

黄河源区典型河网平面形态特征及影响因素
|
李敏慧(1996-), 女, 博士生, 研究方向为河流地貌学。E-mail: li-mh18@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2022-02-07
修回日期: 2022-10-11
网络出版日期: 2022-12-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(51639005)
Planform geometry and controlling factors of river networks in the Yellow River source zone
Received date: 2022-02-07
Revised date: 2022-10-11
Online published: 2022-12-27
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(51639005)
黄河源区不同地貌环境下的河网发育模式、平面形态等具有显著差异,存在羽状、矩形状、对称羽状和树状4种典型的河网类型。选取黄河源区83个典型子流域,计算了河网平面特征参数,探讨了河网参数与地形和气候因子的关系及河网类型的分布规律。结果表明,4类河网平面特征差异性通过流域宽长比、河网密度和流域内河流流向最大频数得到了较好的体现。流域坡度和降雨量对河网密度及流向的影响显著,且能较好解释河网密度及流向最大频数的变化;降雨对流域宽长比的影响显著。羽状主要分布在源区上游北部边缘地带,气候干旱,地表裸露,流域坡度均值为4.5°,流域高差均值为730 m。矩形状集中分布在若尔盖地区,气候相对湿润,且有大量的沼泽湿地,流域坡度和流域高差均值分别为2.3°和177 m。对称羽状处于高山峡谷地带,流域坡度和流域高差均值分别为16.9°和1167 m,降雨量变化范围大。树状分布在黄河源中游山区及中下游的冲积地貌,流域坡度和流域高差均值分别为15.4°和968 m,植被覆盖较好。结合4类河网的空间分布特征及河网参数与环境因子的多元回归分析结果分析,认为地形是决定河网平面形态分异的主要原因;当地形限制减小,气候条件和植被覆盖情况对河网的发展起了重要作用。
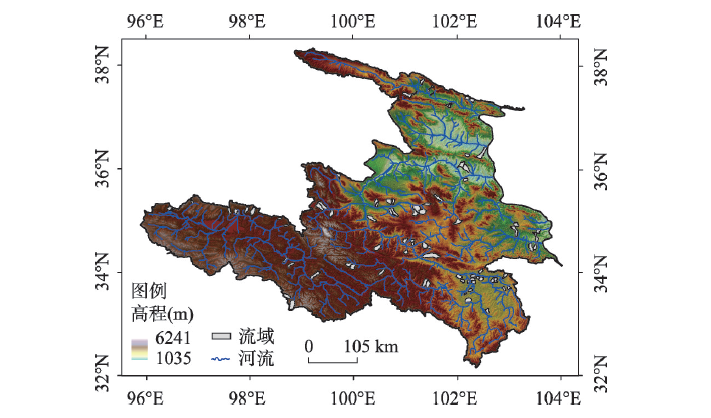
李敏慧 , 吴保生 , 陈毅 . 黄河源区典型河网平面形态特征及影响因素[J]. 地理学报, 2022 , 77(11) : 2878 -2889 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202211012
The landform of the Yellow River source zone is diverse, leading to various drainage patterns. To understand the drivers of planform geometry of river networks in the Yellow River source zone, 83 representative sub-basins, including dendritic, pinnate, rectangular and symmetric pinnate patterns are selected for studies. Attributes to characterize the planform geometry of river networks are calculated. The relationships between river network attributes and environmental factors are examined. The results show that the differences in the characteristics of the 4 drainage patterns are well reflected by the aspect ratio, drainage density and the maximum frequency of flow directions. Changes in drainage density and the maximum frequency of flow directions are well expressed by slope and precipitation variation. Aspect ratio is significantly influenced by precipitation. The pinnate networks are mainly distributed at the northern edge of the upper plateau where the climate is arid and the surface is bare. The mean basin slope of this pattern is 4.5º, and the mean relief is 730 m. The rectangular networks are concentrated in the Zoige basin where the mean basin slope and relief are 2.3º and 177 m, respectively. The climate of the Zoige basin is relatively humid and there are plenty of swamps and wetlands. The symmetric pinnate networks are more likely to occur in the high-relief valleys where the precipitation varies greatly. The average slope and relief of the symmetric pinnate networks are 16.9º and 1167 m, respectively. The dendritic networks are distributed mainly in mountainous areas of the middle reaches and fluvial plains in the northeast part of the source zone. The average slope and relief of the dendritic networks are 15.4º and 968 m, respectively. The vegetation coverage is better than that of the upper plateau. Our analysis suggests that topography is the main factor that leads to the differences of planform geometry among various drainage patterns. Climate and vegetation coverage play an important role in the development of river networks when the constraints of topography are reduced.

表1 河网参数与环境因子的相关系数矩阵Tab. 1 The correlation matrix among river network attributes and environmental factors |
| 流域宽长比 | 河网密度 | 流向最大频数 | 流域坡度 | 流域高差 | 年均降雨量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流域坡度 | -0.096 | -0.671 | -0.356 | - | - | - |
| 流域高差 | -0.253 | 0.016 | 0.055 | 0.276 | - | - |
| 年均降雨量 | 0.283 | -0.389 | -0.581 | 0.063 | -0.171 | - |
| 干旱指数 | 0.203 | -0.566 | -0.596 | 0.283 | -0.164 | -0.836 |
表2 河网参数与环境因子的标准化多元回归系数Tab. 2 Standard multivariate regression coefficients between river network attributes and environmental factors |
| 河网参数 | 流域坡度 | 流域高差 | 年均降雨量 | 干旱指数 | 复相关系数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 流域宽长比 | - | - | 0.283 | - | 0.283 | ||
| 河网密度 | -0.556 | - | -0.409 | - | 0.777 | ||
| 流向最大频数 | -0.321 | - | -0.561 | - | 0.663 | ||
表3 黄河源区所选河网土地利用和岩性Tab. 3 Land-use and lithology of river networks selected in the Yellow River source zone |
| 河网类型 | 土地利用 | 岩性 |
|---|---|---|
| 羽状 | 裸地 | 疏松沉积物和硅质沉积岩 |
| 矩形状 | 草地 | 疏松沉积物 |
| 对称羽状 | 草地和裸地 | 硅质沉积岩和混合沉积岩 |
| 树状 | 草地和森林 | 混合沉积岩 |
| [1] |
[许炯心, 李炳元, 杨小平, 等. 中国地貌与第四纪研究的近今进展与未来展望. 地理学报, 2009, 64(11): 1375-1393.]
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
[刘怀湘, 王兆印. 典型河网形态特征与分布. 水利学报, 2007, 38(11): 1354-1357.]
|
| [19] |
[刘怀湘, 王兆印. 河网形态与环境条件的关系. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 48(9): 1408-1412.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
[杜俊, 王兆印, 李志威, 等. 黄河源同德盆地刺状水系初步研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(2): 129-135.]
|
| [22] |
[李志威, 王兆印, 余国安, 等. 黄河源玛曲河段河型沿程变化及其原因. 泥沙研究, 2013(3): 51-58.]
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[张森琦, 李永国, 尚小刚, 等. 黄河源区新构造运动对生态环境恶化的影响. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2): 213-220.]
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
[叶红, 张廷斌, 易桂花, 等. 2000—2014年黄河源区ET时空特征及其与气候因子关系. 地理学报, 2018, 73(11): 2117-2134.]
|
| [28] |
[汪治桂, 王素萍, 王建兵, 等. 黄河源区近40年参考作物蒸散量变化特征研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2013, 31(6): 169-173, 189.]
|
| [29] |
[李开明, 李绚, 王翠云, 等. 黄河源区气候变化的环境效应研究. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(5): 1183-1192.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
[颜明, 许炯心, 贺莉, 等. 黄河流域河网密度的空间特征及其影响因素. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(2): 288-292.]
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
[李敏慧, 陈毅, 吴保生. 青藏高原典型流域河网特性及控制因素. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 60(11): 951-957.]
|
| [42] |
[刘乐, 王兆印, 余国安, 等. 青藏高原河网统计规律及高原抬升的影响. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 55(9): 964-970.]
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
[黄春长. 若尔盖盆地河流古洪水沉积及其对黄河水系演变问题的启示. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3): 612-625.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |