

基于轨迹数据的多层网络动态社区提取与时空变化分析
|
张媛钰(1998-), 女, 湖南岳阳人, 硕士生, 研究方向为多层时空交互网络。E-mail: yuanyu_zhang@whu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2021-08-02
修回日期: 2022-09-20
网络出版日期: 2023-02-16
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41401453)
Dynamic community detection and evolution analysis in multilayer interaction network based on trajectory data
Received date: 2021-08-02
Revised date: 2022-09-20
Online published: 2023-02-16
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41401453)
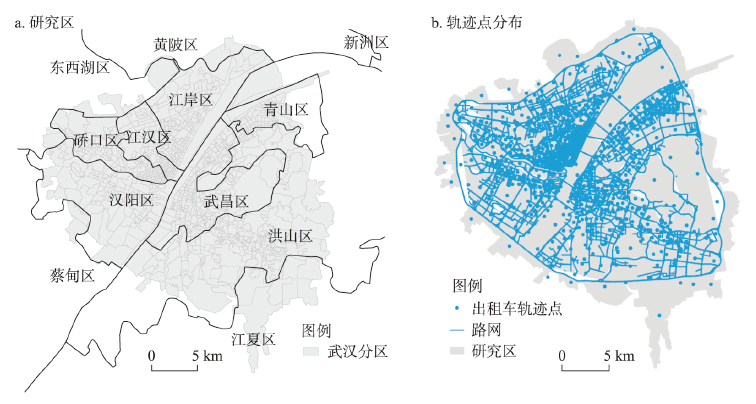
相比于其余部分空间实体,动态社区本质上是彼此之间通过群体移动紧密连接的一系列地理实体的集合,具有生命周期特征。然而目前对于动态社区的时空变化分析仍缺少系统的研究方法。对此,本文首先基于群体出行,对时空交互复杂系统进行网络建模;第二,提取网络中的动态社区,其本质上是由于城市功能活动场所和社会资源分布不均匀、群体出行行为的规律性和多样性导致的动态人地交互而产生的动态城市空间组织;第三,融合景观生态学理论,构建动态社区时空变化模型,分析社区时空变化聚类模式,形成社区提取—动态变化—聚类分析方法框架;最后,以武汉市三环内区域为例应用该方法框架。结果表明:① 基于群体出行活动提取的社区与武汉市现有行政区划具有相似性与差异性,其更能反映以人为中心的城市动态空间组织;② 社区表现出明显的“形成—扩张—稳定—收缩—消亡”的生命周期规律;③ 不同社区时空变化规律具有差异性,通过聚类,其可以被分为短时社区、中时社区与长时社区,且每类社区具有稳定、鞍形、波动等一种或多种形态模式特征,对于城市动态规划管理具有重要意义。本文突破了传统静态社区分析方法的局限性,有助于推动网络动态特征的探索,加深对动态人地交互规律的理解。
张媛钰 , 贾涛 . 基于轨迹数据的多层网络动态社区提取与时空变化分析[J]. 地理学报, 2023 , 78(2) : 490 -502 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202302014
Dynamic community with life cycle is a collection of geographical entities in spatial interaction networks. They connect closely through human movement compared with other spatial entities. However, there is still a lack of systematic approaches for analyzing spatio-temporal variation. In this regard, this paper first constructs the spatio-temporal interaction multilayer network (STIMN) based on human mobility data. Secondly, we extract dynamic communities of STIMN, which reveal the uneven distribution of urban resources and the regularity and diversity of human movement. Thirdly, based on the theories of landscape ecology, we propose a dynamic community evolution model and analyze the clustering patterns, forming the framework of "the community detection - dynamic evolution - clustering analysis". Finally, we apply the framework in the third-ring core area within Wuhan, which shows that: (1) Communities extracted from public activities have similarities and differences with the existing administrative divisions of Wuhan City, which can better reflect the people-oriented urban dynamic spatial organization; (2) Community evolution shows an apparent life cycle of "occurrence - expansion - stability - contraction - disappearance"; (3) The life cycle of different communities is different. Through clustering, communities can be divided into short-term, medium-term and long-term communities. Each type of community has one or more dynamic patterns, such as stability, saddle-shaped and wave-shaped pattern, which are significant to dynamic urban planning and management. This study breaks the limitations of traditional community analysis methods, helps explore the dynamic characteristics of the STIMN and deepens the understanding of the dynamic man-land interaction.

| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
[ 秦昆, 周勍, 徐源泉, 等. 城市交通热点区域的空间交互网络分析. 地理科学进展, 2017, 36(9): 1149-1157.]
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[ 顾朝林, 王颖, 邵园, 等. 基于功能区的行政区划调整研究: 以绍兴城市群为例. 地理学报, 2015, 70(8): 1187-1201.]
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
[ 李萌, 张品超, 陈婕妤. 动态交通分配下潮汐车道方案设置研究. 综合运输, 2015, 37(7): 78-86.]
|
| [21] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |