

20世纪以来中国北方干旱半干旱区针叶树种径向生长动态变化
|
陈峰(1982-), 男, 福建沙县人, 研究员, 博士生导师, 主要从事树轮与水文气候研究。E-mail: feng653@163.com |
收稿日期: 2024-01-09
修回日期: 2024-09-10
网络出版日期: 2024-09-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(32061123008)
Radial growth dynamics of coniferous species in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China since the 20th century
Received date: 2024-01-09
Revised date: 2024-09-10
Online published: 2024-09-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(32061123008)
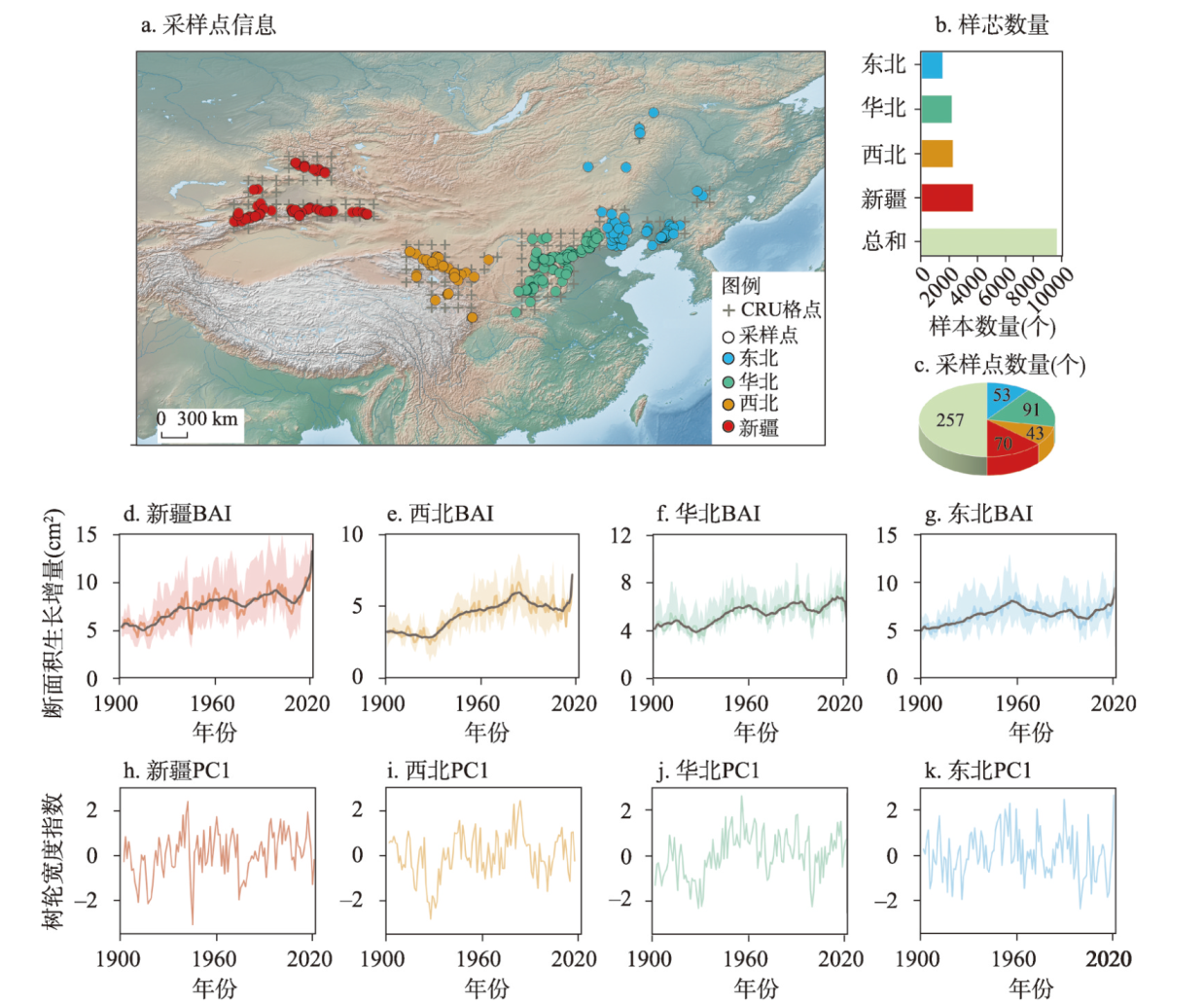
全球变暖不断影响着森林生态系统的结构和功能,其中森林生产力受到大范围极端干旱的限制更为强烈,并表现出显著的空间异质性。本文通过对中国北方干旱半干旱区257个针叶树种年轮样点进行生长趋势检测和气候驱动因子评估,确定了自20世纪以来针叶树种径向生长动态变化及其对气候因子响应模式。滑动平均分析结果表明中国新疆和西北地区针叶树种径向生长呈持续增加趋势,华北地区呈波动式增加,东北地区则在20世纪中叶后呈下降趋势。空间响应模式表明水分对所有区域的针叶树种径向生长存在积极作用,气温上升引起的蒸散发加剧则会抑制径向生长,然而西北地区生长季变化对径向生长的影响受益于暖湿化现象产生的热效应。气候学分析表明大气环流因子从年际到年代际尺度上通过调节全球海温和气压强度变化,对亚洲季风区降水产生显著作用,在一定程度上影响了中国北方针叶树种径向生长动态。CMIP5数据和VS-Lite模型揭示在未来气候变化情景下受全球变暖影响,延长的生长季会促进区域针叶树种径向生长,而低降水量引起的干旱胁迫仍然对径向生长存在限制作用,特别是在水分缺乏的中国西部地区。
陈峰 , 王世杰 , 赵晓恩 , 陈友平 , 胡茂 , 徐阳 , 唐雯卉 , 张合理 , 陈巧湄 , 岳伟鹏 , 侯体源 , 曹红华 , 刘雨欣 , 谌卓岚 , 武心凤 , 魏家昌 , 王赫川 . 20世纪以来中国北方干旱半干旱区针叶树种径向生长动态变化[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(9) : 2341 -2355 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202409012
Continuous global warming has been affecting the structure and function of forest ecosystems, and forest productivity is strongly restricted by large-scale extreme drought and shows significant spatial heterogeneity. Patterns of changes in radial growth dynamics of coniferous species and responses to climatic factors since the beginning of the 20th century were identified by examining growth trends and assessing climatic drivers based on the tree-ring data from the 257 sampling sites in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China. The running average results indicated that radial growth of coniferous species in Xinjiang and northwest China showed a continuous increase, and radial growth of coniferous species showed a fluctuating increase in northern China, and a decline in northeast China was detected after the mid-20th century. Moisture has a positive effect on radial growth of coniferous species in all regions, and increased evapotranspiration induced by warmer temperatures will inhibit radial growth to some extent. The effect of growing season changes on radial growth in northwest China benefits from the thermal effects of warming and humidification phenomena. Climatological analyses showed that atmospheric circulation factors have some vital influences on regional precipitation generated by the Asian monsoon system by regulating global SST and baroclinic intensity changes on interannual to interdecadal scales, and potentially affecting radial growth of coniferous species in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China. CMIP5 data and VS-Lite modeling revealed impacts under future climate change scenarios, the extended growing season due to global warming promotes regional radial growth of coniferous species, and however, drought stress due to less precipitation still have some limiting effects on radial growth, especially in western China.

图1 研究区示意图及20世纪以来中国北方干旱半干旱区针叶树种径向生长情况注:图b~c为各子区域树轮样本和采样点数量分布及总和;图d~k为断面积生长增量(BAI)以及树轮宽度指数(PC1)变化,其中指示各子区域内断面积生长增量均值15 a滑动平均变化,阴影指示各区域内所有样本断面积生长增量的25%~75%范围变化;底图来源于Natural Earth地图数据集(https://www.naturalearthdata.com/features/)。 Fig. 1 Schematic map of the study area and radial growth of coniferous species in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China since the 20th century |
图3 20世纪以来中国北方干旱半干旱区针叶树种径向生长的大尺度环流驱动机制注:图a~h中为观测数据中的空间响应模式,SST和SLP的月份为上年8月至当年7月,点状区域表示5%的显著性水平;图i~n中为CESM-LME模拟数据中的标准化大气环流指数回归的降水(阴影,mm/d)和整层水汽通量(kg/(m/s))的空间模式,点状区域代表超过10%显著性水平,方框表示4个子区域。 Fig. 3 Large-scale circulation-driven mechanisms of radial growth of coniferous species in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China since the 20th century |
图4 基于VS-Lite模型的中国北方干旱半干旱区针叶树种径向生长未来预估注:图a~h中左侧为年表PC1实际值与VS-Lite模拟值对比,阴影表示±1倍均方根误差(RMSE)范围,右侧为21世纪不同排放情景(RCP 4.5和RCP 8.5)下模拟未来树木径向生长情况;阴影表示±2倍标准误差(SE)范围;图i~j为RCP 4.5和RCP 8.5情景下极端干旱(最低降水10年)对树木径向生长的影响(包括当年和次年),箱线图的方框表示25%~75%范围,须线表示±2倍标准差(SD)范围,中线表示平均值,右侧曲线表示正态分布。 Fig. 4 Future projections of radial growth of coniferous species in arid and semi-arid areas of northern China based on the VS-Lite model |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[王锡津, 方克艳, 张仲石. 1901—1950年5—9月北半球CRU数据与树轮资料的对比. 第四纪研究, 2023, 43(5): 1254-1268.]
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
[李心月, 陈显尧. 影响全球平均表面温度的主要过程. 科学通报, 2021, 66(31): 4017-4027.]
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
[周雪城, 姜大膀. 过去千年年代和百年尺度东亚夏季风变化的模拟分析. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(2): 522-535.]
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
[张学珍, 李侠祥, 徐新创, 等. 基于模式优选的21世纪中国气候变化情景集合预估. 地理学报, 2017, 72(9): 1555-1568.]
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
[刘禹, 王财勇, 郝文俊, 等. 利用树轮宽度重建过去238年来内蒙古喀喇沁年降水量. 科学通报, 2011, 56(25): 2052-2059.]
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
[李明启, 邵雪梅, 张永. 392 BC—2017 AD柴达木盆地东北部降水变化及其与太阳活动和强火山喷发的联系. 地理学报, 2023, 78(1): 71-86.]
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
[赵文清, 马耀明, 曹殿斌. 中亚干旱地区降水异常及其影响机制研究. 大气科学学报, 2023, 46(1): 18-29.]
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
[于淑秋, 林学椿, 施晓晖. 东亚夏季风的年际变化及其与环流和降水的关系. 地理学报, 2008, 63(7): 751-760.]
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |