

基于对象空间的地理场景表达模型与组织管理方法及应用
|
靖常峰(1979-), 男, 山东济南人, 博士, 教授, 研究方向为城市空间信息学、时空大数据建模与分析。E-mail: jingcf@cugb.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2024-02-05
修回日期: 2024-07-23
网络出版日期: 2024-09-27
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2021YFB3900902)
Organization and management of geographic scenes based on object space
Received date: 2024-02-05
Revised date: 2024-07-23
Online published: 2024-09-27
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2021YFB3900902)
信息智能化与时空大数据时代拓展了地理信息系统(GIS)的应用边界,给地理场景的描述与表达带来了机遇与挑战。现有的时空数据组织与空间认知模型主要以自下而上思维为主,存在对象抽象表达认知度低、实体对象分区组织割裂等局限性。特别是大数据背景下,地理场景表达中对象与知识的集成度较低、模型与数据的协同计算能力不足等问题更为突出。本文以莱布尼兹(Leibniz)相对时空观为理论基础,提出了对象空间的地理场景组织与管理方法。文章分析了地理场景的概念与发展历程,剖析了地理场景特点,提出了对象空间概念以及对象空间对地理场景的表达方式,建立了层次化对象组织模型、网络化的知识表达技术、按功能分类的模型组织方法,从而构建了“数据—知识—模型”高度集成与协同的地理场景建模理论与技术。结合山东高标准农田土壤含水量监测案例,验证了本文方法的实用性和可行性,为深化地理数据组织模型的理论研究和拓展示范应用场景提供了技术支撑。
靖常峰 , 李佳宁 , 吴森森 , 冯云龙 , 曹一冰 , 陈奕君 , 蒋捷 , 周成虎 . 基于对象空间的地理场景表达模型与组织管理方法及应用[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(9) : 2230 -2245 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202409005
The advent of information intelligence and spatiotemporal big data have significantly broadened the scope of application for geographic information systems (GIS), presenting both opportunities and challenges in the modeling of geographic scenarios. Current paradigms for organizing spatiotemporal data and conceptualizing spatial cognition predominantly rely on a bottom-up approach, which was demonstrated with limitation on low cognition and the fragmented representation of geospatial objects. This is a noteworthy research issue facing the Big Data era, namely the design of new representation models for the integration of objects and knowledge, as well as the collaborative computation of models and objects. This study, inspiring from Leibniz's relative spatiotemporal perspective, establishes an object space-based approach for organization and management of geographic scenarios. The concept of object space was proposed by reviewing the historical evolution of geographic scenarios representation model and literature work on mainstream research domain. Object space is the space of influence of an object, both the inner space of the object and the space of its surroundings. It includes pan spatiotemporal object, object space relationship, calculation and analysis process, which represents object, knowledge and model. For representing and management of object space, a hierarchical model was developed to organize pan spatiotemporal objects according to business requirement and spatial scale. Further, a network model was denoted to represent object space relationship and knowledge, in which node is the objects, and edge is the space relationship. Then, a model classification method based on functional and computational ability was used to organize calculation and analysis process models. Thus, a highly integrated and synergistic "data-knowledge-model" organization and management model was established. The proposed approach was applied in monitoring soil moisture in high-standard farmland in Shandong, which included 44 pan spatiotemporal objects, 2 object space relationship network models and 5 calculation and analysis process models. The results demonstrated its efficacy and feasibility in designing and implementing high-standard farmland intelligent automatic irrigation and drainage systems, thereby offered technical support for advancing theoretical research and expanding practical application in geographic scenarios.

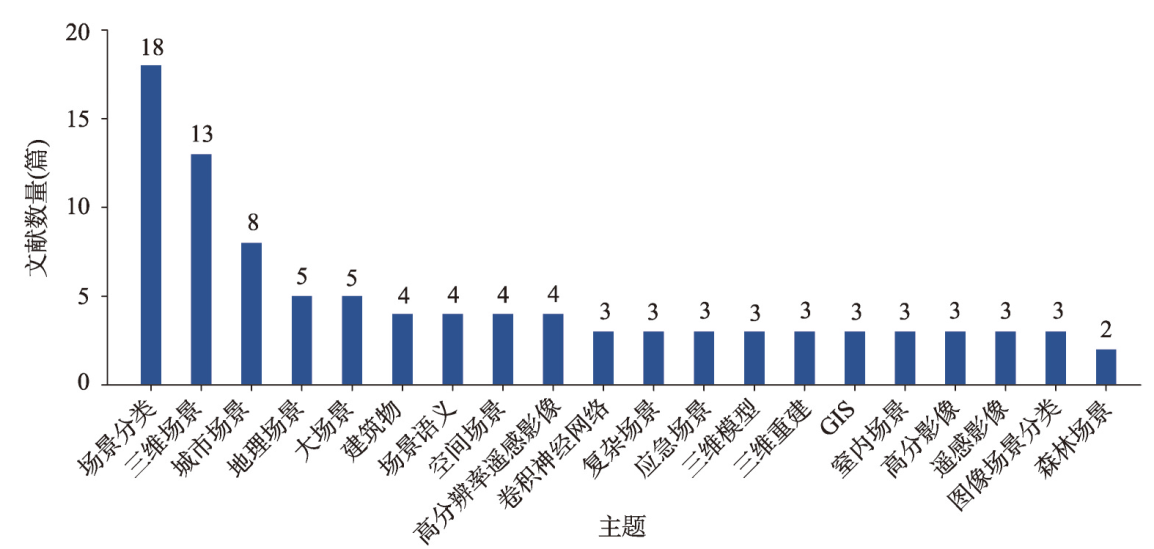
图1 2000—2023年中国知网中文论文中主题分布Fig. 1 Topic distribution in Chinese papers in CNKI from 2000 to 2023 |
表1 地理学及交叉学科JCR一区期刊和行业主流期刊列表Tab. 1 List of geography and interdisciplinary JCR Q1 journals and famous domains' journals |
| 序号 | 期刊名 | 学科分类 | 2022因子 | JCR分区 | 篇数(篇) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nature Reviews Earth & Environment | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 42.1 | Q1 | 0 |
| 2 | Nature Geoscience | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 18.3 | Q1 | 2 |
| 3 | IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine | Remote Sensing, SCI | 14.6 | Q1 | 0 |
| 4 | Remote Sensing of Environment | Remote Sensing, SCI | 13.5 | Q1 | 4 |
| 5 | ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing | Geography, Physical, SCI | 12.7 | Q1 | 7 |
| 6 | Earth-Science Reviews | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 12.1 | Q1 | 16 |
| 7 | Geography and Sustainability | Geography, Physical, ESCI | 9.7 | N/A | 0 |
| 8 | Landscape and Urban Planning | Geography, SSCI | 9.1 | Q1 | 8 |
| 9 | IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing | Remote Sensing, SCI | 8.2 | Q1 | 11 |
| 10 | International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation | Remote Sensing, SCI | 7.5 | Q1 | 16 |
| 11 | GIScience & Remote Sensing | Geography, Physical, SCI | 6.7 | Q1 | 1 |
| 12 | Geo-Spatial Information Science | Remote Sensing, SCI | 6.0 | Q1 | 17 |
| 13 | International Journal of Geographical Information Science | Geography, SSCI | 5.7 | Q1 | 46 |
| 14 | Science China-Earth Sciences | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 5.7 | Q1 | 10 |
| 15 | IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing | Geography, Physical, SCI | 5.5 | Q1 | 14 |
| 16 | International Journal of Digital Earth | Geography, Physical, SCI | 5.1 | Q1 | 19 |
| 17 | Annals of GIS | Geography, ESCI | 5.0 | N/A | 16 |
| 18 | Remote Sensing | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCIE | 5.0 | Q1 | 69 |
| 19 | Applied Geography | Geography, SSCI | 4.9 | Q1 | 10 |
| 20 | Journal of Geographical Sciences | Geography, Physical, SCI | 4.9 | Q1 | 24 |
| 21 | IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters | Remote Sensing, SCI | 4.8 | Q2 | 2 |
| 22 | Regional Studies | Geography, SSCI | 4.6 | Q1 | 0 |
| 23 | Computers & Geosciences | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 4.4 | Q1 | 0 |
| 24 | Journal of Geovisualization and Spatial Analysis | Geography, ESCI | 4.0 | N/A | 1 |
| 25 | Big Earth Data | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, ESCI | 4.0 | N/A | 1 |
| 26 | European Journal of Remote Sensing | Remote Sensing, SCI | 4.0 | Q3 | 6 |
| 27 | Urban Geography | Geography, SSCI | 3.8 | Q1 | 1 |
| 28 | Geocarto International | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, SCI | 3.8 | Q2 | 8 |
| 29 | Applied Computing and Geosciences | Geosciences, Multidisciplinary, ESCI | 3.4 | N/A | 0 |
| 30 | International Journal of Urban and Regional Research | Geography, SSCI | 3.3 | Q2 | 1 |
| 31 | Transactions in GIS | Geography, SSCI | 2.4 | Q2 | 37 |
| [1] |
[周成虎. 全空间地理信息系统展望. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(2): 129-131.]
|
| [2] |
[闾国年, 俞肇元, 袁林旺, 等. 地图学的未来是场景学吗? 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(1): 1-6.]
|
| [3] |
[郭仁忠, 应申. 论ICT时代的地图学复兴. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1274-1283.]
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
[王晓明, 刘瑜, 张晶. 地理空间认知综述. 地理与地理信息科学, 2005(6): 1-10.]
|
| [6] |
[林珲, 胡明远, 陈旻, 等. 从地理信息系统到虚拟地理环境的认知转变. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(4): 662-672.]
|
| [7] |
[袁林旺, 闾国年, 罗文, 等. GIS多维统一计算的几何代数方法. 科学通报, 2012, 57(4): 282-290.]
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
[华一新, 周成虎. 面向全空间信息系统的多粒度时空对象数据模型描述框架. 地球信息科学学报, 2017, 19(9): 1142-1149.]
|
| [11] |
[闾国年, 袁林旺, 俞肇元. 地理学视角下测绘地理信息再透视. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1549-1556.]
|
| [12] |
[华一新, 张江水, 曹一冰. 基于时空域的全空间数字世界时空对象组织与管理研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(1): 76-83.]
|
| [13] |
[霍华骑, 陆璐. 基于空间域和频率域特征融合的场景文本识别. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(Suppl.2): 48-55.]
|
| [14] |
[唐述, 万盛道, 谢显中, 等. 一种多尺度的图像动态场景盲去模糊网络. 软件学报, 2022, 33(9): 3498-3511.]
|
| [15] |
[刘培刚, 孙洁, 杨超智, 等. 密集场景下基于多尺度特征聚合的人群计数方法. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(9): 235-241.]
|
| [16] |
[刘春, 贾守军, 吴杭彬, 等. 点云场景认知模式: 泛化点云. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(4): 556-567.]
|
| [17] |
[孙超, 钟少波, 邓羽. 基于暴雨内涝灾害情景推演的北京市应急救援方案评估与决策优化. 地理学报, 2017, 72(5): 804-816.]
|
| [18] |
[杜方叶, 王姣娥, 靳海涛. 基于个体“移动—接触”的空间交互网络理论构建与疫情风险评估. 地理学报, 2022, 77(8): 2006-2018.]
|
| [19] |
[张雪英, 张春菊, 吴明光, 等. 顾及时空特征的地理知识图谱构建方法. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2020, 50(7): 1019-1032.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[万刚, 武易天. 地图空间认知的数学基础. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 726-738.]
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[张克权, 祝国瑞. 试论地图制图学的理论体系. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 1990, 15(2): 28-33.]
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[薛存金, 周成虎, 苏奋振, 等. 面向过程的时空数据模型研究. 测绘学报, 2010, 39(1): 95-101.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
[曹一冰, 华一新, 郭邵萌. 多粒度时空对象行为特征的描述方法研究. 地理信息世界, 2018, 25(2): 23-29.]
|
| [36] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |