1 引言
1978年改革开放以来,中国城镇化发展取得巨大成就的同时,也促使城乡空间发生剧烈的转型与重构。但长期以来的重城轻乡发展政策,造成了城乡基础设施、人居环境与公共服务配套方面的巨大差距[1],也带来了日趋严重的“城市病”和“乡村病”。城乡发展不平衡不协调,是现阶段中国经济社会发展中最为突出的结构性矛盾[2]。党的“十九大”明确提出“建立健全城乡融合发展体制机制和政策体系,实施乡村振兴战略”,意在更好地解决城乡发展不平衡、农村发展不充分等重大问题[3]。城乡融合发展,是将城市和乡村作为一个有机体,促进城乡要素平等交换和公共资源均衡配置的过程[3]。土地是城乡发展的核心要素,也为城乡发展提供空间支撑[4],土地要素在城乡之间是否流动与平等交换关乎城乡融合发展目标的实现[5]。因此,构建科学合理的城乡聚落规模体系及空间重构方案,是实现城乡融合发展的首要切入点,对于推进乡村振兴战略具有重要理论及现实意义。
城乡聚落体系是指一定地域范围内,一系列不同大小、不同等级的城乡聚落,包括城市、集镇、乡村、部落等各种形式,按照一定组合方式,共同构成的既相互独立、又紧密联系的有机整体[6]。城乡聚落体系是地理学研究的重要内容,国外研究比国内起步较早,国内研究始于20世纪80年代初期,研究内容主要包括城镇体系的时空演变、等级划分、位序规模分布等方面[7]。但是,在长期城乡二元体制的城市偏向影响下[8],关于城乡聚落体系的学术研究也存在明显的城市主导与城乡二元分割特征,城镇体系研究中忽略乡村,村镇体系研究中又忽略城市,没有将城乡紧密结合。关于城乡聚落体系的相关研究多是以城镇为研究对象,重点关注城市、城镇以及城市群。研究内容包括城镇体系等级与规模结构[9,10]、布局优化[11]、时空演变[12]、对比研究[13]以及生态环境效应[14]等,在理论研究及现实应用价值方面取得了显著成果。乡村聚落的研究国内起步较晚,研究内容倾向乡村聚落时空演变特征[15]、聚落空间体系结构[16,17]、空间格局与驱动因素[18]、空间重构[19,20,21]与布局优化[22,23]等方面,研究区域重点关注西部黄土丘陵区[24]、中部传统农区[25]、东部经济发达地区[26]以及干旱绿洲地区[27,28,29]。当前,随着城乡关系步入城乡融合与统筹发展的新时代,城乡聚落将逐步形成相互交错、渗透与融合的有机整体,以往城镇主导及城乡分割的城乡聚落研究思路已经难以适应新形势下的城乡发展要求[30]。现有关于城乡聚落体系的研究成果取得了一定的理论及现实价值,主要研究区及内容重点关注传统农区[31]、东部发达地区[7]以及汾河流域[32]等地区的城乡聚落规模体系及空间结构,鲜有关于西部干旱区绿洲城乡聚落规模体系的相关研究。绿洲是干旱区最重要的人地关系地域系统,绿洲城乡聚落则是绿洲生态系统中人地关系最敏感的关键区域,水土资源胁迫依然是制约干旱区可持续发展所面临的关键问题,而绿洲城乡聚落规模的变化与合理性、适宜性是绿洲水土资源合理配置的重要前提[33,34]。
在工业化与城镇化快速推进的背景下,城乡人地关系失调的问题日趋凸显。形成了以“城乡分割、土地分治、人地分离”为主要特征的城乡人地关系,其中,乡村人地关系问题尤为突出,乡村人口持续流出,但乡村建设用地却持续增加[35,36]。相比于东部城乡聚落而言,干旱区绿洲城乡聚落规模普遍较小、城乡聚落土地资源低效利用特征显著。2009—2018年间渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模扩张较快,但城乡聚落人均占地面积增量反差较大,城镇聚落人均用地面积呈负增长特征,乡村聚落人均用地面积呈正增长特征。乡村聚落空间布局散乱且无序扩张较快,一定程度上造成了乡村聚落用地浪费及城镇用地短缺,将不利于该地区推进城乡融合及经济社会高质量发展。
鉴于此,本文以新疆典型绿洲—渭库绿洲为研究靶区,基于2009年和2018年两期土地利用数据,利用GIS空间分析技术、城市位序—规模法则以及引力模型等方法,考虑到绿洲整体性及城乡联动性,从城镇体系结构—城乡聚落规模—位序规模分布—时空演变特征4个维度刻画渭库绿洲2009—2018年城乡聚落规模体系时空演变特征;结合渭库绿洲城乡聚落位序—规模分布拟合结果与乡村地域多体系统理论,构建基于“网—区—场—极”的乡村振兴多级目标,对渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系进行以土地要素为关键抓手的空间重构及优化调整;对其空间重构路径进行逻辑解析并提出整治方向,以期为渭库及其他典型绿洲城乡聚落规模体系的合理化发展、空间布局优化协调、城乡聚落用地集约高效利用以及城乡聚落融合发展提供理论参考与科学依据。
2 研究区概况与数据来源
2.1 研究区概况
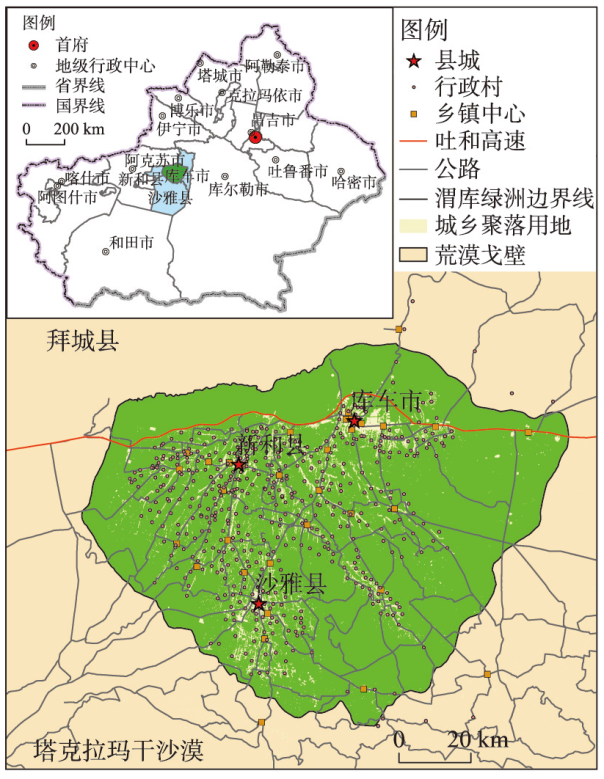
渭库绿洲地处中国西北干旱区塔克拉玛干沙漠北缘、天山中段南部(图1),地理范围介于82°8′20″E~83°39′50″E、40°59′13″N~41°54′35″N,海拔介于950~1300 m,是中国干旱区范围内较为典型的、完整的山前冲积扇平原绿洲。渭库绿洲整体位于新疆阿克苏地区库车市、新和县以及沙雅县境内,绿洲面积为5609.6 km2,占库车新和沙雅三县市总面积的10.7%[37],渭库绿洲是新疆典型的灌溉绿洲,也是南疆经济发展的核心地带之一,截至2018年渭库绿洲社会经济发展及人口现状如表1所示。2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落总规模达396.87 km2,其中城镇聚落规模为85.53 km2,乡村聚落为311.34 km2,10年来乡村聚落规模增量为城镇聚落增量的1.64倍,但城镇人口增量却为乡村人口增量的6.42倍。
图1
表1 2018年渭库绿洲三县市基本情况
Tab. 1
| 乡镇(个) | 行政村(个) | 社区(个) | GDP(亿元) | 总人口(万人) | 城镇人口(万人) | 乡村人口(万人) | 城镇化率(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 渭库绿洲 | 37 | 478 | 95 | 404.3 | 94.7 | 30.7 | 64.0 | 32.4 |
| 库车市 | 18 | 199 | 66 | 269.5 | 48.9 | 17.2 | 31.7 | 35.2 |
| 新和县 | 8 | 126 | 12 | 79.6 | 19.4 | 6.1 | 13.3 | 31.4 |
| 沙雅县 | 11 | 153 | 17 | 55.2 | 26.4 | 7.5 | 19.0 | 28.2 |
2.2 数据来源
研究数据包括以下几方面:① 城乡聚落用地斑块数据。该数据来源于新疆2009年土地调查数据以及2018年土地利用变更数据。通过对比核查可知,两套数据的土地分类标准及分类结果均一致。因此,可直接通过提取两套数据库中地类名称为“建制镇”和“村庄”的斑块作为城乡聚落用地图斑数据,并对相邻斑块进行融合处理。由于聚落图斑面积可以较为客观地反映城乡聚落规模特征,因此,本文利用建制镇—村庄建设用地面积来表征城乡聚落规模。城乡聚落规模体系指的是渭库绿洲范围内由不同等级、规模的城乡聚落图斑组成,且不同层级、同层级之间的城乡聚落图斑具有一定联系的城乡聚落图斑集合;② 地理要素空间数据。研究区县乡级行政区划边界、交通路网、河流水系等数据来源于中国基础地理信息数据库;③ 社会经济统计数据。该数据包括研究区三县市人口、GDP、城乡居民收入等统计数据,来源于历年《新疆统计年鉴》《阿克苏地区统计年鉴》。
2.3 研究方法
借鉴Zipf改进后的位序—规模法则对研究区城乡聚落的规模分布情况进行分析,其公式如下:
式中:r为城乡聚落斑块面积降序排列的位序;Pr为第r位的城乡聚落规模;P1为城乡聚落体系中首位聚落规模;q为齐夫指数,通过线性拟合模型进行估计。对公式(1)两边取对数得到公式(2),为便于表达进一步调整得到公式(3),所有公式如下:
式中:q为常数,是反映城镇规模结构的参数。q = 1,即Zipf认为的城镇规模符合自然状态下的最优分布,城镇聚落体系处于均衡发展状态,达到帕累托最优;q > 1时,表明研究区聚落规模分布比较集中,首位聚落具有较强的垄断地位,中小聚落发育不全,大聚落的优势突出;q < 1时,表示聚落规模分布相对集中,高位次聚落规模不是很突出,中小规模聚落比较发育。
2.3.2 GIS空间分析方法 平均最近邻指数(Average Nearest Neighbor, ANN)是以随机模式的分布状况作为标准,来衡量点状要素的空间分布特征。本文利用平均最近邻指数来判断渭库绿洲城乡聚落的空间分布模式,通过计算城乡聚落斑块中心点与最近邻聚落中心点之间的平均距离,再与假设随机分布的期望平均距离对比,依据计算结果判断城乡聚落之间的集聚离散特征,其计算公式为:
式中:
本文利用局部Getis-Ord Gi*探测局部区域聚落分布状况,进而分析其局部自相关性。Gi*指数可以很好地反映观测值在局部空间区域上的冷热点分布,其计算公式为:
式中:wij为以距离规则定义的空间权重;xi和xj分别是i和j区域的聚落斑块面积。
2.3.3 核密度估计法 核密度估计法(Kernel Density Estimation, KDE)是非参数的方法。核密度分析易于实现并能较好地反映地理现象空间分布中的距离衰减效应。核密度分析用于空间离散数据的连续性表达,分析聚落空间分布密度,直观反映不同地区城乡聚落分布的地域差异。计算公式为:
式中:n为聚落数量;h为带宽。
3 渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系演变特征
3.1 城镇村体系等级结构变化特征
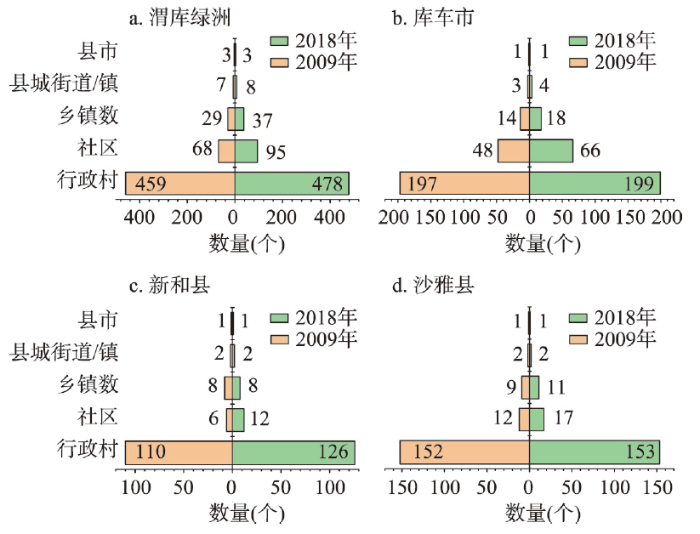
通过梳理渭库绿洲及三县市2009年和2018年城—镇—村体系数量等级结构的演变特征(图2)可知,渭库绿洲城—镇—村体系等级呈现顶尖底宽特征的“金字塔”结构,其中县市数量没有变化,乡镇增加了8个,社区增加了27个,行政村增加了19个。库车市变化较大的是乡镇和社区数量,新和县变化较大的是行政村数量,沙雅县变化较大的是社区数量。城镇村体系等级结构的变化与当地城镇化水平、社会经济发展以及区域发展政策密切相关,库车市已于2019年率先撤县设市,步入了城市发展序列,2009—2018年间渭库绿洲各县市大力推行社区建设等城乡发展政策,但建制镇建设力度不大,城镇主导效应不突出,难以发挥城镇的集聚规模效应。
图2
图2
2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城—镇—村体系等级结构金字塔
Fig. 2
Pyramid of the hierarchical structure of the urban-town-rural system in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
3.2 城乡聚落体系规模变化特征
通过分析渭库绿洲及其三县市城乡聚落体系的规模特征(表2)可知,2009—2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系的规模不断扩大,城乡聚落数量增加了2709个,增幅10.6%,其中城镇聚落增长729个,增幅为76.7%,乡村聚落增长1980个,增幅为8.03%;城乡聚落面积扩大了36.5 km2,增幅为10.1%,其中城镇聚落增长13.49 km2,增幅为20.2%,乡村聚落增长22.1 km2,增幅为7.6%。渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模的平均值以及标准差均有所减小,说明聚落之间的规模差异在缩小。城镇聚落数量和规模增幅均大于乡村聚落,但城镇聚落数量和规模的增量仅占总增量的26.9%和39.4%,渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系规模扩大的主要贡献来自乡村聚落,在渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系演化过程中城镇聚落数量和规模分别由3.7%增长到5.9%和19.7%扩大到21.6%。渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系的演化过程呈现出一定的地域分异特征,库车市城镇聚落和乡村聚落规模均为渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系的首位,沙雅县次之,新和县排序最后。2009—2018年间渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模持续扩张的原因可能与城乡人口增加有较大关系,城镇人口的增量是乡村人口的6倍多,但乡村聚落用地增量却是城镇聚落用地的1.64倍,人均城镇聚落用地减少14.4 m2,人均乡村聚落用地增加27.3 m2。这种城乡人口和土地的变化反差反映了2009—2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系演变具有“乡村人地关系失调”特征。
表2 2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模分布统计分析
Tab. 2
| 聚落规模 体系 | 指标 | 渭库绿洲 | 库车市 | 新和县 | 沙雅县 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009年 | 2018年 | 2009年 | 2018年 | 2009年 | 2018年 | 2009年 | 2018年 | |||||
| 城镇聚落 规模 | 数量(个) | 951 | 1680 | 521 | 977 | 256 | 396 | 174 | 307 | |||
| 总量(km2) | 71.14 | 85.53 | 41.39 | 50.50 | 8.84 | 10.24 | 20.91 | 24.80 | ||||
| 人均(m2) | 292.9 | 278.5 | 261.6 | 293.7 | 270.8 | 168.7 | 401.9 | 332.7 | ||||
| 乡村聚落 规模 | 数量(个) | 24656 | 26636 | 8415 | 9198 | 6055 | 6777 | 10186 | 10661 | |||
| 总量(km2) | 289.24 | 311.34 | 142.01 | 148.11 | 54.81 | 65.97 | 92.41 | 97.25 | ||||
| 人均(m2) | 459.3 | 486.6 | 448.1 | 467.7 | 420.6 | 494.1 | 506.1 | 512.9 | ||||
| 城乡聚落 规模 | 数量(个) | 25607 | 28316 | 8936 | 10175 | 6311 | 7173 | 10360 | 10968 | |||
| 面积(km2) | 360.38 | 396.87 | 183.41 | 198.61 | 63.65 | 76.21 | 113.32 | 122.05 | ||||
| 平均值 | 0.0141 | 0.0140 | 0.0205 | 0.0195 | 0.0074 | 0.0106 | 0.0109 | 0.0111 | ||||
| 标准差 | 0.0593 | 0.0584 | 0.0649 | 0.0633 | 0.0202 | 0.0283 | 0.0683 | 0.0673 | ||||
3.3 城乡聚落规模体系位序—规模分布变化特征
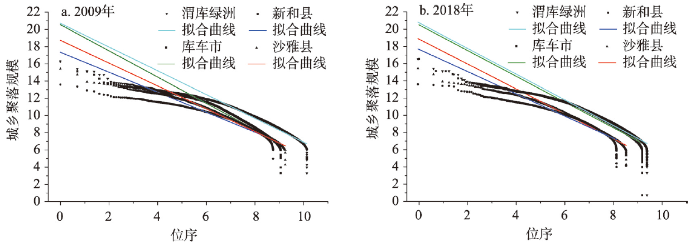
运用城市位序—规模法则拟合渭库绿洲及三县市城乡聚落的规模分布,所有拟合曲线的拟合优度R2均大于0.9,拟合效果较好,表明渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模分布基本符合位序—规模法则。由分析结果(表3、图3)可知,① 渭库绿洲及三县市的齐夫指数均大于1,说明研究区首末位城乡聚落斑块规模趋向分散,聚落斑块规模分布差异较大且首位聚落占垄断地位,中小型聚落发育不突出。2009—2018年除新和县以外其余县市齐夫指数均有所减小,表明新和县首末位聚落规模差距还在扩大,其余县市有所收缩。各县市齐夫指数的地域差异较为明显,其中库车市齐夫指数最大,沙雅县次之,新和县最小,说明三县市中库车市首位聚落垄断性最强,沙雅县次之,新和县最弱,从三县市城镇化水平以及县城建设用地面积的排序也可以反映出这一特征;② 2009年和2018年渭库绿洲及三县市的城市位序—规模分布拟合曲线均呈现“翘首”“伏颈”和“摆尾”现象,首位聚落占垄断地位,但规模大幅低于理论值,中位聚落发育不突出,末位聚落规模分布呈“垂尾”特征已不服从位序—规模法则。10年间位序—规模拟合曲线的变化特征表现为首位聚落规模有所提升但不显著,末位聚落“摆尾”特征进一步加剧,说明渭库绿洲首位聚落规模较小,未来有一定的城镇化发展空间,位序等级最低的零星聚落斑块的数量和规模无序扩张较快,需加以遏制和优化重构;③ 2009—2018年间渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系的齐夫指数均有所下降(除新和县),表明10年来渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系的极化作用不突出,且有所下降,大量新增的聚落用地分布散乱,向首位或高位序等级聚落的集聚特征不明显。
表3 2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落位序—规模法则拟合相关参数
Tab. 3
| 区域 | 方程式:y = -qx+c | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 | 残差平方和 | Pearson's r | 调整后R2 | 斜率 | 截距 | |
| 渭库绿洲 | 2009 | 2301.81 | -0.977 | 0.954 | -1.381 | 20.72 |
| 2018 | 2757.44 | -0.975 | 0.950 | -1.375 | 20.81 | |
| 库车市 | 2009 | 1137.30 | -0.973 | 0.946 | -1.525 | 20.56 |
| 2018 | 1272.24 | -0.972 | 0.945 | -1.498 | 20.51 | |
| 新和县 | 2009 | 848.30 | -0.953 | 0.909 | -1.162 | 17.35 |
| 2018 | 978.38 | -0.955 | 0.912 | -1.190 | 17.71 | |
| 沙雅县 | 2009 | 553.75 | -0.986 | 0.972 | -1.333 | 18.91 |
| 2018 | 423.67 | -0.989 | 0.977 | -1.326 | 18.74 | |
图3
图3
2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系位序—规模分布拟合图
Fig. 3
Fitting curves of the rank-size distribution of the urban-rural settlement scale system in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
3.4 城乡聚落规模体系时空分异特征
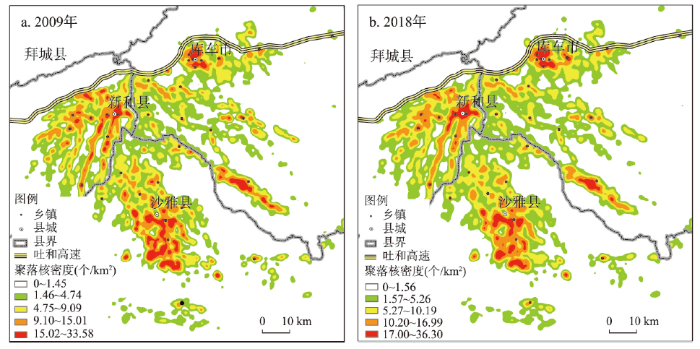
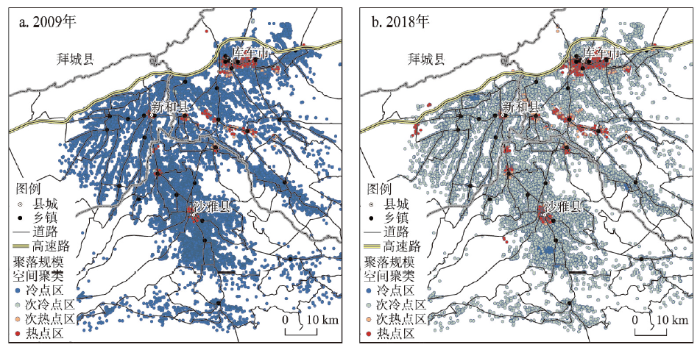
本文首先运用平均最近邻指数方法测算了2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落空间分布特征,发现2009年和2018年R统计值分别为0.305和0.289,标准化Z值分别为-212.73和-228.56(均小于-2.58),P值均为0(表明通过显著性检验),以上结果表明2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落空间分布模式的集聚态势显著且趋势有所加剧。利用核密度分析与空间局部热点探测等方法测度2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落密度分布及聚落规模冷热点分布(图4、图5),发现:① 2009—2018年间渭库绿洲城乡聚落密度整体提高,城乡聚落密度空间分布整体呈集聚分布特征,具体表现为沿干渠、县城、中心镇、交通干线与绿洲内部集聚分布且密度值呈中心高外围低的空间梯度衰减特征;② 2009—2018年间渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模局部冷热点空间分异特征表现为县城以及中心镇是高值集聚的热点区,但10年来高值集聚的热点数量增长及集聚趋势不明显,其周围散落分布着次热点区。10年来广泛分布在绿洲内部及边缘的低值集聚冷点区大部分均转为次冷点区,2018年低值集聚的冷点区仅少量分布在县城以及中心镇的边缘地区。原因是渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系中大量微小零星聚落斑块规模扩张较快,乡镇中心大规模聚落斑块聚合特征不明显,这反映出聚落用地向中心乡镇空间集聚程度不突出,如此将难以发挥土地向城镇集聚所带来的极差地租收益及规模报酬递增效应。
图4
图4
2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落分布核密度图
Fig. 4
Nuclear density map of urban-rural settlements in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
图5
图5
2009年和2018年渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模冷热点空间分布
Fig. 5
Spatial distribution of cold and hot spots at the urban-rural settlement scale in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
4 渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系优化重构
通过刻画渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系特征发现,渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模扩张与人口增长关系存在一定的失调特征。其中,乡村人地关系失调特征尤为突出。若不加以系统规划和引导城乡聚落规模有序增长,将不利于该区域城乡聚落用地高效利用及合理配置。因此,基于对渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系特征的深入研究以及对该区域乡村人地关系失调问题的初步诊断,本文对渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系进行空间重构与优化调整,并提出优化策略及对标乡村振兴多级目标的实际操作层面的空间重构方案。
4.1 基于位序—规模分布拟合的城乡聚落用地优化思路及策略
以位序—规模分布拟合的曲线特征以及数值结果作为渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系优化的依据,并依托相关理论以及实际情况加以检验和校正。通过前文分析可知,渭库绿洲聚落点分布形态总体服从拟合曲线。虽然位序—规模法则的一般原理认为,聚落点位于拟合曲线之下代表实际值小于理论值,城镇化发展潜力较大。但是通过查找首位及位序靠前的聚落点与拟合曲线上的相应值并将对数还原后发现,位于拟合曲线上的点还原成实际值后,面积是现有聚落点的数十倍之巨。结合实际情况来看,渭库绿洲城乡聚落大多分布在绿洲内部,周边分布着大量耕地,首位及位序越靠前的大型聚落进行规模扩张时,势必会侵占周边耕地,耕地保护及农作物产量会受到威胁。因此,在水土资源胁迫、耕地保护及粮食安全的压力下,渭库绿洲首位城镇聚落在短期内难以通过增量用地开发实现大规模扩张而达到理论值,只能在城乡聚落规模体系的存量建设用地中,进行合理精准有序的协调置换建设用地指标以保障各层级不同发展目标下的建设用地需求。
因此,基于审视上述理论结果的客观性以及从实际发展情况出发,依据城乡聚落规模体系位序—规模分布特征及拟合结果所识别出的潜在优化零星斑块规模达5.53 km2。本文认为在现阶段乡村振兴战略提出的农业农村优先发展要求下,渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系重构优化的重点应放在广大乡村聚落,具体优化策略为:① 从位序对数最高的低等级聚落斑块开始逐渐向位序对数较低的高等级聚落斑块推进;② 应采取多级目标来优化不同规模等级的城乡聚落斑块;③ 不同位序等级的聚落斑块应采取不同的优化类型,等级最低的零星斑块散落分布,无序扩张较快且斑块规模均最小,整治难度最低,应列为当前重点整治内容,加强空间管制坚决遏制无序扩张。曲线尾部的微型聚落斑块规模较小数量较多,整治难度加大,应根据实际发展情况及诉求列为优先重构,在充分论证分析并尊重村民意愿的情况下,将区位条件优越且地域邻近的聚落斑块逐步进行空间重组。
4.2 基于乡村振兴多级目标的城乡聚落规模体系空间重构模式探讨
刘彦随提出实施乡村振兴战略,重在实现乡村振兴多级目标,即从边缘到中心由城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极所构成的“网—区—场—极”多级目标体系[3]。依据乡村地域多体系统的理论内涵及相对应的多级目标体系内容,本文尝试以渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系重构为重点内容,结合“人—地—业—路”核心发展要素评价值的空间分异特征来识别乡村振兴极、重构村镇空间场、整治乡村发展区、构建城乡基础网。
(1)基于乡镇影响力测算的乡村振兴极识别。本文基于渭库绿洲乡镇实际发展情况以及对标乡村振兴战略目标,并遵循典型代表性以及可获取性的原则,选取了能够反映乡镇“人—地—业—路”核心发展要素的相关指标,从人口规模、乡镇用地规模、产业发展以及交通路网4个方面通过特尔菲法筛选了10个指标(表4),并借鉴相关文献[41]的方法构建了乡镇影响力指标体系及评价模型。乡镇影响力是对乡镇经济社会发展状况的定量评价,以此评价结果作为识别乡村振兴极的依据,并利用自然断点法将其划分为5个等级。据分析发现(图6),渭库绿洲乡村振兴极空间分异特征表现为:① 1级乡村振兴极分布在县城、高等级公路附近以及本身规模较大、发展基础较好的乡镇;② 2级乡村振兴极大多位于县城周边或远离县城的广大绿洲腹地;③ 3~5级乡村振兴极大多分布于县城附近、县域以及绿洲边缘。
表4 乡村振兴极测度指标体系
Tab. 4
| 目标层 | 准则层 | 指标层 | 指标解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 乡村振兴极识别 | 人口规模 | 总人口数量(人) | 反映人口基础及发展潜力 |
| 城镇人口数量(人) | 反映乡镇城镇化水平 | ||
| 土地规模 | 乡镇建成区面积(km2) | 反映乡镇中心建设用地集聚规模和吸引力 | |
| 耕地面积(km2) | 反映农业发展基础及农业生产要素集聚能力 | ||
| 产业发展 | 乡镇经济收入(万元) | 反映乡镇经济综合实力 | |
| 企业个数(个) | 反映乡镇非农产业发展情况及非农就业吸纳能力 | ||
| 城乡居民人均收入(元) | 反映乡镇人均经济收入水平 | ||
| 企业从业人员(人) | 反映乡镇非农就业水平 | ||
| 交通条件 | 公路里程(km) | 反映乡镇路网交通整体水平 | |
| 路网密度(km/km2) | 反映乡镇路网覆盖度 |
(2)基于加权Voronoi图的村镇空间场影响范围划分。本文通过上述乡镇影响力测度的结果,利用加权Voronoi图划分了渭库绿洲不同乡镇增长点的空间辐射范围,即“村镇空间场”(图6)。研究发现,渭库绿洲各乡镇影响力及其所能辐射的空间范围均存在显著差异。总体来看,发展水平高或处于绿洲腹地及边缘地区的乡镇的空间辐射范围较大,即“村镇空间场”较大。例如,库车市牙哈镇、哈尼喀塔木乡以及塔里木乡,沙雅县的盖孜库木镇、塔里木乡,新和县的新和镇和依其艾日克镇等。而大多发展水平高但处于中心地区的乡镇,其空间辐射能力较低,即“村镇空间场”较小。这一研究结果说明,虽然县城社会经济发展水平最高,但其扩散效应受空间距离的梯度衰减作用和低等级振兴极的替代效应的影响难以到达边缘地区。地处绿洲腹地及边缘地区的乡镇,虽然发展水平不是最高,但其空间辐射能力和扩散效应却很强。渭库绿洲三县市城镇人口占比很低,大多数乡村人口集中分布在广大绿洲腹地。因此,除继续保持县城发展以推进新型城镇化的目标以外,未来渭库绿洲推进乡村振兴的着眼点和重心应放在绿洲腹地的2~3级乡村振兴极上。通过就地城镇化的发展路径,使核心要素集聚,形成基础设施完善、居业协同发展、产业结构合理、生态环境优美以及保留乡村特色和功能的乡村振兴极,以进一步强化其“村镇空间场”的辐射强度和质量。
图6
图6
渭库绿洲乡村地域多级目标空间优化重构
Fig. 6
Spatial optimization and reconstruction of the multilevel objective of rural areas in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
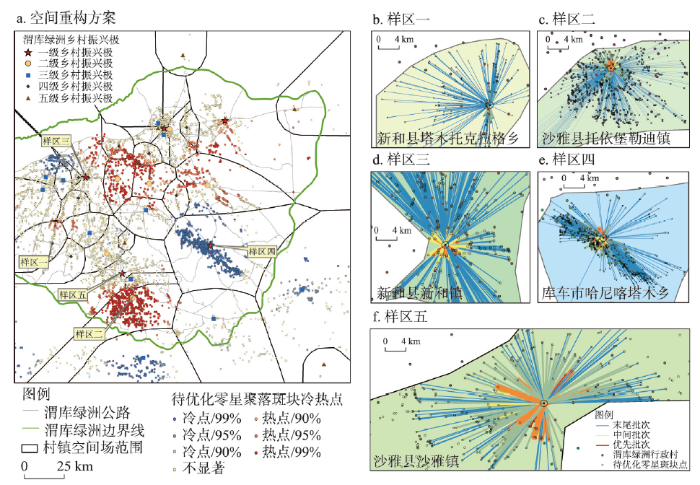
(3)基于引力模型的乡村发展区零星斑块整治重构。本文筛选出渭库绿洲三县市城乡聚落规模体系中“摆尾”部分的异常值(零星斑块)并将其落位到地理空间上,利用空间局部冷热点分析识别零星斑块的冷热点空间分布,结合其地域功能及发展水平选取典型样区。本文以斑块规模代表斑块活跃度,万有引力及空间相互作用理论的一般原理认为,任何两个事物都有相互吸引的作用力,质量越大吸引力越强,质量越小越有可能被吸引。基于空间相互作用理论并利用引力模型测度典型样区空间场范围内零星斑块的引力值并采用自然断点法划分为3个等级,按引力值大小划分牵引次序,优先批次牵引线连接的零星图斑可作为首批重构对象,后者以此类推(表5、图6)。依据引力模型测度结果及其地域特征,本文选取了5个乡镇作为典型样区进行分析。沙雅镇和新和镇均是县政府所在地的城关镇,发展潜力及区位优势较好。因此,其发展目标是推进县域新型城镇化的主要地区,建设用地指标可倾向城区建设及产业发展。哈尼喀塔木乡是渭库绿洲所有乡中人口规模最大,低值集聚的零星斑块也最多,属于1级乡村振兴极且空间场范围较大。托依堡勒迪镇是位于绿洲南部腹地中的2级乡村振兴极,零星斑块呈高值集聚特征。因此,二者空间重构目标为保障就地城镇化发展用地需求,腾退建设用地指标重点倾向“居业协同体”构建的用地保障。塔木托格拉克乡地处绿洲边缘且是4级乡村振兴极,零星斑块集聚特征不显著。因此,其空间重构目标为提升乡村振兴极的极化作用,需要进一步强化土地要素的集聚,形成高等级乡村振兴极,腾退建设用地指标重点倾向基础公服设施的配置。对乡村发展区零星斑块分批次牵引重构的实质就是在不占用耕地或新开发土地的情况下,在现有存量用地中对零星斑块进行复垦整治和空间位移与置换,通过耕地占补动态平衡的思路来获取建设用地指标的过程。实际操作中可采用城乡增减挂与拆旧复垦等政策工具来实施,理论上能够为典型样区节省土地及腾退建设用地指标2.29 km2。
表5 渭库绿洲典型样区零星斑块分层级引力值及规模(km2)
Tab. 5
| 重构样区 | 优先批次 | 中间批次 | 末尾批次 | 总值 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 引力值 | 牵引规模 | 引力值 | 牵引规模 | 引力值 | 牵引规模 | 引力值 | 牵引规模 | ||||
| 沙雅镇 | 12358.69 | 0.0202 | 17675.98 | 0.0886 | 11200.95 | 0.2566 | 41235.62 | 0.3654 | |||
| 新和镇 | 31911.16 | 0.0199 | 28667.09 | 0.0801 | 11655.99 | 0.3297 | 72234.24 | 0.4297 | |||
| 哈尼喀塔木乡 | 8236.68 | 0.0504 | 6604.77 | 0.2106 | 1600.35 | 0.4423 | 16441.80 | 0.7033 | |||
| 托依堡勒迪镇 | 4862.04 | 0.0108 | 5371.95 | 0.0960 | 3818.89 | 0.4814 | 14052.88 | 0.5882 | |||
| 塔木托格拉克乡 | 4679.92 | 0.0072 | 1545.65 | 0.0182 | 1078.36 | 0.1764 | 7303.93 | 0.2018 | |||
(4)基于点—轴系统理论的城乡基础网构建。城乡融合发展的要义在于强化城乡地域系统极化作用的基础上充分发挥扩散效应,构筑城乡命运共同体,形成城乡发展的立体空间和网格结构[3]。因此,需要以乡村振兴极的空间均衡分布为前提,综合考虑各振兴极的区位条件和地域功能,逐步完善渭库绿洲多层级路网体系,进一步强化高等级乡村振兴极,使其成为支撑渭库绿洲整体经济社会发展的核心增长极。促进核心发展要素向中等级乡村振兴极集聚,以强化其辐射带动广大绿洲腹地的重要功能。低等级的乡村振兴极多分布在绿洲边缘,生态敏感性较高,这类振兴极的发展定位应倾向生态功能的完善和环境保护,并结合当地丰富的旅游资源重点发展生态旅游产业,强化其生态服务功能。通过打造多层级乡村振兴极和完善多层级路网体系,来构建促进渭库绿洲城乡融合发展的城乡基础网。
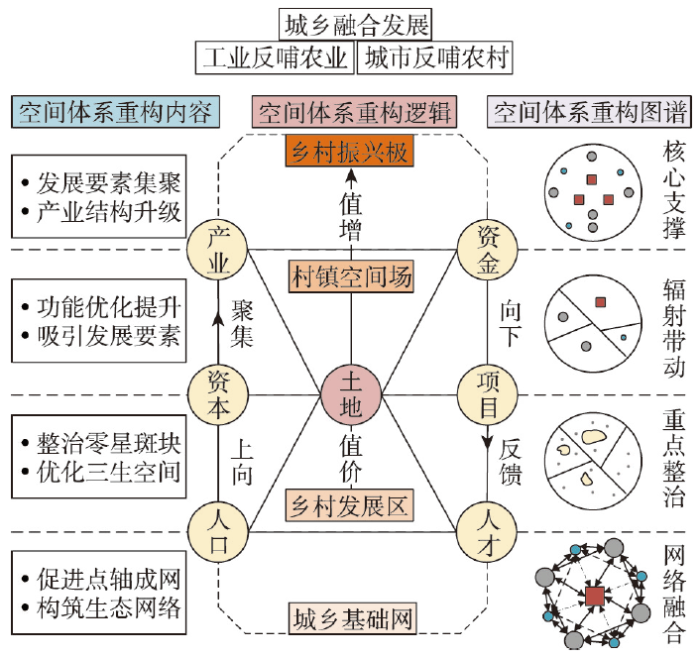
4.3 渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系空间重构路径逻辑解析与整治对策
城乡聚落体系空间重构,即统筹城乡镇村空间体系[20],是实现城乡地域系统各组分功能协调提升、生产要素配置重组以及三生空间格局优化重塑的过程。乡村振兴最终目标是调整人地关系以适应社会经济发展新阶段的生产要素价值变化,而乡村聚落与乡村振兴的关系密切,是乡村人地关系调整的核心和关键抓手,在乡村振兴中起关键作用[42]。因此,以乡村优先发展为表征的城乡关系调整,将促进乡村聚落用地等生产要素在城乡之间的配置[43],对于实现乡村振兴与新型城镇化具有重要现实意义。乡村聚落用地是乡村振兴战略落实的关键,乡村建设用地只有打破区位限制约束,才能分享城市周边土地存在的级差地租收益,形成较高的市场交易价格[44]。部分省市所推广实施的农村建设用地拆旧复垦政策就是该思路的具体实践,其模式主要通过结构重组、空间重构、生产方式变革和生态环境优化等推动乡村振兴[44]。
本文基于城乡聚落规模体系特征的刻画以及乡村振兴多级目标的内涵,按照“网—区—场—极”的分级目标对渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系进行空间重构和优化协调。基于系统梳理渭库绿洲各乡镇影响力水平、地域功能及样区零星斑块整治方向及规模,本文将乡村发展区零星斑块的重构整治方向划分为:① 县城城镇化需求吸引型;② 中心乡镇建设需求吸引型;③ 中心村就地集约化吸引型;④ 特殊功能保留型;⑤ 生态安全保育型。通过设立多层级乡村振兴目标并将目标对应到城乡聚落规模体系中的不同层级,以土地要素为核心的城乡聚落规模体系空间重构的逻辑内涵(图7)就是使核心发展要素“土地”,从乡村不断向上流动到乡镇和县城的过程。在此过程中通过整治零星斑块使其在空间上向各个乡村振兴极集聚,将整治后的零星斑块用以复垦或优化重构乡村发展区三生空间布局,构建以“源地—廊道”为特征的城乡生态融合网络格局,强化生态安全格局。土地要素的空间置换与集聚使土地功能用途发生转变,其价值也随之增加,土地资源逐步转变为资产和资本,各级主体可获得更多土地收益用于乡镇建设和产业发展,就能吸引更多的固定资产投资,土地的流动与集聚牵动其他发展要素的流动与集聚,如此就能在不同层级的核心增长点产生更多经济效益。新型城镇化过程中,县城以外的中心乡镇以就地城镇化发展路径为重点任务,以此促进极化作用,形成支撑当地发展的乡村振兴极。建立以“工农互促、城乡互补、协调发展、共同繁荣”为目标的城镇反哺农村、工业反哺农业的发展理念及政策保障体系。通过政策保障及规划引导,使极化作用带来的资本集聚效应转化为扩散效应,建立资金、产业和基础设施项目以及人才向乡村下沉的渠道,以此推动乡村振兴战略的实施和落地。
图7
图7
渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系空间重构路径逻辑解析
Fig. 7
Logic analysis of the spatial reconstruction path of the urban-rural settlement scale system in the Ugan-Kuqa River Delta Oasis
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
本文以渭库绿洲为研究靶区,利用GIS空间分析技术及城市位序—规模法则等方法探究渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系演变特征,并以渭库绿洲城乡聚落位序—规模分布拟合特征为优化基础,以乡村地域多体系统为理论依据,在实操层面对渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系按“网—区—场—极”分级目标进行空间重构与调整优化,旨在为渭库绿洲及相似地区城乡聚落规模体系空间重构提供科学依据与决策参考。主要结论如下:
(1)渭库绿洲城镇村等级体系结构呈“金字塔”型,2009—2018年间社区增加数量最多,行政村次之,乡镇数量增加最少,城镇建设过程中城镇主导效应不突出。
(2)渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模不断扩大,聚落规模扩张的贡献主要来自乡村聚落。城乡聚落规模扩张与人口增长关系反差明显,乡村人地关系失调特征显著。渭库绿洲城乡聚落分布整体服从位序—规模分布拟合曲线,总体呈“翘首”“伏颈”“摆尾”特征。渭库绿洲齐夫指数呈下降趋势,城乡聚落体系的极化作用不明显。首位聚落占垄断地位,但增长较慢且规模低于理论值,中小型聚落发育不足,位序等级最后的零星聚落呈“摆尾”特征且不断加剧,需要进一步遏制和整治。
(3)渭库绿洲城乡聚落密度分布具有明显的干渠、道路、县城及中心乡镇指向性以及围绕核心的空间梯度衰减特征。城乡聚落规模空间聚类地域差异明显,县城、中心乡镇等热点区集聚趋势不显著,绿洲腹地及外围等连片冷点区聚落规模增长较快,大部分转为次冷点区,聚落用地向乡镇、县城中心的空间聚合特征不突出。零星聚落无序扩张较快,土地集约利用程度低,难以发挥规模集聚效应。渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系中各级核心区均有交通轴线连接,呈点—轴—网空间分布特征,各级核心区聚落规模呈明显的核心—边缘圈层结构。
(4)渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系空间重构与优化应采取乡村优先发展的思路,重点整治零星斑块,并加强空间管制与监测。本文提出了县城城镇化需求吸引型、中心乡镇建设需求吸引型、中心村就地集约化吸引型、特殊功能保留型以及生态安全保育型5种整治方向。通过设立乡村振兴多级目标并依据城乡聚落体系的地域功能、空间组织关系来优化重构零星聚落斑块,理论上能够为典型样区节省建设用地指标228.84 hm2,依托核心支撑、辐射带动、重点整治以及网络融合等分层重构方案及发展措施,能促进以土地要素为核心的城乡要素优化配置,从而有效推进乡村振兴战略与新型城镇化的协同实施。
5.2 讨论
本文以绿洲整体性及城乡联动性为出发点,在探析渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系特征的基础上,对标乡村振兴多级目标进一步提出了城乡聚落规模体系空间重构的具体方案,研究结论能够为该地区城乡聚落规模体系优化提供明确思路及科学依据。城乡融合发展是新时代背景下,乡村振兴与新型城镇化等国家战略协同实施的共同抓手,乡村振兴强调农业农村优先发展,新型城镇化强调以人为核心的城乡互补与协调发展,在实施过程中二者关系应是互为支撑、协同推进。因此,需要将城镇与乡村视为一个有机整体,充分考虑其地域自然、人文特征及联动性,准确研判其演变过程中出现的发展矛盾与关键问题,对标发展目标并利用科学研究方法,按不同阶段因地制宜地提出重构优化方案。当前,城乡聚落规模体系空间重构与优化的过程就是在保障农业农村优先发展及以城带乡的前提下,促进城乡聚落用地以市场配置为主导的平等流动,使区域发展过程中土地资源高效合理配置及集约利用,发挥更大的经济效益,带动其他发展要素向区位条件好的乡镇集中,通过就地城镇化发展路径,强化乡村振兴极对广大乡村的辐射带动作用,促进区域协调发展。
不同于发达地区[7]的是渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模在发展演变进程中具有典型的乡村人地关系失调现象,即空间集聚效应不显著、城乡聚落无序扩张较快,而该特征既是长期以来的城乡二元发展制度的结果,也有悖于推进城乡融合及一体化发展的时代背景。基于对渭库绿洲这一典型发展矛盾的诊断,本文认为渭库绿洲城乡聚落体系的空间重构与优化,首先应着手城乡聚落规模调整及空间布局优化。在充分考虑绿洲自然本底特征及城乡联动性的前提下,厘清渭库绿洲城乡聚落规模体系的演变特征并诊断城乡聚落发展过程中的突出矛盾与问题,是对其进行空间重构的关键所在。空间重构过程中应避免走以往“城镇化”的老路,发展重点倾向乡镇及广大村域。渭库绿洲内聚落形式较为单一且均质性程度较高,以一般城乡聚落为主,除此还有少量的国营农牧场、油田厂区及水利水电站等特殊功能的聚落分布,考虑到这类聚落所占比重极小,所以在空间重构过程中并未剔除。在未来研究中将从以下方面深入开展:① 精准识别乡村振兴极的地域功能,按“三主三分”[45]理论原则精准落实多元类型聚落与多级目标组合的城乡聚落空间重构;② 重点突破土地整治过程中待优化零星斑块的内部属性特征识别及筛选监测技术;③ 重点研究生态安全视角下融合生态安全网络的城乡聚落体系重构优化,以期促进干旱区绿洲人地关系和谐发展。
参考文献
Spatial patterns and influencing factors of urban-rural coordinated development in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2016.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

Integrating urban and rural development is the strategy and mostly significant task of people-oriented urbanization. It is of importance to strengthen research on urban-rural coordinated development, to provide scientific supports for urban-rural planning and policy making. We first proposed the theoretical framework of urban-rural coordinated development and established coordinated index system. Then, by GIS and ESDA methods, spatial patterns and characteristics of urban-rural coordinated development were explored, and its influencing factors were analyzed based on spatial econometric model. The results are shown as follows: 1)The urban-rural coordinated development system consists of four subsystems, which are factors, structures, functions and policies. The coordinated urban-rural development depends on the mutual coordination and cooperation of elements within the subsystem and positive mutual feedback evolvement among the subsystems. 2) Sub-indices such as investment, industry, income and consumption between urban and rural areas take on significant spatial differences, respectively. The degree of variation of investment coordination index, industry coordination index, income coordination index and consume index reduces in turn. 3) Urban-rural integrated coordination index shows obviously spatial differences among the east, middle, northeast and west of China, and takes on spatial agglomeration. High-level areas of coordination index gather in the eastern coastal region and a few cities in the central and western China, while low-level areas are mostly located in the central and western China, especially showed in the provincial map. 4) Economic growth, urbanization, rural investment and domestic consumption had significantly positive effects on urban-rural coordination development, while urban investment had negative effects. Meanwhile, education investment, education level and infrastructure did not have significant effects due to the misallocation of resources between urban and rural areas. These findings are of use to integrate urban and rural development in different aspects. Firstly, we should appropriate urbanization models should be explored in different areas according to the areal characters and its urban-rural development transformation status. Secondly, it is essential for the Chinese authorities to change its traditional planning model and implement rural revitalization plan, especially improving rural infrastructure construction, public services and the comprehensive function of the town. Thirdly, we should reform binary urban and rural managing system gradually and moderately, according to taking a sufficient consideration of the status and trend of inside and outside urban-rural coordinated systems.
中国城乡协调发展格局特征及影响因素
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2016.01.003
[本文引用: 1]

构建城乡协调发展的理论框架与指标体系,基于GIS技术和ESDA方法揭示中国地级市城乡发展协调空间特征,借助空间计量经济学模型探讨城乡协调发展影响因素。研究结果表明:① 城乡发展协调体系由要素、结构、功能、政策等层级构成,具有层级内协调与层级间互馈特征。② 城乡投资、产业、收入、消费等分项指标均存在明显的空间差异,投资协调指数、产业协调指数、收入协调指数、消费协调指数区域间差距依次减小。③ 城乡协调发展综合指数空间集聚特征明显,东中西分异,高值区集聚在东部沿海地区和中西部少数中心城市地区。④ 经济增长、城镇化、对农投资、消费能力的提高有助于城乡协调发展,教育投资、教育水平、基础设施建设对城乡协调发展的作用仍需进一步加强。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 4]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 4]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Land use transition and land management
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201509001
[本文引用: 1]

With the introduction of land use transition to the academic circle of China since the turn of the new millennium, related researches combining with the characteristics of China's socio-economic development have been carried out extensively. Recently, issues related to land use transition in China have attracted interest among a wide variety of researchers as well as the government officials. Land use transition refers to the changes in land use morphology including dominant morphology and recessive morphology of a certain region over a certain period of time driven by socio-economic change and innovation. In general, dominant land use morphology refers to the quantity, structure and spatial pattern of land use, and recessive land use morphology includes land use features in terms of aspects of quality, price, property rights, management mode, input and productive ability, and function. This paper puts forward the theoretical model of regional land use transition as the following: with the socio-economic development, the transformations between different land use types during a certain period of time arise the changes of regional land use morphology pattern from strong conflict to weak conflict, i.e., coordination, which enable a new balance between different land use morphology patterns reflecting the development trend of different economic departments, and then realize the transformation of urban-rural land use system from quantitative change to qualitative change. Then, the mechanism of mutual feedback between land use transition and land management was probed based on a three-fold framework of natural system-economic system-managerial institution system. Generally, land use transition is affected by land management via economic measures, land resources engineering, policy and institution. Land use transition can also contribute to the adjustment of land management measures via socio-ecological feedback. Therefore, policy-makers need to adjust their land management policies taking into account the continuous change of land use morphology and different phases of regional land use transition. Under the background of urban-rural transformation development, the researches of land use transition and land management may focus on how to measure the transitions of land use dominant morphology and recessive morphology and the subsequent transition of the function of land use system, how to measure the socio-economic and environmental effects of land use transitions, how to refine the popular model of regional land use transition, and how to adjust land use transition via socio-economic and engineering measurements. Finally, the author argues that more attentions need to be paid to the recessive morphology of land use, the change of which is the key to policy and institution innovation and improving land management.
论土地利用转型与土地资源管理
DOI:10.11821/dlyj201509001
[本文引用: 1]

自21世纪初土地利用转型这一研究方向引入中国后,土地利用转型已成为当今学术界和国家行政部门十分关注的重要课题。在拓展深化土地利用转型的概念内涵,阐述土地利用转型的理论模式基础上,探讨了土地利用转型与土地资源管理二者之间的互馈机制,进而分析了土地利用转型与土地资源管理二者之间的相互影响。研究指出:决策部门应根据土地利用形态的变化适时调整土地资源管理政策措施,充分考虑目标区域所处的土地利用转型阶段,以增强土地资源管理决策的科学性。在探讨未来土地利用转型与土地资源管理研究方向基础上,强调土地利用隐性形态及其变化应当成为今后土地利用转型与土地资源管理研究关注的焦点,通过管控土地利用隐性形态的变化来创新土地资源管理政策法规及制度,提升土地资源管理水平。
Impacts of land market on urban-rural integrated development in China
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190201 URL [本文引用: 1]
中国土地市场对城乡融合发展的影响
Evolution characteristics and driving mechanism of urban-rural scale system at county level: A case of Zhangjiagang city, Jiangsu province
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20190112 URL [本文引用: 1]
县域城乡聚落规模体系的演化特征及驱动机理: 以江苏省张家港市为例
Evolution paths and the driving mechanism of the urban-rural scale system at the county level: Taking three counties of Jiangsu province as an example
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812009
[本文引用: 3]

In the context of the new era, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to promote urban-rural integrated development and rural revitalization by exploring the evolution paths and the driving mechanism of the urban-rural scale system. In this paper, we examined the evolution paths and the driving mechanism of this system at the county level based on both the land change survey data and remote sensing data in 1995 and 2015, when taking three counties of Jiangsu province as an example, namely developed Zhangjiagang, moderately-developed Taixing, and less-developed Lianshui at different levels of economic development. Based on the empirical study, in this paper, three typical evolution paths of the urban-rural scale system at the county level in Jiangsu province were summarized, and they fell into three types: Developed County, Moderately Developed County, and Less Developed County. In this case, some conclusions can be drawn as follows: (1) the number of settlements in the county decreased, but the total size increased; (2) the total size of rural settlements decreased, and the size of cities and towns increased at different speeds, when the town size gradually exceeded the urban size; (3) the number and the built-up area of high grade settlements increased, while those of low grade settlements decreased; (4) the polarization feature of the county's development became increasingly significant before gradually becoming weak; (5) the characteristics of the spatial cluster concerning the urban-rural scale system became increasingly significant, and the number of hot-points increased in the county area; (6) urban and rural construction land constantly expanded, when Chengguan town and key towns experienced the main change; (7) the spatial pattern of the urban-rural scale system evolved from the single center to double centers, and then to multi-centers. Furthermore, there were two common characteristics, namely urban-dominant effect and clumped-distributive effect, in the developing process of the urban-rural scale system in different counties. Then, based on the analysis of the key influencing factors, in this paper, the driving mechanism of the urban-rural scale system at the county level was put forward. In this study, economic growth, urbanization, transport network, and institutional management stand for four ways to propel progress. They are like the four wheels of a car, reinforcing and depending on one another and forming an integrated whole, in which the urban-rural settlement system constantly evolves.
江苏典型县域城乡聚落规模体系的演化路径及驱动机制
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812009
[本文引用: 3]

新时代背景下,深入开展县域城乡聚落规模体系研究对促进城乡融合发展、推动乡村振兴战略的实施具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。本文从苏南、苏中、苏北选择张家港市、泰兴市、涟水县3个典型县市作为研究案例地,利用1995年和2015年遥感影像数据和土地利用数据,构建了县域城乡聚落规模体系的评价方法,对县域城乡聚落规模体系的时空演化过程进行了实证分析,发现不同类型县域城乡聚落规模体系的演化路径既有明显差异,也存在一般性路径,而且演化路径具有显著的城镇主导效应和集群分布效应。在深入分析经济发展、城镇化、交通网络、制度与管理4种主要影响因素基础上,进一步提炼出县域城乡聚落规模体系演化的“四轮”驱动机制。研究结果有助于深入认识城乡聚落有机整体的系统观,为推动城乡聚落优化重构提供了新的研究视角和方法支撑。
Research on the geography of rural revitalization in the new era
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190133
[本文引用: 1]

Urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development are not only the important strategic themes of China's modernization, but also the main frontier topics of rural regional system research in geography. Facing the problems of urban-rural segregation, human-land segregation and increasingly severe rural diseases in the process of rapid urbanization in China, urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are accelerated to be the national strategies. This research briefly analyses the economic and social background of rural revitalization and its significance in the new era. It is pointed out that the important responsibility of modern geography to face the national strategy and serve the rural revitalization is to deeply explore the major theories and scientific approaches of the coupling of man-land system, the integration of urban-rural development and the fit of the functions of villages-towns, while this paper focuses on the domestic research progress of rural revitalization strategy since it has been proposed for one year and the main contents and characteristics of this special issue. Finally, focusing on giving full play to the advantages and characteristics of geography, this paper expounds the theoretical frontiers and scientific and technological needs of the scientific research on rural revitalization in the new era. The ten frontier issues mainly include the differentiation and integration mechanism of urban and rural regional system; the transformation mechanism and scientific approach of rural regional system; the interaction principle and planning governance of agriculture, farmers and rural areas; the mutual feedback mechanism of rural natural-social-technical system; the coupling process and scenario simulation of rural man-land system; the suitability and carrying capacity of rural spatial reconstruction; and rural transformation developing endogenous power and synergy mechanism; new subjectivity and farmers' organization of rural revitalization; efficiency and transmission mechanism of scientific and technological innovation of rural revitalization; disaster and risk control mechanism of rural regional system. And we put forward some preliminary thoughts and suggestions for deepening the research of rural science and geography on rural revitalization in China.
新时代乡村振兴地理学研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190133
[本文引用: 1]

城乡融合与乡村可持续发展,既是中国现代化建设的重要战略主题,也是地理学乡村系统研究的主要前沿课题。面对快速城镇化进程中城乡分隔、人地分离和日趋严峻的乡村病问题,加快推进城乡融合与乡村振兴上升为国家战略。本文简要分析了新时代乡村振兴的经济社会背景及其重要意义,指出深度探究人地系统耦合、城乡发展融合、村镇功能契合重大理论与科学途径,成为现代地理学面向国家战略、服务乡村振兴的重要责任。重点介绍了乡村振兴战略提出一周年来国内相关研究进展及本专辑论文的主要内容与特点。最后,着眼于发挥地理学优势和特色,阐释了新时代乡村振兴科学研究的前沿问题及科技需求,提出了进一步深化中国乡村科学与乡村振兴地理学研究的初步思考和建议。
Spatiotemporal relationships between urban system and water system in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
京津冀城镇体系与水系结构的时空关系研究
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.003
[本文引用: 1]

京津冀地区人水关系矛盾突出,分形可以有效描述城镇体系和水系时空演化特征,从而揭示两者演化关系,为城市问题的解决提供一些理论和经验依据。论文采用分形理论中的网格维数和多分维谱,首先分别刻画了两者的时空演化特征,其次探讨了城镇体系和水系结构之间的时空关系,最后探究了水系结构退化的影响因素。主要结论有:① 1990—2010年,京津冀地区建设用地的网格维数升高、自相似性增强、从集聚向分散转变,意味着建设用地朝着空间填充程度增强、有序、分散的方向发展,而水系反之,证明两者具有不同的时空演化方向;② 21世纪10年代,京津冀的人水关系十分紧张,南水北调虽然缓和了京津冀用水问题,改善了大尺度上的水系结构,但在小尺度上改善有限;③ 越靠近城市中心,建设用地分形形态发育越成熟,结构越有序,越靠近外围越混乱无序;④ 京津冀地区水系退化,由自然和人为两方面因素造成,21世纪以后人为因素的影响较为显著。针对京津冀地区水系退化,提出如下政策建议:在城市建设过程中,一方面科学规划城市水系,重视低等级水系的保护;另一方面节约集约利用水资源,完善水资源管理机制。未来,需要进一步探索城市发展和水系的非线性关系,为城市可持续发展提供依据。
Evolution of urban system structure scale in central China
中国中部地区城镇体系规模结构演变
Study on urban spatial structure optimization in Henan province
河南省城镇体系空间优化研究
Temporal-spatial characteristics of evolution of the urban system in Jing-Jin-Ji Metropolitan Region
京津冀都市圈城镇体系演化时空特征
Comparative research on regional differences in urbanization and spatial evolution of urban systems between China and India
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706004
[本文引用: 1]

As two rising great powers, China and India have undergone similar development processes, but they also exhibit significant differences in development paths and patterns. The significant differences in political systems, economic systems, and developmental environment between the two countries have attracted great attention from scholars. This research focuses on the regional differences and spatial evolution processes in urbanization and urban systems between the two countries from a geographical perspective. Based on the demographic censuses of both countries and the urban population data from the United Nations, this paper systematically compared and analyzed the spatial characteristics of urbanization and urban systems in China and India using various methods including spatial analysis, parameter estimation, and nonparametric estimation. The results indicate that: (1) Since the 1990s, the regional differences in urbanization in China have transformed from south-north differences to coastal-inland differences, whereas the north-south differences in India have been stable. (2) In terms of the spatial scale at the province (state) level, the population densities and urbanization rates were positively correlated in both countries. The correlation is more significant when the urbanization rate is higher than 50%. However, in recent years, the correlation between population density and urbanization rate kept increasing in China, while such correlation has been decreasing in India. (3) Currently, the urban system is dominated by large and medium-sized cities in China and India, which complies with the characteristics of the rank-size distribution. But the economic reform has exerted significantly different effects on the spatial evolution of the urban systems in the two countries. The economic reform has changed the major driving force for urban development in China from geological and historical factors to the spatial structure of the economic system. However, in India, the driving forces for urban development have always been geological and historical factors, and the economic reform even decreased the effect of the spatial structure of the economic system on urban development.
中印城镇化区域差异及城镇体系空间演化比较
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201706004
[本文引用: 1]

中国和印度作为两个正在崛起的大国,发展历程较为相似,但发展路径和模式差异较大。两个国家政治制度、经济体系、发展环境等的显著差异已经吸引了学者的广泛关注,本文将从地理学视角出发,重点关注两国城镇化及城镇体系的区域差异和空间演化过程。以人口普查和联合国城市人口数据为基础,采用空间分析、参数估计、非参数估计等多种方法,对中印两国城镇化和城镇体系的空间特征进行系统的比较分析,结果表明:① 20世纪90年代以来,中国城镇化的区域差异由南北差异转变为沿海—内部差异,而印度南北差异的格局则基本稳定;② 从省(邦)级空间尺度来看,中国和印度的人口密度和城镇化率都呈现正相关关系,当城镇化率超过50%后,两者的相关性更为显著,但是近年来中国人口密度与城镇化率的相关性不断增强,而印度则呈现降低的趋势;③ 现阶段中印两国以大中城市为主的城镇体系符合位序—规模分布的特征,但是经济改革对于两个国家城镇体系空间演化的影响差异明显,改革使得中国城镇发展的主要驱动力由地理历史因素向经济系统空间结构转变,而印度城镇发展的驱动力始终是地理历史因素,经济改革甚至降低了经济系统空间结构对城镇发展的影响。
Theoretical analysis of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil and coupler control
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912008
[本文引用: 1]

There is an extremely complex nonlinear coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. How to coordinate this relationship has become a global strategic problem and a worldwide scientific problem. First, based on theoretical analysis, this paper revealed the coupling, coupling relationship, coupling degree and coupling tower of interaction between urbanization and eco-environment. Second, by analyzing the main controlling factors, ten kinds of interaction modes between urbanization and eco-environment are summarized. Third, according to the strength of coupling degree, we have identified six coupling types, including low coupling, slight coupling, moderate coupling, high coupling, excellent coupling, and full coupling, which correspond to the random coupling, indirect coupling, loose coupling, synergistic coupling, tight coupling and control coupling, respectively. Then, urbanization and eco-environment coupling tower was formed. Finally, the theory of urbanization and eco-environment coupling coil was established. Through rotating the graph by 10°, we built 45 kinds of coupled graphs, including linear graph, index curve graph, logarithmic curve graph, double index curve graph and S-shaped curve graph. Different graphs represent different urban development modes, stages and characteristics. Among them, S-shaped curve coupled graph is optimal, and it reflects the best state of urbanization and eco-environment coupling. After that, we amplified the S-shaped coupled graph, and then constructed a coupler (UEC) based on the SD model and the complex relationship between different variables. The coupler consists of 11 regulatory elements and 201 variables, and can control the coupling state between urbanization coil and eco-environment coil. In general, the above control types include static control of multiple cities at the same time, dynamic control of a single city at different times, and dynamic control of multiple cities at different times. Through coupler control, urbanization coil and eco-environment coil can keep the best dynamic and orderly state. In addition, if one variable changes, the structure, function and simulation results of the coupler will also be affected. Finally, with the increase of control intensity, the coupler will gradually improve the coupling degree between urbanization coil and ecological environment coil.
城镇化与生态环境耦合圈理论及耦合器调控
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912008
[本文引用: 1]

城镇化与生态环境之间客观上存在着极其复杂的近远程非线性耦合关系,如何协调城镇化与生态环境的关系问题已上升为全球性战略问题和世界性科学难题。本文从理论上揭示了城镇化与生态环境交互作用的耦合性、耦合关系和耦合度;根据主控要素总结出了城镇化与生态环境耦合的10种关系和交互方式;根据耦合度强弱将耦合性分为低度耦合、较低耦合、中度耦合、较高耦合、高度耦合和完全耦合6种类型,分别对应随性耦合、间接耦合、松散耦合、协同耦合、紧密耦合和控制耦合,进而形成城镇化与生态环境耦合塔;创建了城镇化与生态环境耦合圈理论,按每旋转10°生成一个图谱构建了由直线图谱、指数曲线图谱、对数曲线图谱、双指数曲线图谱和“S”型曲线图谱等组合而成的45种耦合图谱,不同图谱对应着不同的城市发展阶段和发展模式。在多种耦合图谱中,认为“S”型曲线耦合图谱是最佳图谱,代表着多种图谱中体现城镇化与生态环境相互作用的最佳耦合状态。以“S”型曲线耦合图谱为依托,借助SD模型及各变量之间存在的一对一、一对多和多对多的复杂关系,构建了由11个调控要素和201个变量构成的耦合调控器(UEC),只要一个变量发生变化,就会牵一发而动全身,影响整个耦合调控器的结构、功能和调控结果。这种耦合调控器包括同一时间多个城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的静态调控、不同时间同一城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的动态调控、不同时间多个城市城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间的动态调控3种时空尺度,通过调控将逐步推动城镇化圈与生态环境圈之间由低级耦合向高级耦合方向演进。
Spatiotemporal change of rural settlement land in the Loess Plateau and influencing factors
黄土高原乡村聚落用地时空演变与影响因素
The rural settlement morphological types and spatial system characteristics in the Jianghan plain
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.013
[本文引用: 1]

Under the background of land space planning reform, the land space of county is divided into three types: Urban space, agricultural space and ecological space. Among them, the planning of rural residential area system is the key to the agricultural space reconstruction. The implementation of Rural Revitalization Strategy requires the construction of rural community system according to the law of rural population migration. The characteristics of rural settlement spatial pattern and the optimized reconstruction mode are the foundation of rural community reconstruction. Based on the land GIS data and the statistical data of villages and towns, the cluster analysis and fractal method are used to explore the form types and spatial system characteristics of rural settlements in the Jianghan Plain. The research shows that the Jianghan Plain has formed ‘two category and four types’ of rural settlement space forms due to the difference of its internal natural environment matrix: One is the balanced mosaic settlement form in the low-hilly and mound areas, which can be divided into two subtypes: high-density & low-hilly point form and medium-density & mound crumb form, this rural settlement present a ‘star point’ spatial structure. Another is shaft-dependent settlement form in the river and ditch network areas, which can be divided into two subtypes: low-density & lake-arc form and medium-low density & river-ditch linear form, this rural settlement presents a ‘point-axis’ spatial structure. The characteristics of ‘two category and four types’ rural settlement form and spatial system in the Jianghan Plain are typical in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River Plain. It can provide theoretical basis and practical guidance for the spatial reconstruction of such rural settlements and the optimization of rural residential area system.
江汉平原乡村聚落形态类型及空间体系特征
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.01.013
[本文引用: 1]

依据国土空间用地GIS数据及村镇统计数据,采用聚类分析及分形学方法,探索江汉平原乡村聚落空间形态类型及空间体系特征。研究表明,江汉平原因其内部自然环境基质的差异,形成了“二类四型”聚落空间形态:低丘岗地地域,主要是均衡镶嵌型聚落空间形态,可分为高密度(斑块)低丘点状形态及中密度(斑块)岗地团块形态2种亚型,此类聚落形态的村镇呈现出“星点”式空间结构;河渠水网地域,主要是轴带依附型聚落空间形态,可分为低密度(斑块)滨湖弧带形态和中低密度(斑块)河渠直线形态2种亚型,此类聚落形态的村镇呈现“点轴”式空间结构。江汉平原“二类四型”乡村聚落形态及空间体系结构在长江中游平原水网农区有一定的典型性,可以为此类乡村聚落空间重构、乡村居民点体系优化提供理论基础及实践指导。
Research on the reconstruction of rural settlement system based on spatial interaction theory at County level: A case study in Changshou district, Chongqing city
基于空间相互作用理论的县域农村居民点体系重构研究: 以重庆市长寿区为例
Spatial patterns and controlling factors of settlement distribution in ethnic minority settlements of southwest China: A case study of Hani terraced fields
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.02.007
[本文引用: 1]

Settlement pattern, an important part of the human-nature system, is the foundation of rural geography, and it has become a hotspot in geographic research. Scientific analysis and characterization of settlement patterns are significant for promoting the development of urbanization, ethnic unity, and well-off society in rural minority areas. However, there is still a lack of research on the settlement patterns of ethnic minority areas, especially in those multi-ethnic group gathered areas. This study depicted the settlement patterns of seven ethnic minority groups (including Hani, Yi, Zhuang, Han, Miao, Yao, and Dai) in the Hani Rice Terraces World Heritage area, which is a typical multi-ethnic group gathered area in the southwest of China. The results show that: 1) In terms of spatial locations, 68% of the settlements in the Hani terraced fields area are located in the west and central parts of the territory, mainly in the areas of Han, Yi, and Zhuang. 2) The ethnic settlement pattern in the Hani terraced fields is characterized by the mix of Hani-Yi, accompanied by the mix of other ethnic groups. 3) In terms of location and the environment, settlements of the seven ethnic groups have significant differences in locational and environmental characteristics such as altitude, slope, temperature, precipitation, distance to river, settlement scale, cultivated land area, distance to administrative center, and grain yields. 4) The main controlling factors of the distribution of Zhuang, Miao, and Yao settlements are economic and administrative and distance to tourism centers (86.4%, 75.3%, and 92.8%); the main controlling factor of the distribution of Yi settlements are air temperature (52.0%); and the main controlling factors of the distribution of Han, Hani, and Dai settlements are precipitation (98.7%, 52.2%, and 97.0%). 5) On the whole, the settlements of Hani terraced fields formed a three-dimensional pattern of multi-ethnic symbiosis vertically, and a multi-ethnic mosaic pattern horizontally. This research can provide a reference for the construction of new rural areas in minority regions, the optimization of settlement patterns, targeted poverty alleviation, and the construction of a well-off society in an all-round way.
中国西南少数民族聚居区聚落分布的空间格局特征与主控因子分析: 以哈尼梯田区为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.02.007
[本文引用: 1]

聚落格局是乡村地理学研究的基础,也是人地地域系统的重要组成部分,更是目前地理学研究的热点之一。科学分析、揭示、刻画少数民族等脆弱地区的聚落格局,对合理、高效推进该区域新型城镇化道路建设,实现民族团结和繁荣,全面建成小康社会具有重要意义。而目前,对于少数民族、尤其是多民族共生区的聚落格局研究还不足。论文以中国西南少数民族聚居的哈尼梯田区为例,从聚落分布的空间位置特征、民族格局特征、区位环境特征及其主控因子等方面,刻画了哈尼梯田区哈尼、彝、壮、汉、苗、瑶、傣等7个民族的聚落格局特征。结果表明:① 在空间位置上,哈尼梯田区68%的聚落分布在区内西中部,主要以哈尼、彝、壮为主。② 在民族格局上,形成了以哈尼—彝混居的大格局,以壮、汉、苗、瑶、傣混居的小格局。③ 在区位环境上,7个民族在海拔、坡度、气温、降水量、与河流距离、聚落规模、耕地面积、与行政中心距离和粮食单产等区位环境特征上具有显著差异。④ 在主控因子上,壮、苗、瑶聚落分布的主控因子为经济、行政、旅游中心距离,贡献率分别为86.4%和75.3%、92.8%;彝族聚落布局的主控因子为气温(贡献率为52.0%);汉、哈尼、傣聚落布局的主控因子为降水量,贡献率分别为98.7%、52.2%、97.0%。⑤ 整体而言,哈尼梯田区聚落格局在垂直向上,形成了多民族共生的立体格局,在水平向上形成了多民族互嵌格局。研究可为少数民族地区新农村建设、聚落格局优化、精准扶贫、全面建设小康社会提供科学参考。
Process and driving factors of rural restructuring in typical villages
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201902009
[本文引用: 1]

Rural restructuring is an important means of implementing and pushing forward the strategy of rural vitalization. A complete process of rural restructuring usually consists of different stages, including initial period, development period, stabilizing period and stable period. Based on the established theoretical framework of analyzing the process of rural restructuring, by introducing the concepts of rural development index, the intensity of rural restructuring and the contribution rate of rural restructuring, the quantitative research and comparative analysis of the driving factors of rural restructuring process at village scale were carried out in the typical villages in metropolitan suburbs and plain farming areas. The results show that: (1) Since the 1990s, along with the transformation of industrial structure from traditional agriculture to industrial mining and tourism service industry, the socio-economic forms and territorial spatial structure of Huangshandian Village have undergone drastic restructuring, and the process of rural restructuring has experienced the initial stage and the development stage successively, and in a stabilizing stage now. The industrial development of Yangqiao Village has experienced the stages of traditional agricultural leading and concurrent farming production. Since 2000, it has taken on a sign of socio-economic restructuring. Recently, the living space has been reconstructed under the promotion of local governments, but the economic form has not changed significantly. At present, the village is still at a low level of development as a whole. (2) The rapid rural restructuring in Huangshandian Village is the results of combined action of exogenous and endogenous factors. The exogenous factors include market requirement pull, government macro-policy guidance, and so on. The endogenous factors include resources and environment, location conditions, behavioral agent, economic foundation, cultural trait, and so on. The restructuring process of Yangqiao Village is mainly dominated by socio-economic development course including urbanization, industrialization and technological progress as well as some exogenous policies such as "building new countryside" and "increasing vs. decreasing balance" land-use policy. The root cause for its relatively slow restructuring speed is lacking of endogenous development impetus.
典型村域乡村重构的过程及其驱动因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201902009
[本文引用: 1]

乡村重构是实施推进乡村振兴战略的重要手段,一个完整的乡村重构过程通常由初始期、发展期、趋稳期、稳成期等不同阶段组成。本文在构建乡村重构过程分析的理论框架基础上,探索引入乡村发展指数、乡村重构强度指数和乡村重构贡献率的概念,选取大都市郊区和平原农区典型村域开展乡村重构过程的定量研究和驱动因素的对比分析。研究表明:① 20世纪90年代以来,伴随产业结构由传统农业向工业采矿业、旅游服务业转型,黄山店村社会经济形态和地域空间结构发生了剧烈重构,乡村重构过程依次经历了初始阶段、发展阶段,目前处于趋稳阶段;杨桥村产业发展经历了传统农业主导、农业兼业化生产阶段,自2000年以来开始出现社会经济重构迹象,近年来在地方政府推动下生活空间发生重构,但经济形态尚未发生明显改观,目前村域整体上仍处于低水平发展阶段。② 黄山店村快速的乡村重构是市场需求牵引、政府宏观政策引导等外源性因素及资源环境、区位条件、行为主体、经济基础、文化特质等内源性因素综合作用的结果;杨桥村的重构历程主要受城镇化、工业化、技术进步等社会经济发展进程以及“新农村建设”“增减挂钩”等外源性政策因素主导,缺乏内生发展动力是导致其重构速度相对缓慢的根源。
Rural restructuring: Theory, approach and research prospect
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 2]

For the sake of adapting to the changes of elements in both kernel system and external system of rural development, rural restructuring is a process of optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements affecting rural development, reshaping social and economic structures in rural areas and optimizing spatial pattern in rural territory, and approaching the structure optimization and function promotion of rural territorial system as well as the structure coordination and function complementation of urban-rural territorial system. Based on elaborating the concept and connotations of rural restructuring and the mechanism of promoting rural restructuring due to the evolution of "elements-structure-function", the paper probed the approaches of rural restructuring from the aspects of spatial restructuring, economic restructuring and social restructuring. In order to meet the current national strategic demands and meet the challenges of rural development in the process of urban-rural development transformation, it is in great urgency to strengthen the study on the patterns and processes, dynamic mechanism, differentiated development models, rural planning technology systems, strategies and policies for rural development, and the impacts of globalization on China's rural restructuring in the future. Finally, focusing on a series of problems in the implementation of some important government intervention policies, which is aimed at boosting the social and economic development of rural areas in recent years, a critical analysis and discussion is carried out.
论乡村重构
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201704001
[本文引用: 2]

快速城镇化进程驱动中国乡村地域发生巨大变化。乡村重构,即为适应乡村内部要素和外部调控的变化,通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局,以实现乡村地域系统内部结构优化、功能提升以及城乡地域系统之间结构协调、功能互补的过程。本文在界定乡村重构的概念内涵,构建基于“要素—结构—功能”演变助推乡村重构的理论框架基础上,从空间重构、经济重构、社会重构视角探讨了乡村重构的实现路径,并着眼于服务当前国家重大战略需求和解决城乡转型发展进程中乡村地域系统面临的现实困境,提出了未来中国乡村重构研究需重点关注的内容。最后,就现有旨在促进乡村社会经济发展的重大引导性战略和政府干预性政策及其在实践操作中引发的一系列问题,展开批判性分析和讨论。
Theoretical thinking of rural restructuring
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 1]

With its focus on the increasingly complicated human-environment relationship under the background of rapid urbanization, rural restructuring study has become an important frontier research area of geography. Rural restructuring is a process of reshaping the socioeconomic forms and spatial patterns in rural areas in respond to the changes of factors both internal and external of the system, by optimally allocating and efficiently managing the material and non-material elements of rural development. It aims at ultimately optimizing the structures and improving the functions within rural territorial systems as well as realizing the structural coordination and functional complementation between urban and rural territorial system. Based on the perspective of "elements-structure-function" of rural territorial system, this article first elaborated the concept of rural restructuring from the aspects of behavioral mainstream, value system, and targets. Then, a framework of rural restructuring mechanism was analyzed, which consisted of inducing mechanism, supporting mechanism, constraining/promoting mechanism, guiding mechanism, and driving mechanism. Furthermore, in view of the guiding role of governments in optimal allocation of critical resources and rural restructuring, this article argued that it is necessary to restructure the contours of state intervention in rural societies and economies. Finally, the research contents of rural restructuring in the future were prospected.
乡村重构的理论认知
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.05.002
[本文引用: 1]

面向快速城镇化进程中乡村地域日益复杂的人地关系,乡村重构成为地理学研究的重要前沿课题。乡村重构即行为主体通过优化配置和有效管理影响乡村发展的物质和非物质要素,重构乡村社会经济形态和优化地域空间格局的过程。本文在已有研究基础上,基于乡村地域系统的“要素—结构—功能”视角,从乡村重构的行为主体、价值取向和目标定位等方面进一步阐释了乡村重构的概念内涵,剖析了由诱发机制、支撑机制、约束/促进机制、引导机制、引擎机制构成的乡村重构作用机制框架。最后,基于政府行为对推动城乡资源要素优化配置和乡村重构的引领作用,认为有必要重构乡村社会经济的政府干预框架,并对未来中国乡村重构需进一步重点关注的研究内容展开探讨。
Layout optimization of rural settlements based on point-axis theory
基于点轴理论的农村居民点布局优化
Evaluation of quality and spatial reconstruction of oasis rural settlements based on micro-scale
微观尺度绿洲乡村聚落质量评价及其空间重构
Analysis on distribution characteristics and evolution mode of rural settlements in the Loess Plateau: A case study on Xiji county, Ningxia
黄土高原地区乡村聚落分布特征与演化模式研究: 以宁夏西吉县为例
Study on the evolution characteristics of the hierarchy and size structure of rural settlements in traditional agricultural areas: A case of Zhoukou in Henan province
传统农区乡村聚落等级规模演变特征研究: 以河南省周口市为例
Characteristics and mechanism of rural settlements spatial reconstruction in developed areas: A case study of southern Jiangsu
发达地区乡村聚落空间重构的特征与机理研究: 以苏南为例
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of oasis rural settlements in Xinjiang, China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190368
[本文引用: 1]

<p id="C3">The study of rural settlements is the core content of rural geography. It is of great theoretical and practical significance to explore the spatial characteristics and influencing factors of regional rural settlements. Based on the remote sensing interpretation data, the spatial pattern and influencing factors of rural settlements in Xinjiang oasis areas were analyzed by using the methods of spatial analysis and geographical detector technique. To reveal the rural settlement spatial influencing mechanism, and explore the rural settlement space reconstruction and optimization approaches, we selected Altay area, north slope of Tianshan Mountains area, Turpan Basin area and Kashgar area as sample areas for further analysis. The results show that: the oasis rural settlements in Xinjiang are small both in density and in scale, and are mainly concentrated in the distribution mode, characterized by a spatial distribution pattern of "dense plain, sparse mountain, no village desert", which presents two major density core belts of oasis on the north and south slopes of Tianshan Mountains. Firstly, rural settlements are mainly distributed in middle- and high-altitude areas (500-3500 m), flat and gentle slope areas (<15 °) and warm areas (annual average temperature 0-10 ℃). Secondly, rural settlements are distributed near the center of towns, which are less affected by the radiation from the center of cities and counties. Finally, rural settlements obviously gather along the roads and rivers, with the feature that the closer they are to the roads and rivers, the larger the number and scale of rural settlements. The spatial distribution of rural settlements in Xinjiang is mainly influenced by factors such as the accessibility of roads to towns, the accessibility of roads to counties, slope, proximity to rivers, temperatures and elevations. In other words, under these extreme geographical and ecological environment conditions in arid areas, the natural environment and geographical conditions are still the main influencing factors, and the traffic factors play an important guiding role, while the influence of economic and social factors are not significant. There are obvious differences in natural conditions and social-economic development levels in the four sample areas, and so do the dominant factors of the distribution of rural settlements. The north slope of Tianshan Mountains area and Kashgar area are affected by road accessibility factors, while Altay area and Turpan Basin area by terrain and water source, respectively. Road accessibility factors have different influences on the spatial distribution of rural settlements in various areas. In the future, the optimization and development of rural settlements should focus on the strengthening of the planning of transportation lines and the improvement of transportation infrastructure, so as to promote the flow and sharing of urban-rural elements, as well as the integration and sustainable development of urban and rural areas.</p>
新疆绿洲乡村聚落空间分布特征及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190368
[本文引用: 1]

乡村聚落研究是乡村地理学研究的核心内容,探讨地域乡村聚落空间特征与影响机理,具有重要的理论与现实意义。利用遥感解译数据,借助空间分析方法揭示新疆绿洲乡村聚落空间分布特征,结合地理探测器技术探讨其空间分异的影响因素;选择阿勒泰样区、天山北坡样区、吐鲁番样区和喀什样区进一步明晰不同自然和社会经济背景下绿洲乡村聚落空间分异的主控因素。结果表明:新疆绿洲乡村聚落密度小、规模小,以集聚模式为主,邻近乡镇中心、道路、河流分布特征明显;乡村聚落空间分布受到乡镇道路可达性、到县城道路可达性、坡度、到河流邻近距离、气温和高程等因素影响,而受社会、经济因素影响不显著。四大样区乡村聚落分布的主控因素存在明显差异,应依据各样区村落发展基础与主控因素,探索不同的乡村聚落空间优化模式与发展振兴方向。
Spatial pattern and driving force of oasis rural settlements in Ebinur Basin
艾比湖流域绿洲乡村聚落空间格局及其驱动力分析
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of oasis rural settlements in inland river basin: A case study in Tarim River Basin
干旱内流区绿洲乡村聚落空间格局及影响因素分析: 以塔里木河流域为例
Revitalize the world's countryside
DOI:10.1038/548275a URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial structure evolution and its mechanism of urban-rural settlement in traditional ruralareas: A case study of Zhoukou city, Henan province
传统农区城乡体系空间结构演变及其形成机制研究: 以河南省周口市为例
Development potential and spatial pattern of urban-rural settlement system in the Fenhe river basin
汾河流域城乡聚落体系发展潜能测度及空间模式探究
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.12.004
[本文引用: 1]

以11 188个自然聚落斑块为研究对象,基于场强模型,定量测度汾河流域城乡聚落体系发展潜能,借助GIS技术和地理探测器模型,分析其空间格局特征及驱动因素,进而探讨流域城乡融合发展空间模式。结果表明:① 城乡聚落斑块发展潜能差异显著,且空间分布极不均衡;纵向上中游流域高于下游流域高于上游流域,横向上河谷盆地区高于周边缓丘区高于两侧山丘区。② 聚落斑块发展潜能具有正向空间自相关性,高值斑块聚类显著;具有空间异质性特征且方向性明显,汾河主河道方向联动效应最强,空间联系最紧密;存在局域热点区,并呈现“主核–廊道–次核”的空间结构形态。③ 自然基础、社会经济发展水平和区位条件共同影响着城乡聚落体系发展潜质及空间结构形态;融合发展采取非均衡增长路径,市、县、镇、村全局考虑,构建“强化核心点–培育发展轴–扶持特色区–带动全流域”的逐层推进式空间发展模式。
Changes in oasis and coordination of resource allocation in Xinjiang
新疆绿洲变化与资源配置协调性分析
Spatio-temporal analysis of urbanization and land and water resources efficiency of oasis cities in Tarim river basin
塔里木河流域绿洲城镇发展与水土资源效益分析
DOI:10.11821/xb201202002
[本文引用: 1]

通过Global Moran's I 指数和Getis-Ord Gi*指数并构建协调发展度模型对塔里木河流域绿洲城镇1995、2000、2005 和2008 年4 个时间点的城镇化水平、土地资源效益和水资源效益的集聚扩散状态及其冷热点空间格局演化与空间联动效应进行分析,得出结论:受塔河流域绿洲分布、气候条件及城镇发展基础等多种因素影响,城镇化和水土资源效益空间格局表现出不尽相同的状态。① 塔河流域城镇化与水土资源效益的集聚扩散状态不一致,城镇发展与自然条件相互作用的时间和力度不同决定了三者空间差异的必然性。② 受城镇化所处阶段、城镇职能与主导产业的影响,各县市水土资源开发的时序不同,城镇化和水土资源效益各自的热点演化格局明显不同,区域联动效应差异显著。③ 城镇化与水土资源效益冷热点区域的数量结构迥异。城镇不平衡发展仍然是主导趋势,土地资源效益滞后于城镇发展,水资源效益敏感性较强。④ 塔河流域范围广,自然条件复杂,各二级流域城镇化与水土资源效益的差异性显著。⑤ 城镇化与水土资源效益协调发展度的类型主要为发展水平低和较低两种,协调发展度的空间格局相比其冷热点区域的空间格局更具稳定性,三者差异显著是协调发展度低的重要原因。
Coupling analysis of rural residential land and rural population in China during 2007-2015
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20171068 URL [本文引用: 1]
2007—2015年中国农村居民点用地与农村人口时空耦合关系
Urbanization can benefit agricultural production with large-scale farming in China
DOI:10.1038/s43016-021-00228-6 URL [本文引用: 1]
Land use and land cover change and its environmental effects in Ugan-Kuqa river delta oasis
干旱区土地利用/覆盖变化与生态环境效应研究: 以渭—库绿洲为例
The changing distribution patterns of rural settlements during the process of urbanization: The case of Gongyi (1929-2013), China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201512002
[本文引用: 1]

Rapid urbanization undergoing in China has caused, and will continue to cause tremendous changes of rural settlements. Regions at various stages of economic development and with various geographical backgrounds may witness different changing patterns. This paper uses data of rural settlements covering 84 years from 1929 to 2013 in a county-level city -- Gongyi in Henan province, China, to examine whether such changes in a traditional rural area have evolved towards the urban structure. As Gongyi was one of the earliest areas of rural industries in China, its rapid industrial growth since the 1980s has dramatically transformed the traditional characteristics of rural settlements. By employing Zipf's index, fractal dimension and Gini coefficient, and village data in the county, we have found that: first, Zipf's indexes based on village sizes of the past 84 years were generally much smaller than results based on cities, but with higher speed. The larger settlements were less prominent, but increasing fast in past two decades. Second, fractal dimensions were big but delaying. The larger size in the settlements, the faster increase in their population. Third, Gini coefficient was small but significantly increasing, especially accelerating after the 1990s. Fourth, the spatial patterns have gradually changed from linear concentration pattern along the Yiluo River to more balanced patterns over the plain and the hills. The increases in large settlements and their sizes, were forming hierarchy of the central place in market principles. Along with the process of urbanization, centralization of population leads to changing patterns of rural settlements, with the first rank settlement dominating rank size hierarchy in a region.
县域聚落分布格局演变分析: 基于1929—2013年河南巩义的实证研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201512002
[本文引用: 1]

基于河南省巩义市1929-2013年的村庄数据,从位序—规模角度着手,使用齐夫指数、分形维数以及基尼系数,分别测度了近百年来县域聚落分布格局的演变。相对于城市,巩义市聚落等级规模具有如下特征:① 齐夫指数偏小但增长较快。大聚落发育不突出,具有农村聚落特征;但聚落规模越大,规模增加的速度越快,且二次项模型优于线性模型。② 分形维数偏大但降速加快。聚落体系等级差异增加,规模分布趋于集中。县域聚落规模只有增加到一定程度才能与城市表现出同样的规律。③ 聚落规模大小的基尼系数相对较小但增加显著,且增长率在1990s后加速,这与当地的城镇化发展过程具有密切关联。在空间上表现如下特征:① 沿河线状格局变化。核心聚落由“沿河平原线状”格局主导逐渐向“平原—丘陵片状”格局转变。② 网络等级结构形成。高等级聚落数量增加且规模增大,聚落等级增加,最终形成市场原则的5级等级结构。③ 核心聚落转移替代。县城迁移、工业化与城镇化带来聚落位序—规模变化,使核心聚落出现空间改变。
A rethink of the rank-size rule for rural settlement in traditional agricultural areas: A case study of Zhoukou city
传统农区村落位序—规模法则的实证研究: 以周口市为例
Study on layout optimization of rural settlements based on the "substance-field" model of village and town space
基于村镇空间“物—场”模型的乡村聚落布局优化研究
The role of rural settlements in rural revitalization: Perspective of economic geography
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

This article started with an analysis of the background of rural decline, and the content and logic of the national strategy of rural revitalization from the perspective of human-land relationship. We proposed that rural recession is the result of the adjustment of human-land relationship lagging behind the process of social and economic development. The ultimate purpose of rural revitalization is to adjust the relationship between human and land to adapt to the change of the value of production factors in the new stage of social and economic development. Then, the review of the literature on rural revitalization found that the existing research has paid more attention to the implementation of its strategic content, but not enough attention to rural settlements that have been the important carrier of rural population. There is a close relationship between rural settlement and rural revitalization. Rural settlements are the focus of human social and economic activities in rural areas, and are the core and starting point of rural human-land relationship adjustment. But in the existing literature on rural settlements, emphasis is placed on development cases and neglecting mechanisms, especially the mechanism of change of rural settlements, which is closely associated with rural revitalization. Therefore, bearing in mind the key role of rural settlements in rural revitalization, this article finally put forward five focus areas of future research: the theory of rural settlement evolution, changing trend of spatial structure in rural settlements, specialization transformation of rural settlements, optimization of rural settlements, and landscape of rural settlements.
乡村振兴下的聚落研究: 来自经济地理学视角
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.001
[本文引用: 1]

论文首先从人地关系视角分析了乡村问题的背景及乡村振兴的内容逻辑,提出乡村衰退是人地关系调整滞后于社会经济发展进程的结果,乡村振兴最终目的就是调整人地关系以适应社会经济发展新阶段的生产要素价值变化。对乡村振兴地理研究的评述发现,多数关注其战略内容的实施,而对乡村人口重要载体的乡村聚落重视不够。事实上,乡村聚落与乡村振兴的关系密切,乡村聚落是乡村地区人类社会经济活动的集中场所,是乡村人地关系调整的核心和关键抓手,在乡村振兴中起关键作用。而已有的乡村聚落地理研究多聚焦空间变化,并且重实证轻机理,尤其是与乡村振兴相关联的聚落演变机理研究尚无成果问世。最后,基于乡村聚落在乡村振兴中关键作用,提出从人地关系协调出发,加强乡村聚落演变理论、乡村聚落空间结构变化趋势、乡村聚落专业化转型、乡村聚落整治优化及乡村聚落风貌景观等5个方面的研究。
Urban and rural element mobility and allocation optimization under the background of rural priority development
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200198
[本文引用: 1]

With the further implementation of the rural revitalization strategy, China's rural areas have entered a critical stage with priority development. It is of great significance for the implementation of the strategy of agricultural and rural priority development to scientifically understand the law of urban and rural element allocation and guarantee approaches under the guidance of rural priority development. This paper is based on the regional system theory of human-land relationship and the developmental logic with "Element-Structure-Function". The scientific connotation for urban-rural relationship and element priority guarantee under the guidance of rural priority development is analyzed in this study. This paper sorts out the evolution characteristics of urban-rural relationship and element flow in China from three aspects, namely, the evolution of urban-rural relationship affecting element flow, the division of element flow stages and the overall characteristics of element flow. In addition, it builds a regulatory framework of priority guarantee of rural element from the aspects of element integration, spatial integration and mechanism coordination. The results show that rural priority development is an evolution process based on rural elements, optimizing rural structure and realizing rural functions. The development of relations between urban and rural areas in China has initially gone through the preferential development in urban areas, the coordinated development between urban and rural areas as well as the integration development for urban and rural areas. What's more, the rural element allocation generally encounters such problems as less types for flow elements, poor element outflow and inflow, as well as unsound element flow. It aggravates the imbalance of the type, direction, scale and efficiency of element flow between urban and rural areas in urgent need of external intervention and regulation. At the current stage, there is an urgent need to expand the types of mobile elements in rural areas, to enhance their mobility, to strengthen the weak links in infrastructure, to dredge the stock of elements flowing into the city, to expand the channel of elements flowing into the countryside as well as to expand the "gray space" in urban and rural areas. It aims to expand the rural flow element types, to enhance its flow property, to improve urban elements into the country and to make a long-term development environment. In the end, the priority allocation targets of rural elements should be achieved, including rural elements flow, urban elements flow and scarce elements, so as to ensure the priority of agricultural and rural development.
乡村优先发展背景下城乡要素流动与优化配置
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020200198
[本文引用: 1]

随着乡村振兴战略的深入实施,中国乡村进入优先发展的关键阶段。科学认知乡村优先发展导向下的城乡要素配置规律与保障途径,对于落实农业农村优先发展具有重要参考意义。立足人地关系地域系统理论及“要素-结构-功能”的发展逻辑,解析乡村优先发展导向下城乡关系与要素优先保障的科学内涵,梳理中国城乡关系与要素流动的演变特征,进而从要素整合、空间融合和机制协同3个层面构建乡村要素优先保障的调控框架。结果表明:乡村优先发展是立足乡村要素、优化乡村结构、实现乡村功能的演变过程;中国城乡关系经历了城市优先发展、城乡协调发展到城乡融合发展阶段,乡村要素配置总体上呈现可流动要素类型少、要素流出难、要素流入难、要素留下更难的“一少三难”状态;在当前阶段,亟需通过扩大乡村可流动要素类型、增强要素流动权能、补齐基础设施短板,以及疏解乡村流入城市的要素存量、扩大要素流入乡村的渠道和扩展城乡“灰色空间”等多种途径,以实现“乡村富余要素流得出、城市要素流得进、稀缺要素留得下”的乡村要素优先配置目标,确保农业农村优先发展。
Capitalization effect of rural land reclamation from the perspective of rural-urban integration: A case study of Guangdong province
城乡融合视角下农村闲置建设用地拆旧复垦的资本化效应: 以广东省为例
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.01.011
[本文引用: 2]

土地问题是乡村振兴战略落实的关键。土地整治和资本化作为提升土地质量、促进城乡融合的重要手段,一直是各方探讨的热点。论文以广东省实施的农村拆旧复垦政策为切入点,分析农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式资本化效应的形成机制,梳理其与乡村振兴、城乡联动的关系。研究发现:首先,在农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式实施中,以市场机制为主的“弱关系”和土地流转为主的“强关系”分别在整治腾退建设用地和复垦农业用地中发挥重要作用,是实现土地资本化的主要路径;其次,农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式主要通过结构重组、空间重构、生产方式变革和生态环境优化等推动乡村振兴;最后,农村建设用地拆旧复垦模式以跨地区市场交易平台为载体,引导城乡之间土地、资金等要素流通,通过设置最低保护价和优先购买权等方式保障乡村的发展权利,实现城乡等价要素联动。
The basic theory and methodology of rural revitalization planning in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

Agricultural and rural modernization is the general goal of the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. The scientific formulation of the rural revitalization planning is related to the implementation effect of the national rural revitalization strategy. How to establish the basic theory of rural revitalization and develop the methods of rural revitalization planning have become important tasks of academic research and government decision-making. This paper constructed the theoretical model and method system of rural revitalization planning, tried to carry out the main function-oriented zoning, dominant type classification and principal purpose classification of rural regional system, and established the spatial system of rural revitalization planning and its optimal adjustment scheme. This system was applied to the overall rural revitalization planning in Yanchi County of Ningxia. By establishing the principle of rural revitalization planning that sticks to ecological priority, adaptation to local condition, industrial support and urban-rural integration, it put forward that the priority should be given to the development of rural professional cooperation organizations and the mixed economy of villages and towns, and the acceleration of the construction of advantageous industrial system characterized by the industrialization of tan-sheep, day lily, and minor cereals, and highlighted by the wisdom of eco-cultural tourism. Moreover, it was encouraged to give prominence to the position of the central town in space, and form the village organism and housing industry coordination body with the county seat and three key towns as the center of integrated industry development. The typical case study of Yanchi County has shown that the main contents and technical points of rural revitalization planning were embodied in the following four aspects: (1) determining the overall orientation of rural revitalization planning, and clarifying the phased development mode, key areas; (2) developing the county area based on the main function-oriented zoning, leading type classification and main purpose classification system, and exploring the territorial pattern and differentiation rules; (3) establishing the county development mode and industrial system, formulating coordination schemes of different main function-oriented zones, and revealing the spatial configuration and structural relationship of different dominant types; (4) exploring the local association and hierarchical system of each dominant type in its scale and level. The main task of implementing the rural revitalization planning is to promote the formation of a new pattern of urban-rural development with factors gathering, reasonable structure and orderly space in accordance with the objective requirements of "industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance and prosperous life". China is facing great differences in rural development and many problems in transformation. Regional disparities and urban-rural differences determine the complexity, diversity and differences of rural governance and rural revitalization planning. China's rural transformation-urban and rural integration-rural revitalization-high quality development will become the major development logic and new normal in the future. The research on rural revitalization planning in the new era should focus on the overall situation of regional coordination and urban-rural integration, and solve the practical problems of "rural disease", so as to serve the national rural revitalization planning and scientific decision-making.
中国乡村振兴规划的基础理论与方法论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

农业农村现代化是实施乡村振兴战略的总目标,科学编制乡村振兴规划事关国家乡村振兴战略的推进及实施成效。《全国乡村振兴战略规划(2018—2022)》提出以来,如何建立符合中国乡村发展基本特点与规律的乡村振兴规划基础理论,研制县域乡村振兴规划方法与方案,成为当前学术研究及政府决策的重要课题和重点任务。基于乡村地域多体系统理论,构建了乡村振兴规划理论模式,提出了“三主三分”乡村振兴规划方法。“三主三分”的基本原理是依据特定区域乡村地域系统结构与格局,进行地域系统主体功能分区、主导类型分类、主要用途分级,确立乡村振兴规划空间体系及其优化调整方案。该体系运用于宁夏回族自治区盐池县乡村振兴总体规划,制定了坚持生态优先、因地制宜、产业支撑、城乡融合的乡村振兴规划原则,提出应重点发展乡村专业合作组织和村镇混合制经济,加快建设以滩羊、黄花、小杂粮产业化为特色、生态文化旅游智慧化为亮点的优势产业体系;在空间上突出中心城镇地位,形成以县城和3个重点镇为中心、“三产”融合发展的村镇有机体、居业协同体。本研究是对创建中国乡村振兴规划体系的有益尝试,可为全国县级乡村振兴规划与乡村发展决策提供参考依据。