

基于省际虚拟水流动的水资源压力及驱动因素
|
房德琳(1990-), 女, 山东济南人, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事城市生态环境耦合模拟相关研究。E-mail: fangd@bnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-09-09
修回日期: 2025-02-05
网络出版日期: 2025-03-25
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42230106)
国家自然科学基金项目(72174029)
中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金
Analysis of water stress and driving factors based on virtual water flows in China
Received date: 2024-09-09
Revised date: 2025-02-05
Online published: 2025-03-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42230106)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(72174029)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
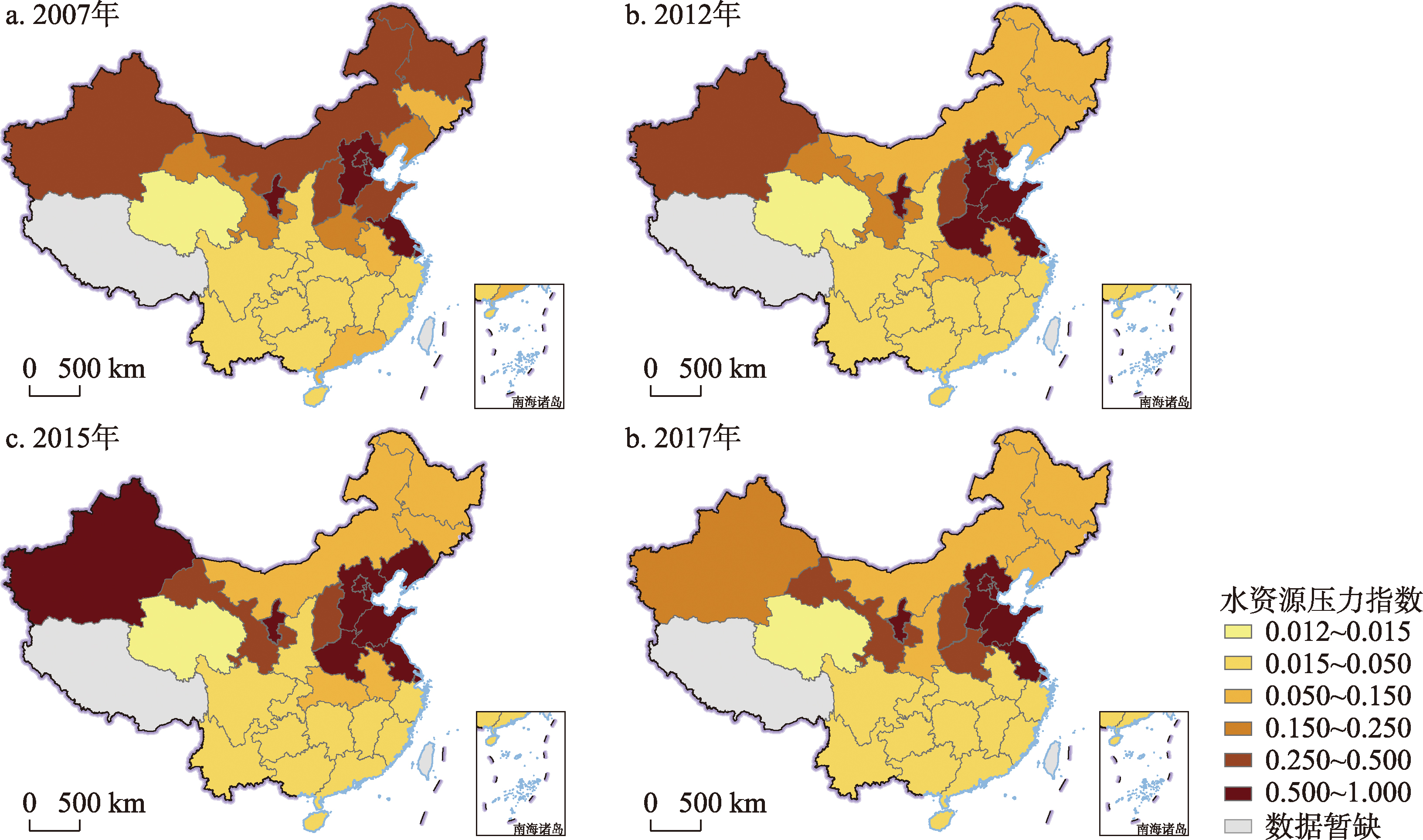
中国各省市资源禀赋、产业发展水平等多因素的空间差异使得各省市面临不同的水资源压力;同时各省市间的经济贸易实现了水资源的再分配,这使得水资源需求差也发生了相应的转移。水资源短缺是限制各地区发展的重要瓶颈,因此分析水资源压力分布现状及格局,并剖析由经济供需链造成的水资源压力转移的重要驱动因素,对地区的可持续发展和生态资源保护具有重要意义。本文聚焦于中国省际水资源压力转移及驱动因素时空变化,分析了2007—2017年中国30个省域(西藏、香港、澳门、台湾地区数据暂缺)的水资源压力转移过程中稀缺蓝水、稀缺灰水流动情况的时空动态,以及其分别对省际水资源压力转移的影响;进一步,本文将省域间水资源压力转移驱动因素分解为技术效应、水资源压力效应、第一至第三产业结构效应和城乡居民消费需求效应等,分析各影响因素对水资源压力的影响贡献。研究结果表明,在各省域最终需求驱动下,隐含在贸易流转中的水资源压力跨区域转移逐渐提高;西南和东南地区自身水资源压力较小,但向其他区域转移较高的水资源压力,这主要由于西南和东南地区进口来自北方水资源压力较大地区的产品,以满足其全产业链的需求;西北地区逐渐成为全国其他地区稀缺蓝水的输出方,中部地区省份由主要稀缺蓝水输出方向主要输入方转变。本文揭示了中国省际水资源压力转移的分布格局和驱动因素影响形式,有助于保障中国的水资源安全,并为中国各地区的可持续发展提供参考意义。
房德琳 , 宋长青 , 黎成航 , 雷頔 , 宋高歌 , 袁嘉露 , 童创路 , 曹力 . 基于省际虚拟水流动的水资源压力及驱动因素[J]. 地理学报, 2025 , 80(3) : 712 -723 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202503009
The spatial disparities in resource endowments and industrial development levels across provincial-level regions in China lead to diverse water resource pressures. Economic trade redistributes water resources, causing spatial shifts in water demand. Water scarcity poses a significant bottleneck to regional development. Thus, examining water resource pressure distributions, patterns, and their drivers within economic supply and demand chains is crucial for sustainable development and ecological conservation. This research explores spatiotemporal changes in inter-provincial water resource pressure transfers and their drivers in China from 2007 to 2017. It analyzes the dynamics of scarce blue and grey water flows among 30 provincial-level regions (excluding Xizang, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan due to the lack of data) and their impacts on inter-provincial transfers. Key drivers such as technological advancements, environmental pressures, industrial structures, and urban-rural consumer demand are decomposed to assess their contributions to water resource pressure. Results show an upward trend in water pressure transfers driven by final demand. Southwest and southeast regions, experiencing lower local water pressures, transfer significant pressures to other areas. Northwest region emerges as major exporters of scarce blue water, while central provinces shift from exporters to importers. This study provides insights into inter-provincial water resource pressure transfers, aiding water security strategies and sustainable development planning in China.

Key words: water stress index; MRIO model; SDA model; blue water-grey water; cluster analysis; China
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
[ 孙才志, 阎晓东. 基于MRIO的中国省区和产业灰水足迹测算及转移分析. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(2): 207-218.]
|
| [5] |
[ 龙爱华, 徐中民, 张志强. 西北四省(区)2000年的水资源足迹. 冰川冻土, 2003(6): 692-700.]
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
[ 田沛佩. 基于MRIO的中国水—能—碳耦合关系研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学(北京), 2021.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
[ 姜秋香, 吴云星, 王子龙, 等. 黑龙江省水足迹时空分布规律及空间均衡分析. 水资源保护, 2022, 38(5): 122-131.]
|
| [14] |
[ 赵勇, 黄可静, 高学睿, 等. 黄河流域粮食生产水足迹及虚拟水流动影响评价. 水资源保护, 2022, 38(4): 39-47.]
|
| [15] |
[ 姜秋香, 李鑫莹, 王子龙, 等. 水足迹及其驱动力研究进展及展望. 生态科学, 2021, 40(1): 192-199.]
|
| [16] |
[ 李艳梅, 张雷. 中国居民间接生活能源消费的结构分解分析. 资源科学, 2008, 30(6): 890-895.]
|
| [17] |
[ 吴彼爱, 高建华, 徐冲. 基于产业结构和能源结构的河南省碳排放分解分析. 经济地理, 2010, 30(11): 1902-1907.]
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
[ 蔡北溟. 中国水足迹时空变化及其驱动机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017.]
|
| [21] |
[ 王光谦, 张宇, 谢笛, 等. 中国绿水格局及其战略意义. 地理学报, 2023, 78(7): 1641-1658.]
|
| [22] |
[ 孙思奥, 王晶, 戚伟. 青藏高原地区城乡虚拟水贸易格局与影响因素. 地理学报, 2020, 75(7): 1346-1358.]
|
| [23] |
[ 刘卫东, 陈杰, 唐志鹏, 等. 中国2007年30省区市区域间投入产出表编制理论与实践. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2012.]
|
| [24] |
Carbon Emission Accounts & Datasets (CEADs). China Multi-Regional Input-Output Table 2012, 2015, 2017.
|
| [25] |
[ 韩琴, 孙才志, 邹玮. 1998—2012年中国省际灰水足迹效率测度与驱动模式分析. 资源科学, 2016, 38(6): 1179-1191.]
|
| [26] |
[ 李飞, 董锁成. 西部地区畜禽养殖污染负荷与资源化路径研究. 资源科学, 2011, 33(11): 2204-2211.]
|
| [27] |
[ 朱兆良. 农田中氮肥的损失与对策. 土壤与环境, 2000(1): 1-6.]
|
| [28] |
[ 王晓萌, 黄凯, 杨顺顺, 等. 中国产业部门水足迹演变及其影响因素分析. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(12): 2114-2126.]
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
[ 田欣, 熊翌灵, 刘尚炜, 等. 中国省际水资源压力的转移模式. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(12): 75-83.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |