

京津冀地区退耕还林还草碳增汇潜力及贡献预估
|
马寅秋(1998-), 男, 辽宁本溪人, 硕士生, 研究方向为生态系统碳汇功能评估。E-mail: mayq.20s@igsnrr.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2022-09-15
修回日期: 2024-02-19
网络出版日期: 2024-04-02
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41977417)
Projecting the carbon sink potential and contribution of Grain for Green Program in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
Received date: 2022-09-15
Revised date: 2024-02-19
Online published: 2024-04-02
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41977417)
退耕还林还草工程(GGP)是中国投资最大、涉及面最广、群众参与程度最高的生态修复项目,也是国土变绿和陆地碳增汇的主要驱动力,然而对其碳增汇潜力及其对碳中和目标的可能贡献仍缺少系统性评估。本文在回溯2000—2020年京津冀地区GGP碳增汇作用基础上,设置由不同气候变化、经济社会、生态规划组合而成的可持续发展、基准、区域竞争3种未来情景,预测双碳目标年(2030年和2060年)GGP的碳增汇潜力及其贡献率。结果表明:① 2000—2020年京津冀地区GGP的碳汇增量超过48.03 Tg C,其中面积占比23.9%的退耕还林碳增汇能力达123.7%。② 2030年京津冀地区GGP年碳汇增量可达5.33~6.20 Tg C a-1,与2020年相比增加95.8%~127.7%,仅能抵消全地区近0.3%的碳排放总量,但对于抵消县域尺度碳排放量的贡献率可达30%。③ 2060年GGP年碳汇增量约4.35~4.88 Tg C a-1,与2020年相比增加59.7%~79.3%,能抵消全地区5.1%~7.2%的碳排放总量,且在县域尺度上对碳排放量的抵消可达到8倍。综上所述,需要正确认识生态修复对京津冀地区双碳目标的作用,特别是西北部生态涵养区的县域可将GGP作为实现碳中和的主要路径。
马寅秋 , 李佳慧 , 曹巍 , 尹川 , 黄麟 . 京津冀地区退耕还林还草碳增汇潜力及贡献预估[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(3) : 732 -746 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202403011
The Grain for Green Program (GGP) is the most invested, policy-oriented, wide-embracing, and public-involving ecological restoration project in China, which has become the main driver of national greening and carbon sink increases; however, the large potential of carbon sink increases and their contribution to the program's carbon neutrality goal still lacks systematic estimation. Here, based on backdating of the GGP effect on increasing carbon sinks in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region over the past 20 years, three scenarios-sustainable development, benchmark, and regional competition-are combined under different climates, socioeconomies, and eco-planning patterns to forecast the potential for increasing carbon sinks and the contribution of the GGP in the "Double Carbon Target" years (2030 and 2060). Our results showed that: (1) During 2000-2020, the increase in carbon sinks exceeded 48.03 Tg C; among them, the ability of increased carbon sinks in the region to restore croplands to forests (GGP-Forest), which accounted for 23.9% of the total area, reached 123.7%. (2) In 2030, the annual increase in carbon sinks resulting from the GGP in the BTH region will reach 5.33-6.20 Tg C a-1, up by 95.8%-127.7% compared with the year 2020. This can offset ~0.3% of the total carbon emissions from this region; however, this contribution can reach 30% at the county scale. (3) In 2060, the annual increase in carbon sinks resulting from the GGP in the BTH region will be about 4.35-4.88 Tg C a-1, up by 59.7%-79.3% compared with 2020 and can offset 5.1%-7.2% of the total carbon emissions from this region; its contribution can reach eightfold at the county scale. In summary, it is essential to correctly quantify the contribution of the Double Carbon Target in the study region resulting from the ecological restoration program, especially in the northwest counties in the ecological conservation area, where the GGP can act as the main method to achieve carbon neutrality.

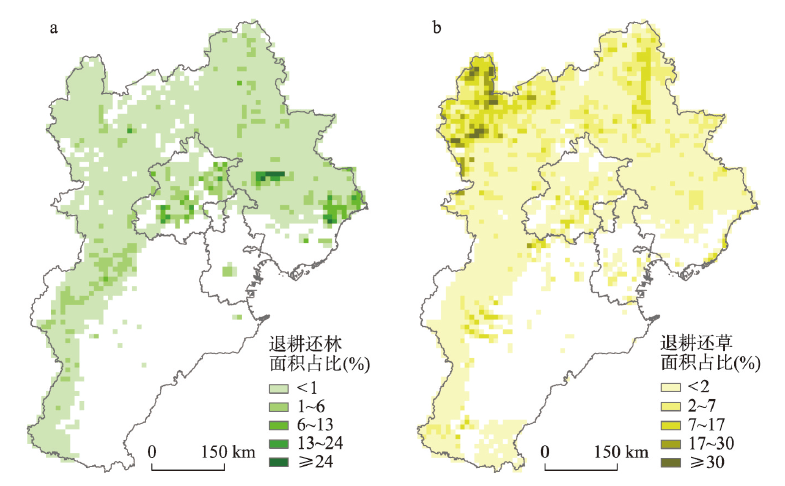
图3 2030年和2060年京津冀地区退耕还林情景空间分布Fig. 3 GGP spatial distribution scenarios of forests in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in 2030 and 2060 |
| [1] |
UNFCCC. The Paris agreement. Paris:The 21st United Nations Climate Change Conference, 2015.
|
| [2] |
The State Council of the People's Republic of China. Opinions of the State Council of the People's Republic of China on Fully, Accurately and Comprehensively Implementing the New Development Concept to Achieve Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutral Work. 2021.
[ 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央、国务院关于完整准确全面贯彻新发展理念做好碳达峰碳中和工作的意见. 2021.]
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
[ 范泽孟. 基于SSP-RCP不同情景的京津冀地区土地覆被变化模拟. 地理学报, 2022, 77(1): 228-244.]
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
[ 黄麟. 造林气候调节效应及其影响机理研究进展. 生态学报, 2021, 41(2): 469-478.]
|
| [15] |
[ 黄麟. 森林管理的生态效应研究进展. 生态学报, 2021, 41(10): 4226-4239.]
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
UNFCCC. Kyoto protocol. Kyoto:The 11st United Nations Climate Change Conference, 1997.
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[ 刘博杰, 逯非, 王效科, 等. 森林经营与管理下的温室气体排放、碳泄漏和净固碳量研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(2): 673-688.]
|
| [30] |
[ 郑芊卉, 韦海航, 陈健, 等. 三北工程四十年碳汇价值评价研究. 林业经济, 2019, 41(2): 67-73, 112.]
|
| [31] |
[ 田育新, 李锡泉, 蒋丽娟, 等. 湖南一期长防林碳汇量及生态经济价值评价研究. 水土保持研究, 2004, 11(1): 33-36, 49.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
[ 樊杰, 廉亚楠, 赵浩. 1980年以来京津冀区域研究进展评论. 地理学报, 2022, 77(6): 1299-1319.]
|
| [36] |
[ 潘梅, 陈天伟, 黄麟, 等. 京津冀地区生态系统服务时空变化及驱动因素. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5151-5167.]
|
| [37] |
[ 王少剑, 方创琳, 王洋. 京津冀地区城市化与生态环境交互耦合关系定量测度. 生态学报, 2015, 35(7): 2244-2254.]
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
[ 姜彤, 王艳君, 袁佳双, 等. Projection of population and economy in the Belt and Road countries (2020-2060). 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(2): 155-164.]
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
[ 张仁平, 郭靖, 张云玲. 新疆草地净初级生产力(NPP)空间分布格局及其对气候变化的响应. 生态学报, 2020, 40(15): 5318-5326.]
|
| [45] |
[ 周广胜, 张新时. 全球变化的中国气候—植被分类研究. 植物学报, 1996, 38(1): 8-17.]
|
| [46] |
[ 张新时. 植被的可能蒸散指标与植被—气候分类(二): 几种主要方法与PEP程序介绍. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1989, 13(3): 197-201.]
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
[ 张学珍, 赵彩杉, 董金玮, 等. 1992—2017年基于荟萃分析的中国耕地撂荒时空特征. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3): 411-420.]
|
| [50] |
[ 刘文超, 刘纪远, 匡文慧. 陕北地区退耕还林还草工程土壤保护效应的时空特征. 地理学报, 2019, 74(9): 1835-1852.]
|
| [51] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |