

中国人—野猪冲突时空特征及对生态系统“反服务”的启示
|
王亚辉(1989-), 男, 安徽亳州人, 博士, 副教授, 硕士生导师, 中国地理学会会员(S110014196M), 主要从事土地利用与国土空间规划研究。E-mail: wangyh1210@swu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2022-09-13
修回日期: 2022-12-29
网络出版日期: 2023-01-16
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42271263)
国家自然科学基金项目(41901232)
国家自然科学基金项目(42071234)
国家自然科学基金项目(41971239)
国家社会科学基金重大项目(19ZDA096)
中央高校基本科研业务费项目(SWU-KT22008)
西南大学创新研究2035先导计划(SWU PilotPlan031)
Spatiotemporal characteristics of human-boar conflicts in China and its implications for ecosystem "anti-service"
Received date: 2022-09-13
Revised date: 2022-12-29
Online published: 2023-01-16
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42271263)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41901232)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42071234)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41971239)
Major Program of National Social Science Foundation of China(19ZDA096)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(SWU-KT22008)
Innovation Research 2035 Pilot Plan of Southwest University(SWU PilotPlan031)
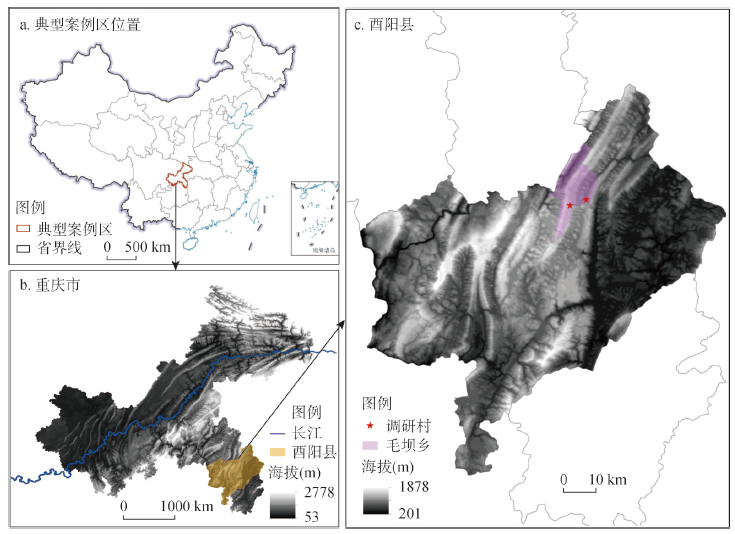
中国农村社会经济转型背景下,生态系统“反服务”现象频现,如何协同生态保护与社会经济发展面临巨大挑战。本文基于收集的733件典型人—野猪冲突(又称野猪“肇事”)事件资料,采用荟萃分析法研究了2000—2021年中国野猪“肇事”事件的时空分布、危害和驱动因素。在此期间,野猪“肇事”的数量、空间范围和危害程度均呈递增趋势,涉及省、市和区(县)数量分别由初期的18个、41个和67个增至近期的25个、147个和399个,相应增幅分别为39%、259%和496%。其中2005年以前野猪“肇事”集中在重庆市和湖北省中西部,之后向四周扩张,2015年以后集中在四川盆地、黄土高原、长江中下游以及长白山等丘陵山区,表现形式以破坏农作物、侵害家禽和致人伤亡为主,尤以对农作物的破坏并导致耕地撂荒最为普遍,并伴随致人伤亡事件的快速增加,约占“肇事”总数量的1/4(23.66%)。目前情况下,野猪“肇事”蔓延趋势和危害性是一种典型的生态系统“反服务”现象,这种现象的加剧是生态恢复、禁猎政策、农地与生态用地界线不清、野猪生存力强且缺少天敌等因素的综合作用结果,对撂荒地利用、农户生计改善以及区域生态安全维持已构成明显威胁,制定野猪数量调控政策和建立野猪“肇事”损失补偿机制迫在眉睫,是新时代乡村振兴工作所亟待应对的新的社会问题。
王亚辉 , 杨遨郗 , 杨庆媛 , 孔祥斌 , 樊辉 . 中国人—野猪冲突时空特征及对生态系统“反服务”的启示[J]. 地理学报, 2023 , 78(1) : 163 -176 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202301011
In the context of social and economic transformation in rural China, the phenomenon of ecosystem "anti-service" has emerged frequently, and it is a great challenge to synergize ecological conservation and socio-economic development. Using the meta-analysis and collecting 733 typical human-boar conflict incidents (also known as wild boar damage incidents), this paper studies the spatiotemporal patterns, hazards and driving factors of wild boar damage from 2000 to 2021. During this period, the number, spatial scope and hazard degree of wild boar damage incidents showed an increasing trend, and the number of provinces, cities and districts (counties) involved increased from 18, 41 and 67 in the earlier stage to 25, 147 and 399 in the recent period, with corresponding increases of 39%, 259% and 496%, respectively. Among them, wild boar damage incidents were concentrated in Chongqing Municipality and central and western parts of Hubei Province before 2005, and then expanded around, and this situation concentrated in the Sichuan Basin, Loess Plateau, middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and hilly mountainous areas such as Changbai Mountains after 2015. The main manifestations were destroying crops, infringing poultry and causing casualties, especially the destruction of crops leading to cultivated land abandonment, accompanied by a rapid increase in casualties, accounting for about 1/4 (23.66%) of the total number of damage incidents. Meanwhile, the spreading trend and harmfulness of wild boar damage is a typical phenomenon of "anti-service" in ecosystem. The aggravation of this phenomenon is the result of ecological restoration, hunting ban policy, unclear boundary between agricultural land and ecological land, strong viability of wild boar and lack of natural enemies. It has posed an obvious threat to the utilization of abandoned cultivated land, the improvement of farmers' livelihood and the maintenance of regional ecological security. It is extremely urgent to formulate the policy of controlling the number of wild boars and establish the compensation mechanism for the loss by wild boars, which is a new social problem that needs to be dealt with urgently in rural revitalization in the new era.

表1 2000—2021年关于人—野猪冲突文献和报道统计Tab. 1 Statistics of literature and reports on human-boar conflict from 2000 to 2021 |
| 文献形式 | 来源 | 数量(条) | 占比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 学术论文 | 中国知网、Web of Science、Elsevier、Springer等 | 88 | 12.01 |
| 政府公告 | 国家林业和草原局、地方政府门户网站 | 8 | 1.09 |
| 领导留言 | 人民网领导留言板 | 11 | 1.50 |
| 新闻网页 | 新华网、凤凰网、南风窗等网站或杂志 | 626 | 85.40 |
| 合计 | - | 733 | 100.00 |
图6 案例区野猪“肇事”与撂荒耕地的空间关系Fig. 6 Spatial relationship between wild boar damage and abandoned cultivated land in typical case areas |
表2 典型案例区耕地撂荒的归因统计Tab. 2 Attribution statistics of abandoned cultivated land in typical case areas |
| 地块类型 | 天仓村 | 双龙村 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地块数量(块) | 占比 (%) | 地块面积(hm2) | 占比 (%) | 地块数量(块) | 占比 (%) | 地块面积(hm2) | 占比 (%) | ||
| 仅因野猪破坏导致撂荒地块 | 85 | 30.14 | 7.24 | 32.01 | 37 | 18.59 | 4.06 | 19.48 | |
| 因野猪破坏等因素导致撂荒地块 | 126 | 44.68 | 10.88 | 48.14 | 123 | 61.81 | 12.13 | 58.11 | |
| 非野猪因素导致撂荒地块 | 71 | 25.18 | 4.49 | 19.85 | 39 | 19.60 | 4.68 | 22.41 | |
| 撂荒地块 | 282 | 100 | 22.61 | 100 | 199 | 100 | 20.87 | 100.00 | |
| 总调研地块 | 437 | 36.88 | 328 | 32.49 | |||||
注:非野猪因素包括家庭劳动力短缺、与家庭距离远、劣等地、自然灾害、水资源短缺、公路占用等因素。 |
审稿专家对本文提出了详实、客观和准确的审稿意见,中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所李秀彬研究员团队提供了山区撂荒区县的调研数据,西南大学资源环境学院阎建忠研究员提出了前期研究建议,中国地质科学院地质力学研究所顾畛逵副研究员对本文提出了建议和修改,特致以诚挚感谢。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[ 王文瑞, 田璐, 唐琼, 等. 生态恢复中生态系统反服务与居民生存的博弈: 以甘肃“猪进人退”现象为例. 地理研究, 2018, 37(4): 772-782.]
|
| [12] |
[ 苗震, 芦欣怡, 周学红, 等. 野猪与人冲突防控对策研究的系统评价. 生态学报, 2022, 42(6): 2501-2509.]
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
[ 邓天鹏, 郑合勋, 曾国仕. 伏牛山北坡野猪(Sus scrofa)泥浴场的生境特征. 生态学报, 2009, 29(2): 1001-1008.]
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
[ 黄杨, 林建忠, 汪国海, 等. 喀斯特生境中野猪活动模式和时间分配. 野生动物学报, 2021, 42(2): 348-354.]
|
| [19] |
[ 江晓萍, 徐基良, 李建强, 等. 基于MaxEnt生态位模型分析江西省人与野猪冲突的空间分布. 森林与环境学报, 2018, 38(3): 334-340.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[ 王亚辉, 辛良杰, 李秀彬. 重庆典型山区耕地资产贬值特征及其发生机理. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(22): 107-114.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
[ 李升发, 李秀彬, 辛良杰, 等. 中国山区耕地撂荒程度及空间分布: 基于全国山区抽样调查结果. 资源科学, 2017, 39(10): 1801-1811.]
|
| [27] |
[ 黄麟, 祝萍, 曹巍. 中国退耕还林还草对生态系统服务权衡与协同的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(3): 1178-1188.]
|
| [28] |
[ 张学珍, 赵彩杉, 董金玮, 等. 1992—2017年基于荟萃分析的中国耕地撂荒时空特征. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3): 411-420.]
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
[ 李焱, 巩杰, 戴睿, 等. 藏西南高原植被覆盖时空变化及其与气候因素和人类活动的关系. 地理科学, 2022, 42(5): 761-771.]
|
| [31] |
[ 李仕冀, 李秀彬, 谈明洪. 乡村人口迁出对生态脆弱地区植被覆被的影响: 以内蒙古自治区为例. 地理学报, 2015, 70(10): 1622-1631.]
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
[ 李薇, 谈明洪. 西南山区人口空间重组及其对植被的影响: 以河流沿线为例. 生态学报, 2018, 38(24): 8879-8887.]
|
| [35] |
[ 李双成, 张才玉, 刘金龙, 等. 生态系统服务权衡与协同研究进展及地理学研究议题. 地理研究, 2013, 32(8): 1379-1390.]
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
[ 周学红, 马建章, 张伟, 等. 珲春自然保护区居民对野猪的容受性及其影响因素分析. 资源科学, 2008, 30(6): 876-882.]
|
| [39] |
[ 董广辉, 仇梦晗, 李若, 等. 探讨过去人地关系演变机制的“支点”概念模型. 地理学报, 2021, 76(1): 15-29.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |