致,计算式(y)为区域产业结构贡献效应,计算式(z)为区域竞争力贡献效应。
2.3 数据来源
本文以北京、天津、河北的市县级行政区为研究对象,鉴于行政区划调整及数据的可获取性,部分建成区做适当调整,得到199个基本研究单元。在进行多年份多地区的GDP比较分析时,GDP实际增长率具有科学意义,因此使用的GDP增长率为实际增长率,来源于《中国统计年鉴》、各省市和地市统计年鉴以及官方公布的社会经济统计公报等资料。地区经济发展路径演变及产业结构演替是一个较为缓慢的过程,为保证研究的科学性,结合企业数据的可获得性,本文选择中国加入WTO后的2002—2019年为研究时段,包括1998年亚洲金融危机和2008年全球金融危机两个事件及其经济复苏期。
各地区各年份产业情况由企业数据汇总获得,企业数据来自于天眼查网站。查询获取2002—2019年研究区企业的注册地址、注册资本、成立时间、营业状态、经营范围等信息数据,共计25074条。整理得到京津冀各地区各行业企业退出、进入的数据库,以反映不同经济韧性阶段地区产业结构的演变。产业分类方面,以中国发布实施的第四版《国民经济行业分类》为依据,将行业门类适当合并为三次产业。参照美国经济学家布朗宁对服务业的分类方法及应用[19,37],将第三次产业分为生产性服务业、流通性服务业、消费性服务业、社会性服务业。其中,生产性服务业是指主要为生产经营主体提供服务的行业,流通性服务业为商品和信息流通提供服务,消费性服务业为个体消费者提供服务业,社会性服务业为群体提供公共性服务。最终形成本文的行业产业分类(表1)。
表1 行业产业分类
Tab. 1
| 产业类别 | 包含的行业 |
|---|---|
| 第一产业 | 种植业、林业、畜牧业、渔业 |
| 第二产业 | 采矿业、制造业、电力燃气及水的生产和供应业、建筑业 |
| 第三产业 | 生产性服务业:金融业、房地产业、租赁和商务服务业 |
| 流通性服务业:交通运输仓储及邮政业、信息传输计算机服务和软件业、批发和零售业 | |
| 消费性服务业:住宿餐饮业、居民服务和其他服务业、文化体育和娱乐业 | |
| 社会性服务业:科学研究技术服务和资质勘探业、水利环境和公共设施管理业、教育、卫生社会保障和社会福利业、公共管理和社会组织、国际组织 |
3 地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的时空关联
3.1 地区经济增长阶段的划分
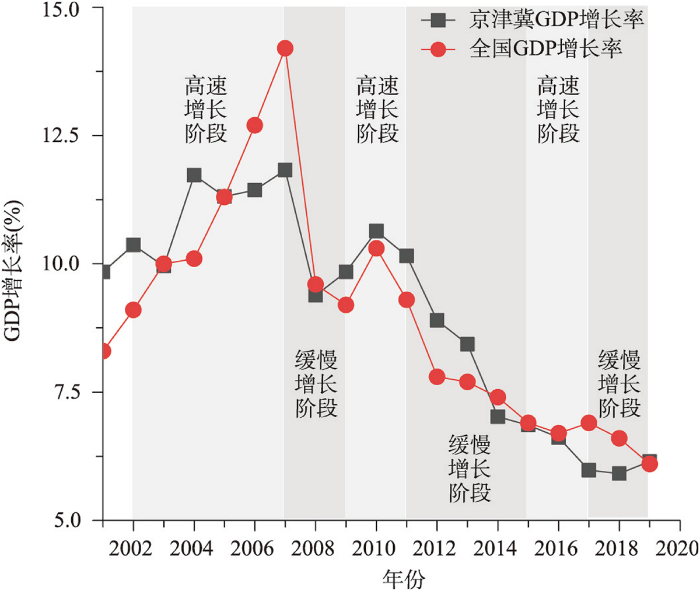
研究时段京津冀地区经济增长可分为3个经济高速增长阶段和3个缓慢增长阶段,依次为:2002—2007年的经济高速增长阶段,2007—2009年经济缓慢增长阶段、2009—2011年经济高速增长阶段、2011—2015年经济缓慢增长阶段、2015—2017年经济高速增长阶段、2017—2019年经济缓慢增长阶段(图2)。总体来看,以上各阶段体现了京津冀地区经济发展外部环境的变化:2002—2007年中国加入WTO后经济增速呈快速上升趋势;而后受2008年全球金融危机的影响经济增速明显下降,直至2010年国家出台“四万亿”政策,经济增速才出现了短暂的回升;2011年以后,经济发展进入“新常态”,国家推动京津冀地区产业结构调整,经济增速又呈现下降的趋势;经过几年的调整,2015年后地区经济增速逐步回升;2017年以来,美国等西方国家加大对中国的技术封锁,引发贸易摩擦,中国及地区经济增长又出现下降的态势。因此,本文基于以上6个经济增长阶段分析区域经济韧性与产业结构的关联性符合中国及地区经济增长的现实背景。
图2
图2
2002—2019年中国及京津冀地区GDP增长曲线及阶段
Fig. 2
GDP growth curves and various stages in China and Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2002 to 2019
3.2 地区经济韧性的空间格局及演变
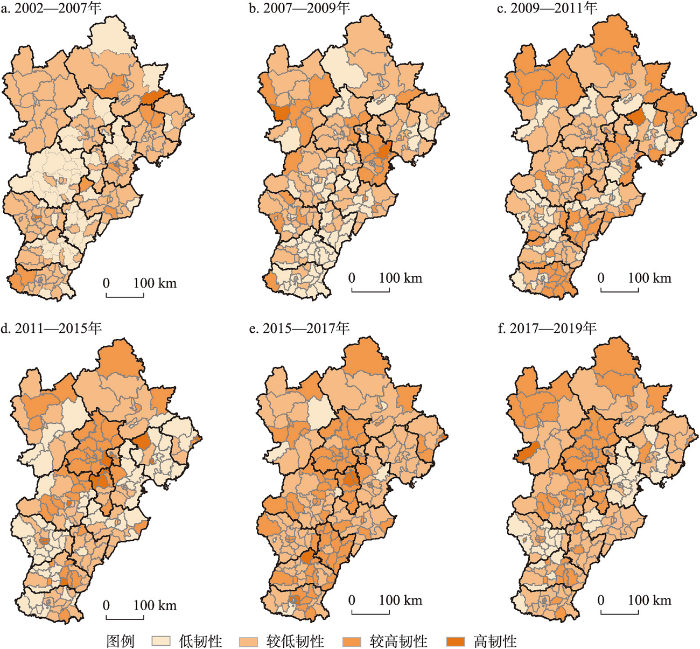
运用经济周期模型方法测度各阶段各地区经济韧性水平,基于ArcGIS自然断裂点法并参考相邻阶段地区GDP增长率的增减幅度将研究单元经济韧性由高到低依次划分为高韧性、较高韧性、较低韧性和低韧性等4种类型(图3)。
图3
图3
2002—2019年京津冀地区各经济增长阶段经济韧性空间格局
Fig. 3
Spatial pattern of regional economic resilience in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region at various economic growth stages from 2002 to 2019
2002—2007年经济高速增长阶段。该阶段是1998年亚洲金融危机以及中国加入WTO以后的经济恢复和高速增长阶段。结果显示(图3a),京津冀地区整体恢复力较弱,经济韧性水平较低。高韧性地区主要有:天津和石家庄市城区、河北宽城等地区;较高韧性地区包括北京西城区、天津部分市区、河北唐山、邯郸、承德、沧州等城市市区、河北滦平;经济韧性较低的地区范围大,除北京和天津外围市区以及河北石家庄、秦皇岛、廊坊、邢台等城市市区少数地区外,其他大部分地区恢复力弱,韧性水平低。总体上,产业结构综合实力强且相对单一的地区经济恢复速度较快,经济韧性较强。
2007—2009年经济缓慢增长阶段。受全球金融危机的影响,京津冀大部分地区在冲击下表现为抵抗乏力。高韧性地区主要有天津市城区、北京顺义、天津宁河、河北怀安;较高韧性地区包括天津其他地区、北京平谷和通州以及河北张家口、保定等少数地区;较低韧性和低韧性区域分布较广,大部分位于北京、天津、石家庄外围以及河北中南部地区(图3b)。结合产业结构分析发现,产业构成外向性强的地区受到外部冲击明显,而其他地区由于受到的冲击小,表现出较强的抵抗力。
2009—2011年经济高速增长阶段。其背景是中国推出“四万亿”经济刺激计划,以保持经济增长。与前一个阶段相比,京津冀55.80%的地区恢复力指数增长,经济韧性水平上升。高韧性和较高韧性区域主要分布在天津、唐山、承德、张家口、秦皇岛、邯郸等地区;较低韧性和低韧性区域集中分布在保定、张家口等河北中西部和延庆、怀柔等北京北部地区(图3c)。分析发现,产业基础好、竞争力强或产业结构相对单一的地区经济恢复较快,表现出较好的恢复力。
2011—2015年经济缓慢增长阶段。世界经济复苏乏力,中国着力调整经济结构,经济发展进入新常态。在此背景下,京津冀大部分地区表现为较差的抵抗力,仅22.60%的地区经济韧性水平增强。总体来看,除北京和石家庄表现出较好的经济韧性外,其他大部分地区经济韧性水平较低。高韧性区域主要分布在河北石家庄、廊坊、唐山;较高韧性区域包括北京、承德和张家口、邢台等部分地区;低韧性区域包括天津以及河北东部、西部和中南部的大部分地区(图3d)。这一阶段的经济韧性更多地体现为国家经济“新常态”下的经济结构调整能力,以传统产业为主、产业结构相对单一的地区受到的影响较大,表现为调整力和适应力不高的低经济韧性。
2015—2017年经济高速增长阶段。该阶段,京津冀64.32%的地区经济韧性水平提升,44.22%的地区为高韧性类型,整体经济韧性增长显著。高韧性区域主要分布在张家口、廊坊、邢台、邯郸的部分地区;北京及其周边的石家庄、廊坊、保定等地区形成较高韧性集中区域;较低韧性地区和低韧性地区分布在从中部高韧性集中区向南到邢台、邯郸部分市区的周围及东西两侧(图3e)。综合来看,经济基础较好、产业结构高级化的地区调整力和适应力较强,能够较快地实现转型发展,表现出较好的适应性经济韧性。
2017—2019年经济缓慢增长阶段。受西方国家技术封锁和贸易摩擦的影响,京津冀地区经济增长再次进入缓慢增长阶段。相比前一阶段,仅有33.70%的地区经济韧性增强,京津冀地区整体上经济抵抗力不强,韧性水平较低。除北京表现出较强的抵抗力韧性外,天津和河北的大部分地区经济韧性不高(图3f)。此外,较低韧性和低韧性的地区数量增加,范围扩大,区域集中分布在天津市以及石家庄市。总体来看,除了北京由于综合实力较强具备较好的抵抗力和恢复力外,其他大部分表现为较低的经济韧性。
总结来看:研究时段内,在外部冲击及国家和地区经济政策的影响下,京津冀地区经济增长、经济韧性以及地区的产业结构状况呈现出较好的一致性;经济高速增长阶段与缓慢增长阶段交替出现,高速增长阶段恢复力提升的地区数量多于缓慢增长阶段抵抗力增强的地区数量,总体经济韧性呈波动上升的趋势。随着京津冀协同发展战略的推进,产业转移有序进行[39],京津冀地区经济增长和经济韧性的协同性进一步加强。但京津冀地区的人口经济主要集中在北京、天津等中心城市,而中心城市周围缺乏相应的产业基础,对产业的吸引力不足[40],使得高经济韧性地区也较为稳定地分布在北京、天津、石家庄市区及其周边地区构成的核心地区,京津冀地区经济增长以及经济韧性依然呈现较为典型的中心—外围结构。此外,经济高速增长阶段和缓慢增长阶段受影响的地区存在显著差异,各地区在抵御经济冲击并做出适应性调整的能力亦存在较大差异;高速增长阶段经济水平较高的北京和天津城市中心区外围地区以及河北大部分地区表现出较好的恢复力,并能够在冲击后积极做出适应性调整;而缓慢增长阶段经济水平较低的外围地区抵抗力也较差,北京、天津及石家庄市区经济韧性较高。
3.3 地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间关联
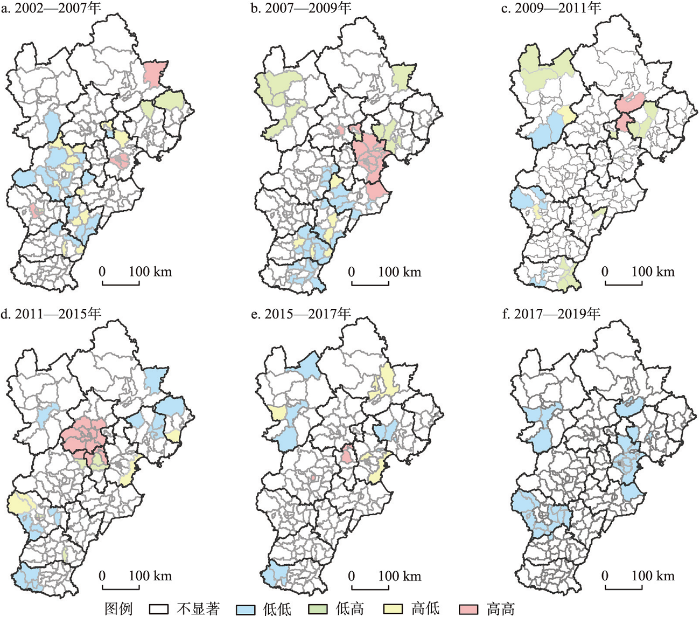
京津冀地区经济韧性空间格局演变分析表明,地区经济韧性呈现显著的空间异质性和中心—外围的空间结构特征。这一特征本质上与各地区产业结构、经济水平、交通网络等要素状况密切相关。由此有必要验证京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间关联性。鉴于产业结构多样化对经济韧性具有显著影响得到学界普遍共识,本文运用GeoDa双变量空间自相关方法,对地区经济韧性与产业多样化指数进行双变量局域空间自相关分析。
结果显示,在p < 0.05的显著性水平之下,2002—2007年经济高速增长阶段、2007—2009年经济缓慢增长阶段、2009—2011年经济高速增长阶段、2011—2015年经济缓慢增长阶段、2015—2017年经济高速增长阶段、2017—2019年经济缓慢增长阶段等6个经济增长阶段的Z统计值的绝对值分别为3.719、5.9771、1.902、5.110、1.962、1.599,对应的Moran's I估计值分别为0.121、0.200、-0.058、0.170、0.060、-0.531,说明2002—2017年间地区经济韧性与产业结构多样化的空间关联集聚性显著;2009—2011年经济高速增长阶段,经济韧性与产业结构多样化的空间关联分散特征显著。总体来看,京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构在空间上呈现长时间序列下的空间自相关关系。
京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构多样化的集聚强度呈现先增强后减弱的趋势,经济较为发达的北京、天津等地区,高经济韧性—高产业结构多样化关联的集聚较为显著。图4显示,2002—2009年京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构多样化的集聚强度逐渐增强,其中高经济韧性—高产业多样化的区域在天津及其周围地区逐渐集聚,其他类型的集聚主要分布在河北南部。2009—2015年天津高经济韧性—高产业多样化集聚现象逐渐减弱,北京及其周边地区集聚效应逐渐增强,其他类型以低经济韧性—低产业多样化集聚类型为主,主要分布在河北西部和东北部等省际边缘地区。从2015年起,产业多样化指数与区域经济韧性的集聚关系逐渐减弱,北京及其周边地区的高经济韧性—高产业多样化集聚现象逐渐减弱,到2019年在河北周边地区出现较为明显的低经济韧性—低产业集聚。
图4
图4
2002—2019年京津冀地区各阶段经济韧性与产业多样化指数双变量局域空间自相关LISA集聚图
Fig. 4
LISA agglomeration pattern of local spatial autocorrelation between regional economic resilience and the industrial diversification index in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region at various stages from 2002 to 2019
4 地区经济韧性与产业结构的演变关联及效应分解
4.1 地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的关联性验证
前文使用双变量空间自相关方法验证了地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间关联,然而地区经济韧性与产业结构均处于不断演变的状态,那么在地区发展路径演化过程中,即在长时段尺度,京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构变动是否存在关联性?对研究时段各地区的经济韧性数值和Lilien指数进行格兰杰因果检验。
表2 单位根检验结果
Tab. 2
| 变量 | ADF统计量 | 1%临界值 | 5%临界值 | 10%临界值 | P值 | 结论 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnX | -22.533 | -3.430 | -2.860 | -2.570 | 0.001 | 平稳 |
| lnY | -27.076 | -3.430 | -2.860 | -2.570 | 0.001 | 平稳 |
表3 格兰杰因果检验结果
Tab. 3
| 原假设 | 滞后期 | 观察数 | F值 | P值 | 结论 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnX不是lnY的格兰杰原因 | 4 | 1194 | 36.271 | 0.001 | 拒绝 |
| lnY不是lnX的格兰杰原因 | 4 | 1194 | 27.182 | 0.001 | 拒绝 |
4.2 地区经济韧性与产业结构演变关联的偏离效应分析
验证了京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间关联及时序关联,进而使用偏离—份额分析回答在地区发展路径演化即经济韧性与产业结构关联演变过程中,各产业发挥的作用。
基于研究时段企业信息数据库,运用偏离—份额分析方法,从偏离效应和联合效应两个方面进行剖析。将区域经济韧性与产业结构进行定量关联,并进一步从产业结构效应与区域竞争力效应两个方面分析细分产业对京津冀地区发展路径演化的影响。结果表明,与产业结构效应相比,绝大多数地区受区域竞争力效应的影响更大(图5)。
图5
图5
2002—2019年京津冀产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应的地区数量占比
Fig. 5
Quantity proportion of the understudied region at industrial structure effect and competitiveness effect from 2002 to 2019
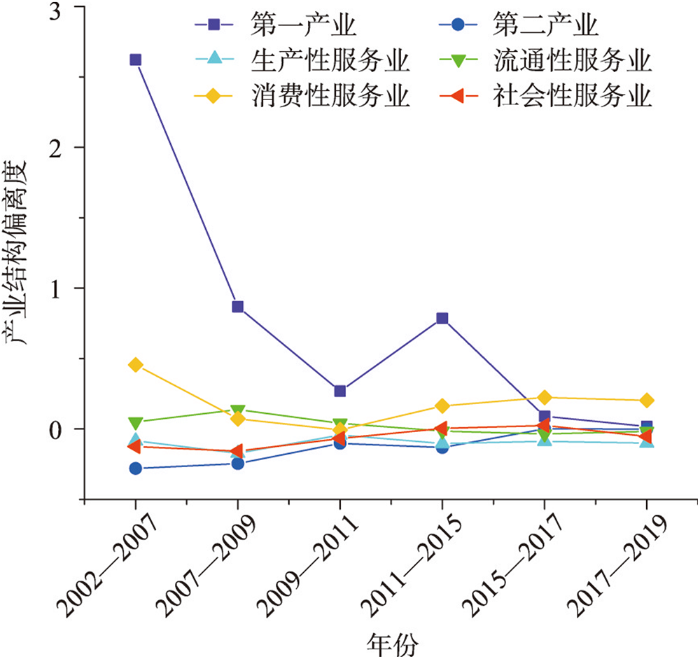
根据产业结构效应可将全区产业分为产业结构良好的正偏离产业与产业结构亟需调整的负偏离产业的假设,研究时段内,京津冀地区产业结构对区域经济韧性的作用有增强趋势。具体来看(图6):首先,第一产业与消费性服务业在长时段内表现为正偏离产业,其中第一产业对区域产业结构的正向促进作用呈减弱趋势,消费性服务业的正向作用逐步凸显;其次,第二产业与生产性服务业在长时段内表现为负偏离产业,并且生产性服务业对产业结构升级的阻碍作用呈波动减弱的态势,而第二产业的阻碍作用呈明显减弱的趋势;最后,流通性服务业与社会性服务业对区域产业结构的作用表现为小范围的波动变化,表现不稳定。由此,各产业对地区经济韧性的影响不仅在趋势上存在差异,且在经济增长的不同阶段其发挥的作用也不同。
图6
图6
2002—2019年京津冀产业结构偏离度
Fig. 6
Industrial structure deviation in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2002 to 2019
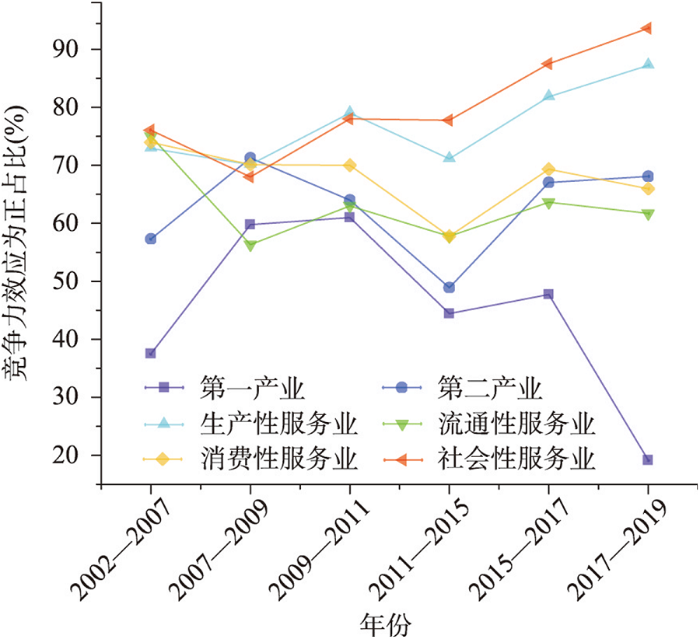
基于区域竞争力效应可将全区产业分为处于区域竞争优势与劣势的扩张型产业、收缩型产业,结果显示(图7):2002—2019年京津冀地区第一产业为扩张型产业的区域比重在减小,说明第一产业对区域经济韧性的贡献呈逐步下降的态势;第二产业、流通性服务业、消费性服务业为扩张型产业的区域比重波动较小,未有明显增加或减少趋势,说明京津冀地区经济韧性的变化受这3种产业的区域竞争力效应的影响较小;而以生产性服务业、社会性服务业为扩张型产业的区域比重呈现大幅增加的特征,表明越来越多的地区经济韧性的提高依赖于这两类产业区域竞争力效应的提高。
图7
图7
2002—2019年京津冀各产业正向区域竞争力效应的区域占比
Fig. 7
Quantity proportion of the understudied regions in which industries exerts positive regional competitiveness effect in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2002 to 2019
4.3 地区经济韧性与产业结构演变关联的联合效应分析
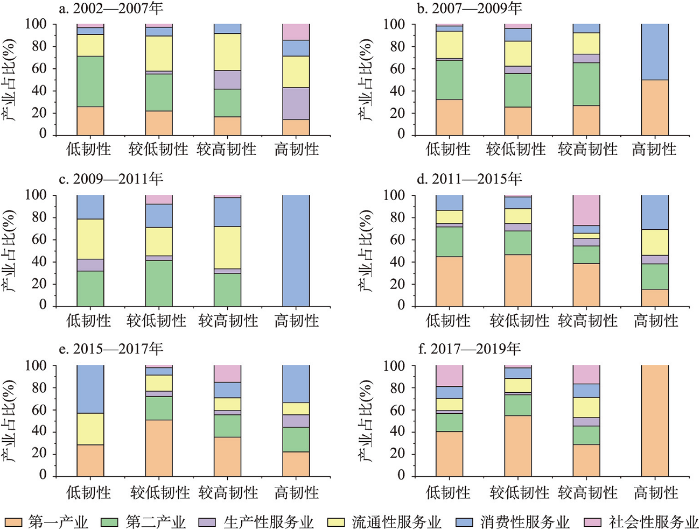
图8
图8
2002—2019年京津冀各阶段不同韧性类型地区结构偏离效应影响最大产业的占比
Fig. 8
The proportion of the industries affected substantially by the structural deviation effect in various resilience types of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region at different stages from 2002 to 2019
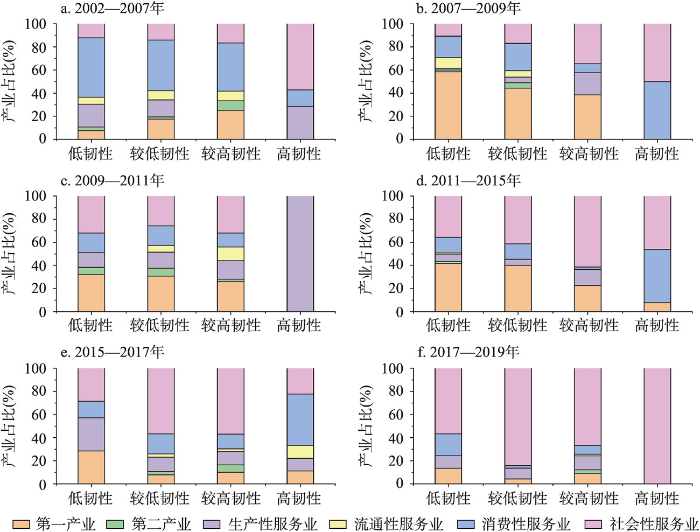
图9
图9
2002—2019年京津冀各阶段不同韧性类型地区扩张型产业的占比
Fig. 9
The proportion of regional expansion industries in various resilience types in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region at different stages from 2002 to 2019
2002—2007年经济高速增长阶段。从产业结构效应来看,此阶段的正偏离产业为第一产业、流通性服务业、消费性服务业。随着地区经济韧性的增强,流通性服务业和消费性服务业对区域经济韧性的贡献在增强,第一产业的贡献在减弱。区域竞争力效应方面,生产性服务业和社会性服务业表现为区域竞争优势,促进了区域经济韧性的提升。因此,此阶段生产性服务业和社会性服务业有利于区域经济韧性的增强。
2007—2009年经济缓慢增长阶段。从偏离效应来看,此阶段的正偏离产业未发生变化,且产业结构效应对经济韧性的影响最为明显。具体来看,流通性服务业偏离效应份额较小,对区域经济韧性的影响较低;第一产业和消费性产业对区域经济韧性的影响较为显著,且起到积极的作用。区域竞争力效应方面,消费性服务业、社会性服务业的区域竞争优势较为显著,有利于区域经济韧性的增强。综上,此阶段产业结构效应的增强伴随着消费性服务业的发展,并提升了区域经济韧性。
2009—2011年经济高速增长阶段。区域竞争力效应对经济韧性的作用较强。具体来看,产业结构效应方面,正偏离产业为第一产业和流通性服务业。其中,流通性服务业对区域经济韧性的产业结构优化的作用显著。区域竞争力效应上,第一产业、生产性服务业以及社会性产业的区域竞争优势明显,其中生产性服务业对区域经济韧性的增强作用最为显著。由此,在此阶段流通性服务业和生产性服务业促进了区域经济韧性的提升。
2011—2015年经济缓慢增长阶段。产业结构效应对区域经济韧性的作用有增长趋势,但仍以竞争力效应为主。具体来看,产业结构效应上,正偏离产业为第一产业和消费性服务业,消费性服务业的正向作用较为显著。区域竞争力方面,消费性服务业、社会性服务业体现出较强的区域竞争优势,且前者强于后者。综上,此阶段区域经济韧性的增强依赖于消费性服务业的正向作用。
2015—2017年经济高速增长阶段。区域产业结构效应的正向作用继续增强。具体来看,产业结构效应方面,第一产业、消费性服务业、社会性服务业为正偏离产业。其中第一产业随区域经济韧性的增强,正向作用逐渐减弱,而消费性服务业的增强作用更为显著。区域竞争力效应方面,社会性服务业和消费性服务业优势突出,其中消费性服务业更有利于区域经济韧性的提升。由此,消费性服务业的发展是此阶段经济增长和经济韧性提升的关键。
2017—2019年经济缓慢增长阶段。从偏离效应来看,此阶段区域产业结构效应的作用在增强,表明京津冀地区产业结构逐步完善。具体来看,产业结构效应方面,第一产业、消费性服务业为正偏离产业,对区域产业结构效应的贡献度较大,且第一产业更有利于区域经济韧性的增强;区域竞争力效应方面,社会性服务业的区域竞争优势更为凸显。因此,此阶段对区域经济韧性提高起到正向作用的产业为第一产业、消费性服务业与社会性服务业。
综上,研究时段内,产业结构效应方面,消费性服务业和第一产业对区域经济抵抗力韧性的增强作用最为显著;相比经济缓慢增长阶段,消费性服务业在经济高速增长阶段对区域经济韧性的正向作用较强,而第一产业在经济缓慢增长阶段是经济增长的基础和保障。区域竞争力效应方面,消费性服务业、社会性服务业在长时段内表现为显著的区域竞争优势,在经济缓慢增长阶段社会性服务业的区域竞争优势更为明显,更有利于区域经济恢复力韧性的增强。由此,京津冀地区第一产业、消费性服务业和社会性服务业在提升区域经济韧性上的作用显著,且发挥积极作用的产业发生了从第一产业到消费性服务业再到社会性服务业的演变,体现了地区产业的转型升级。
5 地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联机理
图10
图10
区域经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联机理
Fig. 10
Mechanism of coupling correlation between the regional economic resilience and industrial structure evolution
时间上的耦合关联方面。当外部冲击发生时,区域首先对其进行抵抗,但经济增长受到抑制,经济发展进入保护阶段,沿着原有发展路径维持低速增长,受到冲击较大的企业行业消退,经济增长主要靠主导产业、基础性行业等产业提供保障,且这些产业向专业化方向发展;之后,区域由抵抗进入恢复时期,经济增长的速度逐步上升,经济发展处于释放阶段并试图突破路径依赖,新的企业行业开始生长,产业多样化发展,产业结构效应首先在区域韧性中发挥积极作用;之后,区域进入调整和重组阶段,经济韧性表现为调整和适应,经济增长表现为缓慢增长或高速增长,企业实现再生并产生更多的企业行业,产业的多样进一步发展并实现产业网络化,区域发展实现路径创造,或者进入新结构下的路径锁定,由产业竞争力生成的区域竞争力效应推动地区韧性提升。另外,在此过程中,伴随着表现为产业空间集聚和产业体系重构、区域经济衰退与复苏、经济要素资源调整以及区域网络重构的区域发展路径演化。就京津冀地区而言,研究时段内,经济增长表现为由缓慢增长阶段进入高速增长阶段以及二者的交替出现,体现了外部冲击的不利影响以及区域由对冲击的抵抗到恢复发展再到调整适应的过程;冲击发生的初期,企业出现消退,具有基础保障性作用的第一产业和消费性服务业维持经济增长以及应对外部冲击的韧性,之后新的企业行业不断生长,产业多样化逐步上升,对区域经济韧性贡献较大的行业从第一产业、消费性服务业转向生产性服务业和社会性服务业,区域经济韧性分解中的产业结构效应不断提升。
空间上的耦合关联方面。冲击发生过程中,区域经济增长出现衰退、复苏及其速度和强度上的差异,伴随着企业的消退与生长,经济要素空间结构随之发生变化,为了降低成本提高竞争力,新的产业在空间上集聚并得到强化或调整,区域产业体系实现重构并进而推动区域网络的重构。以上过程表现为,区域产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应的分化及其导致的内部经济韧性水平的分异和区域空间结构的调整或重构。从京津冀地区来看,研究时段内,京津冀地区经济增长和经济韧性并未实现空间重构,但仍体现了经济韧性与产业结构演变的空间耦合关联:首先,区域竞争力效应对经济韧性的贡献大于产业结构效应,这体现了北京、天津、石家庄市区等较为发达地区的主要产业整体上对区域经济增长和经济韧性的核心支撑作用;其次,在外部冲击较大和自我调整的缓慢增长阶段,北京、天津、石家庄市区等抵抗韧性较强,而在高速增长阶段,中心市区的外围地区恢复韧性较好;在地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间关联方面,高经济韧性—高产业多样化类型的集聚主要分布在北京、天津等地区,自相关强度有减弱趋势,体现了京津冀地区产业和相互作用网络的重构。
区域经济韧性与产业结构关联的实证研究方面,国内主要对长三角和珠三角两个典型地区开展了较多地探讨。研究发现,区域发展路径表现为企业的退出、进入及其导致的产业结构演进,进而与经济韧性形成时空关联。时间关联上,以全球金融危机为代表的外部冲击促使地区不断调整战略耦合形式,不仅推动了产业升级[42],而且形成了地区经济韧性水平的差异[7];地区产业构成不断向资本和技术密集型行业演替[12],创新和非相关多样性成为产业升级的主要方向并影响区域经济韧性的形成[9,16],与此同时,地方制度、文化氛围等因素也会起到积极作用[13]。对比来看,3个地区中,虽然珠三角地区由于对外开发水平更高,在外部冲下,产业结构调整更为迅速、影响因素更加多元化,但经济韧性与产业结构的时间关联与京津冀地区表现了显著的相似性。空间关联上,珠三角地区不仅产业结构呈现明显的核心—边缘模式[22],而且经济韧性强度也表现为“中心—外围”结构[16],长三角地区经济缓慢增长阶段和高速增长阶段的经济韧性的空间格局[43]呈现了与京津冀地区相似的特征。本文以京津冀地区为例,通过细化缓慢增长阶段和高速增长阶段的经济韧性,分解经济韧性的产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应,从时间和空间两个视角进一步深化了区域经济韧性与产业结构演变耦合关联的机理性认识。
综上,区域经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联是由区域发展路径与区域产业结构的相互作用和协同演替实现的,区域产业结构演替驱动了区域发展路径的演化和地区经济韧性的分化,京津冀地区也体现了这一过程和机理。总体来看,京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联以时间上的耦合关联为主,这在经济增长阶段的演替、地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间自相关以及经济韧性的偏离—份额分解上均得到较好地体现;京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构的空间耦合并未实现空间结构的根本性重构。
6 结论与讨论
6.1 结论
本文测度了2002—2019年京津冀地区经济韧性,分析了地区经济韧性空间格局演变,检验了区域经济韧性与产业结构演变的时空关联,进而通过偏离—份额分析,将区域经济韧性分解为产业结构效应和区域竞争力效应,探讨了不同产业在区域经济韧性演变过程中的作用,总结了区域经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联机理。主要结论为:
(1)京津冀地区经济韧性在阶段、类型和空间上发生时空分异。京津冀地区经济韧性总体上呈现波动上升的趋势,并逐步呈现为典型的中心—外围结构;在经济高速增长阶段,经济水平较低的中心城市外围区恢复力韧性较强,经济缓慢增长阶段北京、天津及石家庄市区等经济水平较高的城市地区抵抗力韧性较高。
(2)京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构在演变过程中表现出显著的时空关联性。空间上,京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构之间具有显著的空间自相关关系;在经济较为发达的北京、天津等地区,高经济韧性—高产业结构多样化类型的集聚较为显著。长时段内,区域经济韧性与产业结构之间呈现显著的双向因果关系。
(3)京津冀地区产业结构不断演进,区域竞争力效应对地区经济韧性的作用大于产业结构效应。研究时段内,第一产业与消费性服务业为正偏离产业,生产性服务业和社会性服务业在为扩张型产业。经济高速增长阶段,消费性服务业与社会性服务业对区域经济韧性的提高发挥了较为明显的正向作用;经济缓慢增长阶段,第一产业、消费性服务业、社会性服务业有利于区域经济抵抗力韧性的增强。消费性服务业与社会性服务业的发展有利于增强京津冀地区经济恢复力韧性。
(4)京津冀地区产业结构演替驱动了发展路径的演化,进而表现为地区经济韧性的分化;地区经济韧性与产业结构演变的耦合关联以时间上的耦合关联为主,空间耦合关联并未导致地区空间结构的根本性重构,中心—外围结构仍较为显著。
6.2 讨论
近年来国外学者重点从理论方法上对经济韧性和路径依赖进行架构[1⇓-3,5 -6,34],实证研究则更多地从具体行业的层面探讨产业多样化对区域经济韧性的影响[14-15,42]。国内研究起步稍晚,分别从具体地区某一行业的成长[4,13,22]、区域产业结构内部关联[9,12,19]和外部战略耦合[2,7]等对经济韧性的影响方面进行实证研究,也有学者从城市生命周期的视角尝试开展“产业—企业—空间”协同的城市经济韧性研究[30]。相比已有文献,本文在以下方面做了尝试和拓展:① 区别于单个城市或者国家这样偏微观或过于宏观的研究尺度,本文选择具有中心—外围结构的典型地区开展研究,能够对地区经济韧性与产业结构在空间上如何耦合关联以及是否对原有空间结构带来影响这一问题做出回应;② 区别于以往仅围绕某一行业或者不区分行业的研究,回答了地区在外部冲击下的不同阶段,哪些行业有利于区域经济韧性的提升;③ 将经济韧性适应性循环理论、路径依赖理论与京津冀地区经济韧性与产业结构演变耦合关联过程相结合,既对理论进行了实证,又运用理论阐释了耦合关联的内在机理。
本文具有现实意义。北京、天津及石家庄等地区经济韧性较强,在国家构建新发展格局和国内国际双循环的背景下,应进一步推进京津冀协同发展战略,通过产业网络化和区域联系网络化促进地区经济韧性的网络化、一体化。其次,在经济增长的高速增长阶段和缓慢增长阶段,不同经济水平地区的抵抗力和恢复力表现出明显差异,缓慢增长阶段经济水平较高的中心地区抵抗力更强,高速增长阶段经济水平较低的外围地区恢复力较好,要基于发展水平和阶段的判识,对不同类型地区选择相应产业并完善产业结构,提升地区经济韧性。作为本文研究的延伸,以下问题仍有待进一步探讨。产业分类与本研究的结论密切相关,本文对第二产业的划分还不够细致,一定程度上影响了本文的实际应用价值。其次,本文仅探讨了产业结构对区域经济韧性的影响,制度、文化等其他难以量化的因素以及地区间相互作用等方面不可忽略,这些因素与产业结构如何耦合并影响地区经济韧性仍有待探讨。此外,在空间结构和一体化水平上,京津冀地区与长三角、粤港澳大湾区等中国其他重要区域存在一定差异,这些地区经济韧性与产业结构关联演变机理上的差异有必要深入探究。
参考文献
The economic resilience of regions: Towards an evolutionary approach
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsp029 URL [本文引用: 4]
An analytical framework on regional economic resilience from the perspective of evolutionary strategic coupling
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210293
[本文引用: 3]

In the contexts of on-going global political-economic shifting and shocks of multi-scalar crises, regional economic resilience has become one of the key themes in economic geography for exploring regional development dynamics. Regional economic resilience is not only about local economic configurations and adaptability, but also related to extra-regional dynamics. Thus, it paradigmatically requires adopting a geographically multi-scalar and dynamic network perspective. This paper attempts to integrate the concept of strategic coupling from the GPN theory into the EEG-based regional economic resilience thinking, and to comparatively review the literature related to the two parts by bibliometric methods. Based on that, by focusing on different modes of evolutionary strategic coupling (including coupling, decoupling, and recoupling), the paper constructs an analytical framework of regional economic resilience from the perspective of strategic coupling in evolution. The paper concludes that: (1) any mode of strategic coupling is an agency-based process of strategic change and context-responding, which can be regarded as the core to understand the scalarity and the source of ability for regional economic resilience. (2) The two concepts come across several epistemological similarities on “connectedness”, “contextual sensitivity” and “path development”, and their integration can help to advance the understanding of regional economic resilience. (3) The agent's agency, motives, the degree of embeddedness and modes of strategic coupling are the keys to understand the ability and mechanism of regional economic resilience. This can also help to form a “local-global relational interaction” perspective to comprehensively explore the structural properties (regional advantages), processes (recovery, renewal, and reorientation), ability (recoverability, transformability, and renewal ability), and consequences (multiple development paths) of regional economic resilience. This paper argues that the perspective of strategic coupling in evolution can deconstruct the conventional “regionalism” wisdom of regional economic resilience, which can systematically help explore the causal mechanism of multi-scalarity, multi-agentic processes and multi-factor involved impacts in regional economic resilience. Moreover, this study fosters the integrative innovation between the relational and evolutionary paradigm and makes a practical contribution to corporation decision-making and regional economic development in China under the current “Double Circulation” strategy.
战略耦合演化视角下的区域经济韧性分析框架
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210293
[本文引用: 3]

在全球政治经济变局和多尺度危机冲击语境下,区域经济韧性已成为当下经济地理学探究区域发展动态的核心议题。区域经济韧性不仅有关本地经济属性和适应力,更受到外部联系动态的影响,在范式上需融入多尺度网络动态观。本文将全球生产网络理论中的战略耦合概念纳入到演化经济地理学的区域经济韧性思想中,对两部分文献进行计量分析和梳理对比。在此基础上,以战略耦合不同模式(即耦合、去耦合、再耦合)为切入点,构建了一套基于“战略耦合演化”的区域经济韧性分析框架。研究结论:① 任何一种战略耦合模式,均是一种“战略性求变”和“语境应对”的能动行为过程,是理解区域经济韧性尺度性与能力来源的核心。② 两者在“连接度”“语境敏感性”“路径发展”概念上有较高的思想共性,相互融合可提升区域经济韧性的理论内涵。③ 战略耦合的能动主体、目的、嵌入性程度及方式是理解区域经济韧性特征和机制的关键,有助于从“地方-全球连接互动”的视角来综合分析区域经济韧性的初始属性(区域优势)、过程(恢复、更新和转型)、能力(恢复力、转型力和更新力)和结果(多元路径发展趋势)。本文认为战略耦合演化视角有利于破除以往“区域主义”韧性思想,能更科学地剖析区域经济韧性的多尺度语境依赖、多主体能动过程和多要素互动机制。此外,有利于推动关系与演化经济地理范式的融合创新,对“双循环”战略下中国企业决策和区域经济发展有重要现实意义。
An international literature review of regional economic resilience: Theories and practices based on the evolutionary perspective
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.012
[本文引用: 3]

Regional resilience has become a trendy research branch. However, traditional Chinese research of resilience had been limited within the equilibrium-based epistemology. This article, based on a review of international literature, clarifies different definitions of economic resilience: engineering resilience, ecological resilience, and evolutionary resilience. The article rejects equilibrium-based epistemology of resilience and argues instead the evolutionary perspective. Then, it introduces the formation mechanism of economic resilience from macro and micro aspects; and introduces quantitative measurement of network analysis. This article concludes that resilience should be extended to the economic field and evolutionary-based perspective. Chinese researchers should notice connections between three research branches — namely evolutionary economic geography, innovation geography, and regional resilience. Future research should focus on case studies of urban and regional economies. They should also explore the existing open patent data source to establish the quantitative database of industry space.
国际区域经济韧性研究进展: 基于演化论的理论分析框架介绍
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.11.012
[本文引用: 3]

区域韧性在中国已成为新兴研究热点,然而国内学者依然将韧性研究局限于均衡论的认识论范畴内。本文首先通过回顾国际最新研究动态从认识论层面辨析均衡论和演化论这两种韧性认知视角的本质区别,由此介绍西方经济韧性的演化论转向。然后从宏观和微观角度阐述演化论视角下区域韧性的形成机制,介绍相关定量测度方法;在此基础上形成系统的西方最新有关研究经济韧性的理论分析框架。未来研究应该在演化论视角基础上强化演化经济地理、创新地理(区域知识网络)和区域韧性这三个研究分支的联系,还应该加强产业历史演化过程的案例研究,并利用专利数据等开放数据源构建产业空间基础数据库。
Resilience and resistance of local industry to economic crisis: A case study of China's IT industry
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807004
[本文引用: 4]

Little research has been done on the resilience and resistance of local industries the play a major role in regional economy. This study investigates the main influencing factors of the regional economic resilience of China's IT industry, with a large-scale firm-level survey data from National Bureau of Statistics. Our regression analyses reveal that the firm heterogeneity within the regional industry, the role of local technology gatekeepers, the openness, dynamics and business structure of the local industry jointly exert significantly positive influences on the regional economic resilience of China's IT industry. This suggests that the hub-and-spoke industrial districts may be more resilient than the Marshallian industrial districts under the transitional background of China. Local governments should encourage the co-existence of heterogeneous firms in terms of knowledge base, attract new and younger firms, maintain an open environment for local industries and pay more attention to the leading role of technological gatekeepers so as to enhance the economic resilience of local industries.
地方产业抵御经济危机的弹性影响因素: 以电子信息产业为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807004
[本文引用: 4]

作为区域经济的重要载体,地方产业抵御经济危机的弹性影响机制却鲜少有研究且尚无定论。以电子信息产业为例,利用中国工业企业调查数据库,运用回归分析的法探讨了影响地方产业弹性的主要因素。研究发现:中国电子信息产业的经济弹性存在着地域差异;地方产业内企业的异质性、龙头企业的影响力、地方产业的开放性、动态性和业务结构对电子产业的经济弹性均有显著的正向影响。在中国现阶段的经济制度背景下,轮轴式的地方产业结构可能比小企业为主的产业区更能促进当地的产业弹性。地方政府在扶持地方产业发展的过程中,不仅要保持地方产业内企业的异质性、动态性和开放性,也要注重发挥龙头企业的带领作用。
Towards an evolutionary perspective on regional resilience
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.959481 URL [本文引用: 3]
Regional economic resilience, hysteresis and recessionary shocks
The impact of strategic coupling on regional economic resilience under globalization: A case study of Guangdong province
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210372
[本文引用: 4]

Relational economic geography and evolutionary economic geography, two main genres in nowadays economic geography, are searching for theoretical dialogue and integration. Strategic coupling, a key variable of relational economic geography, is lack of dynamic perspective of regional long-term evolution, while regional economic resilience, a key variable of evolutionary economic geography, neglects the influence on the region of external economy system. Furthermore, the lack of quantitative research in strategic coupling becomes one of the obstacles to integration between the two schools. Therefore, this study takes 21 cities in Guangdong province as examples, preliminarily constructs strategic coupling variables, and uses regression analysis, geographic detector and other methods to explore the impact of strategic coupling on regional economic resilience in combination with existing research results. This study has three main conclusions: (1) Strategic coupling has a significant impact on regional economic resilience. The dependence of production on foreign capital has the greatest impact, followed by the technological advantage of foreign capital. (2) Due to the differences of cooperation modes in strategic coupling, the influence of capital from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan of China and other foreign capital on regional economic resilience is different in terms of production dependence and technological leadership of foreign capital. (3) The traditional globalization variables, such as GDP, FDI and total export, are less important in the study of the relationship between strategic coupling and regional economic resilience, because they cannot accurately locate the interaction among the components of global production network. This study quantifies strategic coupling and global production network, further realizes the theoretical dialogue between relational economic geography and evolutionary economic geography, innovates the quantitative measurement method, and provides a reference for further quantification study of strategic coupling and global production network.
战略耦合对区域经济韧性的影响研究: 以广东省为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210372
[本文引用: 4]

战略耦合与区域经济韧性分别为关系经济地理学派与演化经济地理学派的关键变量,在当下已有的研究中,前者缺乏区域长期演化的动态视角,后者忽视区域外部的经济联系对区域内部的影响,二者缺乏理论对话;同时,战略耦合在当下缺乏定量研究,成为两个学派之间进行融合的阻碍之一。因此,以广东省21个城市为例,基于回归分析、地理探测器等方法,从区域经济中外资的出口主导、生产主导、技术主导3个维度来测度战略耦合程度对区域经济韧性的影响,以此尝试推动两个学派的互动。研究结论:① 证实战略耦合对区域的经济韧性有着显著的影响,其中外资的生产主导影响最为显著,其次是外资的技术主导,影响最小的是外资的出口主导;② 中国港澳台地区投资与其他外资对区域经济韧性的作用机制存在根本性差异,体现在区域韧性变动的过程中,二者在技术主导和生产主导维度上的影响效果相反;③ GDP、FDI、出口总额等传统的全球化程度的测度指标不适合作为测度战略耦合对区域经济韧性影响的重要变量。本研究通过方法的创新,实现了对战略耦合的一次完整的定量测度,进一步实现了关系经济地理学派与演化经济地理学派在方法上的一次理论互动,为全球生产网络后续更加深入的量化研究奠定了基础。
Exploring adaptation and adaptability in uneven economic resilience: A tale of two Chinese mining regions
DOI:10.1093/cjres/rsx012 URL [本文引用: 1]
Specialization, variety and economic resilience of specialized towns in Foshan
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.011
[本文引用: 4]

Since the economic reforms and opening-up, the process of rural industrialization has led to the development of a large number of specialized towns which have significant implications for the Chinese economy. However, due to their labor-intensive, export-oriented and low-tech industrial structure, the economies of the specialized towns became fragile when the financial crisis in 2008 gave rise to a turbulent global market. Specialization of the towns, which used to generate significant effects of localization economies, shows its weakness in coping with the recession after the economic crisis. The sustainable development of the specialized towns in China emerges as an important issue requiring further scholarly enquiry. The newly developed economic resilience theory has provided a valuable and useful framework to explore the development path of the specialized towns, and the article has in turn served as an important empirical study for the theory at the town level. Economic resilience is associated with the capacity to withstand or recover from economic, social, and environmental shocks to its developmental growth path, or to transit to a new, sustainable one. One of the critical factors to shape economic resilience is the attribute of the industrial structure which can define a region’s ability to adjust and adapt to shocks. Despite an ongoing debate on the role played by specialization and variety, it is increasingly agreed that a greater economic diversity is related to a greater resilience of the economies. Based on the panel data of 32 specialized towns in Foshan City and a detailed case study of Xiqiao, a town specialized in textile, this article investigates the relationship between specialization, related/unrelated variety and economic resilience. The regression results suggest that specialization and related variety exert negative effects on economic resilience, whereas unrelated variety plays an active role. Our study supports the argument, which is well-documented in the existing literature, that specialization is more likely to be stuck in negative “lock-in” with adaptation. However, the effect of related variety is not as positive as expected. For low-level labor-intensive industries, their low technology level and weak cooperation among firms have seriously prevented efficient and effective knowledge exchange which is crucial for innovation and resilient ability. The Xiqiao case further indicates that effects of specialization and related variety on economic resilience are limited even the local government has actively intervened in promoting industrial upgrading through a series of approaches such as industrial park construction, labor training, subsidies and other preferential policies. Unrelated variety is conducive to foster the development of new industries, which can help to absorb unemployed labors caused by the shocks and maintain the resilience level. Thus, the specialized towns should consider an industrial structure of greater unrelated variety to boost necessary restructuring process and to engage in new growth paths.
佛山市产业专业化、多样化与经济韧性的关系研究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.09.011
[本文引用: 4]

以2008年和2013年佛山市30个专业镇的数据为基础,分析其在经济冲击抵抗期的经济韧性。分析结果显示,佛山市专业镇在经济危机之后整体经济韧性恢复缓慢,专业化和相关多样化产业的发展不再有助于经济韧性的提升,而非相关多样化则相反。传统专业化的集聚优势式微,以低水平劳动密集型产业为主的专业化易于导致经济的脆弱性;相关多样化因技术含量低和协作关系弱的限制也无法发挥作用,虽然地方政府采取积极干预的手段,但效果并不明显;非相关多样化的发展则有利于培育新的产业结构,弥补受危机影响而流失的劳动力,维持地区的经济韧性。与既往研究相比,研究结果同样支持高度专业化区域经济脆弱性更大、稳健性更低的主流观点,但是传统观点一是多侧重于某个视角,并未将专业化与多样化进行对比分析;二是在多样化研究中并不区分相关多样化和非相关多样化的对经济韧性作用。结论认为,在专业镇持续转型的背景下,发展相关多样化产业不利于提高其经济韧性,而非相关多样化产业则是积极有利的,应该予以大力鼓励。专业镇作为珠三角经济发展的成功经验,其传统发展模式正面临着严峻的挑战,应积极探索建立新的多样化发展模式。
Path-dependence and its implication for regional development
DOI:10.11821/yj2012050002
[本文引用: 1]

Path dependence is an important concept applied in explaining the evolutionary process and dynamics of the social and economic systems,and is also useful for understanding the evolution of economic landscape.Despite this concept has received increasing attention from the fields of economics and management in recent years,we has little knowledge about its implication for economic geography and regional economics.This paper reviews the origin of the path dependence theory and its application in a variety of fields including technological change,institutional evolution and social culture;reviews the literatures of applying the path dependence in explaining some important issues of economic geography;in particular,in understanding the mechanisms of regional economic evolution.This paper argues that there are two mechanisms of path dependence driving the evolution of regional economy: one is that the regional growth is driven by spin-offs and spatial clustering;the other is that over-specialization and the ignoring of external relations together cause regional lock-in.In the final part,the paper points out the short defects of the existing studies of economic geography on path dependence and the future research directions.
路径依赖理论及其地方经济发展隐喻
A comparative analysis of the economic transition process of China's old industrial cities based on evolutionary resilience theory
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804013
[本文引用: 1]

The 2008 international financial crisis had a severe impact on urban economic development globally, which stimulated a new wave of discussion on the importance of urban economic transformation. Compared to the past, Chinese cities are facing tougher challenges in sustaining economic development through transformation because of the slowdown in economic growth nationally. Previous studies mainly focused on the strategies and countermeasures of urban economic transformation, and ignored how local economies develop, adapt, and transform over time. Moreover, there have been no comparative studies among cities in eastern, central and western China. Drawing on the theory of evolutionary resilience, this study examined three typical old industrial cities (Shenyang, Chongqing and Wuhan) to compare and contrast their transformations since 1978 using economic cycle modeling and shift-share methods. Results showed that: (1) economic growth in Chongqing and Wuhan has been above national average since the mid-1990s, whereas that of Shenyang has fluctuated periodically and shown a periodic oscillation phenomenon. (2) Since the 1990s, the shift of industrial structure in Shenyang has been volatile, and the increase in the relative share of the tertiary industry has been mainly the result of the deceleration of growth in the secondary industry. Chongqing and Wuhan, on the other hand, are more stable in industrial restructuring. (3) Since the end of the 1990s, the transformation of the manufacturing industry of Shenyang and Wuhan has been affected mainly by the upgrading of an old path, whilst the transformation of manufacturing industry of Chongqing has been the result of both old and new paths, which contributes to the higher growth rate. (4) Since the beginning of the 21st century, the evolution of the new path in Shenyang has featured a low-end trend, in contrast the evolution of the new path in Chongqing and Wuhan has shown a high-end trend. In conclusion, this paper illustrates the value of applying the resilience theory to the study of urban economic transition and enriches the practical value of the theory.
基于演化弹性理论的中国老工业城市经济转型过程比较
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804013
[本文引用: 1]

运用演化弹性理论(evolutionary resilience)采用经济周期模型法和偏离—份额法,从增长和结构两个方面,比较分析沈阳市、重庆市和武汉市3个典型老工业城市改革开放以来经济发展和转型过程。结果发现:① 重庆市和武汉市经济增长能力水平具有显著地以20世纪90年代中期为分界的阶段性特征;沈阳市经济发展过程呈现出适应循环周期特征,目前处于由维持向释放过渡的阶段。② 20世纪90年代以来,沈阳市3次产业结构转换方向具有较大的波动性,第三产业份额的增加主要是第二产业增长放慢的结果。重庆市和武汉市3次产业结构转换方向具有较强的稳定性。③ 20世纪90年代末以后,沈阳市和武汉市制造业结构演替受老路径增长能力变化影响较大,重庆市制造业结构演替是在新老路径都保持较高增长能力背景下稳步推进的。④ 21世纪初以来,沈阳市新路径的演化呈现出低端化特征,而重庆市和武汉市新路径的演化呈现出高端化特征。本文将弹性理论应用到城市经济转型研究,实证了弹性理论的实践应用价值。
Mechanism of regional economic resilience from the perspective of industrial structure relevance: Taking Jiangsu province as an example
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.02.004
[本文引用: 4]

Exploring the mechanism of regional economic resilience is of great significance for realizing the rapid recovery of the economy after shocks. As a major province of economic activities, Jiangsu Province's industrial structure changes are the epitome of China's economic transformation. An analysis of its resilience changes and the inherent logic can provide a reference for other provinces. This research analyzed the economic resilience level of Jiangsu Province based on a longitudinal comparison. It used network analysis methods to study the multi-year input-output table of the province to clarify the changes in industrial structure and the mechanism of economic resilience, and arrived at the following conclusions: 1) From the longitudinal perspective of self-comparison, the economic resilience of Jiangsu Province has shown a "high-low-medium" state in the face of the impact of economic crises. 2) Core industries and links occupy the main position in the industrial network structure. By stimulating the existing core industries to achieve high resilience of the economy, the essence lies in the interconnections between core industries to induce and drive the overall industrial structural change, but this strategy is difficult to maintain in the long run. 3) Discovering and expanding new economic growth points can effectively improve the overall resilience of the economic system. Its connotation is to neutralize and compensate for declines with stronger growth, thereby reducing the intensity of economic shocks and reducing the risks of subsequent industrial structural reforms. 4) The mechanism of economic resilience can be understood as that, in the face of shocks, an economy maintains the normal operation of its core industrial structure by abandoning network edge industries to concentrate development factors. The damage state of traditional core industries and the growth rate of new industries together determine the effect of regional economic resilience. This research provides a new perspective for regional economic resilience. Based on input-output data, it can effectively interpret regional development status and identify economic resilience.
基于产业结构关联视角的区域经济韧性作用机理研究: 以江苏省为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.02.004
[本文引用: 4]

探讨经济韧性的作用机理有助于增强经济体对冲击的抵抗能力,并提高冲击后的复苏成效。因此,论文从自身对比的纵向角度剖析了江苏省经济韧性水平,并通过网络分析方法研究其多年投入产出表以明晰产业结构变化状况与经济韧性作用机理,得出以下结论:① 从自身对比的纵向角度而言,江苏省经济韧性在经济危机冲击中呈现出“高—低—中”的状态;② 核心行业及其关联占据了产业网络结构中的主要位置,通过刺激现有核心行业能够实现经济体的高韧性;③ 发掘并扩展新的经济增长点能有效提升经济系统的综合韧性,其内涵在于以更强的增长中和、弥补衰落;④ 经济韧性的作用机理可以理解为经济体在面对冲击时,通过放弃网络边缘行业以集中发展要素维系其核心行业架构的正常运转,传统核心行业的受损状态与新型行业成长速度共同决定了区域经济韧性发挥效果。
Path dependence and path creation of industrial evolution about towns from the perspective of economic resilience: Based on the comparative analysis about Zhangmutou and Changping in Dongguan
经济韧性视角下城镇产业演化的路径依赖与路径创造: 基于东莞市樟木头、常平镇的对比分析
Related variety, unrelated variety and regional economic growth
DOI:10.1080/00343400601120296 URL [本文引用: 2]
Institutions and diversification: Related versus unrelated diversification in a varieties of capitalism framework
DOI:10.1016/j.respol.2015.06.013 URL [本文引用: 3]
Industrial diversity, innovation, and economic resilience: Empirical analysis of the Pearl River Delta in the post-financial crisis era
产业多样化、创新与经济韧性: 基于后危机时期珠三角的实证
Regional economic resilience: A new idea to support the variety of industrial structures
区域经济韧性: 支持产业结构多样性的新思想
The economic resilience of Chinese cities and its origin: From the perspective of diversification of industrial structure
中国城市的经济韧性及由来: 产业结构多样化视角
Spatial pattern of urban economic resilience in eastern coastal China and industrial explanation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200486
[本文引用: 4]

Since the global financial crisis in 2008, regional economic resilience has been attracting increasing attention across the world. When facing economic shocks, some regions suffer less and could manage to get through crisis in a short period, while some might be mired in economic stagnation, which mainly depends on the economic resilience of the country. Existing research usually classifies economic resilience into resistance and recovery resilience based on the analysis of a specific economic shock. It is simple and operable in empirical works though, which aims to unravel the economic resilience in a relatively short period and neglects the impacts of longstanding “slow burn” in the urban economy. Thus, this paper divided urban economic resilience into long-term and short-term economic resilience, and further analyzed the features of spatiotemporal distributions of industrial structures (including economic complexity and industrial variety) and urban economic resilience, and explored the impacts of industrial structures on urban economic resilience in different economic development stages with eastern coastal China as a study case. The conclusions are as follows. (1) The economic complexity in the study area is higher in the south and lower in the north, and the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta are the most prominent areas. The distribution of industrial variety is more balanced, while the related variety of center cities is generally higher than that of surrounding cities. Distribution patterns of short-term economic resilience in different periods show great differences, and the long-term economic resilience of the Yangtze River Delta is higher than that in other areas. (2) The elevation of economic complexity and related industrial variety could improve urban long-term economic resilience significantly, while the unrelated variety has no evident impacts, which verifies the importance of knowledge spillover and technology links in the promotion of urban long-term economic resilience. (3) Factors influencing short-term economic resilience vary in different periods. Cities with enormous financial industries were vulnerable to economic shocks in 2008. Comparatively, cities predominated by heavy industries had the lowest economic resilience in the structural adjustment period after 2011. (4) Factors influencing the resistance and recovery resilience on the same shock are different. A higher level of related variety could help cities resist the crisis in 2008, but have no distinct impacts on their recovery, while an elevated level of unrelated variety might harm the recovery from the crisis of 2008. Thus, extending the industrial value chain, establishing local industrial clusters, and upgrading the industrial level are possible ways to raise urban economic resilience.
中国东部沿海地区城市经济韧性的空间差异及其产业结构解释
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200486
[本文引用: 4]

经济韧性的强弱决定着城市在面对冲击时可以快速度过危机还是陷入长期经济发展停滞。本文将城市经济韧性区分为长期经济韧性和短期经济韧性,分析中国东部沿海地级及以上城市的经济韧性和产业结构的时空分异特征,探讨产业结构在不同时期对城市经济韧性的影响。研究发现,东部沿海地区城市不同时期的短期经济韧性及长期经济韧性存在明显的空间差异;长期经济韧性和短期经济韧性的影响因素不同,表征产业整体技术含量的经济复杂度和表征产业关联程度的相关多样化指数能显著提升城市长期经济韧性,短期经济韧性的影响因素则因时期不同而存在差别。延长产业价值链、构建地方产业集群、提升产业层次水平,有助于城市提高经济韧性。
Economic resilience and recovery efficiency in the severely affected area of Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910009
[本文引用: 2]

It is of great significance to enhance disaster prevention and response capacity to reveal the post-disaster economic development and recovery process, and to formulate the control policies and recovery methods for post-disaster economic reconstruction according to the economic resilience. Based on the long-term socio-economic data and ARIMA model, this paper calculated the economic resilience index of severely affected area of Wenchuan earthquake, and adopted the improved Variable Return to Scale (VRS) DEA model and Malmquist productivity index to analyze the efficiency and effect of annual post-disaster recovery. The results show that: (1) The economic resilience index of earthquake severely affected area is 0.877. The earthquake caused a short-term economic recession in the affected areas, but the economy returned to its pre-quake state within two years. In addition, the industrial economy is less resilient than agriculture and service industries. (2) The comprehensive economic recovery efficiency of the disaster-stricken area in the year after the disaster is 0.603. The comprehensive efficiency, pure technical efficiency and scale efficiency of the plain hilly area are significantly higher than those of the plateau mountain area. (3) The annual fluctuation of total factor productivity after the disaster was strong, and the economic recovery efficiency declined significantly, resulting in a short-term economic recession. The TFP index returned to steady state after a decline of 33.7% and 15.2% in the two years after the disaster. (4) The significant decline in the post-disaster recovery efficiency is mainly caused by technological changes, and the renewal of production system is the leading factor in determining the economic resilience after the disaster. With the decline in the scale of economic recovery, the long-term economic recovery in the study areas mainly depends on pure technical efficiency, and the improvement of pure technical efficiency is the driving force to maintain the long-term growth of post-disaster economy. Therefore, in view of the differences between the reconstruction of natural conditions and the stage of economic development, the disaster-stricken areas need to change and readjust their economic structures actively. Meanwhile, we should pay attention to updating production system to enhance the level of technological progress, and give full play to the scale effect of large-scale capital, facilities, manpower and other factors investment, so as to enhance the response to the disaster impact of economic resilience and recovery efficiency.
汶川Ms 8.0地震极重灾区的经济韧性测度及恢复效率
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201910009
[本文引用: 2]

揭示灾后经济发展状态和恢复过程,按照灾区经济韧性科学制定灾后经济重建的调控政策与恢复手段,对增强灾害防范与系统应对能力具有重要意义。以汶川地震极重灾区为案例,基于长时序社会经济面板数据与ARIMA模型,测算灾区经济韧性指数,并运用改进的规模报酬可变DEA模型、Malmquist生产率指数分析灾后年际经济恢复效率及影响效应。结果显示:① 汶川地震极重灾区经济韧性指数为0.877,地震导致灾区短期经济衰退,但2年内恢复至震前水平,工业经济韧性低于农业和服务业。② 受灾当年灾区经济恢复综合效率为0.603,其中,平原丘陵区综合效率、纯技术效率、规模效率均显著优于高原山地区。③ 灾后全要素生产率的年际波动强烈,经济恢复效率显著下降造成短期经济衰退,灾后2年TFP指数下降33.7%和15.2%后恢复至稳态。④ 灾后恢复效率显著下降主因为技术变动因素,而生产体系更新程度决定了灾后经济韧性。随着灾后经济恢复的规模收益下降,灾区经济恢复主要依赖纯技术效率,提升纯技术效率是保持灾后经济长期增长的动力。可见,针对重建自然条件和经济发展阶段的差异性,灾区当地需积极进行经济结构调整和再适应,同时,通过生产体系更新提升技术进步水平,以发挥灾后大规模资金、设施、人力等要素投入的规模效应,从而增强应对灾害冲击的经济韧性与恢复效率。
Regional industrial development and evolution: Path dependence or path creation
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 3]

Regional development is a process in which industries develop, transform and upgrade constantly. Evolutionary economic geography understands the spatial evolution of firm, industry, cluster, network, city and region through the lens of firm entry, growth and exit, and argues that regional industrial evolution is path dependent and determined by inter-industrial technological relatedness. However, path dependence theory overemphasizes the endogenous factors in regional industrial development and ignores the critical role of external linkages and institutional factors, which would bring path creation for regional development. In China, there has been dramatic transformation in regional industrial structure since the economic reform. Empirical studies indicate that technological relatedness has indeed significantly determined regional industrial evolution, suggesting a path dependent process. Meanwhile, marketization, globalization and regional decentralization provide great opportunities to create new industries for regional development. In particular, external linkage, institutional factors and purposeful and strategic actions of local actors would stimulate path creation.
区域产业发展演化:路径依赖还是路径创造
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201807001
[本文引用: 3]

区域发展是区域产业不断演化、转型与升级的过程。近年来发展起来的演化经济地理学旨在通过分析企业进入、成长、衰退和退出等动态过程阐释企业、产业、集群、网络、城市和区域的空间演化,认为区域产业发展演化遵循路径依赖,并决定于产业技术关联。然而路径依赖式演化理论过于强调内生发展过程,忽视了外生因素和制度变革带来的路径创造机会。中国处于经济转型时期,区域产业结构变动剧烈。技术关联推动了区域产业演化,显示中国区域产业演化具有路径依赖性,同时市场化、全球化和分权化的经济转型过程为区域产业发展创造了新路径。外部联系、制度安排、行为主体的战略性行为等促进了路径创造。
Characteristics and path of industrial spatial evolution in Pearl River Delta based on enterprise dynamics
基于企业动态的珠三角产业空间演化特征与路径
Analysis of the regional economic resilience characteristics based on Shift-Share method in Liaoning old industrial base
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180245
[本文引用: 3]

It is of great significance to study the economic resilience characteristics of old industrial bases to promote the revitalization of these decayed old industrial areas and to enhance their capacity on resisting against domestic and global disruptions. This paper uses the concept of regional economic resilience to show the mechanisms underlying the economic development of Liaoning Province. First, it divides the economic growth rate of Liaoning Province from 1990-2015 into different economic cycles. Then, this paper characterizes the regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province by measuring its urban economic resistance and recovery feature in different periods. Meanwhile, the paper explores the mechanism underlying regional economic resilience by decomposing regional economic resilience into two aspects through the Shift-Share method: the industrial structure and the regional competitiveness. We obtained the following three main findings. First, regional economic resilience displays different characteristics which are dynamically changing across different periods. Compared with the whole nation, urban economy of Liaoning Province shows a lower resistance capacity against various disturbance, and it is more vulnerable to these disruptions. Second, both urban industrial structure and regional competitiveness can affect the capacity of regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province. We found that the regional competitiveness plays a more significant role, as the capacity of Liaoning’s regional economic resilience is constrained by its industrial structure and competitiveness. Third, “path dependence” has affected the development of service industry in the province for a long time, which is featured by the low level of industry structure and weak competitiveness. We also discovered that there exists a serious mismatch between the industrial structure level and the competitiveness in the secondary industry. Influenced by the phenomenon of institutional locking under the path dependence, the state-owned economy, which is often of poor management, accounts for a large proportion in the secondary industry. These all restrict the regional economic resilience of Liaoning Province. Aiming at exploring the characteristics and internal mechanism of regional economic resilience, the paper put forward some suggestions for the economic revitalization of Liaoning old industrial base.
基于Shift-Share的辽宁老工业基地区域经济弹性特征分析
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180245
[本文引用: 3]

研究老工业基地经济弹性特征对于增强其应对国内外扰动,促进落后的老工业基地全面振兴具有重要意义。本文采用区域经济弹性概念,在对1990—2015年辽宁老工业基地经济周期划分的基础上,测度各城市不同周期中经济抵抗力和恢复力表征区域经济弹性,借助shift-share分析法将区域经济弹性分解为产业结构分量和区域竞争力分量,揭示区域经济弹性的作用机制,结果发现:在不同时段内的区域经济弹性具有动态差异性特征,辽宁省对冲击扰动的抵抗力较低,容易遭受冲击影响;城市产业结构和区域竞争力均对区域经济弹性产生重要作用,且区域竞争力起主导作用,当前辽宁区域经济弹性受产业结构素质低和竞争力弱双重约束;服务业受老工业基地“路径依赖”影响,长期存在结构水平低和竞争力弱问题,第二产业结构素质和竞争力不匹配问题严重,路径依赖下的制度锁定现象仍旧存在,这都限制了辽宁的区域经济弹性水平。针对区域经济弹性特征和内部机制,提出了促进辽宁老工业基地经济振兴的对策建议。
Review of the research progress in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region since 1980
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206002
[本文引用: 1]

In the past four decades, due to different research contents and spatial governance priorities, the names and scopes of regions such as Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan, Bohai Rim and Greater Bohai Sea have changed many times. As the earliest humanities and economic geography research in China, its object area has attracted more and more attention such as disciplines of economic trade, ecological environment, and urban and rural planning. Based on the academic papers, monographs, and influential scientific research projects, this article reviews the research progress of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in the past 40 years. The progress has experienced a change process of "Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan - Bohai Rim region - Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei". There are four recognizable phases in the research development to date. In the 1980s, economic geography mainly focused on land planning in the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan region, which was relatively limited in scale. In the 1990s, the research area was expanded to the Bohai Rim region, and the intersection of economic and trade science and geography was carried out in the process of economic integration in the eastern (northern) sub-regions. In the first decade of the 21st century, the research field turned to the integration of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, ecological environment science and urban planning science with large-scale intervention. In the 2010s, we started multidisciplinary regional comprehensive research on the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. During this period, the Chinese government carried out a series of major plans in the region, including the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan Land Planning in the 1980s, the Bohai Rim Economic Cooperation Zone in the 1990s, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolitan Region in the 2000s, and the Guidelines for the Coordinated Development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in the 2010s. These major plans have formed a benign interactive relationship with regional research. This interactive relationship not only significantly enhances the scientific nature of regional planning and strategic decision-making, but also effectively promotes the development of humanities and economic geography, and it has also enhanced the research on the evolutionary laws of regional complex systems under the strong interaction between human and nature.
1980年以来京津冀区域研究进展评论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206002
[本文引用: 1]

1980年以来,因研究内容和空间治理重点不同,京津冀、京津唐、环渤海、大渤海等区域名称与区域范围多次变动。作为中国最早开展人文与经济地理学研究的对象区域,越来越受到经济贸易、生态环境、城乡规划等多学科关注。本文基于学术论文和专著、具有影响的科研项目,对1980年以来京津冀及相关区域研究进展进行了综述和评论。归纳起来,研究对象区域经历了“京津唐(塘)—大(环)渤海—京津冀”的变化过程。整体上可分为4个阶段:20世纪80年代面向京津唐地区,国土规划为主的经济地理学区域研究,研究规模有限;20世纪90年代拓展到大(环)渤海地区,面向东(北)亚区域经济一体化进程开展经济贸易科学与地理学交叉研究;21世纪前10年,回归京津冀区域,生态环境科学和城市规划科学大规模介入的融合研究;21世纪10年代京津冀协同发展的多学科区域综合研究。其间,中央政府在该区域开展的一系列重大规划,包括20世纪80年代京津唐国土规划和90年代环渤海经济协作区规划,21世纪前10年京津冀都市圈区域规划和21世纪10年代京津冀协同发展规划,与区域研究形成了良性互动关系,在显著增强空间规划和战略决策的科学性的同时,也有力地促进了人文与经济地理学科发展,推动了人和自然相互间强烈作用状态下区域复杂系统演化规律的研究进展。
Spatio-temporal differentiation and its influencing factors of regional economic growth in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810012
[本文引用: 1]

Spatio-temporal differentiation of regional economic growth viewed from inner functional structure in a typical area is a hot research topic in economic geography in recent years. Based on the core-peripheral theory and the creative methodology framework, we identified the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region into the first central group, the secondary central group and peripheral group, and then displayed the evolution of spatio-temporal differentiation of regional economic growth and disparities in the region from 1994 to 2014 using some indexes which can represent regional economic growth and economic level respectively supported by some statistical indictors and geostatistical analysis methods. The results indicated that there was a positive correlation between accelerating economic growth and widening economic disparities, and the inter-group differences become the main portion of the widening disparities after 2001 in the BTH region. The evolution of spatial differentiation can be divided into four stages according to the characteristics of overall regional economic growth and spatial distribution. In the first stage, economic growth dispersed from the core to peripheral areas. The differences include the intra-group differences, the inter-group differences, and the differences decreased. During the second stage, the economic growth slowed down and clustered in core areas, which resulted in an increase in economic disparities. In the third stage, the overall economic growth rate of the BTH region rose but fluctuated, and the high-speed economic growing regions were mainly distributed surrounding the core. In the last stage, the average economic growth rate declined and the high-speed economic growing regions returned to the core. In summary, the peripheral areas have not yet received the steady and robust driving force emitted from the core. After that, some factors influencing economic growth of three types of groups were estimated in a constructive multiple linear regression model. The coefficient estimates of variables indicated a significant gradient which reflected the gradient of economic structure and economic level among the three groups.
京津冀地区经济增长的时空分异与影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201810012
[本文引用: 1]

空间结构视角下的典型地区内部经济增长时空分异是近年来学界持续探讨和研究的重要议题。基于构建的地区经济增长时空分异研究的理论框架,针对京津冀地区核心—外围结构的3类地区,将地区经济增长与经济水平指标相结合,使用相关统计变量、地统计分析方法以及面板多元回归模型对京津冀地区1994-2014年经济增长的空间分异及近阶段的影响因素进行了探究。结果表明:① 京津冀地区经济增速往往伴随着经济总差异的扩张;地区分组组间差异是总差异的主体成分;地区分组组间差异和京津冀地区经济总差异呈扩张趋势。② 京津冀地区经济增长的空间分异可划分为经济增长空间扩散—地区差异总体收敛、经济增速减缓且空间集聚—地区总差异扩张、经济波动增速并空间扩散—总差异波动上升、经济增速减缓并再次空间集聚—地区经济差异波动缓慢增加等4个阶段。③ 当前,经济增长的空间辐射主要表现为一级核心地区对邻近二级核心地区的带动作用,向外围地区的扩散尚弱。④ 核心与外围不同类型地区的参数估计存在显著差异,这体现了不同类型地区经济结构的梯度差距。
The innovative geographical foundation of the relative decline of economic growth in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206003
[本文引用: 1]

How to raise innovation efficiency to promote the economic development from relative decline to prosperity and then drive the development of the northern hinterland becomes a prominent problem facing the in-depth acceleration of the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region in the new development stage. This paper points out that the inefficiency of innovation is the key to economic stagnation in the BTH region, and empirically demonstrates that the relative inefficiency of innovation geography in the region is the main reason that restricts the innovative efficiency development based on the "Density, Distance, Division, Differentiation" (4D) framework. The strategic proposition of reshaping innovation geography in the BTH region is put forward. First of all, the article analyzes the disparities in the evolution trends of economic efficiency, innovation competitiveness and innovation efficiency in the BTH region, the Yangtze River Delta, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao region, and finds that the economic efficiency in the BTH region is lack of competitiveness and tends to decline, characterized by weak innovative advantage and low innovation efficiency. Secondly, based on the 4D framework, there are several reasons for the relative inefficiency of innovation from a perspective of economic geography. These reasons include the coexistence of low density of economy, population and patent with high concentration imbalance, the wide scope of patent transfer and the low localization level of industry-university-research collaboration, and the severe innovation segmentation with strong spatial heterogeneity, and relatively weak heterogeneous advantage. Finally, the measurement results show that the relative change of 4D factors will significantly affect the fluctuation of innovation relative efficiency, which indicates that the relative inefficiency of innovation geography in the BTH region is the root of innovation relative inefficiency. This paper shows that the reconstruction of innovation economic geography based on 4D framework is vital to improve innovation efficiency and realize innovation-driven development in the BTH region.
京津冀地区经济增长相对衰落的创新地理基础
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202206003
[本文引用: 1]

如何提高创新效率以促进京津冀地区经济发展由相对衰落转向相对兴旺进而带动北方腹地发展,是新发展阶段深入推进京津冀协同发展面临的重大问题。针对这一问题,本文在指出创新相对无效率是京津冀地区经济相对衰落关键的基础上,基于“密度、距离、分割、异质”(“4D”)框架,从经验上论证了京津冀地区创新地理相对无效率是其创新相对无效率的根源,提出了重塑京津冀地区创新地理的战略主张。首先,分析京津冀地区与长三角、粤港澳的经济效率、创新竞争力和创新效率演变趋势差异,发现京津冀地区经济效率低且趋于下降、创新缺乏竞争力、创新效率偏低,处于创新相对无效率状态。其次,基于“4D”框架阐释京津冀地区创新相对无效率的经济地理原因是,经济、人口和专利的低密度与高集聚不平衡程度并存、专利转移空间范围广而产学研协同发展的本地化水平低、创新分割严峻且空间异质性强、异质优势相对薄弱共同导致的创新地理相对无效率。最后,计量分析表明“4D”因素的相对变动将显著影响创新相对效率变动,证实京津冀地区创新地理相对无效率是创新相对无效率的根源。本文研究表明基于“4D”框架重塑创新经济地理是京津冀地区提高创新效率,进而实现创新驱动发展的关键所在。
Pattern evolution and its contributory factor of cold spots and hot spots of economic development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201701008
[本文引用: 1]

The rapid and imbalanced economic development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region has widened the gap between Beijing-Tianjin and surrounding areas since the 1990s, therefore, it is an important social consensus to achieve coordinated development. In this paper, we analyzed the imbalanced economic development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by proposing a GDP Index using the DMSP/OLS nighttime light data to represent the regional economic development. Then the Getis-Ord General G, Global Moran's I and Optimized Hot Spot Analysis were applied to qualify the spatial pattern of the GDP Index. Third, Space Time Pattern Mining, Spatial Lag Model (SLM) and Spatial Error Model (SEM) were employed to identify the dynamics of the spatial pattern and evaluate the effects of four factors, which were natural environment (elevation and gradient), infrastructure (road network), policy (land use cover) and administrative division (urban or rural area), to the imbalance in the economy, respectively. Results show that: (1) the study area can be divided into three groups based on the level of economic development: urban Beijing-Tianjin, rural Beijing-Tianjin and urban Hebei, and rural Hebei. And there are two economic development gaps caused by Siphon Effect between urban and rural Beijing-Tianjin, and Beijing-Tianjin and Hebei, which is different from the previous view that only one economic development gap between Beijing-Tianjin and Hebei. (2) The dynamics of spatial pattern of economic development are mainly constant hot spot, fluctuant hot spot and fluctuant cold spot. The degree of hot spot, which is mostly in Beijing-Tianjin, decreases from urban center to rural area as concentric circles. In contrast, the majority of cold spots, which have no obvious ring structure, are located in rural Hebei. (3) The economic development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region has non-linear relationship with natural environment, infrastructure, policy and administrative division. In the hot spot region where the economy is more developed, all four factors, especially infrastructure, policy and administrative division, are positively correlated with economic development. However, high gradient, insufficient infrastructure and improper policy limit the economic development in the place with less developed economy, i.e. the cold spot region. This research may be helpful to understand the process and current conditions of economic development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, and useful to realize coordinated development in this region.
京津冀地区经济发展冷热点格局演化及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201701008
[本文引用: 1]

为了探讨京津冀地区经济发展失衡,引入DMSP/OLS夜间灯光构建GDP指数,利用优化的热点分析和时空模式挖掘识别经济发展的格局演化,以SLM和SEM模型从自然环境、基础设施及区域开发等方面量化失衡因素。结果表明:① 区域经济发展趋于波动性集聚,经济发展呈明显的京津市区、京津郊区和河北区县城区、河北偏远县乡等3种类型,而京津市区和郊区之间、京津市域和河北省域之间都存在显著的“虹吸效应”所诱发的发展断崖。② 持续的热点、振荡的热点和振荡的冷点是经济发展冷热点的主要演化模式。经济发展热点自中心城区至远郊呈同心圆圈层式弱化,而无明显圈层变化的冷点集中连片地广布在河北乡村。③ 经济发展与自然环境、基础设施和区域开发有复杂非线性关系,经济发展繁荣地区(热点)多受惠于基础设施和区域开发及行政区划的整体优势,而合适的海拔条件次之。经济发展落后地区(冷点)总体受制于坡度条件和基础设施及区域开发的总体劣势。
Analysis on the synergistic development of industrial sectors in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei based on multi-level coupling coordination model
基于多层级耦合协调模型的京津冀工业产业协同发展分析
Theoretical foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

Promoting coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is not only a major national strategy, but also a long-term complex process. It is necessary to apply scientific theories and respect the laws of nature to realize the strategic target of common prosperity, share a clean environment, share the burden of risk of development, and build a world-class metropolis for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. This article examines the scientific foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory, game theory, dissipative structure theory, and catastrophe theory are the theoretical basis of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory is the core theory for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. The coordinated development process of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is a non-linear spiral progress of game, coordination, mutation, game, resynchronization, and mutation. Each game-coordination-mutation process promotes the coordinated development of the urban agglomeration to a higher level of coordination, and the progress fluctuates. This process includes eight stages: assistance phase, cooperation phase, harmonization phase, synergy phase, coordination phase, resonance phase, integration phase, and cohesion phase. Further analysis shows that the real connotation of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is to realize the coordination of planning, transportation, industrial development, urban and rural development, market, science and technology, finance, information, ecology, and the environment, as well as the construction of a collaborative development community. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration will achieve advanced collaboration from low-level collaborative phase through regional coordination on planning, construction of traffic network, industrial development, joint development of urban and rural areas, market consolidation, science and technology cooperation, equal development of financial services, information sharing, ecological restoration, and pollution control. This study may provide a scientific foundation and theoretical basis for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration.
京津冀城市群协同发展的理论基础与规律性分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

推动京津冀城市群协同发展既是一项国家重大战略,又是一个复杂的长期博弈过程,需要遵循科学理论,尊重科学规律,推动京津冀城市群实现共同繁荣昌盛、共享蓝天白云、共担发展风险、共建世界都会的战略目标。本文从理论上提出了京津冀城市群协同发展的科学理论基础与科学规律。认为推进京津冀城市群协同发展应以协同论、博弈论、耗散结构理论和突变论作为科学理论基础,其中协同论为核心理论。京津冀城市群的协同发展过程是一个博弈、协同、突变、再博弈、再协同、再突变的非线性螺旋式上升过程,每一次博弈—协同—突变过程,都将城市群的协同发展推向更高级协同阶段,并呈现出阶段性规律。具体包括协助阶段、协作阶段、协调阶段、协合阶段、协同阶段、协振阶段、一体化阶段和同城化阶段共8大阶段。进一步分析认为,京津冀城市群协同发展的真正内涵是推动城市群实现规划协同、交通协同、产业协同、城乡协同、市场协同、科技协同、金融协同、信息协同、生态协同和环境协同,建设协同发展共同体。本文成果旨在为京津冀协同发展提供科学基础和理论依据。
Economic resilience characteristics of Shenyang city based on a perspective of industry-enterprise-space
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102012
[本文引用: 3]

In the era of China's New Normal, compared with other regions in China, the Northeast region has been in obvious economic downturn featured by its weak adaption, or in other words, weak regional economic resilience. However, there is a lack of study on how middle or micro economic sectors, particularly industries and enterprises could shape the resilience level of regional macro economy. This paper, therefore, tries to fill this gap by analyzing the multi-level characteristics of Shenyang's economic resilience since 1978, with regard to its economic growth, industrial restructuring, and enterprise spatial dynamics. We found that affected by China's development status, resilience level of Shenyang's economy shows a weak-strong-weak cycle, driven by the fluctuation of its secondary industry. There are obvious differences in the resilience level of old and new paths in Shenyang. In particular, due to its low competitiveness, the resilience level of mechanical industry in old paths has weakened and imposed greater impacts on secondary industry. Meanwhile, the survival rate of old and new enterprises indicates that the resilience level of old paths enterprises is stronger than that of the new paths ones under the context of national economy slowing down; except for enterprises in food industry, the resilience level of old enterprises is stronger than that of the new ones. Moreover, this research indicates that new enterprises of technology-intensive industry such as the old paths and the electronic industry in new paths show a spatial path dependence of city center, and spatial agglomeration has positive effects on enterprises' survival.
基于“产业—企业—空间”的沈阳市经济韧性特征
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102012
[本文引用: 3]

新常态背景下,东北地区与其他区域相比经济下行明显,适应能力较差,即区域经济韧性较弱。产业和企业是区域宏观经济的中微观载体,有助于揭示区域宏观经济韧性的中微观特征,却鲜少有研究。本文从宏观经济增量、中观产业增量及结构变化和微观企业空间动态,分析了1978年以来沈阳市经济韧性的特征。研究发现:① 在全国经济周期影响下,沈阳市经济韧性的变化呈现出“弱—强—弱”的周期性特征,主要是受第二产业韧性的波动变化影响。以支柱产业演替为代表的新老路径产业的韧性变化差异明显,其中老路径产业中机械产业韧性的“强—弱”变化对第二产业的韧性变化影响较大,其韧性减弱主要是由自身竞争力不足造成的。② 在全国经济“增速换挡”放缓的影响下,企业存活率的结果表明,老路径产业企业的韧性强于新路径产业企业的韧性;除食品产业外,其余产业老企业的韧性都强于新企业的韧性。另外初步发现,老路径产业和新路径产业中的电子等技术密集型制造业的新进入企业表现出对中心城区的“空间”路径依赖性,“空间集聚”对企业存活存在正向积极作用。
Interdependencies in the dynamics of regional firm entry and exit in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.03.009
[本文引用: 1]

This article investigates the interdependence mechanism between firm entry and exit, which can be categorized into multiplier and competition effects. First, we present the evolutionary process of the spatial distribution of manufacturing enterprises from 1998 to 2013 that indicates the spatiotemporal trend of industry dynamics. The spatial pattern has experienced dramatic changes, demonstrating an agglomeration tendency of same types of enterprises. Using difference-GMM model we conducted a regression analysis on a dynamic panel to test how regional entry and exit rates are affected by previous exit and entry rates. We found different influences of previous exit and entry. Entry rates are determined by competition effect while exit rates are determined by multiplier effect. The impact on entry is delivered immediately and decreases monotonically. However, a delayed effect exists in the impact on exit, which reaches the peak after two years. Further, we found different interdependence relationships in different regions. Competition effect is more intense in eastern coastal cities. In the eastern area, higher exit rate leads to more entries in the next stage, which proves that firm exit is a market action optimizing resource allocation while a higher entry rate will restrain future entry due to the high industry saturation. On the other hand, in the western area where industrial development is only beginning, a certain amount of exits will aggravate the exit rate in the next stage. Finally, the article examines policy implications of the interdependence dynamics. Regions under different economy background should adopt different policies to realize the sustainable development of industries. The eastern areas should set industry entry threshold criteria and lower exit barriers of inefficient enterprises. These actions can facilitate the working of market mechanism and result in creative destruction to promote industrial restructuring and upgrading. The western area should adopt the policy to attract more entries and protect existing firms in order to prevent a butterfly effect of enterprise exit.
中国的地区企业进入与退出关联研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.03.009
[本文引用: 1]

企业的进入退出存在显著的前后关联,关联机制可以分解为竞争效应与乘数效应。本文探讨了1998-2013年间中国制造业企业的空间格局演化过程,发现地级市尺度的企业动态存在明显的时空关联。16年间,企业动态空间格局发生了剧烈演变,逐渐表现出同类型地区集聚现象。利用差分GMM的动态面板模型验证了企业动态在时间上的前后依赖关系。前期的进入与退出对本期企业动态有不同的影响,竞争效应决定企业的进入,乘数效应决定企业的退出。前期企业动态对后期进入的影响会立即显现出来并随时间衰减,而对退出的影响则存在明显滞后效应,在两年之后达到峰值。同时,产业动态关联机制存在显著的空间差异,其中东部地区显示出更强的竞争效应。不同发展水平的地区应采取差别化的政策来指导地区的产业发展,实现产业更新、结构升级和区域经济的可持续发展。东部地区应建立企业准入门槛,降低低效企业退出壁垒;西部地区应该积极吸引新企业进入,并保护在位企业,防止企业退出导致的连锁性萧条。
Review of shift-share analysis
偏离—份额分析法研究进展
Causes of economic rise and fall in the Yellow River Basin after 2000: Based on the shift-share analysis method
新世纪以来黄河流域经济兴衰的原因初探: 基于偏离—份额分析法
How regions react to recessions: Resilience and the role of economic structure
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2015.1136410 URL [本文引用: 2]
The business cycle resilience of the western cape economy: A regional analysis of the 2009 recession and subsequent recovery
Diversity and specialisation in cities: Why, where and when does it matter
DOI:10.1080/0042098002104
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Why are some cities specialised and others diversified? What are the advantages and disadvantages of urban specialisation and diversity? To what extent do the structure of cities and the activities of firms and people in them change over time? How does the sectoral composition of cities influence their evolution? To answer these and related questions, we first distil some key stylised facts from the empirical literature on cities and the composition of their activities. We then turn to a review of different theories looking at such issues, and study the extent to which these theories contribute to the understanding of the empirical regularities.
The resilience of employment in Wales: Through recession and into recovery
DOI:10.1080/00343404.2014.920083 URL [本文引用: 1]
Achievements, problems and path selection of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei coordinated development
京津冀协同发展的成效、问题与路径选择
Study on problems in Beijing,Tianjin and Hebei coordinated industrial development and recommendations
京津冀产业协同发展的问题与建议
中国软科学,
The regional industrial dynamics from the perspective of relatedness
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190995
[本文引用: 1]

Chinese economic development has experienced a rapid transformation since 1978 due to the implementation of the reform and opening-up policy. Arguably the research of regional industry dynamics is at the core of economic geography. Traditional researches in economic geography tend to focus on individuals such as firms, industries and regions, ignoring the relationship between them. Over the past few years, much progress has been made in researches on the relatedness of firms, while the relatedness of industries and regions is still not paid sufficient attentions. From the perspective of relatedness, this paper attempts to shed some light on the linkages of industries and regions, and explore their formation mechanisms. It puts forward that the translocal linkages and resource mobilization on different scales are sources of the relatedness of firms, industries and regions. In addition, this paper also sketches out how industrial relatedness and regional relatedness influences regional industrial dynamics. As for industrial relatedness, evolutionary economic geography (EEG) theories based on a network model named the "product space" have adopted a view that regional spillovers from related, yet not too proximate industries will endogenously induce new industries in a region through processes of recombinatorial innovation. The vast majority of empirical case studies have confirmed these theories. Regional industrial dynamics has thus far largely been conceptualized as an endogenous process, underplaying exogenously-driven forms of regional relatedness. Then, this paper provides a systematic conceptual analysis of the role regional relatedness may play for industrial dynamics in regions. Good connections between the regions improve matching on labour markets, speeding up knowledge flows and plausibly fostering learning which will contribute to the reciprocal industrial dynamics of geographically distant regions. Accordingly, this paper argues that future studies can further investigate the regional development from a relatedness perspective: (1) pay more attention to the industrial relatedness, such as its indirect links, link strengths and industrial relatedness dynamics; (2) enhance the understanding of the properties of regional relatedness and draw on network analysis approaches; (3) forge a link between industrial relatedness and regional relatedness. Emanated from different disciplines, the new perspective of relatedness in the study of regional industry dynamics provides a sound basis for understanding China's special development path and deserves the attention of economic geography scholars. Besides, there is rapidly expanding various data of relatedness which will make the perspective of relatedness more potential in the future.
关联视角下的区域产业动态研究进展与反思
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190995
[本文引用: 1]

区域产业动态是经济地理学的经典研究主题。不同尺度的传统经济地理研究常以企业、产业和区域为研究对象,忽略了不同个体之间的关联。近年来,经济地理学增加了关于企业关联的研究,但对于产业关联和区域关联的关注仍显不足。基于关联视角,本文首先围绕产业关联和区域关联等概念探讨了关联的形成机制,进一步梳理关于产业关联、区域关联与区域产业动态的研究进展,并为未来区域产业动态研究提出相关建议。与企业关联相同,产业和区域关联也与个体间的要素流动有关。现有研究表明产业关联有助于揭示区域产业演化规律,而区域关联会通过区域间要素流动影响区域产业动态。关联视角是区域产业动态研究的新视角,具有较大的研究潜力,值得引起经济地理学者们的关注。
Measuring impact of strategic coupling towards the patterns of industrial upgrading in the Pearl River Delta
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210280
[本文引用: 2]

Existing research on strategic coupling has addressed the interaction mechanism between strategic coupling and regional industrial upgrading under globalization. However, current studies are mainly based on qualitative research and lack of quantitative measurement of relationships between strategic coupling and industrial upgrading. Therefore, based on two dimensions, the enterprise and the region, this study constructs an analytical framework to explore the patterns of industrial upgrading under the influence of strategic coupling. This study also adopts a multiple linear regression model to verify the impacts of strategic coupling on industrial upgrading. The main conclusions are as follows: First, all cities in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) have undergone industrial upgrading. However, there are some intra-regional divergence considering the patterns and extent of upgrading. Among these cities, Shenzhen has shown the best performance of upgrading, an overall regional upgrading. Guangzhou and Zhuhai have less-best upgrading, enterprise upgrading, which is followed by Dongguan with an upgrading related to industrial structure. Significantly, the phenomenon of involution has not yet occurred in the PRD. Second, the difference in the patterns of strategic coupling affects the process of industrial upgrading significantly. The production dependency on Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan-invested enterprises, and the technological dependency towards foreign enterprises are the most prominent influencing factors. Third, after the 2008 financial crisis, the interaction mechanism between strategic coupling and industrial upgrading has changed apparently, which remarked a turning point in the path of regional development. Regions that have higher dependency towards Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan and other general foreign enterprises on industrial production have lower speed of upgrading. However, regions where Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan-invested enterprises have higher technology have more prominent regional upgrading. Nevertheless, the influence of advanced technologies brought by foreign-invested enterprises in fostering regional upgrading have faded out. Overall, this paper helps to advance the theory of industrial upgrading under globalization. It also tentatively explores the use of quantitative methods in relational economic geography.
战略耦合影响下珠三角产业升级模式及测度
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020210280
[本文引用: 2]

现有研究已经初步揭示全球化进程中战略耦合与区域产业升级的互动机制,但战略耦合及其与产业升级的关系仍缺少量化测度。为此本文基于关系经济地理学视角,从企业和区域两个维度构建战略耦合影响下的产业升级模式分析框架,并借助多元线性回归模型初步定量实证战略耦合对产业升级的影响,研究发现:① 珠三角各城市均发生了产业升级,同时也存在地理尺度上的分异。其中,深圳表现出最优的区域整体升级,广州和珠海偏向于次优的企业升级,而东莞接近于产业结构升级,内卷化现象在珠三角城市尚未明显发生。② 战略耦合模式的差异显著影响产业升级进程,其中工业生产对港澳台资的依赖程度和外资企业的技术领先因素的作用最为突出。③ 2008年金融危机之后,战略耦合对产业升级的作用机制发生显著改变,成为区域发展路径的转折点。越依附于港澳台资和其他一般外资进行生产的地区升级越慢,但港澳台资企业的技术领先水平越高的区域则升级更加明显,而一般外资企业的技术领先水平对于升级的促进作用消失。本研究进一步完善了全球化下的产业升级理论,同时也是对关系经济地理学定量研究的一次积极探索。
Multidimensional measurements and analysis of urban economic resilience under the disturbance of economic risks: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta, China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.06.002
[本文引用: 1]

With the increasing economic interaction between cities, disturbance of economic risks has a great impact on their economic resilience. Examining urban economic resilience is crucial for the economic development of cities. Using economic risk disturbances of the Asian financial crisis and the global financial crisis as examples, this study measured economic resilience from four dimensions, including relative-diversity index, relative-specialization index, regional economic connection intensity, and regional economic sensitivity, and analyzed the characteristics and change of the spatial and temporal patterns for cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and their causes. The results show that: 1) The relative-diversity index of most cities declined from 1997 to 2016. The relative specialization developed stably, which promoted the regional industrial division and the improvement of economic resilience. Some of the cities in Anhui Province exhibited structural homogeneity in manufacturing industries. 2) The relative-specialization index showed significant regional differences, which was correlated with dominant industrial structure. The relative-specialization index of the eastern cities was medium, while the western cities mainly developed resource-based economy with high specialization. In the face of economic risk disturbances, some cities in the region tended to strengthen the traditional low-efficiency industry model. These cities had low regional coordination ability, which negatively affected economic resilience and high-quality development. 3) The proportion of total connection between a core city and other cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration decreased year by year, and the agglomeration ability of core cities is still strong, hindering the systematic development of economic resilience. Shanghai was one of the highest regional economic connection intensity cities with its large economic volume, multiple industrial types, and large population, leading to the increasing regional economic gap in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. Spatially, the regional economic connection intensity between eastern cities was higher than that of western cities. 4) The resistance and recoverability of cities in the urban agglomeration were closely related to their economic development models. Export-oriented cities were the first to be seriously affected by economic risk disturbances and had low resistance in the period of urban economic contraction. However, the cities with high-tech industries and domestic demand industries developed rapidly in the period of urban economic expansion. Economic risk disturbances had regional sequential influence on the economic growth of different cities. This paper is helpful to remedy the deficiency of the existing literature on urban economic resilience from the perspective of urban agglomeration, and provides methodological guidance for the high-quality and sustainable development of urban and regional economies in China.
风险扰动下的城市经济韧性多维测度与分析: 以长三角地区为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2022.06.002
[本文引用: 1]

随着城市间经济联系日益密切,风险扰动对城市的经济韧性发展有着较大的冲击影响,深入研究城市经济韧性对于城市经济良性发展和提升经济抵御能力具有重要意义。论文选取亚洲金融危机和全球金融危机两次典型的经济风险扰动,以长三角城市为研究对象,以产业相对多样化、产业相对专业化、区域经济联系强度和地区经济敏感度的多维综合评价法对长三角城市经济韧性进行了测度,并对其时空格局的演化、特征及成因进行了分析,结果表明:① 长三角地区内大部分城市的产业相对多样化指数呈不断下滑趋势,相对专业化整体态势稳定上升,有利于区域产业分工和一体化发展,应对风险扰动的经济韧性能力强,而安徽省内部分城市专业化指数过高且存在产业同构化现象;② 城市产业相对专业化指数区域差距不断增加,与其主导产业结构有显著关系;③ 核心城市与各城市间的联系总量占比逐年降低,核心城市上海的集聚能力仍较高,致使城市间差距增加,不利于城市经济韧性的整体协同;④ 城市抵抗力和恢复力与其经济发展模式密切相关,经济风险扰动对不同城市的经济增长,存在由沿海城市向内部城市的地域先后性影响。论文有助于弥补已有研究在城市群地区尺度经济韧性研究方面的不足,以期为中国城市经济可持续和区域高质量协同发展提供方法指导。