

基于流域系统模拟一情景优化的精细治理决策支持方法
|
秦承志(1977-), 男, 山东蒙阴人, 研究员, 中国地理学会会员(S110005928M), 研究方向为流域分析与模拟的智能化地理计算。E-mail: qincz@lreis.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-07-13
修回日期: 2023-12-05
网络出版日期: 2024-01-29
基金资助
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDA23100503)
国家自然科学基金项目(42101480)
国家自然科学基金项目(41871362)
资源与环境信息系统国家重点实验室自主创新项目(KPI003)
Methods for supporting decision-making of precision watershed management based on watershed system simulation and scenario optimization
Received date: 2023-07-13
Revised date: 2023-12-05
Online published: 2024-01-29
Supported by
Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA23100503)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42101480)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41871362)
Project of Innovation LREIS(KPI003)
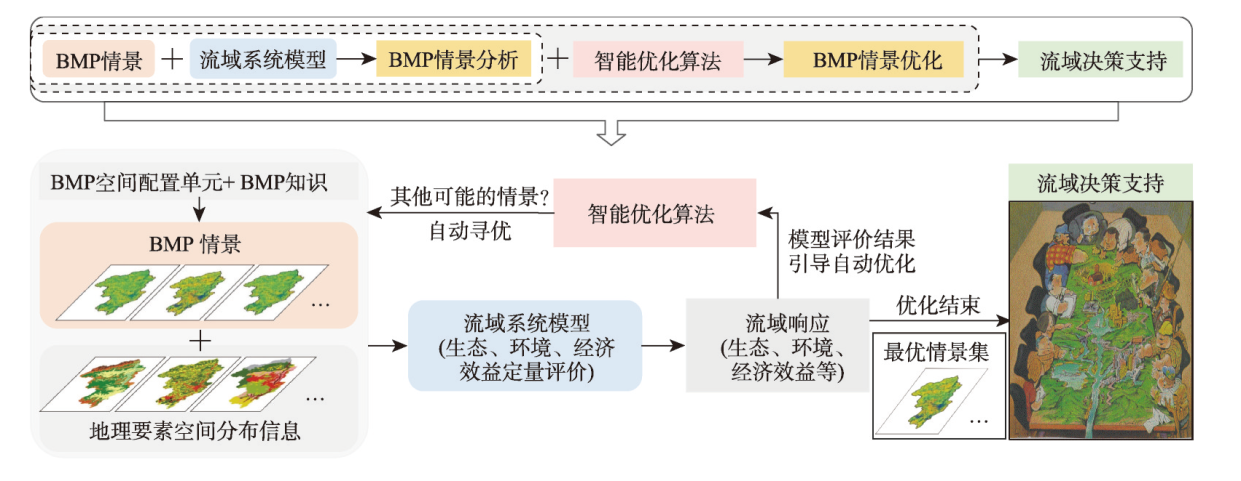
面向美丽中国生态文明建设所需,亟待有效实现流域精细治理的科学决策,以根据流域综合治理愿景目标,优化流域管理措施(BMP)的空间布局方案(即BMP情景)、制定符合实际需求的实施路线图。对此,“流域系统模拟—情景优化”方法框架近年展现出广阔应用前景。本文介绍了该框架在应对实际应用需求中尚存的一系列问题,开展了体系性的方法研究:① 提出新的流域过程建模框架,以兼顾建模灵活性和高性能计算、高效实现流域系统模拟;② 提出以坡位单元作为BMP空间配置单元、并在情景优化过程中可进行单元边界动态调整的BMP情景优化方法,可有效考虑流域综合治理的经验知识,保障优化结果合理性;③ 提出考虑分阶段投资约束的BMP情景实施次序优化方法,可推荐出符合实际落地需求的实施路线图;④ 设计研发用户友好的参与式流域规划系统,供各方利益相关者协商决策。通过典型小流域应用案例验证了上述新方法、工具和原型系统的有效性和实用价值。
秦承志 , 朱良君 , 申申 , 吴彤 , 肖桂荣 , 吴升 , 陈芸芝 , 汪小钦 , 冯险峰 , 朱阿兴 , 陆锋 . 基于流域系统模拟一情景优化的精细治理决策支持方法[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(1) : 58 -75 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202401005
The construction of China's ecological civilization, known as "Beautiful China", necessitates implementing precision watershed management through scientifically informed decision-making. This entails optimizing the spatial distribution of watershed best management practices (the so-called BMP scenario) and proposing multistage implementation plans, or roadmaps that align with practical requirements based on the overarching vision of comprehensive watershed management. The "watershed system simulation-scenario optimization" method framework (the simulation-and-optimization-based framework for short) has demonstrated considerable potential in recent years. To address challenges arising from practical applications of this framework, this study systematically conducted the methodological research: (1) proposing a novel watershed process modeling framework that strikes a balance between modeling flexibility and high-performance computing to model and simulate watershed systems efficiently; (2) introducing slope position units as BMP configuration units and enabling dynamic boundary adjustments during scenario optimization, effectively incorporating practical knowledge of watershed management to ensure reasonable outcomes; (3) presenting an optimization method for determining the implementation orders of BMPs that considers stepwise investment constraints, thereby recommending feasible roadmaps that meet practical needs; and (4) designing a user-friendly participatory watershed planning system to facilitate collaborative decision-making among stakeholders. The effectiveness and practical value of these new methods, tools, and prototype systems are validated through application cases in a representative small watershed. This research contributes to advancing precision watershed management and provides valuable insights for sustainable ecological conservation. The methods proposed within the simulation-and-optimization-based framework in this study are universal methods, which means their application does not depend on the specific implementation, such as the watershed process model, the BMP types considered, the designed BMP configuration strategy, and so on. Further studies should be conducted not only to deepen related theory and method research but also to strengthen promotion and application, especially cooperating with local watershed management agents to provide valuable insights for their sustainable ecological conservation.

图3 中国不同水蚀区的小流域水土保持综合治理模式和模糊坡位信息及坡位单元边界动态调整示意图注:图a~d基于蔡强国等[26]绘制;图e基于Zhu等[27]绘制。 Fig. 3 Integrated watershed management scheme for soil and water conservation in different water erosion regions in China and the schematic diagram of boundary adjustments of slope position units based on fuzzy slope positions along a hillslope |
| [1] |
[傅伯杰. 地理学: 从知识、科学到决策. 地理学报, 2017, 72(11): 1923-1932.]
|
| [2] |
[朱阿兴, 朱良君, 史亚星, 等. 流域系统综合模拟与情景分析: 自然地理综合研究的新范式? 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(8): 1111-1122.]
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
[孟凡德, 耿润哲, 欧洋, 等. 最佳管理措施评估方法研究进展. 生态学报, 2013, 33(5): 1357-1366.]
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[刘军志, 朱阿兴, 秦承志, 等. 论地理规律对流域过程模拟并行计算的指导作用. 地球信息科学学报, 2015, 17(5): 506-514.]
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
[蔡强国, 朱阿兴, 毕华兴, 等. 中国主要水蚀区水土流失综合调控与治理范式. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2012.]
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[史亚星, 朱良君, 秦承志, 等. 基于坡位—地块单元的流域最佳管理措施空间优化配置方法. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(4): 564-575.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
[陈志彪, 陈志强, 岳辉. 花岗岩红壤侵蚀区水土保持综合研究:以福建省长汀朱溪小流域为例. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.]
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
[王学强. 红壤地区水土流失治理模式效益评价及其治理范式的建立[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2008.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |