1 引言
“四个面向”已成为新时代科技工作的指针①(① 习近平. 在科学家座谈会上的讲话. 人民日报. [2020-09-12] (2021-10-01).
治理(governance)是人类干预或应对自然与社会事件的重要行为与生活方式。中文“治理”一词由“治”和“理”组成,早期多以“治”出现,如“既载壶口,治梁及岐”②(② 王世舜. 《尚书译注》. 北京: 中华书局, 1982: 45.),“使帅其属,而掌邦治”③(③ 徐正英, 常佩雨. 《周礼译注》. 北京: 中华书局, 2014: 2.)等。“治理”一词最早出现于春秋战国时期,如“明分职,序事业,材技官能,莫不治理” ④(④方勇, 李波. 《荀子译注》. 北京: 中华书局, 2011: 199.),“其法通乎人情,关乎治理也”⑤(⑤高华平, 王齐洲, 张三夕. 《韩非子译注》. 北京: 中华书局, 2010: 762.)等。“治理”一词与治水活动相联系,具有治国理政之义。英语中“governance”一词由“govern”和表示过程或状态的词缀“-ance”组成,“govern”源自拉丁语“gubernare”,原义为“掌舵、领航”,借用了希腊航海用语“kybernan”[1]。“governance”词源与航海的关联,其实也是与地理的关联。东西方治理思想皆源于人与水共处的经验,所以治理本身具有地理性。治理以地理环境为基础,主要通过工程、规划和政策来实践[2]。当代治理面对的是一个开放的复杂系统[3],涉及全球与地方多个尺度[4],关注自然与社会多个领域[5-6],牵涉政府、市场、社会组织和个人等多主体[7],不同尺度、领域和主体之间的关系错综复杂、互相影响和转化[8]。治理研究需要地理学与管理学、经济学、政治学、社会学、文艺学等人文社会科学和生态学、环境科学、心理学、数据工程学等自然技术科学的广泛联动。
立足重大自然和社会问题,突破学科领域界限,深入研究跨学科视野下全球及地方治理的新理论、方法和实践,探讨实现治理现代化的路径,既是国际研究前沿和趋势,也是国家战略和社会需求。近年来,随着国土空间规划和生态文明建设的深入推进,国内学者对治理进行了积极探索和研究,取得了大量理论和实践成果。本文通过系统归纳和总结近期治理研究的态势,提出面向治理的地理学发展路径,为治理研究以及地理学与治理学科的融合发展提供新的思路。
2 地理学与治理结合研究的态势
2.1 治理成为多学科研究的焦点,但地理学尚未成为治理研究的优势学科
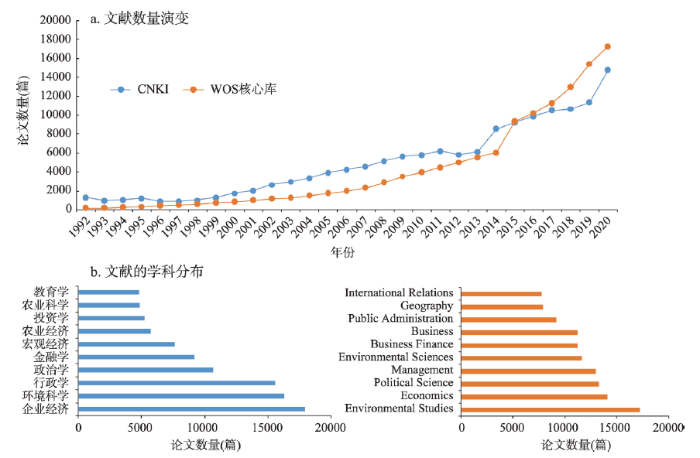
图1
图1
国内外“治理”文献的时间和学科分布
注:检索主题词为“governance”,检索数据库为中国知网(CNKI)和“Web of Science”核心库,时间为2022年1月1日。
Fig. 1
Trends and disciplinary distribution of China and international governance research
地理学尚未成为治理研究的优势学科。在公共知识平台上,国际治理研究有独立的地理学门类,中国地理学的治理研究成果则分布在宏观经济和环境科学中。在成果数量上,国际地理学的治理研究虽然排在前列,但与环境科学、经济学相比仍有差距。中国地理学同样在治理学科群中面临激烈竞争。2000—2022年的国家社会科学基金中,社会学、政治学、管理学、法学、应用经济学的治理研究项目数都在300项以上,地理学申报的项目多挂靠管理学。同时期的国家自然科学基金中,地理学涉及“治理”主题的项目虽然遍及三大分支学科且呈逐年上升趋势,但存在总量少、议题散等问题。
2.2 人地耦合成为治理研究的核心理念,社会—生态治理研究亟需突破
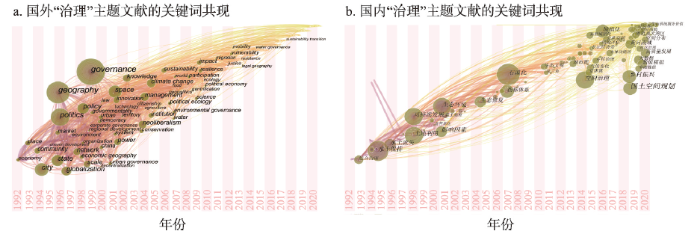
治理面对的不是科学化的表征世界而是自然和社会深刻交织的现实世界,涵盖社会—生态治理的复杂过程和复杂系统研究思想[17]。国际治理研究正在拓展地理学科视野,伦敦政治经济学院(The London School of Economics and Political Science, LSE)、剑桥大学(University of Cambridge)等大学地理学院都开辟了和社会—生态治理有关的研究方向,人地耦合的治理理论创新得到重视并取得理论成果[18⇓⇓⇓⇓-23]。20世纪90年代国际地理学就形成以空间与政治为特色的治理研究(图2a),全球化、新自由主义、气候变化等综合性治理问题是国际地理学研究的重点,近年来,人类世、流动性、韧性等话题成为新的研究热点[24⇓-26]。中国地理学早期以可持续发展为核心(图2b),形成水土治理、生态修复、自然资源管治等偏自然地理领域的治理议题[27⇓⇓-30];近年来以空间治理为核心[31⇓-33],国土空间规划、乡村振兴、新型城镇化等政策热点也成为研究热点[34⇓⇓-37]。总体上,国内外地理学经典治理研究分别侧重自然和社会维度[38-39],近年来都迈向综合性治理议题。
图2
图2
国内外地理学领域治理研究的关键词共现图
注:中文检索主题词为“governance”和“地理”,英文检索主题词为“governance”和“geography”,分别导出论文数据集合,由CiteSpace生成关键词共现网络;检索数据库为中国知网(CNKI)和“Web of Science”核心库,时间为2022年1月1日。
Fig. 2
Keywords co-occurrence for Chinese and international governance research in the field of geography
2.3 尺度视角的治理研究成为热点,尺度交互方法有待创新
2.4 地理大数据与智能技术在治理中得到运用,但应用场景仍待拓展
技术进步是推动学科发展的主要动力,地理学与工程学、心理学等学科技术的融合,不断丰富和创新了地理学的治理手段[59]。一方面,定量和定性相结合的研究技术成为前沿[60-61],“观测—分析—模拟—预测”结合的研究手段成为主流,空间信息技术成为国家治理的重要组成部分。另一方面,研发国际领先的GIS、遥感、大数据产品成为热点[62⇓-64],全球变化遥感、计算机建模、传感器设计、地理可视化的发展推动地理学进行治理推演实验,成为学科创新的前沿领域和核心力量[65⇓-67]。新时期地理学治理效能的切实提升离不开对空间决策支持系统(Spatial Decision Support System, SDSS)(如GIS、RS、GPS)等的有机集成[68]。构建综合的治理平台产品,提升对地理现象的表达、观测、计算、模拟能力,仍是地理学继续探索的方向。同时,服务于政府行政、企业经营、居民生活等不同行动者需求的地理数据容量、精度、时效、适应性仍待提升。
目前国内外地理学对治理的研究处于加速发展阶段,研究议题包括概念和内涵界定、模式提炼、路径优化及对不同区域开展的经验研究等多方面;研究向纵深方向发展,人地耦合成为理论创新焦点;研究尺度涵盖社区、地方、区域、国家、全球等,尺度交互正成为主流;研究方法采用定性和定量相结合,在数据集成和模拟决策上不断深化。
3 地理学进行治理研究的机遇和挑战
3.1 地理学进行治理研究的机遇
地理科学三大二级学科构成自然、人文和技术为一体的交叉学科体系,在治理研究上大有可为。
“四个面向”为治理研究指明方向。面向世界科技前沿,要求治理研究在世界格局中探索中国治理道路。面向经济主战场,要求治理研究以生产力发展作为检验治理成效的标尺。面向国家重大需求,要求以自主创新推动国家治理现代化。面向人民生命健康,要求以人的全面发展作为治理研究的现实归依。
联合国2030年可持续发展目标为治理研究带来机遇。COVID-19疫情的全球蔓延、气候治理与碳中和、“FEW”(food-energy-water)等资源短缺、频发的极端事件和自然灾害对可持续发展产生深刻影响。17个可持续发展目标涉及社会、自然和技术等维度,需要将其贯彻到治理实践中,在不同尺度上制定细致的方案或行动计划。
全面建设社会主义现代化国家新征程为治理研究开辟新战场。十九届四中、五中和六中全会提出大量与治理相关的战略构想亟待实践深化和理论研究(表1)。诸多治理议题要求突破从单一学科出发的治理研究,强调中国式现代化价值导向,围绕人与自然关系协调展开,涉及多尺度的实践和多主体的诉求,呼唤动态智能的技术支撑。
表1 2019年以来国家重大治理议题
Tab. 1
| 议题类别 | 治理内容 |
|---|---|
| 价值 | 政治、法治、德治、自治 |
| 领域 | 经济、网络、科技、文化、社会、风险、污染物、环境和气候、生态系统 |
| 尺度 | 学校、医院、公司、社区、乡村、城市、区域、流域、沉降区、边疆、全球 |
| 方法 | 系统、协同、综合、第三方、源头 |
注:资料来源为
国家自然科学基金委交叉学科战略为面向治理的地理学发展提供了契机。基金委成立交叉科学部,交叉科学四处提出自然科学与人文、社会、管理等领域的研究,面向宏观复杂系统以及经济发展过程中的资源开发利用、生态文明建设、人居环境提升等问题,探究自然与社会的互馈机制、人地系统的动态结构等,解决人类可持续发展中的重大科学问题,为跨学科的治理研究提供了机遇。
3.2 地理学进行治理研究的挑战
地理学进行治理研究面临的主要挑战是没有形成学科融合框架,导致缺乏有影响力的治理理论,无法实现治理方法的集成,不能完全发挥地理技术的治理效力。
治理与地理的关系尚未达成基本共识。一方面,治理的人地关系内涵没有系统梳理。由于治理问题涉及对象的复杂性,治理概念尽管常用但要准确界定却相当困难[69],一些研究符合治理内涵但没有凝练成可与其他学科对话的治理理论,一些研究则披挂治理外衣实则是聚焦政策。而在诸多学科治理研究如火如荼之时,地理学固守对“治理”的认知和话语,许多地理学的治理成果走不出去,其他学科治理理论引不进来。另一方面,地理学主张的治理价值观亟待明晰。治理研究的基本要求是突破实证思维,进行批判性思考和价值判断。中国地理学研究的价值导向已经趋于多元[70],但地理学者结合实际对多元价值进行批判性思考的能力不足[71]。特别是多尺度和多主体参与治理的权责边界尚无定论,对中心与边缘、流动与稳定、趋同与分异辩证关系的认识仍待深化[72]。
学科交叉尚未实现地理学治理思想的重大创新。一方面,治理的学科体系仍处于松散联系状态。治理涉及人类发展和生存环境的各个领域。人文、社会、自然、技术科学领域的治理研究学者往往从各自知识背景出发提出跨学科的治理研究思路,但在研究对象、范畴、话语等元理论方面缺乏综合创新,社会治理与生态治理思想严重分离,社会维度的治理研究缺少“科学”性而自然维度的治理研究缺乏“政治”性。另一方面,地理学围绕治理进行人地关系思想创新的意识不足。地理学习惯将“人”视为要素而不是治理主体,将“地”视作背景而不是治理场域,地理学的综合性面向的是要素—背景的机械关系而不是主体—场域的治理关系。反思各类治理问题的人地关系根源和提出综合性的研究框架成为学界的共识[73]。
地理学方法在治理研究中缺乏集成。从现实世界看,快速变化的治理问题使传统地理学方法的效力下降。地理学为治理做了很多工作,但住房、大气污染等问题始终在不同尺度和空间中转移而得不到根本解决,相对贫困、“双碳”目标等跨尺度治理话题又要求地理学给出新的解决方案。从学科生态看,在经济社会快速发展阶段成长起来的地理学不能适应高质量发展阶段要求,尚未透彻理解共同富裕内涵,过分强调治理的建设和生产属性[74],忽略治理的调节、协商和服务属性,全过程治理缺少综合方法。此外,治理方法研究缺乏长期、大范围的治理经验总结和深层次的方法论探索,研究成果对提升地理科学治国理政能力所起的支撑作用不足。
地理技术的研发力度和社会嵌入不够。随着国土空间规划编制和一系列国土空间开发保护战略制定,对治理技术创新的需求日益扩大[75],但地理学科研人员在技术研发中的能动性得不到解放,研发需要的长期资金支撑和稳定孵化环境都有待完善。而物联网信息技术、AI图像处理技术、空间数据融合技术等先进科技成果转化为治理技术的成本较高也阻碍了地理学的技术创新。这些成本中最关键的是人才成本,在各类机构数字化转型过程中,能够运用新地理技术且具有政治意识、格局观念、共情能力、协商技巧的治理人才短缺,“面向技能”培养模式向“面向治理”培养模式转变需要时间。
4 朝向治理科学:地理与治理融合发展的路径
4.1 面向治理的地理学发展框架
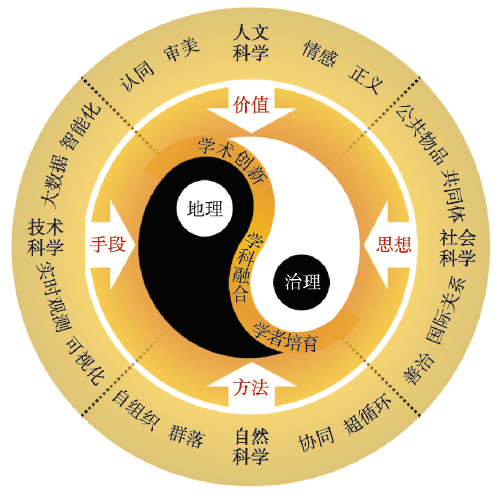
“我们面临着生态问题、城市问题、国际贸易问题,然而我们对此似乎没有什么高见。当我们说话时,却又是庸常之词和荒唐之言。总之,我们的范式已经无效,是时候把它扔到一边去了”[76]。大卫·哈维在1973年针对西方地理学界所说的话并未过时,对当下国内学界也颇具警示作用。治理是地理学回应时代的一个历久弥新的话题。中国地理学必须顺应治理体系和治理能力现代化,明晰治理和地理的关系,推进社会—生态治理理论、尺度交互方法和应用技术的创新,使地理学成为治理研究的优势学科。为此,需要从价值、思想、方法、技术4个维度提出地理学与其他学科融合发展的路径,从基础研究、平台建设、人才培育3个方面发掘面向治理的地理学发展策略(图3)。
图3
图3
地理与治理融合发展的框架
Fig. 3
Framework for integrated development of geography and governance
实践和认识是人类发展的两个基本主题,治理是改造世界的社会实践,地理学是人对地球表层的系统认识。一方面,治理是促进地理学发展的动力,地理学通过参加治理活动吸收多学科的治理研究成果,转化为地理价值、思想、方法和技术。另一方面,地理学始终是治国理政的重要知识来源,地理学调动学科资源构建治理平台和培育具有治理能力的人才,不断推进治理实践。通过提升地理学的治理能力,能够推进从权力到权利、从一元到多元、从中央到地方、从管理到服务的治理转型[8]。从实践和认识辩证统一的角度看待这一框架,治理和地理在人类发展进程中具有明确的定位和相等的地位,4条路径和3种策略从外内两方面推进面向治理的地理学发展,太极图式能够体现学科融合框架在结构上的规则性、运动中的转化性。
4.2 面向治理的地理学发展路径
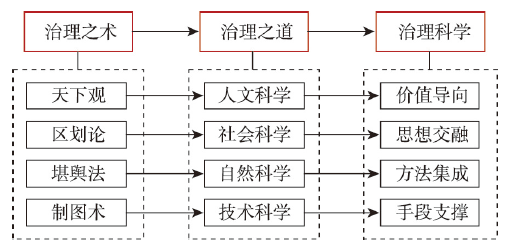
价值、思想、方法、技术4个维度的发展路径共同推进治理研究变革(图4)。中国古代地理学贡献了以天下观、区划论、堪舆法、制图术为核心的治理之术,天下观是以地理空间为基础的文化价值指引,区划论是基于自然和人文要素特征划分空间进行治理的思想,堪舆法是运用系统法则和工具实地考察分析人居世界的方法,制图术是将复杂世界抽象映射为可分析对象的空间信息技术。现代治理研究涉及人文、社会、自然、技术等学科,各学科在专门领域深耕同时也形成条块分割的治理研究格局,现代地理学的治理研究在与不同学科交叉中也逐渐分化。未来通过加强地理学治理研究的法则化、整体化,进而培育一门指导人类有序干预或应对自然与社会事件的治理科学。
图4
图4
从治理之术到治理科学的演进路径
Fig. 4
Evolution paths from governance techniques to governance science
4.2.1 推动人文科学主导的价值融合,树立正确治理观念
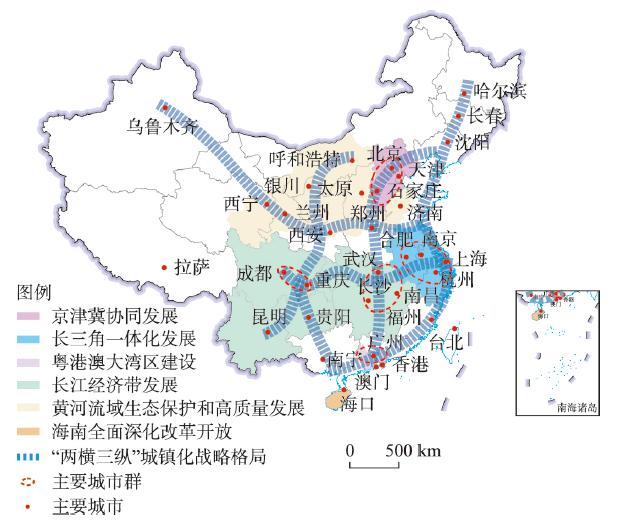
新发展阶段的主要矛盾是人民日益增长的美好生活需要和不平衡不充分的发展之间的矛盾。2020年中国城乡居民人均可支配收入比为2.56,沿海和内陆人均GDP比为1.58①(① 沿海地区包括辽宁省、河北省、北京市、天津市、山东省、江苏省、上海市、浙江省、福建省、广东省、海南省,内地包括除沿海及港澳台地区的其他省市区。数据来源于:国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴(2021). 北京: 国家统计出版社, 2021.)。治理是解决不平衡不充分发展问题的核心动力,“十四五”规划意图构建“两横三纵”城镇化格局和六大区域发展板块(图5),促进国土空间在集聚中均衡发展。地理学必须在国家治理模式整体转型背景下讨论新的空间治理模式[77],要主动与人文科学对话,在治理中突出可持续发展的价值观念。其一,比较治理涉及的多元理论,厘清政治、管理、管制、整治、治理术、善治等概念与治理的关系。其二,梳理治理的价值谱系,明辨东西方治理理论背后的地理学内涵和价值原则,清楚不同地域治理观念的交流分异。其三,聚焦治理的伦理、情感、艺术等维度,聚合伦理学、文艺学等学科知识,把注意力集中在最大限度提高人民的满意度上,提炼新时代的价值支撑。
图5
图5
“十四五”规划期间中国空间治理的格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2020)4626号的标准地图制作,底图边界无修改;资料来源于《中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要》。
Fig. 5
Pattern of spatial governance in China during the 14th Five-Year Plan period
以地理学和伦理学的交叉融合为例。地理学通过超越资本权力逻辑,强化多元主体特别是弱势群体参与策略,寻找将地方置于决策进程的依据,构建决策的正式和非正式框架,明确规划系统在增量与存量、效率与公平等目标中的运行原则,形成一系列价值标准。通过将这些标准和“正义”理论结合,可以定义“空间正义”的内涵。此外,文艺学能启示地理学价值观表达。譬如《诗经》描绘了“民亦劳止,汔可小康。惠此中国,以绥四方” ②(②周振甫. 《诗经译注》. 北京: 中华书局, 2002: 443.)的治理构想,“小康”的价值追寻与空间治理密切关联。通过运用本土话语,向公共领域宣扬地理学的善治立场,将可持续发展的科学观念转化为大众的价值追寻。
4.2.2 推动社会科学主导的思想融合,培育综合治理理论
中国主张人与自然和谐共生的理念,对生态文明与国土空间结构管控优化关系的认识,对“人口资源环境相均衡、经济社会生态效益相统一”原则的理解都亟待跨学科的治理思想创新。一是在开放视野下进行治理思想研究,积极吸收环境法学、政治生态学、生态马克思主义等学科和思潮的理论,与中国传统道法自然等思想结合,明晰地理在治理进程中的作用机理,推动人地关系理论创新。二是扎实进行治理思想总结,利用中国自然和社会多元一体格局的典型性,积极研究塞罕坝林场建设、“千村示范、万村整治”工程、“蚂蚁森林”项目等蕴含的社会—生态治理经验,拓展综合治理思路。三是推进社会—生态治理思想落实,不同尺度的社会—生态治理重点不同,通过借鉴法学、管理学等与行政体制融合的经验,将社会和生态结合的原则贯彻到不同尺度的公共事务中去。
4.2.3 推动自然科学主导的方法融合,创新协同治理方法
中国的空间治理重心经历了从乡村到城市再走向城乡共治和全球治理的过程。在实现多尺度治理的过程中,地理学首先要聚焦“多尺度多主体耦合”的方法集成,不同尺度的治理大致对应特定学科,地理学应该探索在地方、区域、全球治理中与环境心理学、景观生态学、全球变化科学等对接,研究不同尺度的空间治理规律,提升对特定尺度事务的预测、调控能力。其次要强化方法融合,运用自组织、韧性、协同方法,将对象感知和事件情境结合,形成注重公共协商性、过程调控性和层级耦合性的决策支持方法。最终要进行方法论创新,聚焦多要素、多界面、多区域、多尺度、多主体过程和格局的优化调控研究,创新面向地球生命共同体建设的复杂系统方法论。
以地理学和生态学的交叉融合为例。现代韧性研究起源于生态学,近年来,全球灾害发生频率显著上升,韧性成为地理学方法研究的焦点议题[80]。郑州特大暴雨灾害、上海COVID-19疫情冲击表明极端事件对特大型和超大型城市的影响日益加重。更重要的是,甘肃白银马拉松事件表明中小城市抵御风险的能力极弱。全球变化对中西部培育特色发展模式造成的冲击大,是新发展格局中的薄弱环节。综合来看,地理学必须重点关注受风险冲击大、承灾能力弱地区的韧性治理研究[81-82]。在公共安全应急体系建设中,运用韧性方法,重视系统“快变量”和“慢变量”的多时空尺度影响,准确测度转型路径稳健性,以自组织为原则构建多层级治理网络,通过授权、征召、赋利等形式,重组不同尺度治理主体。
4.2.4 推动技术科学主导的手段融合,集成模拟决策技术
随着技术发展和社会进步,人们对治理技术的需求将越来越大,治理的技术研究应该围绕动态化和智能化发展。首先要引进信息领域前沿成果,发展网络空间地理学、人工智能地理学等新分支学科,加强信息技术和田野实验方法集成研究,既要强化运用空间传感器获取实时数据的能力,也要加强对规划实施效果的长期考察分析。其次是合理布局地学数据超算中心,推进平台技术革新、降低研发成本,产出高质量的数据和运用门槛较低的技术产品。最重要的是培育地理学人才综合运用多种治理技术解决现实问题的能力,特别强化人才的技术伦理,提升服务不同尺度特别是全球和社区治理的能力。
4.3 面向治理的地理学发展策略
“在科学上没有平坦的大道,只有不畏劳苦沿着陡峭山路攀登的人,才有希望达到光辉的顶点”[85]。面向治理的地理学发展路径要集成落实到学科发展的具体策略中。立足“十四五”时期地理科学发展战略的宏观背景,统筹价值、思想、方法、技术4大方向,从基础研究、平台建设、人才培育3个方面培育地理学新的学科增长点。
4.3.1 强化学术基础研究
地理学须树立“以治理强学科”观念,推进基础性、急迫性、引领性治理议题研究。① 进行面向现代化的地理学治理价值观研究。系统梳理以治理为主线的地理学思想史,强化“格局—过程—效应—机制—模拟—治理”一体的研究逻辑,构建面向治理的批判性知识体系。② 进行社会—生态治理思想研究。资助依托社区、流域等地理实体的实验性治理项目,基于中国历史地理环境推进人地关系理论创新。③ 进行多尺度、多主体治理方法研究。在深化基于特定尺度的治理方法研究基础上,探索贫困、气候变化等全过程治理问题的多尺度、多主体治理机制,深化复杂网络方法运用。④ 进行关键治理技术创新和推广研究。深化对关键社会和生态过程数据的监测、采集、处理、模拟技术研究,着力聚焦技术与治理单元的耦合路径,提升技术沟通多层级治理单元的中介功能,构建面向国家治理现代化的地学技术支撑网络。
4.3.2 优化学科平台建设
地理学要建设全面开放的学科平台,凸显在治理学科群中的独特地位。① 重塑学科氛围。纠正政策地理学偏向,推进公共地理学发展,统筹国家战略和社会需求两方面研究议题,营造健全的治理研究环境。② 强化学科建设。明确治理在地理学中的位置,谋求人文、自然和信息地理学对治理的研究共识,发挥不同学科与人文、社会、自然、技术科学结合研究的专长,建立治理研究的学科发展系统;促进资源环境管理学、国土空间规划学等分支学科协同发展,在学科评价中提升治理成果的比重,努力培育治理科学一级交叉学科。③ 整合学科基地。基于治理议题涉及的地理单元,推进项目协同申报、数据和设备等的共享(如建设长江经济带科研开放平台);在治理研究基础好的学术机构建设示范基地,整合一批智库平台(如建设长三角地学智库联盟)。
4.3.3 深化学者人才培育
面向治理的地理学须培养具有治国理政才能的知识共同体。① 加快治理人才培养。在招生中增设治理类专业方向,与马克思主义学院、公共管理学院等联合开展跨学科招生;增设法理学、政治学、公共政策学等跨专业课程,详细解析气候变化评估、COVID-19疫情防控、空心村整治、“阿者科”计划等当代地理学治理案例;在人才培养体系中增加在各类治理组织中实践的考核要求,推动地理人才走向世界和扎根基层。② 推动地理学者公共化转型。鼓励学者把握新媒体力量参与治理议题讨论;学科信息平台积极组织地理学者及时发声与交流回应;组织类似底特律地理考察队活动,将教学、科研与实际的社会治理活动有机结合。③ 形成多方共建的治理研讨网络。协调不同年龄、性别、地域、学术背景的学者,引进企业决策者、社会组织成员,建立跨界创新团队。
5 结语
治理是地理学与自然、社会、人文、技术科学交叉的前沿领域。本文围绕地理学如何面向治理进行交叉融合研究这一关键问题,基于人地耦合理念,综合运用资料调查和文献计量方法,系统梳理国内外地理学治理研究的轨迹与特点,认为治理研究正处于加速发展阶段,地理学能在其中发挥关键作用,构建面向治理的地理学框架是首要任务。
地理学要在传承经典治理议题基础上,加强对社会空间的研究,把握地理学的治理内涵和价值观,全面认识现代化进程中的自然和人文要素关系,掌握多尺度、多主体耦合的复杂系统分析方法,创新空间模拟和智能技术,形成并凸显地理学在治理研究上的核心价值、思想、方法和技术。就“十四五”时期乃至更长远的地理科学发展战略而言,必须凝练地理学治理研究的关键命题,构建面向治理的学科体系,形成理论与应用研究并重的人才网络,以此提升中国地理学在国际治理研究中的影响力。促进地理学与其他学科的交叉融合,将自然与人文有机结合的理念应用于社会治理,形成专门的、贯穿理论与实践的治理科学,不但具有重要学术意义,也是服务全球进步、国家战略、区域可持续发展、居民福祉的集中体现。
参考文献
Tentative ideas on the direction and task of the Institute of Geography, Academia Sinica: A report presented at Working Conference of the Institute of Geography, Academia Sinica
中国科学院地理研究所工作方向和任务的初步设想: 在1965年中国科学院地理工作所会议上的报告
The conversion of logic in the modernization of national governance
国家治理现代化的逻辑转换
State governance, global governance and the construction of world order
国家治理、全球治理与世界秩序建构
Introduction to governance and good governance
治理和善治引论
Political economy analysis of global climate governance
全球气候治理的政治经济学分析
Governance: Interpretation of governance
Governance: 治理的阐释
From governance to rural-urban co-governance: Research frontiers, trends, and the Chinese paths
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

Governance has become an important theoretical and practical issue of multi-disciplinary concern. In the context of rapid urbanization and wide rural-urban disparity, rural-urban governance is particularly important for China. Based on the Chinese and international governance theories, the key aspects of governance include: an open system, self-organization, and the interactive relationship between power and rights. Internationally the research frontier focuses on the governance of social-ecological systems, while urban governance has grown significantly, and rural governance has also risen in recent years. The research trend and policy evolution of governance in China indicate that China has undergone a comprehensive transformation from management to governance by top-level design, and rural-urban governance is becoming a key issue. The main path of China's rural-urban governance in the future lies in three aspects. First, it is necessary to shift from power-oriented to rights-oriented governance. Second, equal attention needs to be paid to both ecological environment and social governance instead of focusing only on social, single-dimensional, and urban governance systems, and form a rural-urban co-governance system with the participation of multiple subjects. Third, it should be launched to assist rural and urban vulnerable groups actively. Rural-urban co-governance will become a new growth point for theories, and multi-disciplinary, multi-subject, and multi-department collaboration is much needed.
从治理到城乡治理: 国际前沿、发展态势与中国路径
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.002
[本文引用: 2]

治理已经成为多学科关注的重要理论与现实问题。在快速城镇化和城乡差距居高不下的背景下,城乡治理对中国而言尤为重要。论文通过梳理国内外治理理论,概括治理的要点为开放系统、自组织、权力与权利的交织3个方面。国际研究强调社会生态系统的治理,城市治理增势显著,乡村治理研究开始兴起。中国在顶层设计上经历了从管理到治理的全面转型,城乡治理逐渐成为研究和政策实践的关键议题。未来中国城乡治理的主要路径在于:从权力导向转向权利导向;从只注重社会维度、一元化的、城市偏向的治理模式转向生态环境与社会治理并重,形成多元主体参与的城乡共治体系;积极开展城乡弱势群体的扶持救助工作。城乡共治将会成为新的理论增长点,需要进行多学科、多主体、多部门的协同工作。
'Governance' as a bridge between disciplines: Cross-disciplinary inspiration regarding shifts in governance and problems of governability, accountability and legitimacy
DOI:10.1111/j.1475-6765.2004.00149.x URL [本文引用: 1]
On regional/urban governance of urban agglomeration development areas in China
试论中国城镇群体发展地区区域/城市管治
Governance trends and their impact on human settlements
管治思潮及其对人居环境领域的影响
Study of the system of the space governance on digital city
数字城市空间管治体系模式的探讨
The progress and characteristics of Chinese human geography over the past 70 years
中国人文地理学70年创新发展与学术特色
Progress of applied research of physical geography and living environment in China from 1949 to 2019
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202009001
[本文引用: 1]

Physical geography is a basic discipline of natural science. Since its research object is the natural environment, it is closely related to human survival and development. China's natural environment is complex and diverse; therefore, according to national demand and regional development needs, physical geographers have also made remarkable achievements in applied foundation and application, making important contributions to the planning of national major economic construction and social development, protection of macro-ecosystem and resources and environment, and regional sustainable development. This paper summarizes the practice and application of physical geography in China in the last 70 years (1949-2019), differences between the natural environment and natural zoning, land use/cover change, natural disasters and risk prevention and control, the process of desertification and its administration, lower-yield field transformation of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, engineering construction of permafrost areas, geochemical element abnormity and endemic disease prevention and control, positioning observation of natural geographical factors, geographical spatial heterogeneity identification, and geographical detector. Finally, it proposes the future application research directions of physical geography.
1949—2019年中国自然地理学与生存环境应用研究进展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202009001
[本文引用: 1]

自然地理学是一门以基础研究见长的自然科学,其研究对象是与人类生存和发展密切相关的自然环境。中国的自然环境复杂多样,自然地理学家根据国家需求和区域发展在应用基础和应用研究方面同样取得显著成效,为国家重大经济建设、社会发展的规划,宏观生态系统与资源环境保护及区域可持续发展做出了重要贡献。本文总结了1949—2019年中国自然地理学在自然环境区域差异与自然区划、土地利用与覆被变化、自然灾害致灾因子和风险防控、荒漠化过程与防治、黄淮海中低产田改造、冻土区工程建设、地球化学元素异常和地方病防治、自然地理要素定位观测、地理空间分异性识别和地理探测器等方面的实践与应用,指出了未来自然地理学的应用研究方向。
Information geography: The information revolution reshapes geography
DOI:10.1360/SSTe-2021-0184 URL [本文引用: 1]
信息地理学: 信息革命重塑地理学
Geographic information science development and technological application
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012004
[本文引用: 1]

This study reviews the historical process of the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in the field of geographic information science. From the early survey and cartography research, to the creation of China's geographic information discipline and the establishment of the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information Systems, the development of the institute represents the history of (i) the development of original geographic information theory with Chinese characteristics, (ii) independent research and development of world-class geographic information software, and (iii) geographic information providing solid scientific and technological support for major national strategies. Generally, the development of geographic information discipline was summarized from the aspects of cartography, geoscience remote sensing, geographic information science, geodata sharing, major technological breakthroughs and national strategic support. Finally, from the perspectives of geoscience knowledge graphs, geographic big data analysis, remote sensing artificial intelligence, geographic system simulation and knowledge services, we look forward to the development of new scientific paradigms in geographic science.
地理信息科学发展与技术应用
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012004
[本文引用: 1]

本文回顾了中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所在地理信息科学研究与技术应用方面的历史过程,从早期的测量和制图的研究,到开创中国地理信息学科,建立资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室的历史,是中国特色原创地理信息理论发展的历史,是中国具备自主研发世界级地理信息软件的历史,是地理信息为国家重大战略提供坚实科技支撑的历史。本文主要从地图学、地学遥感、地理信息科学、地学数据共享、重大技术突破和国家战略支撑等方面进行概述,最后从地学知识图谱、地理大数据分析、遥感人工智能、地理系统模拟和知识服务角度展望地理科学发展的新科学范式。
The paradigm transformation of geography from the perspective of complexity sciences
DOI:10.11821/xb201011001
[本文引用: 1]

Geographic System is fundamentally a complex system with properties (e.g. emergence, nonlinearity, feedbacks, self organization, path dependence, adaptation, and multiple scales) that cannot be explained through understanding the components parts individually. Complexity sciences, rising in the 1980s, has brought a new perspective for the paradigm transformation of geography. This paper briefly reviews the development of complexity sciences and the changing paradigm of geography. Then the performance, characteristics, and causes of complexity in geographic system are explained and analyzed thoroughly. Paradigms, including ontology, epistemology and methodology between classical geography and geography from the perspective of complexity sciences are compared. Six methods (i.e. soft computing, simulating, scaling, Geographic Information System, metaphor and meta-synthetic method) are summarized for the study of complexity in geographic system. In the end, the authors conclude that the paradigm transformation of geography from the perspective of complexity sciences lies in the formation of a new and innovative thinking, which is considered a beyond reductionism, holistic and pattern/process based generalized evolutionary thinking.
复杂性科学视角下的地理学研究范式转型
DOI:10.11821/xb201011001
[本文引用: 1]

随着复杂性科学的兴起,地理学研究范式正逐步发生改变。本文在回顾复杂性科学发展历程和当代地理学研究范式变迁的基础上,对地理系统复杂性的表现、特点、成因及其相关的研究方法作了较为详细的解释和说明,比较了传统经典地理学研究范式与复杂性科学视角下地理学研究范式的差异,最后探讨了复杂性地理学思维的创新与发展图景,即超越还原论的地理学整体思维和地学格局与过程的广义进化思维。
Common property institutions and sustainable governance of resources
DOI:10.1016/S0305-750X(01)00063-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Cities and the geographies of "actually existing neoliberalism"
DOI:10.1111/1467-8330.00246 URL [本文引用: 1]
The struggle to govern the commons
DOI:10.1126/science.1091015
PMID:14671286
[本文引用: 1]

Human institutions--ways of organizing activities--affect the resilience of the environment. Locally evolved institutional arrangements governed by stable communities and buffered from outside forces have sustained resources successfully for centuries, although they often fail when rapid change occurs. Ideal conditions for governance are increasingly rare. Critical problems, such as transboundary pollution, tropical deforestation, and climate change, are at larger scales and involve nonlocal influences. Promising strategies for addressing these problems include dialogue among interested parties, officials, and scientists; complex, redundant, and layered institutions; a mix of institutional types; and designs that facilitate experimentation, learning, and change.
Collaborative governance in theory and practice
DOI:10.1093/jopart/mum032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Environmental governance
DOI:10.1146/annurev.energy.31.042605.135621 URL [本文引用: 1]
Governance innovation and the citizen: The janus face of governance-beyond-the-state
DOI:10.1080/00420980500279869 URL [本文引用: 1]
The anthropocene: From global change to planetary stewardship
DOI:10.1007/s13280-011-0185-x URL [本文引用: 1]
The sustainable mobility paradigm
DOI:10.1016/j.tranpol.2007.10.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Resilience for whom? Emerging critical geographies of socio-ecological resilience
DOI:10.1111/gec3.12154 URL [本文引用: 1]
Strategic thinking of modern water management in China based on the "double management" concept
基于“双治”理念的中国现代治水战略思考
Ecosystem science research and ecosystem management
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012006
[本文引用: 1]

Ecosystem ecology is the core content of ecosystem science in the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGNSRR). Our first mission is to develop techniques and methods of ecosystem monitoring and simulation, by which we explore the theories and pathways in solving eco-environmental issues at regional scales. Second, we monitor ecosystem changes, identify the dynamics and patterns, and advance the discipline developments of ecosystem ecology, biogeography ecology, global change ecology, and eco-informatics. Third, we serve for the national and regional ecological constructions by addressing issues related to global changes and regional sustainable developments. To meet national needs, we synthesize and innovate technique and modes of ecosystem management for typical regions of China, i.e. agricultural regions of northern China, hilly red soil forestry regions of southern China, agricultural and pastoral regions of the Tibetan Plateau and Loess Plateau. Utilizing these innovated management modes, we aim to solve fundamental problems in ecological construction and adapt to global changes, and facilitate science advance in regional ecosystem management. Our research directions comprise the following five fields: (1) network monitoring, simulation and ecosystem data management; (2) ecosystem structure, process and function; (3) ecosystem pattern and the underlying mechanism; (4) ecosystem responses and adaptation to global change; (5) ecosystem management and ecosystem services. Centered around the above five foci research directions, we systematically explore theories of ecosystem ecology and their applications, through which we position our research in frontier lines of China and the world.
生态系统科学研究与生态系统管理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012006
[本文引用: 1]

中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所生态系统学科以生态系统生态学研究为核心,通过研制生态系统观测和模拟分析的技术和方法,探索解决区域性/大尺度生态学问题的理论和方法,监测生态系统变化,认知生态系统变化规律,推动生态系统生态学、生物地理生态学、全球变化生态学和生态信息科学技术的发展,创新生态系统管理模式,服务于国家和地方的生态建设、应对全球变化及区域可持续发展。面向国家重大需求,在中国华北平原农业区、南方红壤丘陵林业区、青藏高原农牧区以及黄土高原区等典型区域开展生态系统管理技术与模式的集成与创新研究,着力解决国家生态文明建设和应对全球气候变化中的重大生态学问题,推动区域生态系统管理领域的科技进步。围绕生态系统生态学学科前沿,着重在① 生态系统联网观测、模拟与信息管理,② 生态系统结构、过程与功能,③ 生态系统空间格局与机制,④ 生态系统对全球变化的响应与适应,⑤ 生态系统管理与生态系统服务等五大主要研究方向,系统开展生态系统生态学前沿理论和实践的创新研究,研究成果处于国内和国际生态学研究的科学前沿。
Innovative development and prospect of physical geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012002
[本文引用: 1]

Physical geography (PG) has always been the core discipline of the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGSNRR, CAS) since its establishment in 1940. It aims to serve the grand needs of national development. PG has made significant scientific and technological achievements and progress in the fields of comprehensive physical geography, climatology, geomorphology, hydrology, soil geography, biogeography, chemical geography, etc. These achievements have set up the worldwide priority status of PG, and made great contributions to the scientific and technological innovation, regional sustainable economic and social development. This paper reviews the innovative development of PG in the IGSNRR, summarizes the academic achievements and landmark progress, and looks forward to the future development strategy. Four key points are presented including the interaction mechanism of land surface elements-process, the dynamics of land surface pattern, the comprehensive integration and simulation of process of land surface system, and the sustainable paradigm and regulation mechanism of orderly human activities of land surface system.
自然地理学创新发展与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012002
[本文引用: 1]

自然地理学自中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所建立以来一直是立所的核心学科,长期以服务国家重大需求为使命,在综合自然地理、气候、地貌、水文、土壤地理、生物地理、化学地理等各学科领域取得一批重要科技成果和进展,奠定了自然地理各分支学科在国内外的优势,为国家科技创新、区域经济社会可持续发展做出了重要贡献。本文回顾了中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所自然地理学的创新发展历程,总结了自然地理学取得的学术成就与标志性进展,并展望了中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所自然地理学未来发展,提出以陆地表层要素—过程交互作用机制,陆地表层格局动态研究,陆地表层系统过程的综合集成与模拟,陆地表层系统有序人类活动的可持续范式和调控机制为核心的发展战略。
Unified management of natural resources: A new era, new characteristics, and new trend
DOI:10.18402/resci.2019.01.01
[本文引用: 1]

Both the development goal of beautiful China and the national strategy of ecological civilization construction put forward a higher requirement for the management of natural resources in the new era. It is an inevitable requirement for the harmonious coexistence between human beings and nature to unify management of natural resources. In addition, it is a basic character for the sustainable development of mankind. This study has revealed basic characteristics and significance of natural resources based on integrality, region, systematisms, and property. We also summarize the strategies, foundation, and applications of natural resources science and technology support in the new era of land maintenance. Through the accumulation of relevant study, we further explore the new trend of scientific and technological support for the unified management of natural resources in three aspects: the revelation of the overall characteristics, the recognition of systematic laws, and the discovery of correlation relations.
自然资源统一管理: 新时代、新特征、新趋向
DOI:10.18402/resci.2019.01.01
[本文引用: 1]

自然资源统一管理是人与自然和谐共处的必然要求,也是人类永续发展的基本支撑。本研究通过揭示自然资源的整体性、地域性、系统性、资产性、基础性的特征及时代意义,总结出在新的养地时代自然资源科技支撑所具有的战略性、基础性和应用性。通过相关研究积累,在整体性特征揭示、系统性规律认知和关联性关系发现三个方面探索出自然资源统一管理科技支撑的新趋向。
Economic geography for spatial governance
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408007
[本文引用: 1]

Economic geography is a discipline that studies geographical practices in the real world and plays an important role in supporting the state's strategic decision-making on spatial development and helping to understand spatial issues and solutions in contemporary society. Thus, the discipline's vitality lies with its capability to satisfy the demands of the state and society. At present, the development of economic geography in China is facing two critical challenges or opportunities. First, the Communist Party of China, the ruling party, lists modernization and enhancement of national governance capability as a major target of deepening reforms in China, which indicates reforms in the country are moving from target-oriented (i.e., crossing the river by feeling the stones) to institutional building and capability enhancement. Second, recently the International Council for Science and the International Social Science Council co-launched a large scientific program, i.e. the Future Earth, which calls for inter-disciplinary research for managing the Earth's environment and moving towards sustainable development, and China has established its national committee on Future Earth. The program emphasizes the connection of research to decision-making of both the state and society. Against these two opportunities, this paper suggests an economic geography for spatial governance to lift the discipline's capability to engage with the state and society. Then the paper gives a general discussion of the political, administrative and cultural basis on which China's unique governance structure has developed, as well as a general picture of major tools that the Chinese government has taken for spatial governance, including planning, land, Hukou, and fiscal and tax systems. This paper argues economic geographers can do a better job only if they have a better understanding and theorization of China's national governance structure although they were inclined to do research either at local and global scales or global-local connections and ignored the national scale in the past.
经济地理学与空间治理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408007
[本文引用: 1]

经济地理学是一门研究真实世界的学科,在社会实践中发挥着重要作用。满足国家和社会的需求,是这个学科发展的生命力所在。针对当前全面深化改革的新形势以及“未来地球”计划的提出,本文倡导开展面向空间治理的经济地理学研究,提高该学科服务于国家战略决策的能力。之后本文阐述了中国空间治理的政治文化基础;分析了中国空间治理的主要手段,包括规划体制、土地制度、户籍制度和财税体制。本文认为,只有客观、全面地观察中国的空间治理体系,并将其理论知识化,才能使经济地理学研究具有更大的科学价值和实践意义,也才能为国家提高空间治理能力提供科学支撑。
Spatial governance: Political economy of China's urban and rural planning transformation
空间治理: 中国城乡规划转型的政治经济学
High-end geography and resource think-tank to meet the demands of national development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012008
[本文引用: 1]

Geography and resource think-tank is geared to the demands of national development strategy, combining the discipline characteristic between resources science and geographical science, through long-term scientific research, computational experiments, and the accumulation of experience. It aims at the pressing, realistic and long-term issues in the national development, and submits scientific advice to all levels of governments and policy makers in advance. The construction of think-tank is an important part of the national soft power and the modernization of national governance ability. The geography and resource think-tank has a very important strategic position in the discipline construction and development. Since 80 years ago, geographical science has attained great achievements in the spread of human civilization and sustainable development, and resources science has made a significant contribution to the sustainable use and safety guarantee of national resources. It is the bounden duty and mission of the present and the future to build a new think-tank system of geography and resources with Chinese characteristics to better serve the overall work of the government. This paper reviews the remarkable achievements of the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research (IGSNRR) in think-tank over the past 80 years, especially since 2000. We summarize the key areas and feature directions of the think-tank, including the comprehensive scientific survey and resource environmental bearing capacity evaluation, analysis of national conditions and regional sustainable development, new urbanization and rural revitalization, Beautiful China Initiative and the ecological civilization system, Belt and Road Initiative and national security, eco-environmental protection and disaster prevention and mitigation. Furthermore, we will continue to target at the national development strategic needs, enhance the strategic position of think-tank in the institute development and discipline construction, build think-tank centering on the national "two centenary goals", and achieve the SDGs as the benchmark. We will continue to conduct research centering on the building of a beautiful China and an ecological civilization system, aiming at national major regional development strategies and major emergency events, strengthen the scientific and technological support by geographic simulation and artificial intelligence, and promote the discipline level with the construction of think tanks. We will strive to build the Institute into the most influential national high-end think-tank and become the backbone force of the think-tank products and the support of national development decisions through 5-10 years of efforts.
地理科学与资源科学的国家智库建设
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202012008
[本文引用: 1]

地理科学与资源科学智库建设在地理科学与资源科学发展及学科建设中具有非常重要的战略地位。中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所建所80年来,地理科学与资源科学智库为传播人类文明、保障国家资源安全和持续利用、维护国家和全球可持续发展做出了重大贡献。本文回顾了80年来、尤其是2000年以来地理资源所在高端智库建设方面取得的辉煌成就,以时间为主线,总结了智库建设的重点领域及特色方向,包括综合科学考察与资源环境承载力评价、国家重大区划与规划、国情分析与区域可持续发展、新型城镇化与城市群建设、精准扶贫与乡村振兴、生态文明体制改革与美丽中国建设、“一带一路”建设与国家安全、生态环境保护与科技防灾减灾等方面研究和决策服务;提出要继续瞄准国家发展战略需求,继续提升智库建设在研究所发展与学科建设的战略地位、围绕国家“两个一百年”奋斗目标、对标SDGs实现国家可持续发展目标建好智库,围绕美丽中国与生态文明制度建设、国家重大区域发展战略和应急重大事件建好智库,强化地理模拟技术和智能化技术对智库建设的技术支撑,以智库建设推动地理科学与资源科学建设。力争通过5~10年努力,把研究所建成最具影响力的国家高端智库,成为生产智库产品和支撑国家发展决策的中坚力量。
Geographical thinking on the relationship between beautiful China and land spatial planning
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912004
[本文引用: 1]

Beautiful China is the new goal of ecological civilization construction in the new era of socialism, which can meet the real needs of the people for a better life. National land space planning is a major deployment of the state to coordinate various types of space planning. Beautiful China is the new leading goal of the country's second centenary development. Its connotation is not only "ecological beauty", but also the comprehensive beauty of "economy-politics-culture-society-ecology". The construction of beautiful China needs a differentiated evaluation index system based on the local conditions. Beautiful China is closely related to the land spatial planning. The former provides an important direction for the latter, while the latter provides an important approach and space guarantee for the construction of the former. The establishment of land spatial planning needs to strengthen the further discussion of the regional system of human-environment interaction, point-axis system, the main functional area planning, sustainable development and resource environmental carrying capacity, new urbanization and rural regional multi-body system. This paper puts forward the thinking framework of land spatial planning from the perspective of geography, including scientifically analyzing the natural geographical conditions, economic and social development basis, and the interrelationship between land and space, planing the goal, vision and path of land and space, encouraging the public to participate in and carry out dynamic evaluation, and building an intelligent system platform for land and spatial planning with the goal of beautiful China, which provide ideas for the compilation and implementation of land spatial planning.
美丽中国与国土空间规划关系的地理学思考
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912004
[本文引用: 1]

美丽中国是社会主义新时代生态文明建设的新目标愿景,满足人民群众对美好生活向往的现实需求。国土空间规划是国家统筹涉及空间各类规划的重大部署。美丽中国是国家第二个一百年发展新的引领目标,其内涵不仅是“生态美丽”,也是“经济—政治—文化—社会—生态”综合的大美丽,美丽中国建设要因地制宜构建差异化的评估指标体系。美丽中国和国土空间规划有着密切联系,美丽中国为国土空间规划指引了重要方向,国土空间规划则为美丽中国建设提供了重要途径和空间保障。国土空间规划编制需要加强人地关系地域系统、点—轴系统、主体功能区划、可持续发展与资源环境承载力、新型城镇化、乡村地域多体系统等深入探讨。本文提出了地理学视角下国土空间规划编制的思路框架,科学分析国土空间的自然地理条件、经济社会发展基础、国土空间相互联系,结合美丽中国目标,谋划国土空间的目标、愿景与路径,鼓励公众参与与开展动态评估,构建智能系统平台等,为国土空间规划编制实施提供思路借鉴。
Progress and the future direction of research into urban agglomeration in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408009
[本文引用: 1]

Urban agglomeration has been the inevitable result of China's rapid industrialization and urbanization over the last 30 years. Since the early 2000s, urban agglomeration has become the new regional unit participating in international competition and the division of labor. China has declared urban agglomeration the main spatial component of new types of urbanization over the next decade as clarified at the first Central Urbanization Working Conference and in the National New-type Urbanization Plan (2014?2020). However, research on urban agglomeration remains weak and needs to be strengthened. From 1934 to 2013, only 19 papers published in Acta Geographica Sinica contained the theme of urban agglomeration (0.55% of the total number of articles published) and the first paper on urban agglomeration appeared less than 10 years ago. Despite a small number of divergent studies, this work has contributed to and guided the formation of the overall pattern of urban agglomeration in China. For example, spatial analyses have promoted the formation of the fundamental framework of China's urban agglomeration spatial structure and guided the National New-type Urbanization Plan; spatial identification standards and technical processes have played an important role in identifying the scope and extent of urban agglomeration; serial studies have facilitated pragmatic research; and problems with the formation and development of urban agglomeration have provided a warning for future choices and Chinese development. Future research into urban agglomeration in China should (1) review and examine new problems in China's urban agglomeration options and cultivation; (2) critically consider urban agglomeration when promoting the formation of the 5+9+6 spatial pattern; (3) rely on urban agglomeration to construct new urbanization patterns such as 'stringing the agglomerations with the axis, supporting the axis with the agglomerations'; and (4) deepen national awareness about resources, environment effects and environmental carrying capacity in high density urban agglomerations, management and government coordination innovation, the construction of public finance and fiscal reserve mechanisms, the technical regulation of urban agglomeration planning, and standards for identifying the scope and extent of urban agglomeration.
中国城市群研究取得的重要进展与未来发展方向
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201408009
[本文引用: 1]

中国的城市群是近30年来伴随国家新型工业化和新型城镇化发展到较高阶段的必然产物,自21世纪初期城市群成为国家参与全球竞争与国际分工的全新地域单元之后,中国连续10年把城市群提升为推进国家新型城镇化的空间主体,首次召开的中央城镇化工作会议和《国家新型城镇化规划 (2014-2020年)》进一步明确了城市群作为推进国家新型城镇化的主体地位。然而,城市群在中国的研究目前尚处在亟待加强的薄弱环节。系统总结从1934-2013年的80年间发表在地理学报的城市群主题论文,只有不到19篇,仅占总篇数的0.55%,不仅发表篇数少,而且发表时间短,首次发表城市群研究成果不到10年,研究单位和作者群体集中,研究内容瞄准国家需求但比较发散。即便如此,仅有的城市群研究成果还是对国家城市群总体格局的形成起到了引领作用,做出了重要贡献。具体体现在,提出的城市群空间格局推动国家形成了中国城市群空间结构的基本框架,引导国家新型城镇化规划把城市群作为推进新型城镇化的主体形态,提出的城市群空间范围识别标准与技术流程对界定国家城市群范围起到了重要作用,提出的城市群系列研究领域带动城市群的研究向着纵深与实用方向拓展,提出的中国城市群形成发育中存在的问题对未来城市群的选择与发展起到了警示作用。以这些研究进展和成果为基础,未来中国城市群选择与培育的重点方向为:以问题为导向,深刻反思检讨中国城市群选择与发育中暴露出的新问题;以城市群为主体,重点推动形成“5+9+6”的中国城市群空间结构新格局;以城市群为依托,重点推动形成“以轴串群、以群托轴”的国家城镇化新格局;以国家战略需求为导向,继续深化对城市群形成发育中重大科学问题的新认知,包括深入研究城市群高密度集聚的资源环境效应,科学求解城市群高密度集聚的资源环境承载力,创新城市群形成发育的管理体制和政府协调机制,研究建立城市群公共财政制度与公共财政储备机制,研究制定城市群规划编制技术规程与城市群空间范围界定标准等。
Research progress and prospect on development geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002002
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, we review and sort out research progress on development geography since the 20th century, involving its connotation and theory, fields and methods, and development trends in this paper. Specifically, we systematically reviewed the research and application of development geography in the fields such as in the convergence of underdeveloped countries or regions, the convergence in the process of improving the quality of life in developed countries or regions. Then, in line with the analysis of the research progress on development geography in foreign countries, we indicate the development conditions and disciplinary advantages of development geography in China. Further, we pointed that future development geography research in China should focus more on the latest international academic frontier research and national macro-strategic needs. The future research of development geography should be guided by the theory of sustainable development, with the core of improving the sustainable livelihood capacity and regional green development level in underdeveloped areas, and aiming at constructing industrial policy and development geography theory and interdisciplinary integrated research system, and focusing on research on the spatial pattern, diffusion characteristics and convergence mechanism of regional development, to explore the regulatory policies and scientific paths that serve regional economic construction and industrial development.
发展地理学研究进展与展望
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002002
[本文引用: 1]

本文回顾和总结了20世纪以来发展地理学的研究进展,涉及发展地理学内涵和理论、领域和方法及其发展趋势。系统梳理了发展地理学在欠发达国家或地区发展收敛、发达地区或国家生活品质提升过程中的收敛及其路径等研究内容。通过分析国外研究进展,指出了发展地理学在中国的发展条件与学科优势,并着眼于国际学术前沿最新动向与国家宏观战略需求,提出了今后中国发展地理学研究需重点关注的领域。未来发展地理学研究应以可持续发展理论为指引,以提升欠发达地区可持续生计能力与区域绿色发展水平为核心,以构建发展地理学理论和跨学科综合集成研究体系为目标,聚焦区域发展的空间格局、扩散特征与收敛研究,探索出服务于区域经济建设与产业发展的调控政策与科学路径。
Rural spatial governance and urban-rural integration development
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 1]

The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
论乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006013
[本文引用: 1]

构建现代乡村治理体系成为推动城乡融合发展和乡村振兴的重要内容。破解乡村空间利用过程中出现的发展空间受限、权属关系不明和组织体系不畅等系统性问题,成为乡村空间治理的首要任务。本文从乡村空间“物质—权属—组织”综合治理的视角出发,尝试解析乡村空间治理在推动乡村空间重构、权属关系重塑和组织体系重建中的作用机制,并进一步探讨乡村空间治理优化城乡格局、改善城乡互动关系、推动城乡融合发展的可行路径。结论如下:物质空间治理可作为乡村空间结构和功能优化的重要手段,空间权属治理有助于保障乡村空间不同参与主体的发展权利,空间组织治理可提升乡村空间的组织效率;乡村空间治理导向的“人口—土地—产业”转型过程为“深化空间治理—活化乡村空间—优化人地关系—改善城乡格局”的分析思路创造条件;乡村空间治理推动城乡发展格局不断演化,城乡互动关系改善成为推动城乡融合发展和破解乡村发展困境的重要依据。最后,本文构建了乡村空间治理与城乡融合发展互动分析框架,并探讨了乡村空间治理与国土空间规划的内在关系及研究趋势。
Causes of sand-stormy weather in northern China and control measures
DOI:10.11821/xb200005001
[本文引用: 1]

In northern China, the number of days with sand stormy weather has been decreasing in the past 40 years, but in the spring of 2000, an unprecedented heavy sand stormy weather with high frequency took place, which exerts adverse effect on traffic, environmental management and people’s daily life and work. Especially, it brought direct damage to Beijing, Tianjin and their neighbouring areas, which has aroused even more extensive concern of personages of various circles. Therefore, the reasons and the rational suggestions are proposed in this paper. The sand stormy weather is the result of the special geographic environment and weather conditions. Changes in the number of days of strong wind are the reflections of the periodical change in climate. Why the strong sand stormy weather took place is that the anti El Nin~o case is at top, and the land cover deteriorates in the whole area but with part area improving. The dust weather mainly originated from mid west Inner Mongolia and northwest of Hebei Province. The dust is mainly consisted of soil dust from the origination area and the trace. The ground bare soil and sandy dust from construction site in urban extension areas also supplied materials for the local dust. In order to alleviate and control the dust damage, some suggestions were proposed as following: Firstly, the natural vegetation must be restored through planting tree or grasses in cultivated land instead of planting crops. Especially effective ecological protective shield must be established for Beijing and Tianjin city. The bare land of urban marginal areas must be treated in order to control local dust. Secondly, eco environmental construction must be paid more attention to during implementing Western Development Plan. Ecological benefits must be combined with economic and social benefits. Finally, the system for monitoring and predicting the sand stormy weather must be established and improved. Study on controlling and alleviating the dust disaster also need to be done.
关于我国华北沙尘天气的成因与治理对策
DOI:10.11821/xb200005001
[本文引用: 1]

2000年春季,我国华北沙尘天气次数陡增,影响广泛,损失明显增加。利用长期气象观测数据,结合遥感和GIS技术,对今年华北沙尘天气的成因进行分析,提出造成沙尘天气的原因在于:1北方地区大风日数的增减是气候周期性变化的反映,今年强沙尘天气陡增是因为处于反厄尔尼诺事件的高峰期所致;2我国北方地表覆被状况局部改善、整体恶化也是今年强沙尘天气产生的另一重要原因。影响华北地区的沙尘天气主要发源于内蒙古中西部和河北西北部,发源地及沿途地表粉尘是沙尘的主体,城市扩展区域的地表裸土与建筑沙石则提供了就地扬沙的物质来源。对今后一个时期内沙尘天气的发展趋势进行分析,认为:在全球增暖和我国北方地表植被状况没有根本好转的情况下,今后如再逢反厄尔尼诺事件等引起的强冬季风年,甚至可能出现更严重的沙尘天气。为此提出建议:做好科学的还林还草工作,大范围地恢复自然植被,为京津地区建立减轻和防止沙尘灾害的有效生态屏障。同时治理城市周边地区,抑制就地起沙;西部开发应重视生态环境建设,把生态效益、经济效益、社会效益结合起来考虑;建立和完善沙尘天气的动态监测和预警系统,做好防灾减灾的科学研究工作。
Globalisation as reterritorialisation: The re-scaling of urban governance in the European Union
DOI:10.1080/0042098993466 URL [本文引用: 1]
Disciplinary structure of geographic science in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109001
[本文引用: 1]

The modern international and domestic science advancements have brought forward new opportunities as well as higher requirements to the development of geographic science in China. In planning the disciplinary structure of geographic science in the "Development Strategy of Discipline and Frontier Research in China (2021-2035)", we propose a modified disciplinary structure for the geographic science in the new era. The geographic science in China can be categorized into four secondary disciplines, i.e., integrated geography, physical geography, human geography, and information geography, considering the current situation and development outlook of geographic science. The tertiary disciplines under each secondary discipline are nearly fully developed, and a few quaternary disciplines under tertiary disciplines have already been widely accepted and used. We hope this new disciplinary structure can play a breakthrough role for improving the branches of geographic science, promoting the development of emerging disciplines under the framework of geographic science, and better serving the international and domestic development needs in the new era.
中国地理科学学科体系浅析
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109001
[本文引用: 1]

新的国际和国内形势为地理科学带了新的发展机遇,同时也提出了更高的要求。以《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划为契机,本文系统梳理了新时期地理科学的学科体系。根据地理科学现状和发展趋势,中国地理科学可划分为综合地理学、自然地理学、人文地理学和信息地理学4个二级学科,各二级学科下的三级学科也基本成熟,有些三级学科下的四级学科名称也在普遍使用。我们希望以这一新的学科体系为支点,完善地理科学的学科分支,推动地理科学框架下新兴学科的发展,更好地服务于新时期国际及国家的战略需求。
Disciplinary structure and development strategy of physical geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109002
[本文引用: 1]

Physical geography, one of the branches of geographic science, is the basic discipline of geographic science. And it is the scientific foundation of ecology, environmental science and other related disciplines. Physical geography focuses on spatial characteristics, evolution and regional differentiation of the earth's surface. In the new period of rapid development of social economy, and science and technology, physical geography is more closely and widely connected with human geography and, information geography. Based on "The Development Strategy of Discipline and the Frontier Research (2021-2035)" and geography subject planning, this paper analyzed the forming process of the physical geography, expressed sub-discipline structure of comprehensive physical geography, sectoral physical geography, human survival environment, and proposed the development strategy of physical geography and its branch disciplines, key priority of development goals and directions.
自然地理学学科体系与发展战略要点
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109002
[本文引用: 1]

自然地理学是地理科学的一门基础学科,同时也是生态学、环境科学等相关学科的科学基础。自然地理学重点研究地球表层自然环境的空间特征、演变过程及其地域分异规律,以及过去人—环境相互作用的发展过程。在社会经济和科学技术快速发展的新时期,自然地理学与综合地理学、人文地理学、信息地理学的联系更加密切和广泛。本文结合《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划,分析自然地理学学科的形成过程,阐述综合自然地理学、部门自然地理学、人类生存环境学的分支学科体系,提出自然地理学及其分支学科的学科发展战略布局、优先领域发展目标和重点方向。
Disciplinary structure and development strategy of human geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109003
[本文引用: 1]

Human geography is a discipline which studies the formation and evolution of the geographical distribution pattern of human activities. The main research objects of human geography focus on human activities and human-earth relationship. The scientific questions to be answered by human geography cover both natural science and social science, and thus it has distinctive interdisciplinary features. In China, the economic and social processes of human activities are playing an important role in explaining the law in human geography discipline as human society development is approaching or has entered the post-industrialization stage. The logics and methods of social science have become important tools through which the changes in processes and patterns of human geography can be reasonably discussed and properly understood. Research methodology of human geography shows integration characteristics between natural sciences and social sciences. The outcomes of human geography research reveal scientific laws in geographical distribution pattern and evolution of human activities. It becomes one of primary disciplines for both the national and local governments to manage and optimize the pattern of spatial development and protection. It has wide applications in spatial planning, regional strategy and policy making, and the modernization of spatial governance. The unique feature in integrating academic research and policy-making applications provides human geography discipline in China a superiority of leading the world in the discipline. Besides comprehensive human geography, human geography in China has five subdisciplines, namely, economic geography, urban geography, rural geography, social and cultural geography and political geography. Each subdiscipline has priority and key research fields, and coordinates with the rest of subdisciplines.
人文地理学学科体系与发展战略要点
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109003
[本文引用: 1]

本文属于《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学学科规划的系列成果之一,写作组在对人文地理学学科发展进行系统梳理与分析判研的基础上,在本文中侧重介绍未来15年的中国人文地理学学科体系与发展战略要点。人文地理学是研究人类活动地理分布格局形成和演变规律的一门学科。随着人类发展临近和进入后工业化阶段,人类活动的经济社会过程对人文地理分布规律的影响越来越重要,社会科学研究思维和方法已成为探讨和理解变化的人文地理过程和格局的重要途径,人文地理学研究方法论也呈现出自然科学和社会科学综合集成的特色。人文地理学研究的成果产出,揭示了人类活动地理分布格局和演变的科学规律,成为调控和优化国土空间开发保护格局的科学基础,在国土空间规划、区域战略和区域政策制定、空间治理现代化等方面有着广泛的应用,人文地理学的科学研究与决策应用之间具有紧密的关系。根据学科发展现状、趋势及主要产出结果,中国人文地理学可按照5个分支学科群进行学科战略布局,包括综合人文地理学、经济地理学、城市地理学、乡村地理学、社会文化地理学和政治地理学。各分支学科在新时期地理科学学科体系下,具有其优先发展领域与重点方向,相互协调,不断创新。
The construction of discipline system of science of geography and its significance
地理科学的学科体系构建与内涵
Policy transfer, consultants and the geographies of governance
DOI:10.1177/0309132511417659 URL [本文引用: 1]
The review and prospects of China's human and economic geography: The overview of "high level forum of the development of Chinese human and economic geography under the background of change"
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201608012
[本文引用: 1]

On January 22nd and 23rd, 2016, "High level Forum of the Development of Chinese Human and Economic Geography under the background of change" was held in Beijing. More than 30 professors attended this forum. On the conference, they discussed on the major progress of the development of China's Human and Economic Geography, and the existing problems, restraint factors, opportunities, international path, developing direction, prospects in the development of the discipline. In recent years, Human and Economic Geography has boomed, facing many important opportunities for development. To establish an academic community for joint researches on major issues and collaborative innovation is a significant route. We should embrace domestic and international characteristics, to promote China's Human and Economic Geography to go to the world arena. In the meantime, the construction of various series of talents and the growth of young and middle-aged talents are also of great significance.
我国人文与经济地理学发展回顾与展望: 变化大背景下我国人文与经济地理学发展高层论坛综述
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201608012
[本文引用: 1]

2016年1月22-23日,“变化大背景下我国人文与经济地理学发展高层论坛”在北京召开,与会的30余位专家就近年来我国人文与经济地理学发展的主要进展、学科发展存在的问题和制约因素、面临的发展机遇、学科发展的国际化道路、发展的主要重点方向与前景等议题开展了深入交流和研讨。近年来人文与经济地理学蓬勃发展,当前面临着一系列发展的重要机遇,未来发展有着广阔空间。建立学术共同体,针对重大问题开展联合攻关和协同创新;兼容本土化特色与国际化道路,促进中国人文与经济地理学走向世界;推动各系列人才梯队建设和中青年人才成长。
Research on urban governance models based on decentralization: Focus on new towns and new development areas
基于地方分权的城市治理模式研究: 以新城新区为例
On urban governance
论城市管治研究
Economic globalization research based on scale-construction in western human geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.09.001
[本文引用: 1]

Time-space compression in the context of globalization leads to declining costs of communication and transportation and increasing transnational activities. The emergence of multi-national firms and international organizations, in accordance with increasing boundary-crossing activities, has simultaneously weaken the power of state on economic, political, and cultural processes within its territory. Under such circumstances, some researchers assert globalization as "the end of geography", which sounds like an argument of hyper-globalist. In light of scale construction, human geographers are engaged in reconstructing the global scale and relating it to other scales. It turns out that space matters in the process of globalization. Two key points emerge: (1) Scale construction is not necessarily with hierarchical structures. Relation-based scales provide a better model for globalization, which is featured with horizontal communication rather than vertical regulation. (2) Global shifting exhibits trends both towards globalization and localization simultaneously, much of which appears to be global-local nexus rather than simplex globalizing process. These findings introduce new perspectives into globalization research in human geography: framework based on relational network makes it possible to conduct a trans-territorial analysis and to depict a big picture of the reshaping pattern of global economic landscape. On the other hand, in light of localized globalization, researchers set out to refer regional development to global-local interactions other than local embeddedness and endogenous factors, which offers insight into urban and regional governance in the context of globalization.
尺度重构视角下的经济全球化研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2015.09.001
[本文引用: 1]

全球化的“时空压缩”特征降低了要素流动的空间成本,而为组织和协调跨国经济活动而出现的跨国公司与国际组织,导致象征权利范畴的领土边界对经济、文化和政治的影响力不断削弱,进而引发了极端全球主义式的“地理终结”论调。人文地理学者结合全球化的特征,通过改变尺度结构,明确了全球尺度涉及的主体与内容,凸显出地域单元的意义,避免了全球尺度的抽象理解,从而反驳了地理终结论,形成了两个关键认识:①尺度建构不一定建立在相对性的基础上并构成垂直体系,基于关系建构的全球尺度更契合不同主体和空间联系日趋紧密的特征;②全球化与地方化过程是并存的。全球化并不意味着尺度的垂直叠加,而是全球与地方之间的复杂联系。这两个关键认识为人文地理学参与全球化研究形成了独特的视角:一方面,学者们运用立体网络思维,以关键主体与空间为节点、以关系为纽带,实现“超越边界”式的分析;另一方面,全球化与地方化并存的理念也促使城市与区域发展研究从单纯强调区域差异转向探讨区域内外相互作用,为城市与区域治理提供了新思路。
Discipline and anti-discipline: Spatial politics of urban street vending in Guangzhou since the 1990s
DOI:10.11821/xb201108006
[本文引用: 1]

In the recent Western urban geography, the revanchist or post-justice politics of space targeting urban subaltern groups has become a critical concept for understanding urban changes since the 1980s. Current literature has demonstrated the diversity of the revanchist city or urban revanchism which emerges in specific place with“actually existing”form. However, the excluded disadvantaged groups have been always placed in a passive position where they seem to have no agency to respond to the revanchist politics. This article aims to demonstrate the contrariety and instability of such an exclusionary, revanchist politics of space, through the study of spatial politics of urban street vending in Guangzhou since the 1990s. Based upon Lefebvre's space theory, the analysis is conducted within a structure-agency framework. We integrate the methods of analysis of related policy and institution and observation, semi-structure and in-depth interview of street vendors, city managers, residents and indoor shop owners. It is argued that an exclusionary politics of public space essentially includes mutual-contradictory factors consisting of the structural discipline force and anti-discipline force as agency. On the one hand, the revanchist politics of street vendors has been embedded in the process of urban environment improvement strategy for solving the potential crisis of development in the 1980s. A discipline mechanism with an analogous form of panopticism is appropriated by municipal government to regulate and exclude street vendors for the sake of strategic space. On the other hand, the counter spaces are formed through the everyday and episodic form of resistance by street vendors. The former is characterized by tactics of waiting game and docile inobservance, while the latter is marked by individual violence and collective protest. As a result, strategic space is redefined as a tool space by street vendors for sustaining individual survival, alleviating poverty and pursuing freedom. The contrariety of the revanchist politics of space is in its origin a social product, while the conflict situation it engendered will to a large extent lie on the extent to which the discipline and anti-discipline forces coordinate or confront in the practice.
1990年以来广州市摊贩空间政治的规训机制
Why does China today need world geography more than ever
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2020.01.2019801
[本文引用: 1]

As an important branch of China’s geography, world geography refers to the geographical study on regions or countries outside China, which is a special phenomenon of discipline classification in China. This idea that China’s geography has significant difference from China to outside China has done great harm to the development of world geography, which has been difficult to eliminate till now. Ignoring the study on world geography will impose limitations on research horizons, just like seeing partial trees rather than entire forests. In order to implement the spirit of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, prosperously explore new organization mechanisms of scientific research, create the first-class world geography discipline, and serve the needs of the country's major international strategies, more than 100 experts from domestic universities and research institutes gather to discuss the way to the development of China's world geography. The experts agree that geography can be regarded as the foundation of the country and a magic tool of national development. The accelerated reframing of the current world political and economic structure has brought unprecedented historical opportunities for the development of China’s geography, and has endowed geography, especially world geography with the new major historical missions. To this end, it is necessary to give full play to the advantages and specialties of geography, keep up with the development trend of the country and the world, establish a global perspective, face the needs of major national strategies, combine nature and humanities, face sustainable development, unite relevant domestic units to conduct interdisciplinary research, aiming at lifting world geography to a second-level discipline, building up a theoretical system, logical framework and disciplinary paradigm of world geography with Chinese characteristics, and improving the capability of China’s geography, especially world geography, to serve national and local development.
今天的中国为什么比任何时候都需要世界地理学
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2020.01.2019801
[本文引用: 1]

世界地理作为中国地理学的重要分支学科,特指研究中国以外区域或国家的地理学科,是中国特有的学科分类现象。中国地理学的这种内外有别的思想对世界地理发展危害甚大,至今都难以消弭。忽视世界地理研究,就会有只见树木、不见森林之虞。为了贯彻落实党的“十九大”精神,繁荣探索新型科研组织机制,打造一流世界地理学科,服务国家重大国际战略需求,来自国内高校、科研院所的百余人齐聚一堂,探讨中国世界地理学科发展之路。与会专家一致认为:地理学是国家发展的法宝,是立国之本。当前世界政治经济格局加速重构,为中国地理学发展带来了前所未有的历史机遇,也赋予地理学特别是世界地理学学科新的重大历史使命。为此,须充分发挥地理学科的优势和特长,紧跟国家和世界发展大势,树立全球眼光,面向国家重大战略需求,把自然与人文结合起来,面向可持续发展,团结国内各相关单位,进行跨学科研究,提升世界地理学科为二级学科,构建具有中国特色的世界地理学理论体系、逻辑框架和学科范式,提升中国地理学科,特别是世界地理学科服务国家和地方发展的能力。
A review of Chinese internal migration research under the background of new-type urbanization: Topics and prospects
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

Against the background of new-type urbanization, rural-urban migration becomes one of the vital topics for academia and authorities. Meanwhile, migration, as an important spatial phenomenon, brings new opportunities as well as challenge to Chinese cities and society. This means the studies on floating population will be the key part of understanding new-type urbanization in a long time. Therefore, this article investigates the internal mechanism of how migrants make decision, what motivates them to move, and why they stay and attempt to contribute to a better understanding of new-type urbanization in China. This article reviews the recently migration research in China in 4 aspects: 1) Hukou and migration; 2) Circulation, settlement intention and family migration strategies; 3) Social network and migrant communities; 4) Migration, mobility and the everyday practice of migrants. The main findings are as followed: First, the influence of Hukou system becomes decreased while the accommodation, residential modes, residential space, social interactions, everyday life and practice, and identity construction of migrants will draw more attention in future. Second, we should put more emphasas on microcosmic and the everyday life of migrants from the perspective of new cultural geography. In other words, it is important to understand migrants from individual-level research through the lens of mobility. Last but not least, Chinese migration scholars should seize the opportunities to dig the basic geographical research on migration phenomenon, and critically engage with the migration research in western academia. It is important for Chinese scholars to draw the pictures of contemporary Chinese migrants in the era of globalization and to contribute the “Chinese knowledge” to world migration research.
新型城镇化背景下中国流动人口研究: 议题与展望
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

研究通过4个议题(户籍与人口流动,循环流动、定居意愿及家庭策略,社会网络和移民社区,迁移、流动性和移民的日常生活),回顾了近年来乡城人口迁移的研究。指出:户籍政策对移民在城市中的生计带来的影响将减弱,移民的住房及在城市的居住模式和居住空间、社会交往、生活方式、移民身份建构及生活空间的重构等将会成为新的关注点。新文化地理学中关于移民“微观化”“生活化”的研究应受到更多的重视。换言之,如何理解移民在个体层面的诉求和移民的日常生活,将会是未来流动性研究的重点。如何立足于国内移民地理研究的基础与发展机遇,批判性地与西方移民研究搭建对话空间和平台,结合当前中国崛起过程中所呈现的前所未有的全球化与城镇化契机,为世界移民研究积累和贡献“中国知识”,将成为未来这一领域学者研究的方向。
A review on the research of urban and regional governance in China
中国城市与区域管治研究十年回顾与前瞻
Concept of scale in human geography and politics of scale: Based on anglophone human geography since 1980s
尺度的人文地理内涵与尺度政治: 基于1980年代以来英语圈人文地理学的尺度研究
Geopolitical energy security evaluation method and its application based on politics of scale
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201405005
[本文引用: 1]

Combining the theories of politics of scale from political geography, security theory from international relations and energy security theory, and putting the scale conversion of energy contention, geographical relationship and geo-structure in geo-setting, and the three properties of safety in consideration, this paper rebuilds a geo-energy security evaluation model and uses the model to quantitatively evaluate China's geo-oil energy security in the Russian Pacific oil pipeline construction from 1995 to 2010. Five results could be drawn as follows: (1) from the aspect of time, an up-surging Geo-oil Safety Index of China in the Russian Pacific oil pipeline construction indicated an increasing disadvantage of China in the geo-oil contention by politics of scale. If the United States and South Korea are involved, the competition would be further intensified;(2) from the aspect of geopolitical relationship, a general decrease occurred in the Sino-Japan Energy Competition Index, but a specific increase appeared in the competition of energy imports from Russia by China and Japan individually;(3) from the aspect of regional strategy of energy export, an obvious downward tendency in Energy Export Strategy Index showed that Russia has changed its exports destination off Europe;(4) from the aspect of geosecurity, a relatively steady proportion of China's oil consumption and a friendly comprehensive strategic partnership of cooperation between China and Russia reduced the worries of China's geo-oil energy security to some extent;(5) from the aspect of geopolitical structure, the increasing comprehensive national power in China driven by the rapid economic growth will intensify the geo-oil competition in Northeast Asia.
尺度政治视角下的地缘能源安全评价方法及应用
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201405005
[本文引用: 1]

通过引入政治地理学的尺度政治、国际关系学的安全理论和能源安全理论,考虑到能源争夺中的尺度转换、地缘环境中的地缘关系和地缘结构以及安全的三个属性等因素,重新构建了地缘能源安全评价模型,并基于此模型对1995-2010 年俄罗斯太平洋石油管道建设中的中国地缘石油能源安全进行了定量评价。结果表明:① 从时间上来看,中国在俄罗斯太平洋石油管道建设中的地缘石油安全指数不断攀升,中国在此石油能源尺度政治争夺中越来越处于不利地位,考虑到今后韩国、美国等国家的参与,竞争将更加激烈;② 从地缘关系上看,中日两国能源竞争指数趋于减少,但是两国从俄罗斯进口能源竞争加剧;③ 俄罗斯能源出口战略长期以来一直偏重欧洲,但是已经出现转向的趋势,其能源出口战略指数已显著下降;④ 中国石油消费的比重稳定和中俄之间友好关系在一定程度上缓解了中国地缘石油能源安全;⑤ 从地缘结构上来看,中国经济增长带动下的整体综合国力的增强,将会加剧东北亚地区的地缘石油竞争。
Rescaling: Role changing of the state and spatial production strategy of region in the globalization era.
尺度重组: 全球化时代的国家角色转化与区域空间生产策略
Rural-urban co-governance: Multi-scale practice
DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2020.02.021 URL [本文引用: 1]
Reexamining the explanation of China's spatial transformation from the perspective of new state space framework
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.03.014
[本文引用: 1]

New state space (NSS) framework is the main theoretical framework to explain urban and regional spatial transformation under the background of globalization. Researchers in China have introduced NSS to interpret China's spatial reconfiguration process in recent years. This study reviewed the background, key concepts, main ideas, and research findings of NSS in China and internationally, revealing that NSS can provide a unified perspective to analyze global spatial transformation. However, some defects of NSS would lead to serious ontological problems. First, the concepts of NSS have a tendency of generalization, meanwhile, are lack of falsifiability; second, the lack of flexibility of the framework is hard to capture multifaceted situations; third, NSS may complicate the real-world scenarios sometimes, which would go against the intention of theorization. China has unique national spatial administrative structures, governmental relationship, property right arrangement, promotion system of officials, and market economy development path, therefore NSS may run into difficulties to articulate the intricate Chinese contexts because it was proposed based on the background of Western scenarios. That is to say, there are limitations in using NSS to interpret China's spatial transformation—the differences of territorial administrative framework between China and Western countries may lead to correspondence problems of terms and concepts. Different property right arrangement could result in different dimensions of analysis in spatial restructuring. Finally, the complicated power field in China would have different internal driving forces in the process of regional and urban transformation. These problems would result in dilemmas when discussing and exploring the multiple-scalar practical situations and the underlying logic of state spatial transformation. Further, it would be difficult for Chinese academia to engage in in-depth academic exchanges with scholars from other countries, and to have their voice heard in the theoretical study of Chinese spatial transformation. The NSS might be caught in the involution of dogmatization and instrumentalization if it could not concentrate on several core topics related to the ontology of human geography. China is large and complex in territorial areas with multifarious populations, resources, environment, and so on. The special history and development contexts mean that any theories or frameworks would need to be examined in real and practical situations. Therefore, it is urgent to pay more attention to the localization of spatial transformation and governance theories and propose more universal theoretical frameworks to underpin the study of spatial transformation since 1978.
新国家空间框架解读中国空间转型现象的再审视
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.03.014
[本文引用: 1]

作为全球化背景下城市与区域空间转型的主流理论框架,新国家空间(New State Space, NSS)框架已被国内学者应用于诠释中国国家空间重构过程。论文梳理了NSS框架的提出背景、重要概念、主要观点以及国内外相关研究成果,发现NSS框架虽能为碎片化的全球空间治理研究提供一个统一的分析视角与平台,但却可能因概念泛化且缺乏可证伪性、框架固化而难以捕捉繁复情境、复杂化现象问题等潜在缺陷而引发理论本体模糊。同时,中国存在特殊的国土空间行政结构、政府间关系、所有制安排、地方官员晋升机制以及市场经济发展路径,基于欧美背景的NSS框架难以准确解析中国的本地化场景。此外,国内学界对NSS框架涉及的概念术语尚缺乏必要的辨析,在某种程度上存在对本土现象的机械化解读,可能导致难以深入探究多尺度国家空间转型的实际过程与底层逻辑,不能实现国内外学界的深度学术对话,进而无法掌握改革开放以来中国空间转型研究领域的话语权。未来有必要重新审视NSS框架的内涵外延,理性解读中国空间转型的实践,力争以本土化实践为基础,构建更具普适性的理论框架来兼容不同国家的情境,在国际上发出中国学者的声音。
Urban governance and the production of new state spaces in western Europe, 1960-2000
DOI:10.1080/0969229042000282864 URL [本文引用: 1]
Curriculum design for urban informatics
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008016
[本文引用: 1]

GIScience is facing challenges in defining its discipline-specific knowledge and skills due to the rapid development of computer science. Meanwhile, the research paradigm of urban studies is shifting to more quantitative approaches with the emerging big data and various analytics tools. Based on the development pathways of GIScience, we argued that one direction of the future GIS is urban informatics by taking the advantage of spatial modelling and analysis technologies. The transformation from GIS/Geomatics to urban informatics requires transdisciplinary knowledge, methods, and tools to form a new teaching and research framework. An undergraduate curriculum for urban informatics is proposed in this paper based on the notion of transdisciplinary cooperation among GIS, computer science and urban studies, to foster system thinking, spatial thinking and computational thinking in urban informatics teaching. Researchers and educators from urban studies, geography, geomatics and GIS should work together to promote the development of this emerging discipline, so as to achieve more significant scientific discovery and innovations.
融合式研究趋势下的地理信息教学体系探索
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008016
[本文引用: 1]

城市研究的范式在大数据和人工智能的影响下已经发生了巨大变化。本文根据城市研究及地理信息科学的发展历程和学科脉络,提出城市空间信息学是社会和产业需求导向的一个新兴知识领域,也是融合式研究趋势下地理信息教学和研究的一个发展方向。城市规划和地理信息科学两大类专业虽然具备孵化出城市空间信息学人才的学科基础,但是其学科体系都需要较大的改变才能实现突破;从现有的学科设置的体系看,地理空间信息工程专业由于提供了同时培养学生系统思维、空间思维和计算思维的框架,具备发展城市空间信息学本科教育的入口。本文在此基础上提出了城市空间信息工程本科专业的培养方案设计思路,期望能够对城市空间信息学的学科发展以及教学研究带来讨论契机,并推动地理信息学科和城市规划学科的可持续发展。
A review of spatially integrated humanities and social sciences
空间综合人文学与社会科学研究综述
DOI:10.12082/dqxxkx.2020.200232
[本文引用: 1]

地理信息科学与哲学、历史、文学、艺术、社会学、经济学、政治学、管理学等人文学与社会科学进行了全面的深度融合。一方面,地理信息科学领域的学者积极拓展研究领域,为人文学与社会科学领域的学者提供空间化、可视化的技术手段;另一方面,人文学与社会科学领域的学者积极学习和掌握地理信息技术,在研究中积极引入空间思维和空间可视化方法。同时,一些适用于人文学与社会科学研究者的开放平台、代码和工具不断涌现。本文在对空间综合人文学与社会科学的最新进展进行全面总结的基础上,探讨了空间人文学与社会科学研究的思路和框架,并分别对该框架各分支的研究进展进行了梳理和评述,包括:历史GIS,文学GIS,语言学GIS,GIS与哲学、人类动力学、人文地理学等;以及GIS与政治学及国际关系学,GIS与管理学、空间计量经济学、社会地理计算、空间社会网络与空间交互网络、犯罪地理学、健康地理与公共卫生学等。接着,本文对空间综合人文学与社会科学的研究方法进行了分析,包括:空间思维与空间计量、认知心理学与空间认知、空间可视化与虚拟地理分析、平台研发等。最后,对空间综合人文学与社会科学研究的关键问题和未来发展方向进行了展望。
Rebuild place: The thoughts of place in human geography and their connections with GIS.
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

Place is a very important geographical concept. Scholars especially geographers have conducted extensive studies on place. Focusing on the issues and theories of place, this article explores how to couple human geography with Geographic Information System (GIS), with a focus on geographic issues in large-scale urban space and small-scale communities. This is particularly critical for geographic study in China. The main title of this article, "rebuild place", has three meanings. First, it is necessary to break disciplinary boundaries in order to rediscover the new field of "place", especially based on complex and changing theories and practice of place. Second, we should strive to change the "place" in everyday life according to the new theories. Last but not least, rebuilding place in our lives or minds will be achieved by means of coupling theories and practice, thoughts and technology, as well as human geography and GIS. Through using volunteered geographic information (VGI), 3D-VQGIS, and other new GIS methods, the theories and methods on place research can be enriched with big data and other types of data. The combination of human geography and GIS not only has practical significance, but also helps developing new methodologies. Place and scale are complex in reality and in research. For instance, issues in community and in city interact and can be transformed because some micro-scale individual or community events can affect the whole city or urban culture. Interactions at city level or community level are the same to some extent but often different. In the study of China's urbanization and rural-urban relations, it is urgent to introduce, use, and recreate the theories on place with GIS and multi-scale cases. In terms of methodology, combining human geography with GIS will reshape geography. In addition to being an indispensable concept of geography, place is also closely related to everyday life. Dealing with the challenges from evolving globalization and information and communication technologies, place is changing, and the concepts on place or placelessness are also evolving correspondingly. It is significant in geographic research and practice to couple human geography with GIS and explore the way to apply the methodology to explain changing issues in the real world with different temporal, spatial, and social scales, so as to rebuild the place theoretically and practically.
重建地方: 人文地理与GIS结合研究的路径
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

地方是很重要的地理学概念。中外学界对地方的研究有丰富积累。围绕地方的理论与现实问题,探索人文地理与GIS结合研究的路径和方法对中国地理学尤为重要。“重建地方”旨在打破学科界限,重新发现学术研究的“地方”,并将学术与生活、思想与技术紧密结合起来,反思和重建生活中的“地方”。人文地理与GIS结合研究主要聚焦于流动性的大尺度城市空间与稳定性的小尺度社区空间。通过运用开放的街景地图、3D-VQGIS等新GIS工具和方法,整合大数据与小数据,将定量与定性结合,丰富了地方性研究的方法与理论,使人文地理与GIS结合有新的方法论与可操作的手段。以地方为主题,人文地理与GIS的结合还将重塑这2个子学科,进而促进地理学发展。未来应该大力探索人文地理与GIS结合的思想、理论与方法,实现学科内的交融互动,并将其应用于解释尺度交错的现实问题,进而在理论和实践上重建地方。
Study progress and theorectical framework of virtual geographic environments
虚拟地理环境研究进展与理论框架
The theoretical basis and technical path of cyberspace geography
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201909001
[本文引用: 1]

As a new spatial form of human activities, cyberspace is the common carrier of human and information. Cyberspace security is an important foundation of national security. The scientific description of cyberspace is an important cornerstone of cyber event analysis, cyberspace governance and cyber security guarantee, and also a new field of geographic science research in the information age. In the context of rapid development and fierce competition in global cyberspace, it is urgent to strengthen the intergration of geography and cyberspace security, and to carry out theoretical and methodological innovations based on traditional geosciences, and to create cyberspace geography. Cyberspace geography is the extension of geoscience research content from real space to virtual space. Its theoretical basis has evolved from the traditional theory of man-land relationship to the theory of man-land-network relationship; its research contents include constructing the mapping relationship between cyberspace and real space, redefining the basic concepts of distance and region in cyberspace, constructing the language, model and method system of cyberspace visualization, drawing the cyberspace map and exploring the evolution laws of the structure and behavior of cyberspace; its technical path includes the data collection and fusion of cyberspace elements, the visualization of cyberspace and the intelligent cognition of cyberspace situation and behavior. The intelligent cognition covers the assessment of cyberspace situation, transmission and traceability analysis of network hot events, situation simulation and risk prediction of cyber events, etc. The establishment of cyberspace geography will certainly provide a new perspective for the scientific cognition of cyberspace, the discipline construction of geography and cyberspace security science, as well as the prevention and control of national cyber security and the construction of a community of common future in cyberspace.
网络空间地理学的理论基础与技术路径
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201909001
[本文引用: 1]

网络空间作为人类活动新的空间形态,是人和信息的共同载体,网络空间安全是国家安全的重要基础。对网络空间的科学刻画,是网络事件分析、网络空间治理、网络安全保障的重要基石,也是信息化时代地理学研究拓展的新领域。在全球网络空间激烈竞争的背景下,亟需加强地理学与网络空间安全等学科的交叉融合,在传统地理学的基础上进行理论创新和方法创新,创建网络空间地理学。网络空间地理学是地理学研究内容从现实空间向虚拟空间的延伸,理论基础是从传统地理学的人地关系理论演变为人地网关系理论;研究内容包括构建网络空间、现实空间的映射关系,在网络空间重新定义传统地理学关于距离、区域等基本概念,构建网络空间可视化表达的语言、模型、方法体系,绘制网络空间地图,探究网络空间结构和行为的演变规律等;技术路径包括网络空间要素数据采集与融合、网络空间可视化表达、网络空间态势与行为智能认知等,其中智能认知涵盖了网络空间态势现状评估、网络热点事件传播与溯源分析、网络事件态势模拟与风险预测等。网络空间地理学的创建将为网络空间的科学认知、地理学与网络空间安全等学科建设以及国家网络安全防控和全球网络空间命运共同体的构建提供新视角。
Geography interact with big data: Dialogue and reflection
地理学碰上“大数据”: 热反应与冷思考
Core or edge? Revisiting GIScience from the perspective of geography discipline
DOI:10.1360/SSTe-2021-0050 URL [本文引用: 1]
地理信息科学: 地理学的核心或是外缘
Geographic information science: A step toward geo-governance solutions. International Conference on Information & Communication Technologies: From Theory to Applications
Major advances in studies of the physical geography and living environment of China during the past 70 years and future prospects
近70年来中国自然地理与生存环境基础研究的重要进展与展望
Disciplinary structure and development strategy of information geography in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109004
[本文引用: 1]

The arrival of the information era has exceptionally advanced the development of geographic science. The research scope of the discipline has expanded from the space of traditional physical and human geography to the space of information geography. Meanwhile, the discipline gradually formed three subdisciplines, i.e., geographic remote sensing science, geographic information science, and geographic data science. In the context of preparing the disciplinary structure of geographic science of the "Development Strategy of Discipline and Frontier Research in China (2021-2035)", this paper summarized the history, definition, and disciplinary structure of information geography. Additionally, it highlighted the strategic layout of the discipline, as well as the goals and key directions of its priority development fields. We expect this paper to provide insight into the new discipline that could help promote the developments and applications of remote sensing and geographic information within the framework of geographic science, strengthening the synthesis of geographic research and promoting the integrated development of geographic science.
信息地理学学科体系与发展战略要点
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202109004
[本文引用: 1]

信息时代的到来极大地促进了地理科学的发展,地理科学的研究已从传统的自然地理空间、人文地理空间拓展到了信息地理空间,催生了信息地理学的发展,并逐渐形成了地理遥感科学、地理信息科学和地理数据科学3个分支学科。在《中国学科及前沿领域发展战略研究(2021—2035)》地理科学的学科规划背景下,本文梳理了信息地理学的形成、定义和学科体系,重点阐述了信息地理学的学科发展战略布局、优先领域发展目标和重点方向。以期本文有助于促进遥感、地理信息科学与技术的发展和应用回归地理科学,进一步强化地理科学研究,使其更加系统化、科学化和现代化,促进地理科学的整体发展。
Governance research: Radically reform
治理研究: 正本清源
division: The pluralism and its challenges for contemporary Chinese human geography
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

In last 40 years, Chinese Human Geography has made great achievements in terms of the integrity of disciplinary system, number of research in geographical journals, and social and political impacts of Human Geography graduates. However, there are also many challenges in the development of Chinese Human Geography. The most salient one is the pluralism of Chinese human geographical studies, which leads to the blurred definition, undermined identification and reduced impact of human geography. The article tries to scrutinize and distinguish the types of pluralism in Chinese Human Geography in the aspects of philosophy, theory, method and practice. 3 types of pluralism are summarized and their implications for the future studies are discussed, i.e. the dispersed disagreements (sanjian) which require more communication and integration, the divided ideas (qijian) which need to be unified and bridged, and narrow prejudice (pianjian) which should be dispelled and opened up. This article suggests that Chinese Human Geography should enhance consciousness of raising good research questions and develop more original theories, abandon the excessive worship of new doctrines and methods, promote the communication and combination of qualitative and quantitative methods, improve the rigor of arguments, balance “realistic” and “pragmatic” orientations in policy-making, and integrate diverse research perspectives. We also provide some detailed practical recommendations in future research directions and disciplinary development.
分裂: 论中国人文地理学发展的多元性及其挑战
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

从哲学、理论、方法和实践4个方面梳理了中国人文地理学内部的多元性,并区分了这些多元性的性质,即哪些是缺乏交流和整合的“散见”、哪些是需要统一和弥合的“歧见”、哪些是认识局限导致的“偏见”。据此建议加强中国人文地理学研究的问题意识和原创性理论研究;减少对“主义”的过度推崇和对方法的盲目崇拜;加强定性方法和定量方法的交流及论证过程的严谨性;在政策取向上取得“求真”和“务实”的平衡;提高学科发展的自信和对不同研究视角的包容。此外,应该在研究选题、杂志建设和奖项设置等操作层面推动人文地理学的理论整合。
Problem-dominated versus method-dominated? The reflection on the methodlogy of human geography research in mainland China
问题主导还是方法主导? 对我国人文地理学研究的方法论思考
Reconstructing the theory of cross-border governance: Taking the Yangtze River Delta as a case
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

The world has entered an era of hypermobility and instability. National and social governance is facing enormous new challenges. With the rapid urbanization, the free flow of factors frequently cross borders. Governance needs to transform instability into stability, which highlights the importance of cross-border governance. The interweaving of global, regional and local scales has brought new issues of cross-border governance. Cross-border governance mainly refers to the process of making multiple subjects participate in and jointly govern public affairs through cross-region, cross-department, cross-level and cross-field. By sorting out the relevant theories of cross-border governance, this article redefines the “border”, reconstructs the theoretical logic of cross-border governance, and proposes that cross-border governance mainly involves three pairs of key categories of three scales: Heterogenization and homogenization at the local scale; deborderlization and borderlization at the regional scale; decentralization and centralization at the global scale. Taking the Yangtze River Delta as a case study, this article empirically analyzes the logic of cross-border governance at regional scale.
跨界治理的理论重构: 以长江三角洲地区为例
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2022.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

全球已进入一个超流动与不稳态并行的时代,国家和社会治理面临许多新挑战。伴随着快速城镇化,要素自由流动并频繁“跨界”,而治理需要将不稳定转化为稳定,跨界治理的重要性凸显。全球、区域、地方等尺度交织,使跨界治理的新问题不断涌现。跨界治理主要指通过跨区域、跨部门、跨层级、跨领域使多主体共同参与和联合治理公共事务的过程。通过梳理跨界治理的相关理论,重新界定了“界”,重构了跨界治理的理论逻辑,提出了跨界治理主要涉及3个尺度的3对范畴:在地方层面,去同质化与同质化;在区域层面,去边界化与边界化;在全球层面,去中心化与中心化。运用该框架,以长三角为例,实证分析了区域尺度跨界治理的逻辑。
How to revive geography: Our reflection and practice
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201806001
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is an ancient discipline, yet it is also continuously evolving. Especially in China, geography has been developing rapidly in the past 30 years. However, with the emergence of more and more branches and sub-disciplines, we are facing increasing confusions about geography. For the consideration of construction of geography discipline and its academic community, we are in an urgent need to find a "consensus" on the development of geography and explore the definition of geography community. To this end, we organized a series of workshops and conferences last year to provide a platform for different generations of geographers to express their opinions on how to promote the development of geography in China. This article is a summary of the viewpoints based on the recordings of the conference. In general, several consensuses have been reached as follows: (1) In teaching, we should enhance the comprehensiveness of courses of geography and strengthen the training of methods for geographical investigation and research; (2) In academic research, we should strengthen the summary of the paradigms in geography, provide more comprehensive explanations of "geo" and accelerate the integration and innovation in geographical theories and methods; (3) In disciplinary development, we should highlight the construction of regional geography, emphasize the national and local needs in policy-making, and demonstrate the contribution of geography. We hope that with our joint efforts, both the discipline and community of Chinese geography will be growing stronger in the future.
如何回归地理学: 我的思考与实践
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201806001
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是一门古老的学科,也是一门不断发展变化的学科,尤其在中国,近30年来地理学的发展日新月异。然而,伴随着分支学科越来越多,对地理学的认知也出现了不少困惑。从地理学一级学科建设和学术共同体培育的角度,亟需寻找地理学发展的“共识”,探讨地理学共同体的定义。为此,对地理学充满热爱之情的老中青三代地理学者,对如何推动统一地理学建设提出了各自的见解。这些见解中的共识大体可提炼为以下几点:① 教学上,加强对地理学综合知识体系的传授,加强对地理学调查研究方法的训练;② 研究上,加强对地理学研究范式的总结,加强对“地”的综合解释和理论方法方面的融合与突破;③ 学科发展上,加强区域地理学的建设,加强对国家和地方需求的回馈,彰显地理学的贡献。期待通过学界的共同努力,带动地理学共同体的日益壮大。
Geography: From knowledge, science to decision making support
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

Geography is a subject to explore spatial distribution, time evolution and regional characteristics of geographical elements or geographical complexes. Geography is unique in bridging social sciences and natural sciences, and has characteristics of comprehensiveness, interdisciplinary research and regionalism. With the development of geographical science technology and research methods, geography is in the gorgeous historical process towards geographical science. Research themes of geography are focusing on the comprehensive research on the earth surface. The research paradigms of geography are shifting from geography knowledge description, coupling pattern and process, to the simulation and prediction of complex human and earth system. The development of Chinese geography needs to be rooted in the major needs of national strategy, and plays important roles in the studies of urbanization development, coupling ecological processes and services, water resources management and geopolitics. Under the country's major needs, China's geography tends to achieve the geography theory innovation, new method and technology application and developed disciplinary system with Chinese characteristics, and make more contribution to national and global sustainable development.
地理学: 从知识、科学到决策
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201711001
[本文引用: 1]

地理学是研究地理要素或者地理综合体空间分布规律、时间演变过程和区域特征的一门学科,是自然科学与人文科学的交叉,具有综合性、交叉性和区域性的特点。随着地理信息技术发展与研究方法变革,新时期的地理学正在向地理科学进行华丽转身,研究主题更加强调陆地表层系统的综合研究,研究范式经历着从地理学知识描述、格局与过程耦合,向复杂人地系统的模拟和预测转变。在服务国内重大需求和国际全球战略过程中,地理学正在扮演愈发重要的角色,在新型城镇化、生态环境保护、水土资源管理、地缘政治等领域拥有广阔发展前景。中国地理学正面临前所未有的机遇,需要紧紧围绕国家重大需求,创新发展综合性的理论、方法和技术,逐步形成具有鲜明中国特色、深远国际影响的地理科学体系,为中国和全球的可持续发展服务。
Reform trend and countermeasures of spatial planning under the background of national institutional reform
机构改革背景下我国空间规划的改革趋势与行业应对
Social Justice and the City (Revised Edition)
An empirical research of the registered population transformation in China's megacities
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202007
[本文引用: 1]

From 2020 to 2030, accelerating the citizenization of the floating population is the key to promoting new urbanization and achieving common prosperity. The urbanization rate of registered population in China is roughly 18% lower than that of permanent residents. The aging pressure and lack of labor force make big cities introduce relevant policies to attract talents, and the citizenization process needs to be improved urgently, with the focus on megacities. The transformation number of registered people in megacities varies greatly, and the academic world lacks research on this, which makes the transformation number of registered residents in megacities become an important academic issue. This paper, from both natural and social perspectives, selects concise indicators, and combines the Possibility-Satisfiability model to estimate the urbanization transformation gap of annual household registration, and constructs a panel data model to empirically analyze the factors leading to the gap of household registration in megacities. The main factors affecting the transformation of registered population in megacities are medical service, as well as educational resources and urban water supply. It is urgent for urban and rural administrators to change the passive and rigid institutional mechanisms and realize the flexible and normal governance.
中国超大城市户籍人口转化的实证研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202202007
[本文引用: 1]

“十四五”时期到2030年,加快流动人口市民化是推进新型城镇化和实现共同富裕的关键。中国户籍人口城镇化率与常住人口城镇化率相差约18%,老龄化压力与劳动力市场缺口使大城市纷纷出台“抢人”政策,市民化程度亟待提升,焦点在北上广深等超大城市。超大城市每年户籍人口转化数相差很大,学界对此缺乏研究,使得城市每年能“化”多少户籍人口成为重要学术问题。本文结合自然和社会两个视角,选取简明指标,构建可能—满意度模型,测算4个超大城市年均户籍城镇化转化缺口,构建面板数据模型实证分析超大城市户籍缺口的主导因素。影响超大城市户籍人口转化的因素主要是医疗、教育和供水。城乡治理亟需转变被动和僵化的制度安排,实现弹性的常态化治理。
Legal geography I: Constitutivities, complexities, and contingencies
DOI:10.1177/0309132514527035 URL [本文引用: 1]
Why resilience is unappealing to social science: Theoretical and empirical investigations of the scientific use of resilience
A logical framework of rural-urban governance from the perspective of social-ecological resilience
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.009
[本文引用: 1]

Along with the rapid progress of urbanization, dramatic changes in the ecological environment and profound changes in the social and economic systems have made issues related to China's urban and rural development more prominent. Urban and rural governance faces new challenges. The concept of social-ecological resilience may shed some light on changes in the practice of rural-urban governance, but there is a lack of research on the relationship between them. Focusing on major issues of urban and rural development in China, this study clarified the relationship between social-ecological resilience and urban and rural development, and constructed a logical framework of rural-urban governance from the perspective of social-ecological resilience. The framework aims to promote urban and rural integration and sustainable development by introducing the key characteristics of social-ecological resilience (coupling, self-organization, and learning) into rural-urban governance mechanisms (planning, participation, and policy). In the future, social and ecological issues should be taken into overall consideration in rural-urban governance, with the idea of human-earth system coupling. A multiple-tiered network of coordinated rural-urban governance should be established. Attention should be paid to the cultivation of cooperation and innovation of the participants at different scales, especially to the construction of learning and adaptability of urban and rural communities. In practice, it is necessary to make full use of spatial planning, to incorporate ecosystem services into rural-urban spatial governance and take them as a priority. The goal of enhancing the resilience and adaptive capacity of urban and rural areas to uncertain challenges will be achieved by coordinating the relationship between ecosystem services and human well-being.
社会—生态韧性视角下城乡治理的逻辑框架
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.009
[本文引用: 1]

伴随着快速城镇化,生态环境剧烈变化与社会经济结构深刻转变使中国城乡发展问题愈发突出,城乡治理面临新挑战。社会—生态韧性理论与城乡治理实践存在紧密关联,但对两者关系的研究欠缺。论文以中国城乡发展问题为导向,厘清社会—生态韧性与城乡发展的关系,构建社会—生态韧性视角下城乡治理的逻辑框架。将社会—生态韧性的核心理念(耦合、自组织和学习)引入城乡规划、个体参与和政策制定,将促进城乡融合和可持续发展。在未来的城乡治理中,需要将社会与生态问题统筹考虑,贯彻人地耦合的理念,形成多层级的城乡协同治理网络,促进适应性治理,培育不同尺度城乡治理主体的合作和创新,尤其要重视城乡社区的学习、适应能力构建。实践中需要充分利用空间规划工具,将生态系统服务纳入城乡空间治理范畴,协调城乡生态系统服务与居民福祉的关系,增强城乡对不确定性的缓冲和应对能力。
New reflections on the analysis of regional resilience in geographical sciences from a relational-dynamic perspective
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180256
[本文引用: 1]

Regional resilience is the regional capability of a region to cope with the short- and long-term changes in the development process and to actively adjust and transform itself, which represents the adaptability, innovation and sustainability of the region. As a new concept, regional resilience reflects the new requirements of geographical research on sustainable development and regional studies. A relational-dynamic perspective as a new perspective and a new cognitive method of geographical analysis is introduced in this paper towards an understanding of the complexity of regional resilience. In accordance with the concept of contextuality, path dependence and contingency in Western economic geography as well as the multi-perspectival turns of economic geography during the past decades such as the relational turn, the institutional turn, the cultural turn and the evolutionary turn, the relational-dynamic perspective advocates a comprehensive recognition of the complex process of spatial evolution based on multi-dimensionality, which brings new thinking and new methods of regional resilience cognition. This study attempts to grasp the complexity of regional resilience analytically. It examines the latest findings of the international research progresses in the identification and evaluation of regional resilience in geographical sciences. Based on a relational-dynamic perspective, this study explores the construction of a cognitive framework of regional resilience, summarizes the methodology of the analyses on regional resilience with emphases on both context analysis and process analysis, and attempts to establish an assessment equation to evaluate regional resilience from the economic, social, environmental and institutional dimensions. By analyzing the generality and particularity of the research on regional resilience in China, this study tries to link the theoretical research on regional resilience to the practical Chinese issues in order to make a theoretical contribution to the regional resilience research, to promote the transdisciplinary discussion with knowledge integration and academic discussion of the research on regional resilience, regional development studies and relative cognitive fields in geographical sciences, and thus to provide scientific guidance for national and reginal sustainable development with decision-making reference to relative policies for the governments. It offers a new perspective for regional planners, scientists and policy makers to facilitate regional governance from an interdisciplinary and relational-dynamic perspective based on a resilience-based spatial cognition.
关联演化视角下地理学区域韧性分析的新思考
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180256
[本文引用: 1]

区域韧性是一个区域应对发展进程中短期冲击与长期变化、积极进行自我调适与转型的能力,表征了区域的适应性、创新性与可持续性,作为新兴理念反映了地理学可持续发展与区域研究的新需求。本研究综述了区域韧性研究进展,基于关联演化视角,探索构建区域韧性认知框架,将情境分析与过程分析并重,思考并总结区域韧性分析的方法论,尝试建立区域韧性评估方程,从经济、社会、环境及制度四个维度进行区域韧性评估,将区域韧性应用于中国地理学研究,分析中国区域韧性研究的一般性与特殊性,将区域韧性研究对接中国实际问题,以期对区域韧性研究做出理论贡献,助推地理学区域发展研究及相关认知领域的跨学科讨论、知识集成与学术交流,为国家制定相关区域政策提供参考,并为国家及区域可持续发展提供科学指引。
Big data analysis on COVID-19 epidemic and suggestions on regional prevention and control policy
新冠肺炎疫情大数据分析与区域防控政策建议
Chinese geographers have played an important role in the fight against COVID-19
中国地理学者在抗击新冠肺炎疫情中发挥重要作用