

中国生态地理区划更新和优化
|
王芳(1979-), 女, 山西阳泉人, 副研究员, 主要从事气候变化研究。E-mail: wangf@igsnrr.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2023-09-14
修回日期: 2023-12-22
网络出版日期: 2024-01-29
基金资助
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDA23100400)
Updated scheme for eco-geographical regionalization in China
Received date: 2023-09-14
Revised date: 2023-12-22
Online published: 2024-01-29
Supported by
Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA23100400)
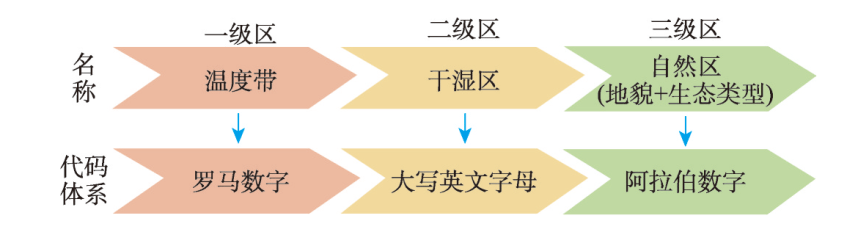
随着全球气候的持续增暖,中国的气候带和生态地理区域呈现出一定程度的变化。本文在已有生态地理区划方法的基础上,利用1991—2020年641个气象台站气候数据,以及高精度的生态地理要素资料,对中国生态地理区域进行了优化,更新了中国生态地理区域图(2023版),将制图比例尺提高至1∶400万。研究结果将中国划分为11个温度带、22个干湿区、50个自然区。与2007版的生态地理区划结果相比,1991—2020年中国生态地理区域的总体格局虽没发生明显变化,但是局部地区的温度带界线、干湿区界线、生态地理区(自然区)界线已经发生了不同程度的变化。首先,温度带的界线变化在东部较明显,特别是长江中下游地区北亚热带和中亚热带之间温度带界线北移较明显;其次,干湿区的界线出现了变动,在第二级地形阶梯的北部半干旱与干旱区的界线有稍微西移,青藏高原上半干旱与半湿润区之间的界线则稍有东南移,都反映半干旱区范围稍有扩大;最后,自然区的界线变化在局地差异较大。本文深化了1991—2020年气候变化和生态地理资料更新对生态地理区域边界变化认识,为指导不同区域生态保护修复工作提供宏观的区域框架。
王芳 , 李炳元 , 田思雨 , 郑度 , 葛全胜 . 中国生态地理区划更新和优化[J]. 地理学报, 2024 , 79(1) : 3 -16 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202401001
With the increasing global warming over the past three decades, the climatic zones and eco-geographical regions characteristics in China have changed. This study used the climatic data of 641 meteorological stations over the past three decades (1991-2020), as well as the high-precision data of eco-geographical elements to optimize the eco-geographical regions in China. The study updated the map of eco-geographical regionalization in China (2023) and increased the scale to 1:4000000. The new map divided China into 11 temperature zones, 22 dry and wet regions, and 50 natural regions. The results show that compared with eco-geographical regionalization in 2007, the overall pattern of eco-geographical regions in China has not changed significantly over the past three decades, but the boundaries of temperature zones, dry and wet regions, and eco-geographical regions (natural regions) in some areas have changed to some extent. Firstly, the boundary change of temperature zones is more obvious in the east. Particularly, in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, the northward shift of the temperature zone boundary between the northern subtropical and the mid-subtropical zones is obvious. Secondly, the boundary between dry and wet regions has changed, and that between semi-arid and arid regions in the north of the second-order landform step has shifted slightly to the west. In addition, the boundary between semi-arid and sub-humid regions in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has shifted slightly to the southeast, reflecting a slight expansion of the scope of semi-arid regions. Finally, boundary changes in natural regions in some areas vary greatly. This study can provide a macro-regional framework for guiding ecological conservation and restoration in different regions.

Key words: climate change; eco-geographical regionalization; shift of boundary; China
表1 中国生态地理区划各级区主要指标及阈值Tab. 1 Main indicators and thresholds of eco-geographical regionalization in China |
| a. 一级区(温度带)指标 | ||||||||||||||||
| 温度带 | 主要指标 | 辅助指标 | 典型植被 | |||||||||||||
| 日平均气温≥10 oC日数(d) | ≥ 10oC积温(oC) | 海拔(m) | 最冷月平均气温(oC) | 最暖月平均气温(oC) | ||||||||||||
| 寒温带I | < 100 | < 1600 | < -30 | < 16 | 针叶林 | |||||||||||
| 中温带II | 100~170 | 1600~3200(3400) | -30~-12(-6) | 16~24 | 针阔叶混交林 | |||||||||||
| 暖温带III | 171~219 | 3200(3400) ~4500(4800) | -12(-6)~0 | > 24 | 落叶阔叶林 | |||||||||||
| 北亚热带IV | 220~239 | 4500(4800) ~5100(5300) | 0~4 | > 24 | 常绿、落叶阔叶混交林 | |||||||||||
| 中亚热带V | 240~285 | 5100(5300) ~6400(6500) (云贵, 4000~5000) | 4~10 | > 24 | 典型常绿阔叶林 | |||||||||||
| 南亚热带VI | 286~365 | 6400(6500)~8000 (云南5000~7500) | 10~15(云南9(10)~13(15)) | > 24 | 季风常绿阔叶林 | |||||||||||
| 边缘热带VII | 365 | > 8000 | 15~18(云南> 13(15)) | > 24 | 热带季雨林 | |||||||||||
| 中热带VIII | 365 | > 8000 | 18~24 | > 24 | 热带雨林 | |||||||||||
| 赤道热带IX | 365 | > 8000 | > 24 | > 24 | 赤道常绿阔叶林 | |||||||||||
| 高原亚寒带HI | < 50 | > 4000 | -18~-10(-12) | < 12 | 高寒草甸 | |||||||||||
| 高原温带HII | 50~180 | > 4000 | -10(-12)~0 | 12~18 | 高寒灌丛、高寒草原 | |||||||||||
| b. 二级区(干湿区)指标 | ||||||||||||||||
| 干湿状况 | 主要指标 | 辅助指标 | ||||||||||||||
| 年干燥指数 | 天然植被 | 年降水量 (mm) | ||||||||||||||
| 湿润A | < 1.00 | 森林 | > 800~900(东北、川西山地> 600~650) | |||||||||||||
| 半湿润B | 1.00~1.49 | 森林 | 400(500)~800(900)(东北400~600) | |||||||||||||
| 半干旱C | 1.50~4.00 1.50~5.00(青藏高原) | 草原 (高寒草原) | 200(250)~400(500) | |||||||||||||
| 干旱D | ≥ 4.00 ≥ 5.00(青藏高原) | 荒漠 | < 200~250 | |||||||||||||
| c. 三级区(自然区)指标 | ||||||||||||||||
| 地形/地貌 | 低海拔(< 1000 m) | 中海拔 (1000~2000 m) | 亚高海拔 (2000~4000 m) | 高海拔 (4000~6000 m) | 极高海拔 (≥ 6000 m) | |||||||||||
| 平原(含台地) | 低海拔平原 | 中海拔平原 | 亚高海拔平原 | 高海拔平原 | 极高山 | |||||||||||
| 小起伏山地(含丘陵)(< 500 m) | 小起伏低山 | 小起伏中山 | 小起伏高中山 | 小起伏高山 | ||||||||||||
| 中起伏山地(500~1000 m) | 中起伏低山 | 中起伏中山 | 中起伏亚高山 | 中起伏高山 | ||||||||||||
| 大起伏山地(≥ 1000 m) | 大起伏中山 | 极大起伏亚高山 | 极大起伏高山 | |||||||||||||
| 其他 | 黄土梁茆 沙丘(流动沙丘、固定半固定沙丘) 风蚀残丘 戈壁 冰川 | |||||||||||||||
| 主要植被 | ||||||||||||||||
| 寒温带针叶林区 | 暖温带落叶阔叶林区 | 热带雨林—季雨林区 | 温带荒漠区 | |||||||||||||
| 温带针阔叶混交林区 | 亚热带常绿阔叶林区 | 温带草原区 | 青藏高原高寒植被区 | |||||||||||||
注:括号内数字表示可能的变幅。 |
图2 中国生态地理区划新版简图注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站GS(2019)1835号的标准地图制作,底图边界无修改。 Fig. 2 New map of eco-geographical regionalization in China |
表2 2023版中国生态地理区域划分方案Tab. 2 Scheme for eco-geographical regionalization in China (2023) |
| 一级区(温度带) | 二级区(干湿区) | 三级区(自然区) |
|---|---|---|
| I寒温带 | A湿润地区 | ⅠAl大兴安岭北部山地落叶针叶林区 |
| Ⅱ中温带 | A湿润地区 | ⅡA1三江平原沼泽区 ⅡA2东北东部山地针阔叶混交林区 ⅡA3东北东部山前台地针阔叶混交林区 |
| B半湿润地区 | ⅡB1松辽中部平原森林草原区 ⅡB2大兴安岭中部山地森林区 ⅡB3大兴安岭西麓北丘陵森林草原区 | |
| C半干旱地区 | ⅡC1西辽河平原草原区 ⅡC2大兴安岭南部草原区 ⅡC3内蒙古东部中平原草原区 ⅡC4呼伦贝尔平原草原区 | |
| D干旱地区 | ⅡD1河套与内蒙古西部中平原荒漠草原区 ⅡD2阿拉善与河西走廊灌木、半灌木荒漠区 ⅡD3准噶尔盆地小乔木、半灌木荒漠区 ⅡD4阿尔泰与额尔齐斯平原山地草原、针叶林区 ⅡD5天山伊犁高山盆地半灌木荒漠、针阔叶混交林区 | |
| Ⅲ暖温带 | A湿润地区 | ⅢA1辽东胶东低山丘陵落叶阔叶林、栽培植被区 |
| B半湿润地区 | ⅢB1鲁中低山丘陵落叶阔叶林、栽培植被区 ⅢB2华北平原栽培植被区 ⅢB3华北山地落叶阔叶林区 ⅢB4汾渭盆地与黄土高原南部落叶阔叶林、栽培植被区 | |
| C半干旱地区 | ⅢC1黄土梁峁与山地草原区 | |
| D干旱地区 | ⅢDl塔里木与东疆盆地灌木、半灌木荒漠区 | |
| Ⅳ北亚热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅣA1淮河中下游平原与大别山地栽培植被、常绿、落叶阔叶混交林区 ⅣA2秦巴山地常绿、落叶阔叶混交林区 |
| Ⅴ中亚热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅤA1长江中下游平原与江南丘陵盆地常绿阔叶林、栽培植被区 ⅤA2南岭与浙闽山地常绿阔叶林区 ⅤA3湘贵高原山地常绿阔叶林区 ⅤA4四川盆地栽培植被区 ⅤA5云南高原常绿阔叶林、松林区 ⅤA6东喜马拉雅南翼山地季雨林、常绿阔叶林区 |
| Ⅵ南亚热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅥA1台中台北山地平原栽培植被、常绿阔叶林区 ⅥA2闽粤桂(华南)低山平原常绿阔叶林、栽培植被区 ⅥA3滇中南亚高山谷地常绿阔叶林、松林区 |
| Ⅶ边缘热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅦAl台南山地平原季雨林、雨林区 ⅦA2琼雷山地丘陵半常绿季雨林区 ⅦA3滇南中山谷地季雨林、雨林区 |
| Ⅷ中热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅧAl琼南低地与东、中、西沙诸岛季雨林、雨林区 |
| Ⅸ赤道热带 | A湿润地区 | ⅨAl南沙群岛珊瑚岛植被区 |
| HI高原亚寒带 | B半湿润地区 | HIBl川青藏高山谷地高寒灌丛草甸区 |
| C半干旱地区 | HICl青南高原宽谷高寒草甸草原区 HIC2羌塘高原湖盆高寒草原区 | |
| D干旱地区 | HID1中昆仑北羌塘高山高原荒漠、荒漠草原区 HID2喀喇昆仑西昆仑高山荒漠半荒漠区 | |
| HII高原温带 | A湿润地区 | HIIA1东喜马拉雅地区高山深谷森林区 |
| B半湿润地区 | HIIBl横断山区高山深谷针叶林 | |
| C半干旱地区 | HIICl祁连青东高山盆地针叶林、草原区 HⅡC2藏南高山谷地灌丛草原区 | |
| D干旱地区 | HⅡD1柴达木盆地半灌木、灌木、盐荒漠区 HⅡD2阿里山地半灌木、灌木荒漠区 |
:感谢自然资源部国土空间生态修复司王磊司长、宋春玉处长、郭义强副处长和国土整治中心相关人员对本文提供的帮助。
| [1] |
[
|
| [2] |
[黄秉维. 中国综合自然区划的初步草案. 地理学报, 1958, 24(4): 14-31.]
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
[郑度, 杨勤业, 吴绍洪, 等. 中国生态地理区域系统研究. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2008: 198-199.]
|
| [7] |
Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Notice on Issuing the "China Land Ecological Basic Zoning (Trial)". Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. 2023.
[自然资源部. 关于印发《中国陆域生态基础分区(试行)》的通知. 2023.]
|
| [8] |
[郑度. 中国自然地理总论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.]
|
| [9] |
[傅伯杰, 刘国华, 陈利顶, 等. 中国生态区划方案. 生态学报, 2001, 21(1): 2-7.]
|
| [10] |
Committee for the Preparation of the Fourth National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Fourth National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Beijing: Science Press, 2022.
[ 《第四次气候变化国家评估报告》编写委员会. 第四次气候变化国家评估报告. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022.]
|
| [11] |
Committee for the Preparation of the Third National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Third National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Beijing: Science Press, 2015.
[ 《第三次气候变化国家评估报告》编写委员会. 第三次气候变化国家评估报告. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.]
|
| [12] |
Committee for the Preparation of the Second National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Second National Assessment Report on Climate Change. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[ 《第二次气候变化国家评估报告》编写委员会. 第二次气候变化国家评估报告. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.]
|
| [13] |
[郑景云, 卞娟娟, 葛全胜, 等. 中国1951—1980年及1981—2010年的气候区划. 地理研究, 2013, 32(6): 987-997.]
|
| [14] |
[郑景云, 尹云鹤, 李炳元. 中国气候区划新方案. 地理学报, 2010, 65(1): 3-12.]
|
| [15] |
[尹云鹤, 吴绍洪, 郑度, 等. 近30年我国干湿状况变化的区域差异. 科学通报, 2005, 50(15): 1636-1642.]
|
| [16] |
[张永, 陈发虎, 勾晓华, 等. 中国西北地区季节间干湿变化的时空分布: 基于PDSI 数据. 地理学报, 2007, 62(11): 1142-1152.]
|
| [17] |
[沙万英, 邵雪梅, 黄玫. 20世纪80年代以来中国的气候变暖及其对自然区域界限的影响. 中国科学D辑, 2002, 32(4): 317-326.]
|
| [18] |
[秦大河, 丁永建, 翟盘茂, 等. 中国气候与生态环境演变. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.]
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
[郑度, 李炳元. 中国生态地理区域图. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2007.]
|
| [23] |
[黄秉维. 中国综合自然区划纲要. 地理集刊, 1989, 21: 10-20.]
|
| [24] |
[黄秉维. 中国综合自然区划图:中国自然保护图集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 155-157.]
|
| [25] |
[任美锷, 包浩生. 中国自然区域及开发整治. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992.]
|
| [26] |
National Weather Science Data Center. Daily values of basic ground meteorological observations in China (1990-2020). http://data.cma.Cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/A.0012.0001.html.
[ 国家气象科学数据中心. 中国地面基本气象观测日值数据(1990—2020). http://data.cma.cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/A.0012.0001.html.]
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
[严中伟, 李珍, 夏江江. 气候序列的均一化: 定量评估气候变化的基础. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(10): 2101-2111.]
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
Editorial Committee of Geomorphological Atlas of the People's Republic of China. Geomorphological Atlas of the People's Republic of China (1∶1000000). Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
[ 中华人民共和国地貌集编辑委员会. 中华人民共和国地貌图集(1∶100万). 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.]
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[侯学煜. 1∶1000000中国植被图集. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 129-132.]
|
| [33] |
National Soil Census Office. Soil map of the People's Republic of China (1∶1000000). 1995.
[ 全国土壤普查办公室. 1∶100万中华人民共和国土壤图. 1995.]
|
| [34] |
[王涛. 中国1:400万冰川冻土沙漠图. 国家冰川冻土沙漠科学数据中心. http://www.ncdc.ac.cn.]
|
| [35] |
[戴声佩, 李海亮, 罗红霞, 等. 1960—2011年华南地区界限温度10℃积温时空变化分析. 地理学报, 2014, 69(5): 650-660.]
|
| [36] |
[张静静, 王岩松, 朱连奇, 等. 近50年来豫西山地亚热带北界变化分析. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(1): 40-49.]
|
| [37] |
[缪启龙, 丁园圆, 王勇. 气候变暖对中国亚热带北界位置的影响. 地理研究, 2009, 28(3): 634-642.]
|
| [38] |
IPCC. Summary for policymakers//Lee L, Romero J. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Geneva, 2023: 1-34. DOI: 10.59327/IPCC/AR6-9789291691647.001.
|
| [39] |
IPCC. Climate Change 2022:Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022.
|
| [40] |
IPCC. Climate Change 2014:Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014.
|
| [41] |
[郑景云, 葛全胜, 郝志新. 气候增暖对我国近40年植物物候变化的影响. 科学通报, 2002, 47(20): 1582-1587.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |