

自然灾害韧弹性社会的理论范式
|
吴绍洪(1961-), 男, 广东潮州人, 博士, 研究员, 博士生导师, 主要从事自然地理学综合研究、气候变化影响与灾害风险研究。E-mail: wush@igsnrr.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2020-09-22
要求修回日期: 2021-03-31
网络出版日期: 2021-07-25
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1508801)
国家重点研发计划(2018YFC1508900)
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDA19040304)
版权
Theoretical paradigm for natural disaster-resilient society
Received date: 2020-09-22
Request revised date: 2021-03-31
Online published: 2021-07-25
Supported by
The National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFC1508801)
The National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFC1508900)
The Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA19040304)
Copyright
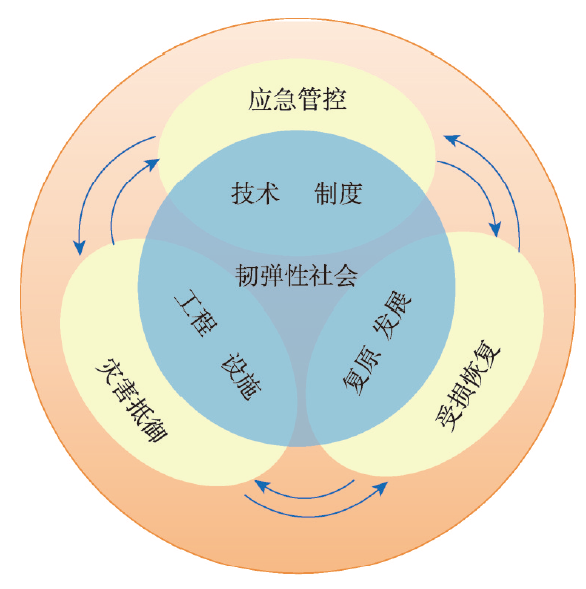
全球环境变化和经济快速发展导致自然灾害的增加,已经成为现代人类社会最严重的环境问题之一。面对自然灾害风险防控的严峻形势,人类社会必须建设得足够强大,以应对可能发生的自然灾害风险。在提出“构筑自然灾害韧弹性社会减轻自然灾害风险”的基础上,本文重点分析韧弹性的确切涵义,通过综合灾害防御、损害恢复和应急管控,诠释自然灾害韧弹性社会的内涵、组分和结构;建立自然灾害韧弹性社会的指标体系和定量表征方法,评估案例区自然灾害韧弹性社会的状况;进而针对城乡差异设计建设自然灾害韧弹性社会的途径。依此,系统性地构建了包括概念—结构—指标—途径的自然灾害韧弹性社会理论范式。建设自然灾害韧弹性社会是人类的必然选择,这与社会经济可持续发展高度一致。研究旨在推动综合应对自然灾害风险,探索建设“更强、更安全、更持续”的自然灾害韧弹性社会途径,支撑国家防灾减灾战略转变、实施“关键领域与薄弱环节九大工程”。
吴绍洪 , 高江波 , 韦炳干 , 张继权 , 郭桂桢 , 王军 , 邓浩宇 , 刘路路 , 贺山峰 , 许尔琪 . 自然灾害韧弹性社会的理论范式[J]. 地理学报, 2021 , 76(5) : 1136 -1147 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202105007
The change of global environment and the rapid development of economy have led to the increase of natural disasters, which have become one of the most serious environmental problems in modern human society. Facing the grim situation of natural disaster risk prevention and control, human society should be built strongly enough to deal with natural disaster risks. On the basis of "building a resilient society to reduce natural disaster risks", this paper focuses on analyzing the exact meaning of resilience, and interprets the connotation, composition and structure of natural disaster-resilient society through integrated hazard defense, damage recovery and emergency governance. The index system and quantitative characterization method of the natural disaster-resilient society was established to evaluate the situation of a natural disaster resilient-society in the case area. According to the differences between urban and rural areas, we designed pathways to build a natural disaster-resilient society. Then a theory paradigm of the natural disaster-resilient society, including concept-structure-index-approach, is systematically constructed. It is an inevitable option for human to build a natural disaster-resilient society, which is highly consistent with the sustainable socio-economic development. The research aims at promoting a comprehensive response to natural disaster risks, exploring ways to build a "stronger, safer and more sustainable" natural disaster-resilient society, supporting the transformation of national disaster prevention and reduction strategies, and implementing the "Nine Key Areas and Weak Links Projects".

表1 苍南县各乡镇自然灾害韧弹性社会指标与涵义Tab. 1 Indicators of NDRS for Cangnan County |
| 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | 涵义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 灾害抵御 | 防备 | 平均每万人拥有病床数 | 医疗救助 |
| 平均每万人拥有医护人员数量 | |||
| 医院覆盖率 | |||
| 储备库覆盖率 | 物资储备 | ||
| 储备库库容面积 | |||
| 人均物资储量 | |||
| 人均避难所面积 | 避难场所 | ||
| 避难所资金投入 | |||
| 救灾设备数量 | |||
| 抗拒 | 堤防工程总长度 | 抗灾工程 | |
| 50 a重现期堤防长度 | |||
| 水泵密度 | |||
| 堤防工程防洪(潮)堤坝比例 | |||
| 水闸密度 | |||
| 重现期30 a及以上防洪水闸 | |||
| 水闸防潮标准 | 建筑设防 | ||
| 交通网络密度 | 基础设施 | ||
| 规避 | 绿地面积增长率 | 生态建设 | |
| 保险赔付率 | 风险转移 | ||
| 受损恢复 | 生活常态 | 农村居民人均消费性支出 | 消费水平 |
| 城镇居民人均消费性支出 | |||
| 生产运转 | 月工业用电量增速 | 经济复苏 | |
| 月三产生产总值增长率 | |||
| 战略性新兴产业总产值 | 新兴产业 | ||
| 社会秩序 | 市政供水能力 | 资源配置 | |
| 市政供气能力 | |||
| 供电能力 | |||
| 网络舆情监控信息情况 | 网络舆情 | ||
| 灾害信息新闻发布次数 | |||
| 治安与刑事案件发案率 | 治安管理 | ||
| 应急管控 | 指挥协调 | 物资运输货车/舟 | 转移安置、物资调配 |
| 救灾志愿者数量 | |||
| 应急救灾部门数量 | 部门合作 | ||
| 应急预案总数量 | 应急预案 | ||
| 社会参与资金投入 | 政策法规 | ||
| 灾害管理法律完善程度 | |||
| 监测预警 | 监测时间分辨率 | 台站观测、移动设备 | |
| 监测设备覆盖率 | |||
| 监测装备投入 | |||
| 预警发布时间分辨率 | 信息发布 | ||
| 预警发布覆盖率 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
World Economic Forum. The Global Risks Report 2019. 2019. https://www.marsh.com/uk/insights/research/the-global-risks-report-2018.html.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
International Monetary Fund. World Economic Outlook. 2019. http://statisticstimes.com/economy/projected-world-gdp-ranking.php.
|
| [10] |
[ 马宗晋, 高庆华. 环境与自然灾害. 地球, 1991(2):17.]
|
| [11] |
[ 高孟潭. 减轻自然灾害—21世纪地球科学家的重要使命. 国际地震动态, 1997,0Z1:41-45.]
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
UNISDR. Living with Risk: A Global Review of Disaster Reduction Initiatives. 2004. https://www.undrr.org/publication/living-risk-global-review-disaster-reduction-initiatives. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.050.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
IPCC. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate, Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
|
| [21] |
[ 吴绍洪, 高江波, 邓浩宇, 等. 气候变化风险及其定量评估方法. 地理科学进展, 2018,37(1):28-35.]
|
| [22] |
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030. 2020. www.preventionweb.net/go/sfdrr.
|
| [23] |
[ 史培军,
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
[ 史培军. 灾害风险科学. 北京:北京师范大学出版社, 2017.]
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
[ 蔡建明, 郭华, 汪德根. 国外弹性城市研究述评. 地理科学进展, 2012,31(10):1245-1255.]
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
National Research Council. National Earthquake Resilience: Research Washington DC: The National Academies Press, 2011.
|
| [41] |
National Research Council. Disaster Resilience: A National Imperative Washington DC: The National Academies Press, 2012.
|
| [42] |
[ 高孟潭, 伍国春, 吴清, 等. 灾害韧弹性:国家的迫切需求. 北京: 地震出版社, 2019.]
|
| [43] |
[ 翟长海, 刘文, 谢礼立. 城市抗震韧性评估研究进展. 建筑结构学报, 2018,39(9):1-9.]
|
| [44] |
[ 吴波鸿, 陈安. 韧性城市恢复力评价模型构建. 科技导报, 2018,36(16):94-99.]
|
| [45] |
[ 邵亦文, 徐江. 城市韧性:基于国际文献综述的概念解析. 国际城市规划, 2015,30(2):48-54.]
|
| [46] |
[ 王冰, 张惠, 张韦. 社区弹性概念的界定、内涵及测度. 城市问题, 2016(6):75-81.]
|
| [47] |
[ 费璇, 温家洪, 杜士强, 等. 自然灾害恢复力研究进展. 自然灾害学报, 2014,23(6):19-31.]
|
| [48] |
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR). 2009 UNISDR Terminology on Disaster Risk Reduction, Geneva, 2009. http://www.unisdr.org/we/inform/terminology.
|
| [49] |
National Research Group on Major Natural Disasters. Natural Disaster and Disaster Reduction. Beijing: Earthquake Press, 1990
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
[ 高等教育出版社. 马克思主义基本原理理论. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2010.]
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
[ 张鹏, 于伟, 张延伟. 山东省城市韧性的时空分异及其影响因素. 城市问题, 2018(9):27-33.]
|
| [57] |
[ 吴洁. 城市内涝灾害防治视阈下社区弹性的度量方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018.]
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
[ 吴绍洪, 潘韬, 贺山峰. 气候变化风险研究的初步探讨. 气候变化研究进展, 2011,7(5):363-368.]
|
| [62] |
[ 刘艳丽, 张建云, 王国庆, 等. 气候自然变异在气候变化对水资源影响评价中的贡献分析. 水科学进展, 2012,23(2):147-155.]
|
| [63] |
[ 高孟潭, 周本刚, 潘华. “5·12”汶川特大地震灾害特点及其防灾启示. 震灾防御技术, 2008,3(3):209-215.]
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |