

铁路功效运输联系空间差异化及区域整合效应
|
李涛(1985-), 男, 山西长治人, 博士, 教授, 主要从事交通运输地理研究。E-mail: taoli-2008@163.com |
收稿日期: 2022-02-28
修回日期: 2022-10-27
网络出版日期: 2023-04-14
基金资助
国家社会科学基金重大项目(20&ZD099)
国家自然科学杰出青年基金项目(42225106)
中央高校基本科研业务费项目(GK202103124)
Spatial differentiation and effect on regional integration of inter-city connections in China
Received date: 2022-02-28
Revised date: 2022-10-27
Online published: 2023-04-14
Supported by
Major Program of National Social Science Foundation of China(20&ZD099)
National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars(42225106)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, SNNU(GK202103124)
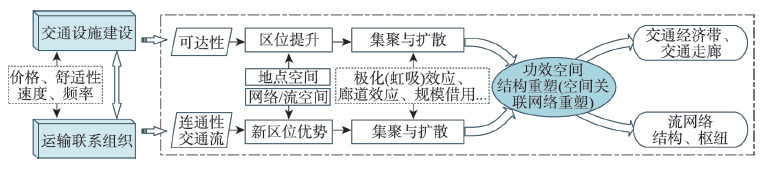
由于速度、票价、合理运距等技术经济特征的差异,高速铁路和普通铁路可以反映不同功效层级的空间运输联系,并对国土空间结构重塑产生影响。本文基于铁路列车时刻表数据,采用客流联系强度模型,研究了基于高铁与普铁服务的差异化空间级联系统秩序,比较了两者对功效空间的区域整合效应。研究结论为:相较普铁而言,高铁的空间布局与全国经济社会发展梯度格局更一致,距离衰减效应更显著,在600 km范围内最具优势;高铁与普铁优势城市分别集中在长江以南和以北,考虑旅客运输需求后显示普铁服务更为均衡。进一步分析发现,在技术经济优势、高铁与普铁竞争以及网络布局影响下,高铁功效空间区域整合呈现出显著的两极分化态势,以邻近区域集聚形态为主,普铁则形成了宏观尺度的南北向和东西向跨区域廊道集聚形态,二者对功效空间区域整合亦分别呈现出多中心等级化与多板块均衡化组织模式。
李涛 , 彭天浩 , 王姣娥 , 黄洁 . 铁路功效运输联系空间差异化及区域整合效应[J]. 地理学报, 2023 , 78(4) : 946 -960 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202304011
There are differences between high-speed rail and conventional rail in technical and economic characteristics such as speed, ticket price and reasonable transport distance. Therefore, they can reflect spatial traffic links at different scales, which have important impact on the reshaping of territorial space. Using train timetable data, this paper analyzes the differential spatial cascading system order of high-speed rail and conventional rail service, and compares the regional integration effect of these two rail modes on the spatial cascading system. The results show that, compared with conventional rail, the spatial layout of high-speed rail is more consistent with the gradient pattern of national economic and social development. The distance decay effect of traffic flows by high-speed rail is more obvious, with an advantage over conventional rail for journeys within 600 km. The advantaged cities of high-speed rail and conventional rail are spatially concentrated to the south and north of the Yangtze River respectively. The conventional rail service presents a more balanced distribution considering the demand of passenger transport. Further analysis shows that, under the influence of technical and economic advantages, competition between high-speed rail and conventional rail, and the network spatial layout, the regional integration effect of high-speed rail on efficiency space shows a significant polarization, with the neighboring regional agglomeration as the main form, while conventional rail has formed cross-regional corridor agglomeration along the north-south direction and east-west direction at the macro level. The regional integration model of high-speed rail and conventional rail also presents the characteristics of multi-center grading and multi-plate equalization respectively.

表1 高铁与普铁技术经济指标与服务特征比较Tab. 1 Comparison of techno-economic indicators and service characteristics between high-speed rail and conventional rail |
| 类型 | 技术标准 | 建设成本 | 速度(km/h) | 基准票价(元/人km) | 单位时间价值(元/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高铁 | 动车、高铁 | 350 km/h:9400万~1.83亿元/km250 km/h:7000万~1.69亿元/km | 新建:≥ 250;既有线改造:≥ 200;200以下动车组 | 350 km/h:0.42~0.48250 km/h:0.29~0.31 | 低收入群体:9.09 中低收入群体:18.09 中等收入群体:27.18 中高收入群体:36.27 高收入群体:90.63 |
| 普铁 | 国铁Ⅰ-Ⅳ级 | 约为高铁的30%~70% | ≤ 200 | 0.11 | |
| 类型 | 列车频次 | 客运量(亿人)及其占比(%) | 周转量(亿人km)及其占比%) | 客运密度(万人km/km) | 覆盖范围 |
| 高铁 | 17.36 | 15.57 (70.7) | 4844.9 (58.6) | 2038.6 | 连接主要城市群,基本连接省会城市和其他50万人口以上大中城市 |
| 普铁 | 7.51 | 6.46 (29.3) | 3421.3 (41.4) | 642.6 | 连接20万人口以上城市,基本覆盖县级以上行政区 |
表2 2019年中国高铁与普铁网络规模统计Tab. 2 Statistics on the size of high-speed rail and conventional rail networks in China in 2019 |
| 类型 | 城市数(个) | 边数(对) | 日发车数(趟/d) | 总联系强度 | 平均联系强度 | 最大值 | 最小值 | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高铁 | 213 | 6006 | 6171 | 73512 | 6.57 | 256 | 0.64 | 2.06 |
| 普铁 | 289 | 12204 | 2312 | 64341 | 2.77 | 61 | 0.64 | 1.66 |
表3 2019年中国高铁与普铁网络空间分布Tab. 3 Spatial distribution of high-speed rail and conventional rail networks in China in 2019 |
| 地区 | 高铁网络 | 普铁网络 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 城市数量(个) | 占比(%) | 客运服务能力 | 占比(%) | 城市数量(个) | 占比(%) | 客运服务能力 | 占比(%) | ||
| 东部 | 79 | 37.09 | 76405 | 51.97 | 88 | 30.45 | 50291 | 39.08 | |
| 中部 | 81 | 38.03 | 48981 | 33.31 | 113 | 39.10 | 53015 | 41.20 | |
| 西部 | 53 | 24.88 | 21638 | 14.72 | 88 | 30.45 | 25377 | 19.72 | |
| 全国 | 213 | 100.00 | 147024 | 100.00 | 289 | 100.00 | 128683 | 100.00 | |
注:东中西三大地带的划分参考文献[16]。 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
[韩增林, 杨荫凯, 张文尝, 等. 交通经济带的基础理论及其生命周期模式研究. 地理科学, 2000, 20(4): 295-300.]
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
[金凤君, 王姣娥. 20世纪中国铁路网扩展及其空间通达性. 地理学报, 2004, 59(2): 293-302.]
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
[蒋海兵, 徐建刚, 祁毅. 京沪高铁对区域中心城市陆路可达性影响. 地理学报, 2010, 65(10): 1287-1298.]
|
| [7] |
[金文纨, 朱晟君, 王翀. 技术关联、交通可达性与企业生产率: 基于公路和铁路的研究. 地理研究, 2022, 41(2): 509-526.]
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
[王姣娥, 焦敬娟, 黄洁, 等. 交通发展区位测度的理论与方法. 地理学报, 2018, 73(4): 666-676.]
|
| [11] |
[焦敬娟, 王姣娥, 金凤君, 等. 高速铁路对城市网络结构的影响研究: 基于铁路客运班列分析. 地理学报, 2016, 71(2): 265-280.]
|
| [12] |
[戴特奇, 金凤君, 王姣娥. 空间相互作用与城市关联网络演进: 以我国20世纪90年代城际铁路客流为例. 地理科学进展, 2005, 24(2): 80-89.]
|
| [13] |
[吴威, 唐昭沛, 梁双波, 等. 空间扩容背景下长三角城市群陆路交通联系时空演化. 人文地理, 2022, 37(3): 163-171, 182.]
|
| [14] |
[钟业喜, 郭卫东. 中国高铁网络结构特征及其组织模式. 地理科学, 2020, 40(1): 79-88.]
|
| [15] |
[马学广, 贾岩. 中国铁路客运流的网络格局与空间特征研究. 中国海洋大学学报(社会科学版), 2020(6): 75-87.]
|
| [16] |
[刘承良, 许佳琪, 郭庆宾. 基于铁路网的中国主要城市中心性的空间格局. 经济地理, 2019, 39(3): 57-66.]
|
| [17] |
[王姣娥, 景悦. 中国城市网络等级结构特征及组织模式: 基于铁路和航空流的比较. 地理学报, 2017, 72(8): 1508-1519.]
|
| [18] |
[金凤君, 焦敬娟, 齐元静. 东亚高速铁路网络的发展演化与地理效应评价. 地理学报, 2016, 71(4): 576-590.]
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[金凤君. 功效空间组织机理与空间福利研究:经济社会空间组织与效率. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 73-75.]
|
| [22] |
[曹小曙, 阎小培. 20世纪走廊及交通运输走廊研究进展. 城市规划, 2003, 27(1): 50-56.]
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
[王姣娥, 杜德林, 金凤君. 多元交通流视角下的空间级联系统比较与地理空间约束. 地理学报, 2019, 74(12): 2482-2494.]
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
[陈伟, 刘卫东, 柯文前, 等. 基于公路客流的中国城市网络结构与空间组织模式. 地理学报, 2017, 72(2): 224-241.]
|
| [36] |
[李涛, 王姣娥, 高兴川. 中国居民工作日与节假日的城际出行网络异同性研究. 地理学报, 2020, 75(4): 833-848.]
|
| [37] |
[赵鹏军, 吕迪, 胡昊宇, 等. 适应人口发展的现代化综合交通运输体系研究. 地理学报, 2020, 75(12): 2699-2715.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |