

河道流量遥感估算研究进展与展望
|
孙文超(1981-), 男, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事遥感水文、水资源与水环境研究。E-mail: sunny@bnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-06-05
修回日期: 2024-03-08
网络出版日期: 2024-04-02
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2021YFC3200102)
国家自然科学基金项目(52179002)
国家自然科学基金项目(41671018)
Estimating streamflow using remote sensing: Progress and prospects
Received date: 2023-06-05
Revised date: 2024-03-08
Online published: 2024-04-02
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2021YFC3200102)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(52179002)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41671018)
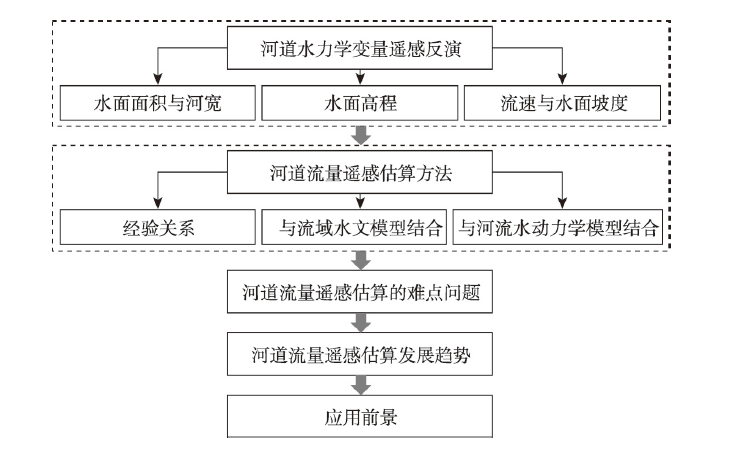
河道流量数据为水文水资源领域科学研究与水利工程规划设计提供重要的科学依据。缺实测资料地区河道流量估算是过去几十年水文学界重点解决的科学问题之一。基于遥感观测的河道流量估算方法是解决水文资料缺乏的有效手段,同时也是定量遥感与水文水资源学科交叉研究的重要领域。本文系统总结了河道水面宽度、水面高程等与河道流量紧密相关水力学变量的遥感反演方法研究现状,梳理了经验关系法、与水文模型结合和与河流水动力模型结合等基于卫星观测的流量估算数学方法研究进展。在此基础上,阐述了河道流量遥感估算研究中流量估算结果误差评估、多星协作提升观测频率与方法普适性评估等难点问题与未来发展趋势。最后,探讨了遥感估算流量方法的应用前景。
孙文超 , 王星灿 , 徐宗学 . 河道流量遥感估算研究进展与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(3) : 565 -583 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202403002
Streamflow data provide vital information for research on hydrology and water resources, as well as for the design of water conservancy and hydropower projects. The lack of streamflow data is an important limiting factor that researchers in the field of hydrology have tried to address in the past decades. Streamflow estimation based on satellite data is an effective way to solve this problem, and it is an important topic for interdisciplinary research on quantitative remote sensing and hydrology. This paper summarizes the current research status of remote sensing inversion methods for hydraulic variables closely related to streamflow, including water surface width and water surface elevation. The research progress of mathematical methods of streamflow estimation based on satellite observations, such as establishing empirical relationships and integrating information with hydrological or hydrodynamic models, is described. The error evaluation of streamflow estimates, increasing observation frequency by multi-satellite collaboration, and the applicability of inversion method are discussed, are the factors that have hindered research into streamflow estimation based on remote sensing. Trends for future studies are elaborated and potential applications for streamflow estimation based on remote sensing are proposed.

Key words: remote sensing; streamflow; ungauged regions; hydraulics; water cycle
表1 遥感河道流量反演常用经验公式Tab. 1 Commonly used empirical equations of streamflow estimation based on remote sensing |
| 分类 | 公式 | 特点及适用范围 | 应用案例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 单 变 量 | We=aQb (1) | 遥感数据来源最为丰富,但不适用于断面近似矩形河道 | Smith等[67]、Pavelsky等[68]、Huang等[69] |
| Q=c(H-H0)d (2) | 与地面水文站水位流量关系类似,对绝大部分河流均适用 | Leon等[70]、Bogning等[71]、 Huang等[69] | |
| 多 变 量 | Q=k1×Wee×Yf×Sg (3) | 对表征流量变化的水力学要素描述最为充分 | Bjerklie等[20]、Birkinshaw等[63]、Tarpanelli等[72] |
| Q=k2×Weh×Y i (4) | 假设河流坡度恒定,避免了坡度遥感误差对流量估算的影响 | Sichangi等[21]、Huang等[69] |
式中:Q为流量;We为河流水面宽度;H为水面高程;H0为河床底部高程;Y为河流平均水深;S为河道坡度;a~i、k1和k2为经验参数。 |
| [1] |
[ 高扬, 于贵瑞. 流域生物地球化学循环与水文耦合过程及其调控机制. 地理学报, 2018, 73(7): 1381-1393.]
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
[ 桑燕芳, 王中根, 刘昌明. 水文时间序列分析方法研究进展. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(1): 20-30.]
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
[ 赵长森, 潘旭, 杨胜天, 等. 低空遥感无人机影像反演河道流量. 地理学报, 2019, 74(7): 1392-1408.]
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
[ 汪伟, 卢麾. 遥感数据在水文模拟中的应用研究进展. 遥感技术与应用, 2015, 30(6): 1042-1050.]
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
[ 李新, 刘绍民, 马明国, 等. 黑河流域生态—水文过程综合遥感观测联合试验总体设计. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(5): 481-498.]
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[ 骆剑承, 胡晓东, 吴田军, 等. 高分遥感驱动的精准土地利用与土地覆盖变化信息智能计算模型与方法研究. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(7): 1351-1373.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
[ 孙芳蒂, 马荣华. 鄱阳湖水文特征动态变化遥感监测. 地理学报, 2020, 75(3): 544-557.]
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
[ 李均力, 陈曦, 包安明. 2003—2009年中亚地区湖泊水位变化的时空特征. 地理学报, 2011, 66(9): 1219-1229.]
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
[ 杨大文, 李翀, 倪广恒, 等. 分布式水文模型在黄河流域的应用. 地理学报, 2004, 59(1): 143-154.]
|
| [79] |
[ 徐宗学, 程磊. 分布式水文模型研究与应用进展. 水利学报, 2010, 41(9): 1009-1017.]
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
[ 张婷, 徐彬鑫, 康爱卿, 等. 流域水文、水动力、水质模型联合应用研究进展. 水利水电科技进展, 2021, 41(3): 11-19.]
|
| [94] |
[ 江春波, 周琦, 申言霞, 等. 山区流域洪涝预报水文与水动力耦合模型研究进展. 水利学报, 2021, 52(10): 1137-1150.]
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
[ 石教智, 陈晓宏. 流域水文模型研究进展. 水文, 2006, 26(1): 18-23.]
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
[ 刘松, 佘敦先, 张利平, 等. 流量数据误差对水文模拟不确定性分析的影响. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2021, 54(1): 1-7.]
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |