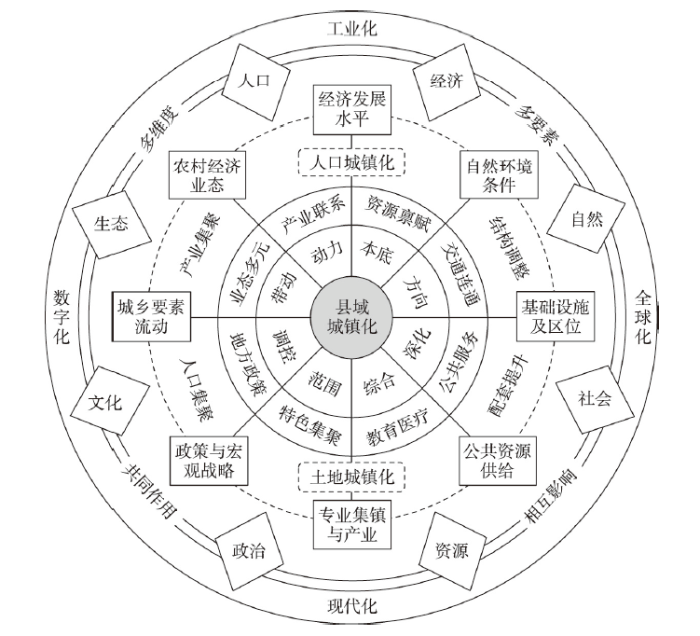
1 引言
随着全球化、工业化和信息化的快速推进,中国城镇化高速发展,城镇数量与规模持续增加和扩大[1],1978—2021年中国城镇化率从17.92%发展到64.72%。城镇化作为城乡融合与乡村转型发展的重要驱动力,关乎特定阶段的城乡关系协调和城镇化发展模式的选择,影响一定地域生产要素、生活方式,以及人居环境、基础设施、土地政策等方面的适应性调整和转变,主要表现为人口、经济、社会、文化等要素从乡村性转向城市性[2],其实质是乡村地域系统转型、乡城关系动态转化,以及城乡生产要素重配、地域结构重塑、空间格局重构的复杂过程。城镇化与城乡发展研究一直是地理学界关注的热点领域,其主要内容聚焦于城镇化发展水平与质量测度[3⇓-5]、城镇化时空过程与城乡转型格局[6⇓-8]、城镇化类型与发展模式路径[9⇓-11]、城镇化影响因素与驱动机制[12⇓-14]等。研究尺度包括了全国、省域、市域、县域及典型流域等,重点关注城镇化演化过程、空间特征和区域差异,侧重探究大城市及大城市群地区的城市化过程及其综合效应,其核心观点是发展大城市并发挥大城市群的辐射带动效应[15],这在一定程度上导致劳动力、资本、土地技术和信息等生产要素,以及交通、物流、市政和生活服务等基础设施配置持续向大城市及城市群地区集聚,中小城市及小城镇则出现各种生产要素持续流失、基础设施配置长期滞后、经济发展缓慢甚至一些地区出现衰败的现象[16]。
县城和重点镇作为县域内城乡互动与要素流动的重要支撑,是实现就地城镇化、城乡要素优化配置与产业融合发展的空间地理单元[17],对于加快县域城镇化、优化城镇化模式起着关键作用[18]。进入21世纪,为应对快速工业化、城镇化进程带来的工农关系不协调、城乡发展不平衡等突出问题,国家相继提出了统筹城乡发展、新农村建设、城乡一体化、精准扶贫、新型城镇化与乡村振兴等重要战略,旨在建立健全城乡融合发展体制机制,加快推进农业转移人口市民化。2022年5月6日,中共中央办公厅、国务院办公厅印发了《关于推进以县城为重要载体的城镇化建设的意见》,明确指出县城是中国城镇体系的重要组成部分,是城乡融合发展的关键支撑,对促进新型城镇化建设、构建新型工农城乡关系具有重要意义。2000—2020年中国县域(包括县、县级市、自治县、旗、自治旗、林区和特区)城镇人口从2.12亿人增至3.86亿人,但其占全国城镇人口比重从46.25%降至42.87%。可见,县域城镇化具有较大的发展空间。以县城和重点镇为支撑推进县域城镇化,能够有效降低农民工市民化成本,是持续推进城镇化水平与质量提升、推动全域乡村振兴与城乡融合发展的关键策略[19],因而对进一步激发县域经济活力、投资能力与消费动力,促进生产要素的城乡有序流动、合理配置与集约利用具有特殊重要的现实意义[20-21]。
当前围绕县域城镇化的研究主要集中在4个方面:① 县域城镇化内涵认识与理论逻辑,包括县域城镇化形成发展过程、内在逻辑、主要思想及科学认知等[22⇓-24],认为县域城镇化是对新型城镇化理论的新发展,强调以县城为载体,通过整合、集聚县域内有限资源,促进县域经济和社会的优化与发展,形成多中心、多层级、组团式的发展模式,不断提升县域经济活力并实现县域现代化发展[25]。② 县域城镇化影响因素及驱动机制,利用人口、资源、环境、经济、社会等多类指标构建县域城镇化发展水平测度体系,揭示县域城镇化的综合动力机制[26-27],验证了工业化、信息化、农业现代化等促进县域城镇化发展[28],特别是现代物流业与电子商务所驱动的县域城镇化成为就地城镇化和乡村转型发展的新动力[29]。③ 县域城镇化时空演变过程、格局与类型,从乡村人口空间转移、非农产业城镇集聚、农业劳动力非农化等方面解析县域城镇化的空间格局与机理[1,30],揭示了不同尺度下县城城镇化时空演变特征[31],并依据产业差异将县域城镇化划分为商业主导型、工业主导型、农业主导型等类型[32]。④ 县域城镇化推进路径与实施策略,认为城市与乡村是一个有机体 [18],通过深入解析城镇化与乡村发展的交互关系[33]、城镇化与农业农村现代化的矛盾冲突问题[34],系统探究了提升县城生产要素吸引力和集聚度,创建完善县城教育、医疗、文化等服务体系,统筹县域城镇和乡村规划建设等重要举措[35],以及创新可持续的公共服务与政策激励机制[36-37]。然而,在现代网络化、信息化和全面推进乡村振兴背景下,亟需深入剖析中国县域城镇化格局演化、发展类型及其优化路径,探明中国县域城镇化发展潜力与未来情景,为科技支撑新时代城乡融合发展与乡村振兴战略决策提供理论参考。
2 数据来源与研究方法
2.1 数据来源
研究基础数据来源于《中国人口普查分县资料》(2000年、2010年、2020年)中各县总人口、城镇人口数据。2000—2020年中国县域单元数量从2074个调整到现在的1871个,其中包括1312个县、388个县级市,以及117个自治县、49个旗、3个自治旗、1个特区、1个林区。2020年中国333个地级市及以上城市的市辖区有973个,虽然市辖区也属于县级区划单位,但因其主体是城市建成区,未列入本文的县域范围。另因数据获取所限,研究范围暂未包括港澳台地区。本文以2020年最新县域单元(1871个)为基础,对行政区划调整导致的数据异常进行了筛查剔除。县域总人口是指2000年、2010年、2020年各县域单元的常住人口数,包括实际经常居住在某地区半年以上的流动人口;城镇人口是指居住在城镇范围内的全部常住人口,包括从事第二、第三产业的人口及其所抚养人口。2000年中国城镇化率计算开始采用常住人口统计方法,体现了非农产业、农村人口向城镇集聚的过程,成为衡量城镇化水平、反映城镇化进程的重要指标。县域城镇化是指县域常住人口城镇化。矢量行政区划数据及影响因素分析数据均来自中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心(
2.2 研究方法
本文应用空间分析法、集中化指数、地理加权回归、回归分析法等对县域城镇化格局演变、区域差异水平、影响因素与发展趋势等进行定量解析和预测分析。
(1)空间分析法。基于ArcGIS 10.5软件平台,对2000年、2010年、2020年中国县域城镇化格局进行可视化分级,揭示2000—2020年、2000—2010年、2010—2020年3个时段的县域城镇化年均变化率空间特征,从而更加直观地反映县域城镇化发展水平的空间格局和演变过程。
(2)集中化指数。旨在探明中国县域人口城镇化发展的区域差异性,采用洛伦兹曲线刻画2000年、2010年、2020年中国县域城镇化发展水平。洛伦兹曲线是用以比较和分析不同发展状况的不平等性,利用县域数量累积百分比和县域城镇化率累积百分比来表示中国县域城镇化发展水平的非均衡性。集中化指数则是基于洛伦兹曲线积分与集中、均匀分布比例关系得到的指数,用以描述城镇化发展水平的地理空间差异程度,该指数越接近0表明发展差距越小,发展水平越趋于均衡。计算公式为:
式中:I为城镇化发展水平的集中化指数;A为城镇化率的累积百分比总和,即洛伦兹曲线的积分;R为城镇化发展水平均匀分布时的累积百分比总和;M为城镇化发展水平集中分布时的累积百分比总和。
(3)地理加权回归。地理加权回归是对普通线性回归模型的扩展,将数据的空间位置嵌入回归方程,能够有效地评估数据的空间自相关性和不同区域的空间异质性。地理加权回归是用回归的原理解释具有空间分布特征的两个或多个变量之间的关系,常用于识别某一地理现象空间分布的影响因素。本文采用该方法探讨中国县域城镇化驱动机制的影响因素,计算公式为:
式中:yi是因变量,表示某一影响因素与县域城镇化的相关性;(μi, vi)为数据点i坐标; βk (μi, vi)为数据点i上的第k个回归参数;εi为随机误差项。本文综合选取了人均GDP、二三产业产值占比、年降水量、坡度、道路里程、电话及宽带数、中小学数量及每万人床位数等可量化的指标,分别探测经济、社会、自然、交通、教育、医疗等对县域城镇化格局演化的影响。
式中:y为城镇化发展水平,即城镇化率;x为人均GDP。
3 中国县域城镇化格局演化与机理解析
3.1 中国县域城镇化格局演化
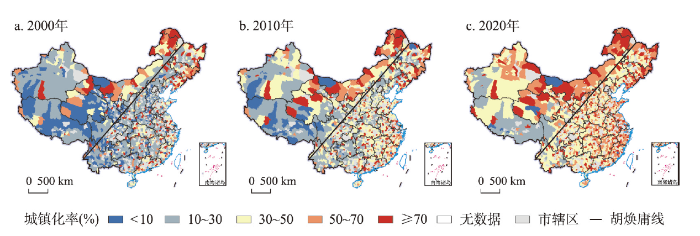
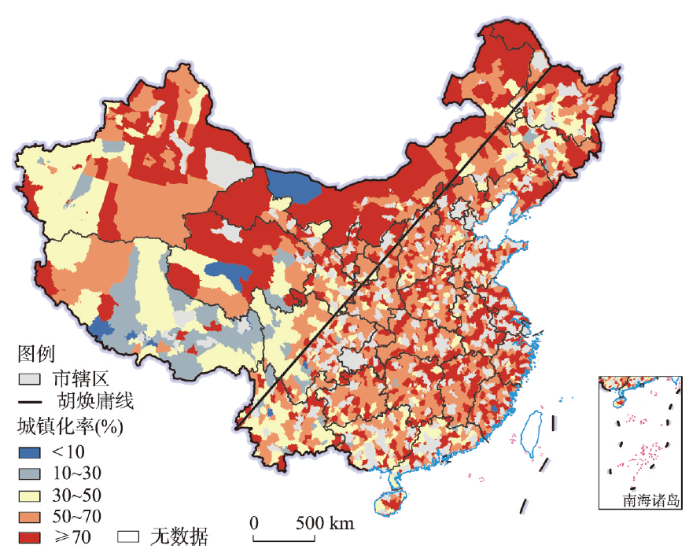
(1)2000年中国县域城镇化率整体偏低,城镇化率在30%以下且区域差异显著(图1a)。城镇化率较高的县域主要分布在内蒙古北方边境地区、东北地区、山东半岛、两湖平原地区、珠三角地区、长三角地区,形成以东部沿海地区、东北地区及西北部分边境地区为核心的点状格局。东部沿海地区高城镇化率的县域逐渐形成,呈现零星分布态势,城镇化率在50%以上的县域数量为93个,占比5.0%。新疆大部分地区、青藏高原南部地区、云贵高原、四川盆地、东南丘陵西部地区、黄土高原中西部、环京津冀地区的县域城镇化率偏低,沿“胡焕庸线”东侧的东北地区、华北地区、黄河中下游及西北、西南地区是县域城镇化率低值区,除省会和少数几个地市之外的县域城镇化率均在30%甚至10%以下,其县域数量达1472个,占比77.7%。
图1
图1
2000年、2010年和2020年中国县域城镇化率空间分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 1
Spatial distribution of the county urbanization rate in China in 2000, 2010 and 2020
(2)2010年中国县域城镇化率较高的地区仍集中在内蒙古北方边境、东北地区、东部及中部地区(图1b)。东部沿海部分县域发展成为高城镇化率地区,城镇化率在50%以上的县域数量达196个,占比10.5%。低城镇化率的县域主要集中在西南地区、西藏及新疆南部等地区,城镇化率仍在30%以下的县域数量为815个,占比43.6%。总体看,中国县域城镇化得到较快发展,高县域城镇化率的县市逐渐从东部沿海地区向中部、西部内陆地区延伸扩展。
(3)2020年中国县域城镇化水平进一步提高,多数地区县域城镇化率比2010年有阶段性提升,沿“胡焕庸线”东侧的东北地区、冀北及晋陕豫地区、川东及云贵地区成为县域城镇化率高值区(图1c)。东部、中部及西北部分地区的县域城镇化率接近或超过50%,而受自然环境、地理区位和产业基础等条件约束,西南地区、西藏及新疆西南部县域城镇化率较低,大部分在50%甚至30%以下。珠三角地区、长三角地区、京津冀地区、成渝都市圈、长江中下游地区、内蒙古边境地区,以及江浙闽东南沿海一带城镇化率超过50%的县域达716个,占比38.3%。
(4)从城镇化发展差异看,2000年、2010年、2020年中国333个地级市及以上城市市辖区(973个)的城镇化率分别为76.68%、77.70%、80.90%,城镇人口分别为2.47亿、3.63亿、5.14亿,占全国城镇人口比重分别为53.75%、54.21%、57.13%;县域城镇化率分别为23.04%、35.45%、49.84%,均低于同期中国城镇化率的36.22%、49.95%、63.89%,城镇人口分别为2.12亿、3.07亿、3.86亿,占全国城镇人口比重分别为46.25%、45.79%、42.87%。2000年、2010年、2020年中国建制镇镇区常住人口分别为1.66亿、2.66亿、3.25亿,占全国总人口比重分别为13.37%、19.98%、23.04%,占全国城镇人口比重分别为36.21%、39.74%、36.09%。可见,以县城及县级市城区、重点镇作为主要载体的县域城镇化,将成为未来城镇化发展的增量所在,具有持续推进中国新型城镇化的巨大潜力。
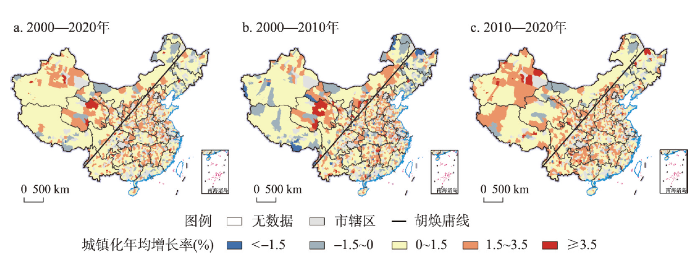
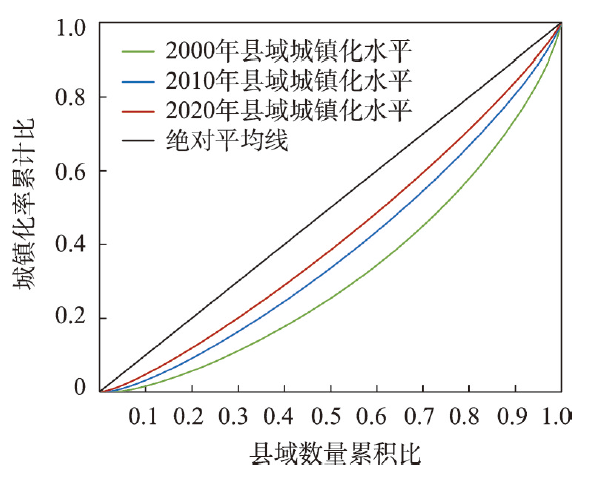
(5)从城镇化时空演化看,2000—2020年中国县域城镇化水平整体呈增长态势。具体而言,2000—2010年除东北地区、新疆西南部,以及西藏北部和南部等地区,中国县域城镇化率年均增长率约为1.3%。2010—2020年中国县域城镇化率持续增长,其中西北地区、中部地区,以及沿“胡焕庸线”东侧的冀北及晋陕豫地区、川东及云贵渝地区成为县域城镇化率快速增长区,部分地区城镇化率年均增长幅度超过1.5%(图2)。对比县域城镇化水平洛伦兹曲线(图3),发现2000—2020年中国县域城镇化的区域差异趋于收敛,城镇化水平集中化指数从2000年的0.36降到2020年的0.17,区域间城镇化发展差异逐渐缩小,中小城镇快速发展很大程度上弥补了区域间城镇发展水平差距。
图2
图2
2000—2020年中国县域城镇化率的年均变化空间分布
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 2
Spatial distribution of the annual change of the county urbanization rate in China from 2000 to 2020
图3
图3
2000年、2010年和2020年中国县域城镇化水平洛伦兹曲线
Fig. 3
Lorenz curve of the county urbanization level in China in 2000, 2010 and 2020
3.2 县域城镇化影响机理
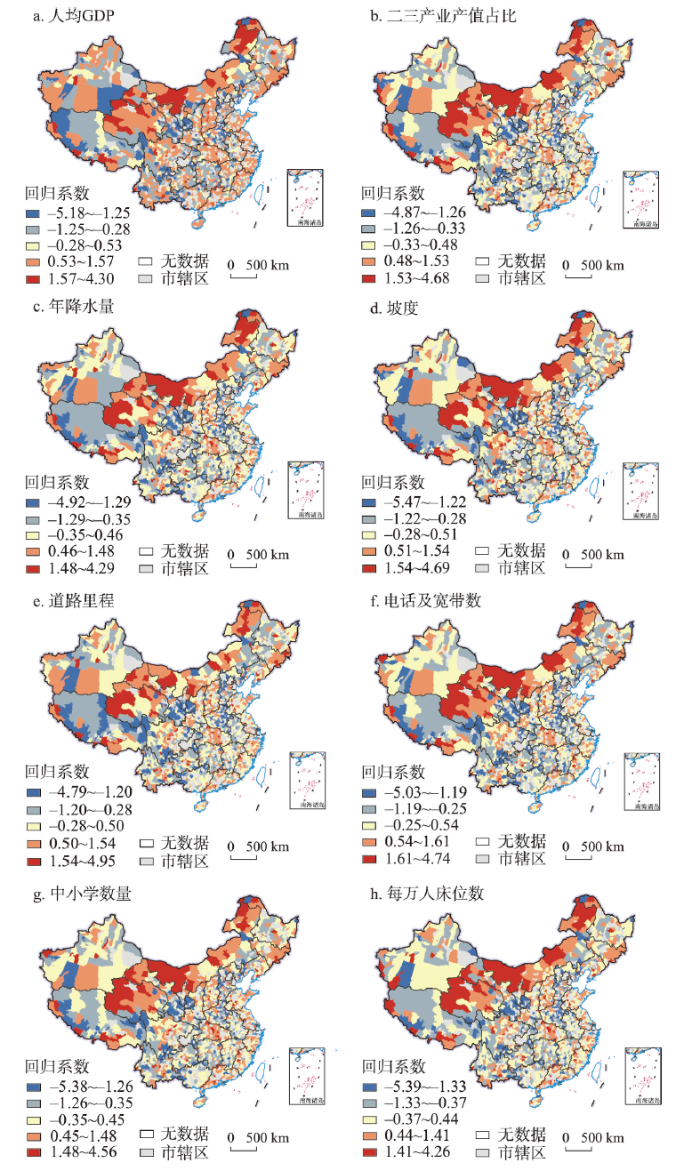
中国县域城镇化发展受到多重因素综合作用与影响,其作用关系与影响程度在不同的历史阶段和地域类型呈现出强弱转换的特征[40]。通过地理加权回归,得出各项指标与县域城镇化率回归的R2值:人均GDP为0.373,二三产业产值占比为0.292,年降水量为0.301,坡度为0.318、道路里程为0.306、电话及宽带数为0.304、中小学数量为0.303、每万人床位数为0.330,而且其空间差异明显(图4)。总体来看,中国县域城镇化是人口、经济、社会、文化等要素综合作用的结果,经济发展水平、自然环境条件、基础设施建设、地理区位条件、公共资源供给、专业创业集群与宏观政策等影响县域城镇化方向、范围和深度,要重视加快县域人口、经济、社会和空间组织结构的调整优化(图5)。
图4
图4
中国县域城镇化影响因素的地理加权回归
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 4
The geographically weighted regression of influencing factors of county urbanization in China
图5
图5
中国县域城镇化发展机理解析模式
Fig. 5
Analytical model of the development mechanism of county urbanization in China
(1)经济发展水平是推动县域城镇化发展的根本动力。县域经济总量规模、人均GDP、产业结构、增长速度等反映了地区经济发展水平,根本上影响着县域城镇化发展。县域工业及服务业发展改变了产业结构与产业布局,尤其是二三产业水平及垂直关联的增强带动地方就业和人口集聚,直接推动了县域城镇化进程。受到大城市、城市群经济辐射带动的周边县市,成为城市产业转移外迁、乡村人口聚集和就地城镇化的主要承接地,县域经济发展水平得到稳步提升,如东部沿海的昆山、江阴、张家港、常熟、晋江、太仓、义乌等县市经济发展迅速,实现了县域人口、产业与土地城镇化的协同发展。而在经济发展水平较低的地区,如中国西北、西南及青藏高原等部分地区,由于缺乏产业和人口等关键要素的集聚,县域城镇化水平整体较低且发展较缓。
(2)自然资源禀赋与环境条件是县域城镇化发展的基础保障。受自然环境本底条件约束,一些地处山地丘陵、资源禀赋较差的西部地区普遍面临农业生产、村镇建设和发展空间不足等实际问题,由于地域资源保障与产业支撑能力弱,导致青壮劳动力跨区县、省市外流,加剧了部分县域人口持续流失。特别是农牧交错带、林草交错带、干旱半干旱区、青藏高原、云贵高原和黄土高原等部分生态脆弱区,由于县域人居环境受限,水资源、土地资源以及生物资源等相对缺乏,致使资源环境承载力偏低,人地关系失衡、功能失调,制约了传统农业、工业、服务业及新型产业的发展壮大,限制了县域发展空间扩展与能力提升,在内外部要素综合作用下造成县域城镇化发展缓慢,部分地区甚至出现了倒退。
(3)交通基础设施及区位条件是县域城镇化空间拓展的核心要素。道路交通网络的通达性事关本地区与外部环境要素的流动与互通,国道、省道等重要交通网络,以及县道、乡镇道路的区域布局,有利于发挥交通基础设施的辐射带动与扩散效应,促使人口、产业及基本公共服务设施沿“线状”延伸,促进了县域城镇化空间拓展与水平提高。地理区位条件对县域城镇化的扩散方向及强度起着关键性作用,如位于京津冀城市群、长三角城市群、珠三角城市群、长江中游城市群、成渝城市群等周边的县域具有临近大都市区的区位优势,其县域发展受到的辐射与带动作用较强,因而城镇化发展水平相对较高且增长速度较快。
(4)教育、医疗等公共服务设施配置是县域城镇化发展的关键条件。作为关系民生事业的教育、医疗、就业、住房等基础条件对县域整体发展具有显著的带动和支撑作用,对县域城镇化的内聚力产生重要影响。教育、医疗等公共服务设施配置的富集度是区域性人口集疏的关键要素,并对区域社会经济发展的环境改善发挥着重要推动作用,进而推进县域城镇化进程的不断加快。县域城镇化不仅是户籍和居住地的城镇化,更是生活水平与服务配套的城镇化,教育、医疗等公共服务设施配置关系着县域城镇化整体质量的改进提升。由于区域间医疗设施配置、优质教育资源不平衡,如西部地区县级医疗服务能力、基础教育水平与周边城市,以及东部地区县市存在较大差距,成为县域人口持续外流及其相关产业发展后劲不足的主要原因,进而制约了县域人口的集聚和城镇化发展。
(5)专业集镇及特色产业发展是县域城镇化发展的推进力量。近些年来,随着网络化、信息化发展,各类专业集镇、特色专业村、文旅产业园等快速兴起,成为壮大县域整体经济实力和促进县域城镇化的重要措施。尤其是数字技术与通讯普及,使得电子商务村(镇)、网红旅游村(镇),以及特色产业村(镇)不断涌现,在珠三角地区、苏南地区以及浙北地区,出现了多功能专业镇集聚现象,呈现出地域特色明显、经济规模较大、产业相对集中、分工配合明确、市场占有率高、以民营企业为主等特点,成为中国小城镇发展新模式。相关研究表明,中国专业村镇在全国范围内广泛分布,尤其在北京、上海、广州、南京、杭州、武汉、成都等大城市周边较为集中,有效带动了县域经济社会发展,实现了就地城镇化[41]。
(6)国家战略与地方相关政策是县域城镇化发展重要的引导因素。在统筹城乡发展、新型城镇化、乡村振兴等国家战略引导下,各地积极探寻实现县域城镇化、城乡融合与乡村振兴的有效路径,涌现出系列具有激励性、创新性的新政策,为推进县域城镇化提供了重要参考和政策引导。中国改革开放与现代化建设,加快了城乡关系重塑和发展格局优化,整体提高了县城吸纳人口与产业的能力。国家战略在宏观层面对县域发展关键性引导和调控作用[42],仍将成为新时期助推县域城镇化、城乡融合发展的重要因素及制度保障。
4 中国县域城镇化发展类型与优化路径
4.1 中国县域城镇化发展预测
(1)2035年中国城镇化率预测。《中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要》提出“人均国内生产总值达到中等发达国家水平”的战略目标,以2035年达到中等发达国家水平的人均GDP 4万美元为标准(按照2021年平均汇率折算成人民币),利用城镇化与经济发展关系模型,预测到2035年中国城镇化率约为76.04%。2020—2035年中国城镇化率预测年均增长0.81个百分点,与2000—2020年中国城镇化率实际年均增长(1.38个百分点)相比,未来中国城镇化发展更加注重质量,增长速度整体放缓。
(2)2035年县域城镇化率预测。2016年以来,《中国县域统计年鉴》具有完整的县域GDP和常住人口数据。2016—2020年中国县域人均GDP从3.95万元增至4.90万元,年均增长率约为5.5%。依据近5年来中国县域人均GDP年均增长率5.5%,并按照现价预测,到2035年中国县域人均GDP为10.18万元。利用城镇化与经济发展关系模型,预测到2035年中国县域城镇化率约为64.38%。结合中国县域城镇化发展变化趋势,预测出2035年中国县域城镇化发展格局如图6所示。总体来看,到2035年中国县域城镇化水平持续提升。城镇化率较低的县域主要集中在东北平原中部、新疆西部、青藏高原,以及四川西部、云南等西南地区。沿“胡焕庸线”西北侧的东北林区、陕蒙宁矿区,以及甘新重点农垦区形成县域城镇化率高值带,东部沿海、长江流域,以及黄淮海等地区城镇化率超过70%的县域数量为480个,占全国县域总数的26.0%。
图6
图6
2035年中国县域城镇化发展格局
注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站审图号为GS(2020)4630号标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。
Fig. 6
The pattern of county urbanization development in China in 2035
4.2 县域城镇化发展类型
县域城镇化发展应遵循一定地域差异特征与分异规律,依据区域资源环境承载力、区位条件、产业基础、社会经济发展水平等综合因素甄别县域城镇化发展类型和地域模式,将县域城镇化划分为5种类型(表1)。
表1 中国县域城镇化发展类型及策略
Tab. 1
| 发展类型 | 发展策略与模式 | 典型区域 |
|---|---|---|
| 大城市周边县域要素集聚型城镇化 | 承接大城市及城市群人口、产业转移和功能耦合,形成与大城市在要素配置、结构优化与功能配套互补的卫星县城,实现就地城镇化、就近园区化 | 珠三角地区、长三角地区、京津冀地区、成渝都市圈、长江中下游地区等 |
| 专业功能县域产业集聚带动型城镇化 | 发挥地方特色产业、资源禀赋和交通区位等综合优势,强化产业集群发展与就业人口吸纳能力,重点建设具有制造优势、人口—产业集聚的专业化县城 | 东部沿海地区、中部及西部主要中心城市周边地区,以及资源型县市等 |
| 农产品主产区县域农业现代化引领型城镇化 | 延长农业产业链、价值链,强化农业与加工业、服务业融合,有效吸纳县域农业从业人口,促成以农产品为支撑的现代化产业体系与市场体系 | 东北平原地区、黄淮海平原地区、长江流域地区、河套平原地区、甘肃及新疆部分地区等 |
| 重点生态功能区县域生态保育型城镇化 | 引导生态敏感区超载人口向县城转移,大力发展县域绿色产业、清洁生产与环保产业,促进生态安全屏障建设和生态产业化发展 | 青藏高原地区、西北干旱及半干旱地区、西南喀斯特地区、黄土高原丘陵沟壑区、陕晋豫黄河“金三角”等 |
| 人口流失县域异地转移集中型城镇化 | 合理利用建设用地,盘活城镇建设用地存量和优化配置增量,促进人口及公共服务设施的区域转移与片区化集中,实现人地协调、居业协同与社会融入 | 东北地区、长江中游地区、华北地区、西南地区、西北地区等 |
(1)大城市周边县域要素集聚型城镇化。大城市周边县城应充分发挥中心城镇、都市圈、城市群经济发展优势与社会资源辐射、扩散效应,促进大城市范围内县城人口集中、产业集聚和土地集约利用,实现重点发展区域的就地城镇化、就近园区化。
(2)专业功能县域产业集聚带动型城镇化。具有资源优势和专业化产业优势的县域应重视促成优势要素向专业集镇、县城转移,以产业集聚带动人口、经济、社会资源的相对集中与集约利用,重点建设具有地域优势的专业化县城及重点镇。
(3)农产品主产区县域农业现代化引领型城镇化。在农产品主产区的县城应延伸农业产业链、融合“三产”,吸引县域农业人口转移,以农业农村现代化促进人口城镇化。
(4)重点生态功能区县域生态保育型城镇化。位于生态敏感区的县城应注重生态环境保护与经济增长、社会发展的有机协调,承接生态脆弱区超载人口的有序转移,重视发展清洁能源与绿色环保产业,加快创建生态保育长效机制,促进生态产业化发展。
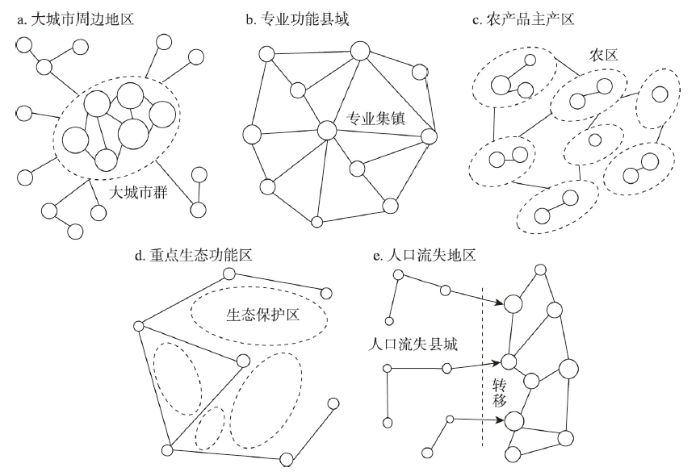
(5)人口流失县域异地转移集中型城镇化。人口流失的县域应积极盘活利用城镇建设用地,有效引导人口、资源和公共服务合理配置与片区化相对集中,实现人地协调、居业协同与社会融入。此外,不同县域城镇化发展类型均具有差异化的空间组织模式,主要体现在县域内外部系统关联、县城与集镇空间组织以及县域城镇化发展方向等方面(图7)。
图7
图7
中国县域城镇化发展类型空间组织模式
Fig. 7
Spatial organization patterns of county urbanization development types in China
4.3 县域城镇化优化路径
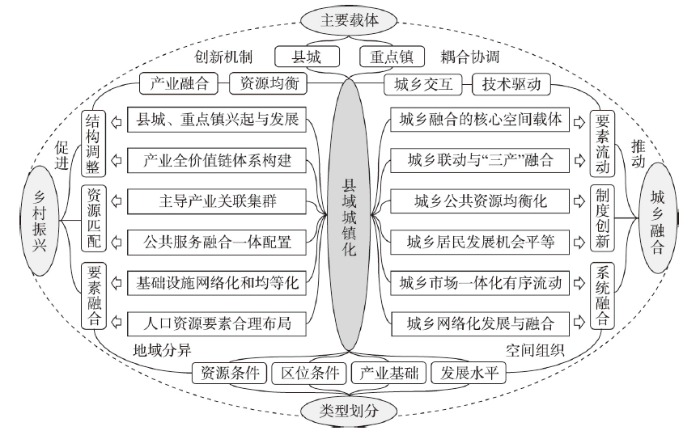
图8
图8
中国县域城镇化发展优化创新路径
Fig. 8
The optimal innovative path for the county urbanization development in China
(1)以空间衔接促进产业融合。城乡融合系统包括地域、市域和县域三个层次,通过城乡基础设施网络进行联通,搭建起联系城乡要素流动与互通的空间组织体系[18]。乡村地域系统是复杂的自然—经济—社会复合巨系统,成为县域城镇化、城乡融合发展与乡村振兴的空间基础。以县城、重点镇(村)为关键空间节点,集中了乡村地域系统资源、人口、产业、资金和技术等关键要素,支撑着城乡融合与乡村居业协同发展。以县域作为城乡联动的基本单元,推进现代农业、工业和服务业等三次产业融合发展,是实现县域产业集群、推动新型城镇化的主要抓手,形成推进构建“三产”融合发展和“三生”(生产、生活、生态)空间体系的城乡融合体、村镇有机体[44]。因地制宜、分类指导、精准施策,实现城镇化的差异化空间组织与多功能耦合。在县域城镇化进程中,产业结构的转型集中体现在农业产业链和价值链的延伸,构建产业全价值链与主导产业关联集群,融合现代化工业技术、信息技术来实现生产增值和功能提升。现代田园综合体、农业观光休闲、生态服务与文化等多功能性日益凸显,在各类功能提升和空间优化下促成县域经济结构与布局优化,并逐渐发展成为城乡系统互通、融合的重要支点。
(2)通过制度创新实现资源均衡配置。伴随着农业生产方式与产业模式变革,相应的土地管理制度和社会治理规程应不断创新[45],例如农村土地三权分置、土地发展权转移等,在不改变土地所有制基础上破除了城乡融合发展的土地空间壁垒,以夯实农业农村现代化基础。常住人口城镇化率与户籍人口城镇化率之间存在较大差距,2020年末中国户籍人口城镇化率仅为45.40%,约低于常住人口城镇化率(63.89%)18.5个百分点。大量进城流动人口难以享受市民化福利待遇,亟需深化改革户籍制度、城镇人口管理制度,探索创建城镇空间体系与城乡融合长效机制,促进进城流动人口市民化。生产方式创新与权利的再组织化,提高了农业生产竞争力及县域经济活力,推动城乡食品、食材和商品有序流动与融合。农业生产水平的提升进而促进县域经济的特色化、专业化和集群化,以及大批专业集镇和特色县城涌现,成为实现县域城镇化的主要动力源。县域数字基础设施的持续建设,以及传统基础设施的网络化与信息化,将进一步推动城乡发展机会均等化和城乡等值化,促进城乡网络化发展和城乡融合一体化进程相融合。
(3)整合要素推动城乡系统耦合。城乡要素流动是加快实现农业农村现代化的重要途经,有利于实现现代农业转型与多功能发展路径衔接,进而形成健全要素—结构—功能传导机制的高质量发展组织模式,促进县域土地利用与经济系统转型,强化人口、土地城镇化带来的城乡融合效应[46]。随着互联网、物联网、大数据和人工智能的快速兴起与应用,县域数字经济与网络经济高速发展,将显著改变以往城乡市场空间相对分离的状况,促使城乡要素、产品与信息等在县域及其以上多层面互通[47]。城乡教育、医疗、科技等公共设施配置及服务水平等差距的逐步缩小,可为其他城乡要素流动提供了基本支撑,尤其是人口资源配置与空间优化布局可为以人为本的城镇化提供发展新机遇。在信息化、网络化新时代,加快构建城乡融合发展及其地域分异的新格局,推进乡村振兴与优化乡村人地关系的新目标[48],以技术革新和创新驱动县域城镇化,优化构建城—镇—村一体化空间体系,成为引领新时代中国城乡融合与乡村振兴的主要路径。
5 结论与讨论
5.1 结论
(1)2000—2020年中国县域城镇化快速发展且区域差异显著。东部沿海地区、中部城郊地区、北方边境地区的县域城镇化率较高,沿“胡焕庸线”东侧的东北地区、冀北及晋陕豫地区、川东及云贵地区成为县域城镇化率高值区,而西南地区、中部农区、西藏及新疆大部分地区的县域城镇化率偏低。2020年中国县域城镇化率为49.84%,低于同期中国城镇化率(63.89%)约14.1个百分点。2020年中国建制镇镇区常住人口为3.25亿,占全国总人口和城镇人口比重分别为23.04%、36.09%。以县城、重点镇为主要载体的县域城镇化建设,在中国城镇化发展中承载着不可替代的重要作用,并具有持续推进中国新型城镇化的巨大潜力。
(2)2035年中国城镇化率为76.04%,县域城镇化率为64.38%,城镇化潜力区相对集中。中国县域城镇化发展受自然、经济、社会和文化等多重因素的综合影响,自然环境条件、经济发展水平、基础设施建设、地理区位条件、公共资源供给、专业集镇产业、宏观政策调控、城乡要素流动成为影响县域城镇化的主导要素。基于城镇化与经济发展关系模型,预测出2035年中国城镇化率约为76.04%,中国县域城镇化率约为64.38%,低于同期中国城镇化率约11.7个百分点,未来县域城镇化发展的潜力区主要集中在沿“胡焕庸线”西北侧的东北林区、陕蒙宁矿区及甘新重点农垦区,以及东部沿海、长江流域、黄淮海等地区区位较优的县域。
(3)未来中国县域城镇化发展要注重分类指导和创新优化路径。中国县域城镇化发展可划分为大城市周边地区、专业功能县域、农产品主产区、重点生态功能区、人口流失地区等5种类型。重视因地制宜、分类指导、精准施策,实现城镇化的差异化空间组织与多功能耦合,成为加快推进中国县域城镇化发展新理念。其创新优化路径包括以空间衔接促进产业融合、通过制度创新实现资源均衡、整合要素推动城乡系统耦合,致力于健全要素—结构—功能传导机制,建立乡村地域系统生产—生活—生态相协调的空间体系。加快推进县域城镇化带动城乡人口、资源、环境、经济、社会等要素优化配置,有利于促进城乡经济社会结构优化调整,推进形成城—镇—村协同、人—地—业耦合的城乡融合体。
5.2 讨论
(1)推进构建中国式城镇化新格局。在快速城镇化和以城市群为主体形态的发展格局下,中国城乡发展不平衡、乡村发展不充分的问题受到广泛关注[49-50]。城镇化是现代化的必由之路,中国式现代化决定着城镇化发展方向与创新路径。中国式城镇化必然是以人为本、城乡融合、区域协调、人地和谐、创新驱动的高质量城镇化。既要坚持大中小城市和小城镇协调发展,又要坚持县域城镇化和乡村振兴协同推进。历史地看,一定乡村地域内从小城镇、小城市到大城市是一个区域城市化过程,从大城市、中心城市到都市圈、城市群是一个都市化过程,而实现一定地域城乡融合发展、城乡融合体建构和共同富裕目标是一个现代化过程。推进中国式现代化应致力于全面构建以城市群为主体形态、以县城为重要载体、以小城镇为基础支撑的中国式城镇化发展新格局。进入新时代,民族要复兴,乡村必振兴。重视回归乡村,推进城乡融合,建设宜居宜业和美乡村,优化新型城镇化空间布局的意义重大。
(2)加快创建县域城镇化空间体系。县域城镇化是新型城镇化的重要方向,更是推进城乡融合与乡村振兴的创新路径。立足“大国小农”的基本国情和“城进乡衰”的现实困境,县域城镇化要立足乡村地域系统多体性[18]、乡城关系演进规律性[43],坚持系统思维、问题导向、健康安全理念,不断强化县城和重点镇的中心功能及其在破解村庄空心化、应对人口老龄化、促进就地城镇化等方面的引导作用,有效扶持“三乡人”(返乡农民工、下乡市民、回乡学子)创新创业和“新农人”宜居宜业,加快创建以县城及县级市城区(1871个)为空间载体,以建制镇(21157个)及乡驻地集镇(8809个)为主要支点,并结网带动中心村(社区)与自然村自组织、网络化的城—镇—村空间体系,全面推动县域城镇化与村镇化、社区化协同耦合发展。建议国家及省市县政府组织编制总体规划,推进多类型县域城镇化机制与模式创建试点,系统开展县域城镇化成效监测与考核评估,以县域城镇化全面推进县域高质量发展,探索形成新时代中国县域城乡融合新方略与乡村振兴新路径。
(3)深入推进城镇化领域综合研究。本文通过县域城镇化格局演化分析、机理解析,以及发展潜力预测、类型剖析,揭示了县域城镇化时空演化过程及其优化路径。对县域城镇化发展预测主要基于经济增长与城镇化关联预判,而未来城镇化发展还将受到与人口老龄化、居住社区化关联的人地系统转型变化,以及生育政策等多重影响,仍需进一步细化县域城镇化发展探测与预测技术方法。同时,亟需充分利用现代大数据、人工智能技术,通过研制乡村人口居业“一码通”系统,绘制“乡流图”与“居业圈”图谱,深入开展复杂乡村地域系统转型协同观测与城镇化格局动态监测,深化县域城镇化类型与潜力、城镇化模式与治理体系、城镇化与乡村振兴“双轮驱动”机理、县域人地业耦合机制与创新路径等前沿问题探究,并作为推进现代地理科学与工程、人地系统科学研究的重要领域,以及创新城乡转型地理学、县域地理学研究的核心内容,努力为推进中国新型城乡关系重塑、城乡融合机制重建、城乡空间格局重构,以及服务新型城镇化、全面乡村振兴和中国式现代化决策提供理论依据。
参考文献
The spatial characteristics and formation mechanism of the county urbanization in China
DOI:10.11821/xb201208001
[本文引用: 2]

The spatial and temporal characteristics and the formation mechanism of the county urbanization in China since 1990 were analyzed systematically, using the methods including regional differences, transect and geography detectors. Results show that the temporal and spatial differences of the county urbanization were significant. The "herringbone" shape region pattern of high county urbanization was gradually highlighted, which were made by the counties along the north border and in eastern coastal areas. The county urbanization process of some regions were accelerated and enhanced, including Wuhan metropolitan region, Chengdu-Chongqing region and Guanzhong-Tianshui region. The low county urbanization level was maintained in Southwest China and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau regions. The differences of urbanization and the change rate of county urbanization were converged in China after 2000, but the rate has slowed down since 2000. The county urbanization trend of transects were significantly different, including Lianyungang-Lanzhou railway and Lanzhou-Urumqi railway transects, the Yangtze River transect, the border of north China transect, 106 National Road transect, and the eastern coastal transect. There are many factors affecting county urbanization, mainly including economic development stage, the level of secondary and tertiary industries, rural net income per capita, population density, leading position of grain production, demographic statistics and special arrangements for counties. The high county urbanization in northern border regions was a typical type of statistical unrealistically high urbanization. In the future county urbanization development should follow the geographical differences, highlight its leading function, and adopt multiple urbanization development models such as promoting urbanization intensively in key urban economic development areas, separating urbanization in cropland and grain producing areas, migrating urbanization in ecological and water resource protection areas, suburban areas and urban-based urbanization and other leading county urbanization patterns.
中国县域城镇化的空间特征与形成机理
DOI:10.11821/xb201208001
[本文引用: 2]

本文综合运用样带、地统计、地理探测器等多种研究方法, 分析了1990 年以来中国县域城镇化的时空特征及形成机理。研究表明:①中国县域城镇化水平时空动态的差异特征显著, 北方边境县域高城镇化和东部沿海县域高城镇化形成的“人字形”空间形态逐渐凸显;以武汉都市圈为中心的两湖地区、成渝地区、关中—天水经济区的县域城镇化水平提升较快, 西南地区、青藏高原地区保持较低的城镇化水平;②2000 年以来中国县域城镇化水平及其变化速度的区域差异逐渐缩小, 陇海兰新线、长江沿线、北方边境、106 国道、东部沿海样带县域城镇化差异明显;县域经济发展阶段、固定资产投资、离中心城市距离、二三产业水平、农民人均纯收入、人口密度是影响县域城镇化空间分异的主要因素, 同时粮食生产主导定位、非农业人口统计口径、城镇设置标准等因素也影响县域城镇化水平及发展过程。未来城镇化发展应遵循地域差异, 凸显主导功能, 推进优化与重点发展区的集约型城镇化、耕地与粮食主产区的分流型城镇化、生态与水源保护区的迁移型城镇化, 以及园区与城镇近郊区的融入型城镇化, 实现城乡土地资源集约利用, 促进城镇化进程中人—地—业耦合与协调发展。
Society: Realizing China's urban dream
DOI:10.1038/509158a URL [本文引用: 1]
Regional disparity and the influencing factors of land urbanization in China at the county level, 2000-2015
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812005
[本文引用: 1]

In the unprecedented urbanization process in China, urbanized land has expanded quickly at the same pace or even faster than the growth of the urban population. Employing both the ordinary least square and geographical weighted regression, we analyzed the spatial patterns and factors influencing land urbanization at the county level in 2000 and 2015. This analysis was assisted by land-use data for China acquired from the resource and environment data cloud platform. The research reveals the following points: (1) The annual growth rate of land urbanization experienced 2.77 percentages on average from 2000 to 2015. About 40% of the counties witnessed an annual increase of 3% or above. Land urbanization was manifested in a pattern of diffusion, which differed from the continued spatial polarization of demographic urbanization in China. (2) Geographically, the north-south differentiation of land urbanization was clearer than the east-west differentiation. And the high-value regions tended to be located to the southeast of "Hu Line". Counties surrounding those metropolitan areas were detected as hotspots of land urbanization. In general, there was a convergent trend of land urbanization among regions in China. (3) The factors of population growth, economic development, industrial structure, city/county features, and geographical location have played significant roles in the spatial disparities of land urbanization at the county level. Besides, the spatio-temporal dependence of their influences were also explored. This study on land urbanization and its influencing factors at the county level advances our theoretical and practical understandings of the new-type urbanization, urban and rural integration, and rural revitalization strategies in contemporary China.
中国县域土地城镇化的区域差异及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201812005
[本文引用: 1]

中国经历了史无前例的快速城镇化进程,与之相伴随的是更加迅猛的土地城镇化过程。基于2000年和2015年中国土地利用现状遥感监测数据,综合运用空间分析、多元回归和地理加权回归的方法,深入分析了中国县域土地城镇化的区域特征及其影响因素。结果表明:① 中国县域土地城镇化率年均增长2.77%,其中近40%的区县城镇化率年均增长大于3%;在空间上呈现出不同于人口城镇化的扩散趋势。② 中国县域土地城镇化的南北分异规律较东西分异更为明显。土地城镇化的高值区域始终集中在胡焕庸线的东南半壁,而围绕主要的城市群地区则形成“组团式”增长的热点区,地区间差异趋于收敛。③ 人口集聚、经济发展、产业结构、城市特性与地理区位等要素对县域土地城镇化空间分异格局的影响较为显著、稳定,各要素对土地城镇化的影响均具有明显的时空依赖特征。分析揭示县域土地城镇化的时空特征及其动力机制,对于科学认识新型城镇化和实施城乡融合、乡村振兴战略,具有重要的理论价值与现实意义。
Revitalize the world's countryside
DOI:10.1038/548275a URL [本文引用: 1]
Demography, urbanization and development: Rural push, urban pull and urban push
DOI:10.1016/j.jue.2015.09.002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Urbanization: Processes and driving forces
DOI:10.1007/s11430-018-9359-y
[本文引用: 1]

Urbanization is becoming the most important human social change in the world, especially in developing countries. However, what is the process of urbanization? What forces are driving the urbanization process? This paper summarizes five main processes of urbanization through various aspects of urbanization in different countries, including economic growth and development, demographic change, social transformation, reshaped and stretched urban spaces, and shrinking cities. Based on the comprehensive method of analyzing urbanization, this paper sorts out five driving forces of urbanization, which are industrialization, modernization, globalization, marketization and administrative/institutional power. The author tries to contribute to the healthy development of urbanization in developing countries through the analysis of process and driving force in urbanization.
The long breadth of cities: Revisiting worldwide urbanization patterns, 1950-2030
DOI:10.1080/00036846.2020.1731410 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial-temporal difference of "townization" of urban population in China
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180497
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, the urbanization of China's population was subdivided into "townization" and "cityization", and the indicators of "townization level" and "townization contribution rate" were adopted. From the perspective of different spatial scales and major function oriented zones, this paper conducted the system analysis on space-time disparity and influencing factors of the development of urban population in China from 1982 to 2015. The main conclusions included: (1) China's urban population's "townization level" and "townization contribution rate" continued to increase. In 2015, townization level was 41.8%, and the townization contribution rate was 55.1% during the period from 2010 to 2015. (2) The urbanization of China's urban population presented significant spatial and temporal differences. The townization-dominated counties and cities were mainly distributed in the central and western regions of China, accounting for more than 70% of the country's total land area. The cityization-dominated counties and cities were mainly concentrated in coastal urban agglomerations, and had a relatively small proportion in the national land area. (3) Looking into the future, China's urban population's "townization level" and "townization contribution rate" would increase steadily but slower and slower. It was necessary to strengthen the exploration of a differentiated development model of small towns based on the differentiation of major function oriented zones.
中国城镇人口“镇化”发展的时空分异
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180497
[本文引用: 1]

将中国人口城镇化细分为城镇人口“镇化”与“城化”,采用“镇化水平”和“镇化贡献率”两个指标,从不同空间尺度及主体功能区视角,系统分析1982-2015年中国城镇人口镇化发展的时空分异及影响因素。主要结论包括:① 中国的城镇人口“镇化水平”和“镇化贡献率”在不断提升。2015年镇化水平为41.8%,2010-2015年期间镇化贡献率为55.1%。② 中国城镇人口镇化呈现显著的时空分异特征。镇化主导型县市主要分布在中西部地区,占全国国土面积的70%以上;城化主导型县市主要集中分布在沿海城市群地区,在全国国土面积中所占比例较小。③ 展望未来,中国城镇人口的镇化贡献率和镇化水平将稳中趋缓,应加强探索出基于主体功能区域分异的差异化小城镇发展模式。
Effect of land-centered urbanization on rural development: A regional analysis in China
The transformations of urban development model in the economic new normal
经济新常态下的中国城镇化发展模式转型
Spatio-temporal change of urban-rural equalized development patterns in China and its driving factors
DOI:10.1016/j.jrurstud.2013.08.004 URL [本文引用: 1]
Re-recognition of precondition and driving mechanism of new-type urbanization
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180444
[本文引用: 1]

This paper analyzes the precondition of urbanization, and concludes that the premise that urban area is better than rural area began to change. The result may be the one-way urbanization process from rural to urban area changes into a reverse or two-way process between rural and urban areas. This paper discusses the driving force and evolving mechanism of the new-type urbanization, and believes that the main driving force of urbanization came from the economies of scale under industrialized production in the early period, which gradually expands from industrial sectors to non-agricultural industries, and changes the organization pattern that the bigger the size is, the better the town is. The paper believes that the organization model of the market in "flow" space under the information condition presents the trend of decentralized layout, which will change the scale-hierarchy structure of traditional space. The paper concludes that the new trend of the mutual integration between industries will change the setting of traditional single-use functions, while emphasizing the complex response of function and space. The paper does not believe that the changes in preconditions and driving mechanisms for urbanization means that urbanization is an inevitable process, and that the higher the level of urbanization, the better, and the larger the city size, the better. The paper finds that the goal of urban development has shifted from economic benefits to comprehensive benefits. The paper concludes that the city level depends on its own attraction and the function based on it, instead of size. The paper does not believe that the residents who are engaged in non-agricultural industries and enjoy non-agricultural lifestyle in new type of rural areas be counted as farmers, but as "semi-urbanization" population. The paper believes that the socio-economic patterns are very complex and highly integrated with each other, so it is difficult to rationally distinguish the connotations of cities or villages from the simple definition of urbanization. The paper proposes that in the semi-urbanized areas, local resources should be used as an advantage, and the main employment forms, public service and infrastructure conditions, lifestyle, and community culture should be promoted in close proximity to the urbanization area. The paper believes that in the future, it is necessary to revise and improve the theory and method of urbanization mode, path, planning and regulation, pay attention to urban and rural characteristics, promote urban and rural equivalent development, and realize the integration of urban and rural factors.
新型城镇化前置条件与驱动机制的重新认知
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020180444
[本文引用: 1]

本文发现:近年来城市比乡村好的城镇化前提开始出现新变化,以前农村-城市单向的城镇化过程,可能会出现城乡之间的反向或双向的过程。城镇化的主要驱动力逐渐从工业部门拓展到整个非农产业,改变了城镇规模越大越好的组织模式;市场在信息化条件下的“流”空间中开始出现分散化布局的组织模式,改变了传统空间的规模-等级结构;产业之间相互融合的新趋势将改变传统单一用地功能的设置,而更强调功能和空间的复合应对;城市发展由经济利益主导向综合效益转变,城市等级的高低取决于自身的吸引力以及在此基础上所形成的功能。建议未来完善城镇化模式、路径、规划、调控的理论方法,注重城乡特色、推进城乡等值化、实现城乡要素交流融合。
The dynamic evolution and its driving mechanism of coordination of rural rejuvenation and new urbanization
DOI:10.31497/zrzyxb.20200902 URL [本文引用: 1]
乡村振兴与新型城镇化耦合协调的动态演进及其驱动机制
Prospects for major issues of China's new urbanization development during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period
“十四五”时期中国新型城镇化发展重大问题展望
The theory and practice of new urbanization in China
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.06.641
[本文引用: 1]

Issue of urbanization is a comphrensive subject which is related to harmonious development of each department of national economy and building a harmonious society. New urbanization is the guarantee of healthy and stable development of urbanization. The research work of the thesis has higher academic meaning and practical value. Urbanization promoted social and economic development of China in the past decades. But some problems arised in the process of urbanization in some areas, such as the rapid pace and disordered state of development, the blind expansion on the edge of cities, degradation of land and water resources, destruction of the ecological environment, and many unsafe, uncomfortable problems in urban environment.From the geographical space and natural resource conservation point of view, this article focuses on three theoretical issues. 1) How to have a good understanding of the basic characteristics and realizing route of new urbanization; 2) How to build a innovation model of new urbanization; 3) In the process of implementing new urbanization, how to understand the development law of China's urbanization, and to take a new road of urbanization with Chinese characteristics.
中国新型城镇化理论与实践问题
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2014.06.641
[本文引用: 1]

城镇化问题是当代中国社会经济发展的综合性课题,是涉及到国民经济各部门如何协调发展,达到一个新的现代化和谐社会发展的根本问题;新型城镇化是中国城镇化健康稳定发展的基本保证,在当前的新形势下,探索中国新型城镇化理论与实践问题,具有重要的学术价值与实践意义。在过去一阶段,虽然城镇化推动了中国社会经济发展取得了巨大成就,并在城市现代化建设与城乡一体化方面也取得了惊人的发展,但在某个时期或一些地区,城镇化过速发展阶段,出现了无序的发展状态,大中城市边缘盲目扩展,水土资源日渐退化,生态环境遭受破坏,特别是有些政府决策人对城镇化的许多制约因素认识不足,甚至决策失误,导致了城市环境出现许多不安全、不舒适的问题。着重从地理空间与自然资源保护的角度,探索中国新型城镇化3个理论与实践问题:① 如何认知中国新型城镇化的基本特征与新的路径;② 在全球经济一体化形势下,如何构建新型城镇化的创新模式;③ 在新型城镇化实施过程中,如何认识中国城镇化本身的发展规律,走具有中国特色的新型城镇化道路。
Foundation, trend and promotion of county's urbanization in China
中国县域城镇化的基础、趋势与推进思路
Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 4]

Cities and villages are components of a specific organism. Only the sustainable development of two parts can support the prosperous development as a whole. According to the theory of man-earth areal system, urban-rural integrated system and rural regional system are the theoretical bases for entirely recognizing and understanding urban-rural relationship. To handle the increasingly severe problems of "rural disease" in rapid urbanization, accelerating rural revitalization in an all-round way is not only a major strategic plan for promoting the urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development, but also a necessary requirement for solving the issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and rural people in the new era and securing a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects. This study explores the basic theories of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization and analyzes the main problems and causes of rural development in the new era, proposing problem-oriented scientific approaches and frontier research fields of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in China. Results show that the objects of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization is a regional multi-body system, which mainly includes urban-rural integration, rural complex, village-town organism, and housing-industry symbiosis. Rural revitalization focuses on promoting the reconstruction of urban-rural integration system and constructs a multi-level goal system including urban-rural infrastructure networks, zones of rural development, fields of village-town space and poles of rural revitalization. Currently, the rural development is facing the five problems: high-speed non-agricultural transformation of agriculture production factors, over-fast aging and weakening of rural subjects, increasingly hollowing and abandoning of rural construction land, severe fouling of rural soil and water environment and deep pauperization of rural poverty-stricken areas. The countryside is an important basis for the socioeconomic development in China, and the strategies of urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are complementary. The rural revitalization focuses on establishing the institutional mechanism for integrated urban-rural development and constructs the comprehensive development system of rural regional system, which includes transformation, reconstruction and innovation in accordance with the requirements of thriving businesses, pleasant living environments, social etiquette and civility, effective governance, and prosperity. Geographical research on rural revitalization should focus on the complexity and dynamics of rural regional system and explore new schemes, models and scientific approaches for the construction of villages and towns, which are guided by radical cure of "rural disease", implement the strategy of rural revitalization polarization, construct the evaluation index system and planning system of rural revitalization, thus providing advanced theoretical references for realizing the revitalization of China's rural areas in the new era.
中国新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201804004
[本文引用: 4]

城市与乡村是一个有机体,只有二者可持续发展,才能相互支撑。依据人地关系地域系统学说,城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统是全新认知和理解城乡关系的理论依据。针对日益严峻的“乡村病”问题,全面实施乡村振兴,既是推进城乡融合与乡村持续发展的重大战略,也是破解“三农”问题,决胜全面建成小康社会的必然要求。本文探讨了新时代城乡融合与乡村振兴的基础理论,剖析了乡村发展面临的主要问题,提出了问题导向的中国城乡融合与乡村振兴科学途径及研究前沿领域。结果表明:① 城乡融合与乡村振兴的对象是一个乡村地域多体系统,包括城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体,乡村振兴重在推进城乡融合系统优化重构,加快建设城乡基础网、乡村发展区、村镇空间场、乡村振兴极等所构成的多级目标体系。② 中国“三农”问题本质上是一个乡村地域系统可持续发展问题,当前乡村发展正面临主要农业生产要素高速非农化、农村社会主体过快老弱化、村庄建设用地日益空废化、农村水土环境严重污损化和乡村贫困片区深度贫困化等“五化”难题。③ 乡村是经济社会发展的重要基础,城乡融合与乡村振兴战略相辅相成,乡村振兴应致力于创建城乡融合体制机制,推进乡村极化发展,按照产业兴旺、生态宜居、乡风文明、治理有效、生活富裕的要求,构建乡村地域系统转型—重构—创新发展综合体系。④ 乡村振兴地理学研究应着眼于乡村地域系统的复杂性、综合性、动态性,探究以根治“乡村病”为导向的新型村镇建设方案、模式和科学途径,为实现新时代中国乡村振兴战略提供理论参考。
Spatial patterns, driving forces, and urbanization effects of China's internal migration: County-level analysis based on the 2000 and 2010 censuses
DOI:10.1007/s11442-015-1165-z URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial pattern and influencing factors of urbanization development in China at county level: A quantitative analysis based on 2000 and 2010 census data
中国县域城镇化发展格局及其影响因素: 基于2000和2010年全国人口普查分县数据
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201604007
[本文引用: 1]

利用2000 和2010 年中国人口普查分县数据,借助空间分析方法揭示近期中国常住人口城镇化格局特征及其动态变化,结合多元回归模型探讨城镇化空间分异的主要影响因素,基于主成分分析和聚类分析进行中国城镇化发展类型区划分。结果表明:① 2000-2010 年,中国常住人口城镇化率不断提高,年均增加1.3 个百分点,32%的县域城镇化水平年均增长超过1.5 个百分点;② 中国城镇化发展存在区域差异性和“低快高慢”的收敛性,东部、东北、中部、西部四大区域城镇化率年均分别增加1.4、0.5、1.4 和1.3 个百分点;③ 60%的中国县域城镇化发展集中在低城镇化率—高增长率、低城镇化率—中高增长率和低城镇化率—中增长率三种类型,且以中、西部地区分布最为密集;④ 中国县域城镇化格局基本未变,仍以珠三角、长三角、京津冀三大增长极的城镇化发展较为突出,东部地区及内陆省会城市周边的城镇化水平也相对较高;⑤ 经济发展水平、产业结构特征、人力资本状况、人口集聚能力、公共服务水平、地理区位特征对县域城镇化空间分异具有显著而稳健的影响;⑥ 中国城镇化格局可分为具有明显区类一致性和区外异质性的5 大类、20 个区域。新时期的城镇化发展应凸显地域功能、提升承载能力、夯实产业基础、强调节约集约。
Spatio-temporal pattern characteristics of relationship between urbanization and economic development at county level in China
DOI:10.1007/s11769-019-1053-z
[本文引用: 1]

The relationship between China's urbanization and economic development (RCUED) is an important concern nationwide. As important actors in regional strategy and policy, county-level regions have played an increasingly significant role in the development of China's social economy. However, the existing research on the RCUED lacks the fine depiction of the county-level administrative units. Using 2000 and 2010 census data and the statistical analysis method, we uncovered the evolution characteristics of China's urbanization and economic development and conducted a quantitative identification for the RCUED with improved methods using the quadrant map approach. In addition, we investigated the spatial correlation effect of the RCUED using the spatial autocorrelation analysis method. The results were as follows: 1) In general, a high degree of matching exists between China's urbanization and economic development at the county level at the significance level of 0.01. The correlation coefficients between China's urbanization and economic development in 2000 and 2010 were 0.608 and 0.603, respectively. 2) A significant regional difference exists in the RCUED at the county level. Based on a comparative analysis of 2276 county units in China in the two years, we found that county units can be categorized as under-urbanized, basic coordination and over-urbanized in various areas. No situation was observed where urbanization seriously lagged behind the economic development level, so the levels of urbanization and economic development appear to be basically coordinated, and the coordination state may be gradually optimized over time. 3) Over time, the spatial dependency of the RCUED has weakened and the spatial heterogeneity has increased. Northeast China has always been an area characterized by over-urbanization. The number of county units classified as under-urbanized has begun to decline in eastern coastal urban agglomeration areas, while counties rich in resources have transformed from having point-shaped over-urbanization to plane-shaped under-urbanization along the northern border, and the number of over-urbanized county units has increased in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. 4) 'Lag-lag' type and 'advance-advance' type accounted for 68% of all counties in China, and these counties were shown to have obvious spatial differentiation characteristics.
The construction of discipline system of science of geography and its significance
地理科学的学科体系构建与内涵
A preliminary study on the internal logic of the new development pattern and high-quality development
新发展格局与高质量发展的内在逻辑
China's regional development pattern oriented toward modernization: The scientific connotation and strategic priorities
DOI:10.2307/141854 URL [本文引用: 1]
面向现代化的中国区域发展格局: 科学内涵与战略重点
The study on comprehensive evaluation and urbanization division at county level in China
DOI:10.11821/yj2012070013
[本文引用: 1]

The China's urbanization,which is in rapid development stage,presents significant regional inequality.Using the counties as basic units can reflect the spatial pattern of China's urbanization,raise the level of understanding of spatial inequality of China's urbanization,and be beneficial to the sound development of China's urbanization. This paper constructs a comprehensive evaluation system for China's county urbanization level in three aspects of urbanization connotation: population,economy and society.Entropy method is adopted to evaluate the comprehensive urbanization levels of 2289 county units in China and levels of their subsystems.Then we transform calculated values into urbanization rate based on min-max normalization and dimensionless method.Urbanization type regions are constructed according to the relationships between population urbanization and economic-social urbanization.The driving force of each urbanization type region is evaluated by partial correlation analysis.Finally,the method of spatial autocorrelation is used to regionalize the level of China's comprehensive urbanization,population urbanization,economic urbanization and social urbanization. The results show that population and economy are two major subtypes reflecting the comprehensive urbanization level of China;the spatial distribution of China's comprehensive urbanization represents a clear administrative hierarchy;China can be divided into four urbanization types,namely,population urbanization lag region;economic-social urbanization lag region,population and economic-social urbanization lag region and comprehensive urbanization non-lag region;spatial autocorrelation is an alternative approach for regionalization researches in the field of human geography.Regionalization of four kinds of urbanization types is different in pattern,mechanism and mode.In regionalization mode of population urbanization type regions,the northern region is higher than the southern region while in regionalization mode of economic and social urbanization type regions,the eastern region is higher than the western region.
中国县域城镇化水平的综合评价及类型区划分
Spatial coupling cooperative analysis of road transport superiority and urbanization at county level in China
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.07.002
[本文引用: 1]

With the fifth and sixth census and road network data, and using a spatial interoperability evaluation model and a spatial lag model, the spatial coupling relationship between China's road transport superiority degree and urbanization rate at the county level was analyzed. The result shows that: (1) Regional difference of China's urbanization rate is significant at the county level. Urbanization rate is low in traditional agricultural areas, poor contiguous mountainous counties (districts), and the spatial mismatch between economic development and labor resources was widespread, with urbanization taking place in areas away from residents’ place of origin in underdeveloped areas. (2) Regional difference of road transport superiority degree is clear between the eastern and western regions and between the transport hubs and peripheries, with a clear “point-axis” spatial structure at the regional level. Road transport superiority degree showed a partial normal distribution at the county level. (3) The overall coverage of highways, national highways, provincial highways, and county and township roads affects road accessibility for production flow, information flow, and non-agricultural market entrance of rural production factors, which affect urbanization development at the county level. Urbanization was obviously facilitated by the presence of highway exits and railway stations. (4) The spatial interoperability grade of road transport superiority degree and urbanization rate shows a partial normal distribution, with significantly mutual influence between urbanization and road transport development levels.
中国县域城镇化的道路交通影响因素识别及空间协同性解析
DOI:10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.07.002
[本文引用: 1]

本文基于人口普查数据和路网数据,利用空间滞后回归模型和耦合协调度模型等,对中国县域城镇化率的道路交通影响及其空间耦合协同性进行分析,研究表明:①中国县域低城镇化水平的县(区)主要集中在传统农区、集中连片贫困山区、高寒经济欠发达区。经济发展水平与人力资源空间上的错位,致使经济欠发达地区的人口倒挂,异地城市化特征显著;②中国县(区)道路交通优势度宏观上呈现出东西部区域差异和交通枢纽与外围区域的差异,“点—轴”地域结构特征显著,县域道路交通优势度数值呈现偏正态分布;③道路交通是城镇间和城镇与区域间联系的核心纽带和产业转型升级发展的传输廊道,开放式的道路系统增强了农村生产要素非农化转型的市场可介入性,对县域城镇化发展有积极作用。高速公路出口、火车站的布局对城镇化影响和带动农村要素非农化作用较为明显;④中国县域交通优势度与城镇化率耦合协调度分级分布为偏正态分布,城镇化发展与交通优势度相互影响显著,呈一定的双向耦合性。
Spatial dynamic mechanism and effect of urbanization in China based on spatial unit data of 2869 counties derived from the sixth census
中国城镇化的空间动力机制与效应: 基于第六次人口普查2869个县域单元数据
The county economic growth effect of government support for migrant workers to return home for entrepreneurship
政府支持农民工返乡创业的县域经济增长效应: 基于返乡创业试点政策的考察
New urbanization from below in China: Rural urbanization driven by e-commerce
新自下而上进程: 电子商务作用下的乡村城镇化
Spatio-temporal pattern and driving forces of urbanization in China's border areas
DOI:10.1007/s11442-020-1755-2 URL [本文引用: 1]
The spatio-temporal heterogeneity of county-level economic development and primary drivers across the loess plateau, China
DOI:10.1007/s11442-021-1851-y
[本文引用: 1]

Unbalanced economic growth is a ubiquitous phenomenon while investigating the regional development at a large spatial scale. Therefore, it is of great significance to analyze the spatio-temporal pattern of regional economic growth and the drivers to understand and facilitate the economic development of low development areas. Taking a county as a fundamental study unit, we used the county-level per capita GDP data on the Loess Plateau from 2005 to 2017, and geographic variables such as slope, elevation, and population density to analyze the spatio-temporal differences and the driving factors of the county-level economic development in the Loess Plateau by employing both conventional and advanced quantitative methods including Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA) and the geographic detector model. Our results suggested that: (1) The selected indicators, including absolute difference, the fluctuation of relative difference and total difference of economic development on the Loess Plateau, all show steady increasing trends, respectively. (2) There are 64.5% of the counties with economic development being below the average level of the whole Loss Plateau region. The relatively high developed counties are distributed in the “A”-shaped regions in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Shaanxi, and Henan provinces, however, the low development counties are mainly located in the “V”-shaped regions in Gansu and Shanxi provinces. (3) GDP, investment in fixed assets and urbanization rate are the major driving factors influencing the regional economic development, and the combined effects are far greater than that of any individual factor.
Local practice and innovation of urbanization in the county region
县域城镇化的地方实践与创新
Quantitative measure and influencing mechanism of land intensive use in China at the county level
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201412001
[本文引用: 1]

Land use issue is an important constraining force for economic sustainable development of China. Urban and rural rapid expansion depletes valued land resources under the background of rapid urbanization. An extensive use pattern might cause a serious waste of land resources. The study on influencing mechanism of land intensive use (LIU) in China at the county level is an important tool for effective LIU practice and policy-making. This paper uses OLS model, Spatial Panel Lagged model and Spatial Panel Error model to characterize the influencing mechanisms of five class factors and 17 variables supported by GIS (Geographic Information System) and MATLAB. And a comprehensive data set, including physical geography attributes and socio-economic information with 2286 counties, was developed. Meanwhile, the spatiotemporal pattern of LIU has been discussed by means of GIS. The results show that Spatial Panel Data models are slightly superior to OLS model in terms of significance and confidence level. Regression results of these models indicate that industrialization, urbanization, economic development level, location, transportation and policy have significant impact on LIU of counties. The variables of physical geography are less significant than socio-economic variables. An ignored variable of historical factor, however, became the most significant factor. In the future, the LIU at the county level should enhance favorable factors and reduce disadvantageous ones, which can be acquired by improving the entire level and quality of industrialization and urbanization. We argued that an efficient and complete land market and operating system should be built to reflect market-oriented activities at the first place. Then, according to regional differences, differential LIU regulation policies and measurements should be optimized. Meanwhile, we should pay close attention to the carrying capacity of local resources and environments when conducting LIU practices.
中国县域国土空间集约利用计量测度与影响机理
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201412001
[本文引用: 1]

土地利用问题日益成为中国经济发展的重要约束力之一。快速城镇化背景下城镇和乡村的快速扩张吞噬了宝贵的土地资源,粗放非集约的利用方式更加剧了土地资源的浪费。从国土空间集约利用的影响机理出发分析中国县域国土空间集约的影响机理对指导集约利用实践以及宏观集约利用政策瞄准和政策矫正都具有特殊意义。综合运用OLS模型、空间面板滞后模型和空间面板自相关模型以GIS和Matlab为技术平台,构建中国县域发展基础数据库 (1992-2010年),定量刻画中国2286个县级单元的空间集约利用度时空变化格局,计量分析社会经济发展、自然环境本底、区位交通地理、宏观战略政策和历史基础5大类变量17项具体因素的影响机理。研究结果表明,空间面板数据模型的整体显著性和可信度检验略高于一般面板数据OLS模型;在固定相关效应后对各因素的影响机制进行了检验,表明工业化、城镇化、经济发展水平、区位、交通和宏观战略政策等因素对县域国土空间集约利用的影响较为明显。自然环境因素弱于社会经济因素。被忽略的历史因素对县域国土空间集约利用具有极显著的影响。未来县域国土空间集约利用应因势利导,强化有利因素,减小不利因素影响。提高工业化和城镇化发展水平和质量。发挥市场的主导作用,完善土地市场和运行机制。优化国土空间集约利用调控政策和管治手段,制定差别化的空间集约利用政策。以资源环境承载力为基础和约束最大限度地提高投入和产出水平。
Urbanisation, natural amenities and subjective well-being: Evidence from US counties
State-sponsored and spontaneous urbanization in Fujian province of China, 1982-2010
DOI:10.1016/j.cities.2016.05.021 URL [本文引用: 1]
Urban density and the metabolic reach of metropolitan areas: A panel analysis of per capita transportation emissions at the county-level
DOI:S0049-089X(16)30115-6
PMID:27194663
[本文引用: 1]

We engage a tension in the urban environment literature that positions cities as both drivers of environmental destruction and loci of environmental protection. We argue that the traditional binary view of cities as either harmful or beneficial is too simplistic; we advance a more nuanced understanding of cities to study their internal and external metabolic effects in terms of carbon emissions from on-road transportation at the county-level across the continental United States between 2002 and 2007. First, utilizing satellite imagery from the National Land Cover Database, we create a novel measure of population density by quantifying the number of people per square mile of impervious surface area. Second, we develop a measure of metropolitan adjacency from the rural classifications datasets published by the USDA. In spatial regression models, we find that while higher density reduces emissions, counties that are geographically isolated from metropolitan areas actually have lower per capita emissions, all else equal. We elaborate on the conceptual, methodological, and practical implications of our study in the conclusion. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Progress of research on urban-rural transformation and rural development in China in the past decade and future prospects
DOI:10.1007/s11442-016-1318-8 URL [本文引用: 1]
Spatial pattern and its influencing factors of specialized villages and towns in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008007
[本文引用: 1]

Specialized villages and towns has significance to agricultural transformation & upgrading and rural vitalization strategy. With the data of "One Village One Product" Demonstration Villages and Towns from the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China, this paper revealed the spatial pattern of specialized villages and towns in the whole country. It also analyzed village-level factors (i.e. topography, resource, location) and region-level factors (i.e. market and economic foundation) from the national and agricultural regionalization scale using Geodetector model. The results showed that: (1) 83.64% of specialized villages and towns mainly concentrated to the southeast of the "Hu Line", presenting central agglomeration and gradient descent from the North China Plain-the Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Plain to south and then to northwest. (2) The products of specialized villages and towns were mainly fruits and vegetables, accounting for 59.45%. They were distributed mainly in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, Guanzhong Plain, the Middle-lower Reaches of Yangtze River Plain, Sichuan Basin, etc., as well as circle distribution centered on the provincial capitals. (3) The distribution of specialized villages and towns was more influenced by region-level factors than by village-level factors, and the explanatory value of market and economic factors was 0.30 and 0.19, respectively. The influence of topographic factor was more obvious than that of other village-level factors, with the explanatory value being 0.15. (4) These factors presented regional differences. The main factor affecting the distribution of specialized villages and towns was market in the northern plain and hilly region; topographic and resource factors dominated the agro-pastoral ecotone and plateau region; market, economic foundation and location factors had a joint effect in the northwestern and Tibetan Plateau regions. There were no prominent factors in the southern hilly and plateau area. This study has important scientific reference value for improving agriculture's level of specialization, identifying and cultivating specialized villages & towns and rural revitalization poles, and realizing the rural vitalization strategy.
中国专业村镇空间格局及其影响因素
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202008007
[本文引用: 1]

探索专业村镇的地域分异格局特征及其影响因素,对实施农业转型升级与乡村振兴战略具有重要参考价值。本文基于农业农村部“一村一品”示范村镇资料揭示了中国专业村镇的空间格局,运用地理探测器模型从全国和农业区尺度分析了地形特征、资源禀赋和区位条件等村域环境因素,以及市场需求和经济基础等区域环境因素对专业村镇分布的影响。研究发现:① 中国专业村镇主要分布在胡焕庸线东南半壁,占83.64%,呈现中心集聚和由华北平原—长江下游平原向南、再向西北梯度递减特征;② 主导产业细分门类以水果、蔬菜为主,占59.45%,主要分布在黄淮海平原、关中平原、长江中下游平原、四川盆地等,且多以省会城市为中心,呈圈带状分布;③ 专业村镇空间分布受区域环境因素的影响强于村域环境因素,市场需求和经济基础因素的解释力值分别为0.30和0.19,村域环境因素中地形特征因素影响相对较大,其解释力值为0.15;④ 影响因素存在明显的区域差异,北方平原—丘陵区主要受到市场需求因素影响,农牧交错—高原区主要受到地形特征和资源禀赋因素的影响,西北—青藏高原区主要受市场需求、经济基础和区位条件的影响,而南方丘陵—高原区解释力较弱。研究可为提高农业生产专业化水平、识别和培育专业村镇和乡村振兴极、推进乡村振兴战略实施提供科学参考。
Evolution analysis of China's spatial development structure and pattern optimization of major function zones
国土空间结构演变解析与主体功能区格局优化思路
Human geography research based on the new thinking of global rural-urban relationship
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 2]

Sustainable rural development is critical to the achievement of global sustainable development goals. Globalization and urbanization, as the key processes, continuously drive the human-earth system to make adaptive responses, promoting the transformation of urban-rural relations. The rural-urban relationship is essentially a mother-child relationship, which is a comprehensive characterization of the transfer of rural humanistic factors, the transformation of man-land relationship and the transformation of urban-rural development in the process of urbanization. However, the traditional cognition of urban-rural relationship ignores the multi-dimensional connections between the rural and the urban as well as the existence of the rural-urban integration system, resulting in prominent drawbacks of rural regions, negatively affecting the urban-rural development rights, and resulting in urban and rural territorial dysfunction and other problems. The key to solve the problems of socio-economic development in China is to reform the urban-biased development strategy, and to innovate the new cognition of rural-urban relationship based on the thinking of "rural maternal effect", which highlights that rural areas nourish the city. Based on the remote coupling and systematic synthesis of the rural human-earth system, modern human geography urgently needs to strengthen the cross-research with physical geography and information geography, create a coordinated observation system of human-earth system supported by the sky-space-ground integration, reshape the global rural development perspective, rural-urban system perspective, and reorganize the global rural human-earth relationship, the rural-urban integration relationship, and the living and employment relationship. Rural human-earth relationship territorial system is the core of rural geography research. The rural human-earth system research should focus on the coupling of rural natural ecosystem and the socio-economic system and their complex interactive processes and effects. Supported by the intersection of multiple disciplines, the expansion of new fields and the cultivation of new disciplines, it should create the collaborative observation technology of human-earth system and methodology of multi-source data fusion computing, the research idea based on process-mechanism-pattern and the technical path of monitoring-simulation-decision support, and explore the organic connection path between rural human-earth system coupling and rural-urban integrated development, regional sustainable development and global common governance.
全球乡城关系新认知与人文地理学研究
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202112001
[本文引用: 2]

全球化、城镇化作为驱动人地系统不断做出适应性调整和改变的关键过程,持续推动着城乡关系的转型与重塑。本文认为乡村孕育了城市,乡城关系实质上是母子关系,是城镇化进程中乡村人文要素转移、人地关系转变、城乡发展转型的一种综合表征,具体体现在不同发展阶段乡村与城市之间土地非农化、人口城镇化、产业园区化、城乡发展一体化等诸多方面;传统的城乡关系认知忽略了城市与乡村之间的内在关系和多维联系,以及城乡融合系统这一重要地理综合体及其功能价值,成为产生乡村短板效应凸显、城乡发展权能受损、城乡地域功能紊乱等突出问题的根源;转变城市偏向发展观念,基于乡村母体思维,创新全球乡城关系新认知是破解当前全球化特别是中国社会经济发展不平衡、不充分问题的关键所在。现代人文地理学迫切需要强化与自然地理学、信息地理学交叉研究,创建天—空—地一体化人地系统协同观测体系,突出乡村人地系统的远程耦合性和系统综合性,重塑全球乡村观、乡城系统观,探究可持续的全球乡村人地关系、城乡融合关系、村镇居业关系。乡村人地系统研究应聚焦乡村自然生态系统、社会经济系统耦合及其复杂交互过程与效应,以多学科交叉、新领域拓展与新学科培育为支撑,创建人地系统协同观测技术与多源数据融合计算方法论,基于过程—机理—格局的研究思路和监测—模拟—决策支持的技术路径,探寻实现乡村人地系统耦合与乡城融合发展、区域可持续发展及全球共同治理的有机衔接路径。
Modern human-earth relationship and human-earth system science
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

In the past 30 years, the theory of human-earth areal system has played an important support and guidance role in promoting the comprehensive research, disciplinary development and serving national strategic decision of geography. This study analyzes the scientific connotation and era value of human-earth areal system, explores the types and environment of modern human-earth system, and puts forward 'human-earth sphere' and the main contents and frontier fields of human-earth system science. The results show that: 1) The modern human-earth system is characterized by complexity, regionalism and dynamicity. The processes, pattern and comprehensive effect of human-earth interaction are undergoing profound changes, and the human-earth system on the surface of the earth has become the critical content and important theme of modern geosciences. 2) To scientifically understand and effectively coordinate the human-earth relationship, it is urgent to explore the coupling pattern and mechanism of human-earth relationship and to analyze the type, structure and dynamic mechanism of human-earth areal system. Based on the urban-rural relationship, the human-earth areal system can be divided into urban regional system, urban-rural integration system and rural regional system. Furthermore, the rural regional system is subdivided into agricultural system, village system, rural system and township system. 3) Modern human activities strongly affect the human-earth system on the surface of the earth, forming a new surface with the coupling and interaction between human and earth. In essence, it is a natural-economic-technological synthesis or human-earth coordination. They are also the main contents of deepening the researches on the coupling of human-earth system and supporting decision-making for coordinated development of human-earth system. 4) Human-earth system science or human-earth science is a new interdisciplinary subject which studies the coupling mechanism, evolution process and complex interaction effect of man earth system. It is the deep intersection and focus of modern geographic science and earth system science. Taking the modern human-earth sphere system as the research object, it is committed to exploring the state of human activities transforming and affecting the surface environment system, the interaction and coupling law of human-earth system, the formation mechanism and evolution process of human-earth coordination.Human-earth system coupling and sustainable development is the core of human-earth system science. Inheriting and innovating the theory of human-earth areal system and developing the human-earth system science will highlight the subjectivity of human on the earth surface, the process of human-earth coordination and the strategy of sustainable development, thus providing scientific guidance for the coordination of human-earth system and sustainable development decision-making.
现代人地关系与人地系统科学
DOI:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2020.08.001
[本文引用: 1]

人地关系地域系统理论系统提出30 a来,对促进地理学综合研究、学科建设和服务国家重大战略决策发挥了重要的科学支撑与导向作用。深入解析了人地关系地域系统理论的科学内涵及时代价值,诠释了现代人地系统的类型与环境,提出了“人地圈”与人地系统科学研究的主要内容和前沿领域。初步研究表明:① 现代人地系统具有复杂性、地域性和动态性特征,人?地交互作用过程、格局及其综合效应正在发生深刻变化,地球表层人地系统成为现代地学综合研究的核心内容和重要主题。② 科学认知和有效协调人地关系,亟需深入探究人地系统耦合格局与机理,探明人地关系地域系统类型、结构及其动力机制。依据城乡关系将人地关系地域类型划分为城市地域系统、城乡融合系统、乡村地域系统。乡村地域系统可细分为农业系统、村庄系统、乡域系统、城镇系统等子系统,分别对应于作土关系、人居关系、居业关系、产城关系。③ 现代人类活动强烈地作用于地球表层人地系统,形成了人地系统耦合与交互作用的地表圈层——“人地圈”,其实质是现代人类活动与地表环境相互联系、耦合渗透而形成的自然–经济–技术综合体或人地协同体。④ 人地系统科学或人地科学是研究人地系统耦合机理、演变过程及其复杂交互效应的新型交叉学科。它是现代地理科学与地球系统科学的深度交叉和聚焦,以现代人地圈系统为对象,致力于探究人类活动改造和影响地表环境系统的状态,以及人地系统交互作用与耦合规律、人地协同体形成机理与演化过程。人地系统耦合与可持续发展是人地系统科学的研究核心。传承创新人地关系地域系统理论和发展人地系统科学,更能凸显地球表层人类的主体性、人地协同的过程性和可持续发展的战略性,为人地系统协调与可持续发展决策提供科学指导。
Urban-rural integrated development and land use transitions: A perspective of land system science
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

The research perspective of land system science can provide a reference for the study of urban-rural integrated development promoted by land use transitions. Based on the review of the development of land system science, this paper discusses the theoretical framework concerning land use transitions affecting urban-rural integrated development guided by land system science, the influential ways and paths of land use transitions on urban-rural integrated development, and the measures of promoting urban-rural integrated development via adjusting and controlling land use transitions. Land system science is committed to monitoring land use change, explaining the driving forces and feedback mechanism, understanding the human-environment interactions occurring on land, and translating scientific findings on land system into solutions for sustainable land use. The operating of land system takes sustainable land use and human well-being as the criterions, and manifests as multi-dimensional effects of land use. Operating well the land system via scientifically adjusting and controlling land use transitions can affect the process of urban-rural integrated development. Land use transitions promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas under the effects of strengthening the whole and reinforcing weak links through four channels, i.e., efficiency improvement, value embodiment, development elements circulation and structure optimization. In order to promote the integrated development of urban and rural areas from the perspective of land system science, the adjustment and control of land use transitions need to reshape the land use rights system, to promote the integrated consolidation of territorial space, and to improve the management and control system of land use transitions.
基于土地系统科学的土地利用转型与城乡融合发展
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202102004
[本文引用: 1]

土地系统科学的研究视角可为促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型研究提供参考借鉴。本文在梳理国际上土地系统科学发展历程基础上,基于土地系统科学研究视角探讨了土地利用转型影响城乡融合发展的理论框架、方式与路径以及促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控途径与措施。土地系统科学致力于监测土地变化,解释驱动因素和反馈机制,理解发生于土地上的人类—环境相互作用,实现将对土地系统的科学发现转化为可持续土地利用解决方案。土地系统运行以土地可持续利用与人类福祉为准绳,显化为土地利用的多维效应。通过科学管控土地利用转型实现土地系统的良好运行能够影响城乡融合发展进程。土地利用转型通过效率提升、价值显化、要素流通与结构优化4大渠道,在“强整体”效应与“补短板”效应的作用下助推城乡融合发展。基于土地系统科学视域下促进城乡融合发展的土地利用转型调控需要重塑土地权能体系,推进国土空间综合整治,健全土地利用转型管控体系。
The basic theory and methodology of rural revitalization planning in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

Agricultural and rural modernization is the general goal of the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. The scientific formulation of the rural revitalization planning is related to the implementation effect of the national rural revitalization strategy. How to establish the basic theory of rural revitalization and develop the methods of rural revitalization planning have become important tasks of academic research and government decision-making. This paper constructed the theoretical model and method system of rural revitalization planning, tried to carry out the main function-oriented zoning, dominant type classification and principal purpose classification of rural regional system, and established the spatial system of rural revitalization planning and its optimal adjustment scheme. This system was applied to the overall rural revitalization planning in Yanchi County of Ningxia. By establishing the principle of rural revitalization planning that sticks to ecological priority, adaptation to local condition, industrial support and urban-rural integration, it put forward that the priority should be given to the development of rural professional cooperation organizations and the mixed economy of villages and towns, and the acceleration of the construction of advantageous industrial system characterized by the industrialization of tan-sheep, day lily, and minor cereals, and highlighted by the wisdom of eco-cultural tourism. Moreover, it was encouraged to give prominence to the position of the central town in space, and form the village organism and housing industry coordination body with the county seat and three key towns as the center of integrated industry development. The typical case study of Yanchi County has shown that the main contents and technical points of rural revitalization planning were embodied in the following four aspects: (1) determining the overall orientation of rural revitalization planning, and clarifying the phased development mode, key areas; (2) developing the county area based on the main function-oriented zoning, leading type classification and main purpose classification system, and exploring the territorial pattern and differentiation rules; (3) establishing the county development mode and industrial system, formulating coordination schemes of different main function-oriented zones, and revealing the spatial configuration and structural relationship of different dominant types; (4) exploring the local association and hierarchical system of each dominant type in its scale and level. The main task of implementing the rural revitalization planning is to promote the formation of a new pattern of urban-rural development with factors gathering, reasonable structure and orderly space in accordance with the objective requirements of "industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance and prosperous life". China is facing great differences in rural development and many problems in transformation. Regional disparities and urban-rural differences determine the complexity, diversity and differences of rural governance and rural revitalization planning. China's rural transformation-urban and rural integration-rural revitalization-high quality development will become the major development logic and new normal in the future. The research on rural revitalization planning in the new era should focus on the overall situation of regional coordination and urban-rural integration, and solve the practical problems of "rural disease", so as to serve the national rural revitalization planning and scientific decision-making.
中国乡村振兴规划的基础理论与方法论
DOI:10.11821/dlxb202006002
[本文引用: 1]

农业农村现代化是实施乡村振兴战略的总目标,科学编制乡村振兴规划事关国家乡村振兴战略的推进及实施成效。《全国乡村振兴战略规划(2018—2022)》提出以来,如何建立符合中国乡村发展基本特点与规律的乡村振兴规划基础理论,研制县域乡村振兴规划方法与方案,成为当前学术研究及政府决策的重要课题和重点任务。基于乡村地域多体系统理论,构建了乡村振兴规划理论模式,提出了“三主三分”乡村振兴规划方法。“三主三分”的基本原理是依据特定区域乡村地域系统结构与格局,进行地域系统主体功能分区、主导类型分类、主要用途分级,确立乡村振兴规划空间体系及其优化调整方案。该体系运用于宁夏回族自治区盐池县乡村振兴总体规划,制定了坚持生态优先、因地制宜、产业支撑、城乡融合的乡村振兴规划原则,提出应重点发展乡村专业合作组织和村镇混合制经济,加快建设以滩羊、黄花、小杂粮产业化为特色、生态文化旅游智慧化为亮点的优势产业体系;在空间上突出中心城镇地位,形成以县城和3个重点镇为中心、“三产”融合发展的村镇有机体、居业协同体。本研究是对创建中国乡村振兴规划体系的有益尝试,可为全国县级乡村振兴规划与乡村发展决策提供参考依据。
Rural regional system and rural revitalization strategy in China
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 1]

Rural regional system is a spatial system with certain structure, function and inter-regional relationship, which is composed of humanity, economy, resources and environment that are connected and interacted with each other. It is a regional multi-body system, including urban-rural integrity, rural synthesis, village-town organism, and housing-industry synergy. Targeting the rural regional system and supporting the rural revitalization strategy provides new opportunities and challenges for innovation of Chinese geography in the new era. Guided by the theory of regional system of human-land system and the science of human-land system, the research on rural revitalization geography should serve national strategy by finding solutions to problems hindering rural sustainable development, and make contribution to the comprehensive study of rural regional system structure, transformation process, evolution mechanism, differentiation pattern, regional function, and rural revitalization path and model under the interaction of surface's human-land system. There is an urgent requirement to better understand and reveal differences in the types of rural regional system and their differentiation law. Taking 39164 townships in China as research object, this paper used quantitative and qualitative methods to detect and identify the dominant factors that restrict the sustainable development of rural regional systems in China. Then we divided the types of Chinese rural regional systems, revealed the pattern of rural regional differentiation and further proposed scientific approaches to rural revitalization in different areas. Results demonstrate that topographic conditions, climate conditions, ruralization level, land resources endowment, population mobility and aging level are the dominant factors restricting the sustainable development of rural regional system, of which reflects the level of resource endowment, endogenous power and external aid of rural development. Through cluster analysis and spatial overlay of dominant factors, China's rural regional system can be divided into 12 first-class zones and 43 second-class zones. The first-class zones are named by means of 'geographical location + driving force of dominant factors', and the second-class zones are named by means of 'regional scope + driving force of dominant factors + economic development level'. The driving force of rural sustainable development in different regional types are varied. The regional pattern and path of rural revitalization in different types of areas are varied, and promoting the rural revitalization strategy should be based on local conditions to realize the coordination and sustainable development of rural economy, society, culture and ecosystem.
中国乡村地域系统与乡村振兴战略
DOI:10.11821/dlxb201912007
[本文引用: 1]

乡村地域系统是由人文、经济、资源与环境相互联系、相互作用下构成的、具有一定结构、功能和区际联系的乡村空间体系,是一个由城乡融合体、乡村综合体、村镇有机体、居业协同体等组成的地域多体系统。以乡村地域系统为对象,服务支撑国家乡村振兴战略,为新时期地理学创新研究提供了新机遇和新挑战。乡村振兴地理学研究,亟需以问题为导向、战略为指向,以人地关系地域系统理论和人地系统科学为指导,致力于地表人地系统交互作用下乡村地域系统结构、转型过程、演变机理、分异格局、地域功能,以及乡村振兴途径与模式综合研究,科学把握乡村地域系统类型及其分异规律。本文以全国39164个乡镇为基本单元,采用定量和定性相结合的研究方法,诊断识别了制约中国乡村地域系统可持续发展的主导因子,划分了中国乡村地域系统类型,揭示了乡村地域系统分异格局,探明了不同类型区乡村振兴科学途径。结果表明:① 地理环境、村镇化水平、资源禀赋、人口流动程度和老龄化水平等是乡村地域系统分异的主导因子,反映了乡村发展自然本底特征以及外援动力、内生动力的大小。② 通过主导要素聚类和空间叠加分析,将中国乡村地域系统划分为12个一级区、43个二级区。一级区采用“地理区位+主导要素驱动力/约束力”的方法命名,二级区采用“地域范围+主导要素驱动力/约束力+乡村经济发展水平”命名。③ 不同类型区乡村振兴地域模式和路径不同,乡村振兴战略与规划的落地要因地制宜、分类施策。
Research on the geography of rural revitalization in the new era
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190133
[本文引用: 1]

Urban-rural integration and rural sustainable development are not only the important strategic themes of China's modernization, but also the main frontier topics of rural regional system research in geography. Facing the problems of urban-rural segregation, human-land segregation and increasingly severe rural diseases in the process of rapid urbanization in China, urban-rural integration and rural revitalization are accelerated to be the national strategies. This research briefly analyses the economic and social background of rural revitalization and its significance in the new era. It is pointed out that the important responsibility of modern geography to face the national strategy and serve the rural revitalization is to deeply explore the major theories and scientific approaches of the coupling of man-land system, the integration of urban-rural development and the fit of the functions of villages-towns, while this paper focuses on the domestic research progress of rural revitalization strategy since it has been proposed for one year and the main contents and characteristics of this special issue. Finally, focusing on giving full play to the advantages and characteristics of geography, this paper expounds the theoretical frontiers and scientific and technological needs of the scientific research on rural revitalization in the new era. The ten frontier issues mainly include the differentiation and integration mechanism of urban and rural regional system; the transformation mechanism and scientific approach of rural regional system; the interaction principle and planning governance of agriculture, farmers and rural areas; the mutual feedback mechanism of rural natural-social-technical system; the coupling process and scenario simulation of rural man-land system; the suitability and carrying capacity of rural spatial reconstruction; and rural transformation developing endogenous power and synergy mechanism; new subjectivity and farmers' organization of rural revitalization; efficiency and transmission mechanism of scientific and technological innovation of rural revitalization; disaster and risk control mechanism of rural regional system. And we put forward some preliminary thoughts and suggestions for deepening the research of rural science and geography on rural revitalization in China.
新时代乡村振兴地理学研究
DOI:10.11821/dlyj020190133
[本文引用: 1]

城乡融合与乡村可持续发展,既是中国现代化建设的重要战略主题,也是地理学乡村系统研究的主要前沿课题。面对快速城镇化进程中城乡分隔、人地分离和日趋严峻的乡村病问题,加快推进城乡融合与乡村振兴上升为国家战略。本文简要分析了新时代乡村振兴的经济社会背景及其重要意义,指出深度探究人地系统耦合、城乡发展融合、村镇功能契合重大理论与科学途径,成为现代地理学面向国家战略、服务乡村振兴的重要责任。重点介绍了乡村振兴战略提出一周年来国内相关研究进展及本专辑论文的主要内容与特点。最后,着眼于发挥地理学优势和特色,阐释了新时代乡村振兴科学研究的前沿问题及科技需求,提出了进一步深化中国乡村科学与乡村振兴地理学研究的初步思考和建议。
Scientific understanding of the major strategy for promoting rural revitalization
科学理解推进乡村振兴的重大战略导向
Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: Achievements, challenges and reflections
DOI:10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.009 URL [本文引用: 1]