

从视觉神经科学的视角看地图视觉变量理论
|
吴明光(1979-), 男, 湖北武汉人, 教授, 主要从事时空大数据可视化、地图认知、地图AI与风格迁移、声音地图等方面的研究与应用。E-mail: wmg@njnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-12-13
修回日期: 2024-08-12
网络出版日期: 2024-09-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41971417)
Revisiting cartographic visual variables from a perspective of visual neuroscience
Received date: 2023-12-13
Revised date: 2024-08-12
Online published: 2024-09-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41971417)
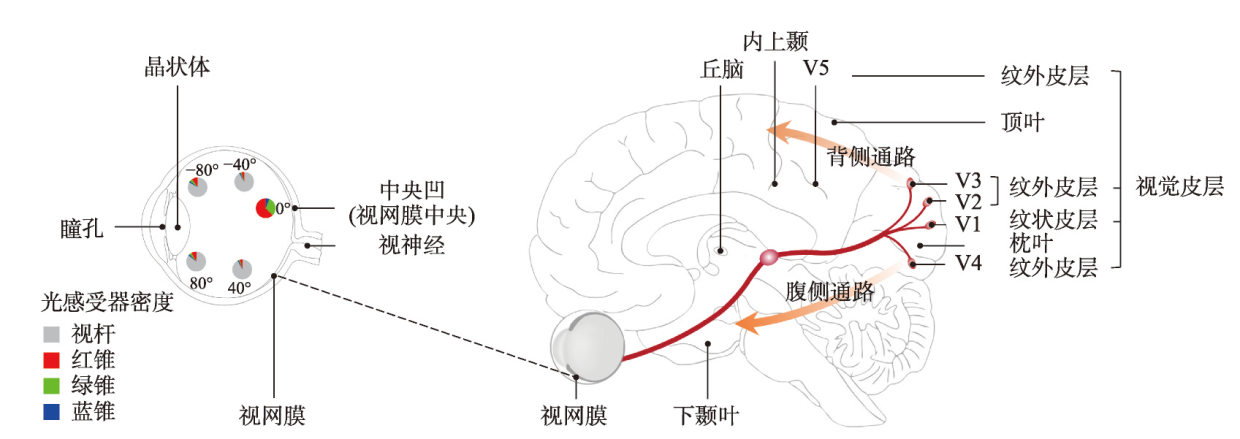
地图是地理学的语言,视觉变量是地图学的基础理论。然而,当前对地图视觉变量的研究主要以经验描述归纳为主,视觉机理解释不足,存在感知顺序不清晰、“形状”视觉变量划分粒度不精细、“位置”视觉变量界定不清楚3个基本问题。本文在总结眼—脑系统中的主要视觉神经元的基础上,详细分析了视觉变量的神经机理,研究发现:① 视觉变量的感知顺序首先是亮度和色彩,其次是简单的位置、方向、尺寸,最后是复杂的形状和纹理;旅游图的眼动实验表明,利用色彩能够被优先感知的特点,可以将色彩作为视觉线索,用于加强地图的视觉层次,引导读者的视觉注意力。② 曲率可作为形状视觉变量的细分变量;可持续发展制图案例表明,曲率视觉变量可以有效用于表达定性、定量信息。③ 位置能够被视觉神经元直接高效识别和处理,应该被定义为一个视觉变量,但是在强调图形位置精度的情况下,它不宜变化。导航地图和印象地图的对比实验表明,位置视觉变量能够引起显著的视觉和情感唤醒度差异。本文研究结果可加深对地图视觉变量理论的理解,可为可持续发展制图、个性创意地图设计等提供新的视觉设计理论。
吴明光 , 乔莉鸽 , 闾国年 . 从视觉神经科学的视角看地图视觉变量理论[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(9) : 2191 -2205 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202409003
Maps are the language of geography and visual variables serve as fundamental theories in the fields of cartography. However, current research on visual variables in cartography predominantly relies on empirical description and induction, and the explanation of visual mechanism is insufficient. There are still three fundamental issues: the perceptual sequence of the visual variables is unclear, the granularity of the "shape" visual variable division is not precise, and the definition of the "location" visual variable is unclear. Based on the summary of the main visual neurons in the eye-brain system, this paper analyzes the neural mechanisms of visual variables in detail. The study uncovers several key findings: (1) The perception sequence of visual variables follows a pattern, starting with value and color, followed by simple location, orientation, size, and finally complex shape and texture. Eye-tracking experiments conducted on tourist maps show that using the feature that color can be perceived first, color can be used as a visual cue to strengthen the visual hierarchy of the map and guide the visual attention of the readers. (2) Curvature can be used as a subdivision variable of shape visual variable. The case study in the context of sustainable development mapping shows that curvature variables can be effectively used to express both qualitative and quantitative information. (3) Location can be directly and efficiently processed and recognized by visual neurons, and thus it should be defined as a visual variable. However, it should not be changed when the accuracy of graphic position is emphasized. Comparative experiments between navigation map and city image map show that the location variable can cause significant evoke differences in visual perception and emotional arousal. The research in this paper contributes to a deeper understanding of the theory of visual variables and provides new visual design theory for sustainable development mapping, creative and personalized mapping.

Key words: visual variables; cartography; visual perception; visual neuroscience
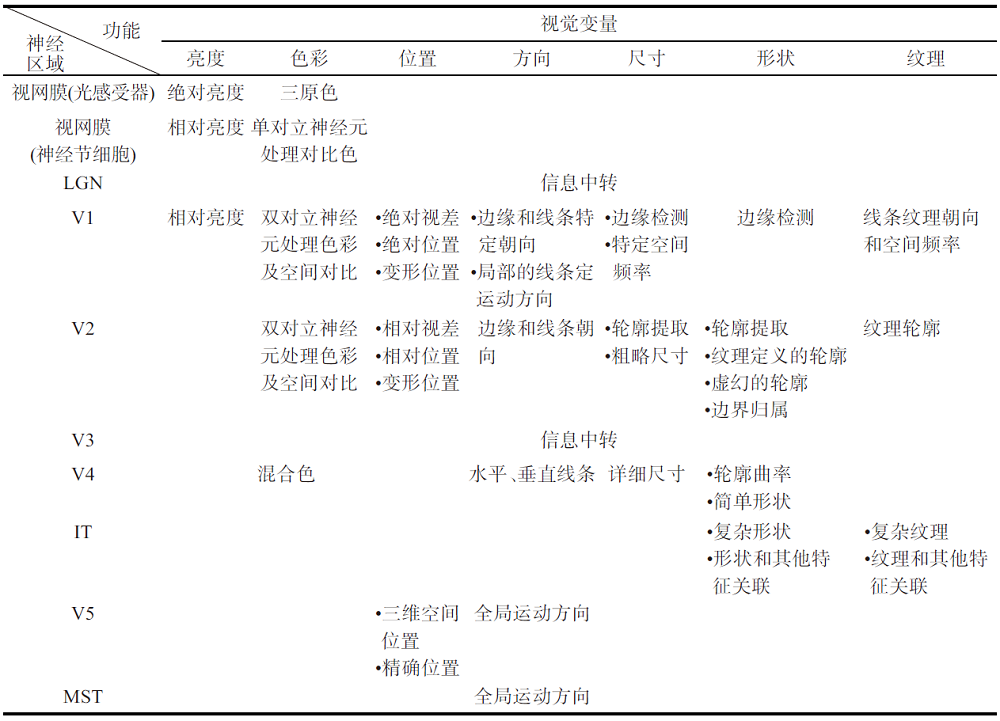
表1 视觉变量涉及的视觉神经区域和主要功能Tab. 1 The visual neural areas involved in visual variables and their primary function |
 |
| [1] |
[王家耀, 武芳, 闫浩文. 大变化时代的地图学. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(6): 829-842.]
|
| [2] |
[郭仁忠, 陈业滨, 马丁, 等. 论ICT 时代的泛地图表达. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1108-1113.]
|
| [3] |
[孟立秋. 地图学的恒常性和易变性. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1637-1644.]
|
| [4] |
[闫浩文, 张黎明, 杜萍, 等. 自媒体时代的地图: 微地图. 测绘科学技术学报, 2016, 33(5): 520-523.]
|
| [5] |
[周成虎. 全息地图时代已经来临—地图功能的历史演变. 测绘科学, 2014, 39(7): 3-8.]
|
| [6] |
[闾国年, 俞肇元, 袁林旺, 等. 地图学的未来是场景学吗? 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(1): 1-6.]
|
| [7] |
[齐清文, 姜莉莉, 张岸, 等. 全息地图建模与多重表达. 测绘科学, 2018, 43(7): 7-14.]
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[乔莉鸽, 吴明光, 闾国年. 地图视觉变量语法结构的神经机理分析. 地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(1): 121-134.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
[董卫华, 廖华, 詹智成, 等. 2008年以来地图学眼动与视觉认知研究新进展. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3): 599-614.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |