

面向富语义复杂事件的时空数据建模
|
刘凤(1990-), 女, 博士生, 主要从事地理信息系统研究。E-mail: liufeng@nudt.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-07-13
修回日期: 2024-06-26
网络出版日期: 2024-07-30
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(U19A2058)
Spatio-temporal data modeling of rich semantic for composite events
Received date: 2023-07-13
Revised date: 2024-06-26
Online published: 2024-07-30
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(U19A2058)
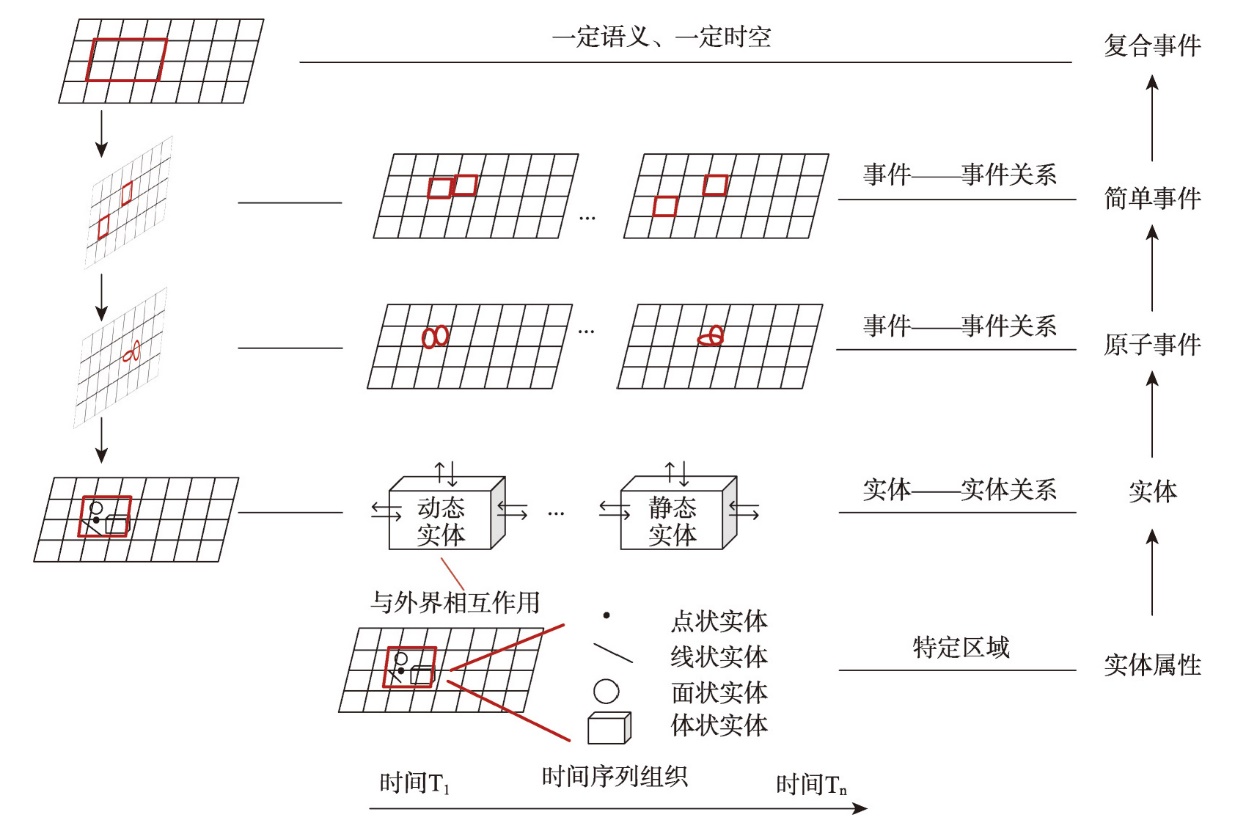
时空是事件的基本特征,复杂事件是多个事件的综合过程,具有多尺度时空特征、多层次语义特征。如何依托时空数据模型,从事件的基本特征出发对复杂事件建模、分析,是实现对事件时空演变知识挖掘与模拟推理的关键途径。由于现有模型难以捕捉事件中跨时空粒度多实体对象间的演变轨迹与时空演化因果关联,缺乏对复杂事件语义动态变化的刻画,无法满足对复杂事件的建模需求。本文主要:① 分析复杂事件中事件的概念,提出富语义事件时空数据模型,拓宽了时空数据模型所表达的事件维度。依据事件的多维度特征,实现了对跨时空粒度的多实体对象伴随事件演变的状态与行为特征描述;② 以事件特征聚合事件层次结构,建立事件由繁至简、由事件本身到其组成要素的多级逻辑框架;③ 刻画复杂事件中事件与事件、实体与实体的关联关系,以时空关系、属性关系的演变推动对事件潜在因果关系的分析;④ 以人类社会历史战争为例,阐述富语义事件时空数据模型的建模与分析方法,依托GIS平台阐述模型表达内容在事件实例中的应用,解释了伴随事件推进引起实体属性演变、实体与实体关系演变,再由上述变化引发新的事件发生的知识推理过程,验证了模型的可行性与实用性。
刘凤 , 钟志农 , 贾庆仁 , 景宁 , 马梦宇 , 杨飞 . 面向富语义复杂事件的时空数据建模[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(7) : 1700 -1717 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202407005
The spatio-temporal feature is a fundamental characteristic of an event. A composite event is the intricate amalgamation of multiple events that have multi-scale spatio-temporal features and multi-level semantic attributes. To effectively model and analyze composite events, it is essential to leverage a spatiotemporal data model that captures the basic features of events and to realize the knowledge mining as well as the simulation and reasoning of the spatio-temporal evolution of events. Existing models often struggle to portray the evolutionary trajectories and causal relationships between entities across different scales of composite events, and lack the ability to capture the dynamically semantic changes of composite events, hindering their ability to meet the requirements for accurate modeling. The primary contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) By analyzing the concept of events within composite events, we propose a rich semantic event spatio-temporal data model that broadens the dimensions of events covered by existing models. We describe the diverse states and behaviors associated with the evolution of multiple entities across various temporal and spatial granularities based on the multidimensional characteristics of events in different domains. (2) We aggregate event hierarchies with their characteristics to establish a multi-level logical framework of events, progressing from complexity to simplicity, from the event itself to its constituent elements. (3) In our model, we depict the associations between events and events, as well as entities and entities within complex events, and analyze the potential causal relationship of the event through the evolution of spatio-temporal relationships and attribute relationships. (4) Finally, we elaborate on the modeling and analysis methods of the rich semantic event spatio-temporal data model by instantiating a historical war in human society. We illustrate the model's application using a GIS platform, demonstrating the knowledge inference process of evolving entity states and changing relationships between entities triggered by events, which lead to the occurrence of new events. Through this process, we validate the feasibility and practicality of our model.

表1 伊拉克战争事件静态实体属性分析Tab. 1 Analysis of static entities' attributes in the Iraq War events |
| 区域名称 | 行政等级 | 交通 | 资源 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 首都 | 重要 城市 | 其他 区域 | 机场 | 公路 | 港口 | 桥梁 | 油田 | 军事 补给 | 国家 机构 | 高层官员 府邸 | 军事 基地 | |||
| 巴格达 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||||||
| 科威特 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||
| 科伊边境 | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 纳西里耶 | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 巴士拉 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||
| 乌姆盖萨尔 | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 法奥半岛 | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||||||||
| 纳杰夫 | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| 卡尔巴拉 | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 萨夫万 | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 萨马瓦 | √ | √ | ||||||||||||
| 伊拉克北部 | √ | √ | √ | |||||||||||
| [1] |
[李欢, 马伯宁, 孔龙星. 军事任务推演的时空模型与驱动机制. 国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(3): 138-143.]
|
| [2] |
[
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[曾梦熊, 华一新, 张江水, 等. 多粒度时空对象动态行为表达模型与方法研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(1): 104-112.]
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
[周成虎. 全空间地理信息系统展望. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(2): 129-131.]
|
| [14] |
[龚健雅, 李小龙, 吴华意. 实时GIS时空数据模型. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(3): 226-232, 275.]
|
| [15] |
[华一新, 赵鑫科, 张江水. 地理信息系统研究新范式. 地球信息科学学报, 2023, 25(1): 15-24.]
|
| [16] |
[华一新, 张江水, 曹一冰. 基于时空域的全空间数字世界时空对象组织与管理研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(1): 76-83.]
|
| [17] |
[谢雨芮, 江南, 赵文双, 等. 基于多粒度时空对象的作战实体对象化建模研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(1): 84-92.]
|
| [18] |
[程昌秀, 史培军, 宋长青, 等. 地理大数据为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇. 地理学报, 2018, 73(8): 1397-1406.]
|
| [19] |
[朱杰, 张宏军. 面向仿真事件的战场地理环境时空过程建模. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(9): 1367-1377, 1437.]
|
| [20] |
[诸云强, 孙凯, 胡修棉, 等. 大规模地球科学知识图谱构建与共享应用框架研究与实践. 地球信息科学学报, 2023, 25(6): 1215-1227.]
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
[周文, 刘宗田, 孔庆苹. 基于事件的知识处理研究综述. 计算机科学, 2008, 35(2): 160-162, 184.]
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
[杜云艳, 易嘉伟, 薛存金, 等. 多源地理大数据支撑下的地理事件建模与分析. 地理学报, 2021, 76(11): 2853-2866.]
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
[薛存金, 苏奋振, 何亚文. 过程: 一种地理时空动态分析的新视角. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(1): 65-79.]
|
| [39] |
[周成虎, 王华, 王成善, 等. 大数据时代的地学知识图谱研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(7): 1070-1079.]
|
| [40] |
[傅伯杰. 地理学: 从知识、科学到决策. 地理学报, 2017, 72(11): 1923-1932.]
|
| [41] |
[邬伦, 刘瑜, 张晶, 等. 地理信息系统:原理, 方法和应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.]
|
| [42] |
[蒋秉川, 黄梓航, 任琰, 等. 基于时序超图模型的战场环境多层次知识建模方法. 地球信息科学学报, 2023, 25(6): 1148-1163.]
|
| [43] |
[朱冬生. 世界经典战例:战争卷. 北京: 解放军出版社, 2010.]
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |