1 引言
京津冀协同发展是习近平总书记亲自谋划、部署和推动的重大国家战略,旨在从区域的经济活动分工和功能结构关系着手,通过区域治理来协调区域发展面临的不均衡矛盾[1-2],实现优势互补,将京津冀城市群打造成具有国际影响力的经济发展共同体和命运共同体[3]。城市群在协同发展过程中不仅是实体形态上的空间连片,更重要的是通过相互吸引、集聚、辐射作用,形成功能紧密联系的流动空间[4],通过增强经济领域的相互作用和联系[5],进而推动城市群在规划、交通、产业、城乡、市场、生态和环境方面的协同发展[6]。目前城市之间的竞争已经不再局限于单体城市的规模,而是越来越取决于城市参与区域分工协作的地位以及在多尺度空间下的功能联系[7]。城市群的发展可以促进单体城市参与区域之间的互联互通,实现区域协同发展[8]。城市群内功能格局是否清晰和互补,功能之间是否实现良性互动,日益成为研究者关注的热点[9]。因此,研究城市功能互动格局无疑是对城市群内城市协同发展和城市群的可持续发展具有重要的理论和实践意义。
京津冀城市群作为中国三大城市群之一,一直受到学者们高度关注,相关研究成果与日俱增。其中,关于城市功能的相关研究大致分为如下3类:① 从京津冀城市群城市功能之间的分工和互补情况进行研究[10-11],发现京津冀城市群尚未真正形成错位发展、功能互补、多中心协同的空间分工格局;② 从城市功能体系的角度进行研究[12-13],发现京津冀城市群各城市间的联合强度不断加大,但城市体系仍存在某一级节点城市的缺失,基本架构仍有待完善;③ 对京津冀城市功能发展的战略做定性讨论[14-15],提出京津冀城市群应成为世界性的重要节点和大城市群之一,内部需要空间重组和整合,雄安新区建设对京津冀城市群功能变化将产生持久影响。
偏离—份额分析模型能较好表达功能互动变化时的漂移映射现象[26],可以弥补土地生态位模型的不足。该模型中的份额—偏离分量以及结构偏离分量能够表达城市的某个功能在城市群中发展的稳定性,而竞争力偏离分量可以表达城市功能的变化趋势。尽管上述模型在一定程度上可以测度城市功能的某种变化特征,但不能全方位刻画城市群城市功能的时空互动特征。目前,尚未发现关于城市功能互动分析研究中提出完善的技术思路和成熟模型。因此,如何在城市功能识别基础上,深入揭示城市间功能互动格局便成为当下亟待解决的科学问题。
综上所述,为了揭示城市功能在京津冀城市群中的互动变化特征,需要对现有的模型进行综合集成。为此,本文在基于POI大数据城市功能识别的基础上,通过研究城市群城市功能互动原理,引入偏离—份额分析模型、改进土地生态位模型、扩展引力模型,设计模型的耦合机制,构建能表征城市功能互动格局的新模型,刻画城市功能互动格局的时空特征,进而针对功能互动格局存在的问题,提出推进京津冀城市协同发展的治理策略,为优化京津冀城市群城市功能和促进区域经济协调发展提供参考。
2 数据来源及处理
2.1 数据来源
本文以京津冀13个地级市为研究对象,包括北京、天津2个直辖市,河北省的张家口、承德、秦皇岛、唐山、沧州、衡水、廊坊、保定、石家庄、邢台、邯郸11个地级市。研究数据主要包括:① POI大数据,也称电子地图兴趣点数据。作为识别城市功能区常用的一类大数据[27],其对每一个地名、建筑、住宅小区、公园、学校、医院、公司、商场等进行统计,信息丰富准确且更新及时。本文选择高德地图POI数据作为城市空间功能分类的基础数据,包含名称、类别、经纬度等信息。使用自编网络爬虫工具获取2010年(共1610384条)、2016年(共3826080条)、2019年(共4457550条)POI数据;② 统计年鉴数据,包括《北京市统计年鉴》《天津市统计年鉴》《河北省统计年鉴》,用于获取城市GDP等相关统计指标;③ 人口数据。为统计附着在指定类型空间功能的人口数量,采用WorldPop(www.worldpop.org)2010年、2016年、2019年的人口数据,其分辨率为100 m×100 m;④ 城市建成区范围数据,来自中国科学院资源环境科学与数据中心[28],用于界定城市边界范围;⑤ 地图与遥感数据,来源与百度地图和Google Earth,用于功能类别验证。
2.2 数据处理
为解决原始POI大数据存在冗余以及坐标偏移等问题,① 先将京津冀POI原始数据进行去重和剔除无意义的点,将火星坐标系转换为WGS84坐标系;② 对城市建成区范围内各类型POI数据进行裁剪,仅保留城市建成区范围内的各类POI点数据;③ 根据《城市用地分类与规划建设用地标准》(GB50137-2011),将POI数据重分类。考虑到北京的核心功能,为了保证能较好的刻画城市功能特征,参考丁彦文等[29]提出的识别城市功能区的方法,使用250 m
本文选用500 m
为进行政策实施前后的比较,本文将京津冀城市群的功能互动划分为两个阶段:第一阶段为非首都功能疏解政策启动前的发展阶段(2010—2016年);第二阶段为非首都功能疏解政策颁布后产生效果的阶段(2016—2019年)。
3 城市群城市功能互动模型构建
3.1 城市群城市功能互动原理
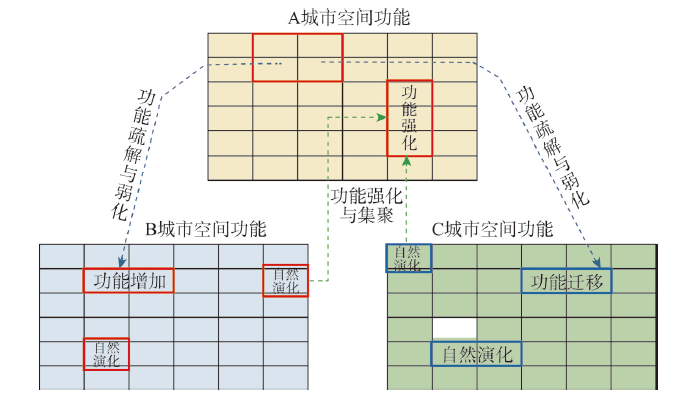
图1
图1
以A为中心城市的城市群功能互动原理示意图
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram of spatio-temporal interactive principle of urban functional interaction in an urban agglomeration (A as the central city)
3.2 城市群城市功能互动耦合模型
3.2.1 城市群城市功能互动耦合模型机制
本文针对传统引力模型无法反映引力作用方向及引力值差异的问题,引入土地生态位模型来衡量城市功能地位的差异性。同时,由于还需要考虑空间对象相互作用传导过程中功能特征变化,进而引入偏离—份额分析模型来揭示城市功能稳定性以及变化特征。考虑到京津冀城市群中的城市发展程度不同,针对北京市非首都功能疏解的迫切需要,本文假设功能发展的稳定性不利于京津冀之间功能的互动,功能的变化有利于京津冀城市之间的功能互动。基于此假设,将前两个分量作为阻力参量加入到耦合模型,后一个分量作为动力参量加入耦合模型。图2展示了城市群城市功能互动耦合模型的耦合机制和过程。
图2
图2
城市群城市功能互动耦合模型
Fig. 2
The coupling model of urban functional interaction in an urban agglomeration
功能互动模型的计算公式为:
式中:Ctij为i城市在t时期(基期年—末期年)对j城市功能迁移作用强度指数;Nti、Pti、Dti为i城市指定功能类型在t时期(基期年-末期年)的份额偏离分量、结构偏离分量以及竞争力偏离分量;dij为i城市与j城市中心的欧式距离;Zij为基期年i城市与j城市对应功能的引力值;Si为i城市基期年指定功能类型对应的面积;Ssum为基期年整个城市群各功能类型的总面积;POPi为i城市基期年指定功能类型上所占有的人口数量;POPsum为基期年整个城市群各功能类型上所占的人口数量之和。
3.2.2 改进土地生态位模型
土地生态位模型可以反映土地利用系统中各类型功能所占据的空间和所处地位。在空间上则表征不同地域单元之间相互作用力大小[32],生态位越大,地域空间单元吸引人流、物流的能力越强。为表征城市功能在城市群中的地位,对土地生态位模型中的变量进行改进,改进后的计算公式为:
式中:Tk为不同空间功能类型k的生态位;SQk、PQk为不同空间功能类型k的态和势;Ak为量纲转换系数(量纲转换系数为0.05)[33]。
式中:P为城市第二产业和第三产业产值总和;Y为城市第二产业、第三产业产值总和的增量;RPk为附着在第k类功能类型上的人口数量。
3.2.3 扩展引力模型
传统引力模型中的关键指标包括两地间的距离、质量和互补性[34]。为了表达功能的相互作用,本文将传统引力模型进行扩展,其计算公式为:
式中:Zij表示加入土地生态位之后的城市i对城市j指定功能的引力值,用于表示指定功能类型的城市间引力强度;Tk为指定功能类型指定城市的功能生态位;i、j为用于计算的城市;n为城市群城市总数。其中i、j城市间的引力值Iij计算公式为:
式中:Wik、Wjk分别为i城市、j城市k功能面积占城市群所有功能的总面积之比;n为城市功能类型的种类数;Pi、Pj分别为i城市、j城市第二、第三产业产值总和;dij为城市中心之间的欧氏距离。Wik计算公式如下:
式中:Gik为i城市k功能区的占地面积;Gi为i城市总功能区面积;Gk为城市群k功能面积;G为城市群所有功能区面积。
3.2.4 引入偏离—份额分析模型
偏离—份额分析模型可将某一区域的经济增长分解为转移和分享两部分,以此来说明区域经济发展和衰退的原因,以及确定区域未来产业调整的方向以及经济发展的规划。由于该模型没有考虑区域之间的空间交互作用,一些学者通过加入空间因素对其进行拓展,提出了偏离—份额分析空间模型[35]。但这些模型仅能表征单一时刻静态的空间功能相互作用。为了刻画城市功能互动的动态变化特征,本文对偏离—份额模型进行了改进。
(1)城市功能基期—末期的竞争力偏离分量Dk为:
式中:ek,0代表城市基期k功能的面积;rk为城市k功能类型的面积基期至末期的变化率;Rk为整个京津冀k功能类型在基期至末期的变化率;ek,t为城市末期k功能类型的面积;Ek,t为城市群总体在末期k功能类型的面积;Ek,0代表城市群总体在基期k功能类型的面积。
(2)城市功能基期—末期的份额偏离分量Nk计算公式为:
式中:
(3)城市功能基期—末期的结构偏离分量Pk的计算公式为:
3.3 模型集成计算
本文使用ArcGIS Pro 2.5进行空间数据的加工处理与计算分析。各种模型计算通过ArcGIS Pro 2.5自带的Arcpy站点包进行二次开发,即基于Python3.6.9编写脚本,在Pandas扩展包的支持下,研制了功能互动模型的计算以及模型参数的传递工具,实现对京津冀13个城市功能区空间数据的处理、计算以及统计。
4 京津冀城市功能空间互动格局分析
4.1 京津冀城市群城市功能总体特征
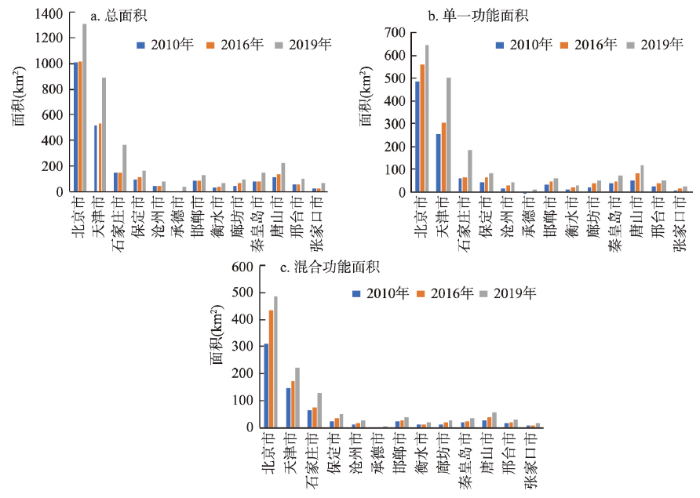
2010—2019年期间,京津冀城市建成区功能稳定快速增长,面积由2010年的2259 km2增长到2019年的3382.75 km2,增加近1.5倍(图3a)。其中,北京、天津与石家庄三市功能总面积占京津冀城市群的70%以上。北京城市建成区在城市群建成区中的占比有所下降,其他城市建成区的增长速度要快于北京。分析单一功能和混合功能变化情况(图3b、3c)发现,城市群内城市单一功能的面积由1145.93 km2增长到1889.75 km2,混合功能由676.19 km2增长到1136.31 km2。京津冀内部13个城市建成区的单一功能区、混合功能区均出现了不同程度的增长,相关研究[36]也得到了类似的结果;同时,单一功能面积均大于混合功能区,且在城市建成区中占据优势地位。
图3
图3
2010年、2016年和2019年京津冀城市功能面积的变化
Fig. 3
Changes of urban functional zones in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region over different periods
4.2 京津冀城市功能互动格局特征
4.2.1 工业与商业功能稳步向京外疏解
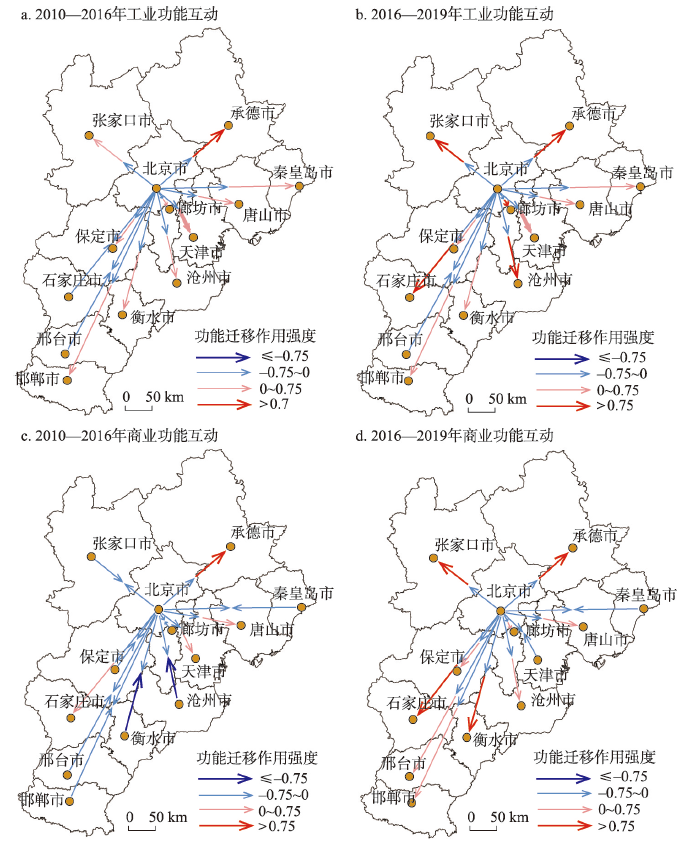
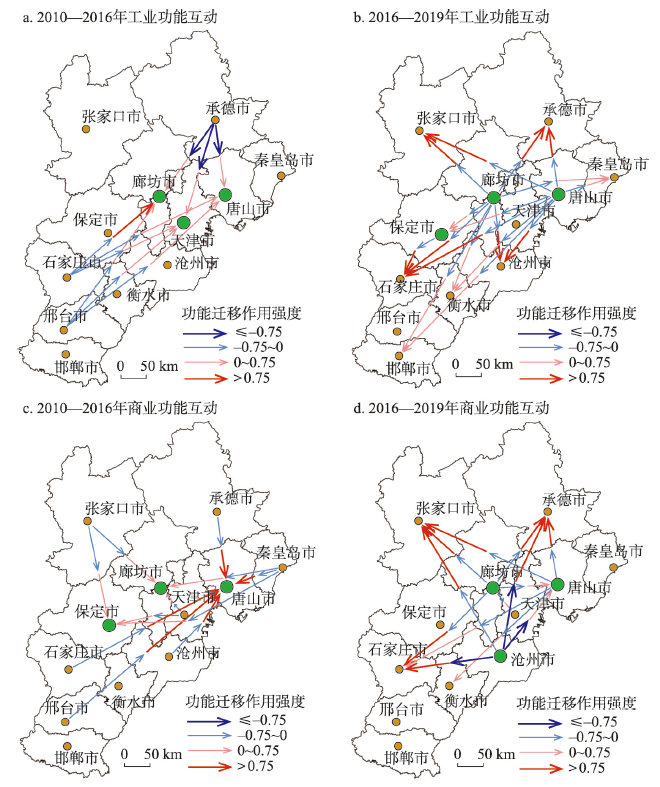
北京市在2010—2016年间对其他城市的工业迁移作用强度均小于0(图4a),表明在非首都功能疏解政策实施之前,北京市的工业功能已经开始向京津冀城市群的其他城市迁移。城市群中的大部分城市也都在吸引从北京市迁移出来的工业功能,从而对北京市的工业功能产生了疏解作用。相比其他城市,承德市对北京市迁移出来的工业功能有着很强的吸引力,而石家庄市和邢台市在该期间向北京市迁移了部分工业功能。
图4
图4
2010—2019年北京市与津冀城市工业和商业功能互动
Fig. 4
Maps of interactive patterns of industrial and commercial functional zones between Beijing and other cities
在非首都功能疏解政策实施之后(2016—2019年),北京市继续向其他城市迁移工业功能(图4b)。除了邢台市,其他城市也在积极地吸引被迁移出来的工业功能。其中张家口市、廊坊市、沧州市和石家庄市吸引工业功能迁移的作用强度显著增加。津冀其他城市对北京市非首都功能疏解政策的响应程度不尽相同,但相比疏解政策实施之前,大部分城市都在积极地吸引被迁移出来的工业功能。由此可知,疏解政策的出台对工业功能的疏解起到了积极的推动作用。
4.2.2 科教、居住、公共服务功能互动明显
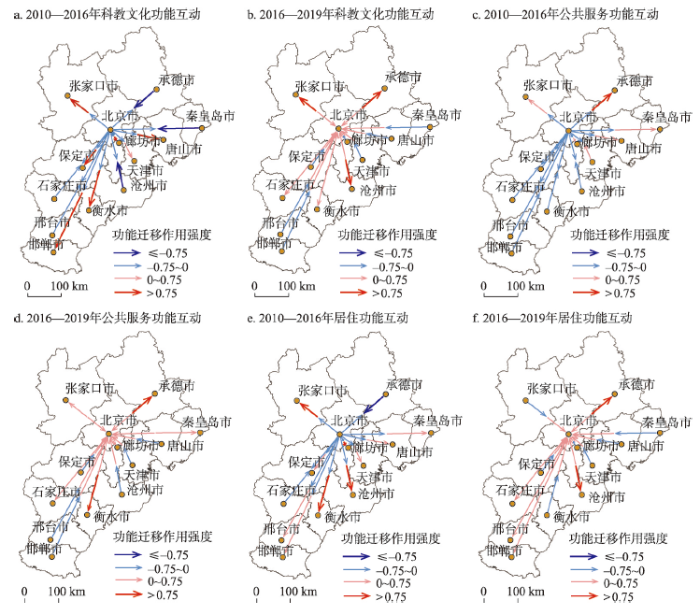
图5
图5
2010—2019年北京与津冀城市科教文化、公共服务和居住功能互动格局
Fig. 5
Maps of interactive patterns of science, education and culture, public services and residential functional zones between Beijing and other cities in 2010-2019
可见,2010—2016年期间,在京津冀城市群中有近一半的城市与北京市呈现科教文化和公共服务功能双向的互动作用(图5),即北京市在向这些城市迁移相关功能的同时,这些城市也在向北京市迁移该功能。而居住功能在该期间内呈现出北京市向外迁移,京津冀其他城市向内吸引的互动特征。在非首都功能疏解政策实施之后,除了科教文化功能开始向北京市聚集外,公共服务和居住功能呈现出吸引和迁移共存的局面。
4.2.3 城市间功能互动存在差异性
表1 2010—2016不同城市吸引力较强的功能统计表
Tab. 1
| 城市 | 对其他城市对应功能吸引力较强的功能 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 张家口市 | 工业 | 公共服务 | 混合 | 居住 | 科教文化 |
| 廊坊市 | 工业 | 公共服务 | 科教文化 | ||
| 衡水市 | 工业 | 科教文化 | 商业 | ||
| 承德市 | 公共服务 | 混合 | 商业 | ||
| 沧州市 | 工业 | 居住 | |||
| 天津市 | 科教文化 | 生态 | |||
| 唐山市 | 科教文化 | ||||
| 邯郸市 | 科教文化 | ||||
| 秦皇岛市 | 公共服务 | ||||
表2 2016—2019年不同城市吸引力较强的功能统计
Tab. 2
| 城市 | 对其他城市对应功能吸引力较强的功能 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 承德市 | 工业 | 公共服务 | 居住 | 科教文化 | 混合 | 商业 |
| 石家庄市 | 工业 | 公共服务 | 居住 | 科教文化 | 生态 | 商业 |
| 张家口市 | 工业 | 公共服务 | 科教文化 | 生态 | 商业 | |
| 沧州市 | 工业 | 居住 | 科教文化 | 混合 | ||
| 唐山市 | 商业 | 生态 | ||||
| 邢台市 | 居住 | 生态 | ||||
| 衡水市 | 公共服务 | |||||
| 秦皇岛市 | 生态 | |||||
| 邯郸市 | 生态 | |||||
图6
图6
2010—2019年京津冀城市群不同功能拥有吸引力较强的城市数量
Fig. 6
The number of cities with strong attractive functions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 2010-2019
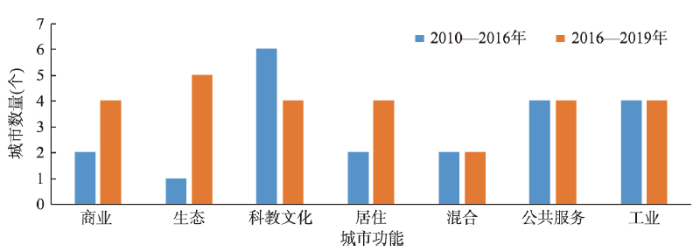
从图6可知,与2010—2016年相比,2016—2019年的商业功能、生态功能、居住功能中吸引力较强的城市数量均有所增长,科教文化功能则有所下降,混合功能、工业功能、公共服务功能则基本持平。这些特征反映了城市间的功能互动(承接、迁移、转化、替换等)是一个复杂的过程。在非首都功能疏解政策实施后,各城市既要对政策进行快速响应,又要考虑城市自身的可持续发展。比如张家口市由于冬季奥林匹克运动会的举办要强化科教文化、商业、居住等功能,从而促使其具有很强的功能互动性。
4.3 京外城市之间的功能互动格局特征
4.3.1 经济发展的城市功能互动明显
分析京外城市之间的功能互动特征,互动强度排名前3的城市(廊坊市、天津市、唐山市)主要位于京津冀城市群的中部(图7)。2010—2016年期间,唐山—廊坊—天津一带向周围城市吸引迁移出来的工业功能和商业功能。2016—2019年期间,唐山—廊坊—天津一带则表现为向其他城市迁移这些功能。这几个城市在京津冀城市群中属于经济发展较好的城市,说明在非首都功能疏解政策开始之前,这些城市因为其经济相对发达而呈现出功能的强化与集聚。在非首都功能疏解政策实施后,它们开始向京津冀其他城市迁移各类功能,说明这些城市在非首都功能疏解的过程中发挥了“二传手”的作用,即一方面在积极承接非首都功能(如工业功能)的疏解,另一方面也在带动京津冀其他城市的功能互动。
图7
图7
2010—2019年京外城市工业和商业功能互动格局
Fig. 7
Maps of interactive patterns of industrial and commercial functional zones among cities except Beijing
4.3.2 南部与中部城市的功能互动不强
2016—2019年期间,位于京津冀城市群北部地区的张家口市与承德市,主要吸引位于城市群中部城市迁移出来的工业功能和商业功能(图7)。而位于南部的邢台市和邯郸市与中部城市的功能互动性不强。石家庄市作为京津冀城市群中相对发达的城市,在吸引从北京市迁移出来的工业功能和商业功能上,强度整体上弱于城市群中部城市;但是,石家庄市则从廊坊和天津等市吸引工业和商业功能。2010—2016年间京津冀南部城市的功能在向京津冀中部的城市集聚,2016—2019年间石家庄市和衡水市开始从京津冀中部的城市吸引工业功能和商业功能。但是,对于南部的邯郸市和邢台市而言,这种作用不甚明显。
5 城市群城市功能互动结果讨论
5.1 城市群城市互动耦合模型的适用性
城市功能格局表现为城市的空间布局、空间形式和空间规模等[37]。围绕这些内容,学者们开展了大量研究。现有研究仅对单个城市功能[38]或者单一时期城市群的功能[39]进行研究,对于城市群内部城市功能的时空变化特征的探究不足。针对这个问题,学者们以指标选择、尺度确定和聚类等刻画空间格局的特征[40],并借助核密度聚类、标准差椭圆、格网分析、空间自相关分析、基尼系数等多角度分析功能格局分布特征[41-42]。由于城市功能不仅受自身发展的影响,也是一种城市之间时空相互影响及动态演变的过程。由于缺乏公认的城市群城市功能时空互动格局分析的成熟模型,本文从问题出发,研究了城市功能互动格局原理,针对原理寻找适合的方法。从上述计算结果可以看出,本文提出的耦合模型不仅可以对城市群功能格局变化总体特征进行分析,也可以对选择性的主题进行分析;既可以分析城市间功能的总体互动,又可以分析单个功能在不同城市间的时空变化特征。城市群城市互动耦合模型在进行城市群甚至区域城市间的功能互动格局分析中具有明显优势和普适性。
5.2 城市群城市互动格局总体特征
对政策的响应程度导致了城市间功能互动格局的差异。张家口市和承德市在2016—2019年期间对大部分功能的吸引力也显著增强。这与张家口市需要及时跟进2022年冬奥会相关配套设施建设有关。承德市因为毗邻北京、天津两座直辖市,为其争取京津共建共享支持提供了便利,并且相关部门也在强化“点对点”精准对接,增加央企、京津企业合作项目。这些举措在一定程度上推进了其对非首都功能疏解政策的响应。
京津冀城市群城市互动以疏解非首都功能为主,京外城市以吸纳非首都核心功能和强化现有功能并存的变化格局。2010—2019年间,在京津冀城市群中有近一半的城市与北京市呈现双向的互动作用。这些特征反映了城市功能互动是一个复杂的过程,既有对政策的快速响应,也有城市自身发展演化和强化,从而促使城市功能的互动。基于大数据对城市功能互动时空格局特征进行分析,可以为优化城区或区域发展提供治理建议。
5.3 城市群城市互动格局局部特征
城市群中相对经济发达的城市(主要位于城市群中部地区)对非首都功能疏解政策落实效果较好,它们充当了“二传手”的作用。这种空间互动关系也得到了已有研究成果的验证[45-46]。唐山—廊坊—天津表现为前期从周围城市吸引工业、商业功能,后期则表现为向其他城市迁移这些功能。位于京津冀南部的石家庄市、邯郸市和邢台市因为距离北京和天津较远,城市功能互动程度不高,已有研究成果验证了该结论[47]。这些结果一定程度上表明京津冀城市群对非首都功能的疏解存在空间门槛,门槛距离约为150 km,即位于距离北京约150 km范围内的城市吸纳疏解功能强,而超出这个范围会出现接力疏解现象。关于这个问题仍有待进一步深入探讨和验证,但这些在距离门槛外的城市想要更好地参与京津冀协同发展需要新思路新方向。
6 京津冀城市功能互动治理策略
京津冀城市群城市功能互动的驱动力及造成空间差异的原因较为复杂。总体上在自然禀赋和行政管辖的背景下,叠加了各种长效或临时性的政策干预。非首都功能疏解政策的确定性与承接功能落地的不确定性共存。城市自身功能演化与城市间功能互动共存。研究结果表明,京津冀城市群的功能区仍然处在发展演变中,尚未真正形成较为稳定的功能互补、协同发展的空间格局。京津冀城市群亟需基于不同城市的功能定位,进一步优化产业分工格局[48]。
为完善京津冀城市功能调控策略,本文提出如下建议:① 政策分层施治。研究发现京津冀城市功能总体和局部特征存在差异。同时在空间上具有一定的门槛现象。因此,在进行功能互动政策编制中,需要充分考虑这种总体政策与局部协同政策的配套。这种配套不能完全通过行政辖区来编制,而要编制跨区域的协同政策。② 优化南部城市功能互动调控政策。由于南部城市功能互动受到“二传手”城市的明显影响,如何通过与“二传手”城市的功能互动成为治理策略的重点。石家庄市作为京津冀城市群的中心城市之一,需要进一步加强承接北京市各类非首都功能,带动京津冀西部以及南部的城市发展。③ 关注城市混合功能发展。城市混合功能的快速发展成为高质量发展的一个新特征。功能混合需要进行合理的引导和优化。同时,还要关注城市功能向边缘区扩展的趋势,通过调控用地布局进行优化功能互动。
7 结论与展望
针对目前用于刻画城市群城市间功能互动的模型相对较少的问题,本文基于POI大数据,集成改进引力模型、土地生态位模型、偏离—份额分析模型和GIS技术,构建了新的城市功能互动耦合模型,旨在揭示以北京非首都功能疏解为核心的京津冀城市群城市功能协同发展特征,进而评估非首都功能疏解政策实施效果以及提出京津冀协同发展的治理策略。
本文得出以下结论:① 2010—2019年间城市群内建成区城市功能区总面积增加1.5倍,其中混合功能区增加了1.7倍,反映未来城市或将出现更多混合功能区。② 北京市工业功能、商业功能正在稳步疏解,居住功能、科教文化功能、公共服务功能仍在聚集与强化。③ 经济相对发达的城市在京津冀城市群功能互动中发挥了关键作用。这些城市对北京市功能的承接效应较好,并且对周围城市功能的辐射作用也较强,在京津冀协同发展中扮演了“二传手”的角色。④ 京津冀南部的城市需要进一步加强与中部城市的功能互动。由于功能互动可能存在空间门槛,石家庄市吸纳疏解功能主要来源于天津和廊坊,具有接力特征。⑤ 在治理策略上需要关注功能互动格局演化趋势来进行精准施策;加强中部与南部城市的功能互动,尽可能发挥京津冀协同带来的积极效应,推进京津冀城市群高质量发展。
城市群城市功能互动格局研究对于城市高质量政策编制具有支撑价值。下一步的研究建议从下面几个方面开展:① 更加精细的功能类别划分;② 开展不同尺度的比较研究;③ 围绕时空变化进行模拟预测研究;④ 优化现有模型并进行工具研发。
参考文献
Fine identification and governance of functional areas of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration supported by big data
大数据支持下京津冀城市群功能区精细识别与治理
Spatial-temporal evolution pattern of unbalanced economic development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region since the 1990s
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201603006
[本文引用: 1]

The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region has been experiencing rapid economic development since 1990. However, development has been imbalanced and has been widening the gaps in economies of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei. To identify the imbalanced pattern of economic development and analyze its dynamics in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during 1992-2012, we first proposed a "GDP per human activity intensity" consisting of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data and the constant price of GDP to map economic development. Second, local Moran's I was applied to classify the economic development pattern into 5 types: HH (high values surrounded by high values), HL (high values surrounded by low values), LH (low values surrounded by high values), LL (low values surrounded by low values), and not significant. Third, the boundary of the HH type was used as the line between rich areas and poor areas, and the dynamics of economic development and its response to administration are analyzed by buffer analysis. The results suggest that the spatial pattern of economic development has been imbalanced during 1992-2012, and the HH type in Beijing-Tianjin and the LL type in Hebei have been increasing in area and intensity. The HL type and the LH type in Hebei and suburban Beijing and Tianjin are growing because of the spillover effect of the development in the urban areas of Beijing and Tianjin. Moreover, having a different view from the previous understanding of "one poverty region around Beijing and Tianjin", we identified wealth gaps on two spatial scales: One is inside Beijing and Tianjin, which is between urban and rural areas, and the other is between Beijing-Tianjin and Hebei. Furthermore, the wealth gap in the former scale is larger than the latter. The imbalanced spatial pattern of economic development is a result of the administrative restrictions among Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei and the urban-rural dual system. Such a result can be attributed to the difference of administrative management and policy exists not only between cities but also between the urban and rural areas of a particular city. In addition, our analysis shows that the latter scale is the main reason for the imbalanced spatial pattern. Therefore, reducing urban-rural differences and administrative constraint is important in realizing balanced economic development in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region.
1990s以来京津冀地区经济发展失衡格局的时空演化
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201603006
[本文引用: 1]

1990s以来京津冀地区经济增长快速,然而经济发展在行政辖区间并不均衡,且逐渐导致环京津贫困带的形成.为识别经济发展失衡格局的演化过程,首先引入DMSP/OLS夜间灯光和可比价GDP,构建"单位开发活动GDP"表征区域经济发展状况;然后运用Local Moran's I将区域经济发展格局划分为五种类型:HH富化扩散,HL富化极化,LH贫化塌陷,LL贫化制约和非显著;最后以HH类型的边界作为京津冀地区经济发展失衡界线,采用缓冲区分析探讨经济发展失衡格局的演化过程和行政区划等人为因素对经济发展的制约效应.结果表明:① 整体上,1990s以来京津冀地区经济发展失衡格局不断加剧,京津富化扩散与河北贫化制约的规模与强度同时增长;局部上,受京津市区经济发展的外溢效应,京津郊区及区位优势显著的部分河北地区经济发展较快.② 与传统认知的"环京津贫困带"不同,在两个空间尺度上识别出经济发展断层,一为京津市区与郊区之间,二为京津与河北之间,且前者的区域经济发展失衡整体上较后者更为严峻.③ 1990s以来京津冀地区经济发展的失衡格局,整体上受制于城乡二元体制带来的城乡隔离效应,局部上受京津冀三地的行政制约.要实现京津冀地区经济发展的协同均衡,关键在于弱化城乡隔离,并辅以消除行政制约.
The theoretical cognition of the development law of China's urban agglomeration and academic contribution
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804005
[本文引用: 1]

Urban agglomeration refers to a highly integrated city and town group. It comes into being with the development of industrialization and urbanization to the advanced stage. The formation and development of urban agglomeration is a long natural process, which is transformed from competition to cooperation. China is in a new stage of urbanization transition, and has entered a new era of leading the global urban agglomeration development in the 21st century. The research and experience model of China's urban agglomeration has been accepted by global urban agglomeration construction as reference. In this paper, the natural law of urban agglomeration is proposed, including developmental gradual law, multi-scale transmission law of space intensive utilization, the combination law of spatial crystal structure, the natural growth of the breeding tree, and the gradient upgrade law of sustainable development. Following these laws, Chinese geographers have made great contributions to the research and development of China's urban agglomerations, which focuses on academic theory, technical method, decision support and planning practice. We developed and scientifically defined the concept of urban agglomeration, and first adopted the identification standard of urban agglomeration space. We established the spatial intensive development and layout simulation decision support technology chain in urban agglomeration, and developed related software chain. We laid out the new pattern of 5+9+6 in the spatial organization of China's urban agglomerations, and formulated the first China's urban agglomeration planning technical regulation. We completed the development plan of most urban agglomerations in China, which has become an important basis for decision-making at the national level. In the future, geographers will play a growing role and shoulder the responsibility in the development of Chinese urban agglomerations. We should combine qualitative and quantitative methods, and use big data and intelligent decision support technology to solve a series of problems in the development of this cause. Only in this way can Chinese geographers make greater contributions to the development of urban agglomerations.
中国城市群形成发育规律的理论认知与地理学贡献
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804005
[本文引用: 1]

城市群是国家工业化和城镇化发展到高级阶段的产物,是高度一体化和同城化的城市群体,城市群形成发育过程是一个各城市之间由竞争变为竞合的漫长自然过程,遵循自然发展规律。中国正处在新型城镇化转型发展的新阶段,已进入21世纪引领全球城市群发展的新时代,中国城市群研究与建设的经验模式正在被全球城市群建设所效仿和借鉴。本文从理论上梳理并提出了城市群形成发育遵循的自然规律,包括城市群形成发育的阶段性规律、城市群多尺度空间集约利用传导规律、城市群空间晶体结构组合规律、城市群自然生长的育树成林规律和城市群可持续发展的梯度爬升规律。地理学家遵循这些发展规律,从学术理论、技术方法、决策支持和规划实践等方面为中国城市群的研究和发展做出了不可替代的重大贡献,主要包括提出并科学界定了城市群概念,提出了城市群空间范围的识别标准,创建了城市群空间集约拓展与布局仿真决策支持技术链,研制了城市群空间集约拓展与布局仿真决策支持系统软件链,提出了中国城市群空间组织的“5+9+6”新格局,研制出国内第一部《城市群规划技术规程》,编制完成了全国多数城市群发展规划,转化为国家决策的重要依据。未来中国城市群的发展与研究中,地理学家发挥作用的空间越来越大,地理学家肩负着不可推卸的责任使命,应责无旁贷地采用定性与定量相结合的研究方法,引用大数据、智能决策支持技术等新手段解决城市群发展面临的一系列问题,一如既往地为城市群发展吸纳众智、献计献策,发挥更大作用,做出更大贡献。
The development degree evaluation of urban network based on functional connection: An empirical analysis of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Chongqing metropolitan areas
基于功能联系的城市网络发育水平综合评价: 对北京、上海、广州与重庆等都市圈的实证分析
Influence of urban agglomeration economic cooperation on regional coordinated development: Based on comparison between Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.04.011
[本文引用: 1]

In essence, regional coordinated development is the process of the interaction of urban economy and the strengthening of economic relations between urban agglomerations. From the perspective of the economic relation, compared Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei with Shanghai-Jiangsu -Zhejiang, the article finds that Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang is superior to Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei in both the echelon structure of the economic development and economic relation with the central city. In Shanghai-Jiangsu-Zhejiang, there is the reasonable hierarchical formation: Shanghai's radiation has contributed to the rise of the surrounding subcentres, and Nanjing, Suzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo as the subcentres, also drive the development of the surrounding cities. However, In Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, there is obvious disparity in the urban comprehensive strength, and all cities maintain close ties with Beijing. As the core city, Beijing’ siphon effect is much greater than the diffusion effect. The polarization effect is so much that although it brings a great deal of factor supply to Beijing, it aggravates Beijing’ urban burden and weakens the radiation effect and driving capacity of other central cities such as Tianjin, Shijiazhuang and Tangshan. Changing the state of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomerations, simply relying on household registration restrictions or industry forced relocation, etc. is not enough. “Easing” and “cultivating”simultaneously are very important. So, taking the Xiongan New Area planning and construction as the opportunity, adjusting the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regional space development strategy and industry structure, fostering innovation driven development new engines, creating a new model of city management, changing the “one city dominant” development mode, enhancing the attractiveness of the urban agglomerations, is the current important route.
论城市群经济联系对区域协同发展的影响: 基于京津冀与沪苏浙的比较
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2018.04.011
[本文引用: 1]

区域协同发展的过程,本质是经济领域相互作用,城市群经济联系不断增强的过程。从经济联系的视角通过对京津冀城市群与长三角地区沪苏浙城市群的对比分析发现,无论是从经济发展的梯次结构还是与中心城市的经济联系,沪苏浙地区都优越于京津冀。立足现实,深化对这一问题的思考,借助雄安新区的规划与建设,就改变京津冀城市群中北京“一城独大”式的发展模式以及带来的一系列负效应,构筑梯次良好、经济互通密切的城市空间布局提出对策建议。
Theoretical foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

Promoting coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is not only a major national strategy, but also a long-term complex process. It is necessary to apply scientific theories and respect the laws of nature to realize the strategic target of common prosperity, share a clean environment, share the burden of risk of development, and build a world-class metropolis for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. This article examines the scientific foundation and patterns of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory, game theory, dissipative structure theory, and catastrophe theory are the theoretical basis of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Synergy theory is the core theory for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. The coordinated development process of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is a non-linear spiral progress of game, coordination, mutation, game, resynchronization, and mutation. Each game-coordination-mutation process promotes the coordinated development of the urban agglomeration to a higher level of coordination, and the progress fluctuates. This process includes eight stages: assistance phase, cooperation phase, harmonization phase, synergy phase, coordination phase, resonance phase, integration phase, and cohesion phase. Further analysis shows that the real connotation of coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration is to realize the coordination of planning, transportation, industrial development, urban and rural development, market, science and technology, finance, information, ecology, and the environment, as well as the construction of a collaborative development community. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration will achieve advanced collaboration from low-level collaborative phase through regional coordination on planning, construction of traffic network, industrial development, joint development of urban and rural areas, market consolidation, science and technology cooperation, equal development of financial services, information sharing, ecological restoration, and pollution control. This study may provide a scientific foundation and theoretical basis for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration.
京津冀城市群协同发展的理论基础与规律性分析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2017.01.002
[本文引用: 1]

推动京津冀城市群协同发展既是一项国家重大战略,又是一个复杂的长期博弈过程,需要遵循科学理论,尊重科学规律,推动京津冀城市群实现共同繁荣昌盛、共享蓝天白云、共担发展风险、共建世界都会的战略目标。本文从理论上提出了京津冀城市群协同发展的科学理论基础与科学规律。认为推进京津冀城市群协同发展应以协同论、博弈论、耗散结构理论和突变论作为科学理论基础,其中协同论为核心理论。京津冀城市群的协同发展过程是一个博弈、协同、突变、再博弈、再协同、再突变的非线性螺旋式上升过程,每一次博弈—协同—突变过程,都将城市群的协同发展推向更高级协同阶段,并呈现出阶段性规律。具体包括协助阶段、协作阶段、协调阶段、协合阶段、协同阶段、协振阶段、一体化阶段和同城化阶段共8大阶段。进一步分析认为,京津冀城市群协同发展的真正内涵是推动城市群实现规划协同、交通协同、产业协同、城乡协同、市场协同、科技协同、金融协同、信息协同、生态协同和环境协同,建设协同发展共同体。本文成果旨在为京津冀协同发展提供科学基础和理论依据。
A rethinking of the theoretical connotation of megaregion in the new era
新时期城市群理论内涵的再认知
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.05.011
[本文引用: 1]

在全球化、信息化背景下,城市之间的竞争已经不再局限于单体城市本身的规模属性,而是越来越取决于城市参与分工协作的地位以及多尺度空间的功能联系,尤其表现在城市网络化、集群化的竞合态势,而城市群已经成为该背景下具有全球意义的空间组合模式。在系统梳理了中西方城市功能地域概念的内在关联基础上,论文认为,中国的城市群概念具有尺度伸缩性,与西方的巨型城市区域、巨型都市区和巨型区域概念是最为接近的。在空间内涵上看,城市群是2个以上城市体系组成的巨型城市地域,是兼具形态连续性和功能内聚力的城市系统,是全球化与本地化显著交互作用的大型经济单元,是当今时代城市与区域分工协作的一种尺度修复。基于此,城市群发育的基本条件主要包括良好的资源环境综合承载能力、大都市区与多个城市系统、地理空间上的邻近性与紧凑性、发达和完善的基础设施网络、深入协调的功能分工与经济联系以及相对一致的社会网络和文化认同。未来,中国城市群研究应更加兼顾形态和功能维度的统一,尤其注重从关系地理与城市网络视角探索城市群的空间集聚效应及其演化规律。
The rethinking of definitions of urban agglomeration in China
中国城市群基本概念的再认知
Urban agglomeration development: New characteristics, new ideas and new directions
城市群发展: 新特点新思路新方向
Study on urban functional division and complementarity under the coordinated development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
[D].
京津冀协同发展下的城市功能分工与互补性研究
[D].
Study on the influence of functional division of urban agglomerations on regional coordinated development: Taking Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration as an example
城市群功能分工对区域协调发展的影响研究: 以京津冀城市群为例
Quantitative simulation and verification of upgrade law of sustainable development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration
京津冀城市群可持续爬升规律的定量模拟及验证
Spatial structure of urban system and its evolution in Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration
京津冀城市群城市体系空间结构及其演变特征
Function orientation and coordinating development of subregions within the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

In this article, we examine the economic linkage and competition among cities in the great metropolitan region of Jing-Jin-Ji. Specifically we demonstrate that Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province have developed their unique industry structures and gained corresponding comparative advantages since the beginning of the reform and opening up. Accordingly, we propose the function orientation of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei Province based on their industrial characteristics and the principle of strategic interest of the country.
京津冀城市群功能定位及协同发展
DOI:10.11820/dlkxjz.2015.03.001
[本文引用: 1]

本文回顾了京津冀大城市群内部各组成部分的经济联系与利益矛盾。阐述了改革开放以来,京津两市和河北省的经济发展特点及已形成的优势。根据各自的特点、优势和符合国家战略利益的原则,提出了京津冀大城市群中北京、天津、河北省的功能定位。
The impact of Xiong'an new area on the evolution of the spatiotemporal pattern of landuse in Beijing
[D].
雄安新区建设对北京市土地利用时空格局演变的影响
[D].
Study on the functional structure of Lanzhou city based on multi-source data
[D].
基于多源数据的兰州主城区功能结构研究
[D].
Identification and evaluation of urban functional land based on POI data: A case study of five districts in Jinan
基于POI数据的城市用地功能识别与评价研究: 以济南市内五区为例
Identifying metropolitan edge in city clusters region using mobile phone data: A case study of Jing-Jin-Ji
基于手机信令数据的城市群地区都市圈空间范围多维识别: 以京津冀为例
A POI data-based study on urban functional areas of the resources-based city: A case study of Benxi, Liaoning
基于POI大数据的资源型城市功能区识别方法与实证: 以辽宁省本溪市为例
Urban functional area division considering POI and land use data
顾及POI与土地利用数据的城市功能区划分
Validating gravity model in multi-centre city: A study based on individual mobile trajectory
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002005
[本文引用: 1]

Due to the lack of empirical studies of scale variables and distance exponents, the effective application of the gravity model in urban study is challenging. With the development of multi-centralized Chinese cities, the gravity model must be validated because several relevant external conditions have changed. The purpose of this study is to validate Huff's Gravity Model using an individual mobile trajectory of mobile communication user in 2015. We follow Huff's two-step validation method: variable validation and parameter correction. Our main conclusions are as follows. First, attractions of commercial and employment centres conform to the law of the gravity model in which the attraction is proportional to the scale of a centre and inversely proportional to the distance from a centre. Second, in the spatial scale of Shanghai central city with spatial units in a 200-m grid, the mean distance exponent for commercial centres is 2.5 and that for employment centres is 3.0. The distance decay for commuting is greater than that for shopping trips, which means commuting is more sensitive to distance. Third, the gravity model can be used to predict the influence areas of adjusted commercial and employment centres based on validated variables and corrected parameters. Our results indicate that the prediction accuracies can reach 78.5% and 71.9% for the commercial and employment centres, respectively. The prediction accuracy for employment centres is slightly lower. This is because the attraction of employment centres is influenced not only by distance but also by factors such as family and housing prices, which will affect the prediction results. Lastly, in this study, we verify the spatial stratified heterogeneity of distance decay and determine that the distance exponent is not a unique constant because it has different values in different areas. Factors such as accessibility, distance to each centre, distance to a subway station and population density will affect distance decay.
基于个体移动轨迹的多中心城市引力模型验证
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202002005
[本文引用: 1]

长期以来由于规模变量、距离衰减系数取值缺乏依据,引力模型在城市研究中的应用容易受到质疑,加之中国城市的多中心化使得模型应用的外部条件发生改变,模型验证工作的必要性再次显现。本文使用2015年移动通信用户的个体移动轨迹数据,使用Huff当年的验证方法,通过变量检验、参数校正两个步骤,验证Huff的引力模型。研究发现:① 城市内部商业中心和就业中心的吸引力与中心的规模呈正比,与距中心的距离呈反比,符合引力模型规律。② 在上海中心城区空间尺度、200 m网格空间单元下,商业中心吸引力的距离衰减系数平均值为2.5,就业中心吸引力的距离衰减系数平均值为3.0,表明居民就业通勤对距离更加敏感,距离衰减比购物出行更加显著。③ 经变量检验、参数校正后的引力模型可用于对商业中心、就业中心优化调整后的势力范围进行预测,预测准确率可分别达到78.5%和71.9%。就业中心势力范围预测准确性略低,这是由于就业中心吸引力衰减除受距离影响外,还受家庭、房价等因素影响,会对预测结果产生扰动。最后,研究还证实了距离衰减系数存在空间分层异质性:距离衰减系数不是唯一值,受道路可达性、至就业(商业)中心距离、至地铁站距离、人口密度影响,不同地区的距离衰减系数存在较显著差异。
Correlation analysis of urban spatial structure based on modified gravity mapping model: A case study of Hubei Province
基于修正引力图谱分析的城市空间关联结构分析: 以湖北省为例
Structural characteristics and formation mechanism of spatial correlation network of grain production in China
中国粮食生产空间关联网络的结构特征及其形成机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202011008
[本文引用: 1]

基于1996—2018年中国省际粮食生产面板数据,在修正的引力模型准确测算粮食生产空间关联关系及构建空间关联矩阵的基础上,首先运用社会网络分析方法从整体特征、个体特征及块模型3个方面具体考察了粮食生产空间关联网络的结构特征,进一步采用二次指派程序方法探讨其形成机制。研究发现:① 省际粮食生产空间关联的密切程度在波动中提高,但仍有提升空间,网络结构呈现较好的稳定性和可达性,溢出效应具有多重叠加特性;② 省际粮食生产空间关联网络呈现主产区、主销区、平衡区“核心—边缘”分布格局,粮食主产区在网络中处于核心地位,粮食主销区和平衡区则处于边缘地位;③ 粮食生产空间关联网络可划分为净溢出、主受益、经纪人和双向溢出4个板块,板块间的溢出效应具有明显的梯度传递特征;④ 自然禀赋条件与社会经济因素的共同作用推动了粮食生产空间关联网络的形成,地理空间邻近性、经济发展水平与农村劳动力规模、机械服务规模、耕地资源的差异、降水量和日照时数的相近性对粮食生产空间关联网络的形成具有显著影响。
A study on the economic niche of land use theory and mechanisms of cropland conservation
土地利用的经济生态位分析和耕地保护机制研究
General niche of land use and its regulating mechanisms
土地利用的生态位及调控机制的研究
Application of the spatial shift-share analysis
偏离—份额分析法空间模型及其应用
Urban research using points of interest data in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.015
[本文引用: 1]

The rising of POI (Point of Interest) data drives an innovation of urban research. In order to sort out the progress of urban research using POI data in China, summarize the directions of research, methods of data analysis and shortcomings, and provide references for the future application of POI data in China’s urban development, CiteSpace was used to analyze 625 related literatures in CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure) database from 2010 to 2019. Result shows that a large number of literatures in urban research using POI data emerged since 2013, and boomed in 2017. According to the results of knowledge map analysis, the main applications of POI data in urban research are identification of urban functional areas, division of urban central areas and boundaries, identification of business agglomeration and recommendation of interested points. While the main methods for analyzing POI data are kernel density analysis, spatial correlation analysis and DBSCAN algorithm. Plenty researches show that POI data is a kind of effective data for urban research, and very helpful for researchers to better understand the spatial structures, distribution patterns and development rules of cities. In future, it can be combined with machine learning and the other algorithms to provide a decision-making method for a long-term development of urban expansion and internal functional structure adjustment. However, POI data can not replace the shape data in some scenarios, and the impact of public awareness should be seriously taken into account individually for different researches.
POI数据在中国城市研究中的应用
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.015
[本文引用: 1]

兴趣点(Point of Interest,POI)数据的兴起带动了城市研究的革新。为梳理中国POI数据在城市研究的应用进展,阶段性总结其应用方向、数据分析方法及尚存不足,并为未来POI数据在中国城市发展中的应用提供思路和借鉴。应用CiteSpace工具对中国知网2010—2019年625篇相关文献进行知识图谱分析,结合分析结果对POI数据应用方向和数据分析方法进行梳理总结。结果表明:时间上,国内应用POI数据进行城市研究的文献在2013年后大量涌现,2017年呈现爆发式增长;应用上,主要用于城市功能区划分、城市中心区和边界识别、查明业态集聚分布以及兴趣点推荐4个方面;方法上,常用的有核密度分析、DBSCAN聚类分析和空间自相关分析3类。研究表明,POI地理大数据是一种研究城市发展的有效数据,有助于研究者深入了解城市的空间结构、分布格局和发展规律,未来可进一步与机器学习等算法结合,为城市外部扩张和内部功能结构调整在更长期的发展上提供一个决策分析手段,但POI数据尚无法代替面数据,研究时也要充分考虑到公众认知度高低对研究的影响。
Research on urban functional area recognition integrating OSM road network and POI data
融合OSM路网与POI数据的城市功能区识别研究
Identify urban functional zones using multi feature latent semantic fused information of high-spatial resolution remote sensing image and POI data
融合高分辨率遥感影像和POI数据的多特征潜在语义信息用于识别城市功能区
Research on measurement method of urban spatial interaction based on GIS and SEM
[D].
基于GIS和SEM的城市空间相互作用测度方法研究
[D].
Application of land economic ecological niche in landscape pattern analysis at county level: A case study of Jinghe County in Xinjiang, China
The theory of land economic ecological niche was used to analyze the regional landscape pattern in this article, with an aim to provide a new method for the characterization and representation of landscape pattern. The Jinghe County region, which is ecologically fragile, was selected as an example for the study, and the Landsat images of 1990, 1998, 2011 and 2013 were selected as remote sensing data. The land economic ecological niche of land use types calculated by ecostate-ecorole theory, combined with landscape ecology theory, was discussed in application of land economic ecological niche in county landscape pattern analysis. The results showed that, during the study period, the correlations between land economic ecological niche of farmland, construction land, and grassland with the parameters, including landscape patch number (NP), aggregated index (AI), fragmented index (FN) and fractal dimension (FD), were significant. Regional landscape was driven by the changes of land economic ecological niche, and the trend of economic development could be represented by land economic ecological niche change in Jinghe County. Land economic ecological niche was closely related with the land use types which could yield direct economic benefits, which could well explain the landscape pattern characteristics in Jinghe County when combined with the landscape indices.
土地经济生态位在县域景观格局分析中的应用: 以新疆精河县为例
Ecological niche-based competition and cooperation relationship among county-level cities in Hexi Corridor
基于生态位理论的河西走廊县域城市竞合关系研究
A study on urban network structure of the urban agglomeration of central-southern Liaoning province based on an improved urban gravity model
基于改进引力模型的辽中南城市群网络结构研究
Spatial structure and taxonomy of decomposition in shift-share analysis
DOI:10.1111/j.1468-2257.2004.00258.x URL [本文引用: 1]
Mixed land use evaluation and its impact on housing prices in Beijing based on multi-source big data
Study on mutual mechanism between urban transport system and urban space pattern: A case study of Guangzhou
城市交通系统与城市空间格局互动影响研究: 以广州为例
Exploring urban functional areas based on multi-source data: A case study of Beijing
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200074
[本文引用: 1]

It has been a trend for the study of urban functional areas to employ multi-source at a finer tempo and/or spatial scale to contribute a niche understanding of the structure and content of the area. Drawing on advancement of technological development of new type and new sources of geo-coded data, the paper proposes a set of indicators to understand urban functional areas, including the intensity of the use of the area, the difference in the use between day and night, and the degree of multifunctionality. The empirical research is taken in Beijing and these indicators are derived by integrating the mobile phone signaling data of 14400 grid areas in the urban area in 2017 and 380975 points of interest (POI) data from Gaode map in 2016. The main research conclusions are as follows. (1) Every standard area in this paper has a square of 250 m×250 m. The number of Beijing's daytime active areas is three times that of nighttime active areas. The nighttime use intensity of restaurant, living, and other service facilities is higher, and the daytime use intensity of financial, tourism, and public service facilities is higher. (2) Tourism (28.2%), residence (12.1%), transportation (11.4%) are the three types of functional areas with the largest proportion of Beijing area, and the smallest area proportion is financial function district (2.8%), showing that the spatial characteristics of tourism, finance, and public functional areas gather, and other functional areas' distribution presents scattered characteristics. (3) Residential, restaurants, living, and other functional services are strongly dependent on each other, while tourism and enterprise functional services show strong exclusivity to other functional types. Except for the tourism functional areas, there appears an obviously different functional mixing pattern in the central urban area of Beijing. In this paper, the area with the highest function mixing degree (greater than 0.98) is defined as the highly mixed functional area, which accounted for 24.6% of the study area. The result of the functional area divisions has a strong practical significance for Beijing urban planning, and also provides an effective method and a richer perspective for the future in-depth study of urban functional areas.
基于多源数据的城市功能区精细化研究: 以北京为例
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200074
[本文引用: 1]

城市功能分区研究在时空尺度上不断细化,多源数据融合有利于推动城市功能分区研究的精细化发展。本文对比国内外城市功能区研究中对多种新型地理数据的内涵挖掘和应用,通过融合北京市2017年14400个栅格区域的手机信令数据和2016年高德地 图380975条兴趣点(POI)数据,量化区域功能使用强度的日夜差异和内部功能混杂程度,完成区域主导功能类型判定及功能混合度评价,并对北京城市功能区划分结果进行分析与验证,主要结论:① 北京的日间活跃区域面积是夜间活跃区域面积的3倍,其中餐饮、生活等服务设施的夜间使用强度更高,金融、旅游、公共服务设施的日间使用强度更高;② 北京市面积占比最大的三类功能区是旅游(28.2%)、居住(12.1%)、交通(11.4%),面积占比最小为金融功能区(2.8%),在空间上呈现出旅游、金融、公共功能区聚集,其他功能区具有离散分布的特征;③ 居住、餐饮、生活等功能服务存在较强的依赖性,而旅游、企业功能服务存在较强的排他性,北京中心城区内除旅游功能区外均存在不同程度的复合功能特征,高度功能混合区约占研究区域的24.6%。功能区划分结果对于北京城市规划具有较强的现实意义,也为今后深入研究城市功能区提供了有效方法和新的视角。
Analysis of functional connection and spatial pattern of Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration based on multi-element factor flows
基于多元要素流的珠三角城市群功能联系与空间格局分析
Method on describing the spatial pattern of land use and its application in China
[D].
土地利用空间格局刻画方法及其在中国的应用
[D].
Stages and spatial patterns of urban built-up land transition in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202007015
[本文引用: 1]

Since the reform and opening-up in 1978, the morphology of urban built-up land (UBL) has been changed significantly due to the rapid socio-economic development in China. Moreover, this change shows an unbalanced variation over space. Based on the UBL area and census data from 1981 to 2015, we use the moving T-test, kernel density estimation and Gini coefficient to identify the abrupt change points over UBL transition process and present its dynamic spatial pattern. This research exhibits four main results. First, there are three identified stages over the transition process, namely, low expansion rate of UBL-decrease of per capita UBL (1981-2000), moderate expansion rate of UBL-slow increasing rate of per capita UBL(1990-2000) and high expansion rate of UBL-high increase of per capita UBL (2000-2015). Second, the spatial pattern of UBL area transition proceeds slowly over the periods of 1990-2000 and 2000-2015. Cities with a high expansion rate of UBL tend to present a spatial pattern of an agglomeration over the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta, and the rest of the regions that tend to show a spatial pattern of an dispersion are provincial capitals in the central and western regions. On the contrary, cities with a high increasing rate of per capita UBL tend to originate from the eastern region to the entire country. Third, the variance of the UBL tends to be smaller during 1990-2000 and then greater during 2000-2015 over space, while the variance of the per capita UBL tends to be smaller during 1990-2000 and then stable during 2000-2015 over space. Lastly, we find that the results correspond to the previous theory of regional land use transition, and the socio-economic transformation phenomenon demonstrates the three identified stages. Moreover, the transition of spatial pattern reveals the fact that the change of national development strategy is from the priority of eastern coastal areas to the regional coordination. This work fills in a gap of quantifying the stage of land use transition, and provide support references to UBL management in the socio-economic transformation in the new era.
中国城市建设用地转型阶段及其空间格局
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202007015
[本文引用: 1]

1978年改革开放以来,社会经济快速发展不断改变着中国城市建设用地形态,并在不同区域表现出非均衡的空间差异。基于中国1981—2015年城市建设用地面积和人口数据,综合运用滑动T检验、K密度估计(KDE)和基尼系数等方法,识别中国城市建设用地转型的关键节点,并揭示其时空特征。结果表明:① 中国城市建设用地形态经历了“面积低速扩张—人均用地收缩”(1981—1990年)、“面积中速扩张—人均用地低速上升”(1990—2000年)、“面积快速扩张—人均用地快速上升”(2000—2015年)3个转型阶段。② 1990—2000年和2000—2015年两个转型阶段,面积转型的空间格局演变缓慢,表现出以东部长三角、珠三角为核心的大聚集和中西部以省会城市为中心的小分散格局,而人均用地转型空间格局呈由东部聚集向全国蔓延的演变趋势。③ 1990—2015年,城市建设用地面积的空间非均衡性表现为先逐渐缩小后逐渐扩大的动态演变特征,人均用地的空间非均衡性表现为先逐渐缩小后趋于稳定的演变特征。④ 中国城市建设用地转型符合区域土地利用转型的理论模式,与社会经济发展阶段转变相对应,空间格局演变揭示了国家发展战略由东部优先向区域协调发展转变的现实情况。研究在内容上弥补了土地利用转型阶段定量识别的不足,可为新时代社会经济转型背景下城市建设用地管控工作提供理论和数据依据。
Spatial pattern and variation characteristics of the production-living-ecological space in Beijing from 2000 to 2020
2000—2020年北京市“三生空间”格局变化特征分析
Application of spatial and temporal entropy based on multi-source data for measuring the mix degree of urban functions
基于多源数据时空熵的城市功能混合度识别评价
A POI data-based study of the urban functional areas of Chongqing and their mix degree recognition
基于POI的城市功能区及其混合度识别研究: 以重庆市核心城区为例
The research of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomerations' spatial connection based on urban relation intensity and urban flow
基于城市联系强度与城市流的京津冀城市群空间联系研究
Evaluation of the quality of economic development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration
京津冀城市群的经济发展质量评价
Research on spatial pattern change of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei services based on standard deviation ellipse analysis
基于标准差椭圆分析法的京津冀服务业空间格局变化研究
Study on the influence of functional division of urban agglomerations on regional coordinated development—taking Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration as an example
城市群功能分工对区域协调发展的影响研究: 以京津冀城市群为例