

天山北坡人类活动强度与地表温度的时空关联性
|
陈泓瑾(1998-), 女, 重庆大足人, 硕士生, 主要从事人类活动强度评估与人地关系研究。E-mail: ZLYZXLX@163.com |
收稿日期: 2021-03-22
修回日期: 2022-02-14
网络出版日期: 2022-07-20
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41461086)
国家自然科学基金项目(41761108)
Spatiotemporal correlation between human activity intensity and surface temperature on the north slope of Tianshan Mountains
Received date: 2021-03-22
Revised date: 2022-02-14
Online published: 2022-07-20
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41461086)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41761108)
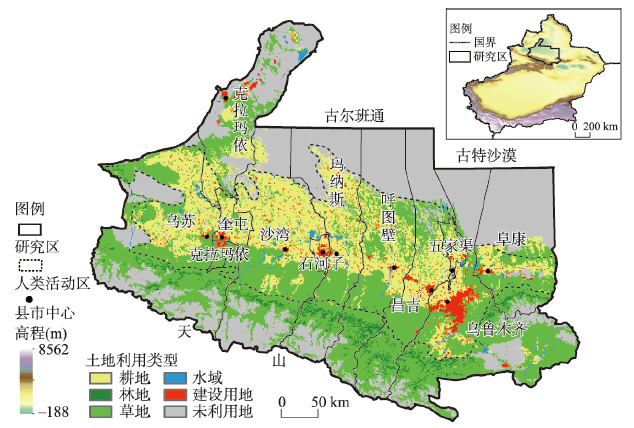
人类活动强度与地表温度的时空关联研究对于充分认识气候变化的成因和机制、积极适应气候变化、合理开发及保护生态环境等均具有重大意义。本文以地处西北干旱区且对气候变化极为敏感的天山北坡为研究区,基于MODIS数据反演地表温度,以夜间灯光数据、人口分布数据及土地利用数据等共同表征人类活动强度,分析2000—2018年人类活动强度与地表温度的演变特征,并进一步探究二者的时空关联性。研究结果显示:① 2000年以来天山北坡平均人类活动强度(0.11)较低,整体呈阶梯式缓慢上升趋势(0.0024 a-1),其中人类活动强度较建设用地和人口规模增加滞后1~2 a。② 天山北坡年均地温为7.18 ℃且呈显著升温态势,变化率(0.02 ℃·a-1)约为全球的2.33倍,春季显著增温(0.068 ℃·a-1)对整体升温的贡献最大;受高程和植被覆盖度等下垫面性状的显著影响,研究区地温空间上呈南低北高特征。③ 天山北坡人类活动区人类活动强度与地表温度显著正相关,呈东强西弱分布特征,其空间分异与相关性的表达受到人类活动范围、表现形式及土地利用变化等因素的综合影响,农林种植、城市绿化和植树造林等与植被相关的人为干预能够有效减弱人类活动造成的地表增温。本文不仅为人类活动强度的精细刻画提出了新思路,更可为区域人地协调和统筹发展等提供科学参考。
陈泓瑾 , 刘琳 , 张正勇 , 刘亚 , 田浩 , 康紫薇 , 王统霞 , 张雪莹 . 天山北坡人类活动强度与地表温度的时空关联性[J]. 地理学报, 2022 , 77(5) : 1244 -1259 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202205014
Research on the spatiotemporal correlation between the intensity of human activities and the temperature of earth surfaces is of great significance in many aspects, including fully understanding the causes and mechanisms of climate change, actively adapting to climate change, pursuing rational development, and protecting the ecological environment. The north slope of Tianshan Mountains, located in the arid area of northwestern China, is a typical area that is extremely sensitive to climate change. This paper takes the area as an example to retrieve the surface temperature of the mountain based on MODIS data, characterized by the effect of the intensity of human activities on the night light, population distribution and land use. The evolution characteristics of human activity intensity and surface temperature in the study area from 2000 to 2018 were analyzed, and the spatiotemporal correlation between them was further explored. It is found that: (1) The average human activity intensity (0.11) has kept relatively low since the beginning of the 21st century, and it has been slowly rising in a stepwise manner (0.0024 a-1); in addition, the increase in human activity intensity has lagged behind that in construction land and population by 1-2 years. (2) The annual average surface temperature in the area is 7.18 ℃ with an obvious growth. The rate of change (0.02 ℃·a-1) is about 2.33 times that of the world. The striking boost in spring (0.068 ℃·a-1) contributes the most to the overall warming trend. Spatially, the surface temperature is low in the south and high in the north, due to the prominent influence of the underlying surface characteristics, such as elevation and vegetation coverage. (3) The intensity of human activity and the surface temperature are remarkably positively correlated in the areas with intense human activity, showing a strong distribution pattern in the east section and a weak one in the west section. The expression of its spatial differentiation and correlation is comprehensively affected by such factors as scopes of human activities, manifestations, and land-use changes. Vegetation-related human interventions, such as farming and forestry planting, urban greening, and afforestation, can effectively mitigate the surface warming caused by human activities. This study not only puts forward new ideas to finely portray the intensity of human activities, but also offers a scientific reference for regional human-land coordination and overall development.

表1 数据来源Tab. 1 Data sources |
| 数据 | 空间分辨率 | 年份 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOD11C3 | 0.05°×0.05° | 2000—2019 | ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/data/search |
| LU | 1 km×1 km | 2005、2010、2015、2018 | http://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx |
| NDVI | 1 km×1 km | 2000—2018 | http://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx |
| DMSP/OLS | 1 km×1 km | 2000—2013 | http://www.resdc.cn/Default.aspx |
| NPP-VIIRS | 500 m×500 m | 2013—2018 | https://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp/downloadV4composites.html |
| PD | 1 km×1 km | 2000—2018 | https://landscan.ornl.gov/landscan-datasets |
表2 土地利用类型权重Tab. 2 Weight of land use types |
| 地类 | 耕地 | 林地 | 草地 | 水域 | 建设用地 | 未利用地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.00 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
[沈永平, 王国亚. IPCC第一工作组第五次评估报告对全球气候变化认知的最新科学要点. 冰川冻土, 2013, 35(5): 1068-1076.]
|
| [3] |
[刘世梁, 刘芦萌, 武雪, 等. 区域生态效应研究中人类活动强度定量化评价. 生态学报, 2018, 38(19): 6797-6809.]
|
| [4] |
[段群滔, 罗立辉. 1990-2015年青藏高原人类足迹数据集. 中国科学数据(中英文网络版), 2020, 5(3): 303-312.]
|
| [5] |
[尹小君, 祝宏辉,
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
[韩美, 张翠, 路广, 等. 黄河三角洲人类活动强度的湿地景观格局梯度响应. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(6): 265-274.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[王鹤饶, 郑新奇, 袁涛. DMSP/OLS数据应用研究综述. 地理科学进展, 2012, 31(1): 11-19.]
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
[胡云锋, 赵冠华, 张千力. 基于夜间灯光与LUC数据的川渝地区人口空间化研究. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(1): 68-78.]
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
[张永年, 潘竟虎. 基于DMSP/OLS数据的中国碳排放时空模拟与分异格局. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(4): 1436-1446.]
|
| [17] |
[管延龙, 王让会, 李成, 等. 天山北麓1963-2010年0 cm最高与最低地表温度变化特征. 干旱气象, 2015, 33(4): 587-594.]
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
[杨贵军, 孙晨红, 历华. 黑河流域ASTER与MODIS融合生成高分辨率地表温度的验证. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(6): 193-200.]
|
| [20] |
[乔治, 黄宁钰, 徐新良, 等. 2003-2017年北京市地表热力景观时空分异特征及演变规律. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3): 475-489.]
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
[张佳华, 侯英雨, 李贵才, 等. 北京城市及周边热岛日变化及季节特征的卫星遥感研究与影响因子分析. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2005, 35(增刊1): 187-194.]
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
[热伊莱·卡得尔, 玉素甫江·如素力, 高倩, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地地表温度时空分布对LUCC的响应. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(20): 259-266.]
|
| [25] |
[陆妍, 喻文兵, 郭明, 等. 黑龙江省漠河地区土地覆被与地表温度时空变化特征研究. 冰川冻土, 2017, 39(5): 1137-1149.]
|
| [26] |
[郭恒亮, 冯珍珍, 赫晓慧, 等. 地表覆被与人口密度变化对城市地表温度的影响分析: 以郑州市为例. 内蒙古师范大学学报(自然科学汉文版), 2019, 48(4): 298-306.]
|
| [27] |
[王刚, 张秋平, 肖荣波, 等. 土地利用、人口密度及海拔对城市热岛的影响. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(1): 82-90.]
|
| [28] |
[沈中健, 曾坚. 闽南三市城镇发展与地表温度的空间关系. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3): 566-583.]
|
| [29] |
[胡李发, 谢元礼, 崔思颖, 等. 关中平原城市群夏季城市热岛特征及驱动力. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8): 3842-3852.]
|
| [30] |
[欧阳斌, 车涛, 戴礼云, 等. 基于MODISLST产品估算青藏高原地区的日平均地表温度. 冰川冻土, 2012, 34(2): 296-303.]
|
| [31] |
[施雅风, 沈永平, 胡汝骥. 西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的信号、影响和前景初步探讨. 冰川冻土, 2002, 24(3): 219-226.]
|
| [32] |
[施雅风, 沈永平, 李栋梁, 等. 中国西北气候由暖干向暖湿转型的特征和趋势探讨. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(2): 152-164.]
|
| [33] |
[管延龙, 王让会, 李成, 等. 基于MODIS数据的天山区域地表温度时空特征. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3): 681-688.]
|
| [34] |
[刘超, 闫小月, 姜逢清. 天山北坡前山带降水分布型对荒漠植被的影响: 基于逐日降水数据和NDVI的分析. 生态学报, 2020, 40(21): 7790-7804.]
|
| [35] |
[齐亚霄, 张飞, 陈瑞, 等. 2001-2015年天山北坡植被覆盖动态变化研究. 生态学报, 2020, 40(11): 3677-3687.]
|
| [36] |
[罗格平, 陈嘻, 胡汝骥. 基于AVHRR/NOAA影像的天山北坡近10a植被变化. 冰川冻土, 2003, 25(2): 237-242.]
|
| [37] |
[孙钦明, 刘彤, 韩志全, 等. 遥感分析天山北部植被覆盖对气候变化的多时间尺度响应. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(15): 248-255.]
|
| [38] |
[潘竟虎, 李俊峰. 基于夜间灯光影像的中国电力消耗量估算及时空动态. 地理研究, 2016, 35(4): 627-638.]
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
[杨任飞. 基于DMSP/OLS与NPP/VIIRS整合数据的城市群发育过程研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018.]
|
| [42] |
[王丽佳, 李加林, 田鹏, 等. 杭州湾南岸围垦土地人类活动强度及对滨海湿地覆被类型的影响. 上海国土资源, 2020, 41(1): 4-10.]
|
| [43] |
[张翠云, 王昭. 黑河流域人类活动强度的定量评价. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(增刊1): 386-390.]
|
| [44] |
[魏凤英. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术. 2版. 北京: 气象出版社, 2007: 29-35.]
|
| [45] |
[刘采, 张海燕, 李迁. 1980-2018年海南省人类活动强度时空变化特征及其驱动机制. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39(4): 567-576.]
|
| [46] |
[仲崇玺, 周跃志. 天山北坡经济带人口分布与经济发展研究. 干旱区资源与环境, 2008, 22(6): 33-38.]
|
| [47] |
[云翔. 全球地表温度数据的改进以及增暖分析[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2019.]
|
| [48] |
[毛炜峄, 陈颖, 曹兴. 单站寒潮降温过程强度评估指标及其在乌鲁木齐市的应用. 气象与环境学报, 2016, 32(5): 139-146.]
|
| [49] |
[黄芳芳, 马伟强, 李茂善, 等. 藏北高原地表温度对气候变化响应的初步分析. 高原气象, 2016, 35(1): 55-63.]
|
| [50] |
[王璞玉, 李忠勤, 李慧林, 等. 天山冰川储量变化和面积变化关系分析研究. 冰川冻土, 2017, 39(1): 9-15.]
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
[李士成, 张学珍. 基于土地利用的长江经济带1970s末至2015年人类活动强度数据集. 中国科学数据(中英文网络版), 2018, 3(3): 15-22.]
|
| [53] |
[荣益, 李超, 许策, 等. 城镇化过程中生态系统服务价值变化及人类活动影响的空间分异: 以黄骅市为例. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5): 1374-1381.]
|
| [54] |
[薛陈利, 张会琼, 邹滔, 等. 中老铁路经济廊带生态质量及其与人类活动的关系. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(2): 638-648.]
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
[陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 吴志峰, 等. 夜间灯光遥感数据应用综述和展望. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38(2): 205-223.]
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
[楚丽霞. 利用遥感卫星数据云平台研究人类活动对沿海环境的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2019.]
|
| [59] |
[王今殊. 北京地区地表温度空间分布特征及其与下垫面关系研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北师范大学, 2008.]
|
| [60] |
[董良鹏. 基于MODIS地表温度的气温估计方法及其在中国东部城市群热岛效应研究中的应用[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2012.]
|
| [61] |
[曾静. 城市土地利用变化对地表温度影响的遥感监测[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2015.]
|
| [62] |
[崔永祥. 辽宁省未利用土地的成因、分布及其改造利用的探讨. 中国土地科学, 1998, 12(2): 12-14.]
|
| [63] |
[夏俊士, 杜培军, 张海荣, 等. 基于遥感数据的城市地表温度与土地覆盖定量研究. 遥感技术与应用, 2010, 25(1): 15-23.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |