

非线性视角下的上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程及动力学特征
|
赵赞(1976-), 女, 广西桂林人, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事旅游地理学教学与科研工作。E-mail: zz7476@126.com |
收稿日期: 2020-03-26
要求修回日期: 2021-07-08
网络出版日期: 2021-10-25
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41930644)
国家自然科学基金项目(41861027)
广西发展战略研究院课题
版权
Evolution and dynamic characteristics of tourism destination complex system from the perspective of nonlinearity: A case study of Shanghai
Received date: 2020-03-26
Request revised date: 2021-07-08
Online published: 2021-10-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41930644)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41861027)
Guangxi Development Strategy Institute
Copyright
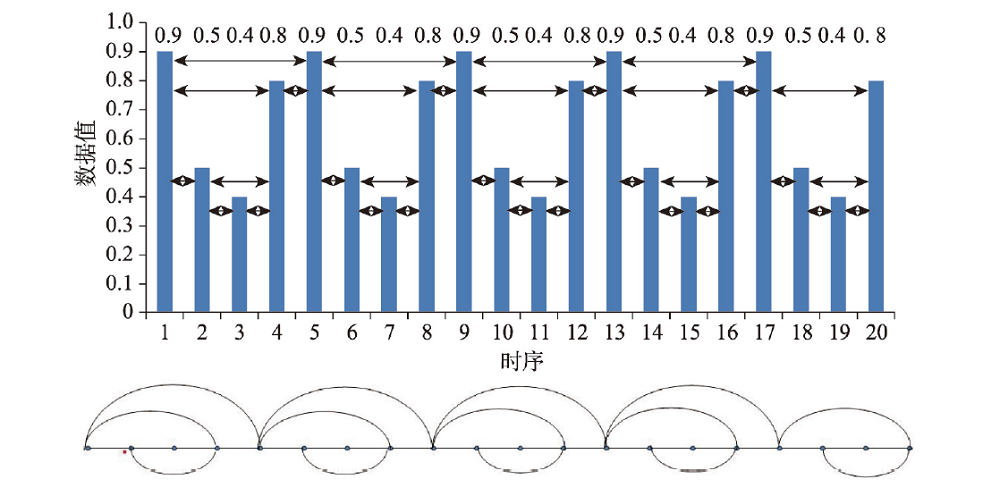
随着旅游地发展复杂性的增加,非线性研究方法成为旅游地演化研究的有效选择。以上海为案例地,运用水平可视图算法,将旅游需求作为旅游地复杂系统动态行为表征,探讨旅游地复杂系统演化过程及动力学特征。研究发现:旅游地复杂系统演化具有小世界和近似无标度网络特性,混沌动态行为特征,表现为混沌确定非线性动力系统;上海旅游地复杂系统演化处于“无序中的有序”混沌或混沌边缘,原有秩序已瓦解,系统新的属性和结构逐渐涌现,有待新的高级有序态生成;旅游地复杂系统遵循“有序—混沌(边缘)—涌现—新有序”,从低级有序向高级有序演化跃升的过程;外部环境和主体系统主导下的重要事件是旅游地复杂系统由低级有序向高级有序演化的“关键要素”,政府学习创新能力的提升对系统阶段性演进起到“推进器”作用,旅游企业开始显现主导地位,成为未来推动上海旅游地复杂系统演替发展的主导力量。上海国际入境旅游客源国(日、韩、新、德、英、法、加、澳)和国内旅游外地游客市场处于不稳定的混沌区域,是影响上海旅游地复杂系统混沌行为的重要因素,应进行混沌控制,加强管理和引导,促进上海旅游地复杂系统新演化阶段有序态的生成。
赵赞 , 陆林 , 任以胜 . 非线性视角下的上海旅游地复杂系统演化过程及动力学特征[J]. 地理学报, 2021 , 76(8) : 2032 -2047 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202108015
With the increasing complexity of tourism destination development, nonlinear research method has become an effective way for tourism destination evolution research. This paper, with Shanghai as a case study, takes the tourism demand as the dynamic behavior representation of the complex system of the tourism destination by using the method of horizontal visibility graph. It explores the evolution process and dynamic characteristics of the complex system of tourism destination. Result shows that the evolution of tourism destination complex system is featured by a small world and approximate scale-free network, which is characterized by chaotic dynamic behavior and chaotic deterministic nonlinear dynamic system. The evolution of the complex system of Shanghai tourism destination is in the chaos of "order in disorder" or the edge of chaos. The original order of the system has collapsed, and new attributes and structures have emerged gradually, and then they will form a new advanced order. The complex system of tourism destination follows the process of "order - chaos (edge) - emergence - new order", from low order to high order. The major events dominated by the external environment and the main system are the "key elements" of the evolution of complex tourism destination system from low-level order to high-level order. The improvement of the government's learning and innovation ability acts as a "propeller" in the system's phased evolution. Tourism enterprises begin to play a critical role and become the leading force to promote the development of complex system of Shanghai's tourism destination in the future. International inbound tourism source countries of Shanghai (Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Germany, Britain, France, Canada, and Australia) and domestic foreign tourism market are in an unstable chaotic region, which is an important factor affecting the chaotic behavior of the complex system of Shanghai's tourism destination. We should control the chaos, strengthen the management and guidance, and promote the formation of orderly state in the new evolution stage of the complex system of Shanghai's tourism destination.

表1 4组时间序列的小世界特性指标表Tab. 1 Small world characteristic index table of four time series |
| 时间序列 | L | Lrond (变异系数) | C | Crond (变异系数) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 5.637 | 3.677(0.015) | 0.588 | 0.030(0.242) |
| Year | 6.289 | 3.159(0.155) | 0.130 | 0.119(0.181) |
| DOM | 6.195 | 3.752(0.021) | 0.594 | 0.031(0.150) |
| INT | 9.390 | 4.035(0.015) | 0.580 | 0.024(0.251) |
表2 各组时间序列度分布指数及95%置信区间Tab. 2 Degree distribution exponents and 95% confidence interval of time series |
| 时间序列 | λ值 | 置信区间(95%) | 变异系数 | Sig(双侧) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 0.264 | 0.022 | - | 0.000 |
| Year | 0.409 | 0.529 | - | 0.059 |
| INT | 0.201 | 0.016 | - | 0.000 |
| DOM | 0.298 | 0.021 | - | 0.000 |
| Rnd | 0.589 | 0.051 | 0.245 | - |
| Fbm | 0.533 | 0.124 | 0.327 | - |
| Lgst | 0.331 | 0.044 | 0.236 | - |
| Lorenz | 0.291 | 0.058 | 0.277 | - |
表3 转折点数值和年份Tab. 3 Turning point value and year |
| 时间序列 | 模块时间节点(年月) | 年份 |
|---|---|---|
| Month | 2008.12,2010.12,2013.11,2016.05 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| Year | 2002,2006,2008,2010,2013,2016 | 2002,2006,2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| INT | 2008.04,2010.10,2013.10,2016.11 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| DOM | 2008.12,2010.12,2013.04,2016.05 | 2008,2010,2013,2016 |
| Month(2013.01—2018.06) | 2013.11,2016.05 | 2013,2016 |
| Year(1998—2013年) | 2002,2006,2008,2010 | 2002,2006,2008,2010 |
表4 上海旅游地复杂系统演化阶段特征Tab. 4 Evolution phase characteristics of tourism destination complex system in Shanghai |
| 演化阶段 | 系统特征(产业结构、规模、业态等) | 转折点 重要事件 | 主导行 动者 | 子系统 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998—2002年 | 旅游业实现“外事接待型”向“经济产业型”转变,成为国民经济新的增长点。以都市旅游观光产品为主,商业、休闲旅游逐步成为都市旅游重要组成部分,会展、工业、农业旅游新兴业态得到一定发展。“非典”疫情爆发后,旅游者人数明显下降。 | 2002年“非典”疫情爆发 | 自然 环境 | 外部 环境 |
| 2003—2006年 | 都市旅游发展格局初步确立,传统观光旅游、工业旅游、农业旅游、休闲度假旅游、会展旅游进一步发展。通过“两节三赛”,创新旅游产品,中国旅游交易会及上海旅游节等节庆活动发展为国际性大型旅游节,上海向国际性大都市迈进,接待旅游者人数呈明显上升态势。 | 2006年举办多项世界国际性活动赛事 | 政府 | 主体 系统 |
| 2007—2008年 | 以“服务奥运”“迎世博”为契机,推动旅游产业集聚,提升旅游自主创新能力,增强旅游国际竞争力。都市旅游成为上海建设大都市的重要途径和形象品牌,节庆会展旅游更趋势国际化;形成国际、国内旅游共同繁荣局面,接待旅游者人数呈显著增长趋势。 | 2008年北京奥运会足球赛事|分会场 | ||
| 2009—2010年 | 世博会的举办,推动上海多中心、多流向、多圈层旅游格局的形成,旅游业成为上海支柱产业。工业旅游、文化旅游等专项产品不断升级,邮轮旅游、农旅等新型旅游业态蓬勃发展,形成一批具有国际影响力的城市旅游品牌,接待旅游者人数都呈迅速大幅增长态势。 | 2010年举办上海世界博览会 | ||
| 2011—2013年 | 以“创新驱动、转型发展”为主旨,大力发展邮轮旅游,邮轮旅游者人数突破百万人大关,成为上海新兴旅游业态的新增长点,出入境旅游者增长120%。注重旅游与相关产业创新融合,智慧旅游、旅游信息服务等旅游公共服务品质日益提升,形成以旅游业为核心、以服务型经济为主的产业结构。 | 2013年举办首届邮轮旅游节,成立中国邮轮旅游发展实验区 | ||
| 2014—2016年 | 以迪士尼开园为契机,大力创新旅游产品,突出上海都市旅游发展核心,形成“旅游+”十大系列产品,实现了从单一观光、休闲向观光、休闲、度假、商务、会议并重的旅游产业发展方式转变和转型升级,逐步形成“大旅游、大产业”的发展格局。 | 2016上海迪士尼开业 | 企业 | |
| 2017年— | 迪士尼溢出带动效应显著,“本土第一、世界精品”的黄浦江旅游休闲区、崇明世界生态岛等由外资、民资及社会资本参与的具有国际性吸引力的重点项目不断涌现;旅游“大旅游、大市场、大产业”产业融合格局基本形成,并由“景区旅游”向“全域旅游”发展格局转变。 | - |
表5 上海国际入境、国内旅游各构成时间序列Granger F值和度分布指数Tab. 5 Granger F value and degree distribution index of international inbound and domestic tourism in Shanghai |
| 构成 | 占比(%) | F值 | λ值 | 置信区间(95%) | sig.(双侧) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 国际 入境 旅游 | 新加坡 | 3.18 | 41.38 | 0.208 | 0.055 | 0.000 |
| 英国 | 2.68 | 23.40 | 0.080 | 0.064 | 0.000 | |
| 德国 | 3.74 | 20.30 | 0.278 | 0.061 | 0.000 | |
| 澳大利亚 | 2.55 | 13.06 | 0.076 | 0.058 | 0.049 | |
| 加拿大 | 2.37 | 11.22 | 0.101 | 0.064 | 0.029 | |
| 法国 | 2.66 | 10.65 | 0.028 | 0.059 | 0.010 | |
| 韩国 | 9.12 | 7.73 | 0.063 | 0.055 | 0.032 | |
| 日本 | 15.12 | 6.93 | 0.132 | 0.064 | 0.019 | |
| 美国 | 9.94 | 3.74 | 0.438 | 0.057 | 0.010 | |
| 国内 旅游 | 国内本地游客 | 42.34 | 19.69 | 0.409 | 0.205 | 0.059 |
| 国内外地游客 | 57.66 | 20.43 | 0.109 | 0.150 | 0.037 | |
中山大学地理科学与规划学院张海洲博士研究生在文章修改过程中提供了帮助,在此表示感谢!
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
[ 黄震方, 俞肇元, 黄振林, 等. 主题型文化旅游区的阶段性演进及其驱动机制: 以无锡灵山景区为例. 地理学报, 2011, 66(6):831-841.]
|
| [15] |
[ 杨春宇, 黄震方, 毛卫东. 基于系统科学的旅游地演化机制及规律性初探. 旅游学刊, 2009, 24(3):55-62.]
|
| [16] |
[ 陆林, 鲍捷. 基于耗散结构理论的千岛湖旅游地演化过程及机制. 地理学报, 2010, 65(6):755-768.]
|
| [17] |
[ 陆林, 鲍捷, 凌善金, 等. 桂林—漓江—阳朔旅游地系统空间演化模式及机制研究. 地理科学, 2012, 32(9):1066-1074.]
|
| [18] |
[ 杨仲元, 徐建刚, 林蔚. 基于复杂适应系统理论的旅游地空间演化模式: 以皖南旅游区为例. 地理学报, 2016, 71(6):1059-1074.]
|
| [19] |
[ 李伯华, 曾荣倩, 刘沛林, 等. 基于CAS理论的传统村落人居环境演化研究: 以张谷英村为例. 地理研究, 2018, 37(10):1982-1996.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[ 颜泽贤, 范冬萍. 系统科学导论: 复杂性探索. 北京: 人民出版社, 2006: 48-49.]
|
| [33] |
[ 米歇尔.沃尔德罗普. 复杂. 北京: 三联书店, 1997: 104-105.]
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
[ 汤胤, 易娜, 毛景慧. 基于有向有限穿越可视图的时间序列伴生网络. 系统工程学. 2017, 32(2):156-264.]
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
[ 李晓佳, 张鹏. 复杂网络中的社团结构. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2008, 5(3):19-42.]
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
[ 张毓, 孙根年. 城市规模与旅游成长空间关系、演变及驱动因子: 长江三角洲城市级别体系新认识. 地理科学, 2016, 36(12):1877-1884.]
|
| [53] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |