

中国区域经济差异时空演变及其多尺度效应
|
王圣云(1977-), 男, 山西河曲人, 研究员, 主要从事区域经济与福祉地理学研究。E-mail: wangshengyun@163.com |
收稿日期: 2023-11-29
修回日期: 2024-08-31
网络出版日期: 2025-04-23
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42061026)
Spatio-temporal evolution and multi-scale effects of regional economic differences in China
Received date: 2023-11-29
Revised date: 2024-08-31
Online published: 2025-04-23
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42061026)
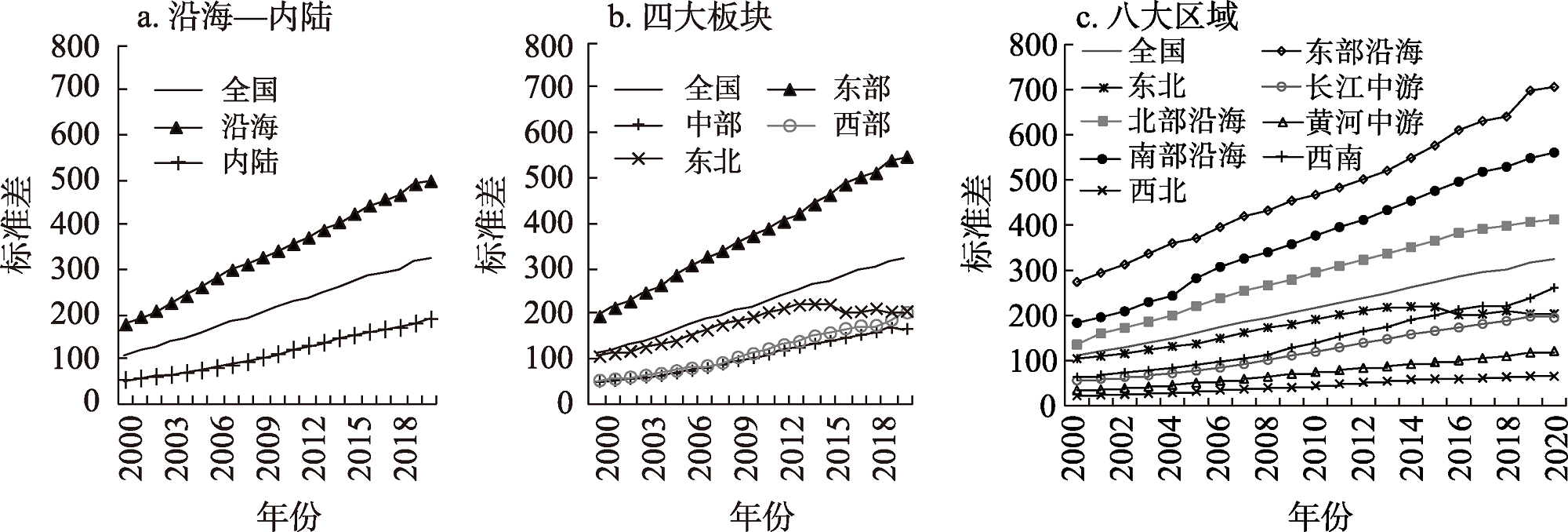
不断缩小区域经济差异,增强区域发展平衡性,是中国实施区域协调发展战略的应有之义。本文融合夜间灯光数据与GDP统计数据构建实际经济指数(GEI),运用泰尔指数、尺度方差模型和空间过滤模型对2000—2020年中国区域经济差异时空演变进行了多尺度分析。研究发现:① 2000—2020年中国区域经济绝对差异逐年扩大,但相对差异整体趋于缩小;② 不同区域划分下,中国区域经济尺度方差均呈现出市级>县级>省级>大区域的递减格局,市级的尺度方差增幅最大且贡献率最高,缩小市间差异是缩小中国区域经济差异的关键;③ 2000—2020年空间自相关对中国区域经济差异的贡献率由23.804%提高至26.079%,不考虑空间自相关因素会导致对中国区域经济差异的高估;④ 空间自相关对区域经济差异的影响具有尺度敏感性,空间尺度越小,区域经济差异对空间自相关的敏感性越强。经空间过滤后,即剔除空间自相关因素后,中国区域经济差异由市间差异最大变为县域间差异最大;⑤ 人力资本、产业结构、消费规模、财政分权对中国实际经济指数的影响显著为正,但这些因素对中国区域经济差异的影响存在明显的区域异质性。本文可为中国实施区域协调发展战略提供多尺度、精细化、差异化的决策参考。
关键词: 区域经济差异; 实际经济指数(GEI); 三阶段嵌套泰尔指数; 尺度方差; 空间过滤模型
王圣云 , 潘柳欣 , 王振波 . 中国区域经济差异时空演变及其多尺度效应[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(4) : 1009 -1030 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202504010
Narrowing the gap of regional economic development and maintaining the balanced development path is the indispensable goals of China's regional coordinated development. In this study, the nighttime light image data and GDP statistical data are integrated to construct the Genuine Economic Index (GEI). Based on GEI, the Theil index, scale variance model, and the spatial filtering model are combined to analyze the spatial and temporal evolution of China's regional economic discrepancy from a multi-scale perspective. The results show that: (1) China's absolute regional economic differences expanded year by year, while the relative regional economic differences tended to shrink overall from 2000 to 2020. (2) Under different regional divisions, the scale variance of China's regional economy is manifested as municipal scale > county scale > provincial scale > regional scale, with the largest increase and highest contribution rate on the municipal scale. Narrowing inter-municipal gap is the key to decrease China's regional economic differences. (3) The contribution rate of spatial autocorrelation increased from 23.804% to 26.079% during 2000-2020. Regardless of spatial autocorrelation factors will lead to an overestimation of China's regional economic differences. (4) The impact of spatial autocorrelation on regional economic differences is scale sensitive, the smaller the spatial scale is, the stronger the sensitivity is. After spatial filtering, inter-county economic differences have been the largest part of China's regional economic differences. (5) Human capital, industrial structure, consumption scale and fiscal decentralization have a significant positive impact on China's Genuine Economic Index, however these factors show an obvious regional heterogeneity. This study could provide a multi-scale, refined and differentiated reference for the implementation of China's regional coordinated development strategy.

感谢周杰文副教授提供部分基础数据,感谢博士生姜婧在建模方面给予的协助,感谢审稿专家细致且有高度的修改建议。
| [1] |
[张军扩. 中国区域政策回顾与展望. 管理世界, 2022, 38(11): 1-12.]
|
| [2] |
[汪晨, 万广华, 张勋. 区域差异与结构变迁: 中国1978—2016. 管理世界, 2019, 35(6): 11-26, 194.]
|
| [3] |
[杨开忠. 中国区域经济差异变动研究. 经济研究, 1994, 29(12): 28-33, 12.]
|
| [4] |
[贺灿飞, 梁进社. 中国区域经济差异的时空变化: 市场化、全球化与城市化. 管理世界, 2004(8): 8-17, 155.]
|
| [5] |
[李小建, 乔家君. 20世纪90年代中国县际经济差异的空间分析. 地理学报, 2001, 56(2): 136-145.]
|
| [6] |
[陈培阳, 朱喜钢. 基于不同尺度的中国区域经济差异. 地理学报, 2012, 67(8): 1085-1097.]
|
| [7] |
[蔡昉, 贾朋. 中国地区差距类型变化及其政策含义. 中国工业经济, 2022(12): 5-13.]
|
| [8] |
[王贤彬, 黄亮雄, 徐现祥, 等. 中国地区经济差距动态趋势重估: 基于卫星灯光数据的考察. 经济学(季刊), 2017, 17(3): 877-896.]
|
| [9] |
[张佰发, 苗长虹, 冉钊, 等. 核心—边缘视角下的黄河流域县域经济差异研究. 地理学报, 2023, 78(6): 1355-1375.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
[杨振, 朱虎啸, 王晓筱, 等. 江苏省区域经济发展空间格局及影响因素的多尺度效应分析. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2024, 47(1):114-123.]
|
| [13] |
[徐康宁, 陈丰龙, 刘修岩. 中国经济增长的真实性: 基于全球夜间灯光数据的检验. 经济研究, 2015, 50(9): 17-29, 57.]
|
| [14] |
[陈梦根, 张帅. 中国地区经济发展不平衡及影响因素研究: 基于夜间灯光数据. 统计研究, 2020, 37(6): 40-54.]
|
| [15] |
Commission for the Rediscovery Geography. Rediscovering Geography:New Relevance to Science and Society. Huang Runhua, trans trans. Beijing: Xueyuan Press, 2002: 108-115.
[重新发现地理学委员会. 重新发现地理学:与科学和社会的新关联. 黄润华, 译. 北京: 学苑出版社, 2002: 108-115.]
|
| [16] |
[李小建. 经济地理学研究中的尺度问题. 经济地理, 2005, 25(4): 433-436.]
|
| [17] |
[李晶晶, 苗长虹, 叶信岳. 区域经济核心—边缘结构多尺度演化机制分析: 以河南省为例. 经济地理, 2016, 36(10): 9-17.]
|
| [18] |
[叶信岳, 李晶晶, 程叶青. 浙江省经济差异时空动态的多尺度与多机制分析. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(9): 1177-1186.]
|
| [19] |
[王少剑, 王洋, 赵亚博. 广东省区域经济差异的多尺度与多机制研究. 地理科学, 2014, 34(10): 1184-1192.]
|
| [20] |
[吴玉鸣. 县域经济增长集聚与差异: 空间计量经济实证分析. 世界经济文汇, 2007, (2): 37-57.]
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[邓小平. 邓小平文选(第三卷). 北京: 人民出版社, 1993.]
|
| [24] |
[周杰文. 中国区域经济差异的尺度效应分析. 北京: 中国社会科学出版社, 2017: 26-29.]
|
| [25] |
[黄少安, 谢冬水. 南北城市功能差异与南北经济差距. 南方经济, 2022(6): 40-63, 76.]
|
| [26] |
[曹子阳, 吴志峰, 匡耀求, 等. DMSP/OLS夜间灯光影像中国区域的校正及应用. 地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(9): 1092-1102.]
|
| [27] |
[胡为安, 刘传立, 詹淇雯. 中国区域NPP-VIIRS年度夜间灯光数据的合成方法与对比验证. 桂林理工大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 141-148.]
|
| [28] |
[董鹤松, 李仁杰, 李建明, 等. 基于DMSP-OLS与NPP-VIIRS整合数据的中国三大城市群城市空间扩展时空格局. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(5): 1161-1174.]
|
| [29] |
[王贤彬, 黄亮雄. 夜间灯光数据及其在经济学研究中的应用. 经济学动态, 2018(10): 75-87.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[魏后凯. 促进区域协调发展的战略抉择与政策重构. 技术经济, 2023, 42(1): 14-24.]
|
| [33] |
[徐建华, 鲁凤, 苏方林, 等. 中国区域经济差异的时空尺度分析. 地理研究, 2005, 24(1): 57-68.]
|
| [34] |
[许召元, 李善同. 近年来中国地区差距的变化趋势. 经济研究, 2006, 41(7): 106-116.]
|
| [35] |
[刘瑜, 汪珂丽, 邢潇月, 等. 地理分析中的空间效应. 地理学报, 2023, 78(3): 517-531.]
|
| [36] |
[严成樑. 现代经济增长理论的发展脉络与未来展望: 兼从中国经济增长看现代经济增长理论的缺陷. 经济研究, 2020, 55(7): 191-208.]
|
| [37] |
[姚先国, 张海峰. 教育、人力资本与地区经济差异. 经济研究, 2008(5): 47-57.]
|
| [38] |
[裴延峰. 中国产业结构变迁的空间不平衡对地区经济差距的影响. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2022, 39(3): 3-23.]
|
| [39] |
[林嵩, 谷承应, 斯晓夫, 等. 县域创业活动、农民增收与共同富裕: 基于中国县级数据的实证研究. 经济研究, 2023, 58(3): 40-58.]
|
| [40] |
[王维国, 王鑫鹏. 创新转化效率、要素禀赋与中国经济增长. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2022, 39(12): 5-25.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |